- 1Department of Population Health and Reproduction, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of California, Davis, Davis, CA, United States
- 2Equii Food, San Leandro, CA, United States
- 3Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, University of California, Davis, Davis, CA, United States
- 4US Department of Agriculture, Eastern Regional Research Center, Wyndmoor, PA, United States
Food waste valorization by recycling and repurposing is critical for lowering the environmental and economic burden of discarded food and facilitating the transition to a circular economy. Several research have focused on recycling technology and end-use products; nonetheless, their economic, environmental, and social impacts are limited. This study employs an integrative review approach to analyze global challenges related to food waste and develop a comprehensive single-source reference on this critical issue. Food supply chain activities, including retail and consumption, microbial and food safety concerns, and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the context of food waste, were evaluated. Despite significant efforts to overcome these challenges, approximately 1.3 billion tons of edible food are lost or wasted annually, leading to the emission of around 3.3 billion tons of greenhouse gases. The environmental impact, ranging from 347 to 2,969 kg CO₂ equivalent per ton of food waste, depends on multiple factors within food supply chains and waste management systems. This review focuses on the following challenges: (1) stress on croplands related to food production and its consequential impacts; (2) limitations of croplands, food production constraints, and waste generation trends at various stages of supply chains; (3) existing strategies for controlling waste by sources and categories, along with the detrimental economic impacts of food waste; and (4) currently available technologies for waste treatment and conversion into value-added products. Overall, food waste is primarily used for energy recovery, biofertilizers, and biomaterials. However, innovative food waste conversion strategies have the potential to create high-value products, foster industrial collaboration, and further support the circular economy.
1 Food waste, hunger, and global challenges: a call for viable solutions
According to United Nations’ projections, the human population will continue to grow over the next few decades. Over the last 70 years, the population has tripled and is projected to reach approximately 10 billion by 2050 (United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, 2022). The expanding human population has greatly raised food demand, yet agricultural land expansion has been limited (Miah et al., 2024; Vorobyova et al., 2024). While the world’s population has increased by 300% in the last 70 years, the overall agricultural land area has increased by approximately 30% (Figures 1a,b). A 30% increase in agricultural land, compared to a 300% rise in population, has significantly stressed croplands necessitating the widespread use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides to boost food production on limited land. Global food production has increased from 0.2 to 1.2 billion tones (FAO, 2024, Ritchie et al., 2023; Figure 1c). A 6-fold increase in global food production in 60 years is indeed a remarkable achievement. The increase in usage of agricultural land has reached a plateau. With the limited scope for expanding agricultural land to increase food production, the real challenge lies in increasing the crop yields through scientific technologies. On the other hand, elevated levels of food waste production have substantial negative impacts on the economy and environment, and controlling it requires improved strategies, which can assist in developing a circular bio-economy (Bhattacharya et al., 2022; Hirbod et al., 2024; Parsa et al., 2024; Parsa et al., 2023). The developed (population 1.4 billion) and developing countries (population 6.2 billion) discarded 670 and 630 million tons of edible foods, respectively (FAO, 2011, 2019, 2021; UNEP, 2021). While globally about 690–829 million people remain hungry and 3 billion cannot afford a healthy diet (Bhattacharya et al., 2022; Parsa et al., 2024). In the United States, 38 million people are food insecure and have already faced hunger (Skaf et al., 2021). Globally, on average, fruits and vegetables contributed about 45% to the total food waste (Figure 1d) (Tiseo, 2017). Usually, this category of food waste, including the peel and skin of fruits, contains a greater amount of bioactive compounds than do the edible portions. In addition, it is also reported that food processing waste is rich in protein, lipids, and carbohydrates; thus, food waste valorization is potential in producing animal feed, cosmetics, and chemicals, as well as prebiotics, and it can play an important role in reducing problems associated with food waste (Moult et al., 2018).
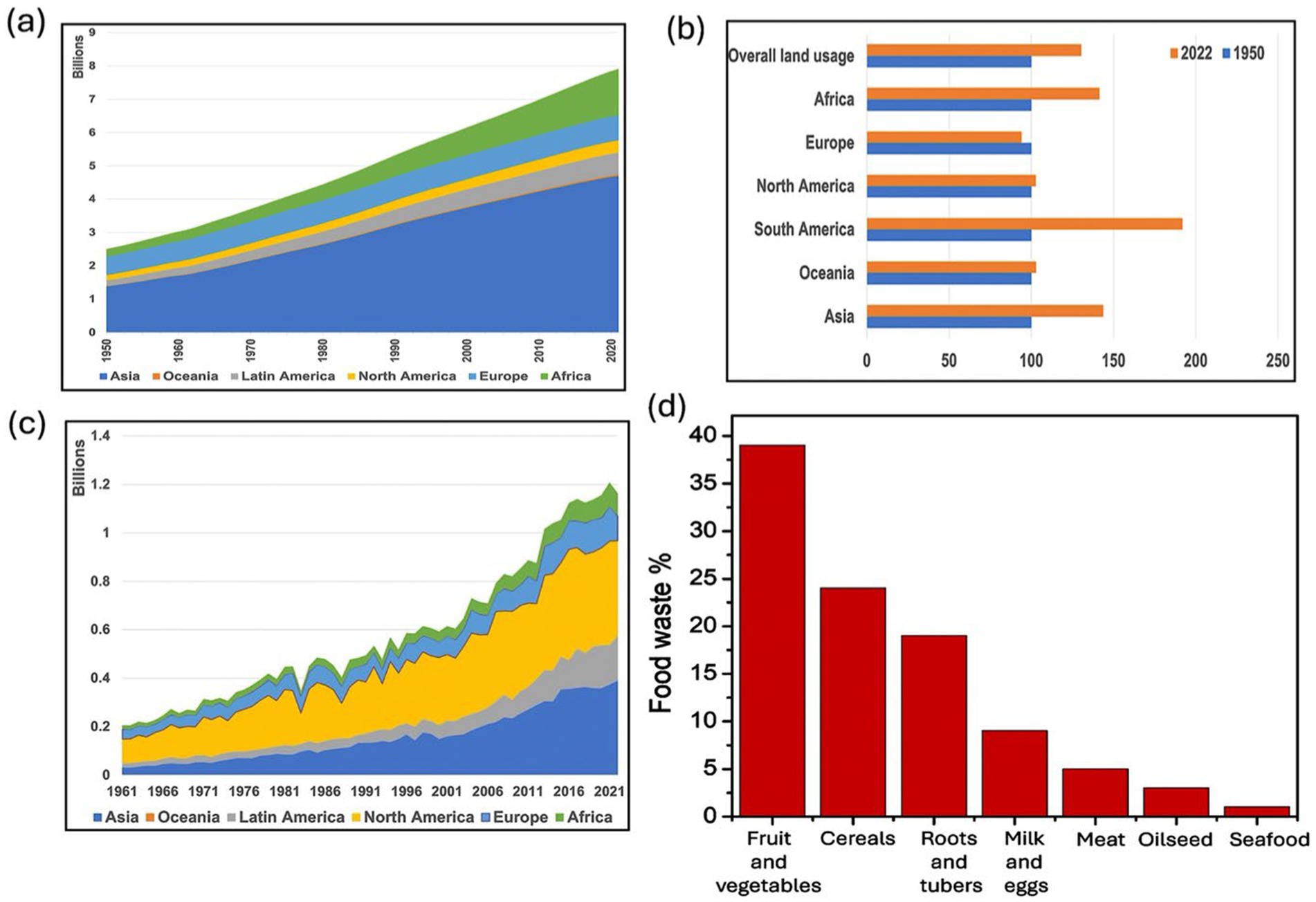
Figure 1. (a) Growth of global population between 1950 and 2021 and regional trends. (b) Percentage change in agricultural land use by continent between 1950 and 2022. (c) Trends in global food production (1961–2021). (d) Breakdown of global food waste by category (data source: UNEP, 2021; FAO, 2019; FAO, 2024; Wani et al., 2024; United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, 2022).
Food waste can be valorized in several ways to generate heat and power, solid or liquid fuels, biomaterials, or chemicals (biofertilizer, biocarbon, activated carbon, graphene, additives, volatile acids, etc.) for various applications depending on their characteristics (Carmona-Cabello et al., 2018; Mohanty et al., 2022). An enormous environmental and socio-economic burden is associated with food waste, which needs to be addressed to ensure the sustainability of food waste as a resource in the circular food economy.
2 Methodology and novelty
This review systematically examines the environmental, economic, and social challenges associated with food waste, offering a comprehensive global reference that underscores its impact on greenhouse gas emissions, cropland stress, and food security. Going beyond traditional assessments, the study evaluates food waste across all stages of the supply chain and highlights the potential of waste-to-value technologies such as biofuels, bioplastics, and biofertilizers. It also explores a range of valorization methods, including thermochemical processes and microbial dynamics, to promote circular bioeconomy frameworks.
Our methodology involves a systematic review of peer-reviewed literature, technical reports, and case studies to thoroughly evaluate food waste management strategies across the entire food supply chain. A comprehensive literature search was conducted using multiple electronic databases, including Web of Science, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. The search strategy combined terms related to food waste and valorization with those related to sustainability, food security, and environmental impact. Keywords were organized into logical categories, including but not limited to: “population growth,” “agricultural land,” “food waste,” “food loss,” “food surplus,” “organic waste,” “recycling,” “composting,” “anaerobic digestion,” “waste valorization,” “bioenergy,” “upcycling,” “food donation,” “animal feed,” “sustainability,” “environmental impact,” “circular economy,” “waste management,” “food security,” “GHG emissions,” “greenhouse gas,” “carbon footprint,” “food safety,” “microbiological,” “machine learning,” “automation,” and “artificial intelligence.” Boolean operators (AND, OR) were used to combine these terms to ensure a broad yet targeted search. For example, search queries included combinations such as (“food waste” OR “food loss”) AND (“composting” OR “bioenergy”) AND (“food security” OR “sustainability”).
This review offers critical insights for policymakers, researchers, and industry stakeholders, supporting the implementation of sustainable food waste management strategies at scale. By providing an in-depth overview of current technologies and identifying research gaps, it serves as a valuable resource for advancing sustainable practices in food waste management.
3 Impact of food waste on the environment
The environmental impact of food waste is profound, contributing to GHG emissions, water waste, and land degradation. Research suggests that food loss and waste account for an estimated 8 to 10% of total global GHG emissions, making it a substantial contributor to climate change (FAO, 2024). Moreover, the carbon footprint of wasted food exceeds the emissions of many individual countries, underscoring the magnitude of its environmental impact (FAO, 2013; Corigliano et al., 2025). Food waste generates GHG emissions at various stages of the food supply chain, including production, processing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. Inefficient agricultural practices, such as overapplication of fertilizers and deforestation for expansion of cropland, contribute to GHG emissions (Vermeulen et al., 2012). Moreover, the decomposition of organic matter in landfills is a large contributor to methane gas, an environmental hazard when considering its potency as a greenhouse gas. According to the US Environmental Protection Agency, 14.3% of methane emissions are from landfills, and this has been on the rise as food waste has been increasing in recent decades. Additionally, the carbon footprint of wasted food encompasses not only the direct emissions associated with its decomposition but also the indirect emissions embedded in its production and distribution (Serra and Fancello, 2020). Addressing food waste presents an opportunity to mitigate GHG emissions and reduce the environmental footprint of the food system. Strategies to minimize food waste include improving agricultural practices to enhance efficiency and productivity, optimizing supply chain management to reduce losses during distribution and storage, implementing policies and incentives to promote sustainable consumption patterns, and investing in infrastructure for food recovery and recycling (Manzoor et al., 2024). By preventing food waste and maximizing resource utilization, these interventions can contribute to climate mitigation efforts and foster a more sustainable food system.
Food waste not only affects the environment and economy but also has implications for human health. In regions where food insecurity is prevalent, the wastage of edible food exacerbates hunger and malnutrition. Furthermore, discarded food that is still safe for consumption but not utilized contributes to unhealthy dietary patterns and foodborne illnesses (Sawaya, 2017; Scherhaufer et al., 2018; Wani et al., 2024).
4 Global problem of food waste
Food waste is a critical global issue that poses significant economic, environmental, and social challenges. The unsustainable disposal of food not only contributes to hunger and malnutrition but also exacerbates resource depletion, GHG emissions, and biodiversity loss (Kohli et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2023). About one-third of the food produced for human consumption worldwide is lost or wasted each year, according to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) (FAO, 2019). This translates to about 1.3 billion metric tons of food wasted globally each year, valued at nearly $1 trillion (FAO, 2019). Food waste is a pervasive issue affecting both developed and developing countries, albeit with differing patterns and causes. In the United States, approximately 30–40% of the food supply is wasted. According to calculations derived from the USDA’s Economic Research Service, this equated to an estimated 31% loss of food at both retail and consumer levels in 2010, amounting to around 133 billion pounds of food and a staggering $161 billion in value (Aziz et al., 2021). In the European Union, the highest proportion of food waste occurs at the consumption stage (46%), followed by primary production (25%) and processing and manufacturing (24%). In contrast, the distribution and retail stages contribute only 5% to the total food waste generated along the supply chain (Figure 2; Sanchez Lopez et al., 2020).
