- 1Department of Neuroscience, Section of Human Anatomy, University of Padua, Padua, Italy
- 2Foundation for Biology and Regenerative Medicine, Tissue Engineering and Signaling - T.E.S. Onlus, Padova, Italy
- 3Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Chettinad Academy of Research and Education (CARE), Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute (CHRI), Chennai, India
Hydrogel-based delivery systems have emerged as a promising strategy to enhance the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) in regenerative medicine. These biomimetic platforms provide a three-dimensional microenvironment that recapitulates key features of native extracellular matrix, supporting MSC viability, retention, and function upon transplantation. Beyond acting as passive carriers, hydrogels can be engineered with tunable biochemical and mechanical properties to modulate MSC behavior, including their differentiation potential, immunomodulatory activity, and paracrine signaling. Recent advances include the development of “smart” hydrogels responsive to physiological stimuli, enabling controlled release of encapsulated cells or bioactive molecules in response to local cues. Preclinical studies have demonstrated enhanced tissue repair in diverse pathological contexts, including musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, dermal, and neural injuries. Importantly, translation to clinical settings is being facilitated by the use of xeno-free, good manufacturing practices (GMP)-compliant components such as platelet derivatives and synthetic polymers. Selected early-phase clinical trials support the feasibility, safety, and therapeutic potential of MSC-laden hydrogels, although further studies are required to optimize delivery parameters and regulatory compliance. This review summarizes current progress in hydrogel-MSC systems across application areas, emphasizing design principles, preclinical outcomes, and translational challenges, with the aim of guiding future developments in stem cell-based tissue regeneration.
1 Introduction
Tissue regeneration remains a significant challenge in modern medicine, particularly for the restoration of structure and function in tissues damaged by trauma, chronic disease, or degenerative conditions related to aging. The intrinsic complexity of tissue architecture and the inflammatory and fibrotic responses following injury often hinder spontaneous healing and limit the efficacy of conventional therapeutic strategies. In this context, regenerative medicine research aims to harness the therapeutic potential of stem cells to develop more effective, biologically integrated strategies for tissue repair and functional restoration (Hoang et al., 2022; Hussen et al., 2024).
Among the various cell types explored for regenerative purposes, mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) have emerged as one of the most promising candidates due to their ease of isolation, multipotent differentiation capacity, secretion of trophic factors, and immunomodulatory properties (Fan X. L. et al., 2020; Barbon et al., 2022; Barbon et al., 2021). These cells can contribute to tissue repair through both direct differentiation into target cell lineages and through paracrine mechanisms that modulate inflammation, promote angiogenesis, and recruit endogenous progenitor cells (Kaviarasan et al., 2024; Xue et al., 2024; Barbon et al., 2023).
However, the effective delivery and retention of MSCs at the injury site remain critical hurdles. Rapid cell death, washout due to mechanical forces, and lack of a supportive microenvironment compromise their regenerative potential (Bagno et al., 2022; Takayama et al., 2023). In particular, recent analyses have highlighted that cell-based interventions alone frequently fail to achieve long-term and uncomplicated wound healing across different tissue contexts. This limitation has been attributed to the transient survival of transplanted MSCs and the short-lived duration of their anti-inflammatory secretory activity, which may be insufficient to sustain the prolonged phases of tissue repair and remodeling (Zhao et al., 2021).
To overcome these barriers, biomaterial-based strategies have been developed to provide scaffolding for cell delivery, with hydrogels standing out as an optimal solution. Hydrogels are water-swollen, crosslinked polymer networks that closely mimic the physical and biochemical properties of the native extracellular matrix (ECM). Their biocompatibility, tunable mechanical strength, and ability to encapsulate and release cells or bioactive molecules make them ideal vehicles for supporting MSC survival and function (Seliktar, 2012).
The combination of MSCs and hydrogels has thus gained considerable attention in regenerative medicine, offering a synergistic approach to enhance tissue regeneration. Recent preclinical and clinical studies have explored the potential of MSC-laden hydrogels in various applications, including cartilage repair, wound healing, and myocardial regeneration (Gnecchi et al., 2016; Liang et al., 2019). Despite promising results, challenges such as optimal hydrogel composition, cell viability, and long-term therapeutic efficacy remain to be addressed.
This literature review examines the current preclinical and clinical research on MSC-laden hydrogels, evaluating their therapeutic outcomes, limitations, and future directions in tissue regeneration. By synthesizing findings from key studies, this review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the translational potential of MSC-hydrogel systems in regenerative medicine. Given the extensive body of research on hydrogel-assisted MSC delivery, this work does not aim to provide an exhaustive systematic review. Instead, a focused narrative approach was adopted, selecting representative preclinical and clinical studies that best illustrate the translational potential of MSC-laden hydrogels. Specifically, we prioritized in vivo investigations in clinically relevant animal models, along with published and ongoing clinical trials in humans. In vitro-only studies, early proof-of-principle experiments, and review articles were excluded from the scope. This strategy allows us to emphasize the therapeutic promise, current limitations, and future perspectives of MSC-hydrogel constructs within a clinically oriented framework.
2 Hydrogel properties enhancing MSC function
Hydrogels play a pivotal role in optimizing the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs for tissue regeneration by providing a biomimetic three-dimensional (3D) microenvironment that closely resembles the native ECM. This supportive niche not only facilitates MSC viability and engraftment but also modulates their paracrine and immunomodulatory functions. The mechanical and biochemical properties of hydrogels significantly influence MSC behavior, including cell survival, proliferation, migration, and lineage-specific differentiation, thereby directly impacting the regenerative process (Garcia-Aponte et al., 2025).
Hydrogels with tunable stiffness, porosity, and degradation kinetics can be engineered to mimic the mechanical properties of specific target tissues (Barbon et al., 2020; Todros et al., 2022a; Todros et al., 2022b). For example, softer hydrogels with elastic moduli in the range of 1–10 kPa have been shown to promote adipogenic or neurogenic differentiation, whereas stiffer matrices ranging from 25 to 40 kPa tend to favor osteogenic commitment (Engler et al., 2006). This mechanosensitivity underscores the importance of substrate stiffness in guiding stem cell fate decisions (Stocco et al., 2019a). Furthermore, pore architecture affects nutrient diffusion, waste elimination, and cell migration, all of which are essential for maintaining a viable and functionally active MSC population in situ (Zhou et al., 2023). Complementing these internal features, hydrogel surface geometry - including features such as roughness, curvature, and micro- or nano-topography - plays a critical role in modulating MSC adhesion, proliferation, and lineage commitment (Xiao et al., 2023; Stocco et al., 2021; Stocco et al., 2024; Di Liddo et al., 2016). These topographical cues can influence cytoskeletal organization and mechanotransduction pathways, thereby directing stem cell differentiation and enhancing tissue-specific integration.
The incorporation of bioactive molecules, such as ECM-derived peptides [e.g., arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD), laminin], growth factors [e.g., vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor-2 (FGF-2), bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2)], and glycosaminoglycans (e.g., hyaluronic acid or chondroitin sulfate), further augments MSC functionality by facilitating cell adhesion, activating integrin-mediated signaling pathways, and enhancing the secretion of regenerative cytokines (Xiao et al., 2023; Porzionato et al., 2019; Di Liddo et al., 2014). These biochemical cues can be spatially and temporally regulated through hydrogel composition or surface modification, allowing more precise control of the cellular microenvironment.
Injectable hydrogels, including those based on natural polymers such as alginate, collagen, gelatin, or hyaluronic acid, enable minimally invasive administration, in situ gelation, and conformation to irregular defect geometries. This ensures precise MSC localization, retention, and protection within injured tissues (Burdick and Murphy, 2012). Synthetic variants such as polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) offer improved mechanical tunability and reproducibility, though often at the expense of bioactivity. Composite hydrogels combining natural and synthetic components aim to leverage the advantages of both material classes.
In addition to traditional natural and synthetic polymers, hydrogels derived from decellularized ECM have gained increasing attention as MSC carriers. These biomaterials closely mimic the native biochemical composition and architecture of tissues, thereby providing a bioactive microenvironment that promotes cell adhesion, survival, and lineage-specific differentiation. However, the intrinsic mechanical weakness and batch-to-batch variability of pure ECM hydrogels may limit their translational application. To address this, bio-hybrid systems combining ECM components with synthetic polymers have been developed, combining the bioactivity of ECM with the tunable mechanical and physicochemical properties of synthetic materials (Stocco et al., 2014; Stocco et al., 2016; Grandi et al., 2018; Stocco et al., 2022). Such composite scaffolds sowed to enhance MSC retention and regenerative capacity across different tissues, including cartilage, intestinal segments, and osteochondral units. In vitro and preclinical evidence further highlighted that ECM-derived hydrogels not only reproduce key integrin-binding and growth factor-retaining motifs, but also demonstrate promising preclinical outcomes in cartilage, bone, cardiac, and cutaneous repair. Based on that, hybrid ECM-synthetic systems emerge as promising next-generation carriers for MSC transport, capable of coupling structural stability with biochemical functionality to better meet the complex demands of tissue regeneration (Soltanmohammadi et al., 2025).
