Abstract
Lung injury is characterized by impaired gas exchange, inflammatory responses, and abnormal tissue repair. In severe cases, it can progress to respiratory failure, posing a threat to public health. Marine natural products, due to their structural and biological activity diversity, show significant potential in the treatment of lung injury. This article systematically reviews the mechanism by which marine-derived natural products improve lung injury by regulating key signaling pathways in vivo. Studies have demonstrated that marine natural products target pathological processes such as inflammatory immunity and oxidative stress by regulating signaling pathways including αvβ3-FAK/Src, TLR4/MyD88, NF-κB, and Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3, thereby exerting a significant protective effect on alveolar structures in lung injury models induced by stimuli such as radiation, OVA, LPS, and cigarette smoke. Currently, there is a lack of marine drugs specifically for lung injury, and in-depth research is needed to promote their translation into clinical medications.
1 Introduction
The lung, as the most vital organ in the human respiratory system, facilitates gas exchange with inhaled air to acquire the oxygen requisite for cellular respiration (Luo et al., 2025). Lung injury refers to the pathophysiological process characterized by impaired gas exchange and inflammatory responses, which is triggered by various damaging factors that induce pulmonary tissue damage, with clinical manifestations of dyspnea (Dubey et al., 2025), hypoxemia (Swenson et al., 2021), cough and expectoration (Guo J. et al., 2024), in severe cases, it can progress to respiratory failure (Fedt et al., 2020). Its pathological core involves increased pulmonary microvascular permeability (Knudsen and Ochs, 2018), alveolar epithelial injury (Swenson et al., 2021), inflammatory cell infiltration (Ma L. et al., 2025), and abnormal tissue repair (D'Agnillo et al., 2021), etc. Based on clinical characteristics, it can be classified into two types: acute injury and chronic injury, as illustrated in Figure 1.
FIGURE 1
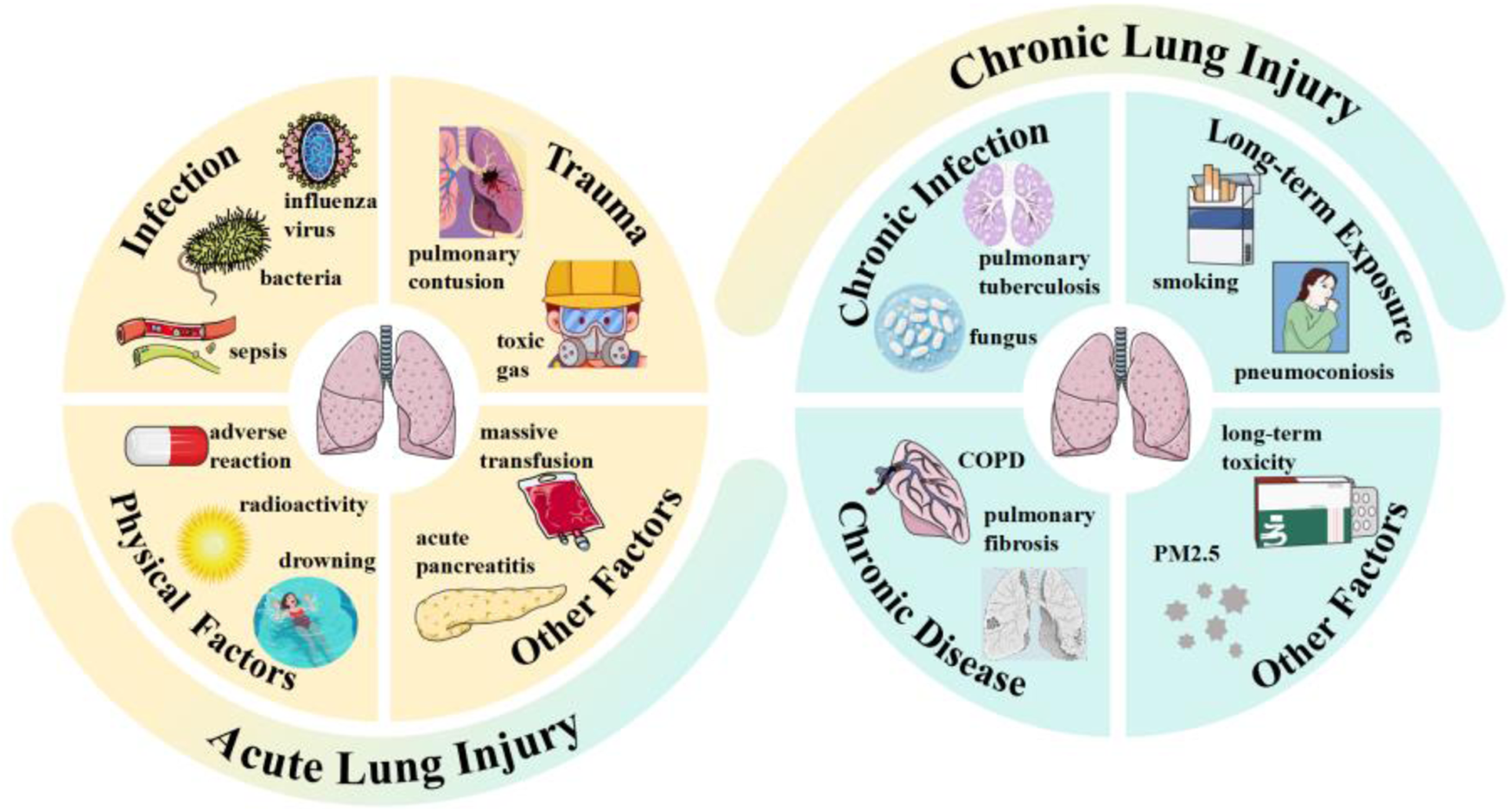
Types and inducing factors of lung injury.
Among them, acute lung injury is associated with high morbidity and mortality, and can progress to acute respiratory distress syndrome with poor prognosis, with a mortality rate as high as 40% (Liao et al., 2021). During the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2002–2003 severe acute respiratory syndrome regional outbreak, the mortality rates of ICU patients who died from acute respiratory distress syndrome reached as high as 67%–85% and 52.2%, respectively (Zhang et al., 2024). According to recent statistical data released by the World Health Organization, it is estimated that due to exposure to air environmental pollution, infections, or genetic backgrounds, the global population will develop acute or chronic lung diseases within the next decade (Bezerra et al., 2023). Even with the rapid advancements in current medical technologies, lung injury-related diseases still pose a significant public health threat.
In recent decades, the potential of marine natural products in the medical field has gained increasing recognition, characterized by extensive chemical activities and biological diversity. Marine microorganisms, algae, and invertebrates constitute the three primary sources of marine natural products (Zhang et al., 2025; Bezerra et al., 2023). These compounds are involved in key in vivo processes such as tumor cell cycle regulation, autophagy, ferroptosis, and gut microbiota programming, exhibiting potent anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor potentials. Furthermore, marine natural products have demonstrated significant antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal activities (Ma M. T. et al., 2025). Such remarkable efficacy may be attributed to their unique functional groups (e.g., brominated and chlorinated alkaloids), complex cyclic structures (e.g., macrolides and polyether compounds), and the presence of sulfate groups (Zhang et al., 2017).
The application of marine natural products in the treatment of lung injury holds theoretical feasibility. From the perspective of pathological mechanisms, the multi-target regulatory properties of marine natural products enable them to specifically address pathological processes associated with lung injury, such as excessive inflammatory responses, oxidative stress damage, and pulmonary fibrosis (Kumar and Adki, 2018). For instance, the carotenoid fucoxanthin can inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines triggered by Mycoplasma pneumoniae and enhance bacterial clearance in mouse models (Li et al., 2020); astaxanthin can reduce the increase in inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and emphysema (Akduman et al., 2021; Bi et al., 2017); and fucoidan significantly alleviates hyperoxia-induced lung injury (Nie et al., 2018). To date, a large number of natural compounds with lung injury-protective activity have been isolated from marine microorganisms, algae, sponges, and other organisms, including alkaloids, terpenoids, polypeptides, polyketides, and pyranones (Zhang Y. et al., 2020; Singh, 2020). However, current research has obvious limitations. On one hand, most studies remain in the stages of compound isolation, identification, and in vitro activity screening, verifying their protective effects on lung epithelial cells, macrophages, etc., through cell experiments or extracellular enzyme experiments, while in-depth in vivo studies are relatively scarce. The in vivo environment is a complex dynamic system involving interactions among various cells, tissues, and physiological processes. On the other hand, the specific molecular mechanisms and targets underlying their therapeutic effects in vivo, especially the regulatory mechanisms of signaling pathways, remain unclear. Therefore, systematically sorting out the mechanistic pathways of marine natural products in the in vivo treatment of lung injury and clarifying the current problems and challenges are of great significance for developing new therapeutic strategies for lung injury and accelerating the development and application of marine natural products.
2 Molecular mechanisms/pathways of lung injury for marine natural products
2.1 Immune response and inflammation
The development of lung injury is closely associated with abnormal activation of the immune system and the inflammatory response. When the lungs encounter external stimuli such as radiation, allergens, pathogens, or chemicals, the innate and adaptive immune systems become activated. This activation leads to a substantial release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Additionally, inflammatory cells such as neutrophils, macrophages, and T-cells infiltrate the lung tissue. This process triggers oxidative stress, tissue edema, and damage to the alveolar structure. These immune-inflammatory responses form a common pathological basis for various types of lung injuries. Currently, several in vivo models are used to study the mechanisms behind lung injury due to immune-inflammatory responses. These models include radiation-induced lung injury, OVA-induced T cell activation, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced lung injury, and cigarette smoke-induced lung injury models. Research has shown that a range of marine natural products exhibited significant protective effects in these four models.
2.1.1 Marine natural products for radiation-induced lung injury
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a common complication that occurs after radiotherapy for thoracic tumors. It is characterized by early-stage alveolar inflammatory exudation, infiltration of immune cells (such as macrophages and neutrophils), and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-6 and TNF-α. In the late stage, RILI features abnormal activation of fibroblasts, deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM), and irreversible remodeling of lung tissue structure (Arroyo-Hernández et al., 2021). Several immune-related signaling pathways play a role in RILI. One significant pathway is the TGF-β/Smad pathway, which, when activated by radiation, triggers fibroblast activation, ECM deposition, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, ultimately leading to irreversible fibrosis in lung tissue (Cao et al., 2017; Park et al., 2015). In addition, the HMGB1/TLR4 pathway serves as a central mechanism driving inflammation in RILI. This pathway amplifies the inflammatory response by activating multiple downstream pathways, including NF-κB and MAPK (Zheng et al., 2020). Research has shown that astaxanthin, a compound commonly found in shrimp, oysters, and other marine organisms, possesses strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. In mouse models of RILI, astaxanthin has been shown to inhibit the progression of pulmonary fibrosis and reduce levels of inflammatory factors. Furthermore, astaxanthin can alleviate RILI by inhibiting cell apoptosis in vitro (Li et al., 2023). As a natural marine product, astaxanthin is highly safe and widely sourced, making it a suitable candidate for adjuvant treatment of RILI.
