- 1Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 2Women+ and Children’s Health Sciences, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 3Applied Biology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
- 4Medical Department, A.Vogel AG, Roggwil, Switzerland
- 5Department of Experimental and Clinical Medicine, University of Florence, Florence, Italy
A Correction on
Respiratory virus-induced bacterial dysregulation in pediatric airway tissue and the dual actions of Echinacea in reducing complications
by Vimalanathan S, Sreya M, Nandanavanam R, Schoop R, Gancitano G, Saberi S, Malikovskaia A and Hudson J (2025). Front. Pharmacol. 16:1579551. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1579551
In the published article, there were errors in Figures 1, 2 as published. The figures were truncated on one side, displaying only part of the images. The corrected Figures 1, 2 and their captions appear below.
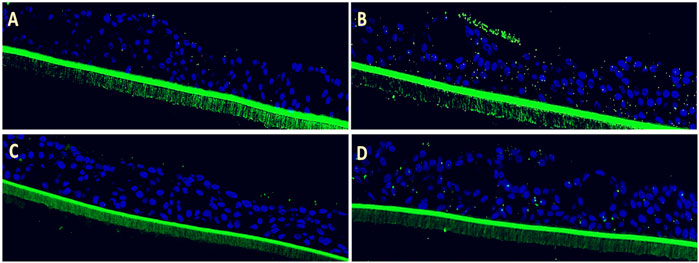
Figure 1. Efficacy of Echinaforce in reducing RSV-induced S. pneumoniae adhesion in pediatric EpiAirway tissue. (A) EpiAirway tissues cultured in an air-liquid interface (ALI) were stained with anti-S. pneumoniae antibody (green) and DAPI for nuclei, visualized at ×20 magnification. Representative images are shown for the following conditions: (A) Vehicle Control + S. pneumoniae, (B) RSV + S. pneumoniae, (C) RSV + EF 1:200 + S. pneumoniae, and (D) RSV + EF 1:400 + S. pneumoniae. (B) Bar chart shows S. pneumoniae adhesion under different conditions: uninfected tissue (infected with S. pneumoniae but not RSV), RSV-infected, and RSV-infected tissues treated with Echinaforce® (EF) at 1:200 and 1:400 dilutions. Data represent ALI-cultured EpiAirway tissues, with statistical significance indicated (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01) ns = not significant.
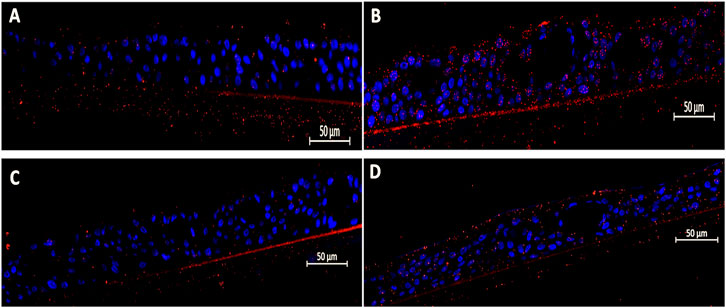
Figure 2. Efficacy of Echinaforce in reducing RSV-induced Hib adhesion in pediatric EpiAirway tissue. (A) EpiAirway tissues cultured in an air-liquid interface (ALI) were stained with anti-Hib antibody (green) and DAPI for nuclei, visualized at ×20 magnification. Representative images are shown for the following conditions: (A) Vehicle Control + Hib, (B) RSV + Hib, (C) RSV + EF 1:200 + Hib, and (D) RSV + EF 1:400 + Hib. (B) Bar chart shows Hib adhesion under different conditions: uninfected tissue (infected with Hib but not RSV), RSV-infected, and RSV-infected tissues treated with EF at 1:200 and 1:400 dilutions. Statistical significance is indicated p < 0.05 (*), ns = not significant.
The original version of this article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: pediatrics, EpiAirway viral-bacterial superinfections, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae type b, respiratory syncytial virus, human parainfluenza virus type 3, rhinovirus, Echinacea purpurea
Citation: Vimalanathan S, Sreya M, Nandanavanam R, Schoop R, Gancitano G, Saberi S, Malikovskaia A and Hudson J (2025) Correction: Respiratory virus-induced bacterial dysregulation in pediatric airway tissue and the dual actions of Echinacea in reducing complications. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1656368. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1656368
Received: 30 June 2025; Accepted: 29 July 2025;
Published: 07 August 2025.
Edited and Reviewed by:
Saravana Kumar Pachaiyappan, Westlake University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Vimalanathan, Sreya, Nandanavanam, Schoop, Gancitano, Saberi, Malikovskaia and Hudson. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Selvarani Vimalanathan, c2VsdmFyYW5pLnZpbWFsYW5hdGhhbkB1YmMuY2E=
 Selvarani Vimalanathan
Selvarani Vimalanathan Mahfuza Sreya
Mahfuza Sreya Ranganayaki Nandanavanam
Ranganayaki Nandanavanam Roland Schoop4
Roland Schoop4