- Department of Agricultural Extension and Education, School of Agriculture, Shiraz University, Shiraz, Iran
General objective of this paper is to develop a methodological approach for comparing and selecting agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks introduced by scholars. Several sub-objectives have been considered, including “identifying and explaining holistic agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks,” “identifying and explaining comparison criteria of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks,” “scoring agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to comparison criteria,” “evaluation of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to comparison criteria,” and finally, “selection of the most appropriate framework.” The results of prioritization and comparison of the frameworks on the basis of comparison criteria using normalized scores and Analytical Hierarchical Process (AHP) demonstrate that, in general, Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) framework has a higher score than other frameworks. Although the present review shows that MCDA (2.144) has a higher overall score than other frameworks, it does not mean that this framework should be considered as one-size-fits-all framework in the field of agricultural sustainability assessment since other methods also have high scores in some (normative, systemic, and procedural) dimensions. For example, Farm-Level Indicators on New Topics (0.351), Sustainability Solution Space (0.351), and Sustainability Assessment of Farming and the Environment (0.267) frameworks have obtained high scores in systemic dimension. Similarly, Ecological Footprint Tool (0.699), Life Cycle Assessment Tool (0.684), and System Dynamic Simulation Tool (0.671) have obtained remarkable scores in the normative dimension, indicating the potential capacity of these frameworks in agricultural sustainability assessments.
1 Introduction
In a world with constant technological developments, agricultural sector is still a vital source of food for human beings (Bonisoli et al., 2018). Development of agriculture helps countries achieve food and national security, economic growth, environmental and ecological health, intergenerational justice goals, and so on (Bijani et al., 2017). However, problems like droughts, climate changes, greenhouse gas emission, increased rate of planet’s population, political conflicts at international level, and risky and inappropriate agricultural practices have faced people’s health with serious challenges. Consequently, the issue of sustainability of agricultural systems has become the focal point of public concerns (Bonisoli et al., 2018). In this regard, agricultural sustainability and its achievement methods are emphasized by international organizations (including Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, World Bank, European Union, and so on) and academics.
Nevertheless, in spite of the widespread agreement on its importance, agricultural sustainability lacks a consensus on both its concept/definition and measurement (Binder et al., 2010; Sinisterra-Solís et al., 2024). Thus, agricultural sustainability experts provide a variety of definitions for this concept, such that some authors doubt the actual usefulness of this concept (Hayati, 2017; Bonisoli et al., 2018; Hansen, 1996). Given the urgent need for agricultural sustainability around the world, developing comprehensive responses to understand the complexities of social, economic, and ecological sustainability seems to be a necessity (Godfray et al., 2010). Although the assessment framework cannot consider all the systemic complexities of agricultural sustainability, it is an invaluable action since it uplifts the horizons of decision-makers beyond crop productivity to include issues of human wellbeing and ecological soundness (Pope et al., 2004; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Measuring agricultural sustainability using assessment indicators is valued in several respects: (1) it develops the discourse of sustainability in practice by measuring sustainability in terms of inputs’ application (Rigby et al., 2001; Hayati et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2024); (2) it increases understanding about the nature of indicators and need for them (de Olde et al., 2016a); (3) it enforces researchers, program planners, decision-makers, farmers, and other stakeholders to be able to deal more practically with the design and validation of indicators in action (Hayati, 2017; Rigby et al., 2001) and this mandatory success leads to more learning and extension of the boundaries of knowledge; and (4) it should be noted that agricultural sustainability assessment can result in appropriate decision-makings by policy-makers (Gasparatos, 2010; Marchand et al., 2014; Hayati, 2017; Benayad et al., 2024). Agricultural sustainability assessment is of significant function in developing the concept of sustainable agricultural systems (Astier et al., 2012). This is because it integrates agricultural sustainability issues in agricultural policy planning and decision making. The main goal of agricultural sustainability assessment is to offer decision-makers an evaluation framework to help determine which practices must or must not be taken (Ness et al., 2007) in an effort to move toward sustainability of agricultural sector (Pope et al., 2004; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Diverse agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks have been presented by researchers and organizations in recent decades (Binder et al., 2010; Schader et al., 2014; de Olde et al., 2016b; Grigoroudis et al., 2024; Abed et al., 2025). These frameworks vary extensively in geographical area, target group, selected indicators, aggregation and weighting methods, and the time required for implementation (Marchand et al., 2014; Schader et al., 2014). Agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks are mainly focused on goals such as research and policy advising, farm monitoring, farm extension, certification, self-assessment, landscape planning, and consumer information (Schader et al., 2014). Although these frameworks differ in terms of their approaches, there is a lack of methodology to enable users to formalize and compare these approaches.
Literature review on agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks reveals that many observers stress the importance of environmental and economic dimensions in sustainability assessment frameworks, but social dimension is usually being overlooked (de Olde et al., 2016b; Binder et al., 2010; Finkbeiner et al., 2010; Lebacq et al., 2013; Marta-Costa and Silva, 2013; Schader et al., 2014). One of the most important reasons for overlooking social dimension stems from the toughness and complexity of dealing with this aspect (Hayati, 2017; de Olde et al., 2016a). Despite the fact that there is still no agreement on the concept of sustainable agriculture, there is a facet commonly pointed out, which is its multiple-dimensional characteristic, including economic, environmental and social aspects (Conway, 1994). This facet reflects that three dimensions of agricultural sustainability (social, economic, and environmental) should be considered in each study addressing agricultural sustainability assessment (Pretty and Hine, 2000). A sustainable farm should fulfill both economic and environmental goals without turning blind eye to social aspects, such as household’s quality of life, human health, relationship with community, farmer’s education and skills, and etc. (Gafsi et al., 2006). According to Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017) and Gafsi et al. (2006), this approach is entitled as “integrative and/or holistic approach.”
As it was mentioned earlier, scholars have constructed various frameworks for measuring agricultural sustainability (Marchand et al., 2014; de Olde et al., 2017; Aghbashlo et al., 2022; Silvestri et al., 2022; Hu et al., 2022; Merheb et al., 2024; Wolcott and Thornsbury, 2025; Kaewchutima et al., 2025). In spite of the fact that development of such frameworks has so many advantages (the most important ones listed in previous paragraphs), “the diversity” of developed tools is really confusing for end-users (e.g., researchers, experts, farmers, practitioners, organizations, and so on) (Valizadeh and Hayati, 2021). In other words, the diversity of tools has hampered the selection of appropriate indicators, accurate measurement of sustainability, and agricultural policy decisions (Alaoui et al., 2022). Since different frameworks use different individual indicators, methodologies, weighing systems, normalization methods, aggregation approaches, stability analysis methods, and so on (Aghbashlo et al., 2022). Therefore, it is not possible to use all of frameworks simultaneously to develop sustainable agricultural assessment indices. In addition, combining them with each other is often not feasible and there should be practical and accurate criteria and steps for comparing and selecting the best agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. Therefore, the lack of a standard methodological approach for comparison and selection of the best frameworks for assessing agricultural sustainability is introduced as the first motivation of present study. This study tries to respond to this challenge by developing and introducing a methodological approach for comparison and selection of the best frameworks. The second motivation for the present study was that very little research (Marchand et al., 2014; de Olde et al., 2016b; Sabiha et al., 2016; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017; Bonisoli et al., 2018) has been done in this area. Through filling this research gap, present study will prevent the users from randomly choosing agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. In other words, they will choose the best framework for their work more consciously. Also, by introducing the comparison and selection methodology for the sustainability assessment of agricultural practices, present study provides a basis for studies whose results are based on more scientific methods. This also makes the results of researchers and studies more reliable. As it was mentioned, very limited studies have been done on the comparison and selection of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks and the focus of analyses and comparisons in the most of these studies was on limited number of tools/frameworks. Addressing this gap was the third motivation of present study. Present study responds to this challenge by incorporating 18 agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. The fourth motivation for the present study was that most of the studies on agricultural sustainability assessment do not provide logical justification or reason for inclusion of given frameworks/exclusion of other frameworks. This systematic review tried to bridge these gaps in the present literature and provide a guideline for users of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks to be able to analyze them from a simple, operational, and objective point of view and finally select a suitable agricultural sustainability assessment framework.
Therefore, 18 holistic agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks are compared, showing diversity of their application and construction. The main reason for choosing those frameworks for comparison was that they have applied Triple Bottom Line Approach of agricultural sustainability. Moreover, there are some other frameworks examining three dimensions of sustainability or have the potential to do so, but since they have not yet been practically applied in the field of agriculture, they were left out of the analysis. More importantly, many of one-dimensional or two-dimensional frameworks (addressing one and/or two dimensions of agricultural sustainability) were also excluded from the analysis. The main objective of this review was to provide a simple and practical guide to answer this question: “How and why should we select a specific agricultural sustainability assessment framework from among a list of frameworks.” Five sub-objectives were determined to achieve this main objective:
1. Identifying and explaining holistic agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks;
2. Identifying and explaining comparison criteria of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks;
3. Scoring agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to comparison criteria;
4. Evaluating agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to comparison criteria, and
5. Selecting the most appropriate framework.
2 Research methodology
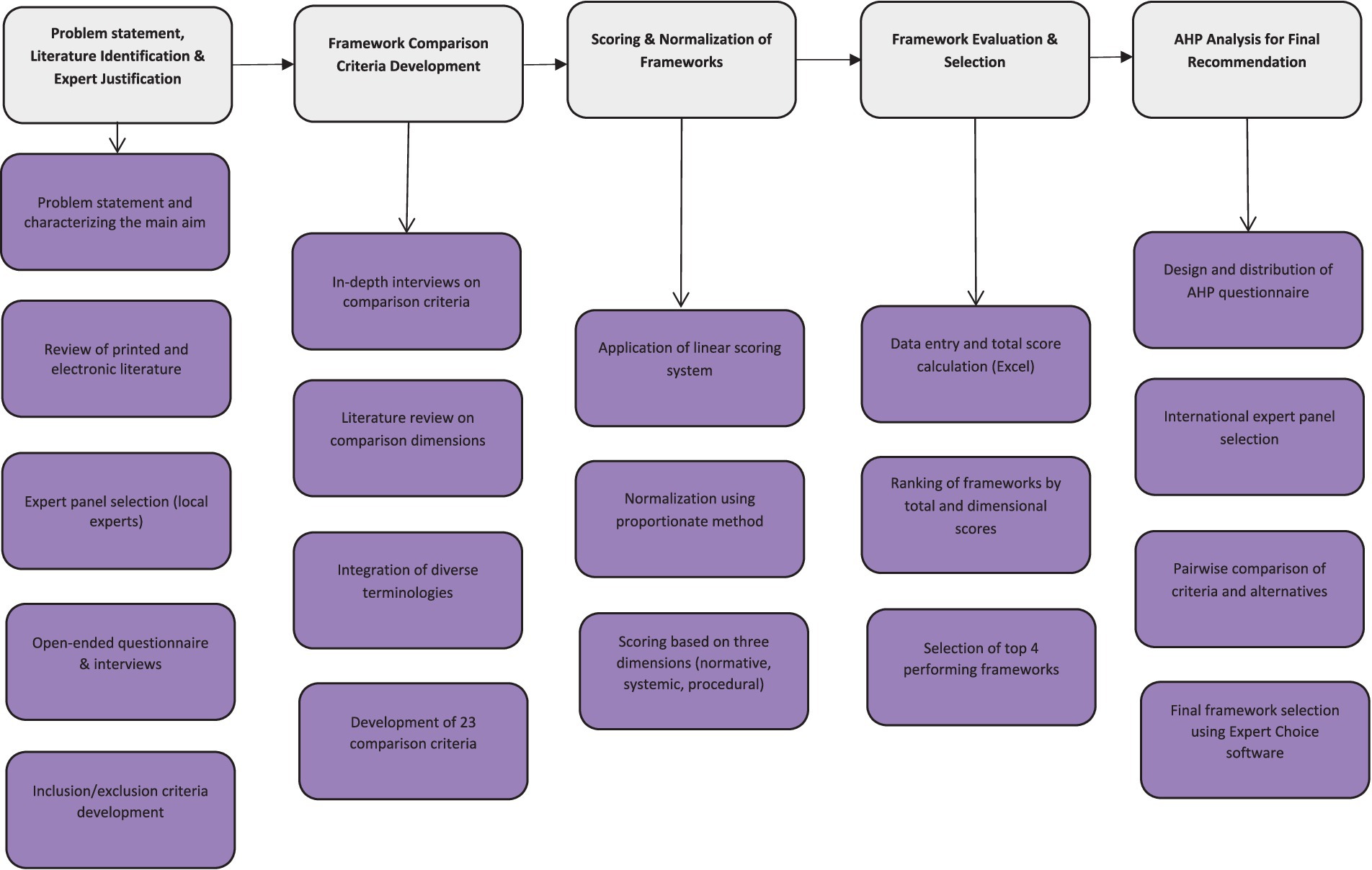
According to the sub-objectives, a five-step process was used for this review. In the first step, printed and electronic literature was reviewed to identify agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. However, due to the large number of frameworks in the literature, a panel of experts was used to determine the justifications for inclusion/exclusion of the frameworks. To this end, an open-ended questionnaire and some in-depth interviews were employed. All participants were experts in agricultural sustainability and sustainability assessment. They were either faculty member of Shiraz University, which is the most remarkable university in southern part of Iran, or faculty member and/or expert in Agriculture and Natural Resources Research and Education Center and Agricultural Organization of Fars province. There were some reasons for selecting the samples from Shiraz University, Agriculture and Natural Resources Research and Education Center, and Agricultural Organization of Fars province. First, present research was part of a Ph. D dissertation conducted in Fars province. Therefore, in order to contextualize the framework with local conditions and identify the local indicators (which were suitable for measuring agricultural sustainability in Fars province), the research team decided to use only the experts of Fars province. Second, given that in phases 1 and 2 mainly in-depth interviews had to be used and this also required inter-organizational coordination and a long time to do the work, collection of information using EMAIL from all over the country was not possible. The limitations related to the financial support was the third important reason that led researchers to use only experts from Fars province to collect the required information in phases 1–2. However, in order to overcome this limitation, an attempt was made to study and cite research papers and articles published by experts from other Iranian universities so that the review reflects their ideas. Snow-ball sampling method was used to select the participants. Therefore, sampling continued until a consensus emerged toward justifications for inclusion/exclusion of the frameworks. The outputs of these interviews resulted in five justifications that will be fully described in the first phase. Subsequently, literature on agricultural sustainability assessment was examined based on these justifications. Due to the fact that different terms, including methods, methodological approaches, frameworks, tools, indices, and so on are being used for describing agricultural sustainability in the literature (Marchand et al., 2014; Schader et al., 2014; Schindler et al., 2015), all these keywords were employed for searching. Search for agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks was fulfilled using Scopus, Google Scholar, Springer and Kluwer, ScienceDirect: Elsevier, Taylor and Francis, Wiley InterScience, Nature, and ProQuest search engines. In the end, 18 agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks were extracted for comparison in next steps.