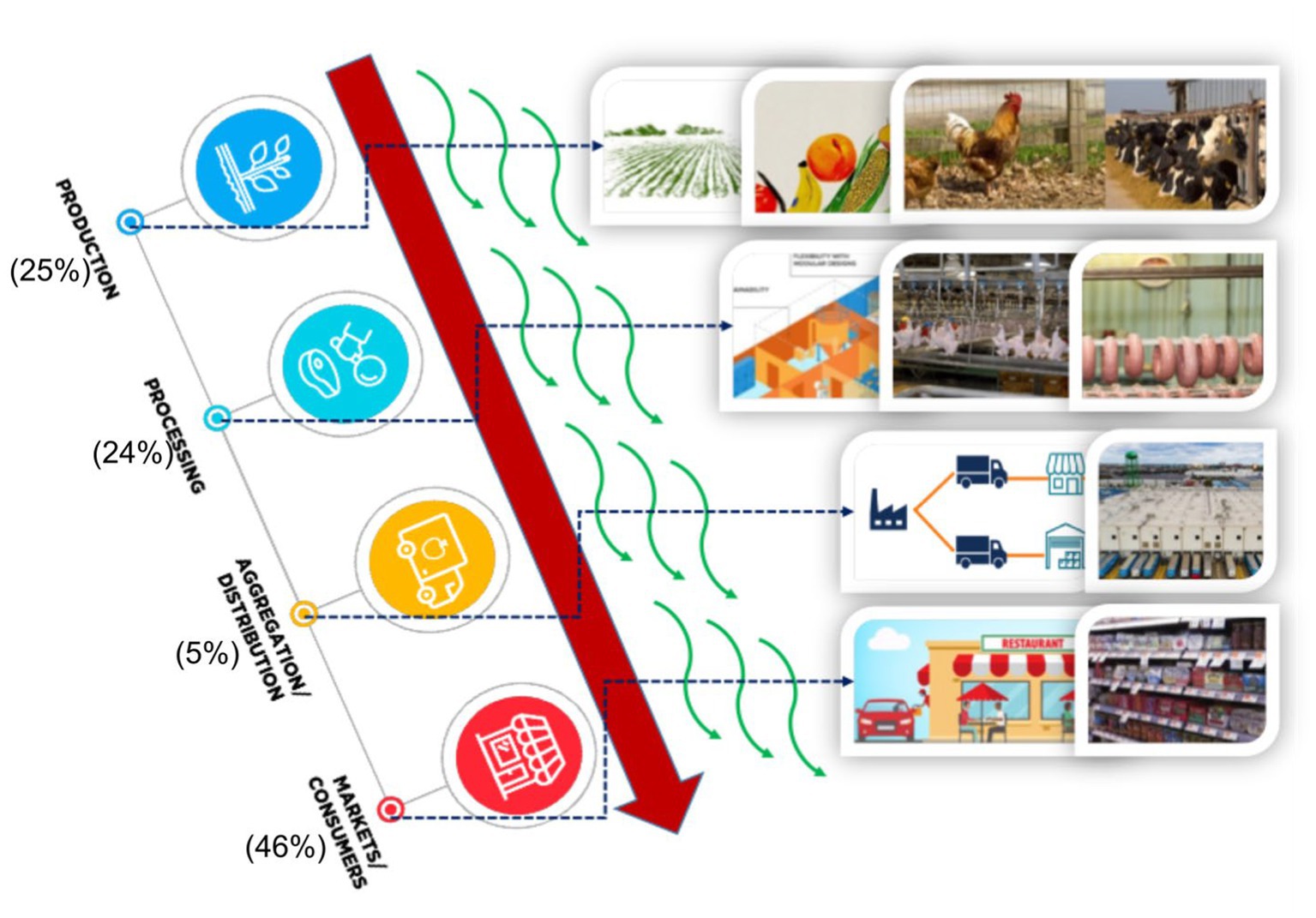
Figure 2. Food waste at different stages of production and supply chain. Percentage values indicate the amount of food waste at that specific stage (Sanchez Lopez et al., 2020).
From production and distribution to consumption and disposal, food waste is an issue at many points in the food supply chain (Figure 2). Consumer behavior and retail practices are major contributors to food waste in developed nations like North America and Europe, making up a large fraction of the total waste (de Camila et al., 2020). On the other hand, inefficient agricultural production, storage, and infrastructure are the main causes of food loss in developing nations like Southeast Asia and sub-Saharan Africa (Sawaya, 2017). Food waste imposes significant economic costs at every stage of the supply chain. For producers, the loss of unsold or unused food represents lost revenue and resources invested in production. At the consumer level, food waste contributes to higher grocery bills and wasteful spending. Additionally, the disposal and management of food waste incur additional costs for waste management systems and taxpayers.
4.1 Food waste at the production and processing levels
The UNEP Food Waste Index Report 2024 shows that in 2022, the world wasted 1.05 billion tons of food, which amounts to one-fifth (19%) of food available to consumers being wasted, at the retail, food service, and household level (United Nations Environment Programme, 2024b). Out of the total food wasted in 2022, households were responsible for 631 million tons, equivalent to 60 percent; the food service sector for 290 million tons; and the retail sector for 131 million tons (United Nations Environment Programme, 2024b). In addition to this, 13% of the world’s food was lost in the supply chain, from post-harvest up to and excluding retail. Parfitt et al. (2021) reported that of all food waste, production waste comprised 20%, and processing contributed 1% (Parfitt et al., 2021). This indicates that a significant portion of food waste occurs during the production and processing stages.
4.1.1 Dominant issues of food waste in production and processing
Various sectors of the food industry, including dairy, fruits and vegetables, seafood, and meat, contribute significantly to food waste. In the dairy sector, waste primarily occurs during product processing and manufacturing. Quality tests can lead to large quantities of product being discarded. Dairy products are semi-perishable, and oversupply often leads to stockpiling and eventual disposal of outdated products (Patra and Duary, 2020; Shrestha et al., 2021). Fruits and vegetables have the highest percentage of waste attributed to product standards, with 20–40% of the total product discarded due to suboptimal size, shape, or color. Retailer and consumer requirements can result in edible food being rejected and wasted. For instance, in the Australian banana industry, up to 40% of total production is rejected due to strict standards and low retail prices, making it unsuitable for farmers to sell (Stanley, 2017). The seafood sector also experiences a high percentage of waste in production. A study of Northern Peru shrimp trawlers operating between Cabo Blanco and Máncora in Northern Peru between April 2019 and March 2020, showed that target species Penaeus californiensis coffee shrimp constituted 17.8% of the overall catch, 82.2% represented bycatch, and 50.6% represented discards (Mendo et al., 2022). Almost 40% of the world’s fish stock is bycatch, resulting in an enormous waste of resources as the fish are generally dead and unsuitable for consumption because they are the wrong species, size, or quality (Davies et al., 2009; Lively and McKenzie, 2023).
In the meat sector, it is estimated that up to 23% of meat production is lost and wasted throughout the entire food chain. This loss and waste occur at various stages of the meat supply chain, with the largest portion occurring at the consumption level, accounting for 64% of the total food waste. This is followed by manufacturing (20%), distribution (12%), and primary production and post-harvest stages (3.5%) (Karwowska et al., 2021). In the Australian food industry, it is suggested that nearly 40% of the total food produced is wasted. This waste represents a significant loss in terms of food that could feed people, but also a loss in resources such as water, labor power, soil nutrients, transportation energy, and so forth (Gustavsson et al., 2011).
By altering raw food to a processed form, the product’s weight is often reduced. Peeling or skinning fruits and vegetables can contribute to 25–30% of waste on the product weight (Kumar et al., 2020). Canning, drying, and freezing also contribute to significant weight losses, and the resultant by-products of these processing methods can increase waste, through unsellable cosmetically damaged products or surplus production that is not consumed. By-products also have the potential to lower the market price of goods due to the increased supply. This can lead to further waste of the primary product, as previously stated with the economics of supply and demand. Processing food has the potential to increase the amount of waste from what is termed as “recovered resources.” Losses throughout the production process are often associated with the economics of supply and demand. If consumer demand is low, there is little incentive for farmers to harvest their entire crop. Often, produce is left in the fields to rot because farmers know that they will not cover the cost of harvest. Other times, crops are oversupplied to the market in an effort to drive down crop prices. Oversupplied crops can lead to lower consumption as consumers are unwilling to purchase large quantities of a good that may spoil. This will further reinforce the cycle of oversupply and low demand (Baker et al., 2019; Minor et al., 2020).
4.2 Food waste at aggregation and distribution levels
Aggregation and distribution are two very important aspects of the food supply chain. Aggregation, according to the defined terminology section of the National Sustainable Agriculture Information Service, refers to small amounts of a product from lots of different producers being assembled into a larger, more efficient amount. This occurs in many countries, such as India, with milk being transported from rural areas over long distances to urban areas in an unorganized fashion. This results in the wastage of large quantities of milk due to spoilage, overproduction, and breakage because the milk is often still in loose form and requires packing in order to qualify as an aggregated product.
Research on the implementation of supply chain management has produced mixed results. For example, a study on the UK fresh produce supply chain concluded that the management of food to longer-lasting product markets and better identification of customer requirements were the key practical changes that could be made to reduce waste (Cao et al., 2020; Fearne and Hughes, 1999; Kaipia et al., 2013). This highlights the complexity of addressing the issue, and also emphasis that multidisciplinary approaches are needed to tackle food waste in production and processing. Other methods that have been identified include more efficient stock and inventory control, supplier-retailer collaboration, and lean production techniques.
This area of the food production chain has received relatively little attention compared to households and is the focus of much recent research. The most cited method to reduce food waste in production and processing is to improve the efficiency of the supply chain (Minor et al., 2020; Parfitt et al., 2010). Previous studies estimated that a 1% reduction in food waste at the retail and consumer levels would result in savings that would outweigh the cost of most initiatives to reduce waste in production (Minor et al., 2020; Parfitt et al., 2010). Food supply chain management and the implementation of quality-based systems such as the ISO 9000 and Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) have been identified as crucial to reducing waste.
Similarly, European aggregation practices have been identified as a key contributor to food waste due to demands for food standardization by supermarkets. This is because the produce that is too large, too small, or misshapen often does not meet these standards and is subsequently left in the field or disposed of at the start of the supply chain. Studies have estimated that up to 30% of UK fruit and vegetable produce (farminguk.com) is not harvested due to the stringent aesthetic standards, with many farmers claiming that they are being forced to overproduce in order to fit the supply agreements at lower prices (Mohan et al., 2023; Kiran et al., 2023). This leads to the wastage of resources such as water and energy, intensifying the impact of the wasted produce. Several studies on traditional supply chains of mango, banana, and tomato produce in India found that around 25, 35, and 40% of the respective crops were wasted at various stages of the supply chain, including aggregation (Mohan et al., 2023; Kiran et al., 2023; Negi and Anand, 2017). This caused the farmers to suffer substantial economic losses as the added value was wasted.
4.2.1 Opportunities and challenges in the aggregation and distribution of food and food waste
An understanding of value chain differences is critical for identifying where and why waste occurs in the aggregation and distribution of food. Such knowledge can be used to pinpoint critical control points for the induction of product shelf life. Unfortunately, the complex and dynamic nature of global food supply chains presents a major obstacle to this understanding. A single commodity can be part of numerous supply chains, each differing in their journey from source to market. These journeys are affected by a vast array of economic, political, social, and environmental factors that differ between countries and regions. As a result, it is often very difficult to visualize or compare supply chain processes and to make generalized assertions about the way particular commodities should be moved and distributed.
Identification of challenges in food waste in aggregation and distribution has been identified as a research priority in response to the need to reduce waste levels and increase the utilization of resources. There are, however, a number of obstacles that prevent greater understanding and resolution of the problem. These can be seen in terms of specific industry issues and limitations of current knowledge and data. Costs associated with food waste are passed down the supply chain all the way to the consumer. When reclamation costs are low, product overstock and redundancy are commonplace. Studies have shown that up to a third of an average supermarket’s inventory are products that will never be bought. Where there is a low cost of disposal, the act of throwing food away becomes the most viable option. This was the case in the UK before landfill tax was introduced; during the 1990s, a rise in real landfill costs did not alter the perceived cost of using landfills for waste disposal. Earmarked grant assistance for capital expenditure on alternative waste treatment methods was an initiative more likely to affect behavior as it aims to make the alternative methods more economically attractive (Bernstein, 1991; Lohri et al., 2014; Gunders and Bloom, 2017).
As food moves from the farm to the local markets and on to retailers, the importance of consistency in the supply of produce becomes more critical. Food waste occurs in the aggregation and early distribution stages largely because the food is not yet a branded product. There is little consequence to canceling an order of generic produce, even when the product is of high quality. Often, when a crop is deemed to have no market value, it is plowed back into the field it came from or is left to rot. A portion of food is lost in post-harvest handling; this is particularly the case with fresh produce.
4.2.2 Efforts on minimizing food waste during aggregation and distribution
There is also potential in the socio-technical systems of innovation theory that can identify pathways to system change that change the relationship between society and the environment to more sustainable practices. A case study done by Germany has investigated how certain innovation niches, as a result of backcasting, scenario development, and transition management, have managed to reduce environmental burdens. The results have shown that radical reductions have taken place as they have managed to reconfigure the rules of the game, with sugar beet and sweet corn, for instance, transforming back into mixed farming. Although the German focus was on food quality and resulted in environmentally friendly food production chains, scenarios out of agricultural intensification into the production of energy/biomass from crops can, at the minimum, maintain food livelihoods and reduce farm surpluses (Quist and Vergragt, 2003; Neuvonen et al., 2014; Quist, 2007). A technical tool called MIPS (Material Input per Service) Analysis, which is designed to measure the material efficiency of a product to provide a service, can provide analytical information for sustainability from these findings.
It is not only at the household level that effective methods can perceive food waste as an opportunity. Lean manufacturing techniques or philosophy can potentially solve the food losses occurring at the time of aggregation and distribution. The concept of lean thinking is essentially to maximize value by minimizing waste. The application of lean manufacturing in the food industry is relatively new (Dora et al., 2013). Lean concepts and tools from manufacturing have high potential to improve efficiency in the food industry. Simulation studies based on linear programming can significantly contribute to reducing food waste by optimizing harvesting time. For instance, studies have shown that using linear programming models can lead to cost reductions of up to 59% in banana plantations (Pechibilski et al., 2024). Additionally, these models help identify profitable seasons for crop harvesting, aiding farmers and agricultural offices in efficient scheduling (Custodio et al., 2024). These tools can greatly reduce overproduction, lead times and inventory, which would subsequently release resources from all levels in the supply chain.
Moreover, recent Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) approaches present significant potential to minimize food waste by improving supply chain efficiency, forecasting demand, and optimizing logistics management (Min et al., 2023; Opara et al., 2024; Clark et al., 2025). Several case studies highlight the effectiveness of AI-driven tools in reducing food waste. Solutions from Shelf Engine and Afresh led to a 14.8% reduction in store-level food waste and prevented 26,705 tons of CO₂ emissions. Similarly, IKEA used AI-powered kitchen monitoring systems to cut its food waste by 30% within a year, demonstrating the strong potential of AI in promoting sustainability across the food supply chain (Onyeaka et al., 2025).
4.3 Market and consumer levels food waste and consequential impacts
A significant portion of this waste occurs at the consumer level and in markets. According to the UNEP, an estimated 931 million tons of food, or 17% of total food available to consumers in 2019, went into the waste bins of households, retailers, restaurants, and other food services (Stancu and Ene, 2024). This waste is equivalent to the weight of 23 million fully loaded 40-tonne trucks, enough to circle the Earth 7 times.
A study commissioned by the IFIC Foundation revealed that 74% of respondents reported leftovers of foods prepared at home were most often wasted. A close second source of waste was produced (67%), while leftovers from restaurants ranked third (50%). The most common reason for food waste at home was spoiled or stale food, as reported by 83% of the respondents. Interestingly, food waste seems to be less of a concern when eating out. Fewer than one in five (19%) report always thinking about food waste while eating out, and nearly two in five (39%) say they never think about it. Consumer behavior in relation to food waste is complex and influenced by multiple factors. The top reason that consumers think about food waste is to reduce the amount of money they spend on food. While reducing food waste can benefit the planet, more people tend to think about how reducing food waste benefits them individually, with saving money outweighing people’s concern for the environment (foodinsight.org/consumers-perception-food-waste).
