- Institute of Agricultural Economics and Development, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China
Introduction: With the rise of the digital economy, e-commerce has become a significant driver of agricultural modernization, offering opportunities to increase farmers’ income by expanding sales channels, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing product value. However, despite growing empirical research, disparities remain in the research findings, and the impact and mechanisms of farmers’ involvement in e-commerce operations on their income require further investigation.
Methods: This study utilizes the 2020 China Rural Revitalization Survey to both theoretically and empirically examine the impact of farmers’ participation in e-commerce on their total household income, while also exploring the mechanisms driving this relationship.
Results: (1) The empirical results of the endogenous switching regression model show that farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations can increase their income. This conclusion remains robust after applying winsorization, the instrumental variable approach, and core variable substitution. (2) Heterogeneity analysis reveals that, under the counterfactual hypothesis, if non-e-commerce households were to participate in e-commerce operations, their average treatment effect in the low-income group would be greater than that in the high-income group. That is, their increase in household income would be larger than that of the corresponding high-income group, suggesting that farmers’ participation in e-commerce would reduce income disparities among farmers. (3) Mechanism analysis indicates that farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations promotes income growth primarily through three channels: enhancing information acquisition capacity, promoting social participation, and saving operating costs.
Discussion: Therefore, this study recommends that the government refine policymaking to facilitate the integration of small-scale agricultural operators into emerging e-commerce models and establish a robust institutional support system. Additionally, efforts should focus on optimizing the rural e-commerce environment, enhancing farmers’ digital awareness and social participation efficiency, and supporting their engagement in e-commerce. Lastly, strengthening rural digital skills education, cultivating and retaining e-commerce talent, and fostering sustained income growth for farmers.
1 Introduction
Sustained income growth among low-income populations is a shared objective of developing countries and a critical factor of social stability and progress. In the Comprehensive Rural Revitalization Plan (2024–2027), the Chinese government emphasizes the importance of consolidating and expanding the achievements of poverty eradication, enhancing measures to increase farmers’ income, accelerating agricultural and rural modernization, and promoting the comprehensive upgrading of agriculture, holistic rural development, and the overall well-being of farmers. In recent years, how to consolidate and expand the achievements of poverty alleviation and sustainably promote the growth of rural household incomes has become a critical issue in implementing the rural revitalization. The core objective of rural revitalization is to ensure farmers’ prosperity through stable income growth. This is not only key to effectively linking poverty alleviation achievements with rural revitalization but also crucial in narrowing the urban–rural income gap and advancing common prosperity. With the rise of the digital economy, the “Internet +” concept has promoted the modern transformation of agriculture and rural areas. E-commerce, as a significant manifestation of the digital economy, has played a vital role in increasing farmers’ income and rural economic development by expanding sales channels, reducing transaction costs and enhancing product added value. In May 2019, the General Office of the Communist Party of China Central Committee and the General Office of the State Council issued the “Digital Rural Development Strategy Outline,” which explicitly identified that digital villages are an important direction for agricultural and rural modernization, and aims to promote rural revitalization and the construction of a digital China by improving farmers’ information skills and applying digital technologies. With the advancement of the “Digital Commerce for Rural Revitalization” initiative, rural e-commerce has become an increasingly crucial tool for the government to promote the development of digital villages and implement the rural revitalization strategy. It plays a significant role in transforming and upgrading rural industries, enhancing product competitiveness, and improving farmers’ incomes and quality of life.
With the gradual implementation of China’s digitalization-related policies, the total national e-commerce transaction volume increased from 4.55 trillion yuan in 2010 to 42.30 trillion yuan in 2021. Among this, online national retail sales rose from 0.51 trillion yuan to 13.09 trillion yuan. Structurally, the proportion of online retail sales in total e-commerce transactions grew from 11.2% in 2010 to 30.9% in 2021, indicating a continued rise in the consumer-end share of the e-commerce structure. This shift demonstrates that consumer-driven e-commerce has gradually become the dominant force.1 In addition, the total number of rural Internet users and the rural Internet access coverage rate serve as important indicators of rural digital infrastructure, indirectly reflecting the penetration level of rural e-commerce in specific regions. These indicators not only reflect the development level of information infrastructure, but also influence the capacity of rural e-commerce to take root and sustain itself at the grassroots level. Furthermore, they provide essential conditions for the extension of e-commerce industrial chains and the innovation of service models. According to the Statistical Report on the Development of China’s Internet, the number of Internet users in China rose from 457 million in 2010 to 1.032 billion in 2021. Among them, rural Internet users increased from 125 million to 284 million, with their share in total Internet users rising slightly from 27.35 to 27.52%. Over the same period, China’s overall Internet penetration rate increased from 34.3 to 73.0%, while the rural penetration rate rose from 17.5 to 57.6%, with the fastest growth from 2018 to 2021.2
The above data reveal several key points. First, between 2010 and 2021, the total number of Internet users in China grew by 125.82%, while rural Internet users increased by 127.20%, slightly surpassing the national average. This marginal difference highlights the positive outcomes of initiatives such as the “Digital Village” strategy and “Internet-Based Poverty Alleviation,” indicating significant improvements in both the coverage and usage frequency of Internet infrastructure in rural areas. Second, although the urban–rural digital divide has narrowed, it still persists. Despite the relatively faster growth of rural Internet users, their share of total Internet users increased only slightly from 27.35% in 2010 to 27.52% in 2021, reflecting a minimal rise of 0.17 percentage points and indicating limited structural transformation. This suggests that although the rural user base has expanded, rural residents remain underrepresented in the national digital landscape, and the digital divide has not been fundamentally bridged. The persistence of this structural disparity may be attributed to several factors, including uneven infrastructure development, lower educational attainment, disparities in digital literacy, and limited access to digital devices. It is worth noting that the rapid spread of the Internet in rural areas carries not only economic significance but also substantial value for social governance. In summary, the continuous growth in both the number of rural Internet users and the Internet penetration rate has laid a solid digital foundation for the development of rural e-commerce. Its influence on farmers’ participation in e-commerce activities warrants further exploration. Whether farmers can achieve income growth through the use of digital tools has become a key research topic in the context of China’s policy design and the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy (see Figure 1).
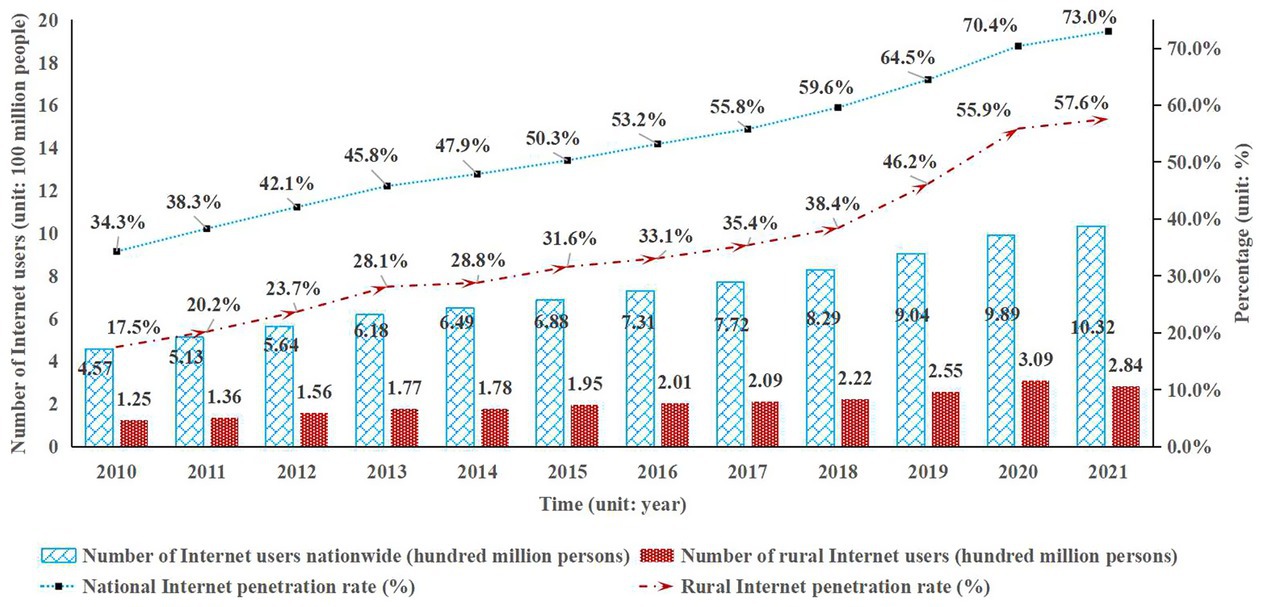
Figure 1. Number of internet users and internet penetration rate in China. Data source: “Statistical Report on the Development of Internet in China”.
