Abstract
Melanin produced by melanocytes, primarily determines human skin color and protects against ultraviolet radiation. However, excessive melanin deposition can lead to skin conditions such as freckles, age spots, and moles, potentially causing aesthetic concerns and psychological distress. Consequently, there is significant research interest in developing safe and effective whitening products that inhibit melanin synthesis. Bioactive peptides represent a promising compound category that effectively reduces melanin synthesis with minimal side effects. This review explores melanin pigmentation, identifies sources of peptides that inhibit melanin synthesis, and elucidates the mechanisms by which these peptides operate, aiming to contribute to developing novel whitening products.
1 Introduction
Melanin is the primary determinant of human skin color and is a biological pigment widely found in animals, plants, and microorganisms (Jung et al., 2015; Sugumaran and Barek, 2016). It is a complex polymer formed by indole or phenolic compounds synthesized within melanosomes-specialized organelles in melanocytes (Li R. et al., 2024; Snyman et al., 2024). Melanosomes are lysosomal organelles (Bissig et al., 2016) that house various enzymes essential for melanin synthesis, including tyrosinase (TYR), which is the rate-limiting enzyme in this process (Aizawa and Yamamuro, 2024). Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: pheomelanin and eumelanin (Le et al., 2021; Boo, 2022; Bento-Lopes et al., 2023; Qiu et al., 2023).
Melanin is a crucial pigment in the human body, influencing the color of human skin, hair, and eyes (Wang et al., 2024). It protects against harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing skin damage (Galibert et al., 2001; Mueller and Neuhauss, 2014; Solano, 2020; Onoda et al., 2024). However, excessive melanin deposition can lead to aesthetic concerns and health issues, such as freckles, moles, melanoma, and senile plaques (Azimi et al., 2024). Additionally, there is growing evidence linking pigmentation disorders with neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease (Tseng et al., 2015; Berg and Berg, 2023).
Recent research into melanin and inhibitors of melanin synthesis has grown exponentially. Various melanin synthesis inhibitors have been developed, offering potential treatments for diseases linked to excessive melanin deposition (Baber et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2023; Veerichetty and Saravanabavan, 2023). Amongst these inhibitors, bioactive peptides have emerged as a significant area of interest due to their efficacy in reducing melanin synthesis with minimal side effects (Errante et al., 2024). In this review, we explore the biosynthesis and regulation of melanin, detail the role of bioactive peptides as melanin synthesis inhibitors, and discuss the mechanisms by which these peptides function, all aimed at developing new whitening products.
2 Biosynthesis of melanin and its regulation
2.1 Melanin synthesis pathway
The specific process of melanin synthesis begins with the conversion of tyrosine into L-Dopa catalysed by tyrosinase, the central glycoprotease in the melanosome region and the only rate-limiting enzyme in this process (Kim et al., 2023). L-Dopa is oxidized to dopaquinone, an active intermediate and crucial precursor for converting melanin into eumelanin and brownish melanin (Olivares et al., 2001). When the ratio of dopaquinone to cysteine is low, L-dopaquinone (L-DQ) undergoes self-cyclization and oxidation to form dopachrome (DC). With the aid of tyrosinase-related protein 2, dopachrome is then converted into 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA), and 5,6-dihydroxyindole (DHI) (Boissy et al., 1998; Olivares et al., 2001). These intermediates eventually combine within melanosomes to form eumelanin.
In conditions where cysteine concentration is high, red-brown melanin is produced. Doboquinone reacts with cysteine to form cysteinyldopa, which further polymerizes to produce brownish melanin (Galvan and Solano, 2016; Wakamatsu et al., 2017). Microphthalmia-related transcription factor (MITF) regulates the expression of tyrosinase and is a primary target for influencing melanin synthesis (Ikarashi et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2021). Phosphorylation of MITF can enhance melanin synthesis (Joyjamras et al., 2022). Moreover, studies have indicated that nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase (NNT) inhibits melanin synthesis by regulating oxidative stress, presenting an alternative to the common TYR pathway and MITF pathway and highlighting the role of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) pathway controlling melanin synthesis (Allouche et al., 2021; Park et al., 2022; Figure 1).
FIGURE 1
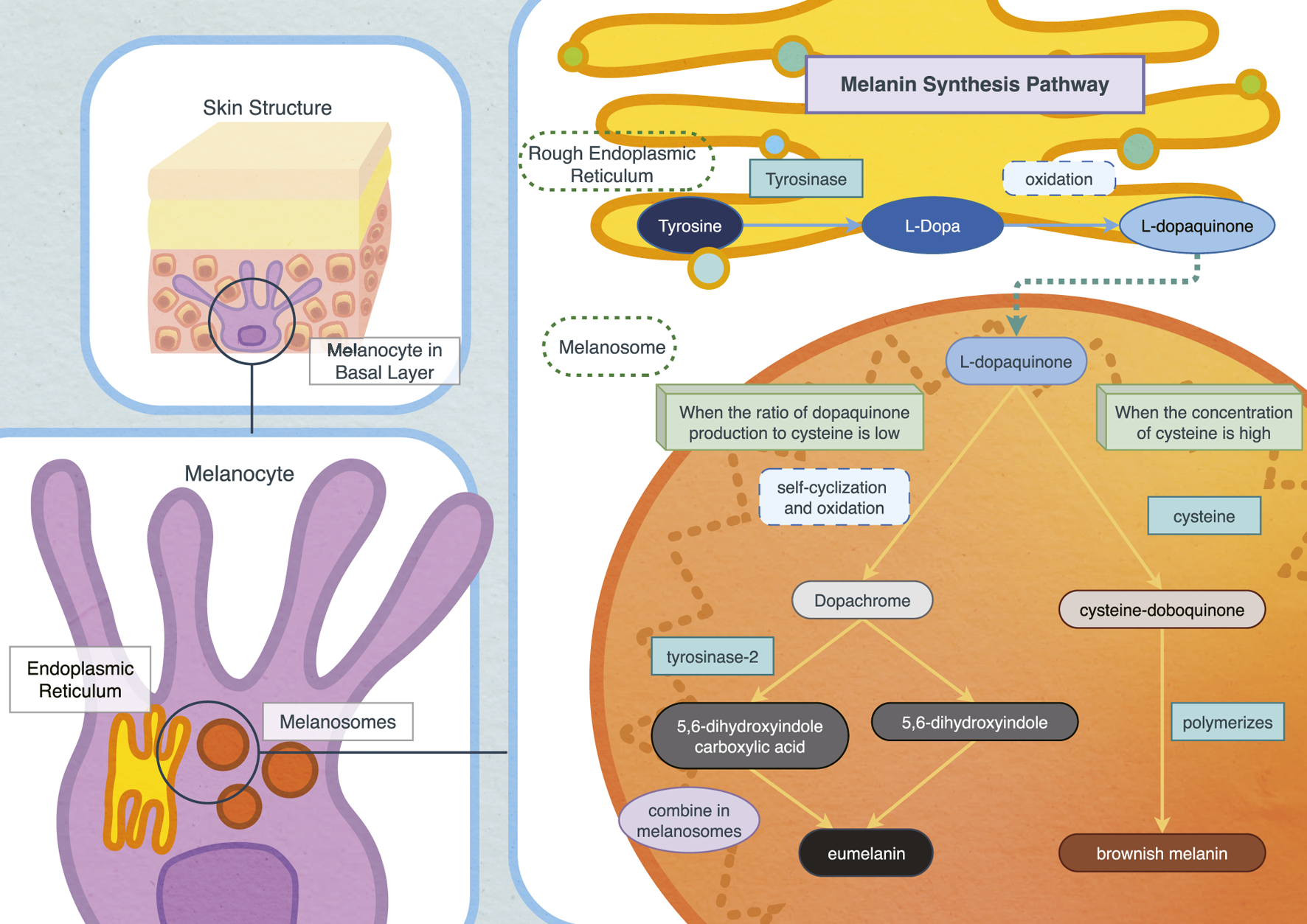
Biosynthesis pathway of melanin in vivo.
2.2 Regulation of pigmentation
Melanin pigmentation is a crucial defense mechanism, protecting humans from external hazards, particularly ultraviolet (UV) rays. It also plays a significant role in the body’s immune response and metabolism, safeguarding against harmful substances (Mueller and Neuhauss, 2014; Koike and Yamasaki, 2020). Pigmentation disorders are the third most common reason for dermatological consultations (Cestari et al., 2014). The primary causes of skin pigmentation disorder include inflammation, ultraviolet radiation, and interactions between specific diseases and medications. This review will further explore the causes of pigmentation, examining the impacts of ultraviolet exposure, inflammation, and genetic inheritance.
2.2.1 Ultraviolet exposure
UV exposure is critical to skin pigmentation (Al-Sadek and Yusuf, 2024). Studies have demonstrated that UV radiation directly stimulates melanocytes, enhancing their melanin secretion. Specifically, UV irradiation increases the release of melanin-inducing factors such as stem cell factor (SCF), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC). POMC is enzymatically hydrolyzed into α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone, where α-MSH binding stimulates eumelanin production (Koike and Yamasaki, 2020; Zhang et al., 2024b).
Ultraviolet A (UVA), with a wavelength of 320 nm–400 nm, has the longest wavelengths in the UV spectrum and can easily penetrate skin tissue (Al-Sadek and Yusuf, 2024). UVA’s strong penetration ability and DNA’s weak absorption capacity for UVA can lead to DNA damage through photosensitive reaction (Agar et al., 2004; D'Orazio et al., 2013). Moreover, the absorption of UVA by the skin generates ROS, inducing oxidative stress, which in turn promotes melanosis (Allouche et al., 2021; Bernerd et al., 2022).
Exposure to Ultraviolet B (UVB), known for causing sunburn, is a significant external factor influencing melanin production (Zhang et al., 2024b). Prolonged UVB exposure activates melanocytes, increasing melanin content, which accelerates pigmentation and potentially contributes to various skin disease such as freckles (Azimi et al., 2024).
2.2.2 Genetic inheritance or inflammation
Pigmentation disorders can result from various factors, including inflammation and genetic inheritance (Hossain et al., 2021; Tearle et al., 2025). Studies have shown that several inflammatory factors are involved in skin pigmentation (Feng et al., 2025). Interleukin-1 (IL-1) a key player in cellular inflammatory responses, and exists in two forms: IL-1α and IL-1β. Keratinocyte growth factor (KGF) facilitates the transport of melanosomes, and when combined with IL-1α, it promotes pigmentation (Cardinali et al., 2005; Chen et al., 2010). IL-1β has been shown to upregulate the expression of tyrosinase and tyrosine-related protein-1 (TRP1), potentially enhancing skin pigmentation by increasing melanin gene expression and promoting the production of additional inflammatory factors (Yang et al., 2022).
IL-4, through the JAK2-STAT6 pathway, reduces MITF and TRP-1 expression in normal human melanocytes (NHM), thereby inhibiting melanin production (Choi et al., 2013). IL-13, which shares similar receptor structures and signaling pathways with IL-4, is also involved in melanogenesis regulation. Epidermal γδ T cells produce both IL-4 and IL-13, with IL-13 being the more abundant cytokine (Renauld, 2001; Nishimura et al., 2008; Kim et al., 2014). Ginsenoside F1 treatment increases IL-13 output from these T cells, contributing to whitening by inhibiting tyrosinase and DCT expression. IL-13 may directly regulate melanogenesis through the JAK2-STAT6 signaling pathway (Han et al., 2014).
While IL-17 alone does not inhibit pigmentation, it significantly amplifies the inhibitory effect of TNF on melanin synthesis through a synergistic interaction (Wang et al., 2013). IL-18 enhances primary human melanocyte growth by inactivating PTEN via the AKT/NF-κB pathway (Zhou et al., 2013; Zhou et al., 2016). IL-33 has been shown to stimulate melanin biosynthesis in NHEM by promoting phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and CREB, leading to increased expression of TYR, TRP-1, and DCT through MITF, ultimately resulting in increased melanin production (Zhou et al., 2014). COX-2 may contribute to the formation of chloasma by activating tyrosinase and melanogenesis-related molecules, therefore promoting melanogenesis (Rodriguez-Arambula et al., 2015).
Gene factors also play a crucial role in inducing pigmentation. For example, differential expression of genes such as SLC24A5 and SLC45A2 influences variations difference in skin color (Soejima and Koda, 2007; Haltaufderhyde and Oancea, 2014).
2.3 Traditional products used to inhibit melanin synthesis
The potential of products that inhibit melanin synthesis, which can have a whitening effect, has long attracted attention. Vitamin C (VC), a well-known free radical scavenger, is the most commonly used, as it effectively neutralizes free radicals caused by oxidative stress from UV irradiation (Gelmi et al., 2022). Other products, such as Vitamin E (VE) and gentisic acid, also serve similar functions (Miao et al., 2019; Sandhu et al., 2023). VC is an acidic compound inhibiting tyrosinase activity through cytoplasm acidification, suppressing melanin synthesis (Nam et al., 2023). As tyrosinase is the key enzyme regulating melanin synthesis, tyrosinase inhibitors are often utilized to inhibit melanin production (Pillaiyar et al., 2017). Natural tyrosinase inhibitors include flavonoids, hydroquinone and its derivatives, stilbene, chalcone, arbutin, kojic acid and coumarin, and some newly synthesized inhibitors (Lee et al., 2016).
While these tyrosinase inhibitors are frequently used in whitening products, studies have highlighted significant side effects (Pillaiyar et al., 2017). For example, long-term use of kojic acid has been shown to have cytotoxic effects, and its instability (due to sensitivity to light, heat, and metal ions) limits its storage and efficacy (Schurink et al., 2007). Hydroquinone use has been associated with several adverse reactions, including allergic dermatitis and depigmentation (Jow and Hantash, 2014). Aminobenzoic acid has also been linked to various side effects, such as headaches, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting (Bala et al., 2018; Kim and Lim, 2023).
3 Peptides are emerging products that inhibit melanin synthesis with little side effect
Numerous studies have identified bioactive peptides as having various benefits, including antibacterial, antiviral, diabetic, and anticancer properties (Kumar et al., 2024; Nikitovic et al., 2024; Zhang S. et al., 2024; Zhao and Song, 2024). Additionally, many bioactive peptides with anti-melanin synthesis properties have been discovered. These peptides have garnered significant interest from researchers worldwide, due to their potential for development into commercial whitening products, and their inherent advantages of low toxicity, low immunogenicity, and high biocompatibility (Lombardi et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2024).
3.1 Melanin-synthesis-inhibiting peptides of anaimal origins
3.1.1 Melanin synthesis-inhibiting peptides from terrestrial animal resources
3.1.1.1 From egg
Phosvitin, a highly phosphorylated protein in egg yolk, contains specific amino acids, with serine accounting for 30% of its composition (Ishikawa et al., 2007; Jie et al., 2018). The unique structure of phosphotoxic protein makes it a potent metal-chelating agent (Okajima et al., 2019; Song et al., 2023). Studies have shown that compounds with metal chelating abilites can also act as melanogenesis inhibitors (Kubo and Kinst-Hori, 1999). In this study, phosphotoxic protein inhibited melanin synthesis by downregulating the expression of MITF, TRP-1, TRP-2, and tyrosinase in B16F10 cells and reducing cAMP levels (Jung et al., 2012). Additionally, phosphotoxic peptide phosphopeptides (PPPs) derived from phosphotoxic protein inhibited α-MSH-induced melanin production in B16F10 melanoma cells. Inhibition rates exceede 30% at a concentration of 3 mg/mL, demonstrating a strong inhibitory effect on tyrosinase activity (Lee et al., 2023).
