- Department of Agricultural Economics, Wolaita Sodo University, Wolaita Sodo, Ethiopia
Introduction: The study aimed at to evaluate the impact of mung bean crop market participation upon asset accumulation of smallholder farmers in lowland areas of South Ethiopia.
Methods: About 384 smallholder mung bean producer farmers were selected from the lowlands of Wolaita, Gamo and Gofa zones following multistage sampling procedures. The composite asset index development was calculated by multiple correspondence analysis whereas endogenous switching regression was used to evaluate the impact of market participation upon households' asset accumulation.
Results: Out of 384 selected mung bean farmers (74.5%) participated in mung bean markets while 25.5% did not participate in mung bean markets. The estimation result revealed that age of the head of household, numbers of family members, livestock population, perception toward social value, quantity of mung bean product, credit utilization, information accessibility, frequent training on agro-practices, road and market distance from home significantly affected mung bean market participation status. In addition, the asset accumulation of the participants was positively and significantly influenced by age of the head of household, quantity of product and distance from all-weather roads whereas information accessibility negatively affected asset accumulation.
Discussion: The farmers who participated in mung bean markets were more likely (positive) impact on asset accumulation from selling of the product. Therefore, the government and market regulatory bodies should encourage farmers through providing credit facilities, information and frequent training about the new emerging beans and developing other infrastructure facilities to increase the asset accumulation for smoothing elongated shocks in SERS, Ethiopia.
1 Introduction
Ethiopia's diverse climate and soil types, combined with three agroecologies, produce various agricultural crops for domestic consumption and commercialization, primarily dominated by smallholder farmers (Addis and Abirdew, 2021; Atnaf et al., 2015; Molla et al., 2022). However, it is still stagnant due to low agricultural technology adoption, weak fallback strategies, imperfect input and output markets, etc. (Atnaf et al., 2015; Rios et al., 2008; Tesfamicheal Wossen, 2015; Jankelova et al., 2017; Adhikari and Khanal, 2021; Getachew, 2019; Simion, 2018). As part of solving the sectorial drawbacks, the agricultural policies, strategic plans, and establishment of the Agricultural Transformation Agency encourage the production of export crops by transforming from subsistence farming to commercialization through the cluster approach (Rios et al., 2008; Tesfamicheal Wossen, 2015; Jankelova et al., 2017; Dinsa et al., 2022; Ogada et al., 2020).
Mung bean is one of the pulse crops in marginal lands, Rift Valley fringes, and river valley areas of Jema, Omo, and their tributaries in Ethiopia (Eze et al., 2022; Kebede, 2020; Teame et al., 2017). Beinshangul regional state, the Bale zone and East Shewa zone in Oromia regional state, the low-land areas of the Wolaita, Gamo, and Gofa zones in South Ethiopia are the major producers (Kaysha et al., 2020; Adhikari and Khanal, 2021; Tehulie et al., 2021; Dinsa et al., 2022; Kebede, 2020; Neda, 2020; Getachew, 2019; Assefa et al., 2022). MH-97-6 (Boreda), Shewa Robit, Rasa (N-26), Arbeke, MH BR-1, NLV-1, and NUL-1 mung bean varieties have been developed by different agricultural research centers and disseminated to farmers for cultivation, and the demand of the farmers has been increasing for improved varieties (Kassa et al., 2021; Dinsa et al., 2022; Baza et al., 2022).
Mung bean is the country's sixth main export item in the commodity market, alongside oil seeds and cereals, driven by smallholder farmers' commercialization efforts (Baker and Yuya, 2020). Its production and export volume have shown a steady increase over the years, with export volumes rising from 2310 tons in 2004 to 22,719 tons in 2013 and reaching 68,818 tons in 2016. Emerging varieties provide additional household income in South Ethiopia, improving food security and soil fertility, supporting construction, providing livestock feed, and serving as fuel (Gata et al., 2024; Tun and Phyo, 2019; Getachew, 2019; Kebede, 2020). All contributions make the mung bean the second low-land pulse next to common bean.
However, this newly introduced crop is trying to make inroads into the existing agricultural system and has faced greater challenges due to various factors. In addition to the potential importance of mung bean, its productivity and export share are low and less popular when compared with other exportable pulse crops in drought-prone areas. In the South Ethiopia region, smallholder farmers produced very small amount of mung bean crops, though they were endowed with favorable agroecological zones. Farmers' uncertainty due to lack of information about the new technology can change the perception of the farmers and adversely affect the probability of adoption (Emeru, 2022). Farmers are producing infinitesimal quantities, thereby challenging the smallholder farmers' market participation. Smallholder farmers are also failing to include it in their local dishes due to adverse perceptions of the nutritional value of the crop (Assefa et al., 2022; Temeche et al., 2022). The marketable surplus of the crop is very low in the country compared with other dry beans. These issues further lead to unexpected outcomes for the smallholder farmers' food security, nutrition and health status, income amount, and other welfare indicators.
There is limited research carried out on the long-term impact of welfare indicators in the area so far, though they simply came across the descriptive analysis of financial analysis (Tun and Phyo, 2019; Wang et al., 2018) and review of market challenges (Kebede, 2020). In addition, landrace and staple crops are usually cultivated for both household consumption and commercialization purposes (Kebede, 2020; Manda et al., 2021; Getachew, 2019), such as common bean (Habte et al., 2021), chickpea (Tabe Ojong et al., 2022), maize and pigeon pea (Sequeros et al., 2021; Mmbando et al., 2015a), and moringa (Meskel et al., 2020). Many previous research studies have found the effects of various crop market participation in welfare indicators, mainly household income (Sequeros et al., 2021; Mmbando et al., 2015a; Meskel et al., 2020; Hashmiu et al., 2022; Abokyi et al., 2020; Zegeye et al., 2022; Biru et al., 2020; Rubhara et al., 2020; Sequeros et al., 2020; Brockington and Brockington, 2021). Short-term income and consumption indicators cannot easily stabilize smallholder farmers' livelihood compared with household asset possession, which is superior on average (Kassa et al., 2021; Baker and Yuya, 2020; Meskel et al., 2020; Zegeye et al., 2022; Li et al., 2020; Mmbando et al., 2015b; Dikr, 2023); however, varieties that are compatible with the harsh environments and high-value crops, such as mung bean varieties, are not given much attention.
Moreover, there is limited knowledge of the impact of mung bean market participation in smallholder agriculture. The claimed benefits of mung bean need to be confirmed by impact analysis for long-term shock smoothing. Finally, the extant literature on market participation did not address the quantitative issues, and the models employed were subjected to biased estimations (Tadele et al., 2022). Hence, analyzing the impact of mung bean market participation on small-scale farmers' welfare would be of policy relevance. Therefore, the study aimed to evaluate the impact of participating in the mung bean market on households' asset accumulation via the models that can handle all impact evaluation challenges in the study area.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
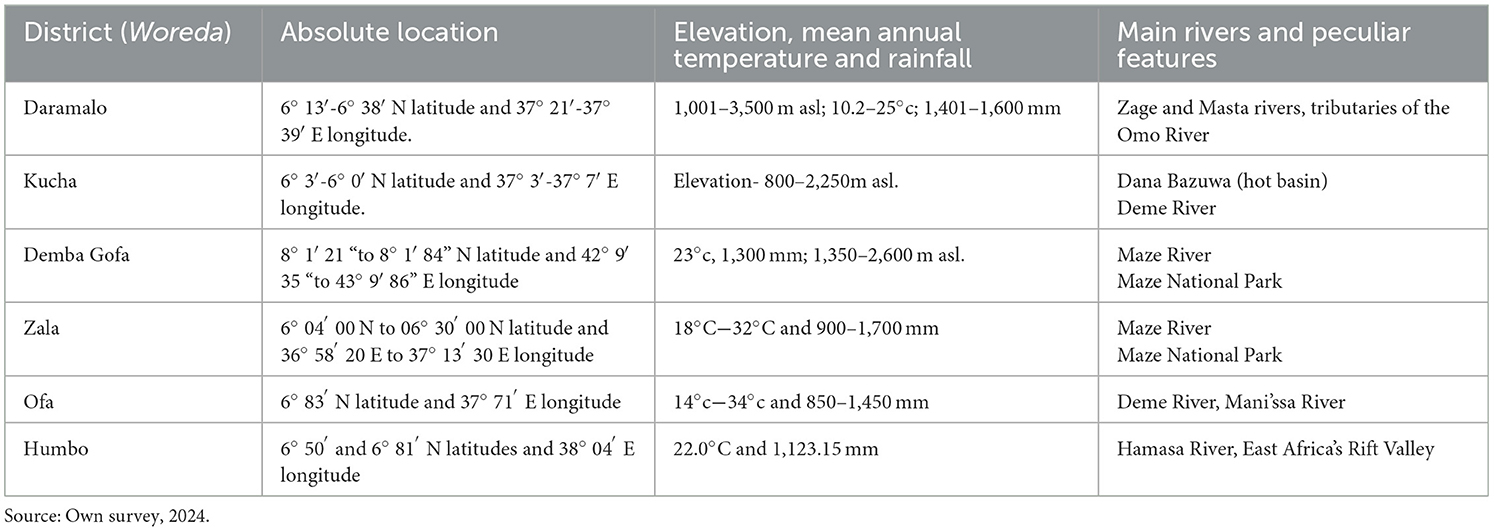
This study was carried out in the Gamo, Gofa, and Wolaita zones, which are the three main producers of mung bean in South Ethiopia Regional State (SERS) after being launched as the sixth export crop in Ethiopia Commodity Exchange Authority (ECX) (Ademe, 2023; Dikr, 2023; Kidane et al., 2022). In the SERS area, production, the yield of crops and private peasant holdings for meher season in 2022 increased to 2,359 ha, 11,805.04 quintals, 10.01 Qt/ha, and 11,344.00 households. They are endowed with natural resources such as permanent and seasonal rivers such as Zage, Masta, Maze, and Deme, in addition to nurturing human beings and the lives of study areas animals, especially Maze National Park dwellers (Chalite, 2020; Isayev et al., 2023; Eze et al., 2022). Dana Bazuwa is a hot area in the basin of the Deme River adjacent to the Kucha, Ofa, and Humbo districts (Baza et al., 2022). Mung bean is one of the major crops grown in low-land areas by rainfall and irrigation schemes for physiological requirements in the study area, like other areas in the world (Isayev et al., 2023; Komarek et al., 2020). Table 1 indicates the geographical and climatic information of the study.
