- 1School of Film, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
- 2Health Management Center, Xiang’an Hospital of Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
- 3School of Art, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of music therapy (MT) in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in the Chinese population through a meta-analysis.
Design: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
Setting: We performed a systematic review according to the PRISMA guidelines. A systematic and comprehensive search was conducted across five databases: PubMed, Web of Science, Chinese Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Science and Technology Journal Database, and Wanfang Database, up to the end of September 2024, that administered MT to children with ASD. Continuous variables were reported as standardized mean differences (SMD) accompanied by 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All analyses were carried out using the Stata statistical software package version 16.0.
Results: Twenty-three studies were included in our meta-analysis. The results showed that MT significantly decreased the total ATEC (autism treatment evaluation checklist) score (SMD = -2.52, 95% CI: -3.69 ~ -1.35, P < 0.001), ABC (autism behavior checklist) (SMD = -1.07, 95% CI: -1.52 ~ -0.61, P < 0.001), and CARS (childhood autism rating scale) score (SMD = -1.50, 95% CI: -2.26 ~ -0.74, P < 0.001). Specifically, MT significantly improved communication skills (SMD = -1.10, 95% CI: -1.54 ~ -0.66, P < 0.001), social interaction skills (SMD = -1.69, 95% CI: -2.59 ~ -0.78, P < 0.001), language ability (SMD = -1.15, 95% CI: -1.56 ~ -0.74, P < 0.001), and cognitive function (SMD = -1.80, 95% CI: -2.73 ~ -0.87, P < 0.001) compared to the control group.
Conclusion: MT can improve communication skills, social interaction skills, language ability, and cognitive function in children with ASD disorders in the Chinese population.
Introduction
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), commonly referred to as autism, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that typically appears before the age of three and is characterized by challenges in social communication, as well as repetitive behaviors and restricted interests (1, 2). ASD includes a variety of disorders with different causes and symptoms, characterized by significant challenges in social interaction and communication, a broad spectrum of severity, and the potential for co-occurring issues such as intellectual disabilities, anxiety, depression, sleep disturbances, epilepsy, and exceptional talents in specific areas, often referred to as savant abilities (3).
Epidemiological surveys reveal a global median prevalence of ASD at 62 per 10,000 individuals, with the 2010 Global Burden of Disease study estimating approximately 52 million people affected worldwide, translating to a prevalence of about 1 in 132 (4). In China, the Second Epidemiological Sample Survey of the Disabled identified around 41,000 children aged 0 to 6 with ASD (5). Furthermore, a recent comprehensive study involving over 120,000 children aged 6 to 12 from eight representative cities in China reported an estimated prevalence of 0.70% (6). The significant increase in ASD prevalence observed over the past two decades raises serious public health concerns.
Music therapy (MT) is a cost-effective and noninvasive adjunct to standard treatment, demonstrating effectiveness in addressing psychiatric disorders across a variety of settings and patient demographics, and it is generally easy to implement (7). Moreover, MT has been shown to enhance cognitive functions such as attention and memory (8). Notably, many children with autism, despite their limited engagement with the external world and occasional language challenges, often exhibit a keen interest in music and may even possess exceptional musical perception and superior sound discrimination skills (9). This unique connection makes MT particularly prominent among interventions for autism.
Therefore, this meta-analysis was conducted to assess the effects of MT on children with ASD in the Chinese population.
Materials and methods
This systematic review adheres to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for reporting and has been prospectively registered in the PROSPERO database under registration number CRD42015029643.
Search strategy and selection criteria
In accordance with the Cochrane Collaboration guidelines, a systematic and comprehensive search was conducted across five databases: PubMed, Web of Science, Chinese Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Science and Technology Journal Database, and Wanfang Database, up to the end of September 2024. The PubMed search combined the terms (“music therapy”[Title/Abstract] OR MT[Title/Abstract]) AND (“autism”[Title/Abstract] OR “autism spectrum disorder”[Title/Abstract]) AND (“children”[Title/Abstract] OR child*[Title/Abstract]) AND (“autism treatment evaluation checklist”[Title/Abstract] OR ATEC (autism treatment evaluation checklist) [Title/Abstract] OR “autism behavior checklist”[Title/Abstract] OR ABC (autism behavior checklist) [Title/Abstract] OR “childhood autism rating scale”[Title/Abstract] OR CARS (childhood autism rating scale) [Title/Abstract]). In Web of Science we applied the analogous query TS = (“music therapy” OR MT) AND TS= (autism OR “autism spectrum disorder”) AND TS = (children OR child*) AND TS = (“autism treatment evaluation checklist” OR ATEC OR “autism behavior checklist” OR ABC OR “childhood autism rating scale” OR CARS). Equivalent strategies using the same concepts translated into Chinese were applied in CNKI, the China Science and Technology Journal Database and the Wanfang Database. Initially, all articles published in English or Chinese were considered for inclusion in the analysis.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) Studies published in peer-reviewed journals investigated the effects of MT delivered by credentialed therapists following established therapeutic protocols on children with ASD; (2) specifically measuring at least on of outcomes using ATEC, ABC, or CARS; (3) Only articles published in English or Chinese and conducted up to September 2024 will be considered. Exclusion criteria: (1) Studies that are not empirical research, including reviews, meta-analyses, case reports or case series; (2) Studies focused on populations other than children with ASD or that do not specifically address MT as an intervention will also be excluded; (3) studies involving non-human subjects.
Data extraction
Duplicate publications were removed using EndNote 21 software, and manual searching of grey literature (e.g., conference abstracts) to reduce publication bias. Two authors independently extracted the data using standardized forms and resolved any discrepancies through discussion until a consensus was reached. Any disagreements were resolved through discussion; if needed, a third author arbitrated. The extracted information included the following: author names, publication year, study location, sample size, age, sex, intervention methods, and duration of intervention.
Quality assessment
The quality of the studies included in this review was assessed by two independent reviewers using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) (10), which evaluates three key parameters: selection, comparability, and exposure, resulting in a score ranging from 0 to 9. Studies received classifications based on their scores, with those scoring 0 to 3 deemed low quality, scores of 4 to 6 categorized as moderate quality, and scores of 7 or higher recognized as high quality. To ensure the integrity of the findings, only studies with NOS scores of 6 or above were included in the analyses, thereby enhancing the reliability of the review’s conclusions and ensuring that they are based on high-quality evidence.