A 2020 study utilized pepsin and trypsin to hydrolyze egg whites, yielding a hydrolysate with strong monophenolase and diphenolase inhibitory activities (Yap and Gan, 2020). Seven peptides were identified as potential inhibitors of melanin synthesis: ILELPFASGDLLML, GYSLGNWVCAAK, YFGYTGALRCLV, HIATNAVLFFGR, FMMFESQNKDLLFK, SGALHCLK and YFGYTGALR (Yap and Gan, 2020).
Additionally, a 2022 study demonstrated that GYSLGNWVCAAK and CEWHdi both reduced intracellular cAMP levels. While GYSLGNWVCAAK inhibited tyrosinase expression, CEWHdi and CEWHmono suppressed the mRNA expressions of Mitf, Tyr, Trp-1, and Trp-2 (Yap et al., 2023).
3.1.1.2 From bee
Many bioactive substances inhibit melanin synthesis by inhibiting the growth of melanoma cells. Bee venom and melittin, a bee peptide, has been shown to inhibit melanoma cell growth and migration (Kim et al., 2018; Lim et al., 2019). Melittin, a 26-amino acid peptide (NH2-GIGAVLKVLTTGLPALISWIKRKRQQ-CONH2) works in conjunction with bee venom to inhibit the growth of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways (Lee and Bae, 2016; Rady et al., 2017; Lim et al., 2019). Melittin decreases the total protein content of the key signal molecules, and its inhibitory effect on melanoma is stronger than bee venom alone. Furthermore, studies indicate that inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway enhances melanoma cell sensitivity to the chemotherapy drug temozolomide (TMZ), suggesting that combining bee venom with TMZ could lead to a more potent inhibitory effect on melanoma (Sinnberg et al., 2009; Niessner et al., 2017).
3.1.1.3 From milk
β-lactoglobulin (BLG), a major milk protein component, has inhibited tyrosinase activity (Mayerhofer et al., 2022). A study in Japan demonstrated that at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, BLG reduced pigmentation in human melanocytes treated with retinol, resulting in only weak pigmentation. However, it remains unclear whether the inhibitory effect was due to the entire BLG protein or a specific component of it.
Subsequent research in Japan found that Lactobacillus helveticus-Fermented Milk Whey (LHMW) could inhibit melanin synthesis (Ikarashi et al., 2020). LHMW inhibited an α-MSH-induced increase in tyrosinase, TRP1, and DCT expression at both protein and mRNA levels in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Moreover, the expression of MITF was decreased when LHMW was applied alone. While LHMW has shown the potential to inhibit melanin synthesis, the precise active components responsible for this effect are still under investigation. Given the rich peptides and protein, content of whey and the strong proteolytic activity of Lactobacillus helveticus, it is speculated that the peptide in LHWN decreased the expression of MITF (Genay et al., 2009; Ikarashi et al., 2020; Irazoqui et al., 2024; Rackerby et al., 2024).
Additionally, studies from South Korea have indicated that bioconverted fermented milk (BCFM) can prevent melanin production by inhibiting the expression of MITF in B16F1 cells induced by α-MSH. It is suspected that peptides within BCFM are responsible for this activity, although the exact peptides involved remain unidentified (Choi et al., 2024).
3.1.1.4 From silkworm
Silk has two main proteins: sericin and fibroin (Jiang et al., 2024; Noda et al., 2024). Most sericin is discarded during processing, accounting for 20%–30% of a cocoon’s quality (Kato et al., 1998; Wu et al., 2008). A study in Japan demonstrated that sericin inhibits tyrosinase activity in silk. The anti-tyrosinase activity of sericin hydrolysate is thought to be linked to copper chelating properties and high serine content (Wu et al., 2008). The relationship between copper chelating activity and tyrosinase inhibition is well established (Cardoso et al., 2021; Jung et al., 2024).
3.1.2 Melanin-synthesis-inhibiting peptides of aquatic origins
3.1.2.1 From fish
Fish is rich in protein, with content ranging from 10% to 25% (Borges et al., 2023; Honrado et al., 2024). Fish by-products constitute about 60% of the total weight of fish and are often considered low-value products. Many by-products, including fish scales and heads, are underutilized or discarded (Ramakrishnan et al., 2023; Shekoohi et al., 2024). Tilapia scale peptides, prepared through enzymolysis and elution, have strong tyrosinase inhibition in vitro. At a 5 mg/mL concentration, the tyrosinase inhibition rate of tilapia scale reached 59.73%, which is significantly higher than the traditional tyrosinase inhibitor arbutin at the same concentration. Furthermore, tilapia scale peptide has demonstrated copper-chelating ability, making it an effective tyrosinase inhibitor (Ju et al., 2022).
In a study conducted in Jiangxi, China, grass carp scale gelatin hydrolyzed by alkaline protease also exhibited significant tyrosinase inhibitory activity. When the fish scale gelatin hydrolysate was used at 5 mg/mL, the tyrosinase inhibition rate was 61.7%. Four new peptides were identified from the hydrolysate using a rapid screening method for tyrosinase inhibitory peptides (TYIPs) via bio-affinity ultrafiltration combined with LC-Orbitrap-MS/MS. DLGFLARGF exhibited high tyrosinase inhibitory activity, with an IC50 value of 3.09 mM. At a 1.6 mg/mL concentration, DLGFLARGF reduced tyrosinase activity by 76.81%, decreasing melanin content (Hu et al., 2022a).
A recent study in South Korea isolated and identified decapeptide (DP, KGYSSYICDK) from the hydrolysate of a Chromis Notate by-product. DP exhibited high antioxidant activity, comparable to or greater than VC in FRAP and ABTS assays. It also inhibited tyrosinase activity and reduced melanin synthesis in α-MSH-induced B16F10 cells in a dose-dependent manner. DP showed strong binding to various tyrosinase residues, reducing the mRNA expression of MITF, tyrosinase, and MC1R (Lee et al., 2024).
Additionally, a peptide T-6(FGFRSP), isolated from TFMH, was studied for its interaction with tyrosinase. Molecular docking revealed that T-6 binds within the TYR cavity, forming hydrogen bonds with Val248, Ala323, Asn320, and Asn81, ionic bonds with Glu322, and pi-pi stacking interactions with Phe192. T-6 may inhibit tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis by binding to the enzyme’s first and second regions (Hu et al., 2024).
3.1.2.2 From shellfish
Shellfish, like fish, is a rich source of high-quality protein and bioactive peptides (Phadke et al., 2021). Meng et al. used alkaline protease from Bacillus licheniformis to hydrolyze Pinctada martensii, yielding 401 peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. These were identified through ultrafiltration and purification. After amino acid sequence identification and molecular docking, three peptides with the lowest binding energy were obtained: WDRPKDDGGSPIK(W1), DRGYPPVMF(W2) and SGGGGGGGLGSGGSIRSSY(W3). At 1–5 mg/mL concentrations, W3 inhibited melanin synthesis by competitively inhibiting tyrosinase activity. Importantly, W3 demonstrated value without affecting the survival of B16F10 cells (Meng et al., 2023).
Additionally, studies have shown that oyster hydrolysate (OH) inhibits melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells by downregulating the cAMP pathway. In C57BL/6J mice treated with OH, both melanin content and the number of melanoma cells were reduced. The sequence of the OH peptide is Ser-Ser-ASP-ASN-ASN-ASP-Glu-Ala-Lys, with a molecular weight of 1036.39 Da (Han et al., 2019).
A 2023 study in Thailand used computer simulation technology to predict eight candidate peptides for tyrosinase inhibition in abalone peptides: TIP1, TIP2, KNN1, KNN2, KNN3, RF1, RF2, and RF3. These peptides showed no cytotoxic effect on mouse melanoma cells. According to AnOxPePred, TIP2, and KNN1 exhibited the best free radical scavenging and ion-chelating activities. At a concentration of 70.83 μM, KNN1 reduced tyrosinase activity in mushrooms by 50% (Kongsompong et al., 2023).
3.1.3 Peptides from amphibians with melanin synthesis-inhibiting activities
Amphibians produce various peptides with diverse structures and functions, many of which have been studied for their antibacterial, antioxidant, and skin wound-healing properties (McMillan and Coombs, 2020; Feng G. et al., 2021; Wang X. et al., 2023). Research on Andrias davidianus (Chinese giant salamander) has gained attention due to its high protein content, which can produce a range of bioactive peptides (Chen et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2023). Among these peptides, antioxidants have been extensively studied, with some also exhibiting melanin-inhibiting properties (Speeckaert et al., 2023; Zhan et al., 2024). However, research on the anti-melanin effects of Andrias davidianus remains limited, with more studies focused on Odorrana andersonii.
A study in China in 2023 reported the first findings on OA-VI12, a peptide derived from Odorrana andersonii which regulates melanin synthesis. OA-VI12 was found to inhibit melanin synthesis in B16 cells. At a concentration of 5 μM, the inhibitory effect of OA-VI12 on melanin production was comparable to that of arbutin, but OA-VI12 showed a significantly stronger inhibitory effect at this concentration. OA-VI12 was shown to promote the expression of miR-122-5p while downregulating the expression of MITF and TYR, suggesting that it inhibited melanin synthesis through the miR-122-5p/MITF/TYR axis. Furthermore, OA-VI12 demonstrated transdermal penetration, inhibiting UVB-induced pigmentation in mouse ears and significantly reducing pigmentation (Wang J. et al., 2023).
Subsequently, another melanin-inhibitory peptide from Odorrana andersonii, (Nigrocin-OA27), was identified. Although its molecular weight is twice that of OA-VI12, Nigrocin-OA27 also exhibited a strong transdermal effect. It decreased tyrosinase activity in B16 cells, inhibited melanin synthesis, and interacted with the catalytic site, preventing its binding with L-Dopa, and thereby reducing the enzyme’s catalytic activity (Li J. et al., 2024) (Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Compound name | Peptide sequence | Source | Mechanism | IC50 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosvitin phosphopeptides | Unknown | Egg | Inhibit the activity of mushroom tyrosinase; Inhibit cell tyrosinase activity and MITF expression | Unknown | Lee et al. (2023) |
| CEWHdi | Unknown | Chicken egg white | Decrease cAMP level and inhibit cell tyrosinase expression | 3.04 mM | Yap et al. (2023) |
| CEWHmono | Chicken egg white | inhibit cell tyrosinase expression | Yap et al. (2023) | ||
| Unnamed | ILELPFASGDLLML | Chicken egg white | Presumably, inhibits monophenolase and diphenolase | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020) |
| Unnamed | GYSLGNWVCAAK | Chicken egg white | Presumably inhibits monophenolase and diphenolase; inhibits tyrosinase expression and reduces cAMP level | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020); Yap et al. (2023) |
| Unnamed | YFGYTGALRCLV | Chicken egg white | Presumably, inhibits monophenolase and diphenolase | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020) |
| Unnamed | HIATNAVLFFGR | Chicken egg white | Presumably, inhibits monophenolase and diphenolase | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020) |
| Unnamed | FMMFESQNKDLLFK | Chicken egg white | Presumably, inhibit monophenolase and diphenolase | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020) |
| Unnamed | SGALHCLK | Chicken egg white | Presumably, inhibit monophenolase and diphenolase | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020) |
| Unnamed | YFGYTGALR | Chicken egg white | Presumably, inhibit monophenolase and diphenolase | Unknown | Yap and Gan, (2020) |
| Melittin | GIGAVLKVLTTGLPALISWIKRKRQQ | Bee | Inhibit PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways; inhibit the growth and migration of melanoma cells | Unknown | Lim et al. (2019) |
| Sericin hydrolysate | Unknown | Silk | Inhibit the activity of mushroom tyrosinase; Chelat ferrous ion | 8.71 mg/mL; 0.128 mg/mL | Wu et al. (2008) |
| Unknown | Unknown | BCFM | Inhibition of melanin synthesis in B16F1 cells; Inhibition of MITF activity in B16F1 cells | Unknown; Unknown | Genay et al. (2009) |
| Tilapia scale peptides | Unknown | Oreochromis niloticus | Chelate copper ions; Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Ju et al. (2022) |
| Unnamed | DLGFLARGF | Grass carp scale gelatin | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | 3.09 mM | Hu et al. (2022a) |
| DP | KGYSSYICDK | Chromis Notate | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Lee et al. (2024) |
| T-6 | FGFRSP | Takifugu flavidus | Inhibit the activity of mushroom tyrosinase; Inhibition of melanin synthesis in melanoma cells | Unknown | Hu et al. (2024) |
| W1 | WDRPKDDGGSPIK | Pinctada martensii | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Meng et al. (2023) |
| W2 | DRGYPPVMF | Pinctada martensii | Mixed inhibition of tyrosine monophenolase activity | Unknown | Meng et al. (2023) |
| W3 | SGGGGGGGLGSGGSIRSSY | Pinctada martensii | Competitive inhibition of tyrosine monophenolase activity | 3.04 mg/mL | Meng et al. (2023) |
| OH | Ser-Ser-Asp Asn-Asn-Asp-Glu-Ala-Lys | Oyster | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Han et al. (2019) |
| TIP1 | TASSDAWYR | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kubglomsong et al. (2018) |
| TIP2 | SAPFMPDAFFRNV | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| KNN1 | NICECMK | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| KNN2 | TSQMSRSSSR | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| KNN3 | KKNYRVSEAYK | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| RF1 | SAPTFFR | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| RF2 | NSSLRVQSR | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| RF3 | SQSNSRSVSR | Haliotis diversicolor | Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Kongsompong et al. (2023) |
| OA-VI12 | VIPFLACRPLGL | Odorrana andersonii | Inhibition of B16 cells and mouse ear melanin synthesis; Inhibition of cell tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Wang J. et al. (2023) |
| Nigrocin-OA27 | ‘GFLSKPLPVGRKIVPWLSGLC’ | Odorrana andersonii | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase; Reduce the content of melanin in B16 cells | 229.2 μM | Li J. et al. (2024) |
Melanin synthesis inhibitory peptides from anaimal origins.
3.2 Melanin-synthesis-inhibiting peptides of plant origins
3.2.1 From pseudostellaria heterophylla
In a 1994 study in Japan, seven cyclic peptides were extracted from the roots of Pseudostellaria heterophylla, all of which exhibited inhibitory activity against mushroom tyrosinase. These peptides were named Pseudostellaria A, B, C, D, E, F, and G (Morita et al., 1994a; Morita et al., 1994b; Morita et al., 1994c). Pseudostellaria C, D and G were found to effectively inhibit melanin synthesis when used to treat melanoma cells cultured in vitro.
