- 1School of Media and Communication, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
- 2Centre for China’s Overseas Interests, Institute of Area and International Communication Studies, College of International Studies, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
- 3China Center for Special Economic Zone Research, College of International Studies, Institute of Area and International Communication Studies, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
- 4College of Economics and Management, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China
Increasing farmers’ income and ensuring food security remain significant challenges in Pakistan’s agricultural sector. Social media adoption offers new opportunities for knowledge sharing, market access, and productivity gains; however, its impact on agricultural income remains underexplored. This study investigates the impact of social media usage during the production stage on crop farmers’ income in Punjab, Pakistan, and explores the underlying mechanisms, including improvements in technical efficiency, land productivity, and agricultural labor efficiency. Using survey data from 480 crop farmers, an endogenous switching regression model is employed to estimate the causal effect of social media usage on agricultural income. Mediation analysis further examines how productivity improvements drive income growth. Social media usage significantly increases agricultural income, with results remaining robust across alternative estimation methods. These income gains are primarily driven by improved technical efficiency and land productivity. They are especially evident among farmers with higher education levels, larger landholdings, and greater initial income. These findings underscore the transformative role of social media in rural development by facilitating better access to information and improved farm performance. To amplify these benefits, policymakers should prioritize expanding digital infrastructure, promoting digital literacy, and improving access to agricultural information, particularly for smallholder and low-income farmers.
1 Introduction
The global agricultural sector faces numerous challenges, including the need to ensure food security, adapt to climate change, and promote sustainable farming practices (Middelberg, 2013; Chand, 2022). As the world’s population grows and food demand rises, transforming agricultural systems has become essential. Sustainable agriculture, which aims to increase food production while minimizing environmental degradation and preserving natural resources, plays a critical role in this transformation (Wang et al., 2024; Chin et al., 2024). In recent years, digital technologies, particularly social media, have emerged as powerful tools for advancing sustainable agricultural practices (Khan et al., 2021). These technologies enhance resource efficiency, improve productivity, and provide farmers with real-time access to climate forecasts, market trends, and best agricultural practices. Social media platforms are reshaping traditional farming by facilitating knowledge sharing, enabling peer-to-peer learning, and expanding farmers’ access to online markets (Ki et al., 2020; Johnson et al., 2020; Cui, 2014). Thus, the integration of digital technologies in agriculture not only boosts farm productivity but also helps address interconnected challenges related to food security, climate change, and rural development (Parra-López et al., 2024). In this context, understanding how social media supports sustainable agricultural growth, particularly among smallholder farmers, is crucial for shaping effective policies and interventions.
Connecting smallholder farmers to modern agricultural practices is essential for rural revitalization and agricultural modernization (Zheng et al., 2022). Several studies have investigated strategies to bridge this gap, including the promotion of farmer cooperatives, the development of agricultural socialized services, and the adoption of innovative land-use models such as land trusteeship and land stock cooperatives (He and Wu, 2019; Khan et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2022). Over the past decade, the integration of digital technologies, especially social media, has accelerated rural development. Governments worldwide have actively promoted the adoption of digital tools in agriculture, enhancing rural information infrastructure and reducing internet costs (Khan et al., 2022). Social media now plays a critical role in rural life by enhancing information exchange and building agricultural networks (Khan et al., 2021). By bridging the gap between farmers and modern innovations, it supports sustainable, broad-based rural development (Misaki et al., 2016). Recent data suggests that social media penetration in rural areas has reached a significant level, increasing farmers’ ability to access critical agricultural information and services. One of the key concerns in rural development is increasing farmers’ income, which is essential for motivating farmers to remain engaged in agriculture and strengthening the sector’s role in economic development. Despite the diversification of rural income sources, agricultural income remains relatively low, leading to a decline in farming enthusiasm (Pandey et al., 2024). The increasing adoption of social media in agriculture has influenced nearly every stage of production, from information gathering to decision-making and market access (Pandey et al., 2024). This shift improves information flow and encourages the adoption of modern technologies in agriculture, and enhancing human capital development in rural areas.
While earlier studies have examined the relationship between social media usage and income generation (Khanal et al., 2015), the majority have concentrated on its effects on overall or non-agricultural income, with comparatively little attention paid to its specific impact on agricultural income (Khanal et al., 2015), Unlike previous studies that focus on social media’s impact on overall or non-agricultural income, this research specifically examines the role of social media in influencing agricultural income through productivity improvements. By employing an endogenous switching model, this research provides robust causal evidence on the mechanisms through which social media enhances agricultural earnings. Some research suggests that social media usage positively influences agricultural production by optimizing production decisions and improving resource allocation (Goyal, 2010). It also enhances market awareness, which can lead to higher selling prices and increased income growth (Goyal, 2010; Siaw et al., 2020). However, other studies argue that social media access does not necessarily translate into higher agricultural income, as it may influence production decisions without significantly altering farmers’ financial outcomes (Aker and Ksoll, 2016). Some findings indicate little to no significant effect of social media usage on household agricultural income (Ma and Wang, 2020; Nguyen et al., 2022). However, these studies often fail to account for the heterogeneous effects of social media usage and the underlying mechanisms driving its impact on agricultural income.
To address this gap, the present study empirically analyzes data from 480 crop farmers in Punjab Province, Pakistan, using an endogenous switching model to examine how social media usage during the production stage affects agricultural income. Additionally, the study explores the mechanisms through which social media enhances income, focusing on its impact on productivity specifically technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor efficiency. The study further investigates the heterogeneous effects of social media adoption among different labor groups of farmers, considering factors such as human capital, farm size, and initial income levels.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Following the introduction, Section 2 provides the theoretical framework and outlines the study’s hypotheses. Section 3 describes the methodology employed, while Section 4 presents the empirical results. Section 5 offers a discussion of the findings, including policy implications and limitations. The final section concludes the study.
2 Theoretical analysis and study hypotheses
2.1 Theoretical analysis
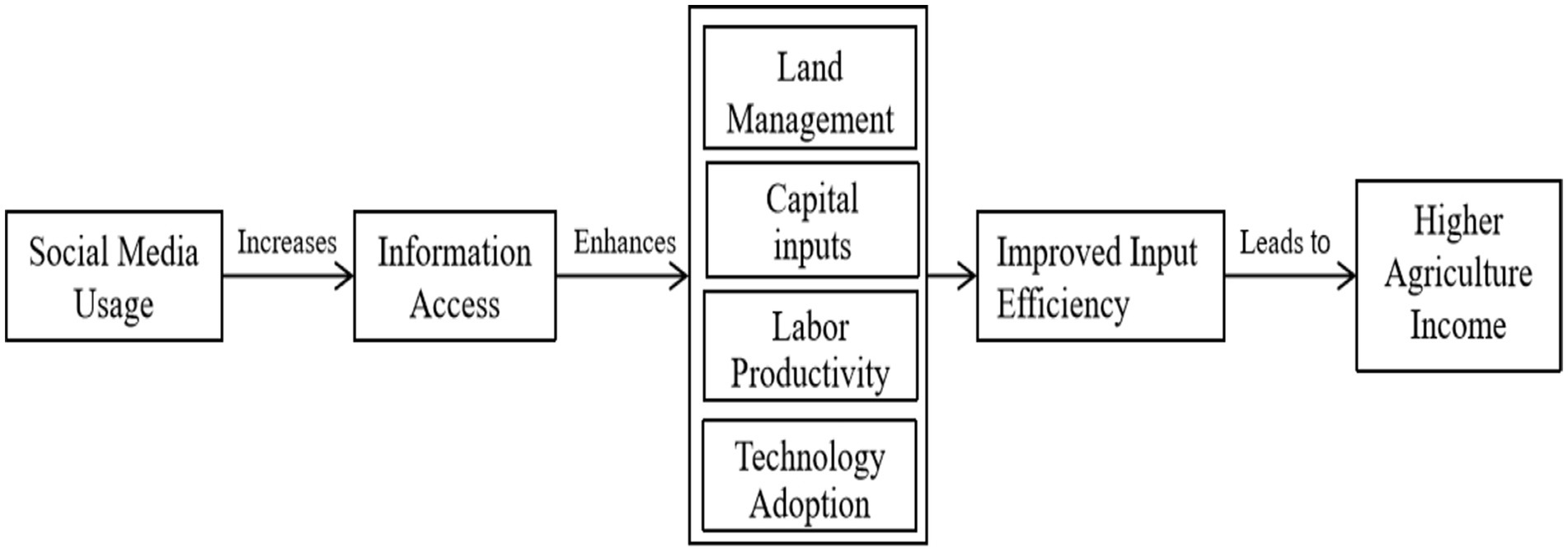
Social media usage has a profound impact on agricultural production by influencing land input, labor input, capital input, and the adoption of advanced agricultural technologies. Farmers, as the primary decision-makers in agriculture, require timely and accurate information to optimize their production processes. Access to relevant agricultural information enhances productivity, reduces uncertainty, and improves decision-making efficiency (Aker et al., 2016). Social media serves as an effective channel for acquiring agricultural knowledge, and facilitating cost-effective access to farming methods, input procurement, land management techniques, weather forecasts, and market trends (Deichmann et al., 2016; Du et al., 2023).
This study adopts the Technology Adoption Theory and Information Diffusion Theory to explain the mechanisms through which social media impacts agricultural income. The Technology Adoption Theory suggests that farmers adopt new technologies when they perceive them as useful and compatible with their existing practices. Social media accelerates this process by disseminating knowledge, reducing barriers to technology adoption, and enhancing farmers’ ability to integrate new agricultural practices. Meanwhile, Information Diffusion Theory explains how knowledge spreads within a farming community, and influences both individual and group decisions. Social media acts as a conduit for agricultural knowledge diffusion, enabling rapid adoption of best practices, modern farming techniques, and improved market access. By improving farmers’ access to timely and relevant agricultural knowledge, social media enhances technical efficiency, which refers to how well farmers utilize available inputs to maximize output. Additionally, it contributes to land productivity by promoting efficient land use practices, ensuring higher agricultural output per unit of land. Furthermore, social media improves labor efficiency by equipping farmers with better techniques, market insights, and mechanized solutions, ultimately increasing output per unit of labor. The agricultural production function can be represented using the Cobb–Douglas production function:
In Equation 1 where i represents the farming household, Yield denotes agricultural output, A captures technological progress, and K, L, and M represent capital, labor, and land inputs, respectively. Social media enhances these factors through improved information dissemination, reducing transaction costs, increasing efficiency, and optimizing input allocation (Nyarko and Kozári, 2021; Zheng et al., 2022). The following subsections detail the specific pathways through which social media impacts agricultural production.