Statistical analysis
All analyses were carried out using the Stata statistical software package version 16.0. Continuous variables were reported as standardized mean differences (SMD) accompanied by 95% confidence intervals (CIs). To assess heterogeneity, either the Chi-square test or the Cochrane Q test was employed, with I² < 50% and P > 0.10 indicating no significant heterogeneity. A fixed-effects model was used when these criteria were satisfied; otherwise, a random-effects model was applied. Furthermore, funnel plots along with the Egger test were utilized to investigate publication bias, where a p-value of < 0.05 was taken as evidence of statistically significant publication bias.
Results
General results of the included studies
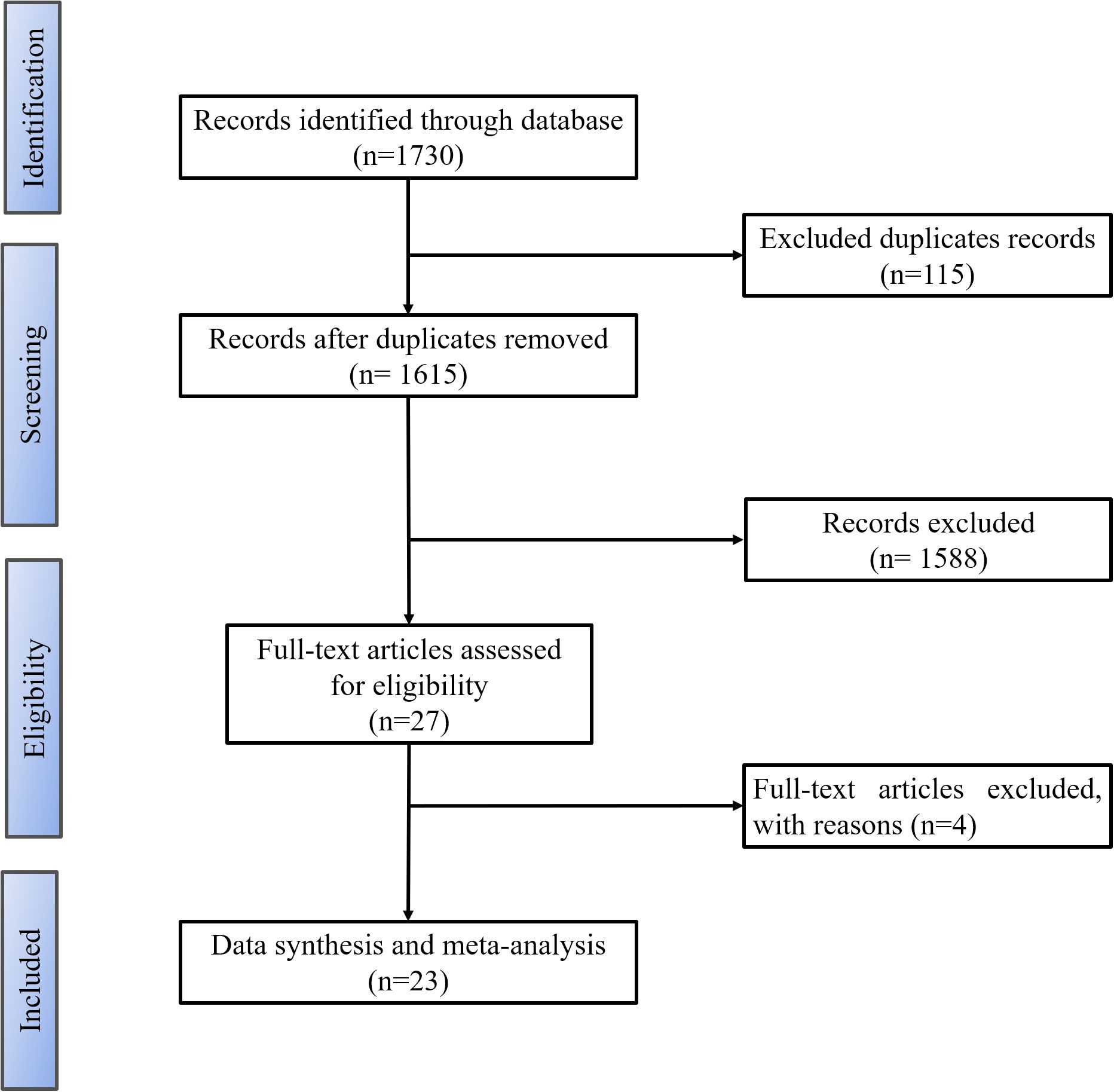
Following the specified inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 1,730 articles were initially obtained. After eliminating 115 duplicates and disregarding 950 articles classified as irrelevant, an additional 177 articles were excluded upon full-text assessment. Finally, 27 articles were chosen for qualitative analysis, with 23 retained for meta-analysis (Figure 1).