3.2.2 From rice
Rice protein and rice bran protein hydrolysates are rich in bioactive peptides (Ochiai et al., 2016; Kubglomsong et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2020). Ruixue Zhang and colleagues used alkaline protease and neutralizing enzymes to hydrolyze rice, and then screened for characteristics, identifying three peptides: LLK, LPK, and PEK. The UVB-induced increase in melanin content and tyrosinase activity was significantly reduced in UVB-irradiated PIG1 cells treated with rice protein hydrolysates. At a 200 μg/mL concentration, both melanin content and tyrosinase activity were lower than those in the positive control group. LLK, LPK, and pEK all reduced melanin content and tyrosinase activity, with PEK exhibiting the strongest inhibitory effect. LLK and pEK downregulated the mRNA expression of TRP-1 and TRP-2 (p < 0.01). These peptides regulate the JNK/β-Trcp/NFκB-p65/MITF signaling pathway at both the mRNA and protein levels to inhibit melanin synthesis (Zhang et al., 2020).
Rice bran protein, a by-product of rice production, has also been explored for its bioactive peptides (Zhang et al., 2024a). Akihito Ochiai isolated three peptides- CT-1, CT-2, and CT-3 from rice bran protein with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Previous research indicated that TH-10 and P4-peptides with similar sequences-share seven identical amino acid residues. TH-10 contains a tyrosine residue at the N- terminal, whereas P4 has tyrosine residue at the center, N- terminal, and C- terminal. Further analysis of P4 showed that the C-terminal tyrosine residues were the most critical for its tyrosinase inhibitory activity (Shen et al., 2019). CT-1, CT-2, and CT-3 all contained C-terminal tyrosine residues and significantly inhibited tyrosinase activity. CT-1 and CT-3 promoted melanin synthesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells, but CT-2 inhibited melanin synthesis without cytotoxicity (Ochiai et al., 2016). Additionally, researchers found that rice bran albumin exhibited higher tyrosinase inhibitory activity than other protein components. After the hydrolysis of rice bran albumin by papain, 13 peptides were obtained by structural analysis, most of which had characteristics of metal-chelating peptides and tyrosinase inhibitors (Kubglomsong et al., 2018).
3.2.3 From flaxseed
Cyclic peptides derived from flaxseed have been proven to possess anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties (Shim et al., 2022; Shim et al., 2024). Recent studies have also demonstrated that a cyclic peptide mixture from flaxseed exhibits tyrosinase inhibitory activity and can inhibit melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells. The proposed mechanism suggests that this effect occurs through the downregulation of the CREB pathway, thereby inhibiting melanin synthesis (Yoon et al., 2023).
3.2.4 From vigna
Zhiwei Shen and colleagues identified a novel peptide, ECGYF (designated EF-5), from Vigna, which exhibits both tyrosinase inhibitory activity and free radical scavenging ability. In both in vivo and in vitro experiments, EF-5 demonstated a stronger inhibitory effect on tyrosinase than glutathione and arbutin. Molecular docking studies revealed that hydrogen bond and hydrophobic interaction between EF-5 and tyrosinase residues influence tyrosinase activity. It is suggested that EF-5 may induce a conformational change in tyrosinase, which differs from the mechanism of glutathione (Shen et al., 2019).
3.2.5 From walnut
Feng et al. researched walnuts by hydrolyzing DWMP with alkaline protease and filtering it through an ultrafiltration membrane to obtain DWMPH. The DWMPH was divided into four components based on molecular weight, and the tyrosinase inhibitory activity of each component was evaluated. Interestingly, the results revealed that all four components inhibited both the monophenolase and diphenolase activity of tyrosinase, which had smaller molecular weights, correlating with greater tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Dwmphs-Ⅳ, with the smallest molecular weight, exhibited the highest inhibitory activity, showing ic50 of 3.52 mg/mL and 2.65 mg/mL for monophenolase and diphenolase respectively. Further purification of DWMPHs-Ⅳ yielded three components, with F2 showing the strongest inhibitory effect. Molecular docking studies were performed to assess the binding affinity of these peptides with tyrosinase, where lower scores indicated more stable and reasonable binding. The tripeptide FPY was identified as the most stable compound, with the highest binding affinity. The ic50 values for tyrosinase monophenolase and bisphenolase by FPY were 1.11 mM and 3.20 mm respectively. FPY was found to be a competitive inhibitor of tyrosinase and was not degraded by digestive enzymes (Feng Y.-X. et al., 2021).
3.2.6 From chaenomeles speciosa
Chaenomeles speciosa is known for its anti-tumor, anti-oxidation, and anti-inflammatory effects, but there is limited research on its anti-melanin synthesis properties (Zhang et al., 2010; Xie et al., 2015). In 2020, Deng et al. hydrolyzed and purified papaya seed proteins, obtained two new peptides: NYRRE (F1-a) and RHAKF(F1-b). RHAKF exhibited stronger DPPH radical scavenging ability and lipid peroxidation abilities in antioxidant activity tests. Molecular docking studies revealed more docking sites between RHAKF and tyrosinase, with a closer binding affinity. The IC values for RHAKF and NYRRE were 8.69 mg/mL and 1.15 mg/mL, respectively. RHAKF may possess an imidazole ring capable of metal chelation (Deng et al., 2020) (Table 2).
TABLE 2
| Compound name | Peptide sequence | Source | Mechanism | IC50 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PseudostellarinsA | Cyclo [GPYLA] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway | 131 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| PseudostellarinsB | Cyclo [GIGGGPPF] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway | 187 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| PseudostellarinsC | Cyclo [GTLPSPFL] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway; Inhibition of melanin production in B16 melanoma cells | 63 μM; 171 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| PseudostellarinsD | Cyclo [GGYPLIL] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway; Inhibition of melanin production in B16 melanoma cells | 100 μM; 49 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| PseudostellarinsE | Cyclo [GPPLGPVIF] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway | 175 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| PseudostellarinsF | Cyclo [GGYLPPLS] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway | 50 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| PseudostellarinsG | Cyclo [PFSFGPLA] | Pseudostellaria heterophylla | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase pathway; Inhibition of melanin production in B16 melanoma cells | 75 μM; 102 μM | Morita et al. (1994c) |
| Unnamed | LLK | Rice protein | Decrease the expression of TRP-1 and TRP-2 to affect melanin synthesis | Unknown | Zhang et al. (2020) |
| Unnamed | LPK | Rice protein | Decrease the expression of TRP-1 and TRP-2 to affect melanin synthesis | Unknown | Zhang et al. (2020) |
| Unnamed | PEK | Rice protein | Decrease the expression of TRP-1 and TRP-2 to affect melanin synthesis | Unknown | Zhang et al. (2020) |
| CT-1 | HGGEGGRPY | Rice bran protein | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Ochiai et al. (2016) |
| CT-2 | LQPSHY | Rice bran protein | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity; Inhibition of melanin synthesis in melanoma | 156 μM; 500 μM | Ochiai et al. (2016) |
| CT-3 | HPTSEVY | Rice bran protein | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | Unknown | Ochiai et al. (2016) |
| TH-10 | Mrsresswy | Rice | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | 102 μM | Shen et al. (2019) |
| P4 | YRSRKYSSWY | Unknown | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity; Inhibition of tyrosine monophenolase activity in mushrooms | 40 μM; 123 μM | Shen et al. (2019), Zhang et al. (2020) |
| Linosorbs | Unknown | Flaxseed | Inhibit the activity of mushroom tyrosinase; Inhibition of melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells | Unknown; Unknown | Yoon et al. (2023) |
| EF-5 | ECGYF | Vinga | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity; Inhibition of melanin synthesis in A375 cells | 0.46 mM; Unknown | Shen et al. (2019) |
| Unnamed | FPY | Walnut | Inhibition of tyrosine monophenolase activity in mushrooms; Inhibition of tyrosine bisphenolase activity in mushrooms | 1.11 mM; 3.22 mM | Feng Y.-X. et al. (2021) |
| F1-a | NYRRE | Chinese quince seed | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | 8.69 mg/mL | Deng et al. (2020) |
| F1-b | RHAKF | Chinese quince seed | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase activity | 1.15 mg/mL | Deng et al. (2020) |
Melanin synthesis inhibitory peptides from plant origins.
3.3 Melanin-synthesis-inhibiting peptides of mushrooms and bacteria
In a 1974 study, a peptide (Madhosingh and Sundberg, 1974) with tyrosinase inhibitory activity was first reported. Madhosnigh and Sundberg isolated two peptides from mushrooms. Naming them Ia and Ib. Their research revealed that Ia is a competitive inhibitor, while Ib is a non-competitive inhibitor. The main hydrolysis products of Ia were phenylalanine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid in a 1: 1: 1 ratio. However, the peptide sequences of Ia and Ib remain unidentified.
Subsequently, Japanese researchers reported the first detailed sequence of a tyrosinase inhibitory peptide in their study on Lactobacillus helveticus. The cyclic peptide, Cycle [Pro-Tyr-Pro-Val], isolated from Swiss lactic acid bacteria, exhibited a tyrosinase IC50 of 1.5 mM, with inhibitory activity stronger than that of arbutin, which had an IC50 of 5.0 mM (Kawagishi et al., 1993) (Table 3).
TABLE 3
| Compound name | Peptide sequence | Source | Mechanism | IC50 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ia | Unknown | Mushroom | Competitive inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase in the presence of DOPA | Unknown | Madhosingh and Sundberg, (1974) |
| Ib | Unknown | Mushroom | Noncompetitive inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase in the presence of DOPA | Unknown | Madhosingh and Sundberg, (1974) |
| Unnamed | Cyclo [PYPV] | Lactobacillus helveticus | Inhibition of mushroom tyrosinase | 1.5 mM | Kawagishi et al. (1993) |
Melanin synthesis inhibitory peptides from mushrooms and bacteria.
3.4 Non-natural peptides with anti-melanin synthesis activities
In an experiment conducted in Italy to develop nontoxic natural tyrosinase inhibitors, reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and ultraviolet detection were used to study the inhibitory effects of various dipeptides on DOPA pigment formation. The results showed that glycyl dipeptides (Gly-Asp, Gly-Lys, Gly-Phe, and Gly-Gly) inhibited melanin formation by directly inhibiting enzymes activity. In contrast, Gly-His inhibited subsequent reactions in converting dopaquinone to melanin. The authors also found that polyphenol oxidase could form binary complexes with substrates, inhibitors, or it can combine them to form ternary complexes. Among the peptides studied, Gly-His exhibited the strongest inhibitory effect (Girelli et al., 2004).
Xiao et al. constructed a pharmacophore model by molecular docking and group simulation to identify key functional groups in natural products that inhibited mushroom tyrosinase (Joompang et al., 2023). Several compounds were identified, including A5 and B16, which showed high tyrosinase inhibitory activity. A5 is similar to dipeptide WY, while B16 features a KFY structure, suggesting that C-terminal tyrosine residues play an important role in the tyrosinase inhibition. Eleven tripeptides derived from KFY were synthesized, with CRY and RCY exhibiting the highest tyrosinase inhibitory activities. The structures of CRY and RCY suggest that they can chelate with Cu ions in the active sites of tyrosinase, making them potential tyrosinase inhibitors.
4 Possible mechanisms of inhibiting melanin synthesis by bioactive peptides
4.1 Known mechanism of inhibiting melanin synthesis
4.1.1 Inhibition of melanin synthesis by mediating oxidation pathway
Melanin plays a protective role in the human body. When ultraviolet rays irradiate the skin, ROS are generated (Chaiprasongsuk and Panich 2022; Yu et al. 2024). Excessive ROS can damage DNA, lipid peroxidation, and cause various issues including cancer (Bickers and Athar 2006; Lee et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2024). Studies have also shown that oxidative stress caused by UV radiation can contribute to hyperpigmentation (Sevilla et al., 2022). Grass Carp Scale Collagen Peptide (FTMGL) demonstrated antioxidant activity similar to kojic acid in B16F10 cells. FTMGL exerts its antioxidant activity by regulating glutathione (GSH) content and enhancing the levels of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, and GPx), which helps reduce the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA)- thus preventing pigment deposition caused by oxidative stress (Hu et al., 2022a). SOD and CAT are key antioxidant enzymes that maintain redox balance within cells (Pudlarz et al., 2020). The direct scavenging of free radicals and the recovery of antioxidant enzyme activity reduced by external stimuli are common antioxidant mechanisms by which peptides inhibit melanin synthesis (Errante et al., 2024).
It is worth mentioning that peptides with strong antioxidant activity often have strong anti-tyrosinase activity. There are abundant hydrophobic amino acids in bioactive peptides, such as Val, Ala, Gly, Iso, Leu, Phe and Pro, which have the ability to scavenge free radicals (Park and Jo, 2019). These amino acids also play an important role in anti-melanin synthesis (Ahuja et al., 2025). At the same time, aromatic amino acids (such as Trp, Leu, Phe, Tyr, Val, Ile) can stabilize active oxygen through direct electron transfer, and Tyr, Phe and Val can significantly enhance TIP's anti-tyrosinase activity (Nie et al., 2017; Shen et al., 2019; Joompang et al., 2020; Thaha et al., 2021; Aizawa and Yamamuro, 2024). Although the antioxidant and anti-melanin production pathways partially overlap, their specific molecular mechanisms have not been fully clarified. It is worth noting that there is still a lack of research on the antioxidant mechanism related to hyperpigmentation induced by environmental factors or endogenous factors (not ultraviolet radiation), which leads to the need to further explore the effectiveness and target of the targeted inhibitory peptide-based hyperpigmentation therapy strategy.
4.1.2 Inhibition of melanin synthesis by mediating inflammatory reaction
Inflammation can also contribute to hyperpigmentation (Hossain et al., 2021). After treatment with substance P, an undecapeptide, the melanin content and tyrosinase activity were significantly downregulated in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells. Substance P may stimulate the phosphorylation of p70 S6K1 and inhibit the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK by activating the NK-1R receptor, thereby inhibiting TRP1 by MITF, thus playing an anti-melanin synthesis role (Ping et al., 2012). Later studies showed that calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) at 500 ng/mL inhibited tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in B16F10 cells in a concentration-dependent manner, especially when combined with substance P (0.1–10 nm). However, CGRP alone did not affect melanin synthesis; its inhibitory effect was mediated by enhancing the expression of NK-1R (Zhou et al., 2015).
In addition to peptides, small molecules can also inhibit abnormal melanin deposition by mediating inflammatory reactions. Asiaticoside (MA) inhibits UV-induced hyperpigmentation by mediating the COX-2 and PGE pathways by inhibiting PAR-2 expression (Jung et al., 2013). Salvianolic acid [CA] has been shown to inhibit melanin deposition in zebrafish skin along with the production and transfer of melanin in skin cells. When CA and LP-GEL were applied together, skin wound healing accelerated, and inflammatory reaction and melanosis were inhibited (Su et al., 2024). Bay 11-7082 inhibits post-inflammatory pigmentation by suppressing inflammation and melanin production (Moon et al. 2025). Solamargine inhibits melanin synthesis in human skin cells induced by UVB by decreasing tyrosinase activity and the expression of MITF, TRP-1, and TRP-2. It also exerts an anti-inflammatory effect by modulating the MAPK/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway (Zhao et al., 2022).
