- School of Business Administration, Guizhou University of Finance and Economics, Guiyang, China
Introduction: Developing climate resilient agriculture is particularly important to reduce food security and climate risks in the context of frequent climate extremes disrupting food production systems.
Methods: Based on the provincial panel data of China from 2011 to 2022, this paper uses dual machine learning model to explore the effect of digital inclusive finance (DIF) on climate resilience of food production (CRFP) and its transmission mechanism.
Results: DIF can significantly improve CRFP, and the conclusion is still valid after endogeneity and robustness tests. The mechanism of action shows that DIF can enhance CRFP by promoting agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services. Heterogeneity analysis show that DIF has a significant effect on promoting CRFP in the eastern region, the main grain-producing areas and the regions with high digital infrastructure.
Discussion: It is necessary to strengthen the construction of digital infrastructure and improve the ecological compensation mechanism to give full play to the role of DIF in improving the climate resilience of grain production. This study provides evidence-based support for the realization of climate-smart agriculture, with policy implications for cracking the food crisis trap in low- and middle-income countries.
1 Introduction
In recent years, global climate change has intensified and extreme weather events have occurred frequently, posing severe challenges to food production security. According to the Global Food Crisis Report released by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) in 2024, the incidence of global food insecurity has risen sharply. By 2023, more than 200 million people around the world will face severe food insecurity, and about 72 million people will be affected by extreme climate events, accounting for 25.6%. In particular, the spatial compound events of heat waves occurring in the same growing season in many parts of the world have a greater impact on global food security. The cumulative intensity of heat waves in the growing season in the global cropland area continues to increase, and the heat wave exposure of total primary productivity of vegetation continues to increase. As a major food producer, China is also one of the countries most affected by climate change-related extreme weather events in the world. In 2022, China’s Yangtze River basin will experience a “flood season reverse drought” due to intensified heat waves, reducing the yield of major crops by at least 20% (Chan et al., 2024). In the summer of 2023, China suffered severe flooding when Typhoon Dokouri hit the North China Plain, producing more than 744.8 mm of precipitation, the highest on record. Building climate-resilient agricultural systems has become a critical issue in light of increasing extreme climate events (Juhola et al., 2017). To achieve this goal is not out of reach. The key is to develop strategies for agricultural adaptation to climate change from a top-level design perspective, supported by science and technology (Bushell et al., 2017; Dookie et al., 2024). In 2022, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment and other ministries jointly issued the National Climate Change Adaptation Strategy 2035, which pointed out that mitigation and adaptation are the two major strategies to cope with climate change, and agriculture should focus on enhancing its adaptability and improving its “resilience” to cope with various adverse climate conditions. Driven by modern scientific and technological innovation and structural transformation, China advocates the development of climate-smart agriculture. These nature-based production solutions, along with agriculture that is resilient to vulnerability, shocks and stress, will be an important direction for global agricultural development.
Digital inclusive finance is a new financial service model that integrates digital technology with the concept of inclusive finance. By using big data, artificial intelligence, blockchain and other information technologies, it can achieve low-cost, efficient and economical financial services, aiming to improve the quality of financial products, break the time and space constraints, and promote the inclusive financial services (Zhou et al., 2023). With the popularization and penetration of DIF in agriculture, its practical role in improving CRFP has become more and more obvious. Especially in climate-changing regions, farmers use digital financial platforms to obtain timely funds, adjust production plans, purchase emergency supplies and introduce disaster resilience technologies, which effectively alleviate the losses caused by extreme weather such as drought and flood (Prasad and Sud, 2019). This innovative form of financial inclusion directly enhances farmers’ financial liquidity, risk response ability and access to resources, enabling them to flexibly adjust production activities in the face of climate disturbances, and ensuring the stability and sustained growth of food production.
In food security research, the concept of resilience has gradually become the core framework to analyze the response of agricultural systems to uncertainty. Some scholars define agricultural resilience as the ability of regional agricultural economy to resist, adapt, recover and transform under external shocks (Volkov et al., 2022; Yao et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2025), which mostly relies on macroeconomic indicators or social network resilience index. However, these studies mostly focus on the mitigation of conventional market risks, often simplify climate risks into homogeneous external variables, and lack in-depth discussion on the particularity of climate shocks and their systemic impacts. Climate resilience of food production refers to the ability of food production system to maintain output, adapt to shocks and recover quickly under extreme climate disturbances (Fang et al., 2024). However, much of the existing research on the climate of food production focuses on the economic consequences of the role of climate change on food security, and there is relatively little quantitative and empirical research on how to improve the climate resilience of food production, which is basically case-based and qualitative.
Digital technologies are becoming an important tool for agricultural systems to cope with climate change (Bhawra et al., 2024; Pappa, 2024). Firstly, digital technologies can monitor key variables such as meteorological changes and environmental humidity in real time by means of sensor networks and remote sensing data (Quarshie et al., 2023), thus improving the ability of agricultural systems to take precautions in the early stages of agricultural production (Goel et al., 2021; Richards et al., 2024). Secondly, models built based on intelligent algorithms can dynamically obtain information on soil moisture and crop growth status (Kalantzopoulos et al., 2024), which can assist farmers to quickly adjust sowing, irrigation and fertilization strategies to enhance the adaptive capacity of agricultural production to climate anomalies (Iaksch et al., 2021). Digital inclusive finance not only continues the basic concept of traditional inclusive finance of “low threshold, low cost and wide coverage” in the financial system, but also takes digital technology as the core driving mechanism, embedding in all aspects of agricultural production, financing and transaction. It has been found that digital inclusive finance in agriculture, on the one hand, reduces farmers’ credit constraints through diversified financing channels (Benami and Carter, 2021), activates farmers’ entrepreneurial vitality (Li et al., 2023; Fu et al., 2024), and enhances farmers’ risk-resistant ability by smoothing consumption and investment with the help of capital (Yi et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2024); On the other hand, DIF relies on digital technology to promote precision farming practices (Mao et al., 2024), optimize machinery substitution (Li and Zhang, 2024), factor allocation (Zheng and Li, 2022; Hong et al., 2024), and low-carbon technology adoption (Liu et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024), thereby realizing environmental benefits and total factor productivity (Guo et al., 2024).
China spans multiple climatic zones, and the types and frequencies of climate disasters vary significantly among provinces, which provides a natural experimental scenario for studying CRFP. At the same time, the provincial DIF level showed a gradient distribution of “leading in the eastern region and catching up in the central and western regions,” which was convenient to analyze the effect differences in different infiltration stages. As a global pioneer in digital financial inclusion, China’s rural mobile payment coverage rate exceeds 86%, and the policy level continues to promote “digital countryside” and “climate-smart agriculture” pilots, providing a rich institutional background for mechanism research. By 2024, China’s digital financial user scale has reached 960 million people, the Internet of Things (IoT) equipment covers more than 40 million mu of farmland, and the coverage rate of drone plant protection services in major agricultural provinces exceeds 60%. At the policy level, the “New Agricultural Digital Infrastructure” plan aims to achieve full coverage of digital finance in counties by 2025, and the No. 1 document of the central government has emphasized the resilience of technology-enabled agriculture for five consecutive years. These advances both highlight the uniqueness of using China as a case study and provide replicable financial solutions for climate adaptation in the global food system. There is a lack of empirical analysis to verify how digital inclusive finance can enhance climate resilience through financial instrument innovation and technology penetration. Therefore, can DIF enhance CRFP? If so, how does it enhance CRFP?
In order to answer the above questions, based on China’s provincial panel data from 2011 to 2022, this paper integrates the financial function and technology enabling effect of DIF into the climate resilience analysis framework, reveals the internal mechanism of DIF enabling CRFP, and fills the research gap mentioned above. Firstly, the dual machine learning model was used to empirically test the direct impact of DIF on CRFP. Secondly, the transmission mechanism of DIF in improving CRFP was comprehensively revealed from the three core mechanisms of agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized service. Finally, in order to further identify the impact of DIF on CRFP in different regions, food functional zones and digital infrastructure levels, the heterogeneity test was conducted.