Parallel to these bio-hybrid strategies, advanced designs such as stimuli-responsive or dynamic hydrogels, incorporate environmental triggers (e.g., pH, temperature, enzymatic activity) to enable the controlled release of encapsulated cells or bioactive factors. These “smart” hydrogels can prolong therapeutic action, support tissue remodeling, and potentially provide on-demand modulation of MSC activity (Lu et al., 2024) (Figure 1).
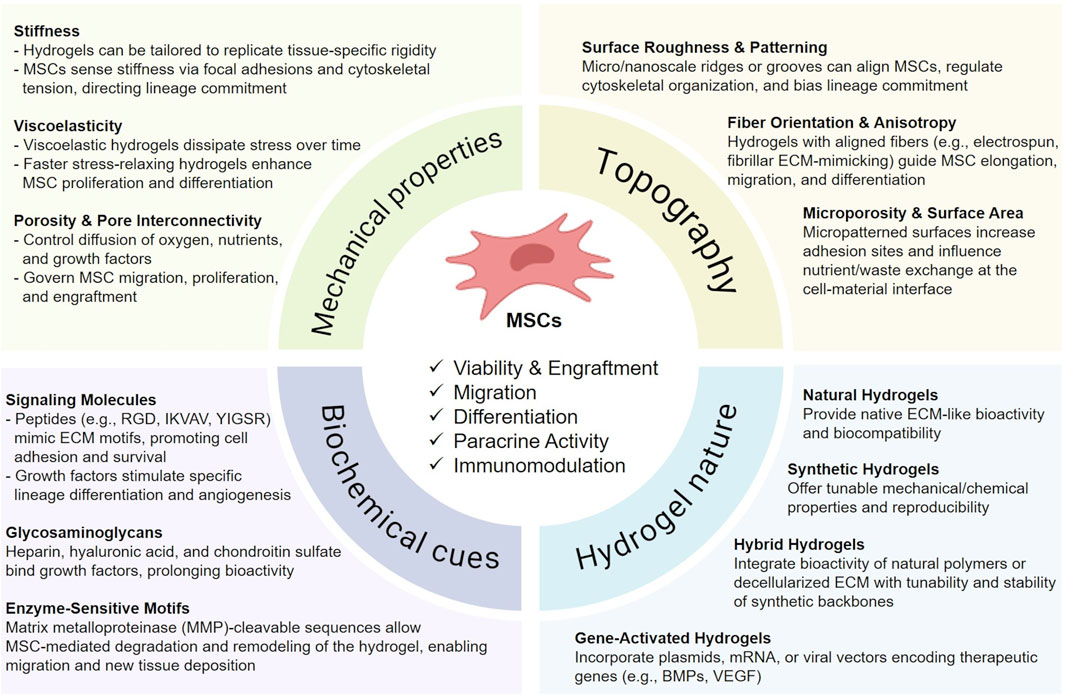
Figure 1. Key hydrogel design parameters influencing MSC therapeutic activity. Schematic overview of hydrogel features that regulate mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC) function and regenerative potential. Mechanical properties such as stiffness, viscoelasticity, and porosity govern MSC survival, migration, and lineage commitment. Topographical cues, including surface roughness, fiber alignment, and microporosity, modulate cell adhesion, elongation, and differentiation. Biochemical signals, provided by peptides, growth factors, glycosaminoglycans, and enzyme-sensitive motifs, enhance MSC survival, angiogenesis, and remodeling capacity. The intrinsic nature of the hydrogel further impacts therapeutic outcomes: natural hydrogels ensure ECM-like bioactivity, synthetic hydrogels provide reproducibility and tunability, hybrid systems combine both advantages, and gene-activated hydrogels enable controlled release of therapeutic genes. Collectively, these design parameters influence MSC viability, engraftment, paracrine activity, and immunomodulation in regenerative applications. This figure was created using BioRender.com.
A promising strategy to further refine hydrogel bioactivity involves engineering matrices with controlled surface or volumetric charge. (e.g., heparinization to confer anionic binding domains or incorporation of cationic moieties) to non-covalently sequester nucleic acids (microRNA, mRNA, plasmid DNA). Such gene-activated hydrogels can prolong local factor residence, protect labile cargos from degradation, and enable cell-responsive release, thereby extending and amplifying MSC paracrine activity in vivo. Preliminary studies further indicate that charge density and spatial distribution critically regulate payload loading/release kinetics and downstream MSC immunomodulation and differentiation (Krasilnikova et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2024).
Despite their potential, hydrogel-based strategies still have to face significant challenges. A key consideration is aligning hydrogel degradation rates with the timeline of native tissue healing to avoid premature scaffold loss or prolonged presence that could hinder integration. Batch-to-batch variability in natural polymers and potential immunogenicity also pose hurdles to clinical translation. Meanwhile, synthetic hydrogels often lack intrinsic bioactivity, requiring functionalization strategies to enhance their biological performance.
Future directions should prioritize the development of clinically scalable, off-the-shelf hydrogel-MSC formulations with optimized degradation kinetics, mechanical resilience, and biofunctionality. Strategies incorporating extracellular vesicles (EVs) or gene editing tools may further enhance therapeutic outcomes by augmenting MSC paracrine signaling or resistance to hostile injury microenvironments.
3 Paracrine signaling and immunomodulation
Mesenchymal stromal cell (MSC)-laden hydrogels exert their regenerative effects primarily through paracrine signaling and immunomodulation rather than direct differentiation. MSCs encapsulated in hydrogels secrete a diverse array of bioactive factors, including growth factors [e.g., VEGF, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β)], cytokines [e.g., interleukin-10 (IL-10), tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6 (TSG-6)], and extracellular vesicles (exosomes), which collectively promote tissue repair by stimulating angiogenesis, reducing fibrosis, and modulating immune responses (Kuppa et al., 2022). The hydrogel matrix serves as a protective niche that prolongs MSC survival and sustains the release of these therapeutic factors, enhancing their local bioavailability compared to free MSC (Caplan and Correa, 2011) (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Mechanisms of MSC delivery and action within hydrogels. Schematic representation of how mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) act when encapsulated in hydrogel scaffolds. Hydrogels provide a protective scaffold that enhances MSC survival and retention, while enabling multiple therapeutic mechanisms. Paracrine signaling through cytokines, exosomes, and growth factors promotes angiogenesis and tissue repair. Immunomodulation drives macrophage polarization from pro-inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes, resulting in reduced inflammation. Differentiation into lineage-specific cells (e.g., chondrocytes, osteoblasts, neurons) and matrix deposition and remodeling contribute to structural regeneration. Collectively, these processes support vascularization, immune regulation, and tissue repair in regenerative medicine applications. This figure was created using BioRender.com.
A key advantage of MSC-laden hydrogels is their ability to polarize macrophages from a pro-inflammatory (M1) to an anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype, which is critical for resolving chronic inflammation in conditions like diabetic wounds or myocardial infarction (Saldanha-Araujo et al., 2020). Hydrogels can be further engineered to amplify these effects by incorporating immunomodulatory agents (e.g., IL-4, interferon gamma (IFN-γ)) or ECM components that synergize with MSC secretions (Xie et al., 2020).
Despite these benefits, challenges include variability in MSC secretomes due to donor differences and culture conditions, as well as the short-lived activity of some paracrine factors. Future strategies may involve genetic modification of MSCs to overexpress specific factors or the use of synthetic hydrogels with controlled release kinetics to optimize immunomodulatory outcomes. Importantly, in the context of wound healing stimulation, these paracrine effects may decrease before tissue repair is stabilized, resulting in incomplete, not functional regeneration. Hydrogel systems are being explored specifically to prolong factor release, modulate local immunity, and synchronize MSC activity with the protracted timeline required for durable and uncomplicated wound closure.
4 Hydrogel-based MSC therapies: preclinical studies
Preclinical studies represent a fundamental step in validating the therapeutic and translational potential of MSC-hydrogel systems across a wide range of disease models. Animal experiments provide essential proof-of-concept data and mechanistic insights into how biomaterial-assisted MSC therapy can overcome limitations such as poor cell survival, retention, and integration. Importantly, the outcomes of these studies depend strongly on the physiological niche in which the therapy is applied. In ischemic tissues, hydrogels protect MSCs from hypoxia and modulate macrophage-driven fibrosis; in neuroinhibitory niches, they attenuate glial scarring and reprogram microglia; in immune-active tissues such as skin and gut, they regulate inflammatory cascades; in mechanically demanding tissues like cartilage and bone, they provide physical support and engage osteo-immune cells; and in sensitive tissues, scaffold selection must minimize excessive immune activation. To reflect this, the following subsections review representative preclinical applications of hydrogel-assisted MSC delivery according to the major biological challenges that influence regenerative success. This integrated perspective highlights both the similarities and the context-specific differences across models, underscoring how hydrogel design can be strategically adapted to distinct tissue environments and host responses, and illustrating the versatility of MSC–hydrogel constructs across a spectrum of regenerative contexts (Table 1).
