Abstract
The medicinal mushroom lion’s mane (Hericium erinaceus) is suggested to have therapeutic potential for neurological disorders due to its neuroprotective and neurotrophic properties. Mycelia of H. erinaceus contain erinacines, a group of cyathane diterpenoids, however no systematic review has explored the broader role of these compounds in mediating the neurobiological effects of the mushroom. This systematic review was therefore performed to enhance the depth of understanding surrounding the neurobiological impact of the various erinacine compounds using various cellular and rodent models. A secondary focus was to assess how study outcomes were influenced by the chemical complexity of the administered treatments. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines were utilized. The findings showed the broader potential of H. erinaceus mycelial formulations, and their derived erinacines, to exert dose-dependent benefits in motor, cognitive, and depression-like behaviours in animal models. Synthesis of records highlighted the ability of both erinacines and H. erinaceus to induce antioxidant responses and activate pro-survival signaling pathways. However, erinacine A and C uniquely induced the accumulation of the transcription factor Nrf2, a key regulator of the antioxidant response. These erinacines were also anti-inflammatory, enhanced neurogenesis and cell survival, and improved cognitive and behavioral outcomes in vivo. These findings suggest the promise of H. erinaceus extracts and individual erinacines as accessible, cost-effective interventions for aging-related and neurodegenerative conditions.

Introduction
Natural therapies have become increasingly popular in recent years as there is a growing list of medicinal plants and mushrooms containing both preventative and restorative neuroprotective compounds (Venturella et al., 2021). Early clinical trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of many medicinal mushrooms for the treatment and management of various diseases including Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), Parkinson’s Disease, depression, anxiety and sleep disorders (Rai et al., 2021; Venturella et al., 2021; Pepe et al., 2023). The therapeutic effects of medicinal mushrooms are often associated with some primary compounds, such as fatty acids and sterols, and secondary metabolites including various terpene/terpenoid compounds (Łysakowska et al., 2023).
Some medicinal mushrooms, such as the agaricomycete Lion’s mane (Hericium erinaceus (Bull.) Pers.), are vital components of traditional Asian medicine (Spelman et al., 2017) and are often used as ingredients in nutraceutical products (Niego et al., 2021). Lion’s mane mushroom, also termed bearded tooth fungus, has garnered interest for its applications in brain health as a nootropic, or “smart drug” (Onaolapo et al., 2019). Nootropics are a heterogenous group of medicinal substances often derived from plants and other organisms that are believed to improve human learning, memory and cognition (Malík and Tlustoš, 2022). The nootropic effects of H. erinaceus were demonstrated in early clinical trials, improving measures in assessments of cognitive ability in both young (19–45) and older (>55) healthy adults (Docherty et al., 2023; Černelič Bizjak et al., 2024) as well as in older adults with mild cognitive impairments (Mori et al., 2009). The efficacy of nootropics is notably increased in cases of learning and memory impairments, where they can serve as potential therapeutics (Schifano et al., 2022).
Hericium erinaceus mushrooms grow primarily on wood-based substrates (Onaolapo et al., 2019). Hericium erinaceus consists of an external fleshy fruiting body that develops from a substrate bound mycelial structure. Both the mycelium and fruiting body of H. erinaceus have neuroprotective properties, although these tissues differ in their composition of bioactive molecules (Corana et al., 2019). H. erinaceus mycelia are rich sources of erinacines, a class of cyathane diterpenoids with fused 5-carbon, 6-carbon, and 7-carbon ring structures, whereas hericenones are a class of meroterpenoids found exclusively within fruiting bodies of this basidiomycete (Corana et al., 2019). Other secondary metabolites that occur in H. erinaceus include hericerins, isoindoline-1-ones, and erinaceolactones (Friedman, 2015). Many of these bioactive constituents exhibit anti-carcinogenic, anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and/or antioxidative properties. Some erinacines and hericenones easily cross the blood brain barrier via passive diffusion, where they function as neurotrophin-stimulating compounds (He et al., 2017; Li et al., 2018). These neurotrophins, or growth factors, such as nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), activate the tyrosine receptor kinase (Trk) family of receptors to promote neuronal survival, plasticity, and repair (Saragovi et al., 2019). To date it is known that hericenones A-H as well as erinacines A-C, H, and I stimulate synthesis of NGF in vitro, but can only do so when administered to glial cells and cannot induce NGF synthesis in neurons alone (Kawagishi et al., 1994; Phan et al., 2014). In addition, erinacine A attenuates neurotoxicity through the upregulation of pro-survival pathways, while decreasing activity of pro-apoptotic pathways (Lee et al., 2020).
Although there have been integrative reports describing H. erinaceus in therapeutic applications, relatively few studies have addressed the unique contribution of individual erinacines to these effects. As such, this review aims to narrow this gap by examining the cumulative literature on the neurobiological effects of H. erinaceus mycelia and, at the same time, provide insights into the molecular actions of specific erinacines and their contribution to the therapeutic profile of H. erinaceus.
Methods
The current systematic review abided by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. Two distinct literature searches were conducted independently by two individuals screening the Web of Science, PubMed and ScienceDirect databases in February 2024 using three strings of search criteria all joined by Boolean commands. The key words consisted of either “erinacine” or “Hericium erinaceus” and (“Neuroprotection” or “Neurotrophins” or “Neuron” or “Neuronal System”). Primary data, free text available, preclinical experimental studies (in vivo and in vitro) published in English in a peer-reviewed journal up to July of 2024 and that also evaluated individual erinacine compounds or H. erinaceus mycelia that reported erinacine concentrations with a neurological focused cellular, molecular, and/or behavioural outcome were included. Exclusion criteria were adopted based on studies that mainly focused on fruiting body administrations, bioavailability, compound isolation, molecular chemistry, cancer research models, non-neurologic outcomes, no reporting of erinacine content, and analysis of alternate Hericium species. Retracted articles, reviews, meta-analyses, conference abstracts, book chapters, and unpublished results were additionally excluded from the analysis. The search initially returned 66 and 123 reports in the erinacine and H. erinaceus searches, respectively, which was reduced to 46 and 107 reports after removal of duplicates. Further screening was then conducted to assess records suitability for inclusion and, after removal of unrelated studies and additional records identified from references, 26 and 66 full-text articles underwent independent screening. Following screening, additional studies were removed after not meeting the inclusion criteria, many of which did not report erinacine concentrations.
Results
After the final synthesis of studies across all searches there were a total of 23 studies included in the review (Figure 1) that were allocated to in vitro or in vivo categories, each of which included either individual erinacines or some type of H. erinaceus mycelial preparation. A total of seven studies investigated treatment outcomes of both in vivo and in vitro analyses. Nine of the included studies evaluated solely in vivo outcomes, whereas seven studies evaluated solely in vitro outcomes.
FIGURE 1
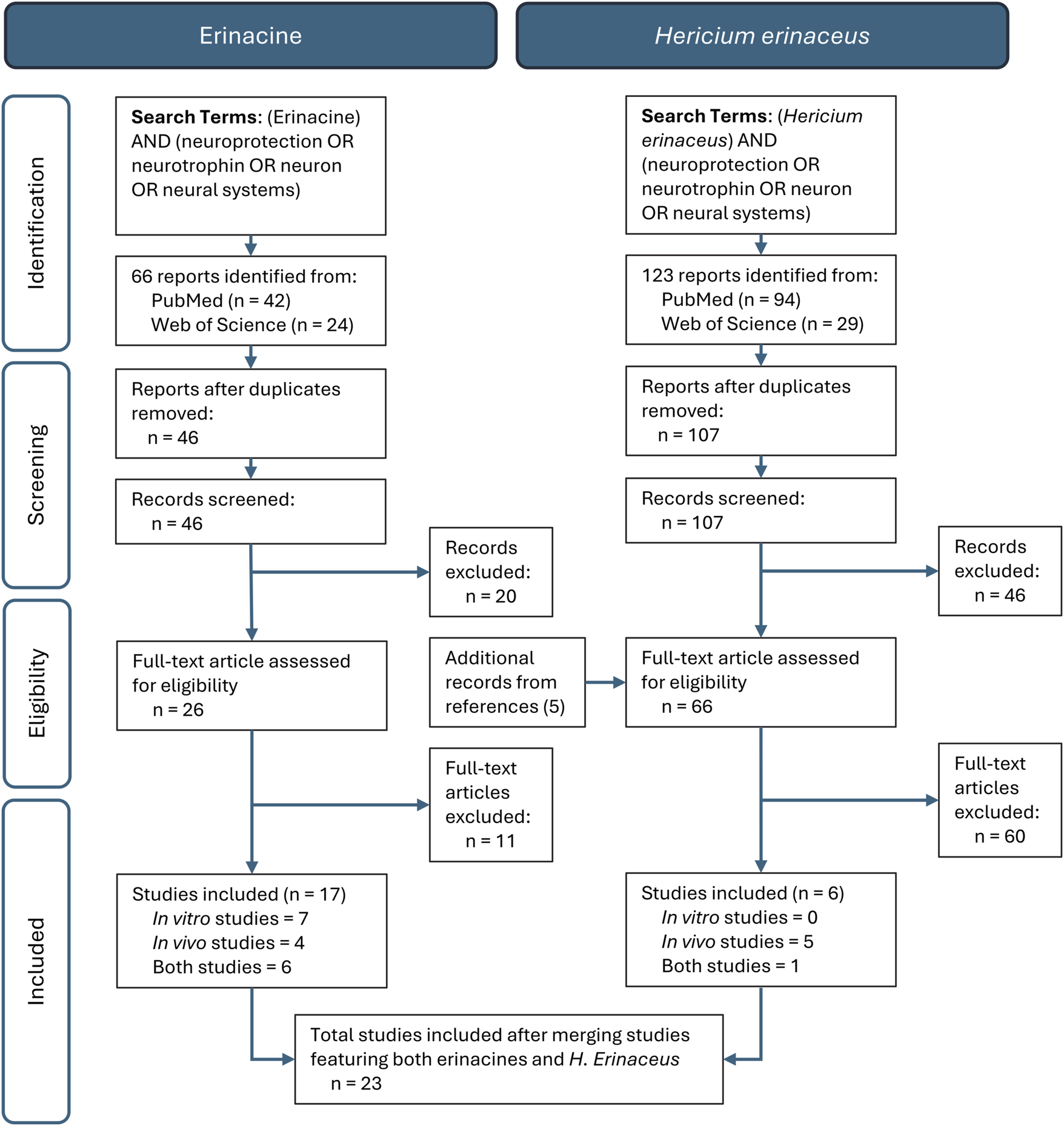
PRISMA Workflow Diagram of a systematic review of the in vitro and in vivo studies related to the neurobiological effects of Hericium erinaceus mycelium whole extracts and the erinacines.
