Abstract
Objective:
This study employed network meta-analysis to evaluate the impact of several exercise interventions on mobile phone addiction. The aim is to determine the most effective exercise intervention measures and provide a reference for future intervention measures to improve mobile phone addiction.
Method:
Systematically search for relevant literatures in domestic and foreign databases such as Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, China Knowledge, Wanfang, etc. We evaluated the risk of bias according to the revised Cochrane Randomized Trial Risk Tool and conducted traditional and web-based meta-analyses using Review Manager 5.3 and Stata 14.0.
Result:
Traditional Meta-results showed that all interventions were superior to the control group in improving mobile phone addiction (SMD= -1.38, 95%CI=-1.75, -1.01). Network meta-analysis shows that Badminton and Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT) have better improvement effects on mobile phone addiction among teenagers than other forms of exercise.
Conclusion:
All kinds of interventions have a significant impact on reducing mobile phone addiction. Badminton and MBT have more advantages in improving mobile phone addiction. However, due to the influence of the sample size and the quality of the included literature, it is recommended to further verify the results in the future.
1 Introduction
Smartphones have become an inseparable part of daily life. Their use makes human life easier because they have many convenient functions and software applications (1). While mobile phones bring convenience, they also bring potential risks, leading to new behavioral problems, among which is mobile phone addiction (2). Mobile phone addiction is the theoretical criterion for defining behavioral addiction, including psychological (craving, cognitive prominence, loss of control, emotional correction), physical dependence (tolerance and withdrawal symptoms), significance, impulsiveness, spotlight behavior, and relapse (3–5). The core signs and symptoms of mobile phone addiction include obsessive thoughts about the phone (craving), spending extra time on the smartphone (tolerance), and experiencing anxiety when the smartphone is unavailable (withdrawal) (6, 7). Mobile phone addiction reduces activity levels and leads to an increase in fat and a decrease in muscle mass (8). It also lowers the sleep quality of teenagers, causes damage to the lens, and leads to immune system dysfunction (9). In addition, teenagers’ skulls are thinner, and their brain tissue is more electrically conductive. They are more likely to absorb mobile phone radiation than adults and have a higher risk of developing brain tumours than adults (10). In addition, mobile phone addiction can also cause anxiety in various aspects, such as self-existence, social interaction, and academic studies. The cognitive dissonance and negative automated thinking it triggers can further exacerbate depression, leading to more suicidal thoughts among teenagers. Furthermore, mobile phone addiction is negatively correlated with the academic performance of adolescents (11). Excessive use of mobile phones can weaken students’ inhibitory control, working memory and attention, affect teaching coherence and hinder establishing a supportive, cooperative learning environment, and those at high risk also find it more challenging to improve school adaptability through self-regulation (12). Mobile phone addiction has seriously affected the physical fitness and intelligence level of teenagers. Relevant reports indicate that mobile phone addiction has become a label for teenagers. Research shows that the incidence of mobile phone addiction among teenagers is 70% (13–15), and 21.3% of college students in China are addicted to smartphones (16). In Italy, 30% of teenagers are addicted to mobile phones (17). Therefore, it is extremely urgent to solve the problem of teenagers’ addiction to mobile phones.
At present, taking scientific and effective measures to reduce teenagers or young adults mobile phone dependence has become the focus of multidisciplinary attention. The existing intervention measures for mobile phone addiction mainly include group counseling intervention, cognitive behavioral intervention and exercise intervention, etc. At present, there are also many clinical randomized controlled trials (RCTS) to verify the intervention effects of various measures (18, 19), and some scholars have conducted research through traditional meta-analysis (20). However, there is a lack of direct comparisons among the intervention effects of different measures. Network meta-analysis (NMA) is an extension of traditional pairwise meta-analysis, with the advantage of simultaneously comparing the effectiveness of multiple interventions for a specific outcome. Even when direct comparisons between two interventions are not available within the network structure, NMA can still calculate indirect comparisons (21). By integrating both direct and indirect evidence, NMA facilitates the ranking of various interventions’ effectiveness (22). However, research on the efficacy of different interventions for mobile phone addiction remains limited. Therefore, we studied and explored the influence of varying intervention methods on mobile phone addiction, and classified the interventions in detail to determine the best intervention methods for improving mobile phone addiction, guiding teenagers or young adults with mobile phone addiction to choose the best intervention methods, and reducing mobile phone addiction among teenagers or young adults.
2 Methods
This study was reported per the PRISMA NMA guidelines (23). The review protocol was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Review (PROSPERO CRD420251127958).
2.1 Search strategy
The computer searched PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, CNKI, and other databases, and the search period was established until April 28, 2025. The search takes the way of combining subject words and free words. We conducted a search using Pubmed as an example. For the search strategy, please refer to the Supplementary Materials (Appendix 1).
2.2 Study selection
The inclusion criteria for study selection were based on the PICOS methodology (Participants, interventions, comparators, outcomes, and study design) (23), shown in Table 1.
Table 1
| Category | Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Teenagers or Young adults who have reached the level of mobile phone addiction after assessment | Medically diagnosed severe mental disorders |
| Interventions | Aerobic Aerobics (AA), Badminton, Baduanjin, Basketball, Biofeedback, Tai Chi (TC), Table tennis (TT), Jump rope (JR), Combined Intervention (CI), Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT), Cognitive Therapy (CT), Sanda, Volleyball, Yoga | |
| Comparisons | Control group (CG) | |
| Outcomes | Using Smartphone Addiction Scale Shortened Version (SAS-SV), The mobile phone addiction index (MPAI). SAS-SV or MPAI has good reliability and validity (24, 25). | |
| Study | Randomized controlled trial; published in English or Chinese | duplicate publications; conference papers and review articles. |
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
The types of interventions were based on the exercise interventions actually reported in the included studies.
2.2 Data extraction
Following database screening, all identified records were imported into Note Express software for duplicate removal. Two independent investigators systematically applied our pre-defined PICOS criteria through title/abstract screening. Potentially eligible studies were then transferred to Zotero software (v6.0.30) for full-text evaluation and data extraction. Discrepancies were resolved through consultation with a third reviewer. Standardized extraction forms captured (1): basic characteristics (first author, publication year, region) (2); participant demographics (sample size, age range) (3); intervention protocols (modality, weekly frequency, duration); and (4) outcome measures with corresponding assessment methods.
2.3 Risk of bias assessment
The risk of bias was assessed independently by two reviewers and by a third reviewer using the tools provided by the Cochrane Collaboration (26), including sequence generation, hidden assignment, blinking, incomplete outcome data, non-selective reporting of results, and other sources of bias. Each criterion was judged to have a low, unclear, or high risk of bias.
2.4 Data analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using Rev Man 5.3 software. The standardized mean difference (SMD) with 95% confidence intervals was selected as the effect measure for continuous outcomes, and a random-effects model was applied to pool effect sizes across studies. A 95% confidence interval (95% CI) represented each effect size. I2 was used to determine the heterogeneity of effect indicators among different studies quantitatively. An I2 >50% or ap value of 0.10 or less for the Q test was interpreted as indicating substantial heterogeneity (26). When the heterogeneity was significant, the random effects model was used; otherwise, the fixed effects model was used. Subgroup analysis was based on movement characteristics and population characteristics. The source of heterogeneity was explored through sensitivity analysis for the studies with significant heterogeneity. Sensitivity analysis was used to test whether the source of heterogeneity was due to one of the original studies.
NMA was also conducted to perform a random-effects multivariate NMA for pooled estimates within the frequentist framework (27). We conduct NMA based on the frequency-based framework through Stata16.0 (network and mvmeta packages). The standardized mean difference (SMD) and its 95% confidence interval were used as combined statistics, and the direct and indirect comparison evidence was integrated through the multivariate random-effects model. The geometry of the network is summarized into a networkplot, in which the lines connecting the nodes represent direct head-to-head comparisons between interventions, and the size of each node and the thickness of each line connecting the nodes are directly proportional to the number of studies. Draw the network contribution graph (netweight package) and calculate the contributions of each direct comparison. The local-global inconsistency test (network meta inconsistency/consistency) is adopted, supplemented by the node splitting method to identify the inconsistency of specific loops. The surface under the cumulative ranking curve (SUCRA) was used to rank and compare the effects of the different interventions. SUCRA values range from 0 to 100, where 100 indicates the best treatment with no uncertainty, and 0 indicates the worst treatment without uncertainty (28). Moreover, a network funnel plot was generated to check for publication bias (netfunnel).
3 Results
3.1 Study selection
Our research obtained a total of 2,784 records. After deleting 436 duplicate records, the titles and abstracts of 2,348 studies were screened. Subsequently, read the remaining 67 articles in full. After reading the full text, we eliminated 35 articles that did not conform to the research. Ultimately, 32 studies were included in the meta-analysis. The research flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1

PRISM flow diagram.
