- 1Department of Agricultural Economics and Agribusiness Management, Faculty of Agriculture, Egerton University, Njoro, Kenya
- 2Department of Economics and Management, University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy
Introduction: The dairy value chain in Kenya is important for income generation and food security, yet smallholder farmers face increasing challenges due to climate change. Climate-smart dairy strategies (CSDS), including improved breeds, feed improvement, health, and manure management, offer promising pathways to enhance productivity and environmental sustainability. While studies have focused on socio-economic factors influencing the adoption of these strategies, the role of entrepreneurial orientation remains underexplored. Entrepreneurial orientation is important in decision-making and enabling agripreneurs to capitalize on growth opportunities.
Methods: This study addresses this gap by assessing the influence of five dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation, namely risk-taking, innovativeness, proactiveness, autonomy, and competitive aggressiveness, on the adoption intensity of CSDS among 385 smallholder dairy farmers in Central Kenya. The study used a cross-sectional research design and a generalised ordered logit model.
Results and Discussion: The results reveal that autonomy and risk-taking significantly increase the likelihood of adopting CSDS (P<0.01) and that various control variables shape them. Autonomy enables farmers to make independent strategic choices, while risk-taking allows them to experiment with CSDS despite uncertainty. Policy interventions should strengthen farmers’ entrepreneurial capacity by promoting training and extension programs that build confidence, decision-making autonomy, and willingness to adopt CSDS. These findings offer clear and actionable recommendations to boost CSDS uptake and support sustainable agriculture in Kenya and other Sub-Saharan African countries.
1 Introduction
The dairy value chain is a vital source of income for many communities in Sub-Saharan countries, particularly in Kenya (Maina et al., 2020). In this country, dairy production ranks the fifth-largest agricultural sub-sector, following meat, horticulture, vegetables, and oils and fats (KIPPRA, 2020). It contributes to approximately 15% of the GDP (KNBS, 2022). Furthermore, the dairy industry, which grows at an annual rate of about 5%, sustains the livelihoods of approximately 1.8 million individuals (MOALF, 2019). With the highest milk consumption in Sub-Saharan Africa, Kenya has an estimated annual per capita consumption of 139 kg (Otieno et al., 2020). This figure is projected to increase by 35% by 2030 (Muunda et al., 2023).
However, climate change risks threaten the dairy value chain despite its importance to Kenya’s economy and livelihoods. Small-scale dairy farmers face climate change-induced shocks, including rising temperatures, erratic rainfall, flash floods, and droughts (Abbas et al., 2022; Odhiambo, 2020). For instance, heat waves have been shown to reduce milk quantity and nutritional composition, lowering the quality of derived dairy products (Gauly and Ammer, 2020). By 2085, heat stress alone could contribute to annual global cattle production losses nearing $40 billion (GCA, 2022). Additionally, climate change negatively affects forage quality and quantity, water availability, disease patterns, cattle reproduction, and biodiversity (Rojas-Downing et al., 2017). Conversely, dairy production is responsible for the highest greenhouse gas emissions per product, mainly due to its low average productivity resulting from poor-quality feeds and breeds (García de Jalón et al., 2017; Rademaker et al., 2016). Therefore, it becomes imperative to reorient the dairy production system to respond to the progressive impacts of climate change effectively.
In this context, implementing CSDS has been recognised as a promising solution to mitigate the impacts of climate change. CSDS aims to boost food security and income production, strengthen resilience, and curtail greenhouse gas emissions (FAO, 2021). These strategies encompass a range of practices such as improved breeding, enhanced feeds and feeding methods, better animal health and welfare, efficient manure management, effective herd size management, grass-legume fodder intercropping, and integrated crop-livestock production systems (Gulwa et al., 2018; Hawkins et al., 2022; Maindi et al., 2020; Mujeyi et al., 2022). For example, the crop-dairy production system is a synergistic climate-smart strategy that allows dairy animals to provide manure for crops. In contrast, in return, crops supply fodder to dairy animals (Mujeyi et al., 2022). Intercropping grass and legume fodder can improve soil quality through nitrogen fixation and increase forage quantity (Ericksen and Crane, 2018; Gulwa et al., 2018). Moreover, strategies such as zero grazing, feed supplementation, enhanced breeding, and improved animal health management can boost milk production and concurrently reduce greenhouse gas emissions (FAO, 2019; Kandulu et al., 2024; Kihoro et al., 2021; Llonch et al., 2017; Richardson et al., 2022; Wilkes et al., 2020). For example, efficient feeding reduces enteric methane emissions, better breeding decreases the number of low-yield animals, and improved health minimises losses and extends productive lifespan, contributing to more sustainable and climate-resilient dairy systems (Ericksen and Crane, 2018; FAO, 2019). Despite the benefits of these strategies in mitigating feed shortages, enhancing soil fertility, and increasing milk production, their adoption remains relatively low and uneven across Sub-Saharan Africa, including Kenya (Korir et al., 2023; Maindi et al., 2020).
Over the past decade, there has been a surge in studies aimed at understanding the factors driving the adoption of CSDS. The majority of the literature has centred on the socio-economic factors (Balcha et al., 2023; Maina et al., 2020; Mokoro et al., 2021), while others have focused on institutional factors influencing adoption in dairy production (Molieleng et al., 2021; Tesfaye et al., 2016; Wodajo and Ponnusamy, 2016). These studies suggest that farm income, off-farm income, access to credit, physical assets, and human capital significantly influence the adoption intensity of CSDS due to resource availability and investment capacity (Akzar et al., 2023; de Vries, 2019; García de Jalón et al., 2017; Mokoro et al., 2021; Musafiri et al., 2022a; Zemarku et al., 2022). Off-farm income, in particular, addresses credit constraints and serves as an alternative to borrowed credit (Chelang’a et al., 2023). Additionally, socio-demographic factors such as age, gender, and education have been reported to influence adoption in diverse ways. For instance, younger and more educated farmers are often more open to adopting innovations due to better access to information and greater risk tolerance (Abegunde et al., 2019), while gender dynamics can affect decision-making power and access to resources, thereby shaping adoption outcomes (Akzar et al., 2023). There is an ongoing debate regarding the influence of large household sizes on adopting climate-smart strategies. While some empirical literature suggests that larger household sizes contribute positively to labour availability (Dhraief et al., 2018; Odhiambo, 2020; Ng’ombe et al., 2024), other studies argue that large households exert financial strain on income allocation, thereby reducing the funds available for the uptake of agricultural technologies (Elahi et al., 2021; Musafiri et al., 2022b). Similarly, access to training and agricultural extension services has been shown to increase the adoption of climate-smart strategies by improving farmers’ knowledge, skills, and awareness of the benefits and application of such practices (Asule et al., 2024; Balcha et al., 2023; Kifle et al., 2022; Maina et al., 2020; Musafiri et al., 2022b). Agricultural extension services also serve as a critical link between farmers and innovations, helping to reduce uncertainty and build trust in new technologies (Dhraief et al., 2018). Group membership has also demonstrated a strong positive correlation with the adoption of climate-smart strategies, as it facilitates knowledge exchange, collective learning, and improved access to production resources such as credit and inputs (Mujeyi et al., 2022; Siraj, 2023; Yang and Wang, 2023). Recently, Rathakrishnan et al. (2022) studied the influence of socio-psychological factors on the adoption of sustainable production practices in dairy farms. They found that farmers who believed they had the ability and were equipped with the right attitude were more inclined to adopt sustainable agricultural practices.
While existing studies have shed light on the factors influencing the adoption intensity of climate-smart agricultural technologies, there is a noticeable gap in research concerning the role of entrepreneurial orientation (Kangogo et al., 2020; Andati et al., 2022), particularly in the context of dairy production. Understanding the role of entrepreneurial orientation in adoption is important because it reflects the mindset and behavioural traits that influence how farmers identify, evaluate, and act on new opportunities, particularly under conditions of risk and uncertainty, such as those caused by climate change. Moreover, there is a scarcity of studies that have examined the adoption of multiple CSDS among smallholder dairy farmers in Kenya. This study assesses the impact of smallholder farmers’ entrepreneurial orientation on the adoption of CSDS in the country, considering other demographic, socio-economic, and institutional variables (control variables), to highlight policy implications and potential actionable measures.
This paper adds value to the literature by exploring the role of entrepreneurial orientation in the adoption of CSDS in the dairy sector. The study, therefore, assesses the influence of entrepreneurial orientation and other factors on the adoption of CSDS among farmers. It expands on previous studies (Kangogo et al., 2020; Andati et al., 2022; Chepng'etich et al., 2024) by evaluating all five dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation, including autonomy and competitive aggressiveness (Suvanto et al., 2020). It highlights how entrepreneurial traits influence CSDS adoption and offers insights for policymakers on enhancing productivity and reducing emissions in Kenya and beyond.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Description of the study area
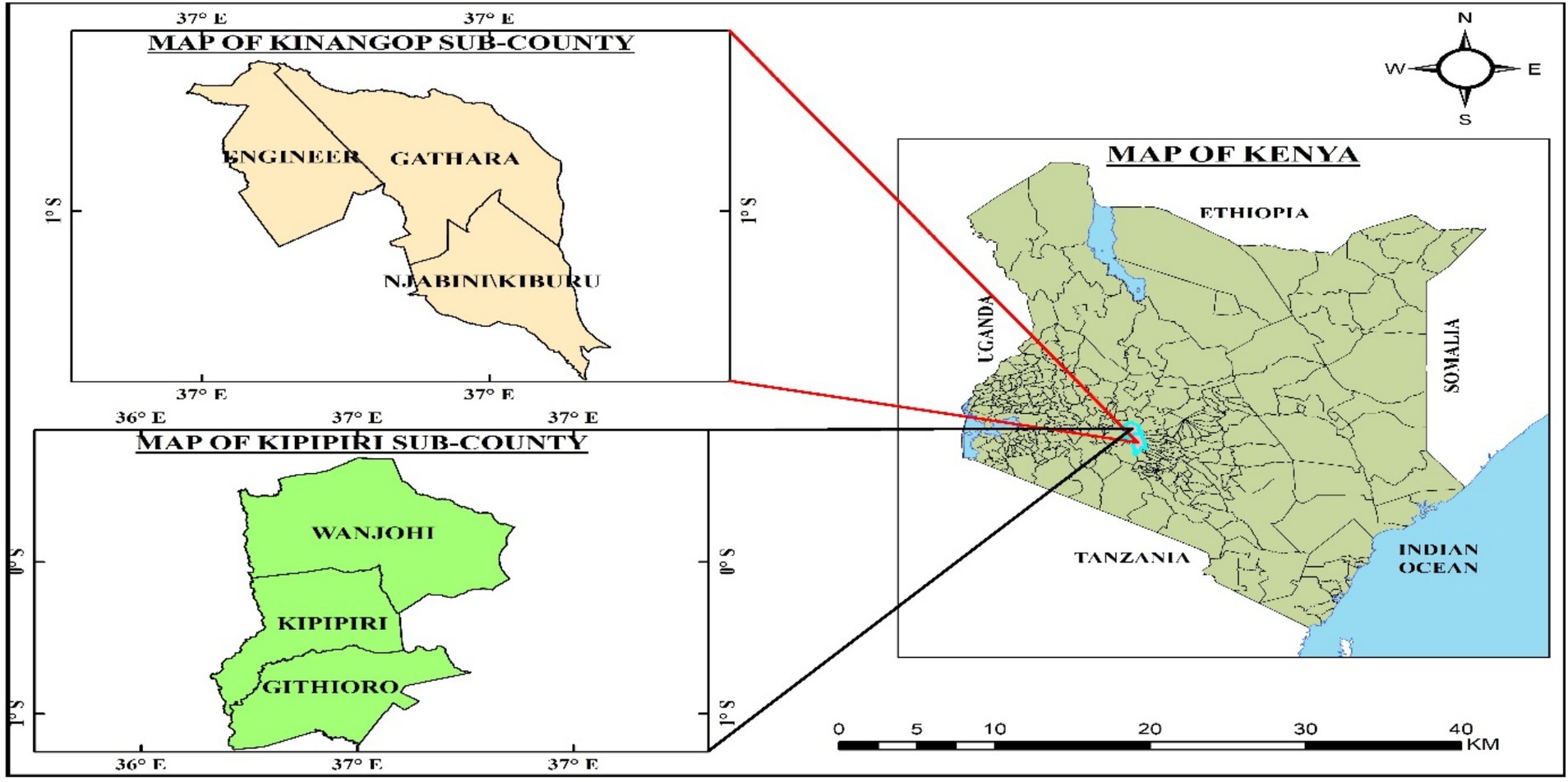
This study was carried out in Nyandarua County (Figure 1). The County is situated between latitude 0°8’ North and 0°50’ South and between longitude 35°13′East and 36°42’ West of central Kenya. It borders Laikipia to the North, Kiambu to the South, Murang’a to the Southeast, and Nakuru to the West. The region experiences an average annual rainfall of approximately 1,700 mm during the long rains and about 700 mm during the short rains. Temperatures are generally moderate, ranging from 12 °C to 25 °C. Dairy and Irish potato production are the main farming activities practised by smallholder farmers. However, climate change has affected this area, decreasing agricultural productivity. As a result, it has become semi-arid, necessitating frequent food and water relief for households and livestock. Recognising this challenge, Nyandarua County, in collaboration with the World Bank, has developed interventions such as climate-smart agriculture to adapt to its unique circumstances. These efforts focus on improving livelihoods while reducing greenhouse gas emissions (County Government of Nyandarua, 2023).