2.1.2 Marine natural products for OVA-induced T cell activation
Ovalbumin (OVA) is the primary protein found in egg white and serves as an exogenous protein that activates the mammalian immune system. It triggers T cell activation and induces a Th2-type immune response, mimicking the immune mechanisms involved in human allergic asthma (Azman et al., 2021). During OVA-induced T cell activation, various immune pathways related to antigen recognition, T cell activation, differentiation, and effector functions are engaged. The T cell receptor pathway is key for antigen recognition and activation (Shin et al., 2021). When CD28 on the surface of T cells binds to B7 on antigen-presenting cells, it enhances the intensity of T cell receptor signaling (Linsley et al., 1993). Additionally, CD28 recruits PI3K, which activates the Akt/mTOR pathway (Efimova and Kelley, 2009). The MAPK pathway is involved in regulating T cell proliferation and differentiation (Jiang et al., 2023). Further, the TGF-β-Smad pathway influences the direction of T-cell differentiation (Liu et al., 2025). In conclusion, OVA-induced T-cell activation results from the synergistic action of multiple pathways. Marine microorganisms produce secondary metabolites with unique structural and therapeutic potential. One such metabolite is alternariol, derived from the marine fungus Alternaria sp. Alternariol has been found to target early T-cell activation, impact T-cell apoptosis, and inhibit T-cell proliferation and inflammatory factor production. Notably, alternariol has demonstrated the ability to alleviate OVA-induced inflammation in mouse lungs by inhibiting T cell activation and preventing T cell metastasis to mouse lungs (Liu et al., 2025). The inhibitory effect of alternariol on OVA-induced T cell activation underscores the potential of marine microbial resources for drug discovery. Blocking T cell activation and migration is one therapeutic strategy for intervening in allergic asthma (Zhang et al., 2022). However, it is essential to focus on specifically modulating pathogenic T cell subsets while preserving the protective immune response to ensure safer and more effective clinical applications.
2.1.3 Marine natural products for LPS-induced lung injury
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a prevalent respiratory condition characterized by increased permeability of the alveolar-capillary membranes. It manifests as noncardiogenic pulmonary edema and severe hypoxemia. The more severe form of ALI is called acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (Long et al., 2022). A classic experimental model for studying ALI and ARDS is the LPS-induced lung injury model. LPS triggers inflammatory gene transcription and cellular stress responses through activating members of the MAPK family (p38, JNK, ERK) (Wang et al., 2018). The activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome further exacerbates inflammatory injury (Ning et al., 2020). Additionally, LPS-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production activates the NLRP3 inflammasome, amplifying the inflammatory response (Liu Y. et al., 2024). The LPS-induced lung injury model also involves the regulation of the JAK-STAT pathway (Hashimoto et al., 2020) and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway (Hu et al., 2020). Together, these mechanisms lead to disruption of the alveolar-capillary barrier, neutrophil infiltration, and the release of numerous proinflammatory factors, closely mimicking the pathologic features of clinical ALI/ARDS. In studies involving mice with LPS-induced acute lung injury, hypobranchial gland extract and the brominated indole compound 6-bromoisatin derived from the marine gastropod molluscs Dicathais orbita have been shown to inhibit inflammatory signaling pathways. These substances work by blocking the translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus and preventing macrophage activation (Ahmad et al., 2017). Furthermore, laminarin, a bioactive polysaccharide found in brown algae, can attenuate sepsis-associated ALI by decreasing M1 macrophage polarization through the downregulation of HIF-1α signaling (Zeng et al., 2025). Thus, marine natural products present significant potential for the treatment of ALI.
2.1.4 Marine natural products for cigarette smoke-induced lung injury
Smoking is responsible for numerous lung diseases, particularly chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer (Durham and Adcock, 2015). The cigarette smoke-induced lung injury model effectively simulates COPD or emphysem Marine natural products for cigarette smoke-induced lung injury a that arises from long-term smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke. This model triggers chronic inflammation of the airways, destruction of alveolar structures, and excessive mucus production due to sustained exposure to smoke, similar to the pathological features of human smokers (Upadhyay et al., 2023). The immune mechanisms involved in this process include the activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes (Zhang et al., 2021), an imbalance between Th17 and regulatory T cells (Tao et al., 2025), and the polarization of macrophages into the M1 subtype (Feng and Zheng, 2023). In addition, oxidative stress exacerbates the inflammatory response by inhibiting the Nrf2 antioxidant pathway (Hikich et al., 2019), creating a vicious cycle of chronic lung injury. Collectively, these pathways reflect the immune-inflammatory cascade characteristic of smoking-related lung diseases. In the coastal region of southern China, a black coral extract from the genus Antipathes is being used to make cigarette holders that filter out some harmful substances in cigarette smoke (Bai et al., 2011a). Studies have shown that ultrasonically aerosolized inhalation of this extract can reduce cigarette smoke-induced inflammation in the lungs of mice with lung injuries, exhibiting both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (Bai et al., 2011b). This black coral extract may have the potential as a protective agent against smoking-associated lung injuries, and nebulized inhalation could prove to be a more effective alternative to traditional oral formulations.
2.2 Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 pathway
2.2.1 Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 signaling in lung injury
The mechanism of action of the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 pathway in lung injury involves several key biological processes, including oxidative stress, inflammatory response, and cell survival. The respiratory system is particularly vulnerable to oxidative stress, making the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway essential for antioxidant defence (Abed et al., 2015). Under normal conditions, Keap1 functions as an adaptor protein for the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, which binds to Nrf2, leading to its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation. This process keeps low levels of Nrf2. However, during lung injury, ROS induce a conformational change in Keap1, resulting in the release of Nrf2. Free Nrf2 then translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to the antioxidant response element and initiates the expression of downstream antioxidant genes, such as HO-1 and glutathione synthetase (Hikichi et al., 2019). HO-1, a crucial target gene for Nrf2, catalyzes the production of heme, which has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and iron metabolism properties (Ghareghomi et al., 2023). Additionally, in the context of lung injury, STAT3 also serves as a target gene for Nrf2 and plays a pivotal role in this pathway. STAT3 can be activated by cytokines or growth factors like IL-6 and IL-10. Once activated, it undergoes phosphorylation, forms a dimer, and moves into the nucleus, where it regulates genes related to inflammation, proliferation and apoptosis. Overactivated STAT3 may promote M1 macrophage polarization and the release of pro-inflammatory factors, intensifying acute inflammation or driving lung fibrosis. On the other hand, moderate activation of STAT3 supports alveolar epithelial cell proliferation, tissue repair, and cell survival through the upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins such as Bcl-2 (Harada et al., 2014). In cases of acute lung injury activating the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway can reduce oxidative damage, while controlling STAT3 activation may help alleviate inflammation.
2.2.2 Marine-derived products in Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 pathway regulation
Astaxanthin and fucoxanthin, two natural carotenoids derived from marine sources, both demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects and protection against iron-mediated cell death in a model of ALI induced by LPS. As astaxanthin was shown to reduce the expression of pro-inflammatory factors, such as COX-2 and iNOS, and to decrease NO release by inhibiting the nuclear translocation of NF-κB in acute and radio-induce lung injury (Luo et al., 2022). Additionally, it activated the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 pathway, which enhanced antioxidant capacity and reversed the abnormal expression of proteins related to iron death, including GPX4, SLC7A11, and FTH1, thus alleviating lung edema and inflammatory cell infiltration (Harada et al., 2014). Similarly, fucoxanthin significantly reduced lipid peroxidation levels and the accumulation of ferrous ions by inhibiting inflammatory markers such as PTGS2 and TNF-α. It also modulated the Nrf2/STAT3 pathway and the glutathione metabolism pathway, resulting in an upregulation of glutathione and its metabolic intermediates such as γ-Glu-Cys, to enhance antioxidant defence (Ding et al., 2024). Both compounds were effective in improving alveolar barrier integrity and mitigating pathological inflammatory responses by modulating Nrf2-associated antioxidant pathways and targeting key proteins involved in iron death. The mechanism by which they alleviated ALI through the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 pathway is illustrated in Figure 2.