Characteristics of included studies
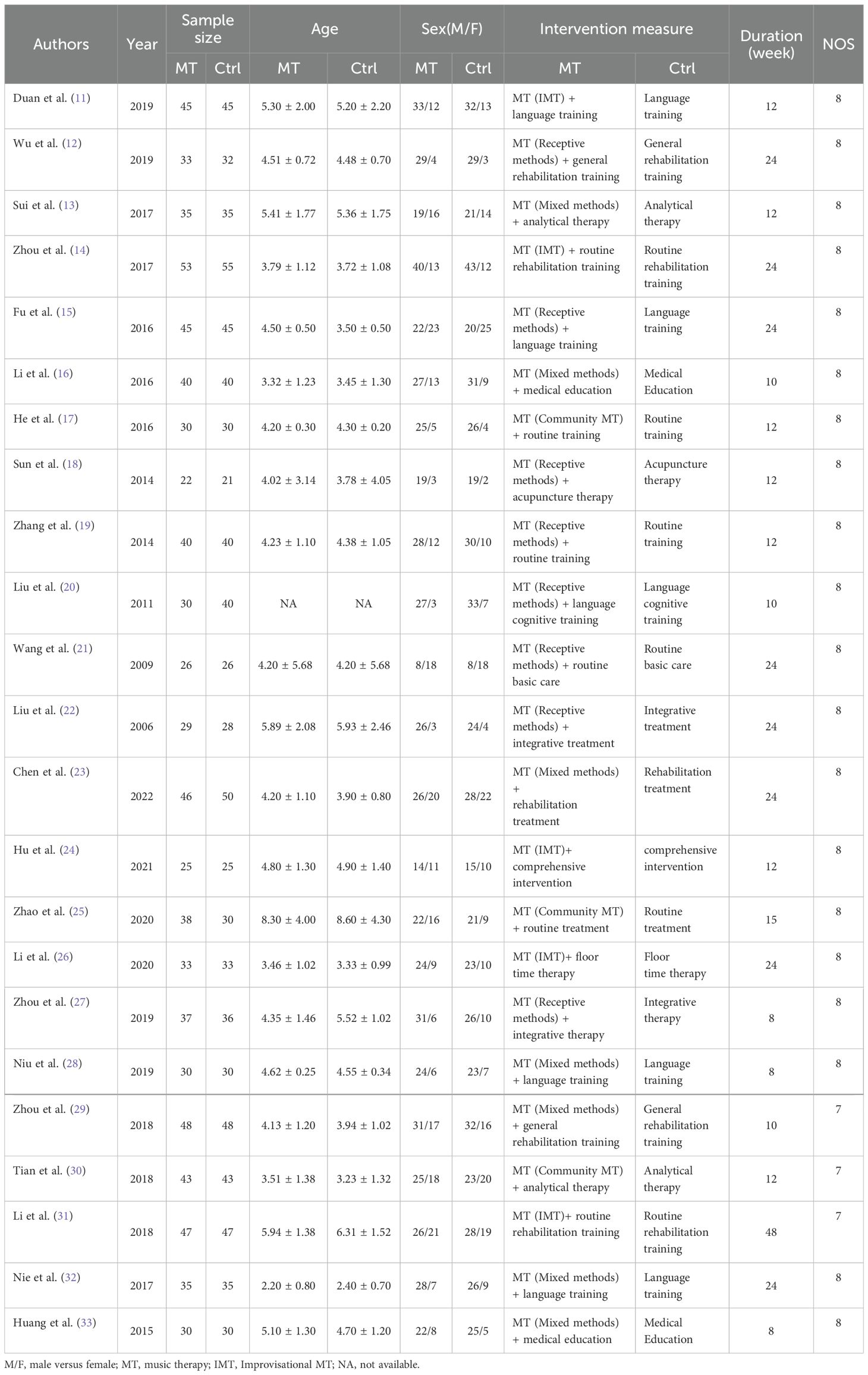
The cohort of the studies that evaluated the included articles comprised a total of 1,684 participants, with 840 individuals in the observation group and 844 individuals in the control group. The quality assessment of the 23 selected articles was conducted using the NOS scale. Among these, 20 articles received a NOS score of 8, while the remaining 3 articles scored 7. This indicates that the overall quality of the articles included in this study is relatively high (Table 1).
The effect of music therapy on ATEC score
Six studies reported the total ATEC score, encompassing 464 cases, with 230 in the experimental group and 234 in the control group. MT significantly decreased the total ATEC score (SMD = -2.52, 95% CI: -3.69 ~ -1.35, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with high levels of heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 2.00, Chi² = 120.67, I² = 96%, P < 0.001) (Figure 2A). Subgroup analyses by intervention duration and modality were conducted to explore heterogeneity sources. MT significantly reduced total ATEC scores in both the >12-week subgroup (SMD = -2.20, P < 0.001; I² = 97.5%, P < 0.001) and the ≤12-week subgroup (SMD = -2.87, P < 0.001; I² = 94.6%, P < 0.001). Similarly, high heterogeneity accompanied the significant benefits observed in both MT + rehabilitation training and MT + language training subgroups. Specifically, eight studies evaluated communication skills, finding that MT significantly improved these skills (SMD = -1.10, 95% CI: -1.54 ~ -0.66, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with considerable heterogeneity among studies (Tau² = 0.34, Chi² = 46.86, I² = 85%, P < 0.001) (Figure 2B). Seven studies assessed social interaction skills, three of which utilized a subscale of the ATEC. MT significantly improved social interaction skills (SMD = -1.69, 95% CI: -2.59 ~ -0.78, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with high levels of heterogeneity (Tau² = 1.42, Chi² = 123.43, I² = 95%, P < 0.001) (Figure 2C). Additionally, seven studies examined language ability. MT significantly enhanced language ability (SMD = -1.15, 95% CI: -1.56 ~ -0.74, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with high heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 0.24, Chi² = 29.60, I² = 80%, P < 0.001) (Figure 2D). Furthermore, seven studies assessed cognitive function, three of which employed a subscale of the ATEC. MT significantly improved cognitive function (SMD = -1.80, 95% CI: -2.73 ~ -0.87, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with substantial heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 1.49, Chi² = 125.11, I² = 95%, P < 0.001) (Figure 2E). Funnel plot asymmetry did not reveal any potential for publication bias (P>0.05) (Supplementary Figure S1).