3.2 Basic information included in the study
As shown in Table 2, a total of 2,891 teenagers or young adults addicted to mobile phones were involved in the 32 included studies. In terms of result measurement, 15 studies used MAPI to assess the severity of mobile phone addiction, 3 studies used SAS-SV for assessment, and 14 studies used MPATS for assessment. 15 studies were published before 2020, and 17 studies were published after 2020.
Table 2
| Author(s) | Publication year | Country | Study population | Age | Intervention method | Sample | Intervention duration | Intervention frequency | Outcome measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liao (29) | 2022 | China | University | 20.12 ± 1.54 | Basketball/CG | 8/8 | 6 Weeks | NA | MPAI |
| Wang (30) | 2021 | China | Middle School | 12-13 | Basketball/CG | 17/16 | 9 Weeks | Twice a week | SAS-SV |
| Yang (31) | 2022 | China | High school student | 16.45 ± 2.02/16.74 ± 1.67/16.28 ± 1.96 | AA/Badminton/CG | 36/36/36 | 12 Weeks | Three times a week | MPAI |
| Zhang (32) | 2023 | China | University | 20.11± 0.64 | CI/TC/CG | 30/30 | 8 Weeks | Three times a week | SAS-SV |
| Zeng (33) | 2024 | China | University | 19.00 ± 0.43/19.00/19.00 ± 0.35 | Badminton/CG | 17/17/17 | 10 Weeks | Twice a week | MPATS |
| Yu (34) | 2023 | China | University | 18.83 ± 0.87/18.87 ± 0.94 | AA/CG | 30/30 | 16 Weeks | Three times a week | MPAI |
| Wu (35) | 2022 | China | University | NA | TT/CG | 10/17/23 | 12 Weeks | Twice a week | MPATS |
| Yang (36) | 2020 | China | University | NA | CI/CG | 30/30 | 8 Weeks | Twice a week | MPATS |
| Ge (37) | 2015 | China | University | 21.24 ± 1.08 | Volleyball/CG | 18/18 | 18 Weeks | Three times a week | MPAI |
| Li (38) | 2020 | China | University | 21.05 ± 1.02/21.05 ± 1.65 | CI/CG | 16/16 | 12 Weeks | Three times a week | MPATS |
| Zhang (39) | 2022 | China | University | 20.27 ± 1.95 | Biofeedback/CI/CG | 17/17/20 | 8 Weeks | Twice a week | MPATS |
| Xie (40) | 2019 | China | University | NA | Baduanjin/CG | 162/152 | 8 Weeks | Five times a week | MPAI |
| Liu (41) | 2019 | China | University | 19.21 ± 1.02/18.95 ± 0.89/18.77 ± 1.29/19.71 ± 1.77 | Basketball/Baduanjin/GC/CG | 31/31/30/34 | 12 Weeks | Three times a week | MPAI |
| Liu (42) | 2022 | China | University | NA | Basketball/Baduanjin/GC/CG | 31/31/30/34 | 10 Weeks | Twice a week | MPAI |
| Sheng (43) | 2017 | China | University | NA | GC/CG | 2/6/6 | 8–10 Weeks | Once a week | MPAI |
| Niu (44) | 2020 | China | University | 21.33 ± 2.05/22.94 ± 2.13 | MBT/CG | 400/400 | 12 Weeks | Twice a week | ,MPAI |
| Li (45) | 2019 | China | University | 20.14 ± 1.33/20.06 ± 1.03 | MBT/CG | 28/31 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Shen (46) | 2022 | China | University | NA | MBT/CG | 34/34 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPAI |
| Du (47) | 2024 | China | University | 20.39 ± 1.20/20.35 ± 1.17 | MBT/CG | 28/31 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Dai (48) | 2018 | China | University | NA | MBT/CT/CG | 27/20/20 | 4 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Feng (49) | 2015 | China | University | NA | GC/CG | 10/10 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Qing (50) | 2019 | China | University | NA | GC/CG | 34/34 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Zhou (51) | 2021 | China | University | NA | GC/CG | 8/41 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Deng (52) | 2016 | China | University | 18.4 ± 0.5/18.9 ± 0.2 | GC/CG | 7/7 | 4 Weeks | Once a week | MPAI |
| Zhou (53) | 2021 | China | University | NA | CT/CG | 12/12 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Tao (54) | 2021 | China | University | 18.95 ± 0.89/19.21 ± 1.02/19.71 ± 1.77 | Basketball/Baduanjin/CG | 33/33/34 | 12 Weeks | Three times a week | MPAI |
| Pal (55) | 2022 | India | University | 20.2 ± 2.2/19.7 ± 1.5 | Yoga/CG | 142/142 | NA | Six times a week | SAS-SV |
| Haihong (56) | 2023 | China | University | 19.1 ± 0.5 | MBT/CG | 28/28 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPAI |
| YUKUN (57) | 2018 | China | University | 21.3 ± 1.3 | MBT/CG | 41/29 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Zhou (58) | 2022 | China | University | 18.93 ± 1.90/19.22 ± 0.86 | Sanda/CG | 121/116 | 10 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
| Zhang (59) | 2020 | China | University | 20.1/20.5 | MBT/CG | 17/15 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPAI |
| An (60) | 2020 | China | University | NA | GC/CG | 8/8 | 8 Weeks | Once a week | MPATS |
Detailed characteristics of the included studies.
3.3 Methodological quality assessment
The methodological quality of the included 32 articles was evaluated. The summary of the risk of bias assessment is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2
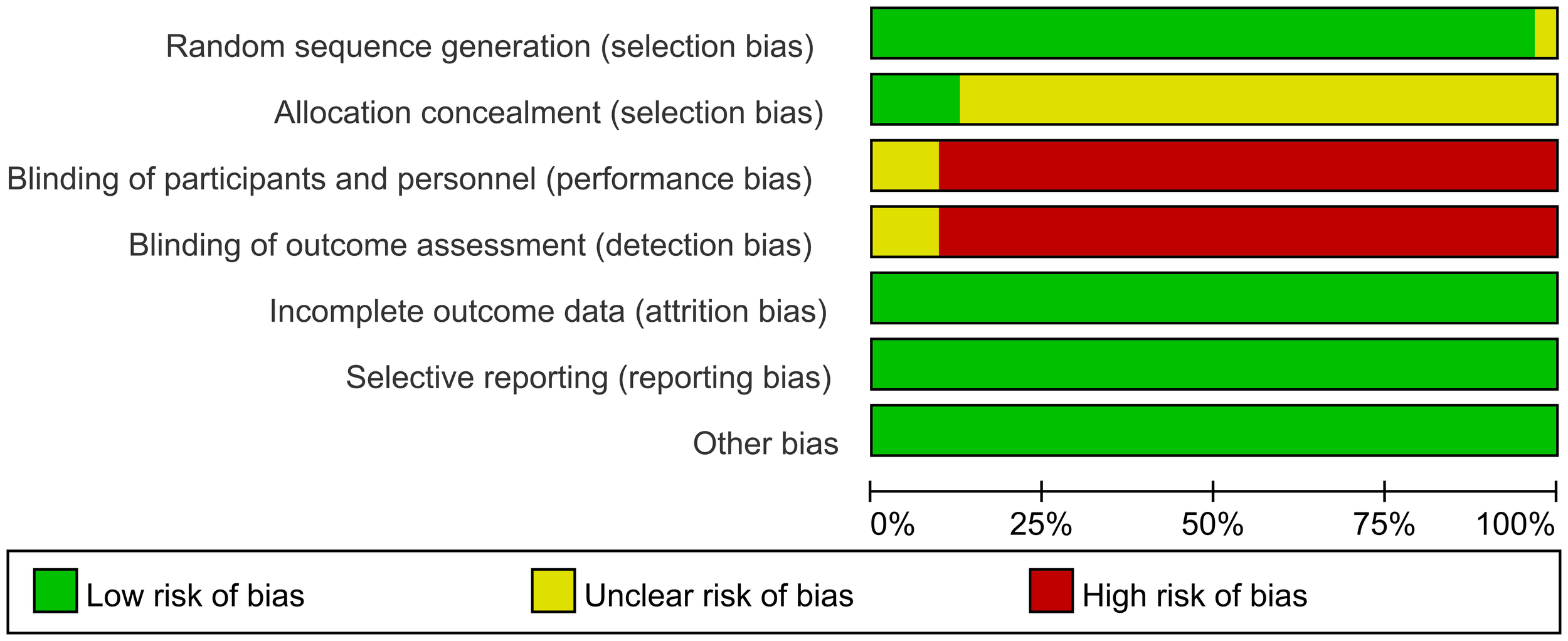
Summary of risk of bias.
