- 1University of Agricultural Sciences, Bengaluru, India
- 2ICAR-National Institute of Seed Science and Technology, Regional Station, Bengaluru, India
- 3University of Agricultural Sciences, Raichur, India
- 4ICAR-Indian Institute of Groundnut Research, Regional Station, Ananthapur, India
- 5ICAR-Central Coastal Agricultural Research Institute, Old Goa, Goa, India
- 6ICAR-National Institute of Abiotic Stress Management, Baramati, India
- 7ICAR-Indian Institute of Farming Systems Research, Modipuram, Meerut, India
- 8ICAR-Indian Grassland and Fodder Research Institute, Jhansi, India
- 9ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi, India
- 10ICAR-National Institute for Research on Commercial Agriculture, Rajahmundry, Andhra Pradesh, India
Nanotechnology offers a sustainable strategy for improving nutrient efficiency and crop productivity. This study hypothesized that green-synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles (Zinc based NPs), derived from weed leaf extracts, could enhance maize performance more effectively than conventional zinc sources. Zinc based NPs (76.89 nm, spherical) were synthesized and characterized, then evaluated through a field experiment using maize hybrid MAH 14–5. Treatments involved seed priming with 800 ppm zinc-based NPs and foliar applications at 200–600 ppm under a randomized complete block design. Results revealed that the combination of seed priming and 500 ppm foliar spray (T5) significantly improved plant height (277.6 cm), leaf area index (2.99), and dry matter production (344 g plant−1). This treatment also recorded the highest kernel yield (8,525 kg ha−1), stover yield (11,803 kg ha−1), and harvest index (0.422), outperforming conventional ZnSO4 treatments. These findings suggest that biogenic nano zinc is a promising, eco-friendly alternative for boosting maize yield and resource use efficiency.
1 Introduction
Zinc (Zn) deficiency is a widespread nutritional challenge affecting nearly one-third of the global population, especially in developing countries like India (Ghosh et al., 2020). Soils in many agro-ecological zones suffer from low zinc availability due to high pH, calcareous nature, low organic matter, and continuous nutrient mining without adequate replenishment (Biradar et al., 2023). This limited zinc availability in soil directly impacts plant uptake, resulting in zinc-deficient crops, which ultimately contributes to malnutrition in humans, particularly in children and women (Khokhar et al., 2024; Rajanna et al., 2023). In plants, zinc plays a crucial role as a cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions, stabilizing protein structures, regulating gene expression, and maintaining membrane integrity, all of which are essential for normal growth and development.
Maize (Zea mays L.), the third-most important cereal crop globally after rice and wheat, is cultivated on approximately 193.7 million hectares with a production of 1,147.7 million tonnes and average productivity of 5.75 t ha−1 (Anonymous, 2021). In India, it spans 9.8 million hectares, producing 33.18 million tonnes with an average yield of 3,199 kg ha−1. Specifically in Karnataka, maize is grown on 17.26 lakh hectares with a production of 53.6 lakh tonnes and productivity of 3,298.5 kg ha−1 (Anonymous, 2022). Despite its adaptability to diverse agro-climatic conditions, maize is highly sensitive to zinc deficiency, often exhibiting symptoms such as poor root development, stunted growth, and interveinal chlorosis in young leaves (Balogun et al., 2020). As an indicator crop for zinc deficiency (Ahsan et al., 2022), maize serves as an ideal system to evaluate zinc nutrition strategies. Addressing zinc deficiency through external sources such as zinc fertilizers is therefore essential to enhance both crop productivity and nutritional value.
Green synthesis of nanoparticles has gained prominence in material and life sciences due to properties such as extremely small size, high surface area-to-volume ratio, and antimicrobial effects (Abdullah et al., 2020; Khan et al., 2020). This eco-friendly method employs phytoconstituents from plant extracts as reducing and stabilizing agents, eliminating the need for high energy inputs or toxic chemicals (Akshay et al., 2024; Ovais et al., 2017). Leaves are commonly used due to their rich composition of polyol and heterocyclic compounds that aid in the reduction and stabilization of metal nanoparticles (El-Naggar et al., 2022). According to the researchers the polyol components present in the plant extract are responsible for the reduction of zinc ions whereas water soluble heterocyclic components stabilize the nanoparticles formed. Appropriate precursors such as zinc nitrate can be used for the reduction of plant extracts. Due to the cost-effective, safe and non-toxic method of nanoparticle synthesis, and the ability of plant extracts to act as capping/stabilizing agents thus reducing particle size and improving reactivity, green synthesis method is preferred (Aksu Demirezen et al., 2019; Iyarin et al., 2024). This method of synthesis will not release any toxic chemicals into the environment during their efficiency. Nano-fertilizers prove to be highly effective in the realm of precision agriculture, as they facilitate precise nutrient management by synchronizing nutrient supply with the varying demands of crop growth stages throughout the entire growth period (Alshaal and El-Ramady, 2017; Ahmed et al., 2023).
While the synthesis of zinc based nanoparticles via green routes has been reported in previous studies, there remains a limited understanding of their agronomic application and optimal concentration for field crops like maize. Moreover, most earlier work focused either on the synthesis or preliminary characterization of nanoparticles, with fewer studies integrating both synthesis and direct agricultural application in a comprehensive manner. This study distinguishes itself by not only employing a green synthesis approach for zinc based nanoparticle production but also evaluating its impact on maize growth and yield under varying concentrations. Hence, the primary contribution of this research lies in both domains—the eco-friendly synthesis of zinc based NPs and their practical application in enhancing maize productivity.
The conventional method of applying fertilizers to the soil, while widely practiced comes with several limitations, primarily related to nutrient accessibility to plants. Green synthesis of nanoparticles aims to reduce waste production and create sustainable methods. The advancement of nanotechnology has recently placed a focus on green methods that employ temperate reaction conditions and non toxic precursors in order to support environmental sustainability (Vitta et al., 2020). The creation of NPs can be done using green synthesis techniques, which have the advantages of lower failure rates, lower costs and simpler characterization. Due to their hazardous by products, physical and chemical methods of creating nanoparticles have placed a number of negative impact on the environment (El-Naggar et al., 2022). A metal salt is made with plant extract and the process takes only a few minutes to a few hours at standard room temperature. This makes plant-based synthesis of nanoparticles quite simple (Yusoff et al., 2020).
Although there have been few instances of improved plant growth and yield, the special characteristics of nanoparticles may lead to dramatically different environmental outcomes and behaviors than those of their bulk counterparts (Akshay et al., 2024). Nanoparticles, due to their high surface area (30–50 m2 g−1), enhanced solubility, and mobility, can increase nutrient absorption by plants and improve physiological performance (Rajiv et al., 2013). Given these advantages, the current study aims to address the issue of zinc deficiency in maize through green-synthesized zinc based nanoparticles. We hypothesize that biogenically synthesized zinc based NPs can improve maize growth, physiological function, and biochemical properties more effectively than conventional zinc fertilizers. The specific objectives are: (i) to synthesize and characterize zinc based nanoparticles using green leaf extract; (ii) to assess their impact on maize growth and physiology; and (iii) to compare their efficacy with traditional zinc applications. By optimizing zinc based NP concentration, this study aims to bridge the gap between lab-scale nanoparticle synthesis and field-scale agricultural utility, contributing to sustainable and efficient crop production systems.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles
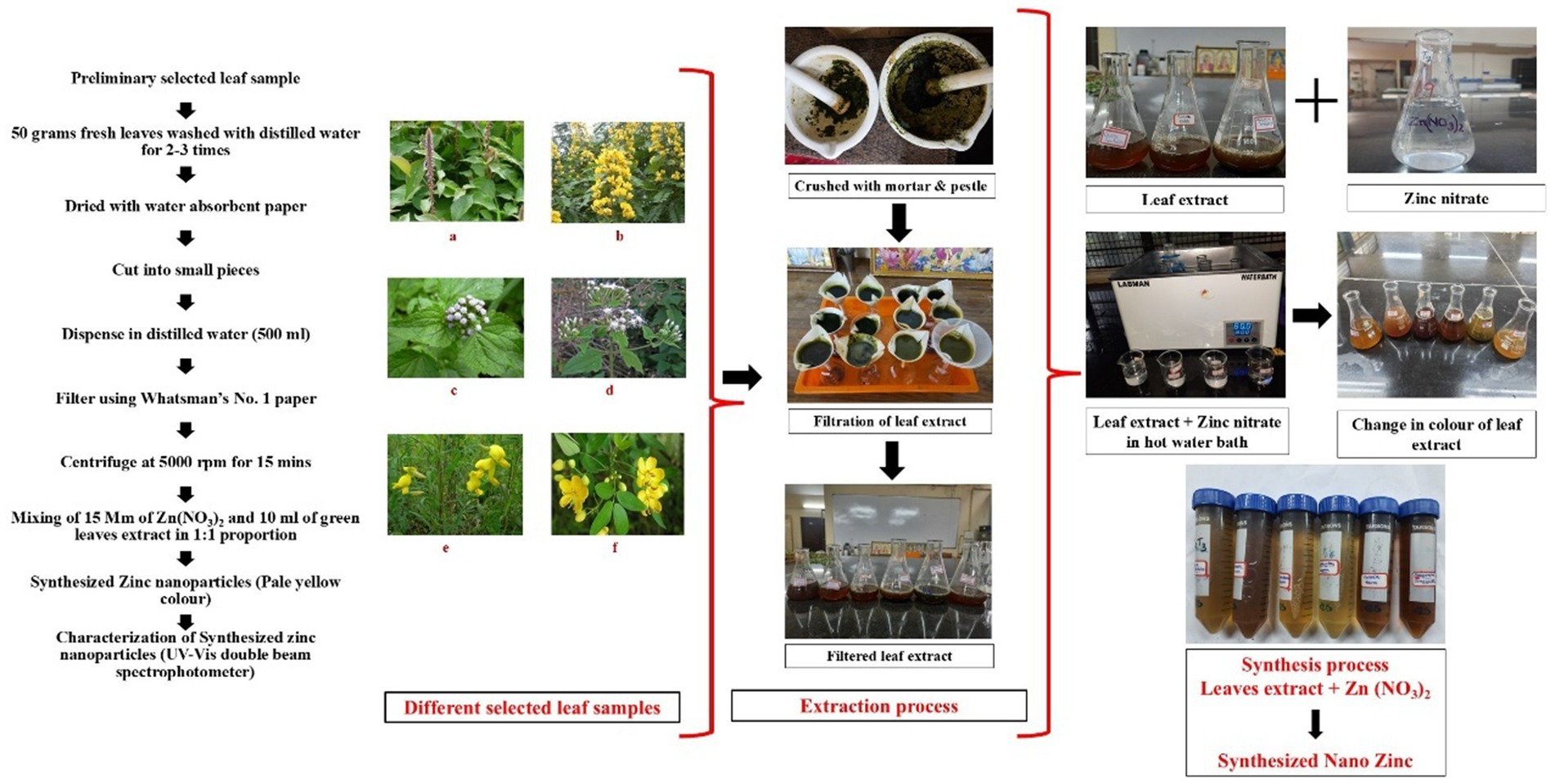
The synthesis of zinc nanoparticles were carried out by collecting fresh, healthy and young leaves of Cassia spectabilis, Crotalaria juncea, Chromolaena odorata, Achyranthes aspera, Ageratum conyzoides, and Cassia tora, collected from the GKVK campus, UAS Bangalore.
Leaves were cleaned, oven-dried and crushed with mortar and pestle. Next the processed leaves (50 g) were heated by taking 500 mL distilled water at 75°C for 10 min which was then cooled, filtered using Whatman No 1 filter paper and stored in refrigerator for further use. Furthermore, the leaves extract was centrifuged at 5,000 rpm for 15 min which was then used directly for the synthesis of zinc nanoparticles.
Zinc oxide nanoparticles were synthesized using the method outlined by Jayachandran et al. (2021). Briefly, 15 mM aqueous solution of Zn (NO3)2 was added to 10 mL of leaves extract in 1:1 proportion in clean sterilized flask (Figure 1). The mixture was continuously stirred at 60°C for 2 h to facilitate the reduction of Zn2+ ions. A gradual change in color to pale yellow indicated the formation of zinc nanoparticles (Figure 2). The solution was then allowed to cool at room temperature and was subsequently centrifuged at 8,000 rpm for 20 min. The pH of the reaction mixture was adjusted to approximately 8.5, as alkaline conditions are known to favor nanoparticle formation and stability, facilitating effective reduction of Zn2+ ions by the phytochemicals present in the extract. The resulting pellet was collected, washed with distilled water and ethanol to remove impurities, and then oven-dried at 60°C for 12 h. The dried nanoparticles were stored in airtight containers for further characterization and application.