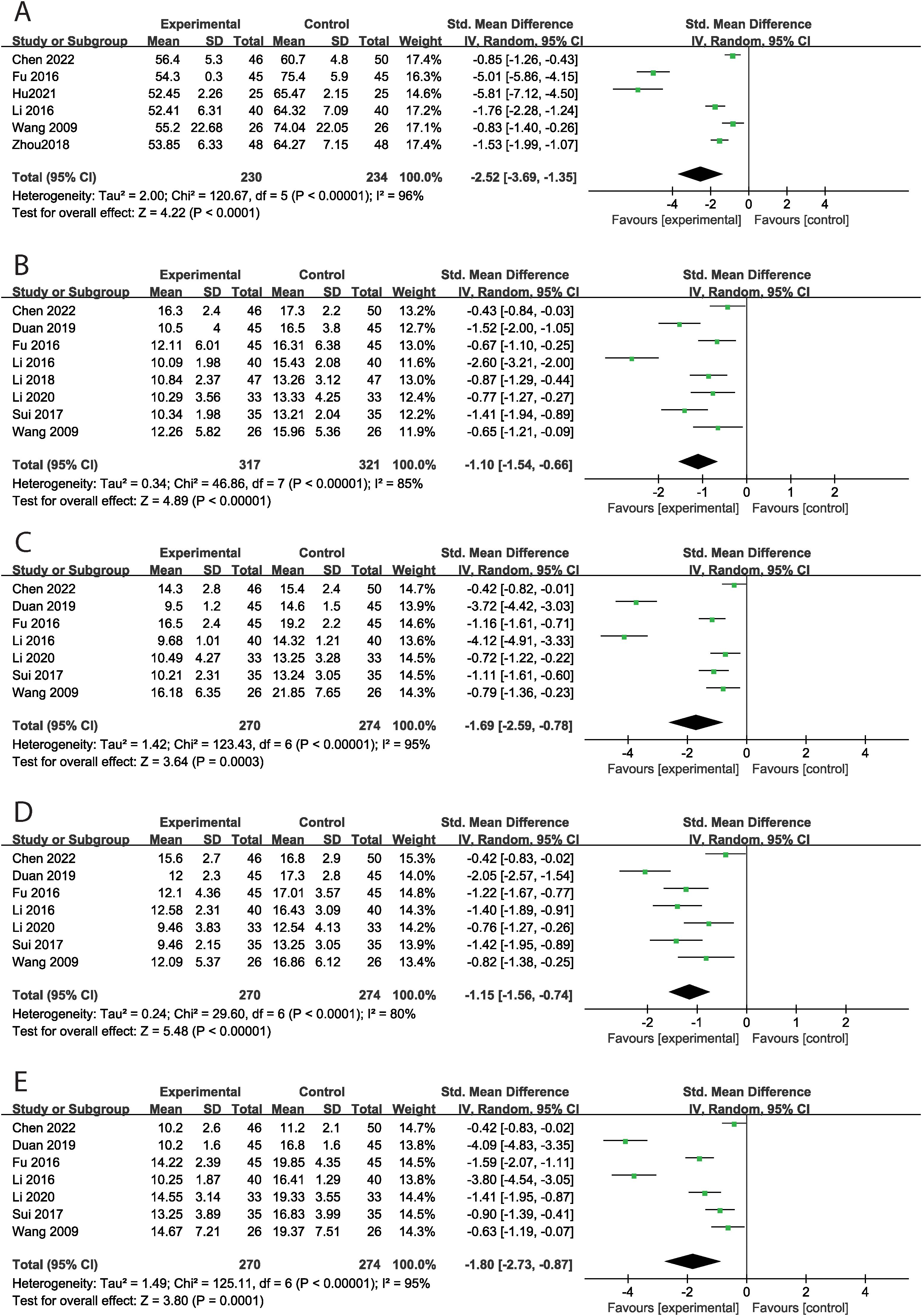
Figure 2. The effect of music therapy on ATEC score [(A) total ATEC score, (B) communication skills, (C) social interaction skills, (D) language ability, (E) cognitive function].
The effect of music therapy on ABC score
Thirteen studies reported the total ABC score, encompassing 815 cases, with 406 in the experimental group and 409 in the control group. MT significantly reduced the total ABC score (SMD = -1.07, 95% CI: -1.52 ~ -0.61, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with high levels of heterogeneity observed across studies (Tau² = 0.58, Chi² = 116.29, I² = 90%, P < 0.001) (Figure 3A). Subgroup analyses by intervention duration were conducted to explore heterogeneity sources. MT significantly reduced total ABC scores in both the >12-week subgroup (SMD = -0.87, P < 0.001; I² = 71.0%, P = 0.002) and the ≤12-week subgroup (SMD = -1.58, P < 0.001; I² = 94.6%, P < 0.001). Specifically, eleven studies focused on the sensory dimension. MT significantly improved sensory outcomes (SMD = -0.84, 95% CI: -1.25 ~ -0.44, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, again with high levels of heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 0.41, Chi² = 76.91, I² = 87%, P < 0.001) (Figure 3B). Twelve studies evaluated the social and self-help dimensions, finding that MT significantly improved these areas (SMD = -0.45, 95% CI: -0.90 ~ -0.01, P = 0.05), despite high heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 0.55, Chi² = 112.89, I² = 90%, P < 0.001) (Figure 3C). Eleven studies assessed body and object use, showing a significant improvement with MT (SMD = -0.88, 95% CI: -1.19 ~ -0.57, P < 0.001), along with high levels of heterogeneity (Tau² = 0.21, Chi² = 43.66, I² = 77%, P < 0.001) (Figure 4A). In terms of language skills, eleven studies also reported significant improvements due to MT (SMD = -1.57, 95% CI: -2.21 ~ -0.94, P < 0.001), with high heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 1.15, Chi² = 190.54, I² = 94%, P < 0.001) (Figure 4B). Furthermore, seven studies assessed the relating dimension; however, no significant difference was found between the experimental and control groups (SMD = -1.67, 95% CI: -2.77 ~ -0.58, P = 0.003), with high levels of heterogeneity evident (Tau² = 2.08, Chi² = 186.23, I² = 97%, P < 0.001) (Figure 4C). Funnel plot asymmetry did not reveal any potential for publication bias (P>0.05) (Supplementary Figure S2).
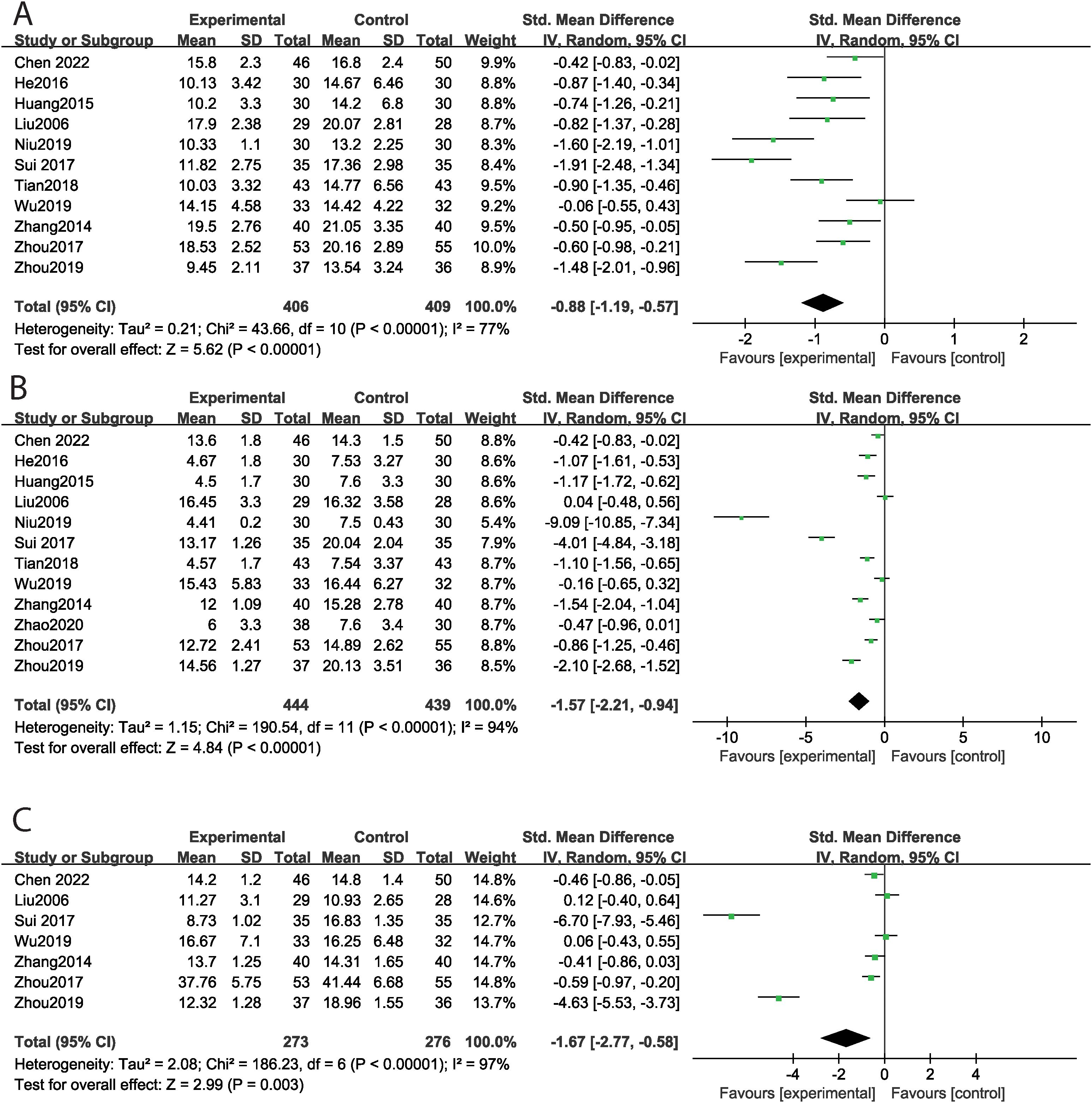
Figure 3. The effect of music therapy on ABC score [(A) total ABC score, (B) sensory, (C) social and self-help].
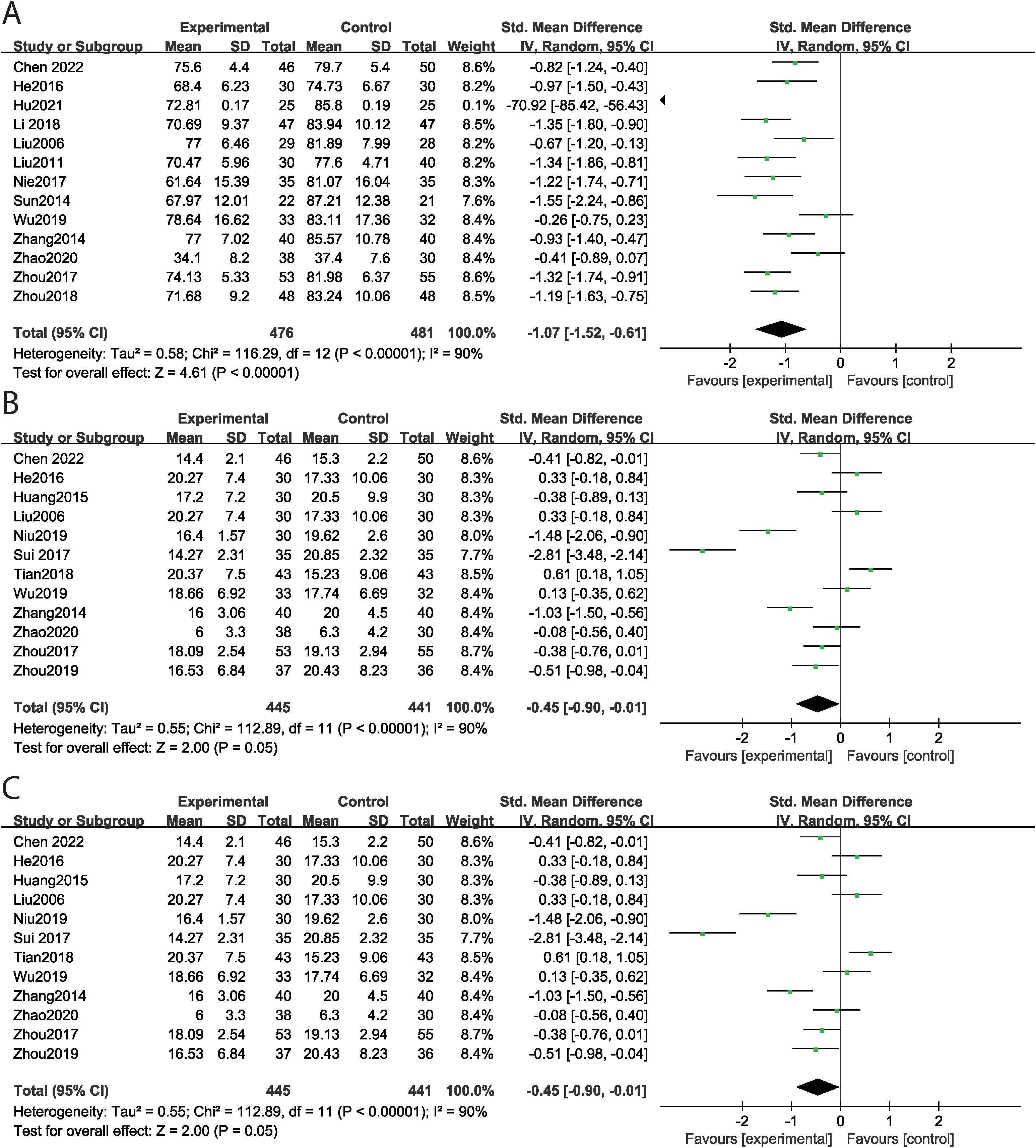
Figure 4. The effect of music therapy on ABC score [(A) body and object use, (B) language skills, (C) relating].
