- 1School of History and Culture, Linyi University, Linyi, China
- 2School of Tourism, Hunan Normal University, Changsha, China
- 3Department of Geography and Environment, Faculty of Human Sciences, Education University of Sultan Idris, Tanjong Malim, Perak, Malaysia
- 4Department of Economics, Faculty of Management and Economics, Education University of Sultan Idris, Tanjong Malim, Perak, Malaysia
- 5School of Art, Ningxia Normal University, Guyuan, China
This study examines the mechanisms underlying the formation and development of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters, using Lanling County in China as a representative case. It addresses how localized innovation strategies contribute to rural industrial transformation within the broader context of national agricultural modernization. Employing a qualitative case study approach, the research integrates field observations, semi-structured interviews, and document analysis. The analytical framework is informed by industrial cluster theory and the regional innovation systems perspective. The study identifies and examines the interactive dynamics among four major drivers: natural and socioeconomic resource endowments, market demand, policy support, and technological innovation. The findings reveal that the emergence and consolidation of the Lanling vegetable innovation cluster is the outcome of synergetic interactions between endogenous innovation capabilities and exogenous enabling conditions. Strategic interventions—such as the construction of intelligent greenhouses, the expansion of specialized production bases, cooperative organization development, and the implementation of quality control systems—have collectively advanced the region's agricultural upgrading. The study contributes to theoretical discourse by extending cluster theory to the agricultural sector and illustrating the applicability of regional innovation systems in rural contexts. Practically, it offers policy-relevant pathways including the enhancement of technological service networks, market responsiveness, environmental governance, and enterprise collaboration. The research provides replicable insights for other regions seeking to promote sustainable agricultural transformation through innovation-driven development.
1 Introduction
The theory of industrial clusters, as advanced by Michael Porter, represents a significant extension of Alfred Marshall's notion of localized industrial specialization (Lepori, 2022). In Warr (1994), Porter formally introduced the concept of industrial clusters, arguing that the spatial concentration of interconnected firms and institutions enhances regional competitiveness through innovation and productivity (Yellice and Türko, 2023). Building on this foundation, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) released its landmark report Boosting Innovation: The Cluster Approach in 1999, which formally conceptualized the idea of “innovation clusters,” emphasizing their pivotal role in driving technological progress and economic development (Kowalski and Mackiewicz, 2021).
In recent years, with increasing attention on the transformative role of science and technology in agricultural modernization (Yadav et al., 2023), a key challenge has emerged: how to integrate the fragmented innovation elements in agriculture (Annosi et al., 2022)—such as R&D, technological diffusion, production systems, and enterprise participation—into a cohesive and dynamic innovation ecosystem. Addressing this challenge is critical not only for enhancing the overall functionality of agricultural systems but also for advancing regional economic development and sustainable agricultural practices (Adisa et al., 2024). As the awareness of the agglomeration effect of innovation in agriculture deepens, the formation and evolution of science and technology-based agricultural clusters has become a prominent topic in both theoretical and empirical research.
Existing research on regional innovation systems has largely focused on industrial and urban contexts, often neglecting the agricultural sector and its particular dynamics in rural regions. This study addresses this gap by investigating how agricultural innovation clusters develop under conditions shaped by local resources, social networks, market dynamics, and institutional arrangements. Using Lanling County as a case study, the research extends the theoretical scope of regional innovation models by showing how rural innovation systems integrate both endogenous capacities and exogenous supports. This provides a more comprehensive understanding of innovation processes in agri-based economies and highlights the adaptive mechanisms through which rural areas foster sustainable development.
This study, therefore, seeks to systematically examine the driving mechanisms behind the formation of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters, with a particular focus on Lanling County, China—a region that has developed a strong specialization in vegetable production. Based on extensive field research, it is observed that Lanling County has entered a new stage of cluster-based development. In response to both domestic and international market demands, the county has proactively leveraged advanced agricultural technologies to enhance the technological content of its vegetable industry. These efforts have culminated in a comprehensive industrial upgrade and the emergence of a well-defined innovation cluster in the vegetable sector, characterized by synergistic integration of enterprises, research institutions, and service organizations.
This study centers on the following scientific question: What are the principal internal and external forces driving the emergence, evolution, and consolidation of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County? By addressing this question, the research seeks to uncover the underlying structural and functional mechanisms that shape innovation-led agricultural clustering. The findings are intended to generate both theoretical contributions to the understanding of rural innovation systems and practical guidance for regional agricultural policy, ultimately aiming to improve productivity, promote sustainability, and strengthen the competitiveness of China's rural economy.
2 The concept and connotation of agricultural industry clusters driven by technological innovation
Agricultural industry clusters, as defined by the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), refer to geographically proximate groups of enterprises and complementary institutions engaged in the production and processing of agricultural products (Medeiros, 2021). These entities form an organic system centered around agricultural production bases through interlinked relationships based on shared or complementary functions. This framework highlights the spatial agglomeration and network-based cooperation among agricultural actors (Wei and Chen, 2024). Agricultural industry clusters into three core sub-clusters: agricultural production, food processing, and agricultural input manufacturing (Foutakis, 2025). This classification has provided a foundational structure for empirical research in North American and European contexts.
