- 1The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha, China
- 2Ningbo Chinese Medicine Hospital, Ningbo, Zhejiang, China
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a leading cause of spinal disorders worldwide. Current clinical therapies for IDD are often constrained by limited efficacy, notable adverse effects, and high treatment costs. Thus, there is a pressing need for safer and more effective treatment strategies. In recent years, natural product-based therapies have garnered increasing attention due to their multi-target mechanisms and relatively low toxicity. This review comprehensively summarizes recent advances in the application of natural products for IDD treatment, with a focus on flavonoids (e.g., quercetin, hyperoside), glycosides (e.g., ginsenosides, notoginsenosides), terpenoids (e.g., aucubin, celastrol), phenolic compounds (e.g., curcumin, resveratrol), and alkaloids (e.g., berberine, evodiamine). These compounds exert their therapeutic effects by modulating critical signaling pathways, including Sirtuin-1 (SIRT1), Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB), Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK), Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B (PI3K/Akt), and Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2–Related Factor 2 (Nrf2). Collectively, they exhibit potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-senescence, and regenerative properties. The insights presented herein provide a robust theoretical foundation to support future preclinical and clinical investigations, highlighting the considerable promise of natural products in IDD management.
1 Introduction
IDD describes a pathological process characterized by progressive structural and functional deterioration of intervertebral disc tissues due to multiple etiological factors. This degenerative condition predominantly affects middle-aged and elderly populations. With global population aging accelerating, IDD has emerged as one of the foremost causes of spine-related disability worldwide (Kos et al., 2019). The intervertebral disc, an integral component of the spinal structure, consists of the annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus (NP), and cartilaginous endplates (CEP), collectively essential for maintaining spinal stability and flexibility. Additionally, IDD is recognized as the primary pathological basis underlying disc herniation (Risbud and Shapiro, 2014). In a healthy state, intervertebral discs exhibit notable elasticity and effective shock-absorbing capabilities. Nevertheless, aging and external pathological factors progressively induce disc degeneration, typified by annular fissures, NP dehydration, and CEP calcification (Sar et al., 2016).
IDD contributes to various spinal disorders, including disc herniation, sciatica, and spinal stenosis. Present therapeutic strategies for IDD primarily aim at symptomatic relief and pain management (Le Maitre et al., 2015), employing both conservative and surgical interventions. Conservative approaches generally involve pharmacological therapies, physical rehabilitation, and lifestyle modifications. However, these methods typically provide only transient symptomatic relief and are largely ineffective in reversing the underlying degenerative processes (Yu et al., 2018). Surgical interventions, including discectomy and artificial disc replacement, can partially restore disc function, yet they carry substantial risks and potential postoperative complications (Cai et al., 2011). Moreover, the substantial economic burden associated with surgical treatment limits its accessibility. Consequently, the development of safer, more effective, and economically viable therapies remains a significant priority among clinicians and researchers. Recently, natural products have attracted considerable attention as potential therapeutic candidates for IDD due to their capability to modulate multiple biological targets involved in disc degeneration.
Natural products are chemical compounds derived from natural sources, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, characterized by a wide range of biological activities and pharmacological properties. Compared with traditional synthetic drugs, natural products offer significant advantages, such as lower toxicity and the capacity for multi-target interventions, making them increasingly attractive as therapeutic options for intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) (Chen et al., 2021). These natural compounds have demonstrated substantial efficacy in reducing inflammation, alleviating oxidative stress, inhibiting apoptosis, and promoting cellular regeneration. Consequently, they may slow down or partially reverse the degenerative processes associated with IDD (Liu Z. et al., 2023; Mavrogonatou and Kletsas, 2024). Notably, flavonoids, glycosides, terpenoids, and phenolic compounds have demonstrated significant therapeutic promise in recent studies (Wan et al., 2025). This review comprehensively summarizes current advancements in utilizing natural products for IDD therapy, focusing specifically on representative compounds and elucidating their underlying mechanisms of action to guide future research and clinical development. These multi-targeted mechanisms and compound classifications are visually summarized in Figure 1.
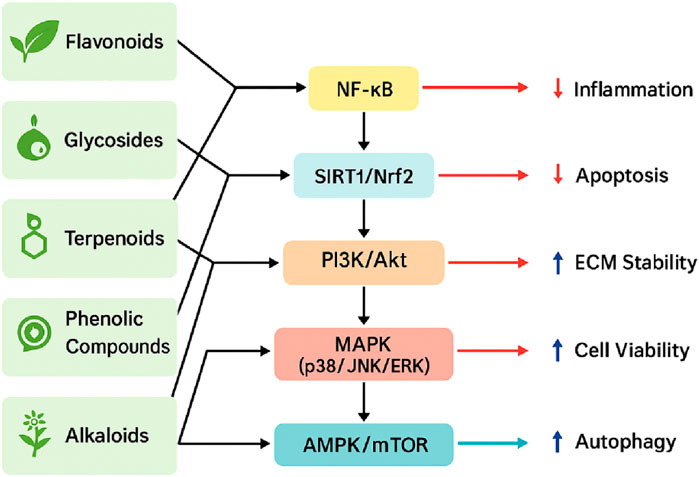
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the major signaling pathways modulated by natural products in the treatment of IDD. Representative compound categories—including flavonoids, glycosides, terpenoids, phenolic compounds, and alkaloids—target key molecular pathways such as NF-κB, SIRT1/Nrf2, PI3K/Akt, MAPK (p38/JNK/ERK), and AMPK/mTOR. These pathways are involved in reducing inflammation and apoptosis, enhancing ECM stability and cell viability, and promoting autophagy, collectively contributing to the attenuation of IDD progression.
Compared to previous reviews that primarily focused on inflammatory modulation or single-pathway mechanisms (Chen et al., 2021; Liu Z. et al., 2023), this study provides a systematic classification of natural compounds, integrates their molecular mechanisms across multiple pathways, and uniquely emphasizes structure-activity relationships and quantitative pharmacological data, offering a comprehensive perspective for future translational research.
A systematic literature search was conducted using PubMed, Web of Science, and Google Scholar, covering the period from January 2000 to May 2025. The following Boolean string was used (“intervertebral disc degeneration” OR “IVDD” OR “IDD”) AND (“natural products” OR “flavonoids” OR “alkaloids” OR “polyphenols” OR “glycosides” OR “terpenoids”). Articles were screened based on title and abstract, and inclusion criteria were: (1) studies reporting in vitro or in vivo effects of plant-derived metabolites on IDD; (2) studies involving known active ingredients with structural and mechanistic data; (3) peer-reviewed journal articles in English.
2 Flavonoids
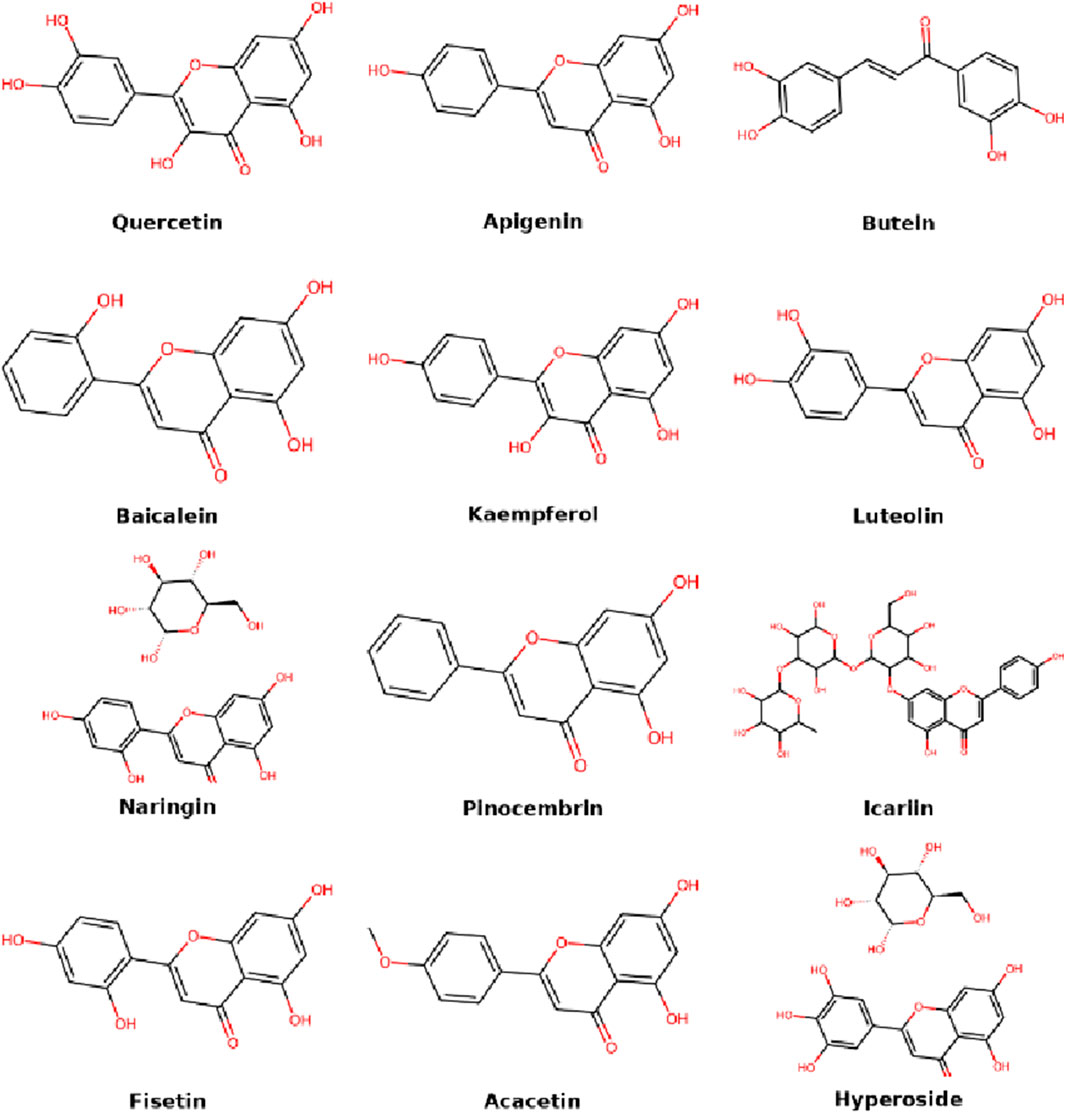
Flavonoids are among the most widely investigated natural compounds in IDD treatment due to their potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and matrix-preserving properties. Their polyphenolic structures allow them to scavenge free radicals, inhibit pro-inflammatory pathways, and modulate ECM metabolism in nucleus pulposus cells. It is worth noting that flavonoids are a subclass of phenolic compounds, sharing similar polyphenolic structures and biological functions such as antioxidation and anti-inflammation. However, flavonoids are often discussed separately due to their extensive subclass-specific research. This section discusses key flavonoids and their specific mechanisms of action, highlighting their therapeutic relevance to disc degeneration (Figure 2).
2.1 Hyperoside
Hyperoside is a natural flavonol glycoside derived from various plant genera, including Hypericum, Filipendula, and Polygonum. It is recognized for its notable anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptotic activities (Xu et al., 2022). SIRT1, an NAD+-dependent deacetylase and key regulator of inflammation in inflammatory and immune responses (Han et al., 2021). Studies have indicated that SIRT1 activation stimulates the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathway, thereby suppressing interleukin (IL)-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation in nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs), and regulating extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling (Qi et al., 2020). Additionally, activation of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress contributes significantly to NPC apoptosis and ECM degradation, thereby playing a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of IDD (Yao et al., 2024). Recent evidence indicates that hyperoside significantly mitigates TNF-α-induced apoptosis in human NPCs by upregulating SIRT1 and Nrf2. Furthermore, hyperoside effectively reduces ECM degradation and apoptosis mediated by ER stress, highlighting its therapeutic potential in the treatment of IDD (Xie et al., 2022a).
2.2 Quercetin
Quercetin, a widely distributed flavonoid, exhibits strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (Li Y. et al., 2016). The p38 MAPK signaling pathway, an essential component of the MAPK family, significantly contributes to the pathological processes underlying intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) (Zhang X. et al., 2023). Studies have shown that quercetin effectively protects NPCs from apoptosis by inhibiting p38 MAPK-mediated autophagy, thereby preventing ECM degeneration and significantly alleviating IDD symptoms in a rat tail puncture-induced IDD model (Zhang S. et al., 2021). Additionally, quercetin exerts protective effects on NPCs by suppressing apoptosis and ECM degradation through activation of the SIRT1-autophagy signaling pathway (Wang D. et al., 2020). Notably, quercetin is recognized as a senolytic agent capable of binding to the Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keap1)–nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) complex, subsequently inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. This action reduces the expression of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors in interleukin (IL)-1β-stimulated NPCs (Shao et al., 2021). Furthermore, a combination therapy involving dasatinib and quercetin has demonstrated efficacy in attenuating age-dependent IDD progression in mouse models (Novais et al., 2021). Quercetin also inhibits oxidative stress-induced senescence in mesenchymal stem cells derived from NPCs through regulation of the miR-34a/SIRT1 axis (Zhao WJ. et al., 2023). Quercetin (100 mg/kg/day) reduced IL-1β by 45% and increased SIRT1 2.1-fold. Network pharmacology studies have further identified quercetin as a critical bioactive component in traditional Chinese medicine formulas commonly employed for lumbar disc herniation treatment (Sun W. et al., 2022). These collective in vitro and in vivo findings underscore quercetin’s promising therapeutic potential for IDD management.
2.3 Apigenin
Apigenin, another flavonoid compound, possesses a broad spectrum of biological activities. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a conserved serine/threonine kinase, has a significant role in various degenerative joint conditions, including IDD (Pal et al., 2015). The mTOR signaling pathway is essential for maintaining homeostasis within the intervertebral disc, and disruptions in autophagic flux are closely linked to NPC senescence and apoptosis during IDD progression (Chen et al., 2023). Apigenin enhances autophagy through the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/mTOR/transcription factor EB (TFEB) signaling cascade, effectively alleviating oxidative stress-induced senescence in NPCs. Moreover, apigenin suppresses the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokines, thereby mitigating disc degeneration in rat models of IDD (Ding and Li, 2020). These findings highlight apigenin as a potentially valuable natural therapeutic candidate for the prevention and treatment of IDD.
2.4 Butein
In addition to mechanical stress, diabetes and the accumulation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) significantly contribute to the progression of IDD (Li S. et al., 2024). Dysregulated glucose metabolism exacerbates IDD by affecting critical cellular processes such as senescence, apoptosis, inflammation, proliferation, and ECM degradation (Jung et al., 2023; Lintz et al., 2022). Butein, a chalcone-type flavonoid isolated from plants belonging to the Anacardiaceae, Asteraceae, and Fabaceae families (Padmavathi et al., 2017), exhibits diverse pharmacological properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, anticancer, and antidiabetic activities (Song et al., 2016). Both in vitro and in vivo studies have revealed that butein activates SIRT1, leading to the suppression of p53 acetylation. This mechanism protects NPCs from apoptosis and senescence triggered by hyperglycemia. Specifically, butein treatment significantly alleviated IDD symptoms in diabetic rat models, as evidenced by increased expression of SIRT1 and decreased acetylation levels of p53 within nucleus pulposus tissues (Zh et al., 2019). These findings indicate butein as a promising candidate for IDD management, particularly in diabetic contexts.
2.5 Baicalein
Baicalein is a prominent flavonoid isolated predominantly from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis, a traditional medicinal herb widely utilized in Chinese medicine (Tsou et al., 2016). It has been extensively studied for its potent hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory properties across diverse disease models (Chen et al., 2014). Research has demonstrated that baicalein effectively inhibits the activation of key signaling pathways such as NF-κB and MAPK. It also reduces the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines, including prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and IL-6 in IL-1β-stimulated NPCs. Baicalein (25–50 μM) reduced cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and PGE2 by 52%–68%. Furthermore, baicalein has shown a dose-dependent capability to counteract ECM degradation, specifically reversing the loss of aggrecan and type II collagen (Col2) (Jin et al., 2019). Complementary in vivo studies employing rat models of needle puncture-induced IDD further validate baicalein’s therapeutic efficacy in mitigating disc degeneration (Jin et al., 2019). Additionally, baicalein suppresses TNF-α-induced apoptosis and catabolic activity in NPCs through activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (Liu Y. et al., 2023). Collectively, these studies underscore baicalein’s significant therapeutic potential as a natural product-based intervention for IDD.
2.6 Kaempferol
Kaempferol is a naturally occurring flavonoid found in tea, as well as many common vegetables and fruits, including legumes, broccoli, cabbage, gooseberries, grapes, kale, strawberries, tomatoes, citrus fruits, Brussels sprouts, apples, and grapefruits (Calderón-Montaño et al., 2011). Its anti-inflammatory properties allow it to be used in treating a range of acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, such as disc degeneration, colitis, postmenopausal bone loss, and acute lung injury (Ren et al., 2019). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) are considered a promising autologous source for regenerating nucleus pulposus tissue. When co-cultured with NPCs, BMSCs can differentiate into NPC-like cells, enhancing their viability and matrix production (Cao et al., 2015). Kaempferol ameliorates IDD progression by suppressing osteogenic, adipogenic, and inflammatory responses induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in BMSCs (Zhu et al., 2017). In an injectable kaempferol-loaded fibrin gel study (Gao et al., 2023), intradiscal injection in IDD rat models demonstrated favorable injectability, sustained release, and biocompatibility. The treatment reduced IDD-associated inflammation and regulated ECM synthesis and degradation. Network pharmacology studies suggest kaempferol may be a key active compound in traditional Chinese medicine for IDD (Wang X. et al., 2023; Liu H. et al., 2023). In IL-1β-induced in vitro IDD models, kaempferol inhibited phosphorylation of ERK1/2, downregulated matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-3 and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs (ADAMTS)-4, while upregulating aggrecan and type II collagen expression. Kaempferol significantly restored cell viability and reduced both ROS accumulation and apoptosis in NPCs (Wang X. et al., 2023).