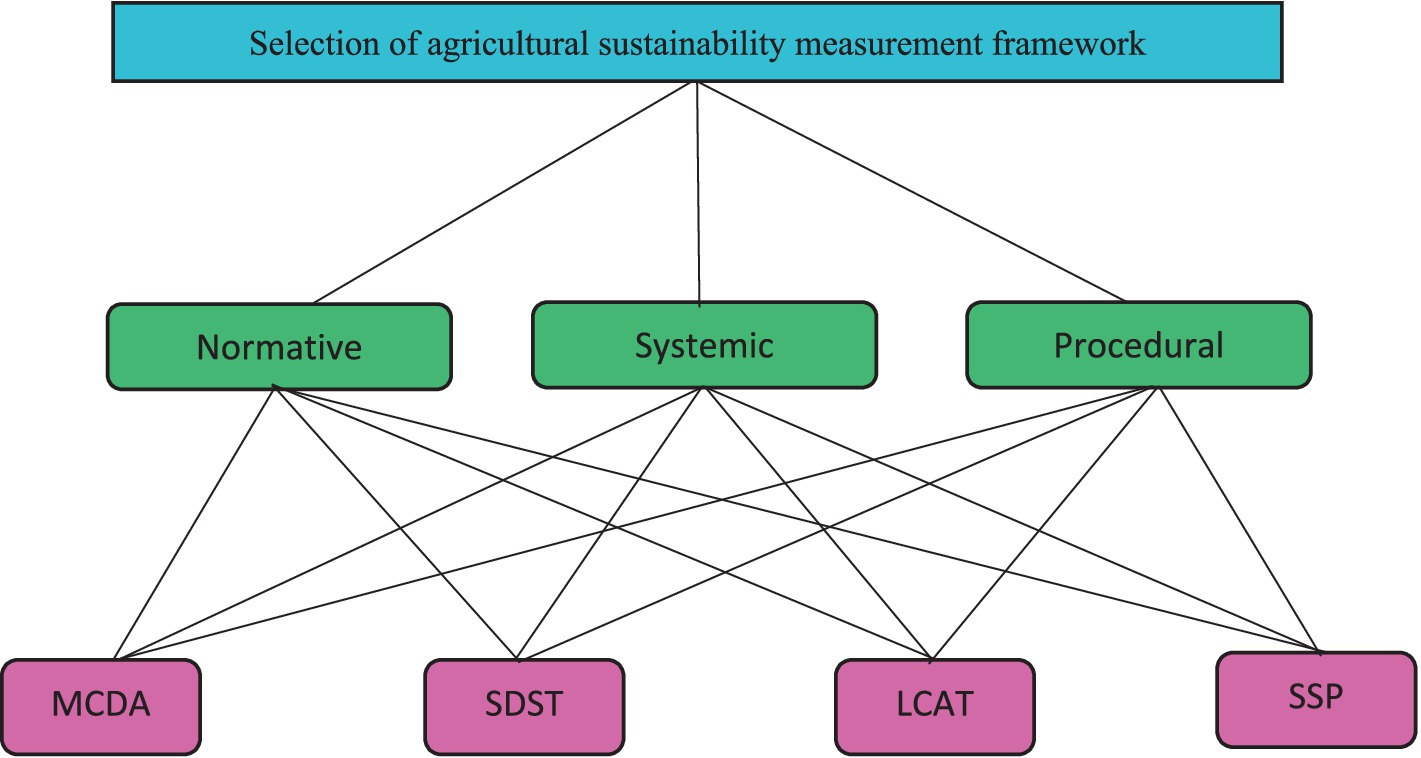
In the second step, several in-depth interviews were carried out with the same sustainability assessment and sustainable agriculture experts (who were interviewed in first step) in order to address the second study sub-objective. Similar to the first step, the selection of these experts was done using snowball sampling method. Sample selection continued until emerging theoretical saturation on comparison criteria. In addition, available printed and electronic literature on comparison criteria of frameworks and indicators of agricultural sustainability were reviewed in order to complete the missing data at this stage. Again, similar to the first step, regarding that diverse terminologies had been used for comparison criteria in literature, a consolidation or integration process was applied. Finally, 23 comparison criteria were generated. These criteria were then divided into three normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions.
In the third step, a linear scoring system was used for comparison of sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to criteria. This scoring system was first developed by Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017) and we have used some scores of this study in our work. Then, the scores of frameworks were normalized by proportionate method with respect to the comparison criteria. Scoring and normalization processes will be completely explained in the third phase.
In the fourth step, the normalized scores of the agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks were introduced into Excel software. In addition, the total scores of each framework were calculated based on the comparison criteria. Also, the scores of all frameworks were calculated based on normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions. Finally, all agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks were compared with each other according to their total scores in order to identify the best framework(s). Four agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with the highest normalized scores in the normative, procedural and systemic dimensions were selected as final recommended methods for measuring agricultural sustainability.
In the fifth step, an Analytical hierarchical Process (AHP) was carried out to introduce a suitable agricultural sustainability assessment method. The objective of hierarchical analysis was to introduce the most appropriate method for measuring agricultural sustainability using experts’ judgment in the field of agricultural sustainability assessment. To this end, a questionnaire was developed, which included pair comparisons of criteria (normative, systemic, and procedural), alternatives (four sustainability methods that obtained the highest scores in the previous step), and the priority of alternatives with respect to criteria. Regarding that AHP is an expert-oriented method and all experts should have expertise in the field of the subject being explored, an international panel of experts was used in this step. The reason to do so was that experts should have extensive familiarity with all alternative and criteria being used in AHP. None of Iranian experts have the experience of applying all four sustainability assessment frameworks in their studies. Accordingly, the questionnaires were sent to 18 international experts, who had publications on the application of four sustainability assessment frameworks. Nine of them filled and returned the questionnaire. Their judgments on agricultural sustainability assessment were analyzed using Expert Choice (EC) software, which is a decision analysis tool. Before performing paired comparisons, the instructions for performing pair comparisons were given to all respondents with respect to the general goal. Their judgments about the importance of a criterion over another were carried out using a 1–9 scale (1: equal importance, 3: weak importance of one over another, 5: strong importance, 6: demonstrated importance, 9: absolute importance, and 2, 4, 6, and 8: intermediate values between two adjacent judgments). Details of the analysis will be given in the fifth phase. Figure 1 shows the procedure of the study.
3 Phase 1: identifying and explaining holistic agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks
Phase 1 was conducted to achieve the first sub-objective. In this phase, agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks existing in academic and international literature were studied and analyzed. Finally, 18 sustainability assessment frameworks were included in the analysis. As it was stated before, most agricultural sustainability studies do not offer clear and reasonable justifications for the inclusion/exclusion of sustainability frameworks (screening process) in their analysis. To fill this gap, after identifying a raw list of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks, some face-to-face interviews were carried out with a panel of sustainability assessment and sustainable agriculture experts in Fars Province, Iran. The results of this interviews set a ground for screening process (justifying the exclusion/inclusion of frameworks). Summarizing these results led to some general criteria and justifications, which were applied for screening the agricultural sustainability frameworks:
1. Regarding that the Triple Bottom Line Approach/holistic approach of agricultural sustainability is almost agreed by most experts, the given framework should focus on three dimensions of agricultural sustainability.
2. Apart from considering the three dimensions of sustainability (potential to be holistic), the given framework should also have actual/in-action ability to measure agricultural sustainability using the triple bottom line approach. This feature reflects the applicability of framework. Existence of at least one study practically applying these dimensions and the given framework was used as a basis for the inclusion/exclusion.
3. To ensure scientific rigor, the frameworks have to be published in a peer-reviewed scientific journal and/or peer-reviewed technical/scientific report.
4. The paper or report has to be written by a tool developer. Therefore, the frameworks that had been published in review works without providing details of framework development were excluded from the analysis.
5. The framework has to have at least one record of application in the field of agriculture. The panel of experts believed that this screening criteria decreases complexity of application and increases feasibility. In other words, they believed that implementation and operationalization of the framework that has been applied in previous agricultural studies is easier than a framework that has been used in a non-agricultural sector (like industry). Furthermore, such frameworks can reflect the reality of agricultural sector more appropriately.
Eighteen frameworks were identified for comparison in the next phase. Their full name, short description of features, and some other information were provided in Table 1.