4.1.3 Inhibition of melanin synthesis by mediating MITF-related pathway
It regulates the transcription of tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP-1), and tyrosinase-related protein 2 (TRP-2), activates various target genes related to melanin synthesis, and influences the reproduction, proliferation, and survival of melanogenic cells (Wellbrock and Marais, 2005; Cheli et al., 2010; Vachtenheim and Borovansky, 2010). Peptides that inhibit melanin synthesis can modulate MITF expression through various pathways in order to inhibit melanin synthesis.
α-MSH binds to MC1R, which: increases cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) of the secondary messenger through adenylate cyclase (AC); stimulates protein kinase A(PKA) to translocate and phosphorylate CREB; activates its transcription activity, increases MITF expression, and then activates tyrosinase, promoting melanin synthesis (Pillaiyar et al., 2017). H89 can inhibit this process (Jian et al., 2011). PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway regulates melanogenesis by reducing MITF expression. CAMP inhibits PI3K, activates AKT, and increases GSK3β activity. After phosphorylation, it inhibits MITF from binding to a tyrosinase promoter and degrades it (Lee et al., 2021; Zhou et al., 2021). MEK/ERK/MITF Pathway, a negative pathway, and the ERK cascade reaction plays a role in cell growth, which can induce MITF phosphorylation and ubiquitination. The α-MSH trigger signal activates ERK after phosphorylation of MEK by cAMP, and p-ERK promotes MITF degradation and inhibits melanin production (Shirasugi et al., 2010; Huang et al., 2017). P38 MAPK is a member of MAPK, which can up-regulate MITF and tyrosinase. CAMP activates p38 MAPK, phosphorylates CREB and promotes MITF expression (Kang et al., 2020; Choi et al., 2022). SB203580 can interrupt p38 MAPK phosphorylation, and Fargesin inhibits melanin production through this pathway and the MEK/ERK/MITF pathway (Huang et al., 2016; Fu et al., 2019).
In addition to the above channels, there are some channels that are less studied. The zebrafish phosphopeptide Pt5 decreased MITF gene expression through the cAMP signaling pathway, inhibiting melanin synthesis (Liu et al., 2017). Dshp inhibits melanin synthesis by activating ERK and promoting MITF degradation (Choi et al., 2016). Sfrp5pepD disrupts the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway by inhibiting the interaction between Axin-1 and β-catenin, affecting the interaction between MITF and β-catenin. This reduces the expression of melanogenic enzymes and ultimately inhibits melanin synthesis (Choi et al., 2024). Additionally, FTMGL not only inhibits the pigment deposition through antioxidant activity, but also reduces MITF expression by modulating p38 and JNK in the cAMP-PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting melanin synthesis in melanoma cells (Pudlarz et al., 2020) (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2
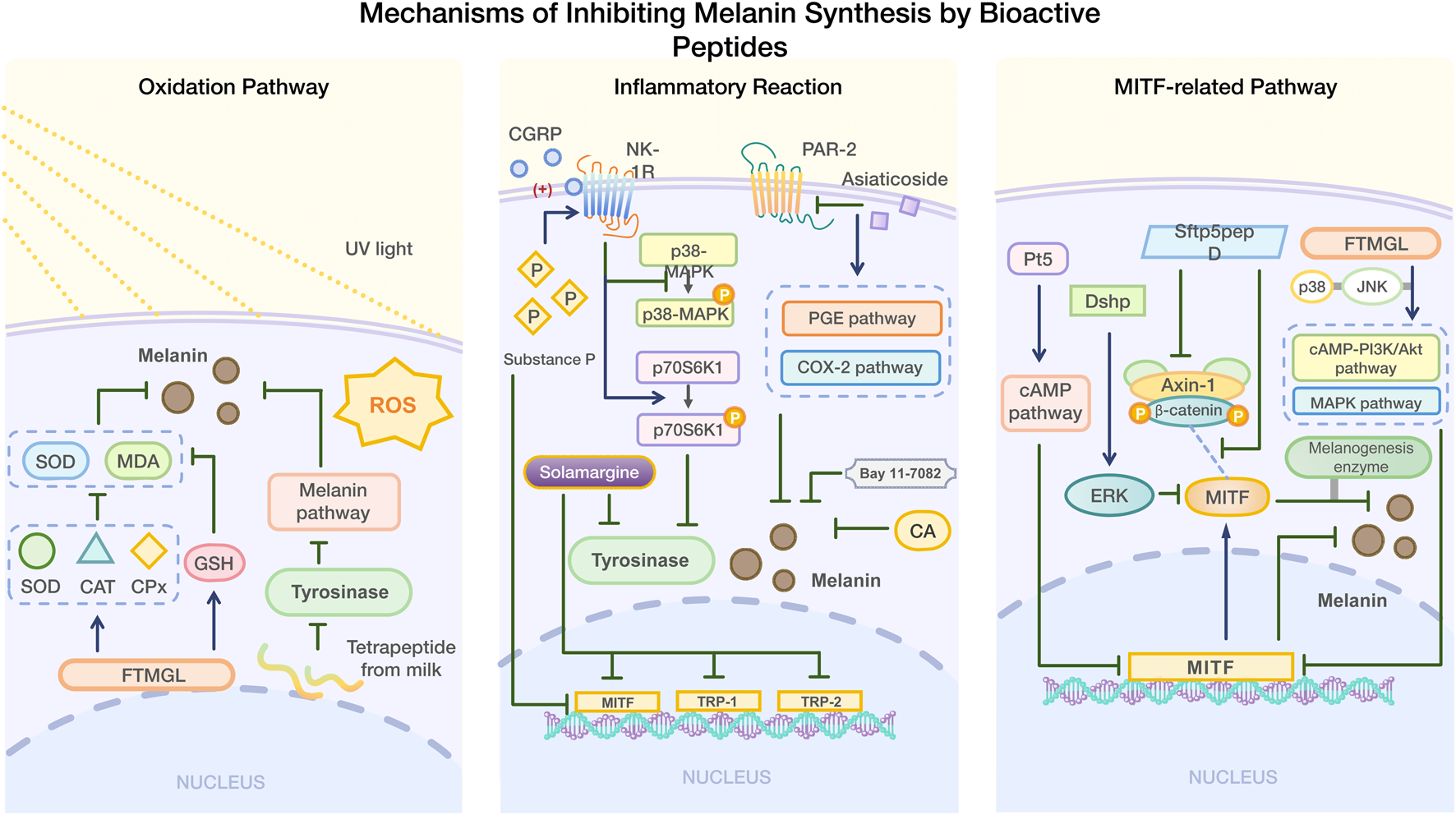
Mechanism of inhibiting melanin synthesis by bioactive peptides.
4.2 Characteristic analysis of melanin synthetic peptides
4.2.1 Key sites of peptide inhibiting melanin synthesis
Peptides inhibit melanin synthesis, mainly by binding with TRP and MITF in melanin biological process. Molecular docking is a selective method used to help understand the drug-forming screening of small molecules such as peptides and macromolecules (Pinzi and Rastelli, 2019; Festa et al., 2020). This technique is used to predict how peptides bind to related targets that inhibit melanin synthesis, to further study its inhibition mechanism (Paggi et al., 2024).
The catalytic core of tyrosinase is composed of H2L2 tetramer, and its active center contains binuclear copper ions, which form a six-coordinated chelating structure through His61, His85, His94(CuA), His259, His263 and His296(CuB) (Baskaran et al., 2021). The redox cycle of Cu2+ is the key step to catalyze the oxidation of L-tyrosine to dopaquinone, which depends on the precise regulation of the hydrophobic environment in the active chamber (Bagherzadeh et al., 2015).
CuA and CuB are connected by an oxygen bridge to form a rigid structure, required for catalytic activity. Peptide inhibitors (such as VY-9) occupy hydrophobic pockets (His85, Phe264, etc.) near the cavity entrance, which prevent the substrate L-tyrosine from entering the active cavity and interfere with the coordination between Cu and His residues (such as the chelation of imidazole ring of His85 with Cu), resulting in the loss of enzyme activity (Baskaran et al., 2021; Sepehri et al., 2022; Sangtanoo et al., 2024). Even if the peptide does not directly bind to Cu, covering His residues (such as His259 and His263) will destroy the stable coordination of Cu and reduce its catalytic efficiency (Joompang et al., 2020). The entrance of the active cavity is composed of His85, Met280, Val283 and other residues, and its steric hindrance and π -π stacking (such as Phe264 and benzyl ring of the substrate) jointly determine the substrate selectivity (Yu and Fan, 2021). Short peptides are embedded in hydrophobic cavities in parallel through aromatic rings, enhancing π -π stacking, simulating the binding mode of natural substrates, and blocking the interaction between copper ion and His residues in hydrophobic cavities (Goldfeder et al., 2014).
Peptide inhibitors destroy tyrosinase function through a hydrogen bond network, hydrophobic interaction and electrostatic interaction, and their mechanisms can be divided into two categories: competitive inhibition and non-competitive inhibition. The aromatic amino acids of peptide (tyrosine) form hydrogen bonds with His263, simulating the interaction between phenolic hydroxyl groups of L-tyrosine and His263 (Goldfeder et al., 2014). The hydrophobic residue of the peptide is embedded in the hydrophobic pocket, which enhances the binding stability by van der Waals force and prevents the substrate from sliding into the active cavity (Hu et al., 2022b). Hydrophobic residues (such as Leu and Ala) cover the surface of the active cavity, which reduces the hydrophobic complementarity between the enzyme and the substrate, and further inhibits the catalytic efficiency (Hu et al., 2022b). The charged residues of peptide (such as Arg/Lys) form a salt bridge with the acidic residues on the enzyme surface (Glu256, Asp322), which induces the conformational change of the active center and destroys the stable coordination of copper ion (Deri et al., 2016).
In addition, peptides (such as FRAF) form a multi-level inhibition network by targeting MITF, TYR and TYRP1/2, and its mechanism goes beyond single target intervention: FRAF forms hydrogen bonds with ASP431 and ALA384 of MITF, blocking the combination of MITF and target gene promoters (such as TYR and TYRP1) and inhibiting the expression of melanin synthesis-related enzymes. FRAF binds to PRO20 and GLU19 of TYR through hydrogen bonds, which interferes with its substrate binding pocket. It forms electrostatic interaction with GLU451 of TYRP1 and GLU63 of TYRP2, which destroys its auxiliary function of TYR and inhibits melanin transport and oxidation (Bai et al., 2024) (Table 4; Figure 3).
TABLE 4
| Peptide | Combine object | Binding site | Binding energy (kcal/mol) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FRAF | MITF TYR TYR1 TYR2 |
hydrogen bonding hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic interactions |
−6.9 −9.1 −9.3 −8.9 |
Bai et al. (2024) |
| YYP | TYR | hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic interactions | −7.6 | Wang W. et al. (2023) |
| PYLK | TYR | hydrogen bonding | −6.9 | Wang W. et al. (2023) |
| PHHF | TYR | hydrogen bonding | −7.3 | Wang W. et al. (2023) |
| FRVK | TYR | hydrogen bonding | −7.0 | Wang W. et al. (2023) |
| VDGYPAAGY | TYR | hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions | −8.3 | Sangtanoo et al. (2024) |
| YPNVY | TYR | Hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic interactions | −10.4 | Lin J. et al. (2024) |
Binding between peptides and MITF, TYR, TYRP1 and TYRP2 proteins.
FIGURE 3
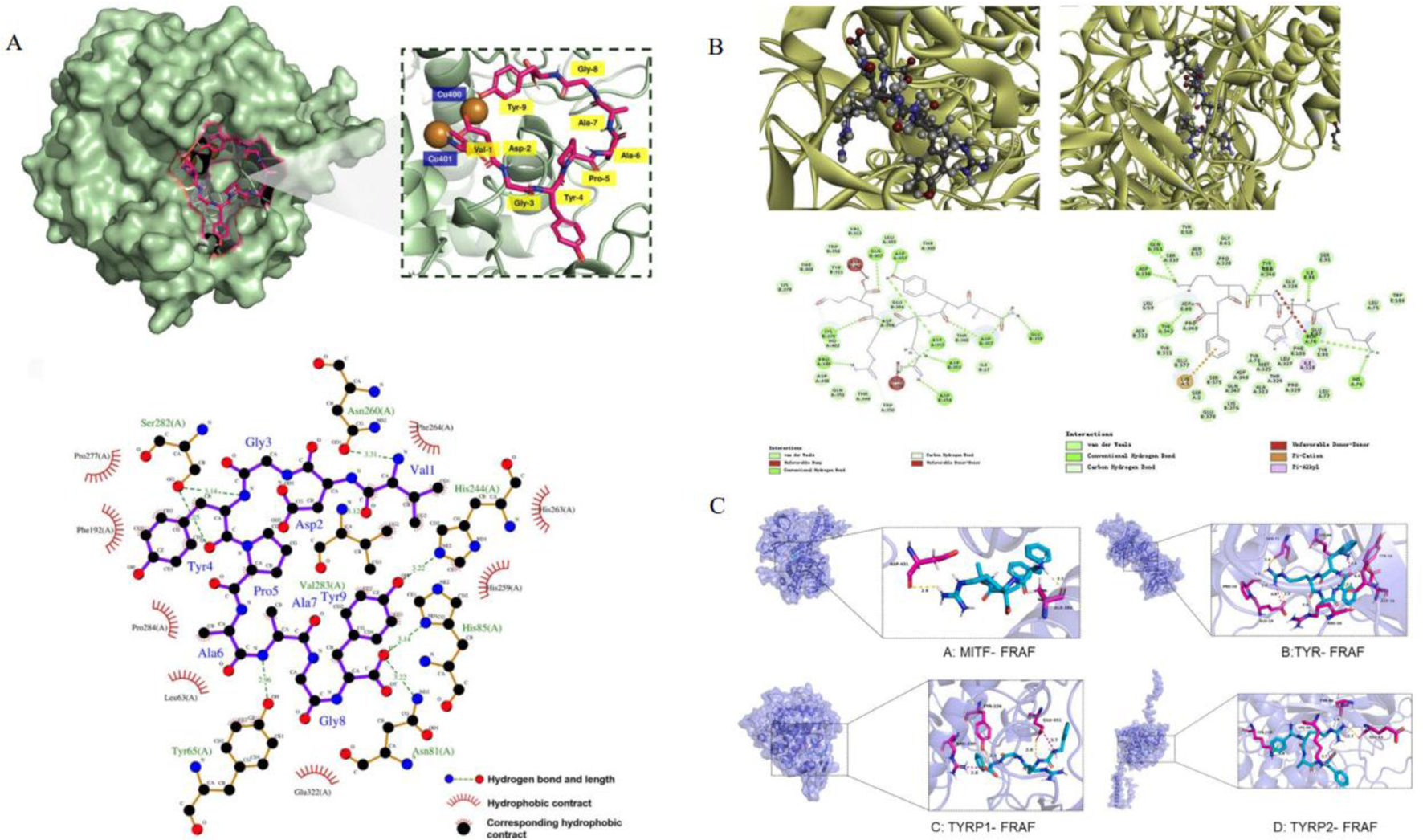
The figure shows the molecular docking diagram of tyrosinase and peptide, where (A) is the 3D and 2D docking model of VY-9 peptide and TYR (Sangtanoo et al., 2024), (B) contains multi-angle views: different conformations of the enzyme-peptide complex (including the docking model of NYRRE, RHAKF and TYR) are at the top Skin-care functions (Deng et al., 2020). (C) is the docking model of FRAF and TYR, MITF, TYR1 and TYR2 (Bai et al., 2024).