2.1.1 Information dissemination and land input
Land is one of the most critical resources in agriculture, and its efficient use significantly affects farm productivity and income. Social media plays a crucial role in improving land management through information dissemination. Farmers can access guidance on soil fertility preservation, organic farming techniques, and precision agriculture methods. They can also learn about land improvement strategies, such as organic fertilizer application, straw return, and land leveling, which enhance soil quality and productivity (Xue and Xue-tao, 2023). Additionally, social media reduces information asymmetry in land rental markets, facilitating smoother transactions and reducing search and negotiation costs. Improving transparency in land leasing and ownership verification, it enhances land market efficiency, enabling optimal resource allocation (Xu et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2022). These factors contribute to increased farming efficiency (Ahmad et al., 2024), ultimately boosting agricultural income (Deininger and Jin, 2005).
2.1.2 Technological innovation and labor input
Social media significantly influences labor input by promoting technological innovation and improving agricultural labor efficiency. Through social media, farmers gain access to a wealth of agricultural knowledge, including modern practices such as mechanization, precision farming, and digital extension services. This facilitates knowledge accumulation, enhances skill development, and encourages the transition toward more efficient farming techniques. Furthermore, social media facilitates peer-to-peer learning, enabling farmers to exchange insights and experiences with their counterparts in other regions. The real-time dissemination of best practices through videos, tutorials, and expert consultations accelerates the adoption of labor-saving technologies. As a result, farmers can allocate labor more efficiently, reducing costs and increasing overall agricultural productivity (Deininger and Jin, 2005).
2.1.3 Market access and capital input
Access to financial resources is essential for sustaining agricultural investments. Social media provides farmers with better access to capital and market opportunities by linking them to financial institutions, microfinance services, and government subsidy programs. Digital platforms enable farmers to access low-cost loans, flexible credit, and government grants for investing in inputs (Qianfeng and Qifeng, 2022). Moreover, social media enhances market integration, allowing farmers to connect directly with buyers, bypass intermediaries, and secure better prices for their produce. Platforms like Facebook, WhatsApp, and YouTube facilitate online marketplaces, enabling farmers to advertise their products, negotiate prices, and expand their customer base. This improved market access leads to higher returns on agricultural investments (Sheng and Wang, 2015; Khan et al., 2022; Hou et al., 2019).
2.1.4 Social media and the adoption of advanced agricultural technologies
Smallholder farmers often struggle with information gaps that hinder their adoption of modern agricultural technologies. Social media bridges this gap by providing real-time access to expert advice, training programs, and virtual demonstration plots. Studies show a strong correlation between social media engagement and increased adoption of agricultural innovations (Aker, 2011). Through social media, farmers can participate in virtual training sessions, access extension services remotely, and receive updates on new farming technologies (Atanu et al., 1994; Adegbola and Gardebroek, 2007). Additionally, real-time problem-solving through farmer networks and expert forums enhances technology uptake, leading to improved productivity and efficiency (Larochelle et al., 2019).
Based on the above discussion, Figure 1 presents the conceptual framework illustrating how social media enhances agricultural income. The framework highlights the key pathways through which social media influences farming outcomes, including improved land management, increased labor productivity (output per unit of labor input, typically measured in yield per labor day), optimized capital inputs, and accelerated technology adoption. These factors collectively contribute to higher farm productivity and sustainable income growth for farmers.
2.2 Hypothesis development
Based on the above theoretical analysis, the current study proposes the following hypotheses:
H1: Social media usage by farmers can increase their agricultural income.
Factor inputs (land management, labor productivity, capital inputs, and technology adoption) and technological progress are key sources of productivity growth. As previously discussed, social media optimizes farmers’ input decisions and technology adoption behaviors, improving agricultural productivity. The increase in agricultural productivity is closely tied to the increase in agricultural income (Block, 2014; Xu et al., 2022). Therefore, to comprehensively analyze the indirect role of productivity in the process by which social media promotes income growth for farmers, this study focuses on three indicators technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity to represent farmers’ productivity. Technical efficiency measures the efficiency of agricultural production management and overall production efficiency (Wouterse, 2010), and using this indicator allows for a comprehensive assessment of farmers’ production efficiency from the perspectives of resource allocation, technology adoption, and decision-making management. Land productivity, with a constant land operating scale, indicates an increase in agricultural output. Similarly, improvements in labor productivity are linked to increased agricultural output or a reduction in the labor cost of family agricultural labor. As discussed earlier, social media usage can encourage farmers to adopt advanced agricultural technologies, optimize resource allocation, and enhance human capital, which will positively affect farmers’ technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity (Deng et al., 2024; Gao et al., 2022; Peng et al., 2022), ultimately raising agricultural income. Thus, this study proposes the second hypothesis:
H2: Social media usage by farmers increases agricultural income by improving technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity.
3 Methodology
3.1 Study area and data collection
Punjab province, located in eastern Pakistan, is the country’s most agriculturally significant region, contributing a substantial share of national crop production. Its fertile soil, extensive irrigation system, and diversified farming practices make it a leading center for agricultural research and innovation. The province produces key staple and cash crops, including wheat, rice, sugarcane, and cotton, which are essential for Pakistan’s food security and agrarian economy (Ali et al., 2022). Compared to other provinces, Punjab has a higher adoption rate of modern agricultural technologies, making it an ideal setting for studying the impact of social media usage on farm performance. While regions such as Sindh, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan also contribute to agriculture, they differ in climate, crop diversity, and irrigation infrastructure. Sindh, for instance, has a greater reliance on the Indus River system, while Balochistan’s agriculture is constrained by water scarcity and arid conditions. Punjab, in contrast, benefits from a well-established canal system and a mix of smallholder and large-scale commercial farms, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of agricultural digitization across different farm sizes. Given Punjab’s central role in Pakistan’s agricultural economy, the findings from this study provide insights that are broadly applicable to other major crop-producing regions with similar agro-economic structures. However, variations in infrastructure, market access, and policy environments across provinces suggest that while Punjab serves as a representative case, future research should explore regional differences to assess the full national impact of social media adoption in agriculture.
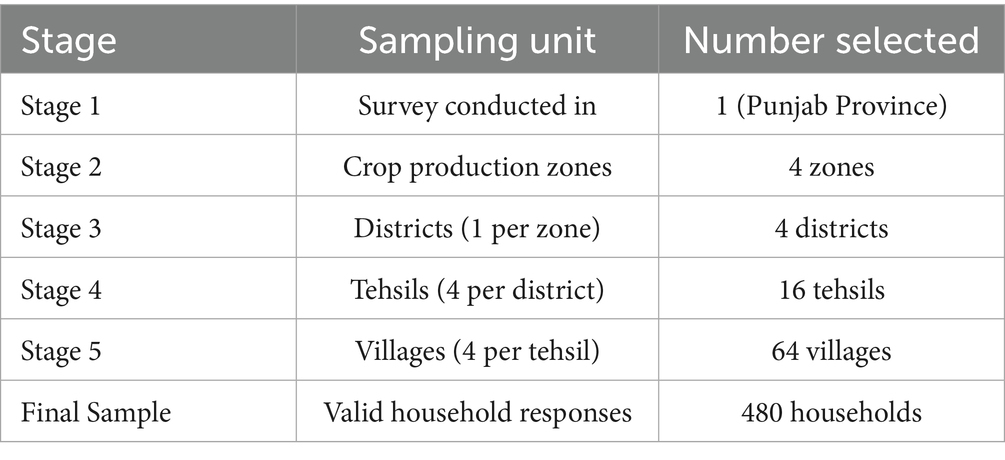
The data for this study was collected through a field survey in Punjab Province, Pakistan, from July to September 2022, targeting crop farming households. A combined stratified and random sampling method was used to ensure representativeness. The sampling followed a hierarchical structure: crop production area, province → districts → tehsils → villages → farmers. Four major crop production areas were identified, from which one district per area was proportionally selected, resulting in four sample districts. Within each district, four tehsils were randomly chosen (16 total), followed by four randomly selected villages per tehsil (32 total). Finally, 15 households per village were randomly chosen, targeting primary agricultural producers and decision-makers (Table 1). To minimize potential biases, the study ensured broad geographical coverage, including both remote and central areas. Random selection at each stage reduced selection bias, while participation bias was mitigated by emphasizing voluntary and confidential participation. Efforts were made to include a diverse mix of smallholder and large-scale farmers to enhance representativeness. A total of 500 questionnaires were distributed, with 480 valid responses, yielding a 96% response rate. These measures strengthen the reliability of the dataset and ensure an accurate reflection of Punjab’s agricultural landscape.
3.2 Model specification
3.2.1 Endogenous switching regression model (ESRM)
Since it is not possible to simultaneously observe the agricultural income of the same farmer in both the social media usage and non-usage states, an endogenous switching regression model (ESRM) was constructed. This model accounts for selection bias by allowing different income determination equations for social media users and non-users, addressing both observed and unobserved heterogeneity as an advantage over OLS and propensity score matching (PSM). The selected instrumental variables, “personal willingness” and “influence of others,” strongly affect social media usage but do not directly influence agricultural income, ensuring validity in addressing endogeneity concerns. The income determination equation for farmers is as follows:
In Equation 2, Incfarm represents the agricultural income of farmer i, Si is the binary variable representing social media usage, where Si = 1 indicates “used,” and Si = 0 indicates “not used.” Xij represents other variables that influence farmers’ income, including personal, family, and village characteristics.
If the decision to use social media by farmers is random, then applying OLS regression to Equation 2 would provide an unbiased estimate of farmers’ income. In this case, α represents the magnitude of the impact of social media usage on farmers’ income. However, the decision to use social media is influenced by external policy environments and farmers’ heterogeneity, leading to a “self-selection” problem. There are also unobservable variables that simultaneously affect farmers’ social media usage and their income levels. Ignoring the impact of sample heterogeneity on decision-making would lead to bias and endogeneity issues.
The ESRM is a two-stage estimation process: In the first stage, a selection estimation equation is established, i.e., the model for estimating social media usage, which verifies the factors influencing farmers’ decision-making. In the second stage, the result equation is used to estimate the income equation for both “used” and “not used” groups separately, verifying income differences under different scenarios.
