- Scientific and Technological Application and Research Center, Aksaray University, Aksaray, Türkiye
The establishment of innovative engineering techniques for meat products is required because of the significant energy requirements associated with freeze-drying of food products. This study is innovative application research on the freeze-drying of meat process and analyses energy efficiency by employing predictive statistical methods. Thermodynamic laws play a crucial role in the thermodynamic analysis of frozen food processes by regulating the essential operations involved in food production. The thermodynamic evaluation of the freeze-drying of meat process was carried out over a total of 40 scenarios covering 24 h (20 scenarios) and 30 h (20 scenarios). The energy efficiency in the 24 h process fluctuated between 38.7 and 43.1% over the 20 scenarios, whereas in the 30 h process, it varied from 36.9 to 41.1% throughout the 20 scenarios. The analysis revealed that the energy efficiency of the 24 h scenarios exceeded that of the 30 h scenarios, suggesting that 24 h is the optimum period for meat drying. This comparative assessment indicates that shortening the drying duration can deliver substantial energy savings without compromising process effectiveness. Future research will look at the application of this technology to enhance food quality and shelf life by applying a comparable freeze-drying technique to meat in various food industries.
1 Introduction
Drying is a fundamental and traditional method for preserving agricultural items, including meats, vegetables, herbs, and cereals, to prevent spoilage (Cengiz et al., 2025). Drying constitutes a significant and energy intensive process, accounting for 20–30% of the total energy consumption in the world economy (Kaveh et al., 2021; Sivakumar et al., 2016). Drying is chiefly employed to eradicate germs, enhance food transit, and guarantee year-round availability and utilization of dried products (Boateng et al., 2021). The significance of utilizing energy has escalated alongside advancements in food production and storage efficiency. Diverse thermal drying methods are available, including microwave drying, forced convection drying, and natural convection drying (Kraiem et al., 2023; Oztuna Taner, 2024a). The study of drying kinetics is critical for optimizing the drying process and increasing product quality, which aids in determining mass and heat transfer during the drying process (Li M. et al., 2025). Furthermore, the effectiveness of the drying kinetics was demonstrated through mathematical modeling (Boateng et al., 2021). While the drying process mitigates unfavorable conditions in foods, freeze-drying (FD) can enhance efficiency by prolonging the shelf life of food products (Donno et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2025). Consequently, drying kinetics influence the efficiency of FD procedures in meat processing.
FD is a widely used method for the shelf life and preservation of high-quality food products (Donno et al., 2025; Li W. et al., 2025; Matondkar et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2025). The demand for energy is on the rise, as food production and storage are more energy intensive. FD meats are considered superior to other dehydrated products due to their rapid water absorption and their capacity to restore a texture and look akin to the original food (Krokida and Philippopoulos, 2005).
This study revealed that FD is a popular technique for preserving various foods, including meat. Several studies have been conducted on the processing of FD meat, with a special emphasis on energy evaluation (Im et al., 2024; Lee et al., 2024; Loskota et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2018; Oztuna Taner, 2024a; Oztuna Taner, 2024b). Previous studies have focused on the characteristics and physicochemical properties of FD meat (Jarunglumlert et al., 2023; Nakagawa et al., 2024; Nowak and Jakubczyk, 2020; Pissia et al., 2022).
FD is a method that extracts moisture from dissolved compounds by directly changing the solvent from a solid to a gas under low pressure. This process conserves resources, reduces mass, and preserves the original quality, potentially exceeding the initial cost (Dai et al., 2022; Oztuna Taner, 2024a). Furthermore, most of the moisture in the sample remained until it crystallized into ice. The procedure was halted upon the solids in the material attaining supersaturation. Vacuum freeze-drying (VFD) maintains the physical and sensory attributes of fruit extracts due to fluctuations in air pressure (Ansar and Azis, 2019; Oztuna Taner, 2024a). Thermal drying methods include natural and forced convection, as well as microwave drying (Kraiem et al., 2023).
VFD is an ingredient preservation method employed in the food business to sustain as well as enhance the quality of food items (Feng et al., 2020; Lammerskitten et al., 2019). In the drying process, the material’s temperature is reduced beneath its freezing point, and water is eliminated through the sublimation of ice to water vapor at pressures below the triple point of water. The interplay of low temperatures and pressures results in excellent preservation of the shape, color, and flavor of the final dried product. Nevertheless, extended drying durations and elevated expenses are necessary to get these advantageous product attributes. The prolonged VFD durations, spanning from hours to days, constrain the effectiveness of industrial VFD systems. Consequently, it is essential to reduce drying time and conserve energy to achieve ideal drying conditions (Cao et al., 2018; Feng et al., 2020; Lammerskitten et al., 2019).
With advancements in the frozen food industry, refrigeration and cold storage facilities have become indispensable. Food storage, refrigeration, and air-conditioning systems stress energy efficiency. Many food-preservation methods use refrigeration and thermodynamics. Refrigeration systems play a crucial role in cold storage and food processing operations, ensuring product safety and quality (Oztuna Taner, 2024a; Selvaraj and Victor, 2020). Oztuna Taner (2024a) reported that the energy efficiency of vacuum freeze-drying (VFD) technology for meat products ranged from 14.3 to 51.9%. Cooling is the use of refrigeration systems and storage methods that are both environmentally friendly and energy efficient (Bhuvaneshwaran and Govindasamy, 2022). Bhuvaneshwaran and Govindasamy (2022) revealed that for a 10°C increase in condenser temperature, the cooling and heating capacity decreases by 28 and 15%, respectively.
Many industrialized countries are experiencing economic development trends in frozen food applications. These methods are very important for the food industry, and it is essential to maintain product quality. Refrigeration and cold storage are indispensable for the expansion of frozen food, and new technologies and optimizations are being focused on, especially in the FD process.
Ensuring the quality and safety of food at a constant temperature is crucial. Temperature fluctuations can lead to deterioration, bacterial growth, and diminished nutritional quality. Compliance with proper refrigeration techniques is essential to maintain food safety and minimize waste (Oztuna Taner, 2024a).
Innovative engineering solutions must be developed to satisfy the substantial energy demands linked to the FD process of beef products. Thermodynamic analysis is fundamental elements in this study of VFD operations. These regulations govern the fundamental processes involved in food production. The purpose of this study was to create various scenarios for FD implementation in a factory. The optimal solution was determined through process optimization by considering various scenarios and using the vacuum FD method. This study is distinguished by integrating thermodynamic modeling and predictive statistical analysis with real industrial-scale data to optimize vacuum freeze-drying of meat products. By systematically comparing 40 scenarios across different drying durations, it demonstrates that shorter processes significantly improve energy efficiency without compromising product quality. This scenario-based framework provides a robust and practical approach to support more sustainable and cost-effective meat drying operations. The specific energy consumption data of the factory were ascertained based on the process energy efficiency (Oztuna Taner, 2024a). Moreover, integrating these findings can enhance both the environment and the economy. Contemporary literature primarily emphasizes the FD of food and various other topics. This study may be revolutionary, as it is the first of its kind.
2 Materials and methods
The meat samples used in this study were boneless beef cuts obtained from a local processing facility in Aksaray, Turkey. To predict the mass input (raw materials) of the products in the FD system, the FD model simulated a total of 40 different scenarios comprising 20 scenarios with a 24 h drying period and 20 scenarios with a 30 h drying period. Based on measurements of the mass loss of the samples during the VFD process, drying curves were plotted as a function of moisture content versus time. The product was frozen to −35°C, and the final vacuum level reached 10 Pa, as recorded in the factory machine data. The enthalpy value (saturated ice at −35°C for −1.475 kJ/kg) for the water energy input calculation was obtained from the thermodynamic table (saturated ice-water-steam), specifically for saturated water at a temperature of −35°C. The mass balance enables the energy balance to be determined and thus the energy efficiency of the system to be explained. FD has a high energy density and uses thermodynamic principles and equations for the computations. Drying curves (parabolic, logarithmic and exponential for graphing) can be evaluated using three different mathematical approaches.
