- 1Department of Management Studies, Graphic Era Deemed to be University, Dehradun, India
- 2Department of Management Studies, Graphic Era University, Dehradun, India
- 3PM Gati Shakti Centre of Excellence in Logistics and Supply Chain Management, School of Management, Doon University, Dehradun, India
Introduction: Transforming agri-food systems toward sustainability and responsible production is essential for achieving Sustainable Development Goal 12, particularly in developing countries. Agri-tech startups play a pivotal role as catalysts of innovation, leveraging technology and novel business strategies to reduce waste, enhance product visibility, and address challenges across the agricultural supply chain.
Methods: This study aims to identify and characterize the critical success factors (CSFs) that influence the effectiveness of agri-tech startups in enabling sustainable agri-food supply chains. Using a Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) approach grounded in the Technology-Organization-Environment (T-O-E) framework, 25 CSFs were extracted and analyzed from the existing literature.
Results: The analysis highlights the most influential CSFs within the cause group, including policy coordination, rural ecosystem readiness, and innovation capacity. These factors collectively determine the capability of startups to scale operations while addressing environmental and operational challenges.
Discussion: Findings demonstrate how local alternative food networks can serve community interests while meeting global sustainability challenges. The study provides practical guidance for assessing startup readiness and scalability and contributes theoretical insights into the integration of technological, organizational, and environmental factors in sustainable agri-food systems.
1 Introduction
The global food system is stressed due to the increasing pressures of climate change, resource scarcity, population growth, and shifting consumption patterns. Traditional agricultural practices are not adequate to meet rising food demands while simultaneously addressing concerns of environmental sustainability, food security, and rural livelihoods. Consequently, agri-tech startups have emerged as pivotal actors in reshaping food production, distribution, and consumption systems, offering innovative solutions that integrate an end-to-end supply chain with digital technologies, data analytics, and sustainable practices. By leveraging tools such as precision farming, blockchain-enabled supply chains, remote sensing, and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven advisory services, these startups not only enhance agricultural productivity but also contribute to the resilience and sustainability of food systems.
The current global food system faces significant challenges stemming from destructive agricultural practices that risk environmental systems, production chain issues, and social crises, which primarily impact developing countries (Devaux et al., 2022). The population needs sustainable approaches that use innovation to empower local communities through food distribution processes (Lisboa et al., 2024).
Local food systems have gained popularity in recent times because they demonstrate the potential to provide security to underserved populations (Horst et al., 2024). The joint approaches between agriculture market initiatives and community programs produce improved results in fresh produce intake and dietary quality (Garrity et al., 2024). Local food programs face obstacles because their growth potential remains restricted due to barriers to entry and cultural practices, which necessitate careful planning for successful implementation (Raihan et al., 2024). Alternative and local food systems frame the essential strategies for developing sustainable food systems that enhance equality (Ruben et al., 2021). Local food initiatives transform the processes of food production, distribution, and consumption through community-supported agriculture, regenerative farming strategies, and digital direct-to-consumer channels (Glaros et al., 2023).
Identification and assessment of Critical Success Factors (CSFs) are essential to ensure the long-term sustainability of agri-tech startups, particularly in developing economies where resource constraints, infrastructural gaps, and smallholder dependency create unique challenges. CSFs provide a structured lens for identifying the most influential factors that determine whether agri-tech ventures can scale beyond pilot projects and deliver measurable impact. By systematically evaluating CSFs, stakeholders can prioritize scarce resources toward high-leverage enablers, creating multiplier effects across the ecosystem. For instance, investments in digital infrastructure enhance connectivity, enabling financial inclusion, advisory services, and traceability systems. Similarly, robust policy frameworks can unlock markets and attract investor confidence, while innovation ecosystems support the development of context-relevant, affordable technologies for farmers. Thus, CSF assessment bridges the gap between startup goals and systemic transformation, offering policymakers, investors, and entrepreneurs a roadmap for building resilient and scalable agri-tech ecosystems that contribute to food security, rural livelihoods, and climate-smart agriculture. Developing sustainable supply chain value requires agri-tech startups to integrate their innovations and models with sustainable operational and value principles (Rialti et al., 2022). Through responsible supply chains, resilience in the food system can be met to fulfill the Sustainable Development Goals SDG 2, SDG 12, and SDG 13 (Michel et al., 2024).
Although the issue of sustainable agri-food systems is gaining considerable consideration, the available literature is primarily centered on single aspects, including technology adoption, organizational preparedness, or ecological regulations. Limited studies are for a comprehensive and analytical examination of related aspects to one another, especially in the developing economies where the supply chain is fragmented, infrastructure is limited, and uncertainty exists in the set policies. Therefore, this study explores the future of sustainable and alternative food systems through the lens of the Technology-Organization-Environment (T-O-E)-based CSFs. However, T-O-E has been implemented in a few studies on agri-tech; the empirical evidence is limited on how the CSFs interact causally to influence the scalability of agri-tech startups and their sustainability. The study has employed Fuzzy DEMATEL, which helps the researchers and policymakers to identify functional relationships between CSFs while establishing strategic priorities and constructing policies (Zhao et al., 2024).
This study is significant as it helps to fill the gaps by adopting a T-O-E-based CSF assessment using Fuzzy DEMATEL methodology, which enables the determination and modeling of causal linkages in agri-tech ecosystems. This contributes to the theoretical understanding of agri-tech-facilitated food system transformations and provides practical knowledge to policymakers, decision makers, investors, and entrepreneurs. Specifically, it identifies strategic leverage points, such as digital infrastructure, enabling policy frameworks, and innovation capacity that can stimulate the rate of change toward the sustainable food system in resource-constrained settings. The study identifies the following particular aims:
1. To systematically identify and categorize the critical success factors (CSFs) influencing the effectiveness and sustainability of agri-tech startups in developing economies.
2. To analyze and model the causal relationships among these CSFs using the Fuzzy DEMATEL Methodology.
3. To derive strategic insights and actionable recommendations for policymakers, investors, and startup founders to strengthen a responsible and resilient agri-tech ecosystem.
The research contributes to the leverage points that can accelerate the role of agri-Tech startups in achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to zero hunger, responsible production, and climate action.
The subsequent parts of this research are as follows: Section 2 discusses a literature review of sustainable food systems and agri-tech innovation. Section 3 details the Fuzzy DEMATEL research methodology. Section 4 discusses results from Fuzzy DEMATEL. Section 5 discusses findings with theoretical and practical implications. Section 6 concludes and provides research recommendations for future study.
2 Literature review
2.1 Technology-organization-environment
The Technology-Organization-Environment (T-O-E) conceptualization, first proposed by Tornatzky and Fleischer (1990), has evolved into a critical theoretical framework guiding analysis of technological innovation and adoption within organizations. Emerging technologies such as precision agriculture, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, AI, and BDA are reshaping food value chains by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive insights, and transparency in supply networks (Klerkx et al., 2019). Similarly, the application of blockchain platforms is increasingly being utilized to enhance traceability and lessen information asymmetry between the farmers, consumers, and intermediaries (Tripoli and Schmidhuber, 2018). Nevertheless, adopting these technologies in agriculture is associated with several obstacles to implementation, including a lack of digital literacy, insufficient connectivity in rural regions, and the high cost of adoption, especially for smallholder farmers (Mhlanga and Ndhlovu, 2023; Touch et al., 2024).