Farmers’ behavioral decision model is expressed as follows:
In Equation 3 Si is the latent variable of the binary indicator Si. When Si > 0, Si = 1; when Si < 0, Si = 0. Zij represents the variable that influences farmers’ decision-making behavior. The income determination equations for farmers are presented in Equation 1:
In the Equation 4 the scenarios “farmers who have used social media choose not to use it” and “farmers who have not used social media but would have used it” are two unobservable “counterfactual” situations. According to the ESRM, the income in these scenarios can be fitted, leading to an estimate of the average treatment effect of farmers choosing to use social media. The Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) for farmers who use social media, had they not used it, is given in Equation 6:
The average treatment effect on the untreated (ATU) for farmers who have not used social media as they used it, is given Equation 7:
3.2.2 Mediation effect model
Theoretical analysis suggests that social media usage has a positive impact on farmers’ agricultural production, including technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity, which in turn promotes agricultural income growth. This effect mechanism requires further empirical testing. Drawing from the mediation effect methodology by Wen and Ye (2014), the model is presented as follows:
In these equations, M represents the mediator variable, which includes the farmer’s production technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity. Y represents the farmer’s agricultural income, and X represents social media usage. In Equation 8, α1 represents the effect of social media usage on agricultural income. If α1 is significantly positive, it indicates that social media usage increases agricultural income, and α1 is the total effect. If γ1 in Equation 9 and β2 in Equation 10 are both significant, a mediation effect exists. The indirect effect, γ1 × β2, represents the indirect impact of social media usage on agricultural income through the mediator variables.
3.3 Variable selection
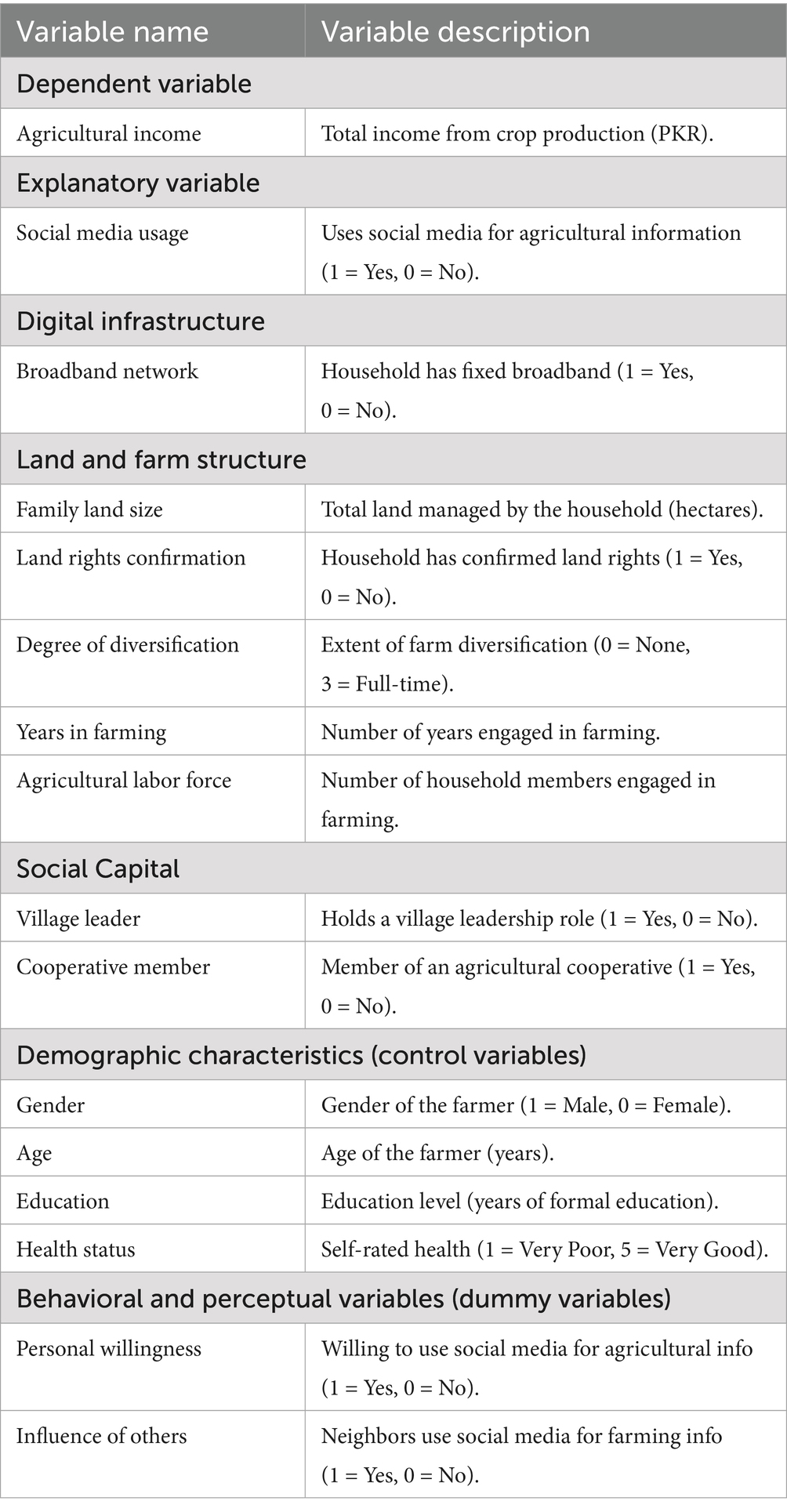
In Table 2 the dependent variable is “farmer agricultural income.” Since the survey targets crop farmers, “agricultural income” is defined as the total income obtained from crop production by the farmer’s household, measured in 10,000 PKR.
The key explanatory variable is “social media usage.” The survey question asked, “Do you use social media to obtain relevant information in the production process (such as agricultural input purchases, land transfer, planting techniques, socialized services, and production material loans)?” A “Yes” response is coded as 1, and “No” as 0, making it a binary variable.
To minimize omitted variable bias, the following control variables are selected: individual characteristics, including the farmer’s gender, age, years of education, health status, years in farming, degree of diversification, whether the farmer is a village leader, and whether they are a member of a cooperative (8 variables); family characteristics, including the family’s land management scale, whether land rights have been confirmed, number of agricultural laborers, and whether the family has fixed broadband social media access (4 variables); and village characteristics, including village terrain and village type (2 variables). Dummy variables are generated in the empirical analysis to control for village-level characteristics. Furthermore, the endogenous switching model requires instrumental variables that influence the selection equation (social media usage) but do not directly impact the outcome equation (agricultural income) (Udimal et al., 2020). The selected instruments “personal willingness” and “influence of others” are appropriate as they directly affect a farmer’s decision to use social media but do not independently determine agricultural income. The survey includes the question: are you willing to obtain necessary information via social media? Which captures a farmer’s intrinsic motivation to engage with digital tools. This willingness influences their likelihood of adopting social media for agricultural purposes but does not directly alter their income unless usage occurs. Similarly, the survey question Do your neighbors use social media to obtain necessary information? Measures peer influence, as farmers surrounded by social media users are more likely to adopt it themselves. However, their neighbors’ social media usage does not directly impact their agricultural income, ensuring the validity of the exclusion restriction (Ma et al., 2022; Li et al., 2024). These instruments effectively capture both internal motivation and external influence while addressing potential endogeneity concerns.
4 Empirical results
4.1 Descriptive statistics
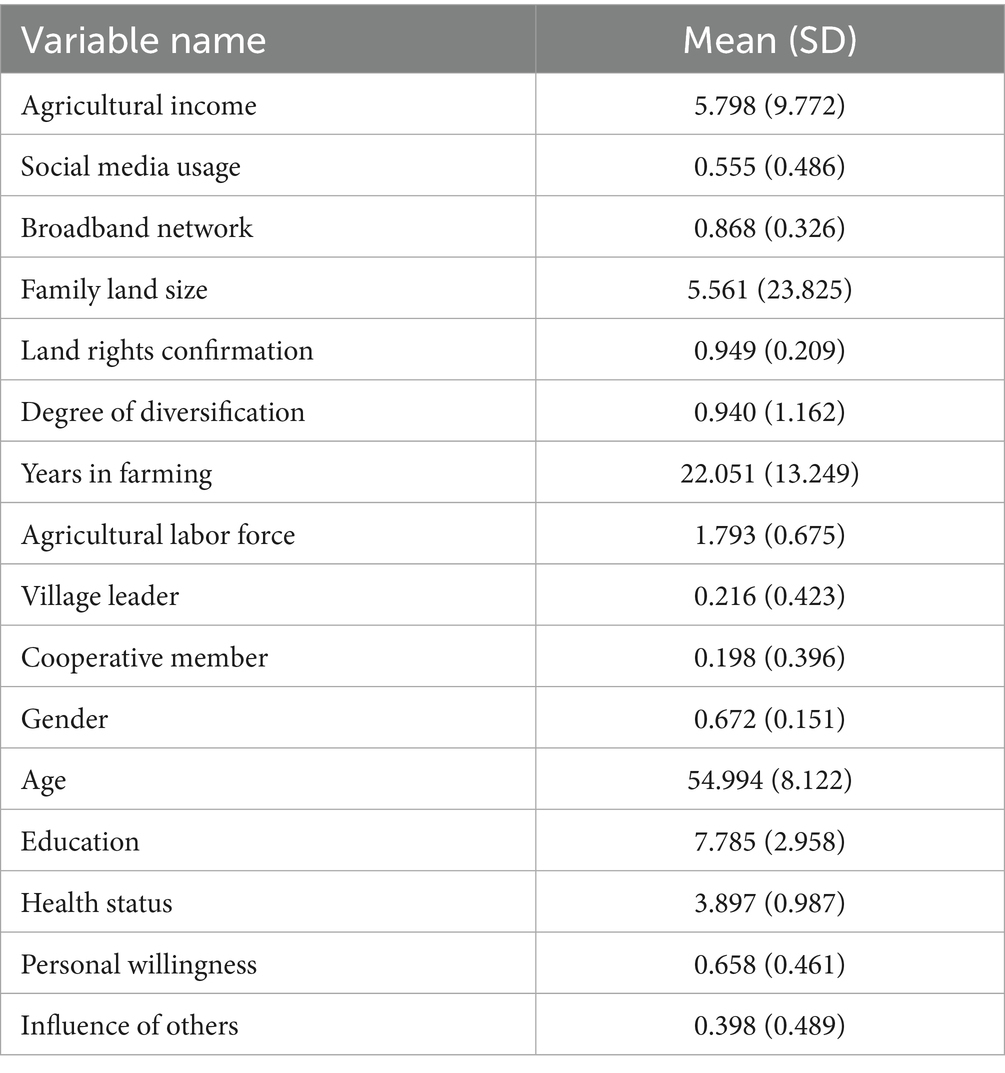
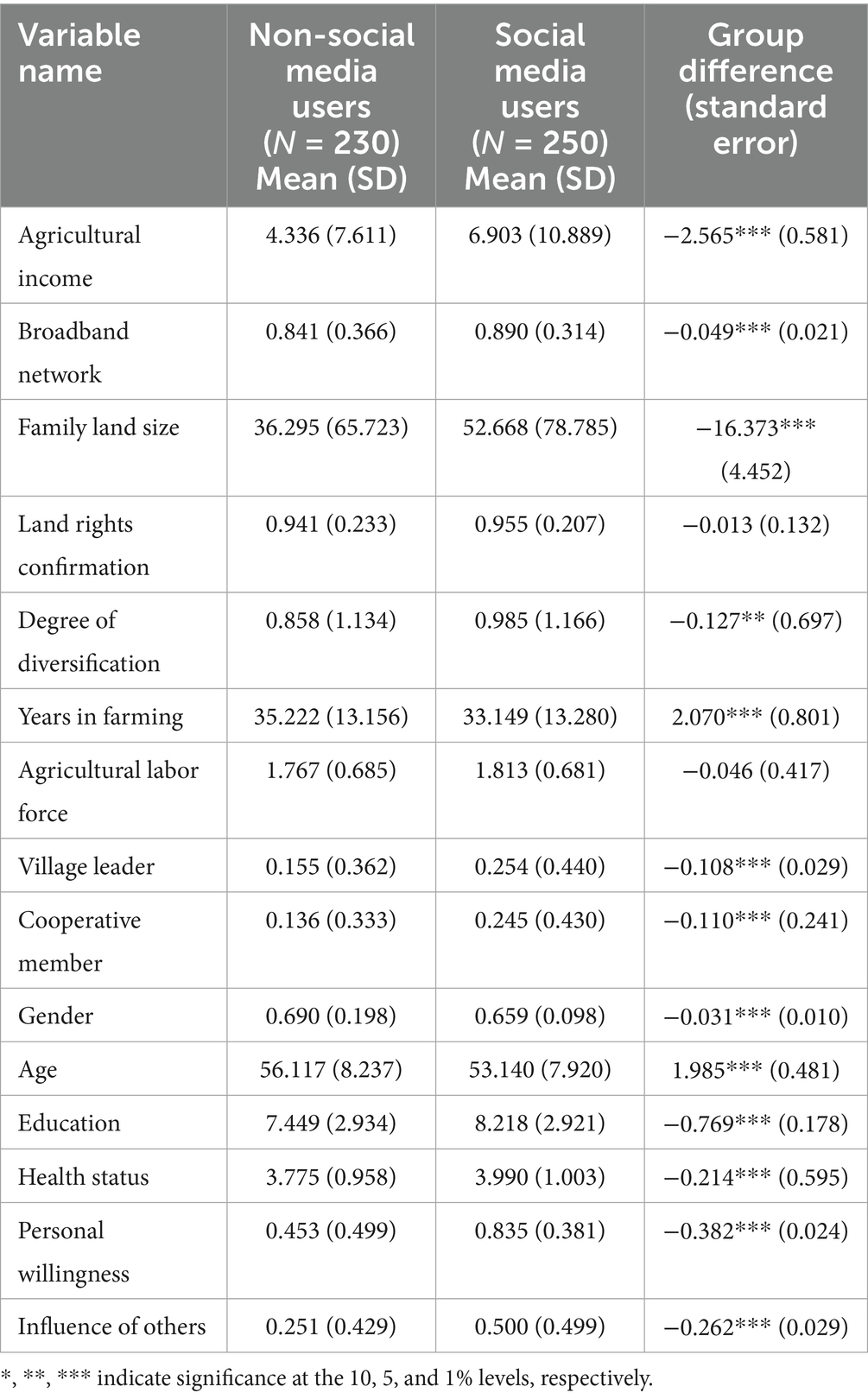
