- 1Cardiovascular Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shuguang Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Cardiovascular Department, Shuguang Hospital of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Department of Pharmacological Sciences, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook, NY, United States
Background: Syringic acid (SA), a naturally occurring phenolic acid, has garnered significant attention for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, the mechanisms underlying these effects and their potential therapeutic applications require further elucidation.
Methods: A comprehensive literature review was conducted using PubMed and Web of Science (1965–2024) to investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of SA, with a focus on oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways. For insights related to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), we referenced Chinese literature. Articles focusing on agriculture, industry, and economics are excluded.
Results: SA exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities through multiple mechanisms. Specifically, it mitigates OS by scavenging free radicals, enhancing endogenous antioxidant defenses, and activating the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway. It also inhibits inflammation by downregulating key mediators, including NF-κB, TLR4, HMGB1, MyD88, and TRAF6. Crosstalk between NRF2, NF-κB, and PI3K/AKT pathways reveals SA’s involvement in cellular pathophysiological processes such as apoptosis, ferroptosis, and endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Conclusion: SA’s robust antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms underscore its promise as a therapeutic agent. Future research should address its pharmacokinetics, safety profile, and clinical potential.
1 Introduction
Natural metabolites from plants are a rich source for drug discovery, with polyphenols serving as potent antioxidants found abundantly in fruits and vegetables (de Araújo et al., 2021). Among them, phenolic metabolites-comprising tannins, flavonoids, phenolic acids, and lignans-are widely known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities (Fu et al., 2022; Milla and Kerpper, 2023). One of the most well-studied phenolic acids is gallic acid (GA), recognized for its strong antioxidant activity and therapeutic benefits in diseases including cardiovascular diseases (Kosuru et al., 2018), cancer (Ashrafizadeh et al., 2021), and diabetes mellitus (Xu, Y. et al., 2021).
SA, a dimethoxybenzene and 3,5-dimethoxy derivative of GA (Figure 1), has demonstrated antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties, as well as protective roles against diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and liver damage (Srinivasulu et al., 2018). First extracted through permanganate oxidation of sinapic lignin (Bland and Logan, 1965), SA is abundantly found in dietary sources such as olives, pumpkins, grapes, blueberries, and honey (Bartel et al., 2023). Additionally, it presents in some medicinal plants such as the seed of Lepidium virginicum L. (“Bei Tinglizi” in Chinese), the seed of Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb. ex Prantl (“Nan Tinglizi” in Chinese), as well as the radix of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. or Paeonia veitchii Lynch (“Chishao” in Chinese) (Hu et al., 2022; Yang, 2020). Both Tinglizi and Chishao are considered to possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities (Hsieh et al., 2020; Parker et al., 2016). Notably, wine-processed Chishao, used for treating dysmenorrhea, exhibits an increased SA content after fermentation, enhancing its anti-inflammatory effects through prostaglandin F2α inhibition, similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (Ferries-Rowe et al., 2020).
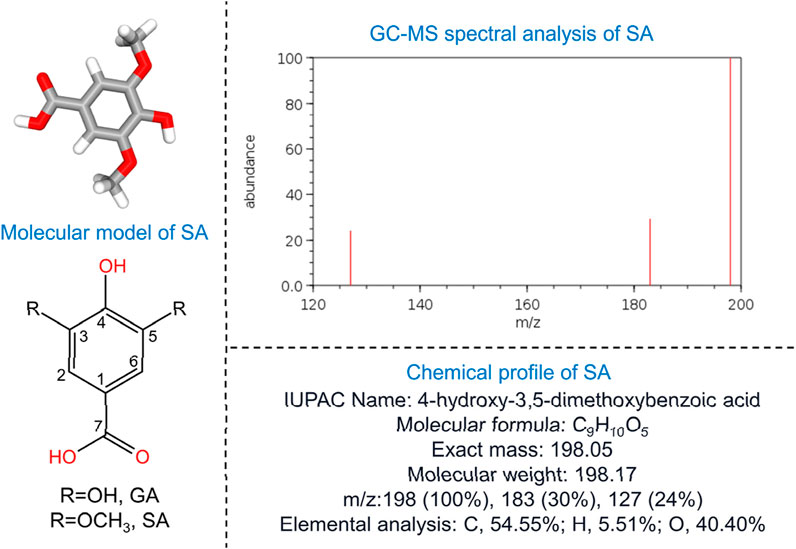
Figure 1. Fundamental characteristics of SA. The left side of the figure illustrates the molecular model of SA, highlighting the substitutions at the 3 and 5 carbon positions: hydroxyl groups denote GA, while methoxy groups indicate SA. The top-right corner displays the GC-MS spectral analysis of SA, and the bottom-right corner provides the chemical profile. GA, gallic acid; GC-MS, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry; SA, syringic acid.
While comprehensive reviews have addressed SA’s occurrence, biosynthesis, pharmacology, and industrial relevance, as well as its role in neurodegenerative and civilization diseases (Bartel et al., 2023; Ogut et al., 2022; Srinivasulu et al., 2018), the precise mechanisms underlying its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects remain unclear. This review aims to elucidate these mechanisms by examining SA’s structure-activity relationships and its complex regulation of NRF2 and NF-κB, providing insights into its direct molecular targets. Additionally, we propose a hypothesis to explain SA’s dual pro- and anti-apoptotic roles in cancer. The review further evaluates SA’s activity on oxidative stress and inflammation-related cellular pathologies, while assessing its pharmacokinetics, safety, and therapeutic potential.
2 Search strategy
A comprehensive literature review was conducted using PubMed and Web of Science (1965–2024) to investigate the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms of SA, with a focus on oxidative stress OS and inflammatory pathways. The search strategy incorporated keywords like “syringic acid,” “oxidative stress,” and “inflammation.” A total of 1,226 articles were identified. Titles and abstracts were screened for relevance, and full texts were assessed according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines. Inclusion criteria focused on studies exploring the pharmacological mechanisms of SA in relation to oxidative stress and inflammation, while exclusion criteria omitted articles centered on agriculture, industry, or economics. In vitro studies were only included if they were clearly linked to or built upon in vivo findings and used primarily for mechanistic exploration. Purely in vitro studies without any in vivo validation were excluded. Chinese literature was referenced for insights related to Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). Data extraction prioritized outcomes addressing SA’s molecular targets, pathways, and therapeutic potential. Two independent reviewers conducted the selection and quality assessment processes, evaluating study design, sample size, methodology, and risk of bias, with discrepancies resolved through discussion. Articles containing suspicious data errors, omissions, or duplications were excluded to ensure the integrity and reliability of the analysis.
3 Antioxidant mechanisms of SA
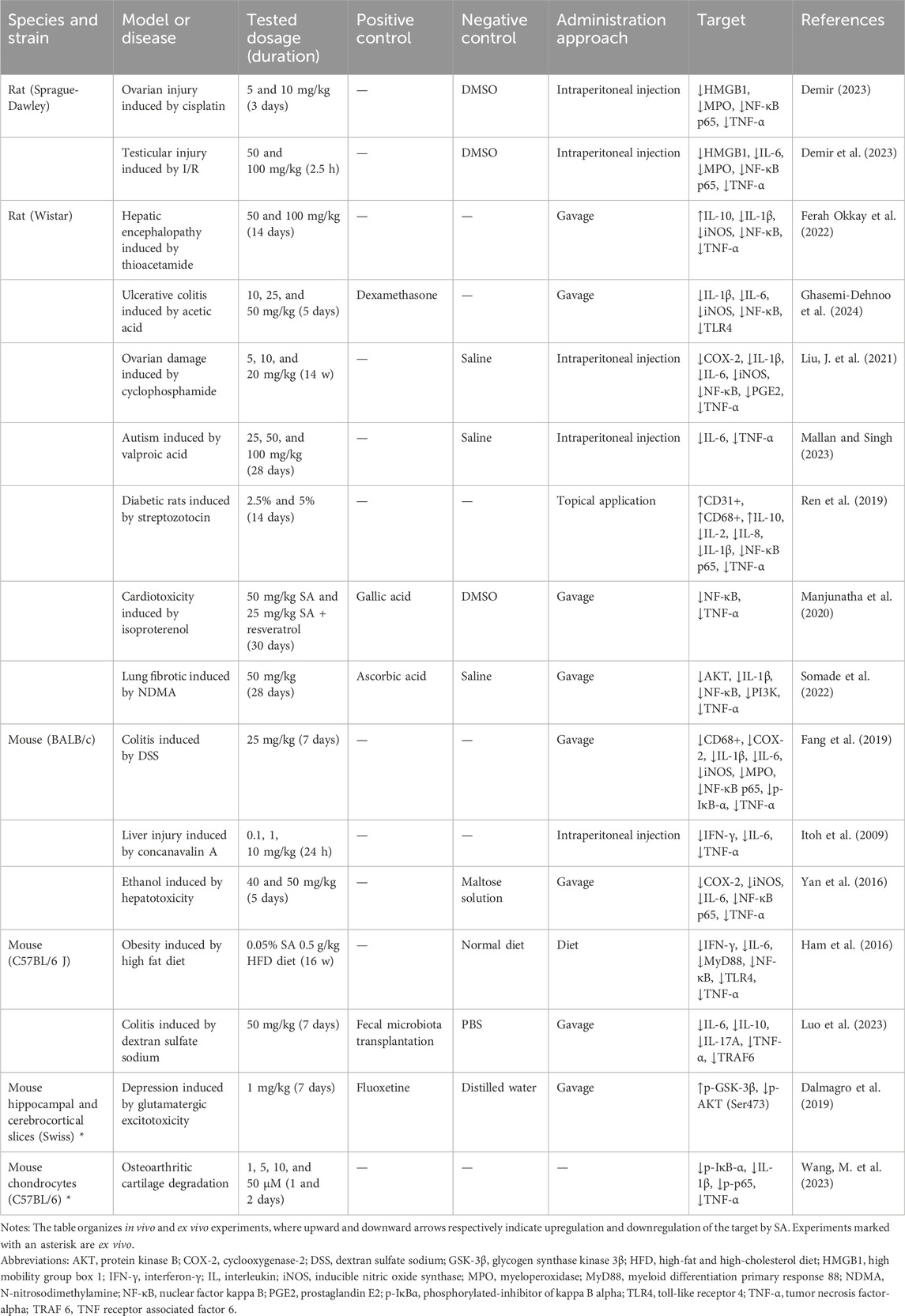
Living cells constantly encounter reactive oxidative molecules from both externally and internally sources. These species, including free radicals or non-radical forms like H2O2, readily capture electrons from surrounding molecules, initiating chain reactions that can damage cellular structures (Filomeni et al., 2015). Under physiological conditions, cells tightly regulate the production of free radicals, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), to maintain redox homeostasis through intrinsic antioxidant defense system (Meulmeester et al., 2022). They are predominantly generated within the mitochondrial electron transport chain, particularly at complexes I and III, where electron leakage facilities the partial reduction of molecular oxygen, leading to the formation of superoxide radicals (Dan Dunn et al., 2015). These superoxide radicals are rapidly converted into the less reactive H2O2 through the catalytic action of superoxide dismutase (SOD). However, under conditions such as elevated flux through the electron transport chain, reduced mitochondrial efficiency, or compromised endogenous antioxidant defense, this redox equilibrium becomes disrupted (Dan Dunn et al., 2015). This imbalance leads to oxidative stress, wherein excess ROS are inadequately neutralized, causing damage on cellular structures and functions. This review explores the mechanisms by which SA mitigates oxidative stress through four key aspects: structural activity, modulation of free radical production, enhancement of the endogenous antioxidant defense system, and activation of molecular signaling pathways. The effects of SA on oxidative stress-related targets are summarized in Table 1.
3.1 Structure-activity relationship of SA
In both in vivo and in vitro settings, the radical scavenging activity of a metabolite is largely determined by its specific molecular structure (Nimse and Pal, 2015). The position and number of hydroxyl groups play a crucial role in enhancing the antioxidant capacity of phenolic acids (Eom et al., 2012).
Gallic acid (GA), characterized by a trihydroxybenzene ring with hydroxyl at positions 3, 4, and 5, is converted to syringic acid (SA) through methylation of the hydroxyl groups at positions 3 and 5, forming methoxy groups (Figure 1). Although the substitution of methoxy groups reduces the antioxidant capacity-evidenced by studies showing GA has a stronger antioxidant capacity than SA (Chen, 2011; Skroza et al., 2022), the presence of methoxy groups in SA still contributes to its significant antioxidant capability. Methoxy groups act as electron-donating substituents that stabilize the phenoxy radical formed during free radical scavenging (Razzaghi-Asl et al., 2013). Specifically, the methoxy groups at positions 3 and 5 (-OCH3) increase the bond dissociation enthalpy (BDE) of the O–H bond in the phenolic moiety, promoting the stabilization of the phenoxy radical generated upon reaction with free radicals (Chen et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2002). Notably, the presence of two methoxy groups flanking the phenoxy radical enhances its stability compared to a single methoxy substituent (Bors et al., 2002). Additionally, the radical-scavenging ability of phenolic metabolites is linked to their acidity, which facilitates proton donation, and the delocalized π-electrons of their benzene ring, which enables electron transfer while maintaining structural stability (Parmar et al., 2011). This dual mechanism—proton donation and electron transfer—underscores the intricate balance that governs SA’s antioxidant efficacy.
3.2 SA modulates the generation of free radicals
Free radicals are highly active intermediates characterized by the presence at least one unpaired electron in their outer shell. Excessive free radicals production within the body acts a catalyst for damage to biological molecules, including DNA, proteins, and cellular membranes, thereby contributing to the development of various diseases (Liu, 2020; Phaniendra et al., 2015). In biological systems, free radicals primarily originate from ROS and RNS (Jomova et al., 2023). Common ROS include hydroxyl radicals (·OH), singlet oxygen (1O2), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and superoxide anion (O2.−). NADPH oxidases (NOXs), a family of membrane-bound enzymes present in various cell types, catalyze the transfer of electrons from NADPH to oxygen molecules, generating ROS, primarily O2.− and the subsequently produced H2O2 (Bedard and Krause, 2007). SA reduces ROS formation by downregulating the expression of p47phox and gp91phox induced by alcohol in the liver. These two components, the cytosolic and membrane components of NOX, respectively, contribute to decreasing the formation of ROS (Yan et al., 2016). In the broader context of oxidative stress and inflammation, lipoxygenases (LOXs) play a pivotal role by catalyzing the metabolism of arachidonic acid to produce eicosanoids, thereby contributing to the ROS pool (Kattoor et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2020). SA acts as an effective LOX inhibitor, exhibiting an IC50 value of 0.009 mM (Habza-Kowalska et al., 2021).
Common RNS include nitric oxide (NO) and peroxynitrite (ONOO−). NO is primarily produced by NO synthase (NOS), which exists in three isoforms: endothelial NOS (eNOS), inducible NOS (iNOS), and neuronal NOS (nNOS) (Stuehr and Haque, 2019). The interaction of O2.− with NO yields ONOO−, a highly reactive oxidant capable of inducing oxidative and nitrative damage (Matsubara et al., 2015). SA reduces NO production by downregulating iNOS expression (Güzelad et al., 2021; Khatun et al., 2023).