In the context of agri-Tech startups, technological scalability and user-focused design are the salient factors of success. Research has shown that technological capability is not sufficient to influence the diffusion of innovations in agri-food systems, which are perceived as easy to use, compatible with current practices, and trustworthy among stakeholders (Rijswijk et al., 2021). Through these technologies, startup companies can provide sustainable services efficiently and transparently throughout the agricultural value chain (Vishnu et al., 2025). The poverty of rural spaces in terms of technology necessitates technological upgrades that would be proportional to the resource issues faced by small-scale farmers (Choruma et al., 2024). The organizational dimension encompasses specific aspects of the firm, such as top management support, the available resources, a talented labor force, and readiness to change. Strong leadership, nimble research, and business inclusion strategies to integrate smallholder farmers as the main organizational motive to agri-tech startup success (Suresh et al., 2024). Cultural aspects are paramount in the organization regarding the process of developing user-centric volatile agri-food products and adapting innovation (Bethi and Deshmukh, 2023). Major challenges that agri-tech startups are currently grappling with are not only a result of regulatory uncertainty but also market fragmentation and a lack of digital literacy among rural farmers, which startups must overcome to create a viable difference.
The T-O-E framework thus serves as both a diagnostic tool and a strategic guide for agri-tech startups seeking to integrate their innovations into responsible and sustainable food systems. By analyzing the technological capabilities, organizational strengths, and environmental opportunities and threats, startups can better align their innovations with Sustainable Development Goal 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) and promote sustainable food security at both global and local scales (Eliseu Benz, 2022; Ogwu et al., 2024). This model enables policymakers and investors to design comprehensive interventions for startups that combine infrastructure development with capacity training, along with policy support, thereby creating an inclusive environment for sustainable agri-tech startup growth (Yontar, 2023).
2.2 Theoretical background
Agri-tech startups and their sustainable food systems receive theoretical support from the interconnected frameworks of socio-technical systems theory, as well as the resource-based view (RBV) and resilient thinking. Each of these lenses provides insights into how technology innovation, organizational strategy, and environmental interaction affect the success of businesses attempting to respond to global food issues through sustainable and ethical solutions.
2.2.1 Socio-technical systems and sustainability transitions
Socio-technical theory focuses on the interdependent evolution of technology, societal structures, regulatory frameworks, and user practices (Angeon et al., 2024). Agri-food systems require radical reform of the entire production-to-distribution-to-consumption flow to evolve sustainably (Camanzi and Troiano, 2021). Such intricate regimes are beneficial to the business ecosystem of agri-tech startups, which aim to bring smart farming solutions to digital marketplaces, transforming the traditional agricultural systems (Andersson et al., 2024). Startups should align their technological solutions with broader institutional developments and cultural shifts to create holistic change (Sarku and Ayamga, 2025).
2.2.2 Resource-based view (RBV) for startups
Resource-based view (RBV) is the argument that the competitive advantages that firms acquire depend on the availability and the strategic use of valuable, rare, inimitable, and non-substitutable (VRINE) resources (Zvarimwa and Zimuto, 2022). In the case of agri-tech startups, such resources encompass technologies such as AI algorithms to optimize yields, as well as expert human resources, including agronomists who are familiar with digital platforms. When they optimize their internal resources, startups build greater potential to expand their business activities and generate significant change in emerging markets that lack external support systems (Zhao et al., 2024).
2.2.3 Resilience thinking and sustainable food system