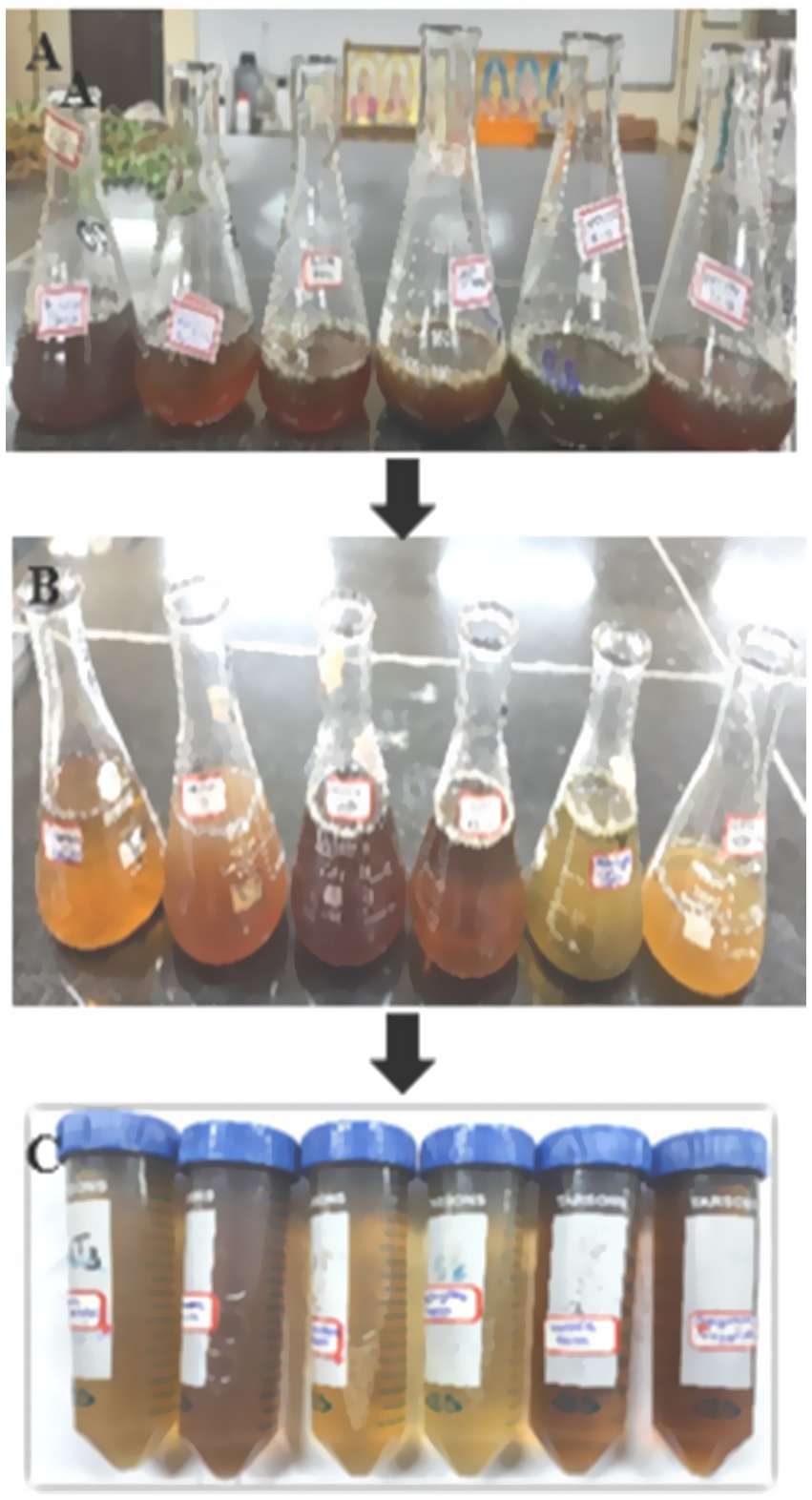

Figure 1. Synthesis of zinc nanoparticles using selected plant leaf extract: (A) Plant leaves extract, (B) Reaction mixture, (C) Synthesized zinc nanoparticles.
2.2 Characterization of synthesized nano zinc particles
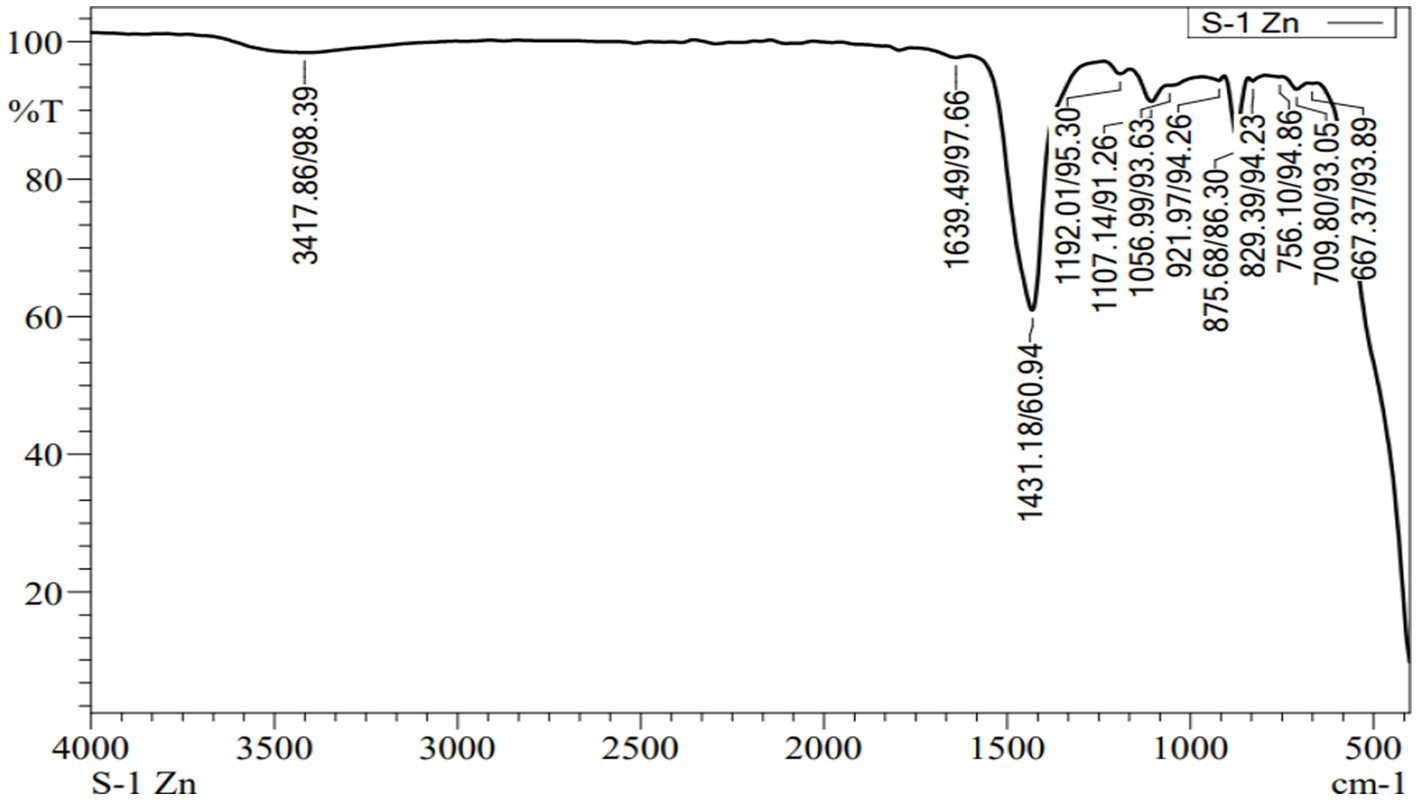
The characterization of the synthesized zinc nanoparticles from green biomass was conducted at the Centre for Nanotechnology, College of Agricultural Engineering, UAS Raichur. For UV–Vis spectroscopy, an aliquot of the nanoparticle suspension was diluted 1:10 with distilled water and the absorbance spectra were measured over the wavelength range of 300–700 nm using a UV–Vis visible spectrophotometer (UV–Vis Spectrophotometer, Shimadzu UV-1800, Japan) (Arularasu et al., 2018) to identify the characteristic absorption peaks of Zn nanoparticles. Particle size and zeta potential were determined using a Zeta sizer (Nano ZS-90, Malvern Instruments, UK) (Bakhtiari et al., 2015), where the sample was diluted 1:20 with distilled water, sonicated briefly to disperse aggregates, and measured at 25°C in triplicate. Morphological analysis was performed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (FEI, Quanta 250, Netherlands) at 80 kV in high contrast imaging mode; a drop of the nanoparticle suspension was placed on a carbon-coated copper grid and air-dried for 12 h before imaging. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) was used to identify functional groups attached to the surface of the zinc nanoparticles by measuring the vibrational frequencies of chemical bonds within the range of 4,000–400 cm−1 (Balogun et al., 2020); the nanoparticle suspension was analyzed directly without further sample processing. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) was conducted using a Bruker Alpha II FTIR spectrometer (Bruker Optik GmbH, Germany) to identify the functional groups associated with the zinc nanoparticles. Spectra were recorded in the range of 4,000–400 cm−1 using the Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR) mode, with a resolution of 4 cm−1 and an average of 24 scans per sample. The resulting spectra displayed prominent absorption bands corresponding to O–H stretching (around 3,400 cm−1), C=O stretching (around 1,650 cm−1), and Zn–O bonding vibrations typically observed below 600 cm−1, confirming the successful capping and stabilization of Zn nanoparticles by the phytochemicals present in the leaf extract (Balogun et al., 2020).
2.3 Zinc content in synthesized nanoparticles
The zinc concentration in the synthesized nanoparticles was quantified using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry (AAS), following the method described by Barzinjy and Azeez (2020). For the synthesis, 50 mL of weed leaf extract was mixed with 50 mL of a 15 mM zinc nitrate [Zn(NO3)2] solution, resulting in a total reaction volume of 100 mL. The theoretical zinc content in the 15 mM Zn(NO3)2 solution was calculated to be 7.2 g per 500 mL. After the completion of synthesis, the resulting colloidal solution was analyzed using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry, which revealed a zinc concentration of 2,188 ppm, indicating successful incorporation of zinc into the nanoparticle formulation.
2.4 Seed germination study
The Paper Towel Method, recommended by the International Seed Testing Association (ISTA), was used to evaluate the effect of synthesized nano-potassium on maize seed germination (Akshay et al., 2024). A Completely Randomized Design (CRD) was implemented with three soaking durations—15, 30, and 45 min—each replicated three times. For the germination test, 10 seeds per trial were placed between two lightly moistened brown corrugated paper towels, ensuring they were damp but not overly wet. The first sheet was laid on a transparent plastic surface, and the seeds were evenly spaced before covering them with the second moistened sheet. The towels were then rolled into a cylindrical shape, secured with butter paper and rubber bands, and placed vertically in a seed incubator maintained at 20–30°C with controlled humidity (approximately 70 ± 5% relative humidity) and proper air circulation, as humidity is a crucial factor influencing seed germination. Seed germination was observed daily and continued until all seeds had sprouted. After 14 days, shoot length, root length, germination percentage, and seed vigor index were recorded. The germination percentage was calculated based on the total number of germinated seeds, while the seed vigor index was determined using a standard formula.
2.5 Field experimental details
Prior to the initiation of the field experiment, the soil at the experimental site was analyzed for its chemical properties. The soil had a slightly acidic pH of 6.31 and low electrical conductivity (0.18 dS m−1), indicating non-saline conditions. The organic carbon content was 0.41%, while the available nitrogen, phosphorus (P2O5), and potassium (K2O) levels were 335.4, 41.32, and 241.7 kg ha−1, respectively, indicating adequate macronutrient availability. The available zinc content was 0.44 ppm, which is near the deficiency threshold for most crops, justifying the application of zinc in the experiment. A field experiment was conducted to study the effect of combined seed treatment and foliar application of synthesized nano zinc on the growth and yield of maize during the summer season of 2023 at the Zonal Agricultural Research Station (ZARS), University of Agricultural Sciences (UAS), GKVK, Bengaluru. The maize hybrid cultivar MAH 14–5 was used for the study. The experiment followed a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with eight treatments and three replications. Each gross plot measured 3.0 m × 2.4 m (7.2 m2), and the net plot measured 1.8 m × 1.8 m (3.24 m2), with plant spacing maintained at 60 cm × 30 cm and a seed rate of 15 kg ha−1. Sowing was done on 1st December 2022, and harvesting took place on 4th April 2023. A recommended fertilizer dose of 150:75:40 kg N: P2O5: K2O ha−1 along with 10 t ha−1 of FYM was uniformly applied to all the treatments. The treatments included seed priming with synthesized nano-zinc at 800 ppm for 30 min alone (T1) and in combination with foliar application of synthesized nano-zinc at concentrations of 200 ppm (T2), 300 ppm (T3), 400 ppm (T4), 500 ppm (T5), and 600 ppm (T6). In addition, conventional zinc sources were used as foliar application of ZnSO4 at 0.5% (T7) and soil application of ZnSO4 at 10 kg ha−1 (T8). The foliar application of synthesized nano-zinc for respective treatments was carried out at 30 days after sowing (DAS).