4.2.2 Structure-activity relationship of melanin inhibitory peptides
The results show that the molecular weight, size and amino acid composition of peptide will significantly affect the anti-tyrosinase ability (Putri et al., 2025). Part A in Figure 4 shows that tyrosinase’s inhibitory ability of short peptides is higher than that of long peptides, and the peptides with good water solubility also have higher tyrosinase inhibitory activity. The result of polypeptides is just the opposite, because polypeptides are generally obtained by enzyme hydrolysis. Part B in Figure 4 shows that the cysteine content is as high as 17.66%, significantly higher than other amino acids. The reason for this may be that it can form disulfide bonds with tyrosinase to stabilize the peptide structure, participate in metal ion coordination, and maintain special conformation. The total amount of hydrophobic amino acids, including L (7.98%), I (3.13%) and V (2.85%), is relatively high, which may be related to the fact that they can form a hydrophobic core with tyrosinase or combine with hydrophobic pockets of tyrosinase. Figure 3B can provide some ideas for us to synthesize new tyrosinase inhibitory peptides. Usually, we will choose enzymes with better degrees of hydrolysis, so that the types of long peptides will be scarce, but too few quantities will lead to deviation in statistics. The cysteine content can be as high as 17.5%, which is significantly higher than other amino acids. The reason for this may be that it can form disulfide bonds with tyrosinase to stabilize peptide structure, participate in metal ion coordination and maintain special conformation. The inhibitory potential of peptides on tyrosinase is closely related to its amino acid composition and structural characteristics. For example, the C-terminal tyrosine residue is particularly critical because it significantly promotes tyrosine binding and inhibition by changing the conformation of the enzyme (Kose and Oncel, 2022). Similarly, tetrapeptides containing a N-terminal cysteine can exert tyrosinase inhibition by chelating with copper ions (Joompang et al., 2023). Basic residues (such as arginine) are paired with nonpolar amino acids (such as proline, alanine, valine and leucine), which have a strong inhibitory effect on tyrosinase (Zu et al., 2023). Many peptides exceed the optimal molecular weight threshold (500 Da) for skin penetration, and the partition coefficients (log P) are usually beyond the range required for effective absorption. This limits their ability to penetrate the skin, which will affect tyrosinase inhibition and skin delivery (Mortazavi and Moghimi, 2022). Peptides from fish scale gelatin and egg whites have proved that smaller peptides (400–600 Da) show higher copper ion chelating activity, highlighting the importance of molecular weights in peptide activity (Yap and Gan, 2020; Xue et al., 2022). In addition, studies have shown that the introduction of D-tyrosine into the N-terminal or C-terminal of pentapeptide-18 can reduce the melanin content by 50% at 500 μM, the tyrosinase activity by 18% at the N-terminal and by 25% at the C-terminal. Adding D-tyrosine can endow short functional cosmetic peptides with an anti-melanin effect, which is of great significance to the research of new cosmetics with whitening/anti-inflammatory and whitening/anti-aging functions (Ge et al., 2023).
FIGURE 4
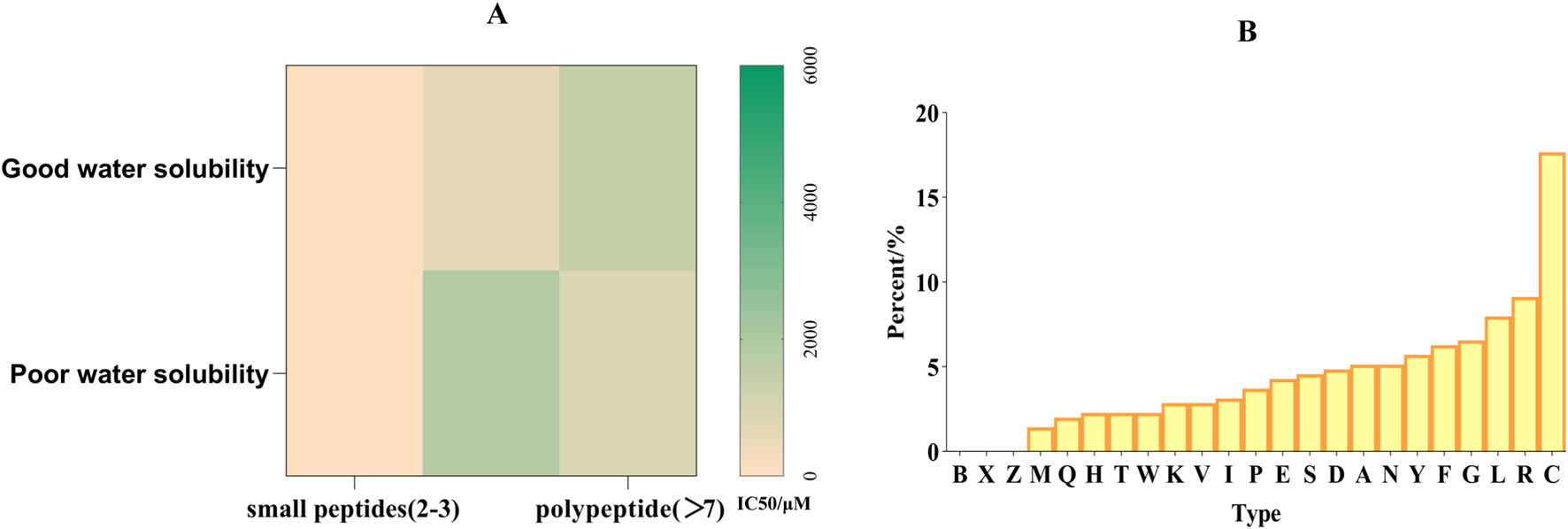
(A) Relationship between tyrosinase inhibitory ability of peptide and its length and hydrophilicity (B). Proportion of amino acids in peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity.
Cyclization of peptides is a strategy that can make peptides have a more stable conformation, enhancing the stability of enzymatic proteolysis and improving the permeability through biological barriers (Karami et al., 2023). The cyclic peptide Massiliamide obtained from Gram-negative bacterium Massilia albidiflava DSM 17472T has an IC50 of 1.15 μM, and its tyrosinase inhibitory activity exceeds that of kojic acid and arbutin in positive control group (Frediansyah et al., 2021). New delivery systems, including liposomes, nanoparticles, nanoemulsions and microneedles, have been used to improve drug solubility, increase skin permeability or reduce skin irritation, thus enhancing the therapeutic effect (Jing-Yan et al., 2020; D'Souza and Shegokar, 2021; Xing et al., 2021; Saadh et al., 2024). The combination of these technologies and peptides will further increase the therapeutic effect of peptides.
5 Conclusion
Although natural and synthetic tyrosinase inhibitory peptides have made remarkable progress in the study of melanin regulation, there are still significant limitations in the existing achievements. The research on natural inhibitors from land and sea is mostly limited to the preliminary screening of known compounds, and their structure-activity relationship and mechanism of action have not been fully clarified - especially the targeting optimization of marine resources (only a small part of which have been verified) and human-specific tyrosinase (which has structural differences with mushroom sources) needs to be broken through. Structural biology research shows that the molecular weight, hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance and cyclization strategy of peptide are very important to the inhibitory effect of TYR. The synergistic effect of aromatic residues, arginine and negatively charged histidine can enhance the stability of enzyme binding, and the regulation of hydrophobic N-terminal residues on aging-related enzyme activities reveals a new optimization direction.
However, the clinical transformation of natural peptides is limited by stability and delivery efficiency, while synthetic peptides need to solve the problems of species-specific differences and long-term safety verification. In the future, we need to focus on three major directions: ① establishing a multi-dimensional screening platform (such as 3D melanocyte models) to accelerate the rational design of humanized peptides; ② Developing a cyclic peptide-liposome co-delivery system to break through the skin barrier and enhance targeting; ③ Identify the regulatory nodes of TYR in melanoma signal pathway through organ-like and preclinical studies, and promote the transformation from basic research to therapeutic application. The collaborative innovation of natural and synthetic peptides will provide a therapeutic paradigm with both efficacy and safety in this field.
Statements
Author contributions
BY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. NW: Writing – review and editing. SC: Writing – review and editing. HY: Writing – review and editing. SS: Writing – original draft. SW: Writing – original draft. YL: Writing – review and editing. LZ: Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2020D01C163) Scientific Research Program for Universities in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XJEDU2021Y30).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Agar N. S. Halliday G. M. Barnetson R. S. Ananthaswamy H. N. Wheeler M. Jones A. M. (2004). The basal layer in human squamous tumors harbors more UVA than UVB fingerprint mutations: a role for UVA in human skin carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.101 (14), 4954–4959. 10.1073/pnas.0401141101
2
Aizawa S. Yamamuro Y. (2024). Tyrosinase deficiency impairs social novelty preference in mice. Neuroreport35 (11), 687–691. 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002055
3
Allouche J. Rachmin I. Adhikari K. Pardo L. M. Lee J. H. McConnell A. M. et al (2021). NNT mediates redox-dependent pigmentation via a UVB- and MITF-independent mechanism. Cell184 (16), 4268–4283.e20. 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.022
4
Al-Sadek T. Yusuf N. (2024). Ultraviolet radiation biological and medical implications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol.46 (3), 1924–1942. 10.3390/cimb46030126
5
Azimi F. Mahdavi M. Khoshneviszadeh M. Shafiee F. Azimi M. Hassanzadeh F. et al (2024). Kinetic studies, molecular docking, and antioxidant activity of novel 1,3-diphenyl pyrazole-thiosemicarbazone with anti-tyrosinase and anti-melanogenesis properties. Bioorg. Chem.152, 107722. 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107722
6
Baber M. A. Crist C. M. Devolve N. L. Patrone J. D. (2023). Tyrosinase inhibitors: a perspective. Molecules28 (15), 5762. 10.3390/molecules28155762
7
Bagherzadeh K. Shirgahi Talari F. Sharifi A. Ganjali M. R. Saboury A. A. Amanlou M. (2015). A new insight into mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors: docking, pharmacophore-based virtual screening, and molecular modeling studies. J. Biomol. Struct. and Dyn.33 (3), 487–501. 10.1080/07391102.2014.893203
8
Bai W. Deng F. Liu X. Yin X. Qiu X. Yang J. et al (2024). Edible bird's nest peptide (EBNP) with high whitening activity: sequences analysis, whitening activity characterization and molecular docking study. J. Funct. Foods123, 106617. 10.1016/j.jff.2024.106617
9
Bala H. R. Lee S. Wong C. Pandya A. G. Rodrigues M. (2018). Oral tranexamic acid for the treatment of melasma: a review. Dermatol. Surg.44 (6), 814–825. 10.1097/DSS.0000000000001518
10
Baskaran R. Chauhan S. S. Parthasarathi R. Mogili N. S. (2021). In silico investigation and assessment of plausible novel tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from sesame seeds. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol.147, 111619. 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111619
11
Bento-Lopes L. Cabaço L. C. Charneca J. Neto M. V. Seabra M. C. Barral D. C. (2023). Melanin's journey from melanocytes to keratinocytes: uncovering the molecular mechanisms of melanin transfer and processing. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (14), 11289. 10.3390/ijms241411289
12
Berg S. Z. Berg J. (2023). Melanin: a unifying theory of disease as exemplified by Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and Lewy body dementia. Front. Immunol.14, 1228530. 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1228530
13
Bernerd F. Passeron T. Castiel I. Marionnet C. (2022). The damaging effects of long UVA (UVA1) rays: a major challenge to preserve skin health and integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (15), 8243. 10.3390/ijms23158243
14
Bissig C. Rochin L. van Niel G. (2016). PMEL amyloid fibril formation: the bright steps of pigmentation. Int. J. Mol. Sci.17 (9), 1438. 10.3390/ijms17091438
15
Boissy R. E. Sakai C. Zhao H. Kobayashi T. Hearing V. J. (1998). Human tyrosinase related protein-1 (TRP-1) does not function as a DHICA oxidase activity in contrast to murine TRP-1. Exp. Dermatol.7 (4), 198–204. 10.1111/j.1600-0625.1998.tb00324.x
16
Boo Y. C. (2022). Metabolic basis and clinical evidence for skin lightening effects of thiol compounds. Antioxidants11 (3), 503. 10.3390/antiox11030503
17
Borges S. Odila J. Voss G. Martins R. Rosa A. Couto J. A. et al (2023). Fish by-products: a source of enzymes to generate circular bioactive hydrolysates. Molecules28 (3), 1155. 10.3390/molecules28031155
18
Cardinali G. Ceccarelli S. Kovacs D. Aspite N. Lotti L. V. Torrisi M. R. et al (2005). Keratinocyte growth factor promotes melanosome transfer to keratinocytes. J. Investigative Dermatology125 (6), 1190–1199. 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2005.23929.x
19
Cardoso R. Valente R. Souza da Costa C. H. da S Gonçalves Vianez J. L. Jr Santana da Costa K. de Molfetta F. A. et al (2021). Analysis of kojic acid derivatives as competitive inhibitors of tyrosinase: a molecular modeling approach. Molecules26 (10), 2875. 10.3390/molecules26102875
20
Cestari T. F. Dantas L. P. Boza J. C. (2014). Acquired hyperpigmentations. An. Bras. De. Dermatol.89 (1), 11–25. 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20142353
21
Chaiprasongsuk A. Panich U. (2022). Role of phytochemicals in skin photoprotection via regulation of Nrf2. Front. Pharmacol.13, 823881
22
Chen N. Hu Y. Li W. H. Eisinger M. Seiberg M. Lin C. B. (2010). The role of keratinocyte growth factor in melanogenesis: a possible mechanism for the initiation of solar lentigines. Exp. Dermatol.19 (10), 865–872. 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.00957.x
23
Chen X. Jin W. Chen D. Dong M. Xin X. Li C. et al (2021). Collagens made from giant salamander (Andrias davidianus) skin and their odorants. Food Chem.361, 130061. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130061
24
Choi H. Han J. Jin S. H. Park J. Y. Shin D. W. et al (2013). IL-4 inhibits the melanogenesis of normal human melanocytes through the JAK2-STAT6 signaling pathway. J. Investigative Dermatology133 (2), 528–536. 10.1038/jid.2012.331
25
Choi J. H. Kwak T. Shin H. Jo Y. H. Kim J. Kim Y. et al (2024). Hydrolyzed cow colostrum extract (BCFM) inhibits alpha-MSH-induced melanogenesis in B16F1 cells via regulation of the MC1R-cAMP signaling pathway. Cytotechnology76 (6), 847–858. 10.1007/s10616-024-00657-8
26
Deng Y. Huang L. Zhang C. Xie P. Cheng J. Wang X. et al (2020). Skin-care functions of peptides prepared from Chinese quince seed protein: sequences analysis, tyrosinase inhibition and molecular docking study. Industrial Crops Prod.148, 112331. 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112331
27
Deri B. Kanteev M. Goldfeder M. Lecina D. Guallar V. Adir N. et al (2016). The unravelling of the complex pattern of tyrosinase inhibition. Sci. Rep.6, 34993. 10.1038/srep34993
28
D'Orazio J. Jarrett S. Amaro-Ortiz A. Scott T. (2013). UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci.14 (6), 12222–12248. 10.3390/ijms140612222
29
D'Souza A. Shegokar R. (2021). Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) for drug delivery: role of liquid lipid (oil). Curr. Drug Deliv.18 (3), 249–270. 10.2174/1567201817666200423083807
30
