- 1Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
- 2Haihe Laboratory of Modern Chinese Medicine, Tianjin, China
- 3KM Science Research Division, Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine, Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Objective: The aim of this study is to review the recent studies on the pharmacology and mechanism of action of Monascus purpureus Went, analyze its medicinal value, and explore future research directions.
Method: A scoping review was conducted by searching the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang database, VIP database, SinoMed, and PubMed from inception until September 2024. The basic information of the included studies, such as study types, disease types, main components, outcomes, and efficacy, was reviewed and summarized. Methodological quality was assessed using the SYRCLE’s risk of bias assessment tool for animal studies and the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool for clinical trials.
Results: We identified 251 studies from the five databases. Among them, 153 were experimental studies, 70 were reviews, and 28 were clinical trials. Of the experimental studies, molecular studies accounted for the largest portion, totaling 80 (52%). Among the reviews, research progress accounted for the most, totaling 41 (59%). The clinical trials studied the effects of Monascus purpureus Went and its related Chinese patent medicines and preparations. Of these, 17 (61%) used Monascus purpureus Went-related Chinese patent medicines and preparations as interventions and 11 (39%) used traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulations of Monascus purpureus Went as interventions. In terms of methodological quality, both animal studies and clinical trials related to Monascus purpureus Went showed deficiencies in randomized allocation sequence generation, allocation concealment, and blinding methods.
Conclusion: We summarized existing studies on the active ingredients and effects of Monascus purpureus Went and found that it is necessary to improve the generation of random allocation sequences and the application of the blinding method in Monascus purpureus Went-related animal studies and clinical trials. When similar studies are conducted in the future, the specific methods of random assignment should be more clearly described, and blinding methods should be applied to improve the objectivity and accuracy of the studies, thereby providing a reference for selecting future research directions and establishing supporting evidence.
1 Introduction
Monascus purpureus Went is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) with a long history, produced through the fermentation of ordinary rice using Monascus species (Chen et al., 2000). It is mainly produced in Fujian, Zhejiang, and Jiangxi. Additionally, Monascus purpureus Went is sweet in taste, warm in nature, and belongs to the liver, spleen, stomach, and large intestine meridians, according to TCM theory. It is recorded in the Supplement to Augmented Materia Medica that Monascus purpureus Went has the effects of “promoting blood circulation and helping digestion, strengthening the spleen and warming the stomach, treating dysentery, and bringing down water.” Clinically, Monascus purpureus Went is mainly used to treat postpartum lochia, abdominal pain with stagnation, food accumulation and fullness, dysentery, and bruises (Song et al., 1999a).
In 2024, Japan’s Kobayashi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. experienced a safety incident involving “health products containing Monascus purpureus Went ingredients.” After investigation, the issue was potentially caused by contamination of the Monascus purpureus Went fermentation raw materials with penicillic acid or by inadequate cleanliness in the production environment, lead to the presence of penicillium mixed. This incident once again brought the efficacy and safety of red yeast into the global social hot spot (Ma 2025; Sun, 2025; Zhu et al., 2025).
Modern pharmacology has discovered that Monascus purpureus Went has lipid-lowering, anti-tumor, antioxidant, anti-osteoporosis, antibacterial, and other effects (Wei et al., 2023). In addition, Monascus purpureus Went has a wide range of applications in brewing, fermented foods, food coloring, and other fields. In recent years, new application fields have been gradually developed, such as animal husbandry and veterinary medicine, feed fermentation, healthy fermented foods, healthy drinks, and healthy seasonings (Xie, 1996). In recent years, the extraction of the lipid-lowering component lovastatin from Monascus purpureus Went (Endo, 1980) has further enhanced the research value of Monascus purpureus Went, attracting great attention from scholars both at home and abroad. The significant lipid-lowering effect and medicinal potential of lovastatin have inspired many scholars to conduct studies on the pharmacology and mechanism of action of this new component in Monascus purpureus Went, resulting in many remarkable findings, such as studying the lipid-lowering mechanism and content determination method of lovastatin (Wen et al., 2001), optimizing the extraction process of lovastatin from Monascus purpureus Went (Wang et al., 2024a), and producing drugs mainly composed of lovastatin, such as Xuezhikang (Kong et al., 2005). At present, the pharmacological research on Monascus purpureus Went still needs to be improved to further understand and develop its medicinal value and expand its application range.
A large number of studies on Monascus purpureus Went have been published, including reviews (Wang et al., 2024b). However, these published reviews lacked a comprehensive literature search, which led to limited references and unreliable evidence evaluation. Such limitations may introduce certain biases into the review, which is not conducive to the reference of other studies. In contrast, this study conducts a scoping review based on evidence-based medicine methods to systematically summarize the recent studies on the pharmacology and mechanism of action of Monascus purpureus Went, analyze its medicinal value, and explore future research directions.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Search strategy
Five databases, namely, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang database, VIP database, SinoMed, and PubMed, were searched from inception to September 2024. The search terms consisted of Monascus purpureus Went, Monascus, Monascus purpureus Went, pharmacology, pharmacological effect, pharmacological mechanism, biological activity, and active ingredient. The full search terms of all databases are shown in Supplementary Add S1.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: Studies focused on Monascus purpureus Went; study types were not limited, and the language was English or Chinese.
Exclusion criteria: Manuscripts with unavailable full text and duplicate publications were excluded. News reports, conference papers, or dissertations were also excluded.
2.3 Study screening and data extraction
The screening and extraction process was as follows: 1) NoteExpress software was used to exclude duplicate studies, 2) two reviewers performed an initial screening after reading the titles and abstracts based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, 3) the full text was reviewed when additional information was needed for screening, and 4) any disagreements were resolved through discussion with a third researcher.
The basic information in the included studies, such as title, authors, year of publication, type of study, subject of study, study population, study method, intervention, duration of treatment, dosage, control measure, measurement index, method of measurement, result, and conclusion, was extracted.
2.4 Data analysis
We analyzed all extracted data fields, including bibliometric statistics, visual data analysis, and evidence graph analysis. We also systematically organized and comprehensively summarized study evidence information.
2.5 Quality assessment
Two reviewers assessed the methodological quality of the included studies, including animal studies and clinical trials, as this is an integral part of evidence-based research. The SYRCLE’s risk of bias assessment tool was used to assess the quality of animal studies, and the Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool was used to assess the quality of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). The evaluation results were indicated as “low risk,” “high risk,” or “unclear risk.”
3 Results
3.1 Search results
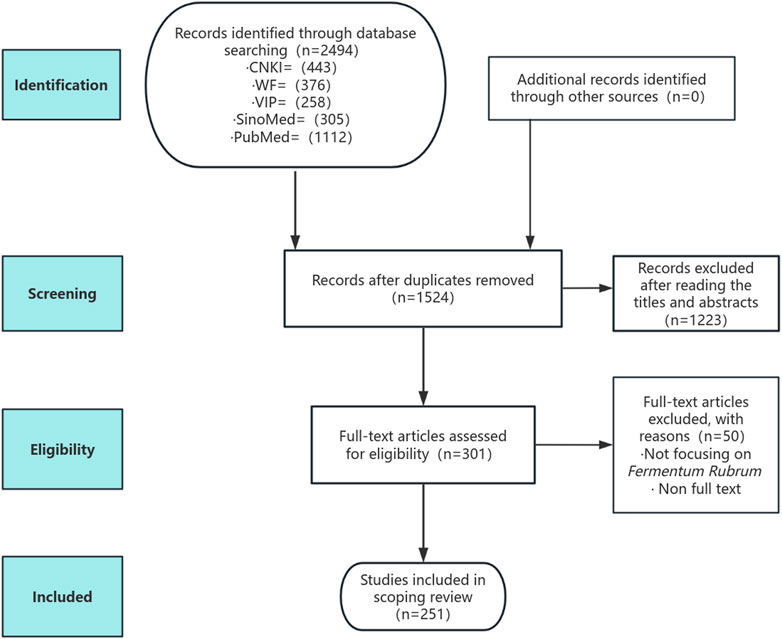
A total of 2,494 studies were initially searched. Among them, 970 were duplicates, and 1,223 were excluded after reading the title or abstract. Among 301 studies assessed in full text, 50 were excluded for the following reasons: not focusing on Monascus purpureus Went (n = 41) and lack of full text (n = 9). Finally, 251 studies were included in the final review.
The study screening process is presented in Figure 1.
3.2 Characteristics of included studies
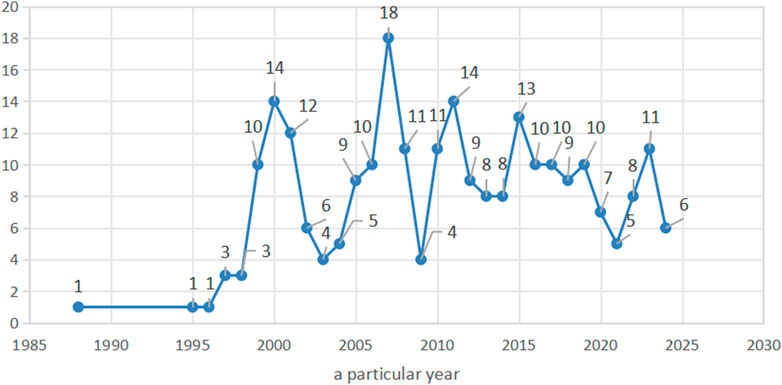
A total of 251 literature studies were included, comprising 242 Chinese publications (96%) and 9 English publications (4%). There were 153 experimental studies (61%), 70 reviews (28%), and 28 clinical trials (11%). The included studies were published between 1988 and 2024, with the highest number published in 2007 (n = 18). The number of studies published each year is presented in Figure 2.