3.3 SA modulates the endogenous antioxidant defense system
The redox equilibrium of cells is maintained by a complex endogenous antioxidant defense mechanism, comprising enzymatic antioxidants like SOD, catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), as well as non-enzymatic components such as glutathione (GSH), and iron-binding proteins such as ferritin and transferrin (Poljsak et al., 2013). SOD plays a critical role by catalyzing the dismutation of superoxide radical anion, a harmful by-product of cellular metabolism, into H2O2, which is less reactive (Wang et al., 2018). CAT then rapidly decomposes H2O2 into water and molecular oxygen preventing its accumulation and potential conversion into more reactive species (Nandi et al., 2019). GPx, a selenium-containing enzyme, further detoxifies H2O2 and organic hydroperoxides by reducing them to water or their corresponding alcohols, utilizing GSH as a cofactor (Brigelius-Flohé and Flohé, 2020). GSH, a tripeptide composed of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine, acts as a critical antioxidant by directly scavenging free radicals and reactive intermediates. It also serves as a substrate for GPx-catalyzed reactions, where it is oxidized to glutathione disulfide (GSSG) during the reduction of H2O2, thereby mitigating ROS-induced damage and maintaining cellular redox homeostasis (Forman et al., 2009).
Oxidative stress is commonly defined as an imbalance between the production and elimination of ROS. The imbalance not only increases free radicals but also impairs antioxidant defense system, leading to reduced activity of these enzymes and molecules (Pérez-Torres et al., 2021). Consequently, these antioxidant indicators are often used to assess the efficacy of antioxidants. Studies have shown that SA significantly enhances the activity of these indicators in response to oxidative stress damage across various systems, including cardiovascular (Güven et al., 2015; Kumar et al., 2012), neural (Cao et al., 2016; Mallan and Singh, 2023), endocrine (Sherkhane et al., 2023), and reproductive systems (Akarsu et al., 2023; Demir, 2023).
Within the cancer microenvironment, although oxidants play roles through various stages of tumor development, excessive accumulation of cellular ROS leads to oxidative stress, which can trigger apoptosis. This mechanism not only limits metastasis but also prevents tumorigenesis (Forman and Zhang, 2021). Furthermore, the surplus of ROS damages cellular components such as DNA, proteins, lipids, membranes, and organelles, acting as a pivotal signal to activate the apoptotic pathways. Increasing evidence indicates that inducing the accumulation of intracellular ROS is a primary strategy underlying the cytotoxicity of anticancer drugs (Redza-Dutordoir and Averill-Bates, 2016). Phenolic metabolites are believed to exert their anticancer activities through such mechanisms (Yang et al., 2020). For instance, high doses of GA in cell culture media can convert O2 into H2O2, increasing ROS levels and inducing selective cytotoxicity in cancer cells (Wang et al., 2016). Both in vivo and in vitro studies, Yang et al. demonstrated that SA can enhance the production of ROS in tumor cells of rat lung cancer, leading to apoptosis (Yang et al., 2020). Similarly, Pei et al. reported that SA reduces the activity of antioxidant enzymes in gastric cancer cells, induces OS, and selectively promotes apoptosis, potentially through the depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential (Pei et al., 2021). Additionally, oral administration of SA to rats with colorectal cancer increased ROS production, decreased antioxidant enzyme activity, and caused DNA damage, as evidenced by elevated levels of 8-OHdG and AP-sites, both of which are significant indicators of oxidative DNA damage (Mihanfar et al., 2021).
In summary, SA exhibits a bidirectional modulation of antioxidant enzyme activity. Specifically, in the context of cancer, it promotes oxidative stress, modulates antioxidant enzyme activity, and induces apoptosis, consistent with the general activities of polyphenols (Chimento et al., 2023). However, the factors determining the selective pro-/anti-oxidant activity of SA in various disease contexts remain unclear. Current research on SA’s anticancer activities has primarily focused on apoptosis. The underlying mechanisms contributing to this duality will be explored in section “5.2 apoptosis”.
3.4 SA modulates KEAP1/NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway
The Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1)/nuclear factor-erythroid related factor 2 (NRF2) signaling pathway is a key regulator of the antioxidant defense system, playing a critical role in protecting cells from oxidative stress. It implicated in various inflammatory diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, and aging (Fão et al., 2019; Lu et al., 2016; Tu et al., 2019). NRF2 is a transcription factor that activates the expression of a range of antioxidant genes, reducing ROS levels and mitigating oxidative stress damage (Hybertson et al., 2011). Under normal condition, NRF2 binds with KEAP1 in the cytoplasm. As part of the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that includes Cullin 3 (Cul3) and RING-box protein 1 (RBX1), KEAP1 promotes the ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of NRF2, thus maintaining NRF2 low levels. However, during oxidative stress or ROS exposure, these oxidants modify KEAP1’s structure, impairing its ability to capture NRF2. Consequently, NRF2 escapes degradation, accumulates, and translocates to the nucleus. In the nucleus, NRF2 forms heterodimers with small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma (sMaf) proteins and binds to antioxidant response elements (ARE), activating the expression of antioxidant genes, including heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1) (Figure 2) (Tonelli et al., 2018).
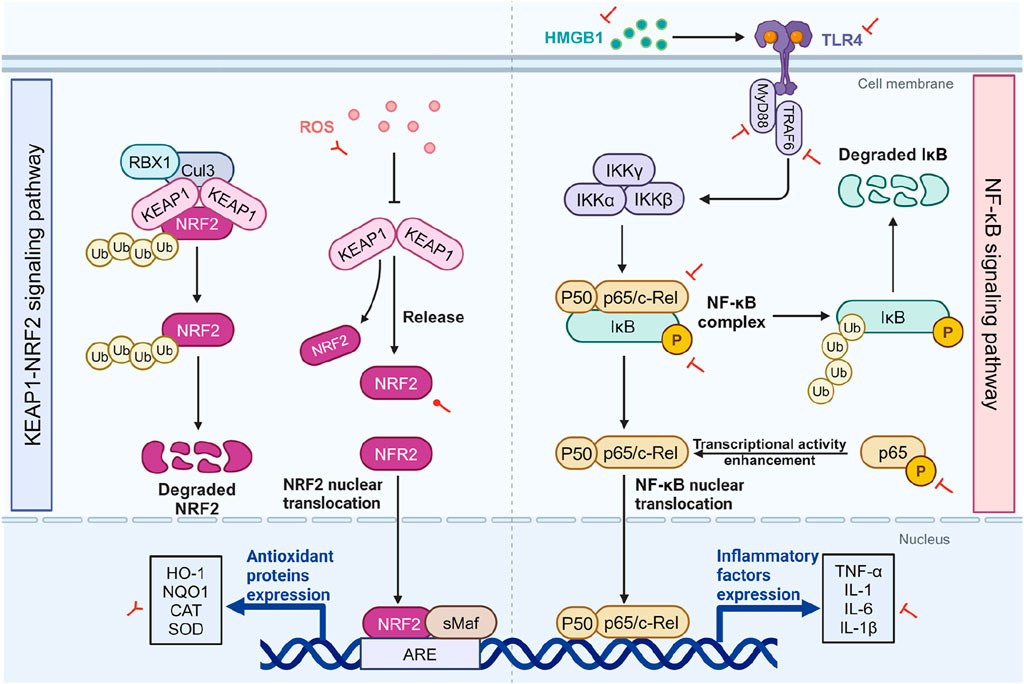
Figure 2. The impact of SA on the KEAP1/NRF2 and NF-κB pathways. The two sides of the diagram respectively depict the KEAP1/NRF2 pathway (left) and the NF-κB pathway (right), as well as the effects of SA on them. Under normal conditions, NRF2 is kept at low levels through its binding with KEAP1 in the cytoplasm, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation. However, OS alters KEAP1, enabling NRF2 accumulation and nuclear migration, where it enhances antioxidant gene expression including HO-1, NQO1, CAT, and SOD. Within the NF-κB signaling cascade, cellular stressors such as the interaction of TLR4 with extracellularly released HMGB1 initiate a complex series of events. This cascade involves the recruitment of the adaptor protein MyD88 and TRAF6, which in turn activates the IKK complex. The activation of IKK results in the targeted phosphorylation of IκB proteins, tagging them for proteasomal degradation and thereby liberating the NF-κB p50/p65 dimers. Under OS and inflammation-related diseases, SA inhibits ROS and activates NRF2, enhancing antioxidant gene expression while concurrently attenuating the NF-κB pathway by reducing the expression of p-IκB-α, p65 and p-p65, as well as downregulating upstream signaling components such as TLR4, HMGB1, MyD88, and TRAF6. In the context of cancer, SA leads to an increase in ROS and decreases the expression of antioxidant genes. Red circular, T-shaped, and bifurcated arrows represent promotion, inhibition, and bidirectional effect by SA, respectively. ARE, antioxidant response element; CAT, catalase; Cul3, cullin-3; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IKK, IκB kinase; IκB, inhibitor κB; KEAP1, cytoplasmic kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1; IL, interleukin; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-kappa B; NQO1, NADPH quinone oxidoreductase enzyme; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; RBX1, ring-box 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; sMAF, small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6. Created in BioRender. Zhejun, Z. (2024) BioRender.com/q25k994.
In an early study by Yan et al., SA intake significantly increased the expression of NRF2 in liver cell nuclei in a mouse model of ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity. This suggests that SA may stabilize intracellular NRF2 molecules, promote its translocation into the nucleus, and regulate antioxidant-related genes (Yan et al., 2016). Similarly, SA ingestion in rats with pulmonary fibrosis significantly increased NRF2 protein expression in lung tissue (Somade et al., 2022). Comparable results were observed in models of testicular damage (Akarsu et al., 2023) and diabetic nephropathy (Sherkhane et al., 2023), where SA enhanced activity of NQO1, a downstream target of NRF2. Furthermore, Ekhtiar et al. found that a higher dosage of SA (50 mg/kg) significantly upregulated the expression of the antioxidant genes NRF2, HO-1, and NQO1, mitigating oxidative and inflammation in a model of experimental ulcerative colitis, while a lower dosages (10 mg/kg) did not elicit the same effect, indicating that SA dose-dependent activation of NRF2 pathway (Ekhtiar et al., 2023).
HO-1, regulated by NRF2, catalyze the rate-limiting step in heme breakdown, producing ferrous ions, biliverdin, and carbon monoxide (Loboda et al., 2016). Biliverdin is rapidly converted into bilirubin by biliverdin reductase (BVR), both of which are widely recognized for their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties (Vijayan et al., 2018). Furthermore, iron homeostasis mechanisms, including the increased in ferritin synthesis, facilitate the safe storage and utilization of these released ferrous ions, protecting cells from oxidative damage (Sha et al., 2023). This aspect will be further discussed in section “5.3 ferroptosis”. Besides regulating antioxidant enzyme expression through NRF2 activation, HO-1upregulation can also enhance the expression of other antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, GPx, and CAT (Ryter, 2022). Studies have shown that HO-1 knockout animal models exhibit elevated lipid peroxidation and oxidized protein levels (Mansouri et al., 2022), highlighting HO-1’s critical role in combating OS and inflammation. Recent in vivo studies have demonstrated that SA activates the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway in inflammatory models. Ekhtiar et al. reported that ulcerative colitis increased pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β, as well as decreased expression of the antioxidant genes HO-1, NRF2, and NQO1. Treatment with SA was able to reverse these effects in a dose-dependent manner (Ekhtiar et al., 2023). Additionally, SA improves ovarian toxicity in rats exposed to CIS, balancing the levels of the antioxidant system, potentially through NRF2/HO-1 pathway activation (Demir, 2023). In summary, SA’s structure underlies its antioxidant capacity, reducing free radical production, enhancing the endogenous antioxidant defense system, and activating the KEAP1/NRF2/HO-1 pathway (Figure 2).
4 Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of SA
Inflammation is the body’s innate response to infection or injury and can be categorized into two types: acute and chronic. Acute inflammation activates the immune system to facilitate rapid recovery clearing invaders and repairing tissues, which is generally beneficial to the host (Joffre and Hellman, 2021; Reuter et al., 2010). However, unresolved inflammation can progress to chronic inflammation, which is associated with various diseases, including cardiovascular diseases (Senoner and Dichtl, 2019), neurodegenerative diseases (Teleanu et al., 2022), diabetes (Poznyak et al., 2020), and cancer (Caliri et al., 2021).
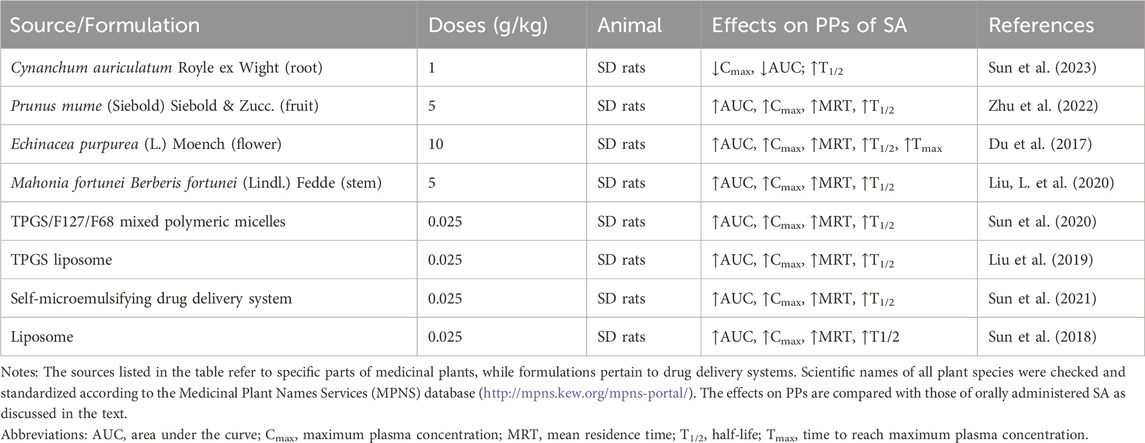
Various inflammatory stimuli trigger the migration of immune cells, such as macrophages and neutrophils, to the site of injury, where they release inflammatory mediators including NO, prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) (Medzhitov, 2008). This process promotes tissue repair and antigen clearance but may also lead to pain and edema. Prolonged inflammation leads to elevated levels of pro-inflammatory mediators such as iNOS, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), PGE2, and various cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, is observed (Alessandri et al., 2013; Watson et al., 2017). Furthermore, the activation of T cells fosters the production of lymphokines, including IL-2 and interferon-γ (IFN-γ), further mobilizing immune cells to combat pathogens and repair tissue (Ding et al., 2022). The specific anti-inflammatory mechanisms of SA will be discussed next, focusing on its regulation of inflammatory mediators and molecular signaling pathways. The effects of SA on inflammation-related targets are summarized in Table 2.