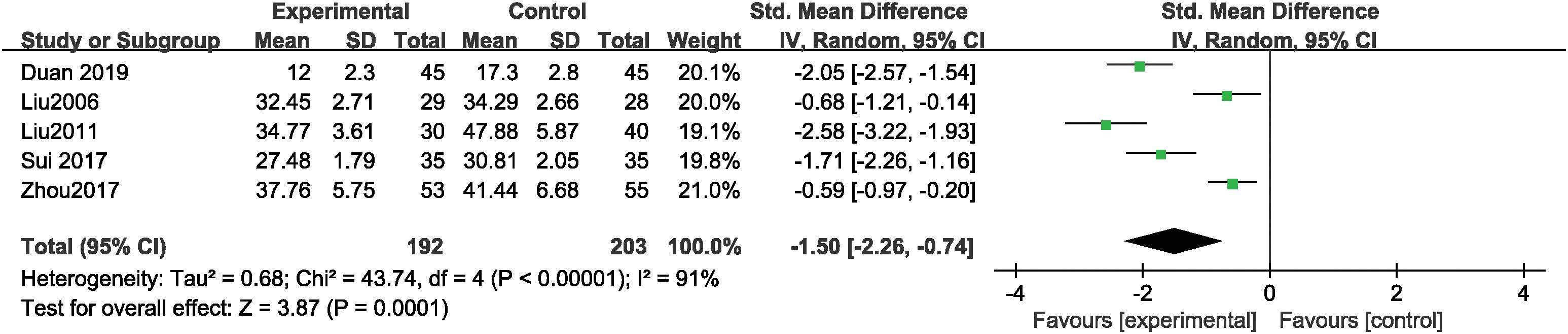
The effect of music therapy on CARS score
Five studies reported the total CARS score, containing 815 cases with 192 cases in the experimental group and 203 in the control group. MT significantly decreased total CARS score (SMD = -1.50, 95% CI: -2.26 ~ -0.74, P < 0.001) compared to the control group, with high levels of heterogeneity across studies (Tau² = 0.68, Chi² = 43.74, I² = 91%, P < 0.001) (Figure 5). Subgroup analyses by intervention duration were conducted to explore heterogeneity sources. MT significantly reduced total CARS scores in both the >12-week subgroup (SMD = -2.09, P < 0.001; I² = 49.9%, P = 0.136) and the ≤12-week subgroup (SMD = -0.62, P < 0.001; I² = 0%, P=0.788). Weights were calculated by the inverse‐variance method, with each study’s contribution proportional to the inverse of its effect-estimate variance. 14 carries the highest weight (21.0%), reflecting its larger sample size more precise estimates are given more influence in the overall effect size calculation. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the total results remained unchanged after excluding each study separately. Funnel plot asymmetry did not reveal any potential for publication bias (P>0.05) (Supplementary Figure S3).
Discussion
The aim of this meta-analysis was to estimate the effectiveness of music therapy (MT) for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in the Chinese population. Our review of twenty-three studies showed that MT was effective in reducing autism-related symptoms as assessed by various standardized tools. Specifically, MT demonstrated significant improvements in key areas such as communication, social interaction, language skills, and cognitive function when compared to control groups. The significant reduction in ATEC scores suggests that MT effectively improves core autism symptoms, including communication, social interaction, and behavioral functioning, reinforcing its potential as a valuable intervention for addressing the multifaceted challenges of ASD. The concurrent decrease in ABC scores further supports MT’s role in reducing maladaptive behaviors, though the comparatively smaller effect implies a stronger impact on socio-communicative domains than behavioral regulation alone. These findings highlight the promising role of MT as an intervention that can enhance various aspects of functioning in children with ASD.
The science of MT represents a multifaceted interdisciplinary field that combines psychology, medicine, music, and education, highlighting music’s vital role in healing and well-being (34). Music’s complexity arises from its ability to engage multiple areas of the brain simultaneously, leading to various proposed mechanisms for its effects. One such mechanism is neuroplasticity, which refers to the brain’s capacity to form new connections and its association with feelings of reward(T. 35). Another important principle is Hebbian theory, which suggests that when two neurons fire together, they are more likely to establish a new connection (36). Key concepts in MT include neuroendocrine theory, resonance theory, psychological mechanisms, and the energy spectrum of music wave theory (37, 38). The acoustic properties of music interact with the limbic system and the reticular formation in the brainstem, enhancing nerve cell excitability. Through rhythm and melody, music produces complex auditory stimuli that can evoke emotional responses, enriching therapeutic experiences. MT is particularly beneficial for promoting brain development in children, aiding in the enhancement of various skills such as attention, memory, imagination, abstract thinking, and language (39, 40). Within the therapeutic framework, musical and emotional attunement fosters synchronization, supports sensory integration and emotional regulation, and enables the sharing of feelings, leading to the creation of a shared narrative among participants (41).
Music interventions can significantly enhance the engagement of children with ASD in learning and social activities. Activities such as singing, playing instruments, rhythm training, music games, and listening to music serve to rebuild, sustain, and promote both mental and physical health while simultaneously fostering language and social skills, improving mood, and enhancing cognitive abilities in children with ASD (42). These findings align with the research conducted by Ghasemtabar et al. (43), which demonstrated an increase in social skills among children who received MT. Similarly, the study by Vaiouli et al. (44) showed improvements in social skills through improvised MT. When implementing MT with children with ASD, careful consideration should be given to the selection of music. Appropriate compositions and rhythms should be chosen based on the child’s age and specific needs, and a blend of group therapy with individualized approaches is often beneficial. The physical movements and musical interactions in MT parallel the musical exchanges typically seen in early childhood, facilitating spontaneous moments of attunement and bodily synchronization (45). Moreover, various elements of music have a profound impact on human physiology; for instance, the tempo of a musical piece can influence cardiovascular responses, while harmonic consonance activates areas of the paralimbic system and cortex, whereas dissonance can evoke feelings of roughness (46). Children who experience disorganized sensory perception, restricted interests, or heightened emotional responses may particularly benefit from methods that focus on sensory integration and affect regulation, laying the foundation for the development of cross-modal perception, body coherence, and self-regulation-key intrapersonal components critical for developing intersubjectivity (47, 48). Thus, greater emphasis should be placed on the bodily-affective regulation of each child during MT sessions. Musical rhythm training challenges children to encode, maintain and update temporal sequences in real time, repeatedly engaging fronto-parietal circuits that underlie working memory (49). Sustained entrainment drives plasticity in executive pathways, enhancing the capacity to hold and manipulate information (50, 51). As working memory improves, children also gain in attention control, language processing and problem-solving, accounting for the robust cognitive benefits of music-based interventions (52, 53).
Recent fMRI research indicates that musical stimulation can simultaneously strengthen under-connected intrinsic networks and dampen hyper-reactive limbic responses in children with ASD. For instance, exposure to structured musical excerpts has been shown to increase functional connectivity among core hubs of the default mode network, such as fronto-temporal brain networks, and auditory and subcortical regions (54, 55). Emotional music also activates the parahippocampal gyrus extending into the amygdala regardless of whether it is happy or sad, and engages the thalamus and adjacent midbrain regions associated with arousal and the processing of temporal complexity (56, 57). By engaging both large-scale social networks and conserved emotional arousal circuits, music therapy may drive the social interaction, communication, and emotional regulation improvements seen in ASD.