FIGURE 2
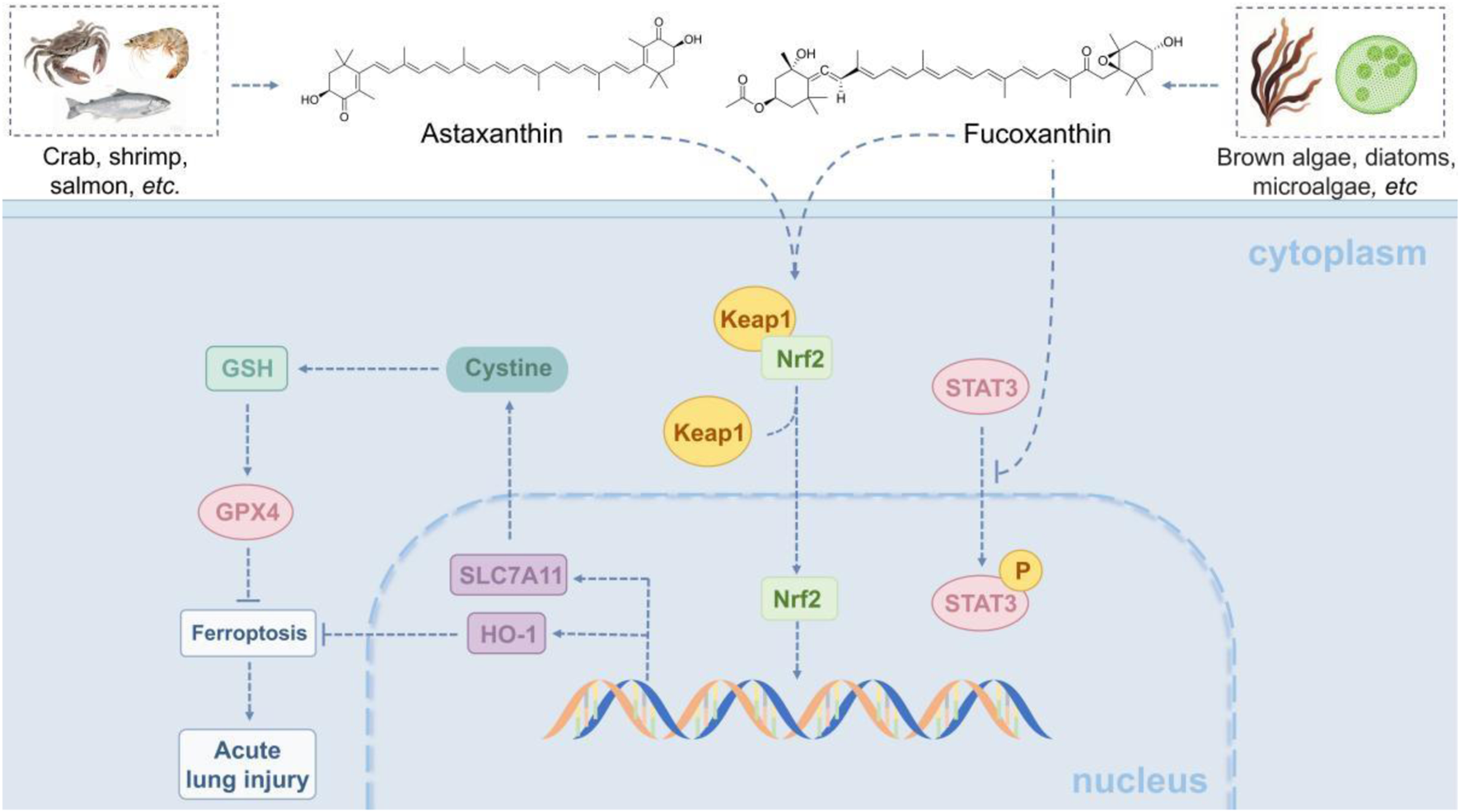
Marine-derived products attenuate acute lung injury (ALI) via the Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 pathway. The Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3 pathway modulates oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell survival in lung injury. Normally, Keap1 degrades Nrf2; upon injury, ROS frees Nrf2, which enters the nucleus to activate HO-1 and other antioxidant genes. HO-1 has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effects. STAT3, an Nrf2 target activated by IL-6/10, regulates related genes-overactivation worsens inflammation, while moderate activation promotes repair via Bcl-2. Marine astaxanthin and fucoxanthin protect against LPS-induced ALI: the former inhibits NF-κB and activates the pathway; the latter reduces lipid peroxidation and modulates Nrf2/STAT3. Both improve alveolar integrity.
2.3 NF-κB-related pathways
2.3.1 NF-κB-related pathways in lung injury
The nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) pathway is a crucial signaling pathway that regulates inflammation and immune response. It plays a significant role in ALI and chronic lung diseases (Millar et al., 2022). When stimulatory factors such as LPS, TNF-α, or IL-1β bind to their respective receptors, they activate the IKK complex. This activation leads to the degradation of the inhibitory protein IκBα and the subsequent release of NF-κB (p50/p65) into the nucleus, where it initiates the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes. In cases of lung injury, the overactivation of NF-κB leads to the upregulation of inflammatory factors. This recruitment of inflammatory mediators results in neutrophil infiltration, damage to the alveolar epithelial and endothelial barriers, and the onset of lung oedema (Li et al., 2022). Additionally, NF-κB promotes the expression of NADPH oxidase and ROS generation. This increase in ROS contributes to lipid peroxidation and DNA damage, thereby exacerbating lung injury (Harijith et al., 2022; Carnesecchi et al., 2011). Chronic activation of NF-κB further stimulates the secretion of factors like TGF-β and PDGF, which activate fibroblasts and can result in lung fibrosis (Liu and Desai, 2015). Moreover, the NF-κB pathway shares common upstream activators with the MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways, and there exists a cross-regulation among these pathways, collectively influencing biological processes such as inflammation, cell survival, proliferation, and apoptosis (Guo Q. et al., 2024).
2.3.2 Marine-derived products in NF-κB-related pathways regulation
Marine natural products offer multiple protective effects in inflammatory lung injury by targeting NF-κB and related signaling pathways. For instance, the extract of the marine brown alga Endarachne binghamiae significantly reduces pro-inflammatory factors like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in macrophages and lung tissues within an LPS-induced ALI model (Lee et al., 2025). This reduction occurs through the inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB activation by blocking IκB phosphorylation and the MAPK (ERK/JNK/p38) pathway. The extract also decreases the expression of iNOS and COX-2 in macrophages and lung tissues, while reducing alveolar edema and inflammatory infiltration (Lee et al., 2025). Similarly, extract from the sea cucumber (Cucumaria frondosa) also lowers IL-1β and TNF-α levels by synergistically inhibiting the phosphorylation of the NF-κB/MAPK/JNK pathways in acute lung injury (Fagbohun et al., 2024). When combined with wild blueberry polyphenols, such as anthocyanins, they further modulate IL-4 expression, which helps TLR4-mediated damage to the alveolar barrier (Fagbohun et al., 2024). Furthermore, 2, 2′-bipyridine compounds (collismycin C and pyrisulfoxin A) from red alga-associated Streptomyces have been effective in reducing alveolar barrier damage caused by particulate matter-induced pulmonary injury (Choi et al., 2019). This is achieved by scavenging PM2.5-induced ROS, inhibiting the p38 MAPK pathway, and activating the PI3K/Akt pathway, thereby attenuating pulmonary microvascular endothelial permeability and leukocyte infiltration (Choi et al., 2019). These studies demonstrate that marine natural products effectively mitigate oxidative stress and inflammation by targeting both the NF-κB pathway and its interconnected signaling components, such as MAPK and PI3K/Akt, thereby highlighting their therapeutic potential for inflammatory lung diseases through a coordinated multi-pathway regulatory mechanism (Figure 3).
FIGURE 3
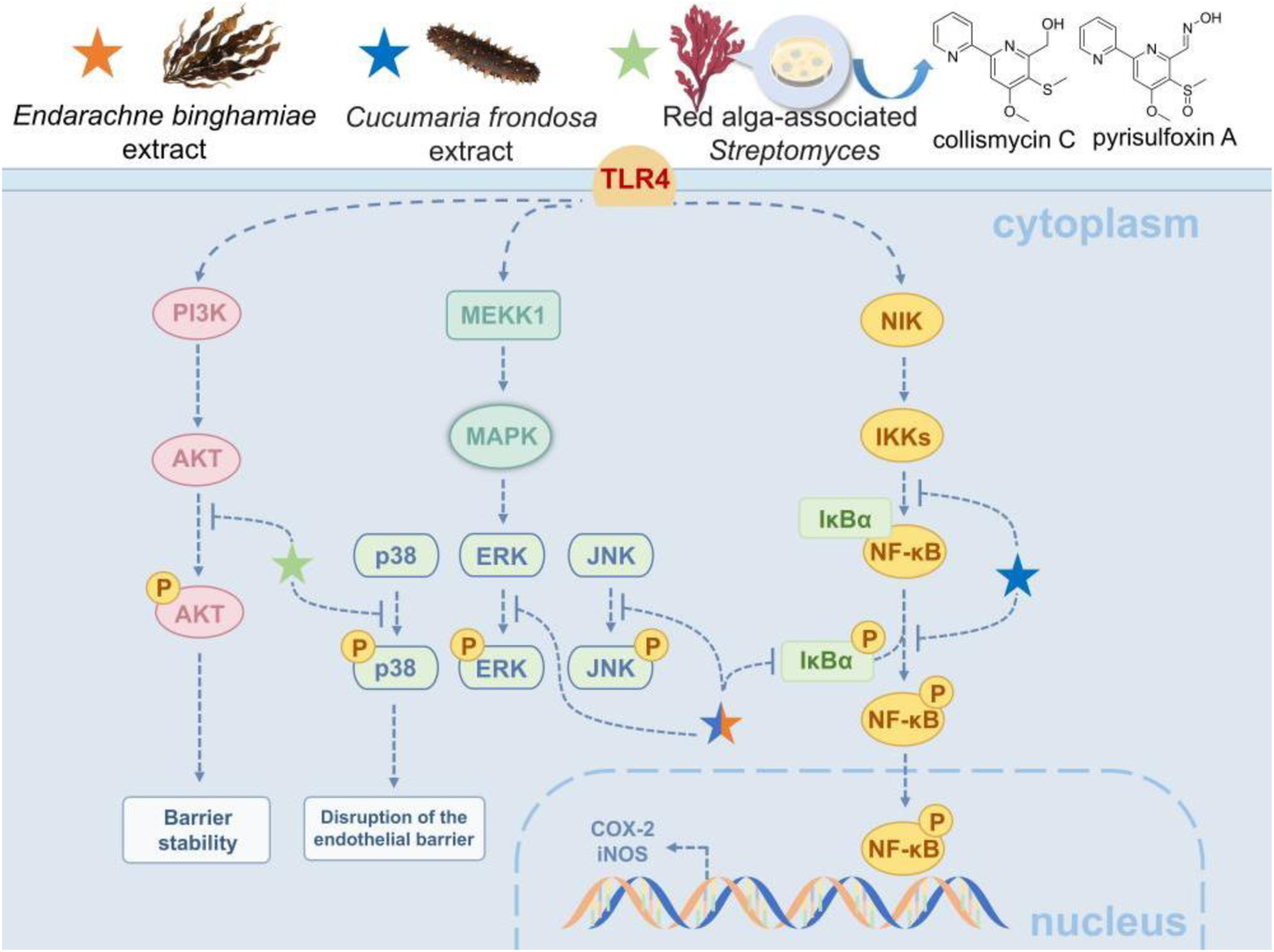
Marine-derived products attenuate ALI via NF-κB-related pathways. The NF-κB pathway, a core regulator of inflammation and immune response, is pivotal in ALI and chronic lung diseases. When LPS, TNF-α or IL-1β binds to receptors, it activates the IKK complex, triggering IκBα degradation and NF-κB nuclear translocation to transcribe pro-inflammatory genes, leading to lung edema and fibrosis. Marine natural products exert protective effects and alleviate injury by targeting NF-κB and related pathways.