Various types of H. erinaceus mycelial formulations and erinacine compounds were assessed in both in vitro (Table 1) and in vivo (Table 2) studies. For the erinacine studies, erinacine A was the most investigated compound, with its biological effects assessed in twelve out of the seventeen in vitro and in vivo studies. Erinacine C and erinacine S were the test compounds in seven and six reports, respectively. Erinacine C was mostly evaluated in vitro, with only two of the seven papers featuring in vivo experiments. The erinacines B, E, F, L, Z1 and Z2 appeared in one record each and therefore only erinacine A, erinacine S and erinacine C were critically evaluated in this review. Six studies that administered H. erinaceus mycelia (HEM) or mycelial extracts (HEME) reported the concentration of erinacine A found within the fungus. All were in vivo studies, with only one of these reporting in vitro analyses. Three studies administered HEM, two studies administered ethanolic HEME, and one study administered both HEM and HEME.
TABLE 1
| Author | Treatment | Focus | Experimental model | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hsu et al. (2022) a | EA | Neuroprotection, astrocyte GLT-1 function, glutamate homeostasis | Oxygen glucose deprived mouse CTX glia-neuron co-culture | Preserved astrocyte enriched GLT-1 function to maintain glutamate homeostasis |
| Huang et al. (2021) | EA, ES, EC | Oligodendrocyte differentiation | Rat CTX OPCs; cerebellar slice cultures | EA & ES: ↑ myelin basic protein expression, ↑ # of mature oligodendrocytes |
| Lee et al. (2024) a | EC | Gene expression, calcium signaling, oxidative stress, Nrf2 | LPS-induced mouse whole brain mixed-glia cultures and BV-2 cells | Nrf2 pathway mediated protection against neuronal injury and microglial activation |
| Lee et al. (2020) a | EA | Parkinson’s disease pathology | MPP + -treated mouse N2a cells or substantia nigra neuron culture | Prevented dopaminergic degeneration and motor dysfunctions through cell survival pathway promotion |
| Lee et al. (2022) a | EA | Neuroinflammation | LPS and/or IFN-γ-induced BV-2 cells, CTX TNA2 cells, N2a cells treated with LPS-treated BV-2 conditioned medium | Inhibited expression of proinflammatory factors involved in activation of glial cells. Suppressed cell death pathways |
| Lin et al. (2024) | EA, EC, ES | Neuroprotection and immunomodulation | LPS-induced BV-2 microglia cells and SH-SY5Y co-cultures | Induces neuroprotection and reduction of inflammation |
| Lin et al. (2023) | ES | Neurite outgrowth and regeneration, gene expression | Mouse CTX neuron culture, rat dorsal root ganglion culture | Enhanced neurite outgrowth and post-injury axon regeneration |
| Rascher et al. (2020) | EC | Transcriptional activation and neurotrophin signaling | PC12 cells cultured with 1321N1 (astrocyte cells) conditioned medium | Enhances expression of NGF and BDNF in glial cells |
| Rupcic et al. (2018) | EA, EB, EC, EZ1, EZ2 | Metabolic profiles, neurotrophin expression | PC12 cells with or without 1321N1 cell conditioned medium | Stimulated neurotrophin production in astrocytic cells |
| Wang et al. (2019) | EC | Neuroinflammation and cell signaling | LPS-induced BV2 microglial cells | Involve activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and inhibition of IκB and iNOS expressions |
| Wei et al. (2023) | EA, EL, EC, EF | Neurotrophic activity and anti-neuroinflammation | PC12 cells, LPS-induced BV2 microglial cells | Showed neurotrophic activity in PC-12 cells and limited NO production in BV2 cells |
| Wu et al. (2023) a | HEME – [EA]: 5 mg/g | Neuroprotection | tBH-induced human neuroblastoma SK-N-SHMJD78 cells and SCA3 cells | ↑ lifespan, ↓ apoptosis via downregulation of p53 and NF-kB |
| Yang et al. (2020) a | EA, ES | Purinoceptor signaling | Human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells, human osteosarcoma cells | ES inhibits ATP-induced rise in [Ca2+] in P2R-mediated signal transduction |
| Zhang et al. (2017) | EA | Neuroprotection and neurite growth | PC12 cells, rat CTX neuron cultures | ↑ NGF-mediated neurite outgrowth through TrkA and Erk1/2 |
Characteristics of the included in vitro studies following PRISMA guidelines.
Indicates studies included in both in vitro and in vivo results.
Abbreviations: CTX, cortex; EA, erinacine A; EB, erinacine B; EC, erinacine C; EF, erinacine F; EL; erinacine L; ES, erinacine S; EZ1, erinacine Z1; EZ2, erinacine Z2; GLT-1, glutamate transporter 1; HE, Hericium erinaceus; HEME, Hericium erinaceus mycelia erinacine extracts; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; Hip, hippocampus; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; IκB, inhibitor of NF-κB; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MPP+, 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO, nitric oxide; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; OPCs, oligodendrocyte precursor cells; P2R, purinoceptor; SCA3, Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3; tBH, tert-butyl hydroperoxide; TrkA, tropomyosin receptor kinase A.
TABLE 2
| Author | Treatment | Focus | Animal species/Model | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen et al. (2016) | EA, ES | Alzheimer’s disease | APP/PS1 mice | ↓ Aβ plaque burden, ↑ cortical insulin-degrading enzyme levels |
| Chiu et al. (2018) | HEME – [EA]: 5 mg/g | Depression | Restraint stress, ICR mice | Normalization of depressive behaviour, ↑ BDNF and modulation of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway |
| Hsu C.-H. et al. (2023) | HEM – [EA]: 30 μg/g | Parkinson’s disease | MPTP-treated C57BL/6 mice | Amelioration of oxidative stress, ↑ dopamine and tyrosine hydroxylase levels |
| Hsu C.-L. et al. (2023) | EA | Traumatic optic neuropathy | Traumatic optic neuropathy, Wistar rats | Neuroprotection and preservation of visual function |
| Hsu et al. (2022) a | EA | Ischemia | tHI-induced C57BL/6 mice | Preserved astrocyte-enriched GLT-1 function to maintain glutamate homeostasis |
| Huang et al. (2021) | EA, EC, ES | Oligodendrocyte maturation | Ex vivo cerebellar slice of SD rats | EA & ES: ↑ myelin basic protein expression, ↑ # of mature oligodendrocytes |
| Lee et al. (2024) a | EC | TBI | TBI-induced SD rats | Nrf2 pathway mediated protection against neuronal injury and microglial activation |
| Lee et al. (2020) a | EA | Parkinson’s disease | MPTP-treated C57BL/6 mice | Prevented dopaminergic degeneration and motor dysfunctions through cell survival pathway promotion |
| Lee et al. (2014) | EA | Ischemia and reperfusion injury | Global ischemia, SD rats | Neuroprotection and free radical scavenging related to endoplasmic reticulum stress signaling |
| Lee et al. (2022) a | EA | LPS-induced inflammation in microglia | SD rats | Prevention of motor dysfunction and ↓ microglia-mediated neuroinflammation |
| Lee et al. (2021) | HEM – [EA]: 5 mg/g | Neuroprotective effects on aging | SAMP8 mouse model of aging | ↑ learning and memory through ↓ oxidative stress and ↓ amyloid aggregation |
| Li et al. (202) | HEM – [EA]: 7.2 mg/g | Sleep disruption | Sleep disturbed C57BL/6 mice | Reversed sleep disturbances and ↓ anxiety-like behaviour |
| Tsai-Teng et al. (2016) | HEM, HEME – [EA]: 19 mg/g, 104.4 mg/g | Alzheimer’s disease | APP/PS1 mice | ↓ Aβ plaque burden, ↑ cortical and hippocampal insulin-degrading enzyme levels, ↑ NGF maturation, ↑ hippocampal neurogenesis |
| Tzeng et al. (2018) | EA, ES | Alzheimer’s disease | APP/PS1 mice | ↑ cortical and hippocampal insulin-degrading enzyme levels, ↑ NGF maturation, ↑ hippocampal neurogenesis. EA; ↓ Aβ production |
| Wu et al. (2023) a | HEME – [EA]: 5 mg/g | Oxidative stress induced by tBH | tBH treated ELAV-SCA3tr-Q78 transgenic Drosophila | ↑ lifespan, ↓ apoptosis via downregulation of p53 and NF-kB |
| Yang et al. (2020) a | EA, ES | Neuropathic pain, neuro-inflammation | C57BL/6 mice with L5 spinal nerve ligation | ES was able to induce better pain-relieving effects when compared to EA |
Characteristics of the included in vivo studies following PRISMA guidelines.