Table 3 presents the variable definitions and descriptive statistics. Among the surveyed farmers, 55.5% use social media for agricultural purposes, showing notable differences in income, demographics, and farm characteristics compared to non-users. On average, social media users earn 25,650 PKR more in agricultural income. They tend to be middle-aged, with a mean age of 54.99 years, rather than young. They have also received more formal education, averaging 7.78 years. Their self-reported health status is higher as well, averaging 3.90 on a five-point scale. Regarding farm characteristics, social media users manage landholdings averaging 5.56 hectares, which is slightly smaller than the overall sample average landholding of 6.30 hectares. This suggests that social media users do not generally have larger farms. Contrary to expectations, social media users are less likely to hold leadership positions, with 21.6% serving as village leaders, compared to 28.4% among all farmers surveyed. Notably, broadband access is significantly higher among social media users, with 86.8% having a fixed broadband connection. Furthermore, 65.8% of social media users express willingness to obtain agricultural information online, and 39.8% report that their neighbors also use social media for agricultural purposes. In terms of farming practices, social media users show a higher degree of diversification, with a mean score of 0.94, but have slightly fewer years of farming experience 22 years than non-users. These descriptive statistics underscore the potential benefits of social media adoption in agriculture and provide a foundation for further empirical analysis.
4.2 Mean differences between two groups of farmers
The statistical characteristics of the sample of farmers reveal several key differences between social media users and non-users in Table 4. The average age of household heads using social media is 53.14, which is younger than 56.11 for non-users, indicating that social media users tend to be younger. Social media users have an average of 8.22 years of education, compared to 7.45 years among non-users, suggesting that social media users generally have a higher level of education. In terms of agricultural income, social media users report an average of 6.90, significantly higher than the 4.34 for non-users, highlighting the positive association between social media use and income. Regarding landholdings, social media users have larger family farms, with an average size of 52.67 acres compared to 36.30 acres for non-users, indicating that larger-scale farmers are more likely to use social media. Additionally, social media users are more likely to be involved in community leadership roles (0.25 vs. 0.15) and are more engaged in cooperative memberships (0.25 vs. 0.14). Social media users also exhibit a higher willingness to adopt new technologies (0.84 vs. 0.45), as well as stronger influence from others (0.51 vs. 0.25), suggesting greater openness to agricultural innovations. These results show that social media users tend to have better resources, higher incomes, and a greater propensity for adopting new agricultural practices compared to non-users.
4.3 Analysis of the income-increasing effect of social media usage
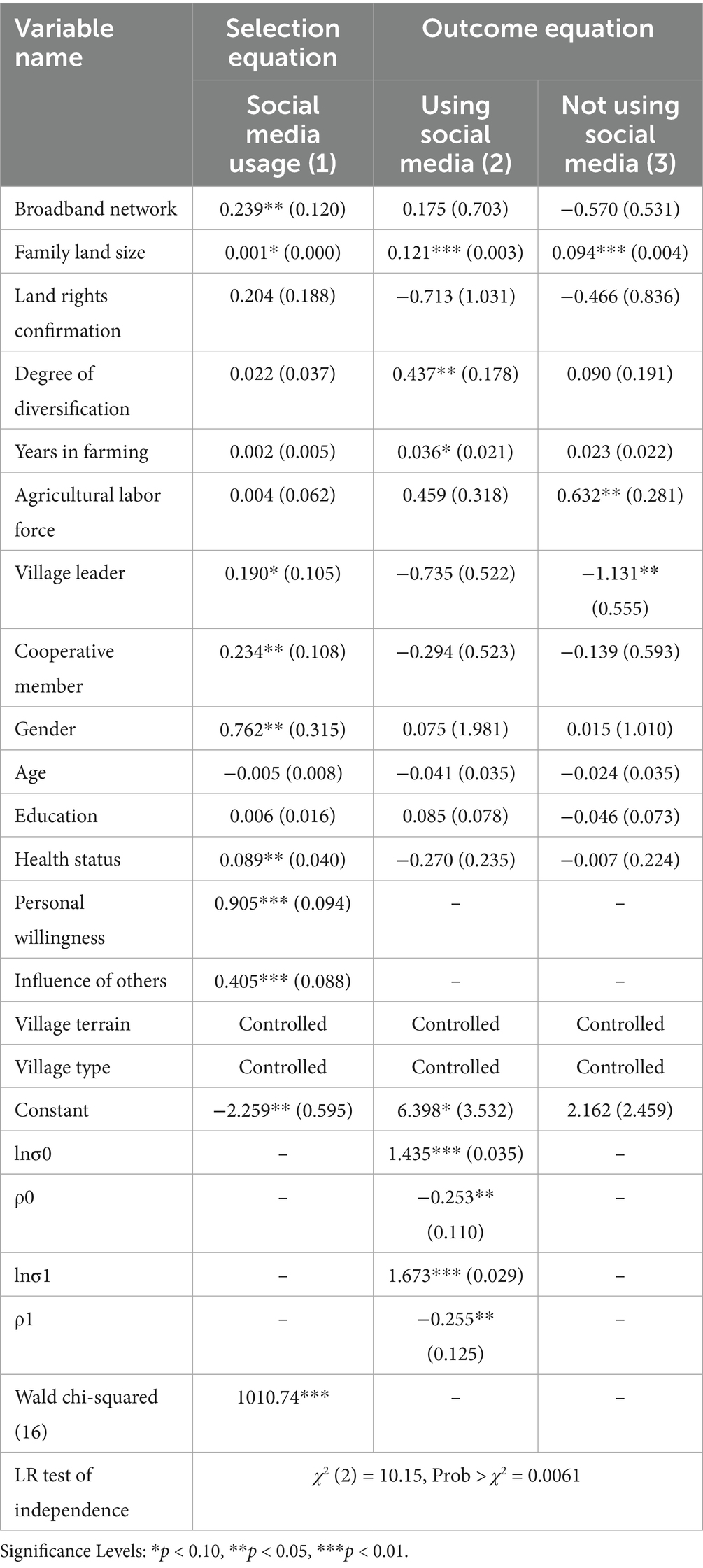
The impact of social media usage on farmers’ agricultural income: The results from the ESRM (Table 5) show that the Wald test rejects the null hypothesis of independence between the selection equation and the outcome equation at the 1% significance level. Both ρ0 and ρ1 are significantly different from zero at the 1% level, indicating that unobservable factors simultaneously influence farmers’ decisions to use social media and their agricultural income. Therefore, it is essential to correct for selection bias to avoid potential errors. This suggests that using the endogenous switching model for empirical estimation is appropriate. Factors influencing farmers’ decision to use social media: As seen in Column (1) of Table 5, the estimation results provide insights into the factors affecting farmers’ decisions to use social media, analyzed from the perspectives of household head characteristics, family operation features, and other relevant factors. The ESRM (Table 5) highlights several factors influencing farmers’ decisions to use social media. Males are more likely to use social media for agricultural information, likely due to higher participation in farming, while healthier farmers are more inclined to engage with online resources. Farmers in leadership roles or those involved in cooperatives have broader access to information channels, increasing their likelihood of social media use. Additionally, farmers with larger land holdings tend to use social media to improve efficiency and profitability, and households with broadband social media access are more likely to engage with online resources. Farmers’ willingness to use social media and the influence of neighbors are both significantly correlated with social media usage, suggesting that personal motivation and social networks play key roles in adoption.