Although previous studies have extensively discussed rural e-commerce, there is still no consensus on its effect in increasing income. From a micro level perspective, rural e-commerce primarily overcomes the geographical limitations of traditional sales models (Goldfarb and Catherine, 2019). Farmers can access a broader consumer base through e-commerce platforms, expand their market coverage and increase product sales (Yu et al., 2023; Kabo-Bah and Bannor, 2025), thereby enhancing their operational income. Secondly, during the transition from an industrial economy to a digital economy, the traditional market transaction mechanism has long been constrained by the structural dilemma of information asymmetry. Information gaps between buyers and sellers in terms of product details, quality verification, and credit assessment lead to high transaction costs for both parties (Chundakkadan and Sasidharan, 2023). With advancements in internet information technology, e-commerce has rapidly permeated various industries. Most scholars agree that e-commerce has significantly improved the ability of both parties involved in transactions to access market information and reduced the costs of information exchange (Huang et al., 2023; Zhai and Chen, 2023; Ji et al., 2023). E-commerce platforms not only offer merchants expanded channels for product dissemination and real-time interaction but also establish efficient product quality feedback mechanisms for consumers, facilitating a bidirectional flow of information (Zaghloul et al., 2024; Liu et al., 2024; Xu et al., 2024). E-commerce operators can even bypass intermediaries and conduct transactions directly with consumers, mitigating the “bullwhip effect” in information flow and increasing profitability (Leong et al., 2016; Zhang L. et al., 2024). Furthermore, the development of rural e-commerce creates new employment opportunities, thereby increasing farmers’ income (Li and He, 2024). In addition, rural e-commerce encourages entrepreneurial activities among farmers, leading to higher business revenues (Han and Li, 2020; Qin et al., 2022). Finally, an empirical study suggests that farmers’ participation in e-commerce significantly elevates marketing prices, fostering income growth (Liu et al., 2021).
At the macro level, e-commerce can be categorized into five types based on macro-level e-commerce measurement methodologies. The first category involves policy evaluation based on e-commerce development policies. Most scholars employ the difference-in-differences (DID) model to assess the impact of China’s E-commerce into Rural Comprehensive Demonstration project on rural residents’ livelihoods and the village economy. Studies indicate that this policy significantly promotes rural e-commerce development (Zhao Z. et al., 2024), fosters urban–rural shared prosperity through digital financial support (Wei X. et al., 2024), stimulates village economic growth (Pen et al., 2021), enhances the economic resilience of family farms (Huang et al., 2024), and ultimately increases rural residents’ income. Additionally, some scholars find that the project expands rural employment opportunities (Zhao J. et al., 2024), fosters entrepreneurship (Dong et al., 2024; Jiang and Qin, 2024), raises rural incomes, and improves residents’ well-being (Wei B. et al., 2024). The second category measures e-commerce development through the number of regional e-commerce villages reported by e-commerce platforms or research institutions. For instance, scholars analyze data from the China Taobao Village Research Report by Alibaba Research Institute, examining the distribution of “Taobao villages” and “Taobao towns” across regions. Existing research has found that Taobao Villages contribute to increasing local farmers’ income, thereby driving regional economic development (Zhang N. et al., 2024). Studies have also shown that in impoverished areas, Taobao Villages primarily increase farmers’ income by raising the proportion of the tertiary sector within the county economy (Li and Qin, 2022). The third category employs an e-commerce development index compiled by research institutions for empirical analysis. A study utilizes the county-level e-commerce development index from Alibaba Research Institute to examine rural e-commerce’s role in county economic growth, highlighting the moderating effect of digital finance (Yao et al., 2022). Another study draws on the China E-commerce Development Index Report, finding that rural e-commerce development increases the likelihood of land transfers and rural entrepreneurship, thereby promoting income growth and alleviating poverty (Tang et al., 2024). The fourth category assesses e-commerce development based on city-level logistics indicators, such as “per capita express delivery volume” and “per capita e-commerce sales.” A study uses per capita express delivery volume at the provincial level as a proxy for e-commerce development, revealing its positive effect on non-agricultural employment and income growth for both urban and rural residents (Li, 2020). Another study finds that while e-commerce expansion raises overall income levels, it also exacerbates the urban–rural income gap (Zhang and Han, 2017). Additionally, some research employs agricultural e-commerce sales and express delivery volume as indicators of regional agricultural e-commerce development, with empirical results showing that traditional wholesale industries derive economic benefits from e-commerce (Yang et al., 2024). The fifth category quantifies e-commerce development using the proportion of e-commerce transaction volume to regional GDP. A study demonstrates that regional logistics density significantly drives e-commerce growth, thereby contributing to the optimization of the regional economic structure (Zeng et al., 2023).
However, some scholars argue that empirical evidence does not fully support the notion that e-commerce significantly increases farmers’ income (Couture et al., 2021; Tang et al., 2022). Empirical results from one study indicate that e-commerce only increases urban residents’ income, with no significant impact on rural residents’ income (Li L. et al., 2021). Additionally, another study’s empirical findings suggest that the growth of e-commerce activities does not contribute to employment promotion (Biagi and Falk, 2017). Furthermore, although e-commerce is theoretically expected to enhance farmers’ access to information, improve their price-searching ability, and reduce transaction costs, its actual impact may be overestimated (Leroux et al., 2001). Moreover, within the e-commerce operational framework, rising logistics fees, packaging expenses, and labor costs have increased farmers’ marketing expenditures, thereby amplifying the cost burden at the end of the supply chain and ultimately affecting overall profitability (Tang and Zhu, 2020; Liu et al., 2021). Lastly, some literature suggests that the role of information and communication technology (ICT) in strengthening trust among agricultural market participants and optimizing farmers’ access to information to drive income growth has yet to be fully validated (Zanello and Srinivasan, 2014; Tadesse and Bahiigwa, 2015).
In summary, in recent years, an increasing number of studies have empirically analyzed the impact of rural e-commerce development on farmers’ income, but there are still differences in the research conclusions. Moreover, most existing studies rely on macro-level data to explore the impact of rural e-commerce on residents’ income. This top-down analytical approach may overlook individual heterogeneity and lead to an indicator synthesis fallacy, thereby limiting the explanatory validity of findings at the microeconomic level. Based on the above, this paper makes two main marginal contributions. First, it theoretically elucidates the intrinsic mechanism through which farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations affects their income, thereby expanding and enriching the theoretical framework of rural e-commerce as a driver of income growth. Second, it distinguishes itself from existing studies that either rely on macro-level e-commerce development indices or are confined to micro-empirical research with narrow geographical coverage and limited sample representativeness. Drawing on nationally representative rural panel survey data, this study accounts for selection bias caused by unobservable factors and empirically examines whether farmers’ engagement in e-commerce operations contributes to income improvement. The findings are both generalizable and robust, providing valuable enrichment to the literature on rural e-commerce and income generation.
2 Theoretical analysis
As a key driver of rural economic digitalization, the rapid development of e-commerce has not only restructured agricultural product distribution channels but also created new growth opportunities for agricultural industry upgrading. As business entities with limited rationality, farmers follow the principle of cost–benefit analysis when making decisions on e-commerce operations. Farmers will only transform their business models based on the principle of utility maximization when the marginal benefits of e-commerce channels significantly exceed the expected returns of traditional sales models. The impact of e-commerce development on farmers’ income can be analyzed from three aspects: (1) Reducing information asymmetry and enhancing information acquisition capabilities; (2) Promoting social participation; (3) Saving operating costs. The specific analysis is as follows.
2.1 Reducing information asymmetry and enhancing information acquisition capabilities
First, farmers operating e-commerce businesses enable direct connections with consumers. The product displays on e-commerce platforms provide consumers with more tangible product descriptions, while the consumer review systems offer reliable references for product information. These features significantly mitigate issues such as price-quality mismatch and quality trust caused by information asymmetry between trading parties (Ahn and Park, 2024; Zhang Y. et al., 2024). Secondly, participation in e-commerce enhances farmers’ capacity to acquire and utilize information and communication technologies. This capacity-enhancing mechanism enables farmers to use online platforms more effectively to obtain production management services and professional technical support, thereby improving operating performance through optimized production and operational decisions and enhanced resource allocation efficiency. Compared with the traditional business model with relatively closed information flows, e-commerce operations enhance farmers’ market adaptability, particularly in product innovation and service optimization. E-commerce platforms provide merchants with extensive consumer data and feedback (Wang et al., 2024), enabling them to monitor market demand in real time and adjust product features or improve after-sales services based on consumer preferences (Ke et al., 2024; Ma and Gu, 2024). This consumer-driven business model not only enhances farmers’ market responsiveness but also promotes product differentiation and personalization, thereby strengthening their competitiveness and ultimately increasing operational income. Moreover, empirical research indicates that farmers’ engagement with e-commerce platforms, particularly through the application of big data technologies, enhances their dynamic capabilities and the prudence of their entrepreneurial decision-making. This, in turn, contributes to increased e-commerce income. Fundamentally, participation in e-commerce strengthens farmers’ ability to access, interpret, and utilize information, thereby promoting income growth (Zeng et al., 2024). Therefore, we argue that improved information acquisition functions as a key mediating mechanism through which e-commerce participation influences farmers’ income.
2.2 Promoting social participation
Social participation mainly refers to individuals actively integrating into social interaction and realizing their own values by participating in various social activities, including politics, economics, and culture (Olsen, 1972). Farmers with a higher degree of social participation generally have more extensive social resources, which can effectively alleviate their investment risks (Yan et al., 2016). The social participation in this study mainly focuses on government participation. Farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations is usually accompanied by cooperation between farmers in production, sales, logistics and information sharing to improve operational efficiency and enhance market competitiveness, which is conducive to the awakening of e-commerce operators’ awareness of participation. Secondly, Moreover, as rural digital governance advances, governments increasingly rely on internet platform for agricultural product quality supervision, land management, market access approvals, and other regulatory functions. Farmers’ participation in e-commerce facilitates their integration into these digital governance systems, thereby strengthening their involvement in government affairs. Some scholars have pointed out that the more actively farmers integrate into village activities, the more opportunities they have to access and control resources, which helps reduce the negative impact of external risks on their livelihoods (Wang and Zhu, 2021). Existing studies have demonstrated that social integration significantly enhances relocated farmers’ access to employment information and market dynamics, strengthens their economic decision-making capacity, and promotes household income growth by improving their non-agricultural employment potential, information acquisition ability, and overall life satisfaction (Zhao et al., 2025). Building on this, social participation, which is a key dimension of social integration, also contributes positively to increasing farmers’ income. Participation in poverty alleviation programs (such as discussions and voting) expands farmers’ social networks and improves their access to information, thereby directly fostering income growth (Lin et al., 2019). Similarly, involvement in collective actions such as village cadre elections and the establishment of cooperatives indirectly improves livelihood standards by enhancing social capital and access to resources (He et al., 2024). Moreover, Other scholars believe that farmers’ integration into the construction of the village’s social order and value system will not only help the village build a fair, efficient and benign institutional environment, but also help to realize personal values and meet psychological needs in social interaction, thereby achieving an organic unity of personal development and community construction (Chen, 2019).