4.1 Ischemic and hypoxic environments
Tissues with limited oxygen supply, such as the heart and intervertebral discs, present severe survival barriers for transplanted MSCs. In the infarcted myocardium, hydrogels derived from Wharton’s Jelly ECM combined with MSCs of the same origin promoted engraftment and enhanced secretion of paracrine factors, which improved left ventricular function, reduced fibrosis, and stimulated neovascularization in rats (Tavajjohi et al., 2025). Similarly, bone marrow-derived MSCs encapsulated in RGD-modified alginate hydrogel showed improved retention and viability in infarcted rat hearts, leading to increased ejection fraction, reduced infarct size, and greater capillary density (Levit et al., 2013; Guo et al., 2020). Beyond structural support, gene-modified MSC therapies have also been investigated. Wu and colleagues (2017) demonstrated that gene-modified MSCs delivered within a small-molecule hydrogel significantly improved angiogenesis and reduced infarct size in a rat model of myocardial infarction (MI), underscoring the synergistic potential of combining MSCs with gene-activated hydrogels in ischemic repair. Comparable challenges exist in the intervertebral disc, where low oxygen and nutrient supply limit regenerative capacity. In a goat model of disc degeneration, hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels encapsulating MSCs restored disc height and stiffness and decreased local inflammation (Zhang et al., 2021). In spinal fusion, gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) carriers were developed to co-deliver MSCs and bone BMP-2, promoting osteogenesis in vitro and bone bridging in vivo (Li et al., 2024). These approaches show that in hypoxic and avascular tissues, hydrogels provide a metabolic buffer that sustains MSC survival and activity while modulating inflammatory macrophage infiltration.
4.2 Neuroinhibitory niches and scar formation
In the central nervous system, regeneration is hindered by glial scar formation and a highly specialized immune environment dominated by microglia.
To address these barriers, Sun et al. (2025) engineered a thermosensitive hydrogel incorporating BMP7-loaded nanoparticles, which promoted neuronal differentiation of bone marrow MSCs, enhanced axonal regeneration, reduced glial scarring, and improved locomotor recovery in rats with spinal cord injury (SCI). In a complementary design, Papa et al. (2018) encapsulated MSCs in a hyaluronic acid hydrogel with controlled release of CCL2, which preserved spinal cord cytoarchitecture, reduced lesion volume, and recruited host cells. Importantly, this system induced macrophage polarization toward a regenerative phenotype, highlighting the immune-modulatory role of hydrogels in the central nervous system.
These findings indicate that hydrogel scaffolds in neuroregeneration must not only sustain MSC viability but also regulate microglia and infiltrating macrophages to counteract inhibitory scar formation.
4.3 Highly immune-active tissues
Tissues such as the skin and gut are highly exposed to inflammation and microbial stress, requiring MSC-hydrogel systems that prolong paracrine signaling and shape immune responses. In a diabetic mouse model, Huang et al. (2025) demonstrated that perinatal MSCs delivered via a hydrogel scaffold accelerated wound closure through the activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) pathway. This resulted in the promotion of keratinocyte migration, angiogenesis, and proliferation. In atopic dermatitis, thiolated hyaluronic acid hydrogels formed in situ after injection, improving MSC engraftment and retention. In treated mice, epidermal hyperplasia and dermal inflammation were significantly reduced, with decreased immune cell infiltration (Lee et al., 2022). Similarly, in gastrointestinal injury, MSCs embedded in hydrogels containing heparan sulfate mimetics (HS-m) named RGTA® showed to retain their immunoregulatory properties and reduced radiation-induced colonic inflammation, enhancing mucosal regeneration and restoring epithelial architecture (Moussa et al., 2019). Together, these studies show that in immune-rich tissues, hydrogels not only deliver MSCs but also provide a platform for reprogramming local macrophages and innate lymphoid cells, thereby facilitating resolution of inflammation.
4.4 Mechanically demanding and avascular tissues
Regeneration of cartilage, osteochondral interface, and bone is particularly difficult due to lack of vasculature, high mechanical stress, and poor intrinsic healing. In rabbits, Seol et al. (2013) reported that thermosensitive poloxamer 407 hydrogels carrying autologous MSCs filled full-thickness cartilage defects and promoted hyaline-like tissue formation with smooth surface morphology and improved histological scores. Hu and colleagues (2024) engineered a nanozyme-functionalized bilayer hydrogel conceptualized not only to promote osteochondral regeneration, but also to modulate the inflammatory microenvironment associate to tissue damage. The upper cartilage-inductive layer was composed of methacrylated gelatin (GelMA) incorporating kartogenin-loaded nanoparticles to stimulate chondrogenesis. The lower layer consisted of oxidized hyaluronic acid (OHA) and adipic acid dihydrazide (ADH) crosslinked hydrogel, embedded with manganese dioxide (MnO2)-based nanozymes to scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reduce local inflammation. This construct significantly enhanced cartilage and subchondral bone repair in rabbits.
Several studies have specifically explored gene-activated MSC scaffolds for osteochondral regeneration. Wang et al. (2010) implanted poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) sponges filled with fibrin gel, bone marrow-derived MSCs, and DNA complexes into rabbit cartilage defects, achieving near-complete filling and formation of hyaline-like tissue. Chen et al. (2011) designed bilayered scaffolds with spatially controlled gene delivery, enabling simultaneous regeneration of articular cartilage and subchondral bone in vivo. Building on this, Li et al. (2013) fabricated PLGA scaffolds containing MSCs and plasmid DNA encoding transforming growth factor beta-1 (TGF-β1), which markedly enhanced cartilage repair quality and ECM deposition. In larger animal models, umbilical cord-derived MSCs embedded in hyaluronic acid hydrogels promoted cartilage repair in minipigs (Ha et al., 2015), while self-assembling peptide hydrogels delivering TGF-β1 induced MSC chondrogenesis and ECM deposition in equine cartilage defects (Kopesky et al., 2014).
Bone regeneration also benefits from gene-activated approaches. Loozen and colleagues (2019) demonstrated that BMP-2 gene delivery in both MSC-laden and even cell-free constructs enhanced osteogenesis in rodent models, showing that sustained morphogen release can substitute for continuous cellular input. Building on this principle, Lin et al. (2017) used projection stereolithography to fabricate BMP-2 gene-activated scaffolds with high spatial precision, achieving robust bone tissue formation. Similarly, Sun et al. (2020) applied an injectable BMP-2 gene-activated scaffold to successfully repair cranial bone defects in mice, highlighting the translational relevance of minimally invasive delivery systems. Beyond gene activation, clinically oriented MSC–hydrogel formulations have been developed to meet regulatory and translational requirements. Vivas and colleagues (2020) designed a good manufacturing practices (GMP)-compliant osteogenic preparation consisting of bone marrow-derived MSCs embedded in a fibrin matrix enriched with micronized bone particles (0.25–1 μm). When implanted subcutaneously in immunodeficient mice, the construct showed no signs of toxicity or adverse immune response, while supporting early osteogenesis and vascularization. Importantly, this work emphasized safety, scalability, and compliance with good manufacturing practices, underlining the feasibility of advancing MSC-hydrogel therapies toward clinical application. Complementing these findings, Black et al. (2020) created a hybrid scaffold that combined a bovine ECM-derived hydrogel with a melt-electro-written polycaprolactone (PCL) framework. In a bovine critical-sized bone defect model, this construct promoted not only extensive new bone formation but also vascular ingrowth and stable integration with host tissue.
In these mechanically demanding tissues, hydrogel systems not only provide structural integration but also coordinate MSC crosstalk with osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and osteal macrophages, underscoring the role of osteo-immunity in skeletal regeneration.
4.5 Immune-sensitive and specialized tissues
Certain tissues present unique regenerative challenges, requiring repair strategies that minimize local immune activation or support complex graft integration. In a preclinical rabbit model of vocal fold scarring, Bartlett et al. (2016) evaluated the therapeutic efficacy and safety of bone marrow-derived MSCs delivered alone or in combination with a hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel (HyStem-VF). The study highlighted that the injection of MSCs alone improved viscoelastic recovery and ECM remodeling, while MSC-hydrogel combinations unexpectedly triggered inflammation and impaired repair. This underscores that in specialized tissues, biomaterial selection must be carefully tuned to avoid counterproductive immune responses.
In pancreatic transplantation, Borg et al. (2016) developed polyethylene glycol (PEG)–heparin cryogels to co-deliver pancreatic islets and MSCs. Implanted subcutaneously in mice, this system preserved insulin secretion and prolonged graft survival, with MSCs providing paracrine and immunomodulatory support.