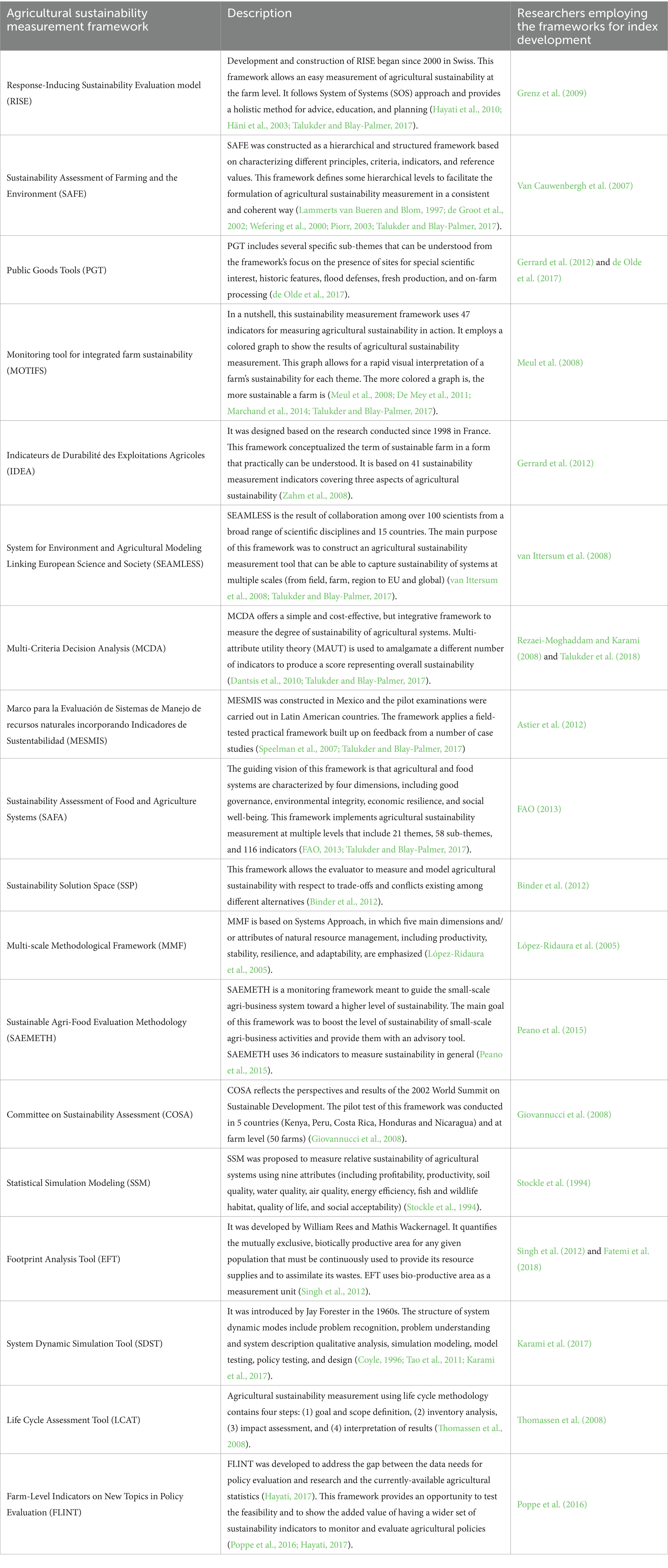
Table 1. The main agricultural sustainability measurement frameworks and researchers employing these frameworks for index development.
It is worth mentioning that some sustainable agricultural assessment frameworks, such as the Life Cycle Assessment Tool (LCAT) and Response-Inducing Sustainability Evaluation model (RISE), have been developed “basically” for environmental purposes. However, according to some studies (see Häni et al., 2003; Grenz et al., 2009; Zamagni et al., 2015; De Luca et al., 2017; Petit et al., 2018), these frameworks are not merely used for environmental sustainability assessments. For example, some researchers (see De Luca et al., 2017; Petit et al., 2018) have recently used the LCAT to measure the three dimensions of agricultural sustainability. The researchers claim that one of the weaknesses of most LCAT-based research is that it focuses mainly on the environmental dimension. In this regard, they have extended the LCAT to include the social and economic dimensions. In addition, according to Häni et al. (2003) and de Olde et al. (2016b), RISE is considered as an integrated framework that considers the three dimensions of social, economic, and environmental dimensions. The researchers believe that using a framework (such as RISE) to analyze environmental dimensions does not mean the “inability” of this framework to consider the three dimensions of sustainability. This was a point that the panel of experts also emphasized, stating that RISE is one of the frameworks mainly used for environmental purposes, but it “can” consider the three dimensions of agricultural sustainability.
It should also be noted that the list provided for agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks in this review does not represent all the frameworks in the literature. For example, the agro-ecosystem health framework was one of the frameworks of the initial list extracted from the literature. However, according to the panel of experts, since this framework is generally focused on the environmental and economic dimensions (it was left out of the analysis). In other words, as mentioned earlier, one of the criteria in screening the extensive list of frameworks extracted from the literature was the consideration of three dimensions of agricultural sustainability.” However, the agro-ecosystem health framework mainly focuses on the environmental and economic dimensions and does not consider the social dimensions. Therefore, based on the recommendation of the panel of experts, it was excluded in the initial screening process. But this does not diminish their importance in the agricultural sustainability literature.
In the initial list extracted from the literature, there were other agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks such as participatory frameworks (see Videira et al., 2010; Xavier et al., 2020; Galván-Martínez et al., 2020). However, they were not included in the final list introduced in this phase. Since according to panel of experts, considering Approach, the ability to measure sustainability in action, publication in a peer-reviewed scientific journal/report, development by a tool developer, and record of application in the field of agriculture were introduced as the most important screening criteria. In other words, the panel did not identify “stakeholders’ participation” as a criterion for inclusion or exclusion of the frameworks. Experts believed that stakeholders’ participation could not be considered as a primary screening criterion for frameworks. Because they believed that the participation or non-participation of stakeholders in the process of framework development often depends on the attitude of the implementers. That is, the implementers of a so-called non-participatory framework can use the participation of different stakeholders if they wish. However, the “stakeholder participation” in the second phase, which was related to the identification of comparison criteria, has been considered.
4 Phase 2: identifying and explaining comparison criteria of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks
This phase was conducted to fulfill the second sub-objective of this review. In this process, two information sources were simultaneously employed. The first information source was sustainable and agricultural sustainability specialists’ opinions in Fars Province, Iran. An open-ended questionnaire was employed in this step. Through some face-to-face in-depth interviews, the respondents were asked to list the criteria of a good sustainability assessment framework. The second information source was literature. In this step, a wide range of printed and electronic sources published in the context of measuring agricultural sustainability was analyzed to identify more criteria.
An important issue about the criteria of a good agricultural sustainability framework is that many of researchers often put less emphasis on them (Meul et al., 2008; Zahm et al., 2008) or ignore these criteria completely (Grenz et al., 2009). This carelessness mainly originates from shallow examination of importance, justification, and reasoning. However, in this review, such criteria are reflected as a key issue in the development of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks as well as comparisons of agricultural sustainability assessment methodologies. This is because they create a link between indicators and the general meaning behind the concept of agricultural sustainability (Bonisoli et al., 2018).
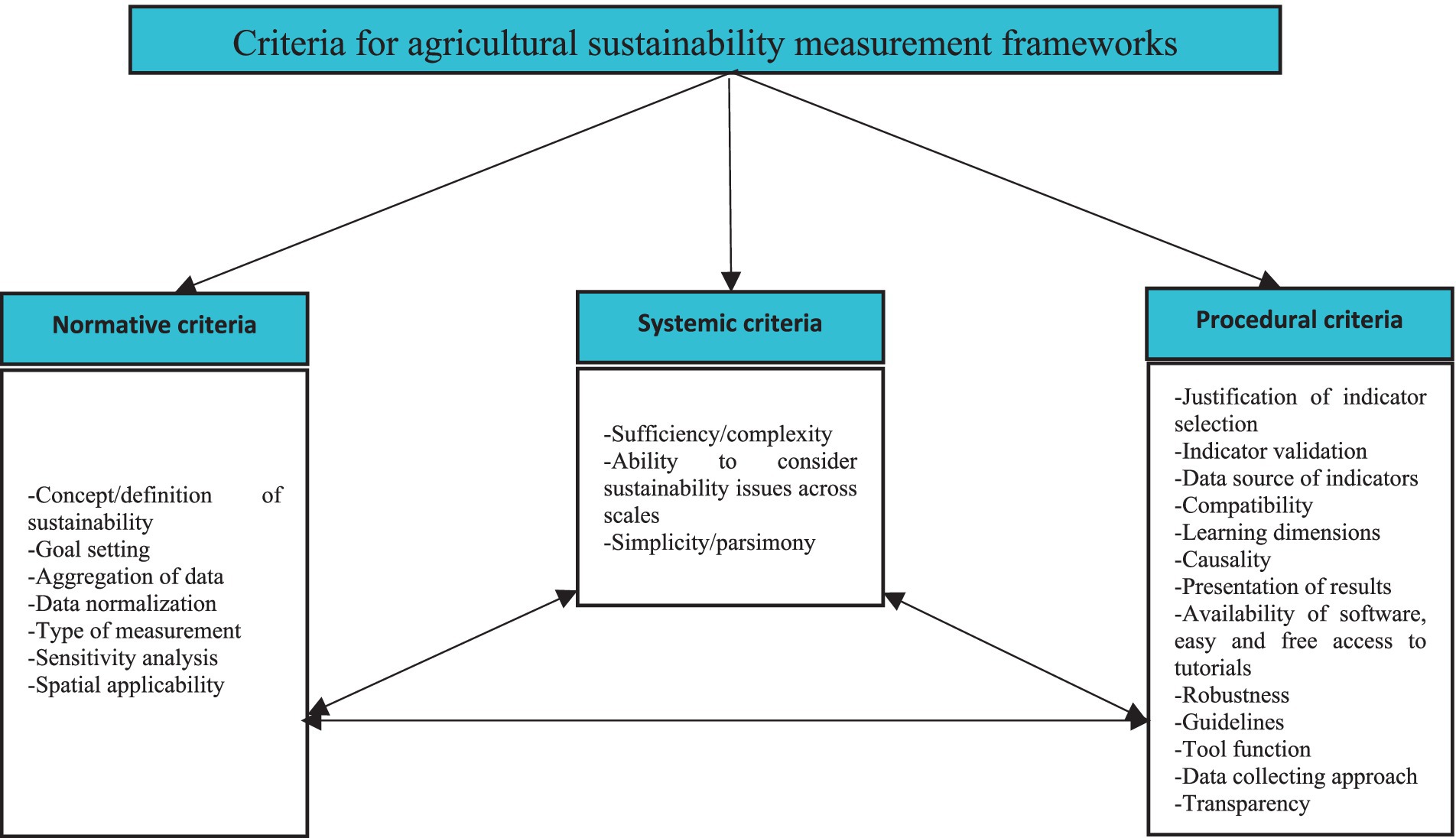
It is worth mentioning that this topic has attracted the attention of some agricultural sustainability researchers in recent years. For example, the study of Binder et al. (2010) is one of the invaluable works in this context. They categorized criteria of agricultural sustainability assessment indicators in normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions. The normative dimension includes criteria like the concept of sustainability, goal setting, and measurement type. On the other hand, systemic dimension is focused on complexity/sufficiency, simplicity/parsimony, and interaction of indicators. Procedural dimension of their framework highlights criteria, like stakeholder involvement, indicator selection, and scale. In general, this study develops and conceptualizes the discourse of agricultural sustainability assessment in a good way. Another notable and really genuine research on criteria development is a recent work by Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017), which properly formulates this knowledge area and makes considerable contributions to the field of criteria development. They divide criteria of agricultural sustainability indicators into two strata, namely, scientific soundness and user-friendliness. However, primary evaluations demonstrate that most scholars addressing criteria for agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks apply Binder et al. categorization (see Bonisoli et al., 2018; Marchand et al., 2014; de Olde et al., 2016b). This is because this framework provides a better understanding of the criteria of sustainability frameworks.
In the present review, the results of face-to-face interviews and literature reviews resulted in a wide range of criteria (over 60 criteria). Regarding the use of different terminologies for each criterion in interviews and literature, a consolidation process was first applied to combine and integrate the vocabulary and set a common language. The reference for consolidation of criteria was Talukder and Blay-Palmer’s work. Regarding that the study of Talukder and Blay-Palmer was so comprehensive in terms of the number comparison criteria, the final names of criteria was mainly selected based on their work. It should be noted that their criteria were adapted to present study and some more criteria were developed for comparison of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. By doing so, 23 criteria were developed for comparing frameworks. Their definitions, justifications, and explanations are highlighted in the following section. In the end, Binder et al. framework was used for simplification of understanding and categorization of comparison criteria (Figure 2).
Normative criteria: This aspect indicates that the agricultural sustainability assessment framework should include a normative guiding concept operationalized in specific targets (Wiek and Binder, 2005). One of the most important challenges in normative dimension is the application of the widely accepted concept of agricultural sustainability to different aspects of an agricultural system (Binder et al., 2010). It should also be mentioned that agricultural sustainability concept used in a framework can have significant effect on the problem and goal orientation (Zahm et al., 2008). Furthermore, these goals and problem orientations can (indirectly) directly influence the agricultural policies and interventions’ direction (de Olde et al., 2016b). Thus, deep understanding of normative dimensions deserves paying more attention if agricultural sustainability assessment is to be beneficial for agricultural development. The concepts of sustainability (Marchand et al., 2014), framework’s function (Schader et al., 2014), methodology used in development of indicator (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017), data aggregation (de Olde et al., 2016b), data normalization (Gómez-Limón and Sanchez-Fernandez, 2010; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017), type of assessment (Bonisoli et al., 2018), and sensitivity analysis (Gómez-Limón and Sanchez-Fernandez, 2010; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017) are considered as the most popular sub-criteria in normative dimension.