The data was obtained from a local plant in Aksaray, a producer of meat products. The plant management, focusing on VFD and meat products, provided the production and energy input–output data for this analysis. VFD is a combination of vacuum and FD processes. In the VFD process, the suspension is frozen at low temperatures. Thus, the VFD is removed from the frozen state by water or solvent sublimation. VFD transfers both thermal energy and mass simultaneously. Various techniques have been applied to improve the rates of heat and mass transfer during the drying process (Waghmare et al., 2021).
The vacuum freeze-drying (VFD) process removes moisture from meat products while preserving their original quality, including color, flavor, and nutrients. In this study, the VFD process was applied to meat batches with masses of 500 kg and 1,000 kg. The unprocessed products typically had a moisture content ranging from 25 to 30%. During the process, the products were frozen to −35°C and maintained under a final vacuum level of 10 Pa. The drying duration varied between 24 and 30 h, as recorded in the factory operational data. Energy efficiency was evaluated based on thermodynamic principles using the measured energy inputs and outputs. Figure 1 provides a schematic overview of the VFD process steps, which include freezing, primary drying under vacuum, and storage preparation. According to factory management, this technique is highly effective for preserving meat quality during large-scale production.

Figure 1. The schematic diagram of a VFD plant process for the meat products drawing by engineering program (this diagram was acquired from factory management).
Figure 1 depicts the layout of the FD facility with respect to meat production. The meat was delivered to the primary processing area in uncooked condition before being relocated to the drying and freezing manufacturing process. Cleaning, cutting, peeling, and loading constitute sequential processes in this operation. The meat was transported to a rapid freezer line where it was freeze-dried in an FD chamber via suction, heating, and freezing. The meat was subsequently transferred to the packaging and inventory department for preparation before dispatch.
Figure 2 depicts the FD process of meat products. The energy demands of the equipment utilized for FD and its by-products fluctuate depending on the product being processed. In the FD energy process, plant power and water serve as energy inputs, whereas energy consumption and evaporator operations constitute energy outputs. This study examines energy-efficient solutions through an analysis of case studies to explore alternative optimization methodologies.
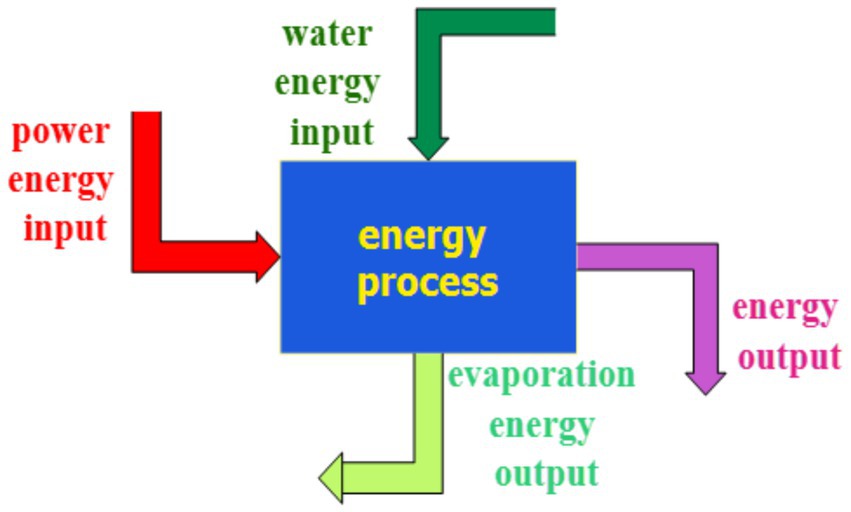
Figure 2. The energy cycle of the FD plant for the flow scheme drawing by engineering drawing program.
2.1 FD system modeling, energy analysis, and mass balance
The FD model simulated a total of 40 different scenarios to predict the mass input () of items in the FD system. The mass balance allows for the determination of the energy balance, thereby elucidating the energy efficiency of the system. FD utilizes thermodynamic principles and equations for computations, exhibiting a high energy density. Drying curves can be assessed using three distinct mathematical approaches. The following equations are employed: parabolic, as shown in Equation 1, and logarithmic, as shown in Equation 2, and exponential as in Equation 3 for graphing (Afolabi et al., 2015; Boateng et al., 2021; Oztuna Taner, 2024a):
The drying moisture can be represented by . The constants of the experiment are , , , and , where is the drying time (Oztuna Taner, 2024a).
Mass balance can be utilized to identify the mass balance and drying products. The flow rate of the cooling water (), which was determined to be 55.0 as the flow rate of the cooling water data from the application of the factory process data, was converted to 15.3 for the mass balance calculation.
The following equations may be utilized to assess the moisture content (MC) on a wet basis of a dried product mass flow rate input (), mass flow rate output (), the evaporation mass flow rate (), the mass of water (), and the total amount of moisture () in meat during processing time () as delineated from Equations 4 to 8 (Abonyi et al., 1999; Afolabi et al., 2015; Boateng et al., 2021; Kaveh et al., 2021; Krokida and Philippopoulos, 2005).
The mass flow rate input () can be formulated from Equation 4 as follows:
where is a dried product mass flow rate inputis the processing time, and is the mass of the product.
The mass output () can be given in Equation 5 as follows:
where is a dried product mass flow rate output, and the MC on a wet basis of a dried product.
The total amount of moisture () can be calculated from Equation 6 as follows:
where is the total amount of moisture.
The mass flow rate output () can be formulated from Equation 7 as follows:
where is a dried product mass flow rate output.
The evaporation mass flow rate () can be determined from Equation 8 as follows:
where is the evaporation mass flow rate output, and is the mass of water.
The energy balance and efficiency were applied to the FD processes. The MC of the meat was determined to be 75.0% and the latent heat of evaporation () was obtained to be 2,257 (Dai et al., 2022). The product was cooled to −35°C and the final vacuum level reached 10 Pa as recorded in the factory FD machine data. The enthalpy value () for the cooling water energy input () was obtained from the thermodynamic table (saturated ice—water—steam), specifically for saturated water at a temperature of −35°C (Cengel et al., 2019). The power input () was determined by the factory’s technical section based on the assumptions of various production meat FD. The work energy input () was measured for 40 FD scenarios (from FDF1 to FDF20 for 24 h, and from FDF21 to FDF40 for 30 h).
The energy balance can be derived from Equation 9 to 14 with regard to the energy consumption of the FD (), evaporation energy (), the cooling water energy (), total energy net (), and overall energy efficiency () of the FD meat process (Abonyi et al., 1999; Baeghbali et al., 2016; Beigi, 2016; Boateng et al., 2021; Cengel et al., 2019). The power input () can be determined from Equation (9) as follows:
where is the power input, and is the work input for FD system.
The cooling water energy () can be calculated from Equation 10 as follows:
where is the cooling water energy, and is the enthalpy value for FD system.
The evaporation energy () can be calculated from Equation 11 as follows:
where is the evaporation energy, and is the latent heat of evaporation for FD system.
The consumption energy () can be obtained from Equation 12 as follows:
where is the consumption energy for FD system.
The total energy net () can be computed from Equation 13 as follows:
where is the total energy net for FD system.
The overall energy efficiency () can be calculated from Equation 14 as follows:
These equations predict and enhance energy and mass characteristics. Consequently, the study models were developed for statistical analysis utilizing Minitab 21.4.2 software, which is specifically tailored for input and output data concerning mass balance.
2.2 Statistical of the mathematical model with predictive numeric analysis of the data
Data analysis was conducted using Minitab version 21.4.2. The current study demonstrated the reliability of scenario mass data and mathematical modeling through the application of statistical approaches for data collection and generation (Oztuna Taner, 2024b). This study calculated mass analysis for 40 scenarios and provided a meat-processing FD configuration. In many studies, the standard formatting of footnotes, especially statistical significance, is indicated by superscript letters (Altmann et al., 2018; Son et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2021; Weththasinghe et al., 2021). In the context of these data, statistical analyses are omitted in this study and the standard formatting of footnotes in tables, especially statistical significance, is indicated by superscript letters.