2.7 Luteolin
There is a close relationship between the intervertebral disc and the adjacent vertebral endplates, and Modic changes, defects, sclerosis, and calcification in these endplates are associated with disc degeneration (Zehra et al., 2019). Degeneration of the endplate may result in abnormal collagen-bone matrix remodeling, spatial reorganization, hypertrophy, and angiogenesis, which in turn promote IDD progression (Zehra et al., 2017). Luteolin, beyond its general antioxidant activity as a flavonoid, exhibits anti-inflammatory, cardiovascular, anticancer, and neuroprotective properties (Huan et al., 2023). It is found in various vegetables, botanical drugs, and fruits such as carrots, broccoli, cabbage, parsley, thyme, mint, basil, celery, artichokes, and apples (Aziz et al., 2020). A study on endplate chondrocytes found that luteolin significantly suppressed the expression of MMP13, p53, and p21 while promoting CDK2, CDK4, and Col2α1 expression. It alleviated chondrocyte senescence, as confirmed by cell cycle analysis, proliferation assays, and β-galactosidase staining (Long et al., 2025). Another study showed that Luteolin dose-dependently reduced NPC apoptosis and reversed TNF-α-induced senescence and inflammation through activating SIRT6 and inhibiting NF-κB (Xie et al., 2022b).
2.8 Naringin
Naringin is a flavonoid compound extracted from citrus fruits, known for its strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (Gan et al., 2023). In a study using degenerative human NPCs from patients with discogenic low back pain, naringin increased aggrecan, bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2, and SRY-box transcription factor 6 (Sox6) expression, while inhibiting TNF-α and MMP3 expression, promoting NPC proliferation and recovery from degeneration (Li N. et al., 2016). Naringin also enhanced autophagy by upregulating LC3 and Beclin-1, reducing oxidative stress-induced NPC apoptosis. Its anti-apoptotic effect was partially reversed by 3-methyladenine, suggesting autophagy is key to its protective action (Zhang et al., 2018). Naringin regulates autophagy via the AMPK pathway, either directly or by indirectly activating SIRT1 (Chen R. et al., 2022), maintaining ECM stability in terms of Col2, aggrecan, and MMP13. In vivo studies showed that naringin alleviated IDD in puncture-induced rat models. In studies on nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells (NPMSCs), naringin at 100 μM for 24 h was non-cytotoxic and reduced H2O2-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway, also mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction, including increased ROS, decreased membrane potential, reduced ATP levels, and altered ultrastructure (Nan et al., 2020a). Naringin suppressed IL-1β-induced MMPs and inflammation in NPCs by downregulating the NF-κB pathway and p53 expression (Gao G. et al., 2019). It also inhibited annulus fibrosus cell apoptosis caused by cyclic stretch by suppressing NF-κB activation, and MRI assessments confirmed IDD alleviation in treated rats (Zhang YH. et al., 2022). Additionally, naringin protected endplate chondrocytes from apoptosis by promoting SIRT3-mediated mitophagy and suppressing NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome activation (Wang J. et al., 2024), which is involved in the IDD pathological process (Chao-Yang et al., 2021). Naringin and its aglycone naringenin are also identified as effective anti-inflammatory agents for treating low back pain and sciatica (Devraj et al., 2019).
2.9 Pinocembrin
Pinocembrin is a major flavonoid compound isolated from various plants, including pine heartwood, eucalyptus, poplar, euphorbia, and Boesenbergia rotunda (Rasul et al., 2013). It exhibits antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, neuroprotective, cardioprotective, and anticancer properties (Elbatreek et al., 2023). A significant study found that pinocembrin alleviated IDD progression in mice and protected the CEP from oxidative stress-induced degeneration and calcification (Wa et al., 2023). In vitro, it activated the Nrf2 pathway, inhibited parkin-mediated mitophagy, and reduced chondrocyte ferroptosis.
2.10 Icariin
Icariin is a flavonoid glycoside extracted from Epimedium, a traditional Chinese medicinal herb, and has gained attention due to its diverse pharmacological activities (Szabó et al., 2022). Widely used in traditional medicine and valued in modern pharmacology, icariin is a promising natural compound for biomedical and tissue engineering applications (Seyedi et al., 2023). It possesses multiple therapeutic effects on bone health, inflammation, cancer, immunity, cardiovascular and nervous system protection, and sexual function (Wang et al., 2021a; Song et al., 2020; Zeng et al., 2022; Si et al., 2024; Fang et al., 2024). Studies indicate that icariin protects NPCs and CEP cells and slows IDD progression by exerting anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic effects and promoting ECM synthesis. It inhibits IL-1β-induced MAPK and NF-κB pathways, reducing proinflammatory factors, degradative enzymes, and oxidative stress (Hua et al., 2018). Moreover, icariin activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to promote mitophagy, inhibit ferroptosis, maintain mitochondrial function and redox balance, and enhance cell survival (Hua et al., 2020; Shao Y. et al., 2022). In vivo, it upregulates chemokines such as insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, and stromal-derived factor (SDF)-1, promoting stem cell migration and tissue repair, mitigating CEP calcification and IDD pathology (Shao Y. et al., 2022; Zhang Z. et al., 2022).
2.11 Fisetin
Fisetin is a natural flavonoid found in many fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, apples, persimmons, and cucumbers (Khan et al., 2013). Due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, anti-aging, and nephroprotective activities (Kashyap et al., 2019; Ren et al., 2021; Wang B. et al., 2024; Ding et al., 2022; Zhou C. et al., 2023), it shows potential in treating various chronic diseases. Fisetin protects both NPMSCs and NPCs by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis, while maintaining ECM integrity (Zhou Q. et al., 2023). Oxidative stress is a major driver of IDD, and fisetin, acting through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, inhibits oxidative stress-induced ferroptosis, reduces cell death, and maintains ECM homeostasis (Li C. et al., 2024). Both in vitro and in vivo studies confirm its effectiveness in protecting disc cells and alleviating disc degeneration in rats (Zhou Q. et al., 2023; Li C. et al., 2024).
2.12 Acacetin
Acacetin is a monomethoxy flavonoid mainly found in Robinia pseudoacacia and various botanical drugs (Singh et al., 2020). It has shown broad therapeutic potential due to its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, anti-obesity, and cardiovascular protective properties (Wu et al., 2022; Zhang G. et al., 2023; Bu et al., 2024; Mu et al., 2022; Liou et al., 2022; Li et al., 2020). Acacetin effectively mitigates NPC degeneration in both in vitro and in vivo models. In vitro, it activates the Nrf2 pathway, upregulates antioxidant proteins such as HO-1, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), and superoxide dismutase (SOD), inhibits ROS production, and reduces COX-2 and iNOS-mediated inflammation. It also prevents aggrecan and Col2 degradation (Wang et al., 2020b; Pan C. et al., 2023). Additionally, acacetin inhibits the phosphorylation of p38, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and ERK1/2, thereby slowing NPC degeneration. In vivo studies using MRI and histopathology confirmed that acacetin significantly ameliorates IDD in puncture-induced rat models (Wang et al., 2020b).
3 Glycosides
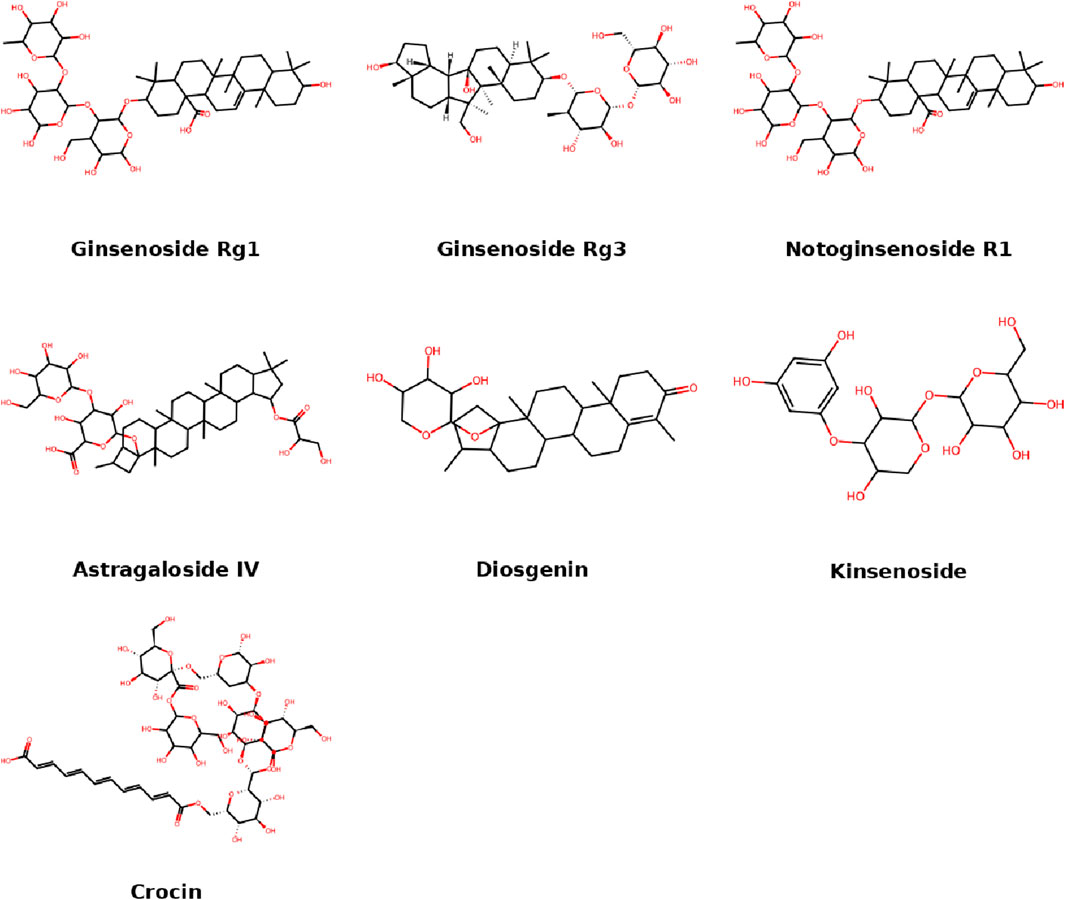
Glycosides, especially saponins, are active components in many traditional herbal medicines. In IDD models, glycosides exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, and anti-apoptotic effects, often through PI3K/Akt or JAK/STAT signaling. Their glycosidic linkages enhance solubility and bioavailability, contributing to their therapeutic potential. This section summarizes representative glycosides and their regulatory functions in IDD (Figure 3).
3.1 Ginsenosides
Ginseng is one of the most widely used herbal nutraceuticals in the world and has a long history of use in traditional Chinese medicine (Shi et al., 2019). Modern pharmacological studies have shown that ginseng has multiple biological effects, including anticancer, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities (Metwaly et al., 2019). Ginsenosides are the main active components of ginseng and are triterpenoid saponins, with more than 180 types identified to date (Yu et al., 2019). Based on the structure of the glycoside moiety, Rg1 is classified as a protopanaxatriol-type dammarane ginsenoside (Kim et al., 2015). Ginsenoside Rg1 has become a major research focus for IDD treatment. It can regulate disc homeostasis and water content, inhibit apoptosis, inflammation, and ECM degradation, thereby delaying the progression of IDD. Rg1 improves NPC proliferation, reduces apoptosis, and enhances aggrecan and type II collagen (Col2α1) expression by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway (Yu et al., 2020). It also suppresses the activation of the Yes-associated protein (YAP)-1/transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ) pathway, thereby preventing IDD progression. Rg1 significantly increases the mechanical and thermal threshold in IDD rats and alleviates histological changes (Yang YH. et al., 2022). Recent studies found that Rg1 ameliorates IDD progression in rats by inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB pathway. In IL-1β-induced NPCs, Rg1 promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and suppresses the expression of IL-6, TNF-α, aggrecan, collagen II, p-p65/p65, and inhibitor of kappa B kinase (IκK) in a dose-dependent manner (Yu et al., 2024). Rg1 (10–50 μM) decreased TNF-α and IL-6 by 60%, and upregulated aggrecan expression by >2-fold. In addition, ginsenoside Rg3, a protopanaxadiol-type saponin, has also been shown to regulate IDD. Treatment with Rg3 reversed IL-1β-induced apoptosis in NPCs and significantly reduced the expression of MMP2, MMP3, ADAMTS-4, and ADAMTS-5 via inactivation of the p38 MAPK pathway. Compared to Rg1, Rg3 not only alleviates NPC degeneration but also restores annulus fibrosus alignment and preserves more proteoglycan-rich matrix (Chen J. et al., 2024).
3.2 Notoginsenoside
The root of Panax notoginseng has been used as a traditional herb for thousands of years, mainly for hemostasis and promoting blood circulation, and it holds a landmark status in traditional Chinese medicine (Zhu and Wan, 2023). Its major pharmacological effects are attributed to notoginsenosides, a group of dammarane-type tetracyclic triterpenes with potent bioactivity (Liu et al., 2020a). Notoginsenosides exhibit a broad range of activities including cardiovascular protection, neuroprotection, antidiabetic effects, hepatoprotection, gastrointestinal protection, pulmonary protection, bone metabolism regulation, renal protection, and anticancer effects (Liu et al., 2020b; Guo et al., 2019). Notoginsenoside R1 (NGR1), a member of the protopanaxatriol group, is the major component of notoginsenosides, with significantly higher content in roots and rhizomes than in other plant parts (Zhu T. et al., 2021). NGR1 enhances alkaline phosphatase activity and mineralized nodule formation in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), and increases estrogen receptor-α expression, thereby regulating the GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway to promote BMSC proliferation, migration, and osteogenic differentiation (Lu et al., 2024). In studies using IDD rat models and NPCs, NGR1 inactivated the NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway, improved NPC function, and inhibited pyroptosis, while promoting ECM synthesis and reducing proinflammatory cytokine mRNA expression both in vitro and in vivo (Tang et al., 2021).
3.3 Astragaloside IV
Astragalosides I, II, and IV are the major saponins found in Astragalus membranaceus, with astragaloside IV (AS-IV) being the most biologically active (Zhang et al., 2020). AS-IV is one of the main active components extracted from Astragalus and is considered a marker compound for quality evaluation of traditional Chinese medicines. It has demonstrated anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective, antifibrotic, and antitumor effects (Liang et al., 2023). In NPCs, miR-223 promotes inflammation and cell injury via the JAK2/STAT1 pathway, and the combined use of AS-IV and tanshinone IIA may protect NPCs by downregulating miR-223 and suppressing JAK2 and STAT1 expression (Du et al., 2021). Other Astragalus derivatives, such as cycloastragenol and AS-IV, have been shown to extend the proliferative capacity and lifespan of NPCs (Hong et al., 2021). These compounds upregulate telomerase expression and improve telomere attrition under high glucose conditions, while enhancing proliferation and morphology of NPCs. In vitro and in vivo studies of IDD have demonstrated that AS-IV reduces IL-1β-induced inflammation, apoptosis, and ECM degradation, and protects against IDD progression in needle-puncture rat models (Tian et al., 2022). AS-IV inhibits IκB-α phosphorylation and NF-κB p65 nuclear translocation, indicating suppression of the NF-κB pathway. It also upregulates Col2, aggrecan, and Bcl-2 while downregulating Bax and cleaved caspase-3 expression and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway (Zhang L. et al., 2023). Furthermore, AS-IV maintains disc height and volume in lumbar instability mouse models, improves matrix metabolism, and restores Col2α1, ADAMTS-5, aggrecan, and MMP-13 expression in degenerated discs. It also suppresses EGFR, p38 MAPK, and caspase-3 expression in annulus fibrosus tissue during IDD progression, possibly via inhibition of the EGFR/MAPK pathway (Chen D. et al., 2024).
3.4 Dioscin
Dioscin is a natural steroidal saponin with bioactivity, extracted from several medicinal botanical drugs (Bandopadhyay et al., 2022). Pharmacological research has demonstrated its anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, and antioxidant effects in various diseases (Tao et al., 2018). In IDD, dioscin inhibits the IL-1β-induced overexpression of MMP1, MMP3, MMP13, and ADAMTS-5, while promoting Col2 and aggrecan synthesis, thereby maintaining ECM homeostasis in cartilage. These effects are associated with inhibition of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways (Ding et al., 2023). Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) is overexpressed in cartilage during osteoarthritis and plays an important role in cartilage degradation (Gómez et al., 2015). Similarly, degenerated NPCs show increased TLR4 expression and respond to LPS-induced TLR4 activation by enhancing proinflammatory cytokine release and reducing ECM content in discs (Rajan et al., 2013). Studies on the potential effects of dioscin in IL-1β-treated NPCs indicate that it suppresses the TLR4/NF-κB pathway to reduce catabolic activity and levels of IL-6 and TNF-α (Wang L. et al., 2020).