Age and ethnicity also seem to impact how often people consider food waste. Those 45 years and younger are more likely to think about food waste while grocery shopping, eating out, and eating at home. Differences were observed between ethnicities, too, with significantly more Hispanic/Latinx-identifying people reporting that they always think about food waste during each of these occasions (foodinsight.org/consumers-perception-food-waste). Sometimes, it is necessary to think about food as a consequence of all the activity done to produce it. Therefore, when food is lost or wasted, it means that all the resources and inputs used in the production of the food are also lost. Food is said to be wasted when it is discarded, whether or not it is still good to eat. This can happen at many stages in the food’s journey from farm to consumer. In terms of the food system, food waste is a consequence of a complex web of interactions among agribusiness, food processing, transportation, retail, and consumption. In the United States, many studies show that food is wasted at the consumer level. Defined as food that reaches the consumer but is discarded instead of being eaten. This was estimated to be 1.4 billion pounds in 1995.
Today, Americans throw away an estimated 25% of the food and beverages they purchase (Gunders and Bloom, 2017; Campbell and Feldpausch, 2022). Considering that everything else is equal, if consumers would reduce food waste by 1%, it would have the same effect as if consumers reduced their food and beverage expenditures by 1%. The small percentage change shows how a relatively small change can have a large impact in terms of resource conservation. In order to prevent food waste, it is necessary to understand the causes and drivers of waste at the consumer level, and research has shown that it is related to food choices and meal management with a complex array of environmental influences. This is where the sociological perspective is valuable in understanding food waste, and it is essential to know how cultural values and practices can affect levels of waste.
5 Technology aspects of food waste treatment technologies and conversion of food waste into value added products
The European Union estimates that 42% of food waste is generated in the home, 39% at the retail level, and 14% in food service outlets (food.ec.europa.eu). Clearly, there is a significant opportunity to reduce waste generated by consumers and retailers. The Waste and Resource Action program of the UK identified a number of opportunities to reduce waste at the consumer level. They suggest improved in-home storage and the judicious use of freezing to extend the life of many foods. Reducing portion sizes can also help reduce waste, given that many people serve more than they can eat. Changing when people eat certain foods can also reduce waste. Food that is damaged or spoiled at the retail level constitutes roughly 17% of the total waste from the distribution and consumption chain (UNEP, 2021). Donations of food that is still fit for consumption to food assistance programs and the conversion of spoiled food to animal feed can be effective in reducing this type of waste. A study of Norwegian consumers’ habits found that throwing away food that was still edible is more likely when they believe food to be unsafe. Improving consumer knowledge about food handling and safety can help reduce the amount of edible food discarded.
5.1 Conventional food waste treatment technologies
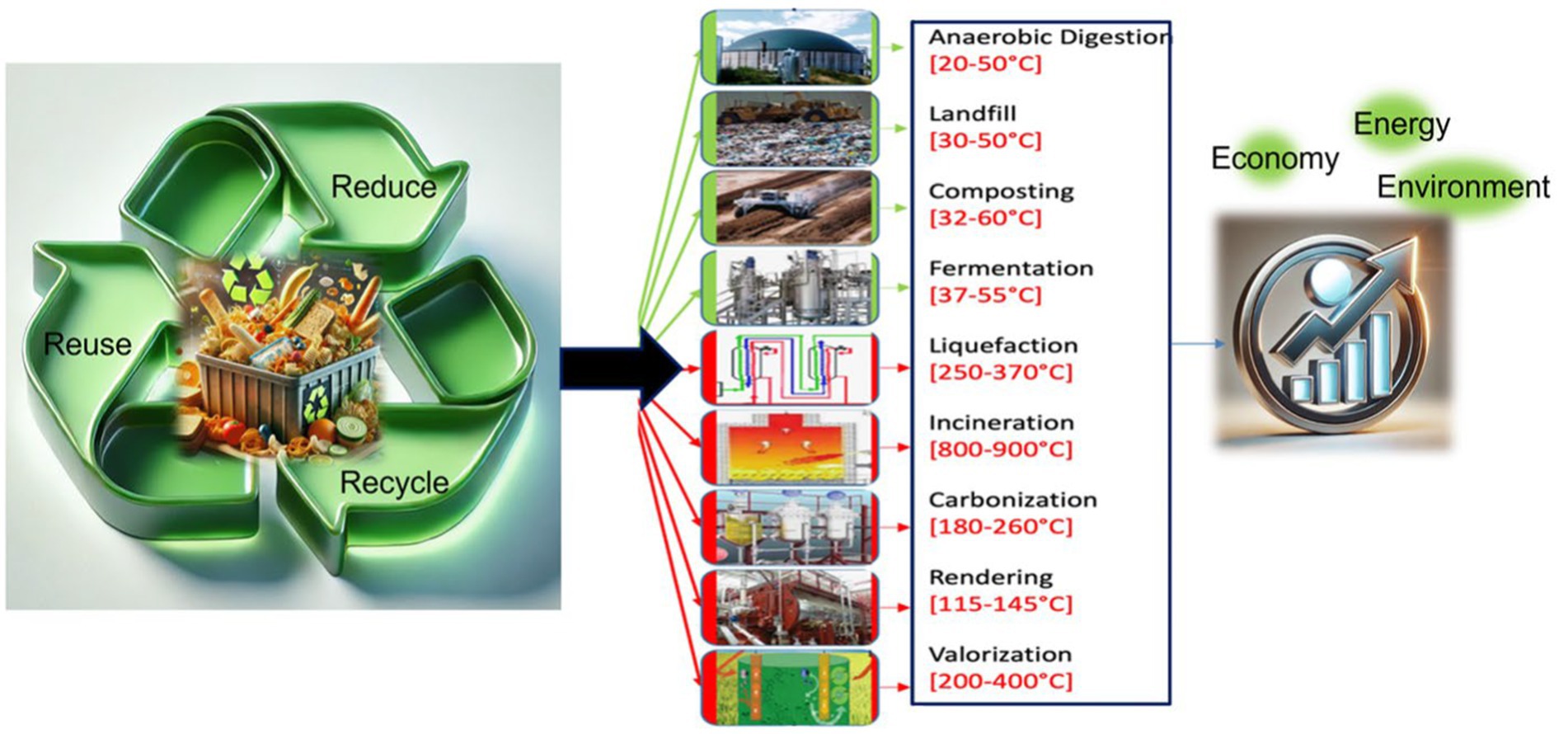
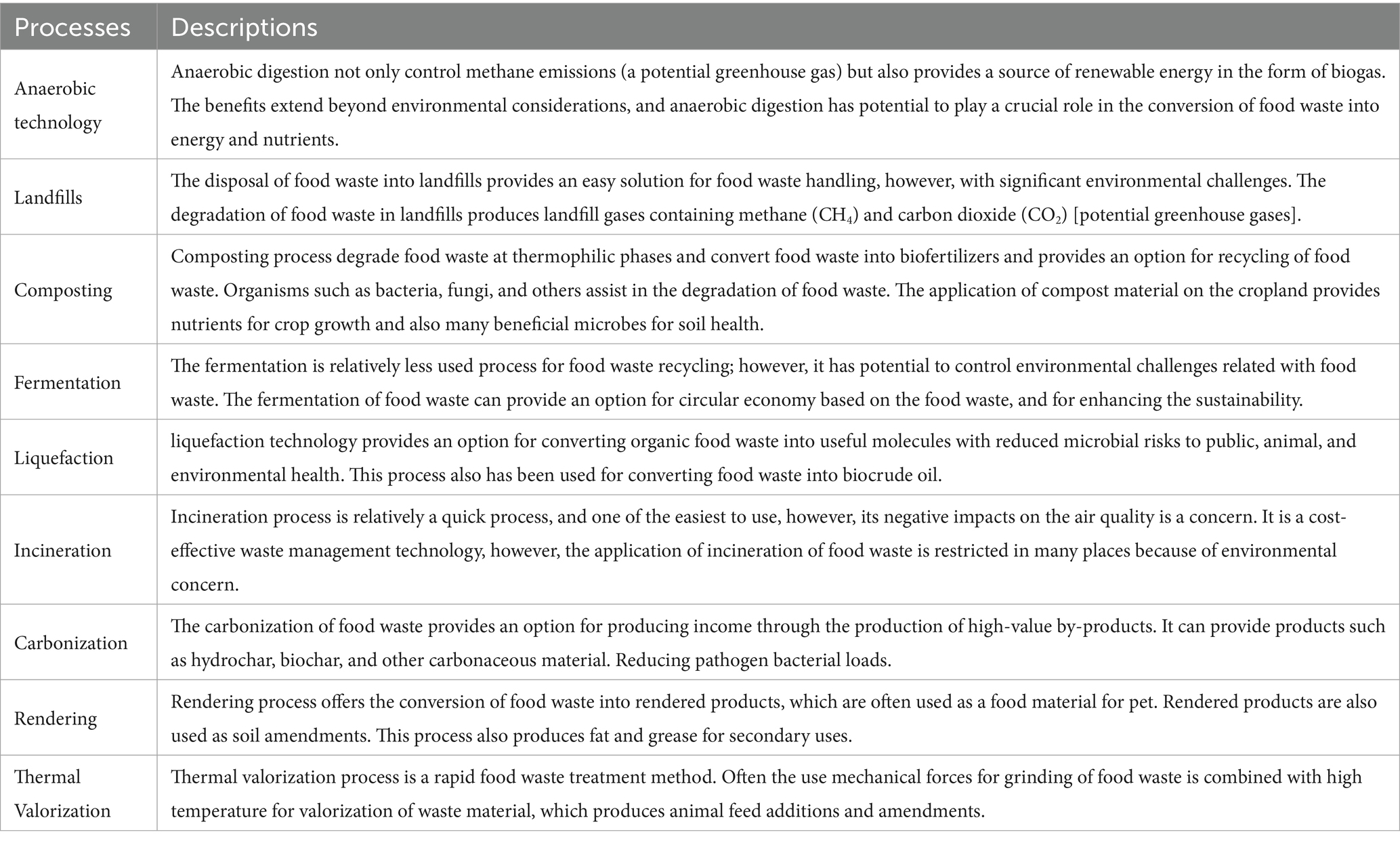
Food waste recycling processes (Table 1) play a crucial role in addressing the environmental, economic, and social challenges associated with food waste management (Shukla et al., 2024). As food waste continues to be a pressing global issue, with significant amounts ending up in landfills and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions, recycling offers a sustainable solution to mitigate these impacts (Lahiri et al., 2023; Ritchie et al., 2024). Different methods are implemented to recycle the food waste (Figure 3).
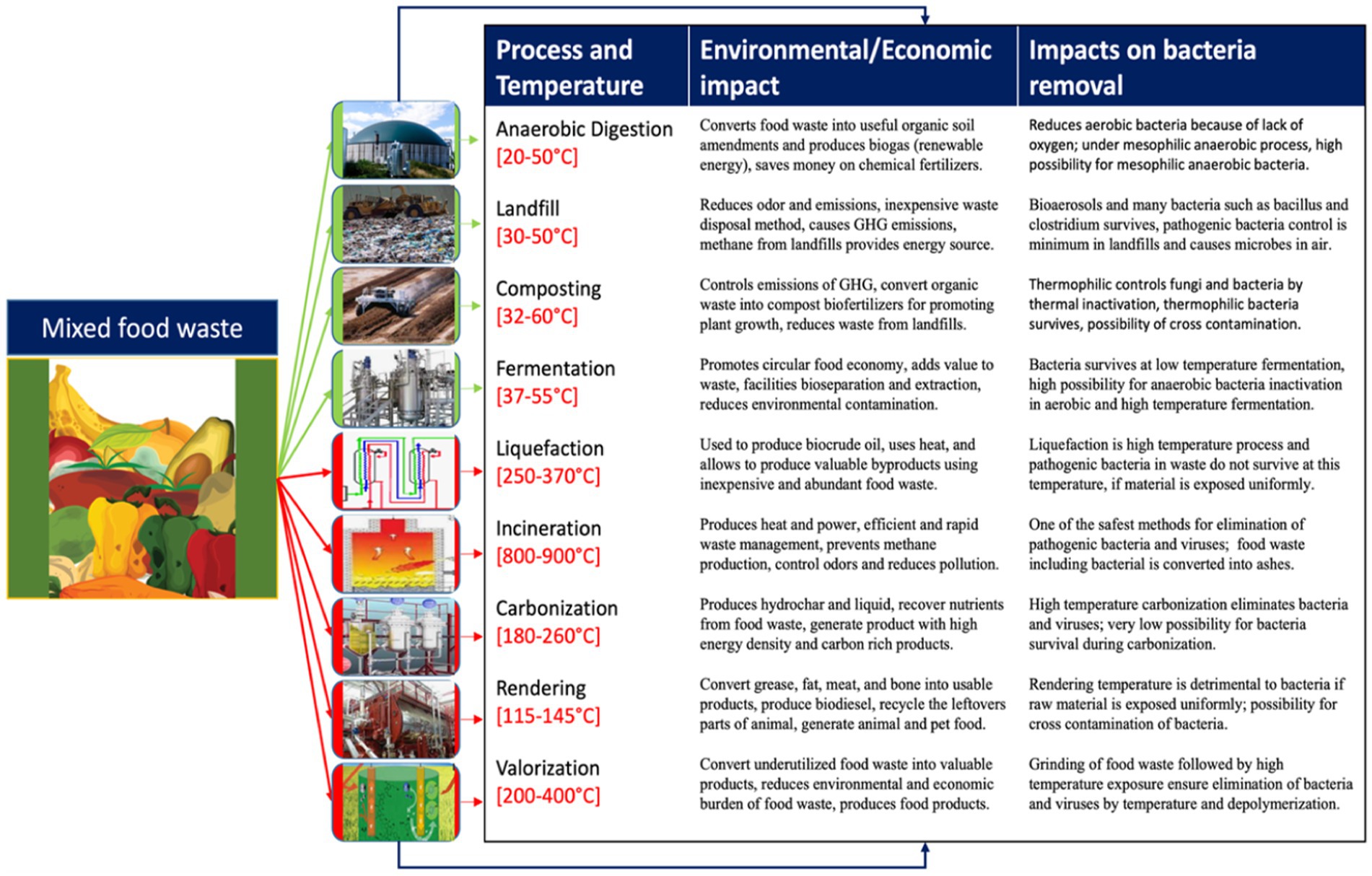
Figure 3. Various food waste recycling methods and their impact on the environment and microbial dynamics.