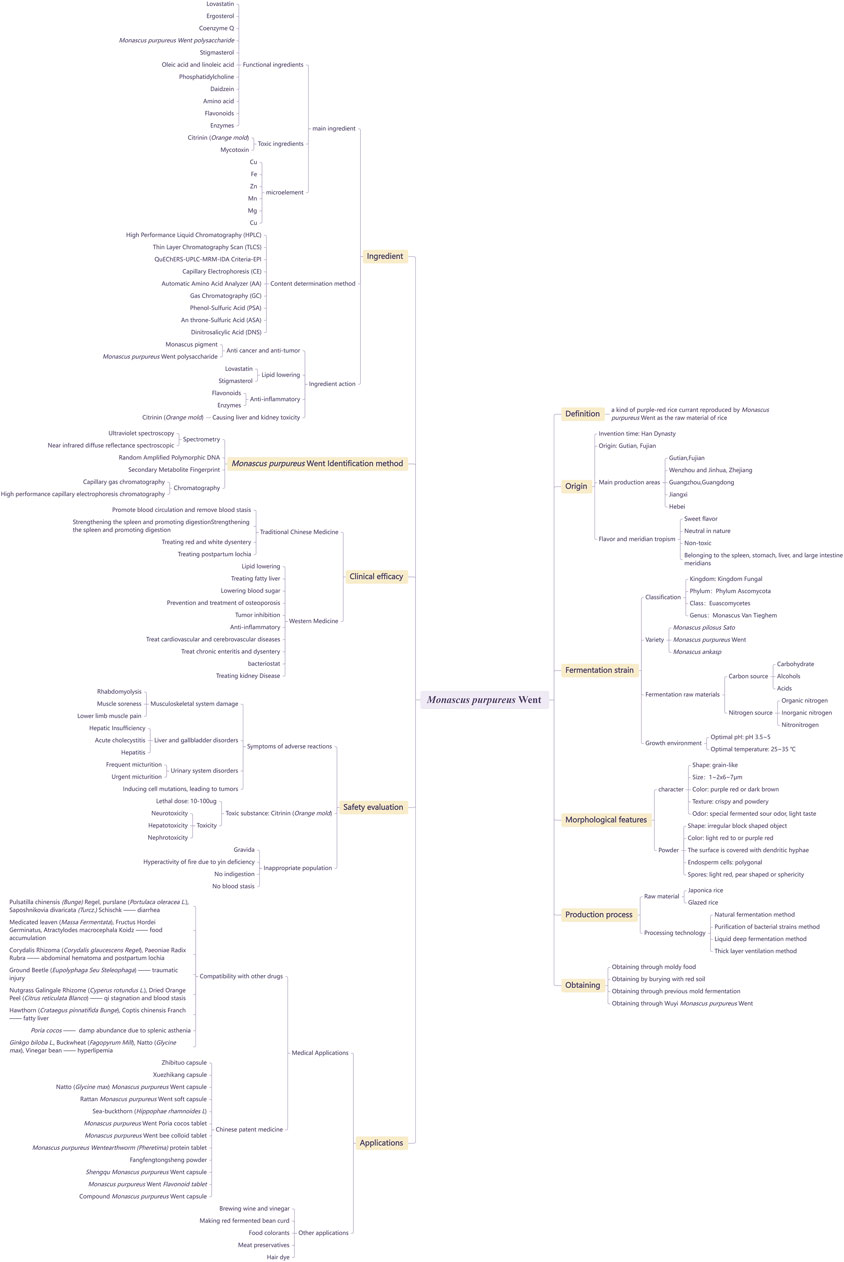
We summarized and generalized evidence from studies on Monascus purpureus Went, including its definition, origin, fermentation strain, morphological features, production process, acquisition methods, ingredients, identification methods, clinical efficacy, safety evaluation, and applications. The chart of evidence from studies on Monascus purpureus Went is presented in Figure 3.
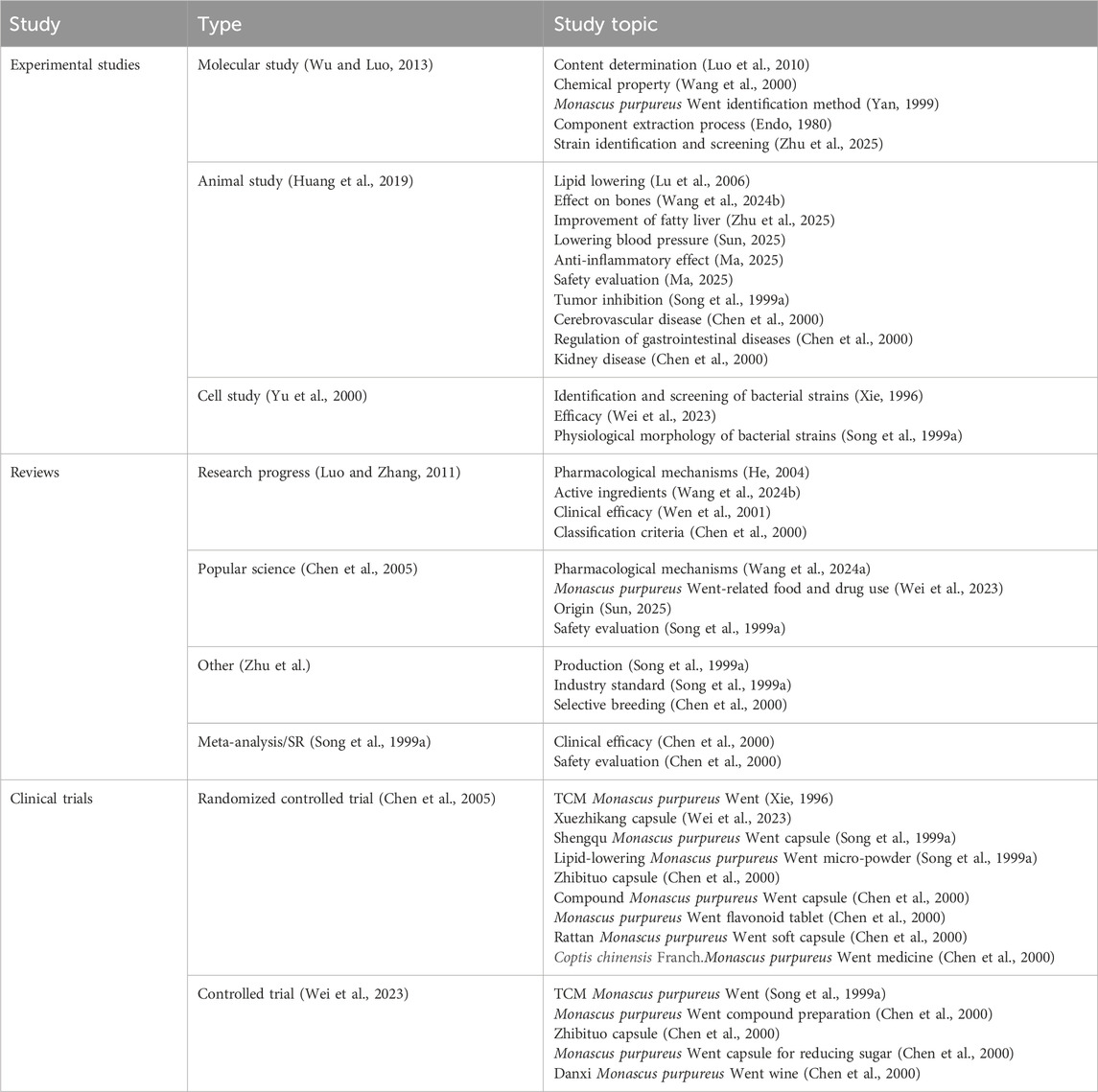
Among the experimental studies, molecular studies accounted for most of them, totaling 80 (52%). Among the reviews, research progress accounted for most of the studies, totaling 41 (59%). Clinical trials studied the effects of Monascus purpureus Went and its related Chinese patent medicine in the treatment of diseases, with 17 (61%) using Monascus purpureus Went-related Chinese patent medicines and preparations as interventions and 11 (39%) using TCM formulations of Monascus purpureus Went as interventions. The details of the research topics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
3.3 Experimental study
3.3.1 Molecular study
Eighty molecular studies related to Monascus purpureus Went were included.
3.3.1.1 Content determination
Forty studies determined the content of active ingredients in Monascus purpureus Went, with lovastatin and citrinin (orange mold) being the most common ingredients. The methods for content determination included high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) (n = 29), thin-layer chromatography scan (TLCS) (n = 2), capillary electrophoresis (CE) (n = 2), automatic amino acid analyzer (AA) (n = 2), gas chromatography (GC) (n = 1), quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, safe–ultra-performance liquid chromatography–multiple reaction monitoring–ion-dependent acquisition–criteria-enhanced product ion (QuEChERS-UPLC-MRM-IDA-Criteria-EPI) (n = 1), phenol–sulfuric acid (PSA) (n = 1), anthrone–sulfuric acid (ASA) (n = 1), dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) (n = 1), flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) (n = 1), and statistical analyses including statistical package for the social sciences principal component analysis and cluster analysis (SPSS PCA and SPSS CA) (n = 1).
3.3.1.2 Chemical property
Fourteen studies examined the chemical properties of the active ingredients in Monascus purpureus Went, including antioxidant activity (n = 5), chemical structure (n = 5), lipid-lowering activity (n = 2), poisoning mechanism (n = 1), and protease and amylase activities (n = 1).
3.3.1.3 Monascus purpureus Went identification method
Thirteen studies examined the methods for identifying different Monascus purpureus Went strains using chromatography (n = 6), spectroscopy (n = 4), random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) (n = 2), and secondary metabolite fingerprint (SMF) (n = 1).
3.3.1.4 Component extraction process
Eight studies investigated the extraction process of active ingredients in Monascus purpureus Went.
(1) Lovastatin: One study used 88% ethanol in an amount 13 times that of the raw material, with reflux extraction for 1.3 hours (n = 1); another study used six times the amount of 95% ethanol, with reflux extraction performed twice, each for 0.5 hours (n = 1); and a third study used 250 mL of ethanol, with reflux for 5 hours (n = 1).
(2) Monacolin K: One study used 70% ethanol (pH 7.5) with a material-to-solvent ratio of 1:30, an extraction time of 1.5 hours, and an extraction temperature of 50°C (n = 1); another study used pure methanol with an extraction temperature 60°C, a liquid-to-solid ratio of 20:1, and ultrasonic extraction for 1 hour (n = 1); and a third used 65% ethanol with a material-to-liquid ratio of 1:20, an extraction temperature of 70°C, and an extraction time of 3 hours (n = 1).
(3) Total flavonoid: One study used analytically pure ethanol and ultrasonic (50 kHz, 250 W) extraction for 20 min, followed by adsorption using 1 g of polyamide powder. The sample was then transferred to a chromatography column (inner diameter 1.0 cm) and eluted with methanol elution (0.5 mL/min) (n = 1).
(4) Monascus purpureus Went pigment: One study used a 70% ethanol aqueous solution with an extraction temperature of 60°C and an extraction time of 2 hours (n = 1).
3.3.1.5 Strain identification and screening
Five studies examined the identification and screening of Monascus purpureus Went strains based on molecular biology.
3.3.2 Animal study
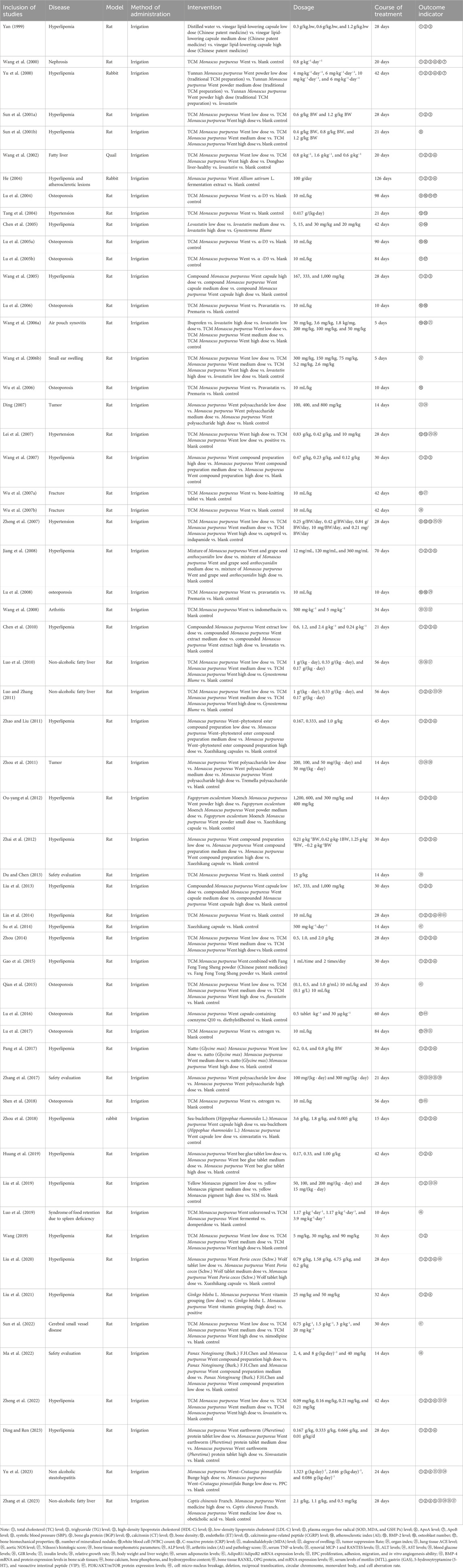
Among the 58 animal studies, 54 used rat models (93%), 3 used rabbit models, and 1 used the quail model. A total of 55 studies determined the efficacy of Monascus purpureus Went, including double-armed studies (n = 6), three-armed studies (n = 10), and multi-armed studies (n = 39). Three studies determined the safety of erythromycin, including a two-armed study (n = 1), a three-armed study (n = 1), and a multi-armed study (n = 1). Fifty-four studies contained a blank control, and four studies did not contain a blank control.