Resilience thinking highlights the capacity of systems to adapt to change and maintain core functions (Charatsari et al., 2022). Resilience emphasizes the importance of diversity, redundancy, decentralized structures, and adaptive governance. Agri-tech startups enhance food system resilience through initiatives promoting crop diversity, enabling users to connect via digital platforms and access data-driven management tools (Aijaz et al., 2025; Karan et al., 2023). Startups that integrate resilience concepts into their business approach by supporting farmer learning, partnering locally, and designing adaptable supply systems yield improved sustainable success (Hokmabadi et al., 2024). By drawing on these theoretical perspectives, the present study conceptualizes the success of agri-tech startups as the outcome of complex interactions between internal resources, dynamic organizational capabilities, systematic barriers and enablers, and ecosystem resilience needs. Through the T-O-E framework, the study structures theoretical constructs into an analytic framework to associate critical success factors with the Fuzzy DEMATEL method analysis.
2.3 Critical success factors
Critical success factors represent key areas that must be effectively addressed to ensure the success and sustainability of agri-tech startups, especially in developing countries. The success of these ventures emerges from the combined effects of numerous technological, organizational, and environmental elements. Understanding these CSFs is crucial for creating resilient, scalable, and sustainable food systems aligned with global development goals (Kohl, 2023).
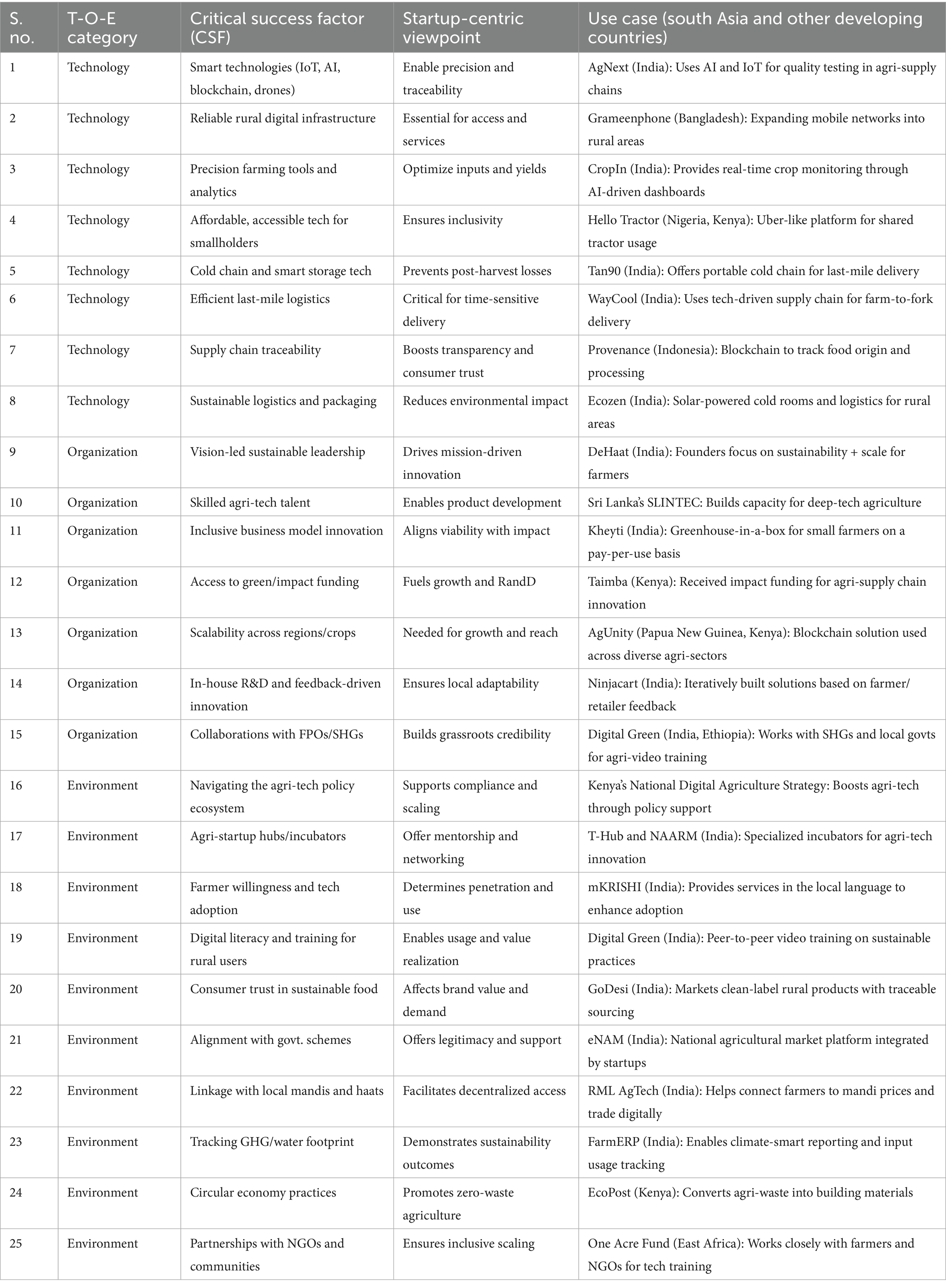
The IoT, AI, and blockchain tracking systems, as well as drone assistance in precision farming, are among the critical factors that enhance the reliability of agriculture (Sharma C et al., 2024; Sharma and Shivandu, 2024). The rural digital infrastructure enables remote farming communities to access innovative solutions, bringing technological benefits to the end-of-mile level (Fehlings et al., 2025). Technologies must be affordable and accessible to smallholder farmers; therefore, businesses must design suitable models and innovations that address economic inequalities (Lidder et al., 2025). Distribution channels facilitate the preservation of food quality through cold chain systems and smart storage technologies, which also reduce post-harvest losses (Huang et al., 2024). The organizational variables play a conclusive role in the evolution of agri-tech startup programs. The tech development assumes a mission-driven direction, characterized by sustainability-oriented leadership that fosters inclusivity (Chaudhary and Suri, 2024). Their investment in R&D processes and the feedback-driven innovation development bodies has a higher local fit, resulting in increased user acceptance and longer market utility (Priyono and Hidayat, 2024). The availability of green and impact-driven capital is a crucial factor that enables startups to mature in financial periods that the new markets face (Addai et al., 2024).
The support of national policy ecosystems directing agri-tech innovation enables startup viability through financial support, incubators, digital strategies, and supportive regulations (Balkrishna et al., 2024). Farmers’ adoption of new technology depends on their willingness, as well as local cultural factors, trust foundations, and strong digital literacy programs (Sindakis and Showkat, 2024). Startups benefit from the market demand of consumers who trust sustainable food sources, motivating them to focus on transparent sustainable practices (Macready et al., 2025). Startups enhance their grassroots credibility through partnerships with NGOs as well as collaborations with farmer organizations and community groups, thereby expanding their operational capacity to scale sustainable impact (Ogbari et al., 2024).
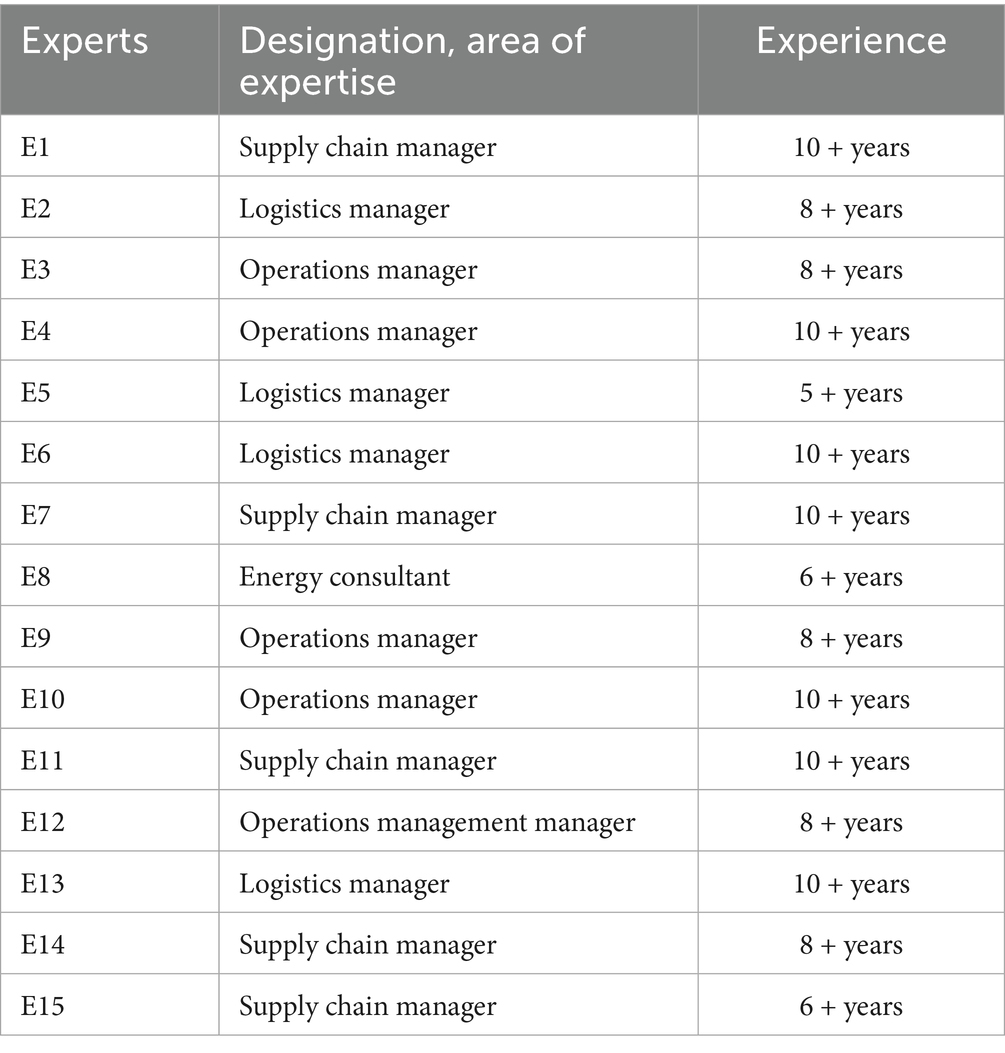
The identification of the 25 CSFs followed a two-step approach. To achieve this, a literature review was conducted across peer-reviewed journals, reports, and conference proceedings related to agri-tech startups, sustainable food systems, and adoption frameworks of technology. Prior studies highlight technological enablers (IoT, AI, blockchain, and drones; Vishnu et al., 2025), organizational determinants (leadership orientations and research and development; Chaudhary and Suri, 2024), and environmental factors such as policy frameworks, incubators, and consumer trust (Balkrishna et al., 2024). This review presented an integrated reservoir of success factors in the T-O-E spheres. Second, the list was validated by consulting 15 domain experts (Table 1) who were selected based on their roles as supply chain managers, operations managers, and consultants. The professionals ensured that contextual consideration of the factors was applied to developing economies. This dual process of the literature, preceded by a peer expert validation process, led to the selection and validation of the 25 final CSFs presented in Table 2.