2.6 Measurement of growth, yield components and yield, nutrient use efficiency and economics of maize
2.6.1 Plant height, leaf area index and dry matter production
At 90 days after sowing (DAS), plant height (cm) was measured from the ground level to the base of the fully expanded top leaf on five randomly selected plants within the net plot area. The leaf area index (LAI) was calculated as the ratio of total leaf area to the ground area occupied by the crop, using the standard formula: LAI = Leaf area per plant (cm2)/Ground area per plant (cm2). Total dry matter production (TDMP) was assessed by collecting leaf, stem, and cob samples from the same plants at 90 DAS. The samples were initially shade-dried for 48 h to allow gradual moisture loss and minimize thermal damage, then oven-dried at 65 ± 2°C to a constant weight, following standard agronomic procedures. After drying, the samples were cooled in a desiccator and weighed using an analytical balance. The final dry weights were recorded and expressed in grams per plant (Tripathi et al., 2017). The 90 DAS stage was specifically chosen because it represents the peak vegetative to early reproductive phase in maize, a critical period during which the plant shows maximum physiological activity, nutrient uptake, and biomass accumulation. Assessing growth parameters at this stage provides a reliable indication of treatment effects and overall crop performance (Alshaal and El-Ramady, 2017; Ahmed et al., 2023).
2.6.2 Yield components and yield
The yield and yield parameters in maize were recorded from tagged plants and the net plot area to assess the crop’s productive performance. Cob length was measured using a linear scale from base to tip and expressed in centimeters. The number of kernel rows per cob was determined by counting the total rows in each cob from tagged plants and averaging the values. Similarly, the number of kernels per row was recorded from five labeled plants, and the total number of kernels per cob was calculated by counting all kernels in each cob and taking the average. Kernel weight per cob was obtained by weighing the kernels from tagged plants and expressing the average in grams. Test weight was recorded as the weight of 100 kernels taken from the tagged plants and expressed in grams. Grain yield and stover yield were recorded from the net plot area, converted to kilograms per hectare. Finally, the harvest index was calculated using the formula suggested by Donald (1962), where Harvest Index = Economic yield (kg ha−1)/Biological yield (kg ha−1), indicating the proportion of total biomass partitioned into economic produce.
2.6.3 Nutrient use efficiency
Nutrient use efficiency was calculated by using following formula and expressed as kg kernel yield per kg nutrient applied. It was separately calculated for each nutrient viz., N, P and K.
2.6.4 Economics
The economic analysis was carried out to assess the profitability of different treatments. The cost of cultivation was computed based on the prevailing prices of inputs and labor during the experimentation period and expressed in ₹ ha−1. Gross returns were calculated by multiplying the grain yield with the market price at the time of harvest. Net returns for each treatment were derived by subtracting the cost of cultivation from the gross returns. The benefit–cost ratio (B:C) was calculated for each treatment by dividing the gross returns by the cost of cultivation, providing a clear measure of the economic viability of each treatment.
2.7 Statistical analysis
Seed germination studies were conducted under controlled conditions using a Completely Randomized Design (CRD) with three replications to ensure the uniform distribution of experimental error. For the field experiment, a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with three replications was employed to minimize the impact of field variability and to obtain more precise treatment comparisons. The experimental data collected from both studies were subjected to rigorous statistical analysis using IBM SPSS Statistics software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Results are reported as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), along with the standard error (SE), critical difference at 5% significance level (CD at 0.05), and the F value derived from the analysis of variance (ANOVA) for each treatment. This comprehensive statistical approach was undertaken to ensure the robustness and reliability of the findings, enabling accurate interpretation of treatment effects.
3 Results
3.1 Confirmation of synthesis of nano particles
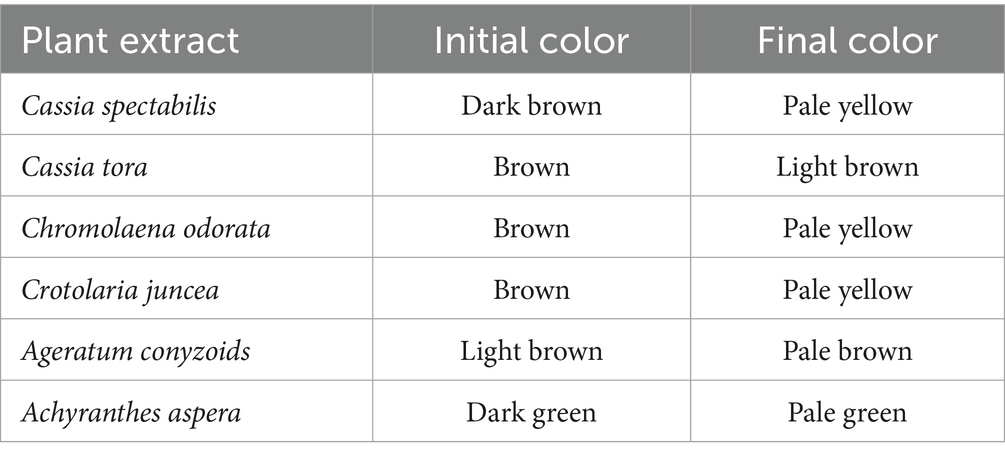
The synthesis of zinc nanoparticles from Cassia spectabilis, Crotolaria juncea, Chromolaena odorata, Achyranthes aspera, Ageratum conyzoids and Cassia tora was done using the standard method. The leaf extract act as reducing as well as capping agent. Zn+2 ions were reduced into Zn nanoparticles when leaves extracts were mixed with Zn(NO3)2 solution. The leaves extract which was initially dark green when mixed with transparent zinc nitrate solution it was changed to pale green then after 1 h it turned to pale yellow within 1 h. This color change indicates the reduction of Zn2+ ions and the nucleation of zinc nanoparticles, with the pale yellow coloration associated with the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) effect of the formed nanoparticles. The absence of further color change after 24 h (Table 1 and Figure 1) suggested the completion of the reduction process and stabilization of the nanoparticles, thus reflecting the efficiency and completeness of the synthesis reaction.
When the zinc nitrate solution is combined with the green leaf extract, natural compounds like flavonoids, phenolics, and terpenoids in the extract help reduce and stabilize the zinc ions. These compounds bind to the Zn2+ ions, which then react with hydroxyl ions (OH−) present in the mixture to form zinc hydroxide as an intermediate. With some heating or over time, this intermediate transforms into zinc based nanoparticles through a dehydration process. Additionally, the plant compounds surround the nanoparticles, stopping them from clumping together and helping control their size and shape (Vitta et al., 2020).
3.2 Characterization of synthesized nano zinc
3.2.1 UV–vis spectrophotometry and zetasizer
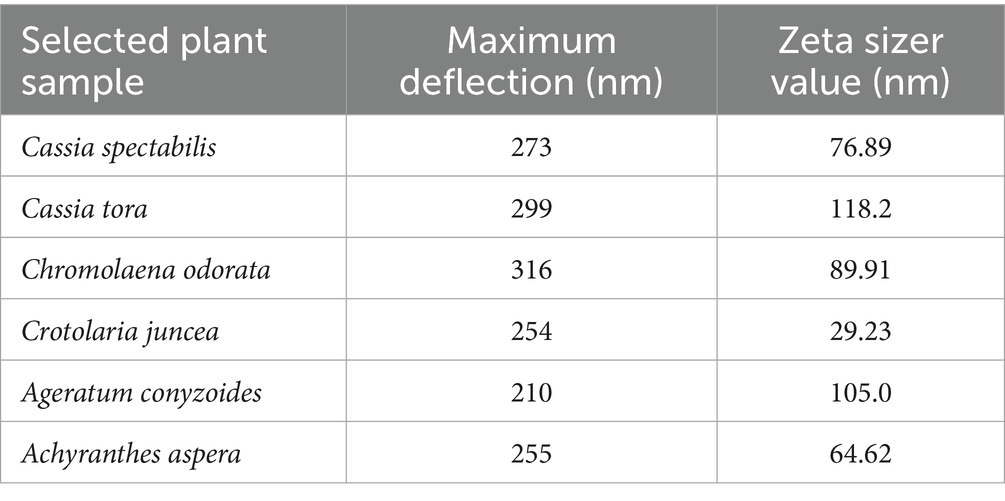
The UV–Vis spectrophotometric analysis, conducted within the wavelength range of 210–316 nm, recorded maximum deflection values at specific wavelengths for different plant sources: 273 nm for Cassia spectabilis, 299 nm for Cassia tora, 316 nm for Chromolaena odorata, 254 nm for Crotolaria juncea, 210 nm for Ageratum conyzoides, and 255 nm for Achyranthes aspera, as presented in Table 2 and depicted in Figure 3. Furthermore, the particle size of the synthesized nano zinc was determined using a Malvern Zeta Sizer Nano ZS90, which operates based on quasi-elastic light scattering. The measured particle sizes and their poly dispersity indices (PDI) were recorded as 76.89 nm for Cassia spectabilis, 188.2 nm for Cassia tora, 89.91 nm for Chromolaena odorata, 29.23 nm for Crotolaria juncea, 105 nm for Ageratum conyzoides, and 64.62 nm for Achyranthes aspera (Table 2). Among the selected plant species used for the synthesis of nano zinc, only Cassia spectabilis (76.89 nm) was chosen for further study, as it exhibited a single peak with a particle size below 100 nm. In contrast, Chromolaena odorata, Achyranthes aspera, and Crotolaria juncea showed two peaks, one above and one below 100 nm, making them less suitable. The results related to this are presented in Table 2 and depicted in Figure 4.
