- Department of Agricultural Extension and Rural Society, College of Food and Agriculture Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
This research aimed to study mango growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems in Al-Hudaydah governorate, Yemen. Data were collected from 323 mango growers using a simple random sampling technique with the help of a pre-tested paper-based questionnaire. The results showed that most mango growers had neutral attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. Moreover, the majority of mango growers were non-adopters. Growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems are determined by farmers' education, social participation, farm size, and adoption. Age, social participation, and adoption significantly positively correlated with growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. Farm size showed a significant negative correlation with growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. The study recommends that the Department of Agricultural Extension promote modern irrigation systems through the active involvement of various stakeholders. In addition, the government should make serious efforts to make modern irrigation technologies available in the market at a highly affordable cost. Overall, the positive attitudes and adoption of modern irrigation technologies by the growers would be advantageous for both the growers as well as the government, as these promising technologies have the potential to enhance agricultural productivity and reduce water scarcity.
1 Introduction
Water is a critical resource for global socio-economic and agricultural development (Aljawzi et al., 2022). However, its availability is increasingly threatened by climate change, rising consumption rates, and unsustainable management practices (Gadain, 2023). Several factors contribute to water scarcity, including excessive groundwater extraction, inefficient use of water resources, inadequate planning for water development and conservation, and unregulated well drilling (Bashir, 2020; Allam and Allam, 2007). Moreover, climate change is projected to disproportionately affect water resources in low-income nations, where weak infrastructure exacerbates vulnerabilities. These regions, which depend heavily on water-intensive sectors, face heightened risks of food insecurity, energy deficits, and chronic water shortages (Dunphy and Rustum, 2024). Sustainable water resource management is further hindered by interconnected challenges such as deteriorating water quality, rapid urbanization, population growth, agricultural expansion, and ecological degradation. Additionally, issues of environmental justice, Indigenous rights, and biodiversity loss complicate governance and policy implementation worldwide (Greenhalgh and Samarasinghe, 2018). Addressing these multifaceted challenges requires integrated strategies that balance developmental needs with long-term resource preservation.
Agriculture is a critical sector in the Republic of Yemen, serving as a primary livelihood source for ~73.5% of households, either directly or through related industries and services (YSEU, 2021). In 2020, it contributed 16.3% to the national gross domestic product (GDP), underscoring its economic significance (YSEU, 2021). Yemen's agricultural production includes a variety of crops, which can be classified into four main categories: fruits, vegetables, cereals, and high-value cash crops. The fruit sector comprises mango, grapes, citrus, banana, papaya, and date, while common vegetables include tomato, potato, watermelon, sweet melon, onion, and cucumber. Cereal production predominantly consists of maize, wheat, sorghum, and barley, whereas high-value cash crops such as sesame, cotton, tobacco, and coffee play a key role in export-oriented agriculture (FAO, 2018).
Yemen is characterized by limited water resources, with approximately two-thirds of its territory classified as hyper-arid, receiving <50 mm of annual rainfall, while the majority of the remaining area is arid, with <200 mm of precipitation (UNDP, 2022). Given its low rainfall and lack of Transboundary Rivers, the country faces severe water scarcity. With only 80 m3 – 86 m3 of renewable water resources per capita, Yemen ranks among the world's most water-scarce nations (Center, 2010; Mccracken, 2012; UNDP, 2021). Despite these constraints, agriculture remains heavily dependent on groundwater, dams, streams, and springs, which supply ~49% of the total cultivated area (Center, 2010). Notably, ~90% of Yemen's freshwater is allocated to agricultural use. The expansion of irrigated land—from 37,000 hectares in the 1970s to 368,000 hectares by 1996—has significantly increased water demand, further straining the sector's sustainability (NWSSIP, 2008). Compounding this issue, groundwater extraction rates exceed recharge by more than two-fold, leading to rapid depletion. If current trends persist, Yemen's groundwater reserves may be exhausted within two decades (UNDP, 2022).
Over the past 50 years, excessive water consumption, coupled with the cultivation of water-intensive crops, has exacerbated shortages, rendering the nation increasingly unable to meet its domestic water demands (UNDP, 2022; Lootsma, 2022). Consequently, Yemen now relies on food imports to sustain its population, with unsustainable resource management contributing to diminished agricultural productivity (Thomas, 2022b). To address water scarcity, the Ministry of Agriculture and Irrigation in Yemen has implemented several initiatives to promote the adoption of sustainable irrigation systems. A key intervention includes a substantial 70% government subsidy for modern irrigation technologies, aimed at incentivizing farmer uptake (Irrigation, 2012). Modern irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation, optimize water use by delivering precise volumes according to crop requirements, thereby minimizing wastage (Al Obidi and Al-Jumaily, 2018; Al-Doan, 2017; Alghawry et al., 2021). Despite their efficiency, localized irrigation methods, including drip systems, remain underutilized, accounting for only 0.1% of irrigated agricultural land in Yemen.
Empirical evidence indicates that drip irrigation reduces water consumption by 30%−60% while offering additional agronomic benefits, such as reduced soil erosion, nutrient retention, and lower labor demands. However, widespread adoption faces barriers, primarily financial constraints and limited farmer awareness (Centre, 2012). These challenges are particularly relevant in Al-Hudaydah governorate, a major mango-producing region yielding ~362,365 metric tons annually, primarily for export to GCC countries (Thomas, 2022a). Despite its agricultural significance, farmers in this region predominantly rely on inefficient flood irrigation (Al Abd Allah and Safwan, 2022). Transitioning to modern irrigation systems could significantly reduce water consumption and enhance sustainability (Zeitoun et al., 2012). This study examines mango growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems in Al-Hudaydah governorate, Yemen, and assesses the influence of socio-economic factors on their adoption. As the first such investigation in the region, the research addresses a critical gap given Yemen's acute water scarcity and unsustainable groundwater depletion. The findings will inform policymakers in designing targeted interventions, such as subsidies, training programs, or awareness campaigns, to overcome adoption barriers. Additionally, the study identifies knowledge gaps and socio-economic constraints, facilitating the development of tailored strategies to enhance water productivity and long-term agricultural resilience.
1.1 Conceptual framework
The conceptual framework of the current study is based on the theory of reasoned action (Fishbein, 1967; Ajzen, 1985) and behavior change theory (Ajzen, 1985; Prochaska et al., 1997). Adults, such as mango growers, are self-directed learners primarily focused on solving and managing their issues and are actively connected to problem-solving learning environments. Behavior change models exhibit that individuals normally go through five phases as they contemplate adopting a new behavior because of innovative technology. The theory of reasoned action explains major constructs, including attitudes and subjective norms. Moreover, it determines whether individuals perceive themselves negatively or positively. Subjective norms explain perceived social pressure to perform an act. Based on the theory of reasoned action, growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems can be influenced by various factors such as perceived benefits, cost, and beliefs. Perceived belief relates to personal attitudes, better understanding, and cultural values (Camargo et al., 2018). Education is a powerful predictor of perceived belief and has strong relationships with attitudes (Fussell, 1996). Rogers and Williams (1983) analyzed that the source of information develops perceptions about the innovations. If the information is gained through trusted sources, then positive attitudes are more likely to develop. The costs and benefits also strongly correlate with attitudes toward innovative technologies such as irrigation technologies. For instance, large landowners would build their attitudes toward modern irrigation systems based on the high benefits. Low benefits of modern irrigation systems would not allow growers to invest in modern irrigation systems (Deininger, 2011).