5.1.1 Anaerobic digestion process
Anaerobic digestion is a natural process that occurs in the absence of oxygen, breaking down organic materials and producing biogas (Archana et al., 2024; Piadeh et al., 2024). This biogas serves as a valuable renewable energy source, while the remaining digestate can be utilized as a fertilizer or soil amendment (Chew et al., 2021). The environmental impact of food waste in landfills, where it generates methane, a potent greenhouse gas, can be mitigated through diverting it to anaerobic digesters. This not only reduces methane emissions but also provides energy offsets by utilizing biogas in lieu of fossil fuels. The benefits extend beyond environmental considerations. Anaerobic digestion can play a crucial role in achieving waste diversion goals, especially considering that food waste constitutes the second-largest category of municipal solid waste sent to landfills in the United States, accounting for about 18% of the waste stream. Anaerobic digestion of food waste presents an opportunity for cost savings in wastewater treatment facilities. These facilities can accept food waste as a feedstock, utilizing biogas to power their operations and even charging a tipping fee for receiving the food waste. Additionally, the digestate can be sold as a valuable product (O'Connor et al., 2022a).
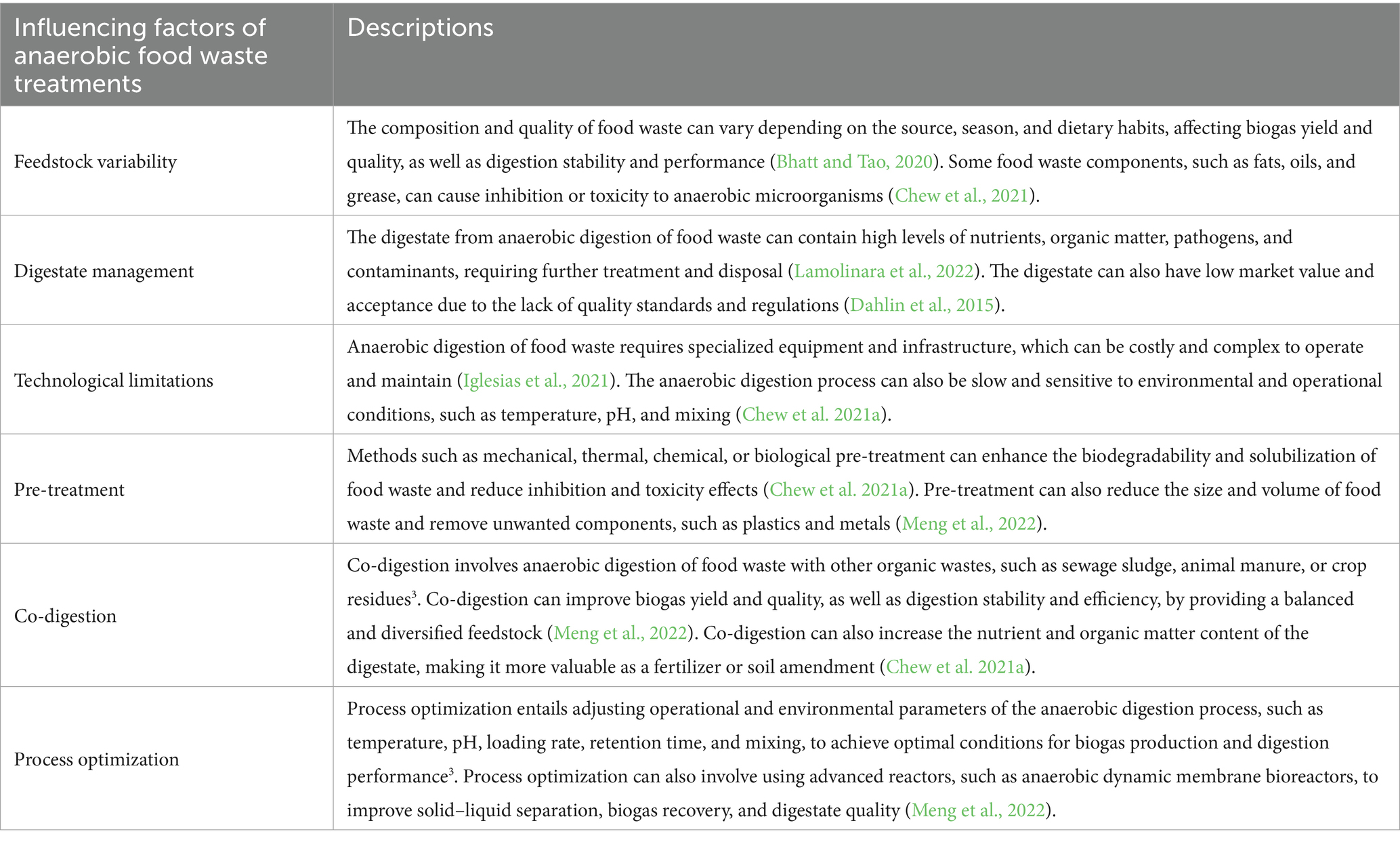
In addition to these environmental benefits, anaerobic digestion also has implications for microbial dynamics. Factors influencing the scope of the anaerobic digestion process are summarized in Table 2. During anaerobic digestion, the microbial community plays a crucial role in the decomposition of organic matter and the production of biogas. Different microorganisms, such as bacteria and archaea, work together in a complex web of interactions to break down organic waste and convert it into methane. The choice of feedstock for anaerobic digestion also affects microbial dynamics and overall process efficiency. For example, the composition of food waste, including its nutrient content and pH, can influence the microbial community structure and metabolic activity within the anaerobic digestion system. The utilization of agricultural residues through bioprocessing technology offers a promising avenue for converting crop residues into valuable bio-products. Using agricultural residues as a source of nutrients for microorganisms can lead to the production of valuable bio-products such as enzymes, organic acids, and other metabolites. These bio-products have diverse applications in various fields and can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to waste management (Sadh et al., 2018). Anaerobic digestion of food waste not only helps reduce environmental impacts associated with waste disposal but also offers the potential for resource recovery through the production of bioplastics and other valuable bio-products (Singhania et al., 2017). One notable example is the coupling of anaerobic digestion with the production of biodegradable thermoplastics, specifically polyhydroxyalkanoates (Du and Yu, 2002). These bioplastics can be derived from the carbon-rich byproducts of anaerobic digestion, such as volatile fatty acids, and offer a sustainable alternative to petroleum-based plastics.
Additionally, methods have been developed to integrate anaerobic digesters with high-temperature fuel cell energy systems, focus on maximizing both the efficiency and sustainability of electricity and heat generation from organic waste streams. The process begins with anaerobic digestion, where organic substrates such as agricultural or industrial waste are biologically converted under controlled conditions to produce biogas, primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide (Sharma et al., 2024). To ensure compatibility with fuel cell systems, this biogas undergoes advanced pretreatment steps-including physical, chemical, and biological methods-to remove contaminants like hydrogen sulfide, siloxanes, and moisture, which can otherwise degrade fuel cell performance and lifespan (Amoo et al., 2023). After purification, the methane-rich biogas is supplied to high-temperature fuel cells such as solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), which operate at elevated temperatures and can directly utilize biogas as fuel. These integrated systems are capable of achieving high electrical and thermal efficiencies, with the added benefit of waste heat recovery for digester heating or other process needs, thus supporting combined heat and power (CHP) applications (Sher et al., 2024).
5.1.2 Landfill systems for food waste disposal
Landfill-based recycling processes involve the disposal of waste in a designated area (landfill) and the subsequent treatment and recycling of that waste. Food waste has consistently constituted a significant proportion of the municipal solid waste (MSW) stream in the United States (Hall et al., 2009). When food waste is disposed of in landfills, it undergoes biodegradation, leading to the production of landfill gas (LFG) containing methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2), both potent GHGs (Chickering et al., 2023). Landfills release a substantial amount of GHGs and other harmful substances into the atmosphere, thereby contributing to global warming (Etezadi et al., 2023). In recent times, several states have implemented recycling objectives and organics management policies, compelling the rechanneling of food waste away from landfills to alternative disposal methods like composting or anaerobic digestion. The heterogeneity and chemical complexity of food waste contribute to distinct impacts on landfill environments. Additionally, the rapid degradation of food waste often outpaces the installation of landfill gas collection infrastructure, leading to the presumption that a considerable portion of the methane produced from food waste is released into the atmosphere (Cusworth et al., 2024).
However, the effect of food waste on the microbiomes in landfills remains unclear and inconsistent (Muhammad and Rosentrater, 2020). To alleviate the environmental and economic consequences of food waste in landfills, it is crucial to explore beneficial uses for food waste biomass, such as converting it into energy (Bhatia et al., 2023). Research has shown that food waste fermentation and utilization in the production of value-added products result in a lower global-warming potential (GWP) impact compared to landfill disposal (Hashar et al., 2021). Therefore, diverting food waste from landfills and exploring alternative management methods can help mitigate the environmental burden.
5.1.3 Composting
Composting, nature’s organic matter recycling method, plays a pivotal role in curbing greenhouse gas emissions. By diverting food waste away from landfills and open dumping sites, composting effectively diminishes the generation of methane. This reduction in methane production is a crucial aspect of climate change mitigation. The positive impact of compost extends to soil health in multiple ways. Initially, it diminishes reliance on chemical fertilizers as it gradually releases essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, fostering robust plant growth. Additionally, compost enhances soil structure, facilitating improved water retention and root penetration. This feature is particularly vital in arid regions where water conservation is paramount. Moreover, the gradual release of nutrients from compost ensures sustained nourishment for plants (Cerda et al., 2018; Saer et al., 2013; Awasthi et al., 2020). Additionally, composting orchestrates a dynamic interplay among a myriad of microbial communities. Bacteria, fungi, and various microorganisms collaborate to dismantle organic matter, transforming it into simpler compounds (Palaniveloo et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2023; Awasthi et al., 2018). The composting process consists of several phases, such as thermophilic, mesophilic, and maturation. In the thermophilic Phase, temperature is increased. Typically ranging between 131°F and 160°F, the thermophilic phase is dominated by thermophilic bacteria. Their prevalence not only expedites the decomposition process but also acts as a potent force in eradicating harmful pathogens (Chang et al., 2006). The mesophilic phase often occurs after the thermophilic phase, the compost undergoes a cooling process. This transition heralds the reign of mesophilic bacteria, which continue the breakdown of organic material, ensuring the refinement of compost constituents (Palaniveloo et al., 2020). The maturation phase occurs after the thermophilic and mesophilic phases. In this phase, compost experiences a slowdown in microbial activity. This final stage results in a product teeming with nutrients, presenting significant benefits for soil health (Palaniveloo et al., 2020).
The profound influence of composting extends to soil microbial communities. Introducing organic matter through compost enriches the soil with a diverse array of microbial species, crucial for nutrient cycling and decomposition. Research indicates that applying food waste compost alters microbial-community composition, impacting factors like pH levels, electrical conductivity, total carbon, and exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) in both water-saturated paddy and unsaturated upland soils (Lee et al., 2019). Composting goes beyond microbial benefits, offering additional environmental advantages. Proper composting not only prevents unpleasant odors but also deters pests, minimizing vermin infestations. Furthermore, by diverting organic waste from landfills, composting reduces the risk of landfill fires.
5.1.4 Fermentation
The recycling of food waste, with a particular emphasis on fermentation processes, plays a pivotal role in addressing environmental concerns, fostering circular food economies, and influencing microbial dynamics. Fermentation, which involves the biological breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, is a key component in various waste treatment strategies. An essential benefit of incorporating fermentation into food waste recycling lies in its contribution to a circular food economy. By transforming food waste into valuable products such as compost, biofertilizers, and biogas, fermentation reduces the environmental impact associated with conventional disposal methods. The circular nature of these processes minimizes the reliance on external inputs, thereby promoting sustainable and self-sufficient waste management systems. Furthermore, fermentation adds value to waste by converting it into products that find utility in agricultural practices. The resulting compost and biofertilizers enhance soil fertility and structure, thereby promoting sustainable agriculture. This added value not only mitigates the economic impact of waste disposal but also contributes to resource efficiency and agricultural productivity (Wang et al., 2020; Han and Shin, 2004; Sabater et al., 2020).
In the realm of microbial dynamics, the conditions within fermentation processes play a crucial role. Low-temperature fermentation environments can support the survival of specific bacteria, adapting to these conditions and influencing the overall microbial composition. Conversely, high-temperature and aerobic fermentation may create environments unsuitable for the survival of anaerobic bacteria. The dynamic interplay of these microbial communities during fermentation is essential for the efficient breakdown of organic matter and the generation of beneficial by-products (Perez-Esteban et al., 2024).
Bioseparation and extraction processes during fermentation further enhance the overall efficiency of food waste recycling. These processes facilitate the separation of valuable compounds from the fermented material, enabling the extraction of bioactive substances and improving the overall economic viability of the recycling system (Hadj Saadoun et al., 2021). Moreover, the integration of fermentation into waste management significantly reduces the environmental risks associated with contamination. Controlled microbial activities in fermentation processes aid in breaking down complex organic compounds, thereby mitigating the potential for leachate generation and groundwater contamination. This environmentally friendly approach aligns seamlessly with the principles of sustainable waste management.
5.1.5 Liquefaction
Food waste recycling processes, particularly liquefaction, have garnered attention due to their potential to transform organic waste into valuable resources while minimizing environmental impact. Liquefaction entails subjecting food waste to elevated temperatures, typically ranging from 150 to 400°C, in the presence of a solvent or water. This process leads to the breakdown of complex organic compounds into simpler molecules. A significant environmental advantage of liquefaction lies in the eradication of pathogenic bacteria, as the high temperatures employed are lethal to many microbial species commonly present in food waste. This aspect enhances the safety of the process, reducing the risk of contamination and the spread of diseases associated with untreated organic waste (Bayat et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2020).
The utilization of liquefaction in food waste recycling has been explored to produce biocrude oil, involving the conversion of organic matter into a liquid fuel that can be further refined and utilized as an energy source. Studies, such as the one conducted by Chen et al. (2016), have delved into the feasibility of employing food waste as a feedstock for biocrude oil production through liquefaction processes (Chen et al., 2016). By converting waste into a valuable energy resource, this approach contributes to decreasing dependence on conventional fossil fuels, thereby mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and addressing energy security concerns. Furthermore, the high-temperature conditions during liquefaction not only eliminate pathogens but also result in the production of valuable byproducts. For instance, Hu et al. (2023) demonstrated that liquefying food waste yields biochar, a carbon-rich material that can be used as a soil amendment to enhance fertility and sequester carbon (Hu et al., 2023). This multifaceted approach enables the simultaneous production of bioenergy and valuable byproducts, creating a more sustainable and resource-efficient food waste recycling system. It is crucial to note that while liquefaction offers environmental benefits, there are challenges and considerations. The energy input required for high-temperature processes must be carefully balanced against the environmental gains achieved. Additionally, the choice of solvents and process parameters can influence the overall environmental footprint of the technology.