The concept of sustainability: Agricultural sustainability assessment heavily depends on the concept or definition of sustainability. The main agricultural sustainability definition can be totally theory-based or developed in an interdisciplinary process, in which, for example, legislative concepts and stakeholders’ opinions can be included (Binder et al., 2012). Most studies use Triple Bottom Line approach or Principles-based approach to measure sustainability. Due to the numerous limitations of Triple Bottom Line Approach, including ambiguity, Principle-based Approach is more suitable for the development of agricultural sustainability concept. A good agricultural sustainability definition can guarantee the selection of the most relevant sustainability indicators and strong agricultural policies (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Methodological approach for the development of indicators/goal setting: This criterion, which is called Goal Setting in some sources (see Bonisoli et al., 2018), defines the methodological approaches in the development of sustainability indicators. Agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks employ top-down, bottom-up, and integrative/trans-disciplinary approaches to develop sustainability indicators (Roy and Chan, 2012). In top-down approach, the goals are predefined and usually theoretically derived from the concept of agricultural sustainability. Bottom-up approach defines indicators and goals by stakeholders in a participatory process. Furthermore, a trans-disciplinary approach integrates bottom-up and top-down approaches (Bonisoli et al., 2018). Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017) claim that sustainability assessment perspective, an approach that derives inputs from both stakeholders and experts, is the most appropriate and effective approach.
Data aggregation: A plethora of aggregation methods does exist and agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks apply one or some of them with respect to their aim, researcher’s creativity, concept of sustainability, and the framework’s target group (Hediger, 1999; Gómez-Limón and Sanchez-Fernandez, 2010). Sustainability assessment frameworks using aggregation methods are extremely beneficial for comparing policy options. This is because they summarize complicated and multi-facet issues of agriculture and offer a holistic picture, without the hazard of information overload. Furthermore, aggregated sustainability assessment frameworks can set the ground for delivering simple massages and running the risk of being misinterpreted (Van Passel and Meul, 2010).
Normalization method: Transforming the base agricultural sustainability assessment indicators into dimensional indicators is a must before aggregation function and makes the indicators mathematically operational (Gómez-Limón and Sanchez-Fernandez, 2010). Most frameworks employ normalization techniques to bring incommensurate indicators into the same scale. However, some of them may not do normalization. Generally speaking, normalization of indicators boosts the reliability of assessment’s results (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Sensitivity analysis: Similar to aggregation and normalization of indicators, there are different methods for sensitivity analysis. This criterion tries to identify the factors that have the most influence on agricultural sustainability (Gómez-Limón and Sanchez-Fernandez, 2010). Regarding that sensitivity analysis helps policy-makers prioritize the agricultural policies by assessing probable options, its consideration in sustainability assessment framework is necessary (Ciuffo et al., 2012).
Spatial applicability: Every agricultural sustainability assessment framework is applicable at least for one spatial scope. Applicability at one, two, and even at more levels depends on factors such as researcher’s opinion, sustainability definition, target group of the framework, and main data sources (de Olde et al., 2016b). The given framework will be much more attractive for decision-makers and policy-makers if it can be implemented at more than one scale (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Type of measurement/Reference values: Reference values reflect the satisfactory level of agricultural sustainability for each assessment indicator (Sauvenier et al., 2006; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017) and sustainability assessment must be based on reference values given or established by research institutions, governmental agencies, experts, and stakeholders (Zhen and Routray, 2003). Reference values can be useful in interpreting the agricultural sustainability indicators’ value and guiding the evolution of the system toward a favorable level defined in the goals of the research. Reference values are requested by stakeholders, because they help interpret the framework’s results (Acosta-Alba and Van der Werf, 2011).
Systemic criteria: According to Wiek and Binder, an agricultural sustainability assessment framework should systemically include a target-related model of system to be assessed (Wiek and Binder, 2005). In general, systemic dimension argues that an agricultural system must be analyzed with as much simplicity as possible and as much complexity as necessary. Simplicity and complexity refer to parsimony and sufficiency, respectively (Bonisoli et al., 2018; Wiek and Binder, 2005). Almost all frameworks introduce these two features as their focal goal since they are trying to provide a framework that is useable by clients. Similarly, due to the fact that the given framework represents a system, it should be able to reflect the systems’ complexity to some extent (de Olde et al., 2016a). In a nutshell, the following sub-criteria were developed to measure the systemic dimension of frameworks.
Simplicity: Simplicity has also been named parsimony in most of the sources (see Binder et al., 2010; Marchand et al., 2014; Bonisoli et al., 2018). Simplicity tries to answer this question: “Is the simplicity of system a representation of the framework objective?” (de Olde et al., 2016b). In other word, simplicity is a crucial factor to achieve an adequate system representation (Marchand et al., 2014). However, it should be noted that a system should not be simplified too much. Because it can undermine the credibility of system.
Complexity: It was mentioned that oversimplification of the system can damage the credibility of system. In this regard, the complexity (sufficiency) of the system should also be considered in its representation. In other word, the indicators and their relations have to reflect the main structures, processes, and functions of social, economic, and ecological aspects of agricultural systems (Binder et al., 2010). Nevertheless, is should not be forgotten that over-complexity of the system can also lead to decrease in user-friendliness of the framework.
Considering sustainability issues across scales: Determining the scale(s) of agricultural sustainability analysis is a significant operation in system boundary definition (Binder et al., 2010). Since agricultural sustainability systems are affected by a range of scales such as farm, local, regional, national, and global scales (Hayati et al., 2010; vanLoon et al., 2005), analyzing agricultural sustainability at only one scale, without paying attention to other scales and their interactions, can be misleading and unrealistic. As a result, considering integration across scales and over the time is of great importance. Large number of policies, management projects, and agricultural sustainability assessment efforts fail because they do not properly consider the issues across scales. Combining sustainability issues across spatial and temporal scales (1 year or a series of years) can help produce a more realistic picture of agricultural sustainability (MEA, 2005; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Procedural criteria: This aspect is mainly focused on the process of conducting assessment endeavor (Marchand et al., 2014). It is believed that the assessment is more likely to produce favorable outcomes if it is developed through a trans-disciplinary approach (Binder et al., 2010; Thompson Klein et al., 2001; Gasparatos et al., 2009). Justification of indicator selection (de Olde et al., 2016b; Binder et al., 2010), data source of indicators (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017), learning dimensions (Binder et al., 2010; Wiek and Binder, 2005), representation of results (Marchand et al., 2014), and so on are among the criteria that can be emphasized in procedural dimension. In sum, the following sub-criteria were developed to measure the procedural dimension of frameworks.
Justification of indicator selection: Providing justification for selection of agricultural sustainability indicators is among the significant requirements of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks (de Olde et al., 2017). Different types of agricultural sustainability assessment indicators are developed using triple bottom line approach, although without an underlying conceptual structure (Van Passel and Meul, 2010; Bonisoli et al., 2018). Regarding that understanding the justifications for indicators’ selection can be really helpful in clarifying their association with agricultural sustainability, the logic of indicators’ selection should be obviously explained in frameworks (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Indicator validation: In general, validation of a framework indicates the extent to which the given framework meets predetermined criteria. However, less effort goes to validation of these sustainability assessment tools (Suresha Adiga et al., 2015; Rigby et al., 2001). Non-validation of a framework can decrease its scientific and practical soundness and user-friendliness. For this reason, every agricultural sustainability assessment framework should be validated in order to identify its strengths and weaknesses.
Data source of indicators: In agricultural sustainability assessment operation, collecting the required data from just one source of information is highly unlikely. In this regard, both primary and secondary sources of information are essential for the development of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks (Gómez-Limón and Sanchez-Fernandez, 2010; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017). The ability to use two sources of information can be considered as a strength for a framework.
Compatibility: This criterion refers to the extent to which the framework is compatible with existing data systems. In other words, an agricultural sustainability assessment framework enjoys compatibility feature if it is fitted into the existing data sources of the system (de Olde et al., 2016b). Compatibility of sustainability assessment frameworks is heavily dependent on required quality of data. However, this feature is among the key comparison criteria of the frameworks.
Learning dimensions: Providing opportunities for communication and learning in the development of a framework is of paramount significance (Marchand et al., 2014). The level of learning and knowledge-sharing depends on methodological approach, function, target group, and sustainability concept of the framework. However, using an agricultural sustainability assessment framework itself is a learning experience. This is because it tackles with many issues (vanLoon et al., 2005). Framework’s focus on addressing the gap in sustainability assessment and demonstrating a straightforward way toward application of the research results is of great significance (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Causality: Causality refers to clear and explicit relationship between an agricultural sustainability indicator and the phenomenon being monitored (sustainability of agriculture) (Bonisoli et al., 2018; Meul et al., 2008). Comprehensible explanation and analysis of the relationships between agricultural sustainability indicators and agricultural sustainability improves the analytical soundness of framework (Meul et al., 2008).
Result representation: The manner in which the results of agricultural sustainability assessment are presented is a dramatically important factor in the framework’s user-friendliness and applicability (de Olde et al., 2016b). Sustainability assessment frameworks employ different kinds of methods for representing the results. Some of them prefer to use visual and graphical representation and others opt to employ numerical representation. It should be noted that there are also some frameworks that use both visual and numerical representations. Due to the fact that users may prefer a particular type of results, the framework should try to meet their information needs (Van Passel and Meul, 2010). But in general, if the results are presented explicitly and in a multi-perspective manner (both graphically and numerically), the framework will be more appropriate for end-users as well as stakeholders (Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Availability of software, easy and free access to tutorials: One of the main challenges of procedural dimension is availability and access to software and tutorials (de Olde et al., 2016b; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017). Availability of online and user-friendly software and tutorials in multiple languages that can combine and analyze the data is necessary in agricultural sustainability assessment (de Olde et al., 2016b). Frameworks that have these features are usually more popular among scholars, organizations, practitioners, and farmers.
Robustness: It refers to relative insensitiveness against anticipated source of interference (Bonisoli et al., 2018). In other word, an agricultural sustainability assessment framework is robust to uncertainty if, despite high standards of uncertainty in the environmental variables, it can achieve a minimum total value (Levy et al., 2000). This criterion, called “solidness” by some scholars (like Niemeijer and de Groot, 2008), is important in designing agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. Consequently, it is logical to be concurred by Moller and Macleod (2013), who demonstrate that an indicator should have a capacity to be affected by few variables and directly link the measures with the cause of change (Bonisoli et al., 2018).
Guideline: Existence of a specific guideline is essential for implementation phase of agricultural sustainability assessment framework. Lack of such guidelines will reduce the executive guarantee and user-friendliness of the frameworks. Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017) pointed out that provision of guidelines allows users apply the frameworks effectively, helps indicator development process, and aids analysis and production as well as the communication of findings. Guidelines must clearly explain or lay out all the steps.
Tool function: An agricultural sustainability assessment framework can have different functions (Langeveld et al., 2007; Schader et al., 2014). Frameworks can induce managerial responses in the field of agricultural sustainability—Management function (Wiek and Binder, 2005; Grenz et al., 2009). They can also fulfill monitoring obligations for statutory control purposes or for product certification-monitoring and certification function (Hülsbergen, 2003; Rodrigues et al., 2010; Marchand et al., 2014). Knowing whether the framework is a certification procedure or an advisory tool aids communicating the results (Hřebíček et al., 2013; Talukder and Blay-Palmer, 2017).
Data collecting approach: Data collection is a must in agricultural sustainability assessment. Data collection methods include quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods. Each of sustainability assessment methods use different types of data collection approach. However, sustainability assessment scholars believe that mixed methods give more realistic picture of the phenomenon (Karami et al., 2017).
Transparency: It refers to the transparency of the tool’s calculations (de Olde et al., 2016b). The meaning of sustainability assessments and mathematical computations should be easy to seize. Ambiguity in these cases has negative effect on the functioning of the framework in action (Bonisoli et al., 2018; Van Cauwenbergh et al., 2007).
After identifying and explaining comparison criteria of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks and their formulation in normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions (Figure 2), the next step is to calculate the scores of agricultural sustainability frameworks with respect to comparison criteria. For this reason, the following phase reflects the scoring and prioritizing system of the frameworks using comparison criteria.