2.2 Sampling technique and data collection
The data for this study come from a cross-sectional research design. A multistage sampling technique was employed in this study. In the first stage, we selected Kipipiri and Kinangop Sub-Counties in Nyandarua County based on milk production and climatic conditions that favour agriculture. In the second stage of our sampling technique, within the selected sub-counties, we purposively chose six wards, namely Engineer, Gathara, Njabini, Kipipiri, Wanjohi, and Githioro, due to their potential for milk production and vulnerability to climate change. Lastly, smallholder dairy farmers were randomly selected from the six wards using a systematic random sampling. Farmers were chosen after every fifth one from the list provided.
Given that the target population of the study area, comprising 9,049 smallholder dairy farmers, was known, the sample size was calculated using Yamane’s (1967) formula with a 5% margin of error. Based on this formula, a representative sample size of 384 farmers was determined. Farmers were selected proportionately across wards to ensure fair representation according to the population size.
This study used secondary and primary data collected through a semi-structured questionnaire. Trained enumerators conducted face-to-face interviews with respondents to ensure accurate and consistent data collection. The survey instrument was developed based on a literature review on climate-smart agriculture and smallholder dairy systems. The final instrument covered socio-demographic characteristics, farm characteristics, adoption of climate-smart strategies, and entrepreneurial orientation. A pretest was conducted in October in Njoro Sub-County to test the reliability and validity of the instruments, followed by the main data collection, which took place between October and November 2023, utilising the ODK Collect software. The pretest aimed to determine the effectiveness, sufficiency, and suitability of the questions in obtaining the required data and played a crucial role in refining the data collection tool, which involved reorganising questions for better coherence and clarity, establishing an optimal number of interviews per day, and strategically placing sensitive questions towards the end of the questionnaire. The response rate from the participants was 89%. For multi-item constructs such as entrepreneurial orientation, internal consistency was tested using Cronbach’s alpha (α = 0.78), indicating acceptable reliability.
We deserved specific attention to the identification of the CSDS. In September 2023, 1 focus group discussion and one key informant interview were conducted to validate and refine the effectiveness of the selected CSDS. The focus group discussion involved eight dairy farmers, including a diverse group of participants: two youths, two women, and four men. Additionally, key informant interviews were held with eight experts, encompassing a range of stakeholders: two Sub-County dairy board members, two dairy cooperative leaders, two extension officers, and two representatives from the Kenya Climate Smart Agriculture Project.
The focus group discussion and key informant interviews were conducted by proficient enumerators fluent in the Kikuyu dialect. These discussions and interviews were instrumental in identifying new CSDS for inclusion and determining which strategies needed refinement or removal. The data collected was cleaned using Excel, and further analysis was conducted using Stata version 18.
2.3 Outcome variable
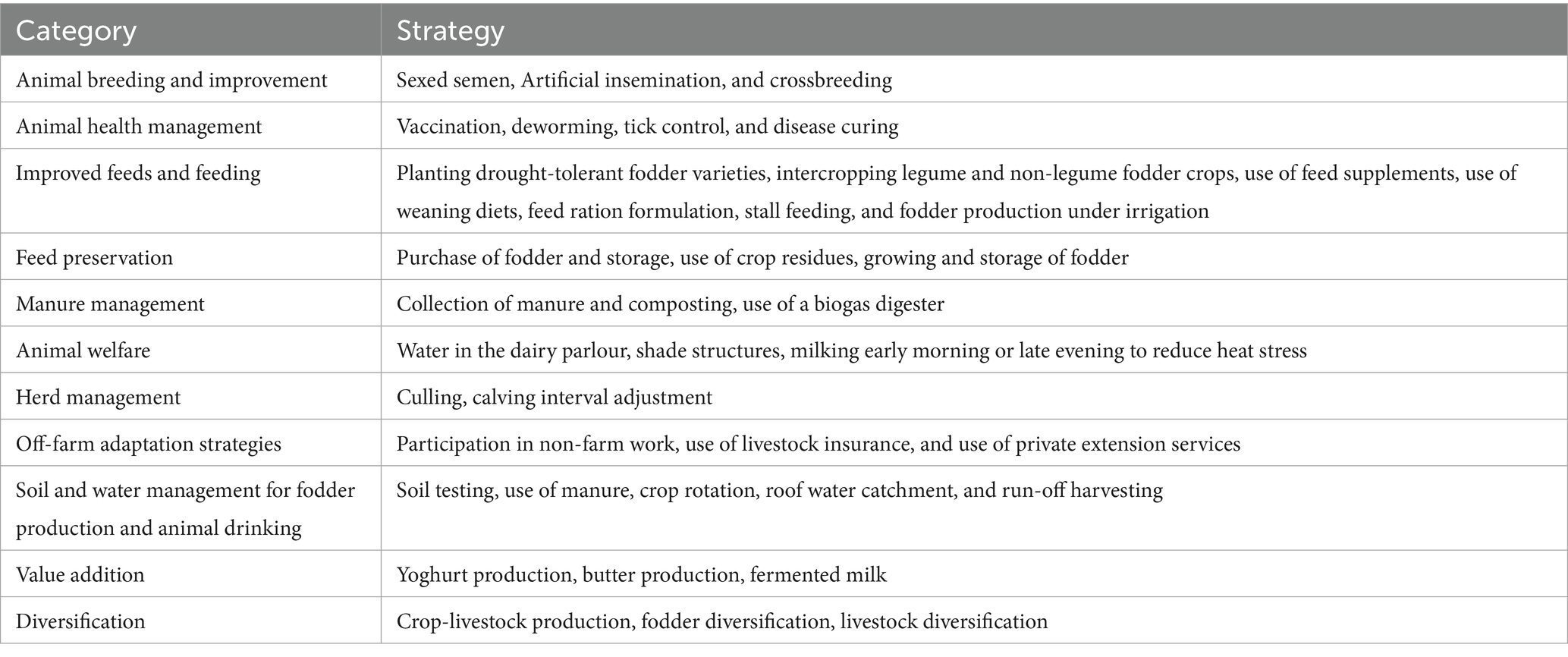
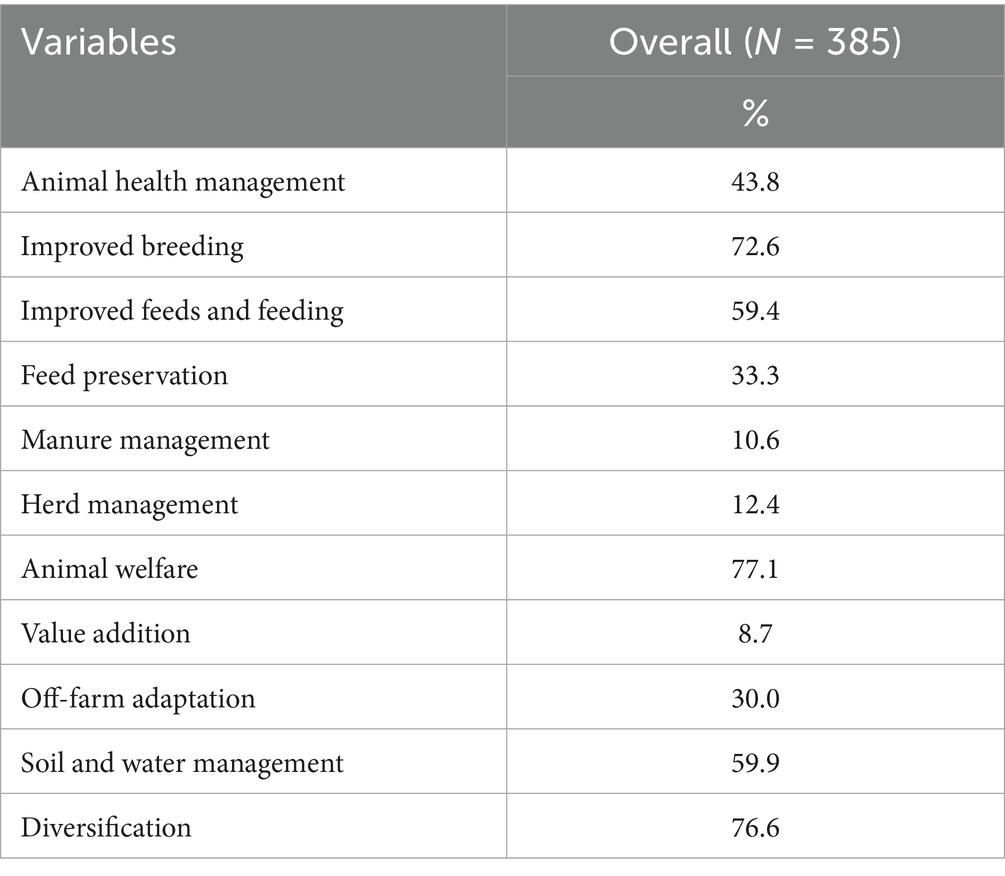
After reviewing the CSDS for the dairy subsector discussed in the literature and several documents of the Kenya Climate Smart Agriculture Project, conducting focus group discussions, key informant interviews, and consulting with researchers, we identified sustainable dairy sector practices for adoption at both farm and off-farm levels. We classified these strategies into eleven broad categories presented in Table 1.
Once strategies were identified, we collected objective responses by asking smallholder farmers to specify whether they adopted each CSDS. Subsequently, an aggregate score of CSDS was calculated by tallying all “yes” responses per household. This served as a proxy for a household’s compliance with CSDS. Following Kumar et al. (2017), the aggregate score for compliance with CSDS for the smallholder farmer is given as shown in Equation 1:
where represents the CSD strategy adopted by the smallholder farmer, is the number of available CSDS available for adoption. Based on the AS, we computed a climate-smart adoption index ( ) as shown in Equation 2. Empirically, the gologit can be specified as shown in Equation 3.
where is the smallholder farmer’s actual score. is the minimum score, and is the maximum score among farmers that were surveyed. This index served as the adoption intensity per household. Farmers were then categorised based on their as low, medium, or high adopters. Dairy farmers with a of 0–50 were classified as low adopters, 50–70 as medium adopters, and 71–100 as high adopters (Kumar et al., 2017).
2.4 Entrepreneurial orientation Likert questions
The entrepreneurial orientation score was calculated based on responses to a series of survey questions administered to smallholder farmers. These questions were designed to evaluate how various dimensions of entrepreneurial orientation, such as risk-taking, proactiveness, competitive aggressiveness, innovativeness, and autonomy, affect their adoption of CSDS. Each dimension was represented by three questions, with responses measured on a five-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). The score for each entrepreneurial construct was derived by averaging the scores of the three corresponding Likert items. As indicated in the literature, each dimension represents a distinct aspect of how individuals approach decision-making and innovation in farming (Kirungi et al., 2023; Suvanto et al., 2020).
Risk-taking assesses a farmer’s willingness to engage in uncertain or high-risk activities in the hope of potential rewards (Chepng'etich et al., 2024). In the context of climate-smart agriculture, this reflects the degree to which farmers are willing to invest in strategies that may mitigate climate change risks. The following questions were used to capture this orientation:
• “I am always ready to adopt new farming strategies”-This question gauges the farmer’s openness to trying new techniques, indicating their readiness to take risks.