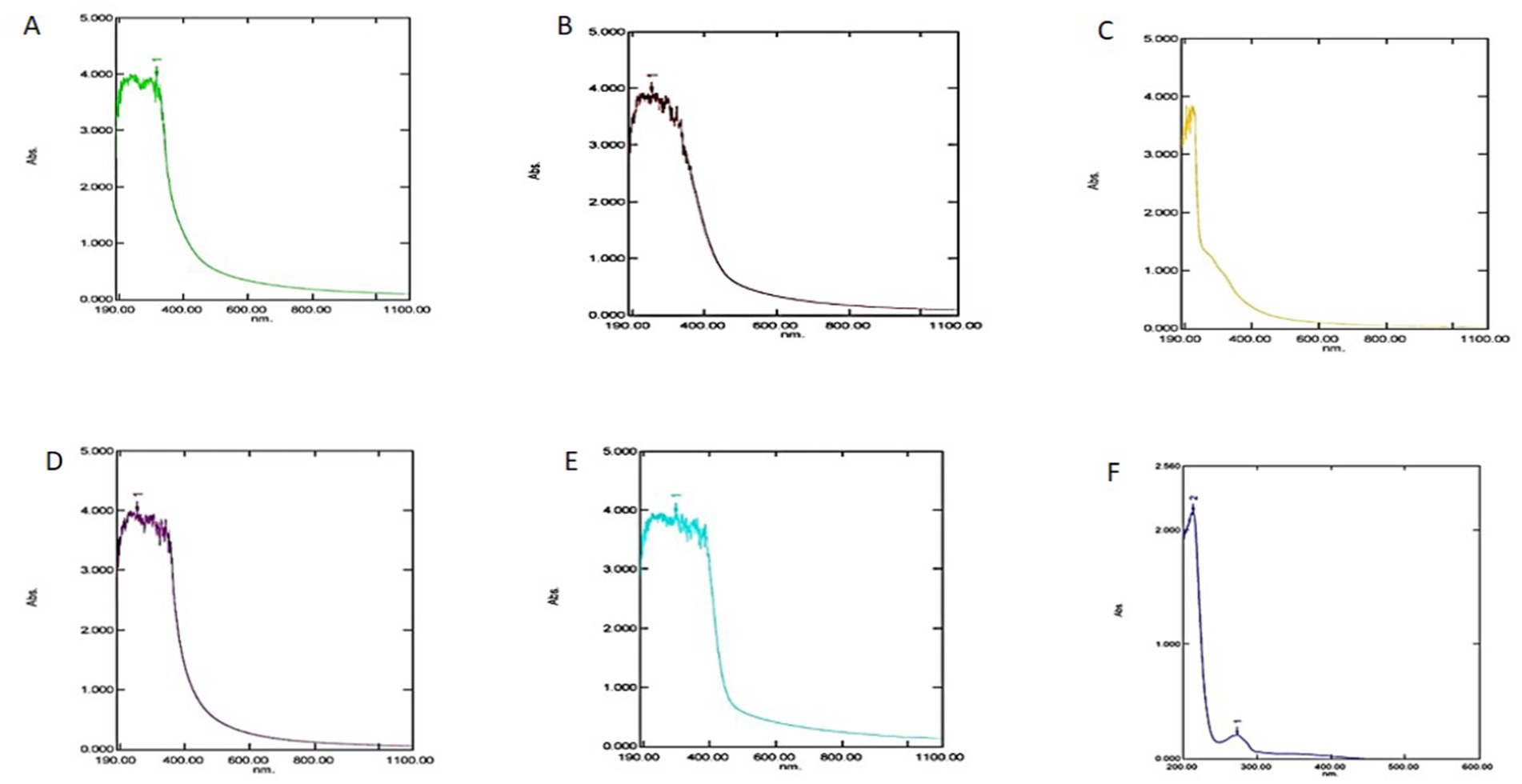
Figure 3. UV–Vis spectra of synthesized nano zinc using weed leaf extracts: (A) Achyranthes aspera, (B) Chromolaena odorata, (C) Ageratum conyzoides, (D) Crotolaria juncea, (E) Cassia tora, (F) Cassia spectabilis,
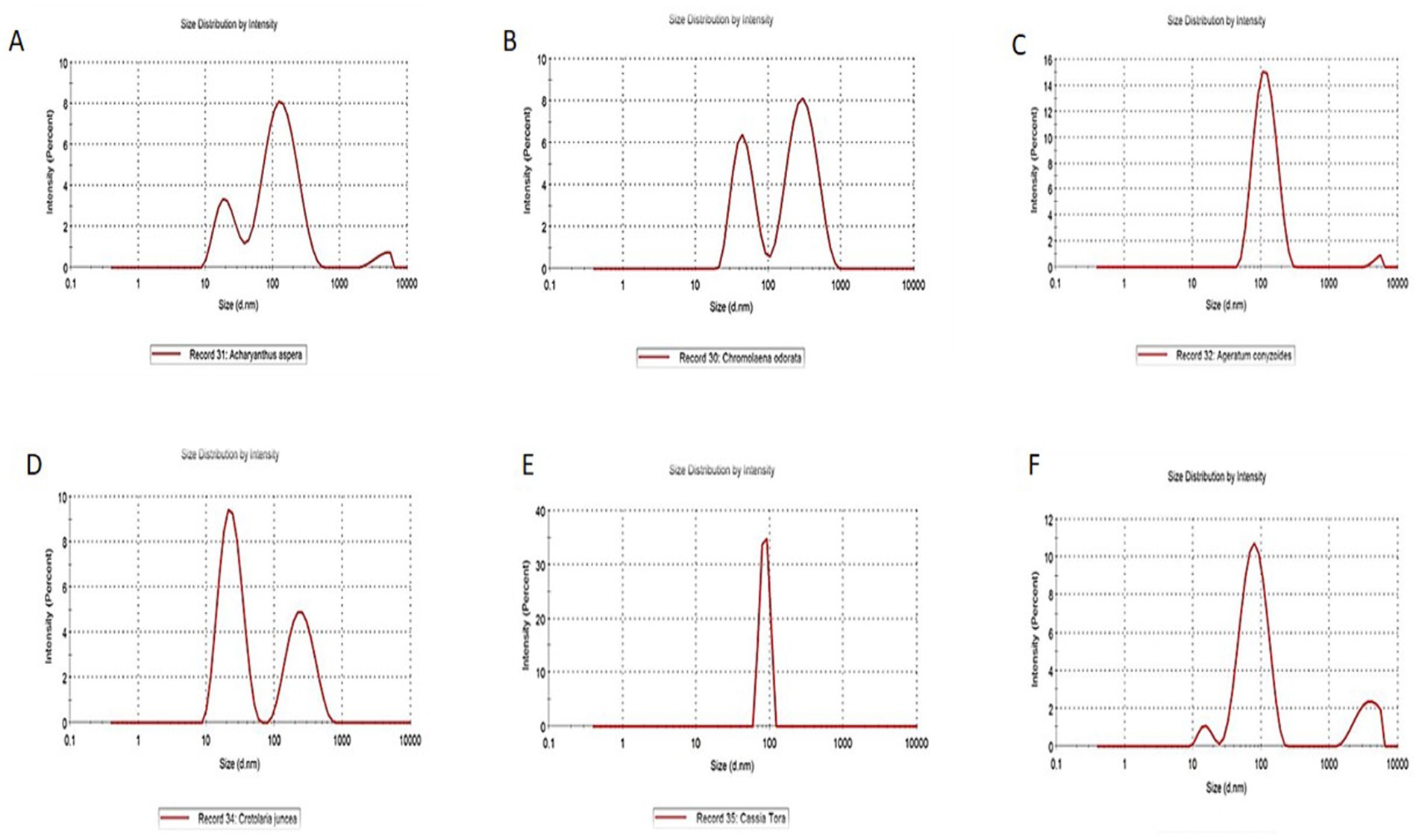
Figure 4. Zeta sizer analysis showing particle size (nm) of synthesized nano zinc using weed leaf extracts: (A) Achyranthes aspera, (B) Chromolaena odorata, (C) Ageratum conyzoides, (D) Crotolaria juncea, (E) Cassia tora, (F) Cassia spectabilis.
3.2.2 Scanning electron microscope analysis result of synthesized zinc nanoparticles
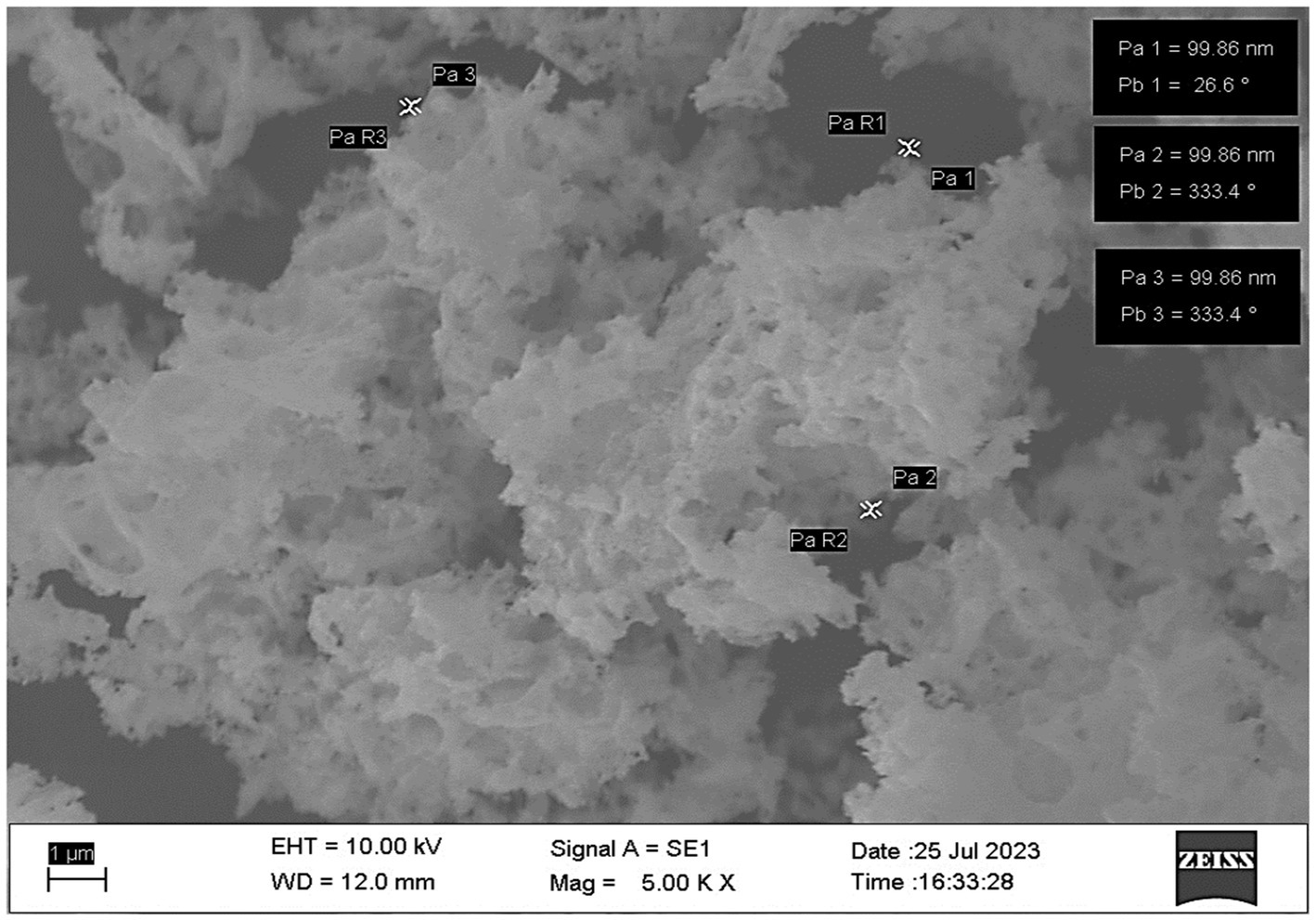
The SEM image (Figure 5) revealed that the nano zinc particles were predominantly in the form of nanospheres with a flower-like structure, a characteristic morphology commonly observed in biosynthesized nanoparticles. These particles were found to be in close contact with each other, forming interconnected chains and clusters. The particle size measured from the image ranged between 50 and 100 nm, with the average diameter of individual particles being approximately 76.89 nm, as observed in the sample synthesized using Cassia spectabilis extract. The SEM image was captured at a magnification of 5,000 × using a ZEISS SEM with an accelerating voltage of 10.00 kV and a working distance of 12.0 mm, employing a secondary electron detector (SE1) to reveal detailed surface topography. The observed aggregation is typical for nanoparticles due to their high surface energy, which promotes Van der Waals attractions leading to cluster formation. Such structural features influence the functional performance of nano zinc in agricultural applications, particularly in enhancing zinc availability, controlled nutrient release, and efficient plant uptake (Figure 6).
3.2.3 FTIR (Fourier transform infrared) spectrum of synthesized zinc nanoparticles
The FTIR spectrum of the synthesized zinc nanoparticles (S-1 Zn) confirms that a broad absorption band around 3,417.86 cm−1 indicates O–H stretching vibrations, suggesting the presence of hydroxyl groups or adsorbed water molecules on the nanoparticle surface. Peaks observed around 1,639.49 and 1,597.86 cm−1 correspond to C=O stretching or N–H bending, which may be attributed to organic molecules or amine groups acting as capping or stabilizing agents. The peak at 1,431.18 cm−1 is indicative of C–H bending or carboxylate interactions. Notably, the strong absorption bands in the region between 875 and 589 cm−1 confirm the presence of Zn–O bonds, which are characteristic of zinc oxide nanoparticles. These findings collectively validate the successful synthesis of zinc based nanoparticles and suggest that organic residues from the synthesis process may aid in enhancing nanoparticle stability and dispersion.
3.3 Effect of synthesized nano zinc on germination and seed vigor of maize
The results of the study showed significant differences among the treatments with respect to germination percentage, shoot length, root length, and seedling vigor index (SVI) in maize (Table 3). Germination percentage ranged from 80.30% (T20: nano zinc @ 1,200 ppm for 45 min) to 90.00% (T11: nano zinc @ 800 ppm for 30 min). Treatments involving seed priming with synthesized nano zinc for 30 min (T8–T14) generally recorded higher germination rates compared to 15- and 45-min durations. Among these, T11 emerged as the most effective, followed closely by T10 (600 ppm for 30 min) and T12 (1,000 ppm for 30 min). In contrast, ZnSO4-based treatments (T7, T14, T21) recorded lower or moderate germination values, indicating comparatively lesser effectiveness.