5 Phase 3: scoring agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to comparison criteria
A purposeful, simple, and linear scoring method was employed to compare the frameworks, criteria and triple-dimensions of evaluation criteria of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks. This scoring method was introduced by Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017) for the first time in agricultural sustainability area. According to Talukder and Blay-Palmer (2017), this scoring method includes 0 = does not exist and 1 = Exists. However, in some cases, depending on the nature and requirements of the desired criterion, a range of 0–3 was also used (see Table 2). To make this process clearer, the scoring method of two criteria is explained. For example, in the case of “goal setting,” it is generally considered best to use top-down and bottom-up approaches simultaneously. In other words, frameworks in which it is possible to use two approaches are considered better than those in which it is possible to use one of the top-down or bottom-up approaches. In this regard, a better score (2) was assigned to the frameworks in which it is possible to use two approaches simultaneously. Meanwhile, the frameworks in which it was possible to use one of the goal setting approaches received a lower score (1). In the frameworks where the possibility of using these approaches was not specified, they received a score of zero. As another example, we can refer to the “data collection approach” criterion. Quantitative and qualitative approaches to data collection are two options that sustainability assessment frameworks can adopt. If a framework allows the user to use two approaches simultaneously, a score of 2 was assigned to it. However, a framework that only allows the use of only one of the approaches was given a score of 1 for it. The method of scoring the rest of the criteria used in this research was similar to this process. The method of scoring each of the criteria is presented in the second column of Table 2.
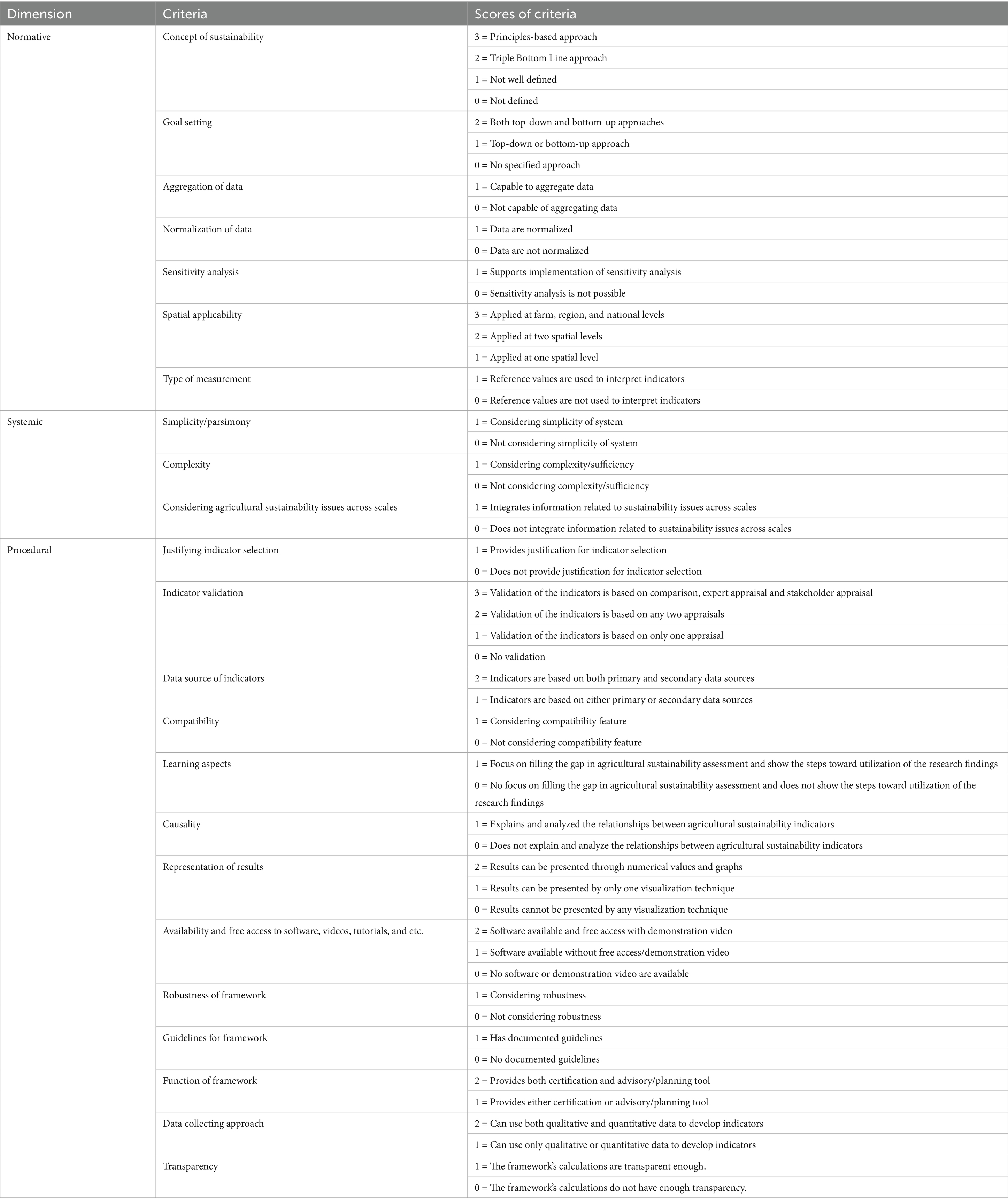
Table 2. Scoring method of criteria and dimensions in agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks.
After specifying numerical values of frameworks in each sub-criteria, the total values of sub-criteria for all framework were calculated by aggregating the scores of individual sub-criteria. Consequently, the values of sub-criteria were normalized using proportionate normalization process (Table 3). The normalization function was carried out by means of Equation 1.
Where:
• N=Proportionate normalization,
• Ci = Criteria value,
• ∑iCi = Sum of criteria values.
6 Phase 4: evaluation of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to normalized comparison criteria
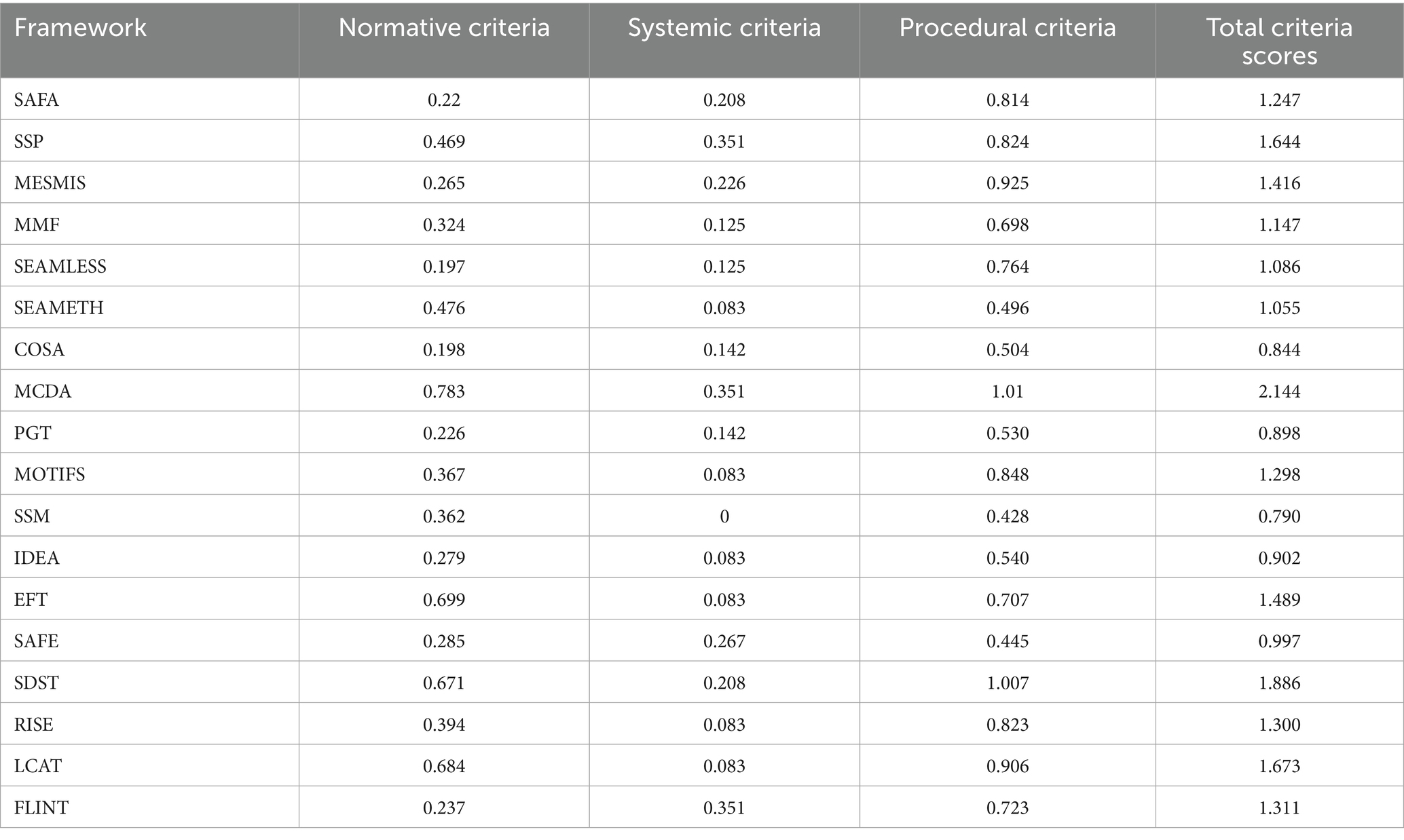
The final normalized total scores for comparison criteria of agricultural sustainability frameworks can be seen in Table 4 and Figures 3A–D. In order to better understand the frameworks’ variations in the first step, the comparison was implemented with respect to normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions. In the second step, the comparison was carried out in general (based on total criteria scores).
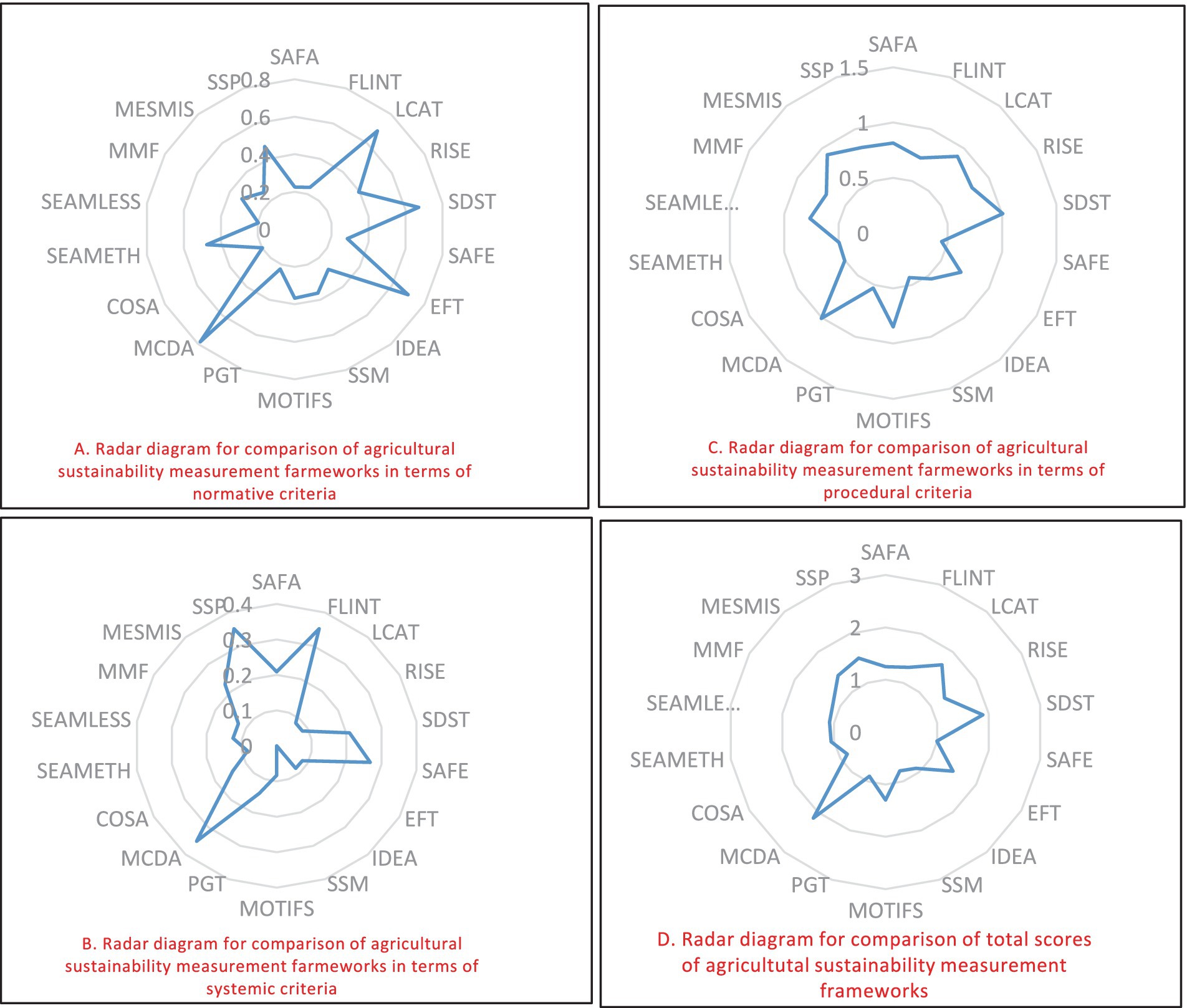
Figure 3. Evaluation of frameworks with respect to normalized normative, procedural, and systemic criteria.
