- College of Economics, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu, China
Introduction: In the digital economy era, the application of digital technologies plays a crucial role in strengthening the food supply chain, especially in ensuring food security. The study of how the digital economy impacts the resilience of the food supply chain is of great practical significance.
Methods: Based on provincial data from China from 2008 to 2023, this research employs fixed effect, mediation effect, and threshold models. These models are utilized to explore the mechanism through which the digital economy improves the resilience of the food supply chain.
Results: The findings indicate that the digital economy has a significant positive effect on enhancing the resilience of the food supply chain. This positive relationship remains stable even after considering potential endogeneity problems. Specifically, the impact of the digital economy is more prominent in major food—producing regions, showing their advantages in using digital development to boost supply chain stability and efficiency. Additionally, information technology adoption acts as an important mediating factor in the relationship between the digital economy and supply chain resilience, and there is a threshold effect of fiscal investment in science and technology on the impact of the digital economy on supply chain resilience.
Discussion: The results suggest that to fully utilize the potential of the digital economy, accelerate the digital and intelligent upgrade of the food supply chain, strengthen its resilience, and promote high—quality agricultural development, the government should take actions. These include accelerating the construction of digital infrastructure, promoting the digital transformation of the food industry, strengthening regional cooperation, and enhancing the resilience of the food supply chain to ensure food security.
1 Introduction
Food security is a critical issue that affects national wellbeing, economic development, and political stability, making it a primary concern for many countries and international organizations. Since the early twenty-first century, global food production has consistently risen, alongside improvements in living conditions, and significant progress has been made toward eliminating hunger and all forms of malnutrition. However, factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russia-Ukraine conflict, and extreme weather events have caused a spike in international food prices, exacerbating the global food security crisis. The 2023 “State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World” report reveals that in 2022, 691 million to 783 million individuals faced hunger, and 2.4 billion people suffered from moderate to severe food insecurity, accounting for about 29.6% of the global population. Amid increasingly complex market conditions and international dynamics, securing food supply and bolstering the resilience of food supply chains are pressing issues that nations must tackle. The burgeoning digital economy offers a historic chance to address these challenges. Therefore, this study seeks to explore the link between the digital economy and food supply chain resilience, offering theoretical insights and empirical evidence to inform the creation of sustainable food security strategies.
China, as a nation with a vast population, faces a significant challenge in feeding 22% of the world's population with ~7% of the world's cultivable land (Chandio et al., 2024). Ensuring food security has consistently been a top priority for national security (Liu et al., 2022). Since 2004, China has achieved an impressive 19-year streak of bumper harvests, with total grain output consistently exceeding 130 million tons for eight consecutive years. The per capita grain possession is ~480 kg, surpassing the internationally recognized benchmark of 400 kg for food security, thereby ensuring the security of staple food supplies.1 However, ensuring national food security requires not only enhancing food supply capacity but also strengthening the establishment of a modern food supply chain system and bolstering governance capabilities related to food security. The food supply chain is a complex system with multiple links and channels. Unlike other supply chains, it is characterized by cross-regional dynamics, long cycles, and a multitude of participants (Yadav et al., 2022). Additionally, the various stages of the supply chain operate relatively independently, resulting in poor information sharing among different entities (Zhang et al., 2023). This lack of coordination among stages increases the risk of supply chain disruptions during emergencies or natural disasters. With international food prices soaring due to the pandemic, extreme weather, and geopolitical conflicts, promoting the modernization of the food supply chain and strengthening its resilience is an urgent task.
The concept of “resilience” originated in physics (Manyena, 2006). Initially adopted in econlogy in the 1970s, Holling (1973) defined ecological resilience as an ecosystem's capacity to withstand disturbances. Over time, it expanded into various fields. Rice and Caniato (2003) first introduced “supply chain resilience”. Christopher and Peck (2004) defined it as recover capacity after external shocks. Ponomarov and Holcomb (2009) categorized it into preparation, response, and recovery phases, later expanded by Hohenstein et al. (2015) and Kamalahmadi and Parast (2016) with a “growth” phase for post—disruption improvement.
Research on “supply chain resilience” has grown across industries. In the food sector, Stone and Rahimifard (2018) defined supply chain resilience as the ability of stakeholders to ensure timely and stable food supply, despite external shocks, due to the chain's unique characteristics. Zhao et al. (2024) recently categorized food supply chain resilience into four stages—preparation, response, recovery, and adaptation (or growth), highlighting the need for adaptability to environmental changes. Drawing on these insights and considering China's context, this article defines food supply chain resilience as the collective ability to withstand shocks, adjust developmental structures, transform operational paradigms, and innovate in the face of market risks and uncertainties. It is characterized by resistance, adaptability, and transformation capabilities, with these aspects interacting during responses to shocks to ensure stable and agile operations for sustainable food provision.
The rapid advancement of digital technologies—big data, artificial intelligence, and blockchain—is driving supply chain digitalization, a key application area for these technologies (Saberi et al., 2019; Gawankar et al., 2020). By leveraging these digital technologies, supply chain participants can share production schedules, inventory, and sales data, reducing information asymmetry. This enables real—time monitoring and enhances supply chain visibility and integration (Ardito et al., 2018), facilitating more effective organizational adjustments and boosting operational efficiency and flexibility (Belhadi et al., 2022; Lee et al., 2023). However, improper adoption of digital technology may result in disruptive changes, introducing high risks and uncertainties to the supply chain. Studies note that digital transformation can transition supply chains from centralized to distributed frameworks (Holmström and Partanen, 2014), potentially shortening supply chains and necessitating swift adaptation by participants to mitigate risks (Yang et al., 2021). Specifically, in the food sector, there is a lack of research directly linking the digital economy to supply chain resilience. Only a few studies have suggested that the digital economy could significantly influence the resilience of the food supply chain. Zhao et al. (2023) explored how the digital economy bolsters supply chain resilience through absorptive, responsive, and recovery capacities. Dayioglu and Turker (2021) showed that digital technology adoption can drive the shift from traditional to smart agriculture, enhancing resilience against external uncertainties like climate change and promoting sustainable development. Using provincial panel data, Hao and Tan (2022) developed a food system resilience index, finding that digital village initiatives enhance China's food system resilience. However, some studies have indicated that digital technology may negatively impact the resilience of the food supply chain. On one hand, some studies indicate impacts. The digital divide can create regional and individual disparities in the digital economy's impact on agricultural development. Regions or groups lacking professional knowledge and digital infrastructure may face relatively higher production costs, reducing their competitiveness within the food supply chain, which in turn affects the overall resilience of the supply chain (Štusek et al., 2017; Shepherd et al., 2020). On the other hand, according to the agricultural treadmill theory (Cochrane, 1958), digital technology compels farmers to adopt new tech, potentially increasing food supply and efficiency. But due to food's low price elasticity of demand, increased supply may lead to price drops, harming supply chain participants' welfare.
Extensive research has explored the interplay between the digital economy and supply chain and agricultural resilience, laying a solid foundation for this study. Yet, the varied impacts of the digital economy on the food system necessitate further examination to determine how it can effectively bolster the food supply chain's resilience. Against this backdrop, this study constructs an econometric model using panel data from 30 Chinese provinces from 2008 to 2023. Utilizing this model, we empirically investigate the impact of the digital economy's expansion on China's food supply chain resilience and the mechanisms involved. The study aims to inform scientific and policy decisions to enhance China's food production distribution and bolster its food security capabilities.
This research innovates in three aspects. Firstly, it develops tailored food supply chain resilience indicators for China, covering resistance, adaptation, and transformation. Secondly, it examines the digital economy's influence on food supply chain resilience through theoretical and empirical lenses. This includes analyzing how information technology adoption enhances supply chain resilience and offering new policy insights. Thirdly, it explores the threshold effects of scientific and technological investments on supply chain robustness within the digital economy, underscoring the nonlinear dynamics.
The paper proceeds as follows: Section 2 details the theoretical mechanisms by which the digital economy bolsters food supply chain resilience and formulates hypotheses; Section 3 measures China's food supply chain resilience and outlines the study's models and data; Section 4 discusses the empirical findings; Section 5 concludes with policy recommendations and future research avenues.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypotheses
2.1 Digital economy and the resilience of food supply chain
The digital economy, a novel socioeconomic development model, is reorganizing global resources, reshaping economic structures, and redefining global competitiveness. From manufacturing and services to agriculture and finance, industries are undergoing digital transformation propelled by the digital economy. Digital technology adoption is spreading, driving innovation and sector upgrades. Global supply chains are trending toward digitalization, networking, and intelligentization (Fu et al., 2023). Therefore, accelerating the digital transformation of the food supply chain is essential. Rooted in computer and internet-based tools, the digital economy enhances food supply chain resilience by leveraging advanced information technologies like blockchain and big data for information sharing and interoperability throughout production, processing, transportation, and sales. This bolsters the supply chain's resistance, adaptability, and transformation capacity. The mechanism of impact is illustrated in Figure 1.
(1) The digital economy enhances the resistance of the food supply chain by optimizing supply-demand matching and stabilizing supply-demand relationships.