2.3 Saving operating costs
First of all, farmers’ e-commerce operations help them master the operation and marketing strategies of e-commerce platforms, enhance their information search capabilities and online operation skills, and leverage the scale advantages of e-commerce platforms to purchase production materials with better cost-effectiveness and guaranteed after-sales services. Secondly, in the traditional production and marketing model, intermediaries gain a competitive advantage in controlling information dissemination and customer resources by separating farmers’ production and marketing functions, thereby weakening the bargaining power of small farmers (Zhao Z. et al., 2024; Zhao J. et al., 2024). E-commerce platforms reduce intermediary involvement and eliminate geographical constraints, and reduce search costs, verification costs, transportation costs, and duplication costs in the traditional procurement model (Goldfarb and Catherine, 2019). These platforms allow farmers to efficiently compare prices and product quality, enabling them to select goods and services with the best cost-performance ratio. Furthermore, rural e-commerce expands sales channels, improves product circulation efficiency, reduces inventory backlog risks, shortens product storage time, and reduces the cost of special assets (Li et al., 2024), particularly for perishable agricultural products. Furthermore, some scholars argue that e-commerce participation enables farmers to communicate more effectively with online vendors concerning the prices and sourcing of organic fertilizers, thereby promoting more rational input procurement and contributing to the reduction of production costs (Wang et al., 2022). Finally, in traditional markets, transactions are often conducted based on verbal agreements or incomplete written contracts, with limited institutional safeguards, leading to a higher risk of default. In contrast, e-commerce platforms employ digital contracting systems to generate standardized, traceable electronic certificates, while third-party intervention mechanisms mitigate transaction uncertainty and significantly reduce time costs.
In summary, this study proposes the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: Farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations can promote income growth.
Hypothesis 2: Information acquisition, social participation and saving operating costs mediate the relationship between farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations and income growth.
3 Research methods
This study uses the endogenous switching regression model (ESR) to analyze the impact of farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations on their total household income. If P* = U1i (participating in e-commerce operations) − U0i (not participating in e-commerce operations) > 0, the farmer chooses e-commerce operations. Based on this, the behavioral decision equation for farmers to participate in e-commerce operations is:
If P* ≤ 0, then Pi = 0; if P* > 0, then Pi = 1. In Equation 1: Pi* is the latent variable of the dummy variable Pi of farmers participating in e-commerce operations; Pi = 1 means that farmer i participates in e-commerce operations, and Pi = 0 means that farmer i does not participate in e-commerce operations. Zi is the control variable; γi is the coefficient of each variable of Zi; μi is the random disturbance term of the decision equation.
The income equation of farmers constructed in this study is:
In Equation 2, the explained variable Yi represents the total household income level of farmer household i; the vector X represents the explanatory variables affecting the total household income of farmers, including the personal characteristics of the head of household, family characteristics and village characteristics; βi and δi are the coefficients corresponding to the Xi and Pi variables respectively; ɛi is the random error term.
If whether farmers participate in e-commerce operations is random, then Equation 2 can accurately estimate the impact of farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations on their total household income. However, whether farmers participate in e-commerce operations is voluntary, that is, whether to participate in e-commerce operations has a “self-selection” problem, and farmers will decide whether to participate in e-commerce operations based on their actual situation. In addition, there may be some unobservable factors that affect both participation in e-commerce operations and total household income. Therefore, the Pi variable cannot be considered exogenous, and directly using the above Equation 2 for OLS estimation will lead to bias.
The endogenous switching regression model can incorporate the bias caused by unobservable factors into the model, and examine the impact of the e-commerce operation group and the non-e-commerce operation group on the total household income, which corrects the sample selection bias to a certain extent. The model contains the behavioral decision Equation 1 and the income determination Equations 3a, 3b.
The estimation steps are: first use the binary choice model to estimate the decision equation of farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations, and then establish an income determination equation to estimate the difference in total household income between farmers who participate in e-commerce operations and those who do not. The income determination equations corresponding to farmers who participate in e-commerce operations and those who do not participate in e-commerce operations are:
In the above formula, Y1i and Y2i represent the total household income of farmers who participate in e-commerce and those who do not, respectively; X1i and X2i are variables that affect the total household income of the two types of farmers; β1 and β2 are the coefficients of X1i and X2i, respectively. The endogenous switching model introduces the inverse Mills ratios λ1i and λ2i, as well as the covariances σ1μ = cov(μi, ɛ1i) and σ2μ = cov(μi, ɛ2i), and uses the full information maximum likelihood method to regress Equations 1, 3a, and 3b to solve the sample selection bias, and then obtain consistent estimates β1 and β2.
Based on Equations 3a, 3b of the endogenous switching regression, the expected value of total household income of farmers who participate in and do not participate in e-commerce operations can be expressed as Equations 4a, 4b. The counterfactual scenarios of the two are the expected income of farmers who participate in e-commerce if they do not participate in e-commerce and the expected income of farmers who do not participate in e-commerce if they participate in e-commerce, which can be expressed as Equations 4c, 4d. The conditional expectation expressions of these four outcome variables are as follows:
Based on Equations 4a, 4c, the average treatment effect (ATT) of the total household income of farmers participating in e-commerce operations is presented in Equation 5a:
Based on Equations 4b, 4d, the average treatment effect (ATU) of the total household income of farmers who do not participate in e-commerce operations is presented in Equation 5b:
Furthermore, in order to examine the mechanisms of information acquisition, social participation, and reduction of operating costs in promoting household income growth through farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations, referring to the research of Jiang (2022), the mediation effect model adopted in this paper is presented in Equation 6:
Among them, ECmediai represents the mediating variables, which are information acquisition, social participation, and reduction of operating costs. θi represents the impact of farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations on the three mediating variables of information acquisition, social participation, and reduction of operating costs.
4 Data sources and definition of the model variables
4.1 Data source
The data for this empirical analysis are derived from the 2020 China Rural Revitalization Survey (CRRS), a large-scale national rural tracking survey conducted by the Rural Development Institute of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. The survey aims to comprehensively capture rural development trends and provide data support for academic research and rural revitalization strategies. It covers various aspects, including rural industrial structure, economic development, household income and expenditure, and residents’ well-being. The survey employed an equidistant random sampling method, covering 10 provinces, including Shandong, Sichuan, Heilongjiang, Henan, and Shaanxi, among others, involving 50 counties (cities) and 156 townships (towns) across the country. After addressing missing values and outliers, 2,245 valid questionnaires were retained for analysis.
4.2 Definition of the model variables
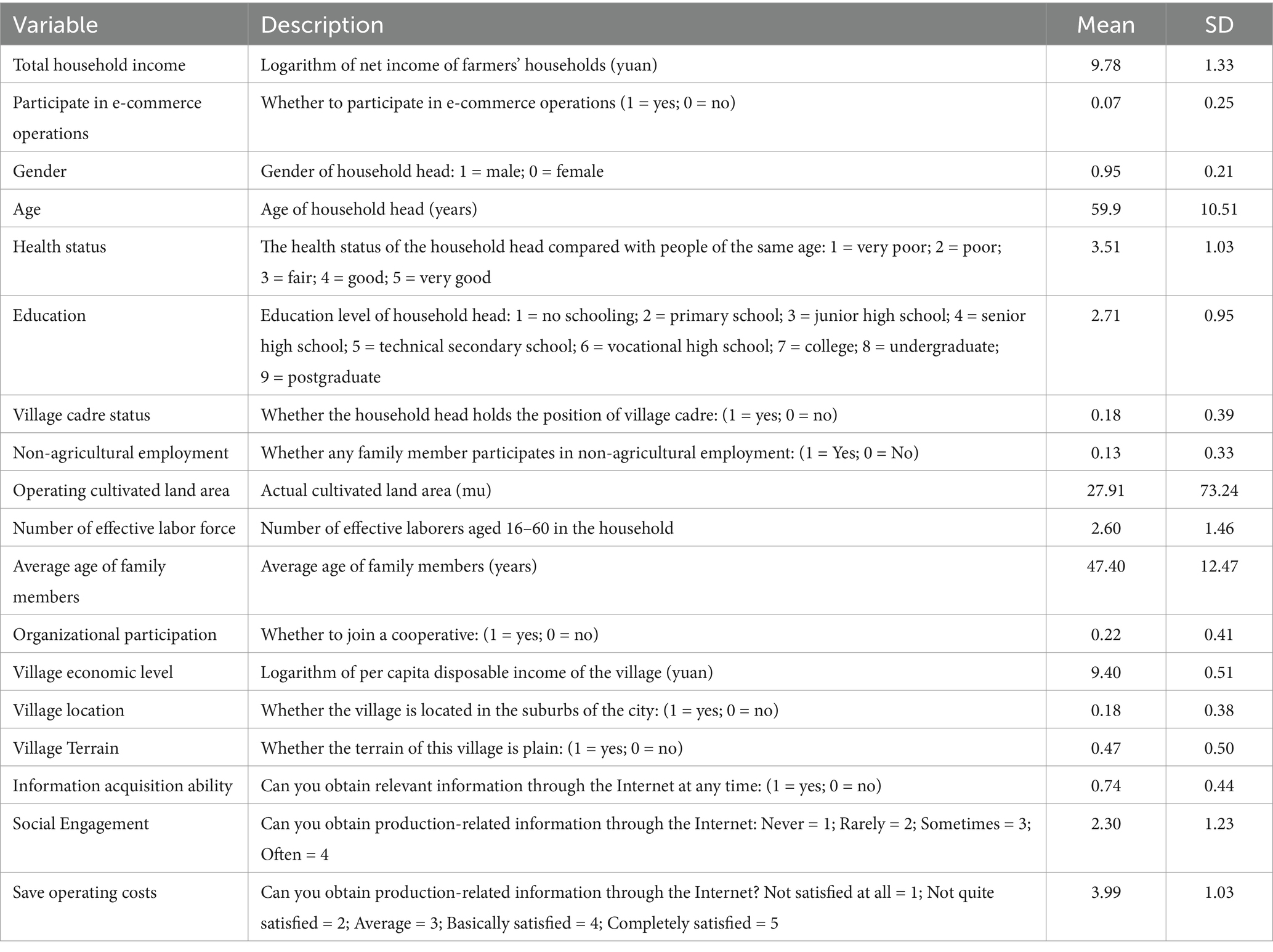
4.2.1 Explained variables
The dependent variable in this study is the total household income of farmers in 2019, measured as net income after deducting production and operational costs. This income is further categorized into agricultural income (comprising crop farming and animal husbandry) and non-agricultural income. To facilitate coefficient interpretation and mitigate heteroscedasticity, the natural logarithm (ln) of total household income is taken.