Normative dimension: MCDA, EFT, LCAT, and SDST had the highest scores in normative dimension (Table 4; Figure 3A). One of the most important reasons of this stems from their particular attention to the sensitivity analysis, goal setting, normalization, and aggregation of data. In terms of sustainability definition, EFT used principle-based concept of sustainability and MCDA, LCAT, AND SDST employed Triple Bottom Line approach. In this regard, from among these four frameworks, EFT provides a definition of sustainability that is economically viable, environmentally sound, and socially just.
SAFA, RISE, and IDEA do also apply Principle-based Approach to define agricultural sustainability. However, poor scores in criteria like goal setting, sensitivity analysis, and aggregation of data led to dramatic decrease in their total scores. For SAFA and IDEA, the goal setting action is carried out through a top-down approach following literature and experts.
SEAMLESS, COSA, SAFA, and PGT had the lowest scores in normative dimension. While COSA and PGT put more emphasis on type of assessment and thus, use extensive reference values and data, their definition of agricultural sustainability was not as strong as the concept of sustainability in SAFA and SEAMLESS. Also, the application of normalization and aggregation methods was not clearly characterized in these four frameworks.
Systemic dimension: The systemic dimension in an agricultural sustainability assessment framework provides insights about the translation of the system’s complexity into indicators and supports simplicity, sufficiency, and indicator interaction (de Olde et al., 2016b; Binder et al., 2010). SSP, MCDA, FLINT, and SAFE had the highest total scores in systemic dimension (Table 3; Figure 3B). SSP, MCDA, and FLINT were the only frameworks that considered all three criteria of systemic dimension (parsimony/simplicity, complexity/sufficiency, and consideration of agricultural sustainability assessment issues across scales). Besides, just PGT and COSA focused on simplicity criterion. LCAT, RISE, EFT, IDEA, MOTIFS, and SEAMETH have implicitly turned a blind eye to simplicity and sustainability issues across scales, and merely emphasized complexity. The fact is that SSM was the only agricultural sustainability assessment framework, in which the three criteria of systemic dimension were not mentioned.
Procedural dimension: MCDA, SDST, MESMIS, LCAT, and MOTIFS had the highest total score in procedural aspect (Table 3; Figure 3C). Considering that procedural dimension is mainly related to the process of assessment and implementation of sustainability assessment, it can be deduced that these frameworks provide a better understanding about the implementation and assessment phases. It is also worth mentioning that most user-friendliness criteria are categorized in procedural dimension. Therefore, if a framework has a high total score in procedural dimension, it will be more likely to be used by different potential users.
SSM, SAFE, SEAMETH, COSA, PGT, and IDEA had the lowest scores in procedural dimension. A closer look at the results of this section shows that the low scores of these six frameworks can be explained by their low scores in criteria like justification of indicator selection, validation of indicators, compatibility, causality, robustness, and providing specific guideline for agricultural sustainability measurement. Moreover, all agricultural sustainability measurement frameworks have paid significant attention to the criteria, such as data sources, data collecting approach, learning dimension, function, and presentation of results.
Summation of the scores of normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions resulted in total criteria scores for sustainability frameworks (Table 4; Figure 3D). The comparison of results of this section revealed that MCDA, SDST, LCAT, and SSP have the highest total scores, respectively. On the other hand, SSM, COSA, PGT, IDEA, and SAFE obtained the lowest total scores with respect to 23 criteria.
7 Phase 5: selection of the most appropriate framework
Agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks that obtained a total score higher than 1.5 in the fourth stage (MCDA, SDST, LCAT, and SSP) were selected as the most appropriate frameworks. However, since it is usually impossible to use different frameworks together to measure agricultural sustainability and users generally prefer to use one specific framework or approach, a hierarchical analysis method was employed as a tool for selecting an appropriate agricultural sustainability assessment approach. Hierarchical analysis is a management decision-making technique proposed by Saaty (1988). The hierarchical analysis method based on pair comparison of all alternatives according to decision criteria provides a basis for choosing the best alternative from among all alternatives (Suresha Adiga et al., 2015) (Figure 4).
Application of the hierarchical analysis process requires determining the relative importance of each of the elements in the model. Each criterion of a level is compared with other criteria at the same level and with respect to an element at a higher level. In this review, the experts of agricultural sustainability assessment compared the normative, procedural and systemic criteria with respect to the general goal (selection of appropriate framework for agricultural sustainability assessment). The results showed that procedural criterion had the highest weight (0.635), followed by normative (0.265), and systemic criteria (0.100), respectively. It should be noted that the level of inconsistency in judgments was estimated to be 0.03, indicating acceptability of judgments. The results of this section indicate that from the standpoint of experts, the procedural criterion (incorporating features such as justification of indicator selection, learning dimensions, presentation of results, tool function, data collecting approach, transparency, and etc.) is the most important criterion in selecting the most suitable framework for measuring agricultural sustainability. Comparison of the weights of criteria reflects that after procedural criterion, the normative criterion can be the most important criterion in selecting the most suitable agricultural sustainability assessment framework. However, it is interesting to note that from the point of view of experts, the systemic criterion has the least importance in choosing the appropriate framework for measuring agricultural sustainability. One of the potential reasons of such perceived low importance for systemic dimension can be related to its complexity.
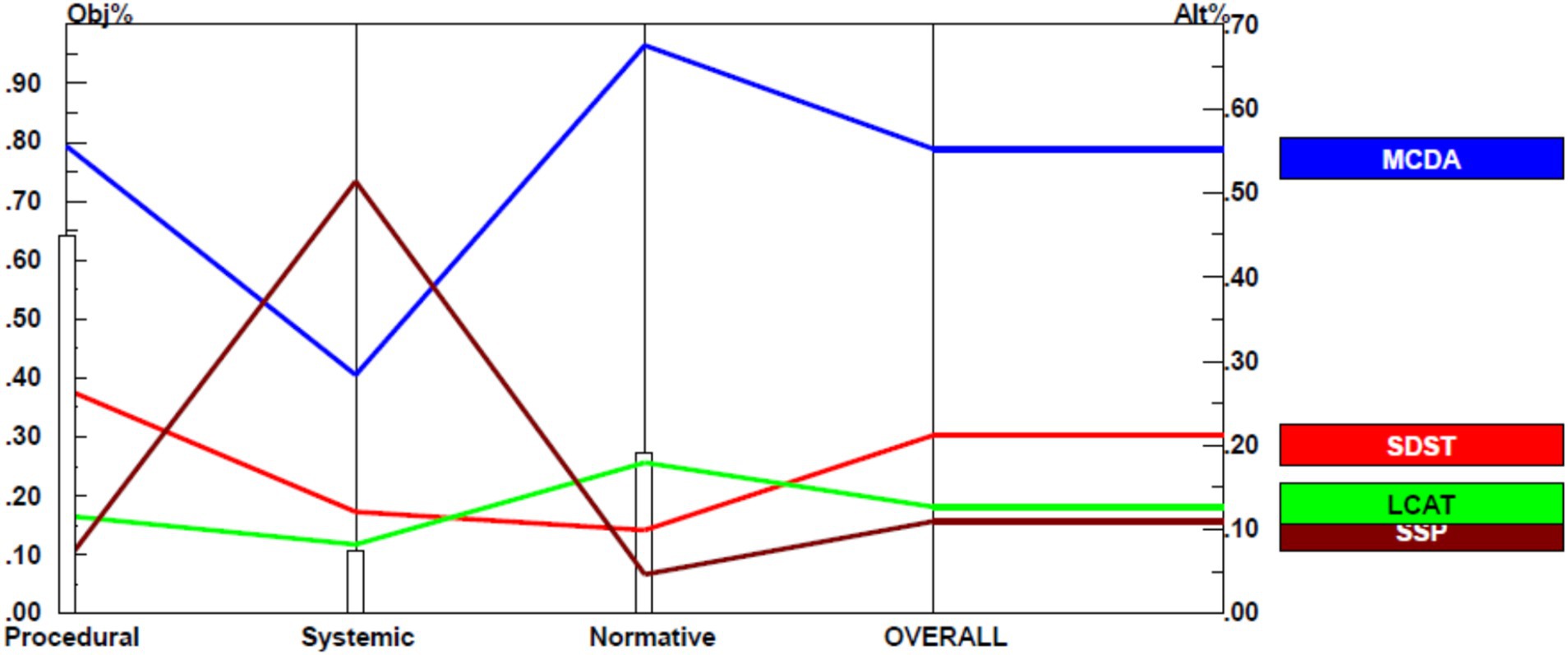
After pair comparison of criteria, the next step was to compare agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks with respect to the criteria. Therefore, paired comparisons were made between the frameworks of agricultural sustainability assessment according to each criterion and the results were summarized in the form of sensitivity analysis (Figure 5). Sensitivity analysis allows researchers to verify the decision results. So, to find out how much alternatives (MCDA, SDST, LCAT, and SSP) are sensitive to changes in weight of the criteria, a sensitivity analysis was performed using the performance method. This analysis was also performed using Expert Choice software. In fact, sensitivity analysis shows the reaction (behavior) of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks (as alternatives) to increase/decrease in the importance (weight) of the criteria.
Figure 5 shows how each alternative is prioritized over other alternatives. This prioritization can be seen for alternatives overall and with respect to each criterion. It is worth mentioning that to see how the best agricultural sustainability assessment framework is compared with other frameworks, the overall priority from the intersection of right y-axis should be used. In this review, MCDA framework (0.552) had the highest priority, followed by SDST (0.212), LCAT (0.127), and SSP (0.110), respectively. In fact, these results show that MCDA is the most appropriate method for measuring agricultural sustainability from the standpoint of agricultural sustainability assessment experts.
8 Conclusion and recommendations
The main goal of this review was to develop a practical and simple guide for choosing a framework from among various sustainability assessment frameworks. The results of prioritization and comparison of the frameworks on the basis of comparison criteria demonstrated that in general, MCDA framework had higher score than other frameworks (see the results of normalized scores in phase 4 and AHP in phase 5). This means that the MCDA-based frameworks are more desirable than other frameworks for measuring agricultural sustainability. One of the main reasons for this is related to their comprehensive consideration and focus on normative, systemic, and procedural dimensions.
MCDA frameworks generally use the concept of Principle-based Approach for defining sustainability in normative dimension and follow an integrative perspective in developing their own indicator since they use both the top-down and the bottom-up approaches. In addition, MCDA agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks enjoy the ability to utilize a variety of methods for aggregation, normalization, and sensitivity analysis, which provide a better understanding of agricultural sustainability as well as the scientific credibility of the tool. These frameworks also have a good reputation for their systemic dimension because they do not make the framework too simple or too complicated. Therefore, provide a plausible and realistic picture of agricultural sustainability. In other words, they try to focus on agricultural sustainability issues across scales. MCDA frameworks also had good and acceptable scores in most procedural dimension criteria (including learning aspects, data collecting approach, causality, transparency, tool function, free access to software and tutorials, etc.). Therefore, MCDA-based frameworks are recommended as coherent, practical, and useful tools for agricultural sustainability assessment purposes. Various potential users, such as decision-makers and agricultural policy-makers, can use it for (re)directing and achieving sustainable agricultural goals. Of course, it is worth noting that lack of a specific guideline for implementation is one of the flaws of these frameworks and researchers often use arbitrary policies and guidelines. One of the reasons for this flaw is related to a variety that is commonly found in MCDA-based frameworks, each with its own guidelines.