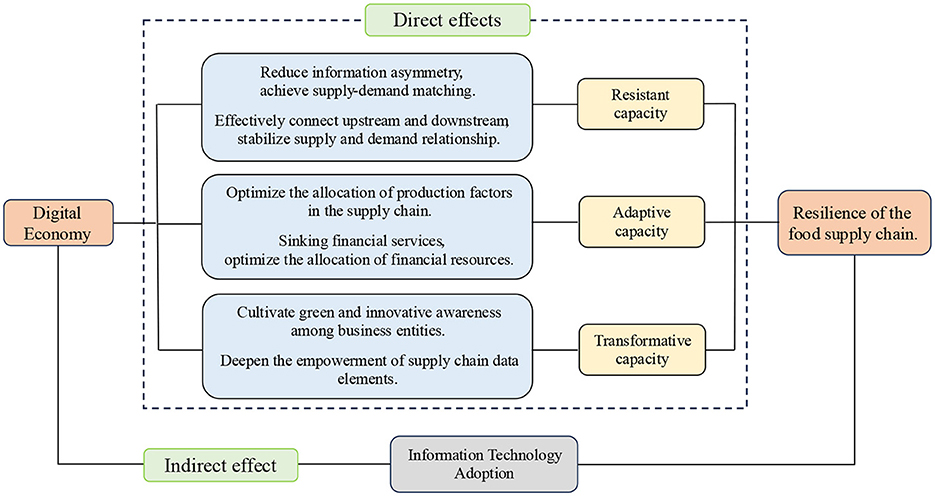
Figure 1. The mechanism of impact of digital economy development on the resilience of the food supply chain.
Effective supply-demand matching and stable relationships are crucial for supply chain resilience. The digital economy connects food supply chain stakeholders, transcending geographical and temporal barriers with technologies like blockchain, big data, and AI. This connectivity enhances information processing, reduces viscosity, breaks down information silos, and fosters upstream-downstream collaboration to align supply with demand, stabilizing relationships and enhancing resilience.
Firstly, the digital economy optimizes supply-demand matching in the food supply chain. In traditional models, information delays can amplify minor downstream demand fluctuations into significant upstream production swings, known as the 'bullwhip effect' (Cachon et al., 2007), leading to overcapacity and supply-demand misalignment. With the digital economy, information technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence facilitate efficient sharing and transmission of information, reducing asymmetry in supply-demand information among producers, processors, and distributors within the food supply chain. This precise alignment of supply and demand enhances operational efficiency and strengthens the supply chain's ability to withstand disruptions.
Secondly, the digital economy stabilizes supply-demand relationships between upstream and downstream enterprises. Supply chain firms are interdependent, with disruptions at any stage potentially affecting the entire system's stability. The digital economy, leveraging digital information platforms, effectively connects the upstream and downstream segments of the food supply chain, achieving a balance between efficiency and inclusiveness. Moreover, digital technology integration fosters an interdependent, connected, and symbiotic supply chain ecosystem (Chen and Liu, 2021), promoting integration across food's lifecycle. This strengthens the stability of collaboration among supply-demand stakeholders within the supply chain, thereby enhancing its resilience.
(2) The digital economy enhances the adaptability of the food supply chain by optimizing resource allocation.
Firstly, the digital economy optimizes input factor allocation in the food supply chain, reducing the lasting impacts of shocks. On the production side, digital technologies enable food producers to implement intelligent agricultural management, allowing for precise monitoring of field conditions, crop growth, and pest and disease information, thereby optimizing the allocation of production resources. This shift toward “intelligent” and “refined” food production reduces sensitivity and exposure to natural risks. On the distribution side, with the support of the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and other technologies, companies can achieve visual monitoring of the entire supply chain, more accurately predict market demand and trends, and adjust inventory levels and logistics strategies to avoid resource wastage caused by information asymmetry.
Secondly, the digital economy enhances adaptability by optimizing financial resource allocation and inclusivity, bolstering the supply chain's post-disruption recovery. On one hand, the digital economy optimizes financial infrastructure, extending the reach of financial resources and leveraging digital technology's inclusive effects to broaden and deepen financial services for supply chain participants, thereby reducing the cost and barriers to accessing financial services (Tang et al., 2022). On the other hand, when the food supply chain is impacted by external shocks, entities at various stages may face funding gaps. Through the application of digital platforms, financial institutions can communicate directly with supply chain entities, understand their specific needs, and provide tailored financial services to bridge these funding gaps, enhancing the risk resistance of various supply chain segments and reinforcing overall resilience.
(3) The digital economy enhances the transformative capacity of the food supply chain by fostering green and innovative awareness among business entities and deepening the empowerment of data elements within the supply chain.
Firstly, the digital economy cultivates green production capabilities and awareness among food producers, promoting sustainable practices. The development of digital technology dismantles information barriers, rapidly spreading knowledge about green, low-carbon, and ecological protection measures. Once food producers recognize that green and low-carbon technologies can reduce resource consumption, improve soil quality, and enhance agricultural ecological benefits, they are more inclined to undergo green transformation for sustainable development (Jiang et al., 2022). In addition, the digital economy cuts down financial service costs, making it easier for food producers to access funds. This enables them to select eco-friendly pesticides and fertilizers, further facilitating green and low-carbon agricultural production.
Secondly, data, as an emerging production factor, offers unique attributes such as virtual substitutability, renewability, and low cost, which may results in increasing returns to scale (Prüfer and Schottmüller, 2021). The deep integration of data elements with other factors promotes the digital transformation of various stages of food production, distribution, and consumption, injecting new momentum into the upgrading of the food supply chain. Moreover, the digital economy can mitigate issues such as information asymmetry and information silos among supply chain entities. It strengthes the collaborative relationships between partners, and improves the operational efficiency and flexibility of the supply chain, and boosts the innovative awareness of entities within the chain. Consequently, these entities are encouraged to engage in innovation and research activities, thereby driving the transformation and upgrading of the food supply chain. Therefore, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1: The digital economy has a positive impact on the resilience of the food supply chain.
2.2 Digital economy, information technology adoption, and the resilience of food supply chain
The Theory of Planned Behavior posits that intentions and actions are influenced by attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control (Ajzen, 1991). Attitudes reflect an individual's assessment of the appeal of a specific behavior. Subjective norms include social pressures and the expectations of others that sway an individual's decision to engage in a behavior. Perceived behavioral control is the perception of how easily a behavior can be performed, considering factors that could facilitate or impede it. In the food supply chain, when entities lack comprehensive information or have a limited understanding of ICTs, adoption is often stymied. Habitual thinking rooted in traditional operational models, coupled with resource constraints such as financial limitations or a shortage of skilled personnel, can reinforce low perceived behavioral control, thereby deterring the adoption of new technologies.
In today's digital economy, new-generation information technologies have a far-researching impact on all aspects of the food supply chain and its various stakeholders. Firstly, technologies like cloud computing, big data, and IoT play a pivotal role in enabling real-time data exchange and seamless collaboration. These technologies transcend geographical boundaries, facilitating the integration of different stages in the supply chain, from production and storage to logistics, processing, and trade. By doing so, they create a more cohesive and interconnected supply chain ecosystem. Secondly, information technology also effectively breaks down the barriers between supply and demand information. It empowers food supply chain entities to access demand data promptly and accurately, allowing for more precise resource allocation. This reduces the inefficiencies and additional intermediaries that often arise due to information asymmetry. Thirdly, the low marginal cost of ICTs allows stakeholders to quickly grasp market dynamics and competitive insights, cutting transaction, information acquisition, learning, and technology dissemination costs, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and competitive advantage (Chen et al., 2022).
Since ICTs effectively reduce information asymmetry and enhance the connectivity and synergy among supply chain links, the adoption and application of ICTs are crucial for the digital economy to strengthen the resilience of the food supply chain. Therefore, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: The digital economy promotes the resilience of the food supply chain by enhancing entities' capacity for information technology adoption.
2.3 The threshold effect of scientific and technological investment
The digital economy operates under a different paradigm compared to the traditional economy, characterized by declining marginal costs and rising marginal returns (Zhao et al., 2020). This unique economic characteristic implies that its influence on food supply chain resilience is not linear but rather exhibits a threshold-based dynamic. Firstly, digital infrastructure, predominantly funded by government fiscal investments, serves as the cornerstone for the development of the digital economy. When financial allocations fall short of meeting the requirements for building and maintaining digital infrastructure, the scope and depth of digital economy applications are inevitably constrained. As a result, the potential of the digital economy to enhance the resilience of the food supply chain remains untapped. Conversely, an increase in government investment propels the advancement of digital infrastructure and platforms. This expansion allows digital technologies to penetrate more deeply into every link of the food supply chain, from production and procurement to distribution and consumption. As digitalization and intelligence levels within the supply chain rise, its ability to absorb shocks and maintain stable operations in the face of disruptions is significantly strengthened.
Secondly, the scale of investment in scientific and technological funds directly influences the level of digital research and development. Insufficient investment may dampen innovation motivation within the food supply chain, hindering digital transformation. However, once investment reaches a certain threshold level, it acts as a catalyst, invigorating the innovation capabilities of supply chain participants. This surge in investment leads to increased digital research and development efforts and enables a more efficient conversion of scientific and technological advancements into market-viable products and services. When digital technologies are applied across all stages of the food supply chain, they drive a profound digital and intelligent transformation, ultimately enhancing the overall resilience of the supply chain. This indicates that the positive effect of the digital economy on boosting food supply chain resilience becomes much more pronounced when scientific and technological investments surpass a specific threshold. Thus, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 3: There is a threshold effect of scientific and technological investment in the influence of the digital economy on the resilience of the food supply chain.