3 Research methodology
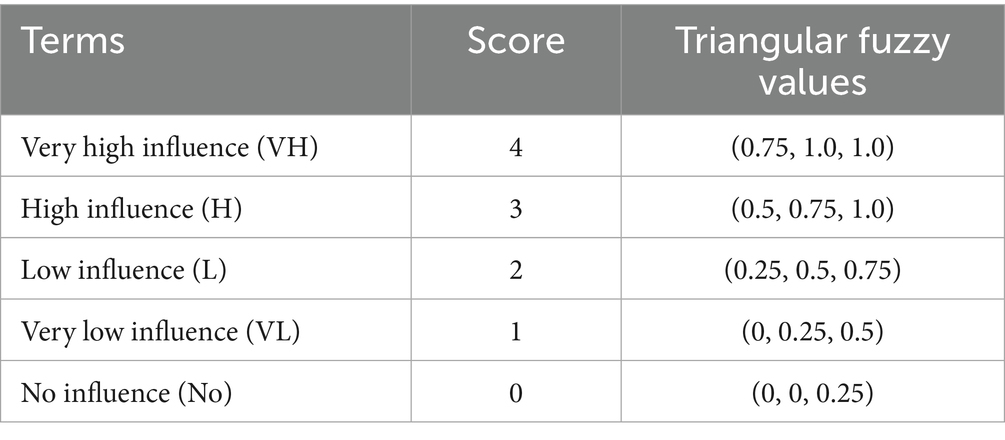
The present study employs the Fuzzy DEMATEL method to systematically analyze the interdependencies among the identified CSFs within agri-tech ecosystems. A panel of 15 experts from supply chain management, logistics, operations, and agri-business was consulted to provide pairwise comparisons of the factors using a five-point linguistic scale shown in Table 3. These linguistic assessments were transformed into triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs) to capture uncertainty and subjectivity in expert judgments. Table 3 presents the linguistic scales.
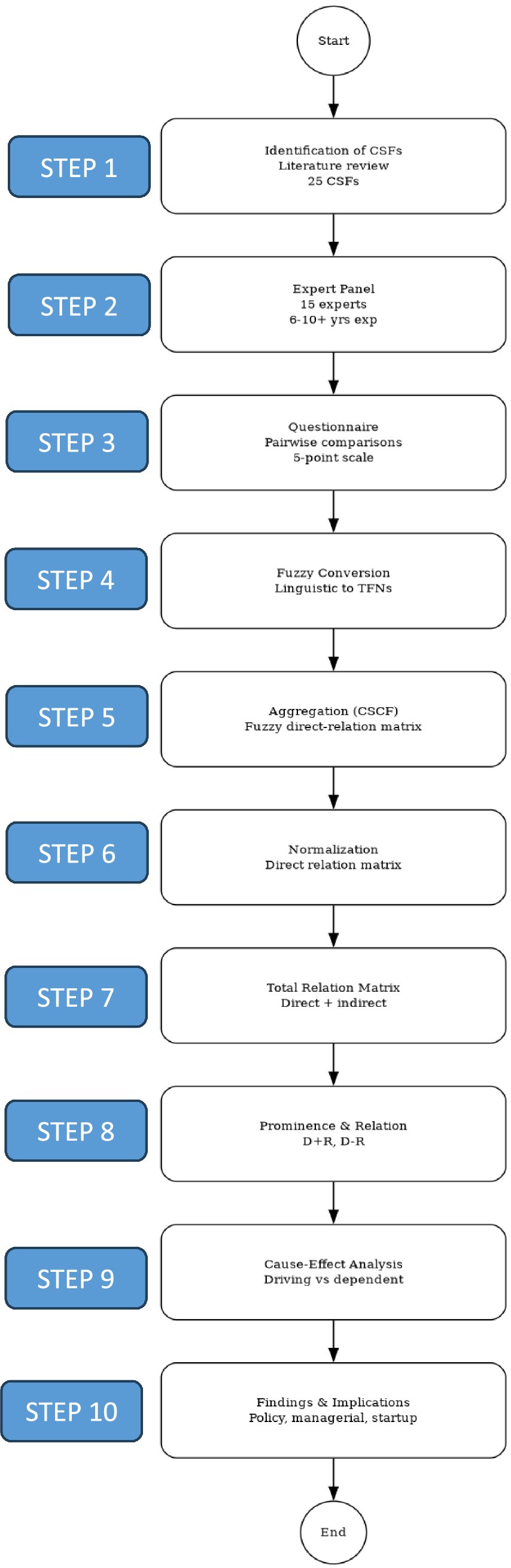
The aggregated responses were then used to construct the fuzzy direct-relation matrix, which was subsequently normalized to ensure comparability. Through iterative computation, the total relation matrix was derived for both direct and indirect influences among the CSFs. Finally, prominence (D + R) and relation (D–R) values were calculated to classify the CSFs into cause-and-effect groups. The research methodology flow is shown in Figure 1.
The fuzzy DEMATEL method enhances the evaluation of ambiguous empirical data. Utilizing fuzzy logic, decision-makers can assess alternatives according to high, medium, and low assessment tiers. This method, with its causal diagram framework, equips decision-makers with the means to identify critical success factors, hence enhancing the methodical examination of the situation. Fuzzy DEMATEL exhibits superior efficacy compared to hierarchical methods in identifying intricate interrelations within multiple systems, despite its utility in the implementation process. Further, it demonstrates adaptability and responsiveness in decision-making, providing advantages to complex information systems with flexible decision-making capabilities (Sharma S. K. et al., 2024). A questionnaire was designed for experts to conduct pairwise comparisons before the implementation of fuzzy DEMATEL. The information regarding the experts’ details is shown in Table 1.
The expert panel for this study was purposely composed of professionals with backgrounds in supply chain management, operations, and agri-business systems, as these individuals possess direct experience in understanding adoption bottlenecks, resource flows, and systemic challenges within agri-tech ecosystems. Their insights were highly valuable for identifying causal linkages between enablers and barriers, which aligns with the objectives of applying Fuzzy DEMATEL to map interdependencies among CSFs. The steps for implementing Fuzzy DEMATEL have been summarized below:
3.1 Steps for F-DEMATEL
The fuzzy DEMATEL method is employed to examine multiple influencing factors within a complex system, providing a systematic framework to explore the interrelationships among these components. The fundamental steps are as follows:
3.1.1 Step 1: expert assessment using a linguistic scale
A panel of domain experts was invited to assess the degree of influence between each pair of factors. The evaluation utilized a five-point linguistic scale, which is detailed in Table 3. This scale captures the perceived causal influence of one factor over another.