Gene-activated constructs have also been applied to skin appendages. Kolakshyapati and collaborators (2017) reported that MSCs seeded in gene-activated matrices regenerated sweat gland-like structures in vivo, suggesting potential for adnexal tissue repair in burn injuries.
4.6 Safety and translational considerations
Clinical translation of hydrogel-MSC systems demands not only therapeutic efficacy but also rigorous demonstration of safety, biocompatibility, and compliance with regulatory standards. Accordingly, Canceill et al. (2023) reported that platelet lysate–based fibrin hydrogels encapsulating MSCs were biocompatible when implanted in immunocompetent rats, showing no acute inflammation, toxicity, or ectopic tissue formation. Platelet-rich formulations, already rich in growth factors and anti-inflammatory mediators, are well-known to enhance MSC activity, serving as valuable xeno-free components that sustain cell viability and function, as well as support tissue repair and immune modulation in a physiologically relevant manner (Barbon et al., 2018; Stocco et al., 2019b). The preclinical data collected by Canceill et al. (2023) exemplify how clinically oriented matrices can serve as advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs), bridging the gap from preclinical testing to human trials.
5 Hydrogel-based MSC therapies: clinical research
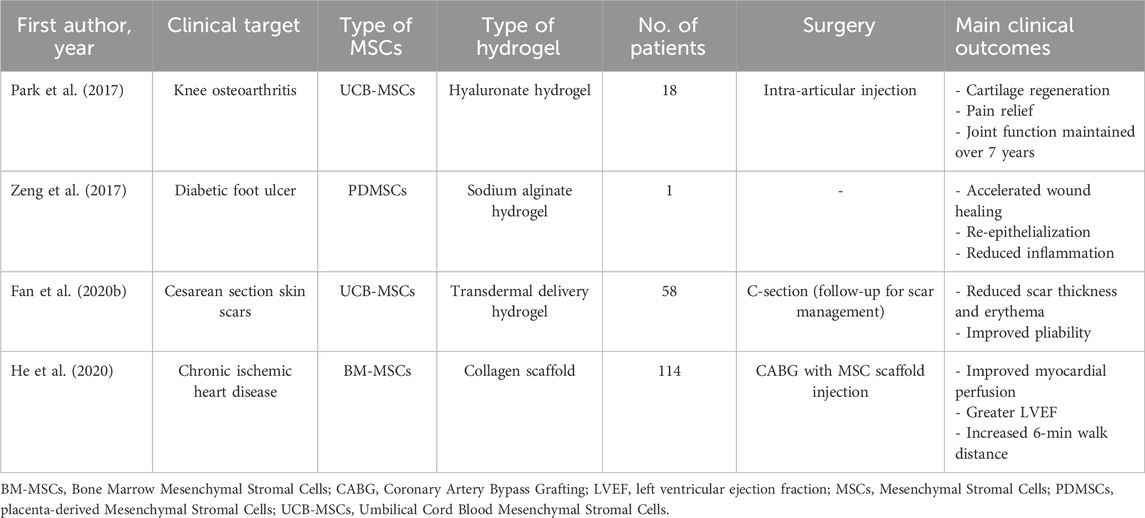
The clinical translation of MSC-based therapies has progressed significantly over the past decade, with numerous trials exploring their potential across various disease contexts. Nevertheless, when the integration of MSCs with hydrogel-based delivery systems is considered, clinical research appears to be in its early stages. Only a limited number of trials have investigated this combinatorial approach in human patients, with encouraging preliminary findings (Table 2). The following sections summarize representative clinical applications of hydrogel-assisted MSC delivery for cardiovascular, dermatological, articular, and chronic wound regeneration (Figure 3).
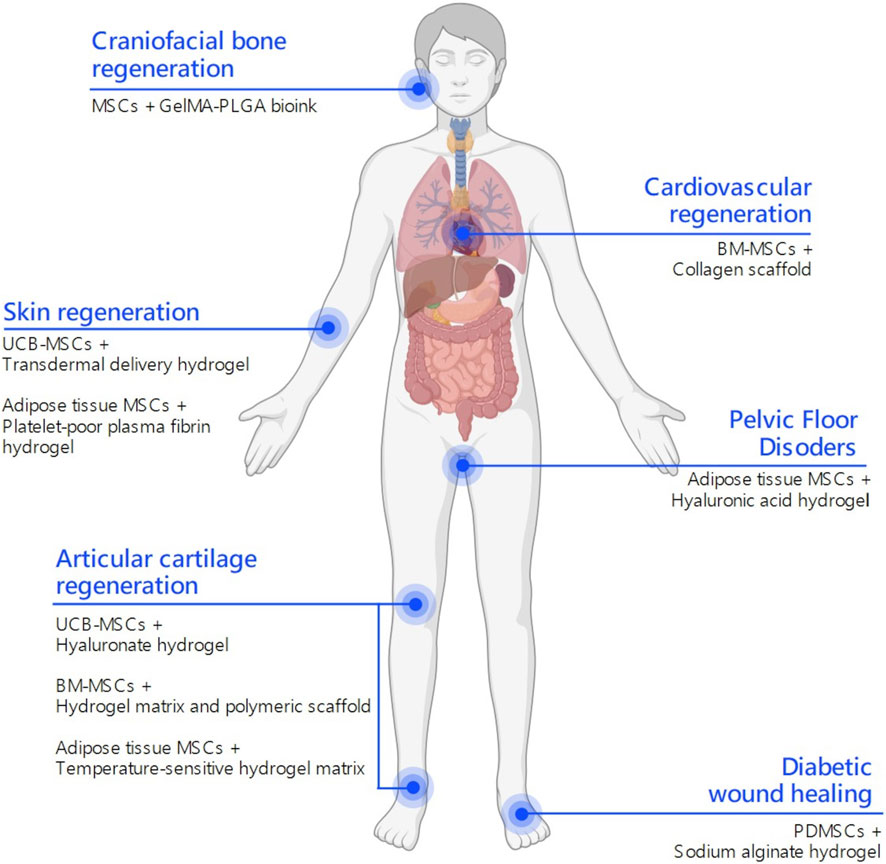
Figure 3. Clinical applications of MSC-laden hydrogels. Schematic representation of published and ongoing clinical trials on hydrogel-assisted mesenchymal stromal cell (MSCs) delivery to stimulate tissue regeneration. Depending on the anatomical site, distinct MSCs and hydrogel formulations are employed to address specific regenerative challenges. This integrative map highlights how hydrogel composition and MSC source can be strategically matched to different tissue microenvironments to improve regenerative outcomes. This figure was created using BioRender.com.
5.1 Cardiovascular regeneration
The clinical translation of regenerative therapies for ischemic heart disease has taken into consideration the integration of cell-based interventions with biomaterial scaffolds to enhance therapeutic efficacy. As already mentioned, this combinatorial approach aims to address the limitations of poor cell retention, survival, and functional integration frequently observed with cell delivery alone. Within this framework, He et al. (2020) conducted a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial involving 114 patients with chronic ischemic heart disease. The intervention group received intramyocardial implantation of MSCs combined with a bioengineered collagen scaffold during coronary artery bypass graft surgery, while the control group received the surgery alone. Over a 12-month follow-up, patients treated with MSCs and scaffold showed significantly improved myocardial perfusion, greater left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and increased 6-min walk distance compared to controls. Importantly, the procedure was well tolerated, with no increase in adverse events.
This trial offers compelling evidence that combining cell therapy with biomaterial scaffolds enhances functional outcomes in ischemic heart disease.
5.2 Skin and scar regeneration
Post-surgical scarring, especially hypertrophic or keloid scars following cesarean sections, presents significant aesthetic and functional concerns. Traditional treatments have limited success in promoting satisfying dermal regeneration. MSCs, with their anti-inflammatory and remodeling capabilities, offer a novel approach to improving scar quality.
Recently, Fan et al. (2020b) conducted a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess the efficacy of umbilical cord-derived MSCs for improving cesarean section scar outcomes. Fifty-eight women were enrolled and randomly assigned to receive intradermal injections of MSCs or placebo along the surgical incision site. The stem cells were delivered in a transdermal hydrogel formulation designed to enhance local retention and therapeutic activity.
At 6 months post-treatment, scar assessments were performed using clinical examination, histological analysis, and the Vancouver Scar Scale (VSS). Results indicated modest improvements in scar appearance among MSC-treated patients, including reduced erythema, improved pliability, decreased scar thickness, and enhanced collagen remodeling. However, these differences did not reach statistical significance compared to the placebo group. Importantly, the treatment was well tolerated, with no adverse events or immune-related reactions reported.
These results suggest that UC-MSCs may be a safe and effective treatment to modulate fibroproliferative responses in human skin wounds. Beyond cosmetic benefits, this approach may reduce functional limitations and discomfort associated with scarring. However, larger trials are needed to standardize dosing and administration strategies.