3 Data and research design
3.1 Data sources
The data used in this study is sourced from the China Socioeconomic Big Data Research Platform (CSYD), the China Economic and Financial Research Database (CSMAR), as well as publications such as the China Statistical Yearbook and the China Rural Statistical Yearbook. The dataset includes provincial panel data from 30 provinces in China (excluding Xizang province) spanning from 2008 to 2023.
3.2 Variable definition
3.2.1 Dependent variable
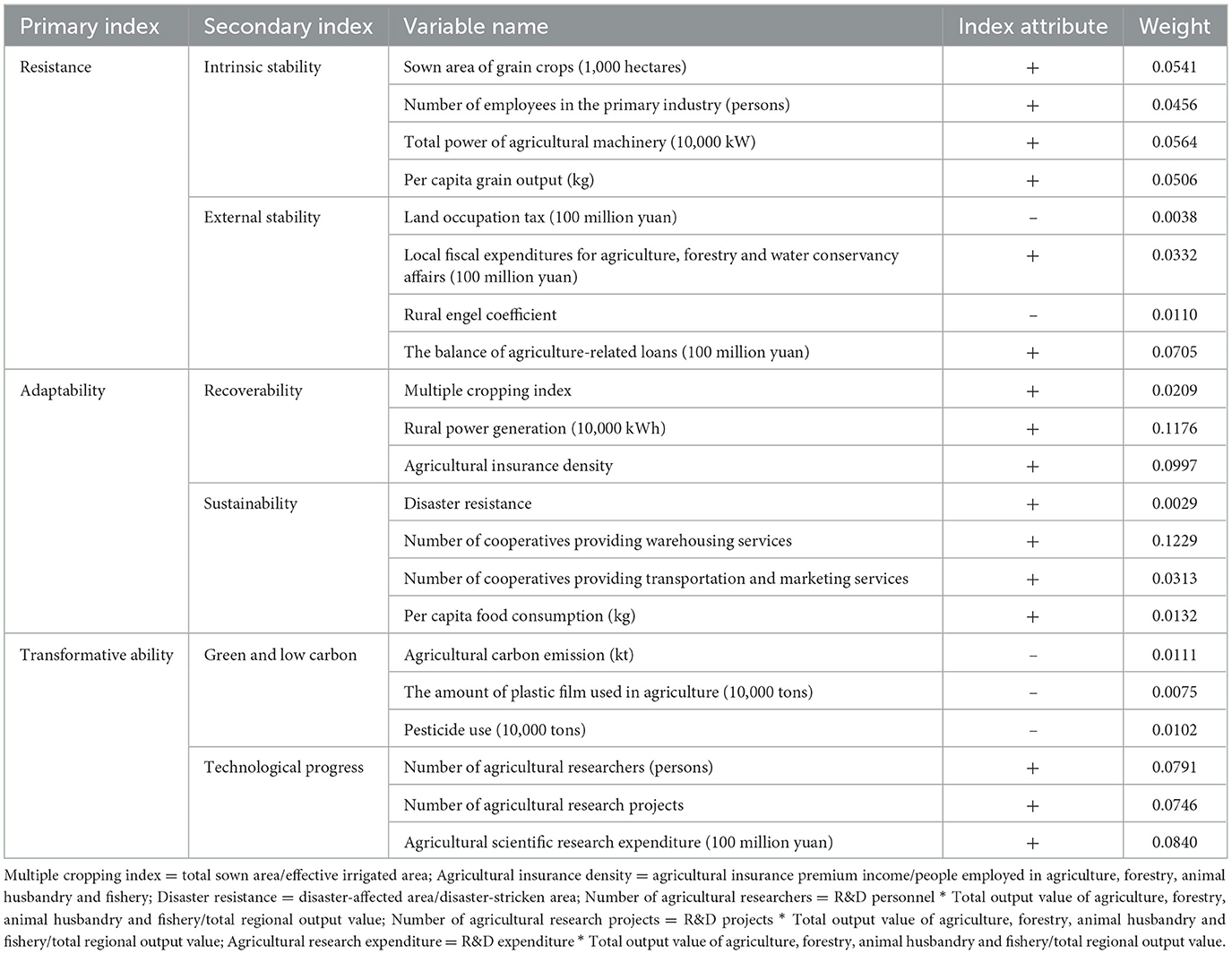
In line with the previously discussed concept of food supply chain resilience, this study selects indicators across three key dimensions: resistance, adaptability, and transformative capacity. We then apply the entropy method to reduce and integrate these variables, culminating in the calculation of resilience scores for the food supply chain in each province. The construction of these indicators and their respective weights are detailed in Table 1.
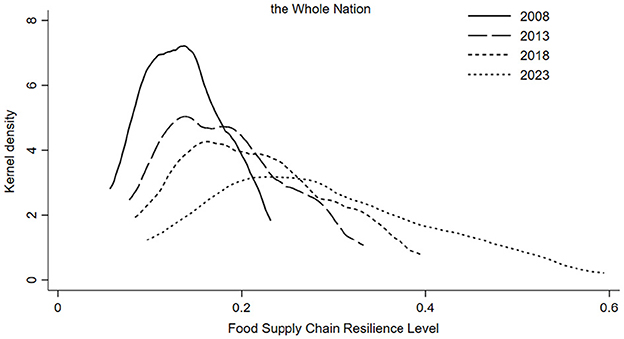
To illustrate the dynamic evolution of the resilience of the grain supply chain, this paper employs Kernel density estimation to depict the dynamic distribution characteristics of grain supply chain resilience over the sample period. Figure 2 shows the changes in the resilience of China's grain supply chain. From a national perspective, the center of the distribution curve exhibits a distinct rightward shift, indicating a continuous improvement in the resilience level of China's grain supply chain. The main peak of the curve decreases in height while its width gradually expands, with a pronounced rightward tail, suggesting that the spatial disparities in the resilience level of the grain supply chain are gradually widening across the country. The curve shape is progressively transitioning toward a unimodal distribution, which implies that the phenomenon of multi-tier differentiation in grain supply chain resilience is decreasing.
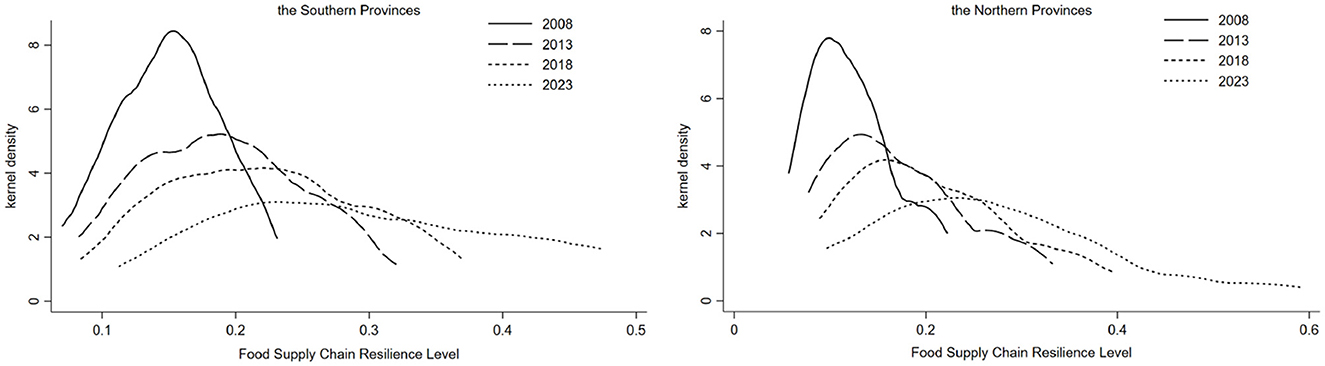
Figure 3 illustrates the dynamic distribution characteristics of the resilience of grain supply chains in the southern and northern regions of China. In terms of distribution position, the Kernel density curves of both southern and northern provinces exhibit rightward shifts to varying degrees, indicating that the resilience of grain supply chains has generally improved across regions. Compared to the southern provinces, the Kernel density curves of the northern provinces show a more pronounced rightward tail, suggesting a more significant gradient difference in the resilience of grain supply chains among northern provinces.