3.4 Meta-analysis
The effect of the intervention measures was compared with that of the control group. A meta-analysis was conducted on 32 studies. The overall result is shown in Figure 3. Compared with the blank control group, exercise intervention had a significant effect on improving mobile phone addiction in adolescents [SMD= -1.38, 95%CI (-1.75, -1.01), p < 0.001], and I2 showed significant heterogeneity (I2 = 94%, p < 0.001).
Figure 3
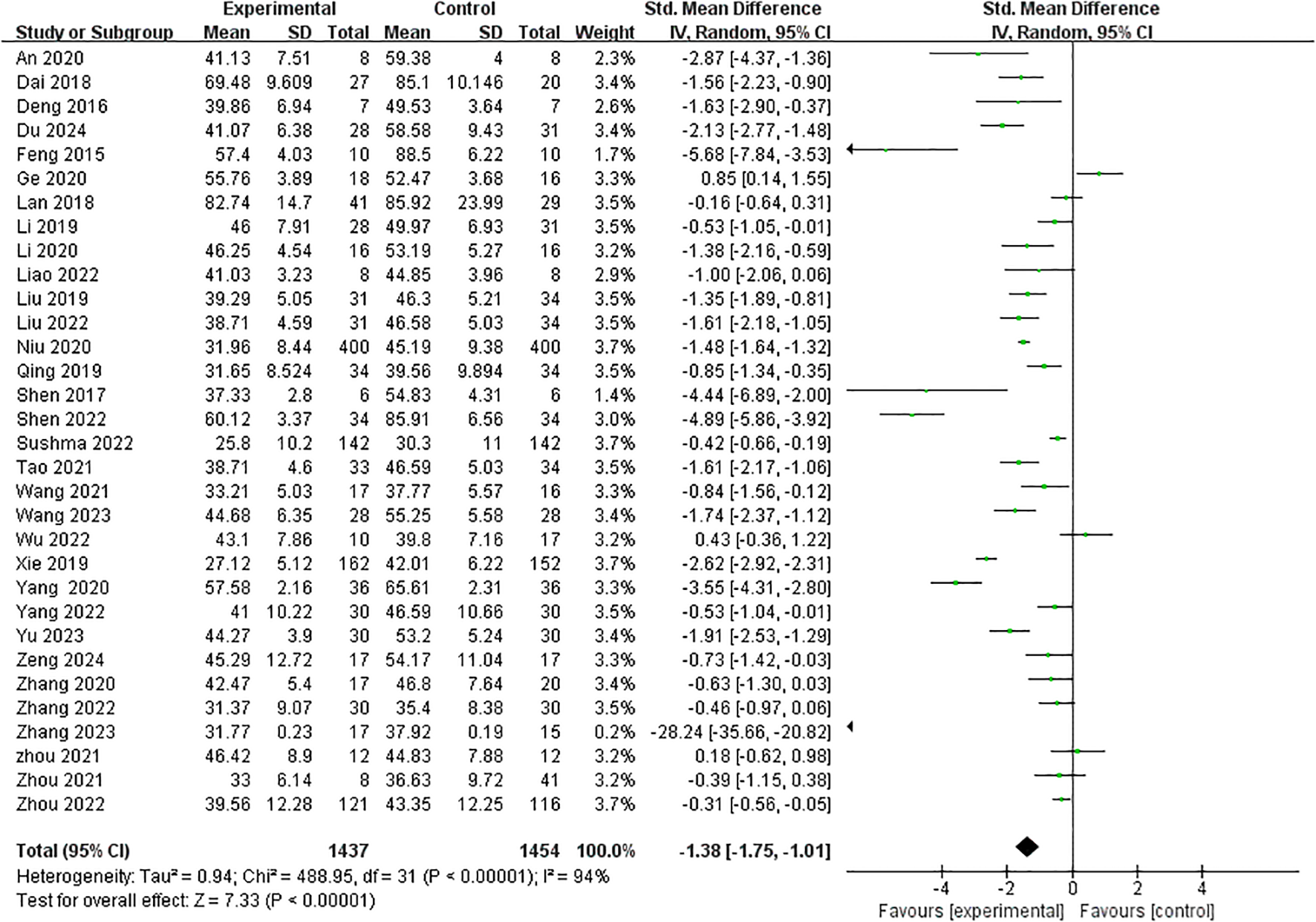
Impact of interventions on Mobile phone addiction.
3.4.1 Subgroup analysis
We conducted subgroup analyses based on sample size, Intervention mode, outcome measurement, Intervention duration, Year of publication, and intervention frequency. There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups in terms of publication year and Intervention frequency, sample size and Intervention duration (P > 0.05). In terms of the outcome measurement, and Intervention mode, the differences between subgroups were statistically significant (p < 0.05), as shown in Table 3.
Table 3
| Variable | Number of trials | Sample size | Meta-analysis | Heterogeneity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental | Control | SMD | CI | Pa | I2 | Chi2 | Pb | ||
| All | 32 | 1437 | 1454 | -1.38 | -1.75, -1.01 | — | 94% | 488.95 | <0.001 |
| Year of publication | |||||||||
| Before 2020 | 15 | 835 | 808 | -1.58 | -2.17, -1.00 | 0.38 | 94% | 229.76 | <0.001 |
| After 2020 | 17 | 602 | 646 | -1.25 | -1.73, -0.76 | 93% | 214.75 | <0.001 | |
| Sample size | |||||||||
| ≤50 | 15 | 198 | 229 | -1.41 | -2.17, -0.66 | 0.87 | 90% | 133.88 | <0.001 |
| >50 | 17 | 1239 | 1225 | -1.48 | -1.93, -1.04 | 95% | 339.17 | <0.001 | |
| Outcome measurement | |||||||||
| MPAI | 15 | 853 | 846 | -1.97 | -2.58, -1.37 | <0.001 | 94% | 236.24 | <0.001 |
| SAS-SV | 3 | 189 | 188 | -4.43 | -6.29, -2.58 | 0 | 0.04 | 0.56 | |
| MPATS | 14 | 395 | 420 | -0.91 | -1.34, -0.53 | 84% | 79.33 | <0.001 | |
| Intervention duration | |||||||||
| 4–8 Weeks | 21 | 952 | 962 | -1.60 | -2.08, -1.11 | 0.14 | 93% | 289.33 | <0.001 |
| 12–16 Weeks | 11 | 485 | 492 | -1.05 | -1.60, -0.50 | 83% | 138.83 | <0.001 | |
| Intervention mode | |||||||||
| Exercise Intervention | 17 | 749 | 748 | -1.04 | -1.53, -0.55 | 0.03 | 94% | 272.90 | <0.001 |
| Psychological Intervention | 15 | 688 | 706 | -1.91 | -2.54, -1.28 | 93% | 194.85 | <0.001 | |
| Intervention frequency | |||||||||
| Once a week | 15 | 409 | 422 | -1.91 | -2.62, -1.19 | 0.14 | 94% | 216.48 | <0.001 |
| 2–3 times a week | 14 | 716 | 730 | -1.06 | -1.50, -0.63 | 90% | 126.40 | <0.001 | |
| Other | 3 | 312 | 302 | -1.36 | -3.06, 0.35 | 98% | 126.09 | <0.001 | |
Subgroup analysis to assess the effect of interventions on adolescents’ intervention addiction.
3.4.2 Sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis of the included literature showed that no single study changed the overall outcome.
3.4.3 Publication bias
The funnel plot showed potential publication bias (Figure 4). We further conducted the test through Begg, and the result of the Egger’s test was P = 0.450 (P > 0.05), indicating that the probability of surface bias in the included studies was relatively low.