3.5 Kinsenoside
Kinsenoside is a glycoside compound extracted from Anoectochilus roxburghii and is considered its primary bioactive constituent (Qi et al., 2018). Anoectochilus is a member of the Orchidaceae family and is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical Asia (Song W. et al., 2021). Kinsenoside possesses hepatoprotective, hypoglycemic, hypolipidemic, anti-inflammatory, vasoprotective, and anti-osteoporotic properties (Han et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2013; Xiang et al., 2016). Its biological effects are associated with pathways such as ERK, MAPK, NF-κB, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling (Luo et al., 2018). In both in vivo and in vitro studies, kinsenoside treatment alleviated T2-weighted signal loss and disc height reduction in IDD rat models, kinsenoside (50 mg/kg) improved disc height index by 22.3%, improved matrix loss and other pathological features, and delayed IDD progression. Kinsenoside activated the AKT–ERK1/2–Nrf2 pathway in NPCs, and in a Nrf2-dependent manner, rescued NPC viability under oxidative stress and protected against apoptosis, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction (Wang Y. et al., 2019).
3.6 Crocin
Crocin is a glycosylated carotenoid compound extracted from Crocus sativus L (saffron) and is the main water-soluble carotenoid responsible for its yellow color (Boozari and Hosseinzadeh, 2022). Crocin has demonstrated antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, anti-retinopathy, anticancer, and antidepressant properties (Heydari et al., 2023; Hashemzaei et al., 2020; Pourmousavi et al., 2024; Tao et al., 2023). Studies have shown that crocin can inhibit inflammation and catabolic processes associated with IDD (Li et al., 2015). In vitro, crocin significantly suppresses the LPS-induced overexpression of MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, ADAMTS-4, ADAMTS-5, and proinflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS, and TLR-2. Crocin (25–100 μM) reduced MMP-13 mRNA by 65%, cytokine levels by >50%. It also inhibits JNK phosphorylation in the MAPK pathway and partially prevents the reduction of chondroitin sulfate and Col2. Ex vivo experiments indicate that crocin protects ECM components in the disc and delays IDD progression (Li et al., 2015).
4 Terpenoids
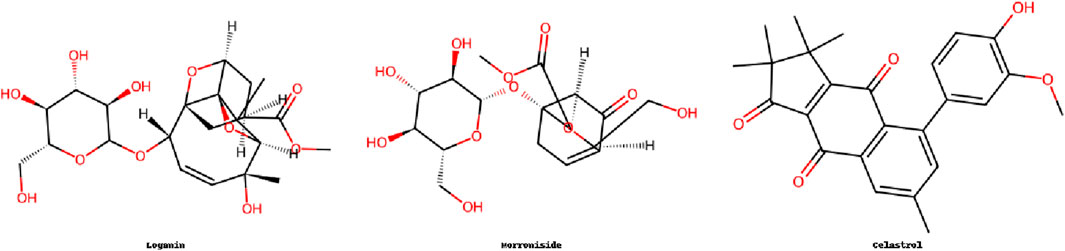
Terpenoids, derived from isoprene units, exhibit diverse bioactivities and have shown promise in IDD therapy. Their mechanisms include the inhibition of inflammatory signaling pathways, protection of ECM components, and modulation of cellular stress responses. Glycosides, especially saponins, sometimes overlap in biological functions with terpenoids, particularly in modulating PI3K/Akt and NF-κB pathways. This overlap indicates possible structural synergy or shared biosynthetic origins. This section highlights key terpenoid compounds and their functions in delaying disc degeneration (Figure 4).
4.1 Aucubin
Aucubin is an iridoid glycoside compound widely found in traditional medicinal botanical drugs such as Eucommia ulmoides Oliv (Eucommiaceae), Aucuba japonica, and Plantago asiatica (Bridi et al., 2023). It exhibits anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anxiolytic and antidepressant, antidiabetic, antifibrotic, antimicrobial, anticancer, antihypertensive, gastroprotective, cardioprotective, and retinoprotective properties (Kartini et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2020d; Shao M. et al., 2022; Yang P. et al., 2022; Feng et al., 2023). Due to its abundant natural sources, high safety, and multiple biological benefits, aucubin holds great potential for applications in health supplements and pharmaceuticals (Zeng et al., 2020). In recent years, microRNAs (miRNAs) have been actively studied in the context of IDD and are considered to play important roles in its pathogenesis through various pathways (Wang et al., 2022). Aucubin inhibits ECM degradation in IL-1β- or TNF-α-stimulated NPCs by downregulating miR-140 expression and modulating its downstream target, cAMP response element-binding protein 1 (CREB1) (Ya et al., 2019). In both in vivo and in vitro experiments using a lumbar instability mouse model, aucubin was found to increase the expression of Col2α1 and aggrecan while reducing MMP-13, p-p65, NLRP3, and caspase-1 expression. It suppressed NF-κB–NLRP3 inflammasome activation in chondrocytes and mitigated ECM degradation in cartilage endplate (CEP) cells, thereby alleviating CEP degeneration (Zou et al., 2023). Aucubin (100 mg/kg/day) increased Col2α1 and aggrecan expression by 2.5-fold, and decreased MMP-13 by 60%. Additionally, aucubin exerts protective effects against IDD by modulating the NF-κB and Wnt signaling pathways, inhibiting cellular senescence, and reducing inflammatory cytokine levels (Li L. et al., 2023).
4.2 Morroniside
Morroniside is an iridoid glycoside extracted from Cornus officinalis, a traditional herb that has been used as food and medicine in China, Korea, and Japan for over 2,000 years (Shi P. et al., 2024). It possesses neuroprotective, osteoprotective, cardioprotective, nephroprotective, and hepatoprotective properties (Yu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2023b; Li W. et al., 2023; Zhang C. et al., 2024), and has demonstrated potential in the prevention and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia, spinal cord injury, Alzheimer’s disease, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, acute myocardial infarction, and diabetes (Jiang H. et al., 2024; Xiao et al., 2023; Qian et al., 2024; Duan et al., 2021; Chen Y. et al., 2024). Recent studies have shown that morroniside significantly ameliorates the progression of IDD. In both in vitro and in vivo studies, morroniside suppressed ROS-induced aberrant activation of the Hippo signaling pathway in NPCs and reduced the expression of senescence markers including senescence-associated β-galactosidase, p53, and p21 (Zhou et al., 2022; Ge et al., 2024). Its mechanisms include inhibition of the phosphorylation of MST1/2 and LATS1/2 within the Hippo pathway, thereby reversing YAP/TAZ suppression, alleviating NPC senescence, and mitigating IDD progression by regulating ECM metabolism and preserving tissue structural integrity (Zhou et al., 2022). Moreover, morroniside reduced NPC pyroptosis by activating the Nrf2/Keap1 pathway, further supporting its therapeutic potential in IDD (Ge et al., 2024). These findings suggest that morroniside may serve as a novel therapeutic agent for IDD by targeting multiple mechanisms, particularly the ROS–Hippo–p53 signaling axis.
4.3 Celastrol
Celastrol is a pentacyclic triterpenoid compound extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. (Celastraceae), and it exhibits a wide range of pharmacological effects (Wang et al., 2023b). It has shown potent anticancer, antitumor, anti-obesity, and antidiabetic properties (Song et al., 2023; Xu H. et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2021; Gu et al., 2023), and has demonstrated unique therapeutic potential for acute and chronic inflammation, brain injury, vascular disorders, immune diseases, renal disorders, skeletal diseases, and cardiac conditions (Li Z. et al., 2022; Li M. et al., 2022; Zhang C. et al., 2021; Shirai et al., 2023; Pan M. et al., 2023). Celastrol effectively suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, reducing IL-1β-induced expression of matrix-degrading enzymes (such as MMP-3, MMP-9, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-4, -5), oxidative stress markers (COX-2, iNOS), and pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, TNF-α) in NPCs (Chen et al., 2017). Celastrol (0.25–1.0 μM) reduced MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 by over 70%. Moreover, in vivo studies have shown that celastrol improves disc structure and significantly enhances T2-weighted MRI signals in a puncture-induced rat model of IDD (Chen et al., 2017).
5 Phenolic
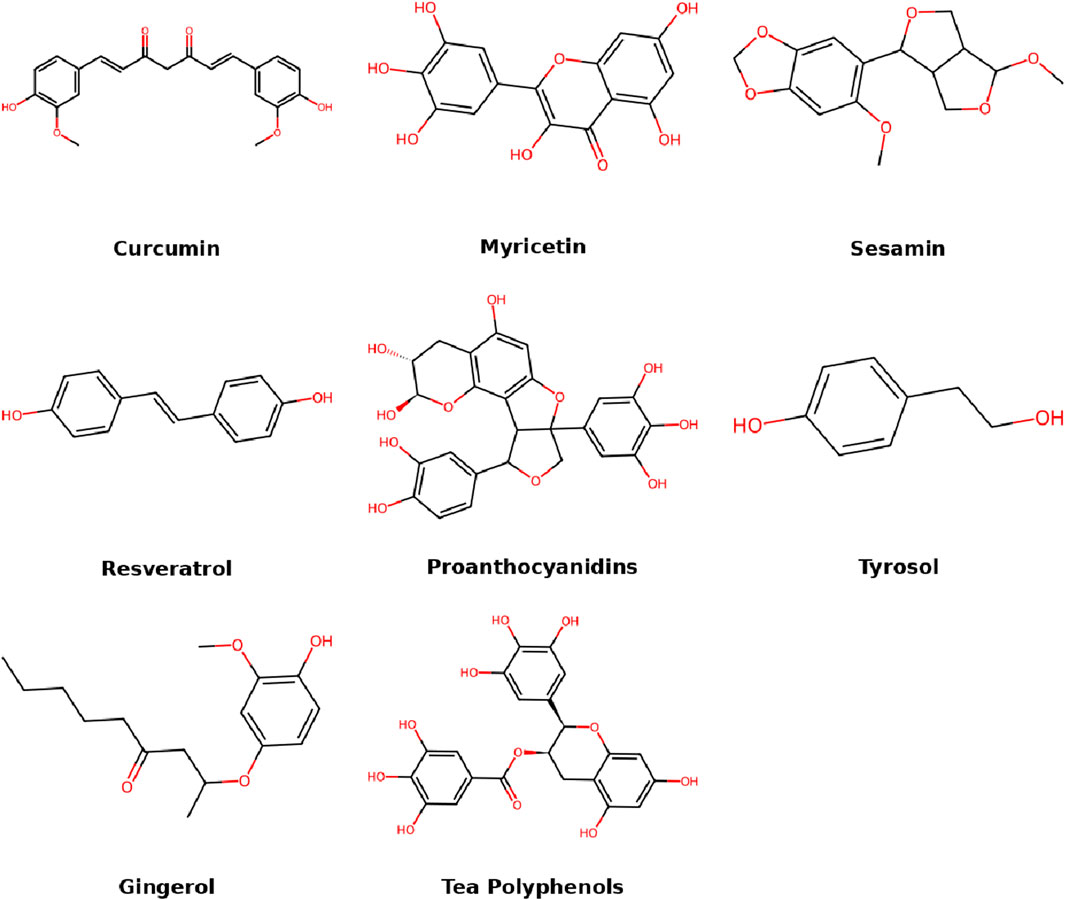
Some terpenoids exhibit similar anti-inflammatory mechanisms to glycosides and phenolics, suggesting cross-class pharmacological activity in IDD management. Phenolic compounds are natural antioxidants widely found in plants. In IDD, they modulate oxidative stress, inhibit inflammatory mediators, and promote ECM synthesis. Their structural diversity, such as hydroxyl group positioning and conjugation, contributes to their differential biological effects. Phenolic compounds as a broad category include flavonoids as a subclass. Their shared hydroxyl-rich structures contribute to their roles in redox regulation and inflammation suppression. This section reviews major phenolic agents involved in IDD management (Figure 5).
5.1 Curcumin
Curcuma longa (Zingiberaceae) is widely used in India, China, and Southeast Asia as an aromatic stimulant, food preservative, and coloring agent. It is now also cultivated in other regions, including Southeast Asia, China, and Latin America (Kotha and Luthria, 2019). Curcumin, a polyphenolic compound extracted from turmeric, possesses a wide range of pharmacological properties, including anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer, antidiabetic, antibacterial, antiviral, antifibrotic, immunomodulatory, and antifungal activities (Zia et al., 2021; Abd et al., 2021; Zhao C. et al., 2023; Nanavati et al., 2022). In recent years, curcumin nanoformulations have attracted increasing attention—such as nanofibers, lipid-based nanostructured carriers, solid self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems, and nanohydrogels—which offer enhanced bioavailability compared to free curcumin (Ataei et al., 2023; Ansari et al., 2023; Araya-Sib et al., 2021). In IDD rat models, curcumin intervention significantly reduced the expression of NF-κB p65 and TNF-α in lumbar disc tissues. MRI and ultrastructural analyses also revealed marked improvements in disc degeneration in the curcumin-treated group (Ma et al., 2015). Further studies found that curcumin protects against IDD progression by decreasing levels of IL-1β, IL-6, iNOS, COX-2, TGF-β1/2, and MMP-9, while promoting the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) (Hu et al., 2017). Curcumin (50 mg/kg) reduced NF-κB and TNF-α by 45%–60%, BDNF ↑2.3-fold. Curcumin regulates the expression of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) factors and enhances ECM synthesis via the Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways in degenerated discs (Cherif et al., 2019). In addition, curcumin upregulates autophagy, inhibits apoptosis, and mitigates phenotype loss in endplate chondrocytes under high-tension mechanical loading, thereby alleviating mechanical imbalance-induced IDD (Xiao et al., 2020). Novel polylactic acid nanoparticles loaded with curcumin—produced using solvent evaporation and water-in-oil emulsion methods—form bioactive hydrogels that overcome curcumin’s hydrophobicity and inhibit TNF-α production, immune cell activation, and inflammation, offering a promising future strategy for IDD therapy (Zamboni et al., 2022).
5.2 Myricetin
Myricetin is both a flavonoid and a phenolic compound. Its structure contains multiple hydroxyl groups, giving it strong antioxidant capacity typical of polyphenols (Jomová et al., 2019). Myricetin is widely distributed in fruits, vegetables, tea, berries, and red wine (Song X. et al., 2021). It exhibits antioxidant, antidiabetic, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antiepileptic, anti-amyloidogenic, and cardiovascular protective properties (Kumar et al., 2023; Pluta et al., 2021; Wang L. et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023c; Rahmani et al., 2023; Sharma et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2022). Studies have shown that myricetin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory responses, reducing the production of proinflammatory mediators such as iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, and IL-6, while regulating ECM component expression—reversing downregulation of aggrecan and type II collagen and suppressing the upregulation of MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 (Xie et al., 2023). Myricetin (25–50 μM) reduced IL-6/iNOS 58%–70%. Additionally, myricetin activates the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and blocks NF-κB activation, protecting NPCs from oxidative stress and inflammation (Mao and Fan, 2024). In both in vitro and in vivo models, myricetin effectively alleviated apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunction, and senescence induced by H2O2 or IL-1β (Xie et al., 2023; Mao and Fan, 2024). These findings highlight myricetin’s significant biological activity in preventing and treating IDD, particularly through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.
5.3 Sesamin
Sesamin is a lipophilic lignan classified as a polyphenol, derived from sesame seeds and oil. It exhibits diverse pharmacological activities including immunomodulation, anti-inflammation, antioxidant, and neuroprotection (Majdalawieh et al., 2022; Dalibalta et al., 2020; Ghaderi et al., 2023). It is commonly used as a dietary supplement to improve blood pressure and lipid levels, mainly by modulating key steps in fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism (Sun Y. et al., 2022; Majdalawieh et al., 2020). In studies of disc degeneration, sesamin protects intervertebral discs from inflammation and ECM damage by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation and MAPK pathway activation, thereby reducing LPS-induced expression of inflammatory cytokines and catabolic enzymes (Li K. et al., 2016). In vivo, sesamin attenuates injury-induced IDD, as demonstrated by preserved MRI signals, suppressed expression of catabolic enzymes, maintained ECM content, and reduced histological degeneration, indicating its potential as an early therapeutic agent for IDD (Li and Lv, 2020). Moreover, sesamin inhibits apoptosis, reverses CASP3, BAX, and BCL2 expression, delays ECM degradation, and promotes cell proliferation, showing protective and therapeutic effects against lumbar disc degeneration (Guo et al., 2023). Recent studies have found that sesamin enhances cell viability and reduces apoptosis by upregulating BECN2 and downregulating autophagy-related genes (ATG14, VPS34, GASP1) and inflammasome proteins (NLRP3, NLRC4, NLRP1, AIM2), alleviating LPS-induced chondrocyte degeneration. These findings support BECN2 as a potential target for IDD therapy (Zhang B. et al., 2024).