3.2.2 Explanatory variables
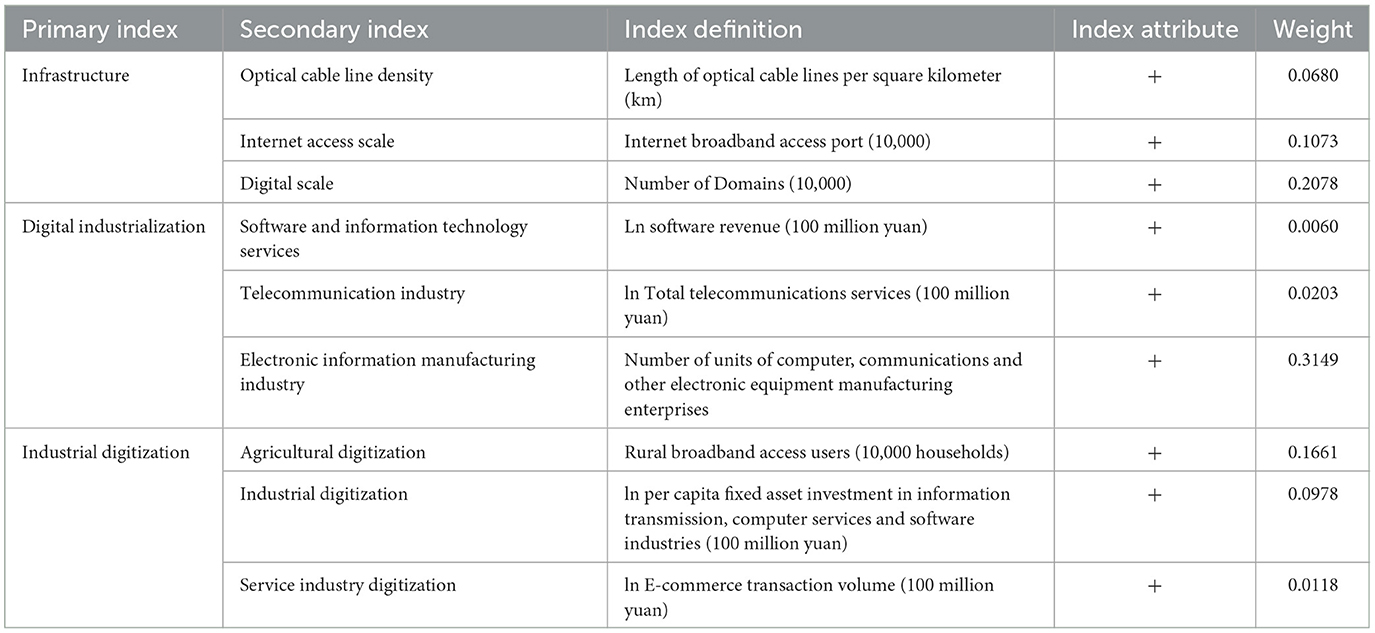
Measuring the digital economy typically involves two approaches. The first uses a single indicator, such as the Digital Inclusive Finance Index (Zhang et al., 2020a,b) or the digital economy sector's value-added (Barefoot et al., 2018), to assess development at national or provincial levels. The second approach constructs an index system with multiple indicators. Xue et al. (2022) and Wang and Li (2023) included dimensions like digital infrastructure, development environment, digital industrialization, and industrial digitization. Stavytskyy et al. (2019) assessed EU countries based on ICT usage by individuals, businesses, and governments. Zhao et al. (2020) created an index system using five indicators: internet penetration rate, internet-related employment, internet-related output, mobile internet user count, and digital inclusive finance development.
Recognizing that a single indicator might not comprehensively reflect the digital economy's development, this study adopts a multidimensional approach inspired by Yi et al. (2022). It selects nine indicators across three key dimensions—digital infrastructure, digital industrialization, and industrial digitization—to assess the digital economy's development level. We then apply the entropy method for dimensionality reduction, constructing a composite score that represents each province's digital economy development. The detailed definitions and weights of these indicators are outlined in Table 2.
3.2.3 Control variables
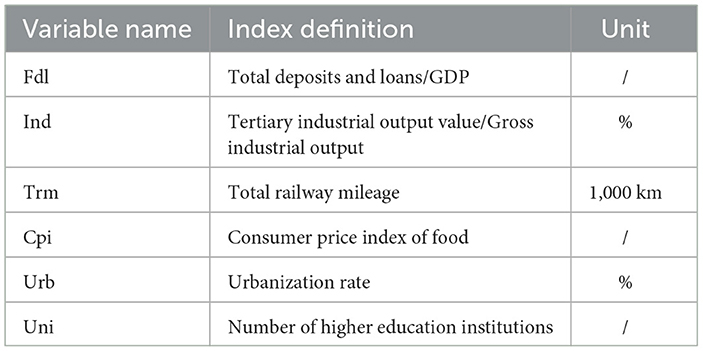
To account for the multifaceted regional development factors that can influence food supply chain resilience, this study includes the following control variables in the econometric model. (1) Financial Development (Fdl). This reflects the region's financial maturity, affecting the financing options, costs, and risk management strategies of food supply chain enterprises, thereby impacting the supply chain's overall operations and resilience. (2) Industrial Structure (Ind). The evolution of the regional industrial structure can influence the allocation of production resources, affecting the supply chain's coordinated operation. (3) Total Railway Mileage (Trm). This indicator represents the region's infrastructure development, closely tied to the supply chain's resilience. (4) Food Consumption (Cpi). It Reflects market demand for food, consumption levels can influence supply chain stability and efficiency. (5) Urbanization (Urb). Urbanization can enhance infrastructure and support the supply chain's development, but it may also lead to decreased agricultural labor and environmental issues, affecting food production and security. It refers to the proportion of urban population to the total population. (6) Education (Uni). The presence of higher education institutions indicates the region's educational resources and research capabilities, which significantly influence the supply chain's transformation and upgrading. The number of higher education institutions in this article includes universities, specialized colleges, and higher vocational and technical colleges. The specific definitions of the indicators are presented in Table 3.
3.2.4 Mechanism variables
To delve into the mechanisms by which Information Technology Adoption (Tech) and Scientific and Technological Investment (Est) affect the resilience of the food supply chain in the digital economy context, this study employs the number of mobile phone subscriptions as a proxy for Tech and the logarithm of fiscal expenditure on science and technology as a proxy for Est. Hypothesis 2 will be tested using a mediation effect model, and Hypothesis 3 will be analyzed through a threshold model regression.
3.3 Econometric model
3.3.1 Baseline regression model
To examine whether the digital economy positively impacts the enhancement of food supply chain resilience and to verify Hypothesis 1, this paper employs a two-way fixed effects panel regression model. The econometric model is specified as follows:
where, Fscrit represents the resilience of the food supply chain, Digit represents the level of development of the digital economy, i and t represent the province and year, respectively. β0, β1, β2 are the parameters to be estimated, Controlit represents the control variables, including the financial development, industrial structure, total railway mileage, food consumption, urbanization, and education. μi represents the individual fixed effect, νt represents the time fixed effect, and εit is the random disturbance item.
3.3.2 Mechanism test model
To explore the mechanism by which information technology adoption influences the impact of the digital economy on food supply chain resilience and to verify Hypothesis 2, this paper adopts a “two-step approach” for analyzing the mechanism. The econometric models are constructed as follows:
where, Techit represents the capacity for information technology, α0, α1, α2 are the parameters to be estimated, and the other terms are defined the same as in Model (1).
3.3.3 Threshold model
To investigate the mechanism by which scientific and technological investment affects the impact of the digital economy on food supply chain resilience and to verify Hypothesis 3, this paper employs a threshold effect model. The econometric model is specified as follows:
where, i and t represent the province and year, respectively, I (·) is an indicator function, Estit represents the threshold variable, and the rest is defined the same as in Model (1). When the threshold variable meets the threshold condition, I = 1, otherwise, I = 0, and qn represents the estimated value of the nth threshold.
4 Results and discussion
4.1 Descriptive statistical analysis
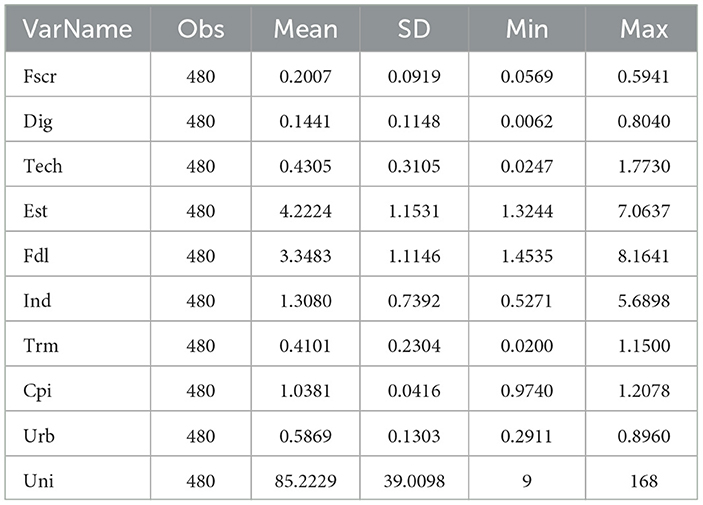
To ensure robust estimation results and mitigate the influence of outliers, a descriptive statistical analysis was conducted for each variable. Table 4 shows that the standard deviations of all variables are smaller than their means, indicating data stability. The food supply chain resilience indicator ranges from 0.0569 to 0.5941, with a standard deviation of 0.0919, reflecting significant regional variation in resilience. The mean resilience value of 0.2007 suggests that the overall capacity of the food supply chain to withstand shocks is relatively weak.
4.2 Baseline regression results
The correlation matrix reveals a significant positive correlation between the digital economy development (Dig) and food supply chain resilience (Fscr), with a coefficient of 0.557. This suggests that progress in the digital economy tends to strengthen the supply chain's resilience. Additionally, all Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) values are below 10, indicating minimal multicollinearity concerns. The correlation matrix details are provided in the Appendix.