5.3 Articular cartilage repair
Degenerative diseases affecting articular cartilage, such as osteoarthritis, are among the most common sources of chronic pain and functional impairment worldwide. Conventional treatments (pharmacologic management, physiotherapy, and surgical interventions) primarily aim to alleviate symptoms but fail in restoring cartilage integrity or halting disease progression. In this context, the integration of MSCs with biocompatible scaffolds, particularly hydrogels, represents a promising regenerative strategy. As part of this growing interest in cartilage regeneration therapies, Park and colleagues (2017) conducted an open-label, single-arm clinical trial in 18 patients with knee osteoarthritis. The treatment consisted of a composite product containing allogeneic umbilical cord blood-derived MSCs mixed with hyaluronic acid hydrogel, injected intra-articularly. Clinical and arthroscopic assessments over 7 years showed sustained improvement in pain and mobility, with imaging revealing the development of hyaline-like cartilage and joint space preservation.
Together, these outcomes emphasize the long-term regenerative potential of MSC-hydrogel therapies in osteoarthritic conditions.
5.4 Diabetic wound healing
Chronic non-healing wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers are a major complication of diabetes, often leading to infection and amputation. Innovative therapies that promote re-epithelialization and vascularization are urgently needed. MSCs have appear to be promising therapeutic candidates due to their regenerative and immunomodulatory effects, particularly when delivered in a hydrogel vehicle.
In this scenario, Zeng et al. (2017) described a single-case application of placenta-derived MSCs embedded in a hydrogel matrix applied topically to a chronic diabetic foot ulcer. The wound was previously unresponsive to standard therapies. Over a 3-week period, the ulcer showed accelerated granulation tissue development, reduced local inflammation, and almost complete re-epithelialization. No complications were observed.
Despite being a case report, the study demonstrates the translational feasibility of topical MSC-hydrogel therapies. The favorable outcome supports further investigation through controlled trials. Numerous polymeric biomaterials are used recently for diabetic wound dressing including hydrogels, collagen-based scaffolds, whose efficacy can be further improved by loading therapeutic molecules, growth factors, and anti-microbial agents that could accelerate the process of wound closure by triggering collagen deposition and vascularization. However, advanced research in this field is essential to enhance the efficacy of polymeric wound dressings for efficient diabetic wound treatment (Sathyaraj et al., 2023). The selection of placenta-derived MSCs suggests a potential for enhanced immunomodulatory action and broader clinical applicability due to their allogeneic compatibility.
5.5 Ongoing clinical trials on MSC-laden hydrogels
Although the number of published clinical trials investigating hydrogel-assisted MSC therapies remains limited, other ongoing studies registered on the databases ClinicalTrials.gov, EudraCT (European Union Drug Regulating Authorities Clinical Trials) and EU Clinical Trials Register underscore the growing translational advancement in this field. These trials explore different hydrogel platforms, cellular sources, and delivery strategies, reflecting the adaptability of MSC-laden hydrogels across a range of regenerative approaches (Table 3).
In the context of autologous regenerative therapies, the multicenter, exploratory trial NCT03113747 entitled “Allogeneic ADSCs and Platelet-Poor Plasma Fibrin Hydrogel to Treat the Patients With Burn Wounds” investigates the safety and preliminary efficacy of a tissue-engineered construct combining allogeneic adipose tissue MSCs embedded in a platelet-poor plasma (PPP)-derived fibrin hydrogel. This study targets patients with deep second- or third-degree burns covering 10%–50% of their body surface. The composite graft is applied directly to wounds within 24 h post-injury to evaluate its potential to accelerate healing and reduce scarring. Specifically, the PPP-derived hydrogel aims to improve local MSC retention and bioactivity, thereby enhancing tissue healing responses. Currently, the study status is listed as “Unknown” due to the absence of updates since April 2017. This suggests possible interruption or prolonged inactivity, underscoring the criticisms often encountered in cell-based product development and clinical translation (Voronin, 2025).
Despite these challenges, further clinical research efforts are being pursued to validate and optimize regenerative therapies based on MSC-laden hydrogels. For example, the EudraCT 2021-002331-34 trial is a multicenter, randomized, double-blind Phase IIb study which evaluates the safety and efficacy of allogeneic adipose-derived MSCs embedded in a hyaluronic acid hydrogel for the treatment of structural fecal incontinence (FI). Patients with a confirmed anal sphincter defect and chronic FI were administered with the investigated MSC-hydrogel product via intralesional injection, comparing 2 cell doses (60 million vs. 120 million adipose tissue-derived MSCs) suspended in a hyaluronic acid matrix. This trial exemplifies the growing clinical interest in MSC-laden hydrogels as a novel treatment strategy for sphincter repair, combining regenerative potential of stem cells with their localized, minimally invasive delivery. Its outcomes may offer valuable insights into the clinical applicability of cell-based biomaterial therapies in pelvic floor disorders (FIMABIS, 2025).
The recent trial NCT06028763 titled “Development of Biomedical Technology for the Treatment of Ankle Cartilage Using Injectable Biocomposite Hydrogel” focuses on adipose tissue-derived MSCs embedded within a customized hydrogel matrix and administered locally for the treatment of ankle cartilage focal injuries. These lesions are particularly difficult to treat due to the avascular nature and limited intrinsic healing capacity of cartilage tissue. The trial addresses these challenges by delivering MSCs in a minimally invasive, injectable hydrogel that solidifies at body temperature, enabling mechanical support, targeted delivery and long-term cellular retention within the ankle joint (Center of National Scientific Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics, 2025).
The clinical challenge of articular cartilage regeneration is also being addressed by a recently registered Phase I clinical trial (EudraCT 2024-512977-28-01), designed to evaluate the safety and feasibility of a novel advanced therapy medicinal product (ATMP). This investigational approach combines autologous bone marrow-derived MSCs with a biocompatible hydrogel matrix and a polymeric scaffold for the treatment of focal femoral condyle cartilage lesions in the knee. The trial aims to assess not only the local tolerability of the composite implant, but also the operational feasibility of its GMP-compliant manufacturing and surgical application. Depending on its specific outcomes, this study may represent a key step toward the clinical translation of MSC-laden hydrogel systems in orthopedic regenerative medicine (Lamina Therapeutics, 2025).
Finally, the trial NCT06533150 titled “Functionalized Bioink Delivering Biomolecules for the Treatment of Craniofacial Diseases (DART-CRAFT)” is developing an advanced Gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) and poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)-based bioink for potential MSC encapsulation and 3D bioprinting applications in craniofacial bone repair procedures. The bioink is applied intraoperatively during reconstructive surgery, where it serves as a moldable and in situ solidifying scaffold, tailored to support bone regeneration by enhancing local tissue integration and possibly incorporating MSCs. This innovative approach merges 3D bioprinting, controlled release technology, and biocompatible materials to address complex craniofacial defects with high precision. By enabling localized therapeutic delivery of growth factors or cells and structural support, the DART-CRAFT platform highlights the future of personalized regenerative strategies in maxillofacial surgery (Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, 2025).
Collectively, these ongoing trials demonstrate the continued evolution and clinical interest in hydrogel-based MSC delivery systems, highlighting their potential to enhance therapeutic efficacy, standardization, and applicability across multiple regenerative medicine applications.
6 Potential research gaps
Despite significant advancements in the preclinical and clinical application of MSC-laden hydrogels for tissue regeneration, several research gaps hinder their full clinical translation. One major challenge is the lack of standardized protocols for hydrogel composition, including optimal mechanical properties, degradation rates, and bioactive molecule incorporation, which vary depending on the target tissue (Burdick and Mauck, 2011). Additionally, while MSC-hydrogel systems have shown promise in preclinical studies, there is limited long-term data on cell survival, engraftment, and functional integration in human clinical trials (Galipeau and Sensébé, 2018). Another critical gap is the insufficient understanding of the paracrine mechanisms by which MSCs exert their therapeutic effects within hydrogels. While MSCs are known to secrete regenerative factors, the precise signaling pathways and their modulation by the hydrogel microenvironment remain unclear (Caplan and Correa, 2011). Furthermore, immune responses to implanted MSC-laden hydrogels, including potential foreign body reactions or unintended immunomodulatory effects, require further investigation (Andrzejewska et al., 2019).
Scalability and manufacturing consistency also pose challenges, as variations in MSC sources (e.g., autologous vs. allogeneic) and hydrogel fabrication techniques can impact therapeutic outcomes (Murphy et al., 2020). Finally, regulatory and ethical considerations surrounding MSC-based therapies necessitate clearer guidelines to facilitate clinical adoption (Sipp et al., 2018). Addressing these gaps through interdisciplinary research will be crucial for advancing MSC-laden hydrogels toward widespread clinical use in tissue regeneration.