This study highlights a predicted numerical analysis of the data. The Weibull probability plot (WPP) method was employed to ascertain the estimated values and rough boundaries of the unknown parameters, which served as initial points in the optimization of the expectation maximization procedure (Wu et al., 2024). The WPP was estimated and illustrated using Minitab software in this study. The data analyzed were evaluated using Minitab software to assess the fit of the distributions and to compare the compatibility and probability of the Weibull, three-parameter Weibull (input and output mass, mass moisture content), minimal extreme, and normal distribution models (Wei, 2024). The WPP has a dependability of 95% across many scientific domains (Jokiel-Rokita and Piaṃtek, 2024). The methodology for determining the initial values and approximate boundaries of each parameter was outlined in the WPP (Wu et al., 2024). The square root of the variance was computed to reverse the variance to its original scale, resulting in the standard deviation. The conclusive formula for the standard deviation can be derived from Equation 15, as demonstrated by Nisbet et al. (2018):
where is the standard deviation, X represents the data point, n is the total number of data points, X signifies the mean, and Σ is the sum of all square deviations from 1 to n. The remaining Fisher statistics (standard error, correlation coefficient, etc.) are only extensions of these two parameters (mean and standard deviation). Thus, it can be observed the inception of the term parametric statistical analysis. The subsequent stage involved deriving a standard probability table (F-distribution) according to the notion of likelihood. F-statistics were employed to assess significant differences between the two datasets (Nisbet et al., 2018). The mixture of the WPP (FDF) can be given cumulatively from Equation 16 and can be computed using Equation 17, as follows (Wu et al., 2024):
where is the reliability function, k is the number of sub-populations, is the shape parameters of the kth sub-population, scale parameters of the kth sub-population, is the weight parameters of the kth sub-population in the mixture Weibull distributions, is the weight factor for the kth sub-population, and is the observed life-time.
The reliability of the corresponding function (R) can be computed using Equation 17, as follows (Wu et al., 2024):
where is the reliability function in the mixture of Weibull distributions.
The WPP initially provides a linear transformation of the empirical reliability function for each individual WPP. The empirical reliability function for the complete failure data is defined by Equation 18 as follows (Jokiel-Rokita and Piaṃtek, 2024; Wu et al., 2024):
where n is the number of data.
For lifetime cases beyond 20, the empirical reliability function, as determined by the Kaplan–Meier technique, can be applied to censored data in Equation 19 (Wu et al., 2024):
where is the number of samples still functioning, and can be observed before time ti, and is the failure time.
This study encompasses 40 scenarios (samples); hence, the Kaplan–Meier technique was employed for these 40 scenarios using the Minitab software.
3 Results and discussion
A methodology for evaluating the mass balance and energy analysis of an FD facility is outlined in this study. The evidence was obtained from a facility that produces FD meat products. Data was collected at an FD facility in Aksaray, which specializes in raw meat preservation. Currently, this energy system is being constructed concurrently. The results of this endeavor seek to enhance the quality of product manufacturing by minimizing the consumption of energy prior to the FD process. This study revealed the significant efficacy of deep learning in forecasting the energy and mass efficiency of industrial operations.
In this study, the FD of meat was applied for energy efficiencies in 500 and 1,000 kg masses, which were investigated and calculated with predictive analysis methods. Reorganize 40 scenarios employing optimization methods to identify improvements in energy efficiency and productivity based on the current input–output data presented in Tables 1, 2. Table 1 shows the details of the parameters altered in Scenarios FDF1-FDF20 for 24 h, and Table 2 presents the details of the parameters altered in Scenarios FDF21-FDF40 for 30 h. In addition, a statistical analysis was conducted on the data derived from the mass balance calculations presented in Tables 1, 2.
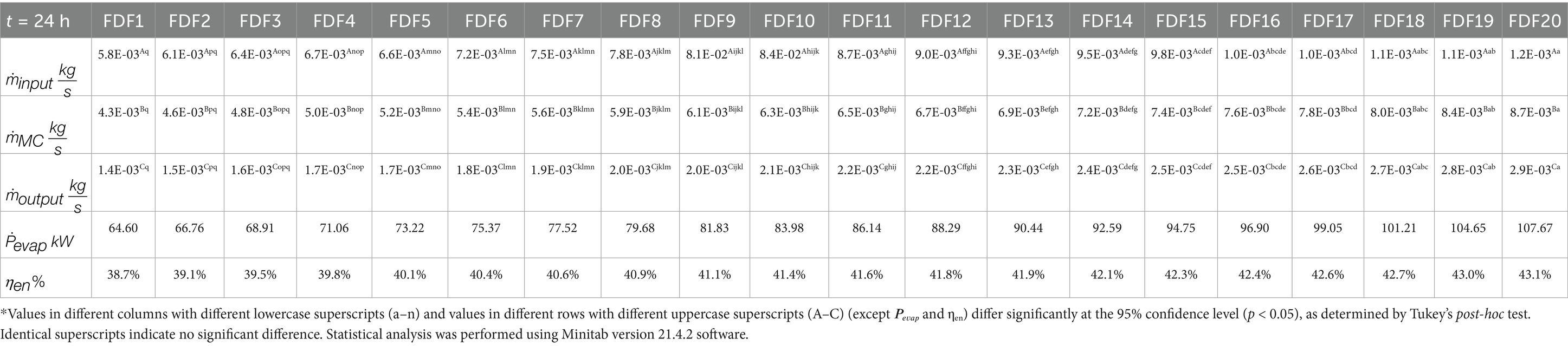
Table 1. Detailing the parameters altered and Statistical analysis of mass balance data by Fisher pairwise comparisons: Scenario (FDFn) 95% confidence in Scenarios FDF1-FDF20 for 24 h.
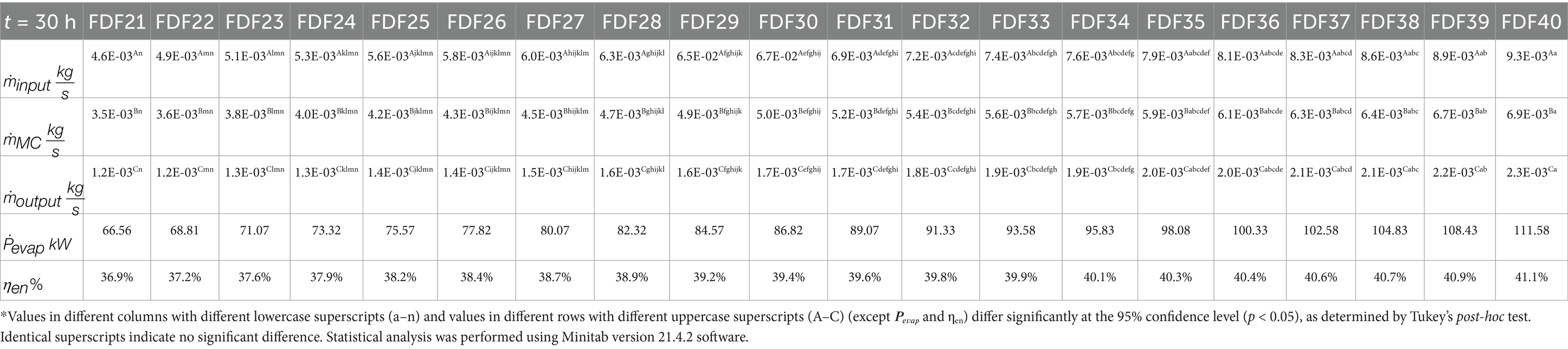
Table 2. Detailing the parameters altered and Statistical analysis of mass balance data by Fisher pairwise comparisons: Scenario (FDFn) 95% confidence in Scenarios FDF21-FDF40 for 30 h.