2.2 Sampling procedures, sample size, and sample size determination
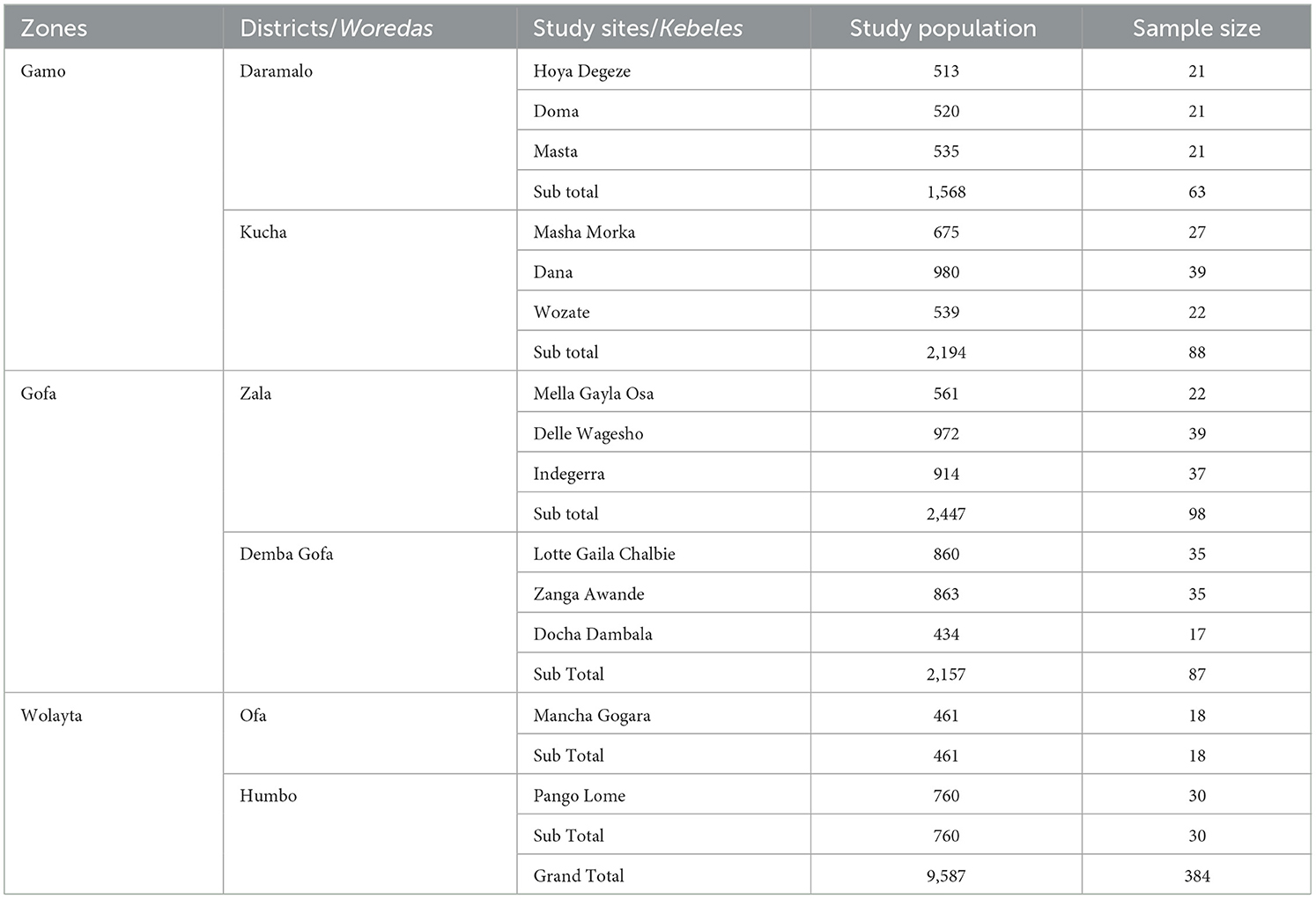
Multistage sampling procedures were employed to select the sampled mung bean farmers in SERS. Among the SERS zones of the Omo and the Rift Valley areas, Wolaita, Gamo, and Gofa were selected in stage one based on large production and the first adopters of the varieties in the regional state. Next, six districts (two from each zone) were selected purposively as part of the study due to the main producers for the ECX (Tabe Ojong et al., 2022). A total of 14 sampled Kebeles. Out of 24 kebeles, only seven kebeles are found to be the major mung bean-producing kebeles in the Daramalo district. These are Hoya Degeze, Masta, Domoa, Shela Shubo, Shela Deda, Nenena Abaya, and Antashe. Out of 24 kebeles, five were identified as the main producers from the Kucha district. Masha Morka kebele, Dana kebele, peri-urban of Selam Ber, and others are the major producers of mung bean. Zala district has 34 rural and one urban kebeles (Simion, 2018).
Demba Gofa, which is adjacent to Maze National Park, is the producer of the crop. Out of 15 rural and four urban kebeles, Mancha Gogara, Sere Esho, and Busha are the main producing kebeles in the catchment area of Dana River in Ofa district (Tehulie et al., 2021; Assefa et al., 2022). Thus, out of the total mung bean-producing kebeles from six districts, three kebeles each were selected from Daramalo, Kucha, Zala, and Demba Gofa districts and one kebele each was selected from Ofa and Humbo districts and that made a total of 14 sampled kebeles those were selected in the third stage through simple random sampling techniques (Table 2).
In the end, from the research population (N), the 384 final sample size (n) with the error term (ε) of 5% value at a 95% confidence level was determined based on the previous literature (Habte et al., 2021; Tabe Ojong et al., 2022; Sequeros et al., 2021).
The study used a proportionate or equalized sampling technique to take a sample from each district, which is specified as follows:
where Pi represents the sample from strata or kebele i; n is the sample size, N is the population, and Xi is the number of households in each kebele i.
2.3 Data types and sources
The study incorporated both primary and secondary data types. A source of primary data was mung bean producers from each Woreda. The primary data survey questionnaire included the mung bean farmers' demographic, socio-economic characteristics, market participation, market-related factors, and asset indicators pertinent to the objective of the study. Secondary data types such as written documents and necessary websites to enrich the literature were also employed from six Woreda offices.
2.4 Data collection and analysis
The household survey was conducted using commonly employed tools such as questionnaire schedules and/or interviews to collect the primary data. Trained and oriented enumerators, such as agriculture office experts from the districts and development agents from sampled kebeles, were assigned and collected, and the data were collected from mung bean farmers under the supervision of the researchers. The smallholder farmer's socio-economic, demographic, and institutional characteristics, market participation, welfare indicators, and other characteristics were summarized by statistical analysis of the center of the distribution, the dispersion, and the shape of data in the first part of the results and finding section. The multivariate statistical algorithm family so-called multiple correspondence analysis (MCA) for the development of household asset accumulation index from the asset lists arranged in a questionnaire based on suitability assessments were used (De Muro et al., 2011). In econometric techniques, the endogenous switching regression (ESR) model was used to estimate the binary equation and the outcome equations simultaneously. Furthermore, due to the sensitivity character of ESR, Instrumental variables (IVs) were selected using the ordinary least square (OLS) estimation technique and binary probit model. The STATA 16 package was used to fit asset indicators in MCA and to estimate the models.
2.5 Model specification for impact evaluation
Outcomes evaluation is a major methodological challenge to cascade because it needs to control potential selection biases/heterogeneity and endogeneity problems. If we apply the classical linear regression model (CLRM) estimation technique to estimate the impact of market participation on farmers' asset accumulation, the result should be biased. Selection biases arose from the observed heterogeneity controlled by the PSM, but the problem of unobserved heterogeneity still remained. Along with PSM, the IVs are able to capture unobserved factors (Maddala, 1992; Mmbando et al., 2015b). In addition, the main limitations of Heckman's model are employed in two successive decision analyses (Willy et al., 2023; De Muro et al., 2011; Koné et al., 2019). Therefore, the current article adopts the model that can be able to handle all impact evaluation challenges, the so-called ESR for the impact of mung bean farmers' participation in the product market upon asset accumulation, by providing both equations simultaneously (Koné et al., 2019; Di Falco et al., 2011).
In stage one of the selection equation in the ESR model, the binary probit model regression method is a suitable model for market participation estimation since it takes dichotomous code “1” (D1) and code “0” (D0) for households that sell their product in the mung bean market for getting benefits from the participation and for households who did not participate in this market, respectively. Therefore, assumed the rational farmers would choose to be participating in order to gain maximum utility (, where = > 0) from that of not participating. Equation 3 represents the selection or participation equation:
where Di is a binary variable that takes values equal “1” and “0” for both participation status; Zi is mung bean farmers; characteristics those assumed to influence binary responses; β is a vector of parameters that indicates the slope change of each variable upon participation decision, and ηi is a random term.
Market participation outcome variable (in this study, the outcome variable was asset accumulation) Yi assumed as the linear function of the variables Xi and Di such that:
where δ and εi are the parameters to be estimated and the error terms, respectively.
The second stage consists of the estimation of both outcome equations: one for those who participate in the market or treated individuals and another for those not participating in the market or for untreated individuals represented following (Hashmiu et al., 2022; Kidane et al., 2022; Koné et al., 2019; Di Falco et al., 2011; Lokshin and Sajaia, 2004) as follows:
where Y1i and Y2i are outcome variables for participants and non-participants, respectively; Xi is a vector of exogenous variables of mung bean i's farmers', expected to influence asset accumulation; β is the coefficient vector; Di is a dummy for market participation, and εi is the residuals.
The selection Equation 3 error term and two regimes error terms in the outcome Equations 5, 6 are assumed to have a tri-variate normal distribution with zero mean and covariance matrix of the following form:
where is the variance of the error term in the selection Equation 3; and are the variances of the error terms in the outcome Equations 5, 6; δ1η and δ2η are the covariance of η, ε1i, and ε2i. Covariance between ε1i and ε2i is not defined since Y1 and Y2 are not observed simultaneously. The FIML method simultaneously estimates binary (the selection equation) and continuous parts of the model (the outcome equations) to yield consistent standard errors.
Based on the literature, the ESR identify the impact of eco-friendly farmers upon asset accumulation of those who participate in the mung bean market (Equation 5) with respect to eco-friendly farmers who do not participate in the mung bean market (Equation 6). Furthermore, the respective two counterfactual hypothetical cases are also examined in the following cases (Case I–Case IV):
Case I: market participants with participation in the mung bean market:
Case II: market participants have decided not to participate in the mung bean market:
Case III: non-market participants without participation in the mung bean market:
Case IV: non-market participants have decided to participate in the mung bean market:
Using these expected outcomes, we derive unbiased treatment effects: the average treatment effect on treated (ATT), which is the difference between Equations 8 and 9, and the average treatment effect on untreated (ATU), which is the difference between Equations 10 and 11.