From the perspective of innovation dynamics, innovation clusters as networks of collaboration between research institutions and industry actors, jointly engaged in technological development and knowledge exchange (Fioravanti et al., 2023). According to the OECD's innovation systems approach, such clusters emerge from complex and continuous interactions among firms, research institutions, educational bodies, and public administration (Klarin et al., 2021). These are referred to as technologically linked innovation clusters, embedded within broader regional innovation ecosystems (Sandoval Hamón et al., 2024). A key feature distinguishing innovation clusters from conventional industrial clusters lies in their intrinsic capacity for generating new knowledge and products (Pinto et al., 2023). Innovation clusters are characterized not only by spatial proximity and industrial specialization but also by knowledge flows, institutional infrastructure, and multi-actor collaboration (Bravaglieri et al., 2025). Within this context, the concept of science and technology innovation clusters denote territorially concentrated networks of scientific and technological resources—including research outputs, projects, and talent—that interact synergistically through shared innovation goals (Rodríguez Ochoa et al., 2025). These clusters facilitate the mobility of knowledge, the co-creation of technologies, and the institutionalization of feedback mechanisms among scientific, technological, and socio-economic agents (Bianchi and Grippi, 2025).
In the agricultural sector, the growing integration of technological innovation has fundamentally transformed traditional industrial cluster structures, giving rise to what is now termed agricultural science and technology innovation clusters (Chen and Li, 2022). These clusters represent a higher stage in the evolution of agricultural industrial clusters, marked by the spatial agglomeration of innovative agricultural entities and the establishment of dynamic linkages with external systems of knowledge, finance, and governance (Bittencourt et al., 2023). An agricultural science and technology innovation cluster can be understood as a spatially organized, innovation-oriented agri-technological network system, where scientific and technological inputs are concentrated, and collaborative interactions are institutionalized. These clusters apply cutting-edge agricultural science and technology to develop new products, adopt modern production methods, and optimize management models, thereby improving the quality and competitiveness of agricultural outputs. In addition to upgrading traditional agricultural industrial clusters, these innovation clusters encompass agricultural science parks, functional agricultural zones, and science-driven agri-innovation ecosystems. The coordinated integration of agricultural innovation with regional planning enhances the formation and growth of such clusters. Ultimately, this convergence facilitates the emergence of comprehensive agricultural innovation complexes, serving as hubs for sustainable rural development and global agri-tech competitiveness.
3 Data collection and analytical procedures
Lanling County, located in Shandong Province, is widely recognized as one of China's leading agricultural production bases, particularly known for its vegetable industry. The county benefits from abundant natural resources, a favorable climate, well-developed agricultural infrastructure, and a long-standing tradition of market-oriented farming. In recent years, Lanling has emerged as a prominent example of an agricultural innovation cluster, characterized by the integration of advanced technologies, cooperative networks, and supportive policy frameworks.
The selection of Lanling County as a case study inevitably raises questions about representativeness and the potential for selection bias. While Lanling represents a highly successful and mature cluster that may not fully reflect conditions in less developed regions, it was intentionally chosen as a critical case to illuminate the mechanisms and enabling conditions behind the formation and consolidation of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters. Rather than constituting a singular outlier, Lanling can be understood as a frontrunner within broader national trends of rural innovation and agricultural modernization, especially under China's rural revitalization strategy. Although the study does not claim universal applicability, it aims to generate transferable insights and hypotheses that can inform comparative research and offer practical lessons for cluster development in diverse regional contexts, both within China and internationally.
The study employed a qualitative case study approach, combining field observations, semi-structured interviews, and document analysis to investigate the formation and dynamics of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County. The interview sample was purposefully designed to capture a broad range of stakeholder experiences. By including farmers, cooperative leaders, enterprise managers, and local government officials, the study ensured that multiple voices were heard, allowing for a more comprehensive understanding of the innovation cluster's development from the ground up. A total of 28 interviews were conducted between November and December 2024 with key stakeholders, including farmers, cooperative leaders, enterprise managers, local government officials, and technical extension agents. The interviews, which ranged from 45 to 90 min, were audio-recorded with the participants' consent and subsequently transcribed in full. The collected data were analyzed thematically using a combination of inductive and deductive approaches. Themes were identified through multiple coding rounds, with the aid of NVivo qualitative analysis software, to ensure consistency and rigor in data interpretation. To enhance validity, triangulation was achieved by integrating interview data with secondary sources, including local government reports, statistical yearbooks, and relevant policy documents. This methodological design provides a robust basis for understanding the mechanisms driving agricultural innovation clustering in the local context.
The data analysis process followed a rigorous thematic analysis framework. After completing the transcription of interview recordings, the research team conducted an initial open coding phase to identify emergent categories and patterns within the data. This was followed by axial coding, which allowed for the clustering of related codes into broader thematic categories aligned with the study's research questions. Throughout this process, NVivo software was employed to organize, code, and manage the qualitative data, enhancing analytical transparency and traceability. To ensure the credibility and consistency of coding, two researchers independently coded a subset of transcripts and resolved discrepancies through discussion and consensus. The analysis also incorporated constant comparison techniques, whereby insights from interview data were systematically cross-checked against field notes, policy documents, and statistical reports to refine interpretations. This multi-layered analytical approach enabled the study to capture the complexity of interactions among actors, institutions, and technologies in the development of agricultural innovation clusters.
To ensure the reliability and validity of the study, several methodological strategies were employed. First, data triangulation was used by integrating multiple sources of evidence, including interview data, field observations, government reports, and statistical records, which allowed for cross-verification of key findings. Second, investigator triangulation was applied during the coding process, with two researchers independently coding a subset of transcripts and subsequently discussing any discrepancies until consensus was reached, thus enhancing coding reliability. Third, member checking was conducted by sharing preliminary findings with selected interview participants to confirm the accuracy and credibility of the interpretations. Finally, detailed documentation of the research procedures and analytic decisions was maintained throughout the study, ensuring transparency and enabling future replication. These combined strategies contributed to strengthening the study's methodological rigor and ensuring the trustworthiness of its conclusions.