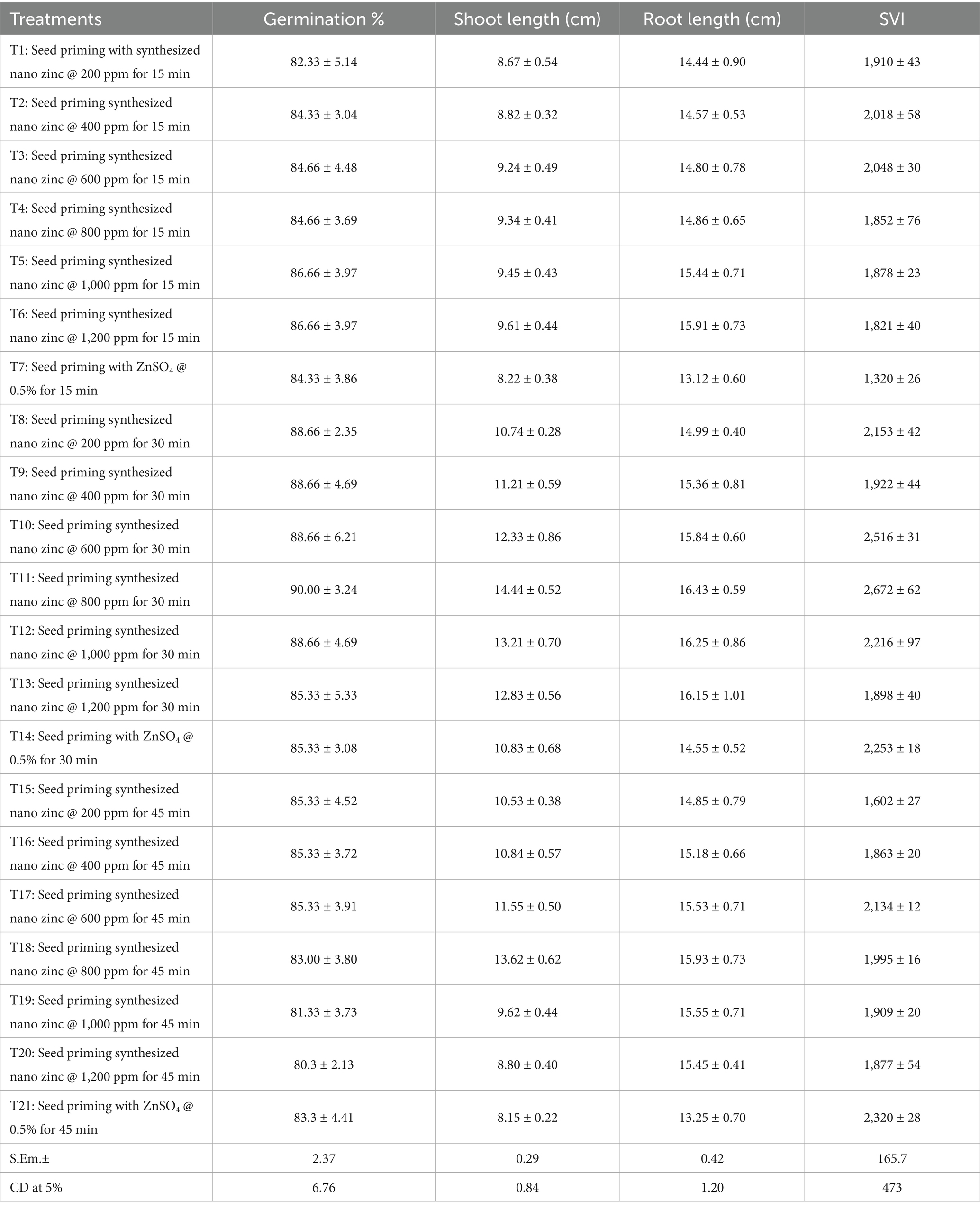
Table 3. Effect of synthesized nano zinc on germination percentage, shoot length, root length and seed vigor index of maize.
Shoot length varied from 8.15 cm (T21: ZnSO4 @ 0.5% for 45 min) to 14.44 cm (T11), while root length ranged between 13.12 cm (T7) and 16.43 cm (T11). Seedling Vigor Index (SVI) followed a similar trend, with the highest value (2,672) recorded in T11, followed by T10 (2,516), T14 (2,253), and T12 (2,216). The lowest SVI was recorded in T7 (1,320), highlighting the comparatively lower performance of ZnSO4-treated seeds. Overall, seed priming with synthesized nano zinc @ 800 ppm for 30 min (T11) consistently showed superior results across all parameters, indicating its potential as the most effective treatment for improving seedling establishment in maize.
3.4 Effect of synthesized nano zinc on growth parameters of maize
The application of synthesized nano zinc significantly influenced the growth parameters of the crop at 90 days after sowing (Table 4). Among the treatments, T5 (seed priming with nano zinc @ 800 ppm followed by foliar spray @ 500 ppm) exhibited superior performance with the tallest plants (277.6 cm), highest Leaf Area Index (2.99), and maximum dry matter production (344.0 g plant−1). This suggests that nano zinc at this concentration effectively enhanced vegetative growth and physiological efficiency. T4 also showed marked improvement in growth attributes, with a plant height of 269.6 cm, LAI of 2.90, and dry matter production of 309.4 g plant−1, indicating a positive response to foliar application of nano zinc @ 400 ppm. Treatments T2 and T3 displayed moderate improvements over T1 (seed priming alone), highlighting the synergistic effect of combining seed priming with foliar application. In contrast, treatments involving conventional zinc sources, especially T8 (soil application of ZnSO4), recorded the lowest plant height (228.9 cm), LAI (2.03), and dry matter production (146.4 g plant−1). These results suggest that synthesized nano zinc, particularly at the 500 ppm foliar application level, is more effective in promoting crop growth than traditional zinc fertilizers.
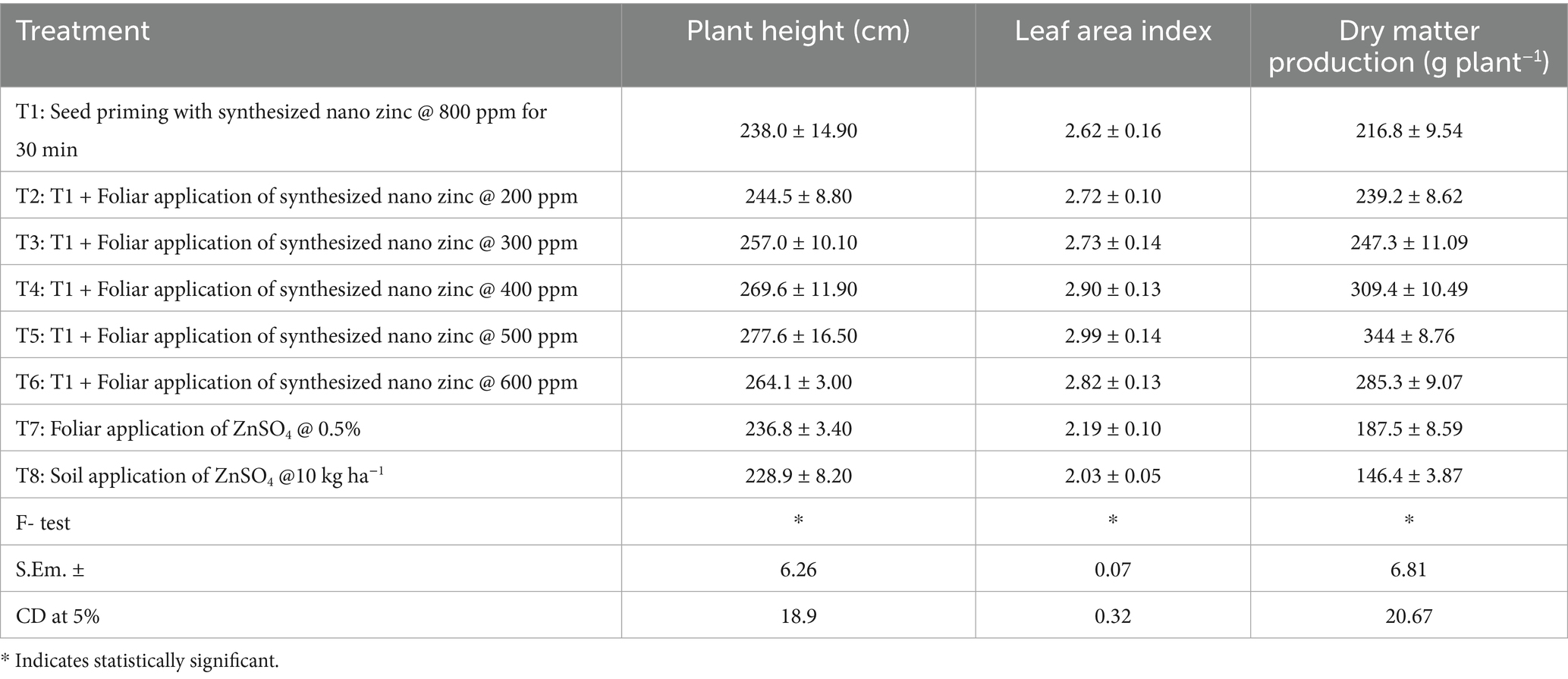
Table 4. Effect of synthesized nano zinc on plant height, leaf area index and dry matter production of maize at 90 DAS.
3.5 Effect of synthesized nano zinc on yield parameters and yield of maize
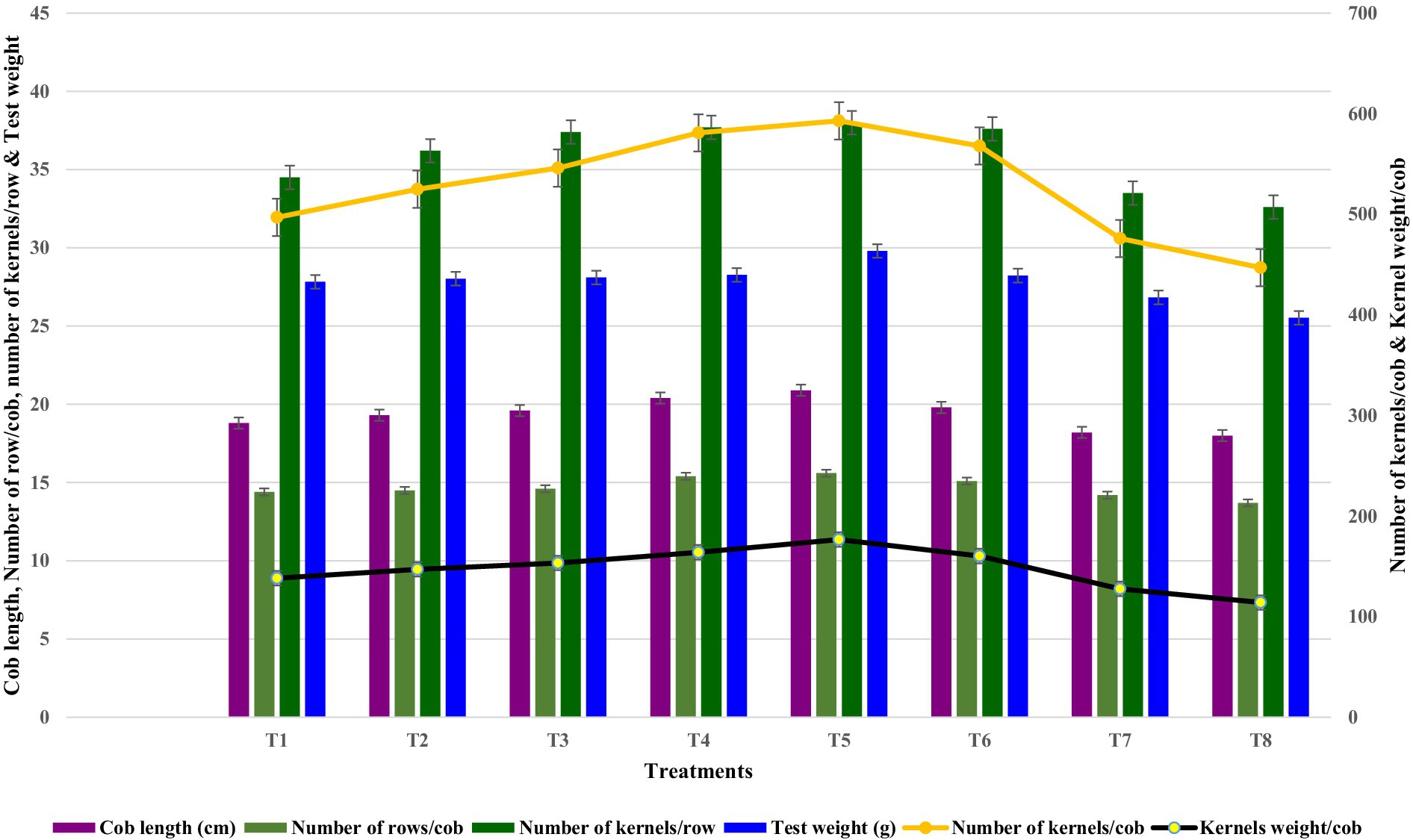
The reproductive parameters of the crop were significantly influenced by different zinc treatments, especially those involving synthesized nano zinc (Figure 7). Among the treatments, T5 (seed priming with nano zinc @ 800 ppm followed by foliar spray @ 500 ppm) consistently outperformed others, showing the highest cob length (20.9 cm), maximum number of rows per cob (15.6), highest number of kernels per row (38.0), and consequently, the greatest number of kernels per cob (593). In addition, T5 recorded the highest kernel weight per cob (176.7 g) and the highest test weight (29.80 g), indicating superior grain filling and overall reproductive efficiency.