The main contributions of this paper are as follows: firstly, this study breaks through the comprehensive risk analysis paradigm of traditional resilience research and focuses on the targeted impact of extreme climate events on food production. At the same time, this study incorporates DIF into the analysis perspective to explore how it reshaped the climate response logic of food production system, and fill the gap of the interdisciplinary research on fintech and climate resilience. Secondly, this paper also explores the transmission mechanism of agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services between DIF and CRFP, and expands the channel of DIF’s effect on CRFP. Finally, we also discussed the different impacts of DIF on CRFP in different regions, food functional zones and digital infrastructure levels.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypotheses
2.1 Direct effect of DIF on CRFP
With the dual characteristics of inclusiveness and digitization, DIF has important structural enabling effects in dealing with extreme weather disruptions to food production systems. First, DIF enables financial services to have strong spatial penetration through channels such as online account opening, identity authentication, and platform access, which can effectively expand the boundaries of financial services and thus enhance financial accessibility in rural areas (Carter, 2022). With the help of digital platforms, inclusive financial services are able to realize cross-regional financial resource dispatch after regional disaster outbreaks, thus enhancing the collaborative recovery capacity of food production systems (Agyekumhene et al., 2018). Secondly, traditional agricultural insurance products have certain shortcomings in terms of claims timing and payout accuracy, making it difficult to adequately match high-frequency and sudden-onset extreme weather events, etc. DIF can promote the transformation of agricultural insurance products from the traditional model to a new form of data-driven, platform-docking (Kirchner and Musshoff, 2024). With the help of remote sensing technology, blockchain, internet and other digital infrastructures, digital agricultural insurance products can more accurately obtain meteorological, geographic, price and other information about the food growing region, thus reducing the risk of adverse selection and improving the science of risk pricing and the timeliness of claims (Richards et al., 2024).
Thirdly, based on digital technology, DIF can effectively alleviate the information asymmetry problem in rural financial services through big data analysis and intelligent risk control (Benami and Carter, 2021). By collecting unstructured information such as farmers’ historical transactions and plot operations, financial institutions are able to establish a multi-dimensional credit evaluation system, thus enabling farmers to obtain low-threshold and high-efficiency financing support (Yu et al., 2020). In the event of extreme climate shocks, farmers can quickly access liquidity funds for key aspects such as replanting, restoration, and replanting, shortening the recovery cycle of the food production system and strengthening its resource deployment capacity in the face of climate perturbations. Fourthly, DIF can effectively improve the transaction efficiency and resource matching capacity within the agricultural system through mobile payments and smart contracts (Ky, 2025). In the event of climate extremes, farmers can use real-time payment tools to complete key links such as agricultural procurement and logistics scheduling to ensure that production inputs are in place in a timely manner. The efficient connectivity of the payment network and the data precipitation effect are also conducive to improving the coordination of the food production chain, thus enhancing the recovery speed of the food production system. In summary, this paper proposes the following core hypotheses:
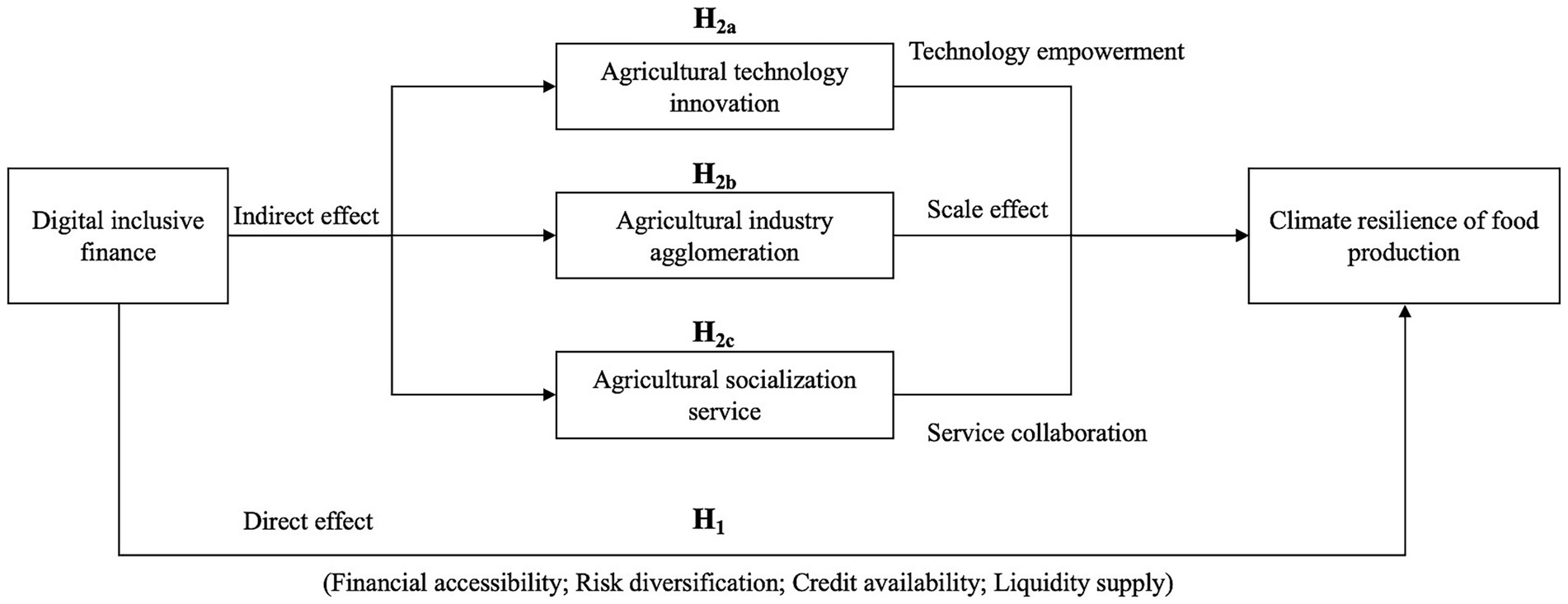
H1: DIF can significantly improve CRFP.
2.2 Mediating effect of DIF on CRFP
2.2.1 Mediating effect of agricultural technological innovation
By providing financial resources, DIF not only lowers the threshold for farmers to adopt new technologies (Mao et al., 2024), but also accelerates the spread of agricultural technologies among farmers. Through the financial inclusion platform, farmers can access advisory services, training and policy guidance related to agricultural technology. In addition, DIF provides financing support for agricultural technology startups through the online platform, accelerating the R&D and promotion of innovative products (Xue et al., 2024).
Agricultural technology innovation has become the core driving force for improving CRFP by optimizing the resource adaptation and risk response of production system. First, the breeding of stress-tolerant varieties directly enhances the physiological resistance of crops. For example, drought-resistant gene editing technology can extend the water use cycle of crops and enable them to maintain basic productivity in the event of sudden changes in precipitation patterns (Wigboldus et al., 2016). At the same time, high temperature resistance can alleviate the inhibitory effect of abnormal temperature on photosynthesis (Clay and Zimmerer, 2020). Second, deeper resilience is due to the redundant design of the system brought about by technology integration, such as the coupling of conservation tillage and intercropping technology, which can not only reduce soil erosion through vegetation cover, but also use biodiversity to spread the risk of disease and insect outbreak, forming a multi-level buffer barrier. Finally, agricultural green technology reduces the carbon footprint of agricultural production by reducing the dependence of agricultural production on chemical fertilizers and pesticides (Li and Gao, 2024), promoting the development of organic agriculture and ecological agriculture. The core value of technological innovation is to transform discrete climate threats into predictable and intervenable control objects, so that agricultural production can shift from vulnerability accumulation to sustainable development path with endogenous resilience. Therefore, the following hypothesis is put forward:
H2a: DIF can enhance CRFP by promoting agricultural technological innovation.
2.2.2 Mediating effect of agricultural industrial agglomeration
On the one hand, DIF can be a key link in the process of investment in the agriculture industry chain, such as agricultural products processing, warehousing, logistics, promote the link to concentrate in a particular area, the formation of the agricultural industry cluster area. At the same time, the DIF can also support the construction of modern agricultural facilities, improve agricultural production efficiency and quality, can attract more concentrated agricultural enterprises and farmers to industrial concentration area, further promote the development of agricultural industry cluster (Xue et al., 2023). On the other hand, agricultural agglomeration can improve the climate resilience of food production through large-scale, specialized and intensive production methods. Specifically, agro-industrial agglomeration can maximize the efficiency of resource use and reduce the waste of resources due to climate change by implementing unified irrigation systems or resource allocation mechanisms. The agricultural industry cluster can bring economies of scale, by focusing on production and the division of labor cooperation, reduces the production cost, improve the enterprises and farmers in the face of climate impacts of economic capacity (Zhang et al., 2022). Secondly, the agglomeration effect promotes the rapid diffusion of technology. New technologies and management experience can spread rapidly in industrial clusters, and the cooperation and knowledge sharing among farmers can shorten the cycle of technology promotion (Wu et al., 2020). Finally, agricultural agglomeration can accelerate the integration of upstream and downstream industrial chains, making supply chains more resilient. For example, grain processing companies can quickly adjust their acquisition plans to cope with grain supply fluctuations caused by climate change and avoid widening yield losses. In addition, agricultural industry agglomeration can often create synergistic effects in ecological protection and restoration, which can help improve the regional ecological environment and enhance CRFP through the promotion of green production models such as organic agriculture and sustainable cultivation (Huang et al., 2022). As a result, put forward the following hypothesis:
H2b: DIF can enhance CRFP by promoting agricultural industrial agglomeration.