4.2.2 Treatment variables
This study uses whether farmers participate in e-commerce as the treatment variable. Combined with the views of previous scholars (Li et al., 2021a), e-commerce business operations are defined as farmers’ online retail activities centered on Internet platforms, such as farmers’ online sales through Taobao, JD.com, WeChat, TikTok and other platforms. Based on this, According to the relevant questions in the questionnaire of the CRRS, whether farmers use e-commerce to operate products is selected as the core variable, and the farmers’ participation in e-commerce is set to 1, and if they do not participate in e-commerce operations, it is set to 0 (see Table 1).
4.2.3 Matching variables
Following Li et al. (2021b) and Qiu and Zhou (2021), and considering the survey structure, the study incorporates multiple matching variables:
Household head characteristics: gender, age, health status, education level, and village cadre status; Household characteristics: cultivated land area, engagement of family members in non-agricultural employment, number of effective laborers, and organizational participation; Village characteristics: economic level, geographical location, and topography; simultaneously, provincial dummy variables are included to control for regional differences in farmers’ household income.
4.2.4 Identification variable
Based on the previous research (Kung, 2002; Deng et al., 2018), this paper selects the proportion of non-interviewed farmers in the same village participating in e-commerce operations as the identification variable. On the one hand, this identification variable meets the relevant conditions with the endogenous covariate, that is, the proportion of other farmers in the village participating in e-commerce operations directly affects the possibility of the target farmers participating in e-commerce operations; on the other hand, this identification variable is not related to the dependent variable, that is, the proportion of other farmers in the village participating in e-commerce operations does not directly affect the total household income of the target farmers.
4.2.5 Intermediary variable
Information acquisition ability: This study assesses information acquisition ability using a relevant question from the CRRS questionnaire: “If you have daily needs, can you obtain relevant information through the Internet at any time?” as the proxy variable of information acquisition ability. This question serves as a proxy variable, coded as follows: yes = 1, no = 0.
Social participation: This study assesses social participation using a relevant question from the CRRS questionnaire: “Do you participate in important public affairs in the village through WeChat groups?” This question serves as a proxy variable for social participation. The variable is coded as follows: never = 1, rarely = 2, sometimes = 3, often = 4.
Saving operating costs: This study measures the impact of e-commerce on operating cost savings using a relevant question from the CRRS questionnaire: “Can you obtain production-related information through the Internet?” This question serves as a proxy variable for saving operating costs. The variable is coded as follows: completely unsatisfied = 1, not very satisfied = 2, neutral = 3, basically satisfied = 4, completely satisfied = 5.
5 Results and analysis
5.1 Model estimation of the impact of participation in e-commerce operations on farm households’ total household income
Table 2 presents the estimated impact of village farmers’ participation in e-commerce on total household income. The first column lists the variable names, the second column reports the estimation results from the ordinary least squares (OLS) method. The third through fifth columns display the results from the endogenous switching regression (ESR) model, including the behavioral decision and income equations.
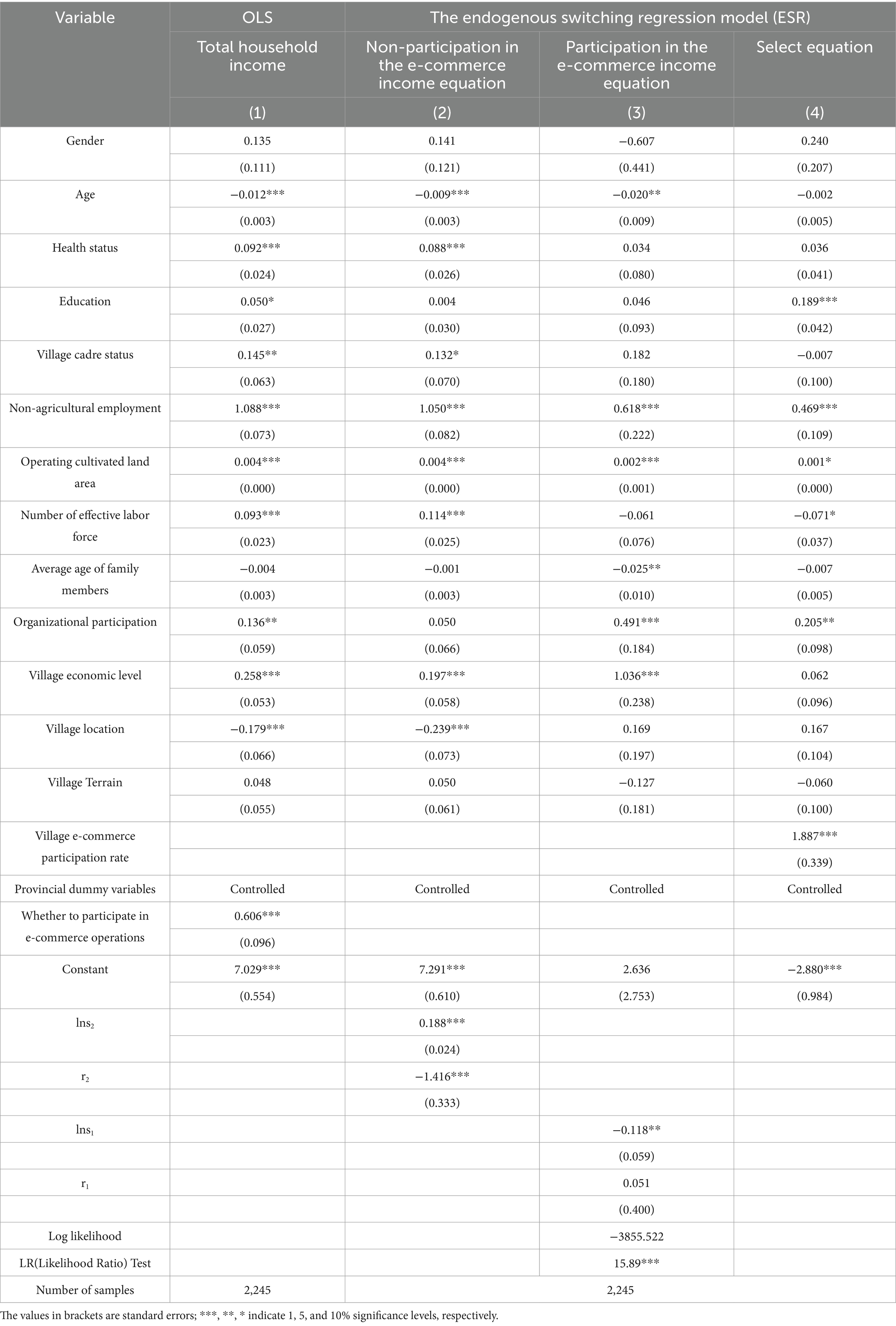
Table 2. Regression results of the impact of participating in e-commerce operations on the total income of farmers’ households (N = 2,245).
According to the OLS estimates in the second column of Table 2, participation in e-commerce operations has a significant positive effect on total household income at the 1% level. Considering that farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations is a self-selection behavior and that unobservable factors may introduce estimation bias, this study uses the village-level e-commerce participation rate as an identification variable for e-commerce participation and employs the endogenous switching regression (ESR) model to analyze total household income. The likelihood ratio (LR) test statistic is 15.89, rejecting the null hypothesis that the behavioral decision and income equations are independent at the 1% significance level.