2.4 TLR4/MyD88
2.4.1 The role of the TLR4/MyD88 pathway in lung injury
When lung tissue is exposed to pathogen-associated molecular patterns, such as bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which acts as an agonist for Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), LPS binds to TLR4. This binding then induces nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) activity either through the Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR)-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β (TRIF) pathway or the myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) pathway. Activated NF-κB triggers an inflammatory response by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). This, in turn, exacerbates pulmonary vascular permeability and alveolar epithelial injury (Doyle and O'Neill, 2006). In addition, the TLR4/MyD88 pathway can also activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, promoting the maturation and secretion of IL-8 and IL-1β, and further amplifying the inflammatory response (Guan et al., 2022). In terms of oxidative stress, this pathway increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by regulating the expression of NADPH oxidase (such as NOX4), leading to oxidative damage of lung tissue. Meanwhile, the excessive activation of the TLR4/MyD88 pathway can also induce apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells and endothelial cells and disrupt lung barrier function by up-regulating the expression of pro-apoptotic proteins (such as Bax) and inhibiting the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins (such as Bcl-2) (Murphy and Caraher, 2015).
2.4.2 Fucoxanthin regulates lung injury through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway
Marine fucoxanthin can significantly inhibit LPS-induced acute lung injury (Li et al., 2020). The core mechanism lies in directly binding to the hydrophobic pocket of the TLR4/MD-2 complex (partially overlapping with the LPS binding site). Molecular conjugating confirmed that this binding depends on the hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions of key amino acids such as LYS-360 and PHE-151, thereby competitive blocking of TLR4 dimerization (Figure 4). This effect effectively inhibits downstream MyD88-dependent signal transduction, reduces the phosphorylation of the NF-κBp65 subunit and blocks its nuclear translocation, and ultimately significantly downregulates the expression of inflammatory mediators such as COX-2 and iNOS, as well as pro-inflammatory factors such as IL-6 and TNF-α. This study confirmed that fucoxanthin regulates the inflammatory storm through the ‘TLR4-MyD88-NF-κB axis’, providing a novel Marine drug candidate strategy for the treatment of acute lung injury.
FIGURE 4
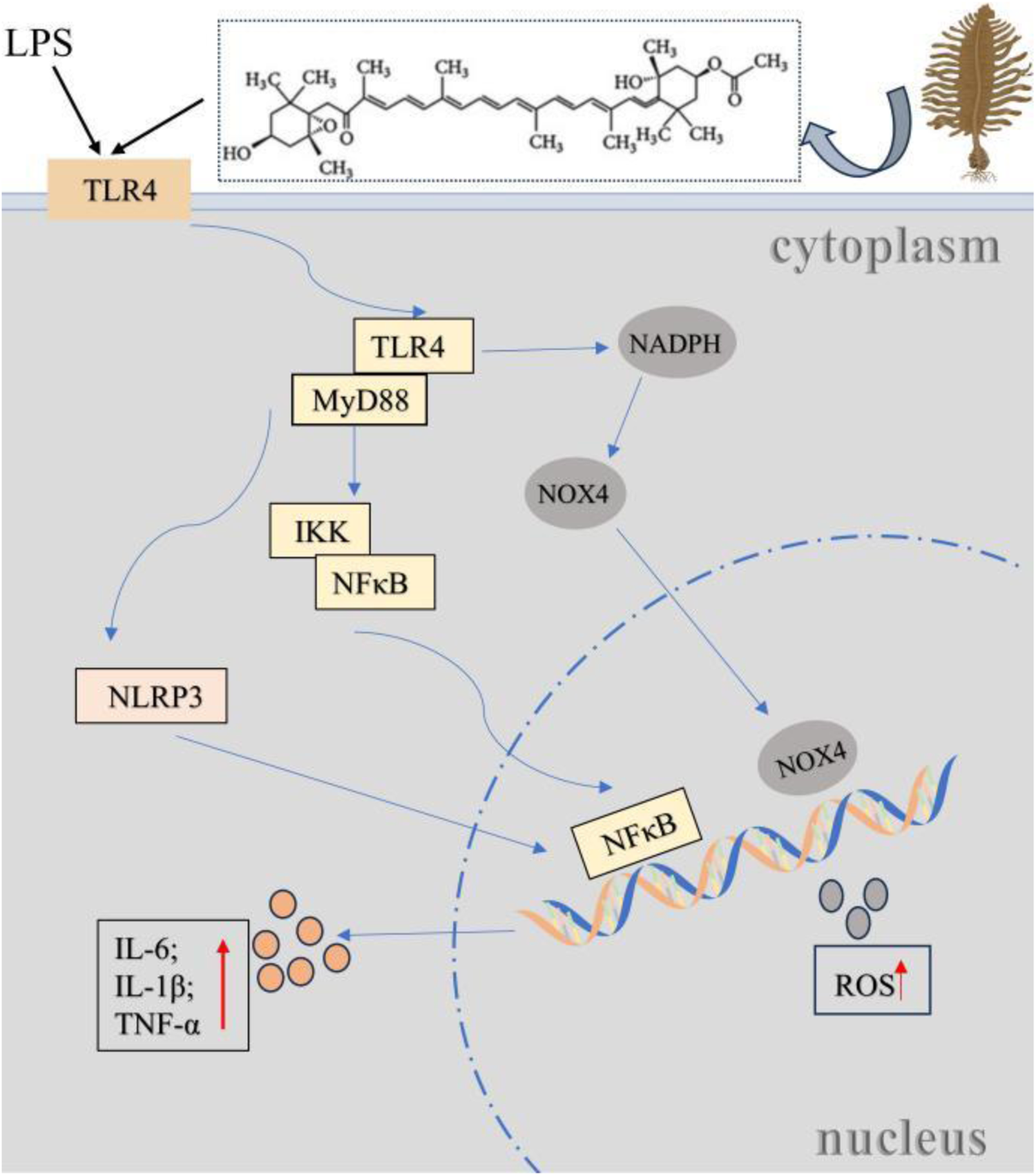
Fucoxanthin regulates lung injury through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Bacterial LPS (a TLR4 agonist) binds to the TLR4/MD-2 complex, activating NF-κB via MyD88 or TRIF pathways to release pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), and triggering NLRP3 inflammasome activation, ROS production and apoptosis, thereby inducing acute lung injury (ALI) through inflammation, oxidative stress, and lung barrier disruption. Marine fucoxanthin inhibits LPS-induced ALI by competitively binding to the TLR4/MD-2 hydrophobic pocket, blocking TLR4 dimerization and MyD88-dependent signaling.
2.5 Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 and fibroblasts
2.5.1 Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 and fibroblasts
The development of pulmonary fibrosis involves complex molecular network regulation, among which the abnormal activation of the Matrix Metalloproteinase family plays a key role. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) are a zinc-dependent endoprotease family that are involved in the degradation and remodeling of extracellular matrix (Cui et al., 2017). In MMP, MMP-9 is particularly worthy of attention because it is elevated in patients with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, and is positively correlated with the severity of lung injury (Lanchou et al., 2003; Hsu et al., 2015; Ricou et al., 1996). The regulatory role of MMP-9 in lung injury shows significant complexity. On the one hand, its excessive activation directly aggravates pulmonary edema and increased permeability by degrading key extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins such as type IV collagen (Torii et al., 1997), the main components of the basement membrane, and destroying the integrity of the alveolar-capillary barrier. Meanwhile, MMP-9 amplifies the inflammatory cascade reaction by cutting and activating multiple pro-inflammatory factors and chemokines, promoting the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells such as neutrophils into lung tissue, and causing tissue damage (Takahashi et al., 2018). On the other hand, the activity of MMP-9 also profoundly affects the process of tissue repair and remodeling. In the later stage of injury, the continuously high expression of MMP-9 not only hinders the normal reconstruction of ECM, but also the fragments produced by its degradation of ECM and the released/activated latent growth factors may instead promote the proliferation, migration and transformation into myofibroblasts of fibroblasts, driving the abnormal pathological fibrosis process (Chapman et al., 2004). Therefore, MMP-9 plays a crucial double-edged sword role in lung injury: early overactivation exacerbates acute inflammatory damage and barrier destruction, while persistent dysregulation in the later stage becomes an important molecule promoting the transformation from inflammation to fibrosis.
2.5.2 Hirsutanol A and fucoidan alleviate lung injury through the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and fibroblast function
Animal experiments have confirmed that in acute lung injury complicated with LPS-induced endotoxemia, Hirsutanol A (HA) derived from the Marine fungus Chondrostereum sp. NTOU4196 can alleviate lung tissue injury conditions (such as edema and inflammatory infiltration) (Jan et al., 2019). Meanwhile, the acute disease behavior is improved by inhibiting the activation of STAT3 and the expression of MMP-9 (Jan et al., 2019) (Figure 5). Another example is fucoidan from brown algae. It alleviates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats by regulating fibroblast differentiation, inhibiting the transformation of lung fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, manifested as a decrease in the expression of α-SMA and collagen I, reduced collagen deposition and pulmonary fibrosis (Zhang B. et al., 2020). HA and Fucoidan respectively alleviate lung tissue damage, fibrosis and oxidative stress by inhibiting the MMP-9-mediated inflammatory cascade and the transformation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, providing potential marine drug strategies for the treatment of lung injury.