Indicates studies included in both in vitro and in vivo results.
Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid-beta; APP, amyloid precursor protein; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; EA, erinacine A; EC, erinacine C; ES, erinacine S; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase-3, beta; GLT-1, glutamate transporter-1; HE, hericium erinaceus; HEM, HE, mycelia; HEME, HEM, erinacine extracts; Hip, hippocampus; ICR, institute of cancer research; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NGF, neuron growth factor; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2; PS1, presenilin 1; SAMP8, Senescence Accelerated Mouse-Prone 8; SD, sprague dawley; TBI, traumatic brain injury; tBH, tert-butyl hydroperoxide; tHI, transient hypoxia-ischemia.
The studies described in this systemic review used various methodologies for the extraction of erinacines. Typically, erinacines extracts derived from H. erinaceus mycelia are cultured on nutritive media (e.g., yeast salt medium) using solid state agar or shaking liquid cultures (Gonkhom et al., 2022). Solvent systems used for erinacine extraction from H. erinaceus mycelia include acetone (Rupcic et al., 2018), and ethyl acetate (Shen et al., 2015) but ethanol (e.g., 75%–95% ethanol) is most often used (Chen et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2024). This includes the reflux of successive ethanolic extraction of mycelia containing erinacines A, C, and S (Tsai-Teng et al., 2016). The molecular structures of these erinacines are provided in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2
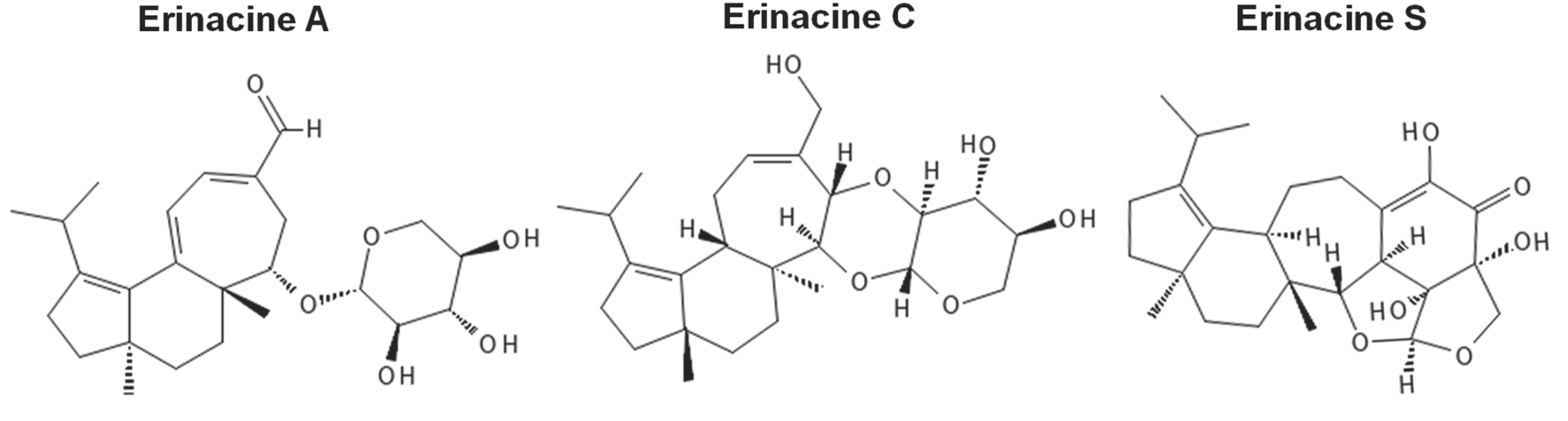
Molecular structures of erinacine A, C and S. Erinacine structures were drawn with the online software PubChem Sketcher, v2.4 (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov//edit3/index.html), accessed on 24 November 2024 (Ihlenfeldt et al., 2009).
Typically, the isolation of erinacines from mycelial extracts is achieved by partitioning against solvents such as ethyl acetate, followed by the subsequent resolution and fractionation on chromatographic media such as silica gel and size exclusion resins (Kawagishi et al., 1994; Chen et al., 2016). Other chromatographic strategies used for erinacine purification include preparative high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or flash chromatography (Rupcic et al., 2018). For many of the studies assessed in this review, the erinacine profiles within HEM were often assessed through HPLC or ultra performance liquid chromatography. The identity of erinacines was confirmed by co-chromatography with authentic standards. In addition, erinacines were identified by mass spectrometry and/or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. It is worth noting that the range of erinacine A concentrations that were detected within HEM varied from 5 to 19 mg/g of freeze-dried or fresh mycelia (Tsai-Teng et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2021; Li et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2023), although Hsu C.-H. et al. (2023), identified a much lower concentration at 30 μg/g dry weight of HEM. Conversely, Tsai-Teng et al. (2016) determined that HEME contained nearly an order of magnitude more erinacine A (i.e., 104.4 mg/g) by comparison. Moreover, this group used HEME that contained 15 times more erinacine A than erinacine C and erinacine S which were each detected at approximately 1 mg/g of mycelial powder.
In vitro studies
Models and treatments
Studies only evaluated the acute effects of a single treatment with erinacines or erinacine-containing mycelia (n = 14) and were conducted most often using the PC12 neuron-like cell line (n = 4) or with BV-2 microglial cells (n = 5). Studies also used primary neuronal cell cultures (n = 5) or other neuron-based cell lines such as mouse N2a cells (n = 2) and human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells (n = 2). Molecular and cellular outcomes were assessed most frequently using Western blotting (n = 10) to identify protein expression, or through various polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques (n = 8) to quantify gene expression in the cells.
Cells were treated with erinacines at concentrations ranging from 0.01 ng/mL to 25 μg/mL, with erinacine A generally delivered at greater concentrations than erinacine C and erinacine S. In vitro HEME was administered from 1.25 to 5 μg/mL and with an erinacine A concentration of 5 mg/g of HEME. There was a general concentration-response trend identified across all groups, with higher concentrations of erinacines and HEME eliciting a stronger cellular response. However, administration of erinacines A, C, or S to SH-SY5Y cells at very high concentrations (>10 μg/mL) decreased cell viability, with as little as 5 μg/mL erinacine S affecting viability in a single study, indicating a biological efficacy window in vitro (Yang et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2024).
Molecular and cellular alterations
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective effects
When looking at the acute effects of erinacines and/or H. erinaceus mycelia in inflammatory and/or disease models, neuroprotective effects were commonly observed. In studies of neuroinflammation models (n = 7), both erinacine A and HEME protected N2a neuronal cells from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-exposed BV-2 conditioned medium-induced cell death through the suppression of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B (NF-κB) activation (Lee et al., 2022). Erinacine A and erinacine C inhibited the expression of proinflammatory factors, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), implicated in the activation of glial cells (Wang et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2022; Wei et al., 2023). Furthermore, erinacine A ameliorated MPP+ -induced apoptosis and degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in a N2a cell model of Parkinson’s Disease. This neuroprotective effect was proposed to be the result of an induction of anti-apoptotic factors such as activated kinase 1 (PAK1), protein kinase B (AKT), lim domain kinase 2 (LIMK2), mitogen-activated protein kinase, and cofilin. This action was also mediated by the inactivation of several proteins that play key roles in pro-apoptotic pathways, such as TNF-α, or in the promotion of oxidative or endoplasmic reticulum stress (Lee et al., 2020).
In primary cortical glia-neuron co-cultures, erinacine A improved neuronal and astrocyte survival and preserved astrocyte glutamate homeostasis in response to oxygen-glucose deprivation via the accumulation of glutamate transporter 1 protein levels (Hsu et al., 2022). The study attributed the inhibition of the NF-κB and AKT signaling pathways as the targets of erinacine A-mediated neuroprotection. In contrast to the findings of Lee et al. (2022), Hsu et al. (2022) found no effect of erinacine A on alterations in the JNK, or ERK1/2 and p38/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. A key role for reduced NF-κB signaling in neuroprotection was also observed following HEME treatment in a tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress human neuroblastoma cell model (Wu et al., 2023). Erinacine S induced neurogenesis in both cortical and dorsal root ganglion primary mouse neuron cultures through the enhanced expression of genes encoding for the metabolism of the neurosteroids pregnenolone and progesterone (Lin et al., 2023).