5.4 Tea polyphenols
Tea polyphenols (TPs) possess anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and antitumor properties (Hong et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2021b; Dai et al., 2023). Major active components such as epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and epicatechin gallate (ECG) have shown promise in treating immune-related disorders and suppressing tumor metastasis (Bag and Bag, 2020). In food processing, TPs interact with proteins, polysaccharides, and lipids, affecting their functional properties (Rana et al., 2022). Further research into their immunomodulatory, antitumor mechanisms, and nutritional interactions will provide scientific evidence for health promotion and disease prevention. Studies have confirmed that TPs activate the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway, enhance the expression of matrix-related genes, and reduce degeneration-associated factors, thereby protecting NPCs from oxidative stress-induced degeneration and effectively delaying IDD in both in vitro and in vivo models (Song D. et al., 2021).
5.5 Resveratrol
Resveratrol exhibits multiple mechanisms of action in delaying or treating IDD, primarily by modulating the SIRT1 pathway, inhibiting ECM degradation and inflammation, and delaying cellular senescence. In degenerated human NPCs, resveratrol significantly upregulates SIRT1, Col2α1, and aggrecan expression while downregulating MMP-1 (Wu et al., 2015). In rabbit IDD models, intradiscal injection of resveratrol improved T2-weighted MRI signals, increased aggrecan expression, and reduced MMP-13 mRNA levels (Kwon, 2013). Mechanistically, resveratrol activates SIRT1, suppresses NF-κB signaling, and in 1,25(OH)2D-deficient mice, reduces TNF-α and IL-1β levels via SIRT1-mediated p65 deacetylation (Wang P. et al., 2023). Furthermore, resveratrol regulates NPC autophagy via the Nampt/NAD+/SIRT1 pathway, restoring LC3 II/I and Beclin-1 expression and delaying degeneration (Shi et al., 2022). Resveratrol (20 μM) increased LC3-II by >2-fold, reduced apoptosis 40%. For delivery, thermosensitive PLGA–PEG–PLGA hydrogels offer controlled release, and co-delivery with tannic acid significantly suppresses local inflammation and promotes ECM regeneration (Liu et al., 2025). Targeted delivery is further improved using CDH2 antibody-loaded nanobubbles with ultrasound, enhancing resveratrol localization and release in NPCs, effectively slowing degeneration (Shen et al., 2018). Resveratrol also exhibits anti-apoptotic, anti-aging, and antioxidant effects, inhibits p21 and p16 expression, promotes cell proliferation, and reduces apoptosis, supporting its potential as a therapeutic agent for IDD (Liu et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2017).
5.6 Proanthocyanidins (PACs)
Proanthocyanidins (PACs) effectively delay the progression of IDD through multi-target mechanisms, exhibiting significant anti-apoptotic, anti-aging, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties (Xu J. et al., 2023). Studies have shown that PACs activate the PI3K/Akt pathway to upregulate Bcl-2 expression and suppress Bax and cleaved caspase-3, thereby reducing IL-1β-induced apoptosis in human NPCs. PACs also inhibit the p53/p21/p16 signaling pathway, thereby reducing cellular senescence (Chen HW. et al., 2022). With respect to mitochondrial homeostasis, PACs help maintain membrane potential by activating the SIRT3/FOXO3 axis, inhibit Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission, and promote the expression of OPA1 and MFN2, significantly reducing caspase-3 activity (Hua et al., 2024). In terms of inflammation regulation, PACs block the binding of LPS to TLR4/MD-2, suppress the NF-κB pathway, and reduce the expression of various inflammatory mediators and matrix-degrading enzymes, while promoting the synthesis of type II collagen and aggrecan (Shang et al., 2020). Despite the current evidence being primarily derived from cellular and animal models, PACs show promising potential as therapeutic candidates for IDD, warranting the development of targeted delivery systems and further evaluation for clinical translation.
5.7 Tyrosol
Tyrosol is a natural phenolic compound with the chemical structure 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)phenol, widely found in marine and terrestrial fungi (e.g., Penicillium species) and plant endophytes (Ferreira et al., 2025). It exhibits a diverse range of activities, including inhibition of pathogenic virulence factor expression, antitumor and anti-inflammatory effects, as well as regulation of intestinal metabolism, showing application potential in antimicrobial, anticancer, and metabolic disease contexts (Chang et al., 2019; Yu et al., 2023; Pal et al., 2023). Tyrosol significantly inhibits IL-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation in human NPCs by upregulating SIRT1 and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway, reducing caspase activity and the levels of TNF-α, IL-6, nitric oxide (NO), and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). It also suppresses MMP expression while promoting the synthesis of type II collagen, SOX-9, and aggrecan. These effects are mediated by SIRT1-dependent modulation of the NF-κB/FOXO3 pathway, suggesting the potential of tyrosol as a therapeutic agent for delaying IDD progression (Qi et al., 2020).
5.8 Gingerol
Gingerols are phenylpropanoid phenolic compounds found in the rhizome of ginger, characterized by an o-methoxyphenol group and an unsaturated C11–C15 carbon chain. They are subclassified into 6-, 8-, and 10-gingerols based on side-chain length (Martin et al., 2017). Gingerols exhibit multiple biological activities, including anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, and antioxidant effects (Nimmakayala et al., 2016; Basith et al., 2016; Orhan et al., 2007). Gingerol derivatives such as D-6-G and 6-gingerol (6-GIN) have shown effectiveness in delaying IDD through multiple mechanisms. D-6-G significantly suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation and GSDMD-mediated pyroptosis, reduces IL-1β and IL-18 secretion, and upregulates IL-10. It also activates the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and preserve mitochondrial function (Xi et al., 2024). 6-GIN simultaneously activates the PI3K/Akt pathway, enhances type II collagen and aggrecan expression, and inhibits MMP-13 along with apoptosis-related signaling, and enhances autophagy to clear damaged mitochondria. Its protective effects on ECM depend on PI3K/Akt signaling, highlighting its anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and matrix-repairing potential in IDD (Nan et al., 2020b).
6 Alkaloids
Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing compounds with strong pharmacological properties. While structurally distinct from polyphenols, alkaloids also exhibit overlapping anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects, expanding the functional convergence among diverse natural compounds. In the context of IDD, they have been shown to reduce oxidative stress, suppress inflammatory cytokines, and protect disc cells from apoptosis. Their small molecular size and lipophilicity facilitate cell penetration and biological activity. This section focuses on key alkaloids and their therapeutic roles in IDD (Figure 6).
6.1 Ligustrazine
Ligustrazine is a benzopyran-type alkaloid with a tetramethylpyrazine structure, derived from the Umbelliferae plant Ligusticum chuanxiong. Its structure is recognized as a clinically effective agent in the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases (Ma et al., 2024), especially in neuroprotective drug development (Jiang et al., 2025). In rat models of disc degeneration induced by prolonged upright posture, pretreatment with ligustrazine effectively restored disc structure, inhibited the expression of collagen type X, MMP-13, and MMP-3, upregulated type II collagen, and decreased levels of inflammatory factors such as IL-1β, COX-2, and iNOS, showing strong tissue-protective and anti-inflammatory effects, ligustrazine (80 mg/kg) reduced MMP-13 and iNOS ∼60%, improved histological scores by 28%. (Liang et al., 2014).
6.2 Berberine
Berberine is an isoquinoline alkaloid widely found in plants of the Berberidaceae family, such as Coptis chinensis and Phellodendron amurense. Berberine and its derivatives have been proven to treat cardiovascular endothelial injury by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, autophagy, platelet dysfunction, and gut microbiota imbalance (Zhang et al., 2025). Berberine also shows therapeutic potential in renal and skin diseases (Fan et al., 2025; A et al., 2025). It reduces TBHP-induced apoptosis in NPCs by activating autophagy, upregulating Bcl-2, and inhibiting pro-apoptotic proteins (Chen et al., 2018). Additionally, it significantly inhibits the expression of MMP-3, MMP-13, and ADAMTS-4/5, reduces ECM degradation, and blocks NF-κB pathway activation, exerting both anti-inflammatory and matrix-protective effects, berberine (10 μM) suppressed cleaved-caspase 3 by 55%, increased Bcl-2 by 1.9-fold, inhibited MMP-13 by 68%. (Lu et al., 2019).
6.3 Sinomenine
Sinomenine is a morphinan alkaloid extracted from the Menispermaceae plant Sinomenium acutum. It has been used in China as an anti-inflammatory agent for over 30 years (Jiang S. et al., 2024). Sinomenine possesses a wide range of pharmacological effects, including anti-inflammatory, immunosuppressive, antitumor, and neuroprotective activities (Li D. et al., 2023; Li JM. et al., 2023; Jiang P. et al., 2024). It induces autophagy in NPCs, reversing TBHP-induced apoptosis and loss of cell viability; this protective effect is attenuated by the autophagy inhibitor 3-MA, indicating that its mechanism is autophagy-dependent. Animal experiments have also confirmed that sinomenine delays IDD progression (Gao Z. et al., 2019).
6.4 Higenamine
Higenamine is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid and a plant-derived β2-adrenergic receptor agonist. Since 2017, it has been listed on the World Anti-Doping Agency’s prohibited substances list (Rangelov et al., 2022). It possesses antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, electrophysiological regulatory, antifibrotic, and lipid-lowering properties (Chen DT. et al., 2022; Wen et al., 2021; Zhang NN. et al., 2022). Higenamine significantly inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in NPCs, reducing the expression of iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α, IL-6, and MMPs (Bai et al., 2019). Moreover, it alleviates apoptosis under inflammatory stimulation by suppressing ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway activation, thus exerting anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effects (Zhu X. et al., 2021).
6.5 Evodiamine
Evodiamine is an indoloquinazoline alkaloid derived from the Rutaceae plant Evodia rutaecarpa, and exhibits anticancer, cardioprotective, anti-inflammatory, and anti-Alzheimer’s effects, as well as digestive system protection (Lin et al., 2024; Solanki and Patel, 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). It upregulates SIRT1 expression and activates the PI3K/Akt pathway, effectively inhibiting LPS-induced apoptosis and ECM degradation in human NPCs, reducing MMP-13 and inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6), and promoting the synthesis of type II collagen, thereby exerting multiple protective effects (Kuai and Zhang, 2022).
6.6 Palmatine
Palmatine is a protoberberine-type isoquinoline alkaloid extracted from the Menispermaceae plant Fibraurea recisa. It exhibits protective effects in cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, and osteoarthritis (Xin et al., 2024; Li et al., 2023f), which are largely mediated through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (Ekeuku et al., 2020). Palmatine activates the transcription factor TFEB to enhance autophagy, reduces CHOP expression to alleviate TBHP-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress, and consequently inhibits NPC apoptosis and ECM degradation. Animal studies have shown that palmatine helps preserve disc tissue morphology, indicating its strong potential for structural protection in IDD (Yu et al., 2025).
7 Discussion and perspectives
Natural products have garnered increasing attention as promising therapeutic candidates for IDD due to their multi-target mechanisms and relatively low toxicity (Sprouffske et al., 2013). The compounds reviewed in this article—spanning flavonoids, glycosides, terpenoids, phenolic compounds, and alkaloids—exert anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-senescent, and ECM-regulating activities, primarily through the modulation of key signaling pathways such as NF-κB, SIRT1, Nrf2, PI3K/Akt, and MAPK (Figure 7) (Chen et al., 2021; Mavrogonatou and Kletsas, 2024). The collective findings provide a compelling preclinical foundation for further development of natural product-based IDD therapies (Table 1).
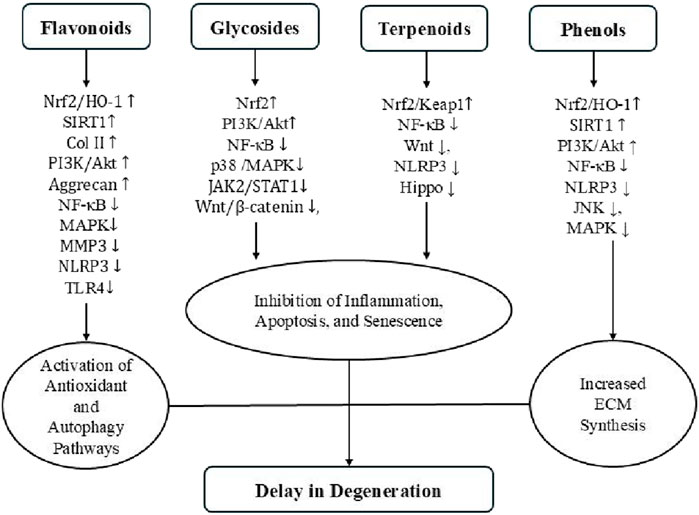
Figure 7. Key signaling pathways and mechanisms of four classes of natural compounds discussed in this review.
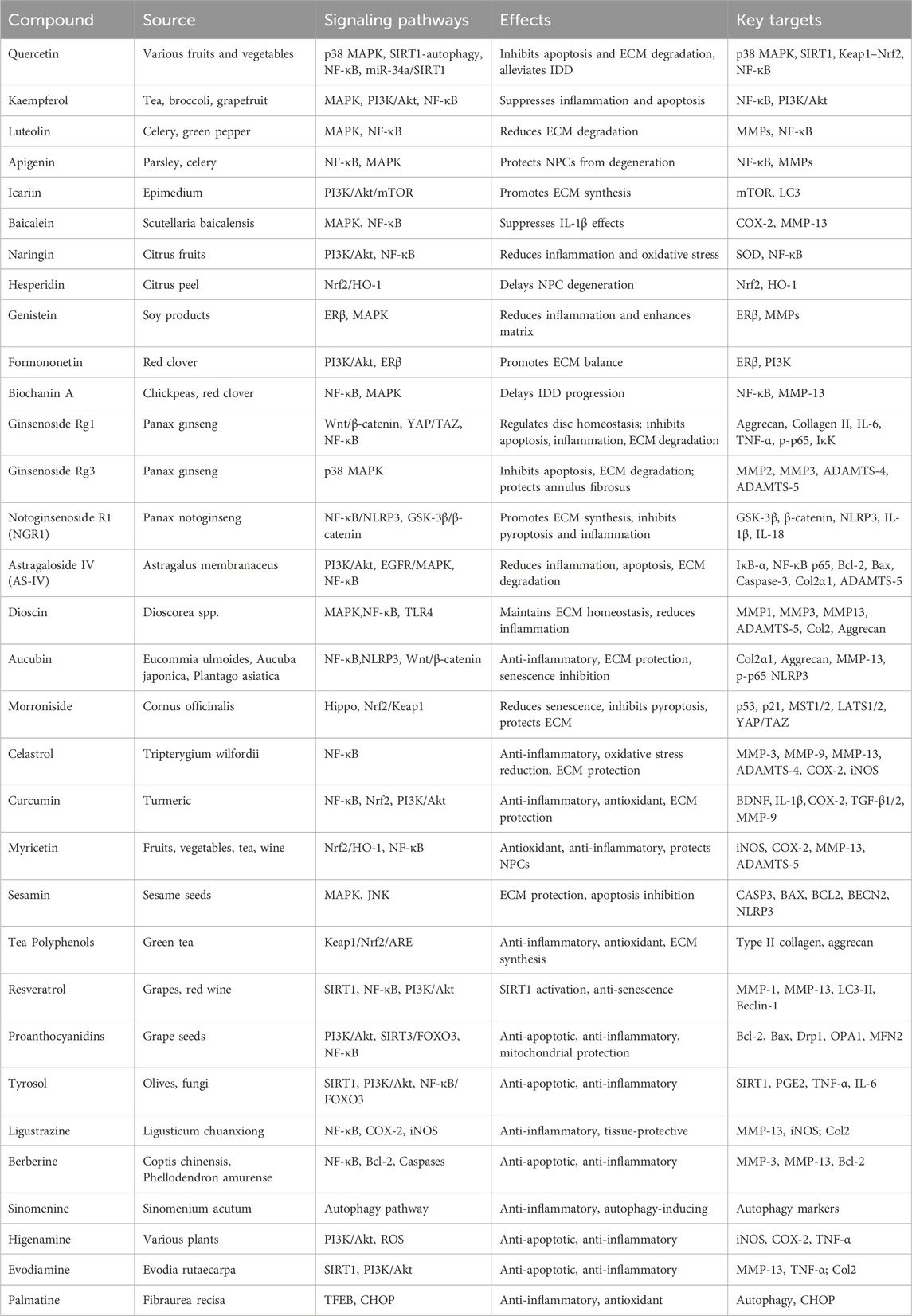
Table 1. Key signaling pathways and mechanisms of five classes of natural compounds discussed in this review.
Despite significant progress in basic and animal research, the clinical translation of natural products remains limited. Most studies are confined to in vitro models or small animal experiments, with a notable lack of human clinical trials directly targeting IDD. For instance, compounds such as curcumin, resveratrol, and quercetin have been assessed in clinical trials for osteoarthritis or systemic inflammation, but no large-scale clinical investigations have addressed their efficacy in IDD (Novais et al., 2021; Ataei et al., 2023; Kwon). Moreover, inconsistencies in dosage, treatment duration, and outcome measures impede direct comparisons and evidence-based application.
Several obstacles hinder the successful translation of natural products from bench to bedside. First, many compounds suffer from poor oral bioavailability, rapid metabolism, and low accumulation within the avascular intervertebral disc environment (Szabó et al., 2022; Araya-Sib et al., 2021). Second, physiological differences between rodent models and the human spine limit the extrapolation of pharmacological responses (Liu Z. et al., 2023). Third, standardized delivery platforms and scalable production processes remain underdeveloped. Addressing these limitations is crucial for advancing natural compounds into clinical practice.