The “effects of base heterogeneity” for the group of farm households that decided to participate (BH1) is:
“The effect of base heterogeneity” (BH2).
The difference between (TT) and (TU) leads to “transitional heterogeneity” (TH). Or it indicates whether the effect of participants is greater than that of the non-participants.
2.6 Variables expected to affect market participation and its impact on asset accumulation
2.6.1 Dependent variable
Treatment variables: Mung bean farmers' market participation was measured by the binary decision of mung bean farmers whether to participate in the output market in selling crops in the survey period (1) or otherwise (0).
Outcome variable: The asset index of households is a continuous outcome variable used in the model. MCA was used to develop a household asset accumulation index based on the asset lists arranged in a questionnaire based on suitability assessments (De Muro et al., 2011).
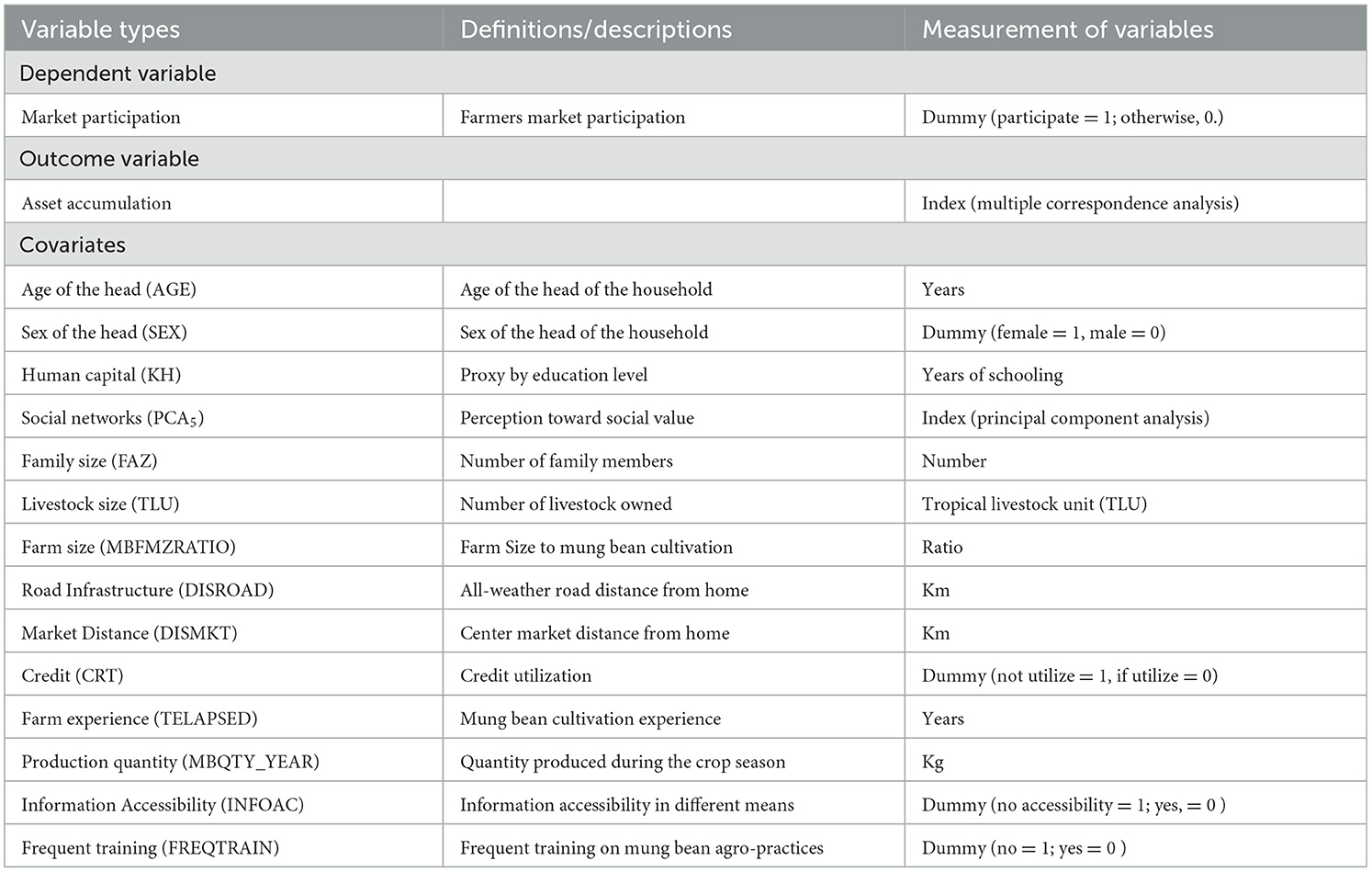
Explanatory variables: The independent variables in this study are classified as control covariates and selection instruments. These are farmers' demographic, socio-economic characteristics, and institutional factors.
Sex of the head of the household (SEX): The sex variable takes the value “1” if the sex of the head of the household is female and the value “0” if the sex of the head of the household is male. Being maleness was expected to influence the binary responses and outcome equations more probably when compared with their counterparts (Cazzuffi et al., 2020).
Age of the head of the household (AGE): The household's age was measured in years. The older farmers are more participating in the mung bean market than their young farmers. According to reports, age is more likely to affect the mung bean market participation (Bezabeh et al., 2020).
Human capital (KH): It was used as a proxy of education level measured by years of schooling. The more educated farmers, the more cash crops are produced, thereby enhancing market supply for household livelihood improvement than less educated farmers (Adhikari and Khanal, 2021). Therefore, a positive relationship is expected.
A number of family members (FAZ): Mung bean production is expected to be labor intensive. If the family members in a single household are large, thus they are expected to produce a large amount of products it should supply to the market. Therefore, it is directly related to market participation (Olounlade et al., 2020).
Perception toward social value (PCA5): The relationship between this perception and the market participation status of new market crop varieties has a positive effect hypothesis (Sánchez-Toledano et al., 2018).
Livestock population (TLU): More holdings of livestock population (TLU) in rural communities are more productive through cultivating commercial crops and thereby supplying more products to the market (Manda, 2016).
Farm size (MBFMZRATIO): Smallholder farmers with relatively large farmland have higher economies of scale and production, encouraging them to rely on market-based institutional arrangements (Mulwa et al., 2017).
Credit utilization (CRT): It is a binary variable that takes code “1” for CRT and “0” for its counterparts. The smallholder households' input demand should be backed by finance, which gives them the power to purchase, thereby increasing the market supply. Hence, it was hypothesized to support households to participate in the mung bean market, thereby increasing asset accumulation (Dagnew et al., 2023).
Quantity of mung bean produced in a year (MBQTY_YEAR): It is expected to be directly related to asset accumulation (Emran et al., 2021).
All-weather road proximity distance from home (DISROAD): The farther the home is from the road, the less it is to supply the farm products to the market than their counterparts (Gikonyo et al., 2022).
Center market distance from home (DISMKT): Center market distance from home takes the approximate distance measurement in kilometers. If center market distance from farmer's residence is very near, it encourages the farmers to supply the products to the market, thus directly related to livelihood improvement strategies (Cazzuffi et al., 2020; Belete and Nigatu, 2023).
Information accessibility (INFOAC): Information accessibility, especially in producing cash crops and marketing in different means, can affect the mung bean market participation decision more likely (Belete and Nigatu, 2023).
Frequent training on mung bean agro-practices (FREQTRAIN): Frequent training takes binary codes 1 and 0 (no = 1 and 0 = there is training). It has a positive impact (Ahsanuzzaman, 2015). However, many meetings with public bodies can complicate the adoption choices of the technology, especially in situations where the improved seed varieties are not provided to the market (Silva and Broekel, 2016). Table 3 depicted types, definitions and measurement of the variables.