In whole-brain mixed glia co-cultures following LPS insult, erinacine C induced the expression of the transcription factor nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), which was correlated with increased protein expression of BDNF and other antioxidant enzymes (Lee et al., 2024). Similarly, in LPS-treated BV-2 microglial cells, erinacine C increased the abundance of nuclear antioxidant/anti-inflammatory Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) protein (Wang et al., 2019).
Neurotrophic effects
Under normal conditions, acute treatments with erinacine A, erinacine C, or erinacine S induced neurite-outgrowth of PC12 neurons in the presence of NGF, and also induced NGF release from astrocytic cells in 1321N1 cell models (Rupcic et al., 2018; Wei et al., 2023). The magnitude of neurite outgrowth was increased when cells were co-treated with erinacines and NGF, compared to NGF alone (Wei et al., 2023). Notably, erinacines did not stimulate NGF synthesis or neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells in the absence of the differentiation inducer NGF. This suggests that erinacine A-induced neurogenesis may be the result of elevated NGF potency as opposed to elevated expression of NGF. However, in primary cortical neuron cultures, erinacine A potentiated NGF-induced neurite outgrowth and was protective against neuronal cell death in the absence of NGF, suggesting erinacine A may serve to acutely mimic the action of neurotrophins (Zhang et al., 2017). NGF-induced neurogenesis of differentiated primary cortical neurons upon treatment with erinacine A was mediated by the TrkA receptor and was extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2)-dependent (Zhang et al., 2017). Erinacine A, erinacine S, or HEME stimulated the differentiation of precursor cells into mature oligodendrocytes and enhanced myelination during the development of dissociated cells (Huang et al., 2021). However, erinacine A was a more potent stimulator of these effects as compared to erinacine S, suggesting that the oligodendrocyte maturation properties induced by HEME were most likely due to the action of erinacine A (Huang et al., 2021). Interestingly, only erinacine C increased BDNF expression in primary mixed-glia cultures and astrocytic cell models (Rupcic et al., 2018; Rascher et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2024).
Summary
In vitro studies on H. erinaceus mycelia and their derived erinacines focused on their effects in neuronal and glial cell cultures, using techniques like protein and gene expression analysis. Both H. erinaceus mycelia and erinacines promoted neurogenesis, protected against inflammation and oxidative stress, and supported cell survival. However, individual erinacine compounds were observed to have differential effects in certain cellular processes compared to others within the same erinacine family.
In vivo studies
Treatments
Erinacines investigated in vivo included erinacine A in nine studies, erinacine S in four studies and erinacine C in two studies. Erinacines were administered through oral gavage at doses ranging from 2.6 mg/kg to 30 mg/kg per day, whereas a smaller range of 1 mg/kg to 10 mg/kg per day erinacines were injected intraperitoneally. H. erinaceus mycelia was administered in vivo as HEME (n = 3) and HEM (n = 4). Doses of HEME were largely based on the original dry weight of HEM prior to extract production. No trends were observed in the studies with respect to the dosage regimen between HEM and HEME. Doses of H. erinaceus for some studies were based on the recommended human intake level and utilization of a 100-fold lower concentration (–1 mg/day of dry HEM). Among the in vivo studies, H. erinaceus was administered orally at a range of 75–1,000 mg/kg per day, however most studies used a dose within the 50–300 mg/kg per day range. H. erinaceus was administered daily for a minimum of 9 days and up to 13 weeks, with most studies using a 30-day administration timeline. No studies evaluated the impacts of acute erinacine or H. erinaceus mycelium treatments.
Behavioural studies
Of the studies examined in vivo (n = 16), nine evaluated behavioural outcomes; five studies assessed erinacine effects, and four studies investigated HEM/HEME effects. Erinacine A was examined in three studies, whereas erinacine S and erinacine C were examined in one study each. Using the rotarod test to evaluate motor function in mice, systemically administered erinacine A (1 mg/kg) alleviated MPTP-induced motor coordination disruption and balance (Lee et al., 2020). Motor improvements following daily oral administration of erinacine A (5.0 mg/kg) for 6 weeks were also reported for amphetamine-injected LPS-induced Parkinson’s disease models (Lee et al., 2022). Similar effects on alleviating motor deficits in the beam walking test were observed following erinacine C treatment in traumatic brain injury (TBI)-induced rats (Lee et al., 2024). In tail suspension test-induced sleep disrupted mice, chronic administration of HEM (150 mg/kg, containing 7.2 mg/g erinacine A, and 3.35 mg/g erinacine C), promoted exploratory behaviour and lowered anxiety-like behaviour in the open field test (Li et al., 2021). However, one study determined that open field associated-locomotor activity was unchanged in stressed mice after a chronic oral administration of HEME (300 mg/kg containing erinacine A at 5 mg/g of HEME), although antidepressant-like effects were present (Chiu et al., 2018). The potential for depression- and/or anxiety-like relief by oral HEM for 9 days was established in a model of continuous sleep disturbance (Li et al., 2021). Results from rodent studies that evaluated anxiety showed increased exploratory activity and reduced anxiety-like behaviour in response to HEM/HEME (Chiu et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021). Erinacine A and HEM also reduced deficits in burrowing and nesting tasks, which are often used to evaluate activities of daily living skills, a sign of natural instinctive behaviour (Tsai-Teng et al., 2016; Tzeng et al., 2018).
With respect to aspects of cognition, erinacine A improved spatial learning and memory in rodent models of AD as evidenced by a reduced escape latency in the Morris water maze task (Tzeng et al., 2018). Associative learning and memory were also enhanced in the passive avoidance task and active shuttle avoidance test after long-term daily HEM (431 mg/kg containing 5 mg/g erinacine A) administration in an accelerated aging mouse model (Lee et al., 2021). Additionally, moderate benefits of erinacine A pretreatment on scores in neurological deficit assessments were observed in a brain ischemia mouse model (Hsu et al., 2022). Moreover, erinacine A ameliorated grip strength deficits following ischemia, but did not lead to increases in basal levels of grip strength (Hsu et al., 2022). Interestingly, following spinal nerve injury, erinacine S promoted an analgesic suppression of neuropathic pain in the von Frey test (Yang et al., 2020).
Molecular and cellular alterations
Models and analyzed tissue
In vivo studies described neuroprotective effects of erinacines and H. erinaceus mycelia in a variety of rodent models through the reduction of neuroinflammation and/or oxidative stress. The most frequently analyzed brain regions were the cerebral cortex (n = 7) and hippocampus (n = 5), followed by the striatum (n = 3) and cerebellum (n = 1). Across all studies, the most often used methodologies (n = 15) were protein quantification by Western blotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and immunohistochemistry within brain tissues. Only one study included both male and female animals that were grouped and analyzed independently. A total of 11 studies used exclusively males, and three studies selectively used females. Of the three studies that employed females, all used APP/PS1 transgenic mice, as the female sex appears more susceptible to the induced pathology.
Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and neuroprotective effects
Sub-chronic administration was evaluated in four studies, where single erinacine compounds or HEME were administered daily for five to 7 days by intraperitoneal injection or oral gavage (Lee et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2024; Hsu et al., 2022). A single rat study analyzed the separate effects of pretreatment with erinacine A and HEME on preventing brain injury during ischemia (Lee et al., 2014). This study revealed that erinacine A prevented neuronal cell death. Moreover, erinacine A effects were mediated through the scavenging of endoplasmic reticulum stress-stimulated free radicals, in addition to inhibiting inflammation via inactivation of iNOS and MAPK, and a reduction in the pro-apoptotic C/EBP homologous protein. In addition, neuroprotective effects of systemic erinacine C were apparent when administered to mice for 6 days following TBI (Lee et al., 2024). This effect was mediated by enhanced activation of the Nrf2/superoxide dismutase type 1 (SOD1) pathway. Increased levels of phosphorylated cAMP response element binding (CREB) protein, in addition to thioredoxin reductase, a key component of the thioredoxin (Trx) neuroprotective pathway, were also observed (Lee et al., 2024). Nrf2 levels were also elevated by erinacine A in the retina and optic nerve of rats following traumatic optic neuropathy, and it was proposed that activation of the Nrf2/HO-1/SOD1 antioxidative stress pathway led to reduced inflammation and apoptosis (Hsu C.-L. et al., 2023). Together these findings suggest that the Nrf2 pathway may be important for the nootropic effects of the erinacines. Studies conducted in healthy rodents showed that erinacine A and erinacine S, promoted the production of myelin basic protein and the maturation of cerebellar oligodendrocytes in neonatal rats, whereas erinacine C had no effect (Huang et al., 2021).