• “I prefer to try new farming strategies on my farm rather than stick to old ones”-This assesses a preference for innovation over traditional methods, reflecting risk-taking in uncertain situations.
• “With the current climate change shocks, I prefer to make further investments on my farm.”-This question measures the willingness to take financial risks or invest despite the challenges posed by climate change.
Proactiveness refers to the tendency to anticipate future challenges or opportunities and take the initiative in addressing them (Kangogo et al., 2020). In farming, this often reflects the ability to foresee the impacts of climate change and adopt strategies proactively. This orientation was evaluated using the following questions:
• “I adopt CSDS because of the future uncertainty of climate change.”-This question highlights a proactive approach where farmers prepare for future risks by adopting climate-smart strategies now.
• “Adopting CSDS will improve my dairy production in the future.”-This reflects the belief that taking proactive steps today will ensure future benefits, showcasing a forward-thinking mindset.
• “I respond more quickly to changes in my environment compared to others”-This captures the individual’s proactiveness in adapting to changing farming conditions, implying quick action.
Competitive Aggressiveness measures how farmers strive to outperform others and take the lead in adopting new practices or technologies, emphasising leadership in a competitive environment (Lumpkin and Dess, 1996). The following questions were used to assess this orientation:
• “I am always among the first people to adopt a practise in my village.”-This question gauges the farmer’s competitive drive to be ahead of others in adopting new farming practices.
• “I like having the latest information on production strategies”-This reflects a desire to stay informed and outpace competitors by accessing and applying the most current information.
• “I am constantly looking for new ways to improve my farm”-This assesses the farmer’s drive for continuous improvement, highlighting their competitiveness in staying ahead.
Innovativeness reflects a farmer’s creativity and willingness to experiment with new methods, products, or processes (Kirungi et al., 2023). In this context, it measures the farmer’s engagement in climate-smart innovations, as indicated by the following questions:
• “I always try new strategies to increase income”-This question evaluates the farmer’s inclination to innovate, linking new strategies with financial benefits.
• “I like to use the latest strategies”-This indicates a preference for up-to-date, innovative methods, reflecting the continuous pursuit of innovation.
• “I always improve my production using available resources”-This measures the farmer’s ability to use innovation to optimise existing resources rather than relying on traditional methods.
Autonomy assesses the extent of a farmer’s independence in decision-making, particularly regarding the adoption of new farming practices like climate-smart strategies (Shahbaz et al., 2022). This orientation was measured using the following questions:
• “I have the capacity to adopt CSDS on my own”-This question reflects the farmer’s self-reliance in decision-making and ability to adopt climate-smart strategies independently.
• “I do not seek permission from my family members to make decisions on the adoption of CSDS”-This assesses the level of autonomy the farmer has in making strategic decisions without family approval.
• “I do not seek guidance from friends to make decisions about adopting CSDS”-This captures the farmer’s independence from social influence, indicating strong personal autonomy in decision-making.
2.5 Other explanatory variables
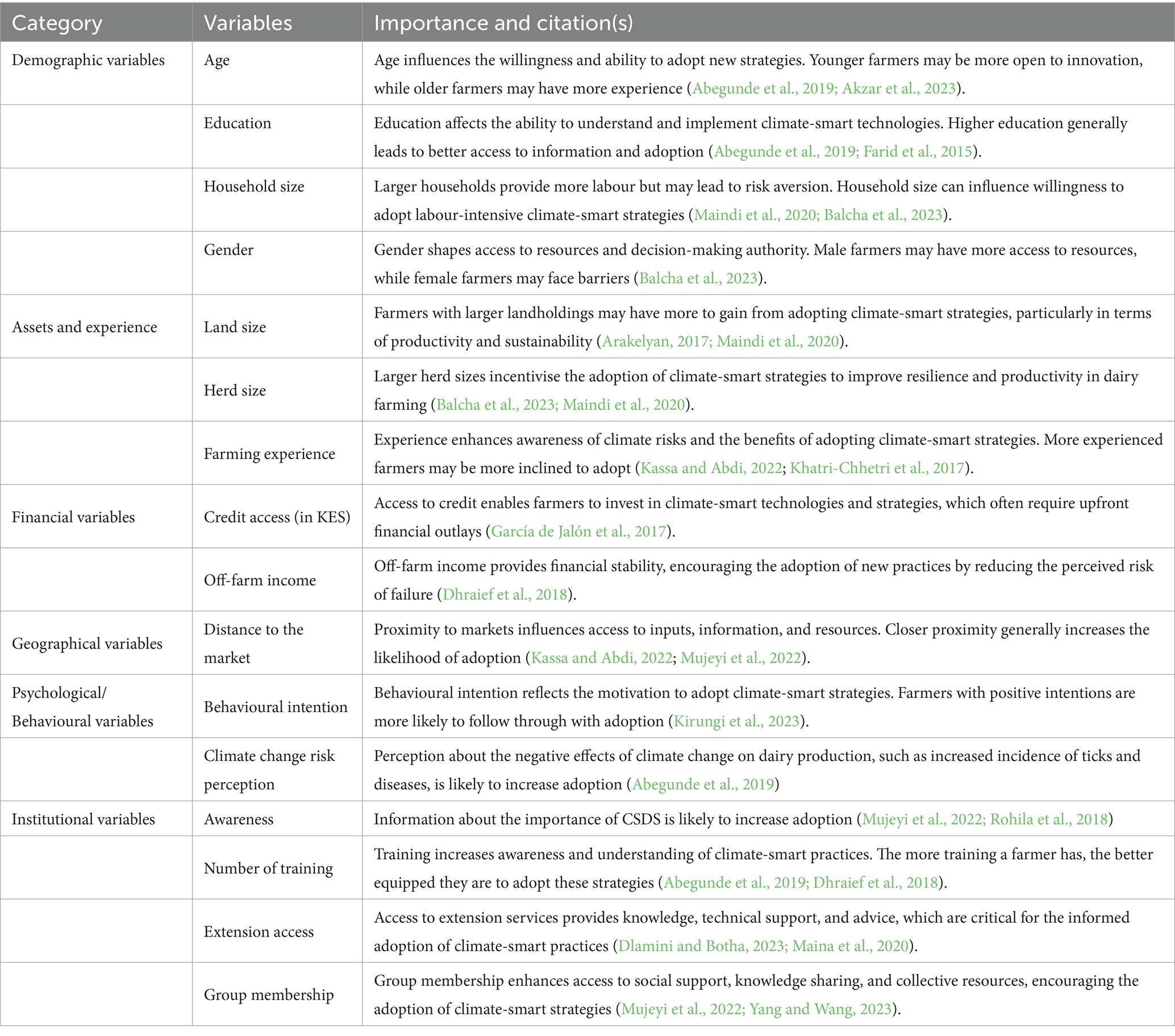
In our empirical model, we include a set of explanatory variables that capture a comprehensive range of factors affecting smallholder farmers’ adoption of CSDS. Demographics shape the basic capacity and willingness to adopt, asset factors representing the farm’s resources, and financial resources influencing the ability to implement new practices. Geographic variables affect access to markets and resources, while psychological and behavioural factors are key to understanding farmers’ motivations. Finally, institutional variables provide a framework for support and access to resources, making them crucial in enabling adoption.
2.6 Empirical strategy
We used a Gologit model to determine the influence of smallholder farmers’ entrepreneurial orientations and other control factors (demographic, socio-economic, and institutional factors) on the low, medium, or high adopters of CSDS, a categorical and ordered variable. This model overcomes limitations inherent in traditional ordered logistic and probit regression models. One major limitation of conventional ordered logistic models is the assumption that relationships between outcome categories are identical, known as the proportional odds assumption (Williams, 2006). This can lead to inaccuracies when the assumption is violated. To address this issue, we used a gologit model, which relaxes the assumption by allowing coefficients to vary across categories, making it more suitable for our analysis.
Empirically, the gologit can be specified as follows:
where is the number of categories of the ordinal dependent variable, that is, 3, is the categorical variable for the adoption level of CSDS. is the intercept, is the coefficient to be estimated and is a vector of independent variables.
This model calculates the probabilities for each adoption category as follows:
Equation 4 gives the probability of the ordinal outcome. is in the first category (category 1 = lower adopter). It states that the probability of being equal to 1 is 1 minus the cumulative probability up to a certain threshold, which is a function of the linear predictor . represents the set of independent variables for observation is a vector of coefficients corresponding to the first threshold, and is the logistic cumulative distribution function. Similarly, Equations 5, 6 give the probability that the ordinal outcome is in the second category (category 2 = medium adopter) and third category (category 3 = high adopter), respectively. Equation 7 represents the observed ordinal outcomes . is the intercept term, are the independent variables, are the corresponding coefficients, and is the error term, typically assumed to follow a standard logistic distribution.
The gologit is equivalent to a series of binary logistic regressions where categories of the dependent variables are combined (Williams, 2006). The model can be thought of as conducting a series of binary logistic regressions, each one contrasting a different grouping of the ordinal categories. For an ordinal outcome variable with M categories, there are binary logistic regressions. We used the gologit2 command in Stata, which estimates this model by fitting a series of binary logistic regressions that compare combined outcome categories. Specifically, for M = 3, the first regression contrasts category 1 (low adopters) vs. categories 2 and 3 combined (medium and high adopters). The second regression contrasts categories 1 and 2 combined vs. category 3 (high adopters).
This approach allows the coefficients to vary across these contrasts, relaxing the proportional odds assumption required in the standard ordered logit model. We tested the proportional odds assumption using the Brant test, which indicated significant violations for some predictors, justifying the use of the generalised ordered logit model. Table 2 presents the variables used in the study and explains their relevance in influencing the adoption of climate-smart strategies among smallholder farmers.
2.7 Data analysis
Data were analysed using Stata software (version 18). Descriptive statistics such as frequencies, means, and standard deviations were used to summarize the farmer and farmer characteristics. The Chi-square test was employed to examine associations between categorical variables. Additionally, the F-test was used to compare means across the adoption groups.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Descriptive analysis
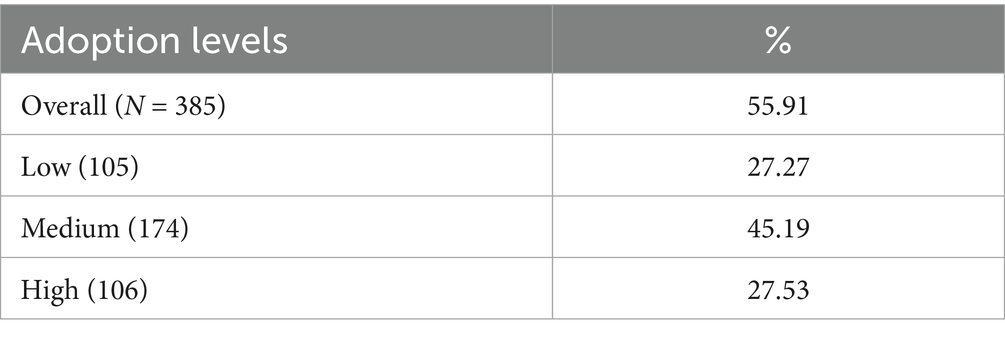
3.1.1 Adoption of CSDS among farmers
Tables 3–5 provide the results for the adoption of CSDS.