3.1.2 Step 2: development of the initial direct matrix based on the score provided by the experts
The expert responses were aggregated to construct the initial direct-relation matrix. In this matrix, the element aij represents the influence of factor i on factor j, as judged by the experts.
3.1.3 Step 3: conversion of linguistic terms into fuzzy numbers
To better capture uncertainty and subjectivity in human judgment, the linguistic terms were transformed into triangular fuzzy numbers (TFNs) using the predefined fuzzy scale (Table 3). Each linguistic value is expressed as a triplet (l, m, u), where l is the lower bound, m is the most probable value, and u is the upper bound.
3.1.4 Step 4: aggregation of expert opinions
The Converting Scale into Crisp Function (CSCF) method was applied to combine the fuzzy variables from multiple experts. This step ensures that all expert evaluations are integrated into a single consensus-based fuzzy direct-relation matrix. The aggregated fuzzy numbers are then averaged across experts.
3.1.5 Step 5: obtaining fuzzy direct relation matrix Z =
Where each is a triangular fuzzy number. Normalization is carried out using:
With
3.1.6 Step 6: constructing the normalized direct relation matrix
To ensure comparability across all factors, the direct-relation matrix is normalized as:
The crisp values are then integrated as:
3.1.7 Step 7: formation of the total relation matrix
The total relation matrix accounts for both direct and indirect effects among factors. It is derived as:
Where N is the normalized direct-relation matrix and I is the identity matrix. This step captures the propagation of influence through the system.
3.1.8 Step 8: calculation of prominence and relation scores
Finally, the prominence and relation of each factor are computed using row and column sums of the total relation matrix:
Row sums (D): the total influence a factor exerts on others.
Column sums (R): the total influence received by a factor from others.
All fuzzy arithmetic and matrix operations were executed using MATLAB, while data aggregation and visualization (cause-and-effect diagrams) were performed in MS Excel.
4 Results from F-DEMATEL
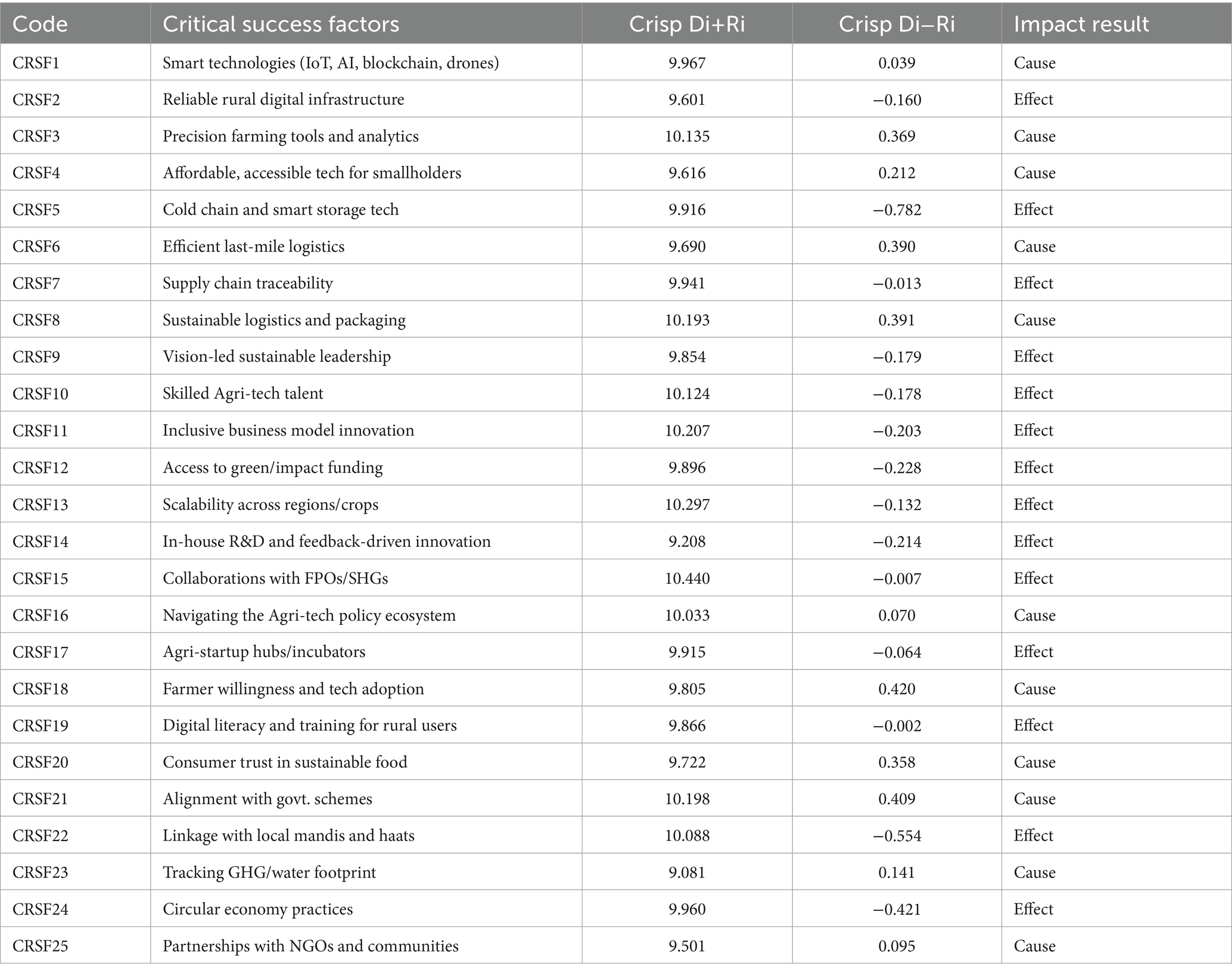
Fuzzy DEMATEL analysis was carried out to explore the causal links between 25 CSFs that determine the scalability and sustainability of agri-tech startups in developing countries. By evaluating the cause-and-effect dynamics through fuzzy logic and expert input, the study classified the factors into two key groups: cause group (influential factors) and effect group (influenced factors). The Initial Direct-Relation Matrix (Z) was created using Equations 1–3, which were developed based on expert responses applying the linguistic scale outlined in Table 3. The fuzzy direct relation matrix is derived from Equations 4–6. Equations 7–9 yield a comprehensive relation matrix, as presented in Appendix Table S1.
Key influential (cause) factors identified include CRSF3 (Technology Infrastructure), CRSF8 (Government Support), and CRSF21 (Policy Frameworks), all of which have high positive (Di–Ri) values, indicating a strong driving impact on the system. Conversely, effect factors such as CRSF11 (Public Engagement) and CRSF24 (Financial Support Mechanisms) showed high (Ri) but relatively lower (Di), suggesting these are outcomes influenced by other variables. The impact results are shown in Table 4.