7 Future clinical research focus
The clinical application of MSC-laden hydrogels holds immense potential for tissue regeneration, yet future research must address key challenges to optimize therapeutic efficacy and translation. A critical focus will be the development of smart hydrogels with tunable biomechanical and biochemical properties that can dynamically respond to the regenerative microenvironment (Daly et al., 2021). Such advanced biomaterials should enhance MSC retention, survival, and controlled differentiation while minimizing immune rejection (Zhu et al., 2022). Importantly, MSC-based therapies alone have shown to often fail to achieve long-term and uncomplicated wound healing across different tissues, largely due to the transient survival of transplanted cells and the short-lived duration of their paracrine signaling. Embedding MSCs within hydrogels directly addresses this limitation, as these systems can provide a supportive matrix that prolongs MSC bioactivity, sustains the release of anti-inflammatory and trophic factors, and better synchronizes cellular functions with the extended phases of tissue repair and remodeling.
Building on this rationale, another priority is the standardization of MSC sources and hydrogel formulations for specific clinical indications, such as osteoarthritis, chronic wounds, and myocardial infarction. Large-scale, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are needed to validate the safety and long-term functional outcomes of MSC-hydrogel therapies compared to conventional treatments (Wei et al., 2023). Additionally, integrating technologies like 3D bioprinting and gene editing could enable patient-specific constructs with spatially controlled MSC delivery (Gungor-Ozkerim et al., 2018).
Understanding the immune-modulatory mechanisms of MSCs within hydrogels will also be essential, particularly in allogeneic applications, to prevent adverse responses and harness their anti-inflammatory potential (Levy et al., 2020). Finally, regulatory frameworks must evolve to accommodate the unique challenges of combination products (cells + biomaterials), ensuring reproducibility and scalability for commercialization (Mendicino et al., 2022). By addressing these priorities, future clinical research can unlock the full regenerative potential of MSC-laden hydrogels.
Author contributions
SB: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SR: Methodology, Writing – original draft. AB: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. PPP: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. RDC: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. VM: Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. AP: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Open Access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Padova University of Padua, Open Science Committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Andrzejewska, A., Lukomska, B., and Janowski, M. (2019). Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: from roots to boost. Stem Cells 37, 855–864. doi:10.1002/stem.3016
Bagno, L. L., Salerno, A. G., Balkan, W., and Hare, J. M. (2022). Mechanism of action of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): impact of delivery method. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 22, 449–463. doi:10.1080/14712598.2022.2016695
Barbon, S., Stocco, E., Grandi, F., Rajendran, S., Borean, A., Pirola, I., et al. (2018). Biofabrication of a novel leukocyte-fibrin-platelet membrane as a cells and growth factors delivery platform for tissue engineering applications. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 12, 1891–1906. doi:10.1002/term.2713
Barbon, S., Stocco, E., Dalzoppo, D., Todros, S., Canale, A., Boscolo-Berto, R., et al. (2020). Halogen-mediated partial oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol for tissue engineering purposes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 801. doi:10.3390/ijms21030801
Barbon, S., Rajendran, S., Bertalot, T., Piccione, M., Gasparella, M., Parnigotto, P. P., et al. (2021). Growth and differentiation of circulating stem cells after extensive ex vivo expansion. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 18, 411–427. doi:10.1007/s13770-021-00330-7
Barbon, S., Stocco, E., Rajendran, S., Zardo, L., Macchi, V., Grandi, C., et al. (2022). In vitro conditioning of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by the endothelial microenvironment: modeling cell responsiveness towards non-genetic correction of haemophilia A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7282. doi:10.3390/ijms23137282
Barbon, S., Banerjee, A., Perin, L., De Caro, R., Parnigotto, P. P., and Porzionato, A. (2023). Editorial: therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in organ and tissue regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1333281. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1333281
Bartlett, R. S., Guille, J. T., Chen, X., Christensen, M. B., Wang, S. F., and Thibeault, S. L. (2016). Mesenchymal stromal cell injection promotes vocal fold scar repair without long-term engraftment. Cytotherapy 18, 1284–1296. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.07.005
Black, C., Kanczler, J. M., de Andrés, M. C., White, L. J., Savi, F. M., Bas, O., et al. (2020). Characterisation and evaluation of the regenerative capacity of Stro-4+ enriched bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells using bovine extracellular matrix hydrogel and a novel biocompatible melt electro-written medical-grade polycaprolactone scaffold. Biomaterials 247, 119998. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119998
Borg, D. J., Welzel, P. B., Grimmer, M., Friedrichs, J., Weigelt, M., Wilhelm, C., et al. (2016). Macroporous biohybrid cryogels for co-housing pancreatic islets with mesenchymal stromal cells. Acta Biomater. 44, 178–187. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2016.08.007
Burdick, J. A., and Mauck, R. L. (2011). Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer.
Burdick, J. A., and Murphy, W. L. (2012). Moving from static to dynamic complexity in hydrogel design. Nat. Commun. 3, 1269. doi:10.1038/ncomms2271
Canceill, T., Jourdan, G., Kémoun, P., Guissard, C., Monsef, Y. A., Bourdens, M., et al. (2023). Characterization and safety profile of a new combined advanced therapeutic medical product platelet lysate-based fibrin hydrogel for mesenchymal stromal cell local delivery in regenerative medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 2206. doi:10.3390/ijms24032206
Caplan, A. I., and Correa, D. (2011). The MSC: an injury drugstore. Cell Stem Cell 9, 11–15. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2011.06.008
Center of National Scientific Center of Traumatology and Orthopedics (2025). Development of biomedical technology for the treatment of ankle cartilage using injectable biocomposite hydrogel. ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT06028763. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06028763 (Accessed on June 29, 2025).
Chen, J., Chen, H., Li, P., Diao, H., Zhu, S., Dong, L., et al. (2011). Simultaneous regeneration of articular cartilage and subchondral bone in vivo using MSCs induced by a spatially controlled gene delivery system in bilayered integrated scaffolds. Biomaterials 32 (21), 4793–4805. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.03.041
Daly, A. C., Prendergast, M. E., Hughes, A. J., and Burdick, J. A. (2021). Bioprinting for the biologist. Cell 184, 18–32. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.002
Di Liddo, R., Paganin, P., Lora, S., Dalzoppo, D., Giraudo, C., Miotto, D., et al. (2014). Poly-ε-caprolactone composite scaffolds for bone repair. Int. J. Mol. Med. 34, 1537–1546. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2014.1954
Di Liddo, R., Aguiari, P., Barbon, S., Bertalot, T., Mandoli, A., Tasso, A., et al. (2016). Nanopatterned acellular valve conduits drive the commitment of blood-derived multipotent cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 11, 5041–5055. doi:10.2147/IJN.S115999
Engler, A. J., Sen, S., Sweeney, H. L., and Discher, D. E. (2006). Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126, 677–689. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.044
Fan, X. L., Zhang, Y., Li, X., and Fu, Q. L. (2020a). Mechanisms underlying the protective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 77, 2771–2794. doi:10.1007/s00018-020-03454-6
Fan, D., Zeng, M., Xia, Q., Chen, J., Liu, R., Wu, Z., et al. (2020b). Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of cesarean section skin scars: a randomized clinical trial. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11, 244. doi:10.1186/s13287-020-01695-7
FIMABIS (2025). A multicenter, randomized, double-blind phase IIb study to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the intralesional administration of two doses of expanded allogeneic adipose tissue adult mesenchymal stem cells (ADTCT), packed in hyaluronic acid hydrogel, as a treatment for patients with fecal incontinence. EU Clin. Trials Regist. EudraCT Number 2021-002331-34. Available online at: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2021-002331-34/ES/ (Accessed on June 29, 2025).
Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS (2025). Functionalized bioink delivering biomolecules for the treatment of craniofacial diseases (DART-CRAFT). ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT06533150. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT06533150 (Accessed on June 29, 2025).