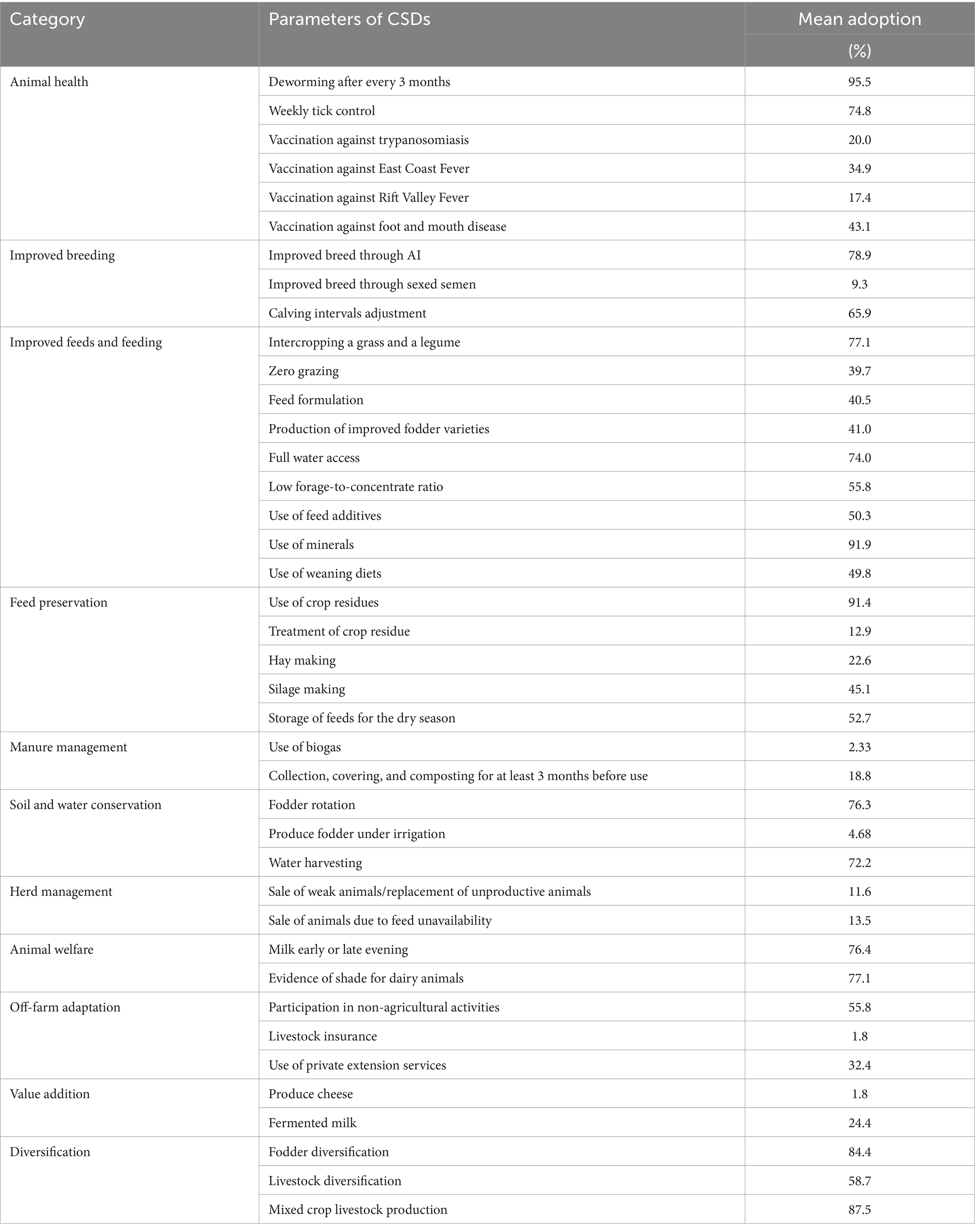
The average adoption level among farmers stood at 56%. The 385 smallholder dairy farmers in our sample consisted of 27% low adopters, 45% medium adopters, and 28% high adopters. Overall, adoption of animal welfare, which includes the presence of a dairy shade, full water access, and milking early and late evening during the hot weather season, recorded the highest score (76%). Similarly, farmers were keen on adopting improved breeds through artificial insemination and sexed semen and had an adoption rate of 72%. Soil and water management strategies, improved feeds, and feeding and animal health management were moderately adopted at about 59, 59 and 44%, respectively. However, value addition, manure management (use of biogas and manure collection, covering, and composting), and culling were poorly adopted, each reporting an adoption level of about 9, 11, and 13%, respectively. Additionally, feed conservation measures, including silage making, hay making, and treatment of crop residue, and off-farm adaptation strategies, such as livestock insurance and participation in non-agricultural activities, reported a low adoption rate of 33 and 30%, respectively.
Regarding individual CSDS attribute uptake levels, Table 6 shows that deworming (96%) and use of minerals (91%) were the most adopted CSDS among farmers. Dairy producers consider deworming a key practise in maintaining good animal health and enhancing production. This finding conforms to the results of García de Jalón et al. (2017), which revealed that deworming had the highest adoption rate among dairy farmers.
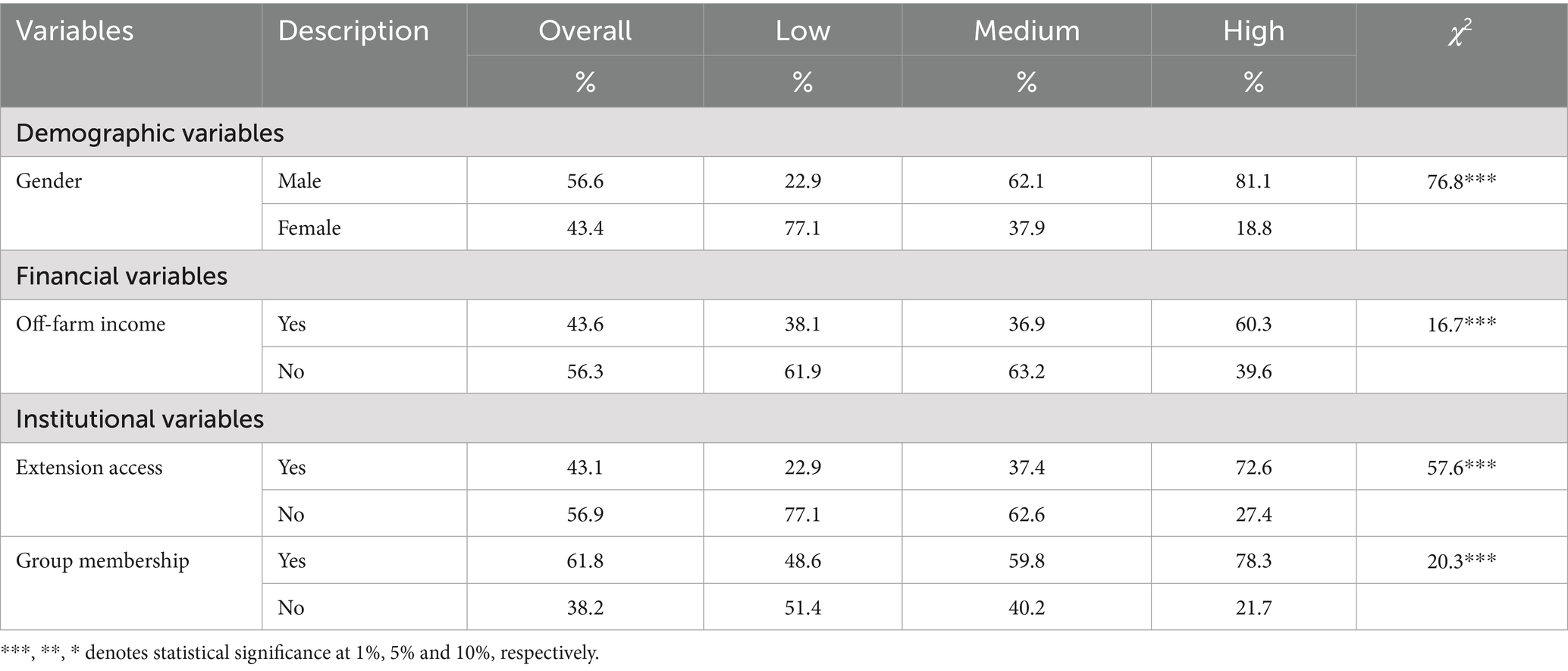
Table 6. Descriptive statistics of categorical variables across three levels of adoption, as well as the overall group.
The adoption rate for sexed semen was 9%. The low adoption level of this strategy could be attributed to the high cost of establishing or servicing. The utilization of sexed semen technology holds the potential to yield a herd where approximately 90% of newborn calves are females. This outcome reduces the production of lower-value male offspring within the breeding program (Henchion et al., 2022). Additionally, livestock insurance, fodder production under irrigation, and the use of biogas reported a low adoption rate (below 5%). Farmers considered fodder rotation and intercropping important in maintaining soil quality for increased forage and had an adoption rate of 76.36 and 77.14%, respectively.
3.1.2 Descriptive statistics of farmers and their farms
Tables 6, 7 present descriptive statistics of entrepreneurial orientation constructs and demographic, socio-economic, institutional, and Psychological factors disaggregated by adoption level.
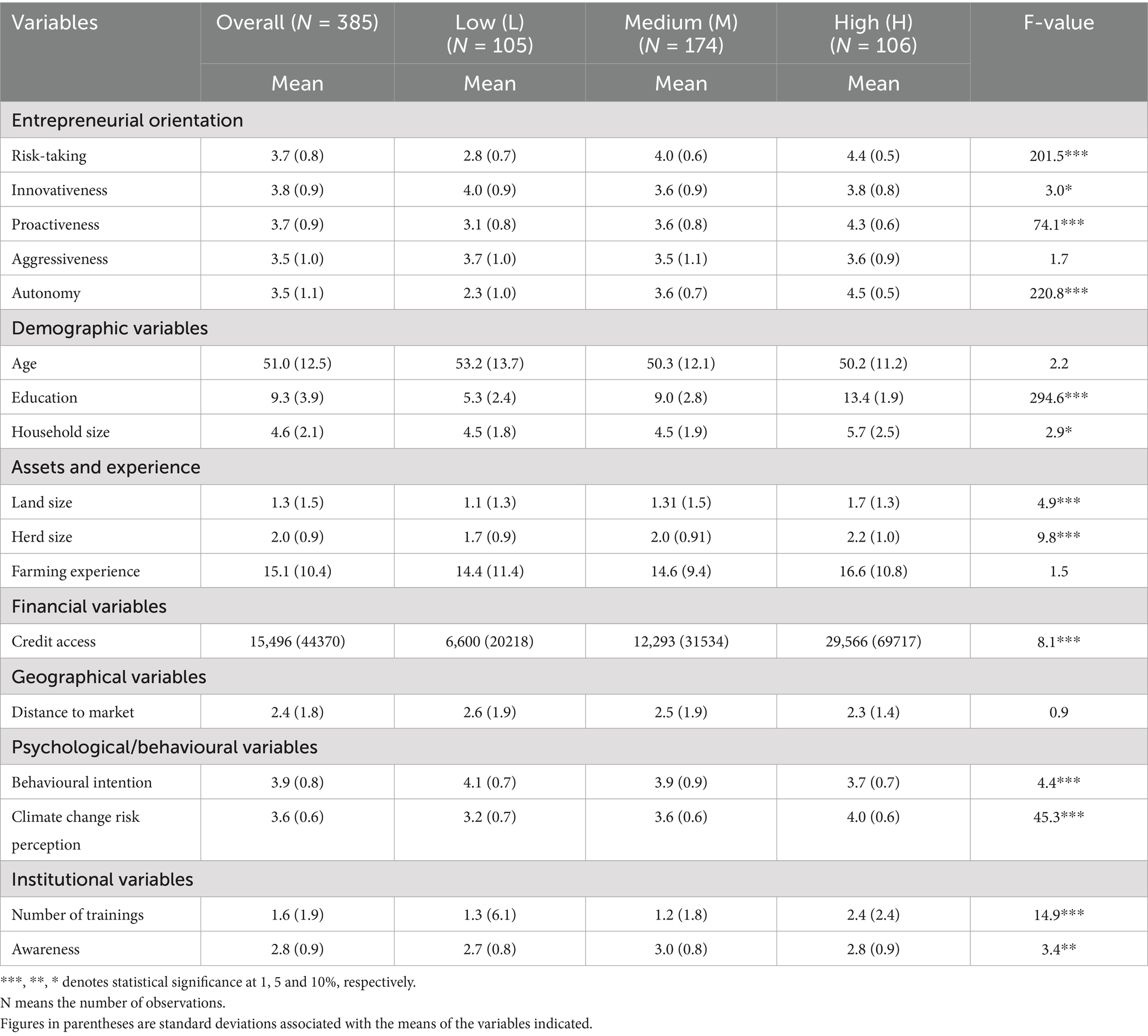
Table 7. Descriptive statistics of continuous variables across the three levels of adoption, as well as the overall group.
The standard deviation indicates variations in the overall sample and the adoption categories for the continuous variables. Additionally, the F-test of the three adoption categories rejected the null hypothesis, meaning that these categories had significant differences for most of the continuous variables. For all the categorical variables, the Chi-Square test with a significance level below 0.05 indicated a significant difference across categories.