Attitude significantly influences the adoption of innovative technologies (Rezaei-Moghaddam et al., 2005). Defined as an individual's positive or negative evaluation of a particular behavior (Hyytia and Kola, 2006; Min et al., 2008), attitude is shaped by the perceived range of alternative actions and the availability of relevant information (Taylor et al., 1988). Empirical evidence suggests that positive attitudes enhance decision-making and increase the likelihood of adopting innovative techniques (Rezaei-Moghaddam and Salehi, 2010). Rogers and Williams (1983) outline the innovation-decision process as a multi-stage progression, beginning with the knowledge stage, followed by the persuasion stage, during which individuals form attitudes toward innovation. At this stage, acceptance or rejection decisions are made, heavily influenced by the credibility of information sources. Trusted sources are more likely to foster positive perceptions and, consequently, favorable attitudes (Al-Zaidi et al., 2014). Attitudes toward technological adoption are not static but are shaped by dynamic factors, including socio-economic characteristics and social learning (Genius et al., 2014). Farm size, for instance, has been identified as a key determinant, with larger-scale farmers exhibiting more positive attitudes due to anticipated productivity gains (Kessler, 2006; Schoengold and Zilberman, 2007). Additionally, socio-economic factors such as age, education level, and access to irrigation facilities significantly influence attitudes (Akter et al., 2017; Idahe and Solomon, 2024). Older and less-educated farmers tend to exhibit lower adoption rates, likely due to limited access to information and resources (Akter et al., 2017). Furthermore, Nahayo et al. (2017) emphasize that information sources and farm size play a critical role in shaping attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. These findings collectively suggest that behavioral change and the adoption of innovative agricultural practices are closely linked to socio-economic conditions (Rogers et al., 2014). Understanding these determinants is essential for designing effective technology diffusion strategies.
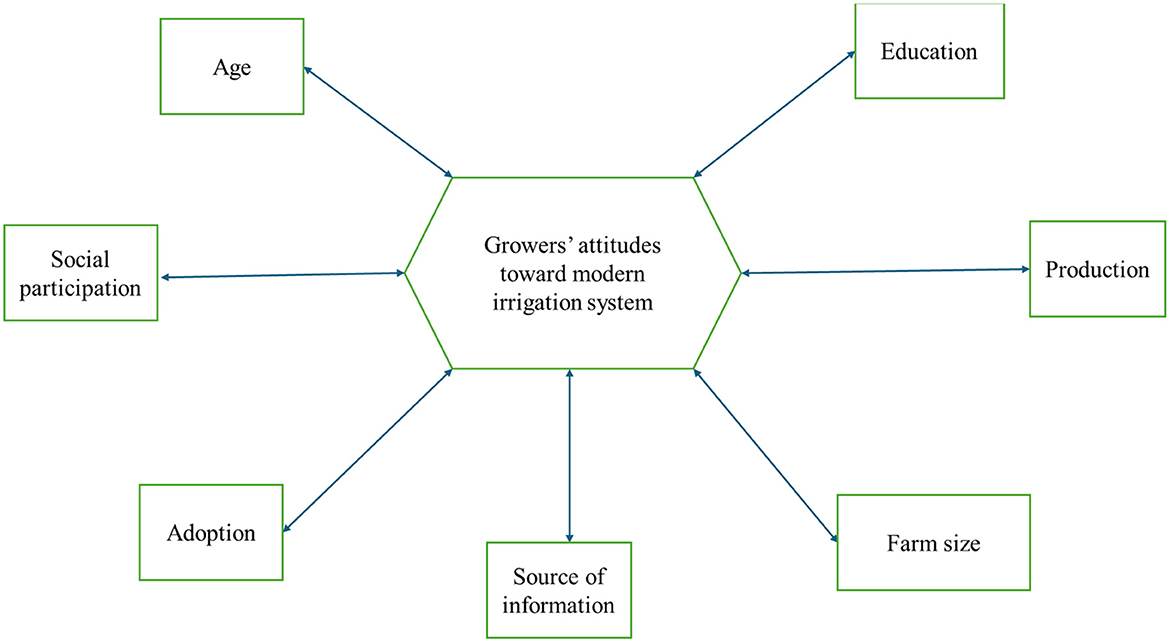
Therefore, according to Figure 1, socio-economic characteristics, including education, age, social participation, adoption, source of information, farm size, and production, were taken as independent variables, and attitudes were taken as dependent variables to achieve the study goal.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Description of the study area
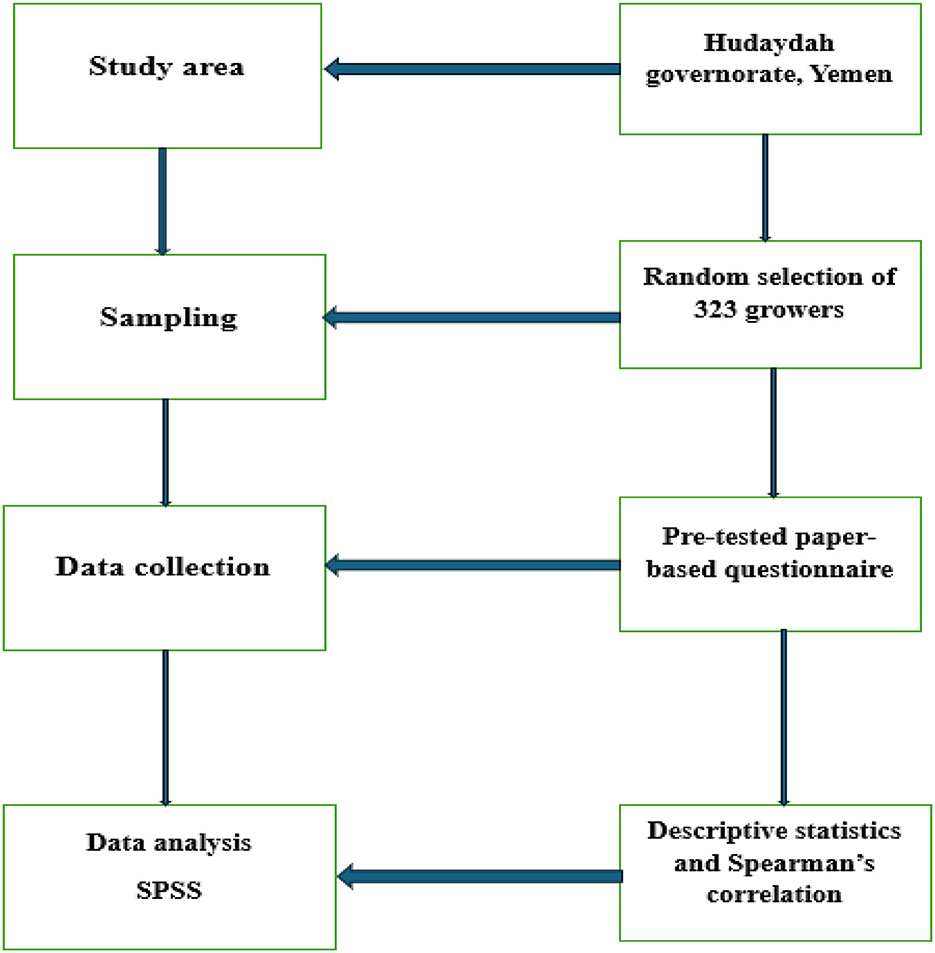
Figure 2 reflects methodological framework including study area, sampling, data collection and statistical analysis. Al-Hudaydah governorate is bordered to the north by Hajjah Governorate, to the south by Taiz Governorate, to the east by Hajjah Governorate, Al-Mahwit, Sana'a, Raymah, Dhamar, and Ibb, and to the west by the Red Sea, which overlooks a coastline of 260 km (Al-Arashi, 2021). Agriculture constitutes the main economic activity in Al-Hudaydah governorate, and the governorate is the largest agricultural producer in Yemen, as it ranks first among the governorates of the Republic in the production of some crops, with a percentage of up to 28.6% of the total production. Its lands are irrigated by valley and well water, and some depend on seasonal rainwater (Center, 2014). Climate change is one of the most important challenges facing agriculture in Al Hudaydah Governorate, as severe floods and torrents have swept through agricultural lands, and high temperatures have burned crops in some of the governorate's districts, exacerbating food insecurity (Programme, 2024).