5.1.1 Results of the ESR model decision equation estimation
The fifth column of Table 2 presents the behavioral decision equation, reporting the regression results for farmers’ participation in e-commerce. Regarding personal characteristics, education level has a significant positive effect on farmers’ decision to participate in e-commerce at the 1% level, whereas gender, age, health status, and cadre status do not exhibit a significant effect. To some extent, this suggests that a higher level of education enhances farmers’ technical comprehension and information-processing abilities, enabling them to acquire and apply e-commerce platform skills and related technologies more efficiently, thereby lowering technical barriers and reducing operational complexity. Additionally, farmers with higher education levels tend to exhibit greater innovation awareness and market sensitivity, allowing them to identify business opportunities in e-commerce more effectively and actively integrate traditional agricultural production with modern marketing strategies, thereby strengthening their market competitiveness. Regarding family characteristics, having a family member engaged in non-agricultural employment significantly influences farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations at the 1% level. This suggests that non-agricultural employment diversifies household income sources and strengthens financial stability, thereby providing a more solid economic foundation for e-commerce participation. The area of cultivated land under management significantly influences farmers’ decision to participate in e-commerce at the 10% level. A larger cultivated land area typically indicates stronger production capacity and higher agricultural output, providing a solid supply of commodities for e-commerce participation. Additionally, farmers with more extensive arable land can expand sales and diversify income sources through e-commerce platforms, which strengthens their motivation to engage in e-commerce operations. Farmers’ participation in cooperatives positively influences their decisions to engage in e-commerce, significant at the 5% level. This suggests that cooperative membership provides farmers with greater access to collective resources, technical support, and market channels, thereby facilitating their use of e-commerce platforms for business operations. Cooperatives offer a platform for information sharing, reducing transaction costs, and enhancing bargaining power, which, in turn, strengthens farmers’ willingness and capacity to participate in e-commerce. Conversely, the number of effective laborers in farming households negatively influences decisions to engage in e-commerce, significant at the 10% level. This may result from an increased reliance on traditional employment as the number of working-age laborers (16–60 years old) rises. Families with more working-age laborers tend to seek stable income through local non-agricultural employment or cross-regional labor migration. A larger labor force suggests that the family has sufficient labor resources and may not feel an urgent need to turn to e-commerce to supplement income. As a result, they are more likely to maintain traditional agricultural practices rather than expand their market presence through e-commerce.
5.1.2 Results of the ESR model income equation estimation
The third and fourth columns of Table 2 present the income equations, reporting the regression results for farmers participating in e-commerce operations and those not participating. First, regarding personal characteristics, health status positively influences the household income of farmers who do not participate in e-commerce, significant at the 1% level. It also has a positive effect on the income of farmers who participate in e-commerce, although this effect is not statistically significant. This may be because non-participating farmers primarily rely on traditional agriculture or physical labor, where health directly impacts their labor capacity and, consequently, their income. In contrast, farmers involved in e-commerce are likely to focus on online sales, management, customer service, and other tasks that require less physical effort, thereby reducing the influence of health on income. Furthermore, the identity of village cadres positively affects the household income of non-participating farmers at the 10% significance level, but does not significantly impact the income of e-commerce participants. This suggests that for non-e-commerce households reliant on the local market, the social network of village cadres may help facilitate connections with buyers, coordinate transportation, and access other resources, thus enhancing family income. Conversely, E-commerce operators access regional and national markets through e-commerce platforms, reducing their dependence on local social networks and diminishing the marginal influence of cadre status. Regarding household characteristics, for both e-commerce and non-e-commerce operators, non-agricultural employment among family members and the size of cultivated land have a significant positive effect on total household income at the 1% level. The number of effective laborers within a household significantly increases the total income of non-e-commerce farmers at the 1% level but has no significant effect on the income of e-commerce participants. This suggests that labor remains the core production factor in traditional agriculture, where the number of effective laborers plays a crucial role in determining household income. In contrast, e-commerce operations depend more on skills and capital rather than the size of the labor force. The participation of cooperatives significantly increases the total household income of e-commerce operators at the 1% significance level but does not have a significant impact on the income of farmers who do not engage in e-commerce. This may be because cooperatives provide effective support for e-commerce operators in areas such as collective procurement, market expansion, brand development, and resource integration. E-commerce operators typically possess strong technological adoption and market expansion capabilities, allowing the empowerment effect of cooperatives to be more fully realized in the e-commerce sector, thereby significantly enhancing income. In contrast, farmers not engaged in e-commerce may lack the capacity to translate cooperative resources into income growth. Engaging in e-commerce requires infrastructure, technological proficiency, and management capabilities, which are often absent among non-e-commerce farmers. Consequently, cooperative empowerment has little or no significant impact on the income growth of these farmers. Regarding village characteristics, village economic conditions significantly influence household income, both for farmers engaged in e-commerce and those who are not, at the 1% level. Additionally, the geographical location of the village has a significant negative effect on the household income of non-e-commerce farmers at the 1% level, whereas the impact on e-commerce participants is not significant. This discrepancy may be attributed to the greater influence of the urban siphon effect on suburban villages, where non-e-commerce farmers are more reliant on urban employment opportunities. Their income levels are subject to fluctuations in the urban labor market, and urban expansion may drive up land and production costs, further diminishing traditional agricultural benefits. In contrast, e-commerce operators mitigate the impact of location constraints by expanding sales channels through online markets and leveraging the city’s advanced logistics and supply chain infrastructure, which helps maintain a relatively stable income level even in suburban areas.
5.2 Analysis of the treatment effect of participating in e-commerce operations on the total income of farmers’ households
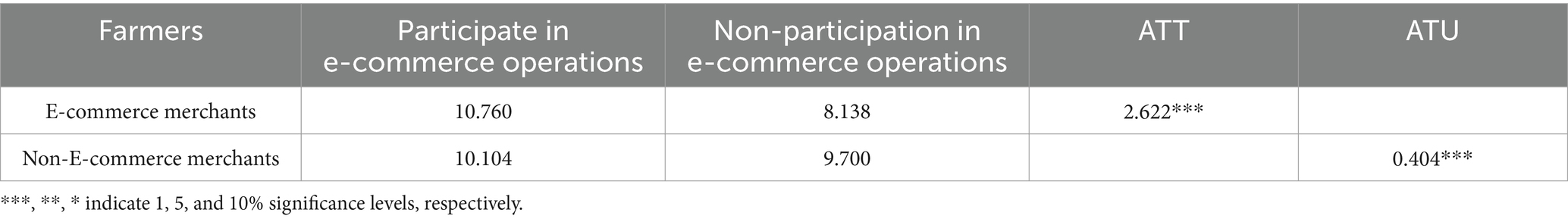
The treatment effect of e-commerce participation on farmers’ total household income is presented in Table 3. The Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) results indicate that e-commerce participation has a statistically significant positive impact on total household income at the 1% significance level. For e-commerce merchants, if they had not participated in e-commerce, their total household income would have decreased by 2.621, representing a decline of 24.35%. Conversely, the Average Treatment Effect on the Untreated (ATU) suggests that if non-e-commerce merchants participated in e-commerce, their total household income would increase by 0.430, corresponding to a rise of 4.24%. These findings demonstrate that e-commerce participation significantly enhances farmers’ income, supporting Hypothesis 1.
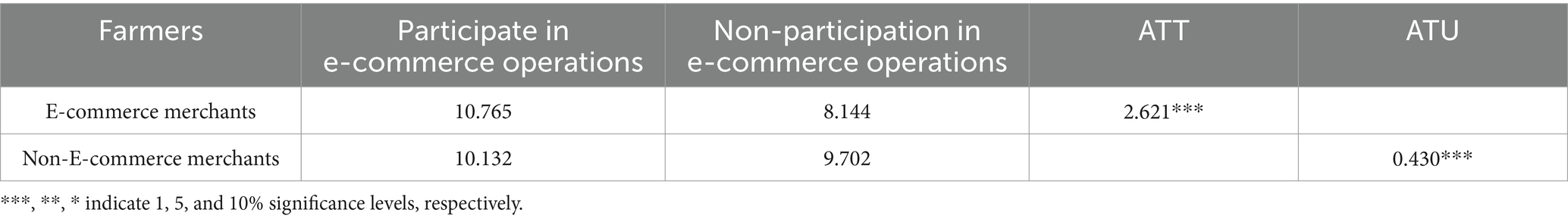
Table 3. Treatment effects of participating in e-commerce operations on the total income of farmers’ households.
5.3 Robustness check
To further verify the robustness of the estimation results of the endogenous switching regression model, this study draws on the methodologies of previous research (Falck et al., 2018; Xue et al., 2022) and conducts robustness checks using three approaches.
1. Robustness Check 1: Winsorization. To eliminate the influence of extreme values, a 5% winsorization is applied to total household income before conducting the analysis. The model is then re-estimated, as presented in Table 4. After implementing a two-sided 5% winsorization on total household income, the estimated treatment effects exhibit only minor variations, and the conclusions remain largely consistent with the findings. Specifically, if e-commerce merchants had not participated in e-commerce operations, their total household income would decrease by 2.622, representing a decline of 24.37%. Conversely, the Average Treatment Effect on the Untreated (ATU) indicates that non-e-commerce merchants, if they were to participate in e-commerce operations, would experience an increase of 0.404 in their total household income, corresponding to a rise of 4.00%.
2. Robustness Check 2: Instrumental Variable Method. First, there may be a causal relationship between participation in e-commerce operations and farmers’ household income, leading to endogeneity issues. Second, endogeneity may arise from omitted variables in the model. To address these two concerns and ensure the robustness of the regression results, the instrumental variable method is employed for robustness testing.
Referring to previous studies, this study uses the proportion of other farmers in the same village engaged in e-commerce operations as an instrumental variable. This variable is correlated with farmers’ participation in e-commerce but is uncorrelated with household income, thus satisfying the criteria for instrumental variables. Table 5 presents the estimation results of the two-stage instrumental variable method. The F-statistic for the weak instrument test is 40.137, exceeding the critical value of 10, which rejects the weak instrument hypothesis. The results indicate that, after addressing potential endogeneity, participation in e-commerce operations significantly enhances farmers’ household income at the 1% level.