4 Typologies of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County, China
The classification of agricultural industry clusters varies depending on the criteria adopted. A review of existing literature reveals multiple typologies based on spatial distribution, industrial organization, and technological attributes. While the emergence of high-tech agricultural clusters built on technological and professional advantages (Li et al., 2022). Currently, three mainstream forms of agricultural clusters have gained significant attention in China: agricultural high-tech parks, leading-enterprise-driven clusters, and market-oriented clusters (Wan, 2022).
Some scholars' application of cluster life cycle theory to the agricultural sector offers an additional perspective, dividing the development of agricultural clusters into four stages: emergence, growth, maturity, and decline (Ostapenko et al., 2024). As agricultural clusters enter the mature stage, technological innovation becomes essential to extend the cluster's life cycle and avoid stagnation. In this context, agricultural science and technology innovation clusters serve as strategic vehicles for upgrading traditional agglomerations.
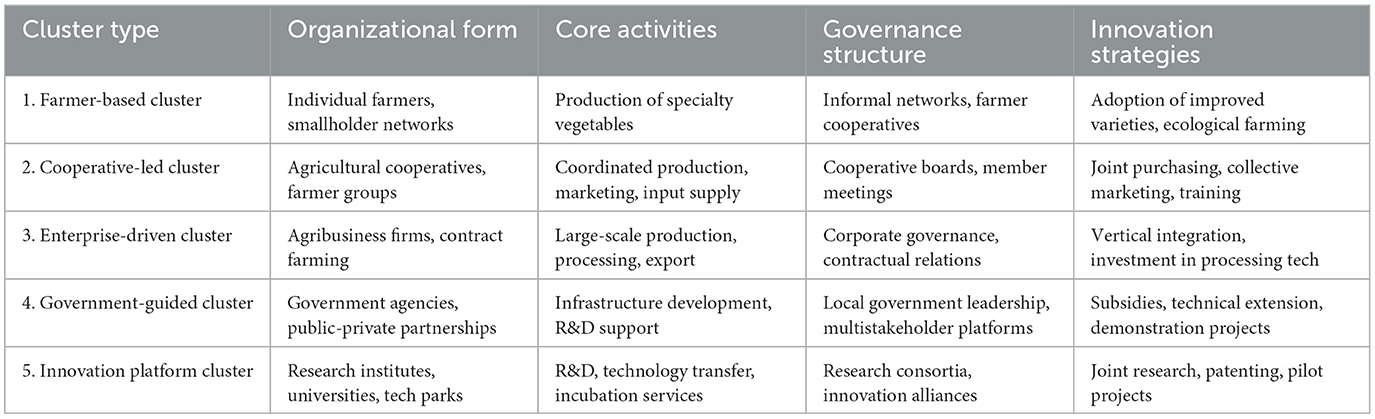
Spatial-temporal categorization of innovation clusters provides further nuance (Wang et al., 2025), while contemporary Chinese scholars have expanded these frameworks by incorporating spatial distribution and techno-economic dimensions. Drawing from both domestic and international studies, this section classifies the vegetable industry cluster in Lanling County into the following five types. To facilitate a clearer understanding of the diversity and organizational dynamics of agricultural innovation clusters in Lanling County, Table 1 provides a comparative summary of the five identified cluster types. The table outlines their main organizational forms, core activities, governance arrangements, and innovation strategies.
4.1 Market-driven clusters
These clusters are characterized by the formation of specialized agricultural markets linked with households and supply/distribution networks. Lanling County currently hosts over 30 specialized vegetable markets, including the prominent Lunan Wholesale Market, with an annual transaction volume exceeding 800 million kilograms. These markets have established stable trade relationships with major urban centers such as Shanghai, Suzhou, and Wuxi. Notable examples include the Changcheng Chili Market, Tianma Winter Melon Market, and Zhuangwu Export Vegetable Market. These trading hubs have accelerated the development of specialized vegetable production zones.
4.2 Leading enterprise-driven clusters
These clusters are formed through the coordination between leading enterprises and farmers, creating loosely or tightly integrated production communities. Companies such as Huangpu Group, Yixing, and Shenda have established vertically integrated value chains encompassing storage, preservation, processing, and logistics. By linking domestic and international markets, these enterprises drive industrial upgrading and foster technology adoption in the vegetable sector.
4.3 Cooperative organization-driven clusters
These clusters rely on cooperative societies or associations that connect farmers with enterprises and markets. Guided by the Farmers' Specialized Cooperatives Law, Lanling County has actively promoted the development of economic cooperation organizations in key vegetable-producing towns. These cooperatives have enhanced farmer organization levels and facilitated contract farming and export-oriented production. One example is the Huibao Cooperative in Shangyan Town, which has successfully linked farmers to stable distribution channels.
4.4 Intermediary- and contract-based clusters
These clusters involve intermediary agencies or agents that serve as coordinators between enterprises and farmers through contract farming arrangements. Since 1999, companies like Nanyuan and Xincheng in Nanqiao Town have signed annual contracts with large buyers such as Shanghai's Baishi Corporation. These agreements involve capital investment, seed provision, and guaranteed purchase prices, promoting the scale-up of contract-based production. By 2023, Lanling County had developed 7,000 hectares of contract-grown vegetables.
4.5 Export-oriented specialization clusters
These clusters are built on aligning foreign market demands with the county's comparative advantages—such as favorable natural conditions, labor intensity, and green certification. For example, Zhuangwu Town has established export-oriented production bases through partnerships with companies like Haidu and Yuanye. These firms import high-quality seed varieties, organize local production, and process the vegetables for export, thus forming an “externally driven” value chain. Zhuangwu has since emerged as a major hub for vegetable export in the region.
This diversified cluster typology not only reflects the multi-scalar and multi-actor nature of agricultural innovation in Lanling County but also illustrates how technology, organization, and market forces interact to shape regionally embedded innovation ecosystems. Understanding these forms provides critical insight into the structural composition and functional mechanisms of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in China's rural economy.