3 Findings and discussion
3.1 Summary statistics of households characteristics in terms of market participation status and asset accumulation
3.1.1 Sampled households characteristics
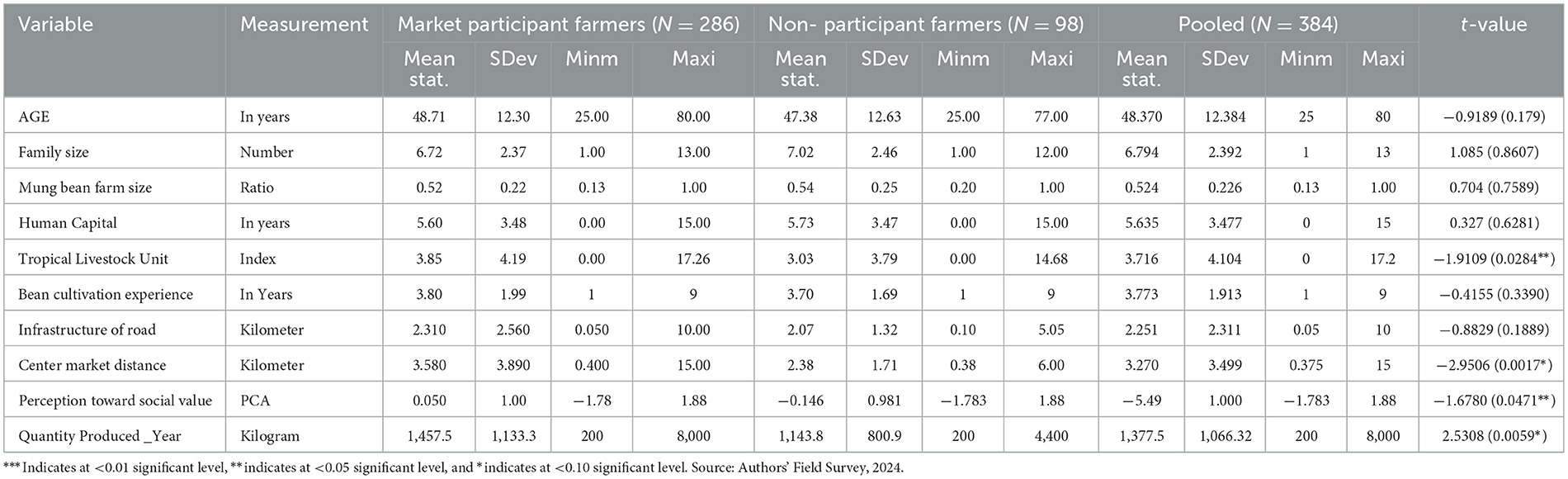
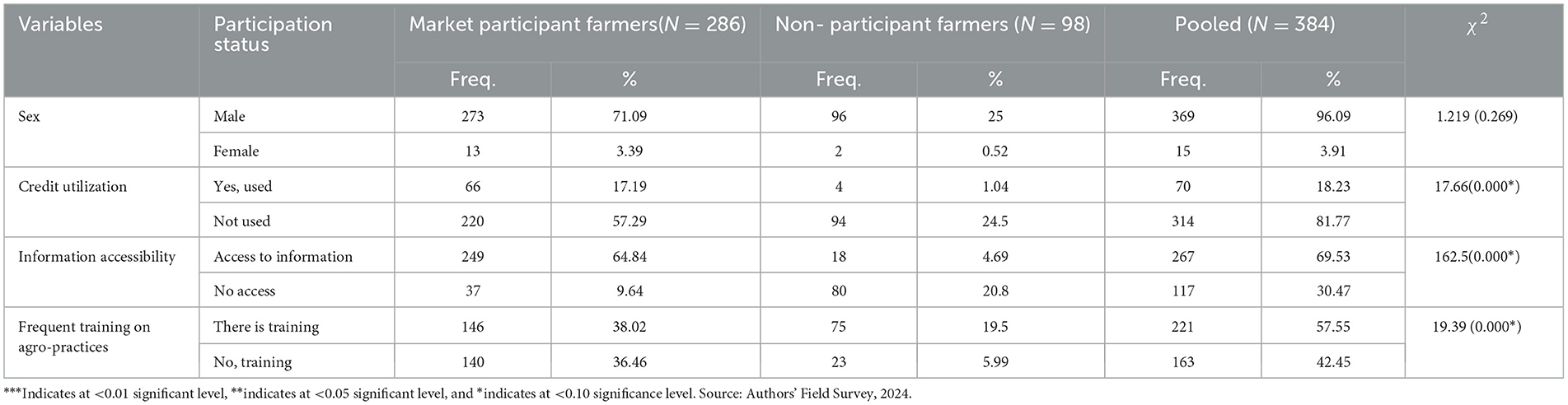
The result revealed that, out of 384 selected mung bean farmers, 74.5% of farmers participated in mung bean markets, while 25.5% of farmers did not participate in mung bean markets (Table 4). The mean age of the total samples, market participants, and non-participants was 48.37, 48.71, and 47.38 years, respectively. The average household size of the total samples, market participants, and non-participants was 6.794, 6.72, and 7.02 years, respectively. The mean education level of the total samples was 5.6 years of schooling. Meanwhile, the mean ratio of total land size to mung bean crop plots was 0.524 ha.
The mean livestock population for overall samples, market participants, and non-participants was 3.716, 3.85, and 3.03, respectively, and the treated and untreated groups are significantly different, as depicted in the t-value. This finding was also confirmed by researchers in the same study area and other regions of the country Ethiopia (Gata et al., 2024). Other researchers also confirmed that farmers who have more livestock holdings (TLU) possess basic assets and are able to handle agricultural implements for cultivation, thereby supplying more products to the market (Manda, 2016). The mean distance of the market center from farmers' homes for the total sample was 3.27 km, for market participants was 3.58 km, and for non-participants was 2.38 km. The farmers' home distance to nearby all-weather roads is a maximum of 10 km. This finding is similar to other drought-prone areas in south Ethiopia (Gata et al., 2024).
Perception toward social aspects in PCA with a mean component for market participants is greater than non-participants. Furthermore, the amount of mung bean products for participants was 1,455.50 kg, while 1,143.80 kg was for the counterparts, and the mean difference was statistically significant at < 0.05 significant levels. This finding indicates that yields produced by participants are larger than the yields produced by non-participants in the study area. This finding was confirmed by Dagnew et al. (2023). A unit increase in the amount of products to market leads households to possess more wealth through market participation (Gikonyo et al., 2022; Durjoy Lal Soren, 2023).
Table 5 presents the characteristics of sampled households in terms of dummy variables and χ2 test for market participant farmers and non-participant farmers. From 384 total samples, 273 farmers were males, while the remaining 13 farmers were females. Out of the total sampled farmers, those who utilized the financial credit were 66 farmers; however, most of the farmers (22 mung bean farmers) did not utilize the credit in the study area. Those who had access to information were 249 mung bean farmers, and the remaining did not have access to market information (37 mung bean farmers). Furthermore, 57.55% of farmers received frequent training on mung bean agro-practices, while the remaining 42.45% did not receive any training during the crop season. It also revealed the existence of statistically significant differences between both groups in cases of CRT [χ2 =17.66 (0.000)] and information accessibility [χ2 = 162.5 (0.000)].
3.1.2 Composite asset index development
Among 53 asset indicators, 38 asset indicators were identified for composite asset index (asset weight) based on suitability assessments to fit for the MCA, whereas 10 asset indicators were excluded from the computation of the asset weight due to possession only by < 10% (few) mung farmers [bee hives (5%), generator (4%), refrigerators (1%), bicycle (2%), computers (2%), remittances (7%), sofa set (15%), water pump (16%), biogas (7%), and irrigation pipe (4%)] and can bias the comparison in the study area; also four asset indicators were also excluded from analysis due to 100% not possessed by mung bean farmers, and one asset indicator was excluded from analysis due 100% possessed by all farmers (Table 6). The most deficient and best-accessed assets were excluded because they brought data outliers and failed to measure asset distribution among the farmers. Moreover, the exclusion of these variables is relevant not only because of low possession or virtually all possessed; rather, the differences in accessibility also can distort the comparison of the farmers across different study districts. Therefore, asset indicators should be removed or adjusted to better meet the fundamental properties of the MCA approach.
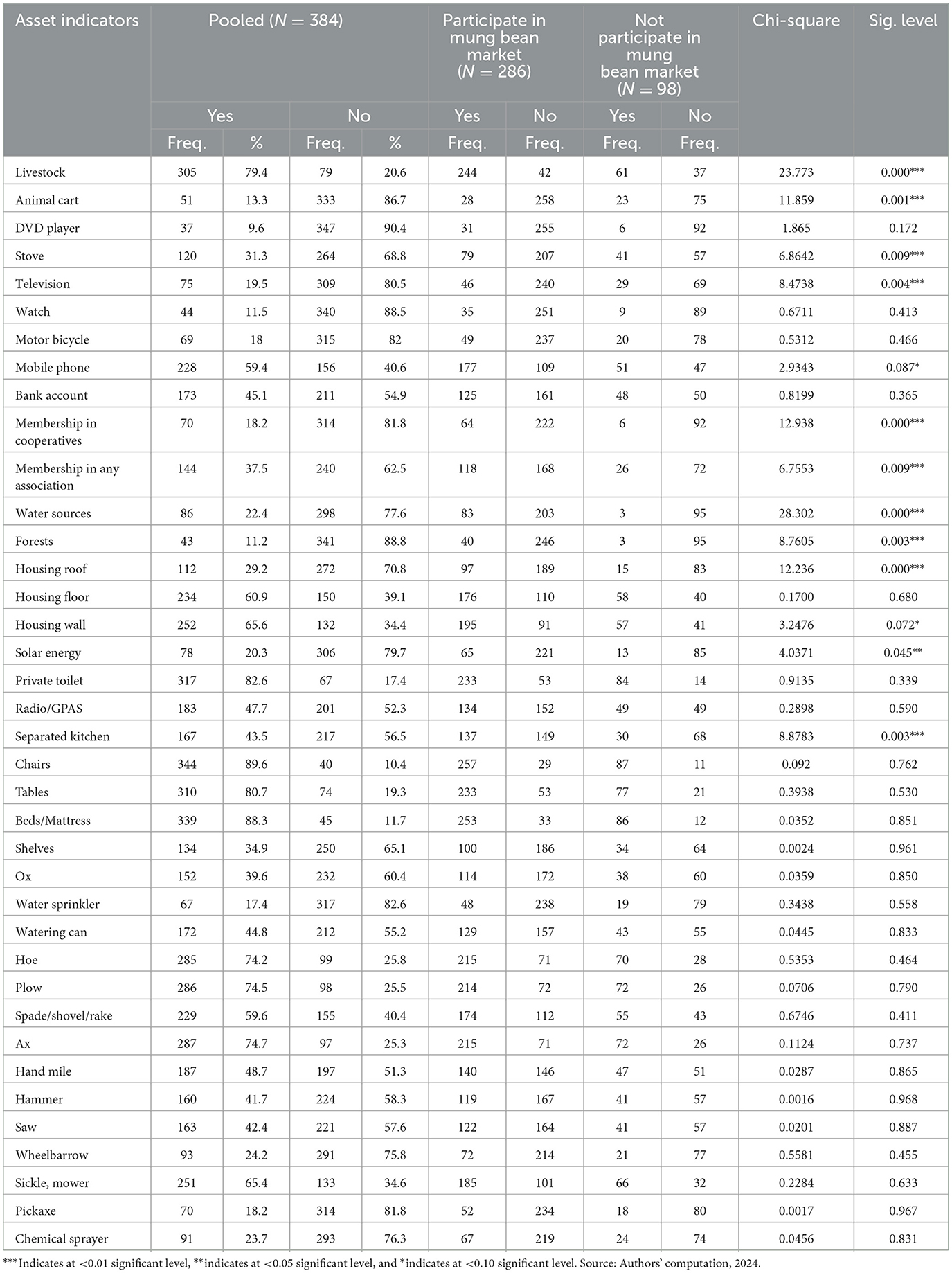
Table 6. Frequency and chi-square test of final asset indicators used for composite asset index development responded by mung bean framers in low-land areas of South Ethiopia.