Among them, 26 studies showed that Monascus purpureus Went had lipid lowering effects, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 5), Monascus purpureus Went compound preparation (n = 3), vinegar bean lipid-lowering capsule (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went earthworm (Pheretima) protein tablet (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went Allium sativum L. fermentation extract (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf tablet (n = 1), compounded Monascus purpureus Went capsule (n = 1), a mixture of Monascus purpureus Went and grape seed anthocyanidin (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went bee glue tablet (n = 1), Xuezhikang capsule (n = 1), lovastatin (n = 1), natto (Glycine max) Monascus purpureus Went (n = 1), Ginkgo biloba L. Monascus purpureus Went vitamin grouping (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went combined with Fang Feng Tong Sheng powder (n = 1), Fagopyrum esculentum Moench Monascus purpureus Went powder (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went–phytosterol ester compound preparation (n = 1), Yunnan Monascus purpureus Went powder (n = 1), compounded Monascus purpureus Went extract (n = 1), yellow Monascus pigment (n = 1), and sea-buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) Monascus purpureus Went capsule (n = 1). Twelve studies showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on repairing bones, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 11) and Monascus purpureus Went capsule-containing coenzyme Q10 (n = 1); five studies showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on improving fatty liver, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 3), Monascus purpureus Went Crataegus pinnatifida Bunge (n = 1), and Coptis chinensis Franch. Monascus purpureus Went medicine (n = 1); four studies showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on lowering blood pressure, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 4); three studies showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on anti-inflammation, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 3); three studies showed a good safety profile of Monascus purpureus Went, involving Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharide (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went extract (n = 1), and Panax Notoginseng (Burk.) F.H.Chen Monascus purpureus Went compound preparation (n = 1); two studies showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on tumor inhibition, involving Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharide (n = 2); one study showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on cerebrovascular disease, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 1); one study showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on regulating the gastrointestinal tract, involving TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 1); and one study showed that Monascus purpureus Went had an effect on treating renal disease, involving Monascus purpureus Went extract (n = 1).
Among these studies, the most commonly used dose was 0.625 g/mL of aqueous Monascus purpureus Went solution, administered via irrigation at 10 mL/kg, and the most commonly used course of treatment was 28 days. The specific information on animal studies is presented in Table 2.
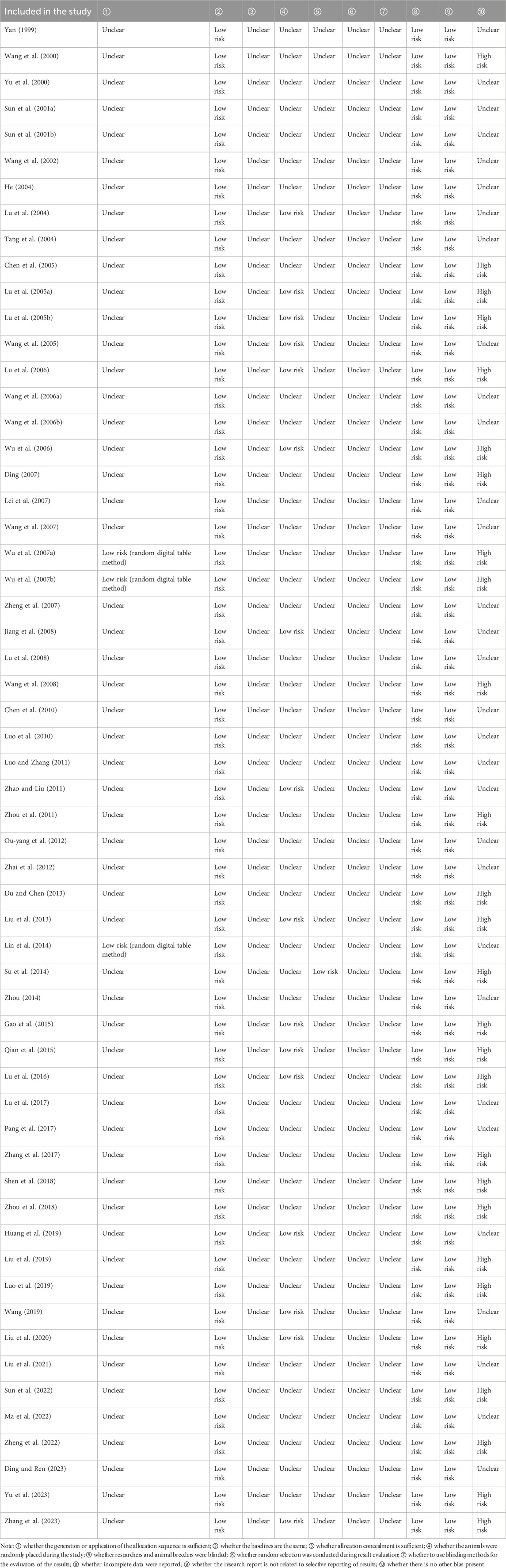
All 58 animal studies were randomized controlled studies. Among them, 55 studies only reported “randomization,” and 3 used the random number table method. A total of 58 studies reported that the experimental group was consistent with the control group at baseline. Fifty-seven studies did not report allocation concealment and blinding, and only one blinded the investigator and the animal keeper. Forty-two studies did not report whether the environments in which the animals were placed were randomized or not, and 16 studies reported that the animals were grown in the same environments; no missing data appeared. The risk of bias assessment of animal studies is presented in Table 3.
3.3.3 Cell study
Fifteen cellular studies related to Monascus purpureus Went were included. Seven studies focused on the identification and screening of Monascus purpureus Went bacterial strains using cell biology techniques. Six studies determined the efficacy of Monascus purpureus Went, including the synthesis and in vitro anticancer activity of Monascus purpureus Went derivatives (n = 1), the blood pressure-lowering mechanism of Monascus purpureus Went (n = 1), the effect of Monascus purpureus Went on the secretion of TNF-alpha by peripheral blood single-nucleated cells of ankylosing spondylitis patients (n = 1), the effect of erythrocytes on the cell growth and molecular mechanisms of HCT-116 cells (n = 1), the effect of Monascus purpureus Went on the proliferation of myocardial fibroblasts (n = 1), and the role of Monascus purpureus Went in inducing apoptosis and autophagy in human colon cancer cells (n = 1).
Two studies examined the physiological characteristics of Monascus purpureus Went and Monascus purpureus Went (n = 1) and the morphological characteristics of TCM Monascus purpureus Went (n = 1).
3.4 Clinical trial
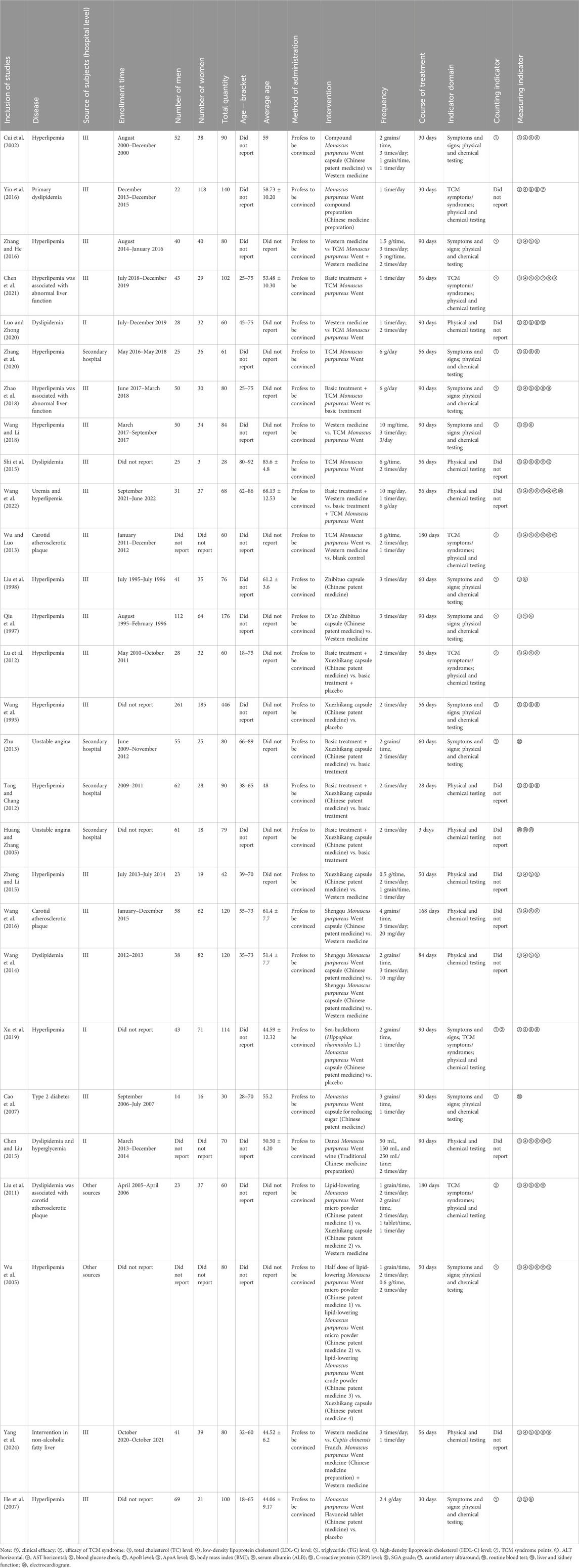
A total of 28 clinical trials studied the effects of TCM Monascus purpureus Went and its related Chinese patent medicine and preparation, including double-armed trials (n = 18), single-armed trials (n = 6), three-armed trials (n = 3), and multiple-armed trials (n = 1). One study was set up with a blank control, and four were set up with a placebo. The mode of administration was oral. Patient sources included tertiary hospitals (n = 19), secondary hospitals (n = 7), and other sources (n = 2). Diseases included dyslipidemia (n = 22), carotid atherosclerotic plaque (n = 3), unstable angina (n = 2), abnormal liver function (n = 2), hyperglycemia (n = 1), type 2 diabetes (n = 1), uremia (n = 1), and fatty liver (n = 1).