To detect heteroskedasticity and assess the suitability of a fixed effects model for regression, White's heteroskedasticity test, the Breusch-Pagan test, and the Hausman test were conducted. Heteroskedasticity, if present, can bias regression coefficient estimates and standard errors, affecting the results' accuracy. The tests' p-values (all < 0.05) confirm heteroskedasticity, underscoring the need for a fixed effects model with robust standard errors. This approach accounts for unobserved individual-specific effects, ensuring more reliable results.
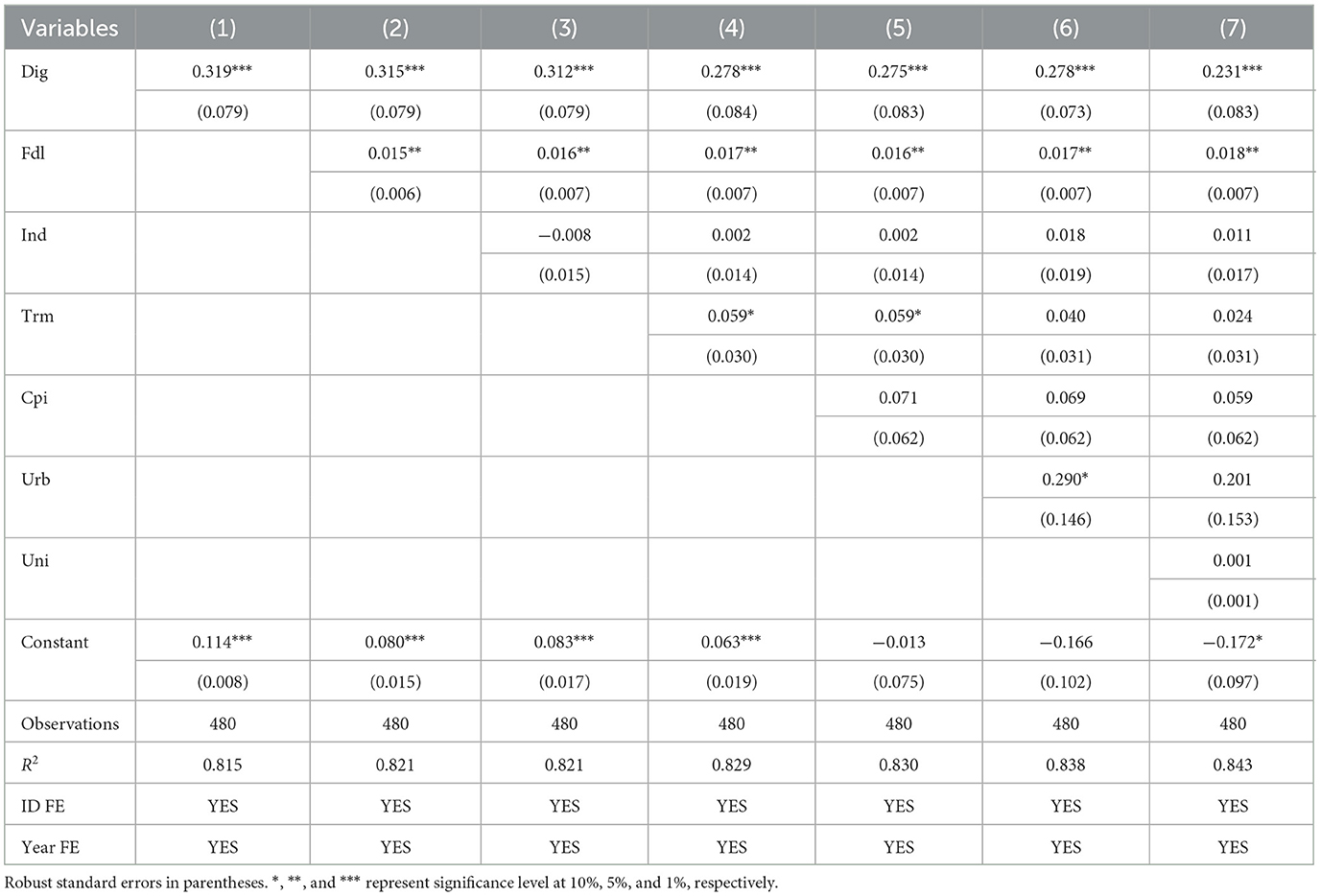
Table 5 displays the panel regression analysis results, adjusted for both time and individual fixed effects. Column (1) shows the results without the inclusion of control variables, where the coefficient of the digital economy is significantly positive at the 1% level. Columns (2)–(7) demonstrate that, even with the gradual introduction of control variables, the coefficient of the digital economy remains significantly positive at the 1% level. This result underscores the digital economy's critical role in bolstering the food supply chain's resilience. Specifically, higher digital economy development is associated with increased supply chain resilience, thereby confirming Hypothesis 1.
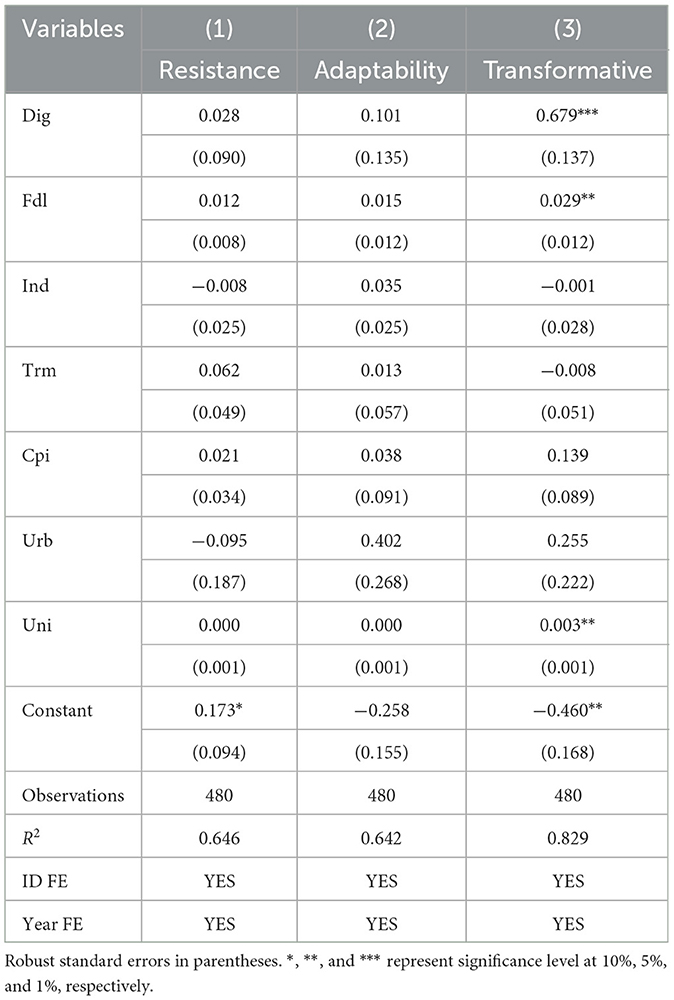
Food supply chain resilience comprises three dimensions: resistance capability, adaptability, and transformative capability. The impact of the digital economy on each dimension varies. Table 6 presents the regression results for these three dimensions. It can be observed that the digital economy has a significantly positive impact on transformative capability, while its impact on resistance and adaptability is positive but not significant. This indicates that the digital economy primarily enhances the overall resilience of the grain supply chain by boosting its transformative capability. The key enablers of this enhancement are digital technologies such as satellite imaging and intelligent irrigation systems. These technologies deepen the empowerment of data elements within the supply chain and promote the digital transformation and upgrading of the grain supply chain, thereby effectively improving its resilience.
4.3 Robustness test
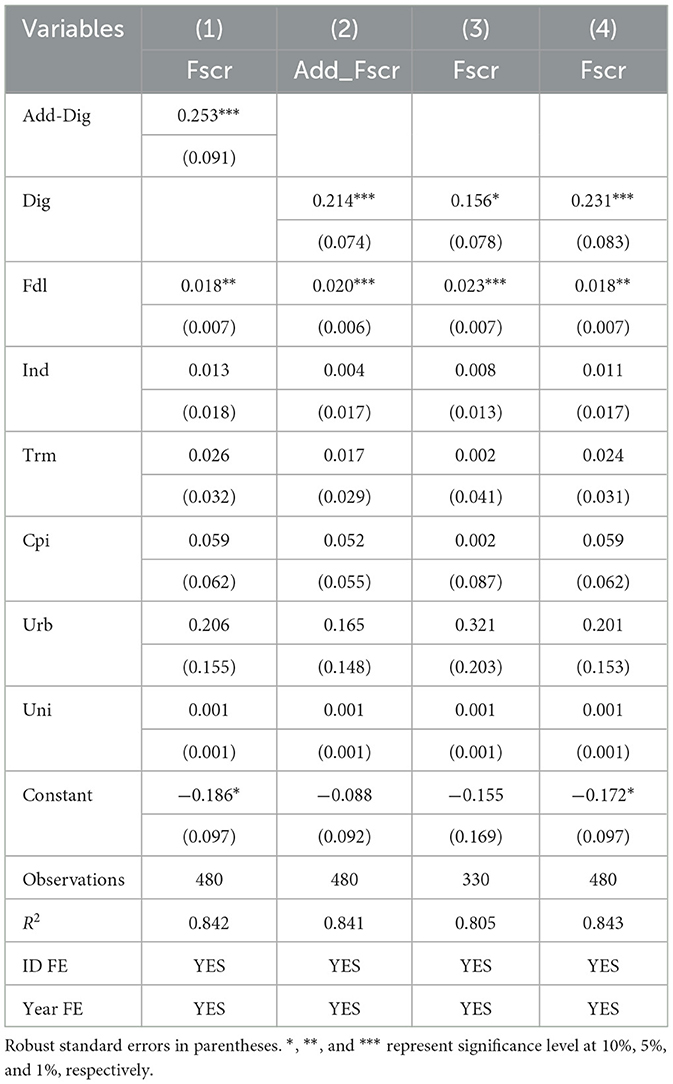
To ensure the robustness of the empirical results, this study recalculates the weights and comprehensive scores for both dependent and independent variables using the coefficient of variation method. These recalculated scores are then utilized in alternative regression analyses. In the Table 7, Model 1 uses an alternative independent variable, and Model 2 uses an alternative the dependent variable. To mitigate the potential biases from extreme values, a 1% bilateral trim is applied to the provincial-level resilience of the food supply chain and the digital economy, with results shown in Model 3. Additionally, to minimize the impact of statistical scale changes on the sample data, the analysis period is adjusted to 2013–2023, and the regressions results are presented in Model 4.