Several critical success factors (CSFs) belong to the cause category because they determine the direction of other system factors. CRSF1, CRSF3, CRSF4, CRSF6, CRSF8, CRSF16, CRSF18, CRSF20, CRSF21, CRSF23, and CRSF25. The systems’ central drivers are CRSF21 with Di+Ri of 10.198 and Di−Ri of 0.409, and CRSF8 with 10.193 and 0.391. When designing intervention strategies, CRSF18 (9.805, 0.420) and CRSF6 (9.690, 0.390) are the highest priority elements. The initiative requires these driving factors to achieve success.
The effect group includes the rest of the factors because their influence stems from outside variables. CRSF2, CRSF5, CRSF7, CRSF9, CRSF10, CRSF11, CRSF12, CRSF13, CRSF14, CRSF15, CRSF17, CRSF19, CRSF22, CRSF24 Some notable effect factors include: A high level of dependency exists between CRSF5 (Di−Ri = −0.782) and CRSF22 (−0.554), which demonstrates these CSFs receive substantial influence from other areas of the healthcare system. The high influence rating (Di+Ri > 10) of CRSF11 and CRSF10 indicates that these factors tend to be system-sensitive rather than driving change elements because they react to changes across the system. The performance indicators function as monitors that help assess system changes resulting from enhancements in the cause group.
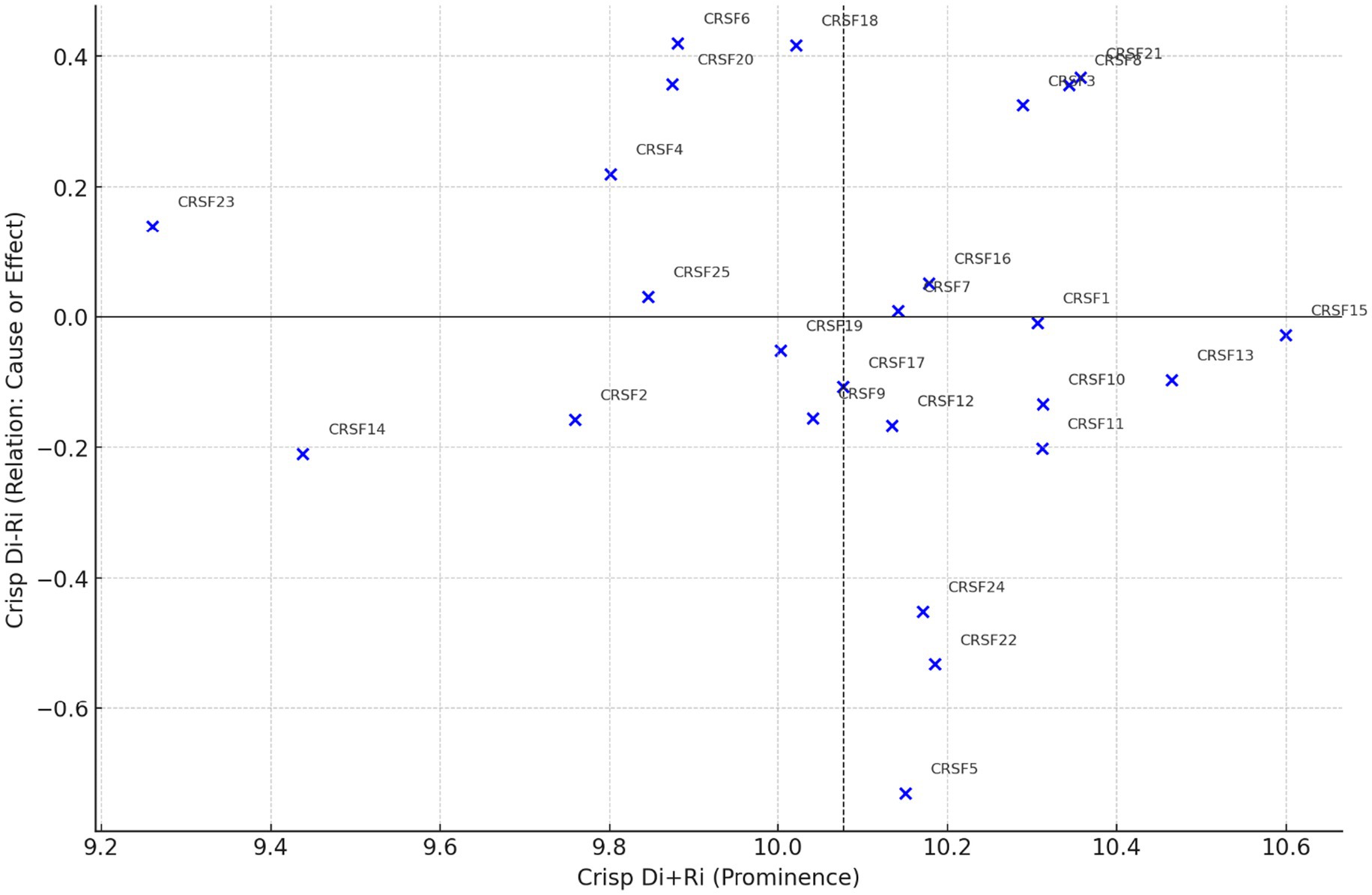
The causal diagram in Figure 2 illustrates strong interdependencies, emphasizing the importance of investing in core enablers such as digital infrastructure, supportive policies, and institutional frameworks to strengthen the entire smart circular economy ecosystem. These insights offer policymakers a prioritized roadmap for informed strategic decision-making.
5 Discussion and implications
The fuzzy DEMATEL analysis enabled a comprehensive assessment of the interdependencies among the 25 CSFs. By categorizing the CSFs into causal and effect groups, the analysis elucidated which factors function as strategic drivers and which are outcomes shaped by systemic interactions.
The cause group comprised CRSF1, CRSF3, CRSF4, CRSF6, CRSF8, CRSF16, CRSF18, CRSF20, CRSF21, CRSF23, and CRSF25, indicating their dominant influence within the system. Notably, CRSF21 (Di − Ri = 0.409), CRSF8 (0.391), CRSF6 (0.390), and CRSF18 (0.420) exhibited both high causality and strong systemic prominence (Di+Ri > 9.6), underscoring their role as key drivers. The analysis reveals crucial aspects about digital infrastructure as well as smart governance and advanced technological capabilities, which enable sustainable transitions (Govindan et al., 2022). Evidence from digital platforms and IoT systems has increased the level of transparency in tracking, which has been supported by CRSF21 and CRSF8 (Singh and Kumar, 2024). The close association between CRSF6 and CRSF18 proves that an efficient stakeholder partnership and information exchange mechanisms are primary factors in the implementation of a circular economy (Wielopolski and Bulthuis, 2023). These drivers are consistent with the strategic enablers discussed in the literature as fundamental core factors that require urgent attention to enhance overall sustainability outcomes (Onukwulu et al., 2025; Falcone et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2022).