For the significance analysis of the mass balance data, two statistical tests were used to evaluate differences among the scenarios. Specifically, the Fisher pairwise comparison test was applied to the 24 h freeze-drying scenarios presented in Table 1. This test was selected because it is appropriate for comparing multiple means when the number of groups is relatively small and provides a straightforward approach to identify significant differences between pairs of scenarios.
For the 30 h scenarios presented in Table 2, the Tukey pairwise comparison test was employed. The Tukey test is particularly suitable for situations involving multiple comparisons, as it controls the family-wise error rate and is more robust when the number of comparisons increases. The selection of these two methods was based on the characteristics of the data sets and the need to ensure rigorous assessment of statistical significance across the different process conditions.
These analyses allowed us to identify which scenarios differed significantly in terms of mass balance parameters and to confirm that the observed variations were not due to random variation alone.
Table 1 indicates the statistical analysis of mass balance data by Fisher pairwise comparisons for 24 h, while Table 2 emphasizes the statistical analysis of mass balance data by Tukey pairwise comparisons for 30 h. Tukey and Fisher pairwise comparisons at the 95% confidence level were applied to organize the data. The individual confidence level for the bulk data was found to be 99.05% (R2). The regression analysis yielded a coefficient of determination (R2) of 0.9905, indicating that 99.05% of the variance in the data was explained by the model.
The analysis of manufacturing and energy data is a major focus of current research. Consequently, a framework was established to create a system for forecasting the production and energy consumption at the FD facility. A fully integrated production-estimation system was created using customizable input parameters. The energy data gathered during the FD manufacturing process served as an input parameter for assessing the output, encompassing mass and total energy. The input parameters were the mass, water content, evaporation, and total energy. This study performed an extensive assessment of the present conditions of graphics, production, and energy input outputs in several situations.
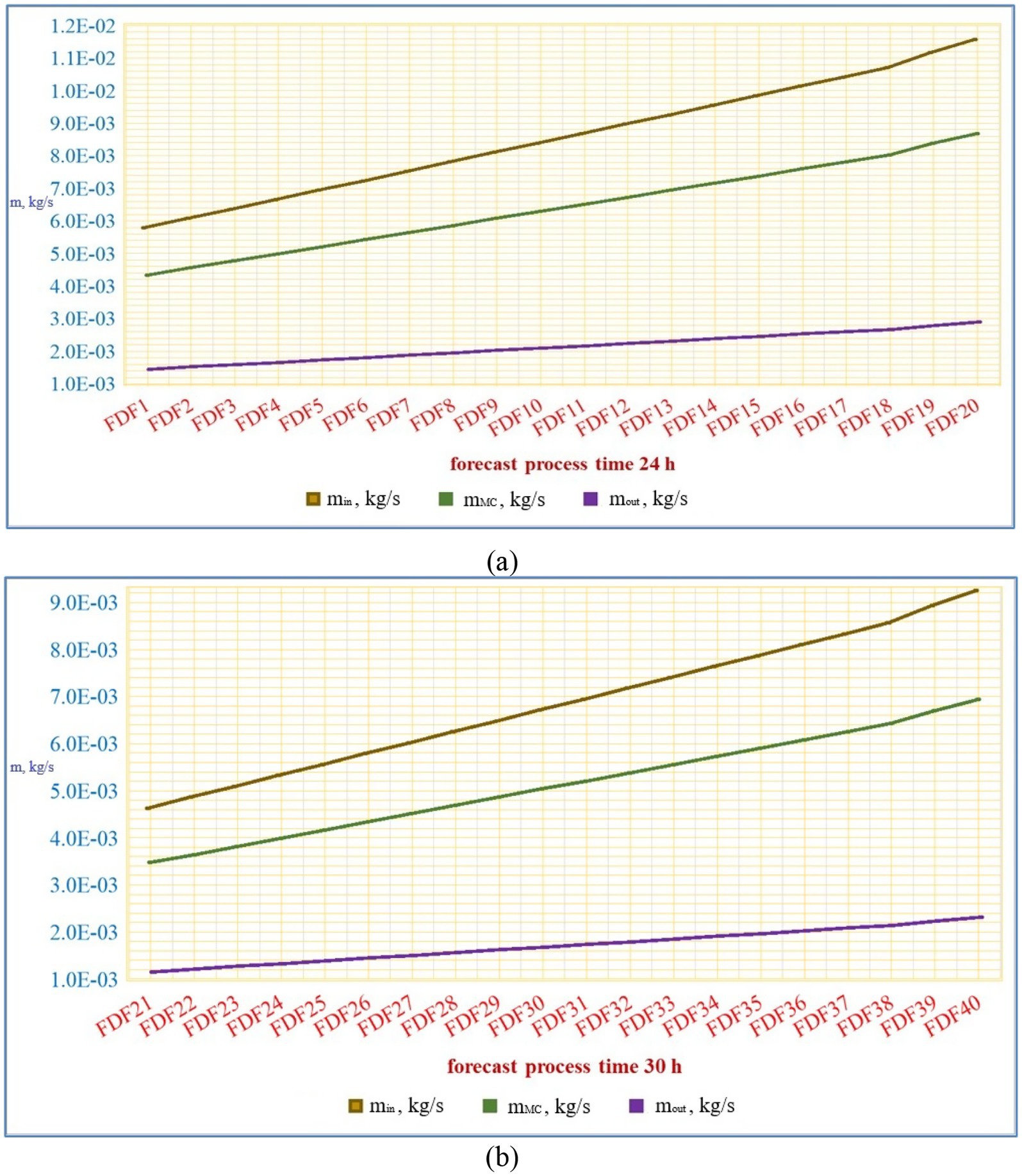
Figure 3 illustrates that augmenting the measurement integral within the manufacturing process of the FD and its derivatives by employing optimization techniques boosts production efficiency. Figure 3A displays the outcomes of 20 scenario assessments conducted over a 24 h period (from FDF1 to FDF20), utilizing current mass and energy efficiency. Figures 3B displays the outcomes of 20 scenario assessments conducted over a 30 h period (from FDF21 to FDF40), using current measures of mass and energy efficiency. The FD yield was determined by evaluating the efficiency of energy production for various FD products and dividing it by the energy analysis production efficiencies of the instruments used to assess the FD facility. The total FD of meat products can be employed to analyze the efficiency of production. 40 scenarios were created utilizing optimization techniques for assessing meat product production in large input and output graphs. The logarithmic slope of the data was plotted on a graph against the nominal factory default parameters.
The mass balance of the FD process over a 24 h period, specifically from FDF1 to FDF20, is displayed in Figure 3A. The mass input was in the range of 0.00579–0.01157 kg/s, whereas the mass output fluctuated between 0.00145 and 0.00289 kg/s. The mass balance of the FD plant 30 h later (from FDF21 to FDF40) is depicted in Figure 3B. The mass input fluctuated between 0.00463 and 0.00926 kg/s, whereas the mass output fluctuated between 0.00116 and 0.00231 kg/s.