The results show statistically significant differences across adoption categories for most entrepreneurial orientation constructs. High adopters scored highest in risk-taking (4), proactiveness (4), and autonomy (5), with significant F-values, indicating that entrepreneurial traits are positively associated with higher adoption levels (Table 7). Similarly, adoption increased significantly with education, from 5 years for low adopters to 13 years for high adopters. Similarly, access to resources such as land, herd size, and credit improves adoption intensity, suggesting that resource endowments and financial access facilitate greater uptake of CSDS. Notably, high adopters accessed more training sessions (2 times on average) and had higher climate change risk perception (4), further underlining the role of institutional support and awareness in influencing adoption.
A significantly higher proportion of high adopters were male (81%) compared to only 22% among low adopters, indicating a gender disparity in adoption (Table 6). Off-farm income was also more prevalent among high adopters (60%), suggesting that additional income sources may support CSDS adoption. Institutional variables such as access to extension services and group membership were positively associated with adoption, with 73% of high adopters having extension access and 78% belonging to a farmer group. These findings emphasise that demographic characteristics, financial capacity, and institutional engagement are key drivers of CSDS adoption among farmers.
3.2 Results on factors influencing the adoption of CSDS
3.2.1 Diagnostic tests
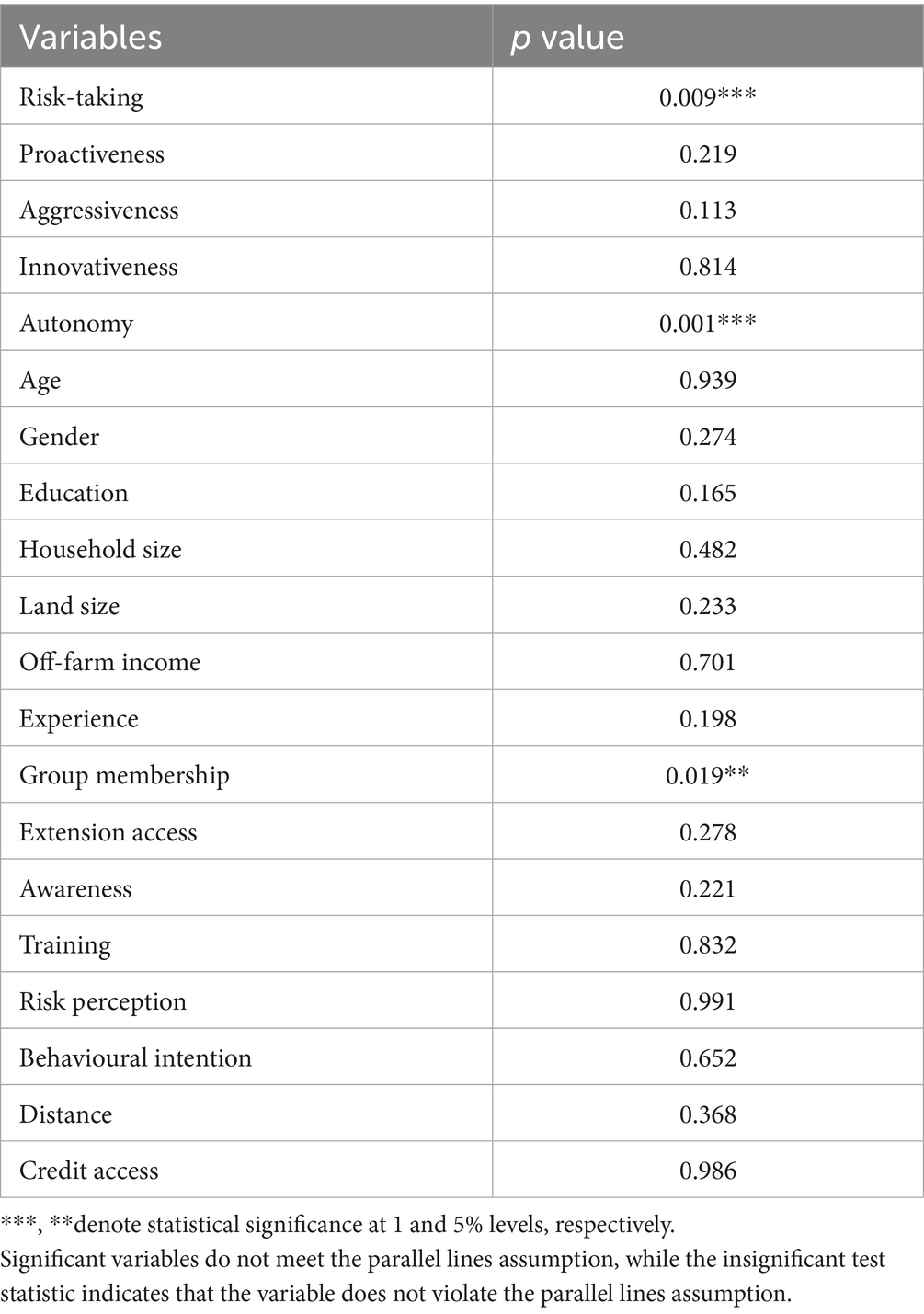
Several pre-estimation diagnostic tests were conducted before the analysis. Based on these results, the gologit2 model was chosen due to violations of the proportional odds assumption for some variables (Table 8). At the same time, diagnostic tests confirmed no issues with heteroscedasticity, multicollinearity, or non-normal residuals. This model offers a robust framework for analysing the relationships between the independent and categorised dependent variables.
3.2.2 Results of the gologit regression
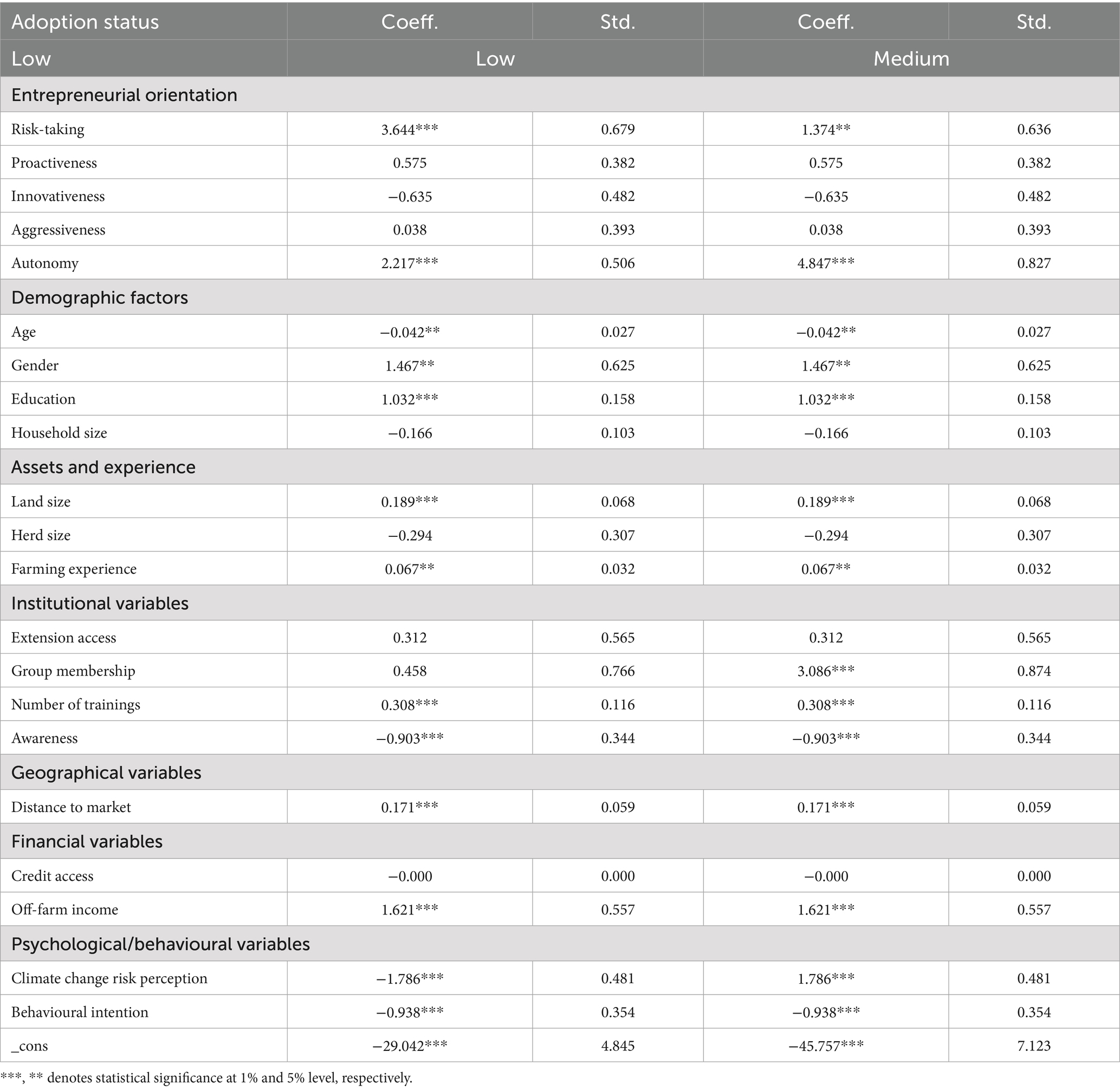
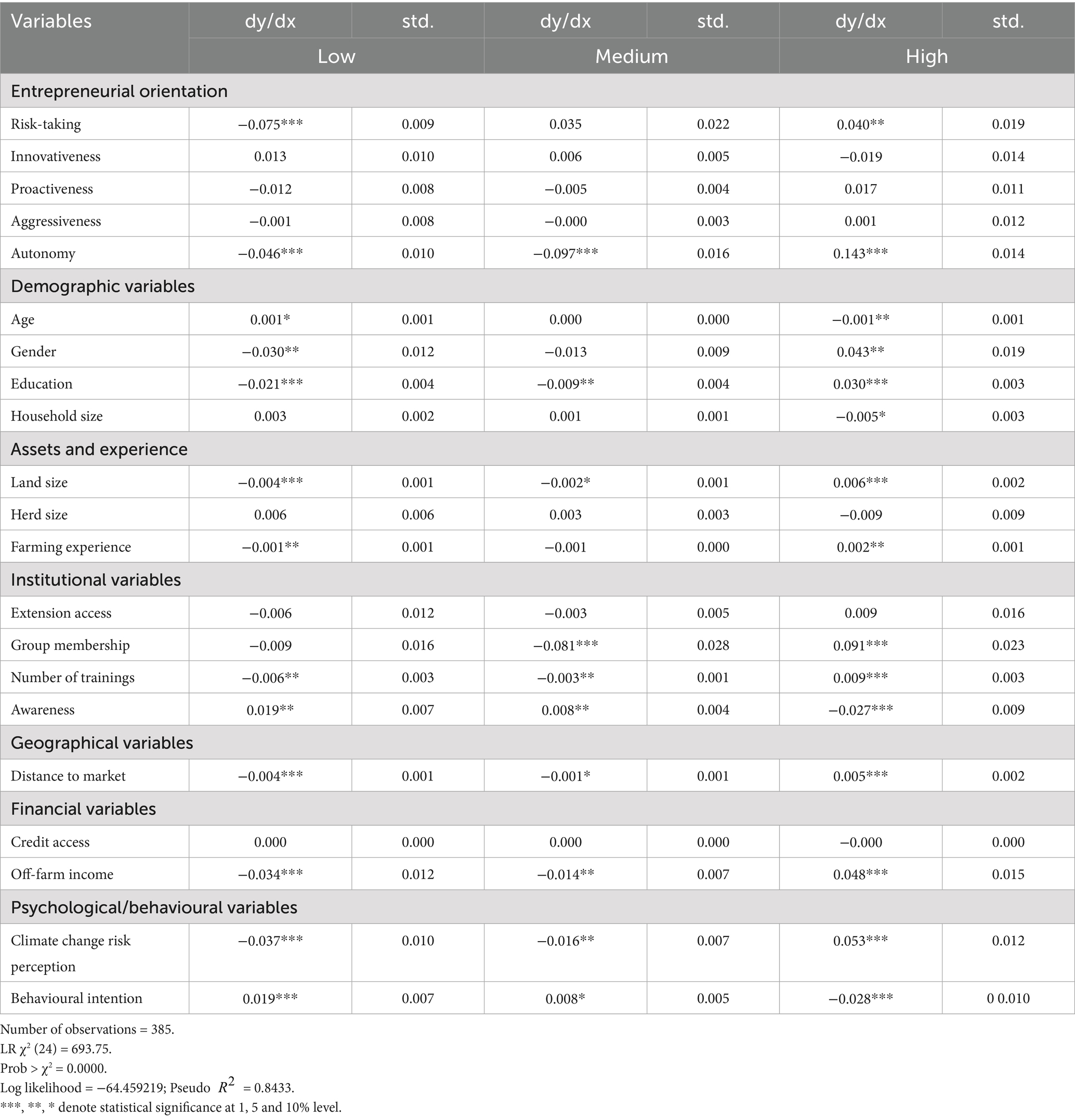
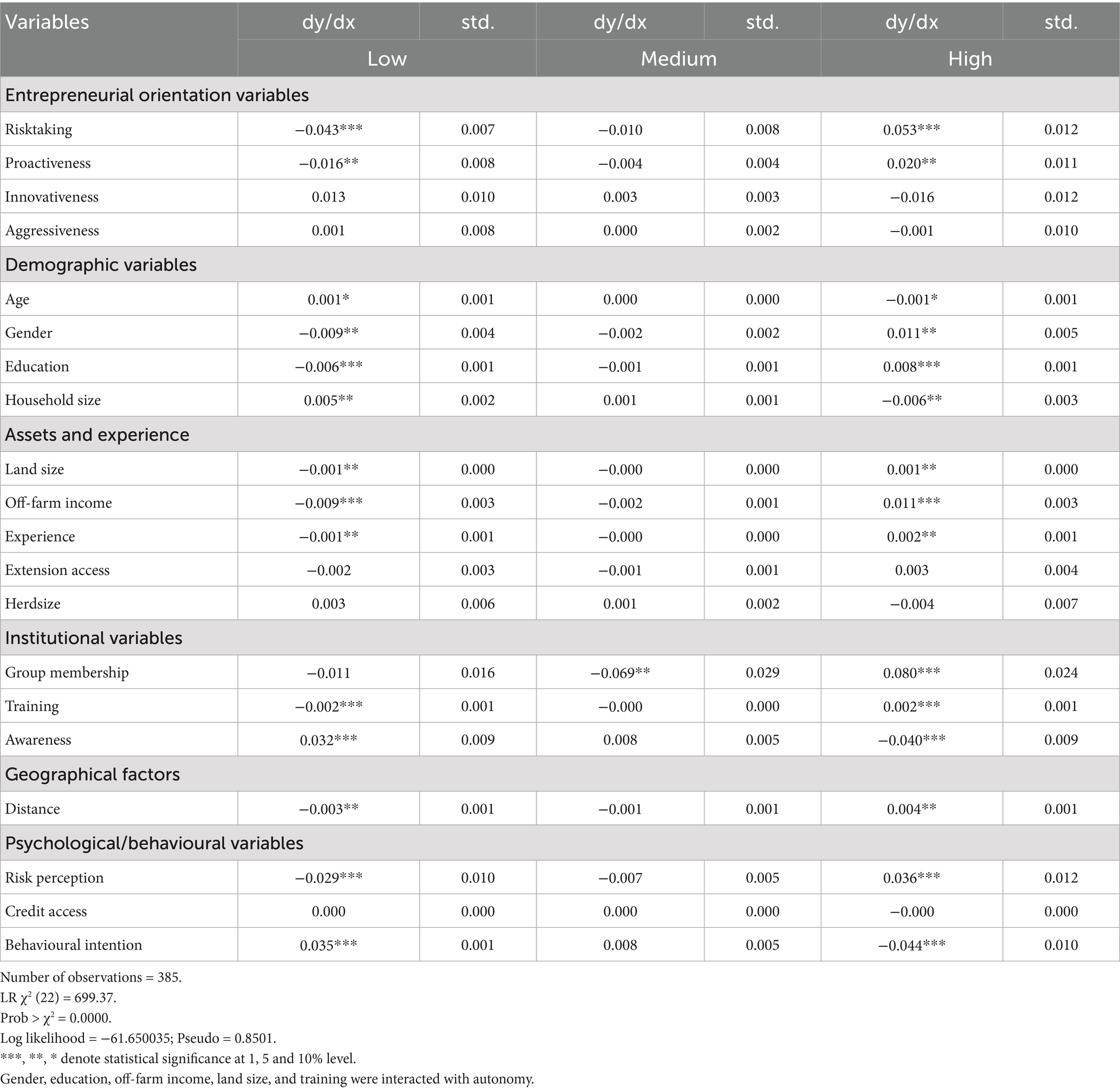
Table 9 presents the results on the determinants of CSDS adoption, while Table 10 shows the marginal effects of the gologit model. Table 11 gives an autonomy disaggregated analysis. In Table 10, the likelihood ratio test for proportionality of odds is highly significant. This suggests that the relationships between the independent and dependent variables differ across categories. Additionally, the significant Wald chi-square test for overall goodness of fit indicates that the independent variables included in the model provide satisfactory explanatory power. The dependent variable was categorised into three groups: low, medium, and high user categories, with the high user category serving as the reference group.
The results suggest that autonomy and risk-taking are the most significant constructs influencing the intensity of adopting climate-smart strategies, with autonomy showing a particularly strong effect on high-intensity adoption. Other factors such as education, gender, off-farm income, and climate change risk perception are crucial in driving high-intensity adoption. In contrast, factors such as age and household size seem to favour lower-intensity adoption. Our findings suggest that addressing risk perceptions, providing risk-mitigating interventions, and empowering farmers through increased autonomy may be crucial in promoting the adoption of climate-smart practices in Kenya’s dairy sector.
The analysis findings show that risk-taking is statistically significant in explaining adoption intensity. Individual farmers’ ability to assign resources to activities whose outcome is uncertain increases the likelihood of being in the higher user category by 4 times and reduces the likelihood of being in the lower user category by about 8 times. This evidence aligns with findings from previous studies examining the role of risk-taking in adopting climate-smart agricultural practices (Aryal et al., 2021; Zakaria et al., 2020). For instance, research on adopting drought-tolerant maize varieties in Africa has shown that risk-averse farmers are less likely to adopt these technologies. Similarly, a study on smallholder farmers’ adaptation strategies to mitigate the effects of drought on maize production in South Africa found that farmers who were more willing to take on risks were more likely to adopt strategies such as changing farming practices and sustainable land management (Muroyiwa et al., 2022). Kangogo et al. (2020) pointed out that risk-taking increased the probability of adopting climate-smart practices that required high financial resources and skilled labour. Our study’s findings are also consistent with other studies highlighting the importance of personal resources and risk-taking in driving the adoption of green technologies and innovative practices in agriculture (Ali et al., 2020). As agriculture becomes increasingly technology-intensive, farmers’ ability and willingness to adapt quickly to exogenous changes like climate change will be key to productivity growth and poverty reduction. In this context, a farmer’s risk-taking propensity can be an important determinant of their adoption of climate-smart practices (Barzola Iza et al., 2019; Bukchin and Kerret, 2018). This suggests that addressing risk perceptions and providing risk-mitigating interventions may be crucial in promoting the adoption of climate-smart practices.
It should also be noted that the heterogeneity in farmer preferences for risk often correlates with their resource endowments and access to services. Better-off farmers with more assets and information are more willing to invest in high-input agriculture. In contrast, resource-constrained farmers are more sensitive to yield variability and prefer low-risk options (Oyinbo et al., 2019).
Improving the design of extension services to provide information on the riskiness of expected outcomes and flexibility in switching between low-risk and high-risk recommendations can help farmers make more informed decisions and improve the uptake of new technologies (Ali et al., 2020; Li et al., 2023).