Conversely, the effect group included CRSF5, CRSF7, CRSF9, CRSF10, CRSF11, CRSF12, CRSF13, CRSF14, CRSF15, CRSF17, CRSF19, CRSF22, and CRSF24, which primarily represent outcomes shaped by systemic dynamics rather than initiators of change. Among these, CRSF5 (Di − Ri = −0.782) and CRSF22 (−0.554) exhibited the greatest dependency, showing that they were more sensitive to upstream drivers. This observation aligns with previous studies that have highlighted the performance measurements of circular economies, i.e., waste reduction, emission mitigation, and resource conservation, depend on the successful experience of upstream enablers, i.e., policy frameworks, leadership commitment, and digital infrastructure (Hartley et al., 2023; Mottet et al., 2020).
Notably, CRSF10 and CRSF11 had a high systemic prominence (Di+Ri > 10) but with negative values of net influence (Di [?]). Ri (0), which means that they are at the center of the system, but are driven externally. This trend underscores the importance of continually monitoring such indicators to assess the effectiveness of circular economy strategies (Govindan and Hasanagic, 2018).
The causal factors identified were CRSF21 (supportive policy frameworks) and CRSF8 (government support). This is consistent with the National Digital Agriculture Strategy of India and the Kenya Agricultural Sector Transformation and Growth Strategy, which indicate that well-designed regulations and strategic digital interventions trigger innovation among startups. In other examples, CRSF6 (digital infrastructure) is a key determinant of success, as in Bangladesh, where Grameenphone has contributed to the delivery of last-mile agri-advisory using its extensive network to rural districts. Furthermore, in Nigeria, Hello Tractor has benefited from the rural penetration of connectivity to support its share machinery system.
CRSF18 (stakeholder collaboration) and CRSF3 (technology infrastructure) are organizational-level drivers that can be seen in initiatives like DeHaat (India) and AgUnity (Papua New Guinea and Kenya), which use digital platforms and farmer-producer organization (FPO) linkages to expand outreach and blockchain-enabled tools to improve the belief participants place in transactions, respectively. The examples suggest that technological possibilities become effective only when incorporated with inclusive sharing practices and culture-relevant business concepts (Alfonsi et al., 2024).
On the effect side, CRSF5 (financial constraints) and CRSF22 (market linkages) have high dependency. The case of East Africa-based One Acre Fund demonstrates that even well-designed digital platforms fail to efficiently serve the population unless farmers have access to financing or markets. Similarly, the example of EcoPost (Kenya), which suggests recycling agricultural waste into building materials, demonstrates that innovative approaches to the circular economy require a comprehensive and robust backup support system in the form of policies and consumer recognition. Although the fuzzy DEMATEL analysis provides structural explanations, the transformative possibilities are related to the capability of modifying causal enablers to create conditions, particularly in developing countries. The policymakers and ecosystem actors should emphasize CSFs that expand digital infrastructure, policy coordination, and inclusive financing to achieve the systemic potential of agri-tech startups in building sustainable food systems. Inclusion, particularly of women, smallholders, and marginalized groups who form the workforce of developing country agriculture, is also a feature of sustainable food systems. It is revealed that factors of stakeholder collaboration, digital literacy, and NGO partnerships directly influence equity outcomes.
The greenhouse-in-a-box program designed by Kheyti in India, and peer-to-peer training activities provided to women in Ethiopia by Digital Green can serve as another example of how the benefits of accessible technology, as well as a knowledge-sharing system, can empower women and smallholders. Similarly, instances of inclusive financing can be observed in programs as One Acre Fund in East Africa, where marginalized farmers can take advantage of adopting innovations. The addition of inclusive practices would enable agri-tech startups to provide benefits to agro-efficiency while also contributing to the fairness and sustainability of food systems.
Recent empirical research further strengthens our findings. A study by Isher et al. (2024) shows that incubation services are strongly linked to the success of agri-tech startups in Indian states through mentorship and infrastructure support. Another study by Isher and Gangwar (2025) corroborates this, highlighting the role of incubators in enhancing job creation and attracting venture funding. Further, Zhao et al. (2025) provide compelling evidence that investments in digital infrastructure in China significantly enhance green agricultural productivity and rural incomes. Similarly, Ofosu-Ampong et al.’s (2025) review reveals that digital agro-advisory tools in the Global South emphasize how behaviorally informed tool design increases farmer uptake.
The empirical grounding of the causal dynamics we identified via fuzzy DEMATEL is further strengthened by the following relevant studies: Kantoğlu et al. (2025) exhibited in Sub-Saharan Africa that agri-tech and value-added agricultural inputs significantly drive sustainability outcomes and emissions mitigation, reinforcing the current study model’s cause group factors. Choruma et al. (2024) and Nxumalo and Chauke (2025) highlight on-ground barriers (digital literacy, infrastructure, financial constraints) alongside success stories, which align with the current study’s effect group and practical barriers. From the Indian context, Dora et al. (2022) identified technology readiness, regulatory compliance, and perceived benefits among key CSFs of AI adoption in the food supply chain, which mirror several of the current study’s CSFs in the technology and organizational categories. Finally, Quayson et al. (2024) applied a fuzzy DEMATEL approach to the cocoa supply chain in Ghana to identify influence relationships among barriers, such as lack of management support, low awareness, and regulatory challenges; these can directly support our recommendations for interventions.
Recent state-level implementations in India also reinforce these trends. For instance, Maharashtra’s MahaAgri-AI Policy (2025–2029) and Andhra Pradesh’s fully digital APAIMS 2.0 scheme employ digital platforms and AI to enhance farmer services and data exchange, highlighting the catalytic role of policy-driven infrastructure (TOI). Lastly, Zafar et al. (2025) suggest methodological advances in data governance, such as privacy-preserving data linkage frameworks, address key ethical and implementation concerns in public–private data collaboration.
5.1 Implications
The transition toward sustainable and responsible agri-food systems represents a crucial pathway to advance Sustainable Development Goal 12, particularly within developing economies. This study demonstrates that agri-Tech startups serve as a catalyst for systemic change, driving the development of ethical, circular, and technology-enabled food systems. By employing the fuzzy DEMATEL method within the TOE framework, several theoretical and practical implications emerge. First, the study explores the most influential CSFs within the “cause group,” including policy coordination, rural ecosystem readiness, and innovation capacity. These findings underscore the importance of government agencies and ecosystem enablers prioritizing coherent regulatory frameworks, targeted investments, and enabling infrastructures that foster startup-driven innovation and ethical supply chain transitions. Second, the results reinforce the central role of technology in building resilient and transparent agri-food systems. Smart integration of digital platforms, precision tools, and sustainable logistics functions enhances supply chain scalability and inclusivity, while simultaneously improving traceability and reducing food waste. To maximize these impacts, investors need not only to provide financial capital but also to support capability-building programs that enable startups to tailor innovations to regional contexts and leverage local opportunities. Third, the “effect group” CSF, such as supply chain coordination outcomes, waste reduction, and consumer-oriented tracking, emphasizes the necessity of systematic performance evaluation. Establishing KPIs and maintaining continuous feedback loops is critical to ensure that upstream innovations translate into measurable sustainability outcomes. Finally, the findings support that local and community-driven alternative food networks, often propelled by local entrepreneurship, represent vital mechanisms for mitigating food insecurity and enhancing resilience at the grassroots level.