2.2 Sampling technique
The formula used for obtaining an appropriate sample size that truly represents the study population is as mentioned below:
where Z represents the value of the Z-score; its value at a 95% confidence level is 1.96; P is the standard deviation (0.5); e is the margin of error (5%); N is the population size (2,036).
The record shows 2,036 mango growers registered in the agricultural extension in Al-Hudaydah governorate; 323 growers were selected with the help of a simple random sampling technique. The sample size calculator was used to determine the sample size (confidence interval, 95%; margin of error, 5%; population proportion, 50%; and population size, 2,036). A questionnaire was prepared in the local language and distributed among mango growers. Mango growers were informed about the aim of the study and confirmed that data would be utilized for research purposes. Out of 323 questionnaires, 272 (~85 %) were completed by the respondents.
2.3 Research instrument
The survey questionnaire consisted of five sections. The first section measured socio-economic characteristics, including age, education level, source of information, profession, farm size, and mango production. The second section included social participation. The third section measured mango growers' perceptions of modern irrigation systems using a five-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, and 5 = strongly agree). In the fourth section, a 3-point scale was used to measure growers' attitudes (1 = negative, 2 = neutral, and 3 = positive). In the fifth section, the adoption of modern irrigation systems was measured by providing two options (1 = adoption and 2 = no-adoption).
2.4 Validity and reliability
Data were collected from 40 growers for a pilot study to test the reliability of the questionnaire, and Cronbach's alpha was calculated to determine the reliability of the Likert scale. Cronbach's alpha is used to analyze the reliability and quality of instruments. Cronbach's alpha is one of the crucial and persistent statistics in research involving test construction. Alpha is generally reported for scales intended to measure attitudes and other affective constructs. Cronbach's alpha of 0.70 and above is acceptable to proceed the research (Schmitt, 1996; Cortina, 1993; Cronbach, 1951). The value of Cronbach's alpha was estimated to be 0.86. After the pilot study, a field survey was initiated to achieve the study objectives.
2.5 Data analysis
Both descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the collected data. The socio-economic characteristics of the growers were summarized using frequencies, percentages, mean and standard deviation. The socio-economic characteristics, attitudes, and adoption of the growers were summarized using frequencies and percentages. Growers' social participations and perception of modern irrigation systems were summarized using frequency, percentage, and mean and standard deviation. To determine the relationship between growers' socio-economic characteristics and growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems, Spearman's correlation statistical analysis was used. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS, version 28.0) was used for running the data analysis.
3 Results
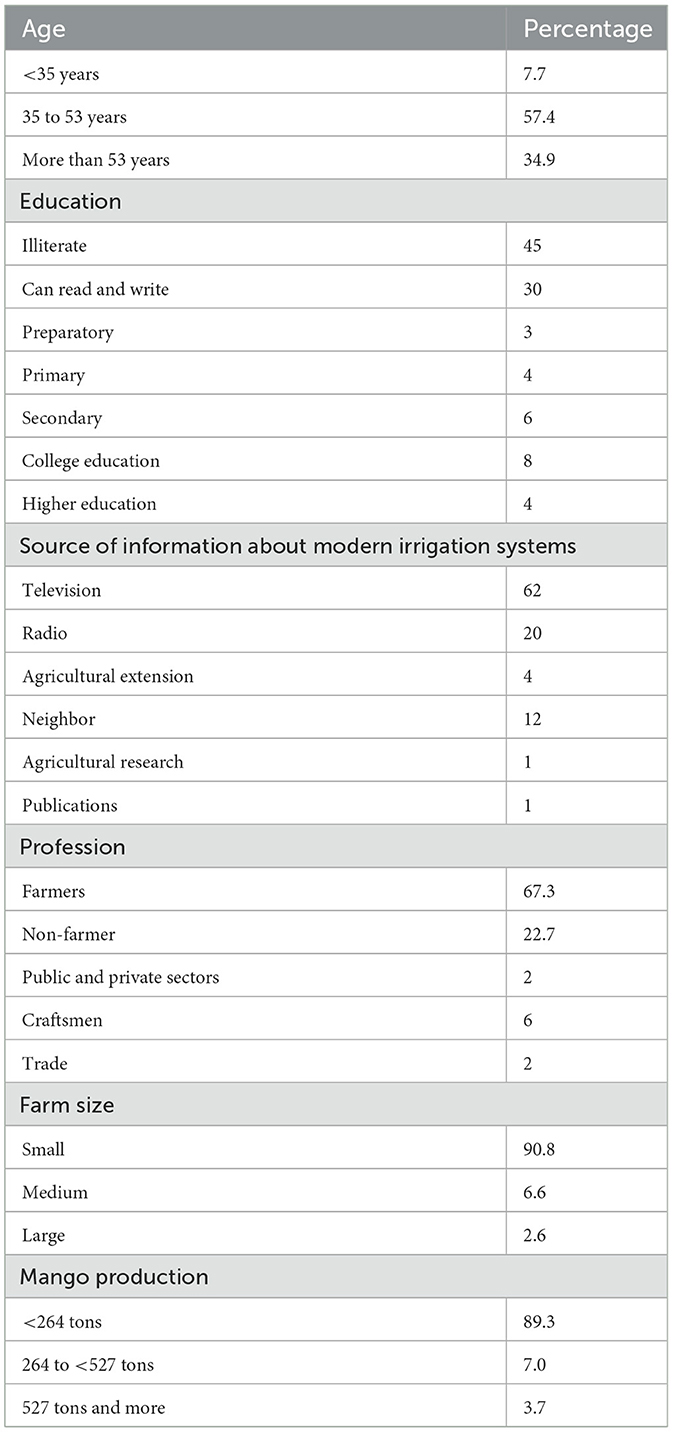
Table 1 shows that more than two-fourths of growers were 35–53 years old. While 34.9% and 7.7% of mango growers belong to the age group more than 53 years old and <35 years old, respectively. Three-fourths of the respondents were illiterate and could read and write. Only one-fourth of growers held preparatory to higher education. More than four-fifths of growers received information about modern irrigation systems from television and radio. Remaining growers received information about modern irrigation systems from the Agricultural extension department, neighbors, and agricultural research and publications.