5.1.6 Incineration
Incineration of mixed food waste at temperatures ranging from 800 to 900°C presents a multifaceted approach to waste management with significant environmental and economic implications. From an environmental standpoint, this process offers several advantages. Firstly, incineration produces heat and power through the combustion of organic matter, thereby contributing to energy generation. This is particularly beneficial in the context of waste-to-energy initiatives, where incineration serves as a renewable energy source. Additionally, the rapid and efficient nature of incineration aids in waste management by reducing the volume of waste and mitigating its impact on landfills. By incinerating food waste at high temperatures, methane production is prevented, thereby helping to mitigate climate change. Furthermore, incineration controls odors associated with decomposing organic matter and reduces air and water pollution by preventing leachate contamination from landfills (O'Connor et al., 2022b; Kowalski et al., 2021).
From an economic perspective, incineration offers cost-effective waste management solutions. While initial setup costs may be significant, the long-term benefits in terms of reduced waste volume, energy production, and environmental conservation outweigh these expenses. Moreover, incineration facilities can generate revenue through the sale of electricity generated from the combustion process.
In terms of microbial dynamics, incineration at temperatures of 800–900°C has profound effects on bacteria removal. The high temperatures achieved during incineration effectively eliminate pathogenic bacteria and viruses present in mixed food waste. Studies have demonstrated that incineration is one of the safest methods for the destruction of microbial contaminants, ensuring that food waste is converted into sterile ashes devoid of harmful pathogens. This microbial sterilization process not only mitigates the risk of disease transmission associated with untreated waste but also minimizes the potential for environmental contamination upon disposal of incineration byproducts.
5.1.7 Carbonization
Carbonization of food waste, typically occurring at temperatures ranging from 180 to 260°C, offers unique environmental and economic benefits. One significant environmental impact of carbonization is the production of hydrochar and liquid byproducts. Hydrochar, a carbon-rich solid material resembling charcoal, can be utilized as a soil amendment or as a precursor to produce activated carbon. The liquid fraction obtained during carbonization contains valuable nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which can be recovered and utilized as fertilizers or bio-based chemicals. By converting food waste into these valuable products, carbonization contributes to resource recovery and reduces the burden on landfills and natural ecosystems (Periyavaram et al., 2023; Saqib et al., 2018; Le et al., 2022; Tradler et al., 2018).
From an economic standpoint, carbonization presents opportunities for generating revenue through the production of high-value products. Hydrochar, with its high energy density and carbon content, can be utilized as a renewable fuel source or as a sustainable substitute for traditional fossil-based materials. Additionally, the recovery of nutrients from food waste through carbonization provides economic benefits by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and promoting circular economy principles (Farru et al., 2024).
In terms of bacteria removal, high-temperature carbonization effectively eliminates microbial contaminants present in food waste. The thermal decomposition process during carbonization involves exposure to temperatures well above the range required for microbial inactivation. Consequently, there is a very low possibility for bacteria survival during carbonization, ensuring the production of sterile end products (Ducey et al., 2017). Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of carbonization in destroying bacteria and viruses, thereby mitigating the risk of disease transmission associated with untreated organic waste (Shimoda et al., 2002). The sterile nature of the hydrochar and liquid products obtained from carbonization further enhances their suitability for agricultural and industrial applications, minimizing the potential for microbial contamination (Sharma et al., 2020; Liu and Zhang, 2025).
5.1.8 Rendering
Rendering, a food waste recycling process, plays a significant role in transforming various organic waste materials into valuable products. One critical aspect of rendering is the temperature at which carbonization occurs, typically ranging between 115 and 145°C. This temperature range is pivotal in driving the breakdown and conversion of organic matter, particularly in the context of grease, fat, meat, and bone (Bedoić et al., 2020; Alexander et al., 2013).
Rendering processes offer both environmental and economic benefits. By converting grease, fat, meat, and bone into usable products, rendering helps mitigate the environmental burden associated with food waste disposal. Instead of ending up in landfills where they contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, these materials are repurposed into valuable commodities. Additionally, rendering can facilitate the production of biodiesel, further reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing carbon emissions (Toldrá-Reig et al., 2020; Canakci, 2007). Moreover, rendering allows for the recycling of leftover animal parts that might otherwise go to waste. This not only minimizes environmental pollution but also contributes to the circular economy by extracting value from by-products that would otherwise be discarded. The generated animal and pet food from rendering not only reduces the strain on natural resources required for conventional feed production but also provides a sustainable solution for pet owners and livestock producers.
The dynamics of microorganisms are significantly impacted by rendering processes, especially when they are performed at the designated temperatures. The elevated temperatures involved in rendering are detrimental to bacteria, effectively sterilizing the raw material if uniformly exposed. This thermal treatment effectively eliminates harmful pathogens, making rendered products safer for consumption and reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses (Pandey et al., 2020). However, it is crucial to recognize the potential for cross-contamination of bacteria during the rendering process. While rendering temperatures are effective at killing pathogens, improper handling or incomplete sterilization can lead to the survival of certain bacteria or the introduction of new contaminants. Therefore, strict adherence to hygiene protocols and quality control measures is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the safety and integrity of rendered products.
5.1.9 Thermal valorization
Valorization in the context of food waste recycling refers to the process of converting underutilized food waste into valuable products, thereby reducing environmental and economic burdens associated with food waste (Liu et al., 2023; du et al., 2018; Van Chhandama et al., 2022; Tropea, 2022; Nayak and Bhushan, 2019). This approach aims to extract maximum value from food waste streams by employing various methods such as thermal, biochemical, or chemical processes. Valorization is increasingly being utilized in food waste recycling due to its effectiveness in converting organic waste into useful products. Among the various methods, thermal valorization, which involves heating food waste at temperatures ranging from 200 to 400°C in the absence of oxygen (pyrolysis), is particularly common (Kim et al., 2020). This process breaks down complex organic molecules into simpler compounds, generating valuable resources such as biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
The temperature range (200–400°C) at which thermal valorization occurs is sufficient to achieve microbial inactivation and reduce the microbial load by breaking down complex organic compounds present in food waste. Overall, thermal valorization processes play a crucial role in not only converting food waste into valuable resources but also in ensuring the safe disposal of potentially harmful microbial contaminants, thereby contributing to environmental sustainability and public health protection.
5.2 Valorization of food waste to produce value-added products
Food waste is a rich source of organic matter that can be converted into value-added products. The conversion of food waste into single cell protein (SCP), biofuel, bioplastics, and other value-added products is a promising approach to waste management and sustainable production.
5.2.1 Single cell protein
Single Cell Protein (SCP) represents a promising nutritional platform with the potential for significant impact, particularly when derived from waste materials. This approach could be considered transformative for sustainable food production. SCP is derived from various microorganisms such as yeast, fungi, or bacteria (Nasseri et al., 2011; Anupama and Ravindra, 2000). The process involves utilizing microorganisms to convert different substrates into microbial cell mass. The resulting microbial protein, or single-cell protein, has various applications, such as human food, animal feed, nutritional supplements, and more (Bratosin et al., 2021; Jones et al., 2020; Sharif et al., 2021). SCP technology is advantageous as it offers upcycling of co-products of the agri-food sector or farms. SCP is not a new protein source, but recent research has demonstrated that co-product streams in the agri-food sector can serve as a carbon source for fermenting organisms to grow biomass. This resulting biomass is highly concentrated in protein, with protein content ranging from 50 and 80% on a dry weight basis. The SCP production from various types of organic waste eliminates the need for treating the organic material for its Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD). Instead, the fermentation of organic waste material transforms low-value waste into high-value single-cell protein (SCP), adding significant value to the production chain (Dharumadurai et al., 2011; Mahan et al., 2018; Ribeiro et al., 2023; Sadh et al., 2023; Thiviya et al., 2022; Tropea et al., 2022). Moreover, as the world’s population continues to grow, there is an urgent need for sustainable and efficient protein sources, and SCP is now at the forefront of this burgeoning field (Ritala et al., 2017).
SCPs are gaining attention due to their high protein content, which is comparable to other protein sources. The protein content in dry matter of algae and yeasts, on conventional substrates, lies between 50 and 60%, for alkane yeasts between 55 and 65%, and for bacteria about 80% (Bratosin et al., 2021; Ritala et al., 2017). The protein content is determined based on total nitrogen, which is multiplied by the factor 6.252. In addition to proteins, SCPs also contain a good balance of essential amino acids. The exact composition of these amino acids can vary depending on the growth medium. SCPs produced using bacteria contain a small amount of sulfur-containing amino acids (Bajpai, 2017). SCPs also contain a significant quantity of dietary fibers in the cell wall and a variety of micronutrients, including vitamins such as thiamine, riboflavin, pyridoxine, nicotinic acid, pantothenic acid, folic acid, biotin, cyanocobalamin, ascorbic acid, β-carotene, and α-tocopherol (Ritala et al., 2017). These vitamins play crucial roles in various biological processes, contributing to the overall health of the consumer.
One of the key advantages of SCP is its exceptional resource efficiency. It can be produced using minimal land, water, and energy resources, making it an environmentally friendly alternative. By utilizing waste materials or low-value substrates, SCP production reduces the burden on traditional agriculture and alleviates environmental degradation (Aidoo et al., 2023; Areniello et al., 2023; Piercy et al., 2023). Moreover, the production of SCP generates fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional protein sources, contributing to mitigating climate change (Bhatia et al., 2023). Recently, multiple entities are in existence offering an option for handling food-related material and conversion of food waste into enhanced material for economic and environmental benefits. Entities such as Solar Foods, which is based in Finland, Solar Foods produce Solein, a protein derived from microbes that consume carbon dioxide and hydrogen. Solein is versatile and can be used in various food products, including meat alternatives, dairy-free goods, and even as an egg substitute. Equii Foods, a US-based food biotech company, manufactures high-protein flours and staple foods like bread and pasta using SCP through sustainable fermentation. Their bread product range includes wheat, multigrain, and fiber-enriched varieties, providing 8–10 grams of protein per slice. Additional companies such as Calysta and Unibio are also instrumental in food-related products. Calysta works in collaboration with Adisseo. Calysta produces FeedKind, a SCP made from natural gas via microbial fermentation. This protein is primarily targeted at the aquafeed market. Uni-bio is a Danish company that produces Uni-Protein, a SCP derived from natural gas. Uni-Protein is designed as a sustainable alternative to traditional animal feeds like fishmeal and soy protein.
5.2.2 Biofuels
Food waste can be significantly used as a raw material for the production of biofuel using various suitable techniques. Carbohydrate, lipid, and other nutrient-containing materials present in food waste can be converted to bioethanol, biodiesel, hydrogen, and methane (Pandey et al., 2022). Given the increasing demand for sustainable energy sources, utilizing food waste for biofuel production presents a promising solution. Biofuels derived from food waste can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and promote circular economy principles (Shaba et al., 2025).
5.2.3 Bioethanol
The process of converting food waste into bioethanol involves three main steps: pretreatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, and fermentation (Bibra et al., 2023; Roukas and Kotzekidou, 2022). The pretreatment process involves the use of mechanical, chemical, and biological methods to maximize sugar recovery from the food waste. This is followed by enzymatic hydrolysis, where a mixture of suitable enzymes (mainly cellulase, β-glucosidase, and pectinase) is used to break down the polysaccharides into fermentable sugars. The final step is fermentation, where microorganisms convert these sugars into bioethanol (Roukas and Kotzekidou, 2022).
However, the production of bioethanol from food waste is not without challenges. The handling of biomass and the application of pretreatment methods to improve the conversion of lignocellulosic materials into fermentable sugars are some of the issues that need to be addressed (Roukas and Kotzekidou, 2022). The biofuel potential of food waste is summarized in Table 3.
5.2.4 Biodiesel
The production of biodiesel from food waste is gaining attention worldwide. Various types of food waste, including waste cooking oil, grease trap waste, and lipid-rich food waste, are being explored for biodiesel production. The extracted lipids are then purified to remove any impurities (Julkipli et al., 2023; Karmee and Lin, 2014). During transesterification, extracted lipids are reacted with an alcohol (usually methanol or ethanol) in the presence of a catalyst to produce biodiesel. The catalyst can be either acidic, basic, or enzymatic (Julkipli et al., 2023; Karmee and Lin, 2014).
However, there are challenges associated with biodiesel production from food waste. These include the variability in the composition of food waste, the need for efficient lipid extraction methods, and the need for effective catalysts for the transesterification process. Despite these challenges, the production of biodiesel from food waste holds great potential. It provides a sustainable solution to the problem of food waste and contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions (Julkipli et al., 2023; Karmee and Lin, 2014). With advancements in technology and process optimization, the production of biodiesel from food waste can become a commercially viable option.
5.2.5 Biogas
The process of converting food waste into biogas involves a set of microbiological reactions and physico-chemical processes known as anaerobic digestion (AD) (Chew et al., 2021; Mirmohamadsadeghi et al., 2019). Anaerobic digestion is a process that involves a set of microbiological reactions and physico-chemical processes to generate biogas, a mixture of predominantly CH4 and CO2 (Chew et al., 2021; Mirmohamadsadeghi et al., 2019). It is commercialized globally; however, AD has limited commercial applications in the U. S. compared to other regions of the world (Chew et al., 2021).
5.2.6 Biohydrogen
The technology used for biohydrogen production from food waste primarily involves two biological methods: dark fermentation and photosynthesis (Bhatia et al., 2024; Mohanakrishna et al., 2023; Tagne et al., 2024). Dark fermentation is a process that involves the breakdown of organic matter by bacteria in the absence of light, producing hydrogen gas as a byproduct (Mohanakrishna et al., 2023). Photosynthesis, on the other hand, involves the conversion of light energy, usually from the sun, into chemical energy in plants, which is then used to fuel the plant’s activities (Bhatia et al., 2024). A more practical option that has emerged is dark-photo sequential fermentation. This approach involves first subjecting the food waste to dark fermentation, followed by photosynthesis (Tamaian, 2023).
Another technology that has been explored for biohydrogen production from food waste is the Separate Hydrolysis and Fermentation (SHF) approach. This method offers several notable advantages, including enhanced hydrolysis efficiency, flexibility and control, improved overall biohydrogen production rates, and nutrient-rich solutions (Tamaian, 2023).