2.2.3 Mediating effect of agricultural socialization service
DIF improves the level of agricultural socialization service through service supply expansion and demand response activation (Xu and Yang, 2025). On the supply side, DIF provides financing tools such as equipment mortgage loan and accounts receivable factoring for professional service subjects to ease their liquidity constraints in asset-heavy operation and expand the service coverage radius. And on the demand side, the digital payment platform service search with the execution of the contract to reduce costs, enable small farmers to on-demand purchase services, disaster prevention and mitigation alternatives to traditional purchasing equipment of the high fixed cost model. In addition, the digital platform integrating various data generation dynamic service recommendation, improve the service efficiency of supply and demand matching (Liu and Yan, 2024). Social services enhance climate resilience through the advantages of specialization and system response agility. Professional level, the service provider focused investment efficient disaster relief equipment, and through practice while learning to accumulate experience in response to specific disasters, decentralized farmers access to marginal cost frontier art technology. At the agility level, IoT devices collect field data in real time, and AI models predict the probability of disaster occurrence and automatically trigger service scheduling, greatly reducing the time lag from risk identification to action intervention. DIF in this mechanism friction by cutting the costs of services trade credit and information, the network embedded in social division of labor and financial instruments to make production system from static disaster to dynamic adaptive management. As a result, put forward the following hypothesis:
H2c: DIF by promoting agricultural socialization service level to enhance CRFP.
The research framework of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
3 Research design
3.1 Model setting
In order to test the effect of DIF on CRFP, this paper selects the dual machine learning model for regression. The traditional linear regression model often has limitations in dealing with nonlinear relationships, and the machine learning model can better capture the nonlinear patterns and interactions in data. At the same time, the model can adapt to different types and sizes of data sets, and has a stronger ability to deal with complex data structure and eliminate bias, thus providing more robust causal inference. Therefore, to build dual machine learning model is as follows:
In the above formula, represents the level of climate resilience of food production, represents the level of digital inclusive finance, and represents various control variables; and denote individual and year, respectively; Let represents the coefficient of DIF and represents the random error term.
The direct use of machine learning algorithm to estimate models (1) and (2) is easy to cause the estimation bias, resulting in the estimation error caused by the function regularization bias. In order to alleviate the above problems, this paper constructs auxiliary regression:
In the above equation, is the regression function of the disposal variable to the high-dimensional control variable. First, the machine learning algorithm is used to estimate the specific form of as , and then the estimated value of its residual is calculated as = . Secondly, the machine learning algorithm is used to estimate the specific functional form of in Equation 1 as , and at the same time, the functional form of the main regression becomes ; Finally, is used as the instrumental variable of the disposal variable ( ) for regression, and unbiased estimates are obtained:
3.2 Measurement of CRFP
3.2.1 Non-expected super-efficiency SBM model
Compared with the traditional DEA model, the non-expected super-efficiency SBM-DEA model considers the slack variables of input and output, and directly incorporates the slack variables into the objective function, which can overcome the problem that the traditional DEA model ignores the environmental and resource factors when measuring efficiency, and improve the accuracy of efficiency calculation. Secondly, the model can handle contains the expected output efficiency evaluation. In the actual production process, in addition to the expected output, there are often some outputs with negative environmental externalities. By incorporating these undesirable outputs into the efficiency evaluation system, the model can more comprehensively reflect the real efficiency of production activities. At the same time, the model can not only evaluate the efficiency of DMUs, but also further decompose and rank the effective DMUs, which breaks through the limitation in the traditional DEA model that when the efficiency value of multiple DMUs is 1 at the same time, the advantages and disadvantages cannot be distinguished. In this study, the climate resilience evaluation system of food production covers multiple inputs, desired outputs and non-desired outputs. In order to further clarify the spatial and temporal variations of climate resilience of food production between regions, this paper adopts the non-expected super-efficiency SBM-DEA model with the following formula:
In the above equation, is the efficiency value, that is, the climate resilience indicator of food production. The larger is, the higher the climate resilience of food production is; denotes the quantity of inputs, denotes the quantity of desired outputs, and denotes the quantity of undesired outputs; , and are slack variables of input, desired output and undesired output, respectively, and represents constraints.
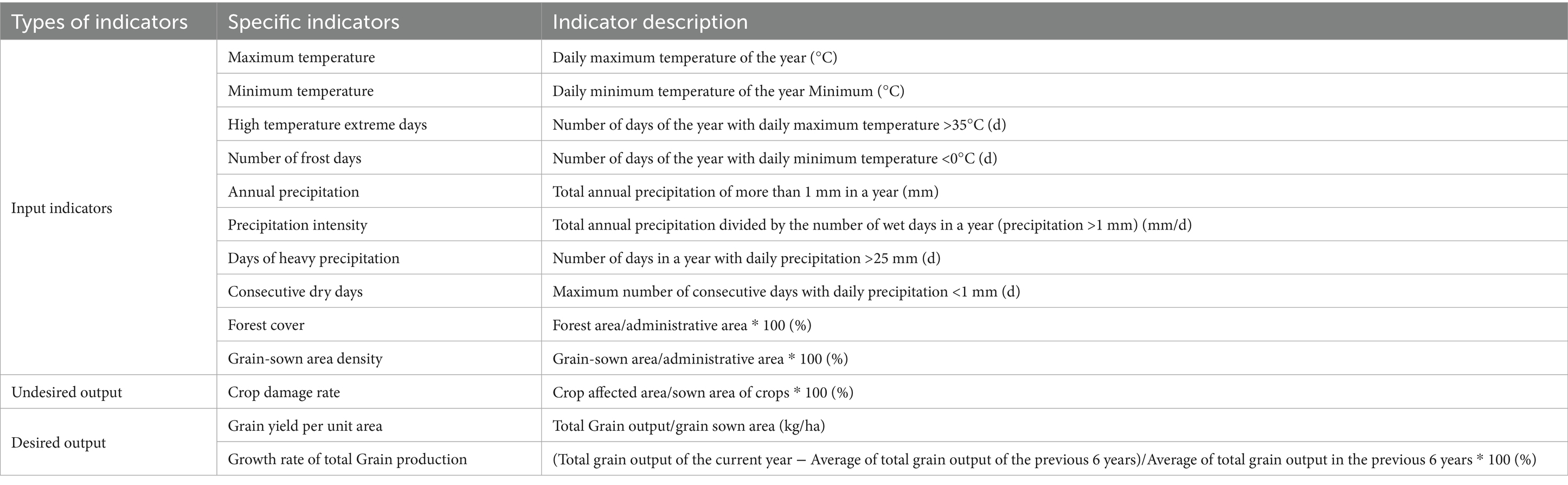
3.2.2 The calculation of CRFP index system
The CRFP indicators are shown in Table 1. Referring to the practice of Fang et al. (2024), the input indicators are composed of climate disasters, disaster environment and disaster burden. Climate disasters including four extreme temperature indicators: the highest and lowest temperatures, extreme number of days in high temperature and frost days; Four extreme precipitation index: annual rainfall, rainfall intensity and precipitation days and days of continuous drought. Forest coverage was used as a proxy indicator for disaster environment. Grain sown area density was selected as the proxy index for disaster undertaking. Output index consists of disaster intensity and disaster recovery. Disaster intensity as unexpected disaster loss rate to measure output indicators selected crops, disaster recovery as expected output indicators using per unit area grain yield and total grain production growth to measure.
3.3 Variable definition
3.3.1 Dependent variable
Climate resilience of food production (CRFP). From the above, this study calculated the CRFP level based on the input-output index of CRFP and through Formula (6).
3.3.2 Independent variable
Digital inclusive finance (DIF). Using the “Peking University Digital Inclusive Finance Index” compiled by the Center for Digital Studies of Peking University (Ren et al., 2023; Hong et al., 2024), in order to ensure that the estimated coefficient value of regression results is appropriate, the digital inclusive financial index is reduced by 100 times.
3.3.3 Mechanism variables
Agricultural Technology innovation (ATECH). The number of agricultural invention patents authorized is used to measure the level of agricultural technology innovation; Agriculture industry agglomeration (AIA). We use the ratio of agricultural output to GDP for the region in that year divided by the ratio of agricultural output to GDP for the whole country in that year to represent (Billings and Johnson, 2012; Zhang et al., 2022); Agricultural socialization service (ASS). The level of agricultural socialization service is expressed as the ratio of the gross value of agricultural services to the number of people employed in agriculture.
3.3.4 Control variables
Considering that the climate resilience of food production will be affected by other factors, this paper refers to the practice of Fang et al. (2024) and selects the following variables as control variables. (1) Grain sown area (AREA), which is represented by the total grain sown area and taken as logarithm; (2) Effective irrigation (IRR), which is expressed as the ratio of effective irrigation area to crop sown area; (3) The amount of agricultural fertilizer (FERT), using the amount of agricultural fertilizer per unit area; (4) Pesticide dosage (PEST), expressed as pesticide dosage per unit area, and taken logarithm; (5) The amount of agricultural plastic film (PLASTIC) was expressed by the amount of agricultural plastic film per unit area, and the logarithm was taken; (6) Rural electricity consumption (ELEC), which is expressed as rural electricity consumption per unit area; (7) Agricultural diesel use (DISEL), which is expressed as the amount of agricultural diesel used per unit area; (8) The proportion of agricultural output (FIRST), which is expressed by the proportion of agricultural output considering the government’s support for agriculture; (9) Extreme high temperature (HEAT) and annual precipitation (PRCP): climate change will lead to fluctuations in the climate resilience of food production, so the extreme maximum temperature and annual precipitation are used to control and take the logarithm.