Following T5, the T4 treatment (foliar nano zinc @ 400 ppm) also exhibited notable performance with a cob length of 20.4 cm, 15.4 rows per cob, and 581 kernels per cob. This indicates that the 400 ppm nano zinc level also significantly improved reproductive growth. Treatments T3 and T2 showed progressive improvements in all yield-related traits compared to the control (T1), confirming the additive benefit of foliar application along with seed priming. On the contrary, the lowest values for all reproductive parameters were observed in T8 (soil application of ZnSO4 @ 10 kg ha−1), where the cob length was only 18.0 cm, the number of rows per cob was 13.7, and the kernel count and weight were significantly lower (447 kernels per cob and 114.1 g kernel weight). Similarly, T7 (foliar ZnSO4) showed slightly better performance than T8 but was still inferior to all nano zinc treatments.
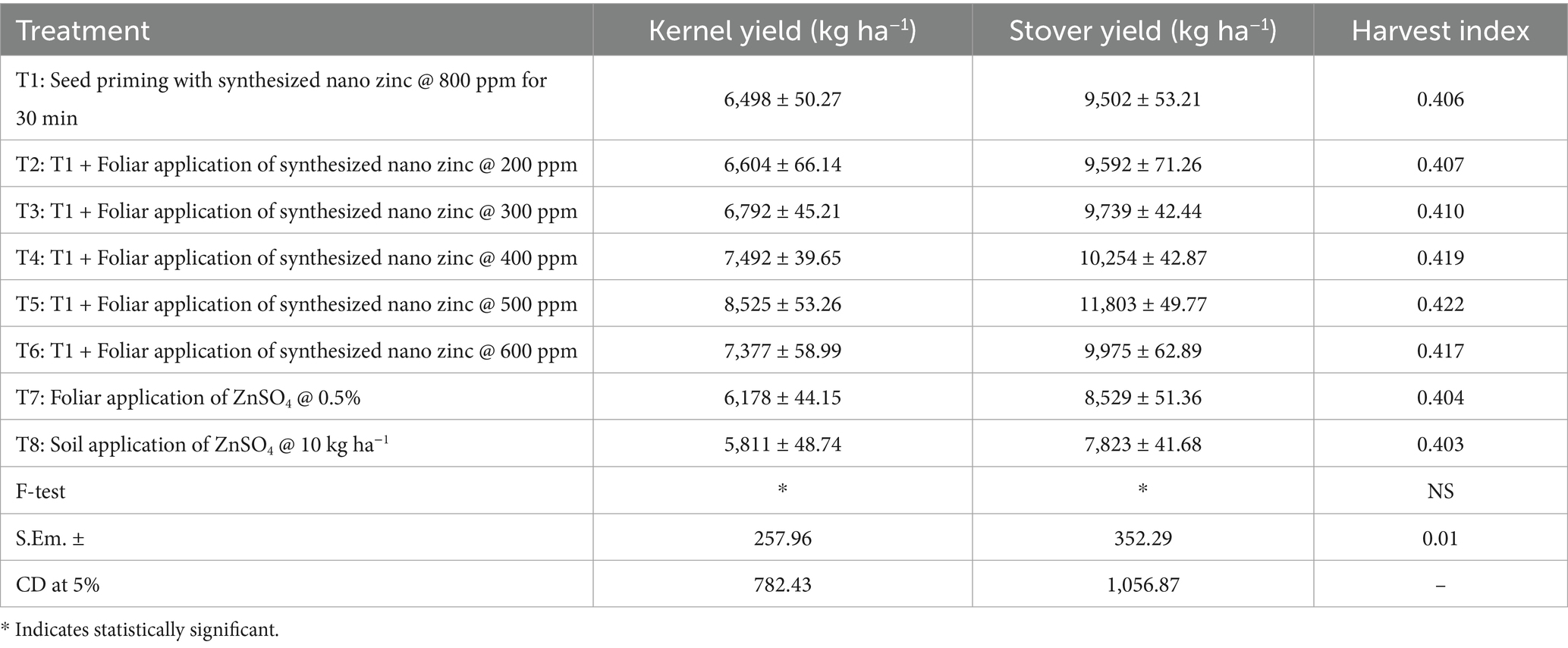
The application of synthesized nano zinc had a marked influence on kernel and stover yields (Table 5). Kernel yield ranged from 5,811 kg ha−1 in the treatment with soil application of ZnSO4 (T8) to 8,525 kg ha−1 in the treatment that included seed priming with synthesized nano zinc @ 800 ppm for 30 min along with foliar application @ 500 ppm (T5). Likewise, stover yield varied from 7,823 kg ha−1 (T8) to 11,803 kg ha−1 (T5), highlighting the superior performance of T5 among all treatments. The harvest index ranged from 0.403 to 0.422, with the highest value also recorded in T5 (0.422), although differences among treatments were relatively small. These findings clearly demonstrate that the combined use of seed priming and foliar application of synthesized nano zinc, particularly at 500 ppm (T5), significantly enhances both kernel and stover yield, recording 8,525 kg ha−1 and 11,803 kg ha−1 respectively, in comparison to conventional ZnSO4 applications.
3.6 Effect of synthesized nano zinc on nutrient use efficiency of maize
The study revealed significant differences among treatments for nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium use efficiencies (Figure 8). The treatment T5, comprising seed priming with synthesized nano zinc @ 800 ppm for 30 min along with foliar application @ 500 ppm, recorded the highest N (57 kg kernel kg−1 N), P (114 kg kernel kg−1 P2O5), and K (213 kg kernel kg−1 K2O) use efficiencies. In contrast, the lowest efficiencies were observed in T8, which involved soil application of ZnSO4 @ 10 kg ha−1. Treatments with foliar application of synthesized nano zinc (T2–T6) consistently outperformed conventional ZnSO4 treatments (T7 and T8), indicating the superior efficiency of nano zinc in enhancing nutrient use. The F-test was significant for all nutrients, and the critical differences at 5% were 4.01, 7.97, and 15.05 for N, P, and K use efficiencies, respectively.
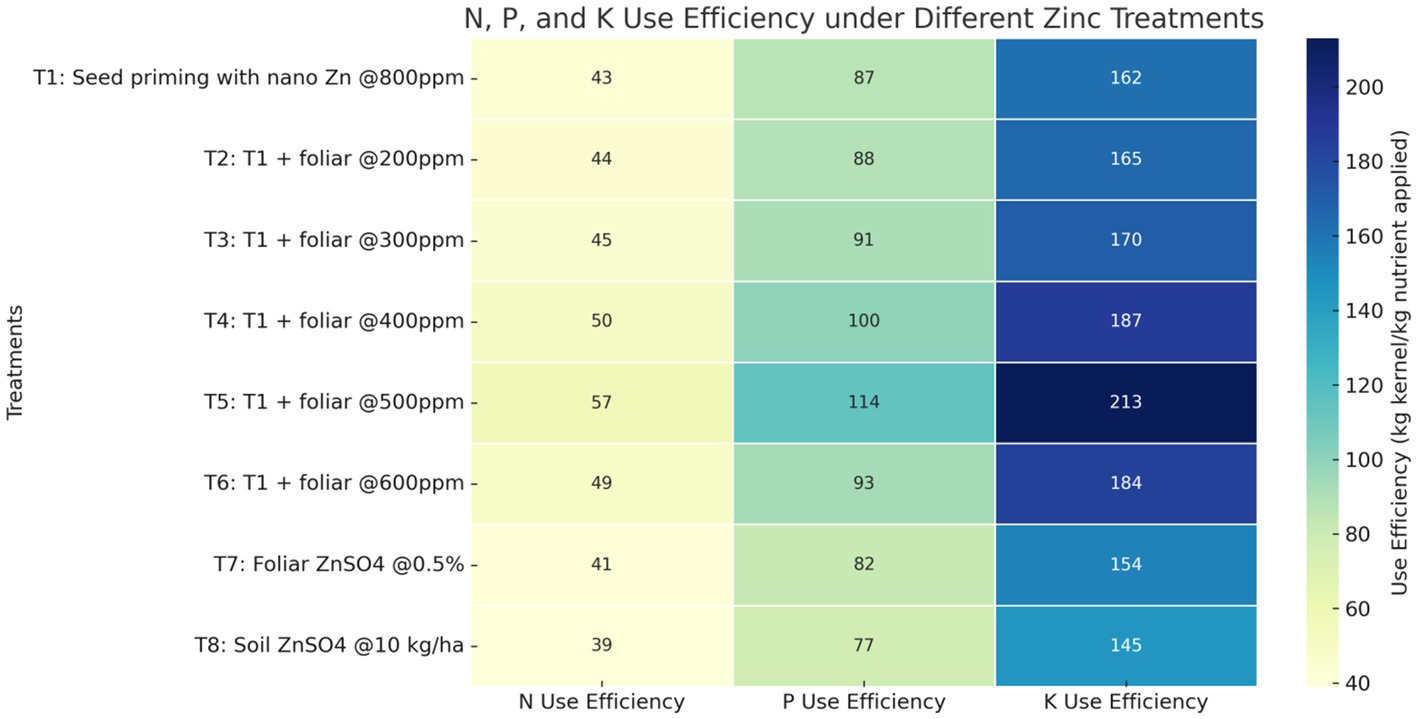
Figure 8. Effects of seed priming and foliar application of synthesized zinc nanoparticles on nutrient use efficiency (Heat map).
3.7 Effect of synthesized nano zinc on economics of maize cultivation
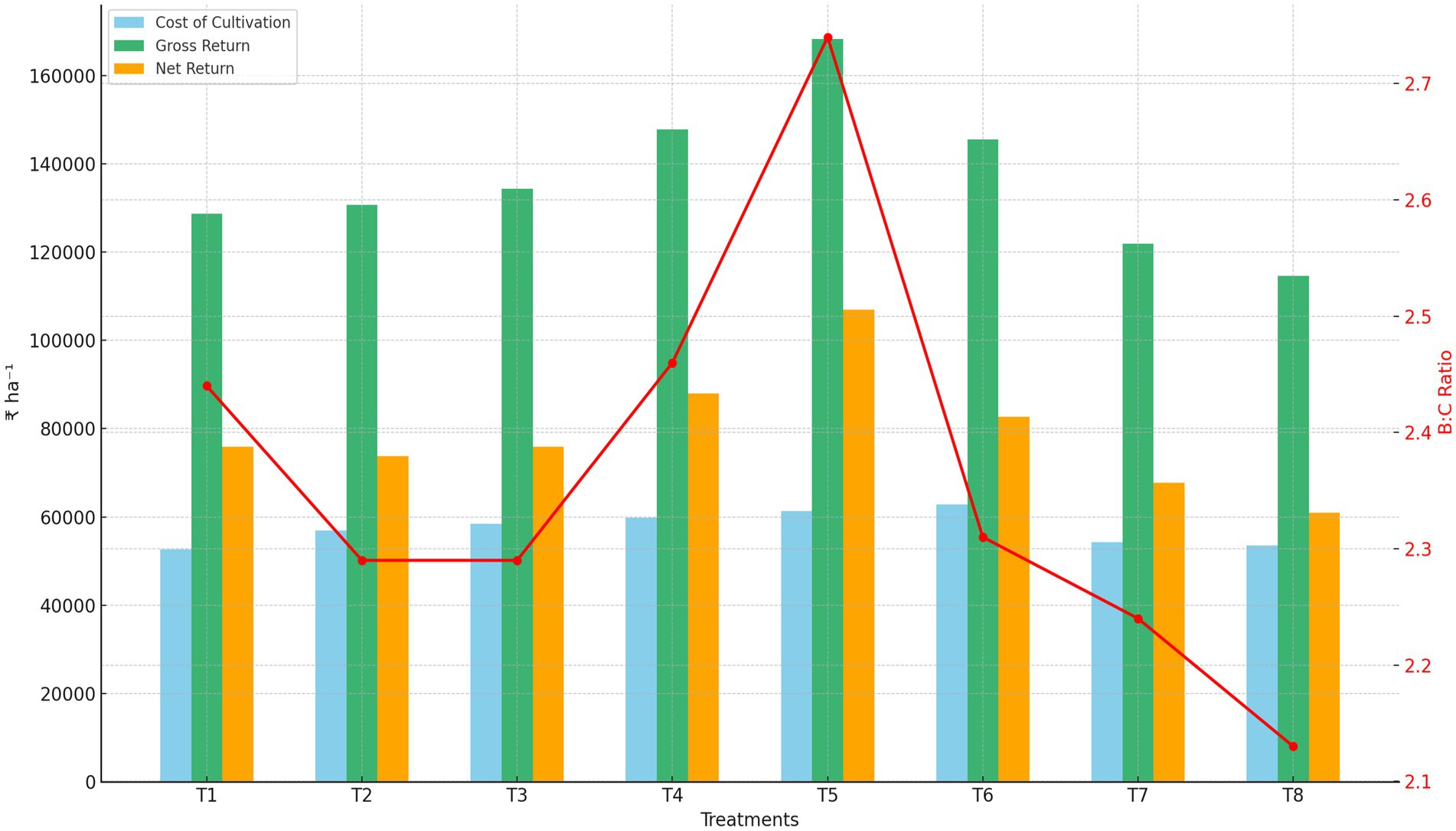
The economic analysis of various zinc application treatments revealed significant differences in cost-effectiveness and profitability (Figure 9). Among all the treatments, T5, which involved seed priming with synthesized nano zinc at 800 ppm for 30 min followed by a foliar application of synthesized nano zinc at 500 ppm, emerged as the most effective. It recorded the highest gross return (₹1,68,276 ha−1) and net return (₹1,06,941 ha−1), with a Benefit:Cost (B:C) ratio of 2.74, indicating excellent economic viability. Although this treatment had a relatively higher cost of cultivation (₹61,335 ha−1), the substantial increase in returns justified the investment.