However, the production of biohydrogen from food waste is not without its challenges. One of the main challenges lies in the conversion of macromolecules, such as starch and protein, into utilizable carbon sources like glucose and free amino nitrogen (FAN) (Osman et al., 2023; Sohrab Hossain et al., 2023). This conversion process, known as hydrolysis, often proves to be the rate-limiting step in most bioprocesses (Osman et al., 2023; Sohrab Hossain et al., 2023). Another challenge is related to the large-scale production of biohydrogen. Issues such as low hydrogen yield, selection of suitable technology, and availability of feedstock for hydrogen production pose significant hurdles (Tamaian, 2023). Furthermore, the most common disposal method of food waste is open dumping in a landfill, which presents additional environmental challenges.
5.2.7 Bioplastics
The production of bioplastics from food and agricultural waste is a rapidly growing field, with significant advancements being made in recent years (Merino et al., 2022; Rajesh Banu and Godvin Sharmila, 2023). Bioplastics, which are biodegradable plastics made from biological substances rather than petroleum, can be created in a more economical and environmentally friendly way from the byproducts of agricultural production (Peydayesh, 2024).
One of the key areas of focus in this field is the use of agri-food waste as an alternative substrate for biopolymer generation (Merino et al., 2022). For instance, Haloferax mediterranei, a highly researched strain, is capable of producing polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB), a type of bioplastic. This strain can grow and produce bioplastic in high-salinity environments without requiring sterilization. Extensive research has been conducted on the genes and pathways responsible for PHB production using H. mediterranei, to understand how fermentation parameters can be regulated to enhance cell growth and increase PHB accumulation (Merino et al., 2022).
Bioplastic production has seen a significant increase over the past decade. In 2014, 1.7 million tons of bioplastics were produced, versus 2.05 million tons in 2017, and it has been estimated that annual bioplastic production will reach 7.5 million tons in 2026 (Ali et al., 2023; Emadian et al., 2017).
6 Conclusion
Addressing the global challenge of food waste is imperative for ensuring environmental sustainability, food security, and economic resilience. Over the past 70 years, while the global population has increased by approximately 300%, agricultural land expansion has only grown by about 30%, placing unprecedented pressure on food systems. Despite a six-fold increase in global food production-from 0.2 to 1.2 billion tons annually-approximately 1.3 billion metric tons of food, or nearly one-third of all food produced for human consumption, is lost or wasted each year (FAO, 2019). This waste is valued at nearly $1 trillion globally and contributes significantly to environmental degradation, accounting for 810% of total global greenhouse gas emissions (FAO, 2024).
In 2022 alone, 1.05 billion tons of food were wasted globally, with households contributing 631 million tons (60%), the food service sector 290 million tons (28%), and the retail sector 131 million tons (12%) (United Nations Environment Programme, 2024a). Concurrently, 13% of the world’s food was lost between post-harvest and retail stages. Such inefficiencies are stark, especially in the face of global hunger, which affects between 690 and 829 million individuals, while 3 billion people cannot afford a healthy diet.
Food waste is not merely a loss of calories-it represents a substantial waste of water, energy, labor, and capital, and leads to environmental pollution through methane emissions, land degradation, and resource depletion. In developed countries, waste predominantly occurs at the consumption level due to consumer behaviors and stringent cosmetic standards, with fruits and vegetables accounting for 45% of global food waste. In contrast, food loss in developing countries is primarily due to limitations in infrastructure and storage during post-harvest and processing stages.
Effective mitigation strategies-such as valorization of food waste into bioenergy, biomaterials, and feedstock; adoption of precision agriculture; improved supply chain logistics; and public policy reforms, can significantly reduce food loss and waste. Emerging energy technologies, including optimized anaerobic digestion, microbial fuel cells, and next-generation bioreactor systems, are enabling more efficient conversion of food waste into bioenergy, biogas, and other value-added energy carriers (Lin et al., 2021; Sikiru et al., 2024; Hidalgo et al., 2025). Holistic interventions must be implemented at each stage of the food supply chain to promote a circular bioeconomy. Collaborative action from governments, industry stakeholders, researchers, and consumers are essential to minimizing food waste, enhancing food system resilience, and contributing to climate change mitigation.
Looking ahead, the integration of automation and AI offers transformative potential to reduce food waste across the entire supply chain. Future strategies should leverage AI-driven predictive analytics for yield forecasting, supply chain optimization, and dynamic pricing to minimize spoilage and overproduction. Advanced automation in sorting, grading, and precision agriculture can further reduce on-farm losses, while smart kitchen technologies and digital food-sharing platforms can curb consumer-level waste. Moreover, AI-enabled optimization of microbial and enzymatic valorization processes presents a promising route to convert food waste into high-value bioproducts. Broad adoption and continued innovation in these areas will be pivotal for transitioning toward a more sustainable, resilient, and resource-efficient global food system.
Author contributions
NR: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BG: Conceptualization, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SD: Resources, Writing – review & editing. VJ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. NA: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Funding provided by Equii Food, San Leandro, California, and UCANR was used for supporting this work.
Acknowledgments
We offer our sincere appreciation to all the team members, individuals, and agencies, including Equii Food, San Leandro, California, California Department of Food and Agriculture (CDFA), University of California Agriculture and Natural Resources (UC ANR), and School of Veterinary Medicine (UC SVM), that were involved in data collection and interpretation. The information, statement, and interpretation presented in the manuscript are authors’ views and do not necessarily reflect the views of the author’s employer, company, institution, or other associated agencies.
Conflict of interest
Authors NR, BG, and SD were employed by the company Equii Food.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aidoo, R., Kwofie, E. M., Adewale, P., Lam, E., and Ngadi, M. (2023). Overview of single cell protein: production pathway, sustainability outlook, and digital twin potentials. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 138:577–598. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2023.07.003
Alexander, C., Gregson, N., and Gille, Z. (2013). “Food waste.” the handbook of food research, vol. 1, 471–484.
Ali, S. S., Abdelkarim, E. A., Elsamahy, T., Al-Tohamy, R., Li, F., Kornaros, M., et al. (2023). Bioplastic production in terms of life cycle assessment: a state-of-the-art review. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 15:100254. doi: 10.1016/j.ese.2023.100254
Amoo, A. O., Ijanu, E. M., Haruna, A., Adeleye, A. O., and Sabo, A. (2023). Review on the pre-treatment advancements of biogas production barriers. UMYU J. Microbiol. Res. 8, 6–30. doi: 10.47430/ujmr.2381.002
Ankathi, S. K., Chaudhari, U. S., Handler, R. M., and Shonnard, D. R. (2024). Sustainability of biogas production from anaerobic digestion of food waste and animal manure. Appl. Microbiol. 4, 418–438. doi: 10.3390/applmicrobiol4010029
Anupama,, and Ravindra, P. (2000). Value-added food: single cell protein. Biotechnol. Adv. 18, 459–479. doi: 10.1016/S0734-9750(00)000450-8
Archana, K., Visckram, A. S., Kumar, P. S., Manikandan, S., Saravanan, A., and Natrayan, L. (2024). A review on recent technological breakthroughs in anaerobic digestion of organic biowaste for biogas generation: challenges towards sustainable development goals. Fuel 358:130298. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130298
Areniello, M., Matassa, S., Esposito, G., and Lens, P. N. L. (2023). Biowaste upcycling into second-generation microbial protein through mixed-culture fermentation. Trends Biotechnol. 41, 197–213. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.07.008
Awasthi, S. K., Sarsaiya, S., Awasthi, M. K., Liu, T., Zhao, J., Kumar, S., et al. (2020). Changes in global trends in food waste composting: research challenges and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 299:122555. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122555
Awasthi, S. K., Wong, J. W. C., Li, J., Wang, Q., Zhang, Z., Kumar, S., et al. (2018). Evaluation of microbial dynamics during post-consumption food waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 251, 181–188. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.040
Aziz, H. A., Abu, S., Vesilind, P. A., Wang, L. K., and Hung, Y.-T. (2021). “Introduction to solid waste management” in Solid waste engineering and management: Volume 1. eds. L. K. Wang, M.-H. S. Wang, and Y.-T. Hung (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–84.
Bajpai, P. (2017). “Nutritional benefits of single-cell proteins” in Single cell protein production from lignocellulosic biomass. ed. P. Bajpai (Singapore: Springer Singapore), 59–63.
Baker, G. A., Gray, L. C., Harwood, M. J., Osland, T. J., and Tooley, J. B. C. (2019). On-farm food loss in northern and Central California: results of field survey measurements. Resour. Conserv. Recycling 149, 541–549. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2019.03.022
Bayat, H., Dehghanizadeh, M., Jarvis, J. M., Brewer, C. E., and Jena, U. (2021). Hydrothermal liquefaction of food waste: effect of process parameters on product yields and chemistry. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:658592. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.658592
Bedoić, R., Špehar, A., Puljko, J., Čuček, L., Ćosić, B., Pukšec, T., et al. (2020). Opportunities and challenges: experimental and kinetic analysis of anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and rendering industry streams for biogas production. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 130:109951. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.109951
Bernstein, J. D. (1991). Alternative approaches to pollution control and waste management: Regulatory and economic instruments. Washington, D.C., USA: World Bank.
Bhatia, L., Jha, H., Sarkar, T., and Sarangi, P. K. (2023). Food waste utilization for reducing carbon footprints towards sustainable and cleaner environment: a review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20:2318. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20032318
Bhatia, L., Sarangi, P. K., Shadangi, K. P., Srivastava, R. K., Sahoo, U. K., Singh, A. K., et al. (2024). A systematic review on photocatalytic biohydrogen production from waste biomass. Bioenergy Res. 17, 932–955. doi: 10.1007/s12155-023-10704-5
Bhatt, A. H., and Tao, L. (2020). Economic perspectives of biogas production via anaerobic digestion. Bioengineering 7:74. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering7030074
Bhattacharya, A., Zutshi, A., and Prajogo, D. (2022). Food waste challenges at downstream interfaces: a triple bottom line dilemma. Aust. J. Environ. Manag. 29, 314–343. doi: 10.1080/14486563.2022.2139768
Bibra, M., Samanta, D., Sharma, N. K., Singh, G., Johnson, G. R., and Sani, R. K. (2023). Food waste to bioethanol: opportunities and challenges. Fermentation 9:8. doi: 10.3390/fermentation9010008
Bratosin, B. C., Darjan, S., and Vodnar, D. C. (2021). Single cell protein: a potential substitute in human and animal nutrition. Sustain. For. 13:9284. doi: 10.3390/su13169284
Campbell, C. G., and Feldpausch, G. L. (2022). Invited review: the consumer and dairy food waste: an individual plus policy, systems, and environmental perspective. J. Dairy Sci. 105, 3736–3745. doi: 10.3168/jds.2021-20994
Canakci, M. (2007). The potential of restaurant waste lipids as biodiesel feedstocks. Bioresour. Technol. 98, 183–190. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2005.11.022
Cao, G., Shah, P., and Ramanathan, U. (2020). “Reducing edible food waste in the UK food manufacturing supply chain through collaboration” in Sustainable supply chains: Strategies, issues, and models. eds. U. Ramanathan and R. Ramanathan (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 291–311.
Carmona-Cabello, M., Garcia, I. L., Leiva-Candia, D., and Dorado, M. P. (2018). Valorization of food waste based on its composition through the concept of biorefinery. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 14, 67–79. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.06.011
Caruso, M. C., Braghieri, A., Capece, A., Napolitano, F., Romano, P., Galgano, F., et al. (2019). Recent updates on the use of agro-food waste for biogas production. Appl. Sci. 9:1217. doi: 10.3390/app9061217
Cerda, A., Artola, A., Font, X., Barrena, R., Gea, T., and Sánchez, A. (2018). Composting of food wastes: status and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 248, 57–67. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.133
Chang, J. I., Tsai, J. J., and Wu, K. H. (2006). Thermophilic composting of food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 97, 116–122. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.013
Chen, W.-H., Lin, Y.-Y., Liu, H.-C., and Baroutian, S. (2020). Optimization of food waste hydrothermal liquefaction by a two-step process in association with a double analysis. Energy 199:117438. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.117438
Chen, W.-T., Tang, L., Qian, W., Scheppe, K., Nair, K., Wu, Z., et al. (2016). Extract nitrogen-containing compounds in biocrude oil converted from wet biowaste via hydrothermal liquefaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 4, 2182–2190. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.5b01645
Chew, K. R., Leong, H. Y., Khoo, K. S., Vo, D.-V. N., Anjum, H., Chang, C.-K., et al. (2021). Effects of anaerobic digestion of food waste on biogas production and environmental impacts: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 19, 2921–2939. doi: 10.1007/s10311-021-01220-z
Chickering, G., Krause, M. J., and Schwarber, A. (2023). Effects of landfill food waste diversion: a focus on microbial populations and methane generation. Biodegradation 34, 477–488. doi: 10.1007/s10532-023-10034-5
Clark, Q. M., Kanavikar, D. B., Clark, J., and Donnelly, P. J. (2025). Exploring the potential of AI-driven food waste management strategies used in the hospitality industry for application in household settings. Front. in Artif. Intell. 7:1429477. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1429477
Corigliano, O., Morrone, P., and Algieri, A. (2025). Navigating the challenges of sustainability in the food processing chain: insights into energy interventions to reduce footprint. Energies 18:296. doi: 10.3390/en18020296
Custodio, J. M., Billones, R. K., Concepcion, R., and Vicerra, R. R. (2024). Optimization of crop harvesting schedules and land allocation through linear programming. Process Integr. Optimiz. Sustain. 8, 123–134. doi: 10.1007/s41660-023-00357-4
Cusworth, D. H., Duren, R. M., Ayasse, A. K., Jiorle, R., Howell, K., Aubrey, A., et al. (2024). Quantifying methane emissions from United States landfills. Science 383, 1499–1504. doi: 10.1126/science.adi7735
Chhandama, M.Van, Lal, A. C., Chetia, K. B., Satyan, S. A., Ruatpuia, J. V L, and Rokhum, S. L. (2022). “Valorisation of food waste to sustainable energy and other value-added products: a review.” Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 17:100945. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2022.100945
Dahlin, J., Herbes, C., and Nelles, M. (2015). Biogas Digestate marketing: qualitative insights into the supply side. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 104, 152–161. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2015.08.013
Davies, R. W., Cripps, S. J., Nickson, A., and Porter, G. (2009). Defining and estimating global marine fisheries bycatch. Mar. Policy 33, 661–672. doi: 10.1016/j.marpol.2009.01.003
de Camila, C. C., de Oliveira Costa, F. H., Pereira, C. R., Roberta, C., Da Silva, A. L., and Delai, I. (2020). Retail food waste: mapping causes and reduction practices. J. Clean. Prod. 256:120124:120124. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120124
Dey, N., and Bhaskarwar, A. N. (2021). “Bioconversion of food waste into ethanol: a review” in Sustainable bioconversion of waste to value added products. eds. Inamuddin and A. Khan (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 45–58.