3.1.3 Distribution of asset accumulation over mung bean market participation
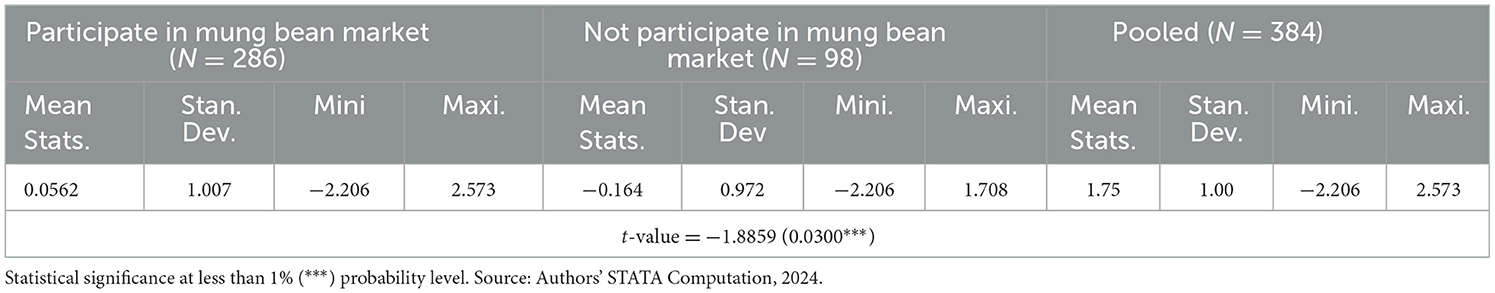
The impact indicator variable, the asset accumulation index, was computed using multiple correspondence analyses and was used as an outcome variable in the models. As depicted in Table 7, the maximum asset index (asset weight) was 2.573, and the minimum asset index was −2.206. The range asset weight was 4.779, which indicates a great uneven distribution of asset accumulation over mung bean market participants in SERS. These kinds of asset variations among rural farmers were also confirmed by Durjoy Lal Soren (2023).
The mean asset accumulation index for total mung bean farmers was 1.75, with a 0.0564 index value for treated and −0.164 for untreated groups. The t-value indicated the significant difference between both groups at < 5% significance level [t-value = −1.8859 (0.0300)]. The level of assets within a community significantly affected its ability to develop and reestablish the low-land people's livelihood improvement during an emergency and after a shock of incidents. The eco-friendly farmers' strength depends on asset accumulation. The more they accumulate the assets, the more they shape the shocks they encounter. In addition, asset accumulation index development is important to address inequality in asset distribution (Islam and Walkerden, 2022).
3.2 Econometric analysis
3.2.1 Driving factors of mung bean market participation _ Stage I: probit model
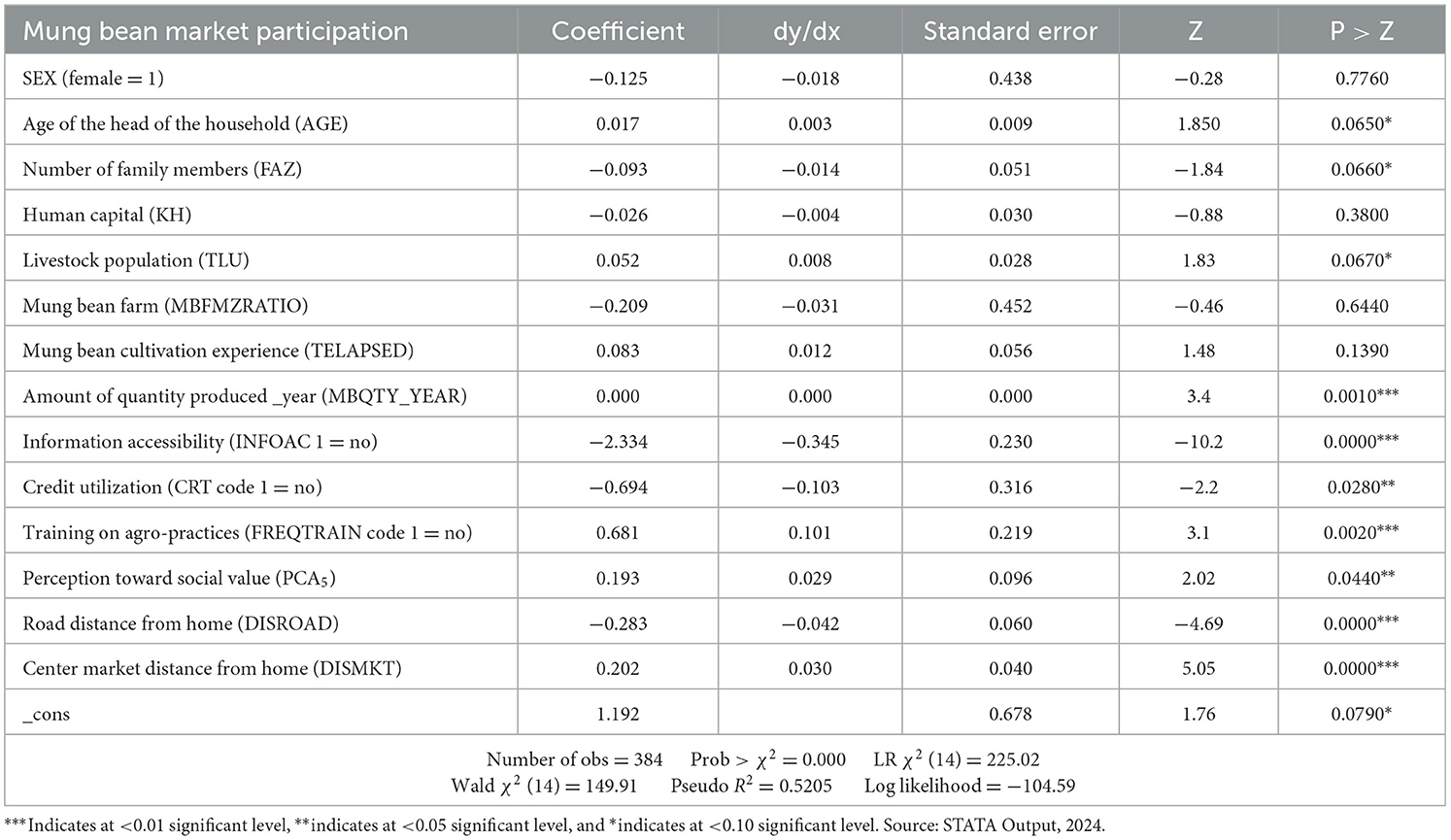
Table 8 indicates the selection equation result of the main driving factors that are influencing mung bean farmers' market participation status. As shown in Table 8, the Chi-square value ( = 225.02) and the log-likelihood ratio [LR χ2 (14) = −104.59] confirmed the final model was appropriate with P < 0.000. McFadden's pseudo R2 given by LR Chi2 (Deviance null – Deviance full) divided by Deviance full and each model Deviance is equal to −2 * the log-likelihood for that model and gave the value of 52.05%, suggests the goodness of fit of the model's adequacy. To treat the heteroscedasticity assumption, some continuous variables are computed by using composite indexes and ratios.
A total of 14 covariates, such as sex, age, CRT, human capital, information accessibility, tropical livestock unit, family size, farm size to mung bean cultivation, how far is the all-weather road from the homestead, center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers, amount of products in kilograms within a year, frequent training on agro-practices, perception toward social value (PC5) and mung bean cultivation experience (TELAPSED) were included into the selection equation to identify the determinates of market participation status. Age, CRT, information accessibility, tropical livestock unit, number of family members, how far is the all-weather road from the homestead, center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers, amount of products in kilograms within a year, frequent training on agro-practices and perception toward social value (PC5) were significantly affected mung bean market participation.
Information accessibility, how far is the all-weather road from the homestead, center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers, amount of products in kilograms within a year, and frequent training on agro-practices were significant (P < 0.01), while perception toward social value (PC5) was significant (P < 0.05) and age, CRT, tropical livestock unit, and a number of family members were significant at < 10% significance level. On the contrary, age, livestock population in TLU, center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers, amount of products in kilograms within a year, frequent training on agro-practices, and perception toward social value were more likely to affect mung bean market participation. This binary probit regression estimation result indicated in Table 8 is almost similar to that of the simultaneous estimation technique of ESR.
The age of the head of the household was highly likely (coeff. = 0.017) and significantly (p > Z = 0.0650) to affect the market participation of mung bean farmers. Holding all the other factors constant, household age increased the likelihood of participating in the mung bean market. One percentage increment in the age of the head of the household increased their likelihood of market participation by 0.30%. This means they get older and older, and they experience more participation in the mung bean market than their counterparts. This might be acquired from a lot of experience in older farmers' mung bean cultivation. This finding was congruent with the findings in the lowlands of southern Ethiopia (Aboye et al., 2023).
Family size of households is less likely (coeff. = −0.093) and significantly influences the market participation status at < 10% (P > z = 0.0660) significant level. A one family member addition on family decreased the likelihood of participating in the mung bean market in the study area by 1.4%, holding all other factors constant. The increasing of the family size retards the market participation. This might be most of the mung bean production required for large family sizes to smooth local dish problems for some early adopters in low-land areas. It is congruent with the finding of Haile et al. (2022).
Holding all the other factors constant, having a large livestock population in TLU is highly likely to increase the probability of participating in the market by 0.8% at p = 0.000. Livestock ownership was found to have a more likely (coef. = 0.052) and significant influence on participation in the mung bean market at < 10% level of significance. Households that have large livestock population support them in purchasing necessary agricultural inputs and implement them through asset accumulation, thereby increasing market surplus, unlike other low-land areas in Ethiopia that practice more pastoralism. The previous studies (Gebiso et al., 2023) confirmed that livestock are mostly vital for asset accumulation.
The quantity of mung bean produced by farmers was statistically significant and more likely affecting market participation for mung bean farmers. Suppose the farmers get more output, and the probability of deciding the supply of beans to the market increases. Increasing the number of products is a significant contributing factor in participating in the output market, thereby enhancing livelihood resilience (Molla et al., 2024). In addition, the production of mung beans is mostly for sale rather than used for local dishes like other regions of the country (Sánchez-Toledano et al., 2018; Manda, 2016).
Households that did not utilize credit for agricultural business influenced the market participation less likely and significantly affected by < 5% significance level than their counterparts. Holding all the other factors constant, a unit change by not utilizing credit services (CRT = 1) decreases their likelihood of participating in the mung bean market by 10.3% at p = 0.028. The current finding is congruent with others (Zakari et al., 2023).
Information accessibility also highly and significantly affected the binary responses at < 1% (p > z = 0.0000). One percentage increment in no-information accessibility (base category) decreased the probability of participating in the center market by 34.5% at p = 0.000. Those farmers who have no information on agro-practices of the mung bean and marketing issues can make the decision to participate in the mung bean market participation decision less likely (coef. = −2.334). This finding is similar to the finding of Belete and Nigatu (2023).
An increase in the frequent training on mung bean crop agro-practices decreased a 10.1% probability of increment, citrusparibus. Frequent training on mung bean crop agro-practices was less likely to affect binary responses. The more training is provided for mung bean crop cultivation, the less advantage it gives the farmers in surplus supply for the market. Though it increases the managing capability of the crop, it does not have access to nearby markets or the ECX market. The finding is inconsistent with the finding of Belete and Nigatu (2023). They stated that the extension services increase the capability of farmers to manage and supply the crops to the market.