Galipeau, J., and Sensébé, L. (2018). Mesenchymal stromal cells: clinical challenges and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 22, 824–833. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.004
Garcia-Aponte, O. F., Kahlenberg, S., Kouroupis, D., Egger, D., and Kasper, C. (2025). Effects of hydrogels on mesenchymal stem/stromal cells paracrine activity and extracellular vesicles production. J. Extracell. Vesicles 14, e70057. doi:10.1002/jev2.70057
Gnecchi, M., Danieli, P., Malpasso, G., and Ciuffreda, M. C. (2016). Paracrine mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair. Methods Mol. Biol. 1416, 123–146. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-3584-0_7
Grandi, F., Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Rambaldo, A., Contran, M., Fascetti Leon, F., et al. (2018). Composite scaffolds based on intestinal extracellular matrices and oxidized polyvinyl alcohol: a preliminary study for a new regenerative approach in short bowel syndrome. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 7824757. doi:10.1155/2018/7824757
Gungor-Ozkerim, P. S., Inci, I., Zhang, Y. S., Khademhosseini, A., and Dokmeci, M. R. (2018). Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: an overview. Biomater. Sci. 6, 915–946. doi:10.1039/C7BM00765E
Guo, Y., Yu, Y., Hu, S., Chen, Y., and Shen, Z. (2020). The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Dis. 11, 349. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2542-9
Ha, C. W., Park, Y. B., Chung, J. Y., and Park, Y. G. (2015). Cartilage repair using composites of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronic acid hydrogel in a minipig model. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 4, 1044–1051. doi:10.5966/sctm.2014-0264
He, X., Wang, Q., Zhao, Y., Li, X., Zhang, W., Chen, Y., et al. (2020). Effect of intramyocardial grafting collagen scaffold with mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw. Open 3, e2016236. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.16236
Hoang, D. M., Pham, P. T., Bach, T. Q., Ngo, A. T. L., Nguyen, Q. T., Phan, T. T. K., et al. (2022). Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7, 272. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01134-4
Hu, C., Huang, R., Xia, J., Hu, X., Xie, D., Jin, Y., et al. (2024). A nanozyme-functionalized bilayer hydrogel scaffold for modulating the inflammatory microenvironment to promote osteochondral regeneration. J. Nanobiotechnol. 22, 445. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02723-x
Huang, J., Deng, Q., Tsang, L. L., Chang, G., Guo, J., Ruan, Y. C., et al. (2025). Mesenchymal stem cells from perinatal tissues promote diabetic wound healing via PI3K/AKT activation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 16, 59. doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04141-8
Hussen, B. M., Taheri, M., Yashooa, R. K., Abdullah, G. H., Abdullah, S. R., Kheder, R. K., et al. (2024). Revolutionizing medicine: recent developments and future prospects in stem-cell therapy. Int. J. Surg. 110, 8002–8024. doi:10.1097/JS9.0000000000002109
Kaviarasan, V., Deka, D., Balaji, D., Pathak, S., and Banerjee, A. (2024). Signaling pathways in trans-differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells: recent advances. Methods Mol. Biol. 2736, 207–223. doi:10.1007/7651_2023_478
Kolakshyapati, P., Li, X., Chen, C., Zhang, M., Tan, W., Ma, L., et al. (2017). Gene-activated matrix/bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells constructs regenerate sweat glands-like structure in vivo. Sci. Rep. 7, 17630. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-17967-x
Kopesky, P. W., Byun, S., Vanderploeg, E. J., Kisiday, J. D., Frisbie, D. D., and Grodzinsky, A. J. (2014). Sustained delivery of bioactive TGF-β1 from self-assembling peptide hydrogels induces chondrogenesis of encapsulated bone marrow stromal cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 102, 1275–1285. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34789
Krasilnikova, O., Yakimova, A., Ivanov, S., Atiakshin, D., Kostin, A. A., Sosin, D., et al. (2023). Gene-activated materials in regenerative dentistry: narrative review of technology and study results. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 16250. doi:10.3390/ijms242216250
Kuppa, S. S., Kim, H. K., Kang, J. Y., Lee, S. C., and Seon, J. K. (2022). Role of mesenchymal stem cells and their paracrine mediators in macrophage polarization: an approach to reduce inflammation in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 13016. doi:10.3390/ijms232113016
Lamina Therapeutics (2025). Feasibility and safety of a combined ATMP comprising a polymeric medical device and autologous bone marrow-derived MSCs in a hydrogel mixture for the treatment of isolated knee femoral cartilage lesions. Strasbourg, France: EU Clinical Trials Register. Available online at: https://euclinicaltrials.eu/search-for-clinical-trials/?lang=en&EUCT=2024-512977-28-01 (Accessed on June 29, 2025).
Lee, H., Lee, T. W., Chandrasekharan, A., Sung, S. E., Yim, S. G., Kim, S., et al. (2022). Injectable self-crosslinkable thiolated hyaluronic acid for stem cell therapy of atopic dermatitis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 8, 1613–1622. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c01374
Levit, R. D., Landázuri, N., Phelps, E. A., Brown, M. E., García, A. J., Davis, M. E., et al. (2013). Cellular encapsulation enhances cardiac repair. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2, e000367. doi:10.1161/JAHA.113.000367
Levy, O., Kuai, R., Siren, E. M. J., Bhere, D., Milton, Y., Nissar, N., et al. (2020). Shattering barriers toward clinically meaningful MSC therapies. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba6884. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aba6884
Li, B., Yang, J., Ma, L., Li, F., Tu, Z., and Gao, C. (2013). Fabrication of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) scaffold filled with fibrin gel, mesenchymal stem cells, and poly(ethylene oxide)-b-poly(L-lysine)/TGF-β1 plasmid DNA complexes for cartilage restoration in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater Res. A 101 (11), 3097–3108. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.34618
Li, T., Zhang, X., Hu, Y., Gao, X., Yao, X., and Xu, Z. (2024). Development of gelatin-methacryloyl composite carriers for bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery: a potential strategy for spinal fusion. J. Biomater. Appl. 39, 195–206. doi:10.1177/08853282241258302
Liang, Y., Zhao, X., Hu, T., Chen, B., Yin, Z., Ma, P. X., et al. (2019). Adhesive hemostatic conducting injectable composite hydrogels with sustained drug release and photothermal antibacterial activity to promote full-thickness skin regeneration during wound healing. Small 15, 1900046. doi:10.1002/smll.201900046
Lin, H., Tang, Y., Lozito, T. P., Oyster, N., Kang, R. B., Fritch, M. R., et al. (2017). Projection stereolithographic fabrication of BMP-2 gene-activated matrix for bone tissue engineering. Sci. Rep. 7, 11327. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11051-0
Liu, J., Xi, Z., Fan, C., Mei, Y., Zhao, J., Jiang, Y., et al. (2024). Hydrogels for nucleic acid drugs delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13, e2401895. doi:10.1002/adhm.202401895
Loozen, L. D., Kruyt, M. C., Kragten, A. H. M., Schoenfeldt, T., Croes, M., Oner, C. F., et al. (2019). BMP-2 gene delivery in cell-loaded and cell-free constructs for bone regeneration. PLoS One 14 (7), e0220028. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0220028
Lu, P., Ruan, D., Huang, M., Tian, M., Zhu, K., Gan, Z., et al. (2024). Harnessing the potential of hydrogels for advanced therapeutic applications: current achievements and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 9, 166. doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01852-x
Mendicino, M., Bailey, A. M., Wonnacott, K., Puri, R. K., and Bauer, S. R. (2022). MSC-Based product characterization for clinical trials: an FDA perspective. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13, 1. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02677-4
Moussa, L., Demarquay, C., Réthoré, G., Benadjaoud, M. A., Siñeriz, F., Pattapa, G., et al. (2019). Heparan sulfate mimetics: a new way to optimize therapeutic effects of hydrogel-embedded mesenchymal stromal cells in colonic radiation-induced damage. Sci. Rep. 9, 164. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-36631-6
Murphy, M. B., Moncivais, K., and Caplan, A. I. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells: environmentally responsive therapeutics for regenerative medicine. Exp. Mol. Med. 52, 1–10. doi:10.1038/s12276-019-0350-4
Papa, S., Vismara, I., Mariani, A., Barilani, M., Rimondo, S., De Paola, M., et al. (2018). Mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated into biomimetic hydrogel scaffold gradually release CCL2 chemokine in situ preserving cytoarchitecture and promoting functional recovery in spinal cord injury. J. Control Release 278, 49–56. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.03.034
Park, Y. B., Ha, C. W., Lee, C. H., Park, K. S., Kang, M. C., Song, J. H., et al. (2017). Cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritic patients by a composite of allogeneic umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and hyaluronate hydrogel: results from a clinical trial for safety and proof-of-concept with 7 years of extended follow-up. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 6, 613–621. doi:10.5966/sctm.2016-0157
Porzionato, A., Barbon, S., Stocco, E., Dalzoppo, D., Contran, M., De Rose, E., et al. (2019). Development of oxidized polyvinyl alcohol-based nerve conduits coupled with the ciliary neurotrophic factor. Materials 12, 1996. doi:10.3390/ma12121996
Saldanha-Araujo, F., Melgaço Garcez, E., Silva-Carvalho, A. E., Carvalho, J. L., Guilmeau-Becker, D., Meirelles, L. S., et al. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cells: a new piece in the puzzle of COVID-19 treatment. Front. Immunol. 11, 1563. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01563