Our findings revealed that autonomy is positively and statistically significant among high adopters of CSDS, while it is negatively associated with low adopters. A possible explanation for this scenario is that autonomous farmers have the discretion to allocate resources to adoption independently. This finding aligns with previous research on the relationship between autonomy and the adoption of agricultural technologies (Zakaria et al., 2020). For instance, a study on adopting improved rice varieties in Ghana found that farmers with more autonomy in decision-making were more likely to adopt these technologies. Furthermore, the positive relationship between autonomy and the intensity of adoption of CSDS suggests that farmers with more control over their farming decisions are more likely to invest in and implement climate-smart practices. This finding emphasises the importance of empowering farmers, particularly in the context of climate change adaptation, to make informed decisions that align with their needs and priorities. In this regard, the literature highlights that farmers who perceive themselves as having more control over their farming decisions are more likely to adopt CSDS (Li et al., 2023). Providing farmers with more autonomy and decision-making power can, therefore, be an effective strategy for promoting the adoption of CSDS (Ali et al., 2020).
The analysis further shows that autonomy significantly increases the likelihood of being in the high CSDS adoption category when interacting with gender, education, land size, off-farm income, and access to training. This suggests that autonomy alone is not uniformly influential; rather, its effect is conditional on enabling demographic and socio-economic contexts. For instance, more educated farmers will likely leverage their autonomy more effectively due to better information processing and decision-making capabilities (Musafiri et al., 2022a). Similarly, male farmers may face fewer social constraints in implementing autonomous decisions since they have rights and control over production resources (Ngetich et al., 2022). Farmers with larger landholdings and access to off-farm income are better positioned to manage the risks and investments associated with adopting new technologies. Likewise, training enhances knowledge and confidence, enabling autonomous individuals to act decisively (Asule et al., 2024). These interaction effects highlight that autonomy becomes more practically meaningful when supported by favourable structural and institutional factors.
In Table 10, proactiveness was not statistically significant. However, once autonomy was interacted with other variables, proactiveness became significant. This suggests that the simpler model may have masked the actual effect of proactiveness due to omitted variable bias or overlapping variance with autonomy. By including relevant interaction terms, the model better captured the complex structure of the data, allowing the independent contribution of proactiveness to emerge.
We also found that innovativeness and aggressiveness do not significantly influence the independent adoption of CSDS. This contradicts existing literature that has generally reported a positive association between leadership characteristics such as idealised influence and innovative behaviour (Kangogo et al., 2020; Sethibe and Steyn, 2017). However, our findings are consistent with those of Zakaria et al. (2020), who found no significant relationship between these traits and the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices among smallholder rice farmers in Sri Lanka. Similarly, Chepng'etich et al. (2024) reported that innovativeness had no significant effect on the adaptive capacity of livestock farmers. One possible explanation is that, while entrepreneurial traits are often expected to drive early adoption, their influence may be muted in contexts where external barriers such as limited access to CSDS-relevant information, credit, or extension services constrain action. Farmers may possess entrepreneurial attributes in Central Kenya’s smallholder dairy sector, but lack the enabling environment to translate them into adoption behaviour. This suggests that the adoption of CSDS is shaped more by institutional and structural factors than by individual entrepreneurial orientation. Consistent with this, Bukchin and Kerret (2018) and Kaua (2020) also found that systemic constraints often outweigh behavioural traits influencing technology adoption. Thus, while entrepreneurial capacity remains relevant, it must be supported by targeted interventions that address underlying structural limitations to enhance CSDS uptake.
Foguesatto et al. (2020) and Zakaria et al. (2020) emphasised the importance of research exploring the complex interactions between personality traits, socio-economic factors, and institutional support in shaping the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices. Our findings confirm that the influence of entrepreneurial orientation on adopting these practices is a multifaceted process shaped by various demographic, asset-related, experiential, geographical, psychological, and institutional factors.
In Kenya, institutional collaboration is central to the adoption of CSDS. Government agencies such as the Kenya Dairy Board and county agricultural departments provide policy, regulation, and public extension. At the same time, research institutions like KALRO and ILRI generate improved technologies, breeds, and feeding practices. Cooperatives aggregate farmers, making accessing inputs, extension, and credit easier, often in partnership with financial institutions (Maindi et al., 2020). NGOs and development projects complement these efforts by piloting innovations, training farmers, and bridging gaps in extension and service delivery, while private actors supply inputs and advisory services. These interactions help overcome key barriers by expanding access to extension, easing credit constraints, improving input supply chains, and closing knowledge gaps through training and farmer-to-farmer learning (Mujeyi et al., 2022). However, challenges remain, including limited public extension capacity, difficulties in accessing formal credit, and weak institutional capacity in some cooperatives (Asule et al., 2024; Mokoro et al., 2021; Ngetich et al., 2022).