Among them, 19 studies examined the effects of Chinese patent medicines and preparations related to Monascus purpureus Went, including Xuezhikang capsule (n = 6), Zhibituo capsule (n = 2), Shengqu Monascus purpureus Went capsule (n = 2), lipid-lowering Monascus purpureus Went micro-powder (n = 2), Monascus purpureus Went compound preparation (n = 1), compound Monascus purpureus Went capsule (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went capsule for reducing sugar (n = 1), Monascus purpureus Went flavonoid tablet (n = 1), rattan Monascus purpureus Went soft capsule (n = 1), Danxi Monascus purpureus Went wine (n = 1), and C. chinensis Franch. Monascus purpureus Went medicine (n = 1); nine studies determined the clinical therapeutic effect of TCM Monascus purpureus Went.
Among them, the most commonly used dose of TCM Monascus purpureus Went was 6 g/dose, administered once daily, with a treatment course of 90 days; the most commonly used dose of Xuezhikang capsule was 2 capsules/dose, administered twice daily, and the course of treatment was 56 days; the most commonly used dose of Zhibituo capsule was 1.05 g/dose, administered thrice daily, with a treatment course of 60 or 90 days; the most commonly used dose of Shengqu Monascus purpureus Went capsule was 2 capsules/dose or 4 capsules/dose, and the course of treatment was 84 or 168 days; and the most commonly used dose of lipid-lowering Monascus purpureus Went micro-powder was 1 capsule/dose, administered thrice daily, with a treatment course of 50 or 180 days.
In terms of indicator domains, physical and chemical testing indicators were applied 28 times, symptom and sign indicators were applied 13 times, and TCM symptom/syndrome indicators were applied six times.
For counting indicators, clinical efficacy was applied 14 times, and TCM evidence efficacy was applied four times. Measurement indicators included lipid levels (n = 25), liver and kidney functions (n = 6), blood routine (n = 2), TCM evidence points (n = 2), blood glucose levels (n = 2), body mass index (n = 2), serum inflammatory factor (n = 2), electrocardiography (n = 1), SGA scores (n = 1), and carotid ultrasound (n = 1). The specific information on clinical trials is presented in Table 4.
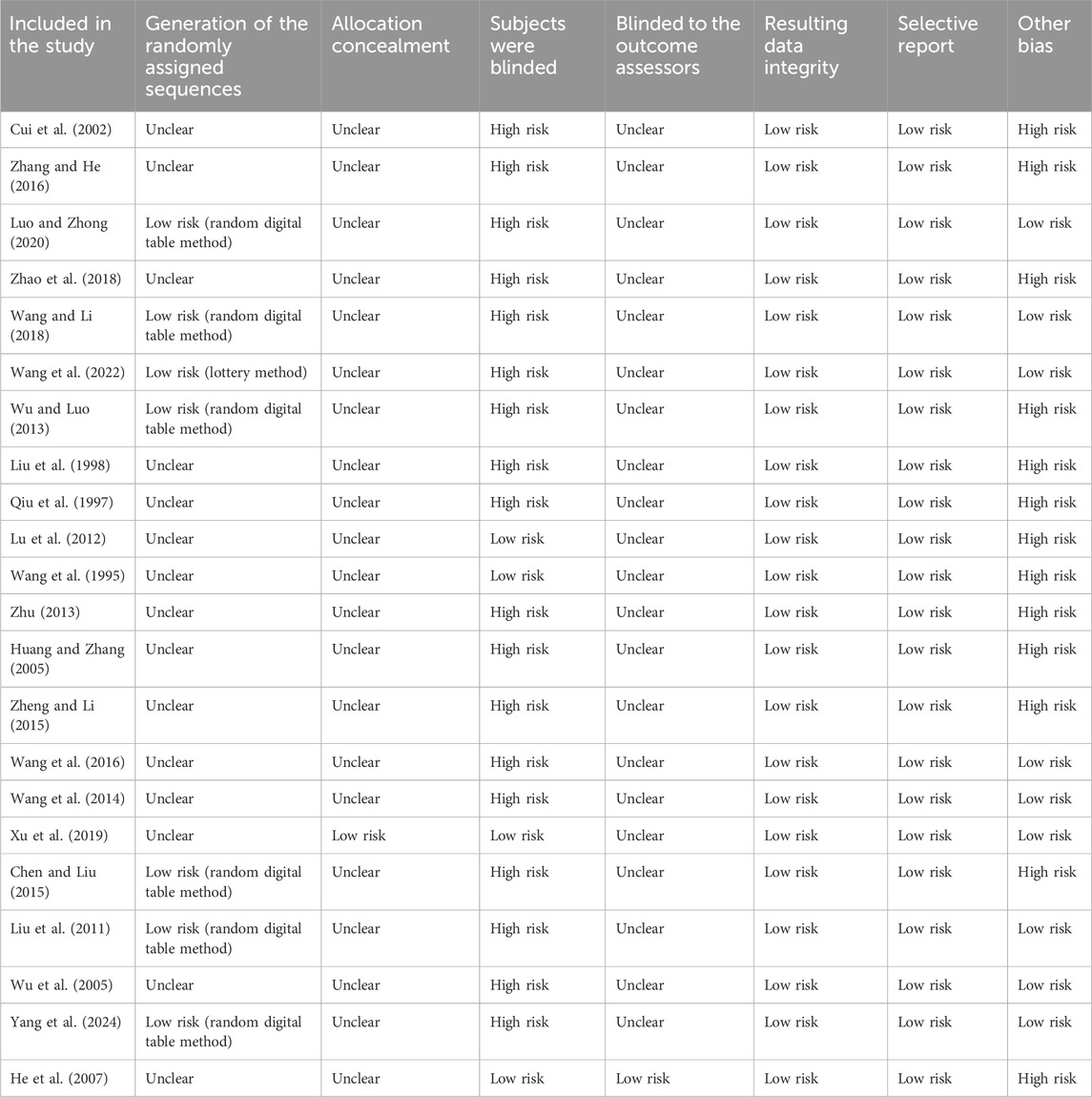
A total of 21 studies were randomized controlled trials (79%), and six were self-controlled trials (21%). Among the 22 randomized controlled trials, only 15 reported “randomization”; six used a randomized numeric table method, and one used lottery method. Only one study performed allocation concealment, four studies blinded patients, and one study blinded outcome assessors. The remaining studies did not perform allocation concealment or apply blinding; no missing data were reported. Thirteen studies exhibited other sources of bias, such as not reporting the source of funding or trial enrollment, while nine studies provided complete reporting. The risk of bias assessment of clinical trials is presented in Table 5.
4 Discussion and analysis
4.1 Content determination method of active ingredients in Monascus purpureus Went
4.1.1 High-performance liquid chromatography
HPLC is the most commonly used method to determine the content of active ingredients in Monascus purpureus Went, particularly lovastatin and citrinin (orange mold) (Wang and Gao, 2006; Wen et al., 2011; Hao et al., 2017; Tan et al., 2015; Qiu et al., 2012; Luo et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2016; Lu et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 1997; Liu, 2007; Fan, 2013; Zhang et al., 2001; Chen and Zhao, 2007; Zhu et al., 2023; Huang, 2000; Chen et al., 2008; Wang, 2014; Gao et al., 2022; Li et al., 2011; Wang, 2000; Song et al., 1999b; Xie et al., 2010; Huang et al., 2014; Wang et al., 2020; Li and Li, 2008; Lv et al., 2020; Li et al., 2010; Li et al., 2019; Qi et al., 2021), and is characterized by simplicity, accuracy, reliability, good repeatability, and high sensitivity.
4.1.2 Thin-layer chromatography scan
TLCS is a method used to determine the content of phosphatidylcholine and daidzein in Monascus purpureus Went and Xuezhikang capsule (Xu et al., 2000; Xu et al., 2001), which is characterized by simplicity and good repeatability and can be used to control the quality of Monascus purpureus Went and its preparations.
4.1.3 Capillary electrophoresis
CE is a method used to determine the contents of lovastatin and citrinin (a compound produced by orange mold) in Monascus purpureus Went (Chen et al., 2007a; Zhang et al., 2008), which is characterized by simplicity, speed, high sensitivity, and good repeatability in detecting certain charged components.
4.1.4 Other methods
AA is a method used to determine the content of amino acids in Monascus purpureus Went (Chen et al., 2007b), which is characterized by high sensitivity and accuracy. GC is a method used to determine the contents of oleic acid and linoleic acid in Monascus purpureus Went (Zhang et al., 2010). QuEChERS-UPLC-MRM-IDA Criteria-EPI is a method used to determine and quantify the content of lovastatin (Wang, 2016). PSA, ASA, and DNS are methods used to determine the content of polysaccharides in Monascus purpureus Went (Fang et al., 2021). FAAS is a method used to determine the content of metal trace elements in Monascus purpureus Went (Lin et al., 2001). SPSS PCA and SPSS CA were used to analyze trace elements in Monascus purpureus Went (Cao and Wu, 2009) to reveal the relationships and distribution patterns between components.
4.2 Chemical ingredients of Monascus purpureus Went
A variety of active ingredients in Monascus purpureus Went provide the material basis for the pharmacological effect of Monascus purpureus Went, mainly including Monascus pigment, monacolin K, ergosterol, stigmasterol, Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharide, and a variety of enzymes.
4.2.1 Monascus pigment
Monascus pigment is a secondary metabolite of Monascus purpureus Went. Monascus pigment not only provides a unique color for Monascus purpureus Went but also possesses physiological activities such as antioxidant, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. So far, as many as 54 types of Monascus pigment have been identified, among which the more intensively studied pigments include yellow Monascus pigment, ankaflavin, rubropunctamine, and monascorubramine. It has been demonstrated that yellow Monascus pigment has a protective effect on the liver of hyperlipemia mice and can regulate blood lipids, and the mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of lipid metabolism and activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway to stimulate fatty acid oxidation (Fang et al., 2021). Monascorubramine can promote the apoptosis of gastric cancer AGS cells, while no obvious inhibitory effect on normal cells was observed, and its therapeutic coefficient is higher than that of paclitaxel, which is a conventional chemotherapeutic drug for gastric cancer (Lin et al., 2001). The safety of Monascus pigment has been proven to be high through acute and chronic toxicity studies, and it has been widely used as an additive ingredient of Monascus pigment in food and cosmetic production processes (Jiang et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2018; Pan et al., 2023).
4.2.2 Statin ingredients
The statin component of Monascus purpureus Went has a wide range of applications in the field of medicine. In the late 1970s, Japanese scientists discovered and isolated a chemical component called monacolin K from the fermentation of Monascus purpureus Went, which can inhibit cholesterol synthesis in the body (Kong et al., 2005). Further studies revealed that the statin component in Monascus purpureus Went is similar to chemically synthesized statins in terms of its lipid-lowering effect. Among them, lovastatin, the most common statin component in Monascus purpureus Went, was formally approved by the FDA in the United States in 1987 and became the first generation of statin lipid-lowering drugs. In addition, lovastatin has an anti-tumor effect, which can induce the activation of the key molecule of apoptosis, caspase 7, and its receptor PARP protein cleavage. Lovastatin can inhibit the proliferation of PC3 cells and induce apoptosis in prostate cancer and has been shown to be efficacious in common tumors, such as gastric cancer, carcinoma of the bile duct, and nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) (Xu et al., 2018).