3.4 Data sources and descriptive statistics
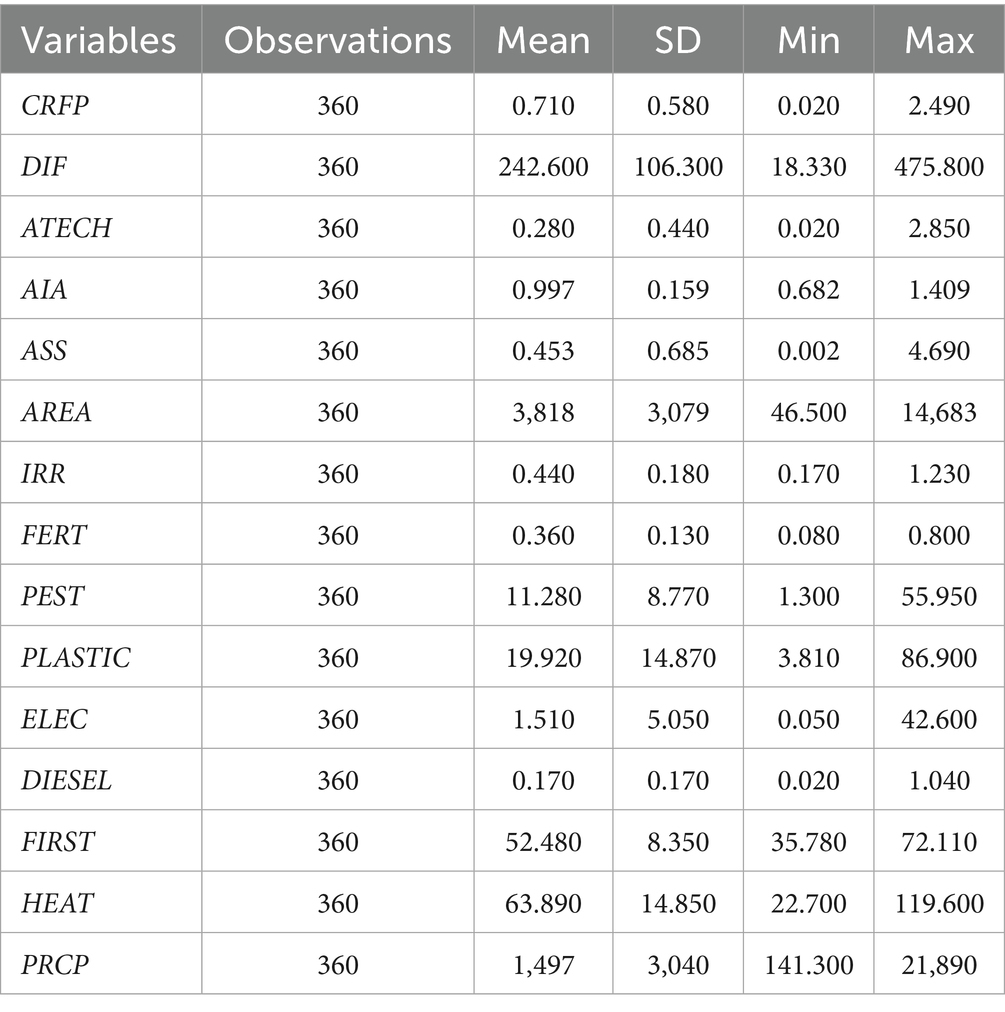
Considering the availability of data, this paper selects panel data from 30 provinces in China, excluding Tibet Autonomous Region and Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan, from 2011 to 2022 as the research sample, and explores the impact of digital financial inclusion on climate resilience of food production. The relevant climate indices are from the National Meteorological Information Center, and the agriculture-related indicators, grain sown area, crop damage area, and total grain output are from the China Statistical Yearbook, China Agricultural Yearbook, China Rural Statistical Yearbook, and China Science and Technology Statistical Yearbook. The digital inclusive financial index is from the Digital Inclusive Financial Index of Peking University. Table 2 shows the descriptive statistical results of each variable. The value of CRFP ranges from 0.02 to 2.49, with mean and standard deviation of 0.71 and 0.58, respectively. The value of DIF ranges from 18.33 to 475.8, with mean and standard deviation of 242.6 and 106.3, respectively. This indicates that there are large differences in CRFP and DIF levels among different regions in China. The statistical values of the above control variables are within a reasonable range, which can be used for further analysis.
4 Empirical results
4.1 Impact of DIF on CRFP
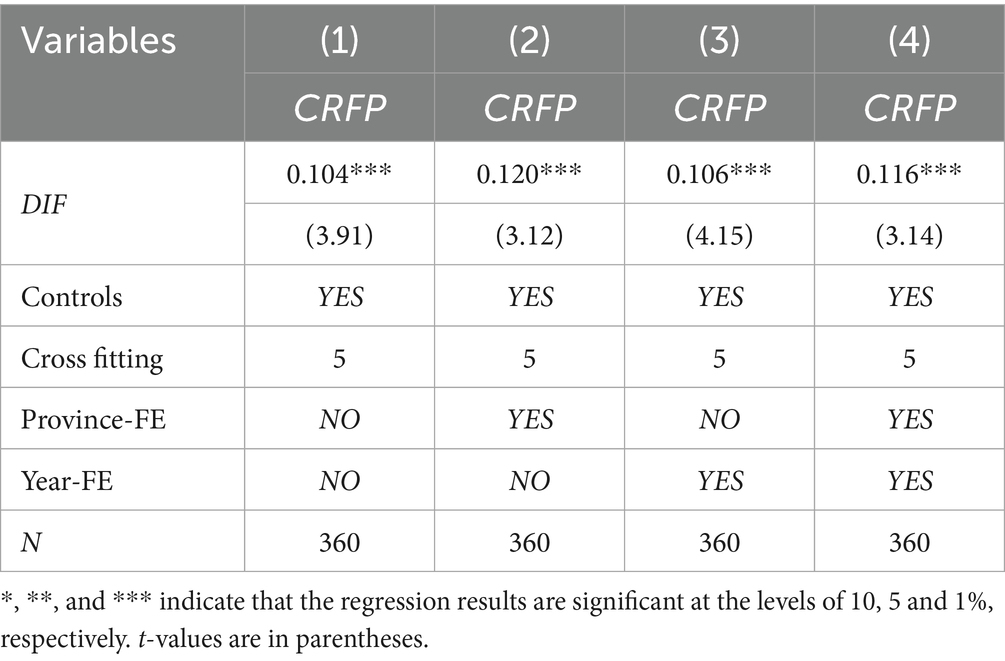
To explore the relationship between DIF and CRFP this study utilized the random forest algorithm of dual machine learning to estimate the parameters of Equations (1–5), and divided the sample ratio into 1:4. The regression results of DIF on CRFP are reported in Table 3, where Column (1) is the regression result when both the year and the province are not fixed, Column (2) is the regression result after fixing only the year, Column (3) is the regression result after fixing only the province, and Column (4) are the regression results after both year and province are fixed. The results show that the estimated coefficients of DIF are all significantly positive, indicating that DIF has a significant enhancing effect on CRFP. Hypothesis 1 is verified.