A 1% increase in perception toward social value increased the likelihood of market participation occurrence by 2.9% with a significance level of p = 0.044. Moreover, positive societal perceptions toward mung bean crop cultivation should be enhanced to produce a large amount of quantity, thereby increasing output supply to the market (Kassa et al., 2021; Emran et al., 2021).
Center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers increased the likelihood of participating in the mung bean market by 3.0% at p = 0.000. A 1-km distance to all-weather roads decreased their likelihood of participating by 4.2%, citrusparibus. Framers' home distance to all-weather roads decreased the probability of participating in the mung bean market. This could be explained by price differentials (Gikonyo et al., 2022). The farmers' willingness to supply his/her products to the market is very less due to the sparsely populated access to road facilities and the large size of farms in low-land areas that are very far from the road. This finding is similar to the finding of Kassa et al. (2021) and Kidane et al. (2022) in market participation of maize, pigeon pea, and mung bean crops.
3.2.2 Impact of mung bean market participation on farmers' asset accumulation _Stage II: results from endogenous switching regression model
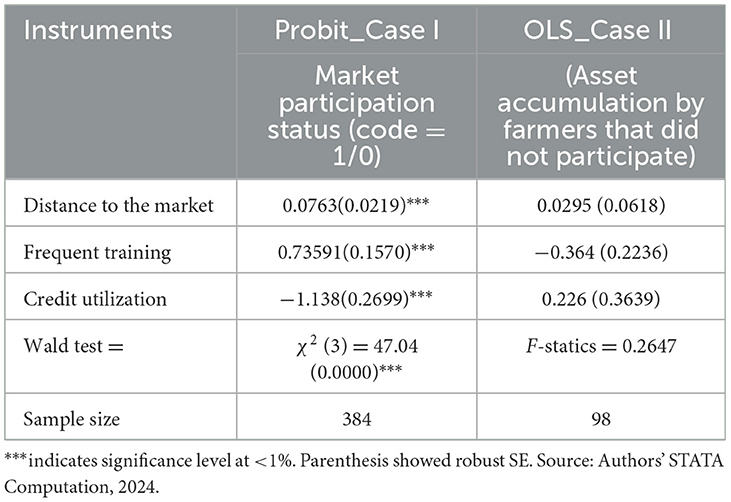
For impact evaluation in stage two, ESR was used to estimate the binary and continuous parts of the equation simultaneously (Cazzuffi et al., 2020; Emran et al., 2021). Its appropriateness is confirmed by the validity test result of selection instrument identification (IVs test). Accordingly, the IVs test confirmed the validity of market distance, frequent training on agro-practices, and CRT status, which were not jointly statistically significant causes of asset accumulation for market mung bean market participants and non-participants. As depicted in Table 9, distance to the market, frequent training on agro-practices, and CRT were statistically significant at < 1% significance level, different from zero, in probit model estimation of the mung bean market participation status of the pooled samples. On the other hand, the OLS estimation showed that these covariates did not affect the asset accumulation of the non-participants group (N = 98). Therefore, the excluded IVs are relevant.
The overall fitness test of the model (Wald χ2 test = 65.54), the correlation coefficient test of the model, such as the Wald test of the independent equation, also significant with χ2 (1) = 6.59; Prob > χ2 = 0.03, which implies that the mung bean market participation was positively correlated with asset accumulations in the study area. The inclusion of at least a few covariates in the selection equation directly affects the mung bean market participation decision but does not affect the outcome equation of the non-participant group. An exclusion restriction is based on economic theories and other previous empirical studies, such as Meskel et al. (2020) and Manda et al. (2020).
The correlation coefficients (ρ1 = 0.504 and ρ0 = −0.304) between participation in the mung bean market and asset accumulation exhibited both signs, and asset accumulation was significant at < 5% level. This indicates that self-selection occurred among the mung bean crop participants and non-participants. Mung bean market participants would have high asset accumulation, and whether they participate in the market, they would be better off if they participated. Relatively, non-participants would have low asset accumulation but would be better off if they preferred to participate in the mung bean market. The positive correlation coefficients between outcome variables and mung bean market participation status also implied that there were both observable and unobservable factors that affected the participation and outcome, such as asset accumulation. The difference in the coefficients of the asset equation between treatment groups shows that heterogeneity influences the value of asset accumulation.
Table 10 presented the full-information maximum likelihood estimates the impact mung bean crop market participation upon asset accumulation The asset accumulation _1 stands for participant farmers, whereas asset accumulation _0 stands for non-participant farmers. Age of the head of household (AGE) was directly affected asset accumulation _1 at < 5% significant level while the amount of products in kilograms within a year at < 1% significant level, and farmers' home proximity to all-weather roads at < 1% significant level. Moreover, asset accumulation _1 was negatively affected by information accessibility at < 1% significant level. On the other hand, accumulation _0 was directly and significantly affected by farmers' home distance from all-weather and information accessibility at < 5% significant level in low-land areas of South Ethiopia.
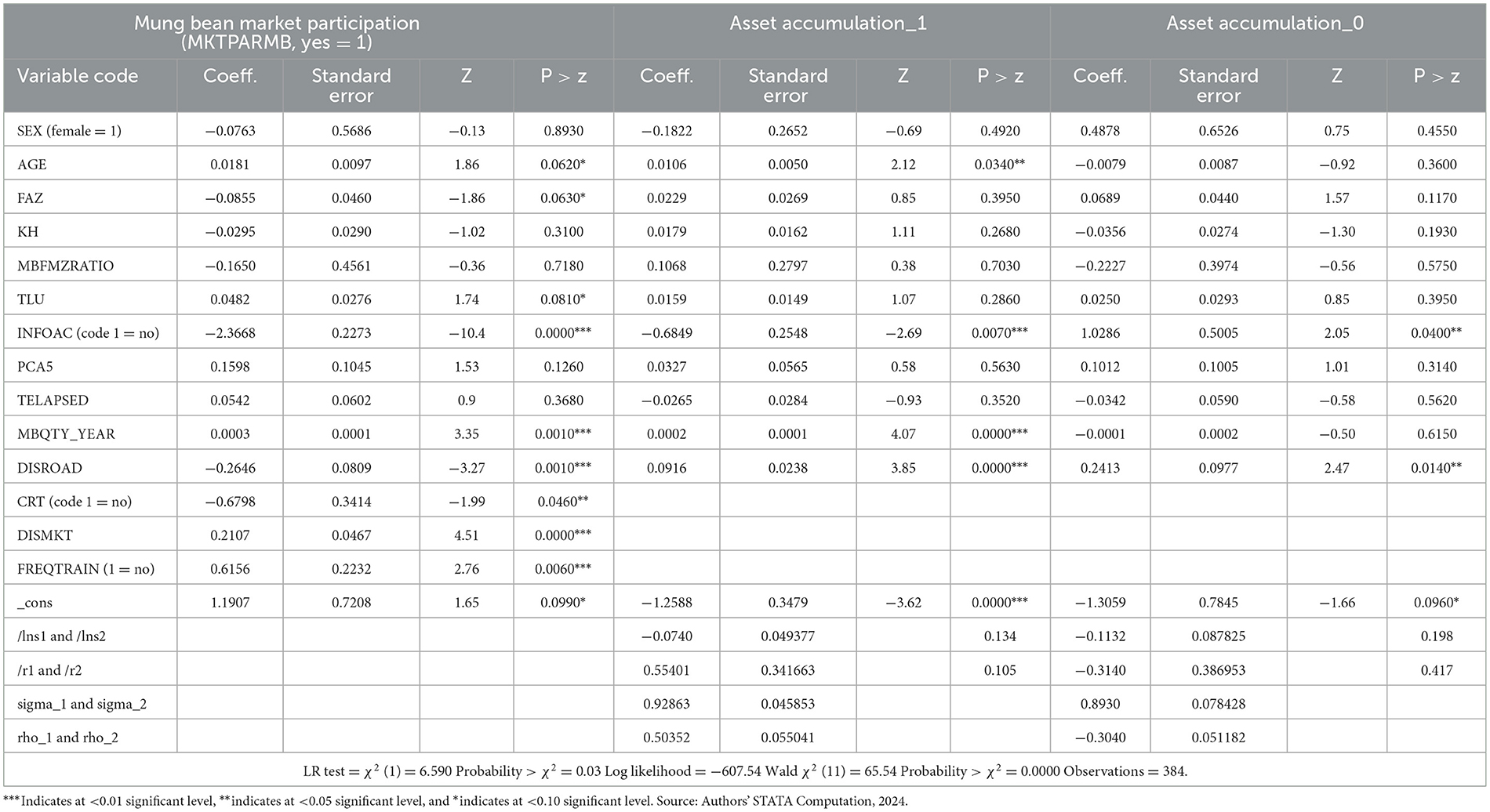
Table 10. Endogenous switching regression (ESR) estimation for asset accumulation of mung bean farmers.
A unit increment in the age of the head of household (AGE) results from the proportional change in an asset accumulation of mung bean market participants by 1.06% (0.0106) whereas decreases an asset accumulation of non-participants by 0.79% (−0.0079). However, it was insignificant. This result is congruent with others (Dagnew et al., 2023). In addition, the age of the household head and amount of products in kilograms within a year only influenced those who did not participate in the mung bean market as depicted in Table 10. These disparities reflect the fact that there is heterogeneity between mung bean market participants and non-participants. The more you produce the mung bean crop, the more supply to the market, thereby boosting asset accumulation by 0.02% (0.0002). It helps increase the living standard of rural households (Bezabeh et al., 2020; Kassa et al., 2021). Furthermore, a mung farmer who did not have access to information on specific crops was less likely to possess more assets than those who had access to information in low-land areas of South Ethiopia.
Finally, the average treatment effect (ATE) in terms of population of the coefficient estimate of participants' farmers in bean market participants and average treatment effect on treated (ATET) for sample impacts on asset accumulation were 0.3200 and 0.3047 and significant at p > z = 0.0490 for nearest-neighbor matching approach, respectively. Meanwhile, the coefficients of ATET were positive and significant at less than a 10% significance level for the regression adjustment approach. These indicate that the one who participated in the mung bean market have a greater probability of increasing asset accumulation than their counterparts.