Multiple studies used rodent model systems to elucidate the therapeutic potential of erinacines in neurodegeneration (n = 5). Studies utilizing transgenic APPswe/PS1dE9 AD model mice (n = 3) determined that erinacine A, erinacine S, or HEME administration reduced amyloid-β plaque formation in the cerebral cortex while elevating levels of insulin degrading enzyme, a protein believed to play a significant role in the clearance of amyloid-β (Chen et al., 2016; Tsai-Teng et al., 2016; Tzeng et al., 2018). However, Tzeng et al. (2018) established that erinacine A was more effective than erinacine S at inhibiting amyloid-β accumulation by reducing insoluble amyloid-β and the C-terminal fragments of amyloid processing protein. Interestingly, HEM that was enriched in erinacine A was more effective than HEME at reducing the brain soluble forms of amyloid-β1-42, whereas HEME was slightly more effective at decreasing the number of amyloid-β10-stained plaques, increasing the level of insulin degrading enzyme, and enhancing hippocampal neurogenesis (Tsai-Teng et al., 2016). Erinacine A pretreatment of LPS-induced, or (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine) MPTP-induced, Parkinson’s Disease model rodents reduced dopaminergic neurotoxicity and protected against microglia-mediated neuroinflammation through the reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression and reactive oxygen species production in the midbrain (Lee et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2022). Moreover, erinacine A treatment ameliorated dopaminergic degeneration in the striatum and substantia nigra of MPTP model mice by reversing the MPTP-induced decrease in pro-survival signaling (Lee et al., 2020). The sole long-term in vivo study analyzed the impact of sub-chronic HEM doses in an accelerated aging mouse model, which revealed similar reductions in oxidative stress and lower amyloid-β plaque aggregation as was seen when using sub-chronic doses (Lee et al., 2021). Notably, this was the one study that evaluated sex differences, but no sex-specific effects were observed (Lee et al., 2021).
Neuromodulator and neurotrophic effects
Erinacine A increased microglial and neuronal survival while preserving astrocytic glutamate machinery in a cerebral ischemic mouse model, with increased expression of glutamate transporter 1 and similar glutamate homeostatic regulators within cells (Hsu et al., 2022). HEME ameliorated stress-induced cellular changes in mice. For example, stress-induced decreases in hippocampal dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine, as well as alterations in plasma IL-6 and TNF-α were ameliorated by the daily administration of HEME (300 mg/kg containing erinacine A at 5 mg/g of dry weight) for 4 weeks (Chiu et al., 2018). Furthermore, HEME supplementation increased hippocampal BDNF levels, activated the AKT signaling pathway to inhibit glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) activity, and induced antidepressant-like behavioral effects (Chiu et al., 2018). Increased BDNF protein expression was evident in whole brain samples following treatment with 150 g/kg HEM (containing 7.2 mg/g erinacine A) to tail suspension test-induced sleep disrupted mice for 9 days (Li et al., 2021). An elevation in hippocampal AKT activity was evident in studies that examined erinacine A and HEME (Chiu et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2020). HEME ameliorated repeated restraint stress or 3-acetylpyridine-induced decreases in monoamine dopamine and serotonin levels (Chiu et al., 2018).
Summary
Studies on H. erinaceus mycelia and erinacines explored their effects on behavioral and molecular outcomes in rodent models. Behaviorally, these compounds showed similar benefits in motor function, cognition, and emotional regulation, with potential applications in neurodegenerative diseases, anxiety, and pain management. Molecular and cellular findings revealed neuroprotective effects, that involved reductions in inflammation, oxidative stress, and amyloid-β accumulation, alongside enhanced neurogenesis and neuronal survival across both erinacine and H. erinaceus mycelial administrations, and with certain erinacines, such as erinacine S, exhibiting novel neurologic effects, particularly as an analgesic.
Discussion
Although the health benefits associated with H. erinaceus are documented to some degree in the scientific literature, there is less information on the contribution of the individual active molecules. As described in this review, in vitro and in vivo studies to date that have examined the short- and long-term effects of the erinacines, particularly erinacine A and C, as well as H. erinaceus mycelia on cellular and behavioral outcomes were evaluated.
Evidence indicates that erinacines or H. erinaceus mycelia have neuroprotective properties that are elicited by the upregulation of cell survival factors and the downregulation of oxidative stress and neuroinflammatory pathways. Similar effects were apparent when comparing the molecular and cellular responses to the administration of single erinacine molecules to those of mycelial extracts. For example, the administration of erinacine A, C, and S, as well as those of HEM/HEME, reduced the abundance of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β (Chiu et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2020; Lin et al., 2024). Erinacine A inhibited TNF-α in an astrocyte cell model of neuroinflammation, but not in microglia, although an effect on iNOS signaling selectively in microglia was evident (Lee et al., 2022). Accordingly, in vivo treatment of HEM containing 5 mg/g of erinacine A inhibited the induced protein expression of cortical and hippocampal iNOS in response to LPS-induced neuroinflammation (Lee et al., 2021). This effect was also observed across studies of erinacine A in vivo (Lee et al., 2014; Lee et al., 2022; Hsu C.-L. et al., 2023) and erinacine C in vitro (Wang et al., 2019), whereas this was not investigated with erinacine S. Other similarities in therapeutic actions were observed between erinacine A and S when compared to HEME (containing 104.4 mg/g of erinacine A) and HEM (containing 19.9 mg/g erinacine A) in neurodegenerative disease models. Each treatment was able to decrease the burden of Aβ plaques, increase the levels of insulin degrading enzyme and induce hippocampal neurogenesis while alleviating behavioural deficits observed in the nesting task (Chen et al., 2016; Tsai-Teng et al., 2016; Tzeng et al., 2018). Interestingly, it was observed that HEME, which was higher in erinacine A concentration was more potent at reducing amyloid-β plaque burden as compared to HEM (Tsai-Teng et al., 2016). This indicates that erinacine A may play a crucial role in the mitigation of amyloid-β accumulation observed in mycelial treatments. Studies using neurodegenerative disease models also showed increased activity of NF-kB, a protein involved in the induction of pro-apoptotic factors (Lanzillotta et al., 2015). Thus, the observed reduction of NF-kB activity by HEME and erinacines may be a key mediator underlying the reported neuroprotective effects across the various treatments (Wang et al., 2019; Lee et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2023).
Both erinacines and H. erinaceus mycelia reduce the production of reactive oxygen species. The suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation were partially mediated by antioxidant-related processes associated with Nrf2, HO-1, and SOD, which act to sequester free radical production and hence inhibit the activation of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that can bind to promoter regions of genes that are essential for antioxidative, cell survival, and cell proliferation signaling, such as BDNF, CAT, SOD1 and TrxR (Hsu C.-L. et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2024). In rodents, Nrf2 protein levels were elevated in optic nerve and cortical samples after administration of erinacine A or erinacine C (Hsu C.-L. et al., 2023; Lee et al., 2024). Conversely, mouse hippocampal Nrf2 levels were lower in vivo following the administration of erinacine-free H. erinaceus primordium extracts and, were unaffected when HT22 hippocampal neurons and BV2 microglia were exposed to an erinacine-free H. erinaceus fruiting body extract in vitro (Kushairi et al., 2019; Roda et al., 2023) suggesting an erinacine-specific effect on Nrf2. Additionally, both erinacine A and HEM protected dopaminergic neurons in models of neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation (Lee et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021). Conversely, the preservation and elevation of dopaminergic activity was also evident following the in vivo administration of fruiting body or mycelia, suggesting erinacines alone are not responsible for the neuromodulatory effects observed in H. erinaceus administration (Chiu et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2020; Chau et al., 2023).
In vivo, both HEME and HEM that contained a high concentration of erinacine A elevated expression of NGF in specific brain regions such as the hippocampus (Tsai-Teng et al., 2016), although this occurred selectively in astrocytes (Zhang et al., 2017; Rupcic et al., 2018; Rascher et al., 2020). In vitro studies using primary cortical neurons suggest that erinacine A can potentially mimic, at least in part, the neurogenic actions of NGF (Zhang et al., 2017). Previous studies have determined that erinacines induce astrocytic NGF protein expression in vitro (Kawagishi et al., 1994; Mori et al., 2008). NGF-dependent neurogenesis was mediated by TrkA receptor activation and partially reliant on ERK1/2, a downstream effector of TrkA and TrkB that is involved in promoting axonal growth and neuronal survival (Mitchell et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2017). HEME or erinacine A-meditated cell survival and growth through both TrkA and TrkB activation may also be mediated by the downstream PI3K/AKT pathway, which regulates essential cellular processes, inhibits apoptosis, and can increase downstream levels of CREB (Li et al., 2015; Chiu et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2020). CREB can be activated through either p38, PI3K/AKT, or ERK signaling, and is critical for increased long-term potentiation (LTP), a process associated with learning and memory, and thus its implication as a key player in H. erinaceus and erinacine-mediated amelioration of cognitive and behavioural deficits in disease models (Ortega-Martínez, 2015). Direct evidence of CREB activation was observed in vivo after erinacine C administration to TBI-model rats (Lee et al., 2024), however erinacine A and S were not directly investigated. There is evidence that the inhibition of GSK-3β, a downstream target of AKT involved in LTP impairment, provides therapeutic benefits in depression and AD models (Llorens-Marítin et al., 2014). Thus, the reported decrease in GSK-3β observed following administration of HEME enriched in erinacine A (Chiu et al., 2018) may also play a significant role in learning and memory improvements.