4.1 SA modulates inflammatory mediators
Cytokines are key regulators of the immune system, comprising both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory types, which play crucial roles in intercellular communication, maintaining homeostasis, and disease progression (Opal and DePalo, 2000). Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IFN-γ, promote inflammatory responses and the development of chronic diseases. Conversely, anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and IL-4 inhibit the inflammatory process by regulating the responses of pro-inflammatory cytokines, maintaining the balance of the immune system (Henshaw et al., 2021; Propper and Balkwill, 2022). The regulation of balance of these cytokines is essential for controlling inflammatory responses. Numerous studies have shown that in various animal models, interventions with SA can exert anti-inflammatory activities by simultaneously downregulating pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, IFN-γ and upregulating anti-inflammatory factors such as IL-10.
In addition to cytokines, other key molecules like COX-2 and PGE2 also play crucial roles in the regulation of inflammatory responses. COX-2, an enzyme upregulated during inflammation, catalyzes the production of prostaglandins, especially PGE2, which is an important mediator of typical symptoms such as inflammation, pain, and fever (Kawahara et al., 2015). In in vivo inflammation models, such as drug-induced liver damage, ovarian injury, and colitis, SA intake significantly downregulated the activity of COX-2 and PGE2 (Fang et al., 2019; Gheena et al., 2022; Liu, J. et al., 2021).
Myeloperoxidase (MPO), an enzyme abundantly present in neutrophils, catalyzes the production of potent oxidants such as hypochlorous acid, which contributes to ROS generation. Activated neutrophils utilize ROS produced by MPO to further modulate the release of inflammatory cytokines, exacerbating the inflammatory response (Aratani, 2018; Hawkins, 2020). In two reproductive system studies by Demir et al., regardless of whether it was a rat ovarian damage model or a testicular damage model, SA intake significantly reduced the activity of MPO (Demir, 2023; Demir et al., 2023). Additionally, the increased activation of immune cells, including neutrophils, macrophages, and T lymphocytes, enhances their recruitment and activation at inflammation site, leading to elevated pro-inflammatory cytokines production (Ozga et al., 2021). Fang et al. demonstrated that in a dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mouse model, SA effectively regulated both the activity and expression of MPO and CD68+, a macrophage marker, suggesting suppression of immune cell activation (Fang et al., 2019). Interestingly, a study on wound healing in diabetic rats produced opposite results, where the topical application of SA significantly upregulated the protein expression of CD68 and the endothelial tissue marker CD31, promoting wound healing (Ren et al., 2019). This discrepancy may be explained by the fact that cytokines produced by macrophages are essential for fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition; their ablation can impair healing and hinder functional recovery (Kessenbrock et al., 2010).
Collectively, these studies suggest that the effects of SA on inflammation are context-dependent. In inflammatory disease models, SA’s anti-inflammatory properties help alleviate tissue damage and inflammation. Conversely, in tissue repair and regeneration contexts, SA promotes wound healing by activating immune cells and enhancing angiogenesis.
4.2 SA modulates NF-κB pathway
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a key signaling pathway that regulates inflammatory responses, immune reactions, and cell survival (Mitchell et al., 2016; Zinatizadeh et al., 2021). The NF-κB family consists of five protein monomers: p65 (RelA), RelB, cRel, p50, and p52, which form homodimers or heterodimers that regulate gene expression by specifically binding to DNA. The classical activation pathway of NF-κB is triggered by upstream signals, including IL-1, TNF, and TLR4 stimulation, which activate the IκB kinase (IKK) complex. IKKβ phosphorylates IκB protein, leading to its degradation and the release of NF-κB dimers, typically the p50/p65 dimer (Zinatizadeh et al., 2021). The NF-κB dimer then enters the nucleus, binds to specific sequences of DNA, recruits coactivators, and initiates the transcription of target genes (Figure 2).
Currently, existing in vivo experiments have widely demonstrated that SA downregulates the expression of NF-κB. For example, in an ethanol-induced liver toxicity mouse model, SA administration reduced NF-κB p65 expression in a dose-dependent manner, without significant impact observed on p50 (Yan et al., 2016). This reduction has also been noted across several inflammatory models, including reproductive system injuries (Demir, 2023; Demir et al., 2023), diabetes (Ren et al., 2019), and colitis (Fang et al., 2019). p65 can be further phosphorylated to p-p65, enhancing its transcriptional activity (Xu, X. et al., 2021). SA can also reduce the phosphorylation of p65 (Wang, M. et al., 2023; Xiang and Xiao, 2022). Meanwhile, once IκB-α is phosphorylated, it is rapidly degraded via the proteasomal pathway, releasing the NF-κB dimer bound to it. Furthermore, SA downregulates p-IκB-α expression in osteoarthritis and colitis models, preventing NF-κB activation (Fang et al., 2019; Wang, M. et al., 2023).
The activation of NF-κB also depends on the recognition and transmission of upstream signals. TLR4, a pattern recognition receptor on the cell surface, recognizes pathogen-associated molecular patterns like LPS, triggering downstream signaling and activating the IKK complex (Ciesielska et al., 2021). Similarly, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), an intracellular DNA-binding protein, can be released extracellularly upon cell stress or death, interacting with TLR4 to amplify inflammatory signaling (Chen et al., 2022). SA can also downregulate the expression of both HMGB1 (Demir, 2023; Demir et al., 2023) and TLR4 (Ghasemi-Dehnoo et al., 2024) in inflammation-related models. Additionally, myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) and tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) are pivotal in bridging TLR4 activation with NF-κB-mediated cellular responses (Cohen and Strickson, 2017). Upon TLR4’s recognition of its ligand, MyD88 is swiftly recruited to the receptor complex, followed by TRAF6, and together they transmit the activation signal to downstream signaling molecules (Deguine and Barton, 2014). Ham et al. also evaluated the expression of TLR4 and MyD88 in the liver tissues of obese mice. SA significantly reduced the gene expression of both, suggesting that by downregulating the TLR4-MyD88 pathway, it decreases the gene expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the liver, including TNF-α and IL-6 (Ham et al., 2016). The inhibitory effect of SA on TRAF6 has also been observed in a colitis model (Luo et al., 2023).
In summary, SA downregulates NF-κB signaling by reducing NF-κB p65 expression and phosphorylation, lowering p-IκB-α levels, and inhibiting nuclear transcription. Additionally, it impacts upstream regulatory mechanisms by suppressing TLR4, HMGB1, and adaptor proteins like MyD88 and TRAF6, highlighting its role in modulating inflammatory responses (Figure 2).
5 Potential crosstalk among different pathways involving SA
Current evidence suggests that SA exhibits significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, its direct molecular targets remain unclear. While SA is well-known for its antioxidant properties, typical of phenolic acids, stronger evidence supports its anti-inflammatory effects. If SA’s antioxidant activity arise from its inherent ROS-scavenging ability, then the reduced oxidative stress should, in theory, restore KEAP1’s ability to capture NRF2. Studies often report increased NRF2 levels following SA intervention, suggesting that SA may stabilize NRF2. Notably, potential publication bias, particularly regarding NF-κB pathway research, cannot be ruled out. Therefore, we will examine NRF2’s upstream regulators and pathway crosstalk to identify SA’s potential direct targets.
5.1 The potential role of SA in modulating crosstalk between NRF2 and NF-κB
Oxidative stress and inflammation are two highly interconnected processes. NRF2 is a crucial molecule in regulating oxidative stress, while inflammation induced by oxidative stress is primarily triggered by the activation of NF-κB (Ahmed et al., 2017).
Their interaction is complex. Similar to NRF2, IKKβ can also bind to KEAP1, leading to its ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Under ROS-rich condition, KEAP1 is inhibited, stabilizing IKKβ, which phosphorylates and degrades I-κBα, thereby activating NF-κB (Lee et al., 2009). Conversely, the NRF2 pathway inhibits NF-κB nuclear translocation of by preventing the proteasomal degradation of IκB-α (Saha et al., 2020). On the other hand, NF-κB inhibits NRF2 activation by reducing the transcription of ARE genes (Cuadrado et al., 2018). NF-κB p65 additionally interacts with KEAP1, promoting its translocation to the nucleus. This process facilitates the separation of NRF2 from the ARE, leading to the increased ubiquitination and degradation of NRF2 (Kim and Jeon, 2022). This reciprocal negative regulation creates a complex interplay between NF-κB and NRF2 (Figure 3). SA’s potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities may stem from a synergistic feedback loop involving NRF2 activation and NF-κB inhibition. Akarsu et al. concurrently evaluated the expression levels of these two molecules. In a rat model of testicular injury induced by lead acetate, a significant downregulation of NRF2 was observed alongside a significant upregulation of NF-κB, indicating the presence of oxidative stress and inflammation. SA intake was able to reverse this condition, suggesting that SA plays a role in regulating the NRF2/NF-κB signaling pathway (Akarsu et al., 2023). However, current research evaluating the simultaneous effects of SA intervention on both NRF2 and NF-κB remain limited. Given the intricate crosstalk between these pathways, the causal relationship is not fully understood, and both pathways may be influenced concurrently. Further studies are needed to elucidate the precise mechanisms and interactions involved.
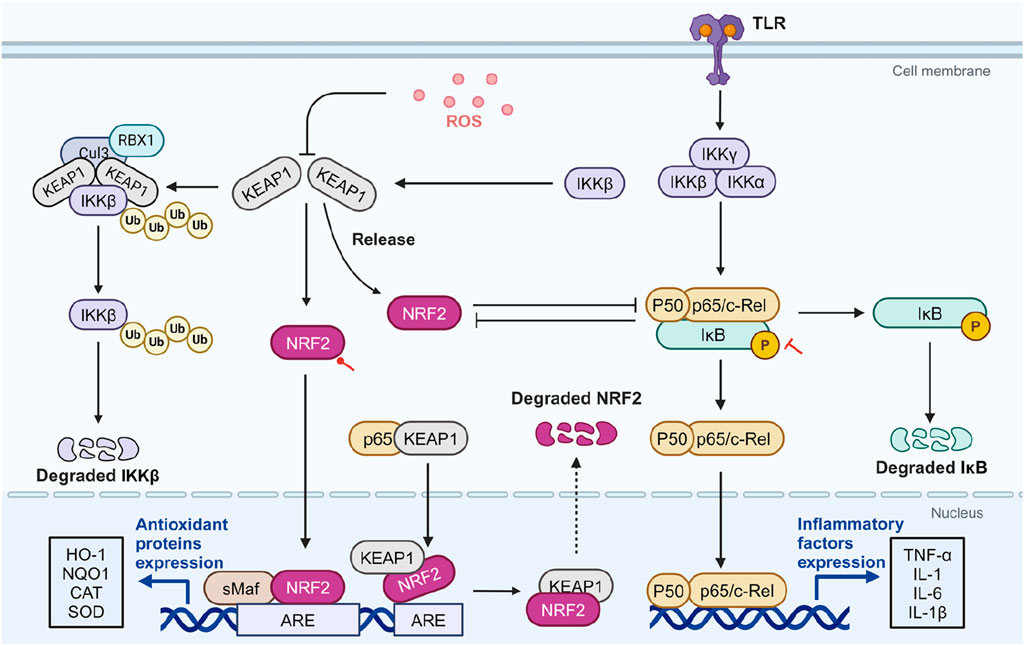
Figure 3. The potential role of SA in modulating crosstalk between NRF2 and NF-κB. ROS-rich conditions inhibit KEAP1, stabilizing IKKβ and leading to NF-κB activation through IκBα degradation. NRF2 inhibits NF-κB’s nuclear translocation by preventing IκBα degradation and reduces NF-κB activation by enhancing antioxidant defenses and lowering ROS levels. Conversely, NF-κB p65 can inhibit NRF2 activation by affecting ARE gene transcription and facilitating NRF2 degradation via interactions with KEAP1. In diseases related to OS and inflammation, SA activates NRF2 and inhibits NF-κB. Red circular and T-shaped arrows represent promotion and inhibition by SA, respectively. Dashed arrows indicate indirect effects. ARE, antioxidant response element; CAT, catalase; Cul3, cullin-3; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; IKK, IκB kinase; IκB, inhibitor κB; KEAP1, cytoplasmic kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1; IL, interleukin; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-kappa B; NQO1, NADPH quinone oxidoreductase enzyme; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; RBX1, ring-box 1; ROS, reactive oxygen species; sMAF, small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α. Created in BioRender. Zhejun, Z. (2023) BioRender.com/n67e000.
5.2 The potential role of SA in modulating crosstalk among PI3K/AKT, NRF2, and NF-κB
NRF2 is an downstream targets of PI3K and can be phosphorylated by activated AKT (Yu and Xiao, 2021). One study indicated that under the action of PI3K inhibitors, there was a reduction in AKT1 phosphorylation, which in turn diminished the accumulation of carnosol-induced NRF2 protein (Martin et al., 2004). The PI3K/AKT/NRF2 pathway is considered a primary route for cells to counteract oxidative stress (Lai et al., 2020). Besides direct activation of NRF2, the PI3K/AKT pathway regulates the activity of NRF2 through glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), a widely distributed serine/threonine kinase (Grimes and Jope, 2001). Activated GSK-3β phosphorylates Fyn tyrosine kinase, promoting its nuclear translocation, where it phosphorylates NRF2 at Tyr568, facilitating its export via chromosomal region maintenance 1 (Crm1) and reducing its transcriptional activity (Culbreth and Aschner, 2018; Rojo et al., 2008). GSK-3β can also phosphorylate NRF2’s Neh6 domain, promoting KEAP1-independent degradation (Rada et al., 2011). Activated AKT phosphorylates GSK-3β at Ser9, leading to its inactivation (Zhou et al., 2013).
SA has been shown to activate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, reducing cellular ROS production and MDA content, thus protecting RGC-5 cells from oxidative damage induced by H2O2 (Song et al., 2016). In another oxidative injury model, the ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury rat model, intervention with SA significantly activated the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway, thereby inhibiting mitochondria-induced apoptosis and alleviating myocardial damage (Liu, G. et al., 2020). In a glutamate-induced neurotoxicity model, SA can significantly increase the phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT, and GSK-3β, producing effects similar to fluoxetine. Moreover, inhibitors of PI3K and GSK-3β can negate these protective effects (Dalmagro et al., 2019). These findings suggest that SA acts as an activator of PI3K and GSK-3β, contributing to NRF2 elevation and antioxidant effect. However, whether SA directly interacts with PI3K and GSK-3β remains to be determined, as the specific binding sites are unknown.
However, in specific disease contexts, the effects of SA on the PI3K/AKT/NRF2 pathway are complex. Another downstream component of AKT is NF-κB (Yu et al., 2017). The PI3K/AKT pathway activates NF-κB by phosphorylating IKK, leading to the degradation of IκB (Burow et al., 2000; Yang et al., 2019). Somade et al. assessed the expression levels of the PI3K/AKT pathway, NRF2, and NF-κB in NDMA-induced pulmonary fibrosis (Somade et al., 2022). In this context, the PI3K/AKT pathway is activated, promoting both fibroblast proliferation and differentiation into myofibroblasts, which play an essential role in fibrotic disease (Conte et al., 2011; Fagone et al., 2011). In this model, the PI3K/AKT pathway is activated, NF-κB significantly increases with NRF2 downregulated. These changes are significantly reversed under SA intervention (Somade et al., 2022). Notably, despite PI3K/AKT activation typically upregulating NRF2, SA’s inhibition of PI3K/AKT coincided with NRF2 stabilization, suggesting that SA may directly stabilize NRF2 or that other upstream factors are involved.