More than three-fifths of growers considered agriculture to be their main profession, while less than one-fifth practiced professions other than agriculture as their main profession and considered agriculture to be their secondary profession. Only 10% were employed in the public and private sectors, as craftsmen, and worked in trade. More than 90% of growers held small agricultural land areas. Only 9.2% of growers held a medium and large agricultural land area. Around 90% of the farmers harvested low production (<264) tons, while 10.7% harvested high production (264–527) tons (527 tons or more).
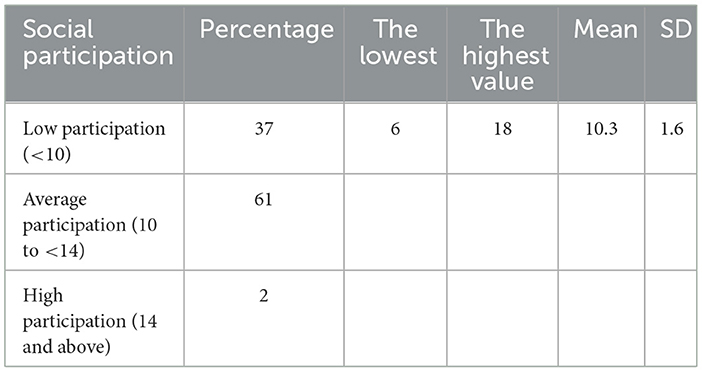
The distribution of mango growers in Table 2 ranged between 6 degrees (the lowest level) and 18 degrees (the highest level), with an arithmetic mean of 10.3 and a standard deviation of 1.6. The respondents have been grouped into three categories as revealed in Table 3. The first category included those with low social participation (<10 degrees), and accounted for were 37%. The second category included those with medium social participation 61%. Only 2% of farmers were in the third category are based on their high participation (14 degrees or more).
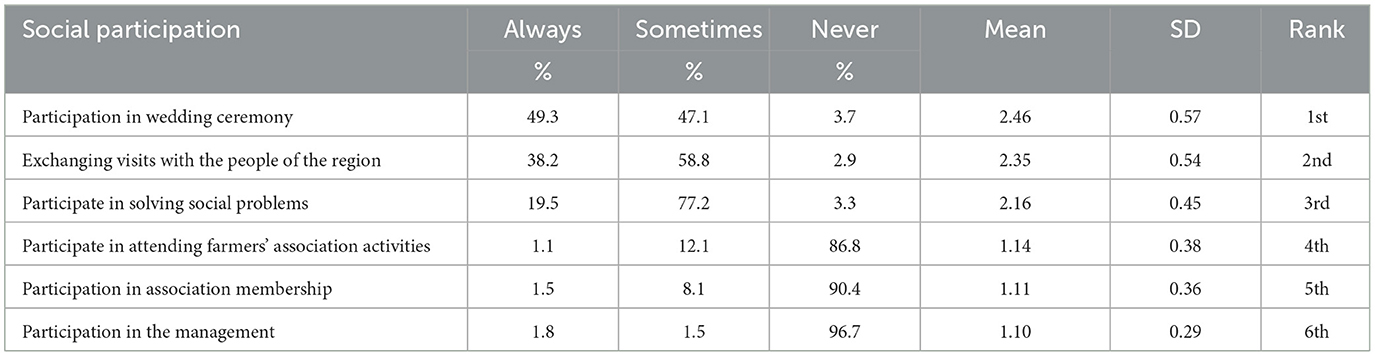
Table 3. Distribution of mango growers' social participation for learning about modern irrigation systems (n = 272).
Table 3 shows mango growers' social participation. All responses were arranged in descending order by the mean score. The results revealed that “participation in wedding ceremony” ranked first with a mean score of 2.46. On the other hand, “Participation in the management” ranked last with a mean score of 1.10.
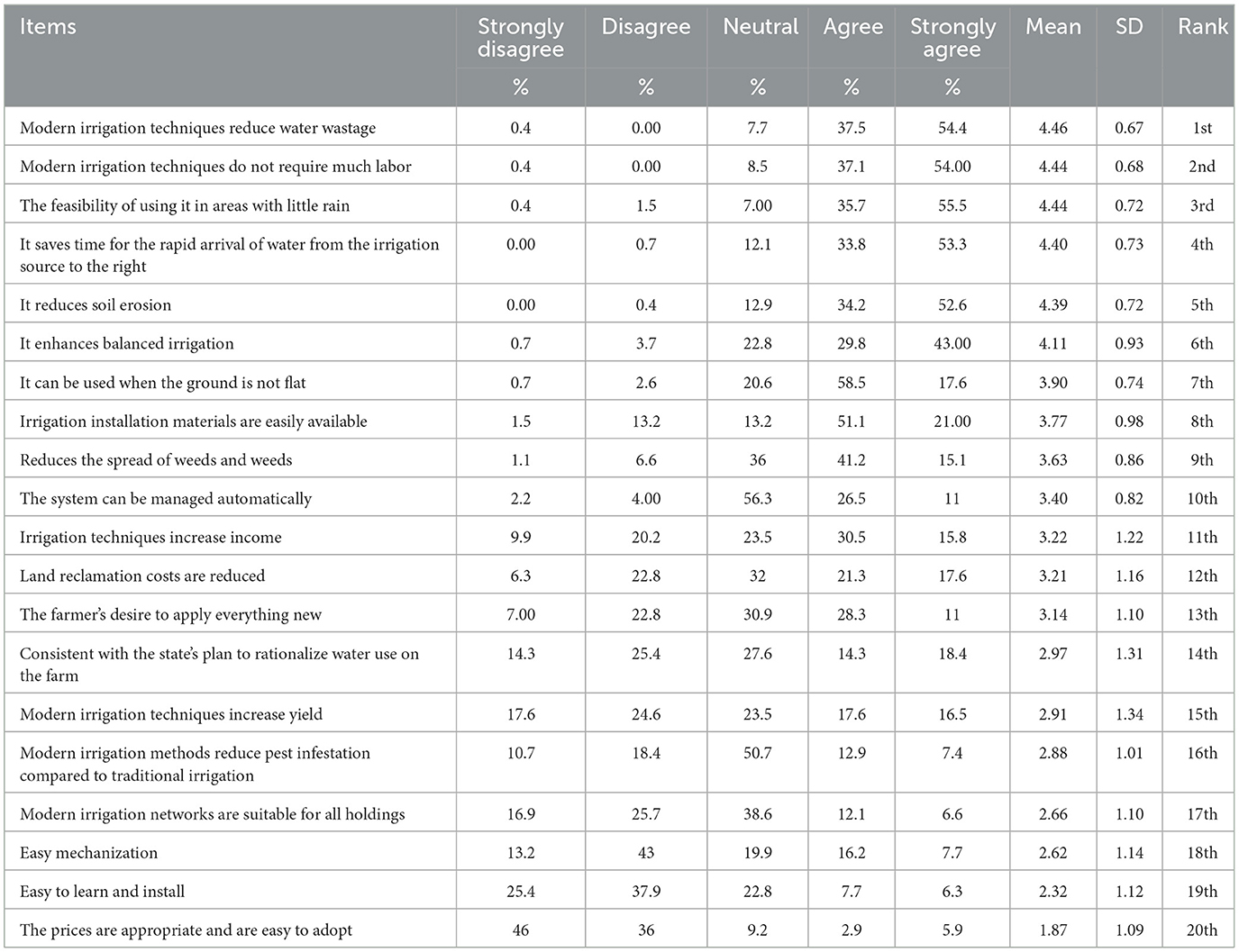
Table 4 shows mango growers' perceptions of modern irrigation systems. All responses were arranged in descending order by the mean score. The results revealed that “modern irrigation techniques reduce water wastage” ranked first with a mean score of 4.46. On the other hand, “the prices are appropriate and easy to adopt” ranked last with a mean score of 1.87.