4 Conclusion and recommendations
4.1 Conclusion
The current aimed to evaluate the impact of mung bean crop market participation on asset accumulation of smallholder households in low-land areas of South Ethiopia. Following the multistage sampling techniques, from the selected six Woredas, a total of 384 samples have been taken for the entire analysis. Based on the above-mentioned findings, the study was drawn the following conclusions:
• About 74.5% of farmers participated in the bean market, while 25.5% of farmers did not participate in the mung bean market out of 384 observations.
• The difference in asset accumulation ranges to 4.779, and it explains the wide uneven possession of households' assets in the three selected zones in SERS.
• The selection equation result revealed that information accessibility, the proximity of an all-weather road from the homestead, center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers, the amount of products in kilograms within a year and frequent training on agro-practices significantly affected market participation at < 1% significance level. Perceptions of social value and CRT were significant at less than a 5% significance level, while the age of the head of household, tropical livestock unit, and family size affected market participation at less than a 10% significance level.
• The mung bean market participation is more likely affected by the age of the household head, CRT, access to market information, tropical livestock unit, center market distance from the residence of mung bean farmers, amount of products in kilograms within a year and perception toward social value. The number of family members, road distance from home, and frequent training on agro-practices were less likely to affect the mung bean market participation.
• The full-information maximum-likelihood method result showed that the asset accumulation of mung bean market participants, outcome equations, was positively and significantly affected by the amount of products in kilograms within a year and farmers' home proximity from all-weather roads and age of household head, whereas information accessibility negatively affected. On the other hand, asset accumulation of non-market participants was positively and significantly affected by farmers' home distance from all-weather and information accessibility.
• The average treatment effects in both cases (population effects and treated) are 0.3200 and 0.3047, respectively. Meanwhile, the coefficients of the average treatment effect on the treated patient are positive. Thus, the farmers who participated in the mung bean market had a greater probability of increasing asset accumulation than their counterparts. However, eco-friendly farmers face various challenges in supplying their products to the market.
4.2 Recommendations
Therefore, based on these findings, it is recommended that credit facilities purchase new farm technology and implements for farmers' agricultural practices to boost its production, information accessibility of the new emerging beans, frequent training on agro-practices, and other infrastructure facilities should get another look by government and non-governmental organizations, ECX and market regulatory bodies to enhance market participation. Increasing market participation of mung bean supports rural households uplifting the improvement of livelihood through increasing asset accumulation for smoothing elongated shocks encountered by eco-friendly farmers in SERS, Ethiopia. In all cases, it is worth mentioning that this study still lacks the support of a large amount of data gathered about this specific crop over different periods to determine the dynamics. A single cross-sectional study may miss significant long-term trends, such as market dynamics, marketing volume and recorded price data of newly emerging mung bean crops, which are crucial for understanding overall market participation.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Wolaita Sodo University Graduate Studies Directorate with a research permit letter of Ref. GSD_596_15. Written informed consent to participate in this study was provided by the [patient/participants' OR patient/participants legal guardian/next of kin].
Author contributions
GG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BK: Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AT: Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abokyi, E., Strijker, D., Asiedu, K. F., and Daams, M. N. (2020). The impact of output price support on smallholder farmers' income: evidence from maize farmers in Ghana. Heliyon 6:e05013. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05013
Aboye, A. B., Kinsella, J., and Mega, T. L. (2023). Farm households' adaptive strategies in response to climate change in lowlands of southern Ethiopia. Int. J. Clim. Change Strat. Manag. 15, 579–598. doi: 10.1108/IJCCSM-05-2023-0064
Addis, Y., and Abirdew, S. (2021). Smallholder farmers' perception of climate change and adaptation strategy choices in Central Ethiopia. Int. J. Clim. Change Strat. Manag. 13, 463–482. doi: 10.1108/IJCCSM-09-2020-0096
Ademe, B. E. (2023). Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L.) production vis-avis market potential in Ethiopia: a review. Asian J. Biol. Sci. 16, 614–622. doi: 10.3923/ajbs.2023.614.622
Adhikari, S., and Khanal, A. R. (2021). Economic sustainability and multiple risk management strategies: examining interlinked decisions of small american farms. Sustainability 13:1741. doi: 10.3390/su13041741
Ahsanuzzaman, A. (2015). “Duration analysis of technology adoption in Bangladeshi agriculture,” in 2015 AAEA and WAEA Joint Annual Meeting, San Francisco, California, 26-28 July 2015, 1–32.
Assefa, Z. B., Dinku, A. M., and Jemal, A. M. (2022). Value chain analysis of Mung Bean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek thrive) in Kalu Woreda, Ethiopia. Agric. Food Secur. 11, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s40066-022-00393-2
Atnaf, M., Tesfaye, K., and Dagne, K. (2015). The importance of legumes in the ethiopian farming system and overall economy: an overview. Am. J. Exper. Agric. 7, 347–358. doi: 10.9734/AJEA/2015/11253
Baker, M. M., and Yuya, B. A. (2020). Determinant of sesame export performance in ethiopia: a panel gravity model application. Turkish J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 8, 714–720. doi: 10.24925/turjaf.v8i3.714-720.3219
Baza, M., Shanka, D., and Bibiso, M. (2022). Agronomic and economic performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties in response to rates of blended NPS fertilizer in Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia. Open Life Sci. 17, 1053–1063. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0461
Belete, A. A., and Nigatu, A. G. (2023). Determinants of market participation among smallholder teff farmers, empirical evidence from central Ethiopia. Environ. Dev. 48:100929. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2023.100929
Bezabeh, A., Beyene, F., Haji, J., and Lemma, T. (2020). Impact of contract farming on income of smallholder malt barley farmers in Arsi and West Arsi zones of Oromia region, Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 6:1834662. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2020.1834662
Biru, W. D., Zeller, M., and Loos, T. K. (2020). The impact of agricultural technologies on poverty and vulnerability of smallholders in ethiopia: a panel data analysis. Soc. Indic. Res. 147, 517–544. doi: 10.1007/s11205-019-02166-0
Brockington, D., and Brockington, D. (2021). Persistent peasant poverty and assets. Exploring dynamics of new forms of wealth and poverty in Tanzania 1999–2018. J. Peasant Studi. 48, 201–220. doi: 10.1080/03066150.2019.1658081
Cazzuffi, C., McKay, A., and Perge, E. (2020). The impact of agricultural commercialisation on household welfare in rural Vietnam. Food Policy 94:101811. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2019.101811
Chalite, G. C. (2020). Management of plant biodiversity in the homegarden agroforestry practices in demba gofa district of south Ethiopia. Int. J. Curr. Res. 12, 14655–14659. doi: 10.24941/ijcr.39900.11.2020
Dagnew, A., Goshu, D., Zemedu, L., and Sileshi, M. (2023). Impacts of contract farming on asset accumulation of malt barley farmers in Northwestern Ethiopia. Cogent Econ. Finance 11:2230724. doi: 10.1080/23322039.2023.2230724
De Muro, P., Mazziotta, M., and Pareto, A. (2011). Composite indices of development and poverty: an application to MDGs. Soc. Indic. Res. 104, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s11205-010-9727-z
Di Falco, S., Veronesi, M., and Yesuf, M. (2011). Does adaptation to climate change provide food security? A micro-perspective from Ethiopia. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 93, 829–846. doi: 10.1093/ajae/aar006
Dikr, W. (2023). Mung Bean (Vigna Radiata L.) production status and challenges in Ethiopia. Glob. Acad. J. Agri. Biosci. 5, 13–22. doi: 10.36348/gajab.2023.v05i02.002
Dinsa, T., Balcha, U., Benya, F., and Fufa, M. (2022). Performance evaluation of improved mung bean (Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek) varieties at low moisture areas East Shewa, Oromia, Ethiopia. J. Sci. Agric. 6, 1–3. doi: 10.25081/jsa.2022.v6.7289
Durjoy Lal Soren, D. (2023). Analyzing the distribution and variation of household assets and amenities in North Bengal municipalities: a construction of assets index (ASI) and Amenity Index (AMI). Int. J. Sci. Res. 12, 996–1007. doi: 10.21275/SR23714062041
Emeru, G. M. (2022). The perception and determinants of agricultural technology adaptation of teff producers to climate change in North Shewa zone, Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. Cogent Econ. Finance 10:2095766. doi: 10.1080/23322039.2022.2095766
Emran, S. A., Krupnik, T. J., Aravindakshan, S., Kumar, V., and Pittelkow, C. M. (2021). Factors contributing to farm-level productivity and household income generation in coastal Bangladesh's rice-based farming systems. PLoS ONE 16:e0256694. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256694
Eze, E., Girma, A., Zenebe, A., Okolo, C. C., Kourouma, J. M., and Negash, E. (2022). Predictors of drought-induced crop yield/losses in two agroecologies of southern Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 12, 1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09862-x
Gata, G., Kuma, B., and Tafesse, A. (2024). Assessment of cumulative incidences of mung bean crop production in lowlands of south Ethiopia through multiple factor analysis. Heliyon 10:e31012. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31012
Gebiso, T., Ketema, M., Shumetie, A., and Leggesse, G. (2023). Drivers of crop commercialization in central and southern Oromia, Ethiopia. Disc. Food 3, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s44187-023-00055-7
Getachew, T. (2019). Pulse crops production opportunities, challenges and its value chain in Ethiopia: a review article. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 9, 20–29. doi: 10.7176/jees/9-1-03
Gikonyo, N. W., Busienei, J. R., Gathiaka, J. K., and Karuku, G. N. (2022). Analysis of household savings and adoption of climate smart agricultural technologies. Evidence from smallholder farmers in Nyando Basin, Kenya. Heliyon 8:e09692. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09692
Habte, E., Katungi, E., Yirga, C., Fenta, B. A, Ratz, B., Mukankusi, C. T., et al. (2021). Adoption of Common Bean Technologies and its Impacts on Productivity and Household Welfare in Ethiopia: Lessons from Tropical Legumes Project Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research. doi: 10.13140/RG.2.2.17130.03524
Haile, B. T., Bekitie, K. T., Zeleke, T. T., Ayal, D. Y., Feyisa, G. L., and Anose, F. A. (2022). Drought analysis using standardized evapotranspiration and aridity index at bilate watershed: sub-basins of ethiopian rift valley. Sci. World J. 2022, 1–14. doi: 10.1155/2022/1181198
Hashmiu, I., Agbenyega, O., and Dawoe, E. (2022). Cash crops and food security: evidence from smallholder cocoa and cashew farmers in Ghana. Agric. Food Secur. 11, 1–21. doi: 10.1186/s40066-022-00355-8
Isayev, S., Malikov, E., Tadjiev, S., Berdiyorov, E., and Pulatova, M. (2023). Modelling effects of irrigation with collector-drainage water on second crop productivity in sample of mung beans. E3S Web Confer. 365:01021. doi: 10.1051/e3sconf/202336501021
Islam, R., and Walkerden, G. (2022). Livelihood assets, mutual support and disaster resilience in coastal Bangladesh. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 78:103148. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.103148
Jankelova, N., Masar, D., and Moricova, S. (2017). Risk factors in the agriculture sector. Agric. Econ. 63, 247–258. doi: 10.17221/212/2016-AGRICECON
Kassa, Y., Mamo, D., Abie, A., Tigabe, A., and Ayele, T. (2021). Scaling up of improved mung bean technology in the potential areas of North Shewa Zone Amhara Region. Int. J. Agric. Extens. 9, 135–141. doi: 10.33687/009.02.3257
Kaysha, K., Shanka, D., and Bibiso, M. (2020). Performance of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties at different NPS rates and row spacing at Kindo Koysha district, Southern Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 6:1771112. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2020.1771112
Kebede, E. (2020). Grain legumes production and productivity in Ethiopian smallholder agricultural system, contribution to livelihoods and the way forward. Cogent Food Agric. 6:1722353. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2020.1722353
Kidane, R., Wanner, T., Nursey-Bray, M., Masud-All-Kamal, M.d., and Atampugre, G. (2022). The role of climatic and non-climatic factors in smallholder farmers' adaptation responses: insights from rural Ethiopia. Sustainability 14:5715. doi: 10.3390/su14095715
Komarek, A. M., De Pinto, A., and Smith, V. H. (2020). A review of types of risks in agriculture: What we know and what we need to know. Agric. Syst. 178:102738. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2019.102738
Koné, S., Bonfoh, B., Dao, D., Koné, I., and Fink, G. (2019). Heckman-type selection models to obtain unbiased estimates with missing measures outcome: theoretical considerations and an application to missing birth weight data. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 19, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12874-019-0840-7
Li, M., Gan, C., Ma, W., and Jiang, W. (2020). Impact of cash crop cultivation on household income and migration decisions: Evidence from low-income regions in China. J. Integr. Agric. 19, 2571–2581. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63161-6
Lokshin, M., and Sajaia, Z. (2004). Maximum likelihood estimation of endogenous switching regression models. Stata J. 4, 282–289. doi: 10.1177/1536867X0400400306
Manda, J. (2016). Econometric Analysis of Improved Maize Varieties and Sustainable Agricultural Practices (SAPs) in Eastern Zambia. Thesis, Wageningen University.