4.2 Robustness test
4.2.1 Replace variable
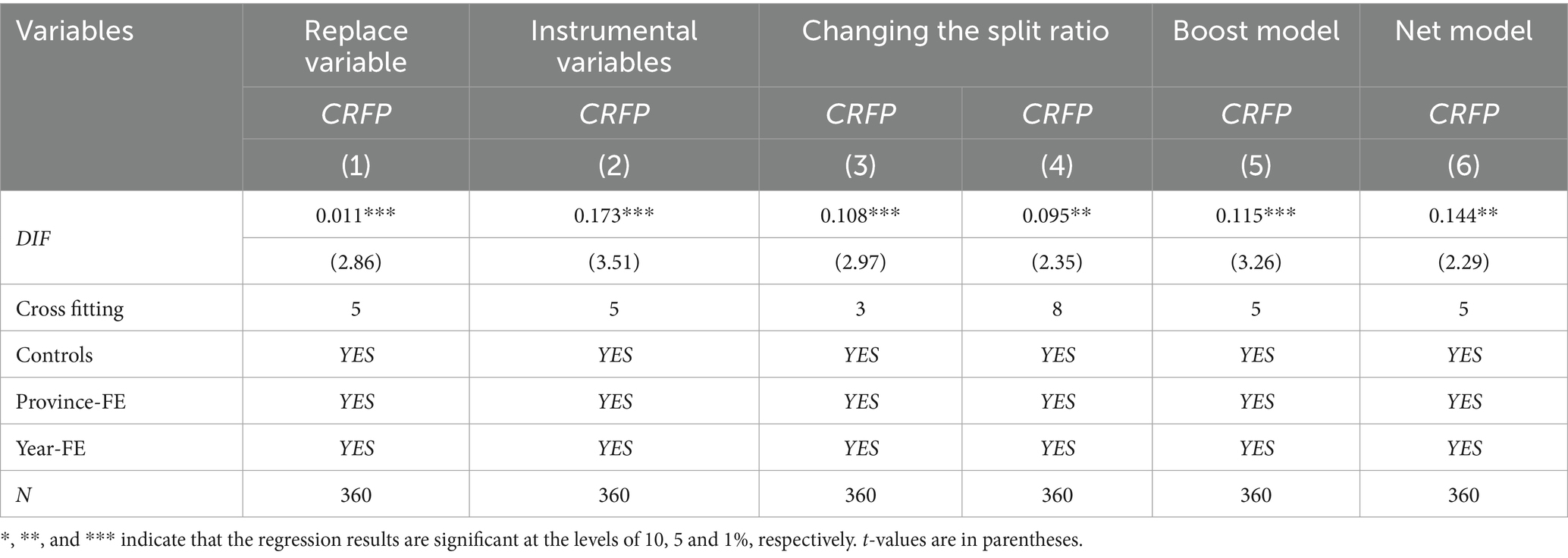
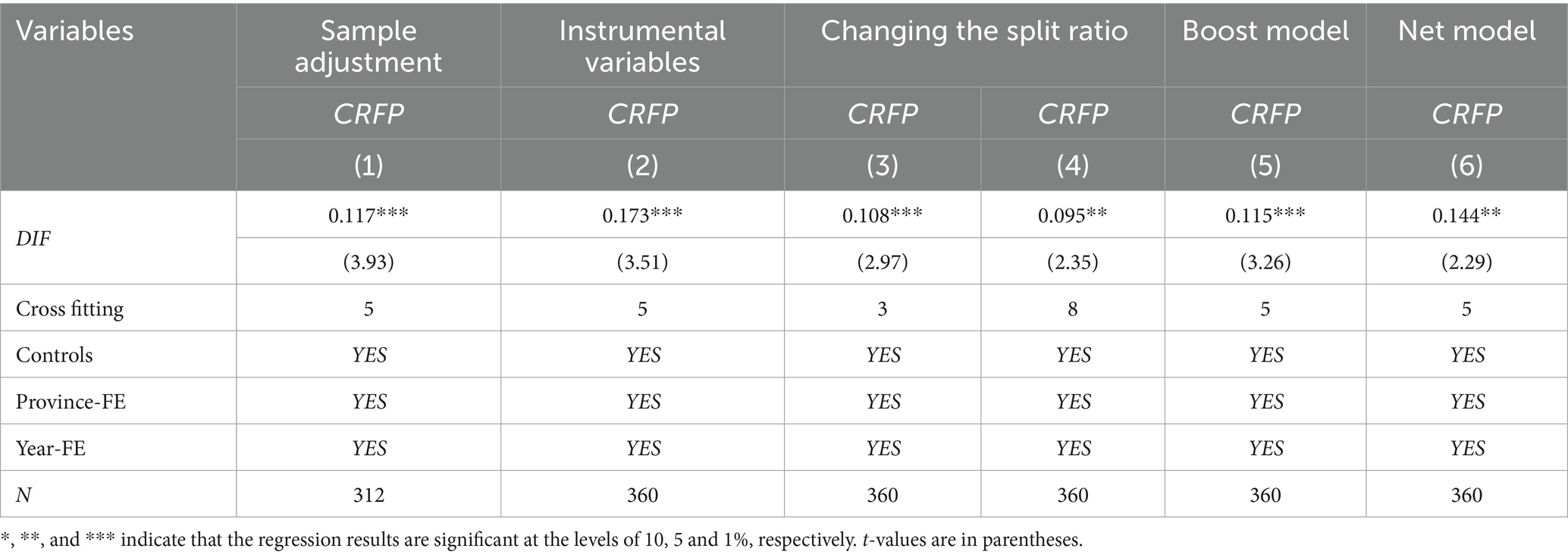
To ensure the robustness of the results, in this paper, the entropy method is used to re-assign weights to each index of CRFP. The entropy method is an objective weighting method that can determine the index weights based on the amount of information of each index value. The CRFP level calculated by the entropy method is used as the surrogate variable. The results are shown in Table 4. The regression coefficient of DIF in column (1) is 0.011, which is significantly positive at the 1% level, and the regression results are still robust, again verifying hypothesis 1
4.2.2 Instrumental variable
Although many variables and years and provinces have been controlled for in the regressions above, there is still the possibility of endogeneity problems due to omitted variables. Since the core vehicle of DIF is highly dependent on Internet access capacity, and regional Internet coverage directly affects the likelihood of farmers’ access to digital financial services, Internet penetration is highly correlated with DIF, whereas Internet penetration is not directly correlated with CRFP, and this paper draws on existing research (Ren et al., 2023; Wang, 2023) to select Internet penetration rate as an instrumental variable is appropriate. Meanwhile, we estimate a partially linear instrumental variable regression model using dual machine learning. Column (2) of Table 4 reports the regression results of the instrumental variables, and the regression coefficient of CRFP remains significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that the result passes the endogeneity test.
4.2.3 Replacing the machine learning model
Since the random forest model is used for regression in the previous section, in order to avoid inconsistent conclusions caused by different dual machine learning model algorithms, this paper carries out the following processing: first, change the sample segmentation ratio in the benchmark regression model, that is, 1:2 and 1:7; The second is to change the Boost model and the Net model for regression comparison. Columns (3) and (4) of Table 5 show the regression results after changing the segmentation ratio, and the regression coefficients of DIF are 0.108 and 0.095 respectively, which are significantly positive at the statistical level of 1 and 5%, respectively. Columns (5) and (6) of Table 5 show the estimated results of the two models, and the regression coefficients of DIF are 0.115 and 0.144, respectively, which are significantly positive at the level of 1 and 5%, respectively. It can be seen that DIF can still significantly improve CRFP after changing the sample splitting ratio and the estimation model, indicating that the above results are reliable to some extent.
4.3 Test of influence mechanism
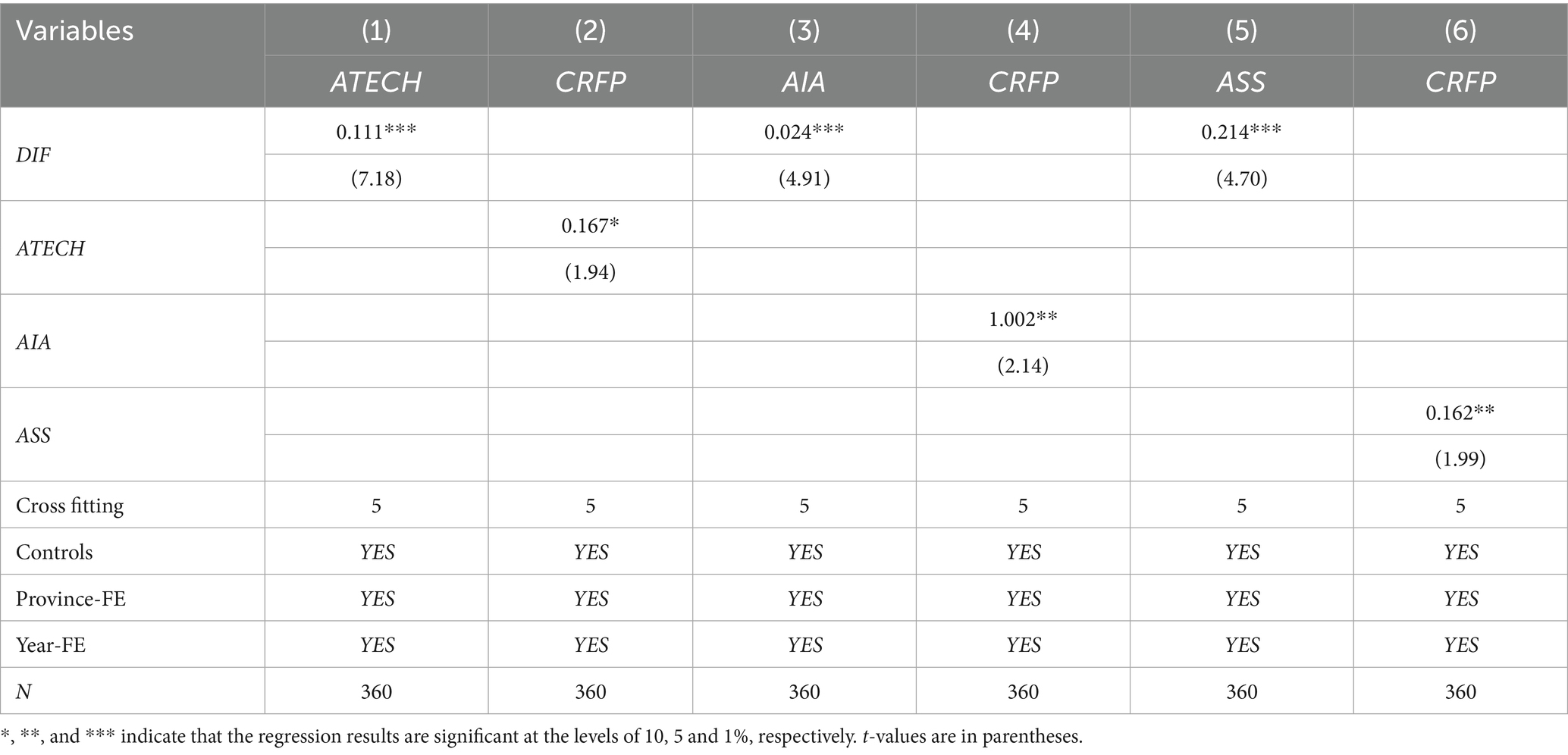
To explore potential mechanisms of DIF effects on CRFP, this study selected agricultural technological innovation, agricultural industrial agglomeration, and agricultural socialized services as mediating variables. The previous theoretical analysis has shown that DIF can improve the climate resilience of food production by promoting agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services. Table 6 reports the results of the mechanism test. Column (1) shows the regression results of DIF’s impact on agricultural technological innovation. The estimated coefficient of DIF is 0.111, which is significantly positive at the level of 1%, indicating that DIF can significantly promote agricultural technological innovation. Column (2) the regression results of CRFP influence for agricultural technology innovation, agricultural technology innovation of estimated coefficient is 0.167, the 10% significant level is positive, according to the column (1) and (2) the results of the analysis of DIF helps promote agricultural technology innovation, and enhance CRFP, empirical results and theoretical analysis; In the same way, the results of columns (3)–(6) show that DIF has a significant promotion effect on agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized service level, and agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized service level also have a significant promotion effect on CRFP. It shows that DIF can improve CRFP by promoting agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services. In conclusion, hypothesis 2 is verified.