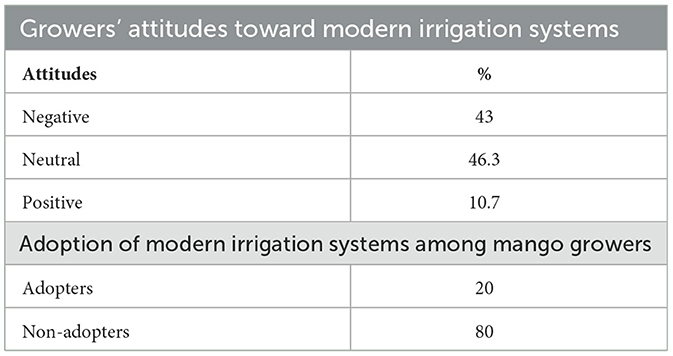
Table 5 shows that most farmers (46.3%) had a neutral attitude toward modern irrigation systems. Meanwhile, 43% and 10.7% of farmers had negative and positive attitudes toward modern irrigation systems, respectively. The majority of mango growers (80%) had not adopted modern irrigation systems in Al-Hudaydah governorate in the Republic of Yemen. Only 20% of mango growers had adopted modern irrigation systems.
Table 6 presents Spearman's rank-order correlation analysis that was run to determine the relationship between the respondents' demographic characteristics, adoption, and attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. Education was significantly correlated with growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems (r = −0.141*, p = 0.02). This means that highly educated growers have a more positive attitude toward modern irrigation systems than those with a lower educational level. Growers' participation in social events significantly correlated with their attitudes toward the modern irrigation system (r = 0.133*, p = 0.03). It means that social participation improved positive attitudes toward modern irrigation systems than those who did not participate. Growers' adoption level significantly correlated with their attitudes toward modern irrigation systems (r = 0.262, **p = 0.00). It means a higher adoption level improved their attitudes than those with a lower one. Farm size was significantly negatively correlated with growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems (r = −0.134, *p = 0.03). It means small land holders have negative attitudes than those who hold large land areas.
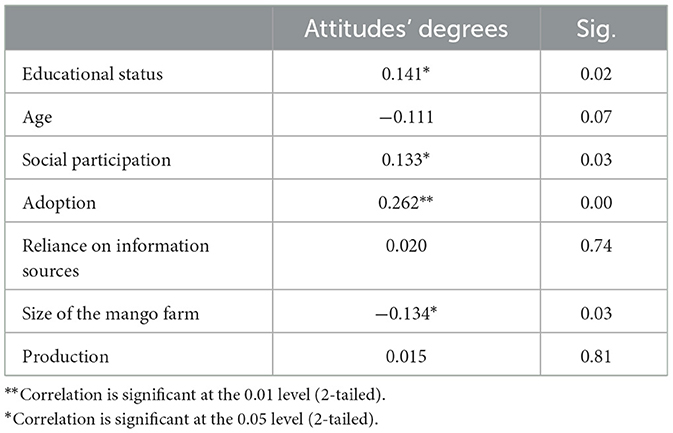
Table 6. Spearman's correlation between the independent variables and farmers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems.
4 Discussion
The current study aims to investigate farmers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems.
4.1 Growers' adoption and attitudes toward modern irrigation systems
The findings of the analysis revealed that the majority of the farmers showed neutral attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. They might be due to growers' low awareness of modern irrigation systems. Awareness has a great impact on attitude building (Wang et al., 2023). It is anticipated that low awareness may keep farmers neutral toward modern irrigation systems. Farmers' attitudes can be improved from neutral to positive by launching educational programs on the advantages of modern irrigation systems. Our arguments are aligned with Al-Zaidi et al. (2014), who suggested that awareness of modern irrigation systems through extension programs among growers could build positive attitudes toward modern irrigation systems.
Growers' neutral attitudes might result from low education. A feature-like attitude could be compatible with traits such as educational level, which means growers with low educational levels may exercise low positive attitudes toward modern irrigation methods, and highly educated farmers may have positive attitudes toward modern irrigation systems, as reported by (Bagheri and Pirmoazzen, 2021; Zhang et al., 2019). This particular study finding is consistent with the outcomes of studies conducted in developing countries and reported by Zhang et al. (2019) and Koundouri et al. (2006).
Findings revealed that the majority of mango growers were non-adopters. Low adoption rates might be a result of low education and knowledge about the advantages of modern irrigation systems. It can be expected that higher education and knowledge could enhance the adoption of modern irrigation systems, as Maru et al. (2022) found that growers with higher education held higher levels of knowledge and adopted modern irrigation systems. Moreover, growers who were well informed about the advantages of modern irrigation systems such as water use efficiency, uniform supply of water in the field, easy application of soluble pesticides and fertilizers, low labor cost, and low soil erosion, adopted modern irrigation systems at a large scale (Maru et al., 2022; Khosravi and Robati, 2025).
4.2 Relationship between education and growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems
The study's findings revealed that the education level improves farmers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. Understandably, education helps farmers decide about adopting innovative technologies (Abdulai and Huffman, 2005). The present finding is consistent with (Koundouri et al., 2006), who noted that educated farmers were positive toward modern irrigation systems. Our findings are consistent with Al-Subaiee et al. (2013), who found that educated farmers exhibited better attitudes and were friendly toward modern irrigation methods. This implies that education is one factor that determines farmers' attitudes toward modern technologies, including irrigation systems. The study findings are in agreement, as reported by Al-Tanoubi (2001). The study conducted by Salazar and Rand (2016) revealed that highly educated farmers might have greater access to effective sources of information, as the authors noticed that educated farmers with higher access to effective sources of information delivered by extension services were more likely to adopt modern irrigation systems. Similar results related to farmers' attitudes on the use of irrigation water have been reported by Ashoori et al. (2016). Similarly, Idahe and Solomon (2024) reported that educated farmers better understood advanced irrigation methods and seemed more likely to adopt modern irrigation technologies.