4.2.3 Sterol composition
Monascus purpureus Went produces a variety of sterol components during the fermentation process, such as ergosterol and stigmasterol. Ergosterol is one of the precursor substances of vitamin D2, which can be converted into vitamin D2 after ultraviolet irradiation, and is involved in the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in the body, which has an obvious effect on the prevention and treatment of rickets in infants and young children and the promotion of calcium and phosphorus absorption in pregnant women and the elderly. Studies have shown that ergosterol can significantly reduce the blood glucose level of diabetic nephropathy model mice, providing a theoretical basis for ergosterol to be used in the clinical treatment of diabetic nephropathy (Xu et al., 2018). Soysterol can competitively inhibit the absorption of cholesterol in the human body and effectively reduce the level of serum cholesterol, which is an important active ingredient in regulating lipid balance and preventing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases (Ge et al., 2012).
4.2.4 Other ingredients
Monascus purpureus Went contains a variety of other active ingredients, such as Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharide, unsaturated fatty acids, a variety of enzymes (e.g., amylase, protease, and lipase), and flavonoids, which also play important roles in the pharmacological effects of Monascus purpureus Went.
For example, Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharides exhibit various physiological activities, such as immunoregulatory, anti-tumor, and lipid-lowering effects; unsaturated fatty acids help lower blood lipids and prevent cardiovascular diseases; and a variety of enzymes promote digestion and absorption of food in the human body.
4.3 Pharmacological mechanism of action of Monascus purpureus Went
4.3.1 Lipid-lowering ability
Monascus purpureus Went has a lipid-lowering effect. This is mainly attributed to the enrichment of statins in Monascus purpureus Went, such as monacolin K, which is the active ingredient of lovastatin. A number of included clinical trials have shown (Yin et al., 2016; Zhang and He, 2016; Chen et al., 2021; Luo and Zhong, 2020; Zhang et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2018; Shi et al., 2015; Gao et al., 2016) that Monascus purpureus Went has a lipid-lowering effect, generally reducing plasma total cholesterol (TC) levels, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels, and triglyceride (TG) levels and also increasing high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels.
4.3.2 Oxidation resistance
Antioxidant components such as polyphenolic compounds and flavonoids in Monascus purpureus Went can scavenge free radicals in the body and reduce cellular damage caused by oxidative stress. Studies have shown that the extracellular polysaccharides of Monascus purpureus Went have the ability to scavenge DPPH-free radicals, confirming the antioxidant effect of Monascus purpureus Went (Cai et al., 2010). This antioxidant effect helps slow down the cellular aging process and protects the cardiovascular system, the liver, and other organs from oxidative damage. In addition, the antioxidant effect of Monascus purpureus Went is complemented by its lipid-lowering effect, which works together to maintain the healthy state of the human body. Included clinical trials have shown that Monascus purpureus Went can reduce ALT and AST levels in patients with hyperlipemia and liver function abnormalities, thus protecting the liver.
4.3.3 Anti-inflammatory action
Monascus purpureus Went has an anti-inflammatory effect, which is closely related to the various anti-inflammatory components it contains. Polyphenols and flavonoids in Monascus purpureus Went have antioxidant and free-radical scavenging ability, which can reduce the inflammatory response caused by oxidative stress. Studies have shown that Monascus purpureus Went can reduce serum TNF-α and CRP levels in inflammatory mouse models, confirming the anti-inflammatory effect of Monascus purpureus Went (Wang et al., 2006a; Wang et al., 2008), which makes Monascus purpureus Went potentially useful in the treatment of non-infectious inflammatory diseases, such as arthritis and dermatitis.
4.3.4 Anti-tumor activity
In recent years, important progress has also been made in research on the anti-tumor effects of Monascus purpureus Went. Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharides and Monascus pigments in Monascus purpureus Went have an effect on inhibiting the growth and proliferation of tumor cells. These components affect the metabolism and signal transduction pathway of tumor cells through different pathways, thus exerting an anti-tumor effect. By determining the tumor inhibition rate, relative growth rate, and index of each organ in loaded mice, it was found that erythrocyte extracellular polysaccharides had a tumor-inhibitory effect on H22-loaded mice in vivo (Zhou et al., 2011). The determination of body weight, tumor weight, tumor suppression rate, and changes in spleen weight and spleen index of the loaded mice indicated that Monascus purpureus Went polysaccharides had a good inhibitory effect on tumor growth in loaded mice (Ding, 2007). Although the application of Monascus purpureus Went in anti-tumor therapy is still in the research stage, its potential should not be ignored.
4.4 Methodological quality
4.4.1 Methodological quality of animal studies
The methodological quality assessment of animal studies related to Monascus purpureus Went found that most studies only reported “randomization,” while a few used the random number table. Assignment concealment and blinding of investigators or animal handlers and evaluators of results were not reported in most studies, which may have led to subjective bias in the expected experimental results, and only a few used assignment concealment and blinding. A number of studies did not report the randomization of the environment in which the animals were placed, which may have influenced objective environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light intensity in different locations on the experimental results. The result data were completely reported. In conclusion, it is necessary to improve the generation of random allocation sequences, allocation concealment, application of blinding, and randomness of the environment in animal studies related to Monascus purpureus Went.
4.4.2 Methodological quality of clinical trials
The methodological quality assessment of clinical trials related to Monascus purpureus Went found that most trials only reported “randomization,” while a few used the random number table and lottery. Assignment concealment and blinding of patients and outcome evaluators were not reported in most trials, which may increase the risk of measurement bias and evaluator bias, and only a few used assignment concealment and blinding. Some trials did not report registration and conflict of interest, which could lead to inappropriate influence from sponsors. Outcome data were completely reported. In conclusion, it is necessary to improve the generation of random allocation sequences, allocation concealment, application of blinding, and reporting of funding sources in clinical trials related to Monascus purpureus Went.
4.4.3 Suggestion for the study design
The common problems of methodological quality deficiencies in both animal studies and clinical trials are obvious, and the following suggestions are made: first, it is suggested that suitable random sequence generation methods, such as the random number table method, should be used to ensure the randomness and fairness of the allocation process. Second, it is suggested that allocation concealment and application of the double-blind method, including blinding of operators and observers, should be implemented. The person in charge of the operation should not know which group each patient is assigned to, in order to eliminate operator-induced subjective bias in the results. The person responsible for data collection and analysis should also not know the specific group to which each patient is assigned. The process of data collection and analysis should be carried out independently to ensure the objectivity and accuracy of the results. In addition, it is suggested that other conditions (e.g., environment and operation) should be strictly controlled for consistency during the study to ensure the reliability and repeatability of results. Finally, during data analysis, care should be taken to control the effect of confounding factors and other biases and to report in detail on the source of funding and registration to ensure the objectivity and accuracy of the results.
4.5 Limitation
There are some limitations to this review. First, the English-language literature obtained from the search was relatively limited. Second, the studies mainly focus on molecular and animal studies, with relatively few clinical trials. Third, some of the studies are of poor quality, and the reference value of their results may therefore be limited. Fourth, excluding studies for which the full texts could not be obtained may lead to data bias. Fifth, some of the clinical trials contained partially unreported information about the subjects, such as the patient source, enrollment time, and age range, which may reduce the strictness of the study. Sixth, only two meta-analyses were obtained and assessed for methodological quality and reporting standards in this study, and the results showed that they were of low quality, but due to their small number, these studies were not examined and described in detail in order to avoid study bias. The assessment of methodological quality and reporting standards for meta-analyses are presented in Supplementary Adds S2, S3.
4.6 Research implications
4.6.1 Clinical safety
Existing studies have shown that the contraindications for Monascus purpureus Went productions mainly include the following: ① patients allergic to monacolin K/lovastatin or any excipients; ② patients with acute liver disease; ③ patients with severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min); ④ patients with various myopathies; and ⑤ pregnant women, lactating women, and women of childbearing age who have not taken effective contraceptive measures (Banach et al., 2022). It is recommended that its importance be emphasized in clinical practice.
4.6.2 Fundamental research challenges
In terms of the bioactive ingredient biosynthetic pathways and regulatory mechanisms of substances produced during Monascus fermentation, the current challenges in the development of Monascus purpureus Went include improving the content of active ingredients like lovastatin and controlling the content of toxic metabolites like citrinin through methods such as optimizing fermentation parameters, mutagenic breeding, and genetic engineering.
4.6.3 Other suggestions
More contamination risks derive from raw materials, microbial metabolism, or processing errors; the suggestions for the production quality control of Monascus purpureus Went are as follows: first, the quality control of raw materials should be optimized, the standardized management of fermentation strains should be strengthened, and high-quality fermentation strains should be accurately identified and screened. Second, the quality detection standard system should be improved, the specifications for the determination of active ingredient contents should be clarified, and the detection scope of safety indicators should be expanded. Third, the production process system must be optimized, the operation process must be standardized, fermentation parameters must be improved, and fermentation conditions must be strictly controlled. Fourth, the construction of the regulatory system must be improved, mandatory third-party safety reviews must be implemented, and the post-market supervision of products must be strengthened.
To promote the high-quality development of Monascus purpureus Went studies, the suggestions are as follows: first, standards should be set up. Unified quality standards for experimental design and efficacy evaluation should be developed to improve comparability between different studies. The production process and quality control of Monascus purpureus Went should be standardized to ensure the stable quality of Monascus purpureus Went products used in research and application. Second, multidisciplinary cooperation should be promoted. Experts in the fields of pharmacy, medicine, biology, and other multidisciplinary fields should be encouraged to cooperate in the studies and explore the pharmacological action mechanism of Monascus purpureus Went in depth from different perspectives. Third, the research and development of new drugs should be encouraged. Modern preparation technology should be actively used to develop new Monascus purpureus Went preparations with more stable efficacy. Fourth, more research on the combination of Monascus purpureus Went and other drugs should be encouraged to observe the therapeutic effect and safety. Fifth, human pharmacokinetic studies and clinical trials should be performed to explore the effective dosage range of Monascus purpureus Went products, validate safety and prevent adverse events, and provide evidentiary support for clinical practice. Concurrently, key procedures, including ethical review and informed consent, must be strictly implemented throughout the process.
5 Conclusion
As a type of traditional Chinese medicine, the pharmacological action mechanism of Monascus purpureus Went is extensive and complex. Given the extensive global use of Monascus purpureus Went products, we have gradually revealed its mechanism of action in regulating blood lipids and exerting anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and anti-tumor effects through modern science research and technology. Moreover, we also need to pay attention to the contraindications and safety issues associated with the use of Monascus purpureus Went to ensure its safety and effectiveness in our daily lives.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
SL: formal analysis, investigation, visualization, and writing – original draft. YX: formal analysis, investigation, visualization, and writing – original draft. JX: formal analysis, investigation, visualization, and writing – original draft. JH: data curation and writing – original draft. YW: methodology, supervision, and writing – review and editing. JZ: project administration, supervision, and writing – review and editing. SL: conceptualization and writing – review and editing. HH: conceptualization, project administration, supervision, and writing – review and editing. LA: conceptualization, supervision, and writing – review and editing. ZJ: conceptualization, project administration, supervision, and writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Promoting Breakthroughs in Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology: “Inheritance and Innovation” - Construction of Evidence-Based Research and Proactive Health in Traditional Chinese Medicine (20217-KL24040101), The first batch of scientific and technological projects of the Modern Traditional Chinese Medicine Haihe Laboratory in 2025 - Construction and Application of an “Artificial Intelligence Agent for Evidence-Based Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine” Based on Large Reasoning Models (/), Tianjin Municipal Education Commission Research Plan Project (2023KJ124) and Chinese Medicine Innovation Team and Talent Support Plan-National Chinese Medicine multidisciplinary Innovation team project (ZYYCXTD-D-202204). Lin Ang and Myeong Soo Lee are supported by the Korea Institute of Oriental Medicine (KSN2122211).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the funding agencies for their support and all the authors for their dedicated contributions and efforts in bringing this study to completion.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1600460/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
AA, automatic amino acid analyzer; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ASA, anthrone–sulfuric acid; CE, capillary electrophoresis; CNKI, China National Knowledge Infrastructure; DNS, dinitrosalicylic acid; FAAS, flame atomic absorption spectroscopy; GC, gas chromatography; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; NPC, nasopharyngeal carcinoma; PSA, phenol–sulfuric acid; QuEChERS-UPLC-MRM-IDA Criteria-EPI; quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, safe–ultra-performance liquid chromatography–multiple reaction monitoring–ion-dependent acquisition–criteria-enhanced product ion; RAPD, random amplified polymorphic DNA; SMF, secondary metabolite fingerprint; SPSS CA, statistical package for the social sciences cluster analysis; SPSS PCA, statistical package for the social sciences principal component analysis; TC, total cholesterol; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; TG, triglyceride; TLCS, thin-layer chromatography scan.