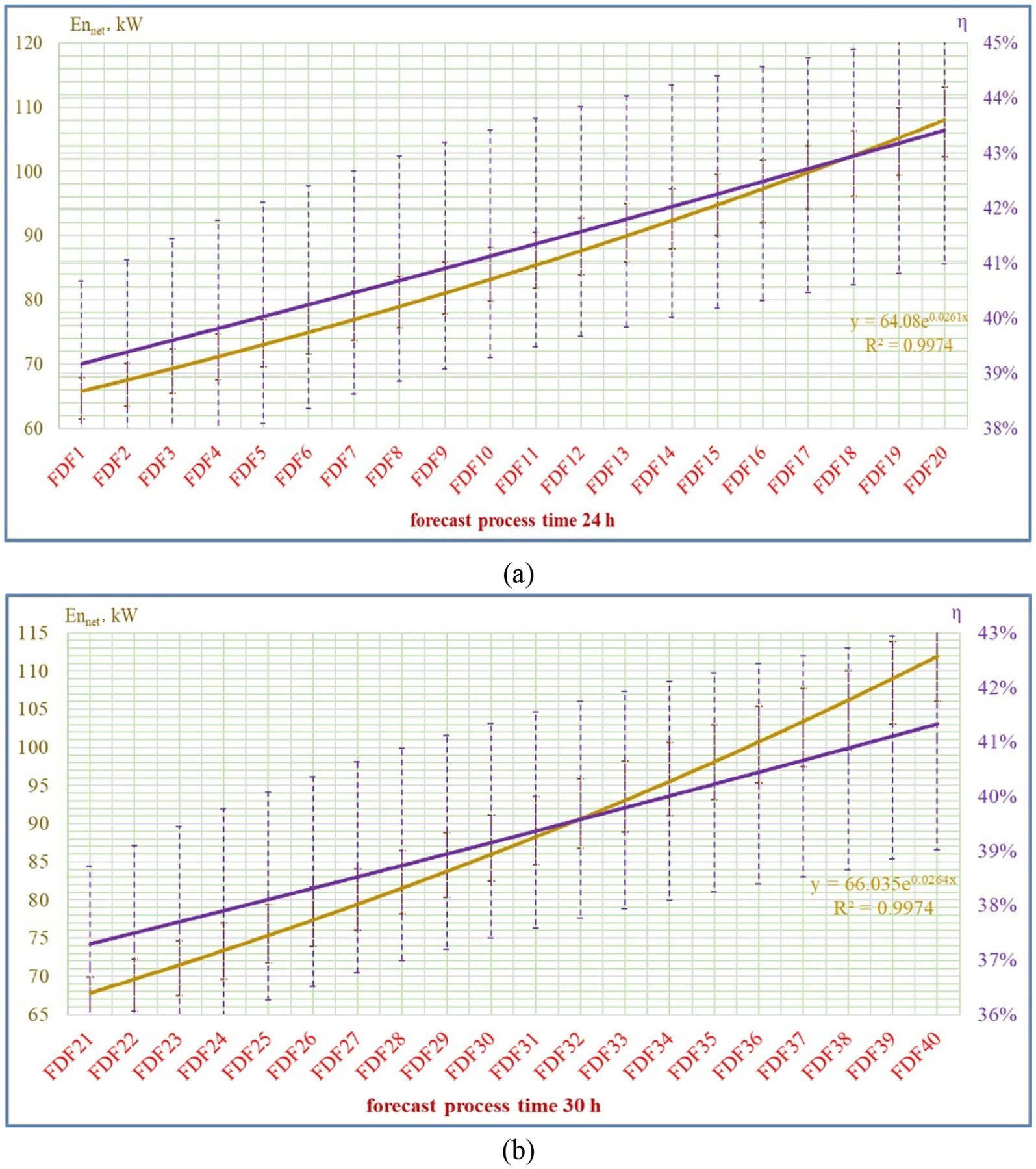
Figures 4A,B depict the energy analysis outcomes of the FD technique for meat. A total of 40 scenarios highlighted the FD process for 24 h (from FDF1 to FDF20) and 30 h (from FDF21 to FDF40).
The production capacity and energy efficiency of the facility were explored in this study through optimization techniques supported by plant data and technical assessments. Quality performance is demonstrated by establishing a process for evaluating productivity and energy efficiency under optimal conditions. This study conducts a comprehensive comparison between the current situation and various scenarios in terms of graphics, production, and energy input–output.
In Figure 4A, the energy efficiency of FD ranged from 38.7 to 43.1% from FDF1 to FDF20 at 24 h, as the net energy of FD ranges from 64.60 to 107.67 kW from FDF1 to FDF20 at 24 h. Figure 4B illustrates the energy efficiency results of the FD plant at 30 h from FDF21 to FDF40, which exhibits an energy efficiency ranging from 36.9 to 41.1%. The net energy of FD ranges from 66.56 to 111.58 kW from FDF21 to FDF40 at 30 h.
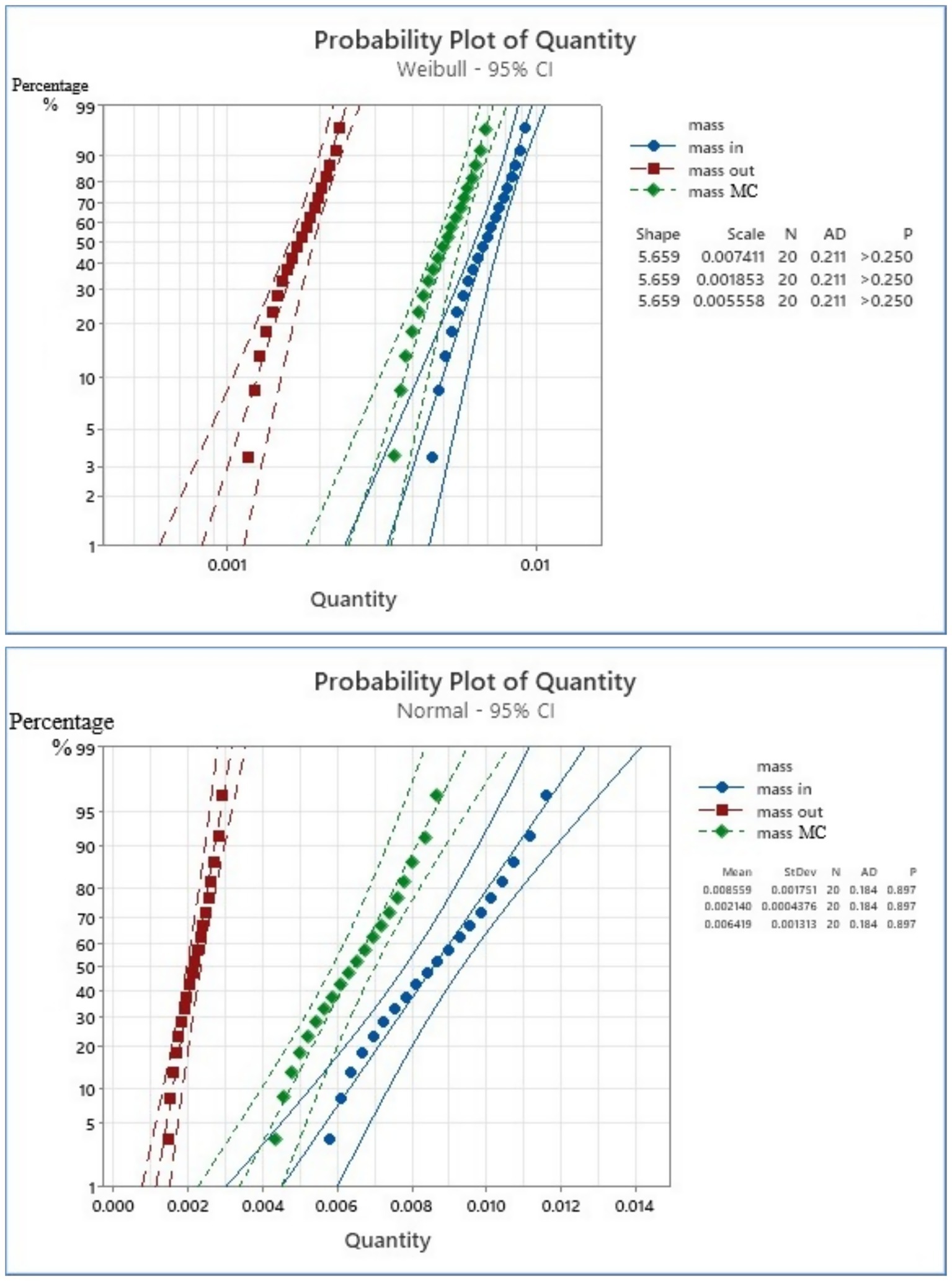
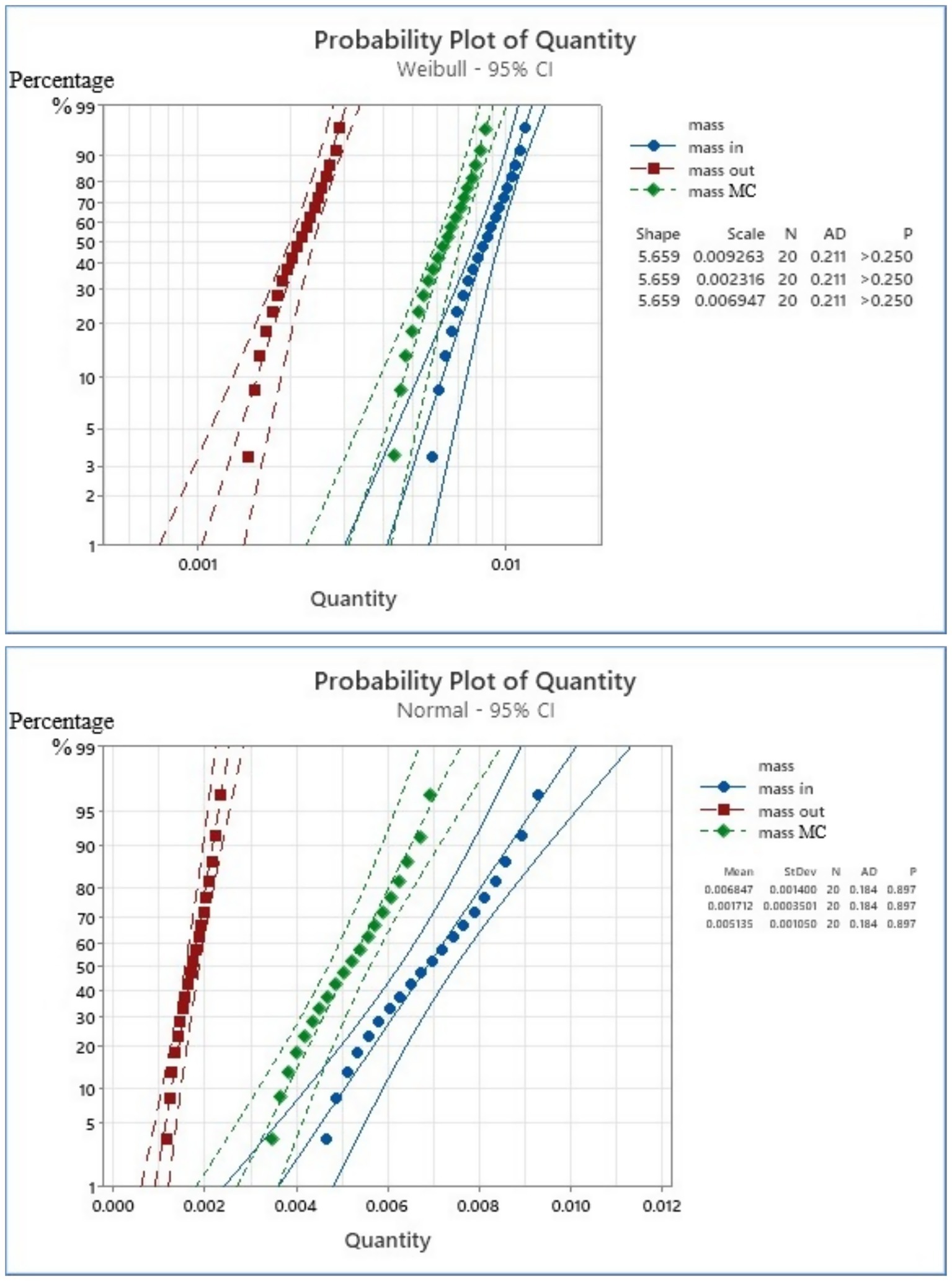
In addition, the predictive model was applied all the results data for the mathematical models. This study conducted mass analysis calculations based on 40 scenarios and determined the FD configuration of meat processing. Weibull distribution model of the data was illustrated in Figures 5, 6, which demonstrate the WPP distribution and the probability plot of the amount of data for the scenario FDF1-FDF40.
These charts illustrate the predictive analysis of the extensive data. These results demonstrate the similarity of the data indices used in the current study. Figure 5 displays the probability plot of the amount of data for scenario FDF1-FDF20 within the range of 0–0014. In Figure 5, the probability plots of quantity for the mass input (mass in), the mass output (mass out), and the mass MC were analyzed utilizing both Weibull and Normal distributions at a 95% confidence level. In both instances, the Anderson-Darling (AD) statistics were minimal (0.211 for Weibull and 0.184 for Normal), and the p values exceeded 0.250 and 0.897, respectively, signifying an excellent match with no substantial divergence from the presumed distributions. Among all groups, the mass input demonstrated the greatest quantities and variability, succeeded by the mass MC, however the mass output displayed the lowest and least variability. The Weibull distribution had a uniform shape parameter (5.659) across all groups, indicating comparable distribution features. Normal distribution yielded marginally elevated the p values, signifying a superior fit for the data. Consequently, both distribution models are statistically valid, with the Normal distribution being slightly more advantageous for subsequent study.