Figure 4
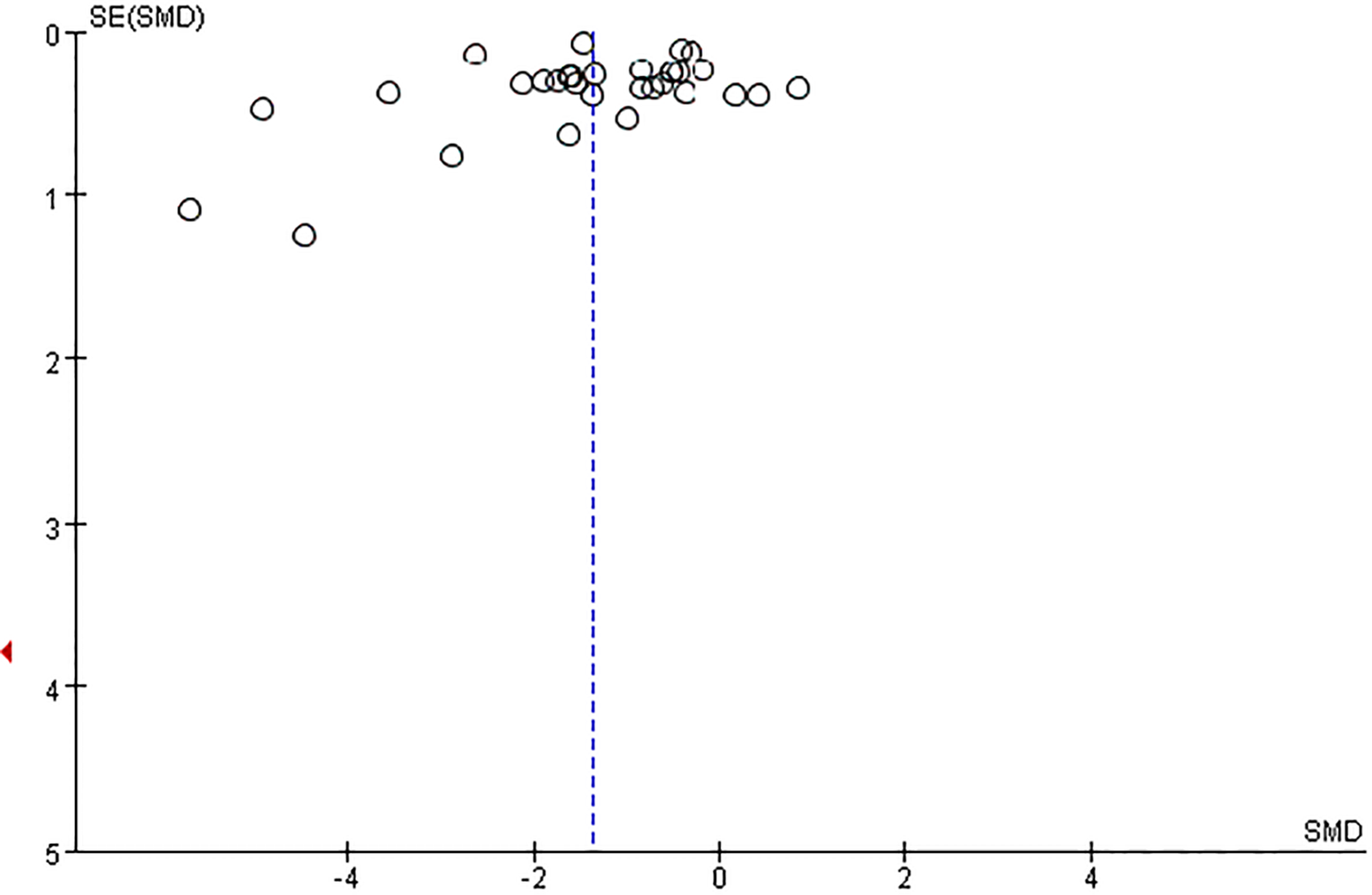
Funnel plot for the publication bias of adolescents’ Mobile phone addiction.
3.5 Network meta-analysis
To examine the differences in effects among the different interventions, network meta-analyses were further performed.
3.5.1 Network diagram
As shown in Figure 5, the dots in the figure represent the number of subjects in each group; the larger the dots are, the larger the sample size of the subjects. The lines connecting the dots represent the number of original studies directly compared in pairs; the thicker the lines are, the more original studies there are.
Figure 5
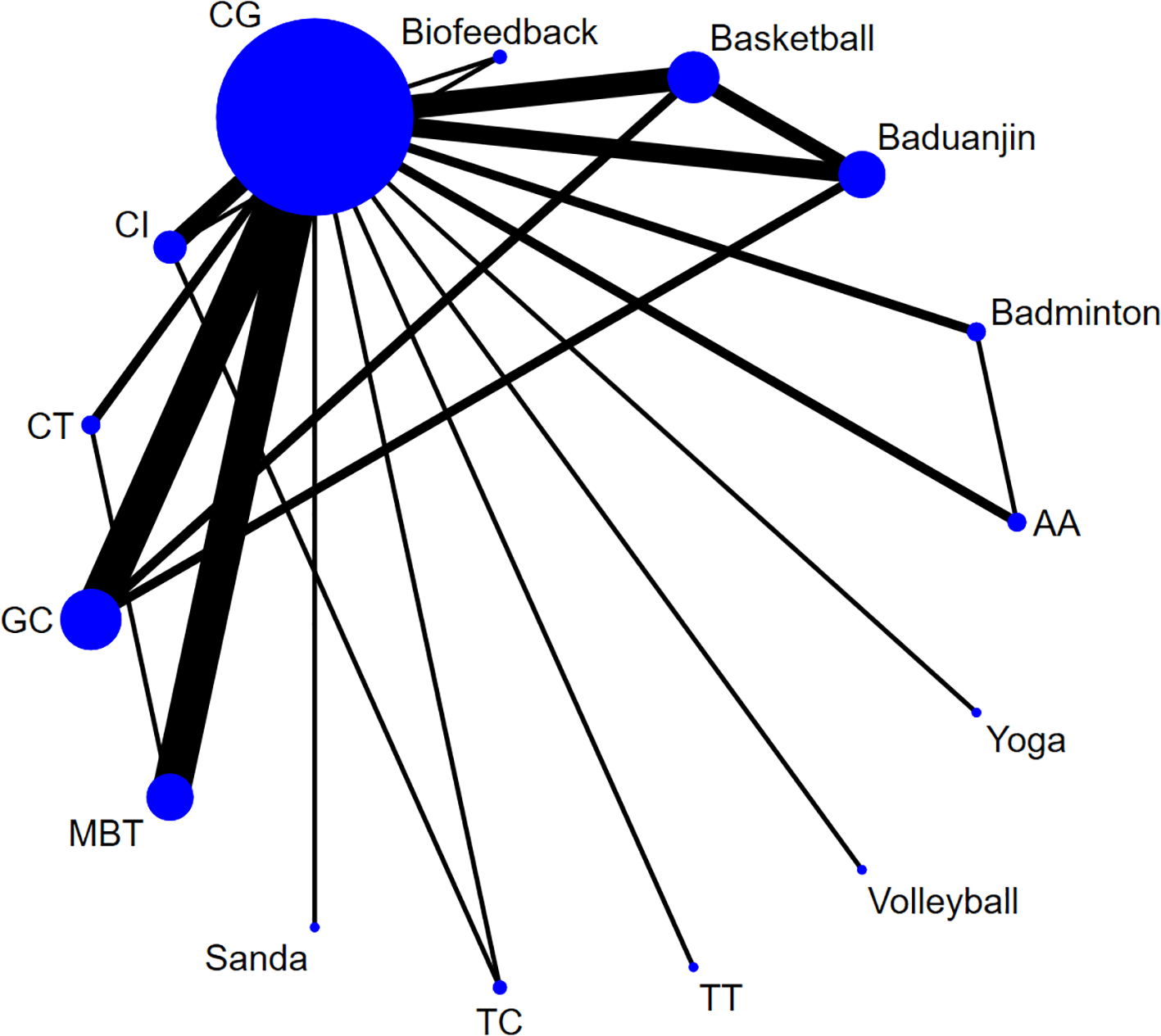
Network diagram of mobile phone addiction. Aerobic Aerobics (AA), Tai Chi (TC), Table tennis (TT), Jump rope (JR), Control group (CG), Combined Intervention (CI), Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT), Cognitive Therapy (CT), Group Counseling (GC).
3.5.2 Inconsistency of the network
The inconsistent model was adopted for verification. The result (P=0.991) indicated that the model inconsistency was not significant. The inconsistency and local inconsistency tests were conducted again. We did not find significant inconsistencies in all the results.
3.5.3 Results of network meta-analysis
Network meta-analysis shows that badminton is significantly superior to CG (SMD -3.86, 95% -6.34 to -1.38) and volleyball (SMD -4.71, 95% -9.07 to -0.34). MBI was significantly superior to CG (SMD -2.37, -3.76 to -0.97), as shown in Figure 6. The forest plots of the comparisons that meet the conditions are shown in Supplementary Materials -Appendix 2.