4.4 Heterogeneity analysis
4.4.1 Heterogeneity analysis of regional division
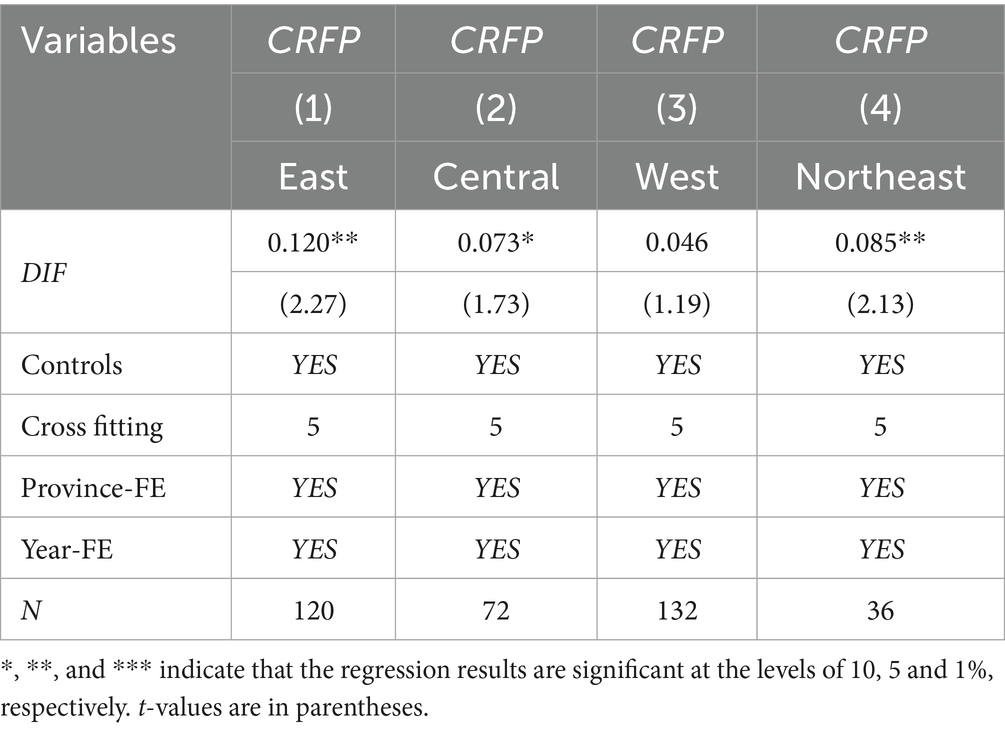
Due to differences in geographical location, climate conditions and resource endowments, the impact of DIF on CRFP may be heterogeneous in different regions. According to the regional division of China, this paper divides the samples into four regions: eastern, northeastern, central, western and northeastern regions. Table 7 shows the results of DIF’s impact on CRFP in these regions. According to the results of columns (1)–(4), DIF plays a significant role in promoting CRFP in the eastern, central and northeastern regions, and the regression coefficient of DIF is the largest in the eastern region (0.12 > 0.085 > 0.073). The reason is that the eastern region has a higher level of climate resilience than other regions, and the development of DIF is relatively fast. Thus, it effectively promoted CRFP. Secondly, the impact of DIF on CRFP in the western region is not significant, which may be due to the backward financial development level, the diverse climate and the relative lack of agricultural resources in this region, which may affect the effect of DIF on CRFP.
4.4.2 Heterogeneity analysis of the division of grain functional zones
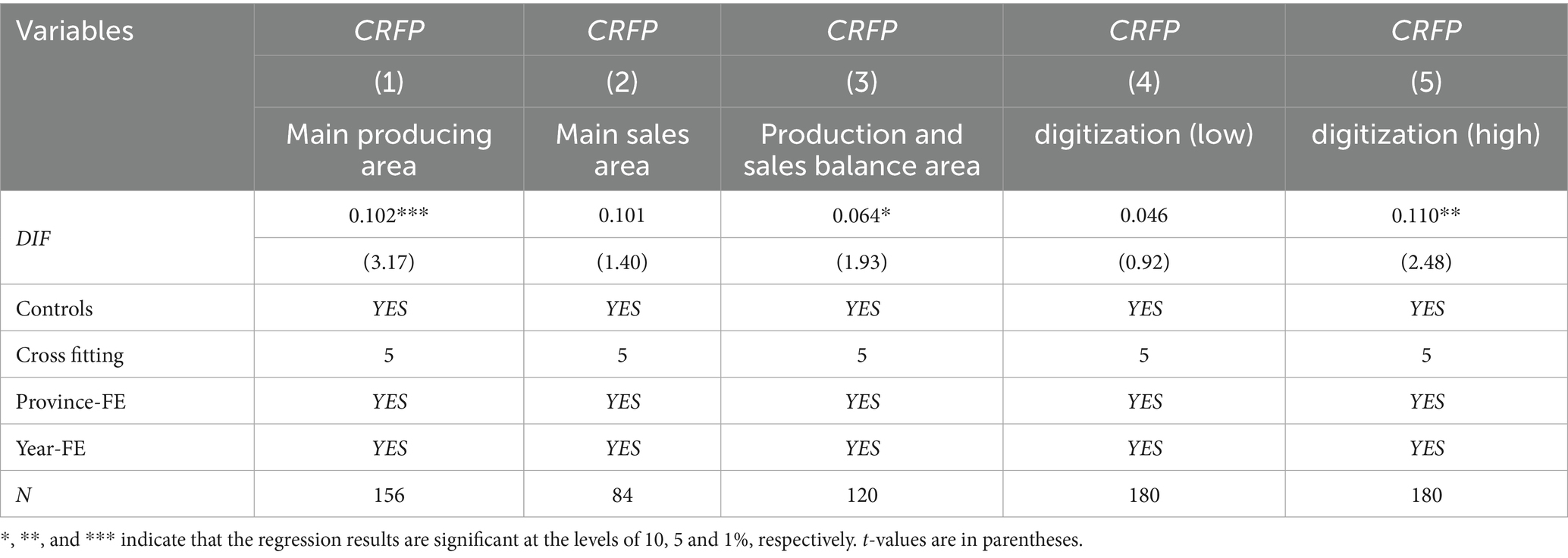
Because of the different functional planning and economic structure of each functional area, the grain production situation of each functional area is quite different. This paper divides each province into main grain producing area, main grain marketing area and balanced grain production and marketing area. From the results of Table 8 (1)–(3), it can be seen that only the DIF in major grain-producing areas and regions with balanced grain production and marketing has a significant increase in the impact on CRFP, and the promotion effect in major grain-producing areas is greater. Although the regression coefficients of grain main selling areas are all positive, they are not significant. This may be related to the agricultural characteristics and development priorities of these regions. Major food marketing regions usually have less arable land and agricultural resources, and agriculture accounts for a lower share of economic activity in these regions. Therefore, the improvement effect of DIF on CRFP is not obvious. The grain production and marketing balance area is between the main producing area and the main selling area, and its agricultural resources are relatively rich, but agriculture is not its main economic pillar. These regions may be more focused on the development of other industries, so the impact of DIF on CRFP is also relatively weak.