Sathyaraj, W. V., Prabakaran, L., Bhoopathy, J., Dharmalingam, S., Karthikeyan, R., and Atchudan, R. (2023). Therapeutic efficacy of polymeric biomaterials in treating diabetic wounds—An upcoming wound healing technology. Polymers 15, 1205. doi:10.3390/polym15051205
Seliktar, D. (2012). Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical applications. Science 336, 1124–1128. doi:10.1126/science.1214804
Seol, D., Magnetta, M. J., Ramakrishnan, P. S., Kurriger, G. L., Choe, H., Jang, K., et al. (2013). Biocompatibility and preclinical feasibility tests of a temperature-sensitive hydrogel for the purpose of surgical wound pain control and cartilage repair. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 101, 1508–1515. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.32981
Sipp, D., Robey, P. G., and Turner, L. (2018). Clear up this stem-cell mess. Nature 561, 455–457. doi:10.1038/d41586-018-06756-9
Soltanmohammadi, F., Mahmoudi Gharehbaba, A., Alizadeh, E., and Javadzadeh, Y. (2025). Innovative approaches to tissue engineering: utilizing decellularized extracellular matrix hydrogels for mesenchymal stem cell transport. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 290, 138893. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138893
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Dalzoppo, D., Lora, S., Sartore, L., Folin, M., et al. (2014). Tailored PVA/ECM scaffolds for cartilage regeneration. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 762189. doi:10.1155/2014/762189
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Radossi, P., Rajendran, S., Dalzoppo, D., Bortolami, M., et al. (2016). Autologous chondrocytes as a novel source for neo-chondrogenesis in haemophiliacs. Cell Tissue Res. 366, 51–61. doi:10.1007/s00441-016-2408-8
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Piccione, M., Belluzzi, E., Petrelli, L., Pozzuoli, A., et al. (2019a). Infrapatellar fat pad stem cells responsiveness to microenvironment in osteoarthritis: from morphology to function. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 7, 323. doi:10.3389/fcell.2019.00323
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Macchi, V., Porzionato, A., Dalzoppo, D., De Caro, R., et al. (2019b). New bioresorbable wraps based on oxidized polyvinyl alcohol and leukocyte-fibrin-platelet membrane to support peripheral nerve neurorrhaphy: preclinical comparison versus NeuraWrap. Sci. Rep. 9, 17193. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53812-z
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Lamanna, A., De Rose, E., Zamuner, A., Sandrin, D., et al. (2021). Bioactivated oxidized polyvinyl alcohol towards next-generation nerve conduits development. Polymers 13, 3372. doi:10.3390/polym13193372
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Zeni, E., Cassari, L., Zamuner, A., Gloria, A., et al. (2022). Development of two-layer hybrid scaffolds based on oxidized polyvinyl alcohol and bioactivated chitosan sponges for tissue engineering purposes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 12059. doi:10.3390/ijms232012059
Stocco, E., Barbon, S., Ceroni, L., Confalonieri, M., Pulzato, G., Pressi, S., et al. (2024). Partially oxidized polyvinyl alcohol + functionalized water soluble multiwalled carbon nanotubes: a new conductive nanocomposite material with promising implications for neuroregeneration. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 9, 100762. doi:10.1016/j.jsamd.2024.100762
Sun, K., Lin, H., Tang, Y., Xiang, S., Xue, J., Yin, W., et al. (2020). Injectable BMP-2 gene-activated scaffold for the repair of cranial bone defect in mice. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9 (12), 1631–1642. doi:10.1002/sctm.19-0315
Sun, X., Zhang, H., Huang, S., Li, K., and Wang, X. (2025). Dual sustained-release BMP7-nanoparticle hydrogel scaffolds for enhanced BMSC neuronal differentiation and spinal cord injury repair. Spine 50, 575–585. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000005307
Takayama, Y., Kusamori, K., Katsurada, Y., Obana, S., Itakura, S., and Nishikawa, M. (2023). Efficient delivery of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells to injured liver by surface PEGylation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 14, 216. doi:10.1186/s13287-023-03446-w
Tavajjohi, Z., Sigaroodi, F., Rabbani, S., Barekat, M., Rouhani, M., Boroumand, S., et al. (2025). Therapeutic performance of hydrogel-derived extracellular Wharton's jelly matrix and Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells in repairing infarcted myocardium of ischemic rats: a preclinical study. Macromol. Biosci. e70007, e70007. doi:10.1002/mabi.202400578
Todros, S., Barbon, S., Stocco, E., Favaron, M., Macchi, V., De Caro, R., et al. (2022a). Time-dependent mechanical behavior of partially oxidized polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels for tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 125, 104966. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2021.104966
Todros, S., Spadoni, S., Barbon, S., Stocco, E., Confalonieri, M., Porzionato, A., et al. (2022b). Compressive mechanical behavior of partially oxidized polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels for cartilage tissue repair. Bioengineering 9, 789. doi:10.3390/bioengineering9120789
Vivas, D., Grau-Vorster, M., Oliver-Vila, I., García-López, J., and Vives, J. (2020). Evaluation of a cell-based osteogenic formulation compliant with good manufacturing practice for use in tissue engineering. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47, 5145–5154. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05588-z
Voronin, A. V. (2025). Allogeneic ADSCs and platelet-poor plasma fibrin hydrogel to treat the patients with burn wounds. ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier NCT03113747. Available online at: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03113747 (Accessed on June 29, 2025).
Wang, W., Li, B., Li, Y., Jiang, Y., Ouyang, H., and Gao, C. (2010). In vivo restoration of full-thickness cartilage defects by poly(lactide-co-glycolide) sponges filled with fibrin gel, bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and DNA complexes. Biomaterials 31 (23), 5953–5965. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.04.029
Wei, W., Dai, H., Zhang, Y., Li, Z., Guo, R., Huang, B., et al. (2023). Hydrogel-based delivery of MSCs for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 19, 112–126. doi:10.1038/s41584-022-00831-8
Wu, Z., Chen, G., Zhang, J., Hua, Y., Li, J., Liu, B., et al. (2017). Treatment of myocardial infarction with gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells in a small molecular hydrogel. Sci. Rep. 7, 15826. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-15870-z
Xiao, L., Sun, Y., Liao, L., and Su, X. (2023). Response of mesenchymal stem cells to surface topography of scaffolds and the underlying mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. B 11, 2550–2567. doi:10.1039/d2tb01875f
Xie, M., Tao, H., Zhu, H., Mei, Y., Chen, L., Wu, A., et al. (2020). Bionic detectors based on low-bandgap inorganic perovskite for selective NIR-I photon detection and imaging. Adv. Mater. 32, 1905362. doi:10.1002/adma.201905362
Xue, Z., Hu, D., Tang, H., Xue, M., Zhu, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2024). Mechanical force regulates the paracrine functions of ADSCs to assist skin expansion in rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 15, 250. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03822-0
Yang, M., Zhang, Z. C., Yuan, F. Z., Deng, R. H., Yan, X., Mao, F. B., et al. (2022). An immunomodulatory polypeptide hydrogel for osteochondral defect repair. Bioact. Mater. 19, 678–689. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.05.008
Zeng, X., Tang, Y., Hu, K., Wang, L., Li, S., Liu, J., et al. (2017). Three-week topical treatment with placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells hydrogel in a patient with diabetic foot ulcer: a case report. Med. Baltim. 96, e9212. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000009212
Zhang, C., Gullbrand, S. E., Schaer, T. P., Boorman, S., Elliott, D. M., Chen, W., et al. (2021). Combined hydrogel and mesenchymal stem cell therapy for moderate-severity disc degeneration in goats. Tissue Eng. Part A 27, 117–128. doi:10.1089/ten.TEA.2020.0103
Zhao, Y., Wang, M., Liang, F., and Li, J. (2021). Recent strategies for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of stem cells in wound healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 12, 588. doi:10.1186/s13287-021-02657-3
Zhou, J., Xiong, S., Liu, M., Yang, H., Wei, P., Yi, F., et al. (2023). Study on the influence of scaffold morphology and structure on osteogenic performance. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1127162. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1127162
Keywords: mesenchymal stromal cells, hydrogels, tissue regeneration, preclinical research, clinical trials
Citation: Barbon S, Rajendran S, Banerjee A, Parnigotto PP, De Caro R, Macchi V and Porzionato A (2025) Mesenchymal stromal cell-laden hydrogels in tissue regeneration: insights from preclinical and clinical research. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1670649. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1670649
Received: 21 July 2025; Accepted: 26 August 2025;
Published: 12 September 2025.
Edited by:
Jian Zhong, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ilya D. Klabukov, National Medical Research Radiological Center, RussiaFatemeh Soltanmohammadi, Tabriz University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Barbon, Rajendran, Banerjee, Parnigotto, De Caro, Macchi and Porzionato. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Silvia Barbon, c2lsdmlhLmJhcmJvbkB1bmlwZC5pdA==
 Silvia Barbon
Silvia Barbon Senthilkumar Rajendran2
Senthilkumar Rajendran2 Antara Banerjee
Antara Banerjee Pier Paolo Parnigotto
Pier Paolo Parnigotto Raffaele De Caro
Raffaele De Caro Veronica Macchi
Veronica Macchi Andrea Porzionato
Andrea Porzionato