Dharumadurai, D., Subramaniyan, L., Subhasish, S., Nooruddin, T., and Annamalai, P. (2011). Production of single cell protein from pineapple waste using yeast. Innov. Roma. Food Biotechnol. 8, 26–32.
Dora, M., Van Goubergen, D., Kumar, M., Molnar, A., and Gellynck, X. (2013). Application of lean practices in small and medium-sized food enterprises. Br. Food J. 116, 125–141. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-05-2012-0107
du, C., Abdullah, J. J., Greetham, D., Fu, D., Yu, M., Ren, L., et al. (2018). Valorization of food waste into biofertiliser and its field application. J. Clean. Prod. 187, 273–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.211
Du, G., and Yu, J. (2002). Green technology for conversion of food scraps to biodegradable thermoplastic polyhydroxyalkanoates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 5511–5516. doi: 10.1021/es011110o
Ducey, T. F., Collins, J. C., Ro, K. S., Woodbury, B. L., and Griffin, D. D. (2017). Hydrothermal carbonization of livestock mortality for the reduction of pathogens and microbially-derived DNA. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 11, 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11783-017-0930-x
Emadian, S. M., Onay, T. T., and Demirel, B. (2017). Biodegradation of bioplastics in natural environments. Waste Manag. 59, 526–536. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2016.10.006
Etezadi, R., Zhao, L., and Tsotsis, T. (2023). “Syngas from food waste” in Advances in synthesis gas: methods, technologies and applications. eds. M. R. Rahimpour, M. A. Makarem, and M. Meshksar. (Netherlands: Elsevier), 1:439–455.
FAO (2011). Global food losses and food waste–Extent, causes and prevention. SAVE FOOD: An initiative on food loss and waste reduction, 9:2011.
FAO (2013). The state of food and agriculture 2019. Food systems for better nutrition. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome.
FAO (2019). The state of food and agriculture 2019. Moving forward on food loss and waste reduction. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome.
FAO (2021). FAO, IFAD, UNICEF, WFP and WHO. 2021. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2021. Transforming food systems for food security, improved nutrition and affordable healthy diets for all. FAO: Rome.
FAO (2024). World food and agriculture – Statistical yearbook 2024. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome.
Farru, G., Scheufele, F. B., Moloeznik Paniagua, D., Keller, F., Jeong, C., and Basso, D. (2024). Business and market analysis of hydrothermal carbonization process: roadmap toward implementation. Agronomy 14:541. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14030541
Fearne, A., and Hughes, D. (1999). Success factors in the fresh produce supply chain: insights from the UK. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 4, 120–131. doi: 10.1108/13598549910279567
Gunders, D., and Bloom, J. (2017) “Wasted: How America is losing up to 40 percent of its food from farm to fork to landfill.” NY, USA: The Natural Resources Defense Council.
Gustavsson, J., Cederberg, C., Sonesson, U., Van Otterdijk, R., and Meybeck, A. (2011) Global food losses and food waste. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
Hadj Saadoun, J., Bertani, G., Levante, A., Vezzosi, F., Ricci, A., Bernini, V., et al. (2021). Fermentation of agri-food waste: a promising route for the production of aroma compounds. Food Secur. 10:707. doi: 10.3390/foods10040707
Hall, K. D., Guo, J., Dore, M., and Chow, C. C. (2009). The progressive increase of food waste in America and its environmental impact. PLoS One 4:e7940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007940
Han, S.-K., and Shin, H.-S. (2004). Biohydrogen production by anaerobic fermentation of food waste. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 29, 569–577. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2003.09.001
Hashar, N. N. H., Kadir, A. A., Loh, K. L., Sarani, N. A., Hassan, M. I. H., Hamid, N. J. A., et al. (2021). In-vessel food waste composting: a review. AIP Conf. Proc. 2339:020089. doi: 10.1063/5.0044305
Hidalgo, D., Urueña, A., Martín-Marroquín, J. M., and Díez, D. (2025). Integrated approach for biomass conversion using thermochemical routes with anaerobic digestion and syngas fermentation. Sustain. For. 17:3615. doi: 10.3390/su17083615
Hirbod, F., Karimi, T., Mohammadnazari, Z., Rabbani, M., and Aghsami, A. (2024). Municipal solid waste management using multiple disposal location-arc routing and waste segregation approach: a real-life case study in England. J. Ind. Prod. Eng. 41, 81–100. doi: 10.1080/21681015.2023.2265925
Hossain, S., Badsha, M. M., Balakrishnan, V., and Shaharun, M. S. (2023, 2023). “A review on bio-hydrogen production from food waste: potential and challenges” in Proceedings of the 1st international conference of new energy: ICNE 2022, 1–2 Dec, Sarawak, Malaysia (Singapore: Springer), 105–114.
Hu, Y., Hu, M., Jiang, H., Yu, P., and Yang, W. (2023). Co-liquefaction of livestock manure and food waste: synergistic effects and product combustion performance. Appl. Energy 341:121073. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2023.121073
Iglesias, R., Muñoz, R., Polanco, M., Díaz, I., Susmozas, A., Moreno, A. D., et al. (2021). Biogas from anaerobic digestion as an energy vector: current upgrading development. Energies 14:2742. doi: 10.3390/en14102742
Jones, S. W., Karpol, A., Friedman, S., Maru, B. T., and Tracy, B. P. (2020). Recent advances in single cell protein use as a feed ingredient in aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 61, 189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2019.12.026
Julkipli, J., Babel, S./., Bilyaminu, A. M., and Rene, E. R. (2023). Hydrogen and biodiesel production from food waste: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 22, 1–23. doi: 10.1007/s10311-023-01674-3
Kaipia, R., Dukovska-Popovska, I., and Loikkanen, L. (2013). Creating sustainable fresh food supply chains through waste reduction. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manage. 43, 262–276. doi: 10.1108/IJPDLM-11-2011-0200
Kapdan, I., Karapinar, F., and Kargi, F. (2006). Bio-hydrogen production from waste materials. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 38, 569–582. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.09.015
Karmee, S. K., and Lin, C. S. K. (2014). Valorisation of food waste to biofuel: current trends and technological challenges. Sustain. Chem. Process. 2, 1–4. doi: 10.1186/s40508-014-0022-1
Karwowska, M., Łaba, S., and Szczepański, K. (2021). Food loss and waste in meat sector—why the consumption stage generates the most losses? Sustain. For. 13:6227. doi: 10.3390/su13116227
Kim, S., Lee, Y., Lin, K.-Y. A., Hong, E., Kwon, E. E., and Lee, J. (2020). The valorization of food waste via pyrolysis. J. Clean. Prod. 259:120816. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120816
Kiran, P. R., Mani, I., Parrey, R. A., and Srivastav, M. (2023). Mapping of supply chain and assessment of pre and postharvest losses of alphonso mango in India. Environ. Conserv. J. 24, 64–74. doi: 10.36953/ECJ.20472555
Kohli, K., Prajapati, R., Shah, R., Das, M., and Sharma, B. K. (2024). Food waste: environmental impact and possible solutions. Sustain. Food Technol. 2, 70–80. doi: 10.1039/D3FB00141E
Kowalski, Z., Kulczycka, J., Makara, A., and Harazin, P. (2021). Quantification of material recovery from meat waste incineration–an approach to an updated food waste hierarchy. J. Hazard. Mater. 416:126021. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126021
Kumar, H., Bhardwaj, K., Sharma, R., Nepovimova, E., Kuča, K., Dhanjal, D. S., et al. (2020). Fruit and vegetable peels: utilization of high value horticultural waste in novel industrial applications. Molecules 25:2812. doi: 10.3390/molecules25122812
Lahiri, A., Daniel, S., Kanthapazham, R., Vanaraj, R., Thambidurai, A., and Peter, L. S. (2023). A critical review on food waste management for the production of materials and biofuel. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 10:100266. doi: 10.1016/j.hazadv.2023.100266
Lamolinara, B., Pérez-Martínez, A., Guardado-Yordi, E., Guillén, C., Diéguez-Santana, K., and Ruiz-Mercado, G. J. (2022). Anaerobic digestate management, environmental impacts, and techno-economic challenges. Waste Manag. 140, 14–30. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2021.12.035
Le, H. S., Chen, W.-H., Ahmed, S. F., Said, Z., Rafa, N., Le, A. T., et al. (2022). Hydrothermal carbonization of food waste as sustainable energy conversion path. Bioresour. Technol. 363:127958. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2022.127958
Lee, C. H., Park, S. J., Hwang, H. Y., Kim, M. S., Jung, H. I., Luyima, D., et al. (2019). Effects of food waste compost on the shift of microbial community in water saturated and unsaturated soil condition. Appl. Biol. Chem. 62, 1–7. doi: 10.1186/s13765-019-0445-1
Lin, R., O'Shea, R., Deng, C., Wu, B., and Murphy, J. D. (2021). A perspective on the efficacy of green gas production via integration of technologies in novel cascading circular bio-systems. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 150:111427. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111427
Liu, Z., de Souza, T. S. P., Holland, B., Dunshea, F., Barrow, C., and Suleria, H. A. R. (2023). Valorization of food waste to produce value-added products based on its bioactive compounds. PRO 11:840. doi: 10.3390/pr11030840
Liu, G., and Zhang, T. (2025). Advances in hydrothermal carbonization for biomass wastewater valorization: optimizing nitrogen and phosphorus nutrient management to enhance agricultural and ecological outcomes. Water 17:800. doi: 10.3390/w17060800
Lively, J. A., and McKenzie, J. (2023). Discards and bycatch: a review of wasted fishing. Adv. Mar. Biol. 95, 1–26. doi: 10.1016/bs.amb.2023.07.001
Lohri, C. R., Camenzind, E. J., and Zurbrügg, C. (2014). Financial sustainability in municipal solid waste management–costs and revenues in Bahir Dar, Ethiopia. Waste Manag. 34, 542–552. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2013.10.014
Mahan, K. M., Le, R. K., Wells, T. Jr., Anderson, S., Yuan, J. S., Stoklosa, R. J., et al. (2018). Production of single cell protein from agro-waste using Rhodococcus opacus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 795–801. doi: 10.1007/s10295-018-2043-3
Manzoor, S., Fayaz, U., Dar, A. H., Dash, K. K., Shams, R., Bashir, I., et al. (2024). Sustainable development goals through reducing food loss and food waste: A comprehensive review. Future Foods, 100362.
Mendo, J., Mendo, T., Gil-Kodaka, P., Martina, J., Gómez, I., Delgado, R., et al. (2022). Bycatch and discards in the artisanal shrimp trawl fishery in northern Peru. PLoS One 17:e0268128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268128
Meng, Q., Liu, H., Zhang, H., Xu, S., Lichtfouse, E., and Yun, Y. (2022). Anaerobic digestion and recycling of kitchen waste: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 20, 1745–1762. doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01408-x
Merino, D., Quilez-Molina, A. I., Perotto, G., Bassani, A., Spigno, G., and Athanassiou, A. (2022). A second life for fruit and vegetable waste: a review on bioplastic films and coatings for potential food protection applications. Green Chem. 24, 4703–4727. doi: 10.1039/D1GC03904K
Miah, M. R., Dong, Y., Wang, J., and Zhu, J. (2024). “Recent Progress on sustainable 2,5-Furandicarboxylate-based polyesters: properties and applications” in ACS sustainable chemistry & engineering (Washington, D.C., USA: American Chemical Society), 2927–2961.
Min, W., Zhou, P., Xu, L., Liu, T., Li, T., Huang, M., et al. (2023). From plate to production: artificial intelligence in modern consumer-driven food systems. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.02400.
Minor, T., Astill, G., Raszap, S., Thornsbury, S., Buzby, J. C., Hitaj, C., et al. (2020). Economic drivers of food loss at the farm and pre-retail sectors: a look at the produce supply chain in the United States. Washington, D.C., USA: Economic Research Service.
Mirmohamadsadeghi, S., Karimi, K., Tabatabaei, M., and Aghbashlo, M. (2019). Biogas production from food wastes: a review on recent developments and future perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 7:100202. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100202
Mohan, A., Krishnan, R., Kaur, A., Vandore, J., and Ramanathan, U. (2023). Management of postharvest losses and wastages in the Indian tomato supply chain—a temperature-controlled storage perspective. Sustain. For. 15:1331. doi: 10.3390/su15021331
Mohanakrishna, G., Sneha, N. P., Rafi, S. M., and Sarkar, O. (2023). Dark fermentative hydrogen production: potential of food waste as future energy needs. Sci. Total Environ. 888:163801. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.163801
Mohanty, A., Mankoti, M., Rout, P. R., Meena, S. S., Dewan, S., Kalia, B., et al. (2022). Sustainable utilization of food waste for bioenergy production: a step towards circular bioeconomy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 365:109538. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2022.109538
Moult, J. A., Allan, S. R., Hewitt, C. N., and Berners-Lee, M. (2018). Greenhouse gas emissions of food waste disposal options for UK retailers. Food Policy 77, 50–58. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2018.04.003
Muhammad, N. I. S., and Rosentrater, K. A. (2020). Comparison of global-warming potential impact of food waste fermentation to landfill disposal. SN Appl. Sci. 2:261. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-2035-6
Nasseri, A. T., Rasoul-Ami, S., Morowvat, M. H., and Ghasemi, Y. (2011). Single cell protein: production and process. Am. J. Food Technol. 6, 103–116. doi: 10.3923/ajft.2011.103.116
Nayak, A., and Bhushan, B. (2019). An overview of the recent trends on the waste valorization techniques for food wastes. J. Environ. Manag. 233, 352–370. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.12.041
Negi, S., and Anand, N. (2017). Post-harvest losses and wastage in Indian fresh agro supply chain industry: a challenge. IUP J. Supp. Chain Manag. 14, 7–23.