FIGURE 5
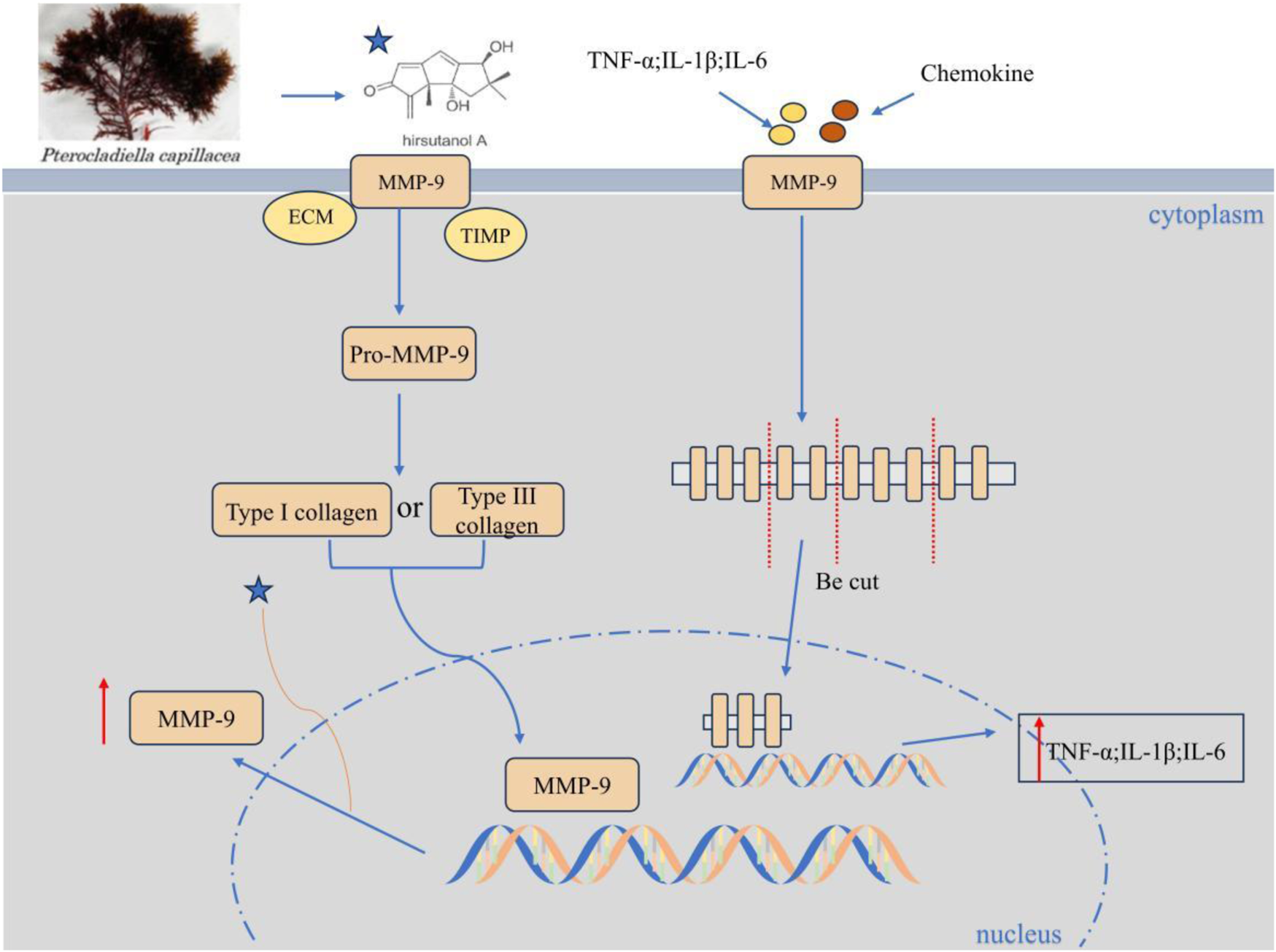
Hirsutanol A inhibits the expression of MMP-9. HA concentration-dependently suppresses LPS-triggered MMP-9-mediated gelatinolysis and its protein/mRNA expression (without affecting TIMP-1 activity), inhibits pro-MMP-9 induction, and significantly attenuates TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β levels.
2.6 αvβ3-FAK/Src pathway
2.6.1 The role of the αvβ3-FAK/Src pathway in lung cancer
Cancer spread mainly occurs through the blood and lymphatic vessels. Many studies have shown that extracellular matrix proteins may be important in the formation of tumor blood vessels and lymphatic vessels (Wasik et al., 2022). In sepsis-induced lung injury, extracellular matrix proteins are abnormally activated, accelerating their binding to the integrin receptor αvβ3, thereby recruiting and phosphorylating focal adhesion kinase (FAK), activating downstream Src family kinases, and forming the FAK/Src signaling complex (Liu Y. S. et al., 2024; Lechertier and Hodivala-Dilke, 2012), Ultimately, it leads to an increase in endothelial permeability and disrupts the integrity of the endothelial barrier. In lung adenocarcinoma, von Willebrand factor (vWF), a multifunctional glycoprotein, inhibits angiogenesis by regulating angiopoietin-2 and integrin αvβ3 (Starke et al., 2011). Studies have shown that targeting and inhibiting αvβ3 or FAK/Src (such as the small molecule inhibitor PF-562271) may be one of the effective ways to slow down lung cancer (Wu et al., 2022).
2.6.2 Isaridin E regulates lung injury complicated with sepsis through the αvβ3-FAK/Src pathway
Isaridin E (ISE) is a marine-derived fungal cyclohexadepsipeptide. It can protect against sepsis through the αvβ3-FAK/Src pathway (Liu Y. S. et al., 2024). In sepsis, the release of vWF from platelets and damaged endothelium significantly increases. After vWF binds to the integrin receptor αvβ3 on the surface of endothelial cells, it activates the downstream focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and Src tyrosine kinase, triggering phosphorylation at the FAK (Y397) and Src (Tyr416) sites (Liu Y. S. et al., 2024). The abnormal activation of this pathway leads to the downregulation of endothelial cell junction proteins (such as VE-cadherin and occludin) expression, disrupts the integrity of the endothelial barrier, increases pulmonary vascular permeability, and triggers pulmonary edema and acute lung injury. ISE blocks this pathological process through dual actions (Figure 6). On one hand, ISE inhibits platelet activation and endothelial injury, reducing the release of vWF; On the other, ISE directly downregulates the expression of αvβ3 receptors in endothelial cells, blocking the binding of vWF to αvβ3, thereby inhibiting the phosphorylation activation of the FAK/Src pathway. Ultimately, ISE maintains endothelial barrier function by inhibiting the αvβ3-FAK/Src signaling axis, thereby alleviating pulmonary vascular leakage and tissue damage.
FIGURE 6
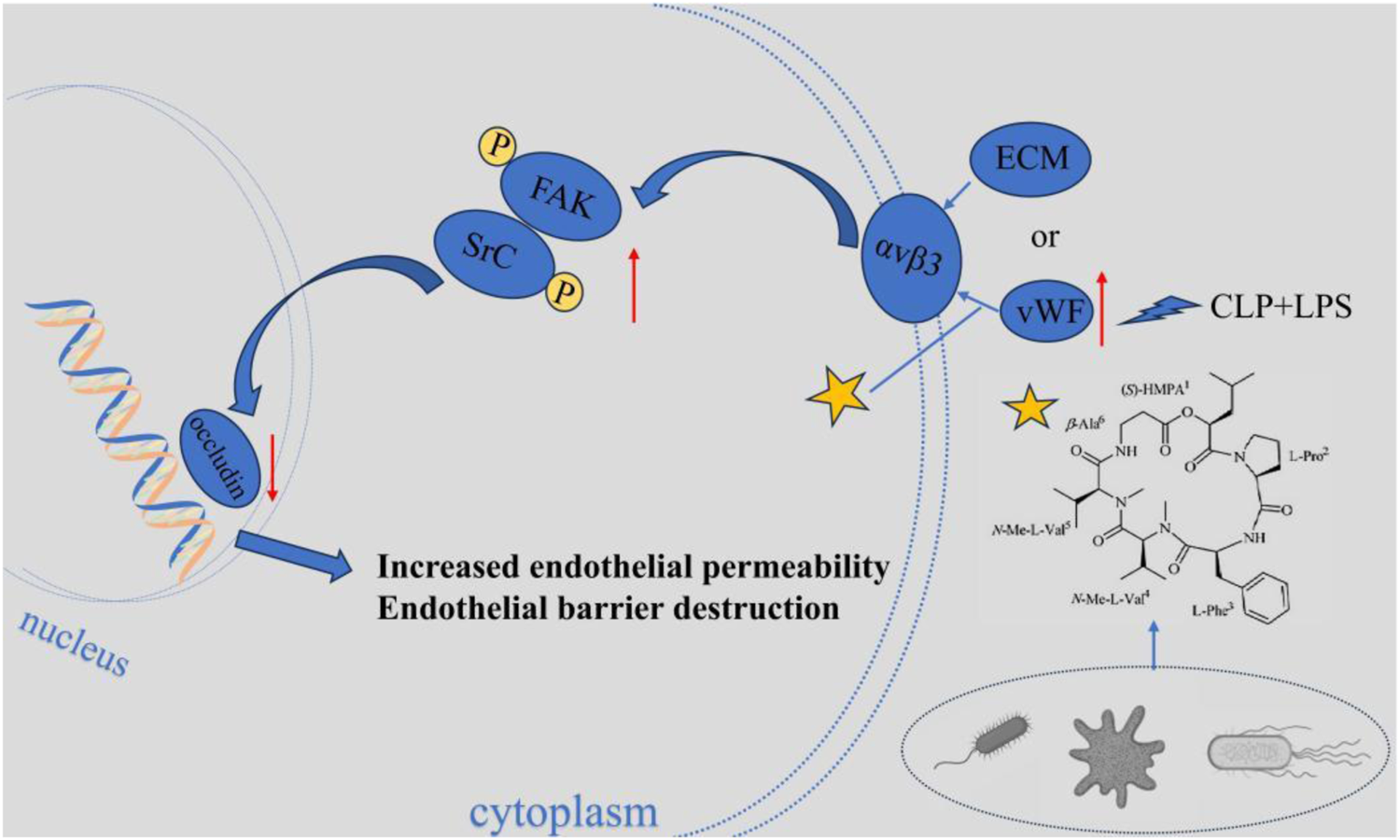
Isaridin E regulates lung injury complicated with sepsis through the αvβ3-FAK/Src pathway. Isaridin E dose-dependently curtails vWF release from activated platelets, inhibits platelet adhesion to LPS-stimulated HUVECs to reduce vWF secretion, and blocks vWF binding to integrin αvβ3 to inhibit downstream αvβ3-FAK/Src pathway activation. These actions collectively mitigate endothelial hyperpermeability, lung injury.
2.7 SP1 pathway
2.7.1 The importance of SP1 in lung cancer
Sp1 is a founding member of the zinc finger transcription factor family (Black et al., 2001). It is famous for its ability to regulate gene expression in many biological processes. It also plays a key regulatory role in the development of lung cancer. It activates or inhibits the transcription of a series of genes involved in the malignant process of tumors by binding to the GC-box in the promoter region of the target gene (Li and Davie, 2010). Studies have demonstrated that Sp1 is overexpressed in various tumor diseases (Vizcaíno et al., 2015). Sp1 can promote cells to enter the S phase and drive the proliferation of tumor cells by activating cyclin, proto-oncogene MYC and growth factor receptor IGF1R. In terms of apoptosis, overexpression of Sp1 can activate anti-apoptotic genes and members of the Bcl-2 family, thereby promoting the survival of tumor cells (O'Connor et al., 2016). The expression level and activity of SP1 are often abnormally elevated in lung cancer tissues, and its high expression is significantly associated with a poor prognosis (Beishline and Azizkhan-Clifford, 2015), To make it a potential therapeutic target, inhibiting SP1 or its downstream pathways has demonstrated anti-tumor effects in preclinical studies.