Errante F. Sforzi L. Supuran C. T. Papini A. M. Rovero P. (2024). Peptide and peptidomimetic tyrosinase inhibitors. Enzym.56, 135–189. 10.1016/bs.enz.2024.06.005
31
Feng G. Wu J. Yang H. L. Mu L. (2021). Discovery of antioxidant peptides from Amphibians: a review. Protein Peptide Lett.28 (11), 1220–1229. 10.2174/0929866528666210907145634
32
Feng J. Song X. Zhang B. Xiang W. (2025). Establishing an animal model for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation following fractional CO2 laser application. Lasers Med. Sci.40 (1), 17. 10.1007/s10103-025-04282-5
33
Feng Y.-X. Wang Z. C. Chen J. X. Li H. R. Wang Y. B. Ren D. F. et al (2021). Separation, identification, and molecular docking of tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from the hydrolysates of defatted walnut (Juglans regia L.) meal. Food Chem.353, 129471. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129471
34
Festa M. Sansone C. Brunet C. Crocetta F. Di Paola L. Lombardo M. et al (2020). Cardiovascular active peptides of marine origin with ACE inhibitory activities: potential role as anti-hypertensive drugs and in prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (21), 8364. 10.3390/ijms21218364
35
Frediansyah A. Straetener J. Brötz-Oesterhelt H. Gross H. (2021). Massiliamide, a cyclic tetrapeptide with potent tyrosinase inhibitory properties from the Gram-negative bacterium Massilia albidiflava DSM 17472<SUP>T</SUP>. J. Antibiotics74 (4), 269–272. 10.1038/s41429-020-00394-y
36
Galibert M. D. Carreira S. Goding C. R. (2001). The Usf-1 transcription factor is a novel target for the stress-responsive p38 kinase and mediates UV-induced Tyrosinase expression. EMBO J.20 (17), 5022–5031. 10.1093/emboj/20.17.5022
37
Galvan I. Solano F. (2016). Bird integumentary melanins: biosynthesis, forms, function and evolution. Int. J. Mol. Sci.17 (4), 520. 10.3390/ijms17040520
38
Ge Z. Liu J. C. Sun J. A. Mao X. Z. (2023). Tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from enzyme hydrolyzed royal jelly: production, separation, identification and docking analysis. Foods12 (11), 2240. 10.3390/foods12112240
39
Gelmi M. C. Houtzagers L. E. Strub T. Krossa I. Jager M. J. (2022). MITF in normal melanocytes, cutaneous and uveal melanoma: a delicate balance. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (11), 6001. 10.3390/ijms23116001
40
Genay M. Sadat L. Gagnaire V. Lortal S. (2009). prtH2, not prtH, is the ubiquitous cell wall proteinase gene in lactobacillus helveticus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.75 (10), 3238–3249. 10.1128/AEM.02395-08
41
Girelli A. M. Mattei E. Messina A. Tarola A. M. (2004). Inhibition of polyphenol oxidases activity by various dipeptides. J. Agric. Food Chem.52 (10), 2741–2745. 10.1021/jf0305276
42
Goldfeder M. Kanteev M. Isaschar-Ovdat S. Adir N. Fishman A. (2014). Determination of tyrosinase substrate-binding modes reveals mechanistic differences between type-3 copper proteins. Nat. Commun.5, 4505. 10.1038/ncomms5505
43
Guo S. Wang J. Wang Q. Wang J. Qin S. Li W. (2024). Advances in peptide-based drug delivery systems. Heliyon10 (4), e26009. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26009
44
Guo Y. Wu W. Yang X. (2023). Coordinated microRNA/mRNA expression profiles reveal unique skin color regulatory mechanisms in Chinese giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). Animals13 (7), 1181. 10.3390/ani13071181
45
Haltaufderhyde K. D. Oancea E. (2014). Genome-wide transcriptome analysis of human epidermal melanocytes. Genomics104 (6), 482–489. 10.1016/j.ygeno.2014.09.010
46
Han J. Lee E. Kim E. Yeom M. H. Kwon O. Yoon T. H. et al (2014). Role of epidermal γδ T-cell-derived interleukin 13 in the skin-whitening effect of Ginsenoside F1. Exp. Dermatol.23 (11), 860–862. 10.1111/exd.12531
47
Han J. H. Bang J. S. Choi Y. J. Choung S. Y. (2019). Anti-melanogenic effects of oyster hydrolysate in UVB-irradiated C57BL/6J mice and B16F10 melanoma cells via downregulation of cAMP signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol.229, 137–144. 10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.036
48
Honrado A. Miguel M. Ardila P. Beltrán J. A. Calanche J. B. (2024). From waste to value: fish protein hydrolysates as a technological and functional ingredient in human nutrition. Foods13 (19), 3120. 10.3390/foods13193120
49
Hossain M. R. Ansary T. M. Komine M. Ohtsuki M. (2021). Diversified stimuli-induced inflammatory pathways cause skin pigmentation. Int. J. Mol. Sci.22 (8), 3970. 10.3390/ijms22083970
50
Hu J. Chen B. Qu S. Liu S. Yang X. Qiao K. et al (2024). Anti-Melanogenic effects of Takifugu flavidus muscle hydrolysate in B16F10 melanoma cells and zebrafish. Mar. Drugs22 (5), 206. 10.3390/md22050206
51
Hu Z.-Z. Ma T. X. Sha X. M. Zhang L. Tu Z. C. (2022b). Improving tyrosinase inhibitory activity of grass carp fish scale gelatin hydrolysate by gastrointestinal digestion: purification, identification and action mechanism. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol.159, 113205. 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113205
52
Hu Z.-Z. Sha X. M. Zhang L. Zha M. J. Tu Z. C. (2022a). From fish scale gelatin to tyrosinase inhibitor: a novel peptides screening approach application. Front. Nutr.9, 853442. 10.3389/fnut.2022.853442
53
Ikarashi N. Fukuda N. Ochiai M. Sasaki M. Kon R. Sakai H. et al (2020). Lactobacillus helveticus-fermented milk whey suppresses melanin production by inhibiting tyrosinase through decreasing MITF expression. Nutrients12 (7), 2082. 10.3390/nu12072082
54
Irazoqui J. M. Santiago G. M. Mainez M. E. Amadio A. F. Eberhardt M. F. (2024). Enzymes for production of whey protein hydrolysates and other value-added products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol.108 (1), 354. 10.1007/s00253-024-13117-2
55
Ishikawa S. I. Tamaki S. Arihara K. Itoh M. (2007). Egg yolk protein and egg yolk phosvitin inhibit calcium, magnesium, and iron absorptions in rats. J. Food Sci.72 (6), S412–S419. 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00417.x
56
Jiang W. Guo K. Dong H. Zhang X. Guo Z. Duan J. et al (2024). Mutation in the Bombyx mori BmGMC2 gene impacts silk production and silk protein synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.274, 133400. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133400
57
Jie Y. Li X. Cai Z. Ma M. Jin Y. Ahn D. U. et al (2018). Phosphorylation of phosvitin plays a crucial effects on the protein-induced differentiation and mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol.118, 1848–1854. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.07.029
58
Jing-Yan W. Shu-Wei M. A. Xin-Yu Z. Jia-Jia C. Yu-Juan L. Li-Li D. et al (2020). Preparation of compound liquorice microemulsion gel and its pharmacodynamics evaluation. China J. Chin. materia medica45 (21), 5193–5199. 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200819.302
59
Joompang A. Anwised P. Klaynongsruang S. Taemaitree L. Wanthong A. Choowongkomon K. et al (2023). Rational design of an N-terminal cysteine-containing tetrapeptide that inhibits tyrosinase and evaluation of its mechanism of action. Curr. Res. Food Sci.7, 100598. 10.1016/j.crfs.2023.100598
60
Joompang A. Jangpromma N. Choowongkomon K. Payoungkiattikun W. Tankrathok A. Viyoch J. et al (2020). Evaluation of tyrosinase inhibitory activity and mechanism of Leucrocin I and its modified peptides. J. Biosci. Bioeng.130 (3), 239–246. 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2020.04.002
61
Jow T. Hantash B. M. (2014). Hydroquinone- induced depigmentation: case report and review of the literature. Dermatitis25 (1), E1–E5. 10.1097/01.DER.0000438425.56740.8a
62
Joyjamras K. Netcharoensirisuk P. Roytrakul S. Chanvorachote P. Chaotham C. (2022). Recycled sericin hydrolysates modified by Alcalase® suppress melanogenesis in human melanin-producing cells via modulating MITF. Int. J. Mol. Sci.23 (7), 3925. 10.3390/ijms23073925
63
Ju X. Cheng S. Li H. Xu X. Wang Z. Du M. (2022). Tyrosinase inhibitory effects of the peptides from fish scale with the metal copper ions chelating ability. Food Chem.390, 133146. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133146
64
Jung H. G. Kim H. H. Paul S. Jang J. Y. Cho Y. H. Kim H. J. et al (2015). Quercetin-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1 → 6)-β-D-glucopyranoside suppresses melanin synthesis by augmenting p38 MAPK and CREB signaling pathways and subsequent cAMP down-regulation in murine melanoma cells. Saudi J. Biol. Sci.22 (6), 706–713. 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.03.009
65
Jung H. J. Park H. S. Kim H. J. Park H. S. Park Y. Chun P. et al (2024). Design, synthesis, and anti-melanogenic activity of 2-mercaptomethylbenzo d imidazole derivatives serving as tyrosinase inhibitors: an in silico, in vitro, and in vivo exploration. Antioxidants13 (10), 1248. 10.3390/antiox13101248
66
Jung S. Kim D. H. Son J. H. Nam K. Ahn D. U. Jo C. (2012). The functional property of egg yolk phosvitin as a melanogenesis inhibitor. Food Chem.135 (3), 993–998. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.113
67
Karami Y. Murail S. Giribaldi J. Lefranc B. Defontaine F. Lesouhaitier O. et al (2023). Exploring a structural data mining approach to design linkers for head-to-tail peptide cyclization. J. Chem. Inf. Model.63 (20), 6436–6450. 10.1021/acs.jcim.3c00865
68
Kato N. Sato S. Yamanaka A. Yamada H. Fuwa N. Nomura M. (1998). Silk protein, sericin, inhibits lipid peroxidation and tyrosinase activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem.62 (1), 145–147. 10.1271/bbb.62.145
69
Kawagishi H. Somoto A. Kuranari J. Kimura A. Chiba S. (1993). A novel cyclotetrapeptide produced by lactobacillus-helveticus as a tyrosinase inhibitor. Tetrahedron Lett.34 (21), 3439–3440. 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)79177-5
70
Kim H.-D. Choi H. Abekura F. Park J. Y. Yang W. S. Yang S. H. et al (2023). Naturally-occurring tyrosinase inhibitors classified by enzyme kinetics and copper chelation. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (9), 8226. 10.3390/ijms24098226
71
Kim K. Han J. Lee T. R. Shin D. W. Chang H. Cho A. R. et al (2014). Comparative analysis of human epidermal and peripheral blood γ δ T cell cytokine profiles. Ann. Dermatology26 (3), 308–313. 10.5021/ad.2014.26.3.308
72
Kim K. M. Lim H. W. (2023). The uses of tranexamic acid in dermatology: a review. Int. J. Dermatology62 (5), 589–598. 10.1111/ijd.16160
73
Kim W.-H. Kim J. Y. Gwon M. G. Gu H. Jeon M. Kim M.-K. et al (2018). Anti-inflammatory effect of melittin on porphyromonas gingivalis LPS-stimulated human keratinocytes. Molecules23 (2), 332. 10.3390/molecules23020332
74
Koike S. Yamasaki K. (2020). Melanogenesis connection with innate immunity and toll-like receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci.21 (24), 9769. 10.3390/ijms21249769
75
Kongsompong S. E-Kobon T. Taengphan W. Sangkhawasi M. Khongkow M. Chumnanpuen P. (2023). Computer-aided virtual screening and in vitro validation of biomimetic tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from abalone peptidome. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (4), 3154. 10.3390/ijms24043154
76
Kose A. Oncel S. S. (2022). Design of melanogenesis regulatory peptides derived from phycocyanin of the microalgae Spirulina platensis. Peptides152, 170783. 10.1016/j.peptides.2022.170783
77
Kubglomsong S. Theerakulkait C. Reed R. L. Yang L. Maier C. S. Stevens J. F. (2018). Isolation and identification of tyrosinase-inhibitory and copper-chelating peptides from hydrolyzed rice-bran-derived albumin. J. Agric. Food Chem.66 (31), 8346–8354. 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01849
78
Kubo I. Kinst-Hori I. (1999). Flavonols from saffron flower: tyrosinase inhibitory activity and inhibition mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem.47 (10), 4121–4125. 10.1021/jf990201q
79
Kumar S. D. Kim E. Y. Radhakrishnan N. K. Bang J. K. Yang S. Shin S. Y. (2024). Enhanced antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and antibiofilm activities of tryptophan-substituted peptides derived from cecropin A-melittin hybrid peptide BP100. Molecules29 (22), 5231. 10.3390/molecules29225231
80
Le L. Sirés-Campos J. Raposo G. Delevoye C. Marks M. S. (2021). Melanosome biogenesis in the pigmentation of mammalian skin. Integr. Comp. Biol.61 (4), 1517–1545. 10.1093/icb/icab078
81
Lee G. Bae H. (2016). Anti-inflammatory applications of melittin, a major component of bee venom: detailed mechanism of action and adverse effects. Molecules21 (5), 616. 10.3390/molecules21050616
82
Lee J.-E. An B. J. Jo C. Min B. Paik H. D. Ahn D. U. (2023). The elastase and melanogenesis inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities of phosvitin phosphopeptides produced using high-temperature and mild-pressure (HTMP) pretreatment and enzyme hydrolysis combinations. Poult. Sci.102 (7), 102680. 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102680
83
Lee S.-G. Hwang J. W. Kang H. (2024). Antioxidant and skin-whitening efficacy of a novel decapeptide (DP, KGYSSYICDK) derived from fish by-products. Mar. Drugs22 (8), 374. 10.3390/md22080374
84
Lee S. Y. Baek N. Nam T. g. (2016). Natural, semisynthetic and synthetic tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhibition Med. Chem.31 (1), 1–13. 10.3109/14756366.2015.1004058
85
Li J. Yin S. Wei Z. Xiao Z. Kang Z. Wu Y. et al (2024). Newly identified peptide Nigrocin-OA27 inhibits UVB induced melanin production via the MITF/TYR pathway. Peptides177, 171215. 10.1016/j.peptides.2024.171215
86
Li R. Li Y. Xu W. Liu W. Xu X. Bi Y. et al (2024). Aabrm1-mediated melanin synthesis is essential to growth and development, stress adaption, and pathogenicity in Alternaria alternata. Front. Microbiol.14, 1327765. 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1327765
87