A comparison of income determinants between social media users and non-users reveals notable differences. For social media users, more years in farming significantly contribute to higher income, as experienced farmers combine their accumulated knowledge with online information to optimize resources. The degree of diversification positively impacts income for social media users, helping part-time farmers balance agricultural and non-farming activities, while non-users see no such effect. Village leader status positively correlates with income for non-users, but not for social media users, suggesting that social media helps village leaders balance governance duties with farming. Both groups show a positive relationship between family land size and income, but social media users benefit more due to improved resource efficiency. Lastly, while non-users see a positive relationship between family labor force size and income, social media usage compensates for smaller labor forces among social media users, enhancing productivity and boosting income. Overall, social media usage enables farmers to optimize practices, improve efficiency, and increase income through better access to information and technology.
4.4 Average treatment effects in two scenarios
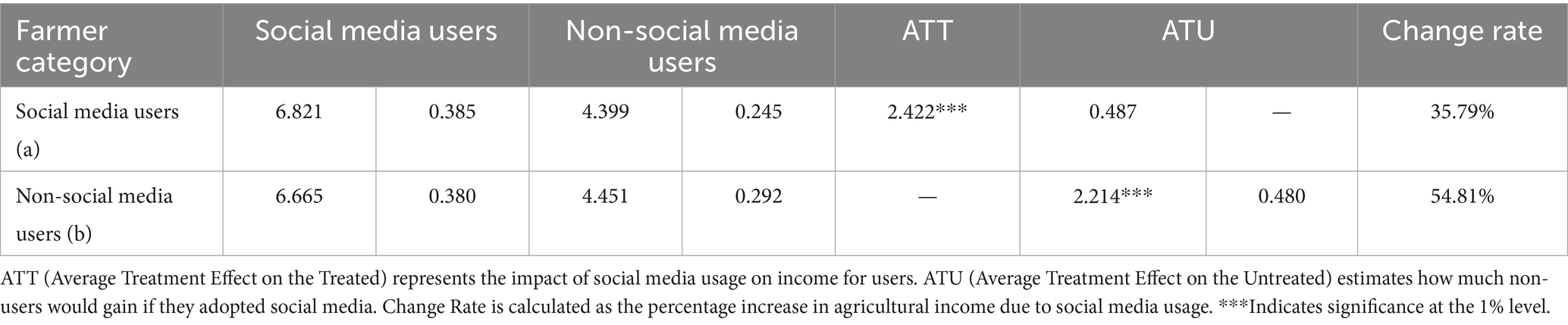
To further assess the impact of social media usage on agricultural income, we calculate the agricultural income for both groups of farmers under “factual” and “counterfactual” scenarios. Table 6 presents the Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) and the Average Treatment Effect on the Untreated (ATU), providing insights into how social media influences income levels. The results indicate that social media users earn significantly higher agricultural income than non-users. The ATT value of 2.422 means that among farmers who already use social media, their income would have been lower by this amount had they chosen not to use it. Similarly, the ATU value of 2.214 suggests that if non-users had adopted social media, their income would have increased by this amount. A notable income gap emerges in the counterfactual scenario. For non-social media users, the analysis reveals that their agricultural income could increase by 54.81% if they adopted social media, underscoring the significant economic potential of digital adoption. Conversely, for current social media users, discontinuing social media usage would lead to a 35.79% income reduction, reinforcing the critical role of social media in sustaining higher agricultural earnings. These findings suggest that non-users could significantly benefit from social media adoption, highlighting the need for digital literacy programs and rural infrastructure investments. Policymakers should support training initiatives to help farmers leverage social media for market access, modern techniques, and financial resources. Additionally, sustained digital inclusion policies are essential to prevent income losses among current users and ensure long-term agricultural resilience.
4.5 Heterogeneity analysis
4.5.1 Different levels of human capital
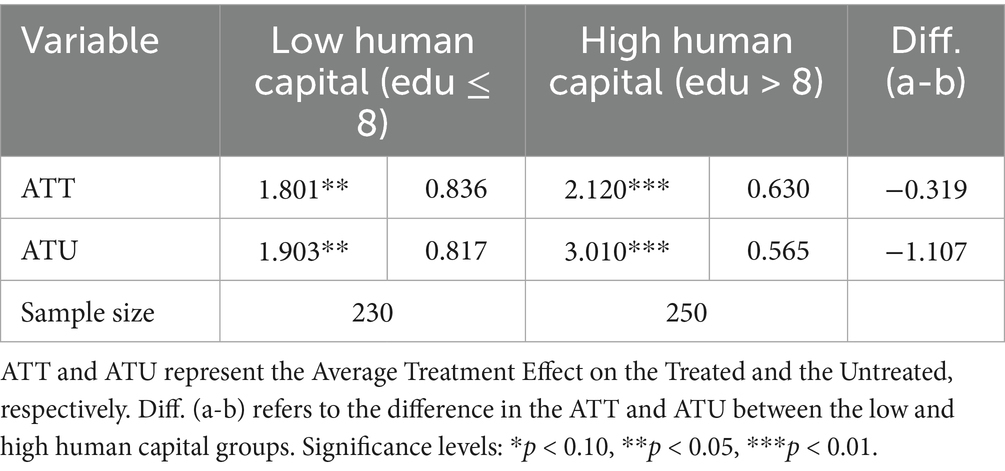
Education, land size, and income levels were selected for subgroup analysis as they significantly influence farmers’ ability to adopt and benefit from social media. Higher education enhances farmers’ ability to interpret and apply online agricultural information, while larger landholdings and higher initial income create greater opportunities for efficiency gains. To assess human capital, we use years of education as an indicator. Farmers are divided into high and low human capital groups based on the sample’s average education level of 8 years. The ability to effectively use information depends on human capital, as supported by empirical results (Table 7), which show that social media usage significantly increases income for both groups (ATT and ATU significant at 1%). However, the negative differences in ATT and ATU between the groups suggest that the income-increasing effect is stronger for farmers with higher education. Although improved digital infrastructure facilitates social media adoption, income growth from social media depends on farmers’ ability to filter, analyze, and apply information effectively. Higher education equips farmers with better analytical and management skills, allowing them to make more informed production decisions. Consequently, the impact of social media on agricultural income varies based on farmers’ human capital levels.
4.5.2 Different household land operation scales
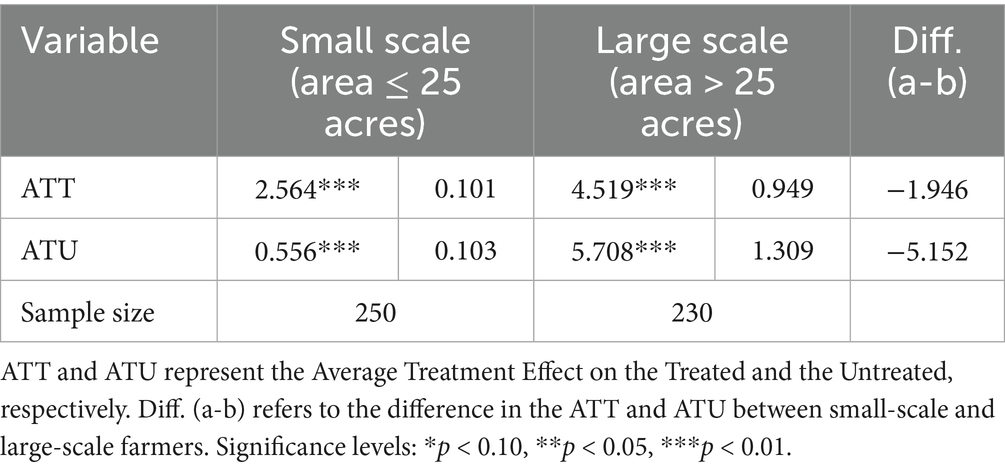
According to the existing policy documents on the definition of “large-scale households,” farmers are categorized into large and small-scale groups based on their family-operated land area, with 25 acres serving as the dividing line. Large-scale farmers typically enjoy significant technical advantages and economies of scale (Hu et al., 2022). Additionally, considering production costs, farmers with larger land operations tend to invest more in agriculture from an input–output perspective (Smidt and Jokonya, 2022). The empirical results (Table 8) further indicate that, for both social media users and non-users, social media usage has a positive income-increasing effect on farmers, regardless of their land operation scale. Both the ATT and ATU for both groups are significant at the 1% level. However, the differences between the ATT and ATU for both groups are negative, suggesting that social media usage has a more pronounced income-increasing effect for large-scale farmers. In other words, the larger the land operation, the more beneficial the use of social media in increasing income. For large-scale farmers, having more abundant resources such as capital and land allows them to leverage social media to optimize the allocation of resources and enhance efficient input. For instance, social media can help integrate fragmented land to improve land productivity or use machinery to replace manual labor, thereby increasing labor productivity and ultimately boosting agricultural output and income.
4.5.3 Different initial agricultural income levels
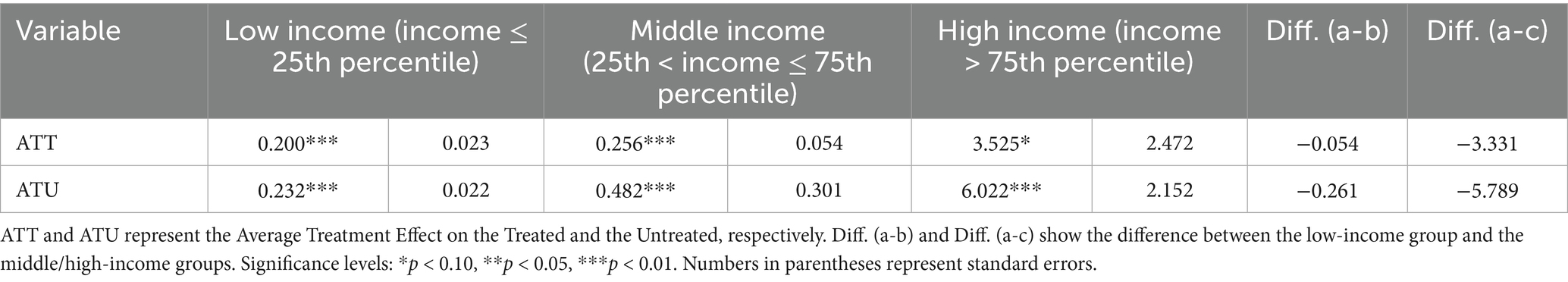
To explore the heterogeneity of the income-increasing effect of social media usage across rural residents with different initial agricultural income levels, we divided the sample based on agricultural income into low-income, middle-income, and high-income groups. A regression analysis was conducted by grouping according to income levels. The empirical results (Table 9) show that social media usage has a positive and significant ATT and ATU for low, middle, and high agricultural income groups, indicating that the income-increasing effect of social media is “inclusive” across all income levels. However, compared to the low-income group, the differences in ATT and ATU between the middle and high-income groups gradually increase. This suggests that the impact of social media usage on agricultural income differs significantly among farmers, with the income-increasing effect being more pronounced for high-income farmers. For low-income farmers, who have fewer initial production resources and face stricter resource constraints, using social media to access production information can enhance their human capital. However, it may not significantly help them leverage their existing resource endowments to achieve greater output. The results suggest that while the “digital dividend” exists across all income levels, the magnitude of its effect varies. Therefore, efforts should be made to assist low-income farmers in using social media to acquire agricultural production information and make efficient use of their inherent resources, maximizing agricultural production efficiency and narrowing the income gap between farmers, thus addressing the “three-level digital divide.”