1. Robustness Check 3: Replacement of the Core Dependent Variable. In this test, the core dependent variable, total household income, was replaced with household per capita income. The likelihood ratio (LR) statistic was 10.87, which rejects the hypothesis that the behavioral decision equation and the outcome equation are independent at the 1% significance level. In the decision equation, factors such as education level, cultivated land area, non-agricultural employment among family members, average age of family members, and participation in cooperatives all significantly influence farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations. In the income equation, age, health status, village cadre status, non-agricultural employment among family members, cultivated land area, number of effective labor force in the family, average age of family members, village economic level, and geographical location significantly impact the per capita income of farmers not engaged in e-commerce operations. Furthermore, in the income equation for farmers engaged in e-commerce, age, non-agricultural employment among family members, participation in cooperatives, cultivated land area, number of effective labor force in the family, average age of family members, and village economic level all significantly affect per capita income. These results are generally consistent with the earlier model, suggesting the robustness of the estimates. Due to space limitations, only the treatment effect of e-commerce participation on farmers’ per capita household income is reported, as shown in Table 6. If e-commerce merchants had not participated in e-commerce operations, their average treatment effect on their per capita household income would have decreased by 2.137, representing a 22.82% reduction. However, if non-e-commerce merchants had engaged in e-commerce, their average treatment effect on per capita household income would have increased by 0.415, equivalent to a 4.72% rise. The findings are broadly consistent with previous research.
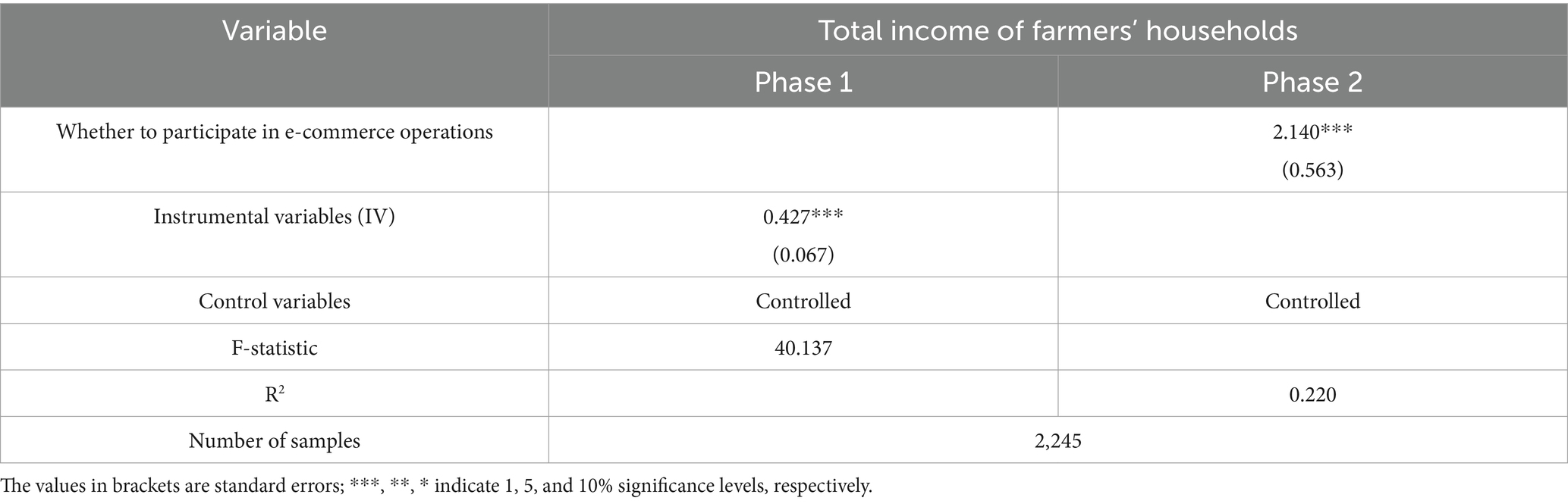
Table 5. Instrumental variable method: the impact of participating in e-commerce operations on the total income of farmers’ households.
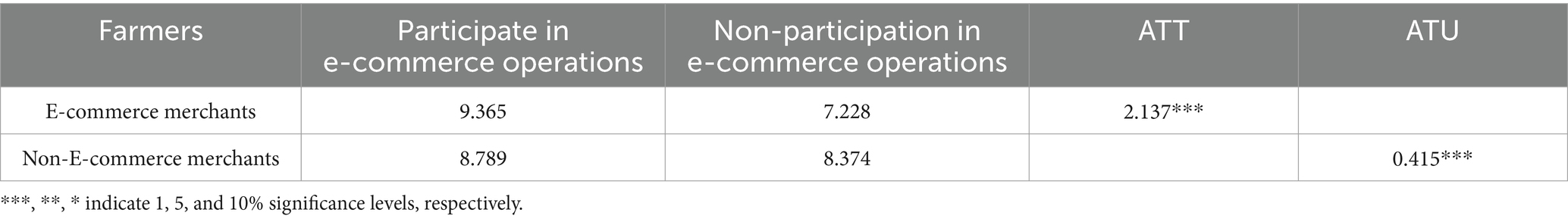
Table 6. Replacement of core variables: treatment effects of participation in e-commerce operations on per capita income of farmers’ households.
5.4 Heterogeneity analysis
This section divides the full sample into low-income and high-income groups based on total household income. The low-income group consists of households whose total income is less than or equal to the sample average, while the high-income group comprises households with total income above the sample average. The treatment effects of participation in e-commerce operations on total household income are estimated separately for these two income groups.
As shown in Table 7, the Average Treatment Effect on the Untreated (ATU) for non-e-commerce merchants, if they participated in e-commerce, would be 0.445 and 0.385 for the low-income and high-income groups, respectively. This indicates that the ATU is larger for the low-income group, suggesting that non-e-commerce merchants in this group would experience a greater increase in household income compared with their high-income counterparts. These findings suggest that participation in e-commerce effectively reduces income disparities among farmers. Conversely, the Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) for e-commerce merchants, if they had not participated in e-commerce, would have been 2.620 and 2.622 for the low-income and high-income groups, respectively. This implies that the decline in household income would be smaller for the low-income group compared with the high-income group, thereby further supporting the significant role of e-commerce participation in narrowing income gaps among farming households.
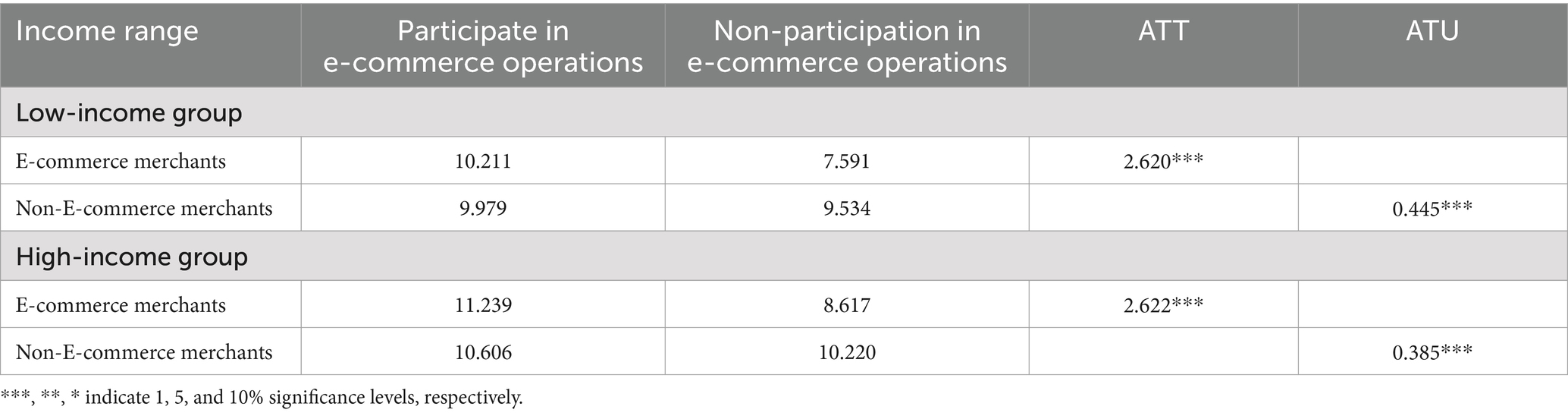
Table 7. Treatment effect of participating in e-commerce business on the total income of farmers in different income ranges.