2.7.2 Naamidine J inhibits the nuclear translocation of SP1 by targeting CSE1L to slow down lung injury
Naamidine J (NJ) is a marine alkaloid and has been identified as a specific inhibitor of the nuclear transport protein CSE1L through chemical proteomics technology. Studies have confirmed that NJ directly binds to the His745 and Phe903 sites of CSE1L, blocking the nuclear translocation process of the transcription factor SP1 mediated by them (Gao et al., 2024). In the LPS-induced macrophage inflammation model, NJ significantly reduces the transcriptional activity of SP1 by inhibiting its nuclear entry, thereby down-regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory factors (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, etc.) and up-regulating anti-inflammatory factors (Figure 7). This study for the first time reveals that the CSE1L-SP1 axis can serve as a therapeutic target for acute lung injury and provides a lead compound for the development of anti-inflammatory drugs targeting CSE1L.
FIGURE 7
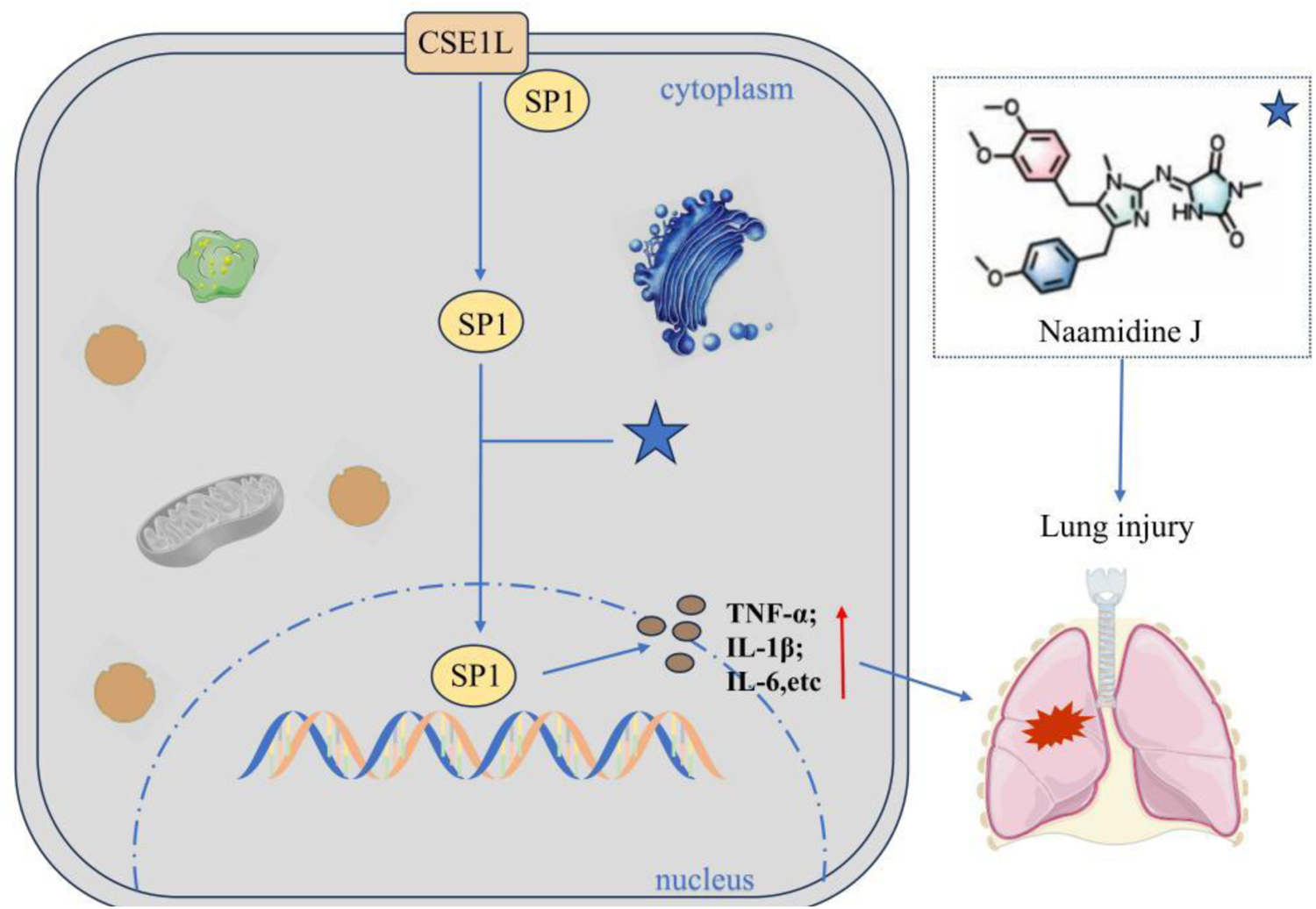
Naamidine J inhibits the nuclear translocation of SP1. Naamidine can directly bind to CSE1L’s His745 and Phe903 sites to block CSE1L-mediated nuclear translocation of the transcription factor SP1, thereby down-regulating pro-inflammatory factors (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and up-regulating anti-inflammatory factors.
3 Discussion
Marine natural products, derived from marine plants, animals, and microorganisms, represent a highly promising and efficient source of pharmaceuticals, exhibiting significant application potential in the field of lung injury treatment. This review systematically summarizes six key mechanistic pathways. Studies have demonstrated that by regulating core signaling pathways such as αvβ3-FAK/Src, TLR4/MyD88, NF-κB, and Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1/STAT3, marine natural products can effectively inhibit the release of inflammatory factors, alleviate oxidative stress responses (Li et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2025; Choi et al., 2019; Jan et al., 2019).
In terms of immunoinflammatory regulation, a variety of marine natural products exert their effects by targeting key pathways in different models, thereby inhibiting inflammatory responses and alleviating lung injury. In the pathways associated with oxidative stress and cell protection, marine-derived carotenoids exhibit prominent performance. They can regulate relevant signaling pathways and metabolic processes, improve the integrity of the alveolar barrier, and mitigate ferroptosis-related damage. Furthermore, as the core of inflammatory regulation, NF-κB-related pathways are synergistically targeted by multiple marine natural products, which inhibit the activation of related pathways. This further confirms the potential of marine natural products in alleviating inflammatory lung injury.
To date, more than 20 marine-derived drugs have been used in clinical practice. Most of the approved marine compounds are indicated for anti-tumor therapy, with a few being applied in the treatment of chronic pain, neuroinflammation, and bacterial infections (Wang et al., 2022), as well as serving as omega-3 fatty acid supplements in diets (Haque et al., 2022). However, drugs specifically for lung injury treatment remain scarce. Existing studies have shown that marine natural products such as astaxanthin, fucoxanthin, brown algal polysaccharides, and coral extracts exhibit high safety profiles and convenient administration routes. Moreover, their multi-target regulatory properties are highly compatible with the complex pathological processes of lung injury, providing new insights and candidate drugs for lung injury treatment and demonstrating certain prospects for clinical translation.
In the future, further in-depth studies on in vivo mechanisms of action should be conducted, and multi-omics technologies can be employed to dissect the panoramic regulatory networks of marine natural products (Leão et al., 2021). In terms of experimental models, it is necessary to establish more clinically relevant composite models and carry out cross-species validation studies to reduce the differences in drug responses between animals and humans. For clinical applications, systematic evaluations of the pharmacokinetic and toxicological properties of marine natural products are required to achieve the synergistic effects of multiple pathways in vivo. Additionally, efforts should be made to develop novel formulations to improve their bioavailability and targeting, while exploring insufficiently studied marine biological resources such as marine microorganisms and symbiotic algae, thereby providing a broader scope for the development of therapeutic drugs for lung injury.
Statements
Author contributions
HW: Writing – original draft. FQ: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declared that financial support was not received for this work and/or its publication.