4.3 Relationship between social participation and growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems
Social participation makes a strong local community and neighborhood engagement (Defrancesco et al., 2008) and may provide an opportunity to learn about modern irrigation systems in the study area. Moreover, the current findings regarding social participation align with Risha (2016), who found a relationship between farmers' attitudes and openness to civilization regarding modern irrigation systems. Social participation builds social networks and social capital (Savari et al., 2023). Moreover, Van Rijn et al. (2012), social participation builds social bonds with norms, values, and trust promotes inter-community ties. According to Yazdanpanah et al. (2022), social participation improved attitudes toward agricultural innovation. Findings by Hunecke et al. (2017) proved that social capital and participation encouraged the attitudes and adoption of modern technologies. According to the researcher, mango growers preferred learning from other farmers. They used to participate in social gatherings, discuss several issues, and try to overcome agricultural problems, including water scarcity. These facts govern data collection. Therefore, social gathering or participation in various ceremonies and agricultural events could affect their attitudes toward modern irrigation. Social gatherings and participation are common practices in Arab countries, including Yemen. Social participation improves farmers' attitudes toward the modern irrigation system. Findings reported by Sulemana and James (2014) and Defrancesco et al. (2008) also support our findings. Social factors influenced decision-making and improved farmers' attitudes toward farming practices.
4.4 Relationship between adoption and growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems
The adoption of modern irrigation systems showed a positive correlation with growers' attitudes. The present results are consistent with Khan et al. (2009) who noted that a positive attitude promotes the adoption of modern technologies. Contradicting our findings, Bagheri and Pirmoazzen (2021) reported that non-adoption of irrigation practices had no relationship with farmers' attitudes. On the other hand, Zhang et al. (2019) revealed that more than 50% of the farmers in Beijing adopted modern irrigation technology and showed positive attitudes toward innovative technologies. Similarly, Al-Zaidi et al. (2014) noted that growers in Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, adopted modern irrigation systems and showed a positive attitude toward innovative and modern irrigation practices. Moreover, the current finding is consistent with Chang et al. (2016) that Italian growers who adopted modern agricultural technologies exhibited positive attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. Growers' decisions about adopting modern irrigation systems mainly depend on the advantages expected from water management and costs (Deveci et al., 2015; Balana et al., 2020). Low advantages of modern technologies discourage adoption among growers and increase negative attitudes. High adoption among growers resulted from low costs and high yields. Many countries around the world, namely, the United States, Spain, the Mediterranean, and Asian countries, provided subsidized modern irrigation systems to growers (Scheierling et al., 2006). It is understandable that subsidized technologies allow growers to experience modern technologies and build positive attitudes after adoption and their economic benefits. These arguments are consistent with our findings.
4.5 Relationship between farm size and growers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems
Findings showed that small farm holders showed negative attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. As Schoengold and Zilberman (2007) revealed that growers with large farms showed positive attitudes toward irrigation technologies because they expected to enhance their crop productivity and incomes. While small landholders showed negative attitudes toward irrigation technologies because modern irrigation systems required large land area and investment to operate modern irrigation technologies (Tohidyan Far and Rezaei Moghaddam, 2015). Large landholders participate in commercial agriculture, have access to wider markets, and earn greater profits (Balana et al., 2020). This economic stability builds their positive attitudes and invests in modern irrigation systems, leading to a positive cycle of agricultural development. During data collection, the researcher noted that large landholders were well-informed about the advantages of modern irrigation systems. Moreover, large landholders experienced high profits after using modern technologies on their farms.
5 Conclusion
The current study aimed to investigate farmers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems in Al-Hudaydah governorate, Yemen. The majority of the farmers did not adopt modern irrigation systems and had neutral attitudes. Improving education, social participation, and adoption levels enhanced farmers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems. Moreover, the decrease in farm size showed negative attitudes. Therefore, the findings of the study have several implications. The extension department needs to plan and organize programs and workshops aimed at raising awareness and helping farmers develop positive attitudes toward modern irrigation systems.
The extension department should undertake educational programs for the farmers by involving more educated farmers to demonstrate different irrigation techniques on their farms. Extension personnel can use a farmer-to-farmer extension approach in areas with similar water resources. More educated farmers can easily train less educated farmers and develop useful contacts with each other. Globally, farmer-to-farmer extension and the concept of field schools have proved very successful and economical. Our study establishes that such extension initiatives hold great potential in developing positive attitudes among the farmers toward modern irrigation systems that would help farmers use scarce water resources in the arid environments of Al-Hudaydah governorate, Yemen—wisely and economically.
The current study selected mango growers only from the Al-Hudaydah governorate, Yemen. The study's outcomes may not be generalizable to growers in other geographical regions. It is, therefore, indicated that a similar study should be conducted in other regions of Yemen that are more prone to water scarcity.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
AD: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Investigation, Project administration. AH: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. YA: Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft. JS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. MM: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Ongoing Research Funding Program, (ORF-2025-1289), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdulai, A., and Huffman, W. E. (2005). The diffusion of new agricultural technologies: the case of crossbred-cow technology in Tanzania. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 87, 645–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8276.2005.00753.x
Ajzen, I. (1985). “From intentions to actions: a theory of planned behavior,” in Action Control. SSSP Springer Series in Social Psychology, eds. J. Kuhl and J. Beckmann (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 11–39.
Akter, S., Rutsaert, P., Luis, J., Htwe, N. M., San, S. S., Raharjo, B., et al. (2017). Women's empowerment and gender equity in agriculture: a different perspective from Southeast Asia. Food Policy 69, 270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2017.05.003
Al Abd Allah, M. S. A. A. A., and Safwan. (2022). Analytical study of the attitudes of irrigated vegetable growers towards the problems affecting production in Swaida governorate. Damascus Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 38.
Al Obidi, R. S. H., and Al-Jumaily, M. H. J. (2018). The level of rationalization of farmers' consumption of irrigation water and its relation with some variables in Salah al-Din Province/Al-Alam distract. Tikrit J. Agric. Sci. 18.
Al-Arashi, A. M. M. (2021). Quantitative evaluation of the efficiency of the paved road network between the administrative cities in the districts of hodeida governorate in the republic of Yemen. J. Arts 20, 457–512. doi: 10.35696/.v1i20.739
Alghawry, A., Yazar, A., Unlu, M., Çolak, Y. B., Iqbal, M. A., Barutcular, C., et al. (2021). Irrigation rationalization boosts wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) yield and reduces rust incidence under arid conditions. BioMed Res. Int. 2021:5535399. doi: 10.1155/2021/5535399
Aljawzi, A. A., Fang, H., Abbas, A. A., and Khailah, E. Y. (2022). Assessment of water resources in Sana'a region, Yemen republic (case study). Water 14:1039. doi: 10.3390/w14071039
Allam, M. N., and Allam, G. I. (2007). Water resources in Egypt: future challeges and opportunities. Water Int. 32, 205–218. doi: 10.1080/02508060708692201
Al-Subaiee, F., Al-Ghobari, H., Baig, M., Ei-Hag, E., and Abu-Riziga, M. (2013). Studies on adoption of irrigation methods by the date palm farmers in Al-Qassim area-Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 19, 1337–1345.