5 Driving mechanisms behind the formation of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County, China
The formation and evolution of agricultural innovation clusters are influenced by a complex interplay of natural endowments, market dynamics, policy interventions, and technological advancement (Annosi et al., 2022). Western scholarship has identified several core drivers—such as geographic and cultural contexts, consumer demand, competitive pressure, and institutional support—as fundamental to cluster development (Rocha and Audretsch, 2022). In particular, the knowledge spillover effect, cumulative learning processes, and paradigm shifts in technology are widely recognized as critical catalysts for innovation clustering (Song et al., 2022).
Drawing from these theoretical frameworks, this section analyzes the driving mechanisms that have underpinned the formation of the agricultural science and technology innovation cluster in Lanling County (Figure 1). Four key forces are identified: resource endowment, market demand, policy and planning, and technological innovation.
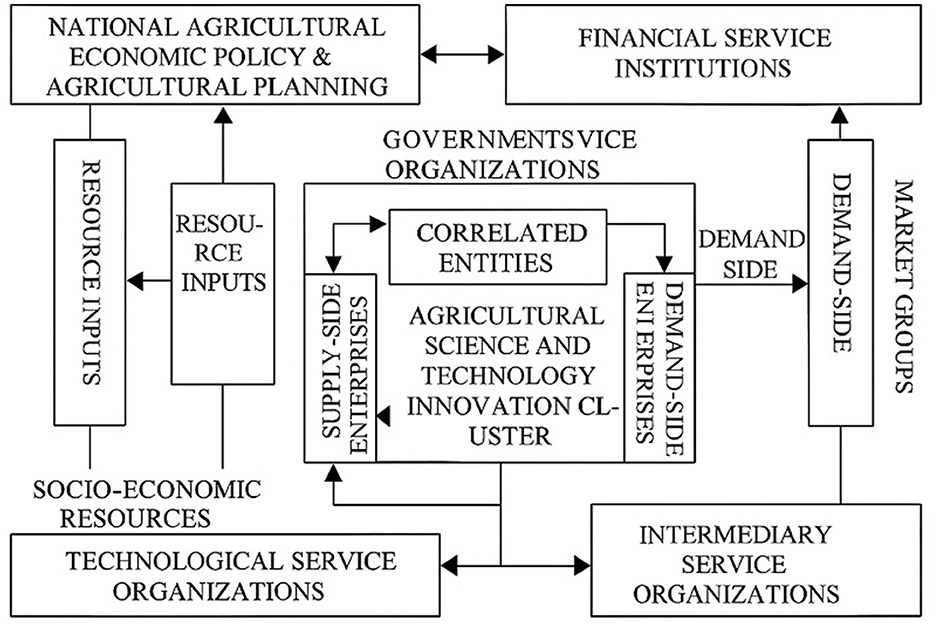
Figure 1. Driving mechanisms behind the formation of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County, China.
5.1 Resource endowment: the foundational basis for cluster formation
Agricultural production is inherently shaped by natural resource conditions, which guide spatial distribution and determine geographic advantages. In a market economy, firms facing competitive pressures and seeking profit maximization are compelled to optimize land use according to resource availability. Resource endowments can be categorized into two types: (1) natural resources—including soil quality, climate, topography, water availability, and geographical location; and (2) socioeconomic resources, such as capital, labor, and knowledge.
Lanling County is uniquely endowed in both respects. It features a diversified landscape of northern hills and southern lowlands, a warm temperate monsoon climate with sufficient sunlight, fertile soil, and clean, abundant water resources. The average annual temperature is 14.4°C, with ~2,473 h of sunshine and 202 frost-free days, making it highly suitable for vegetable cultivation. Moreover, with a population of over 1.16 million and a long-standing tradition in vegetable farming, the region benefits from a rich pool of skilled labor and adaptive knowledge systems. These conditions form the ecological and human capital foundation for innovation-driven cluster development.
Local stakeholders repeatedly emphasized the importance of these resource endowments in interviews. As one farmer noted, “Our soil is fertile and easy to work with, and the climate gives us a long growing season—this is what allows us to produce vegetables that are in high demand even outside the province.” A cooperative leader commented, “The local farming community has accumulated generations of experience in vegetable cultivation, so when new technologies or practices are introduced, people here are quick to learn and adapt.” A government official highlighted, “What makes Lanling competitive is not just the natural conditions, but also the people—hardworking farmers and innovative entrepreneurs who are willing to experiment and improve.” These perspectives underscore that the region's innovation potential stems from the dynamic interplay between ecological advantages and a vibrant, knowledge-rich local workforce.
5.2 Market demand: the primary external driver
The vertical deepening of social division of labor and the expansion of market-oriented agriculture have fueled the rise of large-scale, specialized production zones. As economic growth and urbanization accelerate, stable consumer markets have emerged, both domestically and internationally, creating sustained demand for high-quality agricultural products. The development of specialized agricultural markets in Lanling County has triggered value chain integration, facilitating the alignment of production, logistics, and consumption.
Local stakeholders highlighted how these market dynamics have transformed their operations. A vegetable farmer explained, “We used to sell mainly to local markets, but now, with buyers from big cities and even abroad, we have to upgrade our production methods to meet their standards.” An enterprise manager remarked, “Customized supply chains and contract farming have become the norm here—clients want specific varieties, sizes, and packaging, and we need to coordinate tightly with farmers to deliver on time.” A government official observed, “The development of specialized wholesale markets and cold-chain logistics has not only expanded sales channels but also pushed farmers and enterprises to adopt better technologies, from precision irrigation to improved seed varieties.”