Manda, J., Azzarri, C., Feleke, S., Kotu, B., Claessens, L., and Bekunda, M. (2021). Welfare impacts of smallholder farmers' participation in multiple output markets: empirical evidence from Tanzania. PLoS ONE 16:e0250848. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250848
Manda, J., Khonje, M. G., Alene, A. D., Tufa, A. H., Abdoulaye, T., Mutenje, M., et al. (2020). Does cooperative membership increase and accelerate agricultural technology adoption? Empirical evidence from Zambia. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 158:120160. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120160
Meskel, T. W., Ketema, M., Haji, J., and Zemedu, L. (2020). Welfare impact of moringa market participation in southern Ethiopia. Sustain. Agric. Res. 9:98. doi: 10.5539/sar.v9n3p98
Mmbando, F. E., Wale, E. Z., and Baiyegunhi, L. J. S. (2015a). Determinants of smallholder farmers' participation in maize and pigeonpea markets in Tanzania. Agrekon 54, 96–119. doi: 10.1080/03031853.2014.974630
Mmbando, F. E., Wale, E. Z., and Baiyegunhi, L. J. S. (2015b). Welfare impacts of smallholder farmers' participation in maize and pigeonpea markets in Tanzania. Food Secur. 7, 1211–1224. doi: 10.1007/s12571-015-0519-9
Molla, E., Hailekirstos, E., Mengstie, M., and Zenebe, T. (2022). Determinants of wheat value chain in case of North Shewa Zone of Amhara region, Ethiopia. Cogent Econ. Finance 10:2014639. doi: 10.1080/23322039.2021.2014639
Molla, S. D., Zeleke, M. T., and Tamiru, S. M. (2024). Assessing livelihood resilience in drought-affected areas: lessons from Raya Kobo district, northeast Ethiopia. Heliyon 10:e23399. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23399
Mulwa, C., Marenya, P., Rahut, D. B., and Kassie, M. (2017). Response to climate risks among smallholder farmers in Malawi: a multivariate probit assessment of the role of information, household demographics, and farm characteristics. Clim. Risk Manag. 16, 208–221. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2017.01.002
Neda, E. K. (2020). Grain legumes production in Ethiopia: a review of adoption, opportunities, constraints and emphases for future interventions. Turkish J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 8, 977–989. doi: 10.24925/turjaf.v8i4.977-989.3254
Ogada, M. J., Rao, E. J. O., Radeny, M., Recha, J. W., and Solomon, D. (2020). Climate-smart agriculture, household income and asset accumulation among smallholder farmers in the Nyando basin of Kenya. World Dev. Perspect. 18:100203. doi: 10.1016/j.wdp.2020.100203
Olounlade, O. A., Li, G.-C., Kokoye, S. E. H., Dossouhoui, F. V., Akpa, K. A. A., Anshiso, D., et al. (2020). Impact of participation in contract farming on smallholder farmers' income and food security in rural benin: PSM and LATE parameter combined. Sustainability 12:901. doi: 10.3390/su12030901
Rios, R., Masters, W. A., and Shively, G. E. (2008). “Linkages between market participation and productivity: results from a multi-country farm household sample. Evidencefrom LSMS data,” in Proceedings of the International Association Agricultural Economic Conference China, 16–22 August 2009, 34.
Rubhara, T. T., Mudhara, M., Oduniyi, O. S., and Antwi, M. A. (2020). Impacts of cash crop production on household food security for smallholder farmers: a case of Shamva District, Zimbabwe. Agriculture 10:188. doi: 10.3390/agriculture10050188
Sánchez-Toledano, B. I., Kallas, Z., Palmeros Rojas, O., and Gil, J. M. (2018). Determinant factors of the adoption of improved maize seeds in southern mexico: a survival analysis approach. Sustainability 10:3543. doi: 10.3390/su10103543
Sequeros, T., Ochieng, J., Schreinemachers, P., Binagwa, P. H., Huelgas, Z. M., Hapsari, R. T., et al. (2021). Mungbean in Southeast Asia and East Africa: varieties, practices and constraints. Agric. Food Secur. 10, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s40066-020-00273-7
Sequeros, T., Schreinemachers, P., Depenbusch, L., Shwe, T., and Nair, R. M. (2020). Impact and returns on investment of mungbean research and development in Myanmar. Agric. Food Secur. 9, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s40066-020-00260-y
Silva, K. N. N., and Broekel, T. (2016). Factors Constraining Farmerss Adoption of New Agricultural Technology Programme in Hambantota District in Sri Lanka: Perceptions of Agriculture Extension Officers. SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2910350
Simion, T. (2018). Identification and prioritization of major factors that challenge crop productivity and production system in the case of gamo gofa, segen area people zone and basketo special woreda a review essay. Ann. Soc. Sci. Manag. Stud. 1, 10–15. doi: 10.19080/ASM.2018.01.555553
Tabe Ojong, M. P. J. R., Hauser, M., and Mausch, K. (2022). Does agricultural commercialisation increase asset and livestock accumulation on smallholder farms in Ethiopia? J. Dev. Stud. 58, 524–544. doi: 10.1080/00220388.2021.1983170
Tadele, T. T., Gebremedhin, C. C., Markos, M. U., and Fitsum, E. L. (2022). Stunting and associated factors among 6–23 month old children in drought vulnerable kebeles of Demba Gofa district, southern Ethiopia. BMC Nutr. 8, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00501-2
Teame, G., Ephrem, S., Lemma, D., and Getachew, B. (2017). Adaptation study of Mung Bean (Vigna Radiate) varieties in Raya Valley, Northern Ethiopia. Curr. Res. Agric. Sci. 4, 91–95. doi: 10.18488/journal.68.2017.44.91.95
Tehulie, N. S., Fikadu, T., and Purba, J. H. (2021). Response of mungbean [Vigna radiata (L.)Wilczek] varieties to plant spacing under irrigation at gewane, northeastern Ethiopia. Agro Bali. 4, 1–14. doi: 10.37637/ab.v0i0.613
Temeche, D., Getachew, E., Hailu, G., and Abebe, A. (2022). Effect of Sorghum-Mung bean intercropping on sorghum-based cropping system in the lowlands of north Shewa, Ethiopia. Adv. Agric. 2022, 1–7. doi: 10.1155/2022/6987871
Tesfamicheal Wossen, A. (2015). Climate variability, social capital and food security in sub-saharan Africa : household level assessment of potential impacts and adaptation options. Doctoral Thesis.
Tun, Y. Y., and Phyo, A. (2019). Economic analysis of green mung bean in selected area, Myanmar. J. Encon. Sustain. Dev. 8, 394–401. doi: 10.21275/ART20203145
Wang, Y., Liu, G., Guo, E., and Yun, X. (2018). Quantitative agricultural flood risk assessment using vulnerability surface and copula functions. Water 10:1229. doi: 10.3390/w10091229
Willy, B. T., Beyene, A. B., and Amare, D. M. (2023). The determinants of beef cattle market participation on beef cattle producers' welfare: a case study of west shewa zone, Oromia region, Ethiopia. Adv. Agric. 2023, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2023/8822032
Zakari, S., Moussa, B., Ibro, G., and Abdoulaye, T. (2023). Analyzing the drivers of smallholder farmer's market participation in the Sahelian region of Niger. Cogent Food Agric. 9:2220178. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2023.2220178
Keywords: asset accumulation, ESR, market participation, MCA, OLS, probit
Citation: Gata G, Kuma B and Tafesse A (2025) Impact of mung bean crop market participation on asset accumulation of smallholder households in low-land areas of South Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1562864. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1562864
Received: 18 January 2025; Accepted: 13 June 2025;
Published: 10 July 2025.
Edited by:
Raquel Santiago Barro, Universidade Federal de Viçosa, BrazilReviewed by:
Innocent Osoro Ngare, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, South SudanHabtamu Atalay Wubea, Dire Dawa University, Ethiopia
Copyright © 2025 Gata, Kuma and Tafesse. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Girma Gata, Z2lybWFnZ2FuZWJvQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Girma Gata
Girma Gata Berhanu Kuma
Berhanu Kuma Alula Tafesse
Alula Tafesse