4.4.3 Heterogeneity analysis of digital infrastructure
With the development of digital technology, it plays an important role in the field of agricultural development. Therefore, the difference in the development of digital infrastructure also determines the effect of DIF on CRFP. In this paper, digital infrastructure level is measured comprehensively from three aspects: digital infrastructure construction, digital infrastructure application and digital infrastructure utilization, and the sample is divided into two groups of low level and high level according to the median of digital infrastructure level. Table 8 reports the regression results of the effect of DIF on CRFP for the two groups. According to the results of columns (4)–(5), in the group with high level of digital infrastructure, DIF has a significant effect on promoting CRFP, and the regression coefficient of DIF is 0.11, which is significantly positive at the level of 5%. In the digital infrastructure, low level group, DIF regression coefficient is 0.046, but not significant. The reason is that the difference of digital infrastructure may affect the efficiency of information circulation, the accessibility of technology and the responsiveness of agricultural producers to digital inclusive financial policies. In regions with a high degree of digitalization, agricultural producers can more easily access market information, technical guidance and financial support, so as to cope with the challenges brought by climate change more effectively. However, in less digitized regions, these resources may be relatively scarce, limiting the utilization and response of agricultural producers to digital financial inclusion policies.
5 Discussion and conclusion
5.1 Discussion
Based on the reality of global climate change aggravation threatening food security and the pain point that the traditional financial system is difficult to effectively empower the transformation of agricultural climate adaptation, this study uses China’s provincial panel data from 2011 to 2022 to explore the impact of DIF on CRFP and its mechanism through the comprehensive use the super-efficient SBM-DEA model and dual machine learning methods. The direct effect showed that DIF can significantly improve CRFP. This shows that DIF can break through the physical network restrictions through mobile payment, blockchain and other tools, so that marginal farmers can have low threshold access to climate adaptation technology (Mao et al., 2024). At the same time, by integrating multi-source data such as meteorological and soil data, the big data risk control model can realize the precise drip irrigation of credit resources to climate-vulnerable areas, which is in sharp contrast to the risk-averse tendency of traditional finance.
From the perspective of action mechanism, agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services constitute the core transmission path between DIF and CRFP. On the one hand, DIF by accurate docking agricultural development demand and financial resources, effectively promoted the water-saving irrigation, art varieties, such as technology innovation, and Xue et al. (2024) the conclusion; On the other hand, with the help of digital platforms, DIF optimizes the resource allocation of industrial chain, promotes the agglomeration of agricultural industry, and forms large-scale climate risk response capacity. At the same time, DIF activates the technology diffusion capacity of agricultural machinery cooperatives, plant protection service providers and other entities through supply chain finance tools, forming an ecological transmission chain from financial resources to service network and then to resilience gain, which provides a new perspective for understanding the synergy mechanism between fintech and agricultural organization innovation. Heterogeneity analysis results further reveal the policy effectiveness of boundary conditions. The significant promotion effect of the eastern region and the main grain-producing areas may be due to their high penetration rate of digital infrastructure and advantages of industrial clusters. It is important to note that the threshold of the digital infrastructure effect suggests the necessity of hardware, namely simply increasing digital financial coverage and not improve rural network conditions or digital literacy, could fall into trap “technical suspension.”
This paper makes the following contributions compared with previous studies: firstly, this study breaks through the comprehensive risk analysis paradigm of traditional resilience research and focuses on the targeted impact of extreme climate events on food production. At the same time, this study incorporates DIF into the analysis perspective to explore how it reshaped the climate response logic of food production system, and fill the gap of the interdisciplinary research on fintech and climate resilience. Secondly, this paper also explores the transmission mechanism of agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services between DIF and CRFP, and expands the channel of DIF’s effect on CRFP. Finally, we also discussed the different impacts of DIF on CRFP in different regions, food functional zones and digital infrastructure levels.
Although this study provides a rich and valuable theoretical analysis and empirical test on the impact of DIF on CRFP, there are still some limitations. (1) The limitations of the empirical method. This paper only uses the dual machine learning model to discuss the direct effect and indirect effect of DIF on CRFP, without considering the possible spatial spillover effect of DIF and CRFP. In the future, spatial econometric model can be used to further discuss the spatial spillover effect of DIF on CRFP. (2) Data level and availability limitations. In this paper, the research sample for the Chinese provincial data, the empirical results possible data gathered deviation, county level fails to reflect the DIF with CRFP real interaction. Future studies can explore further from county-level data and empirical data from other developing countries.
5.2 Conclusion
In this study, we select China’s provincial panel data from 2011 to 2022, and use the super-efficient SBM-DEA model and dual machine learning model to explore the role of digital inclusive finance on the climate resilience of food production and its intrinsic mechanism. The results show that DIF can significantly improve CRFP, and the conclusion is still valid after endogeneity and robustness tests. The mechanism of action shows that DIF can enhance CRFP by promoting agricultural technology innovation, agricultural industry agglomeration and agricultural socialized services. Heterogeneity analysis show that DIF has a significant effect on promoting CRFP in the eastern region, the main food-producing areas and the regions with high digital infrastructure. Based on the above conclusions, the following suggestions are put forward:
Firstly, the government should promote the differentiated development of digital inclusive financial service models in accordance with local conditions. In the eastern region, efforts should be made to further promote the deep integration of fintech and agricultural production and enhance the ability of risk identification and dynamic response. The central region should enhance the matching degree between financial products and the actual demands of grain production and improve the service supply system. The western regions should give priority to strengthening infrastructure construction, including Internet access, the deployment of payment terminals, and the popularization of digital financial knowledge among farmers, to enhance the accessibility, usability and effectiveness of digital financial services.
Secondly, encourage the development of tools such as agricultural digital credit, climate-indexed insurance and precision subsidies to strengthen farmers’ resilience in the pre-disaster financing, disaster response and post-disaster recovery phases. Government departments in major production areas should promote the deep integration of digital financial services with farmers’ actual business activities, and enhance the ability of financial services to support the full cycle of agriculture. For the main marketing areas, services such as information docking, storage and transportation management and market early warning can be strengthened to enhance the circulation efficiency and coordination capacity of the grain supply chain under climate shocks.
Thirdly, accelerating the layout of rural 5G networks, the Internet of Agricultural Things, remote sensing monitoring systems and disaster early warning platforms, and improving the ability of agricultural systems to sense and respond to extreme climate change. It will also strengthen infrastructure construction in central and western regions and marginalized areas through financial investment guidance, public service decentralization and government-enterprise collaboration, and promote the full embedding of digital information systems in agricultural production, credit services and insurance claims.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
LL: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Validation, Conceptualization. XL: Software, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the National Social Science Foundation of China (22XGL020).