Another important point in the selection of sustainability frameworks is that although the present review showed that MCDA had a higher overall score than other frameworks, it does not mean that this framework should be considered as the only best framework in the field of agricultural sustainability assessment. This is because other methods also had high scores in some dimensions. For example, FLINT, SSP, and SAFE frameworks obtained high scores in systemic dimension. Similarly, EFT, LCAT, and SDST obtained remarkable scores in the normative dimension, indicating the potential capacity of these frameworks in agricultural sustainability assessments. Therefore, managers, policy-makers, decision-makers and other users (farmers, researchers, practitioners, etc.) of agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks are recommended to consider this issue in the comparison and selection of agricultural frameworks.
This review had also some limitations that should be considered in future studies on agricultural sustainability assessments. In the first and second phases, all agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks and comparison criteria may not be taken into account. Future research can develop these frameworks and comparison criteria by furthering or re-conceptualizing them. Consideration or ignorance of comparison criteria in agricultural sustainability assessment frameworks has been based on literature review, and to some extent, a subjective process. In this regard, future studies are recommended to examine the opinions of experts in the field of agricultural sustainability assessment along with a review of the literature. Doing so can lead to more realistic and precise decisions on comparison criteria and frameworks. The other limitation of the review is related to the selection of samples in phases 1 and 2. As it was mentioned earlier, the participants in these phases were only selected from the faculty members and experts of Fars province. The most important reason to do so was that the target study site was Fars province. Therefore, the selected samples should have been familiar with the local and context-specific requirement of the study. However, future researchers are recommended to repeat the study in large scales and select their samples from the national and international levels. Another limitation is the reliance on secondary data sources in the identification and analysis of sustainability frameworks. While extensive databases were used, the exclusion of non-English literature and gray literature (e.g., reports, theses, and policy briefs) may have limited the comprehensiveness of the review. Future studies should consider incorporating non-English and gray literature sources to broaden the diversity and applicability of findings. Additionally, the AHP employed in the final phase is inherently sensitive to expert judgment, and the number of international experts who participated was relatively limited. Although participants were carefully selected based on their expertise, future research could benefit from involving a larger and more diverse panel to enhance the robustness and generalizability of the AHP results.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors without undue reservation.
Author contributions
NV: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the support of the esteemed Educational Institution-Shiraz University, Iran; this study would not have come to fruition without their technical and financial support. We also would also like to acknowledge the cordial and effective participation and support of the community and research participants in data collection and information dissemination process. The extended cooperation of these groups has enabled us to successfully complete this undertaken review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abed, N., Kakolaki, M. B., Ramesh, M. V., Sankarannair, S., Murugan, R., Soundharajan, B. S., et al. (2025). Assessing farm-level agricultural sustainability in India: a comparative study using a mixed-method approach. Agric. Syst. 224:104223. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2024.104223
Acosta-Alba, I., and Van der Werf, H. (2011). The use of reference values in indicator-based methods for the environmental assessment of agricultural systems. Sustain. For. 3, 424–442. doi: 10.3390/su3020424
Aghbashlo, M., Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H., Shahbeik, H., and Tabatabaei, M. (2022). The role of sustainability assessment tools in realizing bioenergy and bioproduct systems. Biofuel Res. J. 9, 1697–1706. doi: 10.18331/BRJ2022.9.3.5
Alaoui, A., Barão, L., Ferreira, C. S., and Hessel, R. (2022). An overview of sustainability assessment frameworks in agriculture. Land 11:537. doi: 10.3390/land11040537
Astier, M., García-Barrios, L., Galván-Miyoshi, Y., González-Esquivel, C. E., and Masera, O. R. (2012). Assessing the sustainability of small farmer natural resource management systems. A critical analysis of the MESMIS program (1995-2010). Ecol. Soc. 17, 1–25. doi: 10.5751/ES-04910-170325
Benayad, N., Baguare, A., and Abdouh, M. (2024). Developing a composite indicator for agricultural sustainability assessment in the Fes-Meknes region, Morocco. J. Knowl. Econ. 15, 15723–15744. doi: 10.1007/s13132-023-01721-y
Bijani, M., Ghazani, E., Valizadeh, N., and Fallah Haghighi, N. (2017). Pro-environmental analysis of farmers' concerns and behaviors towards soil conservation in central district of Sari County, Iran. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 5, 43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.iswcr.2017.03.001
Binder, C. R., Feola, G., and Steinberger, J. K. (2010). Considering the normative, systemic and procedural dimensions in indicator-based sustainability assessments in agriculture. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 30, 71–81. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2009.06.002
Binder, C. R., Schmid, A., and Steinberger, J. K. (2012). Sustainability solution space of the Swiss milk value added chain. Ecol. Econ. 83, 210–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.06.022
Bonisoli, L., Galdeano-Gómez, E., and Piedra-Muñoz, L. (2018). Deconstructing criteria and assessment tools to build agri-sustainability indicators and support farmers' decision-making process. J. Clean. Prod. 182, 1080–1094. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.055
Chen, Y., Kipkulei, H. K., Xie, Z., and Sieber, S. (2024). Assessment of agricultural sustainability performance in Dali prefecture, China using the DPSIR model. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 22:2401201. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2024.2401201
Ciuffo, B., Miola, A., Punzo, V., and Sala, S. (2012). Dealing with uncertainty in sustainability assessment. Report on the application of different sensitivity analysis techniques to field specific simulation models. EUR 25166, 1–82. doi: 10.2788/57452
Conway, G. R. (1994). Sustainability in agricultural development: trade-offs with productivity, stability and equitability. J. Farm. Syst. Res. Extens. 4, 1–14.
Dantsis, T., Douma, C., Giourga, C., Loumou, A., and Polychronaki, E. A. (2010). A methodological approach to assess and compare the sustainability level of agricultural plant production systems. Ecol. Indic. 10, 256–263. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2009.05.007
De Groot, R., Wilson, M. A., and Boumans, R. M. (2002). A typology for the classification, description and valuation of ecosystem functions, goods and services. Ecol. Econ. 41, 393–408. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(02)00089-7
De Luca, A. I., Iofrida, N., Leskinen, P., Stillitano, T., Falcone, G., Strano, A., et al. (2017). Life cycle tools combined with multi-criteria and participatory methods for agricultural sustainability: insights from a systematic and critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 595, 352–370. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.03.284
De Mey, K., D'Haene, K., Marchand, F., Meul, M., and Lauwers, L. (2011). Learning through stakeholder involvement in the implementation of MOTIFS: an integrated assessment model for sustainable farming in Flanders. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 9, 350–363. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2011.582355
de Olde, E. M., Bokkers, E. A., and de Boer, I. (2017). The choice of the sustainability assessment tool matters: differences in thematic scope and assessment results. Ecol. Econ. 136, 77–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.02.015
de Olde, E. M., Moller, H., Marchand, F., McDowell, R. W., MacLeod, C. J., Sautier, M., et al. (2016a). When experts disagree: the need to rethink indicator selection for assessing sustainability of agriculture. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 19, 1327–1342. doi: 10.1007/s10668-016-9803-x
de Olde, E. M., Oudshoorn, F. W., Sørensen, C. A., Bokkers, E. A., and De Boer, I. (2016b). Assessing sustainability at farm-level: lessons learned from a comparison of tools in practice. Ecol. Indic. 66, 391–404. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.01.047
FAO (2013). Sustainability assessment of food and agriculture systems: Guidelines 3.0. Rome: FAO Press.
Fatemi, M., Rezaei-Moghaddam, K., Wackernagel, M., and Shennan, C. (2018). Sustainability of environmental management in Iran: an ecological footprint analysis. Iran Agric. Res. 37, 53–68. doi: 10.22099/iar.2018.4958
Finkbeiner, M., Schau, E. M., Lehmann, A., and Traverso, M. (2010). Towards life cycle sustainability assessment. Sustainability 2, 3309–3322. doi: 10.3390/su2103309
Gafsi, M., Legagneux, B., Nguyen, G., and Robin, P. (2006). Towards sustainable farming systems: effectiveness and deficiency of the French procedure of sustainable agriculture. Agric. Syst. 90, 226–242. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2006.01.002
Galván-Martínez, D., Espejel, I., Arredondo-García, M. C., Delgado-Ramírez, C., Vázquez-León, C., Hernández, A., et al. (2020). “Sustainability assessment in indigenous communities: a tool for future participatory decision making” in Stewardship of future drylands and climate change in the global south: challenges and opportunities for the agenda 2030 (Cham: Springer), 197–214.
Gasparatos, A. (2010). Embedded value systems in sustainability assessment tools and their implications. J. Environ. Manag. 91, 1613–1622. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.03.014
Gasparatos, A., El-Haram, M., and Horner, M. (2009). The argument against a reductionist approach for measuring sustainable development performance and the need for methodological pluralism. Account. Forum 33, 245–256. doi: 10.1016/j.accfor.2008.07.006
Gerrard, C. L., Smith, L. G., Pearce, B., Padel, S., Hitchings, R., Measures, M., et al. (2012). “Public goods and farming” in Farming for food and water security (Dordrecht: Springer), 1–22.
Giovannucci, D., Potts, J., Killian, B., Wunderlich, C., Soto, G., Schuller, S., et al. (2008). Seeking sustainability: COSA preliminary analysis of sustainability initiatives in the coffee sector. Committee on Sustainability Assessment.
Godfray, H. C. J., Beddington, J. R., Crute, I. R., Haddad, L., Lawrence, D., Muir, J. F., et al. (2010). Food security: the challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 327, 812–818. doi: 10.1126/science.1185383
Gómez-Limón, J. A., and Sanchez-Fernandez, G. (2010). Empirical evaluation of agricultural sustainability using composite indicators. Ecol. Econ. 69, 1062–1075. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2009.11.027
Grenz, J., Thalmann, C., Stampfli, A., Studer, C., and Hani, F. (2009). RISE - a method for assessing. Rural Dev. News 1, 5–9.
Grigoroudis, E., Kouikoglou, V. S., and Phillis, Y. A. (2024). Agricultural sustainability assessment and national policy-making using an axiomatic mathematical model. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 22:100401. doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2024.100401
Häni, F., Braga, F., Stämpfli, A., Keller, T., Fischer, M., and Porsche, H. (2003). RISE, a tool for holistic sustainability assessment at the farm level. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 6, 78–90.
Hansen, J. W. (1996). Is agricultural sustainability a useful concept? Agric. Syst. 50, 117–143. doi: 10.1016/0308-521X(95)00011-S
Hayati, D. (2017). Literature review: a literature review on frameworks and methods for measuring and monitoring sustainable agriculture (No. 22). Rome, Italy: Global Strategy Technical Report.
Hayati, D., Ranjbar, Z., and Karami, E. (2010). “Measuring agricultural sustainability” in Biodiversity, biofuels, agroforestry and conservation agriculture (Dordrecht: Springer), 73–100.
Hediger, W. (1999). Reconciling "weak" and "strong" sustainability. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 26, 1120–1144. doi: 10.1108/03068299910245859
Hřebíček, J., Valtinyová, S., Křen, J., Hodinka, M., Trenz, O., and Marada, P. (2013). “Sustainability indicators: development and application for the agriculture sector” in Sustainability appraisal: quantitative methods and mathematical techniques for environmental performance evaluation (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 63–102.
Hülsbergen, K. J. (2003). Entwicklung und Anwendung eines Bilanzierungsmodells zur Bewertung der Nachhaltigkeit landwirtschaftlicher Unternehmen. Aachen, Germany: Shaker Verlag.