Overall, SA appears to stabilize NRF2 directly while also acting as an activator of PI3K and GSK-3β (Figure 4). However, its effects may vary depending on disease contexts. The causal relationship between SA’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects remains unclear, necessitating further research to identify its direct molecular targets.
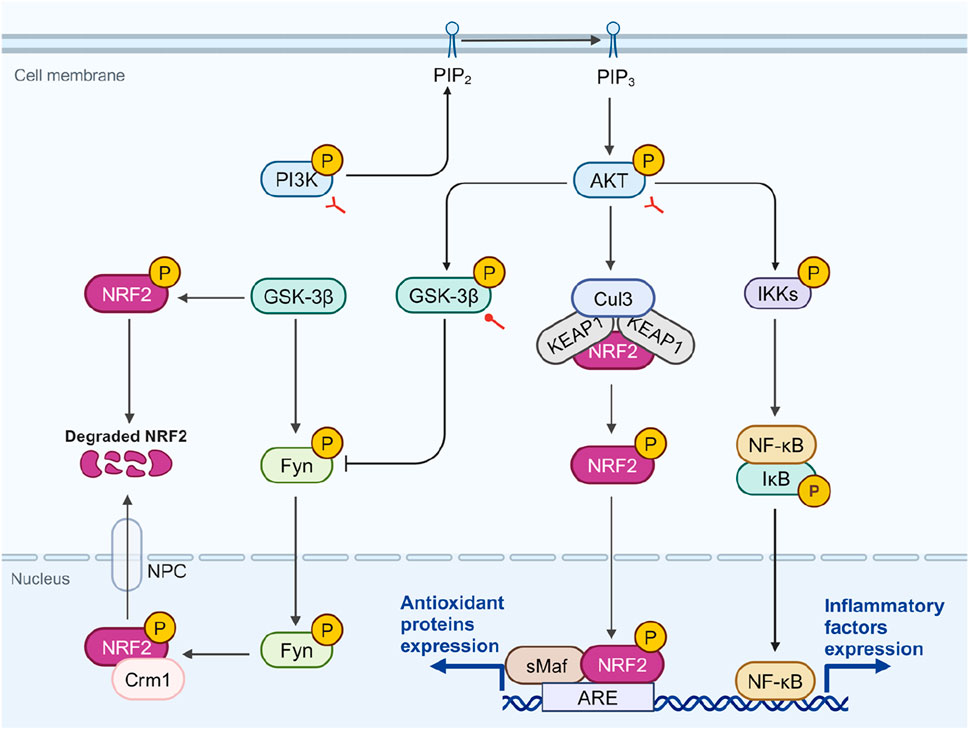
Figure 4. The potential role of SA in modulating crosstalk among PI3K, NRF2, and NF-κB. AKT phosphorylation, stimulated by PI3K, leads to the phosphorylation and inactivation of GSK-3β, which facilitates NRF2’s nuclear retention and antioxidant activity. GSK-3β can phosphorylate Fyn, leading to its nuclear translocation and subsequent phosphorylation of NRF2, which when associated with Crm1, diminishes NRF2’s transcriptional activity. Additionally, AKT-mediated phosphorylation of IKK promotes NF-κB activation and inflammatory response. In diseases related to OS and inflammation, SA promotes the phosphorylation of PI3K, AKT, and GSK-3β. However, in fibrotic diseases, SA inhibits the phosphorylation of PI3K and AKT. Red circular and bifurcated arrows represent promotion and bidirectional effect by SA, respectively. AKT, protein kinase B; ARE, antioxidant response element; Crm1, chromosomal region maintenance 1; Cul3, cullin-3; Fyn, fyn tyrosine kinase; GSK-3β, glycogen synthase kinase 3β; IKK, IκB kinase; IκB, inhibitor κB; NF-κB, Nuclear factor-kappa B; NPC, nuclear pore complex; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate; sMAF, small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma. Created in BioRender. Zhejun, Z. (2023) BioRender.com/r78r058.
6 The regulatory role of SA in OS and inflammation-related cellular pathological processes
SA plays a crucial role in mitigating oxidative stress and inflammation-related cellular pathological processes. Through multiple mechanisms, SA exerts protective effects against endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), apoptosis, and ferroptosis, which are key pathological processes aggravated by oxidative stress and inflammation, partially through modulating NRF2 and NF-κB signaling (Figure 5).
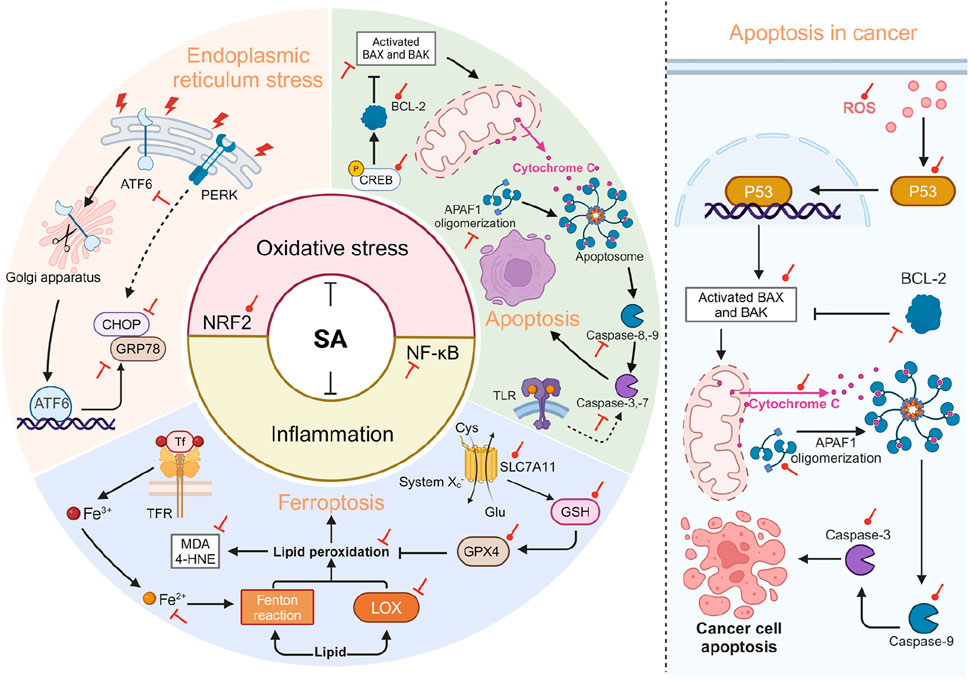
Figure 5. SA is involved in regulating cellular pathological processes related to OS and inflammation. The left side of the diagram illustrates that SA primarily acts to mitigate cellular pathological processes through its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, achieved by enhancing NRF2 and suppressing NF-κB. Specifically, SA alleviates ERS by suppressing the expression of ATF6, CHOP, and GRP78. In terms of apoptosis, SA exerts its anti-apoptotic effect through the mitochondrial-dependent pathway, which includes upregulating Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax, Caspase-3, 8, and APAF1. SA also promotes the phosphorylation of CREB, an upstream activator of BCL-2, thus stabilizing the integrity of the mitochondrial outer membrane. Regarding ferroptosis, SA activates the SLC7A11-GPX4 pathway on one hand and reduces the expression of ferrous ions and LOX on the other, thereby decreasing lipid peroxidation (reductions in MDA and 4-HNE) and mitigating ferroptosis. The right side of the diagram illustrates pro-apoptotic effects of SA in the context of cancer. SA activates the generation of ROS, which promotes the nuclear transcription of p53, thereby activating the mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis pathway. Red circular and T-shaped arrows represent promotion and inhibition by SA, respectively. Dashed arrows indicate indirect effects. 4-HNE, 4-hydroxynonenal; APAF1, apoptotic protease activating factor 1; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; BAX, BCL-2-associated X; BAK, BCL-2-antagonist/killer; BCL-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; Cys, cystine; Glu, glutamate; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GRP78, glucose-regulated protein 78; GSH, glutathione; LOX, lipoxygenase; MDA, malondialdehyde; PERK, protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SA, syringic acid; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; Tf, Transferrin; TLR, toll-like receptor. Created in BioRender. Zhejun, Z. (2024) BioRender.com/g91x518.
6.1 ERS
The ER is essential for cellular functions and survival, overseeing protein synthesis, folding, and trafficking (Oakes and Papa, 2015). ERS occurs when these critical processes are disrupted by pathological events, particularly oxidative stress and inflammation. To restore homeostasis, cells activate the unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway, which is regulated by three sensor proteins: activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1), and protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), respectively (Bettigole and Glimcher, 2015; Chen and Cubillos-Ruiz, 2021). Under normal condition, glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) binds to sensor proteins, keeping them inactive. Upon activation of the UPR, ATF6 migrates to the Golgi apparatus, becomes activated, and then enters the nucleus to increase the expression of proteins like GRP78, GRP94, and CHOP, aiming to restore ER function (Read and Schröder, 2021; Wiseman et al., 2022). However, prolonged PERK activation can induce CHOP expression, suppress the anti-apoptotic gene BCL-2, and promote apoptosis (Marciniak et al., 2004).
Demir et al. demonstrated that SA mitigates rat testicular damage induced by I/R by inhibiting the HMGB1/NF-κB axis and ERS, resulting in a dose-dependent reduction of oxidative stress, inflammation, and key ERS markers (including GRP78, ATF6, and CHOP) (Demir et al., 2023). Similar findings were observed in another study by the same group, showing SA’s protective effects against cisplatin-induced ovarian damage (Demir, 2023). Additionally, in the context of neurodegenerative diseases, SA covalently modify tau protein, inhibit the formation of amyloid fibrils, and alleviate neurotoxicity. Importantly, this study highlighted SA’s inhibitory effects on endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated by tau amyloid proteins (downregulation of ATF6) and apoptosis (downregulation of caspase-8 and caspase-3) (Li et al., 2021).
6.2 Apoptosis
Apoptosis is a precisely regulated form of cell death that occurs via two main pathways: extrinsic and intrinsic (Bertheloot et al., 2021). The intrinsic pathway is triggered by internal stress factors such as DNA damage or ERS, with the key event being the release of cytochrome c from the mitochondria (Ketelut-Carneiro and Fitzgerald, 2022). This pathway is regulated by the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins of the Bcl-2 family (Kesavardhana et al., 2020). In contract, the extrinsic pathway is initiated through the activation of membrane receptors, such as tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1) or toll-like receptors (TLRs) (Amarante-Mendes et al., 2018). Despite their distinct initiation mechanisms, both pathways converge on the activation of caspases, particularly caspase-3, which executes apoptosis.
Oxidative stress and inflammation contribute to apoptosis (Cameli et al., 2020; Kondylis et al., 2017). In such models, SA exerts its anti-apoptotic activity by upregulating BCL-2 and downregulating BAX, caspase-3, 8, and APAF1 (Akarsu et al., 2023; Li et al., 2021; Wang, F. et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2020). Multiple pathway networks are involved in regulating the anti-apoptotic capabilities of SA. For example, in cardiomyocytes, SA activates the PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway to exert anti-apoptotic activities (Liu G. et al., 2020), while in RGC-5 cells, it protects against H2O2-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, suggesting its therapeutic role in diabetic retinopathy (Song et al., 2016). In a rat colitis model, SA alleviates oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/iNOS pathway (Ghasemi-Dehnoo et al., 2024). Most studies on SA’s anti-apoptotic effects focus on the mitochondria-dependent intrinsic pathway. Mitochondrial dysfunction leads to the release of cytochrome C from the mitochondrial membrane into the cytoplasm, resulting in apoptosis (Nakagawa and Tayama, 2000). In the study by Helli et al., bisphenol A-induced mitochondrial dysfunction increases free radicals production, activating the mitochondrial apoptosis signaling pathway. SA’s anti-apoptotic effects were attributed to its potent antioxidant capacity, which scavenges free radicals (Helli et al., 2024). Additionally, SA promotes the phosphorylation of the upstream cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) of Bcl-2, stabilizing the mitochondrial outer membrane and preventing cytochrome c release (Helli et al., 2024; Yan et al., 2022).
Inducing apoptosis is one of the fundamental principles of most current cancer treatments (Ouyang et al., 2012). In cancer cells, SA promotes apoptosis through the mitochondria-dependent pathway, including the downregulation BCL-2, and upregulation of P53, caspase-3, caspase-9, cytochrome C, BAX, and APAF1 (Abijeth and Ezhilarasan, 2020; Li et al., 2023; Velu et al., 2017). This cytotoxic effect often coincides with ROS accumulation (Gheena and Ezhilarasan, 2019; Yang et al., 2020). Structurally similar phenolic acids, such as ferulic and caffeic acids, also increase ROS levels in cancer cells, inducing cytotoxicity (Bao et al., 2023; Rajendra Prasad et al., 2011). ROS can activates P53 translocation to the nucleus and trigger the expression of pro-apoptotic genes (Srinivas et al., 2019). They can also directly affect mitochondria by reducing their membrane potential, promoting the release of cytochrome C and leading to apoptosis (Sinha et al., 2013). Therefore, SA’s ability to regulate ROS accumulation may be central to its anticancer activity.
The pro-oxidant effects of polyphenols in cancer cells are thought to be related to copper-mediated cellular DNA damage (Farhan and Rizvi, 2022). Malignant cells have a higher absolute copper content than non-malignant cells (Ge et al., 2022). In the presence of copper ions, polyphenolic metabolites can act as pro-oxidants. Specifically, plant polyphenols are believed to mobilize chromatin-bound copper, undergoing redox reactions that reduce Cu2+ to Cu1+, which is then re-oxidized by molecular oxygen to produce ROS. Although SA may promote oxidation in this manner, the extent of DNA damage depends on the orientation and number of hydroxyl groups, particularly galloyl groups (Farhan et al., 2015). SA has only one hydroxyl group at the 4-position, with methoxy groups at the 3- and 5-positions. Another possible hypothesis is that the two methoxy groups, as electron donors, push electron density towards the benzene ring through resonance, thereby increasing the electron density on the ring. This makes it easier for the ring to donate electrons to Cu2+, facilitating its reduction to Cu1+ and generating ROS. Additionally, the small molecular size of SA allows it to approach DNA closely, which is essential because hydroxyl radicals have a limited diffusion radius and must be generated near cellular DNA (Pryor, 1988). While SA exhibits significant pro-oxidant effects in cancer cells, the mechanisms underlying its dual anti-oxidant and pro-oxidant activities remain unclear, necessitating further research to validate these hypotheses.