Recent advances in biomaterials have introduced innovative delivery strategies to improve the stability, targeting, and bioactivity of natural products. Notably, nanoparticle encapsulation, thermosensitive hydrogels, and injectable biocompatible gels have demonstrated enhanced efficacy in preclinical IDD models (Ike et al., 2022; Shi S. et al., 2024). For example, kaempferol-loaded fibrin hydrogels and PLGA-PEG-PLGA-based resveratrol systems have shown sustained release profiles and regenerative potential in rat models (Gao et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2025). However, long-term safety, degradation kinetics, and regulatory pathways for these systems remain largely unverified in humans.
To overcome existing challenges, future studies should prioritize:rigorous pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluations in large-animal models. Early-phase clinical trials targeting IDD-specific patient populations. Combination strategies that integrate multiple natural compounds or adjunctive use with conventional treatments (Mavrogonatou and Kletsas, 2024). The development of modular and customizable drug delivery platforms. Furthermore, the integration of computational modeling, high-throughput screening, and network pharmacology may accelerate the identification of synergistic interactions and optimize formulation strategies (Sun W. et al., 2022; Wang X. et al., 2023; Liu H. et al., 2023).
In conclusion, natural products represent a rich and underutilized resource for IDD therapy. With coordinated efforts across pharmacology, materials science, and clinical research, their full therapeutic potential can be more effectively translated into viable interventions for degenerative spinal disorders (Table 2).
8 Conclusion
Natural products regulate multiple critical signaling pathways and exhibit significant anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, and regenerative effects, suggesting their potential to delay or even reverse the pathological progression of IDD. Although research into natural product-based interventions for IDD remains in the preclinical phase, their potential for clinical translation is increasingly recognized. Future studies should focus on optimizing drug delivery systems and exploring combination therapies to facilitate the efficient translation of natural product-based interventions from basic research to clinical application.
It is important to acknowledge that several plant-derived metabolites included in this review—such as flavonoids and polyphenols—are known to fall within the category of pan-assay interference compounds, particularly in in vitro assays. These compounds may produce misleading pharmacological signals by non-specifically interacting with a variety of targets or assay components. Therefore, while this review summarizes mechanistic studies, emphasis was placed on in vivo findings to reduce the overinterpretation of results from PAINS-prone compounds. Further studies using orthogonal assays, target deconvolution, and structure–activity analyses are needed to validate their pharmacological relevance.
Author contributions
ZW: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. JC: Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Investigation. WL: Writing – review and editing. TK: Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Key Project of the Education Department of Hunan Province (Grant No. 23A0285), the Changsha Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. KQ2403107), and the Hunan Provincial Subsidy Project for Health and Wellness (Grant No. 50502/30299).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The AI writing assistant has been utilized to enhance the clarity, fluency, and academic style of the manuscript. The AI tool focuses on improving sentence structure, word choice, grammar, and overall coherence, ensuring that the text adheres to high academic standards.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
A, O. G., Bui, H., Zadu, A., A, M. I., and S, B. A. (2025). The Multifaceted effects of berberine: potential Uses in Dermatology. J. Drugs Dermatol. 24 (3), 298–301. doi:10.36849/JDD.8899
Abd, E. M., El-Saadony, M. T., Swelum, A. A., Arif, M., Abo, G. M., Shukry, M., et al. (2021). Curcumin, the active substance of turmeric: its effects on health and ways to improve its bioavailability. J. Sci. Food AGR 101 (14), 5747–5762. doi:10.1002/jsfa.11372
Ansari, L., Mashayekhi-Sardoo, H., Baradaran, R. V., Yahyazadeh, R., Ghayour-Mobarhan, M., and Askari, V. R. (2023). Curcumin-based nanoformulations alleviate wounds and related disorders: a comprehensive review. Biofactors 49 (4), 736–781. doi:10.1002/biof.1945
Araya-Sibaja, A. M., Wilhelm, K., González-Aguilar, G. A., Vega-Baudrit, J. R., Salazar-López, N. J., Domínguez-Avila, J. A., et al. (2021). Curcumin loaded and co-loaded nanosystems: a review from a biological activity enhancement perspective. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 9 (2), 85–100. doi:10.2174/2211738508666201228150659
Ataei, M., Gumpricht, E., Kesharwani, P., Jamialahmadi, T., and Sahebkar, A. (2023). Recent advances in curcumin-based nanoformulations in diabetes. J. Drug Target 31 (7), 671–684. doi:10.1080/1061186X.2023.2229961
Aziz, N., Kim, M. Y., and Cho, J. Y. (2020). Anti-inflammatory effects of luteolin: a review of in vitro, in vivo, and in silico studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 225 342–358.
Bag, N., and Bag, A. (2020). Antimetastatic properties of tea polyphenols. Nutr. Cancer 72 (3), 365–376. doi:10.1080/01635581.2019.1638426
Bai, X., Ding, W., Yang, S., and Guo, X. (2019). Higenamine inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in human nucleus pulposus cells. Biosci. Rep. 39 (6), BSR20190857. doi:10.1042/BSR20190857
Bandopadhyay, S., Anand, U., Gadekar, V. S., Jha, N. K., Gupta, P. K., Behl, T., et al. (2022). Dioscin: a review on pharmacological properties and therapeutic values. Biofactors 48 (1), 22–55. doi:10.1002/biof.1815
Basith, S., Cui, M., Hong, S., and Choi, S. (2016). Harnessing the therapeutic potential of Capsaicin and its analogues in pain and other diseases. Molecules 21 (8), 966. doi:10.3390/molecules21080966
Boozari, M., and Hosseinzadeh, H. (2022). Crocin molecular signaling pathways at a glance: a comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 36 (10), 3859–3884. doi:10.1002/ptr.7583
Bridi, R., von Poser, G. L., and de Carvalho, M. G. (2023). Iridoids as a potential hepatoprotective class: a review. Mini-Rev Med. Chem. 23 (4), 452–479. doi:10.2174/1389557522666220816130158
Bu, J., Mahan, Y., Zhang, S., Wu, X., Zhang, X., Zhou, L., et al. (2024). Acacetin inhibits inflammation by blocking MAPK/NF-κB pathways and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1286546. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1286546
Cai, H. X., Liu, C., and Fan, S. W. (2011). Routinely using prophylactic antibiotic may not effectively prevent intervertebral disc infection: a new strategy to preventing postoperative intervertebral disc infection. Med. Hypotheses 76 (4), 464–466. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2010.11.021
Calderón-Montaño, J. M., Burgos-Morón, E., Pérez-Guerrero, C., and López-Lázaro, M. (2011). A review on the dietary flavonoid kaempferol. Mini-Rev Med. Chem. 11 (4), 298–344. doi:10.2174/138955711795305335
Cao, C., Zou, J., Liu, X., Shapiro, A., Moral, M., Luo, Z., et al. (2015). Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells slow intervertebral disc degeneration through the NF-κB pathway. Spine J. 15 (3), 530–538. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2014.11.021
Chang, A., Sun, S., Li, L., Dai, X., Li, H., He, Q., et al. (2019). Tyrosol from marine fungi, a novel quorum sensing inhibitor against Chromobacterium violaceum and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Bioorg Chem. 91, 103140. doi:10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103140
Chao-Yang, G., Peng, C., and Hai-Hong, Z. (2021). Roles of NLRP3 inflammasome in intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 29 (6), 793–801. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.02.204
Chen, D., Fan, T., Sun, K., Rao, W., Sheng, X., Wan, Z., et al. (2024b). Network pharmacology and experimental validation to reveal the pharmacological mechanisms of Astragaloside Ⅳ in treating intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 982, 176951. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176951
Chen, D. T., Rao, W., Shen, X., Chen, L., Wan, Z. J., Sheng, X. P., et al. (2022c). Pharmacological effects of higenamine based on signalling pathways and mechanism of action. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 981048. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.981048
Chen, H., Gao, Y., Wu, J., Chen, Y., Chen, B., Hu, J., et al. (2014). Exploring therapeutic potentials of baicalin and its aglycone baicalein for hematological malignancies. Cancer Lett. 354 (1), 5–11. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.08.003
Chen, H. W., Liu, M. Q., Zhang, G. Z., Zhang, C. Y., Wang, Z. H., Lin, A. X., et al. (2022b). Proanthocyanidins inhibit the apoptosis and aging of nucleus pulposus cells through the PI3K/Akt pathway delaying intervertebral disc degeneration. Connect. Tissue Res. 63 (6), 650–662. doi:10.1080/03008207.2022.2063121
Chen, H. W., Zhang, G. Z., Liu, M. Q., Zhang, L. J., Kang, J. H., Wang, Z. H., et al. (2021). Natural products of pharmacology and mechanisms in nucleus pulposus cells and intervertebral disc degeneration. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2021, 9963677. doi:10.1155/2021/9963677
Chen, H. W., Zhou, J. W., Zhang, G. Z., Luo, Z. B., Li, L., and Kang, X. W. (2023). Emerging role and therapeutic implication of mTOR signalling in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Proliferat 56, 13338. doi:10.1111/cpr.13338
Chen, J., Xuan, J., Gu, Y. T., Shi, K. S., Xie, J. J., Chen, J. X., et al. (2017). Celastrol reduces IL-1β induced matrix catabolism, oxidative stress and inflammation in human nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates rat intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 91, 208–219. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.093
Chen, J., Zhang, B., Wu, L., and Xu, J. (2024a). Ginsenoside Rg3 exhibits anti-catabolic and anti-apoptotic effects in IL-1β treated human disc nucleus pulposus cells and in a rat model of disc degeneration by inactivating the MAPK pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. 70 (1), 233–238. doi:10.14715/cmb/2024.70.1.32
Chen, R., Gao, S., Guan, H., Zhang, X., Gao, Y., Su, Y., et al. (2022a). Naringin protects human nucleus pulposus cells against TNF-α-induced inflammation, oxidative stress, and loss of cellular homeostasis by enhancing autophagic flux via AMPK/SIRT1 activation. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 7655142. doi:10.1155/2022/7655142
Chen, Y., Chen, M., Zhu, W., Zhang, Y., Liu, P., and Li, P. (2024c). Morroniside attenuates podocytes lipid deposition in diabetic nephropathy: a network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 138, 112560. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112560
Chen, Y., Zheng, Z., Wang, J., Tang, C., Khor, S., Chen, J., et al. (2018). Berberine suppresses apoptosis and extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates disc degeneration in a rodent model. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 14 (6), 682–692. doi:10.7150/ijbs.24081
Cherif, H., Bisson, D. G., Jarzem, P., Weber, M., Ouellet, J. A., and Haglund, L. (2019). Curcumin and o-Vanillin exhibit evidence of senolytic activity in human IVD cells in vitro. J. Clin. Med. 8 (4), 433. doi:10.3390/jcm8040433
Dai, Y. H., Wei, J. R., and Chen, X. Q. (2023). Interactions between tea polyphenols and nutrients in food. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 22 (4), 3130–3150. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.13178
Dalibalta, S., Majdalawieh, A. F., and Manjikian, H. (2020). Health benefits of sesamin on cardiovascular disease and its associated risk factors. Saudi Pharm. J. 28 (10), 1276–1289. doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2020.08.018
Devraj, V. M., Vemuri, S. K., Banala, R. R., Gunda, S. K., Av, G. R., and Gpv, S. (2019). Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and regenerative efficiency of naringin and naringenin in degenerated human nucleus pulposus cells: biological and molecular modeling studies. Asian Spine J. 13 (6), 875–889. doi:10.31616/asj.2019.0073
Ding, F., and Li, X. (2020). Apigenin mitigates intervertebral disc degeneration through the amelioration of tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) signaling pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, 924587. doi:10.12659/msm.924587
Ding, H., Li, Y., Chen, S., Wen, Y., Zhang, S., Luo, E., et al. (2022). Fisetin ameliorates cognitive impairment by activating mitophagy and suppressing neuroinflammation in rats with sepsis-associated encephalopathy. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 28 (2), 247–258. doi:10.1111/cns.13765
Ding, Q., Zhang, R., Sheng, G., Wang, T., Jing, S., Ma, T., et al. (2023). Dioscin alleviates the progression of osteoarthritis: an in vitro and in vivo study. J. Inflamm-Lond 20 (1), 14. doi:10.1186/s12950-023-00339-w
Du, X., Wang, X., Cui, K., Chen, Y., Zhang, C., Yao, K., et al. (2021). Tanshinone IIA and astragaloside IV inhibit miR-223/JAK2/STAT1 signalling pathway to alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced damage in nucleus pulposus cells. Dis. Markers 2021, 6554480. doi:10.1155/2021/6554480
Duan, F. X., Shi, Y. J., Chen, J., Song, X., Shen, L., Qi, Q., et al. (2021). The neuroprotective role of morroniside against spinal cord injury in female rats. Neurochem. Int. 148, 105105. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2021.105105
Ekeuku, S. O., Pang, K. L., and Chin, K. Y. (2020). Palmatine as an agent against metabolic syndrome and its related complications: a review. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 4963–4974. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S280520
Elbatreek, M. H., Mahdi, I., Ouchari, W., Mahmoud, M. F., and Sobeh, M. (2023). Current advances on the therapeutic potential of pinocembrin: an updated review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 157, 114032. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114032
Fan, Z., Wei, X., Zhu, X., Yang, K., Tian, L., Wang, X., et al. (2025). Unveiling the therapeutic potential of berberine: its therapeutic role and molecular mechanisms in kidney diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1549462. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1549462
Fang, C., You, Y., Luo, F., Li, Z., Shen, Y., Wang, F., et al. (2024). Silk Fibroin encapsulated icariin nanoparticles mitigate Bisphenol A-induced Spermatogenesis dysfunction. Adv. Healthc. Mater 13, 2302899. doi:10.1002/adhm.202302899
Feng, M., Jiang, X., Zhang, Q., Wang, Q., She, C., and Li, Z. (2023). Aucubin protects against retinal ganglion cell injury in diabetic rats via inhibition of the p38MAPK pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 15 (2), 1007–1016.
Ferreira, M. S., Katchborian-Neto, A., Nicácio, K. J., Santos, M., Dias, D. F., Chagas-Paula, D. A., et al. (2025). Phytochemical investigation of Nigrospora zimmermanii isolated from Poincianella pluviosa (Sibipiruna): metabolites characterisation and screening for anti-inflammatory activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 39 (9), 2635–2641. doi:10.1080/14786419.2024.2320733
Gan, J., Deng, X., Le, Y., Lai, J., and Liao, X. (2023). The development of naringin for use against bone and cartilage disorders. Molecules 28 (9), 3716. doi:10.3390/molecules28093716
Gao, G., Chang, F., Zhang, T., Huang, X., Yu, C., Hu, Z., et al. (2019a). Naringin protects against interleukin 1β (IL-1β)-induced human nucleus pulposus cells degeneration via downregulation nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway and p53 expression. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 9963–9972. doi:10.12659/MSM.918597
Gao, W., Bao, J., Zhang, Y., He, D., Zhang, L., Zhang, J., et al. (2023). Injectable kaempferol-loaded fibrin glue regulates the metabolic balance and inhibits inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Sci. Rep-UK 13 (1), 20001. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-47375-3
Gao, Z., Lin, Y., Zhang, P., Cheng, Q., Ye, L., Wu, F., et al. (2019b). Sinomenine ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibition of apoptosis and autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Transl. Res. 11 (9), 5956–5966.