References
Banach, M., Catapano, A. L., Cicero, A., Escobar, C., Foger, B., and Katsiki, N. (2022). Red yeast rice for dyslipidaemias and cardiovascular risk reduction: a position paper of the International Lipid Expert Panel. Pharmacol. Res. 183, 106370. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106370
Cai, Q., Shen, B., Zhang, H., and Cheng, D. (2010). Extraction of extracellular polysaccharides from Fermentum Rubrum and determination of antioxidant activity. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 28 (03), 598–600. doi:10.13193/j.archtcm.2010.03.151.caiq.067
Cao, H., and Wu, Q. (2009). Principal component analysis and cluster analysis for the study of trace element content in traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum. J. Southwest Univ. Natl. Nat. Sci. Ed. 35 (04), 789–792.
Cao, H., Zhu, J., Yang, C., and Wang, R. (2007). Observation on the therapeutic effect of Fermentum Rubrum capsule for reducing sugar on type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 29 (05), 307–308.
Chen, J., Li, Z., Qi, W., Liu, Z., and Li, B. (2007a). High performance capillary electrophoresis analysis method for detecting the content of hesperidin in traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 14, 1412–1415.
Chen, J., Li, Z., Qi, W., Liu, Z., and Li, B. (2008). Determination of citrine in fermentum Rubrum by RP HPLC. West China J. Pharm. Sci. (02), 219–220. doi:10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2008.02.026
Chen, L., Chen, T., and Wu, J. (2007b). Analysis of amino acid composition in Fermentum Rubrum. Str. Pharm. (02), 53–55.
Chen, L., Zhang, S., Deng, Y., and Liu, H. (2021). Clinical observation of the combination treatment of hyperlipidemia and abnormal liver function with Fermentum Rubrum. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 48 (07), 104–107. doi:10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2021.07.029
Chen, W., and Liu, F. (2015). Clinical observation on the effect of dietary therapy with Danxi Fermentum Rubrum liquor on lowering blood lipids and blood sugar. China Naturop. 23 (10), 77–78. doi:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2015.10.063
Chen, X., and Zhao, J. (2007). Determination of monacolin K in Fermentum Rubrum by high performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Bioeng. (Wuhan. China) (12), 74–75+78.
Chen, Y., Chen, C., and Zhang, S. (2005). Effect of Lovastatin from Red Kojic on lipid metabolism and expression of lipoprotein lipase mRNA in hyperlipidemic mice. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 36 (5). doi:10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.2005.05.032
Chen, Y., Peng, D., and Tian, H. (2000). Research and application of Fermentum Rubrum and Aspergillus spp. J. Hubei Agric. Coll. 20 (2).
Chen, Y., Zhang, G., and Ye, Z. (2010). Study on the lipid-lowering effect of compound Fermentum Rubrum extract on hyperlipidemic rats. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 35 (04), 504–507. doi:10.4268/cjcmm20100422
Cui, C., Zhou, K., Yang, L., Zhai, Y., and Qi, X. (2002). Clinical observation on the treatment of 45 cases of hyperlipidemia with compound Fermentum Rubrum capsule. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. (02), 31–34.
Ding, H. (2007). Preliminary study on the anti-tumor effect of Fermentum Rubrum polysaccharides. J. Fungal Res. (03), 171–173. doi:10.13341/j.jfr.2007.03.012
Ding, Y., and Ren, H. (2023). The lipid-lowering effect of Fermentum Rubrum earthworm protein tablet on hyperlipidemic rats. Ind. Microbiol. (Shanghai, China) 53 (04), 104–106.
Du, X., and Chen, Y. (2013). Study on the acute toxicity and mutability of Fermentum Rubrum extract. Food Res. Dev. (Tianjin, China) 34 (05), 4–6+30.
Endo, A. (1980). Monacolin K, a new hypocholesterolemic agent that specifically inhibits 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 33 (3), 334–336. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.33.334
Fan, W. (2013). Determination of lovastatin content in Fermentum Rubrum by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Mod. Med. Health. 29 (16), 2417–2419+2421.
Fang, J., Wang, C., Wang, L., Shi, W., Guo, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Comparative study on the determination methods of polysaccharide content in Fermentum Rubrum Fuling tablets. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 32 (11), 2672–2676.
Gao, S., Huang, C., and He, Z. (2015). Study on the weight loss and lipid-lowering effects of Fengfengtongsheng powder combined with Fermentum Rubrum. Asia Pac. Tradit. Med. 11 (24). doi:10.11954/ytctyy.201524005
Gao, W., Lin, Y., Dai, G., and Zhao, L. (2022). Simultaneous determination of adenosine and three other components in Fermentum Rubrum from different sources by HPLC method. Pharm. Clin. Res. 30 (02), 140–142. doi:10.13664/j.cnki.pcr.2022.02.022
Gao, Y., Yu, C., Yan, G., Lin, X., Lu, F., and Shen, J. (2016). Observation of the therapeutic effect of functional Fermentum Rubrum on hyperlipidemia. Front. Med. 6 (18).
Ge, F., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Yu, H., and Li, C. (2012). Research on the main active components in Fermentum Rubrum. J. Kunming Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. 37 (02), 61–64.
Hao, S., Wang, L., Li, H., Zhang, D., and Xu, H. (2017). Simultaneous determination of lovastatin and lovastatin acid in Fermentum Rubrum and Zhibituo tablets by QAMS. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 23 (5). doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2017050074
He, S., Lou, X., Zhang, R., and Xu, J. (2007). Observation on the clinical effect of Fermentum Rubrum Flavonoids tablets in regulating blood lipids. Chin. Prev. Med. (03), 284–286.
He, Y. (2004). Effect of fermented extract of Fermentum Rubrum garlic on hyperlipemia and arteriosclerosis lesions in cholesterol-loaded rabbits. Int. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (06), 347–348.
Huang, H. (2000). Separation and determination of lovastatin in Fermentum Rubrum by HPLC method. Str. J. Prev. Med. (04), 40–41.
Huang, P., and Zhang, R. (2005). Influence of Xue Zhi Kang on C-reaction albumen of early plasma in unstable colic patients. Chin. Med. Mod. Disrance Educ. China. 3 (12). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-2779.2005.12.022
Huang, X., Chen, P., Chen, L., and Hu, Y. (2014). Determination of Monacolin K content in water soluble Fermentum Rubrum by HPLC method. Zhejiang J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 49 (09), 685–686.
Huang, Y., Zhou, D., and Yu, Q. (2019). Research on the auxiliary lipid-lowering function of Fermentum Rubrum propolis tablets. Food Res. Dev. (Tianjin, China) 40 (08), 195–199.
Jiang, L., Li, S., Liu, Z., Hao, Z., and He, J. (2008). Effect of Fermentum Rubrum and grape seed anthocyanidin mixture on blood lipid in atherosclerotic rats. Food Sci. (Beijing, China) (07), 420–423.
Jiang, Y., Dong, Y., Zhou, F., Chen, J., Zhou, Y., Tian, C., et al. (2021). Research progress on chemical composition, pharmacological effects and clinical applications of Fermentum Rubrum. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 52 (23), 7379–7388.
Kong, Y., Liu, L., and Wu, M. (2005). Research progress on lipid-lowering Fermentum Rubrum at home and abroad. Heilongjiang J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (06), 56–57.
Lei, P., Guo, J., and Jin, Z. (2007). Biochemical mechanism of Fermentum Rubrum in reducing blood pressure in renal vascular hypertension rats. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. (03), 217–218. doi:10.13194/j.jlunivtcm.2007.03.219.leip.147
Li, G., and Li, H. (2008). Determination of lovastatin in fermentation broth of Monascus by HPLC. Guangdong Pharm. J. 24 (3).
Li, X., Xue, L., Zhou, L., Duan, Z., and Guo, S. (2011). HPLC method for detecting kumquat in Xuezhikang capsule. China Pharm. (Wuhan. China) 14 (08), 1088–1090.
Li, Y., Zhang, C., Yang, Y., and Chen, Z. (2019). HPLC determination of seven nucleoside components in Fermentum Rubrum. China Med. Her. 16 (12), 101–104.
Li, Y., Zhang, X., and Qin, M. (2010). HPLC method for determination of Monacolin K, Monacolin K, and dehydromonacolin K in functional Fermentum Rubrum extract. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 41 (08), 1286–1288.
Lin, P., Xing, W., Mi, H., Wang, X., and Wu, H. (2001). Determination of trace elements in the Chinese traditional medicine--Red Kojic by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Pharm. Care Res. 1 (1). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2838.2001.01.014
Lin, X., Zhou, Y., Xu, M., Lin, X., Shao, S., Zhu, X., et al. (2014). The effect of traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum on the expression of PPAR γ and adiponectin receptor in hyperlipidemic rats. Zhejiang Med. J. 36 (21), 1767–1770.
Liu, J., Zhang, J., Liu, X., Zhang, R., Le, N., Zhang, S., et al. (2020). Exploring the effect of Fermentum Rubrum Fuling tablets on rats with spleen deficiency and dampness excess hyperlipidemia based on the theory of dialectical health care. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 13 (11), 1837–1845.
Liu, L., Wu, M., Wang, H., and Zhang, W. (2011). A randomized controlled study of lipid lowering Fermentum Rubrum micro powder in the treatment of dyslipidemia with carotid atherosclerosis. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. Chin. Ed. 31 (09), 1196–1200.
Liu, X. (2007). Determination of lovastatin content in Xuezhikang soft capsules by high performance liquid chromatography. Jiangxi J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 38 (7). doi:10.3969/j.issn.0411-9584.2007.07.054
Liu, Y., Peng, L., and Hu, C. (2021). Study on the lipid regulating efficacy and safety of Ginkgo Fermentum Rubrum vitamin formula. New Chin. Med. 52 (07), 508–512.
Liu, Y., Wu, M., Hu, Y., Wang, X., and Ding, K. (2019). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum flavins on blood lipids and liver AMPK α ACC, PPAR - α, and CPT1 protein expression in hyperlipidemic rats. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Sci. Technol. 26 (03), 351–356.
Liu, Z., Lai, W., Liu, D., Mei, S., and Fu, Y. (2013). Study on the lipid-lowering effect of compound Fermentum Rubrum capsules in rats. J. Food Saf. Qual. 4 (03), 819–822. doi:10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2013.03.029
Liu, Z., Wang, X., and Zhao, K. (1998). Clinical observation of Zhibituo in the treatment of 76 cases of hyperlipidemia. Mod. J. Integr. Tradit. Chin. West. Med. (02), 194–195.