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared that this work was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declared that generative AI was not used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abed D. A. Goldstein M. Albanyan H. Jin H. Hu L. (2015). Discovery of direct inhibitors of Keap1-Nrf2 protein-protein interaction as potential therapeutic and preventive agents. Acta Pharmaceutica Sin. B5 (4), 285–299. 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.05.008
2
Ahmad T. B. Rudd D. Benkendorff K. Mahdi L. K. Pratt K. A. Dooley L. et al (2017). Brominated indoles from a marine mollusc inhibit inflammation in a murine model of acute lung injury. PloS One12 (10), e0186904. 10.1371/journal.pone.0186904
3
Akduman H. Tayman C. Çakir U. Çakir E. Dilli D. Türkmenoğlu T. T. et al (2021). Astaxanthin prevents lung injury due to hyperoxia and inflammation. Comb. Chemistry and High Throughput Screening24 (8), 1243–1250. 10.2174/1386207323666200915092012
4
Arroyo-Hernández M. Maldonado F. Lozano-Ruiz F. Muñoz-Montaño W. Nuñez-Baez M. Arrieta O. (2021). Radiation-induced lung injury: current evidence. BMC Pulmonary Medicine21 (1), 9. 10.1186/s12890-020-01376-4
5
Azman S. Sekar M. Bonam S. R. Gan S. H. Wahidin S. Lum P. T. et al (2021). Traditional medicinal plants conferring protection against ovalbumin-induced asthma in experimental animals: a review. J. Asthma Allergy14, 641–662. 10.2147/JAA.S296391
6
Bai X. Chen Y. Chen W. Lei H. Shi G. (2011a). Volatile constituents, inorganic elements and primary screening of bioactivity of Black coral cigarette holders. Mar. Drugs9 (5), 863–878. 10.3390/md9050863
7
Bai X. Chen Y. Chen W. Lei H. Gao F. Qin Y. et al (2011b). The effect of black coral extraction on acute lung inflammation induced by cigarette smoke in mice. Exp. Lung Research37 (10), 627–632. 10.3109/01902148.2011.627084
8
Beishline K. Azizkhan-Clifford J. (2015). Sp1 and the 'hallmarks of cancer. FEBS Journal282 (2), 224–258. 10.1111/febs.13148
9
Bezerra F. S. Lanzetti M. Nesi R. T. Nagato A. C. Silva C. P. E. Kennedy-Feitosa E. et al (2023). Oxidative stress and inflammation in acute and chronic lung injuries. Antioxidants Basel, Switzerland12 (3), 548. 10.3390/antiox12030548
10
Bi J. Cui R. Li Z. Liu C. Zhang J. (2017). Astaxanthin alleviated acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative/nitrative stress and the inflammatory response in mice. Biomed. and Pharmacotherapy95, 974–982. 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.012
11
Black A. R. Black J. D. Azizkhan-Clifford J. (2001). Sp1 and krüppel-like factor family of transcription factors in cell growth regulation and cancer. J. Cellular Physiology188 (2), 143–160. 10.1002/jcp.1111
12
Cao K. Lei X. Liu H. Zhao H. Guo J. Chen Y. et al (2017). Polydatin alleviated radiation-induced lung injury through activation of Sirt3 and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Cellular Molecular Medicine21 (12), 3264–3276. 10.1111/jcmm.13230
13
Carnesecchi S. Deffert C. Donati Y. Basset O. Hinz B. Preynat-Seauve O. et al (2011). A key role for NOX4 in epithelial cell death during development of lung fibrosis. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling15 (3), 607–619. 10.1089/ars.2010.3829
14
Chapman H. A. (2004). Disorders of lung matrix remodeling. J. Clinical Investigation113 (2), 148–157. 10.1172/JCI20729
15
Choi H. Lee W. Kim E. Ku S. K. Bae J. S. (2019). Inhibitory effects of collismycin C and pyrisulfoxin A on particulate matter-induced pulmonary injury. Phytomedicine International Journal Phytotherapy Phytopharmacology62, 152939. 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152939
16
Cui N. Hu M. Khalil R. A. (2017). Biochemical and biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog. Molecular Biology Translational Science147, 1–73. 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.02.005
17
D'Agnillo F. Walters K. A. Xiao Y. Sheng Z. M. Scherler K. Park J. et al (2021). Lung epithelial and endothelial damage, loss of tissue repair, inhibition of fibrinolysis, and cellular senescence in fatal COVID-19. Sci. Translational Medicine13 (620), eabj7790. 10.1126/scitranslmed.abj7790
18
Ding R. Zhong S. Y. Deng L. Y. Luo L. X. (2024). Fucoxanthin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via Nrf2/STAT3 and glutathione pathways. Am. Journal Chin. Medicine52 (6), 1773–1794. 10.1142/S0192415X24500691
19
Doyle S. L. O'Neill L. A. (2006). Toll-like receptors: from the discovery of NFkappaB to new insights into transcriptional regulations in innate immunity. Biochem. Pharmacology72 (9), 1102–1113. 10.1016/j.bcp.2006.07.010
20
Dubey S. Yu Z. Stephens E. M. Lazrak A. Ahmad I. Aggarwal S. et al (2025). Oxidative damage to lung mitochondrial DNA is a key contributor to the development of chemical lung injury. Redox Biology82, 103624. 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103624
21
Durham A. L. Adcock I. M. (2015). The relationship between COPD and lung cancer. Lung Cancer Amsterdam, Neth.90 (2), 121–127. 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.08.017
22
Efimova O. V. Kelley T. W. (2009). Induction of granzyme B expression in T-cell receptor/CD28-stimulated human regulatory T cells is suppressed by inhibitors of the PI3K-mTOR pathway. BMC Immunology10, 59. 10.1186/1471-2172-10-59
23
Fagbohun O. F. Thilakarathna W. P. D. W. Zhou J. Lehmann C. Jiao G. Rupasinghe H. P. V. (2024). Sea cucumber and blueberry extracts suppress inflammation and reduce acute lung injury through the regulation of NF-κB/MAPK/JNK signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-treated C57BL/6 mice. Mol. Basel, Switzerland29 (7), 1511. 10.3390/molecules29071511
24
Fedt A. Bhattarai S. Oelstrom M. J. (2020). Vaping-associated lung injury: a new cause of acute respiratory failure. J. Adolescent Health Official Publication Soc. Adolesc. Med.66 (6), 754–757. 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.03.019
25
Feng H. Zheng R. (2023). Cigarette smoke prevents M1 polarization of alveolar macrophages by suppressing NLRP3. Life Sciences327, 121854. 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121854
26
Gao C. L. Song J. Q. Yang Z. N. Wang H. Wu X. Y. Shao C. et al (2024). Chemoproteomics of marine natural product naamidine J unveils CSE1L as a therapeutic target in acute lung injury. J. Am. Chem. Soc.146 (41), 28384–28397. 10.1021/jacs.4c09695
27
Ghareghomi S. Moosavi-Movahedi F. Saso L. Habibi-Rezaei M. Khatibi A. Hong J. et al (2023). Modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 by natural compounds in lung cancer. Antioxidants Basel, Switzerland12 (3), 735. 10.3390/antiox12030735
28
Guan Y. Li L. Kan L. Xie Q. (2022). Inhalation of salvianolic acid B prevents fine particulate matter-induced acute airway inflammation and oxidative stress by downregulating the LTR4/MyD88/NLRP3 pathway. Oxidative Medicine Cellular Longevity2022, 5044356. 10.1155/2022/5044356
29
Guo J. Liang J. Guo Z. Bai X. Zhang H. Zhang N. et al (2024). Network pharmacology and transcriptomics to determine danggui yifei decoction mechanism of action for the treatment of chronic lung injury. J. Ethnopharmacology318 (Pt A), 116873. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116873
30
Guo Q. Jin Y. Chen X. Ye X. Shen X. Lin M. et al (2024). NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications. Signal Transduction Targeted Therapy9 (1), 53. 10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9
31
Haque N. Parveen S. Tang T. Wei J. Huang Z. (2022). Marine natural products in clinical use. Mar. Drugs20 (8), 528. 10.3390/md20080528
32
Harada D. Takigawa N. Kiura K. (2014). The role of STAT3 in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers6 (2), 708–722. 10.3390/cancers6020708
33
Harijith A. Basa P. Ha A. Thomas J. Jafri A. Fu P. et al (2022). NOX4 mediates epithelial cell death in hyperoxic acute lung injury through mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Front. Pharmacology13, 880878. 10.3389/fphar.2022.880878
34
Hashimoto R. Kakigi R. Miyamoto Y. Nakamura K. Itoh S. Daida H. et al (2020). JAK-STAT-dependent regulation of scavenger receptors in LPS-Activated murine macrophages. Eur. Journal Pharmacology871, 172940. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.172940
35
Hikichi M. Mizumura K. Maruoka S. Gon Y. (2019). Pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) induced by cigarette smoke. J. Thoracic Disease11 (17), S2129–S2140. 10.21037/jtd.2019.10.43
36
Hsu A. T. Barrett C. D. DeBusk G. M. Ellson C. D. Gautam S. Talmor D. S. et al (2015). Kinetics and role of plasma matrix Metalloproteinase-9 expression in acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock (Augusta, Ga.)44 (2), 128–136. 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000386
37
Hu X. Xu Q. Wan H. Hu Y. Xing S. Yang H. et al (2020). PI3K-Akt-mTOR/PFKFB3 pathway mediated lung fibroblast aerobic glycolysis and collagen synthesis in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Laboratory Investigation; a Journal Technical Methods Pathology100 (6), 801–811. 10.1038/s41374-020-0404-9
38
Jan J. S. Yang C. H. Wang M. H. Lin F. L. Yen J. L. Hsieh I. et al (2019). Hirsutanol A attenuates lipopolysaccharide-mediated matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression and cytokines production and improves endotoxemia-induced acute sickness behavior and acute lung injury. Mar. Drugs17 (6), 360. 10.3390/md17060360
39
Jiang Y. Nguyen T. V. Jin J. Yu Z. N. Song C. H. Chai O. H. (2023). Bergapten ameliorates combined allergic rhinitis and asthma syndrome after PM2.5 exposure by balancing Treg/Th17 expression and suppressing STAT3 and MAPK activation in a mouse model. Biomed. and Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine and Pharmacotherapie164, 114959. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114959
40
Knudsen L. Ochs M. (2018). The micromechanics of lung alveoli: structure and function of surfactant and tissue components. Histochem. Cell Biology150 (6), 661–676. 10.1007/s00418-018-1747-9
41
Kumar M. S. Adki K. M. (2018). Marine natural products for multi-targeted cancer treatment: a future insight. Biomed. and Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine and Pharmacotherapie105, 233–245. 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.142
42
Lanchou J. Corbel M. Tanguy M. Germain N. Boichot E. Theret N. et al (2003). Imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-9 and MMP-2) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1 and TIMP-2) in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients. Crit. Care Medicine31 (2), 536–542. 10.1097/01.CCM.0000048626.02184.F8
43
Leão T. Wang M. Moss N. da Silva R. Sanders J. Nurk S. et al (2021). A multi-omics characterization of the natural product potential of tropical filamentous marine cyanobacteria. Mar. Drugs19 (1), 20. 10.3390/md19010020
44
Lechertier T. Hodivala-Dilke K. (2012). Focal adhesion kinase and tumour angiogenesis. J. Pathology226 (2), 404–412. 10.1002/path.3018
45
Lee S. H. Lee S. S. Lee G. Y. Han S. Y. Kim D. S. Lee B. H. et al (2025). Endarachne binghamiae extract ameliorates inflammatory responses in macrophages through regulation of MAPK, NF-kB and PI3K/AKT pathways, and prevents acute lung injury in mice. Life Basel, Switzerland15 (1), 88. 10.3390/life15010088
46