Figure 6
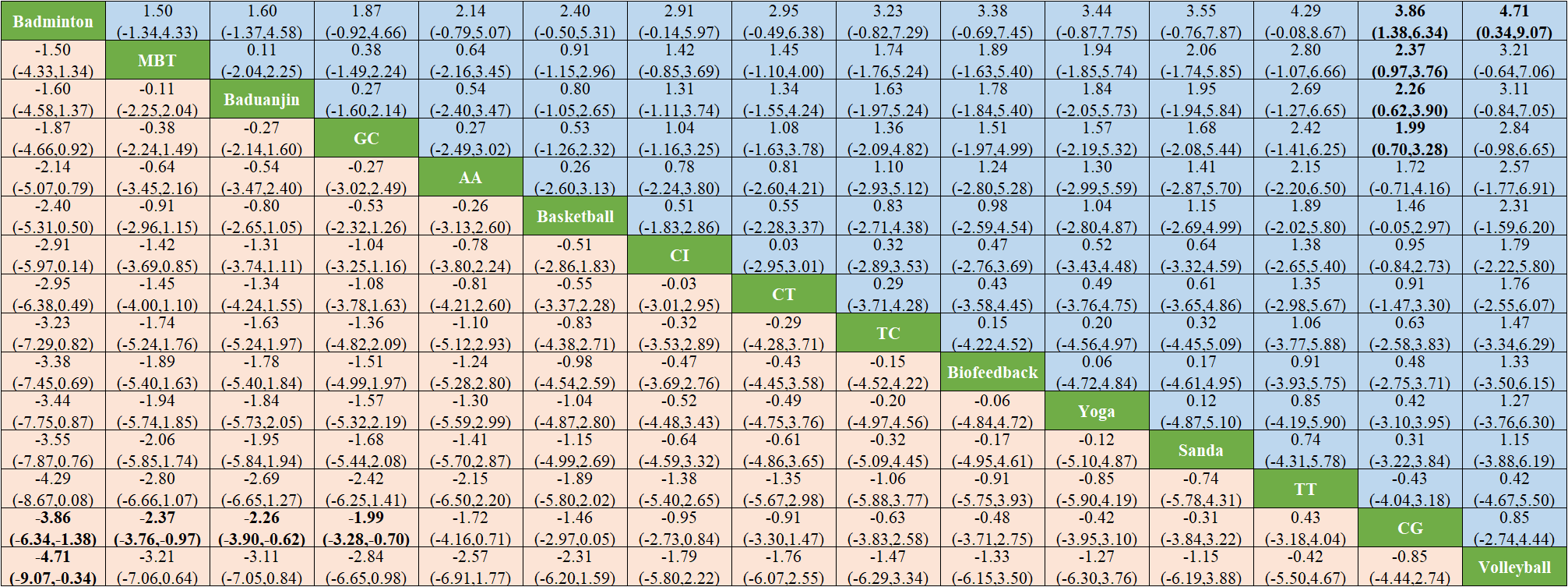
Results of network meta-analysis.
3.5.5 Intervention effect ranking
The SUCRA probability of each intervention in the network is shown in Figure 7. The SUCRA value (Table 4) is the probability that each intervention is among the best of those in the network, with larger values representing higher-ranking probabilities. The SUCRA probability of each intervention in the network is shown in Figure 8. The SUCRA value (Table 4) is the probability that each intervention is among the best of those in the network, with larger values representing higher-ranking probabilities. Badminton (SUCRA=93.8)> MBT(SUCRA=77.3)> Baduanjin (SUCRA=74.3)> GC (SUCRA = 69.6) > Aerobic Aerobics (SUCRA = 62.1) > Basketball (SUCRA = 56.8) > CI (SUCRA = 46.2) > CT (SUCRA = 45.5)> TC (SUCRA = 41.6) >Biofeedback (SUCRA = 39.1) > Yoga (SUCRA = 37.7)> Sanda (SUCRA = 36.3)> TT (SUCRA = 25.7) > CG (SUCRA = 24.0) > Volleyball (SUCRA = 20.0).
Figure 7
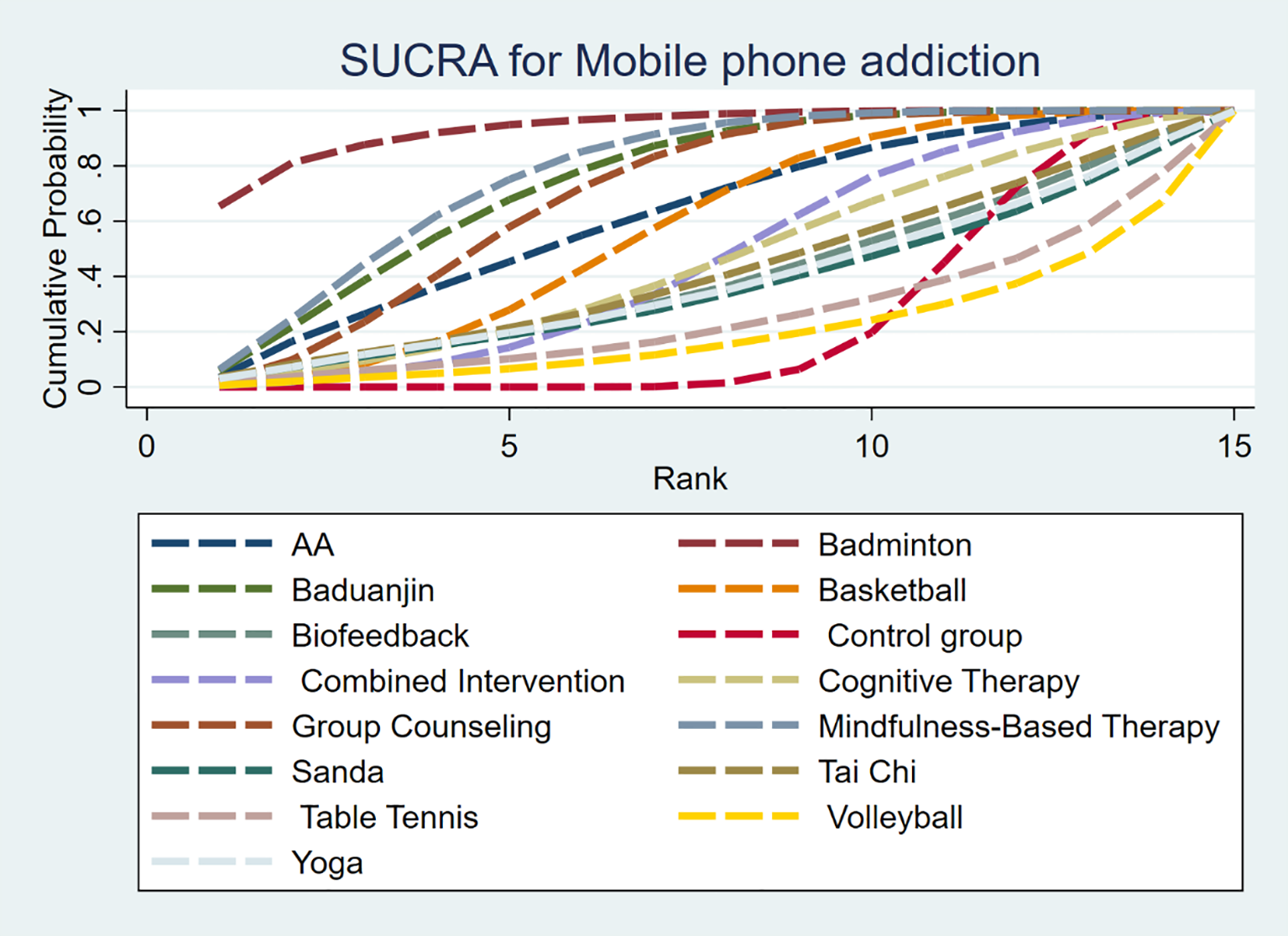
Sucra graph of effectiveness among interventions.
Table 4
| Treatment | SUCRA |
|---|---|
| A= Aerobic Aerobics | 62.1 |
| B= Badminton | 93.8 |
| C= Baduanjin | 74.3 |
| D= Basketball | 56.8 |
| E= Biofeedback | 39.1 |
| F= Control group (CG) | 24.0 |
| G= Combined Intervention (CI) | 46.2 |
| H= Cognitive Therapy (CT) | 45.5 |
| I= Group Counseling (GC) | 69.6 |
| J= Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT) | 77.3 |
| K= Sanda | 36.3 |
| L=Tai Chi (TC) | 41.6 |
| M=Table tennis (TT) | 25.7 |
| N= Volleyball | 20.0 |
| O= Yoga | 37.7 |
The SUCRA values of the interventions.