Lu, J., Lu, Y., Jin, H., Xu, X., Shen, J., Ren, J., et al. (2017). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum on serum ALP, TRAP, and bone tissue TNF - α, RANK expression in osteoporotic rat model after ovariectomy. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Traumatol. Orthop. 25 (09), 5–8.
Lu, J., Qian, X., Hua, J., Hua, W., and Zhu, X. (2008). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum on inducing differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells into osteoblasts. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. (2005-) (06), 541–544.
Lu, J., Wang, W., and Chen, B. (2006). Effect of Fermentum Rubrum on proliferation, differentiation and mineralization function of osteoblasts in vitro. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Traumatol. Orthop. (02), 41–45.
Lu, J., Wang, W., Wu, C., Yang, L., and Wang, J. (2005b). Correlation study of Fermentum Rubrum on bone mineral density and bone mechanics changes in rats. Zhejiang J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. (09), 529–531.
Lu, J., Wu, C., Ni, G., Wang, W., and Wang, J. (2005a). Fermentum Rubrum versus ovariectomized rats BMP experimental studies of expression and osteoblast proliferation. China J. Orthop. Traumatol. (01), 29–31.
Lu, J., Wu, C., Wang, W., Wang, J., and Yang, L. (2004). Effect of Fermentum Rubrum on serum hormone levels, bone density, and bone biomechanics in castrated rats. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Traumatol. Orthop. (04), 22–25.
Lu, S., Yu, Q., and Si-tu, Y. (2016). Protective effect of red yeast rice capsule containing coenzyme Q10 on osteoporosis in rats induced by ovariectomy combined with D-galactose. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 32 (9). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2016.09.013
Lu, S., Zhang, L., He, X., Ding, H., and Wu, T. (2019). Determination of lovastatin and coenzyme Q_ (10) in functional Fermentum Rubrum powder. Guangzhou Chem. Ind. 47 (18), 92–95.
Lu, X., Hu, Y., Wang, X., and Gao, S. (2012). Clinical observation of Xuezhikang in the treatment of hyperlipidemia. Hubei J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 34 (09), 38–39.
Luo, H., and Zhong, Z. (2020). The effect of Tibetan Fermentum Rubrum on blood lipids in patients with dyslipidemia. China Naturop. 28 (16), 57–59. doi:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.2020.1628
Luo, J., Sun, Q., Ma, Z., He, Z., and Li, X. (2019). The gastrointestinal regulatory effects of fermented Fermentum Rubrum on mice with spleen deficiency and food accumulation syndrome before and after processing. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 25 (22), 108–114. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20192252
Luo, R., Sun, K., Xie, S., Han, Y., and Zhao, Y. (2003). Method for determining the total amount of lovastatin in Fermentum Rubrum. J. Hyg. Res. 32 (02), 157–158.
Luo, W., and Zhang, Q. (2011). Tissue and biochemical study of Fermentum Rubrum improving non alcoholic fatty liver in rats. Chin. J. Gen. Pract. 9 (12), 1842–1843+1853. doi:10.16766/j.cnki.issn.1674-4152.2011.12.012
Luo, W., Zhang, Q., and Lv, Z. (2010). Study on the mechanism of Fermentum Rubrum improving insulin resistance in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Tradit. Chin. Drug Res. Clin. Pharmacol. 21 (04), 375–378. doi:10.19378/j.issn.1003-9783.2010.04.014
Lv, S., He, X., Zhang, L., Ding, H., and Wu, T. (2020). Determination of lovastatin content in Fermentum Rubrum capsules by HPLC method. Str. Pharm. 32 (03), 63–66.
Ma, H., Gao, M., Li, X., Zhao, W., and Ying, Y. (2022). Genetic toxicity evaluation of Sanqi Fermentum Rubrum compound preparation. Food Drug 24 (01), 21–25.
Ma, Y. (2025). “The Kobayashi Pharmaceutical scandal in Japan continues to ferment,” in Guangming Dly. Guangming Dly. 008.
Ou-yang, Z., Li, Y., Liang, G., Jin, H., and Kang, D. (2012). The effect of buckwheat Fermentum Rubrum on blood lipid levels in experimental hyperlipidemic rats. J. Yanbian Med. Coll. 35 (01), 25–27. doi:10.16068/j.1000-1824.2012.01.008
Pan, R., Fang, Z., Tang, X., Zheng, L., and Wang, D. (2023). Research progress on secondary metabolites and pharmacological effects of Monascus purpureus. West China J. Pharm. Sci. 38 (03), 345–351. doi:10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2023.03.024
Pang, Z., Li, P., Huang, Y., Liu, Y., and Jiang, Y. (2017). The animal experimental study of Natto-monascus on hyperlipidemia. Mod. Food. 7 (14). doi:10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2017.14.028
Qi, F., Ren, D., Huang, Z., Qin, L., and Zhu, B. (2021). Determination of lovastatin and citrine in Fermentum Rubrum from 16 production areas. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 43 (04), 948–953.
Qian, S., Wang, Y., and Ye, Y. (2015). The effect of alcohol extracted Fermentum Rubrum on BMP-4 mRNA and protein expression during fracture healing in osteoporotic rats. Chin. J. Tradit. Med. Sci. Technol. 22 (03), 284–286.
Qiu, L., Hao, J., and Guan, C. (1997). Observation on the treatment of 112 cases of hyperlipidemia with Fermentum Rubrum extract preparation. China Naturop. (06), 34. doi:10.19621/j.cnki.11-3555/r.1997.06.052
Qiu, W., Liu, X., Zheng, K., and Fu, W. (2012). Immuno-affinity chromatographic purification: the study of methods to test citrinin in monascus products by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. J. Prev. Med. (Beijing). 46 (8), 750–753. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2012.08.017
Shen, J., Lu, J., Xu, X., Jin, H., Ren, J., Lu, Y., et al. (2018). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum on the expression of RANKL, OPG protein and mRNA in bone tissue of ovariectomized rats. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. (2005-). 33 (04), 1370–1372.
Shi, M., Zhao, Y., Hu, G., Bai, H., Liu, Q., and Zhang, J. (2015). Clinical observation on the lipid-lowering effect of Fermentum Rubrumt tea drink on elderly patients. Pract. J. Med. Pharm. 32 (04), 328–329. doi:10.14172/j.cnki.issn1671-4008.2015.04.015
Song, H., Mi, H., and Guo, T. (1999a). Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum. J. Pharm. Pract. (03), 44–46.
Song, H., Mi, H., Guo, T., Wu, W., and Chu, W. (1999b). Determination of lovastatin in Hongqu from various sources by HPLC. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs (2). doi:10.3321/j.issn:0253-2670.1999.02.009
Su, S., Liu, C., Yin, Q., Li, H., Liu, J., and Cheng, M. (2014). The effects of Xuezhikang on the functions of endothelial Progenitor cells isolated from experimental hyperlipidemic rats. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 14 (36). doi:10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2014.36.009
Sun, J., Su, H., Liao, X., Gui, W., Fang, Y., Han, L., et al. (2022). Exploring the mechanism of action of Fermentum Rubrum in treating cerebral small vessel disease based on network pharmacology and animal experiments. Cent. South Pharm. 20 (02), 278–283.
Sun, J. (2025). “Warning and Inspiration from the “Red Yeast Storm” at Kobayashi Pharmaceutical,” in Xinhua Dly. Telegraph. 004
Sun, M., Li, Y., and Yan, W. (2001a). Study on the effect of Fermentum Rubrum on improving hemorheology in hyperlipidemic rats. J. Hyg. Res. 30 (03), 173–175.
Sun, M., Li, Y., and Yan, W. (2001b). Study on the effect of Fermentum Rubrum in lowering blood pressure. J. Hyg. Res. 30 (4). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8020.2001.04.006
Tan, Y., Ma, Y., Liu, Q., Wang, W., and Huang, F. (2015). Research on the quality standards of Qingke Fermentum Rubrum. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 17 (03), 614–619.
Tang, C., and Chang, H. (2012). The effect of Xuezhikang on blood lipids and hemorheology. Chin. Commun. Dr. 14 (22). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2012.22.249
Tang, F., Zhang, J., Zou, J., Sun, W., and Jiao, X. (2004). Fermentum Rubrum Preliminary study on the antihypertensive effect of L-nitroarginine in hypertensive rats. Food Sci. (Beijing, China) (04), 155–157.
Wang, C. (2000). HPLC detection of lovastatin in functional Fermentum Rubrum. J. Beijing Univ. Agric. (02), 48–51. doi:10.13473/j.cnki.issn.1002-3186.2000.02.010
Wang, H., Zhou, D., Xu, S., and Ye, H. (2005). Experimental study on the effect of compound Fermentum Rubrum in regulating blood lipid. Chin. J. Health Lab. Technol. (05), 540–541.
Wang, J. (2014). Simultaneous determination of two configurations of Lovastatin in Fermentum Rubrum by HPLC method. Zhejiang J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 24 (03), 273–274.
Wang, J., Kang, R., Ji-Le-Tu, H., Liang, H., Hong, L., Yan, L., et al. (2020). Determination of total lovastatin in hongmao medicinal wine. J. North. Pharm. 17 (9). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-8351.2020.09.001
Wang, J., Wang, X., and Shi, B. (2016). Observation on the therapeutic effect of Shengqu Fermentum Rubrum capsule on carotid atherosclerosis. Drug Eval. Res. 39 (06), 1054–1057.
Wang, J., Yang, B., Wang, X., and Shi, Z. (2014). Determination of treatment course and observation of efficacy of Shengqu Fermentum Rubrum capsules in the treatment of dyslipidemia. Drugs Clin. 29 (08), 888–890.
Wang, L. (2019). Experimental study on the lipid-lowering effect of Fermentum Rubrum on high-fat rats. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. (Electron. Ed.) 8 (04), 50–51.
Wang, L., Tian, Y., and Mei, C. (2000). Effect of Fermentum Rubrum extract on serum lipid profile and glomerulosclerosis in nephrotic syndrome. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Nephrol. (03), 154–156.
Wang, Q., Qi, F., Bao, B., and Sun, Q. (2024a). Isolation and ITS molecular identification of high-yield Lovastatin producing purple Monascus purpureus. Chin. Pharm. J. 59 (03), 220–226.
Wang, S., Guo, Z., Zhou, B., He, Y., Li, D., Tao, P., et al. (2024b). Research progress on safety and quality control of red yeast rice. Chin. Pharm. J. 59 (13), 1186–1192.
Wang, T., and Li, J. (2018). The treatment of hyperlipidemia with traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum decoction and its effect on vascular endothelial protection. J. Liaoning Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 20 (08), 119–121. doi:10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2018.08.031
Wang, W., Wang, J., Su, M., Lu, Z., and Kou, W. (1995). Clinical observation of Xuezhikang capsules in the treatment of hyperlipidemia. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. (01), 37–41.
Wang, X., Gao, X., Huang, T., and Li, C. (2007). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum compound preparation on blood lipid regulation function in rats. Shaanxi Med. J. (01), 35–37.