Following this, T4 (nano zinc foliar application @ 400 ppm) and T6 (600 ppm) also showed high net returns and respectable B:C ratios of 2.46 and 2.31, respectively. Interestingly, T1, which involved only seed priming, had the lowest cost of cultivation (₹52,703 ha−1) and a decent B:C ratio (2.44), but the returns were significantly lower compared to T5. On the other hand, conventional zinc sulfate applications, T7 (foliar ZnSO4 @ 0.5%) and T8 (soil ZnSO4 @ 10 kg ha−1), resulted in lower gross and net returns and the lowest B:C ratios (2.24 and 2.13, respectively), making them less economically favorable. This analysis clearly demonstrates that nano zinc, particularly at 500 ppm as a foliar spray after seed priming, offers superior profitability and return on investment compared to traditional zinc application methods.
4 Discussion
The present study demonstrates the successful green synthesis and characterization of zinc nanoparticles using aqueous leaf extracts from six different plant species: Cassia spectabilis, Crotalaria juncea, Chromolaena odorata, Achyranthes aspera, Ageratum conyzoides, and Cassia tora. These species were selected due to their rich phytochemical profiles, which include flavonoids, phenolic acids, tannins, alkaloids, saponins, and terpenoids—bioactive compounds known to act as natural reducing and stabilizing agents in nanoparticle synthesis. For instance, Cassia species are rich in anthraquinones and tannins, while Crotalaria and Achyranthes contain high levels of polyphenols and saponins (Selegato et al., 2017). Chromolaena odorata is known for its quercetin content, and Ageratum conyzoides possesses coumarins and essential oils. During the synthesis process, visual color changes from dark green or brown to pale yellow or light brown indicated the bioreduction of Zn2+ ions to zinc based nanoparticles. These observations align with previous studies (Abdullah et al., 2024; Jayachandran et al., 2021; Veeramanikandan et al., 2017), supporting the dual role of plant-derived phytochemicals in both reduction and stabilization, thereby enabling a cost-effective and eco-friendly synthesis approach.
The UV–Vis spectrophotometric analysis further confirmed the formation of nanoparticles, with absorption maxima ranging between 210 and 316 nm depending on the plant species (Barzinjy and Azeez, 2020; Patra and Baek, 2017). These variations in peak wavelengths are attributed to differences in the nature and concentration of bioactive compounds in each extract (Bhattacharjee et al., 2021; Rajakumar et al., 2013). Notably, Cassia spectabilis showed a sharp peak at 273 nm, corresponding to strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR), and had a particle size of 76.89 nm as determined by dynamic light scattering (Bhuvaneshwari et al., 2020). This was within the desired nanoscale range, making it a suitable candidate for further analysis and application.
SEM analysis confirmed nanosphere-shaped particles with flower-like morphology and a size distribution between 50 and 100 nm, consistent with previous findings (Boruah et al., 2023; Rajiv et al., 2013). These structures tended to form aggregates, a common feature in biosynthesized nanoparticles due to high surface energy and Van der Waals forces (Dhanasekaran et al., 2020). Such morphology is favorable for agricultural applications, as it increases surface area, facilitates nutrient absorption, and potentially enhances interaction with plant roots and tissues (El-Shafey et al., 2022; Jayaprakash et al., 2021). FTIR spectral analysis confirmed the presence of various functional groups involved in nanoparticle synthesis and stabilization. The broad O–H stretching peak and distinct Zn–O vibration peaks between 589 and 875 cm−1 verified the formation of zinc based nanoparticles. Additionally, peaks corresponding to C=O, N–H, and carboxylate groups indicate the presence of bio-organic molecules on the nanoparticle surface, which likely originated from the plant extracts and contributed to colloidal stability (Gautam et al., 2016; Hashem et al., 2021).
Collectively, the results suggest that green synthesis using Cassia spectabilis is highly effective for producing stable and functional zinc nanoparticles (Ghidan et al., 2016; Ijaz et al., 2020). The consistent nanoscale size, favorable morphology, and the presence of stabilizing organic compounds highlight the potential of these nanoparticles for use in agriculture, particularly in improving micronutrient delivery, uptake efficiency, and promoting sustainable crop production (Hayat et al., 2022; Hussein et al., 2021).
The study demonstrated that seed priming with synthesized nano zinc significantly enhanced germination and seedling vigor in maize, with the most effective treatment being 800 ppm for 30 min (T11), which consistently recorded the highest germination percentage (90.00%), shoot length (14.44 cm), root length (16.43 cm), and Seedling Vigor Index (2672) (Akshay et al., 2024). Treatments with 30-min priming durations generally outperformed those with 15 or 45 min, suggesting that moderate exposure facilitates optimal zinc uptake without causing stress. The superiority of synthesized nano zinc over conventional ZnSO4 treatments was evident across all parameters, likely due to its smaller particle size and higher bioavailability, enhancing enzymatic activities and nutrient absorption (Makarov et al., 2014; Sharma et al., 2022). The consistently high performance of treatments within the 600–1,000 ppm range for 30 min indicates an optimal window for zinc priming in maize. These findings highlight the potential of nano zinc seed priming as a practical strategy to improve early seedling growth and establishment, particularly in zinc-deficient or low-vigor seed scenarios (Kuppusamy et al., 2016).
The application of synthesized nano zinc significantly enhanced the growth, yield, and nutrient use efficiency of maize, with T5 treatment (seed priming @ 800 ppm + foliar spray @ 500 ppm) consistently emerging as the most effective. The substantial increase in plant height (277.6 cm), Leaf Area Index (2.99), and dry matter accumulation (344.0 g plant−1) under T5 indicates improved vegetative vigor likely driven by enhanced zinc bioavailability, which plays a pivotal role in chlorophyll synthesis, cell division, and enzymatic functions (Akshay et al., 2024; Muruganantham et al., 2022). Reproductive attributes also improved markedly with T5, which recorded the highest cob length (20.9 cm), kernel number (593 per cob), kernel weight (176.7 g), and test weight (29.80 g), reflecting enhanced pollen viability, grain filling, and sink strength. These findings affirm the importance of nano zinc in improving physiological processes and reproductive success in maize (Nasrollahzadeh et al., 2015; Singh et al., 2018). Moreover, nutrient use efficiency was significantly higher under T5, with maximum nitrogen (57 kg grain per kg N), phosphorus (114 kg grain per kg P2O5), and potassium (213 kg grain per kg K2O) efficiencies, suggesting that nano zinc facilitates more efficient uptake and utilization of macronutrients (Tripathi et al., 2017; Santhoshkumar et al., 2017). In contrast, conventional ZnSO4 treatments (T7 and T8) were markedly less effective across all parameters, underscoring the superior performance of nano-formulated zinc in improving both crop productivity and resource efficiency (Raliya et al., 2016). These results collectively highlight the potential of synthesized nano zinc as a sustainable and efficient strategy to boost maize growth, yield, and nutrient use under field conditions (Ramimoghadam et al., 2013).
The economic evaluation of different zinc application strategies in maize cultivation revealed the superior cost-effectiveness of synthesized nano zinc treatments, particularly the combined approach of seed priming and foliar application. Treatment T5, involving seed priming with nano zinc @ 800 ppm for 30 min followed by foliar spray @ 500 ppm, achieved the highest gross (₹1,68,276 ha−1) and net returns (₹1,06,941 ha−1), along with the most favorable Benefit:Cost (B:C) ratio of 2.74. Despite incurring the highest cultivation cost, the significant increase in productivity and profitability justified the investment, highlighting the economic viability of nano zinc use in maize (Akshay et al., 2024). Treatments T4 and T6 also demonstrated strong profitability, indicating that foliar nano zinc application, even at moderate concentrations (400–600 ppm), contributes substantially to economic gains. While T1 (seed priming alone) had the lowest input cost and a moderately good B:C ratio (2.44), its lower yield potential translated into reduced overall returns. In contrast, conventional zinc sources such as ZnSO4 (T7 and T8) were economically less efficient, yielding lower B:C ratios and returns, underscoring the limited benefit of traditional forms in comparison to nano-formulations (Roy et al., 2023).
The outcomes of this study not only affirm the efficacy of green-synthesized nano zinc in enhancing maize growth and yield but also contribute novel insights into its dual-mode application through seed priming and foliar spraying. This integrated approach appears to optimize nutrient availability during both early establishment and critical growth stages, thereby improving physiological efficiency and yield components. Importantly, the use of Cassia spectabilis-based nanoparticles characterized by consistent nanoscale size, favorable morphology, and bioactive surface chemistry—offers a sustainable and scalable alternative to conventional zinc sources. By aligning agronomic performance with economic viability, the study provides a strong case for adopting nano zinc as a precision nutrient strategy in maize cultivation, especially under zinc-deficient or resource-constrained farming systems (Raliya et al., 2016; Rameshraddy et al., 2022).
While the results of this study are encouraging, certain aspects warrant further exploration. The long-term effects of repeated nano zinc application on soil health, microbial communities, and environmental safety remain to be fully understood. Additionally, field validation across different agroecological zones and cropping systems would help confirm the consistency and scalability of these findings. Future studies focusing on environmental fate, residual buildup, and crop-specific responses will be essential to ensure the sustainable integration of nano zinc into agricultural practices.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, zinc nanoparticles synthesized using Cassia spectabilis leaf extract were found to be highly effective in enhancing the growth and productivity of maize. The green synthesis approach produced stable nanoparticles with a size of 76.89 nm, confirmed through UV–Vis, PSA, SEM, and FT-IR analyses. Among the treatments, seed priming with nano zinc @ 800 ppm followed by foliar spray @ 500 ppm (T5) consistently outperformed others in terms of germination, vegetative growth, yield attributes, nutrient use efficiency, and economic returns, recording the highest B:C ratio of 2.74. This indicates that green-synthesized nano zinc is not only agronomically beneficial but also economically feasible. The findings advocate for the integration of nanotechnology in nutrient management strategies to improve input efficiency. Further research is needed to assess long-term impacts on soil health, environmental safety, and nanoparticle behavior under diverse field conditions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
PN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Jayadeva H M: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Somashekharappa P R: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AK: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. Kadalli G G: Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Data curation. AG: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Resources, Validation. Shantharaja C S: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. Sripathy K V: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources. Rajanna G A: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – original draft. Paramesh V: Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. HH: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Resources. MA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology. SC: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Funding acquisition. GG: Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Validation. VT: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Resources. Mahesha H S: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Validation. Vanishree G: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the University of Agricultural Sciences, Bangalore, Karnataka, India, for granting access to the necessary facilities to carry out the experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdullah, J. A. A., Laouini, S. E., Boudjema, A., Alonso-González, M., Guerrero, A., and Romero, A. (2020). Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles by Phoenix dactylifera leaf extract and evaluation of their antioxidant activity. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 17:100280. doi: 10.1016/j.scp.2020.100280
Abdullah, J. A. A., Mohammed, H. A., Salmi, C., Alqarni, Z., Laouini, S. E., Guerrero, A., et al. (2024). Sustainable synthesis of ZnO and FexOy nanoparticles and their nanocomposite ZnFe2O4: comprehensive characterization and applications in antioxidant activity and antibiotics degradation efficiency. Bioorg. Chem. 153:107828. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.107828
Ahmed, S., Qasim, S., Ansari, M., Shah, A. A., Rehman, H. U., Shah, M. N., et al. (2023). Green synthesis of zinc nanoparticles and their effects on growth and yield of Pisum sativum. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 34:102132. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102132
Ahsan, N., Arshad, M., and Arshad, M. (2022). Zinc oxide nanoparticles as an alternative approach for enhancing agricultural productivity: a review. Sci. Prog. 105:00368504221123493. doi: 10.1177/00368504221123493
Akshay, K. K., Jayadeva, H. M., Sannagoudar, M. S., Suresh, K. B., Ayyappa, S., Kumargoud, V., et al. (2024). Eco-friendly green synthesised nano iron particles from weed leaf extract: a potential nutritional source for enhancing the germination and yield of aerobic rice. Cogent Food Agric. 10:2419438. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2024.2419438
Aksu Demirezen, D., Yıldız, Y. S., Yılmaz, S., and Demirezen Yılmaz, D. (2019). Green synthesis and characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using Ficus carica (common fig) dried fruit extract. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 127, 241–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.07.024
Alshaal, T., and El-Ramady, H. (2017). Foliar application from plant nutrition to biofortification. Environ. Biodivers. Soil Secur. 1, 71–83. doi: 10.21608/jenvbs.2017.1089.1006
Anonymous (2021). Area, production and productivity. Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization.