This market pull mechanism has not only promoted economies of scale and agglomeration but also reinforced the need for technological upgrades to meet increasingly differentiated consumer preferences. The proliferation of contract farming, customized supply chains, and export-oriented production has significantly shaped the cluster's industrial structure, embedding technological and organizational innovation deeply within the local agricultural system.
5.3 Government policy and planning: the institutional driver
State policies and strategic planning play a guiding and enabling role in cluster formation, particularly in developing economies. The Chinese government has actively supported regional specialization and modernization through targeted subsidies, infrastructure investment, and agricultural science promotion. In Lanling County, local authorities have leveraged national agricultural industrialization policies to channel resources—land, labor, and capital—toward high-potential sectors.
Local stakeholders consistently underscored the significance of government action. A vegetable farmer noted, “Without government subsidies, we couldn't afford the drip irrigation systems or greenhouses that have boosted our yields so much in recent years.” A cooperative leader observed, “The government's support in setting up cooperatives has been critical—it's allowed small farmers like us to pool resources, access markets, and share new techniques.” An enterprise manager remarked, “Public investment in logistics and cold-chain infrastructure has transformed how we do business, making it possible to ship fresh vegetables across the country and even export them.” A government official reflected, “Our goal is to create the right environment for innovation—by improving roads, supporting agricultural R&D, and offering training programs, we help farmers and companies build competitive capacity.”
Through financial incentives, land-use planning, and institutional support (e.g., cooperatives and technology extension services), the government has helped to reduce coordination costs, mitigate market failures, and strengthen regional comparative advantages. While public intervention cannot substitute for market mechanisms, it plays a vital role in overcoming structural bottlenecks, facilitating public-private partnerships, and promoting collective learning among actors in the cluster.
5.4 Technological innovation: the core internal engine
Technological innovation functions as the core endogenous driver of agricultural innovation clusters, particularly in the polarization stage of development. Advances in biotechnology, precision agriculture, cold chain logistics, and intelligent monitoring systems have reshaped the spatial logic of agricultural production and expanded the scope of high-value cultivation zones.
Stakeholders in Lanling County vividly described the transformative role of technology in interviews. A farmer shared, “The improved seed varieties we use now are much more resilient to pests and weather changes, which means we can plant on land that wasn't suitable before.” A cooperative leader added, “Precision irrigation and greenhouse monitoring systems have allowed us to reduce input costs while improving product quality—this has been a game changer for smallholders.” An enterprise manager explained, “With new cold chain logistics, we can reach markets in big cities and even export fresh produce without worrying about spoilage, which has opened up entirely new opportunities for growth.” A local researcher emphasized, “Our breeding programs are not just about yield but about tailoring crops to local conditions, ensuring that innovation is relevant and applicable on the ground.”
On one hand, scientific breakthroughs in seed quality and crop traits have redefined the ecological adaptability of farming practices, enabling expansion into new geographies. On the other hand, technological progress in storage, processing, and distribution has enhanced the functional integration of the agricultural supply chain, making region-specific specialization more viable.
Furthermore, innovation generates competitive differentiation, creating first-mover advantages for pioneering firms. As new technologies diffuse through demonstration effects and imitation, they promote the cumulative upgrading of the cluster. Due to the spatial stickiness of knowledge spillovers, proximity to innovation sources becomes increasingly important, thereby reinforcing the cluster's spatial concentration and institutional cohesion.
This cumulative feedback loop—where innovation leads to agglomeration, which in turn facilitates more innovation—is consistent with the dynamics described in regional innovation systems (RIS) and technological trajectory theories. In the case of Lanling County, this cycle has supported the emergence of a tightly integrated, innovation-led vegetable industry cluster.
6 Strategic pathways for advancing agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County
The development of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters in Lanling County is shaped by a dynamic interaction of inflow, outflow, and multiplier effects. These forces jointly influence the spatial concentration of innovation factors, the dissemination of knowledge, and the amplification of economic and social value across the region. In order to further strengthen and expand the cluster, it is necessary to optimize its internal structure by improving the key elements linked to the main driving mechanisms. Enhancing cluster cohesion, reinforcing innovation linkages, and upgrading technological infrastructure are fundamental to achieving sustainable growth and competitiveness in agriculture.