Several notable patterns emerged from our analysis. For instance, older farmers are more likely to adopt climate-smart strategies at lower intensities and are less inclined to embrace them at higher intensities. This may reflect a preference for lower-risk or more gradual adjustments, which is often associated with age (Mango et al., 2018; Martey et al., 2020; Oyinbo et al., 2019). Recent research has also highlighted the importance of targeted interventions to empower young women and men in the dairy sector (Bullock and Crane, 2021). However, Asule et al. (2024) found that older age was associated with adopting climate-resilient practices due to experience accumulated over time. While Kenya’s dairy sector is transforming toward more intensive production practices and a greater commercial focus, which presents opportunities and challenges for youth engagement, our study indicates that attention must also be directed toward older farmers. Older people comprised a significant portion of our sample.
On the other hand, male farmers are less likely to adopt climate-smart practices at lower intensities but are more inclined to embrace them at higher intensities. This suggests a tendency toward comprehensive adoption or non-adoption, which may be influenced by differing risk perceptions or decision-making processes between genders (Fahad et al., 2020). More educated farmers are similarly less likely to engage in low- or medium-intensity adoption but exhibit a significantly higher propensity for high-intensity adoption. This pattern likely reflects greater awareness and a deeper understanding of the benefits associated with climate-smart practices among more educated individuals (Fahad et al., 2020). Previous studies have also documented a positive relationship between formal education and adopting agricultural technologies in Africa (Abegunde et al., 2019; Farid et al., 2015).
Larger households may prefer incremental, lower-risk adoption of climate-smart strategies, possibly due to resource constraints or the dynamics of collective decision-making (Kaua, 2020). These households might prioritise strategies that can be implemented gradually rather than more comprehensive but riskier approaches. Conversely, access to off-farm income provides financial security, enabling more extensive adoption of climate-smart strategies by reducing the perceived financial risks associated with higher-intensity adoption.
Perception of climate change risks and behavioural intention are significant drivers of high-intensity adoption, while they negatively influence low-intensity adoption. This observation aligns with the findings of Arakelyan (2017) and Abegunde et al. (2019), suggesting that farmers who perceive greater risks from climate change and exhibit a stronger intention to act are more likely to adopt climate-smart practices comprehensively.
Our results also indicate that increased awareness and proximity to markets significantly enhance the likelihood of high-intensity adoption while reducing the probability of low-intensity adoption. This underscores the critical role of access to information and market opportunities in fostering deeper engagement with climate-smart practices, as supported by previous literature (Alonso et al., 2018).
4 Conclusion
This study provides several targeted policy recommendations to enhance the adoption of CSDS among smallholder farmers in Kenya. First, the results highlight that farmers with high-risk perceptions are more likely to adopt CSDS, suggesting that perceived climate and production-related risks may motivate adoption as a coping or adaptation strategy. To further strengthen this behaviour, policymakers should reinforce climate and market information availability and promote access to CSDS as a credible risk-mitigation option through demonstration farms, success stories, and tailored extension messaging.
Second, the finding that farmer autonomy, when combined with factors like education, gender, land size, off-farm income, and training access, significantly increases the likelihood of high adoption underscores the need for differentiated support policies. Capacity-building programs should equip farmers with technical skills and foster decision-making autonomy through tailored training, peer learning platforms, and digital extension services that provide real-time market and climate information. Extension agents must be trained to recognize socio-economic and gender-based dynamics influencing autonomy and respond with context-sensitive support.
Third, our findings show that access to training and education, particularly when interacted with autonomy, positively influences adoption. Thus, policies should scale up inclusive agricultural education initiatives, focusing on women and youth, and improve the quality and accessibility of training modules on CSDS. These should be embedded within existing cooperative and group structures, which our findings also suggest enhance adoption.
Additionally, access to markets was identified as a key enabler of CSDS adoption. Investments in infrastructure development, such as rural roads, milk cooling facilities, and storage infrastructure, can reduce transaction costs and post-harvest losses, making adoption more economically viable. Further, strengthening farmer linkages to value chains and expanding cooperative marketing models can improve price stability and market access, reinforcing the incentive to adopt sustainable practices.
Lastly, this study affirms that demographic and socio-economic diversity, including differences in gender, landholding size, income sources, and education, shapes farmers’ adoption pathways. Therefore, policies should adopt an equity lens, designing targeted interventions that reflect these variations to avoid leaving vulnerable groups behind in the transition toward climate-smart agriculture.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Commission for Science, Technology and Innovation. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
NC'a: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DO: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
KIPPRA, Kenya Institute for Public Policy Research and Analysis; FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; GDP, Gross Domestic Product; KNBS, Kenya National Bureau of Statistics; MOALF, Ministry of Agriculture, Livestock and Fisheries.
References
Abbas, Q., Han, J., Bakhsh, K., Ullah, R., Kousar, R., Adeel, A., et al. (2022). Adaptation to climate change risks among dairy farmers in Punjab, Pakistan. Land Use Policy 119:106184. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2022.106184
Abegunde, V. O., Sibanda, M., and Obi, A. (2019). Determinants of the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices by small-scale farming households in king Cetshwayo District municipality, South Africa. Sustainability 12:195. doi: 10.3390/SU12010195
Akzar, R., Peralta, A., and Umberger, W. (2023). Adoption of dairy feed technology bundles improves smallholder dairy farmers’ milk production. J. Agribus. Dev. Emerg. Econ. 15, 269–287. doi: 10.1108/JADEE-12-2022-0267
Ali, D. A., Bowen, D., and Deininger, K. (2020). Personality traits, technology adoption, and technical efficiency: evidence from smallholder rice farms in Ghana. J. Dev. Stud. 56, 1330–1348. doi: 10.1080/00220388.2019.1666978
Alonso, S., Muunda, E., Ahlberg, S., Blackmore, E., and Grace, D. (2018). Beyond food safety: socio-economic effects of training informal dairy vendors in Kenya. Glob. Food Secur. 18, 86–92. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2018.08.006
Andati, P., Majiwa, E., Ngigi, M., Mbeche, R., and Ateka, J. (2022). Determinants of adoption of climate smart agricultural technologies among potato farmers in Kenya: does entrepreneurial orientation play a role? Sustainable Technology and Entrepreneurship 1:100017. doi: 10.1016/j.stae.2022.100017
Arakelyan, I. (2017) Climate-smart agriculture and rural livelihoods: the case of the dairy sector in Malawi. [PhD dissertation, Edinburgh university, Edinburgh, UK]
Aryal, J. P., Sapkota, T. B., Rahut, D. B., Marenya, P., and Stirling, C. M. (2021). Climate risks and adaptation strategies of farmers in East Africa and South Asia. Sci. Rep. 11:10489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89391-1
Asule, P. A., Musafiri, C., Nyabuga, G., Kiai, W., Kiboi, M., Nicolay, G., et al. (2024). Awareness and adoption of climate-resilient practices by smallholder farmers in central and upper eastern Kenya. Heliyon 10:e38368. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38368
Balcha, E., Menghistu, H. T., Zenebe, A., Teferi, T., and Hadush, B. (2023). Climate-smart agricultural practices: a case of dairy cooperative farmers in Agula and Maychew, northern Ethiopia. Carbon Manag. 14:2271880. doi: 10.1080/17583004.2023.2271880
Barzola Iza, C. L., Dentoni, D., Mordini, M., Isubikalu, P., Auma Oduol, J. B., and Omta, O. (2019). “The role of farmers’ entrepreneurial orientation on agricultural innovations in the Ugandan multi-stakeholder platform” in The climate-smart agriculture papers. Kampala: investigating the business of a productive, resilient and low emission future, 201–213.
Bukchin, S., and Kerret, D. (2018). Food for hope: the role of personal resources in farmers’ adoption of green technology. Sustainability 10:1615. doi: 10.3390/su10051615
Bullock, R., and Crane, T. (2021). Young women’s and men’s opportunity spaces in dairy intensification in Kenya. Rural. Sociol. 86, 777–808. doi: 10.1111/ruso.12385
Chelang’a, N. C., Kariuki, I. M., Obare, G. A., and Otieno, D. O. (2023). Determinants of adoption of GLOBAL GAP standards: evidence from smallholder French beans farmers in murang’a county, Kenya. Cogent Food Agric. 9:2176949. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2023.2176949
Chepng'etich, E., Ateka, J. M., Mbeche, R., and Obebo, F. (2024). Supporting smallholder livestock farmers’ adaptive capacity to climate change in Kenya: what role does entrepreneurial orientation and uptake of CSA play? Climate Smart Agriculture 1:100007. doi: 10.1016/j.csag.2024.100007
County Government of Nyandarua. (2023). Nyandarua County Integrated Development Plan (CIDP3) draft 1. Nyandarua, Kenya. Available online at: http://www.nyandarua.go.ke/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/CIDP3_DRAFT.pdf
de Vries, M. D. (2019). Vulnerability and adaptation strategies of dairy farming systems to extreme climate events in southwest Uganda: results of CSA-PRA workshops (No. 1141). Wageningen Livestock Research. Available online at: https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wurpubs/547084
Dhraief, M. Z., Bedhiaf-Romdhania, S., Dhehibib, B., Oueslati-Zlaouia, M., Jebali, O., and Ben Youssef, S. (2018). Factors affecting the adoption of innovative technologies by livestock farmers in arid areas of Tunisia. FARA Res. Rep. 3:22.
Dlamini, M., and Botha, M. (2023). Entrepreneurial intention and the three stages of entrepreneurial action: a process approach. Front. Psychol. 14:1184390. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1184390
Elahi, E., Zhang, H., Lirong, X., Khalid, Z., and Xu, H. (2021). Understanding cognitive and socio-psychological factors determining farmers’ intentions to use improved grassland: implications of land use policy for sustainable pasture production. Land Use Policy 102:105250. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.105250
Ericksen, P. J., and Crane, T. A. (2018). The feasibility of low emissions development interventions for the east African livestock sector: Lessons from Kenya and Ethiopia. Nairobi, Kenya: ILRI Research Report.
Fahad, S., Inayat, T., Wang, J., Dong, L., Hu, G., Khan, S., et al. (2020). Farmers’ awareness level and their perceptions of climate change: a case of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province, Pakistan. Land Use Policy 96:104669. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104669
FAO. (2019). Options for Low-Emission Development in the Tanzania dairy sector: Reducing enteric methane for food security and livelihoods. Rome, Italy. Available online at: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/ru/c/CA3215EN. Accessed 15 March 2023.
FAO (2021). Climate-smart agriculture case studies 2020: Projects from around the world. Rome, Italy: FAO, 2021-Rome.