4.6 Robustness check
4.6.1 Changing the estimation model
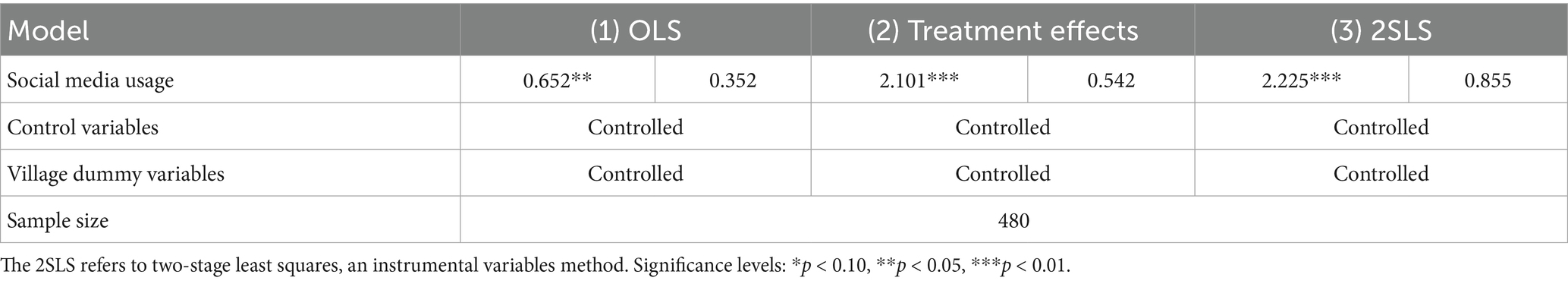
To ensure the robustness of our findings, we conducted multiple robustness checks, including alternative estimation models, different functional forms, and sub-sample analyses. Specifically, we tested the results using Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression, the Treatment Effects Model, and the Two-Stage Least Squares (2SLS) Instrumental Variables (IV) Method, as presented in Table 10. A comparative analysis shows that while OLS regression produces significantly positive coefficients, they are smaller than those from other models, suggesting endogeneity issues and potential bias. The IV method (2SLS) addresses endogeneity but does not fully resolve self-selection bias, while the Treatment Effects Model mitigates self-selection bias but does not fully account for sample heterogeneity. Despite these methodological differences, the results remain consistent, confirming the reliability of our main findings. Additionally, we tested the model’s sensitivity to different functional forms and performed sub-sample analyses to further verify the robustness of our conclusions. These checks ensure that our findings on the impact of social media on agricultural income are not artifacts of model choice or estimation bias.
4.6.2 Changing the dependent variable
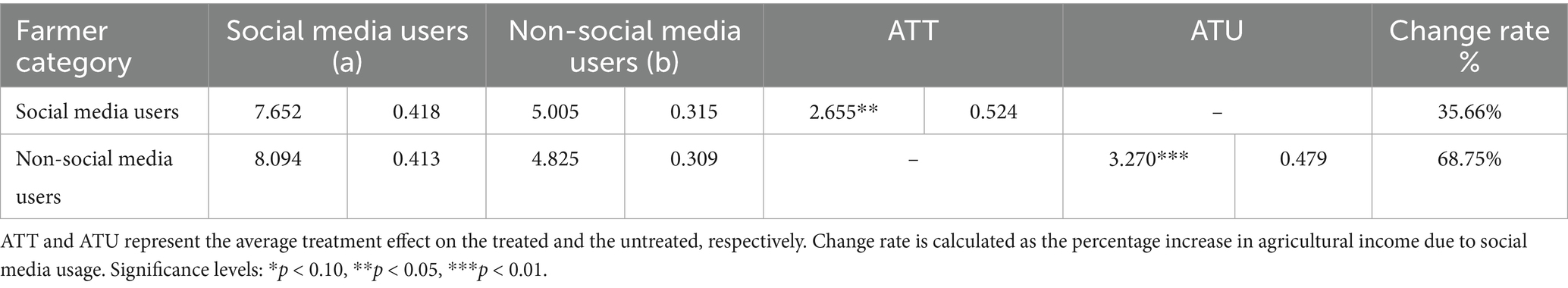
Although the survey targets rice farmers, in practice, farmers do not only grow rice but may also cultivate other crops such as wheat, peanuts, and other food and cash crops. Therefore, we combined the total income from all crops grown by the household and used “household crop income” as the new dependent variable for further testing. Additionally, while the use of social media in agricultural production was initially focused on rice, farmers may also use social media for information related to other crops, thereby increasing their overall crop income. Thus, using the survey data, we calculated the total income from rice, wheat, corn, peanuts, and other food and cash crops grown by the household, while including all previously selected control variables, and applied the endogenous switching model for estimation. The results in Table 11 show that ATT = 2.655, and ATU = 3.270, with change rates of 35.66 and 68.75%, respectively. This indicates that social media usage in the agricultural production process significantly increased household crop income, aligning with the empirical results from the main model, thereby confirming the robustness of the findings.
4.7 Mechanism analysis of the impact of social media usage on farmers’ agricultural income
To analyze the mechanism through which social media usage affects farmers’ agricultural income from a productivity perspective, we used the Stochastic Frontier Approach (SFA) for estimation. Since the primary survey target was rice farmers, the output indicator was total rice production (measured in kilograms), land input was the total area planted with rice (measured in acres), and labor input was the total family and hired labor input (measured in days). Other material inputs included seeds, fertilizers, agricultural films, pesticides, irrigation, machinery use, and fuel. Land productivity and labor productivity were measured by the average yield per acre (kilograms/acre) and average output per labor day (kilograms/day), respectively. Drawing from the mediation effect analysis method by Wen and Ye (2014), we performed non-parametric bootstrap testing to examine the underlying impact mechanism.
Technical efficiency measures agricultural production management efficiency and productivity, reflecting factors such as production potential, cost control during the production process, and competitiveness. It serves as a key indicator of how efficiently farmers utilize available resources. Social media usage contributes to income growth by enhancing technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity. Specifically, social media provides farmers with real-time access to agricultural information, including best farming practices, input selection, weather forecasts, and market prices. This enables them to make more informed decisions, optimize input use, and adopt modern agricultural techniques, reducing inefficiencies and improving production outcomes. Moreover, social media facilitates knowledge-sharing, allowing farmers to learn from peers, agricultural experts, and extension services, further enhancing their ability to allocate resources effectively.
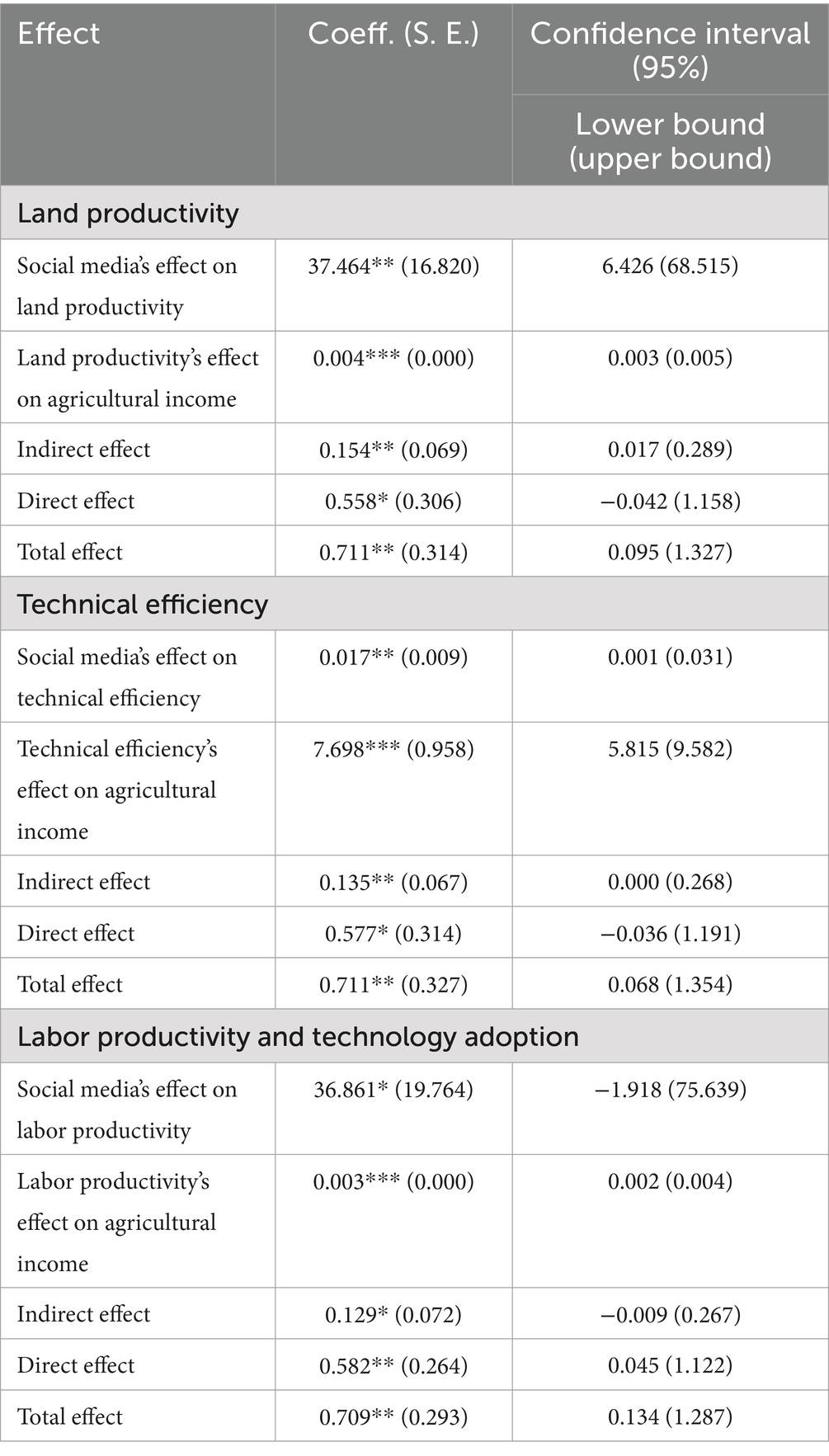
The empirical results in Table 12 show that social media usage significantly improves technical efficiency, with a mediation effect of 0.135, accounting for 18.86% of the total impact on income. This suggests that part of the income increase associated with social media usage is due to improved management practices and better resource utilization. Similarly, social media enhances land productivity, with a mediation effect of 0.154, contributing 21.52% of the total effect. This improvement is driven by farmers gaining access to information on soil fertility management, precision farming, and irrigation techniques, leading to better land utilization and higher yields. Additionally, labor productivity is significantly improved through social media usage, with a mediation effect of 0.129, accounting for 17.00% of the total impact. This indicates that social media helps farmers streamline labor management by adopting mechanization and efficient workforce allocation, ultimately boosting agricultural income. Overall, the total effect of social media usage on agricultural income is 0.709, with its impact distributed across technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity. While social media directly enhances income by improving market access and reducing transaction costs, a significant portion of its effect is mediated through productivity improvements.