6.3 Ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is a form of programmed cell death first identified in 2012, distinct from traditional modes of cell death such as apoptosis and autophagy. Its hallmark features include iron ions dependence and the excessive accumulation of lipid peroxides (Dixon et al., 2012). Current research suggests that ferroptosis is closely associated with oxidative stress (Xie et al., 2016). Iron is an essential element for many metabolic enzymes involved in the production of intracellular ROS. Through the non-enzymatic, iron-dependent Fenton reaction, iron can further catalyze the production of large amounts of ROS, thereby exacerbating the extent of lipid peroxidation and the generation of reactive compounds such as malondialdehyde (MDA) and 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) (Conrad and Pratt, 2019). The excessive accumulation of lipid peroxides disrupts cell membrane integrity, ultimately triggering cell death.
SA has been shown to significantly reduces lipid peroxidation markers, potentially through modulation of the solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11)/glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) axis. SLC7A11 is a critical cystine-glutamate exchanger that constitutes part of system xc−. By regulating the import of cystine (one of the essential precursors for GSH synthesis), SLC7A11 directly influences the synthesis of GSH (Chen et al., 2021; Liu M.R. et al., 2021). As the most abundant antioxidant in mammalian cells, GSH not only scavenges ROS but also acts as a key substrate for GPX4. GPX4 utilizes GSH to convert lipid peroxides into non-toxic molecules, thereby halting the progression of lipid peroxidation reactions and contributing to the cell’s resilience against oxidative stress. Ferroptosis has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including I/R-induced organ damage (Stockwell et al., 2017). In C2C12 subjected to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R), demonstrated that SA can upregulate GPX4 and SLC7A11, while reducing intracellular Fe2+ levels and lipid peroxidation (Wang F. et al., 2023). Additionally, beyond GPX4, other key regulators of Ferroptosis, such as ferroportin and HO-1, are transcriptional targets of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) (Kerins and Ooi, 2018). In fact, many proteins and enzymes responsible for preventing lipid peroxidation and thereby triggering ferroptosis are target genes of NRF2 (Dodson et al., 2019). Notably, NRF2 inhibitors have been explored as potential inducers of ferroptosis-mediated cancer cell death (Roh et al., 2017; Sun et al., 2016). Given the significant effects of SA on modulating NRF2 activity, while direct evidence linking SA to ferroptosis remains limited, there is a strong rationale to investigate this association further.
7 Pharmacokinetics
Ideal pharmacokinetic properties (PPs) are a prerequisite for the clinical application of a botanical drug. Understanding a botanical drug’s PPs helps elucidate its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) processes (Bai et al., 2021). A series of studies have assessed the bioavailability and tissue distribution of SA administered orally in rats and mice (Liu et al., 2019; Sun et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021; Sun et al., 2018). Following a single oral administration of SA in rats, the pharmacokinetic curve shows a rapid and sharp contour, reaching the maximum plasma concentration within 5–15 min, and then swiftly diminishing from the rat plasma. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax), half-life (T1/2), the area under the curve (AUC), and the mean residence time (MRT) ranges between 4.49 and 9.86 μg/mL, 14.29–25.36 min, 200.34–667.22 μg/mL*h, and 34.8–51 min, respectively. Notably, the absolute bioavailability of SA in rabbits was determined to be 86.27%, as calculated by comparing AUC following intraperitoneal administration to that after intravenous injection (Liu et al., 2003). Despite its high bioavailability in rabbits, SA exhibits poor absorption and rapid elimination when taken orally, contributing to its short T1/2 and relatively low bioactivity (Sun et al., 2020). The biodistribution of SA after a single oral dose in mice was also assessed. SA was widely distributed to most organs within 15 min, with the most significant accumulation in the kidneys, followed by the liver, lungs, spleen, and heart. In addition, SA also has the capability to cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). By 120 min, SA had disappeared from most organs. SA primarily distributes to well-perfused tissues such as the liver and kidneys, dependent on blood flow and organ perfusion rates. The significant distribution of SA in the kidneys suggests its clearance mainly through metabolic pathways, while accumulation in the liver reflects a process of passive capture, possibly indicating that part of the drug did not effectively participate in physiological activities. Although direct bioavailability values have not been studied, the rapid elimination rate of the drug, passive accumulation in the liver, and clearance mechanisms through the kidneys could collectively explain the low bioavailability of SA.
SA’s PPs in medicinal plants show significant differences compared to those of the purified metabolite, manifested by varying degrees of increase in AUC, Cmax, MRT, and T1/2 (Table 3). This is attributed to the synergistic effects of various constituents within the extract. Even in scenarios where SA constitutes a minimal proportion of the plant extract, as is the case with Cynanchum auriculatum, where SA accounts for merely 0.01%, the in vivo half-life of SA within rats notably extends to 34.52 h (Sun et al., 2023). It is noteworthy that the study also evaluated the PPs of SA under conditions of functional dyspepsia, finding that the disease state did not significantly impact the PPs of SA. This may imply that the absorption process of SA exhibits a certain degree of robustness, or that its absorption mechanism may rely on pathways not directly affected by the state of the digestive system. It is believed that phenolic metabolites are absorbed mainly through passive diffusion mechanisms or via specific carriers present in the intestine, such as P-glycoprotein and the sodium-glucose linked transporter 1(SGLT1) cotransporter (Lewandowska et al., 2013). However, research on the PPs of SA in vivo under disease conditions remains limited. A deeper understanding of the absorption and metabolism mechanisms of SA in specific health conditions still requires further experimentation and observation. In addition to the synergistic effects between metabolites, existing research has employed various drug delivery system optimization strategies to enhance the oral bioavailability of SA. These include the use of TPGS/F127/F68 mixed polymer microcapsules (Sun et al., 2020), liposomes (Sun et al., 2018), TPGS liposomes (Liu et al., 2019), and self-microemulsifying drug delivery systems (Sun et al., 2021), all of which have been shown to at least double the relative bioavailability.
8 Toxicity and safety assessment
SA is generally considered non-toxic to animals at therapeutic doses (Srinivasulu et al., 2018). A study on the subacute toxicity of SA by Mirza and Panchal, wherein Wistar rats received 1,000 mg/kg/day via oral gavage for 14 days, without significant adverse effects on body weight, food intake, erythropoiesis, leukopoiesis, or the internal organs including the liver, heart, kidneys, pancreas, hippocampus, and sciatic nerve (Mirza and Panchal, 2019). These findings suggest SA is safe within a limited timeframe. However, no clinical studies have been conducted on humans.
An ex vivo study involving 44 individuals, including healthy donors and patients with acute myeloid leukemia, demonstrated that treating peripheral blood mononuclear cells with 10 µM SA for 1 h did not show any signs of cellular damage (Haddadi et al., 2023). Although “Occupational hepatotoxins - Secondary hepatotoxins” describes the potential for a toxic effect in the occupational setting based on human ingestion or animal experimentation (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Syringic-acid), it is important to note that these risks are associated with specific conditions, such as prolonged exposure or high concentrations. Therefore, while passive accumulation of SA in the liver could theoretically contribute to its potential as an occupational hepatotoxin, there is currently no evidence to suggest that such risks are relevant in clinical use, particularly given the therapeutic doses and short exposure times typically involved. According to hazard classification, SA can cause skin, eye, and respiratory irritation (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Syringic-acid). These classifications underline the need for caution when handling SA, especially in occupational environments where exposure risk is higher.
9 Discussion
This review highlights the broad-spectrum pharmacological activities of SA, emphasizing its potent antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties. As elucidated, SA exerts its effects through intricate mechanisms, modulating critical cellular pathways including NRF2, NF-κB, and PI3K/AKT, which play pivotal roles in cellular defense against oxidative stress and inflammation. By influencing these pathways, SA mitigates ERS, apoptosis, and ferroptosis, thereby restoring cellular pathological processes to their normal state. Evidence suggests that SA’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects are primarily mediated through NRF2 activation and NF-κB inhibition.
9.1 Research gap
This review focuses on the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of SA. Despite its promising properties, current research is insufficient, with several critical issues unresolved. Most studies lack systematic in vivo validation, appropriate positive controls, and mechanistic depth. The mechanisms underlying SA’s antioxidant activity remain inadequately elucidated, posing a significant challenge. While SA’s significant anti-inflammatory activity is better supported, the causal relationship between its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities is not well-established. Determining whether SA’s primary action is antioxidant or anti-inflammatory is imperative for future research. Most in vivo studies heavily rely on rats for basic mechanism validation, limiting research depth. Few studies have elucidated the minimum effective antioxidant concentration of SA in vivo. Significant differences exist in the pharmacokinetics of SA derived from medicinal plants compared to the purified metabolite, and its pharmacokinetics in humans remain largely unexplored. Comparative efficacy studies relative to other antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents are scarce. Furthermore, the long-term effects and safety profile of SA, particularly concerning potential hepatotoxicity with prolonged administration, are insufficiently explored.
There also remains a lack of direct target engagement studies, such as protein–ligand interaction assays (e.g., surface plasmon resonance, thermal shift assays, or cellular target validation), to confirm the molecular targets of SA. Structure–activity relationship (SAR) analyses have been insufficiently addressed. Moreover, few studies have directly compared the efficacy of SA with established clinical antioxidants or anti-inflammatory drugs, making it difficult to contextualize its therapeutic relevance.
9.2 Translational potential and challenges in clinical settings
While SA demonstrates substantial antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential in preclinical studies, its translation into clinical settings faces several challenges. SA’s pharmacokinetics, particularly its limited bioavailability, remains a significant hurdle for clinical application. The current research has shown that SA’s bioavailability can be improved via intraperitoneal injection to bypass first-pass metabolism; however, this raises concerns about potential hepatic overexposure and associated toxicity. Optimizing drug delivery methods, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, or polymeric micelles, could improve its therapeutic potential, ensuring better tissue distribution and reducing the risk of toxicity.
Another key challenge is the variability in the pharmacokinetics of SA derived from different sources. The differences in ADME between plant-derived SA and the purified metabolite need to be further studied to understand how these factors may influence clinical outcomes. Additionally, the long-term safety and efficacy of SA, especially with regard to its potential hepatotoxicity after prolonged use, must be carefully evaluated in clinical trials. Furthermore, while SA has demonstrated significant effects in animal models of oxidative stress and inflammation, translating these results to human trials will require robust evidence of its effectiveness and safety at therapeutic doses. There is a need for well-designed clinical studies to establish appropriate dosing regimens and assess the metabolite’s interactions with other therapeutic agents. Combining SA with existing drugs in therapies could also improve treatment outcomes while minimizing side effects.
Future research should prioritize clinical trials to evaluate SA’s efficacy and safety in humans, focusing on its pharmacokinetics, dosage optimization, and potential for synergistic effects with other agents. Mechanistic insights into how SA modulates key signaling pathways such as NRF2, NF-κB, and PI3K/AKT will also be crucial for understanding its therapeutic potential in clinical settings.
9.3 Limitations
Several limitations of this review should be acknowledged. Although this work provides a comprehensive overview of the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of SA, the majority of the included studies are preclinical, with considerable heterogeneity in experimental design, dosage, and model systems. A portion of the included literature is based on in vitro experiments, which, while mechanistically informative, may not fully capture the metabolite’s effects under physiological conditions. Moreover, as SA is a polyphenolic compound, concerns have been raised regarding its potential classification as a pan-assay interference compound (PAINS), known to cause false-positive results in high-throughput or cell-based assays. Nevertheless, structural alert screening using both the ZINC database (https://zinc15.docking.org/) and SwissADME (http://www.swissadme.ch/) revealed no PAINS-associated structural features in SA. While this supports its potential specificity, caution is still warranted when interpreting in vitro findings involving polyphenols.
In addition, potential publication bias cannot be excluded, given that the number of publications highlighting the anti-inflammatory effects of syringic acid substantially exceeds those investigating its antioxidant activity. Studies published in non-English languages or non-indexed journals may have been overlooked. Finally, due to the narrative nature of this review, quantitative comparisons, meta-analyses, or statistical effect size estimations were not performed.
10 Conclusion
In summary, SA has demonstrated considerable antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pharmacological activities, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent. However, further research is needed to clarify its mechanisms of action, optimize its pharmacokinetics, and evaluate its long-term safety and efficacy in clinical settings. By addressing these challenges and focusing on translational research, SA could emerge as a valuable therapeutic option for conditions associated with oxidative stress and inflammation.