Ge, Y., Xie, Y., Chai, J., Ji, W., Lou, X., Tian, K., et al. (2024). Augmented Cornus officinalis levels in Liuwei Dihuang decoction inhibits nucleus pulposus cell pyroptosis to enhance therapeutic efficacy against intervertebral disc degeneration. J. Inflamm. Res. 17, 4453–4465. doi:10.2147/JIR.S465690
Ghaderi, M. A., Emami, S. A., Beirak, O. M., and Javadi, B. (2023). The role of sesamin in targeting Neurodegenerative disorders: a systematic review. Mini-Rev Med. Chem. 23 (6), 756–770. doi:10.2174/1389557522666220523112027
Gómez, R., Villalvilla, A., Largo, R., Gualillo, O., and Herrero-Beaumont, G. (2015). TLR4 signalling in osteoarthritis-finding targets for candidate DMOADs. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 11 (3), 159–170. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2014.209
Gu, J., Shi, Y. N., Zhu, N., Li, H. F., Zhang, C. J., and Qin, L. (2023). Celastrol functions as an emerging manager of lipid metabolism: mechanism and therapeutic potential. Biomed. Pharmacother. 164, 114981. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114981
Guo, J., Shao, M., Lu, F., Jiang, J., and Xia, X. (2017). Role of SIRT1 plays in nucleus pulposus cells and intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 42 (13), E757–E766. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000001954
Guo, J., Xue, J., He, Z., Jia, H., and Yang, X. (2023). The mechanism by which Naru 3 pill protects against intervertebral disc cartilage endplate degeneration based on network pharmacology and experimental verification. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 18 (1), 552. doi:10.1186/s13018-023-04014-x
Guo, S., Xi, X., and Li, J. (2019). Notoginsenoside R1: a systematic review of its pharmacological properties. Pharmazie 74 (11), 641–647. doi:10.1691/ph.2019.9534
Han, F., Li, Z., Han, S., Jia, Y., Bai, L., Li, X., et al. (2021). SIRT1 suppresses burn injury-induced inflammatory response through activating autophagy in RAW264.7 macrophages. J. Invest. Med. 69 (3), 761–767. doi:10.1136/jim-2019-001258
Han, Q., Bing, W., Di, Y., Hua, L., Shi-He, L., Yu-Hua, Z., et al. (2016). Kinsenoside screening with a microfluidic chip attenuates gouty arthritis through inactivating NF-κB signaling in macrophages and protecting endothelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 7, 2350. doi:10.1038/cddis.2016.255
Hashemzaei, M., Mamoulakis, C., Tsarouhas, K., Georgiadis, G., Lazopoulos, G., Tsatsakis, A., et al. (2020). Crocin: a fighter against inflammation and pain. Food Chem. Toxicol. 143, 111521. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111521
Heydari, M., Zare, M., Badie, M. R., Watson, R. R., Talebnejad, M. R., and Afarid, M. (2023). Crocin as a vision supplement. Clin. Exp. Optom. 106 (3), 249–256. doi:10.1080/08164622.2022.2039554
Hong, H., Xiao, J., Guo, Q., Du, J., Jiang, Z., Lu, S., et al. (2021). Cycloastragenol and Astragaloside IV activate telomerase and protect nucleus pulposus cells against high glucose-induced senescence and apoptosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 22 (5), 1326. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10761
Hong, M., Yu, J., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Zhan, S., Wu, Z., et al. (2022). Tea polyphenols as prospective natural attenuators of brain aging. Nutrients 14 (15), 3012. doi:10.3390/nu14153012
Hu, Y., Tang, J. S., Hou, S. X., Shi, X. X., Qin, J., Zhang, T. S., et al. (2017). Neuroprotective effects of curcumin alleviate lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration through regulating the expression of iNOS, COX-2, TGF-β1/2, MMP-9 and BDNF in a rat model. Mol. Med. Rep. 16 (5), 6864–6869. doi:10.3892/mmr.2017.7464
Hua, W., Li, S., Luo, R., Wu, X., Zhang, Y., Liao, Z., et al. (2020). Icariin protects human nucleus pulposus cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis by activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2. BBA-Mol Basis Dis. 1866 (1), 165575. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2019.165575
Hua, W., Xie, L., Dong, C., Yang, G., Chi, S., Xu, Z., et al. (2024). Procyanidin C1 ameliorates acidic pH stress induced nucleus pulposus degeneration through SIRT3/FOXO3-mediated mitochondrial dynamics. J. Transl. Med. 22 (1), 1071. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05805-4
Hua, W., Zhang, Y., Wu, X., Kang, L., Tu, J., Zhao, K., et al. (2018). Icariin attenuates interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory response in human nucleus pulposus cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 23 (39), 6071–6078. doi:10.2174/1381612823666170615112158
Huang, L., Kim, M. Y., and Cho, J. Y. (2023). Immunopharmacological activities of luteolin in chronic diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (3), 2136. doi:10.3390/ijms24032136
Ike, S., Matsuoka, M., Onodera, T., Yokota, I., Iwasaki, K., Hishimura, R., et al. (2022). Primary malignant osseous neoplasms in the hand. Anticancer Res. 42 (3), 1635–1640. doi:10.21873/anticanres.15639
Jiang, H., Wang, W., Mao, Y., Jiang, L., Yu, J., Zhu, X., et al. (2024a). Morroniside-mediated mitigation of stem cell and endothelial cell dysfunction for the therapy of glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Int. Immunopharmacol. 127, 111421. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111421
Jiang, P., Zahra, A., Guo, X., and Wu, J. (2024c). Recent advances in the therapeutic potential of sinomenine for cancer treatment. Pharmacology 109 (2), 76–85. doi:10.1159/000536133
Jiang, S., Li, S., Pang, S., Liu, M., Sun, H., Zhang, N., et al. (2024b). A systematic review: sinomenine. Heliyon 10, 29976. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29976
Jiang, X., Li, S., Wang, N., and Li, J. (2025). Ligustrazine as a multitarget scaffold in drug design and discovery. Bioorgan Med. Chem. 121, 118110. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2025.118110
Jin, H., Wang, Q., Wu, J., Han, X., Qian, T., Zhang, Z., et al. (2019). Baicalein inhibits the IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in nucleus pulposus cells and attenuates disc degeneration in vivo. Inflammation 42 (3), 1032–1044. doi:10.1007/s10753-019-00965-8
Jomová, K., Hudecova, L., Lauro, P., Simunkova, M., Alwasel, S. H., Alhazza, I. M., et al. (2019). A Switch between antioxidant and prooxidant properties of the phenolic compounds myricetin, Morin, 3′,4′-dihydroxyflavone, taxifolin and 4-hydroxy-coumarin in the presence of copper(II) Ions: a spectroscopic, absorption titration and DNA damage study. Molecules 24 (23), 4335. doi:10.3390/molecules24234335
Jung, M., Rospleszcz, S., Löffler, M. T., Walter, S. S., Maurer, E., Jungmann, P. M., et al. (2023). Association of lumbar vertebral bone marrow and paraspinal muscle fat composition with intervertebral disc degeneration: 3T quantitative MRI findings from the population-based KORA study. Eur. Radiol. 33 (3), 1501–1512. doi:10.1007/s00330-022-09140-4
Kartini, K., Irawan, M. A., Setiawan, F., and Jayani, N. (2023). Characteristics, isolation methods, and biological properties of aucubin. Molecules 28 (10), 4154. doi:10.3390/molecules28104154
Kashyap, D., Garg, V. K., Tuli, H. S., Yerer, M. B., Sak, K., Sharma, A. K., et al. (2019). Fisetin and quercetin: promising flavonoids with chemopreventive potential. Biomolecules 9 (5), 174. doi:10.3390/biom9050174
Khan, N., Syed, D. N., Ahmad, N., and Mukhtar, H. (2013). Fisetin: a dietary antioxidant for health promotion. Antioxid. Redox Sign. 19 (2), 151–162. doi:10.1089/ars.2012.4901
Kim, Y. J., Zhang, D., and Yang, D. C. (2015). Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of ginsenosides. Biotechnol. Adv. 33 (6 Pt 1), 717–735. doi:10.1016/j.biotechadv.2015.03.001
Kos, N., Gradisnik, L., and Velnar, T. (2019). A Brief review of the degenerative intervertebral disc disease. Med. Arch. 73 (6), 421–424. doi:10.5455/medarh.2019.73.421-424
Kotha, R. R., and Luthria, D. L. (2019). Curcumin: biological, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and analytical aspects. Molecules 24 (16), 2930. doi:10.3390/molecules24162930
Kuai, J., and Zhang, N. (2022). Upregulation of SIRT1 by evodiamine activates PI3K/AKT pathway and blocks intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol. Med. Rep. 26 (2),265. doi:10.3892/mmr.2022.12781
Kumar, S., Swamy, N., Tuli, H. S., Rani, S., Garg, A., Mishra, D., et al. (2023). Myricetin: a potential plant-derived anticancer bioactive compound-an updated overview. N-S Arch. Pharmacol. 396 (10), 2179–2196. doi:10.1007/s00210-023-02479-5
Kwon, Y. J. (2013). Resveratrol has anabolic effects on disc degeneration in a rabbit model. J. Korean Med. Sci. 28 (6), 939–945. doi:10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.939
Le Maitre, C. L., Binch, A. L., Thorpe, A. A., and Hughes, S. P. (2015). Degeneration of the intervertebral disc with new approaches for treating low back pain. J. Neurosurg. Sci. 59 (1), 47–61.
Li, C., Zhang, Y., Deng, Y., Chen, Y., Wu, C., Zhao, X., et al. (2024b). Fisetin suppresses ferroptosis through Nrf2 and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 964, 176298. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.176298
Li, D., Zhong, Z., Ko, C. N., Tian, T., and Yang, C. (2023d). From mundane to classic: sinomenine as a multi-therapeutic agent. Brit J. Pharmacol. 182, 2159–2180. doi:10.1111/bph.16267
Li, J. M., Yao, Y. D., Luo, J. F., Liu, J. X., Lu, L. L., Liu, Z. Q., et al. (2023e). Pharmacological mechanisms of sinomenine in anti-inflammatory immunity and osteoprotection in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Phytomedicine 121, 155114. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155114
Li, K., Li, Y., Ma, Z., and Zhao, J. (2015). Crocin exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-catabolic effects on rat intervertebral discs by suppressing the activation of JNK. Int. J. Mol. Med. 36 (5), 1291–1299. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2015.2359
Li, K., Li, Y., Xu, B., Mao, L., and Zhao, J. (2016c). Sesamin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and extracellular matrix catabolism in rat intervertebral disc. Connect. Tissue Res. 57 (5), 347–359. doi:10.1080/03008207.2016.1182998
Li, K., and Lv, C. (2020). Intradiscal injection of sesamin protects from lesion-induced degeneration. Connect. Tissue Res. 61 (6), 594–603. doi:10.1080/03008207.2019.1651847
Li, L., Wei, X., Li, K., Gong, H., Zhu, L., Yang, S., et al. (2023a). Traditional Chinese Medicine formula Bu-Shen-Huo-Xue-Fang (BSHXF) protects nucleus pulposus cells against the inflammatory and oxidative stress-induced degenerative changes. J. Pharm. Biomed. 236, 115656. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2023.115656
Li, M., Tian, F., Guo, J., Li, X., Ma, L., Jiang, M., et al. (2023f). Therapeutic potential of Coptis chinensis for arthritis with underlying mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1243820. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1243820
Li, M., Xie, F., Wang, L., Zhu, G., Qi, L. W., and Jiang, S. (2022b). Celastrol: an update on its hepatoprotective properties and the linked molecular mechanisms. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 857956. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.857956
Li, M., Zhang, J., Jiang, L., Wang, W., Feng, X., Liu, M., et al. (2023b). Neuroprotective effects of morroniside from Cornus officinalis sieb. Et zucc against Parkinson’s disease via inhibiting oxidative stress and ferroptosis. BMC Complement. Med. 23 (1), 218. doi:10.1186/s12906-023-03967-0
Li, N., Whitaker, C., Xu, Z., Heggeness, M., and Yang, S. Y. (2016b). Therapeutic effects of naringin on degenerative human nucleus pulposus cells for discogenic low back pain. Spine J. 16 (10), 1231–1237. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2016.05.007
Li, S., Du, J., Huang, Y., Gao, S., Zhao, Z., Chang, Z., et al. (2024a). From hyperglycemia to intervertebral disc damage: exploring diabetic-induced disc degeneration. Front. Immunol. 15, 1355503. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1355503
Li, S., Lv, Q., Sun, X., Tang, T., Deng, X., Yin, Y., et al. (2020). Acacetin inhibits Streptococcus pneumoniae virulence by targeting pneumolysin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 72 (8), 1092–1100. doi:10.1111/jphp.13279
Li, W., Liu, L., Zhang, Z., and Lu, H. (2023c). Morroniside ameliorates endotoxin-induced uveitis by regulating the M1/M2 polarization balance of macrophages. J. Immunol. Res. 2023, 1252873. doi:10.1155/2023/1252873
Li, Y., Yao, J., Han, C., Yang, J., Chaudhry, M. T., Wang, S., et al. (2016a). Quercetin, inflammation and immunity. Nutrients 8 (3), 167. doi:10.3390/nu8030167
Li, Z., Zhang, J., Duan, X., Zhao, G., and Zhang, M. (2022a). Celastrol: a promising agent fighting against cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants-Basel 11 (8), 1597. doi:10.3390/antiox11081597
Liang, Q. Q., Ding, D. F., Xi, Z. J., Chen, Y., Li, C. G., Liu, S. F., et al. (2014). Protective effect of ligustrazine on lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration of rats induced by prolonged upright posture. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2014, 508461. doi:10.1155/2014/508461
Liang, Y., Chen, B., Liang, D., Quan, X., Gu, R., Meng, Z., et al. (2023). Pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV: a review. Molecules 28 (16), 6118. doi:10.3390/molecules28166118
Lin, L., Liu, Y., Tang, R., Ding, S., Lin, H., and Li, H. (2024). Evodiamine: a extremely potential drug development candidate of alkaloids from Evodia rutaecarpa. Int. J. Nanomed 19, 9843–9870. doi:10.2147/IJN.S459510
Lintz, M., Walk, R. E., Tang, S. Y., and Bonassar, L. J. (2022). The degenerative impact of hyperglycemia on the structure and mechanics of developing murine intervertebral discs. JOR Spine 5, 1191. doi:10.1002/jsp2.1191
Liou, C. J., Wu, S. J., Shen, S. C., Chen, L. C., Chen, Y. L., and Huang, W. C. (2022). Acacetin protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by regulating lipid accumulation and inflammation in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (9), 4687. doi:10.3390/ijms23094687
Liu, H., Li, Y., Li, Z., Li, J., Zhang, Q., Cao, S., et al. (2023c). A study based on network pharmacology decoding the multi-target mechanism of Duhuo Jisheng Decoction for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Comput. Intel. Neurosci. 2023, 7091407. doi:10.1155/2023/7091407
Liu, H., Lu, X., Hu, Y., and Fan, X. (2020a). Chemical constituents of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng explain why they differ in therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 161, 105263. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105263
Liu, H., Yang, J., Yang, W., Hu, S., Wu, Y., Zhao, B., et al. (2020b). Focus on notoginsenoside R1 in metabolism and prevention against human diseases. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 551–565. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S240511
Liu, M. Y., Zhang, L., Zang, W. D., Zhang, K. G., Li, H. J., and Gao, Y. Z. (2022). Pharmacological effects of resveratrol in intervertebral disc degeneration: a literature review. Orthop. Surg. 14 (12), 3141–3149. doi:10.1111/os.13560
Liu, Y., Guo, C., Wang, Y., and Kong, Q. Q. (2025). Application of an injectable thermosensitive hydrogel drug delivery system for degenerated intervertebral disc regeneration. Biomacromolecules 26 (1), 209–221. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00965
Liu, Y., Liu, D. K., Wang, Z. W., Zhao, C., and Miao, J. (2023b). Baicalein alleviates TNF-α-induced apoptosis of human nucleus pulposus cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 18 (1), 292. doi:10.1186/s13018-023-03759-9
Liu, Z., Zhu, J., Liu, H., and Fu, C. (2023a). Natural products can modulate inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1150835. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1150835
Liu, Z. L., Liu, Q., Xiao, B., Zhou, J., Zhang, J. G., and Li, Y. (2013). The vascular protective properties of kinsenoside isolated from Anoectochilus roxburghii under high glucose condition. Fitoterapia 86, 163–170. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2013.03.006
Long, L., Tang, X., Wang, Y., Gu, J., Xiong, J., Luo, H., et al. (2025). Network pharmacology and experimental validation to elucidate the pharmacological mechanisms of luteolin against chondrocyte senescence. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 86, 163–170.
Lu, L., Hu, J., Wu, Q., An, Y., Cui, W., Wang, J., et al. (2019). Berberine prevents human nucleus pulposus cells from IL-1β-induced extracellular matrix degradation and apoptosis by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43 (4), 1679–1686. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4105
Lu, W., Shi, Y., and Qian, M. (2024). Notoginsenoside R1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via ERα/GSK-3β/β-catenin signalling pathway. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 105 (1), 4–12. doi:10.1111/iep.12494
Luo, X., Gu, S., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, J. (2018). Kinsenoside ameliorates oxidative stress-induced RPE cell apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis via Erk/p38/NF-κB/VEGF signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 9, 240. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.00240
Ma, J., Liu, J., Chen, Y., Yu, H., and Xiang, L. (2022). Myricetin improves impaired nerve functions in experimental diabetic rats. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 915603. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.915603
Ma, T., Guo, C. J., Zhao, X., Wu, L., Sun, S. X., and Jin, Q. H. (2015). The effect of curcumin on NF-κB expression in rat with lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. 19 (7), 1305–1314.