5.5 Mechanism analysis
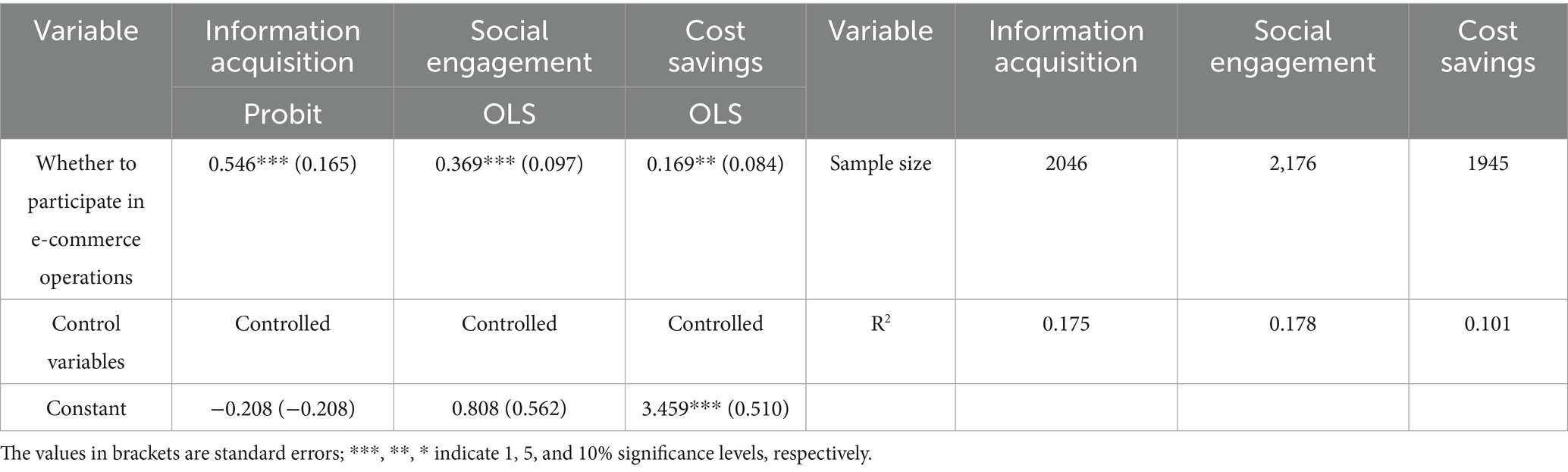
Table 8 presents the results of the mediation effect test. The second column shows that farmers’ participation in e-commerce operations significantly enhances information acquisition at the 1% significance level. This finding suggests that improved access to information serves as a key transmission channel through which e-commerce participation contributes to income growth. Enhanced information acquisition reduces information asymmetry between producers and consumers, facilitates a deeper understanding of market dynamics and price fluctuations, enables timely optimization of production decisions and product structures, expands profit margins, and ultimately increases farmers’ income. The third column indicates that e-commerce participation significantly promotes social engagement at the 1% significance level. By participating in village public affairs, farmers gain more opportunities to access government support policies and technical training, which help them acquire additional production and management resources to increase their income. The fourth column demonstrates that e-commerce participation significantly reduces operating costs at the 5% significance level, highlighting cost savings as an important mechanism through which e-commerce fosters income growth. Farmers engaged in e-commerce are more likely to procure agricultural inputs through online platforms. E-commerce platforms not only reduce intermediaries in transactions, ensuring the rationality of input prices, but also enhance the traceability system to further guarantee the quality of agricultural inputs, thereby reducing agricultural operating costs and increasing farmers’ income. Therefore, Hypothesis 2 is verified.
6 Research conclusions and policy implications
6.1 Research conclusion
The paper uses data from the 2020 China Rural Revitalization Comprehensive Survey and employs an endogenous transformation model to empirically analyze the impact of farmers’ participation in e-commerce on household income. The regression results of the model indicate that if e-commerce merchants had not participated in e-commerce, the Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) on their total household income would decrease by 2.621, representing a decline of 24.35%. Conversely, if non-e-commerce merchants were to participate in e-commerce, the Average Treatment Effect on the Untreated (ATU) would increase by 0.430, corresponding to a rise of 4.24%. This suggests that participation in e-commerce effectively promotes income growth among farmers. The conclusions remain robust after applying winsorization, instrumental variable methods, and replacing core variables. Heterogeneity analysis reveals that, under counterfactual assumptions, the ATU for non-e-commerce merchants participating in e-commerce is 0.445 and 0.385 for the low-income and high-income groups, respectively. This indicates that the ATU is larger for the low-income group, demonstrating that e-commerce participation effectively reduces income disparities among farmers. Similarly, the ATT for e-commerce merchants not participating in e-commerce is 2.620 and 2.622 for the low-income and high-income groups, respectively. This implies that the decline in household income would be smaller for the low-income group compared to the high-income group, further supporting the significant role of e-commerce participation in narrowing income gaps among farming households. Mechanism analysis shows that farmers’ participation in e-commerce primarily promotes income growth through three pathways: enhancing information acquisition capacity, promoting social participation, and saving operating costs.
6.2 Policy implications
Based on the above research findings, the following policy implications can be drawn: First, the government should play a leading role in enhancing the scientific rigor and adaptability of policymaking. This will facilitate the effective integration of small-scale agricultural operators into emerging e-commerce models and establish a complete institutional guarantee system to support rural revitalization. Second, fostering a favorable environment for rural e-commerce development is essential. This includes (1) providing training on e-commerce marketing, business operations, and digital technologies to enhance farmers’ awareness and participation in e-commerce; (2) optimizing rural information networks by expanding broadband access, improving rural road and logistics infrastructure, and offering financial support to enable farmers to engage in e-commerce while leveraging its benefits in information access and cost reduction. Third, Strengthen digital skills education, and form a rural digital education system led by the government, coordinated by enterprises and social entities, and empowered by scientific research institutions. Scientifically improve the comprehensive digital literacy of farmers, eliminate the urban–rural digital divide, actively cultivate e-commerce talents in rural areas, actively support migrant workers and college students returning to their hometowns engage in entrepreneurship and participate in e-commerce operations, attract and retain talents. Leverage the leadership of capable individuals to foster a neighborhood effect, thereby promoting sustained income growth for farmers.
Data availability statement
This study analyzed publicly accessible datasets, which are available in the China Rural Revitalization Survey Database.
Author contributions
MY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by The Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program, grant numbers 10-IAED-08-2025, 10-IAED-RC-04-2025 and also funded by The Key Research Project on Agricultural Science and Technology Strategies in Advanced Countries, grant number Y2025ZZ16.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1597169/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
1. ^Data source: Department of Electronic Commerce, Ministry of Commerce of China.
2. ^Data source: “Statistical Report on the Development of Internet in China” published by China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC).
References
Ahn, H., and Park, E. (2024). The impact of consumers' sustainable electronic-word of-mouth in purchasing sustainable mobility: an analysis from online review comments of e-commerce. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 52:101086. doi: 10.1016/j.rtbm.2023.101086
Biagi, F., and Falk, M. (2017). The impact of ICT and e-commerce on employment in Europe. J. Policy Model 39, 1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.jpolmod.2016.12.004
Chen, S. (2019). The level of public participation and rural construction performance—based on a comparison of two villages in City a, Fujian Province. Popul. Soc. 35, 85–97. doi: 10.14132/j.2095-7963.2019.06.007
Chundakkadan, R., and Sasidharan, S. (2023). The role of government support on E-commerce and firm innovation during pandemic crisis. Econ. Anal. Policy. 78, 904–913. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2023.04.021
Couture, V., Faber, B., Gu, Y., and Liu, L. (2021). Connecting the countryside via e-commerce: evidence from China. Am. Econ. Rev. Insights 3, 35–50. doi: 10.1257/aeri.20190382
Deng, X., Xu, D., Qi, Y., and Zeng, M. (2018). Labor off-farm employment and cropland abandonment in rural China: spatial distribution and empirical analysis. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 15:1808. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15091808
Dong, S., Wang, N., Fan, C., Chen, S., and Zhang, L. (2024). E-commerce and rural women entrepreneurship——based on the quasi-natural experiment of “comprehensive demonstration policy” for E-commerce in rural areas. Econ. Anal. Policy. 83, 749–765. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2024.07.018
Falck, O., Lameli, A., and Ruhose, J. (2018). Cultural biases in migration: estimating non-monetary migration costs. Pap. Reg. Sci. 97, 411–439. doi: 10.1111/pirs.12243
Goldfarb, A., and Catherine, T. (2019). Digital economics. J. Econ. Lit. 57, 3–43. doi: 10.1257/jel.20171452
Han, F., and Li, B. (2020). A new driver of farmers' entrepreneurial intention: findings from e-commerce poverty alleviation. World. Rev. Entrep. Manage. Sustain. Dev. 16, 22–49. doi: 10.1504/WREMSD.2020.105512
He, X., Wu, Y., and Wei, J. (2024). The status of collective action among rural households in underdeveloped regions of China and its livelihood effects under the background of rural revitalization—evidence from a field survey in Shanxi Province. Sustainability 16:6575. doi: 10.3390/su16156575
Huang, Z., Wang, L., and Meng, J. (2024). Does rural e-commerce improve the economic resilience of family farms? Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 95:103505. doi: 10.1016/j.iref.2024.103505
Huang, J., Xu, B., and Yan, X. (2023). Selling mode choice and blockchain adoption in an e-commerce platform with information disclosure. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 62:101331. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2023.101331
Ji, X., Xu, J., and Zhang, H. (2023). Environmental effects of rural e-commerce: a case study of chemical fertilizer reduction in China. J. Environ. Manag. 326:116713. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116713
Jiang, T. (2022). Mediating effects and moderating effects in causal inference. China Ind. Econ. 39, 100–120. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2022.05.005
Jiang, P., and Qin, S. (2024). E-commerce empowers urban entrepreneurial activity—empirical evidence from the construction of national e-commerce demonstration cities. Cities 150:105092. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2024.105092
Kabo-Bah, J. B. W., and Bannor, R. K. (2025). E-commerce among grain traders and its impact on marketing. Sustain. Technol. Entrep. 4:100090. doi: 10.1016/j.stae.2024.100090
Ke, J., Wang, Y., Fan, M., Chen, X., Zhang, W., and Gou, J. (2024). Discovering e-commerce user groups from online comments: an emotional correlation analysis-based clustering method. Comput. Electr. Eng. 113:109035. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2023.109035
Kung, J. K. S. (2002). Off-farm labor markets and the emergence of land rental markets in rural China. J. Comp. Econ. 30, 395–414. doi: 10.1006/jcec.2002.1780
Leong, C., Pan, S. L., Newell, S., and Cui, L. (2016). The emergence of self-organizing E-commerce ecosystems in remote villages of China. Mis. Quart. 40, 475–484. doi: 10.25300/MISQ/2016/40.2.11