Author contributions
ZZ: Investigation, Methodology, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. QY: Methodology, Validation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. YS: Project administration, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. XR: Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82174152), Shanghai Key Clinical Specialty Program (SHSLCZDZK05301), and Project of Shanghai Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Academic Research Studio Construction (SHGZS-202249).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all authors of references.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abijeth, B., and Ezhilarasan, D. (2020). Syringic acid induces apoptosis in human oral squamous carcinoma cells through mitochondrial pathway. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 24 (1), 40–45. doi:10.4103/jomfp.JOMFP_178_19
Ahmed, S. M., Luo, L., Namani, A., Wang, X. J., and Tang, X. (2017). Nrf2 signaling pathway: pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1863 (2), 585–597. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.005
Akarsu, S. A., Gür, C., İleritürk, M., Akaras, N., Küçükler, S., and Kandemir, F. M. (2023). Effect of syringic acid on oxidative stress, autophagy, apoptosis, inflammation pathways against testicular damage induced by lead acetate. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 80, 127315. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127315
Alessandri, A. L., Sousa, L. P., Lucas, C. D., Rossi, A. G., Pinho, V., and Teixeira, M. M. (2013). Resolution of inflammation: mechanisms and opportunity for drug development. Pharmacol. Ther. 139 (2), 189–212. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.04.006
Amarante-Mendes, G. P., Adjemian, S., Branco, L. M., Zanetti, L. C., Weinlich, R., and Bortoluci, K. R. (2018). Pattern recognition receptors and the host cell death molecular machinery. Front. Immunol. 9, 2379. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02379
Aratani, Y. (2018). Myeloperoxidase: its role for host defense, inflammation, and neutrophil function. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 640, 47–52. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2018.01.004
Ashrafizadeh, M., Zarrabi, A., Mirzaei, S., Hashemi, F., Samarghandian, S., Zabolian, A., et al. (2021). Gallic acid for cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms and boosting efficacy by nanoscopical delivery. Food Chem. Toxicol. 157, 112576. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112576
Bai, J., Zhang, Y., Tang, C., Hou, Y., Ai, X., Chen, X., et al. (2021). Gallic acid: pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms involved in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 133, 110985. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110985
Bao, X., Li, W., Jia, R., Meng, D., Zhang, H., and Xia, L. (2023). Molecular mechanism of ferulic acid and its derivatives in tumor progression. Pharmacol. Rep. 75 (4), 891–906. doi:10.1007/s43440-023-00494-0
Bartel, I., Mandryk, I., Horbańczuk, J. O., Wierzbicka, A., and Koszarska, M. (2023). Nutraceutical properties of syringic acid in civilization diseases-review. Nutrients 16 (1), 10. doi:10.3390/nu16010010
Bedard, K., and Krause, K. H. (2007). The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 87 (1), 245–313. doi:10.1152/physrev.00044.2005
Bertheloot, D., Latz, E., and Franklin, B. S. (2021). Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: an intricate game of cell death. Cell Mol. Immunol. 18 (5), 1106–1121. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-00630-3
Bettigole, S. E., and Glimcher, L. H. (2015). Endoplasmic reticulum stress in immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 33, 107–138. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-032414-112116
Bland, D. E., and Logan, A. F. (1965). The properties of syringyl, guaiacyl and p-hydroxyphenyl artificial lignins. Biochem. J. 95 (2), 515–520. doi:10.1042/bj0950515
Bors, W., Kazazic, S. P., Michel, C., Kortenska, V. D., Stettmaier, K., and Klasinc, L. (2002). Methoxyphenols—Antioxidant principles in food plants and spices: pulse radiolysis, EPR spectroscopy, and density functional theory calculations. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 90 (2), 969–979. doi:10.1002/qua.985
Brigelius-Flohé, R., and Flohé, L. (2020). Regulatory phenomena in the glutathione peroxidase superfamily. Antioxid. Redox Signal 33 (7), 498–516. doi:10.1089/ars.2019.7905
Burow, M. E., Weldon, C. B., Melnik, L. I., Duong, B. N., Collins-Burow, B. M., Beckman, B. S., et al. (2000). PI3-K/AKT regulation of NF-kappaB signaling events in suppression of TNF-induced apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 271 (2), 342–345. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.2626
Caliri, A. W., Tommasi, S., and Besaratinia, A. (2021). Relationships among smoking, oxidative stress, inflammation, macromolecular damage, and cancer. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 787, 108365. doi:10.1016/j.mrrev.2021.108365
Cameli, P., Carleo, A., Bergantini, L., Landi, C., Prasse, A., and Bargagli, E. (2020). Oxidant/antioxidant disequilibrium in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis. Inflammation 43 (1), 1–7. doi:10.1007/s10753-019-01059-1
Cao, Y., Zhang, L., Sun, S., Yi, Z., Jiang, X., and Jia, D. (2016). Neuroprotective effects of syringic acid against OGD/R-induced injury in cultured hippocampal neuronal cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 38 (2), 567–573. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2016.2623
Chen, J., Yang, J., Ma, L., Li, J., Shahzad, N., and Kim, C. K. (2020). Structure-antioxidant activity relationship of methoxy, phenolic hydroxyl, and carboxylic acid groups of phenolic acids. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 2611. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-59451-z
Chen, R., Kang, R., and Tang, D. (2022). The mechanism of HMGB1 secretion and release. Exp. Mol. Med. 54 (2), 91–102. doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00736-w
Chen, X., and Cubillos-Ruiz, J. R. (2021). Endoplasmic reticulum stress signals in the tumour and its microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 21 (2), 71–88. doi:10.1038/s41568-020-00312-2
Chen, X., Yu, C., Kang, R., Kroemer, G., and Tang, D. (2021). Cellular degradation systems in ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ. 28 (4), 1135–1148. doi:10.1038/s41418-020-00728-1
Chen, Y. (2011). Studies on the fermentation process of mulberry wine and the antioxidant activity of phenolics[D]. Xi’an, China: Northwest University.
Chimento, A., De Luca, A., D’Amico, M., De Amicis, F., and Pezzi, V. (2023). The involvement of natural polyphenols in molecular mechanisms inducing apoptosis in tumor cells: a promising adjuvant in cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24 (2), 1680. doi:10.3390/ijms24021680
Ciesielska, A., Matyjek, M., and Kwiatkowska, K. (2021). TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 78 (4), 1233–1261. doi:10.1007/s00018-020-03656-y
Cohen, P., and Strickson, S. (2017). The role of hybrid ubiquitin chains in the MyD88 and other innate immune signalling pathways. Cell Death Differ. 24 (7), 1153–1159. doi:10.1038/cdd.2017.17
Conrad, M., and Pratt, D. A. (2019). The chemical basis of ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 15 (12), 1137–1147. doi:10.1038/s41589-019-0408-1
Conte, E., Fruciano, M., Fagone, E., Gili, E., Caraci, F., Iemmolo, M., et al. (2011). Inhibition of PI3K prevents the proliferation and differentiation of human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts: the role of class I P110 isoforms. PLoS One 6 (10), e24663. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024663
Cuadrado, A., Manda, G., Hassan, A., Alcaraz, M. J., Barbas, C., Daiber, A., et al. (2018). Transcription factor NRF2 as a therapeutic target for chronic diseases: a systems medicine approach. Pharmacol. Rev. 70 (2), 348–383. doi:10.1124/pr.117.014753
Culbreth, M., and Aschner, M. (2018). GSK-3β, a double-edged sword in Nrf2 regulation: implications for neurological dysfunction and disease. F1000Res 7, 1043. doi:10.12688/f1000research.15239.1
Dalmagro, A. P., Camargo, A., Severo Rodrigues, A. L., and Zeni, A. L. B. (2019). Involvement of PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway in the antidepressant-like and neuroprotective effects of Morus nigra and its major phenolic, syringic acid. Chem. Biol. Interact. 314, 108843. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2019.108843
Dan Dunn, J., Alvarez, L. A., Zhang, X., and Soldati, T. (2015). Reactive oxygen species and mitochondria: a nexus of cellular homeostasis. Redox Biol. 6, 472–485. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2015.09.005
de Araújo, F. F., de Paulo Farias, D., Neri-Numa, I. A., and Pastore, G. M. (2021). Polyphenols and their applications: an approach in food chemistry and innovation potential. Food Chem. 338, 127535. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127535
Deguine, J., and Barton, G. M. (2014). MyD88: a central player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 6, 97. doi:10.12703/P6-97
Demir, E. A. (2023). Syringic acid alleviates cisplatin-induced ovarian injury through modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation and Nrf2 pathway. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 82, 127356. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2023.127356
Demir, E. A., Demir, S., Kazaz, I. O., Kucuk, H., Alemdar, N. T., Gecici, O. F., et al. (2023). Syringic acid ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced testicular injury in rats via suppressing of HMGB1/NF-κB axis and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 49 (3), 1595–1602. doi:10.1007/s00068-023-02227-7
Ding, H., Wang, G., Yu, Z., Sun, H., and Wang, L. (2022). Role of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and IFN-γ receptor 1/2 (IFNγR1/2) in regulation of immunity, infection, and cancer development: ifn-γ-dependent or independent pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 155, 113683. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113683
Dixon, S. J., Lemberg, K. M., Lamprecht, M. R., Skouta, R., Zaitsev, E. M., Gleason, C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149 (5), 1060–1072. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Dodson, M., Castro-Portuguez, R., and Zhang, D. D. (2019). NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 23, 101107. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101107
Du, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, L., Gao, M., Wang, L., Gan, C., et al. (2017). Simultaneous determination of seven phenolic acids in rat plasma using UHPLC-ESI-MS/MS after oral administration of Echinacea purpurea extract. Molecules 22 (9), 1494. doi:10.3390/molecules22091494
Ekhtiar, M., Ghasemi-Dehnoo, M., Mirzaei, Y., Azadegan-Dehkordi, F., Amini-Khoei, H., Lorigooini, Z., et al. (2023). The coumaric acid and syringic acid ameliorate acetic acid-induced ulcerative colitis in rats via modulator of Nrf2/HO-1 and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Int. Immunopharmacol. 120, 110309. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110309
Eom, T. K., Senevirathne, M., and Kim, S. K. (2012). Synthesis of phenolic acid conjugated chitooligosaccharides and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 34 (2), 519–527. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2012.05.004
Fagone, E., Conte, E., Gili, E., Fruciano, M., Pistorio, M. P., Lo Furno, D., et al. (2011). Resveratrol inhibits transforming growth factor-β-induced proliferation and differentiation of ex vivo human lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts through ERK/akt inhibition and PTEN restoration. Exp. Lung Res. 37 (3), 162–174. doi:10.3109/01902148.2010.524722
Fang, W., Zhu, S., Niu, Z., and Yin, Y. (2019). The protective effect of syringic acid on dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in BALB/c mice. Drug Dev. Res. 80 (6), 731–740. doi:10.1002/ddr.21524
Fão, L., Mota, S. I., and Rego, A. C. (2019). Shaping the Nrf2-ARE-related pathways in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 54, 100942. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2019.100942
Farhan, M., and Rizvi, A. (2022). Understanding the prooxidant action of plant polyphenols in the cellular microenvironment of malignant cells: role of copper and therapeutic implications. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 929853. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.929853
Farhan, M., Zafar, A., Chibber, S., Khan, H. Y., Arif, H., and Hadi, S. M. (2015). Mobilization of copper ions in human peripheral lymphocytes by Catechins leading to oxidative DNA breakage: a structure activity study. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 580, 31–40. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2015.06.019
Ferah Okkay, I., Okkay, U., Gundogdu, O. L., Bayram, C., Mendil, A. S., Ertugrul, M. S., et al. (2022). Syringic acid protects against thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy: behavioral, biochemical, and molecular evidence. Neurosci. Lett. 769, 136385. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136385
Ferries-Rowe, E., Corey, E., and Archer, J. S. (2020). Primary dysmenorrhea: diagnosis and therapy. Obstet. Gynecol. 136 (5), 1047–1058. doi:10.1097/AOG.0000000000004096
Filomeni, G., De Zio, D., and Cecconi, F. (2015). Oxidative stress and autophagy: the clash between damage and metabolic needs. Cell Death Differ. 22 (3), 377–388. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.150
Forman, H. J., and Zhang, H. (2021). Targeting oxidative stress in disease: promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 20 (9), 689–709. doi:10.1038/s41573-021-00233-1
Forman, H. J., Zhang, H., and Rinna, A. (2009). Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med. 30 (1-2), 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006
Fu, Y. P., Zou, Y. F., Lei, F. Y., Wangensteen, H., and Inngjerdingen, K. T. (2022). Aconitum carmichaelii debeaux: a systematic review on traditional use, and the chemical structures and pharmacological properties of polysaccharides and phenolic compounds in the roots. J. Ethnopharmacol. 291, 115148. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2022.115148
Ge, E. J., Bush, A. I., Casini, A., Cobine, P. A., Cross, J. R., DeNicola, G. M., et al. (2022). Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 22 (2), 102–113. doi:10.1038/s41568-021-00417-2
Ghasemi-Dehnoo, M., Amini-Khoei, H., Lorigooini, Z., AnjomShoa, M., Bijad, E., and Rafieian-Kopaei, M. (2024). Inhibition of TLR4, NF-κB, and INOS pathways mediates ameliorative effect of syringic acid in experimental ulcerative colitis in rats. Inflammopharmacology 32 (1), 795–808. doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01387-7
Gheena, S., and Ezhilarasan, D. (2019). Syringic acid triggers reactive oxygen species-mediated cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 38 (6), 694–702. doi:10.1177/0960327119839173
Gheena, S., Ezhilarasan, D., Shree Harini, K., and Rajeshkumar, S. (2022). Syringic acid and silymarin concurrent administration inhibits sodium valproate-induced liver injury in rats. Environ. Toxicol. 37 (9), 2143–2152. doi:10.1002/tox.23557
Grimes, C. A., and Jope, R. S. (2001). The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog. Neurobiol. 65 (4), 391–426. doi:10.1016/s0301-0082(01)00011-9
Güven, M., Aras, A. B., Topaloğlu, N., Özkan, A., Şen, H. M., Kalkan, Y., et al. (2015). The protective effect of syringic acid on ischemia injury in rat brain. Turk J. Med. Sci. 45 (1), 233–240. doi:10.3906/sag-1402-71
Güzelad, Ö., Özkan, A., Parlak, H., Sinen, O., Afşar, E., Öğüt, E., et al. (2021). Protective mechanism of syringic acid in an experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Metab. Brain Dis. 36 (5), 1003–1014. doi:10.1007/s11011-021-00704-9
Habza-Kowalska, E., Kaczor, A. A., Bartuzi, D., Piłat, J., and Gawlik-Dziki, U. (2021). Some dietary phenolic compounds can activate thyroid peroxidase and inhibit lipoxygenase-preliminary study in the model systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (10), 5108. doi:10.3390/ijms22105108
Haddadi, N., Mirzania, M., and Ansarihadipour, H. (2023). Syringic acid attenuates oxidative stress in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Nutr. Cancer 75 (3), 1038–1049. doi:10.1080/01635581.2023.2170432
Ham, J. R., Lee, H. I., Choi, R. Y., Sim, M. O., Seo, K. I., and Lee, M. K. (2016). Anti-steatotic and anti-inflammatory roles of syringic acid in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 7 (2), 689–697. doi:10.1039/c5fo01329a
Hawkins, C. L. (2020). Hypochlorous acid-mediated modification of proteins and its consequences. Essays Biochem. 64 (1), 75–86. doi:10.1042/EBC20190045
Helli, B., Navabi, S. P., Hosseini, S. A., Sabahi, A., Khorsandi, L., Amirrajab, N., et al. (2024). The protective effects of syringic acid on bisphenol A-induced neurotoxicity possibly through AMPK/PGC-1α/Fndc5 and CREB/BDNF signaling pathways. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 7767–7784. doi:10.1007/s12035-024-04048-0
Henshaw, F. R., Dewsbury, L. S., Lim, C. K., and Steiner, G. Z. (2021). The effects of cannabinoids on Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines: a systematic review of in vivo studies. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 6 (3), 177–195. doi:10.1089/can.2020.0105
Hsieh, P. C., Kuo, C. Y., Lee, Y. H., Wu, Y. K., Yang, M. C., Tzeng, I. S., et al. (2020). Therapeutic effects and mechanisms of actions of Descurainia sophia. Int. J. Med. Sci. 17 (14), 2163–2170. doi:10.7150/ijms.47357
Hu, J. H., Weng, L. L., Wu, Y. X., and Chen, T. L. (2022). Study on chemical composition difference and analgesic effect of Paeonia lactiflora before and after being processed with wine. China Pharm. 33 (22), 2738–2742.