Of the analyzed in vivo studies, there was widespread similarity in the behaviours observed in response to administration of the erinacines or H. erinaceus mycelia, with both inducing improvements in motor functioning, learning and memory, and/or natural instinctive behaviour in the various models examined. However, there was variation in the potency of the cellular effects of the individual erinacines. Although erinacine A was the focus of most of the studies, the in vivo effects of erinacine S and erinacine C treatment were also investigated in some reports. The erinacines studied had some similarities in their biological impacts. Amelioration of neuroinflammation by erinacines A, C and S was mediated through the reduced activation of glial cells and decreased release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and likely involve TrkA receptors (Lee et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2022; Rascher et al., 2020). In addition to NGF/TrkA, HEM administration to healthy mice can also induce TrkB activation through increased abundance of BDNF, an effect shown to involve erinacine C, but not erinacine A (Rupcic et al., 2018). In stressed mice, suppressed BDNF levels in whole brain or hippocampus were not only normalized, but elevated beyond that observed in non-stressed controls following HEM administration (Chiu et al., 2018; Li et al., 2021). Importantly, both H. erinaceus ethanolic and aqueous fruiting body extracts increase expression of BDNF protein in models of stress, indicating that erinacines are not the only BDNF-inducing compound found within H. erinaceus (Chong et al., 2021; Chau et al., 2023). Erinacine A and erinacine S were also implicated in their ability to stimulate maturation of oligodendrocytes and myelination in healthy models, whereas erinacine C was unable to potently do so (Huang et al., 2021). Interestingly, erinacine A and erinacine S differed in their therapeutic efficacy in the AD mouse model studies. Erinacine A was more potent at inhibiting amyloid-β plaque formation than erinacine S, particularly within the plaque core formation stage and the production of amyloid-β (Tzeng et al., 2018). Conversely, in a spinal nerve ligation mouse model, erinacine S had a greater ability to suppress ATP-induced purinoceptor activation and produce greater pain alleviating effects than erinacine A (Yang et al., 2020). Given the limited overlap between the erinacine studies, there were many effects attributed to single erinacine molecules that were not investigated using others. For example, erinacine A was seen to maintain astrocytic glutamate homeostasis through preservation of GLT-1 function and to increase expression of excitotoxicity protection machinery in a cerebral ischemia model (Hsu et al., 2022) whereas erinacine S was shown to increase accumulation of neurosteriods in primary cortical mouse neurons (Lin et al., 2023). Taken together, these findings suggest that although erinacines share a cyathane backbone within their chemical structure, they can vary in their potency as well as in their ability to alter select cellular functions. A general trend within the studies was that H. erinaceus or erinacines exerted their effects in a dose-dependent manner, although some exceptions have been reported. Evidence of a a therapeutic effect of H. erinaceus fruiting body extract was apparent in certain disease models, such as in temporal lobe epilepsy model mice (Jang et al., 2019), suggesting there may be an optimal dose range for H. erinaceus, as well as for the erinacines. In vitro evidence also suggests treatment with erinacines at high concentrations can negatively affect cell viability (Lin et al., 2024). Interestingly, erinacine S decreased cell viability more potently than erinacine A or C when administered at the same concentration to BV-2 microglia and SH-SY5Y neuron co-cultures, suggesting the erinacines may have different toxic dose ranges (Lin et al., 2024). However, this was unsupported by in vivo studies, where no dose of erinacines – oral or systemic – decreased the abundance of cell survival markers. The cell viability effects reported in vitro may be a possible reflection of the lack of cellular complexity in these models.
Future considerations
It is noteworthy that sex effects were, for the most part, not evaluated in the in vivo studies. A single study considered the sex-dependent effects of erinacines or H. erinaceus (Lee et al., 2021), whereas the vast majority of studies focused on one sex, most often male subjects. This lack of representation of both sexes may lead to missed therapeutic opportunities and lack of identification of potential sex-specific effects, particularly among females that are most often understudied. Indeed, many studies report sex differences in learning and memory, as well as in several disorders and diseases such as autism spectrum disorders, depression, or neurodegenerative disorders (Altemus et al., 2014; Williams et al., 2021; Aggarwal and Mielke, 2023; Fleischer and Frick, 2023).
In addition to the lack of sex inclusion, there is a lack of quantification of the chemical constituents within H. erinaceus studies in the general literature. This lack of erinacine quantification led to the exclusion of a large majority of H. erinaceus focused studies prior to analysis. This is particularly problematic as numerous factors contribute to the chemical fingerprint of mushrooms, such as the strain used, availability of carbon and nitrogen sources (Dudekula et al., 2020), growth conditions (Corana et al., 2019), as well as the chemical extraction procedure. Strain identification and reporting were not featured across studies. This, together with the lack of consistent reporting of growth conditions, makes it challenging to directly compare the H. erinaceus studies as the ratio of compounds would invariably differ between reports. With respect to extraction methods, the lack of standardization across extract formulations presents a significant limitation. Hot-water, ethanol and methanol-based extraction of mycelium were common approaches, as well as administration of lyophilized crude extracts, each of which would result in differing concentrations of erinacines administered across studies, limiting repeatability and reliability. Additionally, when reporting doses, some studies referred to the dry weight of HEM prior to concentration whereas others referred to the final extract creating confusion for future applications. Taken together, the lack of erinacine concentration reporting given the variability of strain, cultivation, extraction and dosing greatly reduces the translatability and reproducibility of studies using H. erinaceus mycelia. Therefore, future studies should establish standardized protocols for batch-to-batch consistency in HEME formulation.
The use of pure compounds may present a logical alternative for therapeutics given the challenge in creating extracts with the same chemical compositions between laboratories or facilities. A more thorough characterization of the neuroprotective and neurogenic pathways induced by erinacines is required as are investigations into the pharmacokinetics and safety profiles of these compounds. Moreover, although the broad neuroprotective effects of erinacine A, C and S have been identified, the actual binding target(s) of the compounds remain unknown. Future studies should attempt to identify the direct receptor and/or targets in which erinacines associate to produce their neuroprotective effects to gain a deeper understanding of their mechanism of action prior to clinical implementation. Future research should assess erinacine A, C or S administration in parallel with HEM or HEME administrations using equivalents of the individual compounds to dose. In this way it would be possible to discern directly how the biological effects of the whole mushroom or mycelium differs from the individual molecule; that is, whether there is an “entourage effect” from the other sparsely studied compounds such as hericerins and erinacerins.
This systematic review highlights the neuroprotective actions of erinacine compounds in H. erinaceus. We found that erinacines uniquely activate Nrf2 pathways to promote neuroprotection through various signaling mechanisms, with erinacine C demonstrating promise as a neuroprotective agent by elevating BDNF signaling. Additionally, erinacine S yielded analgesic effects for neuropathic pain, underscoring the compound’s potential relevance to public health challenges like neurodegenerative diseases and chronic pain management. Through their observed neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects, associated with reductions in neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, evidence supports the use of erinacines and erinacine-containing compounds as potential therapeutics in neurodegenerative diseases and in preventing overall neurocognitive decline. Furthermore, given the apparent high tolerability observed with HEM/HEME administration, alongside the low cost and accessibility, the study of H. erinaceus for broader therapeutic applications, such as for TBI, anxiety disorders, or major depressive disorder, is recommended.