Figure 8
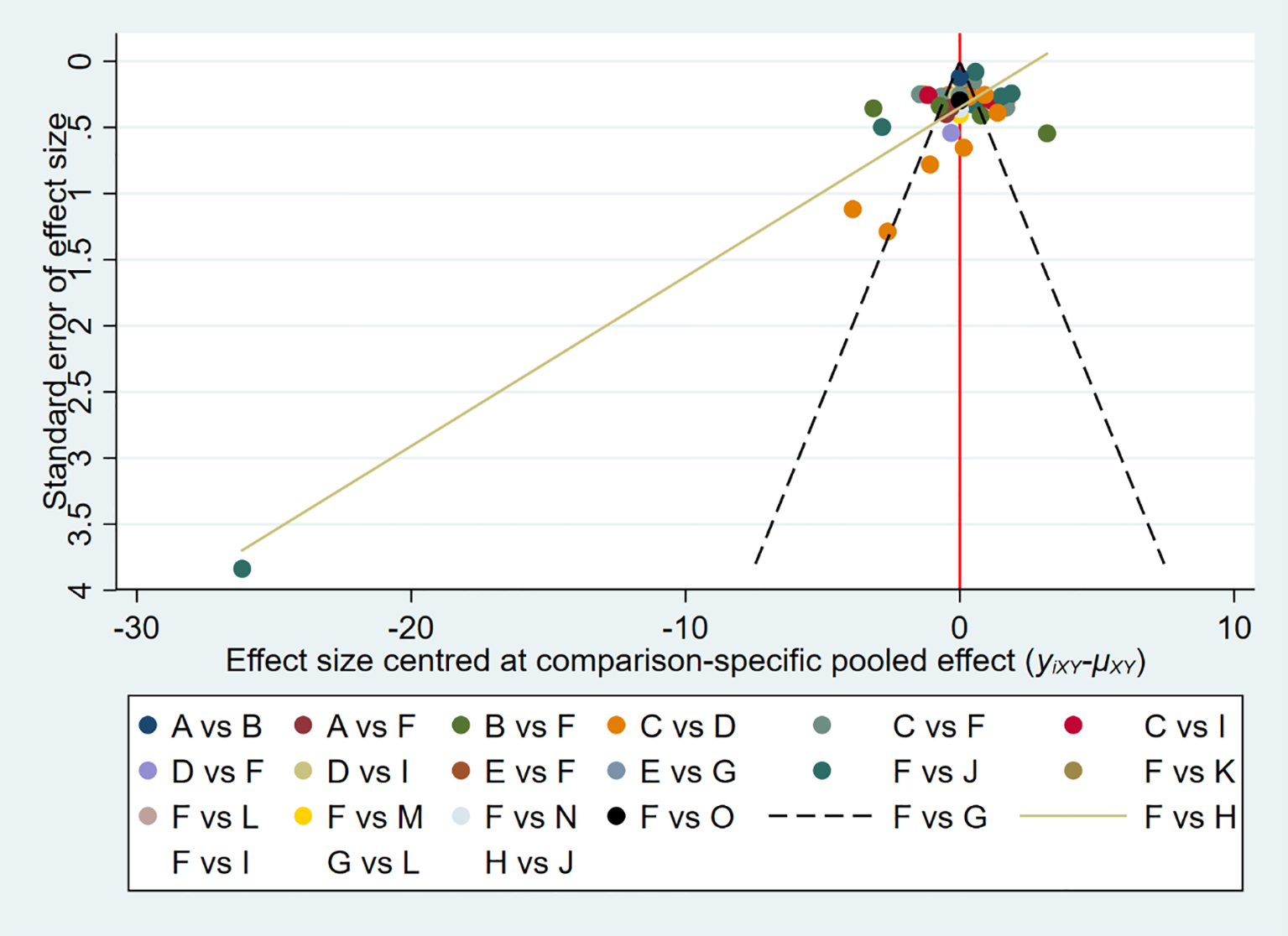
Comparison-adjusted funnel plot of adolescent Internet addiction scores. (A) = Aerobic Aerobics, (B) =Badminton, (C) =Baduanjin, (D) = Basketball, (E) = Biofeedback, (F) =Control group (CG), (G) = Combined Intervention (CI), (H) = Cognitive Therapy (CT), (I) = Group Counseling (GC), (J) = Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT), (K) = Sanda, (L) =Tai Chi (TC), (M) =Table tennis (TT), (N) = Volleyball, (O) = Yoga.
3.5.6 Risk of bias across studies
The publication bias was illustrated by funnel plots (Figure 8). According to the network meta-analysis, the funnel plot showed slight asymmetry.
4 Discussion
Mobile phone addiction seriously endangers the physical and mental health of teenagers or young adults, reduces academic performance and intelligence levels (10, 27). Therefore, it is of great significance to improve mobile phone addiction among teenagers or young adults. This study includes 32 randomized controlled studies. A traditional meta-analysis was conducted on 32 studies to evaluate the effects of the intervention measures and the control group. Furthermore, a network meta-analysis was conducted on the included studies to analyze the direct and indirect comparisons among different intervention measures.
This meta-analysis is based on 32 randomized controlled trials to evaluate the impact of intervention measures on mobile phone addiction among adolescents or young adults. The results showed that compared with the blank control group, all intervention measures (Combined Intervention (CI), Cognitive Therapy (CT), Group Counseling (GC), Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT), Exercise intervention) significantly improved adolescent mobile phone addiction. Total amount effect for [SMD = 8.78, 95% CI (10.64, 6.91), p < 0.001), Similar to the results reported by Wu (61) et al. (2023) [SMD= -2.88, 95%CI: (-3.78 to -1.97)] and Pan et al (20) (2023). [SMD=-3.214, 95%CI (-4.293 to -2.135)]. The differences in the subgroup analysis based on Outcome measurement, Intervention duration, and Intervention mode were statistically significant (P < 0.05). However, the differences were not statistically significant in the subgroup analyses of Year of publication, Sample size, and Intervention frequency (p > 0.05). Due to the significant heterogeneity of the analysis results, further analysis and verification are needed.
The conventional meta-analysis confirmed that various interventions demonstrated significantly greater improvement in smartphone addiction compared to control groups. However, this approach is inherently limited to pairwise comparisons, preventing comprehensive evaluation of relative effectiveness across different interventions (20). As an extension of traditional methods, NMA overcomes this limitation by synthesizing both direct and indirect evidence, enabling simultaneous comparison of multiple interventions and identification of the optimal therapeutic strategy (21). Our NMA results show that badminton is superior to other interventions in improving mobile phone addiction among teenagers or young adults. Apart from walking and jogging, badminton is one of the most participated sports among Chinese mass sports enthusiasts, with a participation rate as high as 42.6%. Regular participation in badminton can not only cultivate the reaction ability of both participants but also develop the ability to cooperate with teammates. The interaction during the sport can meet social needs and reduce teenagers’ reliance on obtaining social satisfaction through mobile phones (62). In addition, badminton is characterized by strong competitiveness, high confrontation, and diverse offensive and defensive variations. Badminton participants devote themselves wholeheartedly and pay less attention to their mobile phones (62). Badminton is a moderate-intensity sport. Compared with low-intensity and high-intensity sports, moderate-intensity sports help strike a balance between the benefits of cardiometabolic metabolism and the promotion of pleasant experiences, achieving the promotion of physical and mental health and the replacement and satisfaction of need (63, 64).
Furthermore, our research found that Mindfulness-Based Therapy (MBT) ranked second only to badminton in improving mobile phone addiction among teenagers or young adults. Mind-based intervention is a long-term and delicate training process. During this process, people with an addiction are expected to gradually change their wrong concepts and establish new and objective resistance to inappropriate mobile phone usage behaviors (65). The current mindfulness training process adopts a group mutual assistance model, that is, group members deepen their understanding of positive beliefs and internal viewpoints during the communication process, thereby improving the efficiency of the training (56). During the discussion process, questions need to be answered and mistakes need to be corrected, which enhances the self-control motivation of people with an addiction. Early studies on event-related potential (ERP) have also confirmed that the attention bias caused by the high sensitivity of Internet addiction patients to specific addiction-related cues may be an essential basis for the generation and maintenance of their addictive behaviors (66). The intervention of MBT on mobile phone addiction can be explained from the aspect of attention bias (67). Through MBT, attention bias was trained to a large extent. Attention bias is one of the strong predictors of the recurrence of addictive behaviors.
Although our research found that badminton and MBT have a better effect on improving mobile phone addiction among adolescents or young adults, due to the relatively few randomized controlled trials involving badminton and MBT in this study, the impact of these intervention measures on adolescent Internet addiction still needs to be further explored. Due to the small number of included studies, the results of this study must be preliminarily considered.