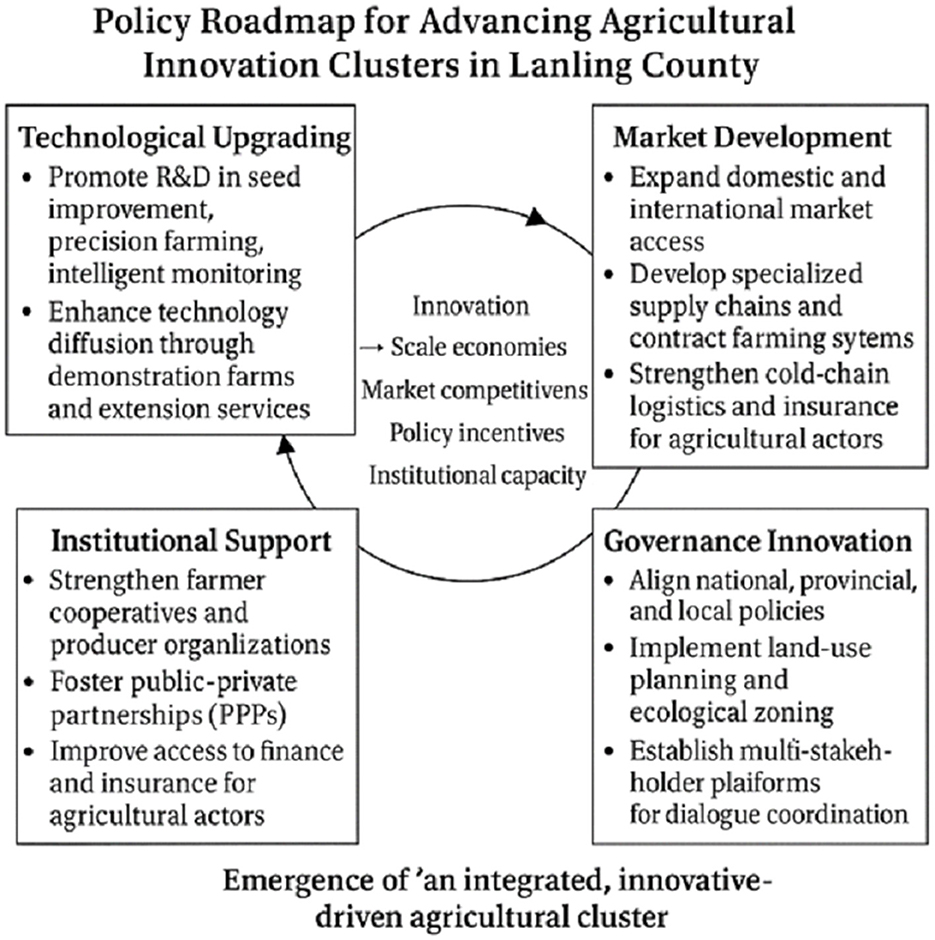
To improve the accessibility and policy relevance of the strategic pathways, a conceptual framework has been developed to visually summarize the main findings. As shown in Figure 2, the framework integrates four interrelated domains—technological upgrading, market development, institutional support, and governance innovation—that together drive the emergence and consolidation of agricultural innovation clusters. By mapping the interactions and feedback loops among these dimensions, the framework provides a practical roadmap for policymakers and development practitioners seeking to promote agricultural modernization and rural transformation in China and beyond.
6.1 Strengthening production bases to enhance the scale and quality of vegetable cultivation
To build a more robust foundation for agricultural clustering, it is imperative to strengthen the construction of high-quality vegetable production bases. This involves formulating long-term development plans, optimizing regional planting structures, and promoting specialized cultivation at the township and village levels. Emphasis should be placed on leveraging the county's natural advantages to expand base areas, introduce superior vegetable varieties, and develop intelligent greenhouse systems. At the same time, demonstration zones focusing on early-, peak-, and off-season vegetable cultivation should be established to support experimental application of novel breeding techniques and advanced agronomic practices. Ecological approaches such as biogas utilization and organic cultivation methods also play a critical role in promoting green production. With the support of leading enterprises and coordinated government planning, these bases have become platforms for regional innovation diffusion, enabling large-scale, standardized, and modernized vegetable production.
6.2 Enhancing market responsiveness and improving product quality
Improving the responsiveness of agricultural production to evolving market demands is essential for sustaining the competitiveness of the cluster. This requires the construction of a multi-tiered technical service system, integrating county-level coordination, township-level implementation, and village-level outreach. By strengthening the linkage between market information, production guidance, and technology extension, farmers can be equipped with the necessary tools to adjust their practices to shifting consumer preferences. The integration of modern technologies—such as precision fertilization, micro-irrigation, biological pest control, seedling automation, and soilless cultivation—can significantly enhance production efficiency and product quality. In parallel, quality assurance mechanisms must be improved through the establishment of regular testing, rapid quality inspection stations, and environmental monitoring networks. These efforts not only ensure food safety but also protect the ecological integrity of major production zones. By aligning production with quality standards and consumer expectations, Lanling County can further consolidate its reputation as a leading supplier of premium vegetables.
6.3 Advancing technological innovation to increase value and productivity
Accelerating the application of agricultural science and technology is vital for enhancing the innovation capacity of the cluster. A comprehensive technology service network should be developed, linking public institutions, agricultural enterprises, and grassroots organizations to form an integrated system that supports continuous learning and technology dissemination. The promotion of high-quality varieties, expansion of protected agriculture (particularly greenhouse systems), and integration of multiple advanced technologies into production processes can effectively drive the modernization of vegetable cultivation. Furthermore, collaboration with specialized institutions—such as the Shandong Agricultural Product Quality Supervision Center—will facilitate the establishment of a more robust monitoring and evaluation system. Technological upgrading not only enhances production efficiency but also lays the groundwork for a knowledge-based, innovation-driven rural economy.
6.4 Creating a supportive policy and institutional environment
Government intervention is essential in providing strategic direction and cultivating an enabling environment for innovation clusters. Policymakers must develop scientifically grounded plans for the growth of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters, identify leading sectors based on local strengths, and prioritize infrastructure investment to support logistics, storage, and irrigation systems. At the same time, regulatory frameworks and policy instruments should be refined to facilitate inter-firm trust, coordinated development, and positive competitive dynamics. An open, transparent, and innovation-friendly institutional environment encourages cooperation among cluster participants, reduces transaction costs, and supports long-term collaboration between public and private actors. By aligning policy incentives with development goals, the government can effectively stimulate endogenous innovation and ensure the sustainable evolution of the cluster.
6.5 Developing circulation channels to support industrialized operations
A well-functioning market system is a cornerstone of cluster industrialization. The rational planning and restructuring of local markets are crucial to ensure orderly trading and eliminate unregulated and low-standard outlets. Upgrading wholesale markets to include sorting, cleaning, environmentally friendly packaging, and value-added services will better align supply with the demands of urban consumers. Meanwhile, the introduction and integration of large-scale, high-tech processing enterprises will further promote the industrial chain extension and value enhancement. In addition, the development of farmer-led marketing cooperatives and rural distribution networks should be prioritized to improve logistics efficiency and expand market reach. These initiatives will enable Lanling's vegetable industry to strengthen its competitiveness in both domestic and international markets, laying the foundation for a resilient and innovation-oriented agricultural economy.