These robustness checks are crucial for confirming that the results are not methodological artifacts. By recalculating variables, addressing biases through trimming, and adjusting the sample period, the study verifies that the observed relationship between the digital economy and food supply chain resilience is consistent and not influenced by these factors. The consistent results across these tests bolster the credibility of the findings, indicating that the positive link between the digital economy and supply chain resilience is a robust empirical observation.
4.4 Endogeneity test
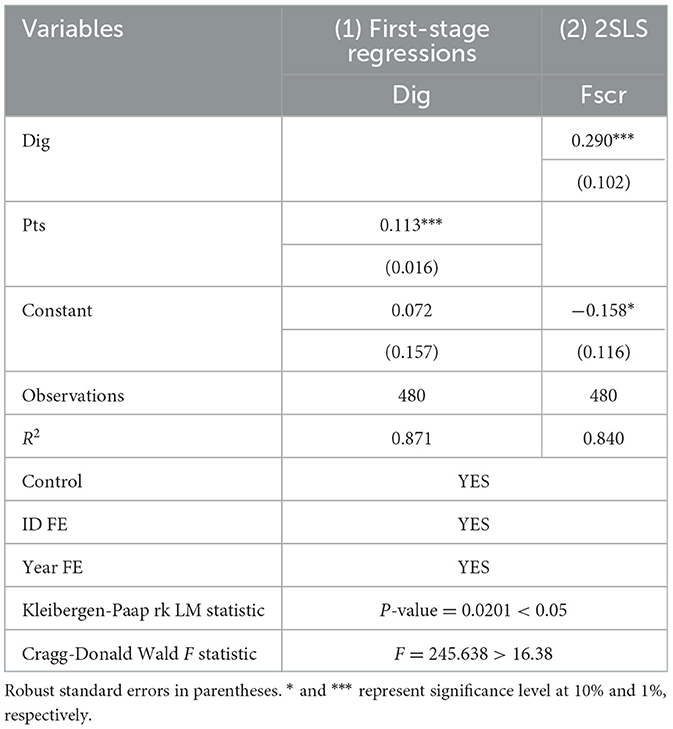
To address the potential endogeneity in the regression analysis, this study employs the two-stage least squares (2SLS) estimation method with an instrumental variable (IV). The total volume of postal and telecommunications services (Pts), measured in ten—thousand—yuan units, is selected as the IV. This variable reflects the development and utilization of ICT infrastructure in a region, having a close association with the advancement of the digital economy. With the improvement of ICT applications and network infrastructures, the growth in postal and telecommunications services usually accompanies higher levels of digitalization.
Nevertheless, the total volume of these services is more susceptible to external factors like policy changes, technological innovations, and demands for communication services, which have no direct influence on the resilience of the food supply chain. This characteristic of independence makes it a suitable IV candidate. The results, as shown in Table 8, confirm that the IV passes both the identification test and the weak IV test. The 2SLS estimation reaffirms the significant positive impact of the digital economy on the food supply chain's resilience after accounting for endogeneity.
4.5 Heterogeneity analysis
4.5.1 Geographic heterogeneity
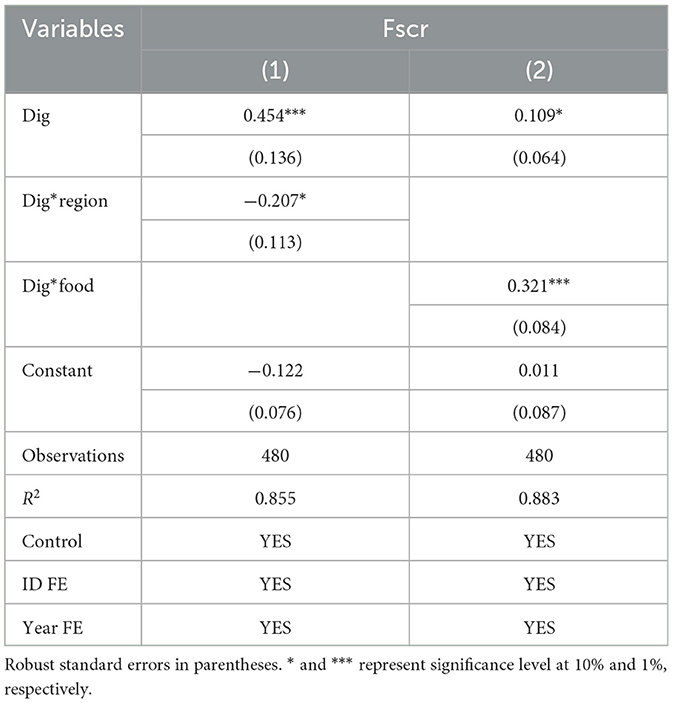
Due to significant differences in socio-economic development and resource endowments between the northern and southern regions of China, coupled with the dynamic changes in agricultural resources, China's grain production and supply have formed a pattern of “grain moving from the north to the south”.2 To explore whether there are regional differences in the role of the digital economy in enhancing the resilience of the grain supply chain, this study divides the sample into southern and northern provinces. A dummy variable, Region, is constructed. Southern provinces are assigned as the treatment group (Region = 1), while northern provinces are assigned as the control group (Region = 0). An interaction term between the digital economy (Dig) and the regional dummy variable (Region) is incorporated into the regression model. The regression results are shown in Column (1) of Table 9. The results indicate that the coefficient of the interaction term is significantly negative, suggesting that the digital economy has a more pronounced effect on enhancing the resilience of the grain supply chain in northern provinces. The possible reason is that the northern region has flat terrain and abundant arable land, which leads to significant economies of scale in grain production. In recent years, northern provinces have actively promoted the development of the digital economy, with gradually improved digital infrastructure and information platforms. This has endowed northern provinces with higher potential and room for integration between the digital economy and the grain system, thereby more significantly enhancing the resilience of the grain supply chain.
4.5.2 Food production functional zones heterogeneity
Agricultural production conditions and grain production structures vary markedly across different regions in China, leading to diverse agricultural development orientations and functions. Major grain-producing areas play an indispensable role in safeguarding national food security, distinguishing them from non-core grain-producing regions. Using the classification by China's National Development and Reform Commission, a dummy variable, Food, is created. Thirteen main food-producing provinces (Heilongjiang, Henan, Shandong, Sichuan, Jiangsu, Hebei, Jilin, Anhui, Hunan, Hubei, Inner Mongolia, and Liaoning) are designated as the experimental group (Food = 1), while the remaining seventeen provinces as the control group (Food = 0). An interaction term, Dig*Food, between the digital economy development level and the main food-producing area variable is incorporated into the regression model. The analysis results, as detailed in Column (2) of Table 9, show that the interaction term's coefficient is significantly positive. This suggests that the digital economy's positive effect on food supply chain resilience is more pronounced in the main food-producing areas than in non-main producing regions. In these critical areas, the advancement of digital technology and the expansion of the digital economy significantly enhance the supply chain's resilience and stability. Main food-producing areas typically have relatively well-developed agricultural infrastructure and a higher propensity to adopt new technologies. The introduction of digital technologies enables intelligent management of the grain system, reduces resource wastage, and enhances the operational efficiency of the grain supply chain, thereby strengthening its resilience.