4.3 Strengths and limitations
It is crucial to identify and explain some advantages and limitations of this study. Our research results confirmed the effectiveness of intervention measures (exercise intervention, MBT, CT, GC) in improving mobile phone addiction among adolescents, and further explored through network element analysis which intervention measure has the best effect on improving mobile phone addiction. First of all, we conducted a comprehensive and systematic search of the published literature to reduce bias and identify potential related studies. Secondly, in this study, the retrieval method was adopted to search seven databases, and the retrieved literature was analyzed. We conducted a strict literature screening. We included 32 studies, and many of the included studies were published in Chinese. Due to the influence of cultural background, their global application is limited. Caution should be exercised when inferring the results. The studies included in this analysis demonstrated unclear allocation concealment and inadequate blinding procedures, methodological limitations that may have introduced performance bias and detection bias, thereby compromising the overall quality of the evidence. We strongly recommend that future studies adhere strictly to standardized reporting of randomization processes and blinding protocols to enhance methodological rigor. Furthermore, our study has high heterogeneity (I²= 94%), and high heterogeneity can affect the validity of the meta-analysis results and the reliability of the validity interpretation. Finally, the intervention measures were ranked based on the average score of SUCRA. This does not necessarily mean that the intervention measures with higher rankings are statistically significantly superior to those with lower rankings. Therefore, the research results should be interpreted with caution. Our research confirms that badminton and MBT have a very good effect on improving mobile phone addiction. However, the optimal intervention cycle and frequency remain to be further explored. In future research, attention should be paid to the mobile phone addiction behaviors of different groups of people. The impact of various interventions on the addiction problems of other groups in society should be understood from multiple dimensions, and the health and quality of life of the target population should be improved in a targeted manner. Therefore, in the future, more rigorous, comprehensive and high-quality randomized controlled trials with different cultural backgrounds need to be carried out to provide a reliable theoretical basis for the research update in this field. The mechanism of mobile phone dependence behavior is complex. However, the research has only focused on the impact of psychological intervention and exercise intervention on mobile phone addiction. In the future, the physiological mechanism should be further explored from the perspectives of physiology and imaging.
5 Conclusion
According to our research results, all intervention measures have a significant impact on improving Internet addiction. Based on the results of NMA, badminton and MBT may be the best intervention measures. Mobile phone addiction has brought many adverse effects on the physical and mental health of teenagers. In the future, schools should promptly screen for mobile phone addiction among teenagers or young adults, adopt a combination of physical intervention and psychological strategies, and form a comprehensive and systematic intervention system to prevent and reduce the risk of mobile phone addiction among teenagers. However, our research is also subject to some limitations, such as a majority of studies in China, high heterogeneity, and unclear optimal intervention duration/frequency. Therefore, future research should focus on conducting multi-center, cross-cultural randomized controlled trials to further verify the dose-effect relationship of the optimal intervention plan under different cultural backgrounds.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. QZ: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. DT: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1629251/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Zhong Y Ma H Liang YF Liao CJ Zhang CC Jiang WJ . Prevalence of smartphone addiction among Asian medical students: A meta-analysis of multinational observational studies. Int J Soc Psychiatry. (2022) 68:1171–83. doi: 10.1177/00207640221089535
2
Ezoe S Toda M Yoshimura K Naritomi A Den R Morimoto K . Relationships of personality and lifestyle with mobile phone dependence among female nursing students. Soc Behav Personality: an Int J. (2009) 37:231–8. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2009.37.2.231
3
Yen CF Tang TC Yen JY Lin HC Huang CF Liu SC et al . Symptoms of problematic cellular phone use, functional impairment and its association with depression among adolescents in Southern Taiwan. J Adolesc. (2009) 32:863–73. doi: 10.1016/j.adolescence.2008.10.006
4
Panova T Carbonell X . Is smartphone addiction really an addiction? J Behav Addict. (2018) 7:252–9. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.49
5
Billieux J Maurage P Lopez-Fernandez O Kuss DJ Griffiths MD . Can disordered mobile phone use be considered a behavioral addiction? An update on current evidence and a comprehensive model for future research. Curr Addict Rep. (2015) 2:156–62. doi: 10.1007/s40429-015-0054-y
6
Kim J-H Seo M David P . Alleviating depression only to become problematic mobile phone users: Can face-to-face communication be the antidote? Comput Hum Behav. (2015) 51:440–7. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.05.030
7
Zhang A Xiong S Peng Y Zeng Y Zeng C Yang Y et al . Perceived stress and mobile phone addiction among college students: The roles of self-control and security. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 13:1005062. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1005062
8
Kim SE Kim JW Jee YS . Relationship between smartphone addiction and physical activity in Chinese international students in Korea. J Behav Addict. (2015) 4:200–5. doi: 10.1556/2006.4.2015.028
9
Xie X Dong Y Wang J . Sleep quality as a mediator of problematic smartphone use and clinical health symptoms. J Behav Addict. (2018) 7:466–72. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.40
10
Hardell L Carlberg M Hansson Mild K . Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology. (2013) 20:85–110. doi: 10.1016/j.pathophys.2012.11.001
11
Samaha M Hawi NS . Relationships among smartphone addiction, stress, academic performance, and satisfaction with life. Comput Hum Behav. (2016) 57:321–5. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.12.045
12
Kwon HE So H Han S Oh W . Excessive dependence on mobile social apps: A rational addiction perspective. Inf Syst Res. (2016) 27:919–39. doi: 10.1287/isre.2016.0658
13
Chóliz M . Mobile phone addiction: a point of issue. Addiction. (2010) 105:373–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02854.x
14
de Freitas BHBM Gaíva MAM Bernardino FBS Diogo PMJ . Smartphone addiction in adolescents, part 2: scoping review—Prevalence and associated factors. Trends Psychol. (2021) 29:12–30. doi: 10.1007/s43076-020-00040-4
15
Lu G-L Ding Y-M Zhang Y-M Huang H-T Liang Y-P Chen C-R . The correlation between mobile phone addiction and coping style among Chinese adolescents: a meta-analysis. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. (2021) 15:60. doi: 10.1186/s13034-021-00413-2
16
Mehmood A Bu T Zhao E Zelenina V Alexander N Wang W et al . Exploration of psychological mechanism of smartphone addiction among international students of China by selecting the framework of the I-PACE model. Front Psychol. (2021) 12:758610. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.758610
17
Cali MAA Fernandez-Lopez L Navarro-Zaragoza J Caravaca-Sánchez F Falcon M . Smartphone addiction among adolescents in southern Italy and correlation with other risky behaviors. Actas Esp Psiquiatr. (2024) 52:632–40. doi: 10.62641/aep.v52i5.1664
18
Janssen I Carson V Lee IM Katzmarzyk PT Blair SN . Years of life gained due to leisure-time physical activity in the U.S. Am J Prev Med. (2013) 44:23–9. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2012.09.056
19
Rebar AL Stanton R Geard D Short C Duncan MJ Vandelanotte C . A meta-meta-analysis of the effect of physical activity on depression and anxiety in non-clinical adult populations. Health Psychol Rev. (2015) 9:366–78. doi: 10.1080/17437199.2015.1022901
20
Hua P Meng Z Jian-Rong H . A meta-analysis on effectiveness of intervention of mobile phone addiction in college students. Occupand Health. (2023) 39:260–9. doi: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2023.0043
21
Lee A . The development of network meta-analysis. J R Soc Med. (2022) 115:313–21. doi: 10.1177/01410768221113196
22
Efthimiou O Debray TP van Valkenhoef G Trelle S Panayidou K Moons KG et al . GetReal in network meta-analysis: a review of the methodology. Res Synth Methods. (2016) 7:236–63. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1195
23
Hutton B Salanti G Caldwell DM Chaimani A Schmid CH Cameron C et al . The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
24
Hidalgo-Fuentes S Martínez-Álvarez I Llamas-Salguero F Pineda-Zelaya IS Merino-Soto C Chans GM . Psychometric properties of the smartphone addiction scale-short version (SAS-SV) in Honduran university students. PloS One. (2025) 20:e0327226. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327226
25
An X Chen S Zhu L Jiang C . The mobile phone addiction index: Cross gender measurement invariance in adolescents. Front Psychol. (2022) 13:894121. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.894121
26
Higgins JP Altman DG Gøtzsche PC Jüni P Moher D Oxman AD et al . The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Bmj. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
27
Salanti G . Indirect and mixed-treatment comparison, network, or multiple-treatments meta-analysis: many names, many benefits, many concerns for the next generation evidence synthesis tool. Res Synth Methods. (2012) 3:80–97. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1037
28
Chen X He H Xie K Zhang L Cao C . Effects of various exercise types on visceral adipose tissue in individuals with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of 84 randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. (2024) 25:e13666. doi: 10.1111/obr.13666
29
Ziyan L Zhengzifeng M Zhengjie C . Effects of basketball and aerobic exercise intervention on improvingSmartphone addiction and mental health of college students. Bull Sport Sci Technol. (2022) 30:160–162 + 171. doi: 10.19379/j.cnki.issn.1005-0256.2022.06.043
30
Fan W . The influence of basketball dbbling training on self-control of mobile phone addicts: A case study of junior one students thesis (2021). Guangzhou Sport University. doi: 10.27042/d.cnki.ggztc.2021.000029
31
Chao Y . Experimental study on the effects of aerobic aerobicsand badminton on moderate mobile phone addictionamong secondary vocational school students thesis (2022). Yangzhou University. doi: 10.27441/d.cnki.gyzdu.2022.000378
32
Kexin Z . Effects of aerobic exercise and tai chi chuan on college students with mobile phoneAddictionand the potential role of gut microbiota: A randomized controlled trial thesis (2023). Anhui Medical University. doi: 10.26921/d.cnki.ganyu.2023.000374
33
Zhiyi Z . Research on the impact of badminton on negative attention bias of college students addicted to mobile phones thesis (2024).