Neuvonen, A., Kaskinen, T., Leppänen, J., Lähteenoja, S., Mokka, R., and Ritola, M. (2014). Low-carbon futures and sustainable lifestyles: a backcasting scenario approach. Futures 58, 66–76. doi: 10.1016/j.futures.2014.01.004
O'Connor, J., Mickan, B. S., Rinklebe, J., Song, H., Siddique, K. H. M., Wang, H., et al. (2022a). Environmental implications, potential value, and future of food-waste anaerobic digestate management: a review. J. Environ. Manag. 318:115519:115519. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115519
O'Connor, J., Mickan, B. S., Siddique, K. H. M., Rinklebe, J., Kirkham, M. B., and Bolan, N. S. (2022b). Physical, chemical, and microbial contaminants in food waste management for soil application: a review. Environ. Pollut. 300:118860. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.118860
Onyeaka, H., Akinsemolu, A., Miri, T., Nnaji, N. D., Duan, K., Pang, G., et al. (2025). Artificial intelligence in food system: innovative approach to minimizing food spoilage and food waste. J. Agric. Food Res. 21:101895. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2025.101895
Opara, I. K., Opara, U. L., Okolie, J. A., and Fawole, O. A. (2024). Machine learning application in horticulture and prospects for predicting fresh produce losses and waste: a review. Plan. Theory 13:1200. doi: 10.3390/plants13091200
Osman, A. I., Deka, T. J., Baruah, D. C., and Rooney, D. W. (2023). Critical challenges in biohydrogen production processes from the organic feedstocks biomass convers. Biorefin 13, 8383–8401. doi: 10.1007/s13399-020-00965-x
Palaniveloo, K., Amran, M. A., Norhashim, N. A., Mohamad-Fauzi, N., Peng-Hui, F., Hui-Wen, L., et al. (2020). Food waste composting and microbial community structure profiling. PRO 8:723. doi: 10.3390/pr8060723
Pandey, P., Vidyarthi, S. K., Vaddella, V., Venkitasamy, C., Pitesky, M., Weimer, B., et al. (2020). Improving biosecurity procedures to minimize the risk of spreading pathogenic infections agents after carcass recycling. Front. Microbiol. 11:623. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00623
Pandey, K., Yadav, A. K., and Goel, C. (2022). Utilization of food waste for biofuel production. In Food Waste to Green Fuel: Trend \u0026amp; Development (pp. 1–23). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
Parfitt, J., Barthel, M., and Macnaughton, S. (2010). Food waste within food supply chains: quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 365, 3065–3081. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0126
Parfitt, J., Croker, T., and Brockhaus, A. (2021). Global food loss and waste in primary production: a reassessment of its scale and significance. Sustain. For. 13:12087. doi: 10.3390/su132112087
Parsa, A., Van De Wiel, M., Schmutz, U., Fried, J., Black, D., and Roderick, I. (2023). Challenging the food waste hierarchy. J. Environ. Manag. 344:118554. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118554
Parsa, A., Van De Wiel, M., Schmutz, U., Taylor, I., and Fried, J. (2024). Balancing people, planet, and profit in urban food waste management. Sustain. Prod. Consumpt. 45, 203–215. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2024.01.003
Patra, F., and Duary, R. K. (2020). “Waste from dairy processing industries and its sustainable utilization” in Sustainable food waste management: concepts and innovations, Singapore: Springer, 127–154.
Pechibilski, N. W., Brandes, L. A., Knop, M. L., Ramos, F. M., and Cembranel, P. (2024). Production optimization through linear programming in agricultural properties. Environ. Dev. Sustain., 1–19. doi: g/doi: 10.1007/s10668-024-04757-5
Perez-Esteban, N., Vives-Egea, J., Peces, M., Dosta, J., and Astals, S. (2024). Temperature-driven carboxylic acid production from waste activated sludge and food waste: co-fermentation performance and microbial dynamics. Waste Manag. 178, 176–185. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2024.02.026
Periyavaram, S. R., Uppala, L., Sivaprakash, S., and Reddy, P. H. P. (2023). Thermal behaviour of hydrochar derived from hydrothermal carbonization of food waste using leachate as moisture source: kinetic and thermodynamic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 373:128734. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2023.128734
Peydayesh, M. (2024). Sustainable materials via the assembly of biopolymeric nanobuilding blocks valorized from Agri-food waste. Sustain. For. 16:1286. doi: 10.3390/su16031286
Piadeh, F., Offie, I., Behzadian, K., Rizzuto, J. P., Bywater, A., Córdoba-Pachón, J.-R., et al. (2024). A critical review for the impact of anaerobic digestion on the sustainable development goals. J. Environ. Manag. 349:119458. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119458
Piercy, E., Verstraete, W., Ellis, P. R., Banks, M., Rockström, J., Smith, P., et al. (2023). A sustainable waste-to-protein system to maximise waste resource utilisation for developing food-and feed-grade protein solutions. Green Chem. 25, 808–832. doi: 10.1039/D2GC03095K
Quist, J. (2007). Backcasting for a sustainable future: the impact after 10 years : Eburon Uitgeverij BV. Utrecht: Eburon Academic.
Quist, J., and Vergragt, P. J. (2003). “Backcasting for industrial transformations and system innovations towards sustainability: is it useful for governance?” in The 2003 Berlin conference on the human dimensions of global environmental change, 1–26.
Rajesh Banu, J., and Godvin Sharmila, V. (2023). “Review on food waste valorisation for bioplastic production towards a circular economy: sustainable approaches and biodegradability assessment.” Sustainable Energy Fuels.
Ribeiro, G. O., Rodrigues, L. A. P., dos Santos, T. B. S., Alves, J. P. S., Oliveira, R. S., Nery, T. B. R., et al. (2023). Innovations and developments in single cell protein: bibliometric review and patents analysis. Front. Microbiol. 13:1093464. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1093464
Ritala, A., Häkkinen, S. T., Toivari, M., and Wiebe, M. G. (2017). Single cell protein—state-of-the-art, industrial landscape and patents 2001–2016. Front. Microbiol. 8:2009. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02009
Ritchie, H., Rosado, P., and Roser, M. (2023). Agricultural production, our world in data Global Change Data Lab, UK.
Ritchie, H., Rosado, P., and Roser, M. (2024). Greenhouse gas emissions : Our World in Data. Global Change Data Lab, UK.
Roukas, T., and Kotzekidou, P. (2022). From food industry wastes to second generation bioethanol: a review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 21, 299–329. doi: 10.1007/s11157-021-09606-9
Sabater, C., Ruiz, L., Delgado, S., Ruas-Madiedo, P., and Margolles, A. (2020). Valorization of vegetable food waste and by-products through fermentation processes. Front. Microbiol. 11:581997. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.581997
Sadh, P. K., Chawla, P., Kumar, S., Das, A., Kumar, R., Bains, A., et al. (2023). Recovery of agricultural waste biomass: a path for circular bioeconomy. Sci. Total Environ. 870:161904. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.161904
Sadh, P. K., Duhan, S., and Duhan, J. S. (2018). Agro-industrial wastes and their utilization using solid state fermentation: a review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 5, 1–15. doi: 10.1186/s40643-017-0187-z
Saer, A., Lansing, S., Davitt, N. H., and Graves, R. E. (2013). Life cycle assessment of a food waste composting system: environmental impact hotspots. J. Clean. Prod. 52, 234–244. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.03.022
Sanchez Lopez, J., Caldeira, C., De Laurentiis, V., Sala, S., and Avraamides, M. (2020) Brief on food waste in the European Union Joint Research Centre, European Commission.
Saqib, N. U., Baroutian, S., and Sarmah, A. K. (2018). Physicochemical, structural and combustion characterization of food waste Hydrochar obtained by hydrothermal carbonization. Bioresour. Technol. 266, 357–363. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.06.112
Sarkar, N., Jeon, B.-H., Chatterjee, P. K., and Ganguly, A. (2020). Food waste, a good option for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Utiliz. Bioprocess, 267–273. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-1607-8_25
Scherhaufer, S., Moates, G., Hartikainen, H., Waldron, K., and Obersteiner, G. (2018). Environmental impacts of food waste in Europe. Waste Manag. 77, 98–113. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.04.038
Serra, P., and Fancello, G. (2020). Towards the IMO’S GHG goals: a critical overview of the perspectives and challenges of the main options for decarbonizing international shipping. Sustain. For. 12:3220. doi: 10.3390/su12083220
Sawaya, W. N. (2017). Impact of food losses and waste on food security. Water, energy and food sustainability in the middle east: The sustainability triangle, 361–388.
Sharif, M., Zafar, M. H., Aqib, A. I., Saeed, M., Farag, M. R., and Alagawany, M. (2021). Single cell protein: sources, mechanism of production, nutritional value and its uses in aquaculture nutrition. Aquaculture 531:735885. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735885
Sharma, P., Bano, A., Singh, S. P., Atkinson, J. D., Lam, S. S., Iqbal, H. M., et al. (2024). Biotransformation of food waste into biogas and hydrogen fuel–a review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 52, 46–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.08.081
Sharma, R., Jasrotia, K., Singh, N., Ghosh, P., Srivastava, S., Sharma, N. R., et al. (2020). A comprehensive review on hydrothermal carbonization of biomass and its applications. Chem. Africa 3, 1–19. doi: 10.1007/s42250-019-00098-3
Sher, F., Smječanin, N., Hrnjić, H., Karadža, A., Omanović, R., Šehović, E., et al. (2024). Emerging technologies for biogas production: a critical review on recent progress, challenges and future perspectives. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2024.05.138
Shimoda, M., Kago, H., Kojima, N., Miyake, M., Osajima, Y., and Hayakawa, I. (2002). Accelerated death kinetics of Aspergillus niger spores under high-pressure carbonation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 4162–4167. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.8.4162-4167.2002
Shrestha, S., Khatiwada, J. R., Sharma, H. K., and Qin, W. (2021). “Bioconversion of fruits and vegetables wastes into value-added products” in Sustainable bioconversion of waste to value added products, 145–163.
Shukla, K. A., Abu, A., Singh, A., Chen, W. H., Show, P. L., and Chan, Y. J. (2024). Food waste management and sustainable waste to energy: current efforts, anaerobic digestion, incinerator and hydrothermal carbonization with a focus in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 448:141457. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141457
Sikiru, S., Abioye, K. J., Adedayo, H. B., Adebukola, S. Y., Soleimani, H., and Anar, M. (2024). Technology projection in biofuel production using agricultural waste materials as a source of energy sustainability: a comprehensive review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 200:114535. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2024.114535
Singhania, R. R., Patel, A. K., and Pandey, A. (2017). “Biotechnology for agricultural waste recycling” in Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (Amsterdam, Netherlands Elsevier), 223–240.
Skaf, L., Franzese, P. P., Capone, R., and Buonocore, E. (2021). Unfolding hidden environmental impacts of food waste: an assessment for fifteen countries of the world. J. Clean. Prod. 310:127523. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127523
Stanley, R. (2017). Commercial feasibility of Banana waste utilisation in the processed food industry. Sydney, Australia: Hort Innovation.
Shaba, E. Y., Jiya, M. J., Andrew, A., Salihu, A. M., Mamma, E., Anyanwu, S. K., et al. (2025). Biomass Valorisation: A Sustainable Approach Towards Carbon Neutrality and Circular Economy. In Biomass Valorization: A Sustainable Approach towards Carbon Neutrality and Circular Economy, Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 99–122.
Stancu, A., and Ene, C. (2024). Highlights of food waste consumer behaviour in households and food services sector. In Contemporary marketing and consumer behaviour in sustainable tourism (pp. 63–98). Routledge.
Tagne, R. F. T., Costa, P., Casella, S., and Favaro, L. (2024). Optimization of biohydrogen production by dark fermentation of African food-processing waste streams. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 49, 266–276. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.07.348
Tamaian, R. (2023). “Enhanced biohydrogen production from food waste via separate hydrolysis and fermentation: a sustainable approach” in Biology and life sciences forum, (Basel, Switzerland: MDPI), 31:14.
Thiviya, P., Gamage, A., Kapilan, R., Merah, O., and Madhujith, T. (2022). Single cell protein production using different fruit waste: a review. Separations 9:178. doi: 10.3390/separations9070178
Tiseo, I. (2017). Share of food wasted globally as of 2017, by food category. Statista. Available online at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/519611/percentage-of-wasted-food-by-category-global/ (Accessed March 23, 2022).
Toldrá-Reig, F., Mora, L., and Toldrá, F. (2020). Trends in biodiesel production from animal fat waste. Appl. Sci. 10:3644. doi: 10.3390/app10103644
Tradler, S. B., Mayr, S., Himmelsbach, M., Priewasser, R., Baumgartner, W., and Stadler, A. T. (2018). Hydrothermal carbonization as an all-inclusive process for food-waste conversion. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2, 77–83. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2018.04.009
Tropea, A., Ferracane, A., Albergamo, A., Potortì, A. G., Lo, V., and Di Bella, G. (2022). Single cell protein production through multi food-waste substrate fermentation. Fermentation 8:91. doi: 10.3390/fermentation8030091
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2022). World Population Prospects 2022: Summary of Results. UN DESA/POP/2022/TR/NO. 3.
United Nations Environment Programme (2024a). Emissions Gap Report 2024: No more hot air … please! With a massive gap between rhetoric and reality, countries draft new climate commitments. Nairobi. doi: 10.59117/20.500.11822/46404
United Nations Environment Programme (2024b). Food Waste Index Report 2024. Think Eat Save: Tracking Progress to Halve Global Food Waste. Available at: https://wedocs.unep.org/20.500.11822/45230
Vorobyova, V., Skiba, M., Anastasiya, K., and Vasyliev, G. (2024). The type III deep eutectic solvents: physicochemical properties and applications for the extraction of value-added compounds from spent coffee grounds. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 16, 1821–1837. doi: 10.1007/s12649-024-02771-2
Vermeulen, S. J., Campbell, B. M., and Ingram, J. S. (2012). Climate change and food systems. Annual review of environment and resources, 37, 195–222.
Wang, P., Han, S., and Lin, Y. (2023). “Role of microbes and microbial dynamics during composting” in Current developments in biotechnology and bioengineering (Amsterdam, Netherlands: Elsevier), 169–220.
Wang, Q., Li, H., Feng, K., and Liu, J. (2020). Oriented fermentation of food waste towards high-value products: a review. Energies 13:5638. doi: 10.3390/en13215638
Wani, N. R., Rather, R. A., Farooq, A., Padder, S. A., Baba, T. R., Sharma, S., et al. (2024). New insights in food security and environmental sustainability through waste food management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31, 17835–17857. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-26462-y
Keywords: food waste, cropland, recycling, environment, economy, population, sustainability
Citation: Rai N, Pavankumar TL, Ghotra B, Dhillon S, Juneja V, Amaly N and Pandey P (2025) Essential recycling and repurposing of food waste for environment and sustainability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1575113. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1575113
Edited by:
Çağrı Akyol, Ghent University, BelgiumReviewed by:
Amita Shakya, Amity University, IndiaOrlando Corigliano, University of Calabria, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Rai, Pavankumar, Ghotra, Dhillon, Juneja, Amaly and Pandey. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pramod Pandey, cGtwYW5kZXlAdWNkYXZpcy5lZHU=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Navneet Rai
Navneet Rai Theetha L. Pavankumar
Theetha L. Pavankumar Baljit Ghotra2
Baljit Ghotra2 Pramod Pandey
Pramod Pandey