Ma, Z., Zhang, H., Zhao, F., Li, K., Dong, N., and Sang, W. (2024). Safety and effectiveness of Salvia miltiorrhiza and ligustrazine injection for acute cerebral infarction in Chinese population: a PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1425053. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1425053
Majdalawieh, A. F., Dalibalta, S., and Yousef, S. M. (2020). Effects of sesamin on fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism, macrophage cholesterol homeostasis and serum lipid profile: a comprehensive review. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 885, 173417. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173417
Majdalawieh, A. F., Yousef, S. M., Abu-Yousef, I. A., and Nasrallah, G. K. (2022). Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of sesamin: mechanisms of action and future directions. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 62 (18), 5081–5112. doi:10.1080/10408398.2021.1881438
Mao, T., and Fan, J. (2024). Myricetin protects against rat intervertebral disc degeneration partly through the Nrf2/HO-1/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem. Genet. 62 (2), 950–967. doi:10.1007/s10528-023-10456-z
Martin, M., Béjar, J., Esposito, G., Chávez, D., Contreras-Hernández, E., Glusman, S., et al. (2017). Markovian analysis of the sequential behavior of the spontaneous spinal cord dorsum potentials induced by acute nociceptive stimulation in the anesthetized cat. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 11, 32. doi:10.3389/fncom.2017.00032
Mavrogonatou, E., and Kletsas, D. (2024). Plant-derived senotherapeutics for the prevention and treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration and aging. Metabolites 14 (3), 146. doi:10.3390/metabo14030146
Metwaly, A. M., Lianlian, Z., Luqi, H., and Deqiang, D. (2019). Black ginseng and its saponins: preparation, phytochemistry and pharmacological effects. Molecules 24 (10), 1856. doi:10.3390/molecules24101856
Mu, J., Chen, H., Ye, M., Zhang, X., and Ma, H. (2022). Acacetin resists UVA photoaging by mediating the SIRT3/ROS/MAPKs pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 26 (16), 4624–4628. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17415
Nan, L. P., Wang, F., Liu, Y., Wu, Z., Feng, X. M., Liu, J. J., et al. (2020b). 6-gingerol protects nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells from oxidative injury by activating autophagy. World J. Stem Cells 12 (12), 1603–1622. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v12.i12.1603
Nan, L. P., Wang, F., Ran, D., Zhou, S. F., Liu, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2020a). Naringin alleviates H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Connect. Tissue Res. 61 (6), 554–567. doi:10.1080/03008207.2019.1631299
Nanavati, K., Rutherfurd-Markwick, K., Lee, S. J., Bishop, N. C., and Ali, A. (2022). Effect of curcumin supplementation on exercise-induced muscle damage: a narrative review. Eur. J. Nutr. 61 (8), 3835–3855. doi:10.1007/s00394-022-02943-7
Nimmakayala, P., Abburi, V. L., Saminathan, T., Alaparthi, S. B., Almeida, A., Davenport, B., et al. (2016). Genome-wide diversity and association mapping for capsaicinoids and fruit weight in Capsicum annuum L. Sci. Rep-UK 6, 38081. doi:10.1038/srep38081
Novais, E. J., Tran, V. A., Johnston, S. N., Darris, K. R., Roupas, A. J., Sessions, G. A., et al. (2021). Long-term treatment with senolytic drugs dasatinib and quercetin ameliorates age-dependent intervertebral disc degeneration in mice. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 5213. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25453-2
Orhan, I., Naz, Q., Kartal, M., Tosun, F., Sener, B., and Choudhary, M. I. (2007). In vitro anticholinesterase activity of various alkaloids. Z Naturforsch C J Biosci. 62 (9-10), 684–688. doi:10.1515/znc-2007-9-1010
Padmavathi, G., Roy, N. K., Bordoloi, D., Arfuso, F., Mishra, S., Sethi, G., et al. (2017). Butein in health and disease: a comprehensive review. Phytomedicine 25, 118–127. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2016.12.002
Pal, B., Endisha, H., Zhang, Y., and Kapoor, M. (2015). mTOR: a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis? Drugs R&D 15 (1), 27–36. doi:10.1007/s40268-015-0082-z
Pal, P. P., Begum, S. A., Basha, A. S., Araya, H., and Fujimoto, Y. (2023). A new lignan (Polonilignan) and inhibitors of nitric oxide production from Penicillium polonicum, an endophytic fungi of Piper nigrum. Chem. Biodivers. 20, 202200840. doi:10.1002/cbdv.202200840
Pan, C., Hou, W., Deng, X., Liu, J., Chi, R., Shang, X., et al. (2023a). The pivotal role of Nrf2 signal Axis in intervertebral disc degeneration. J. Inflamm. Res. 16, 5819–5833. doi:10.2147/JIR.S432575
Pan, M., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Jiang, X., Fan, Y., Gong, F., et al. (2023b). Celastrol alleviated acute kidney injury by inhibition of ferroptosis through Nrf2/GPX4 pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 166, 115333. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115333
Pluta, R., Januszewski, S., and Czuczwar, S. J. (2021). Myricetin as a promising molecule for the treatment of post-ischemic brain neurodegeneration. Nutrients 13 (2), 342. doi:10.3390/nu13020342
Pourmousavi, L., Asadi, R. H., Zehsaz, F., and Jadidi, R. P. (2024). Potential therapeutic effects of crocin. N-S Arch. Pharmacol. 397, 7395–7420. doi:10.1007/s00210-024-03131-6
Qi, C. X., Zhou, Q., Yuan, Z., Luo, Z. W., Dai, C., Zhu, H. C., et al. (2018). Kinsenoside: a promising bioactive compound from Anoectochilus species. Curr. Med. Sci. 38 (1), 11–18. doi:10.1007/s11596-018-1841-1
Qi, W., Ren, D., Wang, P., Song, Z., Wu, H., Yao, S., et al. (2020). Upregulation of SIRT1 by tyrosol suppresses apoptosis and inflammation and modulates extracellular matrix remodeling in interleukin-1β-stimulated human nucleus pulposus cells through activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 88, 106904. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106904
Qian, L., Huang, S., Liu, X., Jiang, Y., Jiang, Y., Hu, Y., et al. (2024). Morroniside improves the symptoms of post-stroke depression in mice through the BDNF signaling pathway mediated by MiR-409-3p. Phytomedicine 123, 155224. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155224
Rahmani, A. H., Almatroudi, A., Allemailem, K. S., Alwanian, W. M., Alharbi, B. F., Alrumaihi, F., et al. (2023). Myricetin: a significant emphasis on its anticancer potential via the modulation of inflammation and signal transduction pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (11), 9719. doi:10.3390/ijms24119719
Rajan, N. E., Bloom, O., Maidhof, R., Stetson, N., Sherry, B., Levine, M., et al. (2013). Chahine: Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) expression and stimulation in a model of intervertebral disc inflammation and degeneration. SPINE 38 (16), 1343–1351. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e31826b71f4
Rana, A., Samtiya, M., Dhewa, T., Mishra, V., and Aluko, R. E. (2022). Health benefits of polyphenols: a concise review. J. Food Biochem. 46, 14264. doi:10.1111/jfbc.14264
Rangelov, K. V., Ivanov, K., and Ivanova, S. (2022). Higenamine in plants as a source of unintentional doping. Plants-Basel 11 (3), 354. doi:10.3390/plants11030354
Rasul, A., Millimouno, F. M., Ali, E. W., Ali, M., Li, J., and Li, X. (2013). Pinocembrin: a novel natural compound with versatile pharmacological and biological activities. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 379850. doi:10.1155/2013/379850
Ren, J., Lu, Y., Qian, Y., Chen, B., Wu, T., and Ji, G. (2019). Recent progress regarding kaempferol for the treatment of various diseases. Exp. Ther. Med. 18 (4), 2759–2776. doi:10.3892/etm.2019.7886
Ren, Q., Tao, S., Guo, F., Wang, B., Yang, L., Ma, L., et al. (2021). Natural flavonol fisetin attenuated hyperuricemic nephropathy via inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 and TGF-β/SMAD3 signaling. Phytomedicine 87, 153552. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153552
Risbud, M. V., and Shapiro, I. M. (2014). Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 10 (1), 44–56. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2013.160
Sarath, B. N., Krishnan, S., Brahmendra, S. C., Venkata, S. G., Gurava, R. A., and Idris, M. M. (2016). Quantitative proteomic analysis of normal and degenerated human intervertebral disc. Spine J. 16 (8), 989–1000. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2016.03.051
Seyedi, Z., Amiri, M. S., Mohammadzadeh, V., Hashemzadeh, A., Haddad-Mashadrizeh, A., Mashreghi, M., et al. (2023). Icariin: a promising natural product in biomedicine and tissue engineering. J. Funct. Biomater. 14 (1), 44. doi:10.3390/jfb14010044
Shang, P., Tang, Q., Hu, Z., Huang, S., Hu, Y., Zhu, J., et al. (2020). Procyanidin B3 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via interaction with the TLR4/MD-2 complex. J. Cell Mol. Med. 24 (6), 3701–3711. doi:10.1111/jcmm.15074
Shao, M., Kuang, Z., Wang, W., Li, S., Li, G., Song, Y., et al. (2022b). Aucubin exerts anticancer activity in breast cancer and regulates intestinal microbiota. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2022, 4534411. doi:10.1155/2022/4534411
Shao, Y., Sun, L., Yang, G., Wang, W., Liu, X., Du, T., et al. (2022a). Icariin protects vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and degeneration via activating Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 937502. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.937502
Shao, Z., Wang, B., Shi, Y., Xie, C., Huang, C., Chen, B., et al. (2021). Senolytic agent quercetin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the Nrf2/NF-κB axis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 29 (3), 413–422. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2020.11.006
Sharma, S., Tomar, V. R., and Deep, S. (2023). Myricetin: a potent anti-amyloidogenic polyphenol against superoxide dismutase 1 aggregation. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 14 (13), 2461–2475. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.3c00276
Shen, J., Zhuo, N., Xu, S., Song, Z., Hu, Z., Hao, J., et al. (2018). Resveratrol delivery by ultrasound-mediated nanobubbles targeting nucleus pulposus cells. Nanomedicine-UK 13 (12), 1433–1446. doi:10.2217/nnm-2018-0019
Shi, P., Zheng, B., Zhang, S., and Guo, Q. (2024a). A review of the sources and pharmacological research of morroniside. Front. Pharmacol. 15, 1423062. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1423062
Shi, Q., Xu, L., and Zeng, X. (2022). Sirtuin 1 participates in intervertebral disc degeneration via the nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase/nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide/sirtuin 1 pathway responsible for regulating autophagy of nucleus pulposus cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 23 (4), 267. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11193
Shi, S., Ou, X., Liu, C., Li, R., Zheng, Q., and Hu, L. (2024b). Nanotechnology-enhanced Pharmacotherapy for intervertebral disc degeneration treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 19, 14043–14058. doi:10.2147/IJN.S500364
Shi, Z. Y., Zeng, J. Z., and Wong, A. (2019). Chemical structures and pharmacological profiles of ginseng saponins. Molecules 24 (13), 2443. doi:10.3390/molecules24132443
Shirai, T., Nakai, A., Ando, E., Fujimoto, J., Leach, S., Arimori, T., et al. (2023). Celastrol suppresses humoral immune responses and autoimmunity by targeting the COMMD3/8 complex. Sci. Immunol. 8 (81), eadc9324. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.adc9324
Si, Y., Li, Y., Gu, K., Yin, H., and Ma, Y. (2024). Icariin ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by targeting Cullin 3/Nrf2/OH pathway for osteoclast inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 173, 116422. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116422
Singh, S., Gupta, P., Meena, A., and Luqman, S. (2020). Acacetin, a flavone with diverse therapeutic potential in cancer, inflammation, infections and other metabolic disorders. Food Chem. Toxicol. 145, 111708. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111708
Solanki, R., and Patel, S. (2024). Evodiamine and its nano-based approaches for enhanced cancer therapy: recent advances and challenges. J. Sci. Food AGR 104 (14), 8430–8444. doi:10.1002/jsfa.13612
Song, D., Ge, J., Wang, Y., Yan, Q., Wu, C., Yu, H., et al. (2021c). Tea polyphenol attenuates oxidative stress-induced degeneration of intervertebral discs by regulating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 6684147. doi:10.1155/2021/6684147
Song, J., He, G. N., and Dai, L. (2023). A comprehensive review on celastrol, triptolide and triptonide: insights on their pharmacological activity, toxicity, combination therapy, new dosage form and novel drug delivery routes. Biomed. Pharmacother. 162, 114705. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114705
Song, L., Chen, X., Mi, L., Liu, C., Zhu, S., Yang, T., et al. (2020). Icariin-induced inhibition of SIRT6/NF-κB triggers redox mediated apoptosis and enhances anti-tumor immunity in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 111 (11), 4242–4256. doi:10.1111/cas.14648
Song, W., Sun, Y., Xu, L., Sun, Y., Li, T., Peng, P., et al. (2021a). Synthesis of nature product kinsenoside analogues with anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorgan Med. Chem. 29, 115854. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2020.115854
Song, X., Tan, L., Wang, M., Ren, C., Guo, C., Yang, B., et al. (2021b). Myricetin: a review of the most recent research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 134, 111017. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111017
Song, Z., Shanmugam, M. K., Yu, H., and Sethi, G. (2016). Butein and its role in chronic diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 928, 419–433. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-41334-1_17
Sprouffske, K., Athena, A. C., Radich, J. P., Carroll, M., Nedelcu, A. M., and Maley, C. C. (2013). An evolutionary explanation for the presence of cancer nonstem cells in neoplasms. Evol. Appl. 6 (1), 92–101. doi:10.1111/eva.12030
Sun, W., Chen, Y., and Li, M. (2022a). Systematic elaboration of the pharmacological targets and potential mechanisms of ZhiKe GanCao Decoction for preventing and delaying intervertebral disc degeneration. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2022, 8786052. doi:10.1155/2022/8786052
Sun, Y., Ren, J., Zhu, S., Zhang, Z., Guo, Z., An, J., et al. (2022b). The effects of sesamin supplementation on obesity, blood pressure, and lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 13, 842152. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.842152
Szabó, R., Rácz, C. P., and Dulf, F. V. (2022). Bioavailability improvement strategies for icariin and its derivates: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (14), 7519. doi:10.3390/ijms23147519
Tang, K., Su, W., Huang, C., Wu, Y., Wu, X., and Lu, H. (2021). Notoginsenoside R1 suppresses inflammatory response and the pyroptosis of nucleus pulposus cells via inactivating NF-κB/NLRP3 pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 101 (Pt B), 107866. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107866
Tao, W., Ruan, J., Wu, R., Zhao, M., Zhao, T., Qi, M., et al. (2023). A natural carotenoid crocin exerts antidepressant action by promoting adult hippocampal neurogenesis through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Adv. Res. 43, 219–231. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2022.02.015
Tao, X., Yin, L., Xu, L., and Peng, J. (2018). Dioscin: a diverse acting natural compound with therapeutic potential in metabolic diseases, cancer, inflammation and infections. Pharmacol. Res. 137, 259–269. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2018.09.022
Tian, Y., Chu, X., Huang, Q., Guo, X., Xue, Y., and Deng, W. (2022). Astragaloside IV attenuates IL-1β-induced intervertebral disc degeneration through inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 17 (1), 545. doi:10.1186/s13018-022-03438-1
Tsou, L. K., Lara-Tejero, M., RoseFigura, J., Zhang, Z. J., Wang, Y. C., Yount, J. S., et al. (2016). Antibacterial flavonoids from medicinal plants covalently inactivate type III protein secretion substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138 (7), 2209–2218. doi:10.1021/jacs.5b11575
Wan, C., Liu, S., Zhao, L., Chang, C., Li, H., Li, R., et al. (2025). Curcumin protects rat endplate chondrocytes against IL-1β-induced apoptosis via Bcl-2/Bax regulation. J. Mol. Histol. 56 (2), 111. doi:10.1007/s10735-025-10390-x
Wang, B., Yang, L. N., Yang, L. T., Liang, Y., Guo, F., Fu, P., et al. (2024b). Fisetin ameliorates fibrotic kidney disease in mice via inhibiting ACSL4-mediated tubular ferroptosis. ACTA Pharmacol. SIN. 45 (1), 150–165. doi:10.1038/s41401-023-01156-w
Wang, C., Cui, L., Gu, Q., Guo, S., Zhu, B., Liu, X., et al. (2022). The mechanism and function of miRNA in intervertebral disc degeneration. Orthop. Surg. 14 (3), 463–471. doi:10.1111/os.13204
Wang, C., Dai, S., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Gong, L., Fu, K., et al. (2023b). Celastrol as an emerging anticancer agent: current status, challenges and therapeutic strategies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 163, 114882. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114882
Wang, C., Ouyang, S., Zhu, X., Jiang, Y., Lu, Z., and Gong, P. (2023c). Myricetin suppresses traumatic brain injury-induced inflammatory response via EGFR/AKT/STAT pathway. Sci. Rep-UK 13 (1), 22764. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-50144-x
Wang, D., He, X., Wang, D., Peng, P., Xu, X., Gao, B., et al. (2020a). Quercetin suppresses apoptosis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration via the SIRT1-autophagy pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 8, 613006. doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.613006
Wang, H., Jiang, Z., Pang, Z., Zhou, T., and Gu, Y. (2020b). Acacetin alleviates inflammation and matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 14, 4801–4813. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S274812
Wang, H., Liu, X., Yang, H., Jing, X., Wang, W., Liu, X., et al. (2023). Activation of the Nrf-2 pathway by pinocembrin safeguards vertebral endplate chondrocytes against apoptosis and degeneration caused by oxidative stress. Life Sci. 333, 122162. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122162
Wang, H., Zhou, X. M., Wu, L. Y., Liu, G. J., Xu, W. D., Zhang, X. S., et al. (2020d). Aucubin alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation via Nrf2-mediated signaling activity in experimental traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 17 (1), 188. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-01863-9