Figure 6 depicts the probability plot of the amount of data for the scenario FDF21-FDF40 within the range of 0–0012. Figure 6 presents probability charts that depict the distribution characteristics of quantity data for the mass input, the mass output, and the mass MC according to both Weibull and Normal distribution models. In both instances, a robust statistical fit is evident, corroborated by elevated the p values (>0.250 for Weibull and 0.897 for Normal) and minimal AD statistics. Nevertheless, the Normal distribution exhibits a greater goodness-of-fit, as evidenced by markedly elevated p-values and narrower confidence intervals surrounding the fitted line. This outcome indicates that the quantitative data for all three assessed categories more closely adhere to Normal distributions than to a Weibull distribution under the specified conditions (FDF21–FDF40 scenario). Consequently, for subsequent statistical analysis or modeling, supposing Normal distributions will probably produce more precise and dependable results.
Jokiel-Rokita and Piaṃtek (2024) utilized the AD test to confirm the null hypothesis that the observed failure times are derived from random variables following the Weibull distribution. The p-value obtained from this test was 0.8257, hence it cannot be rejected at the 0.05 significant level (Jokiel-Rokita and Piaṃtek, 2024). Wu et al. (2024) utilized a Weibull distribution with a shape parameter of 2.5 for 30 samples and 4 for the remaining 70 samples. Nisbet et al. (2018) established the utilization of distribution models with p values ranging from 0 to 1. The findings of this investigation about the Weibull distribution align with existing literature.
This study indicates that the energy efficiency of FD varied from 38.7 to 43.1% across FDF1 to FDF20 during a 24 h, with the net energy of FD ranging from 64.60 to 107.67 kW during the same timeframe. The energy efficiency outcomes of the FD plant at 30 h, from FDF21 to FDF40, demonstrate a range of 36.9–41.1%. The net energy of FD varies from 66.56 to 111.58 kW between FDF21 and FDF40 for a duration of 30 h. Comparative literature research indicated that the VDF procedure led to a decrease in energy consumption between 17.67 and 35.66% (Li et al., 2024). The energy efficiency of the drying process ranges from 35 to 45% (Crichton et al., 2017). An independent analysis revealed that the application of ultrasound and other FD pretreatments reduced the drying time by 25.0–62.50% and decreased overall energy consumption by 24.28–62.35% (Xu et al., 2021). Another study indicates that the energy efficiency of the FD methods for food products typically varies from 14.3 to 51.9% (Oztuna Taner, 2024a).
The primary importance of experimental design is in its scenario-based methodology, which methodically compares 24 h and 30 h freeze-drying processes across different input masses under regulated industrial settings. By maintaining a consistent drying length within each group and varying the input quantities, the study effectively isolated and assessed the impacts of processing time and mass load on energy efficiency. This paradigm offers a more thorough comprehension of operational dynamics than single-condition trials.