Hybertson, B. M., Gao, B., Bose, S. K., and McCord, J. M. (2011). Oxidative stress in health and disease: the therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activation. Mol. Asp. Med. 32 (4-6), 234–246. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2011.10.006
Itoh, A., Isoda, K., Kondoh, M., Kawase, M., Kobayashi, M., Tamesada, M., et al. (2009). Hepatoprotective effect of syringic acid and vanillic acid on concanavalin a-induced liver injury. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 32 (7), 1215–1219. doi:10.1248/bpb.32.1215
Joffre, J., and Hellman, J. (2021). Oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction in sepsis and acute inflammation. Antioxid. Redox Signal 35 (15), 1291–1307. doi:10.1089/ars.2021.0027
Jomova, K., Raptova, R., Alomar, S. Y., Alwasel, S. H., Nepovimova, E., Kuca, K., et al. (2023). Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 97 (10), 2499–2574. doi:10.1007/s00204-023-03562-9
Kattoor, A. J., Pothineni, N. V. K., Palagiri, D., and Mehta, J. L. (2017). Oxidative stress in atherosclerosis. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 19 (11), 42. doi:10.1007/s11883-017-0678-6
Kawahara, K., Hohjoh, H., Inazumi, T., Tsuchiya, S., and Sugimoto, Y. (2015). Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: relevance of prostaglandin E receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1851 (4), 414–421. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.07.008
Kerins, M. J., and Ooi, A. (2018). The roles of NRF2 in modulating cellular iron homeostasis. Antioxid. Redox Signal 29 (17), 1756–1773. doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7176
Kesavardhana, S., Malireddi, R. K. S., and Kanneganti, T. D. (2020). Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and pyroptosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 38, 567–595. doi:10.1146/annurev-immunol-073119-095439
Kessenbrock, K., Plaks, V., and Werb, Z. (2010). Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 141 (1), 52–67. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.015
Ketelut-Carneiro, N., and Fitzgerald, K. A. (2022). Apoptosis, Pyroptosis, and Necroptosis-Oh My! The Many Ways a Cell Can Die. J. Mol. Biol. 434 (4), 167378. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167378
Khatun, A., Panchali, T., Gorai, S., Dutta, A., Das, T. K., Ghosh, K., et al. (2023). Impaired brain equanimity and neurogenesis in the diet-induced overweight mouse: a preventive role by syringic acid treatment. Nutr. Neurosci. 27, 271–288. doi:10.1080/1028415x.2023.2187510
Kim, M. J., and Jeon, J. H. (2022). Recent advances in understanding Nrf2 agonism and its potential clinical application to metabolic and inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (5), 2846. doi:10.3390/ijms23052846
Kondylis, V., Kumari, S., Vlantis, K., and Pasparakis, M. (2017). The interplay of IKK, NF-κB and RIPK1 signaling in the regulation of cell death, tissue homeostasis and inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 277 (1), 113–127. doi:10.1111/imr.12550
Kosuru, R. Y., Roy, A., Das, S. K., and Bera, S. (2018). Gallic acid and gallates in human health and disease: do mitochondria hold the key to success? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 62 (1). doi:10.1002/mnfr.201700699
Kumar, S., Prahalathan, P., and Raja, B. (2012). Syringic acid ameliorates (L)-NAME-induced hypertension by reducing oxidative stress. Naunyn Schmiedeb. Arch. Pharmacol. 385 (12), 1175–1184. doi:10.1007/s00210-012-0802-7
Lai, T. T., Yang, C. M., and Yang, C. H. (2020). Astaxanthin protects retinal photoreceptor cells against high glucose-induced oxidative stress by induction of antioxidant enzymes via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Antioxidants (Basel) 9 (8), 729. doi:10.3390/antiox9080729
Lee, D. F., Kuo, H. P., Liu, M., Chou, C. K., Xia, W., Du, Y., et al. (2009). KEAP1 E3 ligase-mediated downregulation of NF-kappaB signaling by targeting IKKbeta. Mol. Cell 36 (1), 131–140. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.07.025
Lewandowska, U., Szewczyk, K., Hrabec, E., Janecka, A., and Gorlach, S. (2013). Overview of metabolism and bioavailability enhancement of polyphenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61 (50), 12183–12199. doi:10.1021/jf404439b
Li, D., Luo, D., Hu, S., Zhao, H., and Peng, B. (2023). Syringic acid suppressed proliferation, invasion, and migration via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinases expression on glioblastoma cells by promoting apoptosis. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 24 (2), 310–316. doi:10.2174/1389201023666220513100129
Li, X., Zhang, X., Xing, R., Qi, F., Dong, J., Li, D., et al. (2021). Syringic acid demonstrates promising protective effect against tau fibrillization and cytotoxicity through regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated pathway as a prelude to Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 192, 491–497. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.173
Liu, G., Zhang, B. F., Hu, Q., Liu, X. P., and Chen, J. (2020). Syringic acid mitigates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 531 (2), 242–249. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.047
Liu., J., Wang, W., Chen, L., Li, Y., Zhao, S., and Liang, Y. (2021). Chemoprotective effect of syringic acid on cyclophosphamide induced ovarian damage via inflammatory pathway. J. Oleo Sci. 70 (5), 675–683. doi:10.5650/jos.ess21023
Liu, L., Cui, Z. X., Yang, X. W., Xu, W., Zhang, Y. B., Li, F. J., et al. (2020). Simultaneous characterisation of multiple Mahonia fortunei bioactive compounds in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS for application in pharmacokinetic studies and anti-inflammatory activity in vitro. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 179, 113013. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2019.113013
Liu, M. R., Zhu, W. T., and Pei, D. S. (2021). System Xc(-): a key regulatory target of ferroptosis in cancer. Invest New Drugs 39 (4), 1123–1131. doi:10.1007/s10637-021-01070-0
Liu, Y., Guo, X., Lü, Z., and Xie, W. (2003). Study on the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of syringic acid in rabbits. Zhong Yao Cai 26 (11), 798–801.
Liu, Y., Sun, C., Li, W., Adu-Frimpong, M., Wang, Q., Yu, J., et al. (2019). Preparation and characterization of syringic acid-loaded TPGS liposome with enhanced oral bioavailability and in vivo antioxidant efficiency. AAPS PharmSciTech 20 (3), 98. doi:10.1208/s12249-019-1290-6
Liu, Z. Q. (2020). Bridging free radical chemistry with drug discovery: a promising way for finding novel drugs efficiently. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 189, 112020. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.112020
Loboda, A., Damulewicz, M., Pyza, E., Jozkowicz, A., and Dulak, J. (2016). Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 73 (17), 3221–3247. doi:10.1007/s00018-016-2223-0
Lu, M. C., Ji, J. A., Jiang, Z. Y., and You, Q. D. (2016). The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: an update. Med. Res. Rev. 36 (5), 924–963. doi:10.1002/med.21396
Luo, Q., Gong, P., Shi, R., Chen, W., Wang, C., Zhang, C., et al. (2023). Syringic acid alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by modulating gut microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71 (22), 8458–8470. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02441
Mallan, S., and Singh, S. (2023). Syringic acid alleviates valproic acid induced autism via activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase: possible molecular approach. Environ. Toxicol. 38 (10), 2400–2415. doi:10.1002/tox.23876
Mansouri, A., Reiner, Ž., Ruscica, M., Tedeschi-Reiner, E., Radbakhsh, S., Bagheri Ekta, M., et al. (2022). Antioxidant effects of statins by modulating Nrf2 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in different diseases. J. Clin. Med. 11 (5), 1313. doi:10.3390/jcm11051313
Manjunatha, S., Shaik, A. H., E, M. P., Al Omar, S. Y., Mohammad, A., and Kodidhela, L. D. (2020). Combined cardio-protective ability of syringic acid and resveratrol against isoproterenol induced cardio-toxicity in rats via attenuating NF-kB and TNF-α pathways. Sci. Rep. 10 (1), 3426. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-59925-0
Marciniak, S. J., Yun, C. Y., Oyadomari, S., Novoa, I., Zhang, Y., Jungreis, R., et al. (2004). CHOP induces death by promoting protein synthesis and oxidation in the stressed endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 18 (24), 3066–3077. doi:10.1101/gad.1250704
Martin, D., Rojo, A. I., Salinas, M., Diaz, R., Gallardo, G., Alam, J., et al. (2004). Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and the Nrf2 transcription factor in response to the antioxidant phytochemical carnosol. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (10), 8919–8929. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309660200
Matsubara, K., Higaki, T., Matsubara, Y., and Nawa, A. (2015). Nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16 (3), 4600–4614. doi:10.3390/ijms16034600
Medzhitov, R. (2008). Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454 (7203), 428–435. doi:10.1038/nature07201
Meulmeester, F. L., Luo, J., Martens, L. G., Mills, K., van Heemst, D., and Noordam, R. (2022). Antioxidant supplementation in oxidative stress-related diseases: what have we learned from studies on alpha-tocopherol? Antioxidants (Basel) 11 (12), 2322. doi:10.3390/antiox11122322
Mihanfar, A., Darband, S. G., Sadighparvar, S., Kaviani, M., Mirza-Aghazadeh-Attari, M., Yousefi, B., et al. (2021). In vitro and in vivo anticancer effects of syringic acid on colorectal cancer: possible mechanistic view. Chem. Biol. Interact. 337, 109337. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109337
Milla, E., and Kerpper, I. (2023). Effectiveness of standardized red Orange extract. Ger. J. Vet. Res. 3 (2), 35–40. doi:10.51585/gjvr.2023.2.0057
Mirza, A. C., and Panchal, S. S. (2019). Safety evaluation of syringic acid: subacute oral toxicity studies in wistar rats. Heliyon 5 (8), e02129. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02129
Mitchell, S., Vargas, J., and Hoffmann, A. (2016). Signaling via the NFκB system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 8 (3), 227–241. doi:10.1002/wsbm.1331
Nakagawa, Y., and Tayama, S. (2000). Metabolism and cytotoxicity of bisphenol A and other bisphenols in isolated rat hepatocytes. Arch. Toxicol. 74 (2), 99–105. doi:10.1007/s002040050659
Nandi, A., Yan, L. J., Jana, C. K., and Das, N. (2019). Role of catalase in oxidative stress- and age-associated degenerative diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 9613090. doi:10.1155/2019/9613090
Nimse, S. B., and Pal, D. (2015). Free radicals, natural antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. RSC Adv. 5 (35), 27986–28006. doi:10.1039/c4ra13315c
Oakes, S. A., and Papa, F. R. (2015). The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 10, 173–194. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-012513-104649
Ogut, E., Armagan, K., and Gül, Z. (2022). The role of syringic acid as a neuroprotective agent for neurodegenerative disorders and future expectations. Metab. Brain Dis. 37 (4), 859–880. doi:10.1007/s11011-022-00960-3
Ogut, E., Sekerci, R., Akcay, G., Yildirim, F. B., Derin, N., Aslan, M., et al. (2019). Protective effects of syringic acid on neurobehavioral deficits and hippocampal tissue damages induced by sub-chronic deltamethrin exposure. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 76, 106839. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2019.106839
Opal, S. M., and DePalo, V. A. (2000). Anti-inflammatory cytokines. Chest 117 (4), 1162–1172. doi:10.1378/chest.117.4.1162
Ouyang, L., Shi, Z., Zhao, S., Wang, F. T., Zhou, T. T., Liu, B., et al. (2012). Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: a review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 45 (6), 487–498. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2184.2012.00845.x
Ozga, A. J., Chow, M. T., and Luster, A. D. (2021). Chemokines and the immune response to cancer. Immunity 54 (5), 859–874. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.01.012
Parker, S., May, B., Zhang, C., Zhang, A. L., Lu, C., and Xue, C. C. (2016). A pharmacological review of bioactive constituents of Paeonia lactiflora pallas and Paeonia veitchii Lynch. Phytother. Res. 30 (9), 1445–1473. doi:10.1002/ptr.5653
Parmar, A., Singh, K., Bahadur, A., Marangoni, G., and Bahadur, P. (2011). Interaction and solubilization of some phenolic antioxidants in pluronic® micelles. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 86 (2), 319–326. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2011.04.015
Pei, J., Velu, P., Zareian, M., Feng, Z., and Vijayalakshmi, A. (2021). Effects of syringic acid on apoptosis, inflammation, and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Front. Nutr. 8, 788929. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.788929
Pérez-Torres, I., Castrejón-Téllez, V., Soto, M. E., Rubio-Ruiz, M. E., Manzano-Pech, L., and Guarner-Lans, V. (2021). Oxidative stress, plant natural antioxidants, and obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (4), 1786. doi:10.3390/ijms22041786
Phaniendra, A., Jestadi, D. B., and Periyasamy, L. (2015). Free radicals: properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 30 (1), 11–26. doi:10.1007/s12291-014-0446-0
Poljsak, B., Šuput, D., and Milisav, I. (2013). Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 956792. doi:10.1155/2013/956792
Poznyak, A., Grechko, A. V., Poggio, P., Myasoedova, V. A., Alfieri, V., and Orekhov, A. N. (2020). The diabetes mellitus-atherosclerosis connection: the role of lipid and glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (5), 1835. doi:10.3390/ijms21051835
Propper, D. J., and Balkwill, F. R. (2022). Harnessing cytokines and chemokines for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 19 (4), 237–253. doi:10.1038/s41571-021-00588-9
Pryor, W. A. (1988). Why is the hydroxyl radical the only radical that commonly adds to DNA? Hypothesis: it has a rare combination of high electrophilicity, high thermochemical reactivity, and a mode of production that can occur near DNA. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 4 (4), 219–223. doi:10.1016/0891-5849(88)90043-3
Rada, P., Rojo, A. I., Chowdhry, S., McMahon, M., Hayes, J. D., and Cuadrado, A. (2011). SCF/{beta}-TrCP promotes glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent degradation of the Nrf2 transcription factor in a Keap1-independent manner. Mol. Cell Biol. 31 (6), 1121–1133. doi:10.1128/MCB.01204-10
Rajendra Prasad, N., Karthikeyan, A., Karthikeyan, S., and Reddy, B. V. (2011). Inhibitory effect of caffeic acid on cancer cell proliferation by oxidative mechanism in human HT-1080 fibrosarcoma cell line. Mol. Cell Biochem. 349 (1-2), 11–19. doi:10.1007/s11010-010-0655-7
Razzaghi-Asl, N., Garrido, J., Khazraei, H., Borges, F., and Firuzi, O. (2013). Antioxidant properties of hydroxycinnamic acids: a review of structure-activity relationships. Curr. Med. Chem. 20 (36), 4436–4450. doi:10.2174/09298673113209990141
Read, A., and Schröder, M. (2021). The unfolded protein response: an overview. Biol. (Basel) 10 (5), 384. doi:10.3390/biology10050384
Redza-Dutordoir, M., and Averill-Bates, D. A. (2016). Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1863 (12), 2977–2992. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012
Ren, J., Yang, M., Xu, F., Chen, J., and Ma, S. (2019). Acceleration of wound healing activity with syringic acid in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 233, 116728. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116728
Reuter, S., Gupta, S. C., Chaturvedi, M. M., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2010). Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 49 (11), 1603–1616. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.09.006
Roh, J. L., Kim, E. H., Jang, H., and Shin, D. (2017). Nrf2 inhibition reverses the resistance of cisplatin-resistant head and neck cancer cells to artesunate-induced ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 11, 254–262. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.010
Rojo, A. I., Sagarra, M. R., and Cuadrado, A. (2008). GSK-3beta down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf2 after oxidant damage: relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress. J. Neurochem. 105 (1), 192–202. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05124.x
Ryter, S. W. (2022). Heme oxygenase-1: an anti-inflammatory effector in cardiovascular, lung, and related metabolic disorders. Antioxidants (Basel) 11 (3), 555. doi:10.3390/antiox11030555
Saha, S., Buttari, B., Panieri, E., Profumo, E., and Saso, L. (2020). An overview of Nrf2 signaling pathway and its role in inflammation. Molecules 25 (22), 5474. doi:10.3390/molecules25225474
Senoner, T., and Dichtl, W. (2019). Oxidative stress in cardiovascular diseases: still a therapeutic target? Nutrients 11 (9), 2090. doi:10.3390/nu11092090
Sha, W., Zhao, B., Wei, H., Yang, Y., Yin, H., Gao, J., et al. (2023). Astragalus polysaccharide ameliorates vascular endothelial dysfunction by stimulating macrophage M2 polarization via potentiating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 112, 154667. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154667
Shahzad, S., Mateen, S., Naeem, S. S., Akhtar, K., Rizvi, W., and Moin, S. (2019). Syringic acid protects from isoproterenol induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 849, 135–145. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.01.056
Sherkhane, B., Yerra, V. G., Sharma, A., Kumar, K. A., Chayanika, G., Kumar, A. V., et al. (2023). Nephroprotective potential of syringic acid in experimental diabetic nephropathy: focus on oxidative stress and autophagy. Indian J. Pharmacol. 55 (1), 34–42. doi:10.4103/ijp.ijp_671_22
Sinha, K., Das, J., Pal, P. B., and Sil, P. C. (2013). Oxidative stress: the mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 87 (7), 1157–1180. doi:10.1007/s00204-013-1034-4
Skroza, D., Šimat, V., Vrdoljak, L., Jolić, N., Skelin, A., Čagalj, M., et al. (2022). Investigation of antioxidant synergisms and antagonisms among phenolic acids in the model matrices using FRAP and ORAC methods. Antioxidants (Basel) 11 (9), 1784. doi:10.3390/antiox11091784
Somade, O. T., Adeyi, O. E., Ajayi, B. O., Asunde, O. O., Iloh, P. D., Adesanya, A. A., et al. (2022). Syringic and ascorbic acids prevent NDMA-Induced pulmonary fibrogenesis, inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress through the regulation of PI3K-Akt/PKB-mTOR-PTEN signaling pathway. Metabol. Open 14, 100179. doi:10.1016/j.metop.2022.100179
Song, M., Du, Z., Lu, G., Li, P., and Wang, L. (2016). Syringic acid protects retinal ganglion cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis through the activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 62 (6), 50–54.