4.6 Further analysis
4.6.1 Mechanism effect
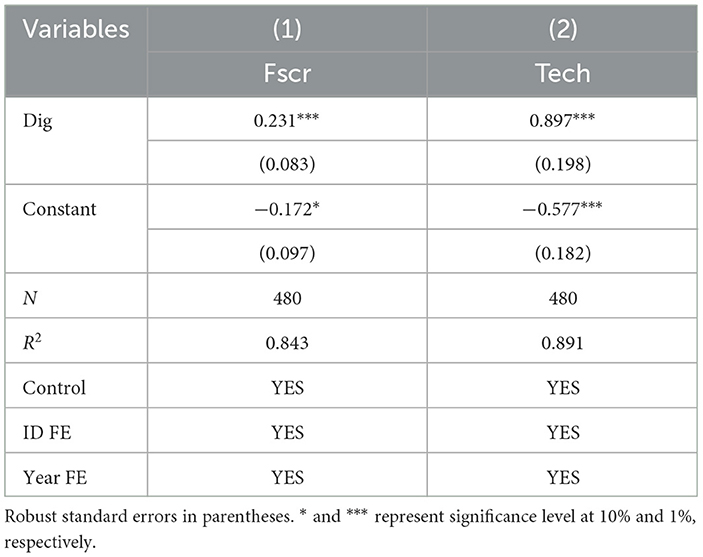
The theoretical framework suggests that the digital economy primarily strengthens food supply chain resilience through the adoption of information technology by agricultural entities. To explore this mechanism, this study uses the number of mobile phone subscriptions as a proxy for information technology adoption, allowing us to examine the mediating role of IT adoption capacity in the relationship between the digital economy and supply chain resilience. The mechanism analysis results are detailed in Table 10.
As presented in Table 10, the coefficient for the digital economy's development level on IT adoption capacity is significantly positive, providing empirical support for hypothesis 2. The growth of the digital economy drives regions to invest in information infrastructure, which serves as the bedrock for agricultural entities to embrace new technologies. This foundational support is crucial as it addresses one of the key barriers to technology adoption, thereby facilitating a smoother transition toward digital transformation. In addition, the digital economy offers accessible and efficient IT tools and platforms, reducing the costs and barriers to technology adoption. The adoption of IT by agricultural entities, in turn, facilitates the digital transformation of the food supply chain, empowering it with enhanced abilities to manage natural disasters and market fluctuations. Digital platforms, for instance, enable supply chain operators to optimize production schedules, streamline marketing strategies, and eliminate redundant intermediaries. This transformation improves the supply chain's resilience, making it more adaptable and responsive to challenges. In conclusion, the digital economy enhances the food supply chain's resilience by bolstering the capacity of supply chain operators to adopt and utilize information technology.
4.6.2 Threshold effect
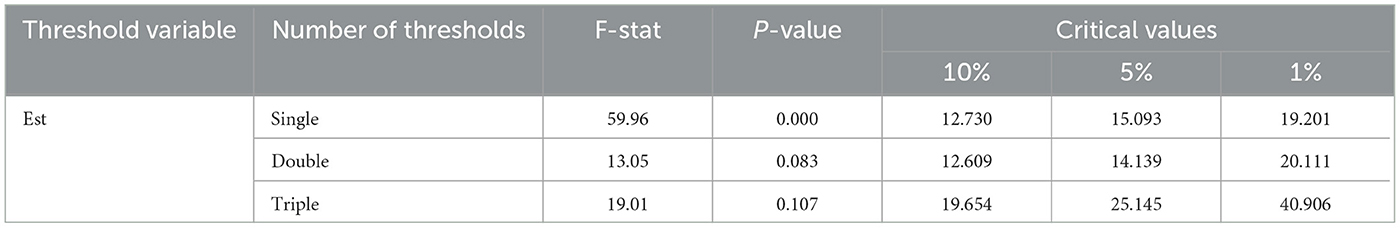
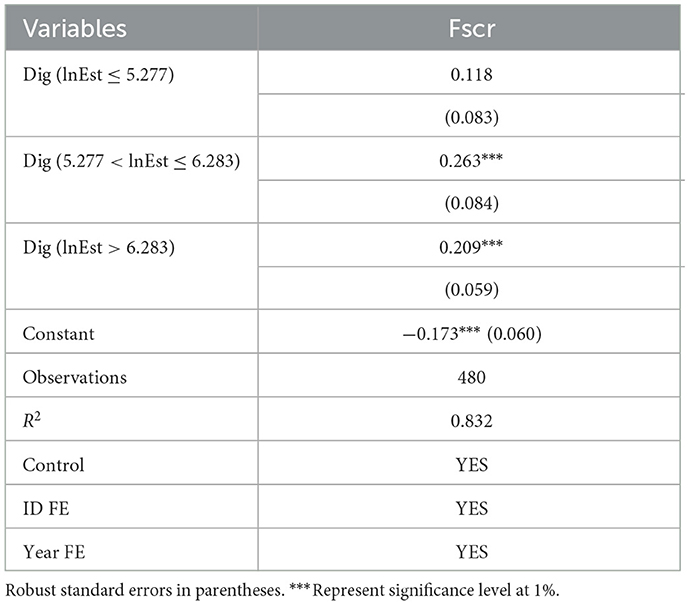
To explore the potential nonlinear dynamics between the digital economy and food supply chain resilience, this study examines the threshold effect of fiscal investment in science and technology. The objective is to understand how different levels of investment modulate the digital economy's impact on supply chain resilience. Prior to conducting the threshold regression analysis, a threshold effect test with 400 bootstrap resampling iterations was performed. Table 11 shows a significant double threshold effect at the 1% significance level, suggesting that the influence of the digital economy on food supply chain resilience undergoes distinct changes at two specific levels of fiscal investment, which are identified as 5.277 and 6.283.
Table 12 demonstrates the estimated impact of the digital economy on food supply chain resilience, considering the threshold variable of science and technology investment. The empirical results strongly validate the presence of a significant threshold effect, providing support for Hypothesis 3. In particular, when lnEst ≤ 5.277, the impact of the digital economy on the food supply chain resilience is statistically insignificant. When 5.277 < lnEst ≤ 6.283, the digital economy has a significant positive impact on the level of resilience of the food supply chain, with an impact coefficient of 0.263. Notably, when lnEst > 6.283, although the impact coefficient remains significantly positive, it decreases to 0.209. These findings underscore the necessity of a certain level of scientific and technological investment to effectively harness the promoting effect of the digital economy on the food supply chain resilience.
In 2023, 18 regions, mostly located in central and western China, had investment levels below the first threshold, while 12 regions, mainly in the eastern coastal areas, exceeded this threshold. This spatial disparity suggests that regions with higher science and technology investments are better positioned to capitalize on the digital economy's potential for enhacing food supply chain resilience. Based on these empirical findings, it is recommended that Chinese government, especially in the central and western regions, increase government investment in science and technology. Such investments should be directed toward improving digital infrastructure and accelerating the digitalization and intelligentization of the food supply chain, thereby maximizing the digital economy's role in strengthening supply chain resilience.
5 Research conclusions and policy recommendations
Leveraging digital technologies is crucial for bolstering the food supply chain within the digital economy, particularly for ensuring food security. This study, using provincial data from China spanning 2008 to 2023, explores how the digital economy enhances supply chain resilience. Key findings indicate that the digital economy significantly strengthens China's food supply chain resilience, with a robust effect even after addressing endogeneity. The digital economy's impact is especially pronounced in major food-producing regions, suggesting these areas are well-positioned to use digital advancements to improve supply chain stability and effectiveness. The adoption of information technology plays a crucial mediating role between the digital economy and supply chain resilience. There is also a threshold effect of fiscal investment in science and technology on the digital economy's impact on supply chain resilience, indicating a necessary investment level to maximize benefits.
To fully harness the potential of the digital economy and enhance the digitalization and intelligence of the food supply chain, and enhance its resilience for high-quality agricultural development, this study proposes strategic policy recommendations. First, policymakers must prioritize the establishment and enhancement of agricultural digital infrastructure, with a strong emphasis on accelerating digital development in major food-producing regions. This entails increasing financial investments in these areas and actively promoting the integration of advanced information technologies, such as agricultural Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, and cloud computing, across all stages of food production, distribution, and processing. For example, in vast grain—growing areas, IoT sensors can be deployed to monitor soil conditions and crop growth in real-time, while big data can optimize inventory management and delivery routes during distribution.
Second, efforts should be concentrated on cultivating agricultural talent and enhancing the digital technology application capabilities of food production entities. This can be accomplished through targeted training programs and demonstration projects. These initiatives should aim to elevate farmers' and food-related enterprises' awareness of information technology and equip them with practical application skills, thereby expediting the widespread adoption of digital solutions throughout the food sector. Third, leveraging the advantages of the digital economy, cross-regional collaborative systems need to be refined by establishing a comprehensive national information-sharing network. This network will enhance connectivity between major food-producing regions and other areas, enabling efficient resource allocation and facilitating prompt adjustments to supply chain plans during emergencies. Finally, it is crucial to encourage the integrated development of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries while streamlining the food supply chain. This requires the seamless integration of assets, capital, and expertise from different sectors to improve resource utilization efficiency and foster the creation of a comprehensive, secure, and stable agricultural growth ecosystem. Simultaneously, special attention should be paid to enhancing transportation and logistics infrastructure, as it serves as a vital foundation for promoting advanced agricultural development.
This study, offering a broad analysis of the digital economy's impact on China's food supply chain resilience based on provincial data, recognizes its limitations in capturing farm-level nuances. Future research should explore the detailed dynamics of how IT adoption contributes to supply chain resilience and investigate the digital economy's effects in other agricultural sectors, including its potential to mitigate climate change's impact on agriculture. Additionally, a global comparative study could reveal the digital economy's wider effects on agricultural supply chains across different countries.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZD: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Social Science Fund of China (No. 21CGL026).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1589133/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^Data Source: National Food and Strategic Reserves Administration of China.