During the identical time intervals, the findings indicated that reduced drying durations consistently attained superior energy efficiency, irrespective of input mass. Statistical analysis demonstrated significant differences among scenarios at the 95% confidence level (p < 0.05), as denoted by the superscript annotations in Tables 1, 2. The increase in mass load led to a small decrease in efficiency due to the additional energy needed for sublimation and vacuum maintenance; however, this effect was less significant than that of drying time. The regression analysis, exhibiting R2 value of 0.9905, indicated that most of the variance in efficiency could be accounted for by the synergistic effects of drying time and input mass. The findings are substantiated by thermodynamic principles, which demonstrate that prolonged processing time correlates with increased cumulative energy consumption, chiefly due to the continuous running of refrigeration and vacuum systems. Thus, optimizing cycle duration is a more efficacious approach to enhancing energy efficiency than merely modifying batch size.
The results of this study have been presented in literature. Consequently, this study includes several comparable energy efficiency studies conducted in FD industries. The scenario evaluations correspond with prior studies, demonstrating that the application of optimization techniques in FD industries can boost energy efficiency in response to evolving conditions.
4 Conclusion
This study effectively utilized thermodynamic analysis and predictive statistical modeling to enhance the FD process of meat products, tackling the substantial energy requirements commonly linked to these activities. The results indicated that a 24 h FD period produced greater energy efficiency, varying from 38.7 to 43.1%, in contrast to the 30 h, which attained efficiencies between 36.9 and 41.1%. The utilization of probability distribution analyses employing both Weibull and Normal models yielded robust statistical validation of the experimental data. Both models had a satisfactory match at the 95% confidence level; however, the Normal distribution displayed marginally enhanced performance, evidenced by elevated p-values (0.897) and reduced AD statistics (0.184). Mass input demonstrated the most variability among the measured parameters, succeeded by mass MC, while mass output displayed the least variability. Furthermore, it was noted that energy efficiency improved with extended process duration but diminished with increased mass load, highlighting the necessity of balancing operating parameters to attain best results.
The results indicate that reduced processing times improve energy efficiency and that predictive models serve as excellent instruments for analyzing and improving critical process variables, including mass input, mass output, and mass MC. These findings enhance the current knowledge base by illustrating the efficacy of model-based methodologies in augmenting process efficiency, decreasing production expenses, and prolonging the shelf life of FD of meat products.
Subsequent study ought to concentrate on modifying and broadening the suggested modeling framework to encompass other food products and investigating real-time optimization techniques. Subsequent investigations may enhance process parameters and assess long-term product quality results, thereby fostering more sustainable and economical FD technologies in the food sector.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
OO: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
This study is innovative scientific research on the energy efficiency of the vacuum freeze-drying technology for meat processing, incorporating different scenarios. The Ak-Çav Holding Company’s Traditional Vegetable and Fruit Drying Plant supported this project of the study during the installation phase as a research topic focusing on energy efficiency. The author also expresses gratitude for their invaluable guidance and support throughout this investigation.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abonyi, B. I., Tang, J., and Edwards, C. G. (1999). Evaluation of energy efficiency and quality retention for the refractance window drying system. Res. Rep., 1–38.
Afolabi, T. J., Tunde-Akintunde, T. Y., and Adeyanju, J. A. (2015). Mathematical modeling of drying kinetics of untreated and pretreated cocoyam slices. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52, 2731–2740. doi: 10.1007/s13197-014-1365-z
Altmann, B., Neumann, C., Velten, S., Liebert, F., and Mörlein, D. (2018). Meat quality derived from high inclusion of a micro-alga or insect meal as an alternative protein source in poultry diets: a pilot study. Foods 7:34. doi: 10.3390/foods7030034
Ansar, N., and Azis, A. (2019). Effect of vacuum freeze-drying condition and maltodextrin on the physical and sensory characteristics of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis sims) extract. IOP Conf. Ser 355:012067. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/355/1/012067
Baeghbali, V., Niakousari, M., and Farahnaky, A. (2016). Refractance window drying of pomegranate juice: quality retention and energy efficiency. LWT Food Sci Technol. 66, 34–40. doi: 10.1016/J.LWT.2015.10.017
Beigi, M. (2016). Energy efficiency and moisture diffusivity of apple slices during convective drying. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 36, 145–150. doi: 10.1590/1678-457X.0068
Bhuvaneshwaran, K., and Govindasamy, P. K. (2022). Technical assessment of novel organic Rankine cycle driven cascade refrigeration system using environmental friendly refrigerants: 4E and optimization approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 35096–35114. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-24608-y
Boateng, I. D., Soetanto, D. A., Yang, X., Zhou, C., Saalia, F. K., and Li, F. (2021). Effect of pulsed-vacuum, hot-air, infrared, and freeze-drying on drying kinetics, energy efficiency, and physicochemical properties of Ginkgo biloba L. seed. J. Food Process Eng. 44:e13655. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.13655
Cao, X., Zhang, M., Mujumdar, A. S., Zhong, Q., and Wang, Z. (2018). Effects of ultrasonic pretreatments on quality, energy consumption and sterilization of barley grass in freeze drying. Ultrason. Sonochem. 40, 333–340. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.06.014
Cengel, Y. A., Boles, M. A., and Kanoglu, M. (2019). Thermodynamics: an engineering approach. 9th Edn. New York, NY: Mcgraw-Hill Education.
Cengiz, N., Abdulvahitoğlu, A., and Abdulvahitoğlu, A. (2025). Comparative analysis of different drying methods on strawberry aroma compounds via multi-criteria decision-making techniques. Appl. Sci. 15:815. doi: 10.3390/app15020815
Crichton, S., Shrestha, L., Hurlbert, A., and Sturm, B. (2017). Use of hyperspectral imaging for the prediction of moisture content and chromaticity of raw and pretreated apple slices during convection drying. Dry. Technol. 36, 804–816. doi: 10.1080/07373937.2017.1356847
Dai, J., Sameen, D. E., Zeng, Y., Li, S., Qin, W., and Liu, Y. (2022). An overview of tea polyphenols as bioactive agents for food packaging applications. LWT 167:113845. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113845
Donno, D., Neirotti, G., Fioccardi, A., Razafindrakoto, Z. R., Tombozara, N., Mellano, M. G., et al. (2025). Freeze-drying for the reduction of fruit and vegetable chain losses: a sustainable solution to produce potential health-promoting food applications. Plants 14:168. doi: 10.3390/plants14020168
Feng, Y., Ping Tan, C., Zhou, C., Yagoub, A. E. A., Xu, B., Sun, Y., et al. (2020). Effect of freeze-thaw cycles pretreatment on the vacuum freeze-drying process and physicochemical properties of the dried garlic slices. Food Chem. 324:126883. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126883
Im, C., Song, S., Cheng, H., Park, J., and Kim, G.-D. (2024). Changes in meat quality and muscle fiber characteristics of beef striploin (M. longissimus lumborum) with different intramuscular fat contents following freeze-thawing. LWT 198:116081. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.116081
Jarunglumlert, T., Chantanuson, R., Hayashi, R., Katano, Y., Kusakari, T., Nagamine, S., et al. (2023). Techno-economic assessment of plant-based meat analogue produced by the freeze alignment technique. Future Foods 8:100269. doi: 10.1016/j.fufo.2023.100269
Jokiel-Rokita, A., and Piaṃtek, S. (2024). Estimation of parameters and quantiles of the Weibull distribution. Stat. Pap. 65, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s00362-022-01379-9
Kaveh, M., Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y., and Nowacka, M. (2021). Comparison of different drying techniques and their carbon emissions in green peas. Chem. Eng. Process. 160:108274. doi: 10.1016/j.cep.2020.108274
Kraiem, K., Abdelmoumen, S., and Ben-Ali, S. (2023). Dehydration study of apple slices by a non-thermal process. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 40620–40628. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-27517-w