Li L. Davie J. R. (2010). The role of Sp1 and Sp3 in normal and cancer cell biology. Ann. Anatomy = Anatomischer Anzeiger Official Organ Anatomische Gesellschaft192 (5), 275–283. 10.1016/j.aanat.2010.07.010
47
Li X. Huang R. Liu K. Li M. Luo H. Cui L. et al (2020). Fucoxanthin attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury via inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88 signaling axis. Aging13 (2), 2655–2667. 10.18632/aging.202309
48
Li W. Li D. Chen Y. Abudou H. Wang H. Cai J. et al (2022). Classic signaling pathways in alveolar injury and repair involved in sepsis-induced ALI/ARDS: new research progress and prospect. Dis. Markers2022, 6362344. 10.1155/2022/6362344
49
Li J. She X. Ding Z. Yao L. Yang Y. Tang H. et al (2023). Astaxanthin protects the radiation-induced lung injury in C57BL/6 female mice. Radiat. Protection Dosimetry199 (17), 2096–2103. 10.1093/rpd/ncad208
50
Liao S. Y. Casanova N. G. Bime C. Camp S. M. Lynn H. Garcia J. G. N. (2021). Identification of early and intermediate biomarkers for ARDS mortality by multi-omic approaches. Sci. Reports11 (1), 18874. 10.1038/s41598-021-98053-1
51
Linsley P. S. Ledbetter J. A. (1993). The role of the CD28 receptor during T cell responses to antigen. Annu. Review Immunology11, 191–212. 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.001203
52
Liu R. M. Desai L. P. (2015). Reciprocal regulation of TGF-β and reactive oxygen species: a perverse cycle for fibrosis. Redox Biology6, 565–577. 10.1016/j.redox.2015.09.009
53
Liu C. Gu F. Zou Z. Wang F. Li D. Song J. et al (2025). Marine-derived alternariol suppresses inflammation by regulating T cell activation and migration. Mar. Drugs23 (3), 133. 10.3390/md23030133
54
Liu Y. Zhang Y. You G. Zheng D. He Z. Guo W. et al (2024). Tangeretin attenuates acute lung injury in septic mice by inhibiting ROS-Mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation via regulating PLK1/AMPK/DRP1 signaling axis. Inflamm. Research Official Journal Eur. Histamine Res. Soc.73 (1), 47–63. 10.1007/s00011-023-01819-8
55
Liu Y. S. Chen W. L. Zeng Y. W. Li Z. H. Zheng H. L. Pan N. et al (2024). Isaridin E Protects against Sepsis by Inhibiting Von Willebrand Factor-Induced Endothelial Hyperpermeability and Platelet-Endothelium Interaction. Mar. Drugs22 (6), 283. 10.3390/md22060283
56
Long M. E. Mallampalli R. K. Horowitz J. C. (2022). Pathogenesis of pneumonia and acute lung injury. Clin. Science Lond. Engl. 1979136 (10), 747–769. 10.1042/CS20210879
57
Luo L. Huang F. Zhong S. Ding R. Su J. Li X. (2022). Astaxanthin attenuates ferroptosis via Keap1-Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury. Life Sci.311, 121091. 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121091
58
Luo Z. Wang Q. Fan X. Koh X. Q. Loh X. J. Wu C. et al (2025). ROS-driven nanoventilator for MRSA-induced acute lung injury treatment via in situ oxygen supply, anti-inflammation and immunomodulation. Adv. Science Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger.12 (18), e2406060. 10.1002/advs.202406060
59
Ma M. T. Chu Z. Q. Quan H. Y. Li H. Zhou Y. Han Y. et al (2025). Natural products for anti-fibrotic therapy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: marine and terrestrial insights. Front. Pharmacol.16.1524654. 10.3389/fphar.2025.1524654
60
Ma L. Chen F. Chen S. Hu Y. Nie S. He X. et al (2025). Inflammation-targeting nanoparticles impede neutrophil infiltration and scavenge ROS for acute lung injury alleviation. Int. Journal Pharmaceutics673, 125359. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125359
61
Millar M. W. Fazal F. Rahman A. (2022). Therapeutic targeting of NF-κB in acute lung injury: a double-edged sword. Cells11 (20), 3317. 10.3390/cells11203317
62
Murphy M. P. Caraher E. (2015). Mcl-1 is vital for neutrophil survival. Immunol. Research62 (2), 225–233. 10.1007/s12026-015-8655-z
63
Nie M. Wang Y. Lu Y. Yuan Y. Liu Y. Li X. (2018). Protective effects of fucoidan against hyperoxic lung injury via the ERK signaling pathway. Mol. Medicine Reports17 (1), 1813–1818. 10.3892/mmr.2017.8022
64
Ning L. Wei W. Wenyang J. Rui X. Qing G. (2020). Cytosolic DNA-STING-NLRP3 axis is involved in murine acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Clin. Translational Medicine10 (7), e228. 10.1002/ctm2.228
65
O'Connor L. Gilmour J. Bonifer C. (2016). The role of the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor Sp1 in tissue-specific transcriptional regulation and in disease. Yale Journal Biology Medicine89 (4), 513–525.
66
Park S. A. Kim M. J. Park S. Y. Kim J. S. Lee S. J. Woo H. A. et al (2015). EW-7197 inhibits hepatic, renal, and pulmonary fibrosis by blocking TGF-β/Smad and ROS signaling. Cell. Molecular Life Sciences CMLS72 (10), 2023–2039. 10.1007/s00018-014-1798-6
67
Ricou B. Nicod L. Lacraz S. Welgus H. G. Suter P. M. Dayer J. M. (1996). Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. Journal Respiratory Critical Care Medicine154 (2 Pt 1), 346–352. 10.1164/ajrccm.154.2.8756805
68
Shin S. H. Cho K. A. Yoon H. S. Kim S. Y. Kim H. Y. Pewzner-Jung Y. et al (2021). Ceramide synthase 2 null mice are protected from ovalbumin-induced asthma with higher T cell receptor signal strength in CD4+ T cells. Int. Journal Molecular Sciences22 (5), 2713. 10.3390/ijms22052713
69
Singh K. S. (2020). Pyrone-derived marine natural products: a review on isolation, bio-activities and synthesis. Curr. Org. Chem.24 (4), 354–401. 10.2174/1385272824666200217101400
70
Starke R. D. Ferraro F. Paschalaki K. E. Dryden N. H. McKinnon T. A. Sutton R. E. et al (2011). Endothelial von Willebrand factor regulates angiogenesis. Blood117 (3), 1071–1080. 10.1182/blood-2010-01-264507
71
Swenson K. E. Ruoss S. J. Swenson E. R. (2021). The pathophysiology and dangers of silent hypoxemia in COVID-19 lung injury. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc.18 (7), 1098–1105. 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202011-1376CME
72
Takahashi E. Indalao I. L. Sawabuchi T. Mizuno K. Sakai S. Kimoto T. et al (2018). Clarithromycin suppresses induction of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and improves pathological changes in the lungs and heart of mice infected with influenza A virus. Comp. Immunology, Microbiology Infectious Diseases56, 6–13. 10.1016/j.cimid.2017.11.002
73
Tao P. Su B. Mao X. Lin Y. Zheng L. Zou X. et al (2025). Interleukin-35 inhibits NETs to ameliorate Th17/Treg immune imbalance during the exacerbation of cigarette smoke exposed-asthma via gp130/STAT3/ferroptosis axis. Redox Biology82, 103594. 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103594
74
Torii K. Iida K. Miyazaki Y. Saga S. Kondoh Y. Taniguchi H. et al (1997). Higher concentrations of matrix metalloproteinases in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am. Journal Respiratory Critical Care Medicine155 (1), 43–46. 10.1164/ajrccm.155.1.9001287
75
Upadhyay P. Wu C. W. Pham A. Zeki A. A. Royer C. M. Kodavanti U. P. et al (2023). Animal models and mechanisms of tobacco smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). J. Toxicology Environmental Health. Part B, Crit. Reviews26 (5), 275–305. 10.1080/10937404.2023.2208886
76
Vizcaíno C. Mansilla S. Portugal J. (2015). Sp1 transcription factor: a long-standing target in cancer chemotherapy. Pharmacol. and Therapeutics152, 111–124. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.05.008
77
Wang W. Weng J. Yu L. Huang Q. Jiang Y. Guo X. (2018). Role of TLR4-p38 MAPK-Hsp27 signal pathway in LPS-induced pulmonary epithelial hyperpermeability. BMC Pulmonary Medicine18 (1), 178. 10.1186/s12890-018-0735-0
78
Wang X. Qiu H. Yang N. Xie H. Liang W. Lin J. et al (2022). Fascaplysin derivatives binding to DNA via unique cationic five-ring coplanar backbone showed potent antimicrobial/antibiofilm activity against MRSA in vitro and in vivo. Eur. Journal Medicinal Chemistry230, 114099. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2021.114099
79
Wasik A. Ratajczak-Wielgomas K. Badzinski A. Dziegiel P. Podhorska-Okolow M. (2022). The role of periostin in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in tumors. Cancers14 (17), 4225. 10.3390/cancers14174225
80
Wu X. Wang J. Liang Q. Tong R. Huang J. Yang X. et al (2022). Recent progress on FAK inhibitors with dual targeting capabilities for cancer treatment. Biomed. and Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine and Pharmacotherapie151, 113116. 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113116
81
Zeng L. Zhang J. Song R. Dong X. Wei Z. Li X. et al (2025). Laminarin alleviates acute lung injury induced by LPS through inhibition of M1 macrophage polarisation. J. Cellular Molecular Medicine29 (5), e70440. 10.1111/jcmm.70440
82
Zhang B. Zhang T. Xu J. Lu J. Qiu P. Wang T. et al (2020). Marine sponge-associated fungi as potential novel bioactive natural product sources for drug discovery: a review. Mini Reviews Medicinal Chemistry20 (19), 1966–2010. 10.2174/1389557520666200826123248
83
Zhang J. Zhang H. Alexandre Muehlmann L. Jiang C. S. Guo Y. W. (2017). Synthesis and structural modification of marine natural products. Mol. Basel, Switzerland22 (6), 882. 10.3390/molecules22060882
84
Zhang M. Y. Jiang Y. X. Yang Y. C. Liu J. Y. Huo C. Ji X. L. et al (2021). Cigarette smoke extract induces pyroptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells through the ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Life Sciences269, 119090. 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119090
85
Zhang J. Zou Y. Chen L. Xu Q. Wang Y. Xie M. et al (2022). Regulatory T cells, a viable target against airway allergic inflammatory responses in asthma. Front. Immunology13, 902318. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.902318
86
Zhang J. Guo Y. Mak M. Tao Z. (2024). Translational medicine for acute lung injury. J. Translational Medicine22 (1), 25. 10.1186/s12967-023-04828-7
87
Zhang T. Ouyang Z. Zhang Y. Sun H. Kong L. Xu Q. et al (2025). Marine natural products in inflammation-related diseases: opportunities and challenges. Med. Research Reviews45 (5), 1375–1406. 10.1002/med.22109
88
Zhang Y. Du H. Yu X. Zhu J. (2020). Fucoidan attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in newborn rats by mediating lung fibroblasts differentiate into myofibroblasts. Ann. Translational Medicine8 (22), 1501. 10.21037/atm-20-6601
89
Zheng L. Zhu Q. Xu C. Li M. Li H. Yi P. Q. et al (2020). Glycyrrhizin mitigates radiation-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4 signalling pathway. J. Cellular Molecular Medicine24 (1), 214–226. 10.1111/jcmm.14703
Summary
Keywords
in vivo , inflammatory response, lung injury, marine natural products, signaling pathway
Citation
Wang H and Qiu F (2026) Signaling pathways of marine-derived natural products on lung injury: from the in vivo perspective. Front. Pharmacol. 16:1716898. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1716898
Received
07 October 2025
Revised
03 December 2025
Accepted
08 December 2025
Published
05 January 2026
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Venkata Ramireddy Narala, Yogi Vemana University, India
Reviewed by
Katarzyna Kaczynska, sakowski Medical Research IPolish Academy of Sciences, Poland
Chen Chen, Anhui Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2026 Wang and Qiu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Qiu, qiufeng19951102@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.