Hu, S., Yang, Y., Zheng, H., Mi, C., Ma, T., and Shi, R. (2022). A framework for assessing sustainable agriculture and rural development: a case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 97:106861:106861. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106861
Kaewchutima, N., Suttinun, O., Sinthipong, U., and Musikavong, C. (2025). A legal and SAFA-based framework for improving the environmental integrity toward Thailand's agriculture sustainability. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 26:100681:100681. doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2025.100681
Karami, S., Karami, E., Buys, L., and Drogemuller, R. (2017). System dynamic simulation: a new method in social impact assessment (SIA). Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 62, 25–34. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2016.07.009
Lammerts van Bueren, F., and Blom, F. (1997). Hierarchical framework for the formulation for sustainable forest management standards: principles, criteria and indicators. Wageningen, Netherlands: Tropenbos Foundation.
Langeveld, J. W. A., Verhagen, A., Neeteson, J. J., Van Keulen, H., Conijn, J. G., Schils, R. L. M., et al. (2007). Evaluating farm performance using agri-environmental indicators: recent experiences for nitrogen management in the Netherlands. J. Environ. Manag. 82, 363–376. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.11.021
Lebacq, T., Baret, P. V., and Stilmant, D. (2013). Sustainability indicators for livestock farming. A review. Agronomie 33, 311–327. doi: 10.1007/s13593-012-0121-x
Levy, J. K., Hipel, K. W., and Kilgour, D. M. (2000). Using environmental indicators to quantify the robustness of policy alternatives to uncertainty. Ecol. Model. 130, 79–86. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00226-X
López-Ridaura, S., Keulen, H. V., Ittersum, M. V., and Leffelaar, P. A. (2005). Multiscale methodological framework to derive criteria and indicators for sustainability evaluation of peasant natural resource management systems. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 7, 51–69.
Marchand, F., Debruyne, L., Triste, L., Gerrard, C., Padel, S., and Lauwers, L. (2014). Key characteristics for tool choice in indicator-based sustainability assessment at farm level. Ecol. Soc. 19, 46–57. doi: 10.5751/ES-06876-190346
Marta-Costa, A. A., and Silva, E. (2013). “Approaches for sustainable farming systems assessment” in Methods and procedures for building sustainable farming systems: application in the European context (Dordrecht: Springer), 21–29.
MEA, M. E. A. (2005). Ecosystems and human well-being: wetlands and water. Washington, DC, USA: World Resources Institute.
Merheb, M., Cudennec, C., and Nardi, F. (2024). Can we use indicator-based farm sustainability assessment tools for the WEFE Nexus? Proc. IAHS 385, 91–96. doi: 10.5194/piahs-385-91-2024
Meul, M., Van Passel, S., Nevens, F., Dessein, J., Rogge, E., Mulier, A., et al. (2008). MOTIFS: a monitoring tool for integrated farm sustainability. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 28, 321–332. doi: 10.1051/agro:2008001
Moller, H., and MacLeod, C. J. (2013). Design criteria for effective assessment of sustainability in New Zealand's production landscapes. The NZ sustainability dashboard research report 13/07 : ARGOS.
Ness, B., Urbel-Piirsalu, E., Anderberg, S., and Olsson, L. (2007). Categorising tools for sustainability assessment. Ecol. Econ. 60, 498–508. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2006.07.023
Niemeijer, D., and de Groot, R. S. (2008). A conceptual framework for selecting environmental indicator sets. Ecol. Indic. 8, 14–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2006.11.012
Peano, C., Tecco, N., Dansero, E., Girgenti, V., and Sottile, F. (2015). Evaluating the sustainability in complex agri-food systems: the SAEMETH framework. Sustain. For. 7, 6721–6741. doi: 10.3390/su7066721
Petit, G., Sablayrolles, C., and Yannou-Le Bris, G. (2018). Combining eco-social and environmental indicators to assess the sustainability performance of a food value chain: a case study. J. Clean. Prod. 191, 135–143. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.156
Piorr, H. P. (2003). Environmental policy, agri-environmental indicators and landscape indicators. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 98, 17–33. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8809(03)00069-0
Pope, J., Annandale, D., and Morrison-Saunders, A. (2004). Conceptualising sustainability assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 24, 595–616. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2004.03.001
Poppe, K. J., Vrolijk, H. C. J., Dolman, M. A., and Silvis, H. J. (2016). FLINT farm-level indicators for new topics in policy evaluation: an introduction. Stud. Agric. Econ. 118, 116–122. doi: 10.7896/j.1627
Pretty, J., and Hine, R. (2000). The promising spread of sustainable agriculture in Asia. Nat. Res. Forum 24, 107–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-8947.2000.tb00936.x
Rezaei-Moghaddam, K., and Karami, E. (2008). A multiple criteria evaluation of sustainable agricultural development models using AHP. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 10, 407–426. doi: 10.1007/s10668-006-9072-1
Rigby, D., Woodhouse, P., Young, T., and Burton, M. (2001). Constructing a farm level indicator of sustainable agricultural practice. Ecol. Econ. 39, 463–478. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8009(01)00245-2
Rodrigues, G. S., Rodrigues, I. A., de Almeida Buschinelli, C. C., and de Barros, I. (2010). Integrated farm sustainability assessment for the environmental management of rural activities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 30, 229–239. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2009.10.002
Roy, R., and Chan, N. W. (2012). An assessment of agricultural sustainability indicators in Bangladesh: review and synthesis. Environmentalist 32, 99–110. doi: 10.1007/s10669-011-9364-3
Saaty, T. L. (1988). What is the analytic hierarchy process?. In Mathematical models for decision support (pp. 109–121). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
Sabiha, N. E., Salim, R., Rahman, S., and Rola-Rubzen, M. F. (2016). Measuring environmental sustainability in agriculture: a composite environmental impact index approach. J. Environ. Manag. 166, 84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.10.003
Sauvenier, X., Valckx, J., Van Cauwenbergh, N., Wauters, E., Bachev, H. I., Biala, K., et al. (2006). Framework for assessing sustainability levels in Belgian agricultural systems-SAFE. Part 1: sustainable production and consumption patterns. Final report-SPSD II CP 28 (no. UCL-Université Catholique de Louvain). Brussels, Belgium: Belgian Science Policy. p. 125.
Schader, C., Grenz, J., Meier, M. S., and Stolze, M. (2014). Scope and precision of sustainability assessment approaches to food systems. Ecol. Soc. 19, 42–56. doi: 10.5751/ES-06866-190342
Schindler, J., Graef, F., and König, H. J. (2015). Methods to assess farming sustainability in developing countries. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 1043–1057. doi: 10.1007/s13593-015-0305-2
Silvestri, C., Silvestri, L., Piccarozzi, M., and Ruggieri, A. (2022). Toward a framework for selecting indicators of measuring sustainability and circular economy in the agri-food sector: a systematic literature review. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 29, 1446–1484. doi: 10.1007/s11367-022-02032-1
Singh, R. K., Murty, H. R., Gupta, S. K., and Dikshit, A. K. (2012). An overview of sustainability assessment methodologies. Ecol. Indic. 15, 281–299. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2011.01.007
Sinisterra-Solís, N. K., Sanjuán, N., Ribal, J., Estruch, V., Clemente, G., and Rozakis, S. (2024). Developing a composite indicator to assess agricultural sustainability: influence of some critical choices. Ecol. Indic. 161:111934:111934. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2024.111934
Speelman, E. N., López-Ridaura, S., Colomer, N. A., Astier, M., and Masera, O. R. (2007). Ten years of sustainability evaluation using the MESMIS framework: lessons learned from its application in 28 Latin American case studies. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 14, 345–361. doi: 10.1080/13504500709469735
Stockle, C. O., Papendick, R. I., Saxton, K. E., Campbell, G. S., and Van Evert, F. K. (1994). A framework for evaluating the sustainability of agricultural production systems. Am. J. Altern. Agric. 9, 45–50. doi: 10.1017/S0889189300005555
Suresha Adiga, M., Ananthan, P. S., Ramasubramanian, V., and Kumari, H. D. (2015). Validating RAPFISH sustainability indicators: focus on multi-disciplinary aspects of Indian marine fisheries. Mar. Policy 60, 202–207. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2015.06.032
Talukder, B., and Blay-Palmer, A. (2017). “Comparison of methods to assess agricultural sustainability” in Sustainable agriculture reviews (Cham: Springer), 149–168.
Talukder, B., Hipel, K. W., and vanLoon, G. W. (2018). Using multi-criteria decision analysis for assessing sustainability of agricultural systems. Sustain. Dev. 26, 781–799. doi: 10.1002/sd.1848
Tao, G., Xiaojian, Z., and Tiexin, C. (2011). Evaluation of wetland ecological restoration project based on SD: a case study on Qilihai wetland in Tianjin. Procedia Environ. Sci. 10, 2587–2593. doi: 10.1016/j.proenv.2011.09.402
Thomassen, M. A., van, K. J., Smits, M. C., Iepema, G. L., and de Boer, I. J. (2008). Life cycle assessment of conventional and organic milk production in the Netherlands. Agric. Syst. 96, 95–107. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2007.06.001
Thompson Klein, J., Grossenbacher-Mansuy, W., Häberli, R., Bill, A., Scholz, R. W., and Welti, M. (2001). Transdisciplinarity: joint problem solving among science, technology, and society: an effective way for managing complexity. Germany, Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Valizadeh, N., and Hayati, D. (2021). Development and validation of an index to measure agricultural sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 280:123797. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123797
Van Cauwenbergh, N., Biala, K., Bielders, C., Brouckaert, V., Franchois, L., Garcia, V., et al. (2007). SAFE-A hierarchical framework for assessing the sustainability of agricultural systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 120, 229–242. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2006.09.006
Van Ittersum, M. K., Ewert, F., Heckelei, T., Wery, J., Alkan, J., Andersen, E., et al. (2008). Integrated assessment of agricultural systems-a component-based framework for the European Union (SEAMLESS). Agric. Syst. 96, 150–165. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2007.07.009
Van Passel, S., and Meul, M. (2010). Multilevel sustainability assessment of farming systems: a practical approach. In Building sustainable rural futures: the added value of systems approaches in times of change and uncertainty. 9th European IFSA symposium, Vienna, Austria, 4–7 July 2010 (pp. 791–800). BOKU-University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences.
Videira, N., Antunes, P., Santos, R., and Lopes, R. (2010). A participatory modelling approach to support integrated sustainability assessment processes. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 27, 446–460. doi: 10.1002/sres.1041
Wefering, F. M., Danielson, L. E., and White, N. M. (2000). Using the AMOEBA approach to measure progress toward ecosystem sustainability within a shellfish restoration project in North Carolina. Ecol. Model. 130, 157–166. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(00)00205-2
Wiek, A., and Binder, C. (2005). Solution spaces for decision-making-a sustainability assessment tool for city-regions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 25, 589–608. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2004.09.009
Wolcott, E., and Thornsbury, S. (2025). Adapting farm-level sustainability assessment: challenges for Florida strawberry agriculture. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 26:100653. doi: 10.1016/j.indic.2025.100653
Xavier, J. H. V., Gomes, M. C., Anjos, F. S. D., Scopel, E., Silva, F. A. M. D., and Corbeels, M. (2020). Participatory multicriteria assessment of maize cropping systems in the context of family farmers in the Brazilian Cerrado. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 18, 410–426. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2020.1788253
Zahm, F., Viaux, P., Vilain, L., Girardin, P., and Mouchet, C. (2008). Assessing farm sustainability with the IDEA method-from the concept of agriculture sustainability to case studies on farms. Sustain. Dev. 16, 271–281. doi: 10.1002/sd.380
Zamagni, A., Feschet, P., De Luca, A. I., Iofrida, N., and Buttol, P. (2015). Social life cycle assessment: methodologies and practice. In Sustainability assessment of renewables-based products: methods and case studies, Edited by Dewulf Jo, De Meester Steven and Alvarenga Rodrigo A. F. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 229–240.
Keywords: evaluation criteria, assessment frameworks, agricultural sustainability, sustainability indicators, multi-criteria decision analysis
Citation: Valizadeh N and Hayati D (2025) A systematic review on selection and comparison of holistic agricultural sustainability assessment approaches. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1559503. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1559503
Edited by:
Marzia Ingrassia, Università degli Studi di Palermo, ItalyReviewed by:
Mehdi Rahimian, Lorestan University, IranMoslem Savari, Khuzestan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Valizadeh and Hayati. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dariush Hayati, aGF5YXRpQHNoaXJhenUuYWMuaXI=
†ORCID: Naser Valizadeh, orcid.org/0000-0003-1608-0853
Dariush Hayati, orcid.org/0000-0003-1608-0853
 Naser Valizadeh
Naser Valizadeh Dariush Hayati
Dariush Hayati