To complement these policy recommendations, it is worth considering possible risks and challenges that could emerge during implementation, particularly concerning the balance between public support and market-based mechanisms. While the paper highlights the important role of government in providing infrastructure, strategic planning, and institutional support, it is equally important to acknowledge potential challenges and risks associated with such interventions. One concern is the possibility of over-reliance on top-down support, which may undermine local initiative and entrepreneurial dynamics within the cluster. Excessive dependence on government subsidies or directives can also lead to inefficiencies or distortions in resource allocation. Moreover, questions of long-term sustainability arise, particularly regarding the cluster's ability to maintain competitiveness once initial public investments taper off. Ensuring the resilience of the cluster will require a balanced approach that fosters not only state-led coordination but also bottom-up innovation, private sector engagement, and adaptive capacity among local actors. Recognizing these challenges can enrich the analysis and provide more nuanced policy recommendations for achieving sustainable agricultural innovation clusters.
7 Conclusion and future directions
This study explored the driving mechanisms and development pathways of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters, using Lanling County in China as a representative case. Grounded in industrial cluster theory and the broader framework of regional innovation systems, the research addressed the central scientific question: What are the key internal and external forces that drive the emergence and consolidation of agricultural innovation clusters in a region with strong agricultural specialization? Through a comprehensive review of the theoretical foundations, cluster typologies, and empirical evidence from Lanling's vegetable industry, the study identified four major drivers: resource endowment, market demand, institutional support, and technological innovation. These factors interact dynamically to shape the spatial and organizational structure of innovation clusters and foster a cumulative cycle of agglomeration, learning, and value creation.
Beyond its practical and policy contributions, this study offers theoretical insights that enrich current debates in agri-food innovation research. The case of Lanling County illustrates how innovation in peripheral regions is shaped by a combination of path dependency, where historical resource configurations and institutional arrangements condition present trajectories, and adaptive responses that help avoid innovation lock-in. Furthermore, the findings highlight the capacity of rural areas to become sites of periphery-driven innovation, where localized experimentation, learning, and multi-actor collaboration can generate novel development pathways. By situating the empirical findings within these broader theoretical discussions, the study contributes to a more nuanced understanding of the complexities and adaptive dynamics underpinning agricultural innovation systems in developing country contexts.
The findings suggest that Lanling County's success in developing a science-driven agricultural cluster lies in its ability to integrate localized production systems with advanced technological services, responsive market mechanisms, and enabling policy environments. The county's strategic deployment of greenhouses, cooperative organizations, processing enterprises, and quality control infrastructure has transformed its vegetable industry from fragmented production into a coordinated innovation ecosystem. Moreover, the case of Lanling illustrates how endogenous innovation capacity—amplified by external policy support and global market linkages—can catalyze rural transformation and agricultural modernization.
From a theoretical perspective, this study contributes to the growing literature on innovation clusters in non-metropolitan contexts. While most existing research on innovation agglomerations focuses on manufacturing or urban-based high-tech sectors, this study underscores the relevance of cluster theory in agriculture and rural development. The results affirm the applicability of concepts such as knowledge spillover, institutional thickness, and innovation system integration within the agricultural domain. This study makes a theoretical contribution by refining the regional innovation systems framework to better capture the complexities of agricultural cluster development in rural regions. The Lanling County case shows that the evolution of agricultural innovation clusters is driven by the dynamic interaction between local assets, institutional flexibility, and market orientation, combined with the selective adoption of advanced technologies. These findings call for a rethinking of conventional innovation models to account for the specific governance patterns, resource dependencies, and innovation trajectories observed in agri-based systems. By bridging the gap between theory and rural practice, this study provides a robust foundation for future comparative research on innovation in diverse peripheral regions.
Looking forward, several avenues for future research remain open. First, longitudinal studies are needed to assess the evolutionary trajectory of agricultural innovation clusters and to evaluate the long-term impacts of government interventions. Second, quantitative models—such as spatial econometrics and system dynamics—can be applied to further analyze the feedback loops and spillover effects across regions. Third, comparative case studies between counties with different agro-ecological conditions, governance capacities, and market structures would enrich our understanding of the contextual factors shaping cluster formation. Finally, as digital agriculture continues to evolve, future research should examine how smart technologies and data-driven innovation platforms can be embedded into existing agricultural clusters to enhance their resilience, efficiency, and sustainability.