Wang, J., Jing, X., Liu, X., Chen, F., Ge, Z., Liu, X., et al. (2024a). Naringin safeguards vertebral endplate chondrocytes from apoptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through SIRT3-mediated mitophagy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 140, 112801. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112801
Wang, L., Gu, Y., Zhao, H., Chen, R., Chen, W., Qi, H., et al. (2020c). Dioscin attenuates interleukin 1β (IL-1β)-Induced catabolism and apoptosis via modulating the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling in human nucleus pulposus cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 26, 923386. doi:10.12659/MSM.923386
Wang, L., Wu, H., Yang, F., and Dong, W. (2019b). The protective effects of myricetin against cardiovascular disease. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 65 (6), 470–476. doi:10.3177/jnsv.65.470
Wang, P., Yang, C., Lu, J., Ren, Y., Goltzman, D., and Miao, D. (2023d). SIRT1 protects against intervertebral disc degeneration induced by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D insufficiency in mice by inhibiting the NF-κB inflammatory pathway. J. Orthop. Transl. 40, 13–26. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2023.04.003
Wang, S., Li, Z., Ma, Y., Liu, Y., Lin, C. C., Li, S., et al. (2021b). Immunomodulatory effects of green tea polyphenols. Molecules 26 (12), 3755. doi:10.3390/molecules26123755
Wang, S., Ma, J., Zeng, Y., Zhou, G., Wang, Y., Zhou, W., et al. (2021a). Icariin, an up-and-coming bioactive compound against neurological diseases: network pharmacology-based study and literature review. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 15, 3619–3641. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S310686
Wang, X., Tan, Y., Liu, F., Wang, J., Liu, F., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023a). Pharmacological network analysis of the functions and mechanism of kaempferol from Du Zhong in intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). J. Orthop. Transl. 39, 135–146. doi:10.1016/j.jot.2023.01.002
Wang, Y., Zuo, R., Wang, Z., Luo, L., Wu, J., Zhang, C., et al. (2019a). Kinsenoside ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration through the activation of AKT-ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 11 (18), 7961–7977. doi:10.18632/aging.102302
Wen, J., Li, M., Zhang, W., Wang, H., Bai, Y., Hao, J., et al. (2021). Role of higenamine in Heart diseases: a Mini-review. Front. Pharmacol. 12, 798495. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.798495
Wu, C., Yan, J., and Li, W. (2022). Acacetin as a potential protective compound against cardiovascular diseases. Evid-Based Compl Alt. 2022, 6265198. doi:10.1155/2022/6265198
Wu, J. W., Wang, J. J., Chen, J. B., Huang, Y. L., Wang, H., Liu, G. H., et al. (2015). Resveratrol could reverse the expression of SIRT1 and MMP-1 in vitro. Genet. Mol. Res. 14 (4), 12386–12393. doi:10.4238/2015.October.16.5
Xi, H., Weng, Y., Zheng, Y., Wu, L., and Han, D. (2024). Diacetoxy-6-gingerdiol protects the extracellular matrix of nucleus pulposus cells and ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting the IL-1β-mediated NLRP3 pathway. Heliyon 10, 37877. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37877
Xiang, M., Liu, T., Tan, W., Ren, H., Li, H., Liu, J., et al. (2016). Effects of kinsenoside, a potential immunosuppressive drug for autoimmune hepatitis, on dendritic cells/CD8(+) T cells communication in mice. Hepatology 64 (6), 2135–2150. doi:10.1002/hep.28825
Xiao, J., Han, Q., Yu, Z., Liu, M., Sun, J., Wu, M., et al. (2023). Morroniside inhibits inflammatory bone loss through the TRAF6-mediated NF-κB/MAPK signalling pathway. Pharmaceuticals-Base 16 (10), 1438. doi:10.3390/ph16101438
Xiao, L., Ding, B., Gao, J., Yang, B., Wang, J., and Xu, H. (2020). Curcumin prevents tension-induced endplate cartilage degeneration by enhancing autophagy. Life Sci. 258, 118213. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118213
Xie, T., Pan, R., Huang, W., Dong, S., Wu, S., and Ye, Y. (2023). Myricetin alleviates H2O2-induced senescence and apoptosis in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Folia Histochem Cyto 61 (2), 98–108. doi:10.5603/FHC.a2023.0007
Xie, T., Yuan, J., Mei, L., Li, P., and Pan, R. (2022a). Hyperoside ameliorates TNF-α-induced inflammation, ECM degradation and ER stress-mediated apoptosis via the SIRT1/NF-κB and Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 26 (2), 260. doi:10.3892/mmr.2022.12776
Xie, T., Yuan, J., Mei, L., Li, P., and Pan, R. (2022b). Luteolin suppresses TNF-α-induced inflammatory injury and senescence of nucleus pulposus cells via the Sirt6/NF-κB pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 24 (1), 469. doi:10.3892/etm.2022.11396
Xin, L., Tan, G. Y., Zhang, Q., and Zhang, Q. (2024). Protective effects of Phellodendron species on bone health: a novel perspective on their potentials in treating osteoporosis and osteoarthritis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 30 (4), 379–384. doi:10.1007/s11655-023-3751-8
Xu, H., Zhao, H., Ding, C., Jiang, D., Zhao, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2023a). Celastrol suppresses colorectal cancer via covalent targeting peroxiredoxin 1. Signal Transduct. TAR 8 (1), 51. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01231-4
Xu, J., Shao, T., Lou, J., Zhang, J., and Xia, C. (2023b). Aging, cell senescence, the pathogenesis and targeted therapies of intervertebral disc degeneration. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1172920. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1172920
Xu, S., Chen, S., Xia, W., Sui, H., and Fu, X. (2022). Hyperoside: a review of its structure, synthesis, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicity. Molecules 27 (9), 3009. doi:10.3390/molecules27093009
Xu, S., Feng, Y., He, W., Xu, W., Xu, W., Yang, H., et al. (2021). Celastrol in metabolic diseases: progress and application prospects. Pharmacol. Res. 167, 105572. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105572
Yang, P., Zhang, Q., Shen, H., Bai, X., Liu, P., and Zhang, T. (2022b). Research progress on the protective effects of aucubin in neurological diseases. Pharm. Biol. 60 (1), 1088–1094. doi:10.1080/13880209.2022.2074057
Yang, S., Li, L., Zhu, L., Zhang, C., Li, Z., Guo, Y., et al. (2019). Aucubin inhibits IL-1β- or TNF-α-induced extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cell through blocking the miR-140-5p/CREB1 axis. J. Cell Physiol. 234 (8), 13639–13648. doi:10.1002/jcp.28044
Yang, Y. H., Gu, X. P., Hu, H., Hu, B., Wan, X. L., Gu, Z. P., et al. (2022a). Ginsenoside Rg1 inhibits nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis, inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation via the YAP1/TAZ pathway in rats with intervertebral disc degeneration. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 17 (1), 555. doi:10.1186/s13018-022-03443-4
Yao, D., Chen, E., Li, Y., Wang, K., Liao, Z., Li, M., et al. (2024). The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and their crosstalk in intervertebral disc degeneration. Cell Signal 114, 110986. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110986
Yu, H., Chen, K., Li, X., Liang, J., Jin, Y., Bao, Y., et al. (2025). Palmatine activation of TFEB enhances autophagy and alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in intervertebral disc degeneration. Phytomedicine 139, 156431. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156431
Yu, H., Xu, H., Yang, X., Zhang, Z., Hu, J., Lu, J., et al. (2023). Gut microbiota-based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study and molecular mechanism of specnuezhenide in the treatment of colorectal cancer targeting carboxylesterase. J. Pharm. Anal. 13 (9), 1024–1040. doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2023.06.012
Yu, H., Yao, S., Zhou, C., Fu, F., Luo, H., Du, W., et al. (2021). Morroniside attenuates apoptosis and pyroptosis of chondrocytes and ameliorates osteoarthritic development by inhibiting NF-κB signaling. J. Ethnopharmacol. 266, 113447. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2020.113447
Yu, L., Hao, Y., Peng, C., Zhang, P., Zhu, J., Cai, Y., et al. (2020). Effect of Ginsenoside Rg1 on the intervertebral disc degeneration rats and the degenerative pulposus cells and its mechanism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 123, 109738. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109738
Yu, L., Hao, Y. J., Ren, Z. N., Zhu, G. D., Zhou, W. W., Lian, X., et al. (2024). Ginsenoside Rg1 relieves rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inhibits IL-1β-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and inflammation via NF-κB signaling pathway. Vitro Cell Dev-An 60 (3), 287–299. doi:10.1007/s11626-024-00883-6
Yu, P. F., Liu, J. T., Ma, Z. J., Zhong, M., Li, X. C., and Jiang, H. (2018). Logistic regression analysis on the outcome predictive factors of ruptured lumbar disc herniation. Zhongguo Gu Shang 31 (6), 522–527. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1003-0034.2018.06.008
Yu, S. E., Mwesige, B., Yi, Y. S., and Yoo, B. C. (2019). Ginsenosides: the need to move forward from bench to clinical trials. J. Ginseng Res. 43 (3), 361–367. doi:10.1016/j.jgr.2018.09.001
Zamboni, F., Ren, G., Culebras, M., O’Driscoll, J., O’Dwyer, J., Ryan, E. J., et al. (2022). Curcumin encapsulated polylactic acid nanoparticles embedded in alginate/gelatin bioinks for in situ immunoregulation: characterization and biological assessment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 221, 1218–1227. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.09.014
Zehra, U., Flower, L., Robson-Brown, K., Adams, M. A., and Dolan, P. (2017). Defects of the vertebral end plate: implications for disc degeneration depend on size. Spine J. 17 (5), 727–737. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2017.01.007
Zehra, U., Noel-Barker, N., Marshall, J., Adams, M. A., and Dolan, P. (2019). Associations between intervertebral disc degeneration grading schemes and measures of disc function. J. Orthop. Res. 37 (9), 1946–1955. doi:10.1002/jor.24326
Zeng, X., Guo, F., and Ouyang, D. (2020). A review of the pharmacology and toxicology of aucubin. Fitoterapia 140, 104443. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104443
Zeng, Y., Xiong, Y., Yang, T., Wang, Y., Zeng, J., Zhou, S., et al. (2022). Icariin and its metabolites as potential protective phytochemicals against cardiovascular disease: from effects to molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 147, 112642. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112642
Zhang, B., He, Z., Guo, J., Li, F., Huang, Z., Zheng, W., et al. (2024b). Sesamin-mediated high expression of BECN2 ameliorates cartilage endplate degeneration by reducing autophagy and inflammation. Aging (Albany NY) 16 (2), 1145–1160. doi:10.18632/aging.205386
Zhang, C., Tong, Q., Liu, K., Mao, T., Song, Y., Qu, Y., et al. (2024a). Morroniside delays the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by promoting AMPK-mediated lipophagy. Phytomedicine 129, 155703. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155703
Zhang, C., Zhao, M., Wang, B., Su, Z., Guo, B., Qin, L., et al. (2021b). The Nrf2-NLRP3-caspase-1 axis mediates the neuroprotective effects of celastrol in Parkinson’s disease. Redox Biol. 47, 102134. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.102134
Zhang, G., Dong, J., Lu, L., Liu, Y., Hu, D., Wu, Y., et al. (2023b). Acacetin exerts antitumor effects on gastric cancer by targeting EGFR. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1121643. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1121643
Zhang, J., Wu, C., Gao, L., Du, G., and Qin, X. (2020). Astragaloside IV derived from Astragalus membranaceus: a research review on the pharmacological effects. Adv. Pharmacol. 87, 89–112. doi:10.1016/bs.apha.2019.08.002
Zhang, L., Gao, J., Li, Z., Liu, J., Zhang, C., Liu, J., et al. (2023c). Astragaloside IV relieves IL-1β-induced human nucleus pulposus cells degeneration through modulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Medicine 102, 34815. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000034815
Zhang, N. N., Li, Z. J., and Zhu, H. B. (2022c). Higenamine as a potential pharmacologic stress agent in the detection of coronary artery disease. Chin. Med. Sci. J. 37 (3), 275–281. doi:10.24920/003936
Zhang, S., Liang, W., Abulizi, Y., Xu, T., Cao, R., Xun, C., et al. (2021a). Quercetin alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by modulating p38 MAPK-mediated autophagy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 6631562. doi:10.1155/2021/6631562
Zhang, W., Guo, S., Dou, J., Zhang, X., Shi, F., Zhang, C., et al. (2025). Berberine and its derivatives: mechanisms of action in myocardial vascular endothelial injury - a review. Front. Pharmacol. 16, 1543697. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1543697
Zhang, X., Zhang, Z., Zou, X., Wang, Y., Qi, J., Han, S., et al. (2023a). Unraveling the mechanisms of intervertebral disc degeneration: an exploration of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1324561. doi:10.3389/fcell.2023.1324561
Zhang, Y., Cai, J., Ruan, H., Pi, H., and Wu, J. (2007). Antihyperglycemic activity of kinsenoside, a high yielding constituent from anoectochilus roxburghii in streptozotocin diabetic rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 114 (2), 141–145. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2007.05.022
Zhang, Y. H., Shangguan, W. J., Zhao, Z. J., Zhou, F. C., Liu, H. T., Liang, Z. H., et al. (2022a). Naringin inhibits apoptosis induced by cyclic stretch in rat annular cells and partially attenuates disc degeneration by inhibiting the ROS/NF-κB pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 6179444. doi:10.1155/2022/6179444
Zhang, Z., Lin, J., Nisar, M., Chen, T., Xu, T., Zheng, G., et al. (2019). The SIRT1/P53 Axis in diabetic intervertebral disc degeneration pathogenesis and therapeutics. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 7959573. doi:10.1155/2019/7959573
Zhang, Z., Qin, F., Feng, Y., Zhang, S., Xie, C., Huang, H., et al. (2022b). Icariin regulates stem cell migration for endogenous repair of intervertebral disc degeneration by increasing the expression of chemotactic cytokines. BMC Complement. Med. 22 (1), 63. doi:10.1186/s12906-022-03544-x
Zhang, Z., Wang, C., Lin, J., Jin, H., Wang, K., Yan, Y., et al. (2018). Therapeutic potential of naringin for intervertebral disc degeneration: Involvement of autophagy against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 46, 1561–1580. doi:10.1142/S0192415X18500805
Zhao, C., Zhou, X., Cao, Z., Ye, L., Cao, Y., and Pan, J. (2023b). Curcumin and analogues against head and neck cancer: from drug delivery to molecular mechanisms. Phytomedicine 119, 154986. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154986
Zhao, W. J., Liu, X., Hu, M., Zhang, Y., Shi, P. Z., Wang, J. W., et al. (2023a). Quercetin ameliorates oxidative stress-induced senescence in rat nucleus pulposus-derived mesenchymal stem cells via the miR-34a-5p/SIRT1 axis. World J. Stem Cells 15 (8), 842–865. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v15.i8.842
Zhou, C., Huang, Y., Nie, S., Zhou, S., Gao, X., and Chen, G. (2023a). Biological effects and mechanisms of fisetin in cancer: a promising anti-cancer agent. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28 (1), 297. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01271-8
Zhou, C., Yao, S., Fu, F., Bian, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., et al. (2022). Morroniside attenuates nucleus pulposus cell senescence to alleviate intervertebral disc degeneration via inhibiting ROS-Hippo-p53 pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 942435. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.942435
Zhou, Q., Zhu, C., Xuan, A., Zhang, J., Zhu, Z., Tang, L., et al. (2023b). Fisetin regulates the biological effects of rat nucleus pulposus mesenchymal stem cells under oxidative stress by sirtuin-1 pathway. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 11 (5), e865. doi:10.1002/iid3.865
Zhou, Z., Zhou, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhao, M., Hu, C., Yang, L., et al. (2024). Progress on the effects and underlying mechanisms of evodiamine in digestive system diseases, and its toxicity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytomedicine 132, 155851. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155851
Zhu, J., Tang, H., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Qiu, C., Zhang, L., et al. (2017). Kaempferol slows intervertebral disc degeneration by modifying LPS-induced osteogenesis/adipogenesis imbalance and inflammation response in BMSCs. Int. Immunopharmacol. 43, 236–242. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2016.12.020
Zhu, T., and Wan, Q. (2023). Pharmacological properties and mechanisms of Notoginsenoside R1 in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin. J. Traumatol. 26 (1), 20–26. doi:10.1016/j.cjtee.2022.06.008
Zhu, T., Wang, L., Feng, Y., Sun, G., and Sun, X. (2021a). Classical active ingredients and extracts of Chinese herbal medicines: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and molecular mechanisms for ischemic stroke. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 8868941. doi:10.1155/2021/8868941
Zhu, X., Liu, S., Cao, Z., Yang, L., Lu, F., Li, Y., et al. (2021b). Higenamine mitigates interleukin-1β-induced human nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis by ROS-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol. Cell Biochem. 476 (11), 3889–3897. doi:10.1007/s11010-021-04197-z
Zia, A., Farkhondeh, T., Pourbagher-Shahri, A. M., and Samarghandian, S. (2021). The role of curcumin in aging and senescence: molecular mechanisms. Biomed. Pharmacother. 134, 111119. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111119
Keywords: natural products, IDD (intervertebral disc degeneration), mechanistic, hyperoside, quercetin
Citation: Wu Z, Chen J, Luo W and Kuang T (2025) Natural products for intervertebral disc degeneration: mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1605764. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1605764
Received: 03 April 2025; Accepted: 09 July 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Javier Echeverria, University of Santiago, ChileReviewed by:
Juan Carlos Sepúlveda-Arias, Technological University of Pereira, ColombiaWeimin Gao, Barrow Neurological Institute (BNI), United States
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Chen, Luo and Kuang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tao Kuang, OTk1NzExNjQwQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Zenghan Wu
Zenghan Wu Jiang Chen2
Jiang Chen2