Statements
Author contributions
ES: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. GB: Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work has been supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (to GGB and MLP). The authors declare that this study received funding from Whitecrest Innovations Inc. (to GGB and MLP). The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article, or the decision to submit it for publication.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the land in Ontario, Canada, on which this research was performed, the ancestral lands of the Attawandaron people, and the treaty lands and territory of the Mississaugas of the Credit First Nation. We also offer our respect to all of the First Nations, Inuit, and Métis peoples, acknowledging their spirituality, traditional knowledge, and cultural diversity. We offer our gratitude for their environmental stewardship from time immemorial.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
- AD
Alzheimer’s Disease
- AKT
Protein kinase B
- APP
Amyloid precursor protein
- ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
- BDNF
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- CREB
cAMP response element-binding protein
- CTX
Cortex
- C/EBP
CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins
- EA
Erinacine A
- EB
Erinacine B
- EC
Erinacine C
- EF
Erinacine F
- EL
Erinacine L
- ERK1/2
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2
- ES
Erinacine S
- EZ1
Erinacine Z1
- EZ2
Erinacine Z2
- GLT-1
Glutamate transporter 1
- GSK-3β
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta
- HE
Hericium erinaceus
- HEM
Hericium erinaceus mycelia
- HEME
Hericium erinaceus mycelia extracts
- Hip
Hippocampus
- H2O2
Hydrogen peroxide
- HO-1
Heme oxygenase-1
- ICR
Institute of Cancer Research
- IFN-γ
Interferon-gamma
- IL-6
Interleukin-6
- iNOS
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- JNK
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- LIMK2
LIM domain kinase 2
- LPS
Lipopolysaccharide
- MAPK
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MPP+
1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium
- MPTP
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
- NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- NGF
Nerve growth factor
- Nrf2
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- NT-3
Neurotrophin-3
- OPC
Oligodendrocytes progenitor cell
- PAK1
p21-activated kinase 1
- PCR
Polymerase chain reaction
- PI3K
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- pCREB
Phosphorylated CREB
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses
- PS1
Presenilin 1
- SAMP8
Senescence Accelerated Mouse-Prone 8
- SCA3
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 3
- SD
Sprague Dawley
- SOD1
Superoxide dismutase 1
- TBI
Traumatic brain injury
- tBT
Tert-butyl hydroperoxide
- tHI
Transient hypoxia-ischemia
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- Trk
Tyrosine receptor kinase
- TrkA
Tyrosine receptor kinase A
- TrkB
Tyrosine receptor kinase B
- Trx
Thioredoxin
- TrxR
Thioredoxin reductase
References
1
Aggarwal N. T. Mielke M. M. (2023). Sex differences in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Clin.41, 343–358. 10.1016/j.ncl.2023.01.001
2
Altemus M. Sarvaiya N. Epperson C. N. (2014). Sex differences in anxiety and depression clinical perspectives. Front. Neuroendocrinol.35, 320–330. 10.1016/j.yfrne.2014.05.004
3
Černelič Bizjak M. Jenko Pražnikar Z. Kenig S. Hladnik M. Bandelj D. Gregori A. et al (2024). Effect of erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus supplementation on cognition: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. J. Funct. Foods115, 106120. 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106120
4
Chau S. C. Chong P. S. Jin H. Tsui K. C. Khairuddin S. Tse A. C. K. et al (2023). Hericium erinaceus promotes anti-inflammatory effects and regulation of metabolites in an animal model of cerebellar ataxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 6089. 10.3390/ijms24076089
5
Chen C.-C. Tzeng T.-T. Chen C.-C. Ni C.-L. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. et al (2016). Erinacine S, a rare sesterterpene from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceus. J. Nat. Prod.79, 438–441. 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b00474
6
Chiu C.-H. Chyau C.-C. Chen C.-C. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. Liu J.-L. et al (2018). Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelium produces antidepressant-like effects through modulating BDNF/PI3K/akt/GSK-3β signaling in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 341. 10.3390/ijms19020341
7
Chong P. S. Poon C. H. Roy J. Tsui K. C. Lew S. Y. Phang M. W. L. et al (2021). Neurogenesis-dependent antidepressant-like activity of Hericium erinaceus in an animal model of depression. Chin. Med.16, 132. 10.1186/s13020-021-00546-8
8
Corana F. Cesaroni V. Mannucci B. Baiguera R. M. Picco A. M. Savino E. et al (2019). Array of metabolites in Italian Hericium erinaceus mycelium, primordium, and sporophore. Molecules24, 3511. 10.3390/molecules24193511
9
Docherty S. Doughty F. L. Smith E. F. (2023). The acute and chronic effects of lion’s mane mushroom supplementation on cognitive function, stress and mood in young adults: a double-blind, parallel groups, pilot study. Nutrients15, 4842. 10.3390/nu15224842
10
Dudekula U. T. Doriya K. Devarai S. K. (2020). A critical review on submerged production of mushroom and their bioactive metabolites. 3 Biotech.10, 337. 10.1007/s13205-020-02333-y
11
Fleischer A. W. Frick K. M. (2023). New perspectives on sex differences in learning and memory. Trends Endocrinol. Metab.34, 526–538. 10.1016/j.tem.2023.06.003
12
Friedman M. (2015). Chemistry, nutrition, and health-promoting properties of Hericium erinaceus (Lion’s Mane) mushroom fruiting bodies and mycelia and their bioactive compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem.63, 7108–7123. 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02914
13
Gonkhom D. Luangharn T. Hyde K. Stadler M. Thongklang N. (2022). Optimal conditions for mycelial growth of medicinal mushrooms belonging to the genus Hericium. Mycol. Prog.21, 82. 10.1007/s11557-022-01829-6
14
He X. Wang X. Fang J. Chang Y. Ning N. Guo H. et al (2017). Structures, biological activities, and industrial applications of the polysaccharides from Hericium erinaceus (Lion’s Mane) mushroom: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.97, 228–237. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.040
15
Hsu C.-H. Liao E.-C. Chiang W.-C. Wang K.-L. (2023). Antioxidative activities of micronized solid-state cultivated Hericium erinaceus rich in erinacine A against MPTP-induced damages. Molecules28, 3386. 10.3390/molecules28083386
16
Hsu C.-L. Wen Y.-T. Hsu T.-C. Chen C.-C. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. et al (2023). Neuroprotective effects of erinacine A on an experimental model of traumatic optic neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24, 1504. 10.3390/ijms24021504
17
Hsu P.-C. Lan Y.-J. Chen C.-C. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. Wang Y.-C. et al (2022). Erinacine A attenuates glutamate transporter 1 downregulation and protects against ischemic brain injury. Life Sci.306, 120833. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120833
18
Huang H.-T. Ho C.-H. Sung H.-Y. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. Chen Y.-W. et al (2021). Hericium erinaceus mycelium and its small bioactive compounds promote oligodendrocyte maturation with an increase in myelin basic protein. Sci. Rep.11, 6551. 10.1038/s41598-021-85972-2
19
Ihlenfeldt W. D. Bolton E. E. Bryant S. H. (2009). The PubChem chemical structure sketcher. J. Cheminformatics1, 20. 10.1186/1758-2946-1-20
20
Jang H.-J. Kim J.-E. Jeong K. H. Lim S. C. Kim S. Y. Cho K.-O. (2019). The neuroprotective effect of Hericium erinaceus extracts in mouse hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20, 859. 10.3390/ijms20040859
21
Kawagishi H. Shimada A. Shirai R. Okamoto K. Ojima F. Sakamoto H. et al (1994). Erinacines A, B and C, strong stimulators of nerve growth factor (NGF)-synthesis, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceus. Tetrahedron Lett.35, 1569–1572. 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)76760-8
22
Kushairi N. Phan C. W. Sabaratnam V. David P. Naidu M. (2019). Lion’s Mane mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. -induced oxidative damage and LPS-induced inflammation in HT22 hippocampal neurons and BV2 microglia. Antioxidants8, 261. 10.3390/antiox8080261
23
Lanzillotta A. Porrini V. Bellucci A. Benarese M. Branca C. Parrella E. et al (2015). NF-κB in innate neuroprotection and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurol.6, 98. 10.3389/fneur.2015.00098
24
Lee K.-F. Chen J.-H. Teng C.-C. Shen C.-H. Hsieh M.-C. Lu C.-C. et al (2014). Protective effects of Hericium erinaceus mycelium and its isolated erinacine A against ischemia-injury-induced neuronal cell death via the inhibition of iNOS/p38 MAPK and nitrotyrosine. Int. J. Mol. Sci.15, 15073–15089. 10.3390/ijms150915073
25
Lee K.-F. Hsieh Y.-Y. Tung S.-Y. Teng C.-C. Cheng K.-C. Hsieh M.-C. et al (2024). The cerebral protective effect of novel erinacines from Hericium erinaceus mycelium on in vivo mild traumatic brain injury animal model and primary mixed glial cells via Nrf2-dependent pathways. Antioxidants13, 371. 10.3390/antiox13030371
26
Lee K.-F. Tung S.-Y. Teng C.-C. Shen C.-H. Hsieh M. C. Huang C.-Y. et al (2020). A derived diterpenoid of H. erinaceus, attenuates neurotoxicity in MPTP model of. Antioxidants9, 137. 10.3390/antiox9020137
27
Lee L.-Y. Chou W. Chen W.-P. Wang M.-F. Chen Y.-J. Chen C.-C. et al (2021). Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelium delays progression of age-related cognitive decline in senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) mice. Nutrients13, 3659. 10.3390/nu13103659
28