Leroux, N., Wortman, M. S. Jr., and Mathias, E. D. (2001). Dominant factors impacting the development of business-to-business (B2B) e-commerce in agriculture. Int. Food. Agribus. Manag. Rev. 4, 205–218. doi: 10.1016/S1096-7508(01)00075-1
Li, H. (2020). E-commerce development, non-agricultural employment transfer and farmers' income growth. Guizhou Soc. Sci. 10, 126–134. doi: 10.13713/j.cnki.cssci.2020.10.018
Li, X., Chen, Z., and Xia, X. (2021a). Spatial spillover effects of participating in E-commerce on farmers' green production awareness——analysis based on the two-zone spatial Durbin model. Aust. J. Agric. Econ. 7, 49–64. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.2021.07.004
Li, X., Guo, H., Jin, S., Ma, W., and Zeng, Y. (2021b). Do farmers gain internet dividends from E-commerce adoption? Evidence from China. Food Policy 101:102024. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2021.102024
Li, W., and He, W. (2024). Revenue-increasing effect of rural e-commerce: a perspective of farmers' market integration and employment growth. Econ. Anal. Policy. 81, 482–493. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2023.12.015
Li, G., and Qin, J. (2022). Income effect of rural E-commerce: empirical evidence from Taobao villages in China. J. Rural. Stud. 96, 129–140. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.10.019
Li, L., Zeng, Y., Ye, Z., and Guo, H. (2021). E-commerce development and urban-rural income gap: evidence from Zhejiang Province, China. Pap. Reg. Sci. 100, 475–495. doi: 10.1111/pirs.12571
Li, Q., Zhu, P., and Zheng, J. (2024). Can participation in e-commerce promote the green production offacility vegetable growers? Based on a micro-survey of five cities and 11 counties in Shandong Province. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 34, 106–118. doi: 10.12062/cpre.20230719
Lin, J., Zhang, Z., and Lv, L. (2019). The impact of program participation on rural household income: evidence from China’s whole village poverty alleviation program. Sustainability 11:1545. doi: 10.3390/su11061545
Liu, S., Jin, Y., and Zheng, F. (2024). Did product certification and e-commerce benefit agricultural producers in China? Food Policy 127:102688. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2024.102688
Liu, M., Min, S., Ma, W., and Liu, T. (2021). The adoption and impact of E-commerce in rural China: application of an endogenous switching regression model. J. Rural. Stud. 83, 106–116. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.02.021
Ma, X., and Gu, X. (2024). New marketing strategy model of E-commerce enterprises in the era of digital economy. Heliyon 10:e29038. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29038
Olsen, M. E. (1972). Social participation and voting turnout: a multivariate analysis. Am. Sociol. Rev. 37, 317–333. doi: 10.2307/2093471
Pen, C., Ma, B., and Zhang, C. (2021). Poverty alleviation through e-commerce: village involvement and demonstration policies in rural China. J. Integr. Agr. 20, 998–1011. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63422-0
Qin, F., Wang, J., and Xu, Q. (2022). How does the digital economy affect farmers’ income?——Evidence from the development of rural E-commerce in China. China Econ. Q. 22, 591–612. doi: 10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2022.02.12
Qiu, Z., and Zhou, Y. (2021). The mechanism of the role of E-commerce in increasing rural household income: an analysis based on a Micro empirical test of the interaction between demand and supply. Chin. Rural. Econ. 4, 36–52. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2021.04.003
Tadesse, G., and Bahiigwa, G. (2015). Mobile phones and farmers’ marketing decisions in Ethiopia. World Dev. 68, 296–307. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.12.010
Tang, L., Chen, M., Tang, Y., and Xiong, Y. (2024). Can E-commerce development alleviate farm household poverty vulnerability: evidence from rural China. Cities 153:105297. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2024.105297
Tang, K., Xiong, Q., and Zhang, F. (2022). Can the E-commercialization improve residents’ income?--evidence from “Taobao counties” in China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 78, 540–553. doi: 10.1016/j.iref.2021.12.019
Tang, W., and Zhu, J. (2020). Informality and rural industry: rethinking the impacts of E-commerce on rural development in China. J. Rural. Stud. 75, 20–29. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2020.02.010
Wang, L., Pertheban, T. R. A., Li, T., and Zhao, L. (2024). Application of business intelligence based on big data in E-commerce data evaluation. Heliyon 10:e38768. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38768
Wang, C., Wang, H., Xia, C., and Ali, A. (2022). Does E-commerce participation increase the use intensity of organic fertilizers in fruit production? Evidence from China. PLoS One 17:e0273160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273160
Wang, H., and Zhu, Y. (2021). Impact of social capital on multi-dimensional poverty of farmers: analysis of intermediary effect based on labor mobility. J. China. Agric. Univ. 26, 240–254. doi: 10.11841/j.issn.1007-4333.2021.04.22
Wei, X., Yang, Z., Yan, Y., and Sun, J. (2024). Rural E-commerce, digital finance, and urban–rural common prosperity: a quasi-natural experiment based on China's comprehensive demonstration of E-commerce entering rural areas policy. Financ. Res. Lett. 69:106237. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2024.106237
Wei, B., Zhao, C., and Luo, M. (2024). Online markets, offline happiness: E-commerce development and subjective well-being in rural China. China Econ. Rev. 87:102247. doi: 10.1016/j.chieco.2024.102247
Xu, X., Fan, R., Wang, D., Wang, Y., and Wang, Y. (2024). The role of consumer reviews in e-commerce platform credit supervision: a signaling game model based on complex network. Electron. Commer. Res. Appl. 63:101347. doi: 10.1016/j.elerap.2023.101347
Xue, P., Han, X., Wang, Y., and Wang, X. (2022). Can agricultural machinery harvesting services reduce cropland abandonment? Evidence from rural China. Agriculture 12:901. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12070901
Yan, T., He, K., and Zhang, J. (2016). Analysis of social capital influencing farmers’ willingness of environmental protection investment: evidence from empirical study on reusing agricultural wastes in Hubei rural areas. China population, resources and environment. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 26, 158–164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2104.2016.01.021
Yang, R., Liu, J., Cao, S., Sun, W., and Kong, F. (2024). Impacts of Agri-food E-commerce on traditional wholesale industry: evidence from China. J. Integr. Agr. 23, 1409–1428. doi: 10.1016/j.jia.2023.10.020
Yao, L., Yi, F., and Sun, Y. (2022). Rural E-commerce and digital inclusive finance synergize to Promote County economic growth. Res. Financ. Econ. Issues. 11, 67–76. doi: 10.19654/j.cnki.cjwtyj.2022.11.007
Yu, A., Cao, J., She, H., and Li, J. (2023). Unveiling the impact of E-commerce on smallholder livestock marketing: insights on egg price premiums and mechanisms. Econ. Anal. Policy. 80, 1582–1596. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2023.10.024
Zaghloul, M., Barakat, S., and Rezk, A. (2024). Predicting E-commerce customer satisfaction: traditional machine learning vs. deep learning approaches. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 79:103865. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2024.103865
Zanello, G., and Srinivasan, C. S. (2014). Information sources, ICTs and price information in rural agricultural markets. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 26, 815–831. doi: 10.1057/ejdr.2014.1
Zeng, S., Fu, Q., Haleem, F., Han, Y., and Zhou, L. (2023). Logistics density, E-commerce and high-quality economic development: an empirical analysis based on provincial panel data in China. J. Clean. Prod. 426:138871. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138871
Zeng, Y., Li, B., Li, L., and Zhang, G. (2024). The drivers and income effect of big data use by e-commerce farmers: evidence from China. Electron. Commer. Res. doi: 10.1007/s10660-024-09914-6
Zhai, M., and Chen, Y. (2023). How do relational bonds affect user engagement in e-commerce livestreaming? The mediating role of trust. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 71:103239. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103239
Zhang, L., and Han, L. (2017). Has E-commerce economy development expanded urban-ural residents income gap? Res. Econ. Manag. 38, 3–13. doi: 10.13502/j.cnki.issn1000-7636.2017.05.001
Zhang, N., Yang, W., and Ke, H. (2024). Does rural e-commerce drive up incomes for rural residents? Evidence from Taobao villages in China. Econ. Anal. Policy 82, 976–998. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2024.04.023
Zhang, L., Zhang, Z., and Liu, T. (2024). Can E-commerce participation promote quality certification of agricultural products among farmers?——An analysis of apple-producing farmers in the loess plateau advantageous region. J. Northwest. A. F. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Edit). 24, 127–136. doi: 10.13968/j.cnki.1009-9107.2024.04.13
Zhang, Y., Zhang, T., and Yan, X. (2024). Understanding impulse buying in short video live E-commerce: the perspective of consumer vulnerability and product type. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 79:103853. doi: 10.1016/j.jretconser.2024.103853
Zhao, Z., Liu, R., and Wang, Q. (2024). Place-based polices and e-commerce development in rural China. China Econ. Rev. 83:102085. doi: 10.1016/j.chieco.2023.102085
Zhao, C., Tang, M., and Wang, C. (2025). How social integration affects the income of relocated households: evidence from China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8, 8–24. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1520548
Keywords: rural e-commerce, e-commerce operations, farmers, income growth, income growth channels
Citation: Yin M, Han X, Yan Y and Wang X (2025) Can farmers increase their income by participating in e-commerce? Evidence from rural China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1597169. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1597169
Edited by:
Rose Nyikal, University of Nairobi, KenyaReviewed by:
Pengfei Cheng, Jeonbuk National University, Republic of KoreaHui Wang, Beijing Forestry University, China
Copyright © 2025 Yin, Han, Yan and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiudong Wang, d2FuZ3hpdWRvbmdAY2Fhcy5jbg==
 Mingyang Yin
Mingyang Yin Xinru Han
Xinru Han Yan Yan
Yan Yan Xiudong Wang
Xiudong Wang