Srinivas, U. S., Tan, B. W. Q., Vellayappan, B. A., and Jeyasekharan, A. D. (2019). ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox Biol. 25, 101084. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2018.101084
Srinivasulu, C., Ramgopal, M., Ramanjaneyulu, G., Anuradha, C. M., and Suresh Kumar, C. (2018). Syringic acid (SA) ‒ A review of its occurrence, biosynthesis, pharmacological and industrial importance. Biomed. Pharmacother. 108, 547–557. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.069
Stockwell, B. R., Friedmann Angeli, J. P., Bayir, H., Bush, A. I., Conrad, M., Dixon, S. J., et al. (2017). Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 171 (2), 273–285. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
Stuehr, D. J., and Haque, M. M. (2019). Nitric oxide synthase enzymology in the 20 years after the nobel prize. Br. J. Pharmacol. 176 (2), 177–188. doi:10.1111/bph.14533
Sun, C., Li, W., Ma, P., Li, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). Development of TPGS/F127/F68 mixed polymeric micelles: enhanced oral bioavailability and hepatoprotection of syringic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 137, 111126. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2020.111126
Sun, C., Li, W., Zhang, H., Adu-Frimpong, M., Ma, P., Zhu, Y., et al. (2021). Improved oral bioavailability and hypolipidemic effect of syringic acid via a self-microemulsifying drug delivery system. AAPS PharmSciTech 22 (1), 45. doi:10.1208/s12249-020-01901-y
Sun, C., Yuan, Y., Omari-Siaw, E., Tong, S., Zhu, Y., Wang, Q., et al. (2018). An efficient HPLC method for determination of syringic acid liposome in rats plasma and mice tissues: pharmacokinetic and biodistribution application. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 14 (1), 41–52. doi:10.2174/1573412912666160926101220
Sun, J., Meng, X., Huang, D., Gong, Z., Liu, C., Liu, T., et al. (2023). Pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of four major bioactive components of Cynanchum auriculatum extract: a UPLC-MS/MS study in normal and functional dyspepsia rats. Front. Pharmacol. 14, 1279971. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1279971
Sun, X., Ou, Z., Chen, R., Niu, X., Chen, D., Kang, R., et al. (2016). Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 63 (1), 173–184. doi:10.1002/hep.28251
Teleanu, D. M., Niculescu, A. G., Lungu, I. I., Radu, C. I., Vladâcenco, O., Roza, E., et al. (2022). Neurotransmitters-key factors in neurological and neurodegenerative disorders of the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (11), 5954. doi:10.3390/ijms23115954
Tokmak, M., Sehitoglu, M. H., Yuksel, Y., Guven, M., Akman, T., Aras, A. B., et al. (2017). The axon protective effects of syringic acid on ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat sciatic nerve model. Turk Neurosurg. 27 (1), 124–132. doi:10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.14656-15.5
Tokmak, M., Yuksel, Y., Sehitoglu, M. H., Guven, M., Akman, T., Aras, A. B., et al. (2015). The neuroprotective effect of syringic acid on spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Inflammation 38 (5), 1969–1978. doi:10.1007/s10753-015-0177-2
Tonelli, C., Chio, I. I. C., and Tuveson, D. A. (2018). Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid. Redox Signal 29 (17), 1727–1745. doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7342
Tu, W., Wang, H., Li, S., Liu, Q., and Sha, H. (2019). The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis. 10 (3), 637–651. doi:10.14336/AD.2018.0513
Velu, P., Vinothkumar, V., Babukumar, S., and Ramachandhiran, D. (2017). Chemopreventive effect of syringic acid on 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene induced hamster buccal pouch carcinogenesis. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 27 (8), 631–640. doi:10.1080/15376516.2017.1349227
Vijayan, V., Wagener, F., and Immenschuh, S. (2018). The macrophage heme-heme oxygenase-1 system and its role in inflammation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 153, 159–167. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2018.02.010
Wang, F., Qi, Y., Gao, Y., Wang, Z., Shen, X., and Wu, H. (2023). Syringic acid suppresses ferroptosis of skeletal muscle cells to alleviate lower limb ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via the HMGB1 pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 102 (6), 1387–1398. doi:10.1111/cbdd.14326
Wang, M., Gao, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhao, Q., Tan, X., Wu, S., et al. (2023). Syringic acid promotes cartilage extracellular matrix generation and attenuates osteoarthritic cartilage degradation by activating TGF-β/Smad and inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 38, 1000–1012. doi:10.1002/ptr.8089
Wang, M. H., Hsiao, G., and Al-Shabrawey, M. (2020). Eicosanoids and oxidative stress in diabetic retinopathy. Antioxidants (Basel) 9 (6), 520. doi:10.3390/antiox9060520
Wang, S., Mateos, R., Goya, L., Amigo-Benavent, M., Sarriá, B., and Bravo, L. (2016). A phenolic extract from grape by-products and its main hydroxybenzoic acids protect Caco-2 cells against pro-oxidant induced toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 88, 65–74. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2015.12.005
Wang, Y., Branicky, R., Noë, A., and Hekimi, S. (2018). Superoxide dismutases: dual roles in controlling ROS damage and regulating ROS signaling. J. Cell Biol. 217 (6), 1915–1928. doi:10.1083/jcb.201708007
Watson, N., Ding, B., Zhu, X., and Frisina, R. D. (2017). Chronic inflammation - inflammaging - in the ageing cochlea: a novel target for future presbycusis therapy. Ageing Res. Rev. 40, 142–148. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2017.10.002
Wiseman, R. L., Mesgarzadeh, J. S., and Hendershot, L. M. (2022). Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell 82 (8), 1477–1491. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2022.03.025
Xiang, S., and Xiao, J. (2022). Protective effects of syringic acid on inflammation, apoptosis and intestinal barrier function in Caco-2 cells following oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury. Exp. Ther. Med. 23 (1), 66. doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10989
Xie, Y., Hou, W., Song, X., Yu, Y., Huang, J., Sun, X., et al. (2016). Ferroptosis: process and function. Cell Death Differ. 23 (3), 369–379. doi:10.1038/cdd.2015.158
Xu, X., Lei, Y., Chen, L., Zhou, H., Liu, H., Jiang, J., et al. (2021). Phosphorylation of NF-κBp65 drives inflammation-mediated hepatocellular carcinogenesis and is a novel therapeutic target. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40 (1), 253. doi:10.1186/s13046-021-02062-x
Xu, Y., Tang, G., Zhang, C., Wang, N., and Feng, Y. (2021). Gallic acid and diabetes mellitus: its association with oxidative stress. Molecules 26 (23), 7115. doi:10.3390/molecules26237115
Yan, J., Zhang, Y., Wang, L., Li, Z., Tang, S., Wang, Y., et al. (2022). TREM2 activation alleviates neural damage via Akt/CREB/BDNF signalling after traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neuroinflammation 19 (1), 289. doi:10.1186/s12974-022-02651-3
Yan, S. L., Wang, Z. H., Yen, H. F., Lee, Y. J., and Yin, M. C. (2016). Reversal of ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity by cinnamic and syringic acids in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 98 (Pt B), 119–126. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2016.10.025
Yang, L., Hu, X., and Mo, Y. Y. (2019). Acidosis promotes tumorigenesis by activating AKT/NF-κB signaling. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 38 (1-2), 179–188. doi:10.1007/s10555-019-09785-6
Yang, N., Qiu, F., Zhu, F., and Qi, L. (2020). Therapeutic potential of zinc oxide-loaded syringic acid against in vitro and in vivo model of lung cancer. Int. J. Nanomedicine 15, 8249–8260. doi:10.2147/IJN.S272997
Yang, X. W. (2020). Material basis research of anti-COVID-19 huashibaidu granule gormula. Mod. Chin. Med. 22 (05), 672–689.
Yu, C., and Xiao, J. H. (2021). The Keap1-Nrf2 system: a mediator between oxidative stress and aging. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 6635460. doi:10.1155/2021/6635460
Yu, M., Qi, B., Xiaoxiang, W., Xu, J., and Liu, X. (2017). Baicalein increases cisplatin sensitivity of A549 lung adenocarcinoma cells via PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 90, 677–685. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.001
Zhang, H., Qin, H., Zhou, C., Feng, Q., Yang, Y., Sui, J., et al. (2020). Gene expression profile of lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells reversed by syringic acid. Mol. Med. Rep. 22 (6), 5012–5022. doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11632
Zhang, H. Y., Sun, Y. M., and Wang, X. L. (2002). Electronic effects on O-H proton dissociation energies of phenolic cation radicals: a DFT study. J. Org. Chem. 67 (8), 2709–2712. doi:10.1021/jo016234y
Zhou, X., Wang, H., Burg, M. B., and Ferraris, J. D. (2013). Inhibitory phosphorylation of GSK-3β by AKT, PKA, and PI3K contributes to high NaCl-induced activation of the transcription factor NFAT5 (TonEBP/OREBP). Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 304 (7), F908–F917. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00591.2012
Zhu, Y., Wei, S., Cao, X., Wang, S., Chang, Y., Ouyang, H., et al. (2022). Multi-component pharmacokinetic study of Prunus mume fructus extract after oral administration in rats using UPLC-MS/MS. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 954692. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.954692
Zinatizadeh, M. R., Schock, B., Chalbatani, G. M., Zarandi, P. K., Jalali, S. A., and Miri, S. R. (2021). The nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB) signaling in cancer development and immune diseases. Genes Dis. 8 (3), 287–297. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2020.06.005
Glossary
4-HNE 4-hydroxynonenal
AKT Protein kinase B
APAF1 Apoptotic protease activating factor 1
ARE Antioxidant response element
ATF6 Activating transcription factor 6
BAX BCL-2-associated X
BAK BCL-2-antagonist/killer
BCL-2 B-cell lymphoma 2
BVR Biliverdin reductase
CAT catalase
CHOP C/EBP homologous protein
CO Carbon monoxide
COX-2 Cyclooxygenase-2
CREB cAMP response element-binding protein
Crm1 Chromosomal region maintenance 1
Cul3 cullin-3
Cys cystine
ERS Endoplasmic reticulum stress
Fyn Fyn tyrosine kinase
GA Gallic acid
Glu Glutamate
GPx Glutathione peroxidase
GRP78 Glucose-regulated protein 78
GSH Glutathione
GSK-3β Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
GST Glutathione S-transferase
HMGB1 High mobility group box 1
HO-1 Heme oxygenase-1
H/R Hypoxia/reoxygenation
IFN-γ Interferon-γ
IKK IκB kinase
IκB Inhibitor κB
IL Interleukin
iNOS Inducible nitric oxide synthase
I/R Ischemia/reperfusion
IRE1 Inositol-requiring enzyme 1
KEAP1 Cytoplasmic kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1
L-NAME Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester
LOX Lipoxygenase
MDA Malondialdehyde
MPO Myeloperoxidase
MyD88 Myeloid differentiation primary response 88
NADPH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
NDMA N-nitrosodimethylamine
NF-κB Nuclear factor-kappa B
NO Nitric oxide
NOS NO synthase
NOX NADPH oxidase
NQO1 NADPH quinone oxidoreductase enzyme
NRF2 Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
OGD/R Oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation
PERK Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
PGE2 Prostaglandin E2
PI3K Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase
PIP2 Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate
PIP3 Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate
PPs Pharmacokinetic properties
RBX1 Ring-box 1
RNS Reactive nitrogen species
ROS Reactive oxygen species
SA Syringic acid
SLC7A11 Solute carrier family 7 member 11
sMAF small musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma
SOD Superoxide dismutase
TAS Total antioxidant status
TCM Traditional Chinese medicine
Tf Transferrin
TLR Toll-like receptor
TNF-α Tumor necrosis factor-α
TNFR1 Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1
TOS Total oxidant status
TRAF6 Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6
UPR Unfolded protein response.
Keywords: syringic acid (PubChem CID 10742), oxidative stress, inflammation, pharmacological activity, pharmacokinetics, toxicity
Citation: Zhao Z, Yang Q, Sun Y and Ruan X (2025) Unveiling the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of syringic acid: mechanistic insights and pathway interactions. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1615294. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1615294
Received: 21 April 2025; Accepted: 16 June 2025;
Published: 09 July 2025.
Edited by:
Mithun Rudrapal, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology and Research, IndiaReviewed by:
André Mauricio De Oliveira, Federal Center for Technological Education of Minas Gerais, BrazilKratika Singh, Centre of Bio-Medical Research (CBMR), India
Copyright © 2025 Zhao, Yang, Sun and Ruan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanlong Sun, c3VueXVhbmxvbmdAc2h1dGNtLmVkdS5jbg==; Xiaofen Ruan, cnVhbnhpYW9mZW5nQHNodXRjbS5lZHUuY24=
 Zhejun Zhao
Zhejun Zhao Qiuhua Yang
Qiuhua Yang Yuanlong Sun
Yuanlong Sun Xiaofen Ruan
Xiaofen Ruan