Anonymous (2022). Agricultural Statistics at a Glance 2022. Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Department of Agriculture, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India.
Arularasu, M. V., Devakumar, J., and Rajendran, T. V. (2018). An innovative approach for green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: characterization and its photocatalytic activity. Polyhedron 156, 279–290. doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2018.09.036
Bakhtiari, M., Moaveni, P., and Sani, B. (2015). The effect of iron nanoparticles spraying time and concentration on wheat. Biol. Forum Int. J. 7, 679–683.
Balogun, S. W., James, O. O., Sanusi, Y. K., and Olayinka, O. H. (2020). Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using bashful (Mimosa pudica) leaf extract: a precursor for organic electronics applications. SN Appl. Sci. 2:504. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-2127-3
Barzinjy, A. A., and Azeez, H. H. (2020). Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus globulus Labill. leaf extract and zinc nitrate hexahydrate salt. SN Appl. Sci. 2:991. doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-2813-1
Bhattacharjee, S., Habib, F., Darwish, N., and Shanableh, A. (2021). Iron sulfide nanoparticles prepared using date seed extract: green synthesis, characterization and potential application for removal of ciprofloxacin and chromium. Powder Technol. 380, 219–228. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.11.055
Bhuvaneshwari, M., Pavani, T., Anupama, P., Vasantha, K. V. V., and Kumari, K. S. (2020). Biosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of iron oxide nanoparticles using Tridax procumbens plant extract. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 11, 7789–7794. doi: 10.26452/ijrps.v11i4.3557
Biradar, B., Jayadev, H. M., Halli, H. M., and Sannagoudar, M. S. (2023). Mapping of soil test-based spatial fertilizer recommendations for paddy and maize using GIS, GPS and STCR approaches in a micro-watershed of Karnataka, India. Curr. Sci. 124:1160. doi: 10.18520/cs/v124/i10/1160-1166
Boruah, P. K., Kumar, D., Yadav, K. K., Sharma, R., Maurya, P. K., Renuka, N., et al. (2023). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Garcinia pedunculata fruit extract and their antibacterial, antifungal and photocatalytic activities. Mater. Chem. Phys. 286:127557. doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2022.127557
Dhanasekaran, D., Thajuddin, N., and Panneerselvam, A. (2020). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica leaf extract and evaluation of antibacterial and cytotoxic properties. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 206:111882. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.111882
El-Naggar, M. E., Hussein, M. Z., and El-Kemary, M. (2022). Green synthesis of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles and their environmental applications: a review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 17:100650. doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100650
El-Shafey, R. A., El-Esawi, M. A., Hassan, M. E., El-Samad, L. M. A., Eladawy, H. A., and El-Gawad, H. A. A. (2022). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles by Eruca sativa leaf extract for sustainable removal of heavy metals from wastewater. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32, 4029–4042. doi: 10.1007/s10904-021-02139-4
Gautam, A. K., Singh, R., Chauhan, D. K., and Varma, A. (2016). Iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized via green route using Ficus religiosa leaf extract and its applications in dye removal. J. Mol. Liq. 219, 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2016.03.045
Ghidan, A. Y., Bani-Ahmad, M. A., and AL-Momani, F. (2016). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles via leaf extract of Lawsonia inermis and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Mater. Lett. 164, 179–182. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2015.10.088
Ghosh, A., Singh, A. K., Kumar, S., Manna, M. C., Bhattacharyya, R., Agnihortri, R., et al. (2020). Differentiating biological and chemical factors of top and deep soil carbon sequestration in semi-arid tropical Inceptisol: an outcome of structural equation modeling. Carbon Manag. 11, 441–453. doi: 10.1080/17583004.2020.1796143
Hashem, A. H., Salem, S. S., Alamri, S., Alghamdi, S., Ali, M. I. A., Attia, M. S., et al. (2021). Eco-friendly synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Klebsiella pneumoniae and their biomedical applications. Molecules 26:5864. doi: 10.3390/molecules26205864
Hayat, K., Menhas, S., Bundschuh, J., Al-Muhtaseb, A. H., Niazi, N. K., Rehman, M. Z. U., et al. (2022). A review on green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles: applications to agroecosystems and environmental remediation. Arab. J. Chem. 15:103543. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103543
Hussein, H. E., El-Naggar, M. E., and Kamal, A. M. (2021). Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Euphorbia milii leaf extract and their application as anticancer and antibacterial agents. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 16:100516. doi: 10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100516
Ijaz, F., Shahid, S., Khan, S. A., and Ahmad, W. (2020). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Ficus carica leaf extract and their antimicrobial activity. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 9, 7673–7683. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.05.030
Iyarin, T. M. E., Aravind Kumar, B. N., Babu, R., Nirmalnath, P. J., Hebsur, N. S., Halli, H. M., et al. (2024). Nanocomposite based slow-release atrazine effectively controlled Striga asiatica incidence, and enhanced sugarcane yield. Sci. Rep. 14:30821. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81117-3
Jayachandran, A., Aswathy, T. R., and Achuthsankar, S. (2021). Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Cayratia pedata leaf extract. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 26:100995. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100995
Jayaprakash, N., Owais, M., Bukhari, S. N. A., Arunachalam, K. D., and Ramaswamy, S. (2021). Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Solanum nigrum leaf extract for antimicrobial and anticancer applications. Mater. Lett. 305:130840. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130840
Khan, Z., Singh, D., Hussain, J. I., and Hashmi, A. A. (2020). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Catharanthus roseus leaf extract and their applications as antimicrobial agents. Mater. Lett. 264:127359. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.127359
Khokhar, J. S., Broadley, M. R., and Ander, E. L. (2024). Soil zinc surveillance frameworks can inform human nutrition studies: opportunities in India. Front. Soil Sci. 4:1421652. doi: 10.3389/fsoil.2024.1421652
Kuppusamy, P., Yusoff, M. M., Maniam, G. P., and Govindan, N. (2016). Biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant derivatives and their new avenues in pharmacological applications – an updated report. Saudi Pharm. J. 24, 473–484. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2014.11.013
Makarov, V. V., Love, A. J., Sinitsyna, O. V., Makarova, S. S., Yaminsky, I. V., Taliansky, M. E., et al. (2014). “Green” nanotechnologies: synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Acta Nat. 6, 35–44. doi: 10.32607/20758251-2014-6-1-35-44
Muruganantham, T., Sumathi, S., Ramachandran, R., and Sivakumar, P. (2022). Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum leaf extract and its antibacterial activity. Surf. Interfaces 31:102010. doi: 10.1016/j.surfin.2022.102010
Nasrollahzadeh, M., Sajadi, S. M., Rostami-Vartooni, A., and Bagherzadeh, M. (2015). Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles using Nasturtium officinale leaf extract and their photocatalytic activity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 24, 279–284. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2014.09.011
Ovais, M., Khalil, A. T., Raza, A., Khan, M. A., Ahmad, I., Islam, N. U., et al. (2017). Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles via plant extracts: beginning a new era in cancer theranostics. Nanomedicine 12, 315–328. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2016-0429
Patra, J. K., and Baek, K. H. (2017). Green nanobiotechnology: factors affecting synthesis and characterization techniques. J. Nanomater. 2017:4178204. doi: 10.1155/2017/4178204
Rajakumar, G., Abdul Rahuman, A., Roopan, S. M., Elango, G., Kamaraj, C., Zahir, A. A., et al. (2013). Fungus-mediated biosynthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their activity against pathogenic bacteria. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 110, 133–137. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.03.005
Rajanna, G. A., Dass, A., Singh, V. K., Choudhary, A. K., Paramesh, V., Babu, S., et al. (2023). Energy and carbon budgeting in a soybean–wheat system in different tillage, irrigation and fertilizer management practices in South-Asian semi-arid agroecology. Eur. J. Agron. 148:126877. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2023.126877
Rajiv, P., Rajeshwari, S., and Venckatesh, R. (2013). Bio-fabrication of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Parthenium hysterophorus L. and its size-dependent antifungal activity against plant fungal pathogens. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 112, 384–387. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.04.072
Raliya, R., Tarafdar, J. C., and Biswas, P. (2016). Enhancing the mobilization of native phosphorus in mung bean rhizosphere using ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by different methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 3111–3118. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b05224
Rameshraddy, T., Krishnappa, M., Jyothi, A. N., Somashekarappa, H. M., Somashekar, R., and Nataraj, S. K. (2022). Green synthesis and characterization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Adiantum philippense extract and evaluation of their antibacterial and anticancer properties. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32, 2011–2023. doi: 10.1007/s10904-021-02121-0
Ramimoghadam, D., Bagheri, S., and Abd Hamid, S. B. (2013). Progress in mesoporous zinc oxide-based nanostructures: synthesis and applications. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 189, 26–51. doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.05.035
Roy, D., Sengupta, K., Mondal, R., Gunri, S. K., Ali, O., and Madhu, H. S. (2023). Effect of nano-fertilizers on growth, yield and economics of summer hybrid maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Bioresour. Stress Manag. 14, 1321–1330. doi: 10.23910/1.2023.4790
Santhoshkumar, J., Kumar, S. V., and Rajeshkumar, S. (2017). Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using plant leaf extract against urinary tract infection pathogen. Resour. Eff. Technol. 3, 459–465. doi: 10.1016/j.reffit.2017.05.001
Selegato, D. M., Monteiro, A. F., Vieira, N. C., Cardoso, P., Pavani, V. D., Bolzani, V. S., et al. (2017). Biological and chemical aspects of Senna spectabilis. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 28, 415–426. doi: 10.21577/0103-5053.20160322
Sharma, P., Urfan, M., Anand, R., Sangral, M., Hakla, H. R., Sharma, S., et al. (2022). Green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Eucalyptus lanceolata leaf litter: characterization, antimicrobial and agricultural efficacy in maize. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 28, 363–381. doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01136-0
Singh, J., Dutta, T., Kim, K. H., Rawat, M., Samddar, P., and Kumar, P. (2018). ‘Green’ synthesis of metals and their oxide nanoparticles: applications for environmental remediation. J. Nanobiotechnol. 16:84. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0408-4
Tripathi, D. K., Singh, S., Singh, S., Pandey, R., Singh, V. P., Sharma, N. C., et al. (2017). An overview on manufactured nanoparticles in plants: uptake, translocation, accumulation and phytotoxicity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 110, 2–12. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.07.030
Veeramanikandan, V., Madhu, G., Pavithra, V., Jaianand, K., and Balaji, P. (2017). Green synthesis, characterization of iron oxide nanoparticles using Leucas aspera leaf extract and evaluation of antibacterial and antioxidant studies. Int. J. Agric. Innov. Res. 6, 242–250.
Vitta, P., Edachery, B., Kumar, S. G., and Khan, M. M. (2020). Sustainable and ecofriendly synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles for environmental remediation and energy storage applications: recent advances and future perspectives. Chemosphere 253:126653. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126653
Keywords: innovative zinc source, leaf extract, characterization, eco-friendly, weeds
Citation: Nayak P, Jayadeva H M, Sannagoudar MS, Somashekharappa P R, Kurdekar AK, Kadalli G G, George A, Shantharaja C S, Sripathy K V, Rajanna G A, Paramesh V, Halli HM, Arif M, Chand S, Gupta G, Tyagi V, Mahesha H S and Vanishree G (2025) Biogenic zinc nanoparticles from weeds as an innovative zinc source for boosting growth, yield, and profitability in maize. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1613410. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1613410
Edited by:
Prakash Kumar Jha, Mississippi State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Domingos Lusitâneo Pier Macuvele, Federal University of Santa Catarina, BrazilMuhammad Omer Iqbal, Ocean University of China, China
Anuj Saraswat, Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, India
Copyright © 2025 Nayak, Jayadeva H M, Sannagoudar, Somashekharappa P R, Kurdekar, Kadalli G G, George, Shantharaja C S, Sripathy K V, Rajanna G A, Paramesh V, Halli, Arif, Chand, Gupta, Tyagi, Mahesha H S and Vanishree G. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Manjanagouda S. Sannagoudar, bXNzYWdyb25AZ21haWwuY29t
 Parthivi Nayak1
Parthivi Nayak1 Manjanagouda S. Sannagoudar
Manjanagouda S. Sannagoudar Anjitha George
Anjitha George Shantharaja C S
Shantharaja C S Hanamant M. Halli
Hanamant M. Halli Subhash Chand
Subhash Chand Gaurendra Gupta
Gaurendra Gupta Vishal Tyagi
Vishal Tyagi