Several limitations exist in our study. Firstly, only articles published in English and Chinese were considered, which may introduce publication bias. Additionally, there has been a decline in the number of published studies in recent years, suggesting the possibility of selective publication. Some trials combined music therapy with other interventions, such as language training, making it difficult to isolate the effects of music therapy alone. The broad age range across studies limits our ability to draw conclusions about age-specific efficacy. Most included studies did not report the music therapists’ credentials or training levels, limiting our ability to assess the influence of therapist expertise on intervention outcomes. The primary outcomes assessed varied significantly among studies, and the lack of consistent measures of interaction further adds to the heterogeneity observed. To establish the effectiveness of MT for children with ASD, future research needs to feature large sample sizes, employ rigorous methodologies, and implement long-term observation and follow-up periods. Furthermore, adopting standardized research designs is essential for drawing more robust conclusions regarding the benefits of MT in the treatment of children with ASD.
Conclusions
The results of the meta-analysis indicate that music therapy significantly enhances the overall symptoms of autism spectrum disorder in children from the Chinese population, particularly by improving communication skills, social interaction, language abilities, and cognitive function within existing high-quality studies. These robust findings support the integration of structured music therapy into pediatric rehabilitation protocols. However, the heterogeneity among the studies included and the low methodological quality of some research underscore the necessity for further well-designed randomized controlled trials with larger sample sizes to confirm and solidify these findings.
Author contributions
YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1611182/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Lord C, Brugha TS, Charman T, Cusack J, Dumas G, Frazier T, et al. Autism spectrum disorder. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2020) 6:55. doi: 10.1038/s41572-019-0138-4
2. Willsey HR, Willsey AJ, Wang B, and State MW. Genomics, convergent neuroscience and progress in understanding autism spectrum disorder. Nat Rev Neurosci. (2022) 23:323–3415. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00576-7
3. Hirota T and King BH. Autism spectrum disorder: A review. JAMA. (2023) 329:157–1685. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.23661
4. Baxter AJ, Brugha TS, Erskine HE, Scheurer RW, Vos T, and Scott JG. The epidemiology and global burden of autism spectrum disorders. Psychol Med. (2015) 45:601–13. doi: 10.1017/s003329171400172x
5. Wang L, Peng JL, Qiao FQ, Cheng WM, Lin GW, Zhang Y, et al. Clinical randomized controlled study of acupuncture treatment on children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:5549849. doi: 10.1155/2021/5549849
6. Zhou H, Xu X, Yan W, Zou X, Wu L, Luo X, et al. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder in China: A nationwide multi-center population-based study among children aged 6 to 12 years. Neurosci Bull. (2020) 36:961–9715. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00530-6
7. Solanki MS, Zafar M, and Rastogi R. Music as a therapy: role in psychiatry. Asian J Psychiatr. (2013) 6:193–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2012.12.001
8. Ho YC, Cheung MC, and Chan AS. Music training improves verbal but not visual memory: cross-sectional and longitudinal explorations in children. Neuropsychology. (2003) 17:439–50. doi: 10.1037/0894-4105.17.3.439
9. Shi Z-M, Lin G-H, and Xie Q. Effects of music therapy on mood, language, behavior, and social skills in children with autism: A meta-analysis. Chin Nurs Res. (2016) 3:137–1415. doi: 10.1016/j.cnre.2016.06.018
10. Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
11. Yi D. A study on the effect of music therapy combined with language training on autism. Pract Clin J Integrated Traditional Chin Western Medicin. (2019) 19:45–6. doi: 10.13638/j.issn.1671-4040.2019.11.021
12. Li W, Li Z, Zhou G, and Ni Z. Research on the efficacy duration of auditory integration training in the treatment of children with autism spectrum disorder. Chin J Child Health Care. (2019) 27:565–5675.
13. Guanghong S. Effect of Music Therapy on Autistic Children. Tianjin: Tianjin Medical University, Cnki (2017).
14. Zhou Q, Jing Y, Gan X, Gu J, and Song M. Rehabilitation effect of music therapy on children with autistic spectrum disorders. Chin Primary Health Care. (2017) 31:68–69+76.
15. Fu Y, Zhang F, and Wang F. Study on the influence of music on the treatment of autism in children. J Clin Med Literature. (2016) 3:8505+8508.
16. Li R, Xiaoyan Y, and Chunhong C. The efficacy observation of music therapy combined with speech training in the language rehabilitation of autistic children. Chin Sci J Hearing Speech Rehabil. (2016) 14:220–2235.
17. Hui H. Observation and empirical research on the clinical effect of music therapy intervention on children with autism. China Rural Health. (2016) 02):27.
18. Sun Yuyan HC, Jian L, Shunying P, Guoling Z, Yan L, Yuanyue Z, et al. Effects of auditory integrative training and psychological nursing on low-functional autistic children. China Modern Doctor. (2014) 52:37–39+42.
19. Zhang J and Zhang Q. Effect of auditory integration training on the rehabilitation of children with autism. Chin J Child Health Care. (2014) 22:321–4.
20. Liu Z and Li N. (2011). Music therapy combined with scalp acupuncture for autism, in: The 10th Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Music Therapy Association, Guangzhou, China, (Gunagzhou: Proceedings of the 10th Annual Academic Conference of the Chinese Music Therapy Association).
21. Wang J, Zhang X, and Zhang J. The effect on childhood autism with melodic intonation therapy. J Henan University(Medical Science). (2009) 28:60–615.
22. Gang L. Clinical observation and experimental study on acupuncture combined with music therapy in the treatment of autism. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Cnki (2006).
23. Chen Y, Zeng L, and Zhang Y. Effects of visual music training on children with autism spectrum disorders. Med J Chin People's Health. (2022) 34:58–605.
24. Hu S, Wu J, and Yinjia Z. Effect of language cognitive training combined with music therapy on improving language expression and comprehension abilities in children with autism. Modern Pract Med. (2021) 33:802–8045.
25. Zhao Y, Wen C, Qi Y, Shi N, and Li E. Clinical sffects of group music therapy on children with infantile autism. J Pract Traditional Chin Internal Med. (2020) 34:23–265.