Lee S.-L. Hsu J.-Y. Chen T.-C. Huang C.-C. Wu T.-Y. Chin T.-Y. (2022). Erinacine A prevents lipopolysaccharide-mediated glial cell activation to protect dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory factor-induced cell death in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23, 810. 10.3390/ijms23020810
29
Li I.-C. Lee L.-Y. Tzeng T.-T. Chen W.-P. Chen Y.-P. Shiao Y.-J. et al (2018). Neurohealth properties of Hericium erinaceus mycelia enriched with erinacines. Behav. Neurol.2018, 5802634. 10.1155/2018/5802634
30
Li T.-J. Lee T.-Y. Lo Y. Lee L.-Y. Li I.-C. Chen C.-C. et al (2021). Hericium erinaceus mycelium ameliorate anxiety induced by continuous sleep disturbance in vivo. BMC Complement. Med. Ther.21, 295. 10.1186/s12906-021-03463-3
31
Li X. Lavigne P. Lavoie C. (2015). GGA3 mediates TrkA endocytic recycling to promote sustained Akt phosphorylation and cell survival. Mol. Biol. Cell26, 4412–4426. 10.1091/mbc.E15-02-0087
32
Lin C.-Y. Chen Y.-J. Hsu C.-H. Lin Y.-H. Chen P.-T. Kuo T.-H. et al (2023). Erinacine S from Hericium erinaceus mycelium promotes neuronal regeneration by inducing neurosteroids accumulation. J. Food Drug Anal.31, 32–54. 10.38212/2224-6614.3446
33
Lin J.-Y. Chen Y.-P. Lin T.-W. Li T.-J. Chen Y.-W. Li I.-C. et al (2024). Discovery of a new compound, erinacerin W, from the mycelia of Hericium erinaceus, with immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects. Molecules29, 812. 10.3390/molecules29040812
34
Liu M. Liu L. Song X. Zhou Y. Peng Y. Xie C. et al (2024). Isolation and evaluation of erinacine A contents in mycelia of Hericium erinaceus strains. Foods13, 1649. 10.3390/foods13111649
35
Llorens-Marítin M. Jurado J. Hernández F. Ávila J. (2014). GSK-3β, a pivotal kinase in Alzheimer disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci.7, 46. 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00046
36
Łysakowska P. Sobota A. Wirkijowska A. (2023). Medicinal mushrooms: their bioactive components, nutritional value and application in functional food production-a review. Molecules28, 5393. 10.3390/molecules28145393
37
Malík M. Tlustoš P. (2022). Nootropics as cognitive enhancers: types, dosage and side effects of smart drugs. Nutrients14, 3367. 10.3390/nu14163367
38
Mitchell D. J. Blasier K. R. Jeffery E. D. Ross M. W. Pullikuth A. K. Suo D. et al (2012). Trk activation of the ERK1/2 kinase pathway stimulates intermediate chain phosphorylation and recruits cytoplasmic dynein to signaling endosomes for retrograde axonal transport. J. Neurosci.32, 15495–15510. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5599-11.2012
39
Mori K. Inatomi S. Ouchi K. Azumi Y. Tuchida T. (2009). Improving effects of the mushroom Yamabushitake (Hericium erinaceus) on mild cognitive impairment: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother. Res.23, 367–372. 10.1002/ptr.2634
40
Mori K. Obara Y. Hirota M. Azumi Y. Kinugasa S. Inatomi S. et al (2008). Nerve growth factor-inducing activity of Hericium erinaceus in 1321N1 human astrocytoma cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull.31, 1727–1732. 10.1248/bpb.31.1727
41
Niego A. G. Rapior S. Thongklang N. Raspé O. Jaidee W. Lumyong S. et al (2021). Macrofungi as a nutraceutical source: promising bioactive compounds and market value. J. Fungi7, 397. 10.3390/jof7050397
42
Onaolapo A. Y. Obelawo A. Y. Onaolapo O. J. (2019). Brain ageing, cognition and diet: a review of the emerging roles of food-based nootropics in mitigating age-related memory decline. Curr. Aging Sci.12, 2–14. 10.2174/1874609812666190311160754
43
Ortega-Martínez S. (2015). A new perspective on the role of the CREB family of transcription factors in memory consolidation via adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci.8, 46. 10.3389/fnmol.2015.00046
44
Pepe M. Hesami M. de la Cerda K. A. Perreault M. L. Hsiang T. Jones A. M. P. (2023). A journey with psychedelic mushrooms: from historical relevance to biology, cultivation, medicinal uses, biotechnology, and beyond. Biotechnol. Adv.69, 108247. 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108247
45
Phan C.-W. Lee G.-S. Hong S.-L. Wong Y.-T. Brkljača R. Urban S. et al (2014). Hericium erinaceus (Bull.: Fr) Pers. cultivated under tropical conditions: isolation of hericenones and demonstration of NGF-mediated neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via MEK/ERK and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. Food Funct.5, 3160–3169. 10.1039/c4fo00452c
46
Rai S. N. Mishra D. Singh P. Vamanu E. Singh M. P. (2021). Therapeutic applications of mushrooms and their biomolecules along with a glimpse of in silico approach in neurodegenerative diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother.137, 111377. 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111377
47
Rascher M. Wittstein K. Winter B. Rupcic Z. Wolf-Asseburg A. Stadler M. et al (2020). Erinacine C activates transcription from a consensus ETS DNA binding site in astrocytic cells in addition to NGF induction. Biomolecules10, 1440. 10.3390/biom10101440
48
Roda E. De Luca F. Ratto D. Priori E. C. Savino E. Bottone M. G. et al (2023). Cognitive healthy aging in mice: boosting memory by an ergothioneine-rich Hericium erinaceus primordium extract. Biology12, 196. 10.3390/biology12020196
49
Rupcic Z. Rascher M. Kanaki S. Köster R. W. Stadler M. Wittstein K. (2018). Two new cyathane diterpenoids from mycelial cultures of the medicinal mushroom Hericium erinaceus and the rare species, Hericium flagellum. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 740. 10.3390/ijms19030740
50
Saragovi H. U. Galan A. Levin L. A. (2019). Neuroprotection: pro-survival and anti-neurotoxic mechanisms as therapeutic strategies in neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci.13, 231. 10.3389/fncel.2019.00231
51
Schifano F. Catalani V. Sharif S. Napoletano F. Corkery J. M. Arillotta D. et al (2022). Benefits and harms of ‘smart drugs’ (nootropics) in healthy individuals. Drugs82, 633–647. 10.1007/s40265-022-01701-7
52
Shen T. Morlock G. Zorn H. (2015). Production of cyathane type secondary metabolites by submerged cultures of Hericium erinaceus and evaluation of their antibacterial activity by direct bioautography. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol.2, 8. 10.1186/s40694-015-0018-y
53
Spelman K. Sutherland E. Bagade A. (2017). Neurological activity of lion’s mane (Hericium erinaceus). J. Restor. Med.6, 19–26. 10.14200/jrm.2017.6.0108
54
Tsai-Teng T. Chin-Chu C. Li-Ya L. Wan-Ping C. Chung-Kuang L. Chien-Chang S. et al (2016). Erinacine A-enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelium ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in APPswe/PS1dE9 transgenic mice. J. Biomed. Sci.23, 49. 10.1186/s12929-016-0266-z
55
Tzeng T.-T. Chen C.-C. Chen C.-C. Tsay H.-J. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. et al (2018). The cyanthin diterpenoid and sesterterpene constituents of Hericium erinaceus mycelium ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease-related pathologies in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci.19, 598. 10.3390/ijms19020598
56
Venturella G. Ferraro V. Cirlincione F. Gargano M. L. (2021). Medicinal mushrooms: bioactive compounds, use, and clinical trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22, 634. 10.3390/ijms22020634
57
Wang L.-Y. Huang C.-S. Chen Y.-H. Chen C.-C. Chen C.-C. Chuang C.-H. (2019). Anti-inflammatory effect of erinacine C on NO production through down-regulation of NF-κB and activation of Nrf2-mediated HO-1 in BV2 microglial cells treated with LPS. Molecules24, 3317. 10.3390/molecules24183317
58
Wei J. Li J.-Y. Feng X.-L. Zhang Y. Hu X. Hui H. et al (2023). Unprecedented neoverrucosane and cyathane diterpenoids with anti-neuroinflammatory activity from cultures of the culinary-medicinal mushroom Hericium erinaceus. Molecules28, 6380. 10.3390/molecules28176380
59
Williams O. O. F. Coppolino M. Perreault M. L. (2021). Sex differences in neuronal systems function and behaviour: beyond a single diagnosis in autism spectrum disorders. Transl. Psychiatry11, 625–629. 10.1038/s41398-021-01757-1
60
Wu Y.-L. Chen S.-C. Chang J.-C. Lin W.-Y. Chen C.-C. Li C.-C. et al (2023). The protective effect of erinacine A–enriched Hericium erinaceus mycelium ethanol extract on oxidative Stress–Induced neurotoxicity in cell and Drosophila. Biol. Med.195, 1–12. 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.12.005
61
Yang P.-P. Chueh S.-H. Shie H.-L. Chen C.-C. Lee L.-Y. Chen W.-P. et al (2020). Effects of Hericium erinaceus mycelium extracts on the functional activity of purinoceptors and neuropathic pain in mice with L5 spinal nerve ligation. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med.2020, 2890194. 10.1155/2020/2890194
62
Zhang C.-C. Cao C.-Y. Kubo M. Harada K. Yan X.-T. Fukuyama Y. et al (2017). Chemical constituents from Hericium erinaceus promote neuronal survival and potentiate neurite outgrowth via the TrkA/Erk1/2 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci.18, 1659. 10.3390/ijms18081659
Summary
Keywords
erinacine, Hericium erinaceus , neuroprotection, neuroinflammation, cognitive function, neurodegenerative diseases
Citation
Spangenberg ET, Moneypenny A, Bozzo GG and Perreault ML (2025) Unveiling the role of erinacines in the neuroprotective effects of Hericium erinaceus: a systematic review in preclinical models. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1582081. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1582081
Received
23 February 2025
Accepted
03 June 2025
Published
23 June 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Miao Liu, Harvard Medical School, United States
Reviewed by
Ulrike Lindequist, University of Greifswald, Germany
Kinga Sałaciak, Jagiellonian University Medical College, Poland
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Spangenberg, Moneypenny, Bozzo and Perreault.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: M. L. Perreault, perreaum@uoguelph.ca
†ORCID: M. L. Perreault, orcid.org/0000-0002-5775-8950
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.