2. ^The south and the north are divided by the Qinling Mountains and the Huaihe River. The northern provinces include Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Liaoning, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Shandong, Henan, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang 15 provinces.
References
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Org. Behav. Hum. Dec. Proc. 50, 179–217. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Ardito, L., Petruzzelli, A. M., Panniello, U., and Garavelli, A. C. (2018). Towards Industry 4.0: mapping digital technologies for supply chain management-marketing integration. Bus. Proc. Manag. J. 25, 323–346. doi: 10.1108/BPMJ-04-2017-0088
Barefoot, K., Curtis, D., Jolliff, W., Nicholson, J. R., and Omohundro, R. (2018). Defining and Measuring the Digital Economy. Washington, DC: US Department of Commerce Bureau of Economic Analysis, 210.
Belhadi, A., Kamble, S. S., Venkatesh, M., Jabbour, C. J. C., and Benkhati, I. (2022). Building supply chain resilience and efficiency through additive manufacturing: an ambidextrous perspective on the dynamic capability view. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 249:108516. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2022.108516
Cachon, G. P., Randall, T., and Schmidt, G. M. (2007). In search of the bullwhip effect. Manuf. Serv. Operat. Manag. 9, 457–479. doi: 10.1287/msom.1060.0149
Chandio, A. A., Ozdemir, D., Gokmenoglu, K. K., Usman, M., and Jiang, Y. (2024). Digital agriculture for sustainable development in China: the promise of computerization. Technol. Soc. 76, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2024.102479
Chen, J., and Liu, Y. (2021). Operations management innovation enabled by digitialzation and intellectualization: from supply chain to supply chain ecosystem. J. Manag. World 37, 227–240+14. doi: 10.19744/j.cnki.11-1235/f.2021.0180
Chen, X. D., Liu, Y., and Zhou, K. (2022). Research on the path of digital economy to improve China's industrial chain resilience. Reform Econ. Syst. 1, 95–102.
Christopher, M., and Peck, H. (2004). Building the resilient supply chain. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 15, 1–13. doi: 10.1108/09574090410700275
Cochrane, W. W. (1958). Farm Prices: Myth and Reality. Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press.
Dayioglu, M. A., and Turker, U. (2021). Digital transformation for sustainable future-agriculture 4.0: a review. J. Agric. Sci. 27, 373–399. doi: 10.15832/ankutbd.986431
Fu, S., Liu, J., Tian, J., Peng, J., and Wu, C. (2023). Impact of digital economy on energy supply chain efficiency: evidence from Chinese energy enterprises. Energies 16:568. doi: 10.3390/en16010568
Gawankar, S. A., Gunasekaran, A., and Kamble, S. (2020). A study on investments in the big data-driven supply chain, performance measures and organisational performance in Indian retail 4.0 context. Int. J. Prod. Res. 58, 1574–1593. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2019.1668070
Hao, A., and Tan, J. (2022). Impact of digital rural construction on food system resilience. J. South China Agric. Univ. 21, 10–24. doi: 10.7671/j.issn.1672-0202.2022.03.002
Hohenstein, N. O., Feisel, E., Hartmann, E., and Giunipero, L. (2015). Research on the phenomenon of supply chain resilience: a systematic review and paths for further investigation. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 45, 90–117. doi: 10.1108/IJPDLM-05-2013-0128
Holling, C. S. (1973). Resilience and stability of ecological systems. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 4, 1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.04.110173.000245
Holmström, J., and Partanen, J. (2014). Digital manufacturing-driven transformations of service supply chains for complex products. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 19, 421–430. doi: 10.1108/SCM-10-2013-0387
Jiang, Q., Li, J., Si, H., and Su, Y. (2022). The impact of the digital economy on agricultural green development: evidence from China. Agriculture 12:1107. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12081107
Kamalahmadi, M., and Parast, M. M. (2016). A review of the literature on the principles of enterprise and supply chain resilience: major findings and directions for future research. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 171, 116–133. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.10.023
Lee, C. C., Zeng, M., and Luo, K. (2023). Food security and digital economy in China: a pathway towards sustainable development. Econ. Anal. Policy 78, 1106–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2023.05.003
Liu, F., Xiao, X., Qin, Y., Yan, H., Huang, J., Wu, X., et al. (2022). Large spatial variation and stagnation of cropland gross primary production increases the challenges of sustainable grain production and food security in China. Sci. Total Environ. 11, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.151408
Manyena, S. B. (2006). The concept of resilience revisited. Disasters 30, 434–450. doi: 10.1111/j.0361-3666.2006.00331.x
Ponomarov, S. Y., and Holcomb, M. C. (2009). Understanding the concept of supply chain resilience. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 20, 124–143. doi: 10.1108/09574090910954873
Prüfer, J., and Schottmüller, C. (2021). Competing with big data. J. Indust. Econ. 69, 967–1008. doi: 10.1111/joie.12259
Rice, J. B., and Caniato, F. (2003). Building a secure and resilient supply network. Supp. Chain Manag. Rev. 7, 22–30.
Saberi, S., Kouhizadeh, M., Sarkis, J., and Shen, L. (2019). Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 57, 2117–2135. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2018.1533261
Shepherd, M., Turner, J. A., Small, B., and Wheeler, D. (2020). Priorities for science to overcome hurdles thwarting the full promise of the ‘digital agriculture'revolution. J. Sci. Food Agricul. 100, 5083–5092. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9346
Stavytskyy, A., Kharlamova, G., and Stoica, E. A. (2019). The analysis of the digital economy and society index in the EU. TalTech J. Eur. Stud. 9, 245–261. doi: 10.1515/bjes-2019-0032
Stone, J., and Rahimifard, S. (2018). Resilience in agri-food supply chains: a critical analysis of the literature and synthesis of a novel framework. Supp. Chain Manag. Int. J. 23, 207–238. doi: 10.1108/SCM-06-2017-0201
Štusek, J., Kubata, K., and Očenášek, V. (2017). Strategic importance of the quality of information technology for improved competitiveness of agricultural companies and its evaluation. AGRIS On-line Papers Econ. Inform. 9, 109–122. doi: 10.7160/aol.2017.090411
Tang, X., Ding, S., Gao, X., and Zhao, T. (2022). Can digital finance help increase the value of strategic emerging enterprises? Sustain. Cities Soc. 81:103829. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2022.103829
Wang, X., and Li, J. (2023). Heterogeneous effect of digital economy on carbon emission reduction. J. Clean. Prod. 429:139560. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.139560
Xue, Y., Tang, C., Wu, H., Liu, J., and Hao, Y. (2022). The emerging driving force of energy consumption in China: does digital economy development matter? Energy Policy 165:112997. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2022.112997
Yadav, V. S., Singh, A. R., Gunasekaran, A., Raut, R. D., and Narkhede, B. E. (2022). A systematic literature review of the agro-food supply chain: challenges, network design, and performance measurement perspectives. Sustain. Prod. Consump. 29, 685–704. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.11.019
Yang, M., Fu, M., and Zhang, Z. (2021). The adoption of digital technologies in supply chains: drivers, process and impact. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 169:120795. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120795
Yi, M., Liu, Y., Sheng, M. S., and Wen, L. (2022). Effects of digital economy on carbon emission reduction: new evidence from China. Energy Policy 171:113271. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2022.113271
Zhang, X., Sun, P., Xu, J., Wang, X., Yu, J., Zhao, Z., et al. (2020a). Blockchain-based safety management system for the grain supply chain. IEEE Access. 8, 36398–36410. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2975415
Zhang, X., Wan, G., Zhang, J., and He, Z. (2020b). Digital economy, financial inclusion and inclusive growth. China Econ. 15, 92–105. doi: 10.19602/j.chinaeconomist.2020.05.07
Zhang, Y., Wu, X., Ge, H., Jiang, Y., Sun, Z., Ji, X., et al. (2023). A blockchain-based traceability model for grain and oil food supply chain. Foods 12:3235. doi: 10.3390/foods12173235
Zhao, G., Vazquez-Noguerol, M., Liu, S., and Prado-Prado, J. C. (2024). Agri-food supply chain resilience strategies for preparing, responding, recovering, and adapting in relation to unexpected crisis: a cross-country comparative analysis from the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Bus. Logist. 45:e12361. doi: 10.1111/jbl.12361
Zhao, N., Hong, J., and Lau, K. H. (2023). Impact of supply chain digitalization on supply chain resilience and performance: a multi-mediation model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 259:108817. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2023.108817
Keywords: digital economy, information technology adoption, supply chain resilience, food, China
JEL: O13, Q01, Q10
Citation: Ding Z, Yue H and Liu J (2025) Examining the role of digital economy on supply chain resilience: an empirical analysis of China's food sector. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1589133. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1589133
Received: 07 March 2025; Accepted: 02 June 2025;
Published: 26 June 2025.
Edited by:
Siphe Zantsi, Agricultural Research Council of South Africa (ARC-SA), South AfricaReviewed by:
Mohammad Ali Yamin, Jeddah University, Saudi ArabiaJingsuo Li, Qingdao Agricultural University, China
Sani Ega Priani, Bandung Islamic University, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Ding, Yue and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhao Ding, emRpbmdAc2ljYXUuZWR1LmNu
 Zhao Ding
Zhao Ding Hongxia Yue
Hongxia Yue Jiawei Liu
Jiawei Liu