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the efforts and patient comments from the editors and reviewers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1612111/full#supplementary-material
References
Agyekumhene, C., de Vries, J. R., van Paassen, A., Macnaghten, P., Schut, M., and Bregt, A. (2018). Digital platforms for smallholder credit access: the mediation of trust for cooperation in maize value chain financing. NJAS-Wageningen J. Life Sci. 86-87, 77–88. doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2018.06.001
Benami, E., and Carter, M. R. (2021). Can digital technologies reshape rural microfinance? Implications for savings, credit, & insurance. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 43, 1196–1220. doi: 10.1002/aepp.13151
Bhawra, J., Elsahli, N., and Patel, J. (2024). Applying digital technology to understand human experiences of climate change impacts on food security and mental health: scoping review. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 10:e54064. doi: 10.2196/54064
Billings, S. B., and Johnson, E. B. (2012). The location quotient as an estimator of industrial concentration. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 42, 642–647. doi: 10.1016/j.regsciurbeco.2012.03.003
Bushell, S., Buisson, G. S., Workman, M., and Colley, T. (2017). Strategic narratives in climate change: towards a unifying narrative to address the action gap on climate change. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 28, 39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.erss.2017.04.001
Carter, M. R. (2022). Can digitally-enabled financial instruments secure an inclusive agricultural transformation? Agric. Econ. 53, 953–967. doi: 10.1111/agec.12743
Chan, F. K. S., Zhu, Y. G., Wang, J., Chen, J., Johnson, M. F., Li, G., et al. (2024). Food security in climatic extremes: challenges and opportunities for China. Cell Reports Sustainability 1:100013. doi: 10.1016/j.crsus.2023.100013
Clay, N., and Zimmerer, K. S. (2020). Who is resilient in Africa’s green revolution? Sustainable intensification and climate smart agriculture in Rwanda. Land Use Policy 97:104558. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104558
Dookie, D. S., Conway, D., Dessai, S., and Oliner, E. (2024). Organisational perceptions of adapting to a changing climate. Clim. Risk Manag. 45:100637. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2024.100637
Fang, D., Chen, J., Wang, S., and Chen, B. (2024). Can agricultural mechanization enhance the climate resilience of food production? Evidence from China. Appl. Energy 373:123928. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123928
Fu, C., Sun, X., Guo, M., and Yu, C. (2024). Can digital inclusive finance facilitate productive investment in rural households? –an empirical study based on the China household finance survey. Financ. Res. Lett. 61:105034. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2024.105034
Goel, R. K., Yadav, C. S., Vishnoi, S., and Rastogi, R. (2021). Smart agriculture–urgent need of the day in developing countries. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 30:100512. doi: 10.1016/j.suscom.2021.100512
Guo, J., Chen, L., and Kang, X. (2024). Digital inclusive finance and agricultural green development in China: a panel analysis (2013–2022). Financ. Res. Lett. 69:106173. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2024.106173
Hong, X., Chen, Q., and Wang, N. (2024). The impact of digital inclusive finance on the agricultural factor mismatch of agriculture-related enterprises. Financ. Res. Lett. 59:104774. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2023.104774
Huang, D., Zhu, Y., and Yu, Q. (2022). Spatial spillover effects of agricultural agglomeration on agricultural non-point source pollution in the Yangtze River basin. Sustainability 14:16390. doi: 10.3390/su142416390
Iaksch, J., Fernandes, E., and Borsato, M. (2021). Digitalization and big data in smart farming–a review. J. Manag. Anal. 8, 333–349. doi: 10.1080/23270012.2021.1897957
Juhola, S., Klein, N., Kayhko, J., and Neset, T. S. S. (2017). Climate change transformations in Nordic agriculture? J. Rural. Stud. 51, 28–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2017.01.013
Kalantzopoulos, G., Paraskevopoulos, P., Domalis, G., Liopa-Tsakalidi, A., Tsesmelis, D. E., and Barouchas, P. E. (2024). The Western Greece soil information system (WΕSIS)—a soil health design supported by the internet of things, soil databases, and artificial intelligence Technologies in Western Greece. Sustainability 16:3478. doi: 10.3390/su16083478
Kirchner, E., and Musshoff, O. (2024). Digital opportunities for the distribution of index-based microinsurance: evidence from a discrete choice experiment in Mali. J. Agric. Econ. 75, 794–815. doi: 10.1111/1477-9552.12584
Ky, S. S. (2025). Empowering sub-Saharan farmers: the transformative effect of mobile money in agriculture. J. Rural. Stud. 117:103637. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2025.103637
Li, B., and Gao, Y. (2024). Impact and transmission mechanism of digital economy on agricultural energy carbon emission reduction. Int. Rev. Econ. Finance 95:103457. doi: 10.1016/j.iref.2024.103457
Li, H., Tian, H., Liu, X., and You, J. (2024). Transitioning to low-carbon agriculture: the non-linear role of digital inclusive finance in China’s agricultural carbon emissions. Hum. Soc. Sci. Commun. 11, 1–14. doi: 10.1057/s41599-024-03354-1
Li, F., Zang, D., Chandio, A. A., Yang, D., and Jiang, Y. (2023). Farmers' adoption of digital technology and agricultural entrepreneurial willingness: evidence from China. Technol. Soc. 73:102253. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2023.102253
Li, X., and Zhang, J. (2024). Rural digital credit and residential energy consumption: evidence from the agricultural production perspective. Energy 290:130111. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.130111
Liu, Y., Deng, Y., and Peng, B. (2023). The impact of digital financial inclusion on green and low-carbon agricultural development. Agriculture 13:1748. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13091748
Liu, Q., and Yan, T. (2024). How do digital media strengthen the role of social networks in promoting farmers' adoption of climate change mitigation measures? China Agric. Econ. Rev. 16, 445–467. doi: 10.1108/CAER-05-2023-0118
Lu, Q., Liao, C., Chen, M., Shi, V., Hu, X., and Hu, W. (2024). Platform financing or bank financing in agricultural supply chains: the impact of platform digital empowerment. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 315, 952–964. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2023.12.024
Mao, H., Chai, Y., Shao, X., and Chang, X. (2024). Digital extension and farmers' adoption of climate adaptation technology: an empirical analysis of China. Land Use Policy 143:107220. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2024.107220
Pappa, F. (2024). Sounding the alarm for digital agriculture: examining risks to the human rights to science and food. Neth. Q. Hum. Rights 42, 276–296. doi: 10.1177/09240519241270408
Prasad, R. S., and Sud, R. (2019). Implementing climate change adaptation: lessons from India’s national adaptation fund on climate change (NAFCC). Clim. Pol. 19, 354–366. doi: 10.1080/14693062.2018.1515061
Quarshie, P. T., Abdulai, A. R., Duncan, E., Kc, K. B., Roth, R., Sneyd, A., et al. (2023). Myth or reality? The digitalization of climate-smart agriculture (DCSA) practices in smallholding agriculture in the bono east region of Ghana. Clim. Risk Manag. 42:100553. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2023.100553
Ren, X., Zeng, G., and Gozgor, G. (2023). How does digital finance affect industrial structure upgrading? Evidence from Chinese prefecture-level cities. J. Environ. Manag. 330:117125. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117125
Richards, C., Messner, R., and Higgins, V. (2024). Digital technology and on-farm responses to climate shocks: exploring the relations between producer agency and the security of food production. Agric. Hum. Values 42, 53–67. doi: 10.1007/s10460-024-10624-w
Volkov, A., Morkunas, M., Balezentis, T., and Streimikiene, D. (2022). Are agricultural sustainability and resilience complementary notions? Evidence from the north European agriculture. Land Use Policy 112:105791. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105791
Wang, J. (2023). Digital inclusive finance and rural revitalization. Financ. Res. Lett. 57:104157. doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2023.104157
Wigboldus, S., Klerkx, L., Leeuwis, C., Schut, M., Muilerman, S., and Jochemsen, H. (2016). Systemic perspectives on scaling agricultural innovations. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 36, 1–20. doi: 10.1007/s13593-016-0380-z
Wu, J., Ge, Z., Han, S., Xing, L., Zhu, M., Zhang, J., et al. (2020). Impacts of agricultural industrial agglomeration on China’s agricultural energy efficiency: a spatial econometrics analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 260:121011. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121011
Xu, Z., and Yang, J. (2025). Impact of digital finance on rural industry revitalization. Int. Rev. Econ. Finance 97:103820. doi: 10.1016/j.iref.2024.103820
Xue, Z., Hou, Y., Cao, G., and Sun, G. (2024). How does digital transformation drive innovation in Chinese agribusiness: mechanism and micro evidence. J. Innov. Knowl. 9:100489. doi: 10.1016/j.jik.2024.100489
Xue, Y., Hu, D., Irfan, M., Wu, H., and Hao, Y. (2023). Natural resources policy making through finance? The role of green finance on energy resources poverty. Resources Policy 85:104023. doi: 10.1016/j.resourpol.2023.104023
Yang, Z., Li, Y., and Wu, C. (2025). Population aging, fintech, and agricultural economic resilience. Int. Rev. Econ. Finance 97:103756. doi: 10.1016/j.iref.2024.103756
Yao, R., Ma, Z., Wu, H., and Xie, Y. (2024). Mechanism and measurement of the effects of industrial agglomeration on agricultural economic resilience. Agriculture 14:337. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14030337
Yi, F., Yao, L., Sun, Y., and Cai, Y. (2023). E-commerce participation, digital finance and farmers' income. China Agric. Econ. Rev. 15, 833–852. doi: 10.1108/CAER-03-2023-0053
Yu, L., Zhao, D., Xue, Z., and Gao, Y. (2020). Research on the use of digital finance and the adoption of green control techniques by family farms in China. Technol. Soc. 62:101323. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2020.101323
Zhang, H., Zhang, J., and Song, J. (2022). Analysis of the threshold effect of agricultural industrial agglomeration and industrial structure upgrading on sustainable agricultural development in China. J. Clean. Prod. 341:130818. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130818
Zheng, H., and Li, X. (2022). The impact of digital financial inclusion on carbon dioxide emissions: empirical evidence from Chinese provinces data. Energy Rep. 8, 9431–9440. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.07.050
Keywords: digital inclusive finance, food production, climate resilience, machine learning, agricultural industry agglomeration
Citation: Liu L and Li X (2025) How does digital inclusive finance improve the climate resilience of food production? Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1612111. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1612111
Edited by:
Songyu Jiang, Rajamangala University of Technology Rattanakosin, ThailandReviewed by:
Xiaomin Wu, Hebei University, ChinaJiahao Wang, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiang Li, eGlhbmdsaUBtYWlsLmd1ZmUuZWR1LmNu
 Liangcan Liu
Liangcan Liu Xiang Li
Xiang Li