26. Li P. Application of music care in the care of autistic children. Henan Med Res. (2020) 29:549–51.
27. Fan Z. Analysis of the clinical application of music therapy in the rehabilitation of autistic children. Renowned Doctor. (2019) 11):71.
28. Yuan N. The application value of music therapy in the rehabilitation of autistic children. Northern Music. (2019) 39:248–9.
29. Yuhang Z. Effect of music therapy combined with language training on the rehabilitation of language function in children with autism. Chin J Convalescent Med. (2018) 27:1157–9.
30. Liyuan T. Analysis of the rehabilitation effect of music intervention therapy on language disorders in children with autism. Clin Res. (2018) 26:108–9.
31. Li Q and Chao G. Observation on the effect of music therapy in the rehabilitation treatment of children with autism. Med J Chin People's Health. (2018) 30:69–70.
32. Li NM. The effect of music therapy on rehabilitation training of childhood autism. China Continuing Med Educ. (2017) 9:192–3.
33. Lingyi H. Rehabilitation applications of music therapy in children with autism. China Continuing Med Educ. (2015) 7:153–4.
34. Shalit L, Elefant C, and Roginsky E. Exploring music in the everyday lives of autistic women: An Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis. Nordic J Music Ther. (2024) 34(3):225–44. doi: 10.1080/08098131.2024.2396105
35. Zaatar MT, Alhakim K, Enayeh M, and Tamer R. The transformative power of music: Insights into neuroplasticity, health, and disease. Brain Behavior Immun - Health. (2024) 35:100716. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100716
36. Talukdar S and Ghosh S. Biophysics of Brain Plasticity and Its Correlation to Music Learning. In: Advances in Speech and Music Technology: Computational Aspects and Applications, edited by Anupam Biswas, Emile Wennekes, Alicja Wieczorkowska and Rabul Hussain Laskar, 269-282. Springer International Publishing, Cham (2023).
37. Bowling DL. Biological principles for music and mental health. Trans Psychiatry. (2023) 13:374. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02671-4
38. Sun Y, Zhang Y, Li R, Cai D, Zhang W, and Yang Z. Intracranial dissemination in a primary small cell carcinoma of the brain: a case report and literature review. Front Oncol. (2023) 13:1222961. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1222961
39. Xiao X, Chen W, and Zhang X. The effect and mechanisms of music therapy on the autonomic nervous system and brain networks of patients of minimal conscious states: a randomized controlled trial. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1182181. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1182181
40. Sun Y, Zhang Y, Cai D, Zhang W, and Yang Z. Middle ear neuroendocrine tumor with multiple brain metastases: a case report and literature review. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1392610. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1392610
41. Daniel S, Wimpory D, Delafield-Butt JT, Malloch S, Holck U, Geretsegger M, et al. Rhythmic relating: bidirectional support for social timing in autism therapies. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:793258. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.793258
42. Kossyvaki L and Curran S. The role of technology-mediated music-making in enhancing engagement and social communication in children with autism and intellectual disabilities. J Intellect Disabil. (2020) 24:118–38. doi: 10.1177/1744629518772648
43. Ghasemtabar SN, Hosseini M, Fayyaz I, Arab S, Naghashian H, and Poudineh Z. Music therapy: An effective approach in improving social skills of children with autism. Adv BioMed Res. (2015) 4:157. doi: 10.4103/2277-9175.161584
44. Vaiouli P, Grimmet K, and Ruich LJ. Bill is now singing: joint engagement and the emergence of social communication of three young children with autism. Autism. (2015) 19:73–83. doi: 10.1177/1362361313511709
45. Birnbaum JC, Kandler Z, Aslan M, Fu JHY, and Turry A. Music therapy with autistic children: creating an intersubjective field of play through improvisation. Psychoanalytic Inq. (2023) 43:232–2465. doi: 10.1080/07351690.2023.2185070
46. Schaefer H-E. Music-evoked emotions—current studies. Front Neurosci. (2017) 11:600. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00600
48. Meltzoff AN. Foundations for developing a concept of self: The role of imitation in relating self to other and the value of social mirroring, social modeling, and self practice in infancy. (1990). (Chicago).
49. Zanto TP, Johnson V, Ostrand A, and Gazzaley A. How musical rhythm training improves short-term memory for faces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2022) 119:e2201655119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201655119
50. Yurgil KA, Velasquez MA, Winston JL, Reichman NB, and Colombo PJ. Music training, working memory, and neural oscillations: A review. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:266. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00266
51. Thaut MH, Peterson DA, and McIntosh GC. Temporal entrainment of cognitive functions: musical mnemonics induce brain plasticity and oscillatory synchrony in neural networks underlying memory. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2005) 1060:243–54. doi: 10.1196/annals.1360.017
52. Rodriguez-Gomez DA and Talero-Gutiérrez C. Effects of music training in executive function performance in children: A systematic review. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:968144. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.968144
53. Bentley LA, Eager R, Savage S, Nielson C, White SLJ, and Williams KE. A translational application of music for preschool cognitive development: RCT evidence for improved executive function, self-regulation, and school readiness. Dev Sci. (2023) 26:e13358. doi: 10.1111/desc.13358
54. Sharda M, Tuerk C, Chowdhury R, Jamey K, Foster N, Custo-Blanch M, et al. Music improves social communication and auditory-motor connectivity in children with autism. Transl Psychiatry. (2018) 8:231. doi: 10.1038/s41398-018-0287-3
55. Padmanabhan A, Lynch CJ, Schaer M, and Menon V. The default mode network in autism. Biol Psychiatry: Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. (2017) 2:476–4865. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2017.04.004
56. Koelsch S, Fritz T, and Schlaug G. Amygdala activity can be modulated by unexpected chord functions during music listening. Neuroreport. (2008) 19:1815–9. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32831a8722
Keywords: music therapy, children, autism spectrum, meta-analysis, ATEC, CARS
Citation: Yang Y, Wang Y, Li W and Su L (2025) Effect of music therapy on children with autism spectrum disorders in the Chinese population: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 16:1611182. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1611182
Received: 13 April 2025; Accepted: 26 June 2025;
Published: 25 July 2025.
Edited by:
Fabrizio Stasolla, Giustino Fortunato University, ItalyReviewed by:
Weijia Yang, Yonsei University, Republic of KoreaFerdinando Suvini, Conservatorio di Musica Girolamo Frescobaldi, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Wang, Li and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Li Su, bGlzdXNjaWVuY2VAb3V0bG9vay5jb20=
 Yajing Yang1
Yajing Yang1 Li Su
Li Su