Al-Tanoubi, M. O. (2001). Adaptation of Modern Agricultural Technology to the Requirements of Development in Developing Countries. Alexandria, Egypt: Technical Radiation Press.
Al-Zaidi, A. A., Baig, M. B., Elhag, E. A., and Al-Juhani, M. B. A. (2014). “Farmers' attitude toward the traditional and modern irrigation: methods in Tabuk Region—Kingdom of Saudi Arabia,” in Science, Policy and Politics of Modern Agricultural System: Global Context to Local Dynamics of Sustainable Agriculture, eds. M. Behnassi, S. Shahid, and N. Mintz-Habib (Dordrecht: Springer), 109–122.
Ashoori, D., Bagheri, A., Allahyari, M. S., and Michailidis, A. (2016). Understanding the attitudes and practices of paddy farmers for enhancing soil and water conservation in Northern Iran. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 4, 260–266. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2016.09.003
Bagheri, A., and Pirmoazzen, S. (2021). Potato growers' attitudes and perceptions towards precision irrigation technologies in Ardabil County, Iran. Int. J. Agric. Manag. Dev. 11, 65–78. doi: 10.22004/ag.econ.335147
Balana, B. B., Bizimana, J.-C., Richardson, J. W., Lefore, N., Adimassu, Z., and Herbst, B. K. (2020). Economic and food security effects of small-scale irrigation technologies in northern Ghana. Water Resour. Econ. 29:100141. doi: 10.1016/j.wre.2019.03.001
Bashir, A. M. (2020). Agriculture in Yemen, Community Partnership Conference for Sustainable Development in Yemen. Cairo.
Camargo, M. C., Lima-Silva, T. B., Ordonez, T. N., Batistoni, S. S. T., Yassuda, M. S., De Melo, R. C., et al. (2018). Beliefs, perceptions, and concepts of old age among participants of a University of the Third Age. Psychol. Neurosci. 11:417. doi: 10.1037/pne0000117
Center, N. I. (2010). Agriculture in Yemen. Available online at: https://yemen-nic.info/agri/agrin_yemen/ (accessed December 20, 2022).
Centre, F. M. (2012). Innovations in Water Management Needed to Sustain Cities. FAO Media Centre: Innovations in Water Management Needed to Sustain Cities. Food and Agriculture Organization, 12 Mar. 2011. Available online at: https://www.fao.org/newsroom/detail/Innovations-in-water-management-needed-to-sustain-cities/en (accessed July 23, 2024).
Chang, G., Wang, L., Meng, L., and Zhang, W. (2016). Farmers' attitudes toward mandatory water-saving policies: a case study in two basins in northwest China. J. Environ. Manage. 181, 455–464. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.07.007
Cortina, J. M. (1993). What is coefficient alpha? An examination of theory and applications. J. Appl. Psychol. 78:98. doi: 10.1037//0021-9010.78.1.98
Cronbach, L. J. (1951). Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika 16, 297–334. doi: 10.1007/BF02310555
Defrancesco, E., Gatto, P., Runge, F., and Trestini, S. (2008). Factors affecting farmers' participation in agri-environmental measures: a Northern Italian perspective. J. Agric. Econ. 59, 114–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-9552.2007.00134.x
Deininger, K. (2011). Challenges posed by the new wave of farmland investment. J. Peasant Stud. 38, 217–247. doi: 10.1080/03066150.2011.559007
Deveci, O., Onkol, M., Unver, H. O., and Ozturk, Z. (2015). Design and development of a low-cost solar powered drip irrigation system using systems modeling language. J. Clean. Prod. 102, 529–544. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.04.124
Dunphy, E., and Rustum, R. (2024). “Challenges faced by developing economics to mitigate the impacts of climate change on water resources,” in Living with Climate Change (Elsevier), 149–172.
FAO (2018). Yemen Plan of Action 2018–2020 Strengthening Resilient Agricultural Livelihoods. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Fishbein, M. (1967). Attitude and the Prediction of Behavior. Readings in attitude theory and measurement.
Fussell, W. (1996). The value of local knowledge and the importance of shifting beliefs in the process of social change. Commun. Dev. J. 31, 44–53. doi: 10.1093/cdj/31.1.44
Gadain, H. (2023). Being the Change in Yemen: Improving Integrated Water Resources Management for Food Security. Available online at: https://reliefweb.int/report/yemen/being-change-yemen-improving-integrated-water-resources-management-food-security-enar (accessed January 20, 2025).
Genius, M., Koundouri, P., Nauges, C., and Tzouvelekas, V. (2014). Information transmission in irrigation technology adoption and diffusion: social learning, extension services, and spatial effects. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 96, 328–344. doi: 10.1093/ajae/aat054
Greenhalgh, S., and Samarasinghe, O. (2018). Sustainably managing freshwater resources. Ecol. Soc. 23. doi: 10.5751/ES-10233-230244
Hunecke, C., Engler, A., Jara-Rojas, R., and Poortvliet, P. M. (2017). Understanding the role of social capital in adoption decisions: an application to irrigation technology. Agric. Syst. 153, 221–231. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.02.002
Hyytia, N., and Kola, J. (2006). Finnish citizens' attitudes towards multifunctional agriculture. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 9, 1–22. doi: 10.22004/ag.econ.8203
Idahe, D., and Solomon, Z. (2024). Smallholder farmers' participation in small-scale irrigation system: insight from Lume district, Ethiopia. Heliyon 10:e39638. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39638
Irrigation, M. O. A. A. (2012). National Agriculture Sector Strategy (2012–2016), prepared in cooperation with the United Nations Development Programme, and Economic Diversification Support Program (Agriculture Sector).
Kessler, C. A. (2006). Decisive key-factors influencing farm households' soil and water conservation investments. Appl. Geograp. 26, 40–60. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2005.07.005
Khan, N., Akram, M., Pervaiz, U., and Jan, I. (2009). Impact of education on diffusion of dates palm orchards in Northwest Pakistan. Sarhad J. Agric. 25, 495–500.
Khosravi, S., and Robati, A. (2025). Groundwater level simulation using hybrid model. Int. J. Agric. Biosci. 14, 424–435. doi: 10.47278/journal.ijab/2025.024
Koundouri, P., Nauges, C., and Tzouvelekas, V. (2006). Technology adoption under production uncertainty: theory and application to irrigation technology. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 88, 657–670. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8276.2006.00886.x
Lootsma, A. (2022). Foreword from Resident Representative United Nations Development Program (UNDP) Yemen. A Holistic Approach to Addressing Water Resources Challenges in Yemen UNDP Strategic Framework. Available online at: https://www.undp.org/sites/g/files/zskgke326/files/2022-11/2022%20Nov%20Water%20Resources%20Challenges%20in%20Yemen.pdf (accessed January 20, 2025).