Farid, K. S., Tanny, N. Z., and Sarma, P. K. (2015). Factors affecting adoption of improved farm practices by the farmers of northern Bangladesh. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 13, 291–298. doi: 10.22004/ag.econ.235292
Foguesatto, C. R., Borges, J. A. R., and Machado, J. A. D. (2020). A review and some reflections on farmers’ adoption of sustainable agricultural practices worldwide. Sci. Total Environ. 729:138831. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138831
García de Jalón, S., Silvestri, S., and Barnes, A. P. (2017). The potential for adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices in sub-Saharan livestock systems. Reg. Environ. Chang. 17, 399–410. doi: 10.1007/s10113-016-1026-z
Gauly, M., and Ammer, S. (2020). Challenges for dairy cow production systems arising from climate changes. Animal 14, 196–203. doi: 10.1017/S1751731119003239
GCA (2022). Global Centre on adaptation. State and trend in adaptation report 2022. Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
Gulwa, U., Mgujulwa, N., and Beyene, S. T. (2018). Benefits of grass-legume inter-cropping in livestock systems. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 13, 1311–1319. doi: 10.5897/AJAR2018.13172
Hawkins, J. W., Komarek, A. M., Kihoro, E. M., Nicholson, C. F., Omore, A. O., Yesuf, G. U., et al. (2022). High-yield dairy cattle breeds improve farmer incomes, curtail greenhouse gas emissions and reduce dairy import dependency in Tanzania. Nat. Food 3, 957–967. doi: 10.1038/s43016-022-00633-5
Henchion, M. M., Regan, A., Beecher, M., and Macken-Walsh, A. (2022). Developing ‘smart’dairy farming responsive to farmers and consumer-citizens: a review. Animals 12:360. doi: 10.3390/ani12030360
Kandulu, J. M., Zuo, A., Wheeler, S., Dusingizimana, T., and Chagunda, M. G. (2024). Influence of climate-smart technologies on the success of livestock donation programs for smallholder farmers in Rwanda. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 29:24. doi: 10.1007/s11027-024-10120-w
Kangogo, D., Dentoni, D., and Bijman, J. (2020). Determinants of farm resilience to climate change: the role of farmer entrepreneurship and value chain collaborations. Sustainability 12:868. doi: 10.3390/su12030868
Kassa, B. A., and Abdi, A. T. (2022). Factors influencing the adoption of climate-smart agricultural practice by small-scale farming households in Wondo Genet, Southern Ethiopia. Sage Open, 12:21582440221121604. doi: 10.1177/21582440221121604
Kaua, C. G. (2020). Determinants of adoption of indigenous strategies for climate change adaptation among the Tharaka people in Tharaka Nithi County, Kenya. East Afr. J. Environ. Nat. Resour. 2, 31–40. doi: 10.37284/eajenr.2.1.139
Khatri-Chhetri, A., Poudel, B., Shirsath, P. B., and Chaudhary, P. (2017). Assessment of climate-smart agriculture (CSA) options in Nepal. CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), New Delhi, India. Available online at: https://cdkn.org/sites/default/files/files/Assessment-of-CSA-in-Nepal_CCAFS-LI-BIRD-FINAL_0.pdf
Kifle, T., Ayal, D. Y., and Mulugeta, M. (2022). Factors influencing farmers’ adoption of climate-smart agriculture to respond to climate variability in Siyadebrina Wayu District, central highlands of Ethiopia. Clim. Serv. 26:100290. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2022.100290
Kihoro, E. M., Schoneveld, G. C., and Crane, T. A. (2021). Pathways toward inclusive low-emission dairy development in Tanzania: producer heterogeneity and implications for intervention design. Agric. Syst. 190:103073. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103073
KIPPRA (2020). Exploring the Kenyan dairy industry for job creation for the Youth. Nairobi, Kenya. Available online at: https://kippra.or.ke/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Exploring-Kenya-Dairy-Industry-for-Job-Creation-for-the-Youth-DP232.pdf
Kirungi, D., Senyange, B., Wesana, J., Sseguya, H., Gellynck, X., and De Steur, H. (2023). Entrepreneurial and attitudinal determinants for the adoption of climate-smart agriculture technologies in Uganda. Cogent Food Agri. 9:2282236. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2023.2282236
KNBS. (2022). Economic Survey 2022. Nairobi, Kenya. Available online at: https://www.knbs.or.ke/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/2022-Economic-Survey1.pdf. (Accessed June 10, 2023)
Korir, L., Manning, L., Moore, H. L., Lindahl, J. F., Gemechu, G., Mihret, A., et al. (2023). Adoption of dairy technologies in smallholder dairy farms in Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1070349. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1070349
Kumar, A., Thapa, G., Roy, D., and Joshi, P. K. (2017). Adoption of food safety measures on milk production in Nepal: impact on smallholders’ farm-gate prices and profitability. Food Policy 70, 13–26. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2017.05.002
Li, J., Liu, G., Chen, Y., and Li, R. (2023). Study on the influence mechanism of the adoption of smart agriculture technology behavior. Sci. Rep. 13:8554. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35091-x
Llonch, P., Haskell, M. J., Dewhurst, R. J., and Turner, S. P. (2017). Current available strategies to mitigate greenhouse gas emissions in livestock systems: an animal welfare perspective. Animal 11, 274–284. doi: 10.1017/S1751731116001440
Lumpkin, G. T., and Dess, G. G. (1996). Clarifying the entrepreneurial orientation construct and linking it to performance. Acad. Manag. Rev. 21, 135–172. doi: 10.5465/amr.1996.9602161568
Maina, K. W., Ritho, C. N., Lukuyu, B. A., and Rao, E. J. O. (2020). Socio-economic determinants and impact of adopting climate-smart Brachiaria grass among dairy farmers in eastern and Western regions of Kenya. Heliyon 6:e04335. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04335
Maindi, N. C., Osuga, I. M., and Gicheha, M. G. (2020). Advancing climate smart agriculture: adoption potential of multiple on-farm dairy production strategies among farmers in murang’a county, Kenya. Livest. Res. Rural. Dev. 32:63.
Mango, N., Makate, C., Tamene, L., Mponela, P., and Ndengu, G. (2018). Adoption of small-scale irrigation farming as a climate-smart agriculture practice and its influence on household income in the Chinyanja triangle, southern Africa. Land 7:49. doi: 10.3390/land7020049
Martey, E., Etwire, P. M., and Kuwornu, J. K. (2020). Economic impacts of smallholder farmers’ adoption of drought-tolerant maize varieties. Land Use Policy 94:104524. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104524
MOALF (2019) National Livestock Policy Draft. Available online at: https://repository.kippra.or.ke/bitstream/handle/123456789/483/
Mokoro, A. N., Adede, O. W., Omasaki, S. K., and Evans, B. A. (2021). Factors affecting adoption of climate-smart agricultural technologies: evidence from Nandi County, Kenya. Int. J. Res. Soc. Sci. Humanities 2, 1–16. doi: 10.47505/IJRSS.2021.9207
Molieleng, L., Fourie, P., and Nwafor, I. (2021). Adoption of climate-smart agriculture by communal livestock farmers in South Africa. Sustainability 13:10468. doi: 10.3390/su131810468
Mujeyi, A., Mudhara, M., and Mutenje, M. J. (2022). Adoption patterns of climate-smart agriculture in integrated crop-livestock smallholder farming systems of Zimbabwe. Clim. Dev. 14, 399–408. doi: 10.1080/17565529.2021.1930507
Muroyiwa, B., Masinda, N., and Mushunje, A. (2022). Smallholder farmers’ adaptation strategies to mitigate the effect of drought on maize production in the OR Tambo District municipality. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 14, 459–471. doi: 10.1080/20421338.2020.1847385
Musafiri, C. M., Kiboi, M., Macharia, J., Ng’etich, O. K., Kosgei, D. K., Mulianga, B., et al. (2022b). Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices among smallholder farmers in Western Kenya: do socio-economic, institutional, and biophysical factors matter? Heliyon 8, e08677. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08677
Musafiri, C. M., Kiboi, M., Macharia, J., Ng'etich, O. K., Okoti, M., Mulianga, B., et al. (2022a). Does the adoption of minimum tillage improve sorghum yield among smallholders in Kenya? A counterfactual analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 223:105473. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2022.105473
Muunda, E., Mtimet, N., Bett, E., Wanyoike, F., and Alonso, S. (2023). Milk purchase and consumption patterns in peri-urban low-income households in Kenya. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1084067. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1084067
Ng’ombe, A., Sithole, M., Musafiri, C. M., Kiboi, M., Sales, T., Kayira, M., et al. (2024). Uptake determinants of climate-smart agricultural practice for greening smallholder groundnut value chain: evidence from Malawi. Cleaner Circular Bioeconomy 9:100123. doi: 10.1016/j.clcb.2024.100123
Ngetich, F. K., Mairura, F. S., Musafiri, C. M., Kiboi, M. N., and Shisanya, C. A. (2022). Smallholders’ coping strategies in response to climate variability in semi-arid agro-ecozones of upper eastern Kenya. Soc. Sci. Humanit. Open 6:100319. doi: 10.1016/j.ssaho.2022.100319
Odhiambo, C. O. (2020). Determinants of Adaptive Strategies to Climate Change Among Smallholder Dairy Farmers of Migori County, Kenya [Doctoral dissertation, Maseno University]. Maseno University Available online at: https://repository.maseno.ac.ke/handle/123456789/3994
Otieno, G. O., Muendo, K., and Mbeche, R. (2020). Smallholder dairy production, motivations, perceptions, and challenges in Nyandarua and Nakuru counties, Kenya. J. Agric. Vet. Sci. 13, 42–50. doi: 10.9790/2380-1301024250
Oyinbo, O., Chamberlin, J., Vanlauwe, B., Vranken, L., Kamara, Y. A., Craufurd, P., et al. (2019). Farmers’ preferences for high-input agriculture supported by site-specific extension services: evidence from a choice experiment in Nigeria. Agric. Syst. 173, 12–26. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2019.02.003
Rademaker, C. J., Bebe, B. O., Van Der Lee, J., Kilelu, C., and Tonui, C. (2016). Sustainable growth of the Kenyan dairy sector: a quick scan of robustness, reliability, and resilience. Wageningen Livestock Research. Available online at: https://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wurpubs/508760
Rathakrishnan, T., Suntharalingam, C., Shern, L. Y., Keng, L. S., Lee Hai, Y., Kok, T. K., et al. (2022). Adoption of sustainable agricultural practices among smallholder dairy farmers in Malaysia: contributing factors and smart farming prospects. J. Smart Sci. Technol. 2, 16–31.
Richardson, C. M., Amer, P. R., Quinton, C., Crowley, J., Hely, F. S., Van Den Berg, I., et al. (2022). Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through genetic selection in the Australian dairy industry. J. Dairy Sci. 105, 4272–4288. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-21277
Rohila, A. K., Shehrawat, P., and Malik, J. (2018). Awareness, constraints, and prospects of climate smart agricultural practices (CSAP). J. Agrometeorol. 20, 167–171.
Rojas-Downing, M. M., Nejadhashemi, A. P., Harrigan, T., and Woznicki, S. A. (2017). Climate change and livestock: Impacts, adaptation, and mitigation. Climate Risk Management. 16, 145–163. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2017.02.001
Sethibe, T., and Steyn, R. (2017). The impact of leadership styles and the components of leadership styles on innovative behaviour. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 21:1750015. doi: 10.1142/S1363919617500153
Shahbaz, P., Ul Haq, S., Abbas, A., Batool, Z., Alotaibi, B. A., and Nayak, R. K. (2022). Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices through women’s involvement in the decision-making process: exploring the role of empowerment and innovativeness. Agriculture 12:1161. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12081161
Siraj, N. (2023). Practices and determinants of adoption of Climate Smart cattle production among smallholder farmers -The case of Damboya Woreda, KembataTambaro Zone, and SNNPR, Ethiopia. Ethiopia: Hawassa University.
Suvanto, H., Niemi, J. K., and Lähdesmäki, M. (2020). Entrepreneurial identity and farmers’ protein crop cultivation choices. J. Rural. Stud. 75, 174–184. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2020.01.022
Tesfaye, A., Mamo, T., Getahun, W., Fikadu, T., Alemu, T., Bediye, S., et al. (2016). Adoption analysis of smallholder dairy production technologies in Oromiya region. Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR). Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. Available online at: http://publication.eiar.gov.et:8080/xmlui/bitstream/handle
Wilkes, A., Wassie, S., Fraval, S., and van Dijk, S. (2020). Variation in the carbon footprint of milk production on smallholder dairy farms in Central Kenya. J. Clean. Prod. 265:121780. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121780
Williams, R. (2006). Generalised ordered logit/partial proportional odds models for ordinal dependent variables. Stata J. 6, 58–82. doi: 10.1177/1536867X0600600104
Wodajo, W. A., and Ponnusamy, K. (2016). Determinants of improved dairy practices adoption in the west Shewa zone of Oromia, Ethiopia. Indian Res. J. Ext. Educ. 16, 73–83.
Yang, W., and Wang, L. (2023). Impact of farmer group participation on the adoption of sustainable farming practices-: spatial analysis of New Zealand dairy farmers. Ann. Public Coop. Econ. 94, 701–717. doi: 10.1111/apce.12404
Zakaria, A., Azumah, S. B., Appiah-Twumasi, M., and Dagunga, G. (2020). Adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices among farm households in Ghana: the role of farmer participation in training programmes. Technol. Soc. 63:101338. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101338
Keywords: entrepreneurial orientation, climate-smart strategies, dairy, smallholder farmer, Kenya
Citation: Chelang’a NC, Mathenge M, Okello Otieno D and Sassi M (2025) Does entrepreneurial orientation influence the adoption intensity of climate-smart dairy strategies? Evidence from smallholder farmers in Central Kenya. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1569193. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1569193
Edited by:
Salome Migose, University of Embu, KenyaReviewed by:
Collins Musafiri, Research Centre for Smallholder Farmers, KenyaMoses Mwito, University of Embu, Kenya
Copyright © 2025 Chelang’a, Mathenge, Okello Otieno and Sassi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Naomi Chebiwot Chelang’a, bmFvbWljaGViaTA5QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Naomi Chebiwot Chelang’a
Naomi Chebiwot Chelang’a Mary Mathenge1
Mary Mathenge1