In the context of limited land operation scales and a higher number of agricultural laborers on relatively small plots of land, labor productivity is a more accurate reflection of how farmers optimize the allocation and use of agricultural labor compared to land productivity. As previously discussed, social media usage helps compensate for income losses caused by a reduction in labor, highlighting its role in improving agricultural income. Building on this analysis, the improvement in labor productivity reflects, to some extent, that farmers not only increase labor productivity through social media usage but also enhance agricultural output. The empirical results (Table 12) show that social media usage significantly boosts labor productivity. The mediation effect is 0.129, indicating that part of the impact of social media usage on farmers’ increased agricultural income is mediated through the improvement in labor productivity, with the mediation effect accounting for 18.00% of the total effect. Therefore, consistent with theoretical expectations, social media usage in the agricultural production process, by providing necessary information, encourages farmers to adopt advanced agricultural technologies, optimize resource allocation, and enhance their human capital. This optimizes farming practices, leading to improvements in technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity all contributing to higher agricultural income.
5 Discussion
The findings of this study provide robust evidence that social media usage has a significant positive impact on agricultural income among crop farmers in Punjab, Pakistan. The results from the endogenous switching model confirm that social media adoption enhances income levels by facilitating improved access to agricultural information, promoting better resource allocation, and increasing efficiency in production processes. The discussion below elaborates on these findings by comparing them with existing literature and analyzing their theoretical and practical implications. The results align with prior studies that highlight the role of digital technologies in agricultural development. Several scholars have emphasized the transformative potential of information and communication technologies, including social media, in improving farmers’ decision-making processes, optimizing input usage, and enhancing market access (Deichmann et al., 2016; Aker and Ksoll, 2016). This study extends this literature by empirically demonstrating that social media usage significantly increases agricultural income through improvements in technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity. This finding is consistent with previous research showing that access to digital information contributes to increased farm productivity and income (Zheng et al., 2022; Khan et al., 2021). However, some studies have reported mixed or insignificant effects of technology adoption on agricultural income (Aker and Ksoll, 2016; Ma and Wang, 2020). The discrepancy between these findings and our results may stem from differences in contextual factors such as the availability of digital infrastructure, farmers’ digital literacy levels, and variations in agricultural practices. In contrast to regions with low social media penetration, this research focuses on Punjab, where digital connectivity has improved significantly, and allowing farmers to leverage social media more effectively.
This study contributes to the theoretical understanding of digital adoption in agriculture by providing empirical evidence on the mechanisms through which social media enhances agricultural income. The findings support the information diffusion theory, which posits that access to timely and relevant information can lead to better decision-making and increased efficiency (Rogers et al., 2014). Specifically, social media usage enables farmers to obtain critical information on weather forecasts, pest control strategies, optimal planting techniques, and market trends, ultimately improving farm productivity. Additionally, the results corroborate the theory of rational inattention, which suggests that individuals allocate their limited cognitive resources to acquiring information that maximizes their economic returns (Sims, 2003). Farmers who use social media effectively prioritize relevant agricultural information, allowing them to optimize resource allocation and enhance income. This insight highlights the need for policies that promote digital literacy and ensure that farmers can filter and apply information effectively.
The study’s findings have several practical implications for policymakers, extension services, and agricultural stakeholders. First, governments should invest in expanding rural digital infrastructure to ensure broader access to social media platforms. Policies aimed at reducing internet costs and improving connectivity can enhance farmers’ ability to use digital tools for agricultural decision-making. Second, targeted training programs should be designed to improve farmers’ digital literacy and ability to leverage social media for agricultural purposes. Extension services can play a crucial role by integrating digital training modules that help farmers navigate social media platforms and extract valuable agricultural insights. Third, policymakers should ensure that digital interventions are inclusive, particularly for smallholder farmers with lower initial income levels and limited education. Providing subsidies for digital devices, offering localized content in regional languages, and facilitating peer-learning networks can help bridge the digital divide. In the context of Punjab’s rural areas, where many farming communities face infrastructural challenges and rely heavily on traditional information sources, digital strategies should be closely aligned with local realities ensuring content relevance, language accessibility, and mobile-based platforms compatible with commonly used devices.
While this study provides valuable insights, it has certain limitations. First, the cross-sectional nature of the data limits the ability to capture the long-term effects of social media usage on agricultural income. Future studies should employ longitudinal data to analyze the sustained impact of digital adoption in farming. Second, the study focuses on agricultural income as the primary outcome variable, without considering other potential benefits of social media usage, such as improvements in farmers’ bargaining power, reduced transaction costs, and enhanced market integration. Further research could explore these additional dimensions. Third, although the endogenous switching model helps address selection bias, a more detailed discussion of its assumptions is necessary. This model accounts for self-selection bias by estimating counterfactual outcomes and controlling for observable factors. However, unobserved external factors, such as policy changes, internet penetration, and variations in government support programs, could still influence the relationship between social media usage and agricultural income. While instrumental variables mitigate these concerns, future research could use longitudinal data or experimental designs to further validate causality. This study highlights the substantial benefits of social media usage in enhancing agricultural income among crop farmers in Punjab. By improving technical efficiency, land productivity, and labor productivity, social media serves as a powerful tool for rural development. Policymakers and stakeholders must capitalize on these findings to design interventions that expand digital access, enhance digital literacy, and ensure equitable benefits for all farmers.
6 Conclusion
This study, based on survey data from 480 crop farmers in the Punjab Province of Pakistan, employs an endogenous switching model to empirically assess the impact of social media usage on agricultural income. It also conducts a heterogeneity analysis considering farmers’ human capital, family landholding scale, and initial agricultural income, while exploring the mechanisms through which social media usage promotes income growth. The findings reveal several key insights. First, both individual and family characteristics significantly influence farmers’ decisions to use social media, and notable differences exist in its impact of social media usage on agricultural income between users and non-users. Second, social media usage is found to significantly boost agricultural income. In a counterfactual scenario, social media users would experience a decline in income if they did not use social media, while non-users would see income increases if they began using it. These results remain consistent even after re-estimating with alternative models and dependent variables. Third, the impact of social media usage on income is generally inclusive, but it is more pronounced for farmers with higher human capital, larger landholdings, and higher initial agricultural income. Finally, social media usage increases agricultural income by enhancing technical efficiency, as well as land productivity and labor efficiency. Future research should use longitudinal data to examine how farmers’ social media usage and income evolve over time. This would provide deeper insights into the causal relationships and long-term effects, helping to understand how sustained engagement with social media influences agricultural productivity and economic outcomes. Additionally, exploring regional variations and incorporating other digital technologies could further enrich the findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. IU: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. NK: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This paper is a phased achievement of the major project entitled Study on the Impact of the Situation in the Bay of Bengal Region on the Safety of China’s’ East Data and West Computing ‘Project (Project No.: 22ZDA181) funded by the National Social Science Foundation in 2022.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. Because the authors are not native speakers use AI for English improvement.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adegbola, P., and Gardebroek, C. (2007). The effect of information sources on technology adoption and modification decisions. Agric. Econ. 37, 55–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-0862.2007.00222.x
Ahmad, B., Zhao, Z., Jile, X., Gultaj, H., Khan, N., and Yunxian, Y. (2024). Exploring the influence of internet technology adoption on the technical efficiency of food production: insight from wheat farmers. Front. Sust. Food Syst. 8:1385935. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1385935
Aker, J. C. (2011). Dial “a” for agriculture: a review of information and communication technologies for agricultural extension in developing countries. Agric. Econ. 42, 631–647. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-0862.2011.00545.x
Aker, J. C., and Ksoll, C. (2016). Can mobile phones improve agricultural outcomes? Evidence from a randomized experiment in Niger. Food Policy 60, 44–51. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2015.03.006
Aker, J. C., Ghosh, I., and Burrell, J. (2016). The promise (and pitfalls) of ICT for agriculture initiatives. Agric. Econ. 47, 35–48. doi: 10.1111/agec.12301
Ali, M. A., Hassan, M., Mehmood, M., Kazmi, D. H., Chishtie, F. A., and Shahid, I. (2022). The potential impact of climate extremes on cotton and wheat crops in southern Punjab, Pakistan. Sustainability 14:1609. doi: 10.3390/su14031609
Atanu, S., Love, H. A., and Schwart, R. (1994). Adoption of emerging technologies under output uncertainty. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 76, 836–846. doi: 10.2307/1243745
Block, S. (2014). “The decline and rise of agricultural productivity in sub-Saharan Africa since 1961” in African successes, Volume IV: Sustainable Growth. eds. D. Acemoglu, I. N. Chaves, P. Osafo-Kwaako, and J. A. Robinson (Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press), 13–67.
Chand, R. (2022). Agricultural challenges and policies for the 21st century. NABARD Res. Policy Series 2:36.