Lim H. N. Baek S. B. Jung H. J. (2019). Bee venom and its peptide component melittin suppress growth and migration of melanoma cells via inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR and MAPK pathways. Molecules24 (5), 929. 10.3390/molecules24050929
88
Lin H. Li F. Kang J. Xie S. Qin X. Gao J. et al (2024). In vitro in silico screening strategy and mechanism of novel tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from nacre of Hyriopsis cumingii. Mar. Drugs22 (9), 420. 10.3390/md22090420
89
Lombardi L. Falanga A. Del Genio V. Galdiero S. (2019). A new hope: self-assembling peptides with antimicrobial activity. Pharmaceutics11 (4), 166. 10.3390/pharmaceutics11040166
90
Lu L. Hu C. Min X. Liu Z. Xu X. Gan L. (2023). In vitro and in vivo biological evaluation of indole-thiazolidine-2,4-dione derivatives as tyrosinase inhibitors. Molecules28 (22), 7470. 10.3390/molecules28227470
91
Madhosingh C. Sundberg L. (1974). Purification and properties of tyrosinase inhibitor from mushroom. FEBS Lett.49 (2), 156–158. 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80500-4
92
Mayerhofer H. Zednik K. Pali-Schöll I. (2022). Der erweiterte Bauernhofeffekt: Das Milchprotein Beta-Lactoglobulin im Stallstaub schützt vor Allergien. Allergologie45 (4), 252–258. 10.5414/alx02246
93
McMillan K. A. M. Coombs M. R. P. (2020). Review: examining the natural role of Amphibian antimicrobial peptide magainin. Molecules25 (22), 5436. 10.3390/molecules25225436
94
Meng J. Liu J. Lu J. Jiang P. Bai Y. Liu X. et al (2023). Isolation, identification, and preparation of tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from Pinctada martensii meat. Biotechnol. Lett.45 (11-12), 1495–1511. 10.1007/s10529-023-03437-0
95
Miao F. Su M. Y. Jiang S. Luo L. F. Shi Y. Lei T. C. (2019). Intramelanocytic acidification plays a role in the antimelanogenic and antioxidative properties of Vitamin C and its derivatives. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev.2019, 2084805. 10.1155/2019/2084805
96
Moon J. Moon I. J. Hyun H. Yoo J. M. Bang S. H. Son Y. et al (2025). Bay 11-7082, an NF-κB inhibitor, prevents post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation through inhibition of inflammation and melanogenesis. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.38 (1), e13207
97
Morita H. Kayashita T. Kobata H. Gonda A. Takeya K. Itokawa H. (1994a). Pseudostellarins A - C, new tyrosinase inhibitory cyclic peptides from Pseudostellaria heterophylla. Tetrahedron50 (23), 6797–6804. 10.1016/s0040-4020(01)81333-8
98
Morita H. Kayashita T. Kobata H. Gonda A. Takeya K. Itokawa H. (1994b). Pseudostellarins d-f, new tyrosinase inhibitory cyclic-peptides from pseudostellaria-heterophylla. Tetrahedron50 (33), 9975–9982. 10.1016/s0040-4020(01)89612-5
99
Morita H. Kobata H. Takeya K. Itokawa H. (1994c). Pseudostellarin-g, a new tyrosinase inhibitory cyclic octapeptide from pseudostellaria-heterophylla. Tetrahedron Lett.35 (21), 3563–3564. 10.1016/s0040-4039(00)73238-2
100
Mortazavi S. M. Moghimi H. R. (2022). Skin permeability, a dismissed necessity for anti-wrinkle peptide performance. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci.44 (2), 232–248. 10.1111/ics.12770
101
Mueller K. P. Neuhauss S. C. F. (2014). Sunscreen for fish: co-option of UV light protection for camouflage. Plos One9 (1), e87372. 10.1371/journal.pone.0087372
102
Nam S.-H. Choi J. H. Kim G. C. (2023). Topical application of no-ozone cold plasma in combination with Vitamin C reduced skin redness and pigmentation of UV-irradiated mice. Biomedicines11 (6), 1563. 10.3390/biomedicines11061563
103
Niessner H. Kosnopfel C. Sinnberg T. Beck D. Krieg K. Wanke I. et al (2017). Combined activity of temozolomide and the mTOR inhibitor temsirolimus in metastatic melanoma involves DKK1. Exp. Dermatol.26 (7), 598–606. 10.1111/exd.13372
104
Nikitovic D. Kukovyakina E. Berdiaki A. Tzanakakis A. Luss A. Vlaskina E. et al (2024). Enhancing tumor targeted therapy: the role of iRGD peptide in advanced drug delivery systems. Cancers16 (22), 3768. 10.3390/cancers16223768
105
Nishimura Y. Nitto T. Inoue T. Node K. (2008). IL-13 attenuates vascular tube formation via JAK2-STAT6 pathway. Circulation J.72 (3), 469–475. 10.1253/circj.72.469
106
Noda M. Danshiitsoodol N. Kanno K. Sugiyama M. (2024). Silk-derived sericin/fibroin mixture drink fermented with plant-derived Lactococcus lactis BM32-1 improves constipation and related microbiota: a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health43 (3), 282–292. 10.12938/bmfh.2023-102
107
Ochiai A. Tanaka S. Tanaka T. Taniguchi M. (2016). Rice bran protein as a potent source of antimelanogenic peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. J. Nat. Prod.79 (10), 2545–2551. 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00449
108
Okajima S. Hamamoto A. Asano M. Isogawa K. Ito H. Kato S. et al (2019). Azepine derivative T4FAT, a new copper chelator, inhibits tyrosinase. Biochem. Biophysical Res. Commun.509 (1), 209–215. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.105
109
Olivares C. Jiménez-Cervantes C. Lozano J. A. Solano F. García-Borrón J. C. (2001). The 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid (DHICA) oxidase activity of human tyrosinase. Biochem. J.354 (Pt 1), 131–139. 10.1042/0264-6021:3540131
110
Onoda Y. Nagahashi M. Yamashita M. Fukushima S. Aizawa T. Yamauchi S. et al (2024). Accumulated melanin in molds provides wavelength-dependent UV tolerance. Photochem. and Photobiological Sci.23 (9), 1791–1806. 10.1007/s43630-024-00632-4
111
Paggi J. M. Pandit A. Dror R. O. (2024). The art and science of molecular docking. Annu. Rev. Biochem.93, 389–410. 10.1146/annurev-biochem-030222-120000
112
Park H. J. Byun K. A. Oh S. Kim H. M. Chung M. S. Son K. H. et al (2022). The combination of niacinamide, Vitamin C, and PDRN mitigates melanogenesis by modulating nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase. Molecules27 (15), 4923. 10.3390/molecules27154923
113
Phadke G. G. Rathod N. B. Ozogul F. Elavarasan K. Karthikeyan M. Shin K. H. et al (2021). Exploiting of secondary raw materials from fish processing industry as a source of bioactive peptide-rich protein hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs19 (9), 480. 10.3390/md19090480
114
Pillaiyar T. Manickam M. Namasivayam V. (2017). Skin whitening agents: medicinal chemistry perspective of tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Enzyme Inhibition Med. Chem.32 (1), 403–425. 10.1080/14756366.2016.1256882
115
Pinzi L. Rastelli G. (2019). Molecular docking: shifting paradigms in drug discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci.20 (18), 4331. 10.3390/ijms20184331
116
Putri S. A. Maharani R. Maksum I. P. Siahaan T. J. (2025). Peptide design for enhanced anti-melanogenesis: optimizing molecular weight, polarity, and cyclization. Drug Des. Dev. Ther.19, 645–670. 10.2147/DDDT.S500004
117
Qiu Z. Wang S. Zhao J. Cui L. Wang X. Cai N. et al (2023). Synthesis and structural characteristics analysis of melanin pigments induced by blue light in Morchella sextelata. Front. Microbiol.14, 1276457. 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1276457
118
Rackerby B. Le H. N. M. Haymowicz A. Dallas D. C. Park S. H. (2024). Potential prebiotic properties of whey protein and glycomacropeptide in gut microbiome. Food Sci. Animal Resour.44 (2), 299–308. 10.5851/kosfa.2024.e12
119
Rady I. Siddiqui I. A. Rady M. Mukhtar H. (2017). Melittin, a major peptide component of bee venom, and its conjugates in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett.402, 16–31. 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.05.010
120
Ramakrishnan S. R. Jeong C. R. Park J. W. Cho S. S. Kim S. J. (2023). A review on the processing of functional proteins or peptides derived from fish by-products and their industrial applications. Heliyon9 (3), e14188. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14188
121
Renauld J. C. (2001). New insights into the role of cytokines in asthma. J. Clin. pathology54 (8), 577–589. 10.1136/jcp.54.8.577
122
Rodriguez-Arambula A. Torres-Álvarez B. Cortés-García D. Fuentes-Ahumada C. Castanedo-Cázares J. P. (2015). CD4, IL-17, and COX-2 are associated with subclinical inflammation in malar melasma. Am. J. Dermatopathol.37 (10), 761–766. 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000378
123
Saadh M. J. Shallan M. A. Hussein U. A. R. Mohammed A. Q. Al-Shuwaili S. J. Shikara M. et al (2024). Advances in microscopy characterization techniques for lipid nanocarriers in drug delivery: a comprehensive review. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Archives Pharmacol.397 (8), 5463–5481. 10.1007/s00210-024-03033-7
124
Sandhu A. Jyoti D. Sharma H. Phull T. Khurana N. S. Tiwana J. K. (2023). Efficacy of topical Vitamin C application on healing after gingival depigmentation by scalpel: a case series. Cureus15 (11), e48417. 10.7759/cureus.48417
125
Sangtanoo P. Srimongkol P. Saisavoey T. Puthong S. Buakeaw A. Suttisuwan R. et al (2024). Bee pollen peptides as potent tyrosinase inhibitors with anti-melanogenesis effects in murine b16f10 melanoma cells and zebrafish embryos. Sci. Rep.14 (1), 30834. 10.1038/s41598-024-81495-8
126
Schurink M. van Berkel W. J. H. Wichers H. J. Boeriu C. G. (2007). Novel peptides with tyrosinase inhibitory activity. Peptides28 (3), 485–495. 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.11.023
127
Sepehri N. Khoshneviszadeh M. Farid S. M. Moayedi S. S. Asgari M. S. Moazzam A. et al (2022). Design, synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking study of thioxo-2,3-dihydroquinazolinone derivative as tyrosinase inhibitors. J. Mol. Struct.1253, 132283. 10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.132283
128
Shekoohi N. Carson B. P. Fitzgerald R. J. (2024). Antioxidative, glucose management, and muscle protein synthesis properties of fish protein hydrolysates and peptides. J. Agric. Food Chem.72 (39), 21301–21317. 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02920
129
Shen Z. Wang Y. Guo Z. Tan T. Zhang Y. (2019). Novel tyrosinase inhibitory peptide with free radical scavenging ability. J. Enzyme Inhibition Med. Chem.34 (1), 1633–1640. 10.1080/14756366.2019.1661401
130
Shim Y. Y. Kim J. H. Cho J. Y. Reaney M. J. T. (2024). Health benefits of flaxseed and its peptides (linusorbs). Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.64 (7), 1845–1864. 10.1080/10408398.2022.2119363
131
Shim Y. Y. Tse T. J. Saini A. K. Kim Y. J. Reaney M. J. T. (2022). Uptake of flaxseed dietary linusorbs modulates regulatory genes including induction of heat shock proteins and apoptosis. Foods11 (23), 3761. 10.3390/foods11233761
132
Sinnberg T. Lasithiotakis K. Niessner H. Schittek B. Flaherty K. T. Kulms D. et al (2009). Inhibition of PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling sensitizes melanoma cells to cisplatin and temozolomide. J. Investigative Dermatology129 (6), 1500–1515. 10.1038/jid.2008.379
133
Snyman M. Walsdorf R. E. Wix S. N. Gill J. G. (2024). The metabolism of melanin synthesis-From melanocytes to melanoma. Pigment Cell and Melanoma Res.37 (4), 438–452. 10.1111/pcmr.13165
134
Soejima M. Koda Y. (2007). Population differences of two coding SNPs in pigmentation-related genes SLC24A5 and SLC45A2. Int. J. Leg. Med.121 (1), 36–39. 10.1007/s00414-006-0112-z
135
Solano F. (2020). Photoprotection and skin pigmentation: melanin-related molecules and some other new agents obtained from natural sources. Molecules25 (7), 1537. 10.3390/molecules25071537
136
Song Y. Li J. Tian H. Xiang H. Chen S. Li L. et al (2023). Copper chelating peptides derived from tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) skin as tyrosinase inhibitor: biological evaluation, in silico investigation and in vivo effects. Food Res. Int.163, 112307. 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.112307
137
Speeckaert R. Bulat V. Speeckaert M. M. van Geel N. (2023). The impact of antioxidants on vitiligo and melasma: a scoping review and meta-analysis. Antioxidants12 (12), 2082. 10.3390/antiox12122082
138
Sugumaran M. Barek H. (2016). Critical analysis of the melanogenic pathway in insects and higher animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci.17 (10), 1753. 10.3390/ijms17101753
139
Tearle R. G. Chen T. Brien F. D. (2025). A 3-bp deletion in the SLC45A2 gene is associated with loss of fleece pigmentation in black-fleeced Suffolk sheep. Anim. Genet.56 (1), e13495. 10.1111/age.13495
140
Tseng T.-S. Tsai K. C. Chen W. C. Wang Y. T. Lee Y. C. Lu C. K. et al (2015). Discovery of potent cysteine-containing dipeptide inhibitors against tyrosinase: a comprehensive investigation of 20 × 20 dipeptides in inhibiting dopachrome formation. J. Agric. Food Chem.63 (27), 6181–6188. 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b01026
141
Veerichetty V. Saravanabavan I. (2023). Molecular docking study of nuciferine as a tyrosinase inhibitor and its therapeutic potential for hyperpigmentation. Genomics and Inf.21 (3), e43. 10.5808/gi.23054
142
Wakamatsu K. Nagao A. Watanabe M. Nakao K. Ito S. (2017). Pheomelanogenesis is promoted at a weakly acidic pH. Pigment Cell and Melanoma Res.30 (3), 372–377. 10.1111/pcmr.12587
143
Wang C. Q. F. Akalu Y. T. Suarez-Farinas M. Gonzalez J. Mitsui H. Lowes M. A. et al (2013). IL-17 and TNF synergistically modulate cytokine expression while suppressing melanogenesis: potential relevance to psoriasis. J. Investigative Dermatology133 (12), 2741–2752. 10.1038/jid.2013.237
144
Wang F. Ma W. Fan D. Hu J. An X. Wang Z. (2024). The biochemistry of melanogenesis: an insight into the function and mechanism of melanogenesis-related proteins. Front. Mol. Biosci.11, 1440187. 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1440187
145
Wang J. Li Y. Feng C. Wang H. Li J. Liu N. et al (2023). Peptide OA-VI12 restrains melanogenesis in B16 cells and C57B/6 mouse ear skin via the miR-122-5p/Mitf/Tyr axis. Amino Acids55 (11), 1687–1699. 10.1007/s00726-023-03341-x
146