In conclusion, the development of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters presents a viable pathway for revitalizing rural economies and achieving sustainable agricultural transformation in China and beyond. By systematically identifying and reinforcing the multidimensional drivers of cluster development, policymakers and practitioners can better design place-based innovation strategies tailored to the specific needs and potentials of local agricultural systems.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AX: Software, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. YY: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Supervision. FC: Formal analysis, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. NR: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Validation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. YM: Writing – original draft, Visualization, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the National Social Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21BGL150). The funder provided financial support for the research but had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adisa, O., Ilugbusi, B. S., Adelekan, O. A., Asuzu, O. F., and Ndubuisi, N. L. (2024). A comprehensive review of redefining agricultural economics for sustainable development: overcoming challenges and seizing opportunities in a changing world. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 21, 2329–2341. doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2024.21.1.0322
Annosi, M. C., Ráez, R. M. O., Appio, F. P., and Del Giudice, T. (2022). An integrative review of innovations in the agricultural sector: the roles of agency, structure, and their dynamic interplay. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 185:122035. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2022.122035
Bianchi, C., and Grippi, N. (2025). Developing collaborative ecosystem platforms to trigger sustainable “place-based” value creation: a dynamic performance governance approach. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manage. 74, 1052–1078. doi: 10.1108/IJPPM-10-2023-0580
Bittencourt, B. A., Zen, A. C., Prévot, F., and Schmidt, V. K. (2023). How to be more innovative in clusters? The influence of geographical agglomerations on its firms. J. Knowl. Econ. 14, 2603–2629. doi: 10.1007/s13132-022-00975-2
Bravaglieri, S., Åberg, H. E., Bertuca, A., and de Luca, C. (2025). Multi-actor rural innovation ecosystems: definition, dynamics, and spatial relations. J. Rural Stud. 114:103492. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2024.103492
Chen, X., and Li, T. (2022). Diffusion of agricultural technology innovation: research progress of innovation diffusion in Chinese agricultural science and technology parks. Sustainability 14:15008. doi: 10.3390/su142215008
Fioravanti, V. L. S., Stocker, F., and Macau, F. (2023). Knowledge transfer in technological innovation clusters. Innov. Manage. Rev. 20, 43–59. doi: 10.1108/INMR-12-2020-0176
Foutakis, D. (2025). Identification and visualization of clusters using network theory methods: the case of the greek production system. Economies 13:15. doi: 10.3390/economies13010015
Klarin, A., Sharmelly, R., and Suseno, Y. (2021). A systems perspective in examining industry clusters: case studies of clusters in Russia and India. J. Risk Financ. Manage. 14:367. doi: 10.3390/jrfm14080367
Kowalski, A. M., and Mackiewicz, M. (2021). Commonalities and differences of cluster policy of Asian countries; discussion on cluster open innovation. J. Open Innovat. Technol. Mark. Complex. 7:21. doi: 10.3390/joitmc7010021
Lepori, D. (2022). Location competitiveness in specific pioneering theories: a condensed overview. Comp. Rev. Int. Bus. J. 32, 142–154. doi: 10.1108/CR-11-2020-0138
Li, E., Xu, Y., Ren, S., and Lee, J. (2022). Spin-offs, innovation spillover and the formation of agricultural clusters: the case of the vegetable cluster in Shouguang city, Shandong province, China. Land 11:279. doi: 10.3390/land11020279
Medeiros, E. (2021). Development clusters for small places and rural development for territorial cohesion? Sustainability 14:84. doi: 10.3390/su14010084
Ostapenko, S., Africano, A. P., and Meneses, R. (2024). Cluster dynamics and firms' strategies–an integrative framework. EuroMed J. Bus. 19, 366–397. doi: 10.1108/EMJB-01-2022-0014
Pinto, H., Guerreiro, J. A., and Fernández-Esquinas, M. (2023). Sources of knowledge in the firm: a review on influential, internal and contextual factors in innovation dynamics. SN Bus. Econ. 3:57. doi: 10.1007/s43546-023-00430-7
Rocha, H., and Audretsch, D. B. (2022). Entrepreneurial ecosystems, regional clusters, and industrial districts: historical transformations or rhetorical devices? J. Technol. Transf. 1–24. doi: 10.1007/s10961-022-09920-6
Rodríguez Ochoa, D., Arranz, N., and de Arroyabe, M. F. (2025). Assessing regional innovation strategies (RIS3) through competitive public project networks: the case of Aragón 2014–2020. Economies 13:71. doi: 10.3390/economies13030071
Sandoval Hamón, L. A., Ruiz Peñalver, S. M., Thomas, E., and Fitjar, R. D. (2024). From high-tech clusters to open innovation ecosystems: a systematic literature review of the relationship between science and technology parks and universities. J. Technol. Transf. 49, 689–714. doi: 10.1007/s10961-022-09990-6
Song, H., Hou, J., and Zhang, Y. (2022). Catalytic capacity of technological innovation: multidimensional definition and measurement from the perspective of knowledge spillover. Technol. Soc. 68:101898. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101898
Wan, Z. (2022). “Promoting urban-rural integration with new agricultural modernization-a case study of Liaocheng City, Shandong Province,” in China's Reform and New Urbanization, eds. Y. Li, and Z. Cheng (Cham: Springer), 239–255. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-4916-5_15
Wang, Y., Liang, H., Dong, L., Zhu, Y., and Wang, Y. (2025). Harmonizing new-type urbanization and eco-efficiency: spatial-temporal coupling coordination in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 107014. doi: 10.1007/s10668-025-06089-4
Warr, P. G. (1994). Comparative and competitive advantage. Asia-Pac. Econ. Lit. 8, 1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8411.1994.tb00091.x
Wei, X., and Chen, B. (2024). Spatial association network structure of agricultural carbon emission efficiency in Chinese cities and its driving factors. Sci. Rep. 14:31810. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83041-y
Yadav, R., Kumar, R., and Kumar, U. (2023). Technological advancements driving agricultural transformation. Int. J. 1, 05–11.
Keywords: agricultural innovation cluster, technological upgrading, regional development, innovation systems, Lanling county, policy-driven modernization, rural transformation
Citation: Xie A, Yang Y, Che Leh F, Rambeli N and Miao Y (2025) Exploring the driving mechanisms behind the formation of agricultural science and technology innovation clusters: a case study of Lanling County, China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1607580. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1607580
Received: 07 April 2025; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 30 June 2025.
Edited by:
Fuyou Guo, Qufu Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Jia Liu, Ocean University of China, ChinaGuosheng Han, Shandong University, Weihai, China
Chengcai Tang, Beijing International Studies University, China
Copyright © 2025 Xie, Yang, Che Leh, Rambeli and Miao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Youbao Yang, cWR5eWIxOTg3QDEyNi5jb20=
 Ailiang Xie
Ailiang Xie Youbao Yang2*
Youbao Yang2*