Chin, C. F., Goh, E. V., Clarke, A. C., Ang, M. L. E., Show, P. L., Supramaniam, C. V., et al. (2024). Transforming food systems in maritime Southeast Asia and Pacific Small Island developing states to support food security and sustainable healthy diets. Front. Sust. Food Syst. 8:1304317. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1304317
Cui, Y. (2014). Examining farmers markets' usage of social media: an investigation of a farmers market Facebook page. J. Agric. Food Syst. Commun. Dev. 5, 1–17. doi: 10.5304/jafscd.2014.051.008
Deichmann, U., Goyal, A., and Mishra, D. (2016). Will digital technologies transform agriculture in developing countries? Agric. Econ. 47, 21–33. doi: 10.1111/agec.12300
Deininger, K., and Jin, S. (2005). The potential of land rental markets in the process of economic development: evidence from China. J. Dev. Econ. 78, 241–270. doi: 10.1016/j.jdeveco.2004.08.002
Deng, X., Huang, M., and Peng, R. (2024). The impact of digital economy on rural revitalization: evidence from Guangdong, China. Heliyon 10:e28216. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28216
Du, X., Wang, X., and Hatzenbuehler, P. (2023). Digital technology in agriculture: a review of issues, applications and methodologies. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 15, 95–108. doi: 10.1108/CAER-01-2022-0009
Gao, X.-p., Zhang, Y.-h., Zhang, M.-l., and Liao, W.-m. (2022). Analysis of the impact of use of internet information technology on agricultural productivity: a case study of rice farmers in Jiangxi Province, China. Agric. Econ. Dev. 34, 2809–2822. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1524.2022.12.24
Goyal, A. (2010). Information, direct access to farmers, and rural market performance in Central India. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2, 22–45. doi: 10.1257/app.2.3.22
He, Y., and Wu, S. (2019). Connection is empowerment: practice and thinking on the connection between small farmers and modern agriculture. Rural Economy 6, 28–37.
Hou, J., Huo, X., and Yin, R. (2019). Does computer usage change farmers’ production and consumption? Evidence from China. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 11, 387–410. doi: 10.1108/CAER-09-2016-0149
Hu, Y., Li, B., Zhang, Z., and Wang, J. (2022). Farm size and agricultural technology progress: evidence from China. J. Rural. Stud. 93, 417–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2019.01.009
Johnson, M. O., Cozart, T., and Isokpehi, R. D. (2020). Harnessing knowledge for improving access to fruits and vegetables at farmers markets: interactive data visualization to inform food security programs and policy. Health Promot. Pract. 21, 390–400. doi: 10.1177/1524839919877172
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Sargani, G. R., Ihtisham, M., Khayyam, M., and Ismail, S. (2021). Current progress and future prospects of agriculture technology: gateway to sustainable agriculture. Sustain. For. 13:4883. doi: 10.3390/su13094883
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Kassem, H. S., and Ihtisham, M. (2021). Toward cleaner production: can mobile phone technology help reduce inorganic fertilizer application? Evidence using a national level dataset. Land 10:1023. doi: 10.3390/land10101023
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Zhang, S., Osabuohien, E., and Ihtisham, M. (2022). Influence of mobile phone and internet technology on income of rural farmers: evidence from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Technol. Soc. 68:101866. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101866
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Kassem, H. S., Ihtisham, M., Siddiqui, B. N., and Zhang, S. (2022). Can cooperative supports and adoption of improved technologies help increase agricultural income? Evidence from a recent study. Land 11:361. doi: 10.3390/land11030361
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Kassem, H. S., and Zhang, S. (2022). Mobile internet technology adoption for sustainable agriculture: evidence from wheat farmers. Appl. Sci. 12:4902. doi: 10.3390/app12104902
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Kassem, H. S., Khan, F. U., Ihtisham, M., and Zhang, S. (2022). Does the adoption of mobile internet technology promote wheat productivity? Evidence from rural farmers. Sustainability 14:7614. doi: 10.3390/su14137614
Khanal, A. R., Mishra, A. K., and Koirala, K. H. (2015). Access to the internet and financial performance of small business households. Electron. Commer. Res. 15, 159–175. doi: 10.1007/s10660-015-9178-3
Ki, C.-W. C., Cuevas, L. M., Chong, S. M., and Lim, H. (2020). Influencer marketing: social media influencers as human brands attaching to followers and yielding positive marketing results by fulfilling needs. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 55:102133. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102133
Larochelle, C., Alwang, J., Travis, E., Barrera, V. H., and Dominguez Andrade, J. M. (2019). Did you really get the message? Using text reminders to stimulate adoption of agricultural technologies. J. Dev. Stud. 55, 548–564. doi: 10.1080/00220388.2017.1393522
Li, Y., Xu, J., Liu, F., and Zhang, X. (2024). Impact and mechanism of digital information selection on farmers’ ecological production technology adoption: a study on wheat farmers in China. Agriculture 14:713. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14050713
Ma, W., and Wang, X. (2020). Internet use, sustainable agricultural practices and rural incomes: evidence from China. Aust. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 64, 1087–1112. doi: 10.1111/1467-8489.12390
Ma, Q., Zheng, S., and Lu, Q. (2022). Social network, internet use and farmers’ green production technology adoption behavior. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ 36, 16–21.
Middelberg, S. (2013). Sustainable agriculture: a review of challenges facing the south African agricultural sector. J. Hum. Ecol. 42, 163–169. doi: 10.1080/09709274.2013.11906590
Misaki, E., Apiola, M., and Gaiani, S. (2016). Technology for small scale farmers in Tanzania: a design science research approach. Electr. J. Inf. Syst. Dev. Countries 74, 1–15. doi: 10.1002/j.1681-4835.2016.tb00538.x
Nguyen, T. T., Nguyen, T.-T., and Grote, U. (2022). Internet use, natural resource extraction and poverty reduction in rural Thailand. Ecol. Econ. 196:107417. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2022.107417
Nyarko, D. A., and Kozári, J. (2021). Information and communication technologies (ICTs) usage among agricultural extension officers and its impact on extension delivery in Ghana. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 20, 164–172. doi: 10.1016/j.jssas.2021.01.002
Pandey, S. C., Modi, P., Pereira, V., and Fosso Wamba, S. (2024). Empowering small farmers for sustainable agriculture: a human resource approach to SDG-driven training and innovation. Int. J. Manpow. 46, 652–675. doi: 10.1108/IJM-11-2023-0655
Parra-López, C., Abdallah, S. B., Garcia-Garcia, G., Hassoun, A., Sánchez-Zamora, P., Trollman, H., et al. (2024). Integrating digital technologies in agriculture for climate change adaptation and mitigation: state of the art and future perspectives. Comput. Electron. Agric. 226:109412. doi: 10.1016/j.compag.2024.109412
Peng, J., Zhao, Z., and Liu, D. (2022). Impact of agricultural mechanization on agricultural production, income, and mechanism: evidence from Hubei province, China. Front. Climate Change Agricultural System Response 10:838686. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.838686
Qianfeng, L., and Qifeng, Z. (2022). A study of the influence and mechanism of internet use on peasant household income growth. Econ. Surv 39, 34–44.
Rogers, E. M., Singhal, A., and Quinlan, M. M. (2014). “Diffusion of innovations” in An integrated approach to communication theory and research. eds. D. W. Stacks, M. B. Salwen, and K. C. Eichhorn (London: Routledge), 432–448.
Sheng, A., and Wang, Y. (2015). Manufacturing and engineering technology. London: CRC Press/Balkema.
Siaw, A., Jiang, Y., Twumasi, M. A., and Agbenyo, W. (2020). The impact of internet use on income: the case of rural Ghana. Sustain. For. 12:3255. doi: 10.3390/su12083255
Sims, C. A. (2003). Implications of rational inattention. J. Monet. Econ. 50, 665–690. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3932(03)00029-1
Smidt, H. J., and Jokonya, O. (2022). Factors affecting digital technology adoption by small-scale farmers in agriculture value chains (AVCs) in South Africa. Inf. Technol. Dev. 28, 558–584. doi: 10.1080/02681102.2021.1975256
Udimal, T. B., Liu, E., Luo, M., and Li, Y. (2020). Examining the effect of land transfer on landlords' income in China: an application of the endogenous switching model. Heliyon 6:e05071. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05071
Wang, W., Huang, Z., Fu, Z., Jia, L., Li, Q., and Song, J. (2024). Impact of digital technology adoption on technological innovation in grain production. J. Innov. Knowl. 9:100520. doi: 10.1016/j.jik.2024.100520
Wen, Z., and Ye, B. (2014). Analyses of mediating effects: the development of methods and models. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 22:731. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1042.2014.00731
Wouterse, F. (2010). Migration and technical efficiency in cereal production: evidence from Burkina Faso. Agric. Econ. 41, 385–395. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-0862.2010.00452.x
Xu, L., Chandio, A. A., Wang, J., and Jiang, Y. (2022). Does farmland tenancy improve household asset allocation? Evidence from Rural China. Land 12:98. doi: 10.3390/land12010098
Xu, J., Li, Q., Qi, J., and Jin, J. (2024). ICT, land transfer and farm’s income increase. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 18, 19–26.
Xue, J., and Xue-tao, S. (2023). The impact of internet use on the supply of agricultural ecological products: theoretical analysis and evidence from farmers. J. Nat. Resour. 38, 1833–1847. doi: 10.31497/zrzyxb.20230713
Zhang, F., Bao, X., Deng, X., and Xu, D. (2022). Rural land transfer in the information age: can internet use affect farmers’ land transfer-in? Land 11:1761. doi: 10.3390/land11101761
Zheng, Y.-Y., Zhu, T.-H., and Wei, J. (2022). Does internet use promote the adoption of agricultural technology? Evidence from 1 449 farm households in 14 Chinese provinces. J. Integr. Agric. 21, 282–292. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(21)63750-4
Keywords: social media usage, farmers’ income, endogenous switching regression model, mediation effect, food production
Citation: Hamza A, Yonghong D, Ullah I and Khan N (2025) Assessing the impact of social media on farmers’ income: evidence from Punjab, Pakistan. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1555584. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1555584
Edited by:
Chiedza Zvirurami Tsvakirai, University of South Africa, South AfricaReviewed by:
Sukoluhle Mazwane, University of Mpumalanga, South AfricaSurya Mani Dhungana, Agriculture and Forestry University, Nepal
Humaira Gultaj, Jilin University, China
Copyright © 2025 Hamza, Yonghong, Ullah and Khan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dai Yonghong, ZGFpeWgxOTk5QDEyNi5jb20=
 Amir Hamza1
Amir Hamza1 Nawab Khan
Nawab Khan