Krokida, M. K., and Philippopoulos, C. J. (2005). Rehydration of dehydrated foods. Dry. Technol. 23, 799–830. doi: 10.1081/DRT-200054201
Lammerskitten, A., Wiktor, A., Siemer, C., Toepfl, S., Mykhailyk, V., Gondek, E., et al. (2019). The effects of pulsed electric fields on the quality parameters of freeze-dried apples. J. Food Eng. 252, 36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2019.02.006
Lee, S., Han, S., Jo, K., and Jung, S. (2024). The impacts of freeze-drying-induced stresses on the quality of meat and aquatic products: mechanisms and potential solutions to acquire high-quality products. Food Chem. 459:140437. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.140437
Li, W., An, N., Yu, H., Li, D., Wang, L., and Wang, Y. (2025). Enhancing okra drying quality and efficiency through combined freeze and pulsed spouted microwave vacuum drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 18, 2585–2601. doi: 10.1007/s11947-024-03618-3
Li, M., Wang, B., Li, Y., Nie, X., Mao, J., Guo, Q., et al. (2025). Exploration of the impact of different drying methods on the quality of Gastrodia elata: a study based on drying kinetics and multidimensional quality evaluation. Food Chem. 464:141628. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141628
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Dong, H., Sun, T., Liu, Y., Cheng, S., et al. (2024). Effects of ultrasonication and freeze–thaw pretreatments on the vacuum freeze-drying process and quality characteristics of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L. cv. Diaoganxing). Food Chem. 22:101357. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101357
Loskota, E., Gramatina, I., and Kince, T. (2023). A review: application of freeze-drying in meat processing. Res. Rural Dev. 38, 77–81. doi: 10.22616/rrd.29.2023.011
Ma, Y., Wu, X., Zhang, Q., Giovanni, V., and Meng, X. (2018). Key composition optimization of meat processed protein source by vacuum freeze-drying technology. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 25, 724–732. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2017.09.013
Matondkar, P. M., Rane, P., and Aher, P. J. (2025). Exploring isochoric food preservation as a novel approach to enhance quality of freezed foods. Curr. Food Sci. Technol. Rep. 3, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s43555-025-00054-y
Nakagawa, K., Chantanuson, R., Boonarsa, P., Seephua, N., and Siriamornpun, S. (2024). Meat analogue preparation from cricket and rice powder mixtures with controlled textural and nutritional quality by freeze alignment technique. Food Chem. 22:101402. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2024.101402
Nisbet, R., Miner, G., and Yale, K. (2018). “Numerical prediction” in Handbook of statistical analysis and data mining applications 2nd ed. New York: Academic Press, 187–213. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-416632-5.00010-4
Nowak, D., and Jakubczyk, E. (2020). The freeze-drying of foods—the characteristic of the process course and the effect of its parameters on the physical properties of food materials. Foods 9:1488. doi: 10.3390/foods9101488
Oztuna Taner, T. (2024a). Vacuum freeze dryer technology for extending the shelf life of food and protecting the environment: a scenario study of the energy efficiency. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 38573–38584. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-30398-8
Oztuna Taner, T. (2024b). Enhancement of the energy and exergy analysis capabilities of the yoghurt process: a case study of the dairy industry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1450653. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1450653
Pissia, M.-A., Matsakidou, A., Paraskevopoulou, A., and Kiosseoglou, V. (2022). Structural characteristics and physicochemical properties of freeze-dried snail meat. LWT 155:112980. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112980
Selvaraj, D. A., and Victor, K. (2020). Vapour absorption refrigeration system for rural cold storage: a comparative study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 34248–34258. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-11214-z
Sivakumar, R., Saravanan, R., Elaya Perumal, A., and Iniyan, S. (2016). Fluidized bed drying of some agro products – a review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 61, 280–301. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.04.014
Son, S.-H., Yang, S.-J., Jeon, H.-L., Yu, H.-S., Lee, N.-K., Park, Y.-S., et al. (2018). Antioxidant and immunostimulatory effect of potential probiotic Lactobacillus paraplantarum SC61 isolated from Korean traditional fermented food, jangajji. Microb. Pathog. 125, 486–492. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.018
Waghmare, R. B., Perumal, A. B., Moses, J., and Anandharamakrishnan, C. (2021). Recent developments in freeze drying of foods, Innovative Food Processing Technologies (Volume 3). Innovative Food Processing Technologies, Elsevier: New York, 82–99. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-815781-7.00017-2
Wang, P., Lv, W., and Wang, H. (2025). Effects of freeze-hot air drying on physicochemical properties and anti-tyrosinase activity of quince peels. Food Chem. 463:141507. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141507
Wei, Y. (2024). Application of Weibull analysis in the optimization of civil aviation aircraft engineering reliability management. Acad. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 7, 68–73. doi: 10.25236/AJETS.2024.070111
Weththasinghe, P., Lagos, L., Cortés, M., Hansen, J. Ø., and Øverland, M. (2021). Dietary inclusion of black soldier fly (Hermetia Illucens) larvae meal and paste improved gut health but had minor effects on skin mucus proteome and immune response in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). Front. Immunol. 12:599530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.599530
Wu, Y., Lu, Z., and Wu, J. (2024). Reliability evaluation of components with multiple failure modes based on mixture Weibull distribution using expectation maximization algorithm. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 38, 649–660. doi: 10.1007/s12206-024-0113-1
Xu, X., Zhang, L., Feng, Y., Zhou, C., Yagoub, A. E. A., Wahia, H., et al. (2021). Ultrasound freeze-thawing style pretreatment to improve the efficiency of the vacuum freeze-drying of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) and the quality characteristics of the dried product. Ultrason. Sonochem. 70:105300. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2020.105300
Yang, Q., Fong, L.-A., Lyu, W., Sunkara, L. T., Xiao, K., and Zhang, G. (2021). Synergistic induction of chicken antimicrobial host defense peptide gene expression by butyrate and sugars. Front. Microbiol. 12:781649. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.781649
Glossary
AD - Anderson-Darling
FD - freeze-drying
FDF - scenario freeze-drying
MC - moisture content, %
VFD - vacuum freeze-drying
WPP - Weibull probability plot
, , , - constants of the experiment
- cooling water energy input,
- evaporation energy,
- total energy net,
- power input,
- total amount of moisture with dry basis,
- flow rate of cooling water,
- evaporation mass flow rate output,
- dried product mass flow rate input,
- dried product mass flow rate output,
- latent heat of evaporation, 2,257
- enthalpy value,
- energy consumption of the FD,
- reliability function (mixture Weibull distributions)
- reliability function in the mixture of Weibull distributions
- work energy input,
- failure time
- mass input of the product, kg
- mass output of the product, kg
- mass of water, kg
- number of samples still functioning
- processing time,
- drying time, s
- scale parameters of the kth sub-population (mixture Weibull distributions)
- shape parameters of the kth sub-population (mixture Weibull distributions)
- overall energy efficiency,
- weight parameters of the kth sub-population (mixture Weibull distributions)
k - number of sub-populations reliability function (mixture Weibull distributions)
n - total number of data points
R - reliability of the corresponding function
- data point
- sum of all squared deviations from 1 to n
- life-time
- weight factor for the kth sub-population (mixture Weibull distributions)
- standard deviation
Keywords: freeze-drying, energy efficiency, food industry, meat, predictive model
Citation: Oztuna Taner O (2025) Advancing the thermodynamic approach with the predictive model for the freeze-drying of meat. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1549287. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1549287
Edited by:
Poonam Rani, Moorepark Food Research Centre, Teagasc Food Research Centre, IrelandReviewed by:
Hany El-Mesery, Jiangsu University, ChinaPrakash Kumar, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India
Copyright © 2025 Oztuna Taner. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Oznur Oztuna Taner, b290YW5lckBha3NhcmF5LmVkdS50cg==
 Oznur Oztuna Taner
Oznur Oztuna Taner