Maru, C., Trivedi, S., and Lakhlani, C. (2022). Awareness and adoption level of farmers for sprinkler irrigation system. Int. J. Sci. Env. 8, 1208–1214.
Mccracken, M. (2012). The impact of the water footprint of Qat on Yemen's water resources. (Master's thesis). School of International Development, University of East Anglia, Norwich, England.
Min, Q., Ji, S., and Qu, G. (2008). Mobile commerce user acceptance study in China: a revised UTAUT model. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 13, 257–264. doi: 10.1016/S1007-0214(08)70042-7
Nahayo, A., Omondi, M. O., Zhang, X.-H., Li, L.-Q., Pan, G.-X., and Joseph, S. (2017). Factors influencing farmers' participation in crop intensification program in Rwanda. J. Integr. Agric. 16, 1406–1416. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61555-1
NWSSIP (2008). National water sector strategy and investment programme, 2005–2009 Republic of Yemen. Ministry of Water and Environment Final draft 17 December.
Prochaska, J. O., Diclemente, C. C., and Norcross, J. C. (1997). “In search of how people change: applications to addictive behaviors,” in Addictive Behaviors: Readings on Etiology, Prevention, and Treatment, eds. G. A. Marlatt and G. R. VandenBos (American Psychological Association), 671–696. doi: 10.1037/10248-026
Programme, U. N. D. (2024). Building Resilience: Supporting Farmers to Face the Impact of Climate Change in Yemen, FSRRP Interventions Transform Agricultural Production in Yemen. Available online at: https://www.undp.org/arab-states/stories/building-resilience-supporting-farmers-face-impact-climate-change-yemen (accessed December 30, 2024).
Rezaei-Moghaddam, K., Karami, E., and Gibson, J. (2005). Conceptualizing sustainable agriculture: Iran as an illustrative case. J. Sustain. Agric. 27, 25–56. doi: 10.1300/J064v27n03_04
Rezaei-Moghaddam, K., and Salehi, S. (2010). Agricultural specialists' intention toward precision agriculture technologies: integrating innovation characteristics to technology acceptance model. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 5, 1191–1199.
Risha, M. A. (2016). Farmer's adoption of drip irrigation system in Bahariya Oasis. Egypt. J. Desert Res. 66, 405–423. doi: 10.21608/ejdr.2016.29646
Rogers, E. M., Singhal, A., and Quinlan, M. M. (2014). “Diffusion of innovations,” in An Integrated Approach to Communication Theory and Research (Mahway, MJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates).
Salazar, C., and Rand, J. (2016). Production risk and adoption of irrigation technology: evidence from small-scale farmers in Chile. Latin Am. Econ. Rev. 25, 1–37. doi: 10.1007/s40503-016-0032-3
Savari, M., Eskandari Damaneh, H., and Eskandari Damaneh, H. (2023). The effect of social capital in mitigating drought impacts and improving livability of Iranian rural households. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 89:103630. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.103630
Scheierling, S. M., Young, R. A., and Cardon, G. E. (2006). Public subsidies for water-conserving irrigation investments: hydrologic, agronomic, and economic assessment. Water Resour. Res. 42. doi: 10.1029/2004WR003809
Schmitt, N. (1996). Uses and abuses of coefficient alpha. Psychol. Assess. 8:350. doi: 10.1037//1040-3590.8.4.350
Schoengold, K., and Zilberman, D. (2007). “Chapter 58 the economics of water, irrigation, and development,” in Handbook of Agricultural Economics, eds. R. Evenson and P. Pingali (Elsevier), 2933–2977.
Sulemana, I., and James, H. S. Jr. (2014). Farmer identity, ethical attitudes and environmental practices. Ecol. Econ. 98, 49–61. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2013.12.011
Taylor, J. G., Stewart, T. R., and Downton, M. (1988). Perceptions of drought in the Ogallala aquifer region. Environ. Behav. 20, 150–175. doi: 10.1177/0013916588202002
Thomas, E. (2022b). Food Security in Yemen: The Role of the Private Sector in Promoting Domestic Food Production. London: ODI. Available online at: www.odi.org/en/publications/food-security-in-yemen/
Tohidyan Far, S., and Rezaei Moghaddam, K. (2015). Attitudes of farmers toward participation in irrigation and drainage projects: the structural equations modeling analysis. Iran Agric. Res. 34, 80–91. doi: 10.22099/iar.2015.3085
UNDP (2021). Water Availability in Yemen. Literature Review of the Current and Future Water Resources and Water Demand in Yemen. Final Report.
UNDP (2022). A Holistic Approach to Addressing Water Resources Challenges in Yemen. UNDP Strategic Framework. Available online at: https://www.undp.org/yemen/publications/strategic-framework-holistic-approach-addressing-water-resources-challenges-yemen
Van Rijn, F., Bulte, E., and Adekunle, A. (2012). Social capital and agricultural innovation in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agric. Syst. 108, 112–122. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2011.12.003
Wang, J., Liu, L., Zhao, K., and Wen, Q. (2023). Farmers' adoption intentions of water-saving agriculture under the risks of frequent irrigation-induced landslides. Clim. Risk Manag. 39:100484. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2023.100484
Yazdanpanah, M., Klein, K., Zobeidi, T., Sieber, S., and Löhr, K. (2022). Why have economic incentives failed to convince farmers to adopt drip irrigation in southwestern Iran? Sustainability 14:2055. doi: 10.3390/su14042055
YSEU (2021). “Yemen Socio-Economic Update, Agriculture in Yemen - The Key for Future Food and Social Security,” in ed. M. O. P. A. I. C. E. S. F. Sector.
Zeitoun, M., Allan, T., Al Aulaqi, N., Jabarin, A., and Laamrani, H. (2012). Water demand management in Yemen and Jordan: addressing power and interests. Geogr. J. 178, 54–66. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4959.2011.00420.x
Keywords: modern irrigation systems, mango growers, attitudes, water resources, extension plans
Citation: Dabiah AT, Hasan Herab A, Alotibi YS, Shaman Alfridi J and Muddassir M (2025) Farmers' attitudes toward modern irrigation systems: a case study of the Republic of Yemen. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1556204. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1556204
Received: 06 January 2025; Accepted: 20 May 2025;
Published: 02 July 2025.
Edited by:
Weiping Chen, Renmin University of China, ChinaReviewed by:
Muhammad Mubashar Zafar, Hainan University, ChinaHina Firdous, Northwest University, China
Copyright © 2025 Dabiah, Hasan Herab, Alotibi, Shaman Alfridi and Muddassir. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdulaziz Thabet Dabiah, YWRhYmlhaEBrc3UuZWR1LnNh; Muhammad Muddassir, bXJhanBvb3RAa3N1LmVkdS5zYQ==
 Abdulaziz Thabet Dabiah*
Abdulaziz Thabet Dabiah* Ahmed Hasan Herab
Ahmed Hasan Herab Muhammad Muddassir
Muhammad Muddassir