Wang, X., Zou, D., Li, H., and Li, D. (2022). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum on blood lipids and nutritional status of hemodialysis patients. Chin. J. Gerontol. 42 (23). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2022.23.015
Wang, Y. (2016). QuEChERS UPLC-MRM-IDA criteria EPI determination of lovastatin in Fermentum Rubrum. China Licens. Pharm. 13 (10), 21–24+39.
Wang, Y., and Gao, X. (2006). Research on the quality standards of Zhibituo capsule. Sichuan Med. J. (05), 451–452. doi:10.16252/j.cnki.issn1004-0501-2006.05.006
Wang, Y., Wei, W., and Li, C. (2002). The therapeutic effect of special Fermentum Rubrum on experimental fatty liver disease in quail. Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. (04), 293–295.
Wang, Y., Zhao, Z., Huang, F., and Ren, J. (2006a). Research on the anti-inflammatory mechanism of Fermentum Rubrum. Chin. Rem. Clin. (05), 350–352.
Wang, Y., Zhao, Z., Huang, F., and Ren, J. (2006b). Experimental study on the anti-inflammatory effect of Fermentum Rubrum. Chin. J. New Drugs. (02), 96–98.
Wang, Y., Zhao, Z., Wang, L., and Huang, F. (2008). The anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of Fermentum Rubrum on collagen induced arthritis rats. Chin. J. New Drugs. (14), 1217–1221.
Wei, R., Zhang, X., Hu, S., Zhang, Q., and Zhang, W. (2023). Reconstructed herb —— Fermentum Rubrum. Jilin J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 43 (02), 222–224. doi:10.13463/j.cnki.jlzyy.2023.02.025
Wen, J., Chang, P., Gu, X., and Jin, Z. (2001). Research progress on physiological activity and determination methods of Fermentum Rubrum and Lovastatin. China Food Addit. (01), 12–19.
Wen, Z., Zhang, F., Huang, Y., Xie, J., Luo, J., Wei, Z., et al. (2011). Determination of Fermentum Rubrum content in Zhibitai capsules. China Pharm. 20 (13), 21–23.
Wu, C., Huang, J., Wang, W., and Lu, J. (2007a). Bone tissue morphometric observation of Fermentum Rubrumt promoting fracture healing in experimental rats. J. Zhejiang Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. (01), 41–43. doi:10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2007.01.015
Wu, C., Huang, J., Wang, W., and Lu, J. (2007b). Experimental study on the treatment of experimental rat fractures with Fermentum Rubrum. Fujian J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (01), 42–44.
Wu, C., Lu, J., Wang, W., and Chen, B. (2006). The effect of Fermentum Rubrum on BMP-2 expression in cultured rat osteoblasts in vitro. J. Tradit. Chin. Orthop. Traumatol. (05), 5–6+79.
Wu, M., Wang, W., Zhang, W., Zheng, G., and Liu, L. (2005). Clinical study on the treatment of hyperlipidemia with lipid-lowering Fermentum Rubrum micro powder. J. Shandong Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. (06), 433–435. doi:10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.2005.06.009
Wu, X., and Luo, D. (2013). Observation on the clinical effect of Fermentum Rubrum on carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 5 (22), 7–8.
Xie, J., Li, D., Wang, M., Chen, Z., and Yuan, W. (2010). Determination of Lovastatin content in Xuezhikang capsule by HPLC method. China Pharm. (Chongqing, China). 21 (45), 4287–4289.
Xie, Z. (1996). Further study on traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum by modern technology. China Med. news. 22, 13–14.
Xu, H., Ruan, J., Gao, F., and Li, M. (2019). Clinical study on the treatment of hyperlipidemia with Shateng Fermentum Rubrum soft capsules. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 39 (05), 61–64. doi:10.13424/j.cnki.mtcm.2019.05.019
Xu, S., Shao, Y., and Wu, T. (2018). Overview of research on anti-tumor active ingredients extracted from Fermentum Rubrum. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 11 (06), 973–978.
Xu, Y., Wei, L., He, D., and Wang, M. (2000). Determination of phosphatidylcholine content in Fermentum Rubrum and its preparation Xuezhikang. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. (12), 16–17.
Xu, Y., Wei, L., He, D., and Wang, M. (2001). Thin layer scanning method for determining the content of daidzein in Fermentum Rubrum and its preparation Xuezhikang. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 26 (1). doi:10.3321/j.issn:1001-5302.2001.01.010
Yan, S. (1999). Development of vinegar bean capsule and the effect of lowering blood lipid. Fujian J. Tradit. Chin. Med. (01), 39–40.
Yang, Y., Liu, J., Zhang, Y., Guo, Z., Luo, Y., Chen, D., et al. (2024). Observation of clinical efficacy and network pharmacological mechanism analysis of Coptis chinensis-Fermentum Rubrum drug in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Shaanxi Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 47 (02), 76–82. doi:10.13424/j.cnki.jsctcm.2024.02.015
Yin, M., Ye, H., Feng, S., and Zhang, X. (2016). Retrospective analysis of Fermentum Rubrum compound preparation in the treatment of primary dyslipidemia of phlegm turbidity and blood stasis type. Mod. Clin. Tradit. Chin. Med. 23 (04), 8–11.
Yu, L., Xu, J., Zheng, J., and Lu, B. (2023). Exploring the mechanism of action of Fermentum Rubrum hawthorn in treating NASH based on network pharmacology and verifying the mechanism of NF - κ B signaling pathway. J. Zhejiang Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 47 (09), 986–1001. doi:10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2023.09.003
Yu, Y., Qu, X., Li, Z., and Guo, Z. (2000). Yunnan Fermentum Rubrum powder modulates blood lipid and anti-atherosclerotic plaque formation. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. (05), 587–588.
Zhai, P., Zhao, J., Zhou, D., and Hong, X. (2012). Experimental study on the lipid-lowering effect of traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum compound preparation. J. Zhejiang Univ. Tradit. Chin. Med. 36 (01), 70–72. doi:10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2012.01.032
Zhang, J., Meng, F., Miao, T., Ji, L., and Zhang, J. (2017). Study on the effects of Fermentum Rubrum polysaccharides on several important physiological indicators in rats. Heilongjiang J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. (05), 203–205. doi:10.13881/j.cnki.hljxmsy.2017.0434
Zhang, Q., Wang, J., Bai, G., Wang, H., and Cui, H. (2016). HPLC-DAD/FLD determination of the active ingredient Lovastatin and toxic ingredient kumquat in Fermentum Rubrum. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 27 (04), 816–819.
Zhang, Q., Wei, Q., Tang, B., Jin, Q., and Liu, H. (2008). Determination of Lovastatin content in Fermentum Rubrum capsule by capillary electrophoresis. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. (11), 4–6. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2008.11.005
Zhang, S., Mi, W., and Chen, L. (2020). Observation on the therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum on hyperlipidemia of different TCM constitution types. J. Pract. Tradit. Chin. Intern. Med. 34 (08), 56–59. doi:10.13729/j.issn.1671-7813.Z20200152
Zhang, W., and He, W. (2016). Clinical observation on the treatment of 80 cases of simple hyperlipidemia with Fermentum Rubrum. Heilongjiang J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 45 (06), 21–22.
Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., and Luo, Y. (2023). Study on the effect of Coptis chinensis-Fermentum Rubrum medicine on regulating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to improve non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. China J. Tradit. Chin. Med. Pharm. (2005-) 39 (04), 19–24. doi:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.20230307.002
Zhang, X., Zhou, F., and Shi, J. (1997). Determination of lovastatin content in Xuezhikang capsules and Fermentum Rubrum by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin. Med. News. (16), 23–24.
Zhang, Y., Hou, T., and Zhang, S. (2001). The Dtermination of lovastatin in red yeast rice by HPLC. Food Sci. (Beijing, China) 22 (7). doi:10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2001.07.017
Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., and Wu, C. (2010). Determination of oleic acid and linoleic acid content in traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum by GC method. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae. 16 (02), 23–25. doi:10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2010.02.010
Zhao, J., Fei, Y., and Shao, Y. (2018). The effect of traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum on blood lipids and liver function in patients with hyperlipidemia and liver dysfunction. J. Med. Theor. Pract. 31 (21), 3226–3228. doi:10.19381/j.issn.1001-7585.2018.21.031
Zhao, J., and Liu, X. (2011). Study on the lipid-lowering effect of Fermentum Rubrum plant sterol ester compound preparation. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 42 (11), 2296–2299.
Zheng, J., Guo, J., and Jin, Z. (2007). Study on the hypotensive mechanism of Fermentum Rubrum on spontaneously hypertensive rats. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. (03), 207–208+236.
Zheng, W., Lin, J., Lin, F., and Wu, L. (2022). Comparison of lipid-lowering efficacy of functional Monascus and lovastatin. China Brew. 41 (4). doi:10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.04.019
Zheng, Y., and Li, Y. (2015). Clinical study on the treatment of hyperlipidemia with Fermentum Rubrum extract preparation. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 7 (09), 36–37.
Zhou, D. (2014). The effect of traditional Chinese medicine Fermentum Rubrum on blood lipids in high-fat diet rats. China Mod. Med. 21 (16), 19–21.
Zhou, F., Zhu, X., Pan, P., Chen, Y., and Cheng, D. (2011). Study on the anti-tumor activity of extracellular polysaccharides from Monascus purpureus. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med. 29 (01), 123–124. doi:10.13193/j.archtcm.2011.01.125.zhoufm.063
Zhou, X., Wang, M., Luo, W., Wang, L., Gao, F., and Wei, P. (2018). Experimental study on the lipid-lowering effect of Seabuckthorn Fermentum Rubrum capsules. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 34 (05), 116–118. doi:10.13412/j.cnki.zyyl.2018.05.028
Zhu, Q. (2013). Observation of the clinical efficacy of Xuezhikang capsule in the treatment of 40 cases of unstable angina Pectoris. Everyone’s Health (Late Ed.) 7 (2).
Zhu, W., Jing, G., Zhao, R., Bi, T., Zhao, D., Wang, S., et al. (2023). Simultaneous determination of 10 fungal toxins in Fermentum Rubrum by HPLC tandem mass spectrometry. China Pharm. 32 (03), 89–93.
Keywords: Monascus purpureus Went, pharmacological effects, pharmacological mechanisms, scope review, evidence
Citation: Liu S, Xu Y, Xie J, Hu J, Wang Y, Zhang J, Lee MS, Hu H, Ang L and Ji Z (2025) The pharmacology and mechanism of action of Monascus purpureus Went: a scoping review. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1600460. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1600460
Received: 26 March 2025; Accepted: 11 June 2025;
Published: 30 July 2025.
Edited by:
Ruyu Yao, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Yanfeng Liu, Jiangnan University, ChinaSabreena Safuan, Universiti Sains Malaysia Health Campus, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Xu, Xie, Hu, Wang, Zhang, Lee, Hu, Ang and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haiyin Hu, eWlueWluMjEzQHFxLmNvbQ==; Lin Ang, YW5nbGluMjgwOEBraW9tLnJlLmty; Zhaochen Ji, cm9iaW5fam9obnNvbkBmb3htYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Sitong Liu
Sitong Liu Yaxin Xu
Yaxin Xu Jinhan Xie
Jinhan Xie Jing Hu
Jing Hu Yuetong Wang
Yuetong Wang Junhua Zhang
Junhua Zhang Myeong Soo Lee
Myeong Soo Lee Haiyin Hu
Haiyin Hu Lin Ang
Lin Ang Zhaochen Ji
Zhaochen Ji