34
Yu L Xia J Guozhong Y . Research on comprehensive intervention of aerobics on mobile phone addiction of female college students Vol. 42. Chengdu, China: Sichuan Sports Science (2023) p. 70–3.
35
Hua W . Brain mechanism of different exercise intervention methods on mobile phone dependent College Students thesis (2022). Jiangxi Normal University. doi: 10.27178/d.cnki.gjxsu.2022.000358
36
Jiahao Y . Empirical study on mobile phone addiction exercise intervention in college students thesis (2020). Fujian Normal University. doi: 10.27019/d.cnki.gfjsu.2020.001221
37
Ge R-K Xiao-mei Z Rong C . Influence of exercise intervention on mobile phone dependence in university students. Modern Prev Med. (2015) 42:3919–21.
38
Yuanyuan L . Research on the impact of exercise intervention on the cognitive function of college students with mobile phone dependence thesis (2020). Chengdu Sport University. doi: 10.26987/d.cnki.gcdtc.2020.000054
39
Jia-rui Z Lie-yu H Jing-jiao L Na H Tao W . Intervention effect of biofeedback and exercise intervention on college students’ mobile phone addiction. Occup Health. (2022) 38:2981–5. doi: 10.13329/j.cnki.zyyjk.2022.0584
40
Fei X . Current status of mobile phone addiction among nursing students and intervention study of Baduanjin health education thesis (2019). Shanxi Medical University.
41
Shijie L . Effect of different Motor Skills,Group Cognitive Behavior for college students’Mobile Phone Dependence thesis (2019). Wuhan University of Technology. doi: 10.27381/d.cnki.gwlgu.2019.001621
42
Shijie L Yanu L Lin W . Exercise intervention and cognitive-behavioral therapy towards mobile phone dependence in college students. Chin J School Health. (2022) 43:825–9. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2022.06.007
43
Xiaoran S . The Study on the Intervention of Integrated Sandplay Therapy for MobilePhone Addiction ofCollege Students thesis (2017). Liaoning Normal University.
44
Linhong N . The influence of mindfulness therapy on the interpersonal relationship and empathy ability of college students with mobile phone-dependent. J Of Int Psychiatry. (2020) 47:1161–5. doi: 10.13479/j.cnki.jip.2020.06.020
45
Yi L . Effects of mindfulness training on reaction inhibition in college students with mobile phone addiction: evidence from ERPs thesis (2022). Guizhou Medical University. doi: 10.27045/d.cnki.ggyyc.2022.000397
46
Yanfei S . The influence of mindfulness training on attentional bias of college students dependent on mobile phone thesis (2022). North China University of Science and Technology. doi: 10.27108/d.cnki.ghelu.2022.000031
47
Meijie D Yi L Wanzhu Z . Effects of mindfulness training intervention on negative emotions of medical students with smart phone addiction. J Of Guizhou Med Univ. (2024) 49:235–41. doi: 10.19367/j.cnki.2096-8388.2024.02.011
48
Yuan D . (2018)., in: A randomized controlled study on how mindfulness training reduces the level of mobile phone dependence among mobile phone addicts thesis, Zhejiang Normal University.
49
Qing F . The intervention study of cognitive-behavioral group counseling on college students’ SmartMobile phone addiction thesis (2015). Central China Normal University.
50
Zaihua Q Caihong W Jianping C . Research on the intervention effect of cognitive behavioral group counseling on college students’ Mobile phone addiction. J Mudanjiang Normal Univ. (2019) 2:126–31. doi: 10.13815/j.cnki.jmtc(pss).2019.02.014
51
Zhenghong Z Tao Z Dong Z . Research on the impact of group psychological intervention based on introspective cognitive therapy on mobile phone addiction and self-control of vocational college students. Health Vocational Educ. (2021) 39:152–4.
52
Zhengxing D Dan W Lei D . Research on cognitive behavioral group intervention for college students’ Mobile phone dependence. Theory Pract Contemp Educ. (2016) 8:145–7. doi: 10.13582/j.cnki.1674-5884.2016.11.046
53
Qian Z . The Relationship among Mobile PhoneAddiction, Psychological Capitaland Academic Burnout of College Students and Intervention Research thesis (2021). Hebei Normal University. doi: 10.27110/d.cnki.ghsfu.2021.000422
54
Xiao T Jiao C Yao J Yang L Zhang Y Liu S et al . Effects of basketball and baduanjin exercise interventions on problematic smartphone use and mental health among college students: A randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:8880716. doi: 10.1155/2021/8880716
55
Pal S Sharma SK Singhal A Telles S . Smartphone Excessive Use, Sleep, and Beliefs about Well-being in University Students who Practice Yoga Compared with Those with No Experience of Yoga. Indian J Community Med. (2022) 47:292–5. doi: 10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_601_21
56
Wang H Chen X . Intervention effect of mindfulness-based mental health education therapy on adolescents mobile phone addiction and cognitive tendency. Iran J Public Health. (2023) 52:2563–71. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v52i12.14317
57
Lan Y Ding JE Li W Li J Zhang Y Liu M et al . A pilot study of a group mindfulness-based cognitive-behavioral intervention for smartphone addiction among university students. J Behav Addict. (2018) 7:1171–6. doi: 10.1556/2006.7.2018.103
58
Haili Z Biao L Jiawei Z . The influence of Sanda sports intervention on the psychological resilience and mobile phone addiction tendency of freshmen in higher vocational colleges. J Jincheng Polytechnic. (2023) 16:66–69 + 83.
59
Miaoyin Z . Alleviating effect of mindfulness group training on college students’ dependence on mobile phones thesis (2020). Sichuan Normal University. doi: 10.27347/d.cnki.gssdu.2020.000546
60
Jia A Sizhe C Jinyan Z Huiying L Yuwei H . Research on the effective intervention of peer group psychological counseling on college students’ Mobile phone dependence: A case study of a university in shanxi province. Psychologies Magazine. (2020) 15:9 + 11. doi: 10.19738/j.cnki.psy.2020.01.005
61
Qiong W Lin-Sheng M Miao M Endong Q . Relative effectiveness of exercise prescription: A network meta analysis of the effects of different methods on mobile phone dependence intervention in college students. J Harbin Sport Univ. (2023) 41:77–86.
62
Chao Y . Experimental Study on the Effects of Aerobic Aerobicsand Badminton on Moderate obile Phone Addiction among Secondary Vocational School Students thesis (2022). Yangzhou University. doi: 10.27441/d.cnki.gyzdu.2022.000378
63
Liu S Xiao T Yang L Loprinzi PD . Exercise as an alternative approach for treating smartphone addiction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of random controlled trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:3912. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16203912
64
Li S Wu Q Tang C Chen Z Liu L . Exercise-based interventions for internet addiction: neurobiological and neuropsychological evidence. Front Psychol. (2020) 11:1296. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01296
65
Yanli Z . A randomized controlled study on improving psychological resilience of middle school students by mindfulness-based mental health education. Adv Psychol. (2023) 13:217–23. doi: 10.12677/AP.2023.131027
66
Shenyi D Qingguo M Xiaoyi W . The attention bias of online game addicts towards addictive cues: An ERP study. J psychol Sci. (2011) 34:1302–7. doi: 10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2011.06.006
67
Garland EL Howard MO Froeliger B . Mindfulness training applied to addiction therapy: insights into the neural mechanisms of positive behavioral change. Neurosci Neuroeconomics. (2016) 5:55–63. doi: 10.2147/NAN.S89257
Summary
Keywords
mobile phone addiction, teenagers, young adult, network analysis, meta
Citation
Li Y, Zhang Z, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Luo Z and Tao D (2025) The influence of different intervention measures on improving mobile phone addiction among teenagers or young adults: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Psychiatry 16:1629251. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1629251
Received
18 May 2025
Accepted
18 August 2025
Published
17 September 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Aviv M. Weinstein, Ariel University, Israel
Reviewed by
André Luiz Monezi Andrade, Pontifical Catholic University of Campinas, Brazil
Riza Hayati Ifroh, Northeast Normal University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Luo and Tao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiuyan Zhang, zhangqiuyan@bwu.edu.cn
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.