Wang W. Lin H. Shen W. Qin X. Gao J. Cao W. et al (2023). Optimization of a novel tyrosinase inhibitory peptide from Atrina pectinata mantle and its molecular inhibitory mechanism. Foods12 (21), 3884. 10.3390/foods12213884
147
Wang X. Duan H. Li M. Xu W. Wei L. (2023). Characterization and mechanism of action of amphibian-derived wound-healing-promoting peptides. Front. Cell Dev. Biol.11, 1219427. 10.3389/fcell.2023.1219427
148
Wu J.-H. Wang Z. Xu S. Y. (2008). Enzymatic production of bioactive peptides from sericin recovered from silk industry wastewater. Process Biochem.43 (5), 480–487. 10.1016/j.procbio.2007.11.018
149
Xie X. Zou G. Li C. (2015). Antitumor and immunomodulatory activities of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Chaenomeles speciosa. Carbohydr. Polym.132, 323–329. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.046
150
Xing M. Wang X. Zhao L. Zhou Z. Liu H. Wang B. et al (2021). Novel dissolving microneedles preparation for synergistic melasma therapy: combined effects of tranexamic acid and licorice extract. Int. J. Pharm.600, 120406. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120406
151
Xue W. Liu X. Zhao W. Yu Z. (2022). Identification and molecular mechanism of novel tyrosinase inhibitory peptides from collagen. J. Food Sci.87 (6), 2744–2756. 10.1111/1750-3841.16160
152
Yang C.-Y. Guo Y. Wu W. J. Man M. Q. Tu Y. He L. (2022). UVB-induced secretion of IL-1β promotes melanogenesis by upregulating TYR/TRP-1 expression in vitro. Biomed Res. Int.2022, 8230646. 10.1155/2022/8230646
153
Yap P.-G. Gan C.-Y. (2020). Chicken egg white-advancing from food to skin health therapy: optimization of hydrolysis condition and identification of tyrosinase inhibitor peptides. Foods9 (9), 1312. 10.3390/foods9091312
154
Yap P.-G. Gan C. Y. Naharudin I. Wong T. W. (2023). Effect of chicken egg white-derived peptide and hydrolysates on abnormal skin pigmentation during wound recovery. Molecules28 (1), 92. 10.3390/molecules28010092
155
Yoon J. H. Jang W. Y. Park S. H. Kim H. G. Shim Y. Y. Reaney M. J. T. et al (2023). Anti-melanogenesis effects of a cyclic peptide derived from flaxseed via inhibition of CREB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci.24 (1), 536. 10.3390/ijms24010536
156
Yu F. Lu Y. Zhong Z. Qu B. Wang M. Yu X. et al (2021). Mitf involved in innate immunity by activating tyrosinase-mediated melanin synthesis in pteria penguin. Front. Immunol.12, 626493. 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626493
157
Yu Q. Fan L. (2021). Understanding the combined effect and inhibition mechanism of 4-hydroxycinnamic acid and ferulic acid as tyrosinase inhibitors. Food Chem.352, 129369. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129369
158
Zhan J.-q. Wu J. X. Fu J. J. Li G. S. Wu F. Chen Y. W. (2024). Antioxidant synergistic anti-inflammatory effect in the MAPK/NF-κB pathway of peptide KGEYNK (KK-6) from giant salamander (Andrias davidianus). J. Sci. Food Agric.104 (14), 8613–8620. 10.1002/jsfa.13689
159
Zhang L. Cheng Y. X. Liu A. L. Wang H. D. Wang Y. L. Du G. H. (2010). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anti-influenza properties of components from chaenomeles speciosa. Molecules15 (11), 8507–8517. 10.3390/molecules15118507
160
Zhang R. Wei Y. Li M. Cai M. Gu R. Ma Y. et al (2020). Melanogenesis effects of rice protein hydrolysate and its characteristic peptides Leu-Leu-Lys, Leu-Pro-Lys, and pyroGlu-Lys on UVB-induced human epidermal melanocyte cells. Food and Funct.11 (10), 8757–8767. 10.1039/d0fo01808b
161
Zhang S. Huang C. Li Y. Li Z. Zhu Y. Yang L. et al (2024). Corrigendum: anti-cancer immune effect of human colorectal cancer neoantigen peptide based on MHC class I molecular affinity screening. Front. Immunol.15, 1514836. 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1514836
162
Zhang Y. Hu Y. Lei L. Jiang L. Fu C. Chen M. et al (2024b). UVB-induced TRPS1 regulates MITF transcription activity to promote skin pigmentation. Biochimica Biophysica Acta-Molecular Basis Dis.1870 (7), 167445. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167445
163
Zhang Y. Li D. Diao Y. Xu W. Wang G. Hu Z. et al (2024a). Effect of rice bran protein on the foaming properties and foaming characteristics of rice bran protein-sodium caseinate and rice bran protein nanoparticles-sodium caseinate. Foods13 (15), 2328. 10.3390/foods13152328
164
Zhao H. Song G. (2024). Antiviral peptide-generative pre-trained transformer (AVP-GPT): a deep learning-powered model for antiviral peptide design with high-throughput discovery and exceptional potency. Viruses-Basel16 (11), 1673. 10.3390/v16111673
165
Zhou J. Ling J. Wang Y. Shang J. Ping F. (2016). Cross-talk between interferon-gamma and interleukin-18 in melanogenesis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology163, 133–143. 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.08.024
166
Zhou J. Shang J. Song J. Ping F. (2013). Interleukin-18 augments growth ability of primary human melanocytes by PTEN inactivation through the AKT/NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biochem. and Cell Biol.45 (2), 308–316. 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.11.008
167
Zhou J. Song J. Ping F. Shang J. (2014). Enhancement of the p38 MAPK and PKA signaling pathways is associated with the pro-melanogenic activity of Interleukin 33 in primary melanocytes. J. Dermatological Sci.73 (2), 110–116. 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.09.005
168
Zu X.-Y. Xiong G. Q. Cai J. Liao T. Li H. L. (2023). Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) scales collagen peptides (SCPs): preparation, whitening activity screening and characterization. Foods12 (7), 1552. 10.3390/foods12071552
169
Yu Z.-W. Zheng M. Fan H. Y. Liang X. H. Tang Y. L. (2024). Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: a double-edged sword in cancer development and therapy. Molecular biomedicine5 (1), 49–49. 10.1186/s43556-024-00209-8
170
Bickers D. R. Athar M. (2006). Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of skin disease. Journal of Investigative Dermatology126 (12), 2565–2575. 10.1038/sj.jid.5700340
171
Chen H. Lin C. Wu Y. Wang B. Kui M. Xu J. et al (2024). Protective effects of degraded Bletilla striata polysaccharides against UVB-induced oxidative stress in skin. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules277, 134462, 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134462
172
Sevilla A. Chéret J. Slominski R. M. Slominski A. T. Paus R. (2022). Revisiting the role of melatonin in human melanocyte physiology: A skin context perspective. Journal of Pineal Research72, e12790, 10.1111/jpi.12790
173
Pudlarz A. M. Czechowska E. S Karbownik M. Ranoszek-Soliwoda K. Tomaszewska E. Celichowski G. et al (2020). The effect of immobilized antioxidant enzymes on the oxidative stress in UV-irradiated rat skin.Nanomedicine15 (1), 23–39. 10.2217/nnm-2019-0166
174
Park S. H. Jo Y.-J. (2019). Static hydrothermal processing and fractionation for production of a collagen peptide with anti-oxidative and anti-aging properties. Process Biochemistry83, 176–182. 10.1016/j.procbio.2019.05.015
175
Ahuja K. Raju S. Dahiya S. Motiani R. K. (2025). ROS and calcium signaling are critical determinant of skin pigmentation. Cell Calcium125, 102987, 10.1016/j.ceca.2024.102987
176
Nie H. Liu L. Yang H. Guo H. Liu X. Tan Y. et al (2017). A Novel Heptapeptide with Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity Identified from a Phage Display Library. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology181 (1): 219–232. 10.1007/s12010-016-2208-3
177
Thaha A. Wang B. S. Chang Y. W. Hsia S. M. Huang T. C. Shiau C. Y. et al (2021). Food-Derived Bioactive Peptides with Antioxidative Capacity, Xanthine Oxidase and Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity. Processes9, 747, 10.3390/pr90507475).
178
Ping F. Shang J. Zhou J. Song J. Zhang L. (2012). Activation of neurokinin-1 receptor by substance P inhibits melanogenesis in B16-F10 melanoma cells. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology44 (12), 2342–2348. 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.09.025
179
Zhou J. Feng J. Y. Wang Q. Shang J. (2015). Calcitonin gene-related peptide cooperates with substance P to inhibit melanogenesis and induces apoptosis of B16F10 cells. Cytokine74 (1), 137–144. 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.01.034
180
Jung E. Lee J. A. Shin S. Roh K. B. Kim J. H. Park D. (2013). Madecassoside Inhibits Melanin Synthesis by Blocking Ultraviolet-Induced Inflammation. Molecules18 (12), 15724–15736. 10.3390/molecules181215724
181
Su H. Yang F. Lu K. Ma J. Huo G. Li S. et al (2024). Carnosic acid ameliorates postinflammatory hyperpigmentation by inhibiting inflammatory reaction and melanin deposition. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie180, 117522–117522. 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117522
182
Zhao J. Dan Y. Liu Z. Wang Q. Jiang M. Zhang C. et al (2022). Solamargine Alleviated UVB-Induced Inflammation and Melanogenesis in Human Keratinocytes and Melanocytes via the p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway, a Promising Agent for Post-inflammatory Hyperpigmentation. Frontiers in Medicine9, 10.3389/fmed.2022.812653
183
Wellbrock C. Marais R. (2005). Elevated expression of MITF counteracts B-RAF-stimulated melanocyte and melanoma cell proliferation. Journal of Cell Biology170 (5), 703–708. 10.1083/jcb.200505059
184
Cheli Y. Ohanna M. Ballotti R. Bertolotto C. (2010). Fifteen-year quest for microphthalmia-associated transcription factor target genes.” Pigment Cell & Melanoma Research23 (1), 27–40. 10.1111/j.1755-148X.2009.00653.x
185
Vachtenheim J. Borovansky J. (2010). “Transcription physiology” of pigment formation in melanocytes: central role of MITF. Experimental dermatology19 (7), 617–627. 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2009.01053.x
186
Jian D. Jiang D. Su J. Chen W. Hu X. Kuang Y. et al (2011). Diethylstilbestrol enhances melanogenesis via cAMP-PKA-mediating up-regulation of tyrosinase and MITF in mouse B16 melanoma cells. Steroids76 (12), 1297–1304. 10.1016/j.steroids.2011.06.008
187
Lee H.-R. Jung J. M. Seo J. Y. Chang S. E. Song Y. (2021). Anti-melanogenic property of ginsenoside Rf from Panax ginseng via inhibition of CREB/MITF pathway in melanocytes and ex vivo human skin. Journal of Ginseng Research45 (5), 555–564. 10.1016/j.jgr.2020.11.003
188
Zhou S. Yotsumoto H. Tian Y. Sakamoto K. (2021). α-Mangostin suppressed melanogenesis in B16F10 murine melanoma cells through GSK3β and ERK signaling pathway. Biochemistry and biophysics reports26, 100949–100949. 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100949
189
Shirasugi I. Kamada M. Matsui T. Sakakibara Y. Liu M. C. Suiko M. (2010). Sulforaphane Inhibited Melanin Synthesis by Regulating Tyrosinase Gene Expression in B16 Mouse Melanoma Cells. Bioscience Biotechnology and Biochemistry74 (3), 579–582. 10.1271/bbb.90778
190
Huang H.-C. Lin H. Huang M. C. (2017). The lactoferricin B-derived peptide, LfB17-34, induces melanogenesis in B16F10 cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine39 (3), 595–602. 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2884
191
Kang B. Kim Y. Park T. J. Kang H. Y. (2020). Dasatinib, a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces melanogenesis via ERK-CREB-MITF-tyrosinase signaling in normal human melanocytes. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications523 (4), 1034–1039. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.01.051
192
Choi H. Yoon J. H. Youn K. Jun M. (2022). Decursin prevents melanogenesis by suppressing MITF expression through the regulation of PKA/CREB, MAPKs, and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β cascades. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy147, 112651, 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112651
193
Huang H.-C. Liao C. C. Peng C. C. Lim J. M. Siao J. H. Wei C. M. et al (2016). Dihydromyricetin from Ampelopsis grossedentata inhibits melanogenesis through down-regulation of MAPK, PKA and PKC signaling pathways. Chemico-Biological Interactions258, 166–174. 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.08.023
194
Fu T. Chai B. Shi Y. Dang Y. Ye X. (2019). Fargesin inhibits melanin synthesis in murine malignant and immortalized melanocytes by regulating PKA/CREB and P38/MAPK signaling pathways. Journal of Dermatological Science94 (1), 213–219. 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2019.03.004
195
Liu Y.-Y. Su X. R. Liu S. S. Yang S. S. Jiang C. Y. Zhang Y. et al (2017). Zebrafish phosvitin-derived peptide Pt5 inhibits melanogenesis via cAMP pathway. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry43 (2), 517–525. 10.1007/s10695-016-0306-3
196
Choi H. R. Kang Y. A. Lee H. S. Park K. C. (2016). Disulfanyl peptide decreases melanin synthesis via receptor-mediated ERK activation and the subsequent downregulation of MITF and tyrosinase. International Journal of Cosmetic Science38 (3), 279–285. 10.1111/ics.12291
Summary
Keywords
melanin, excessive deposition, inhibition, tyrosinase, whitening, bioactive peptides
Citation
Yu B, Wang N, Cai S, Yan H, Sun S, Wang S, Li Y and Liang Z (2025) Research progress on peptides that inhibit melanin synthesis. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1610623. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1610623
Received
12 April 2025
Accepted
26 May 2025
Published
02 July 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Wei Chen, Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals, China
Reviewed by
Aphichart Karnchanatat, Chulalongkorn University, Thailand
Huali Wu, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Yu, Wang, Cai, Yan, Sun, Wang, Li and Liang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhengting Liang, liangzhengting@xjmu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.