5.2 Practical recommendations for policymakers and decision makers
This study offers various practical suggestions for enhancing sustainable agri-tech ecosystems in developing economies, based on its findings. The findings highlight to policymakers the need to develop logical and facilitating policy conditions that encourage the use of technologies by subsidizing, easing regulations, and enabling programs. Moreover, the expansion of rural digital infrastructure, in terms of broadband and mobile connectivity, is crucial for establishing equal access opportunities to the digital transition with smallholders and marginalized groups. It should also focus on gender-sensitive policies to ensure women farmers have equal access to innovation adoption, as they are significantly affected by systemic obstacles to innovation adoption.
In the case of the startup ecosystem, research suggests that partnerships with farmer-producer organizations, cooperatives, and NGOs are crucial, as they strengthen grassroots outreach and establish credibility. Startups must implement business models that allow greater penetration of small-scale producers. Inclusive business models: pay-per-use, bundled services, and micro-leasing could make advanced technologies accessible and affordable. The enhancement of knowledge-sharing mechanisms, such as those based on incubators and accelerators, can also be used to scale innovations in various contexts.
Funding agencies and investors should pay attention to impact-driven funding mechanisms, such as green funds, blended finance, microcredit, and credit, which can help decrease one of the barriers to funding for both startups and farmers. Additionally, capacity-building projects that enhance the managerial, technical, and computer skills of the entrepreneurs are vital to long-term viability. Incorporating zero hunger sustainability targets, SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and SDG 13 (Climate Action) in investment portfolios will help keep financial flows viable and sustainable. Collectively, these recommendations emphasize the importance of recognizing that technological breakthroughs alone are insufficient to change food systems. A favorable policy environment, supportive entrepreneurial ecosystems, and bespoke funding facilities are also vital in allowing agri-tech entrepreneurs to become agents of fundamental change, directing food systems toward sustainable production and equitable access.
6 Conclusion
This study employed the T-O-E framework and fuzzy DEMATEL to analyze 25 CSFs for agri-tech startups in developing economies. The findings reveal that systemic enablers such as supportive policy frameworks, robust digital infrastructure, and innovation capacity emerge as dominant enablers. Conversely, financial access, market linkages, and consumer adoption appear to be dependent factors that improve only when causal enablers are addressed. The findings highlight that startups alone cannot drive transformation; supportive policies, robust infrastructure, and inclusive innovation systems are required to achieve scalable and sustainable outcomes in developing economies. The findings not only offer theoretical insights but also provide actionable guidance for stakeholders, including policymakers, investors, and startup founders, who are working toward building resilient, responsible, and inclusive food systems. For policymakers, this study suggests investing in rural connectivity, creating national digital agriculture strategies, and ensuring inclusive regulatory frameworks that reduce adoption barriers for smallholders and women farmers. Investors and funding agencies must de-risk early-stage ventures through blended finance, green funds, and incubation support, while aligning capital flows with measurable SDG outcomes. Startup founders, in turn, need to focus on affordable, context-sensitive business models, collaborate with cooperatives and FPOs to build trust, and embed user-driven R&D to ensure scalability. Concisely, these targeted actions can strengthen agri-tech ecosystems and position startups as catalysts for resilient and equitable food systems.
However, this study has a few limitations. First, the analysis relies on expert judgment. Although expert inputs capture structured knowledge, they may introduce subjectivity and potential bias, especially when experts share similar professional backgrounds or perspectives. Second, the sample of experts undertaken is limited in size and diversity; this may underrepresent other important ecosystem actors such as grassroots farmers, community organizations, and policymakers at local levels. Third, the study does not incorporate empirical validation from farmer surveys, startup field data, or impact assessments of ongoing agri-tech interventions. Future research should address these gaps by integrating larger and more diverse stakeholder groups, including farmers, agri-startups, and rural extension workers, to improve representativeness. The methodology can be extended by combining expert judgment with real-world startup performance data (e.g., investment levels, user growth, supply chain emissions) to validate and refine the fuzzy DEMATEL model. In addition, a mixed-method approach combining expert-based modeling with field surveys, case studies, and secondary adoption data would strengthen the credibility and practical relevance of the findings. Finally, the dynamic nature of agri-tech ecosystems may lead to changes in these success factors over time that need to be assessed. While technology is a central theme, this study does not explore in-depth distinctions between types of digital tools (e.g., AI, IoT, blockchain), which may have different levels of impact on agri-food sustainability. Future researchers can conduct time-series analyses to observe how the influence of CSFs evolves as agri-tech startups mature and external conditions (e.g., policies, market forces) change. The study can be replicated in a broader sample of countries, especially emerging economies in Latin America, Southeast Asia, and Africa. It can also be extended to explore sector-specific startups (e.g., aquaculture, urban farming). The study is insightful for developing systems dynamics or agent-based simulation models to explore how different policy interventions affect the readiness and impact of agri-tech startups over time.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Navneet Rawat, Rajesh Tiwari, Nagendra Sharma. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
MS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PG: Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SJ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1621741/full#supplementary-material
References
Addai, K., Yufenyuy, M., and Kifem, F. L. (2024). Do green finance and digital technology matter for sustainable agricultural development? Insights from sub-Saharan Africa. Discover Agric. 2:29. doi: 10.1007/s44279-024-00039-w
Aijaz, N., Lan, H., Raza, T., Yaqub, M., Iqbal, R., and Pathan, M. S. (2025). Artificial intelligence in agriculture: advancing crop productivity and sustainability. J. Agric. Food Res. 20:101762. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2025.101762
Alfonsi, R. M., Naidoo, M., and Gasparatos, A. (2024). Stakeholder perspectives for information and communication technologies (ICTs) for sustainable food systems in South Africa: challenges, opportunities and a proposed ICT framework. Environ. Dev. Sustain., 1–34. doi: 10.1007/s10668-024-04838-5
Andersson, J., Lennerfors, T. T., and Fornstedt, H. (2024). Towards a socio-techno-ecological approach to sustainability transitions. Environ. Innov. Soc. Trans. 51:100846. doi: 10.1016/j.eist.2024.100846
Angeon, V., Casagrande, M., Navarrete, M., and Sabatier, R. (2024). A conceptual framework linking ecosystem services, socio-ecological systems and socio-technical systems to understand the relational and spatial dynamics of the reduction of pesticide use in agri-food systems. Agric. Syst. 213:103810. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2023.103810
Balkrishna, A., Singh, S. K., Pathak, R., and Arya, V. (2024). E-governance paradigm in the Indian agricultural sector. Discover Agric. 2:1. doi: 10.1007/s44279-024-00012-7
Bethi, S. K., and Deshmukh, S. S. (2023). Challenges and opportunities for Agri-Tech startups in developing economies. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 15, 12661–12666.
Camanzi, L., and Troiano, S. (2021). The evolutionary transformation of modern Agri-food systems: emerging trends in consumption, production, and in the provision of public goods. Agric. Food Econ. 9:1. doi: 10.1186/s40100-021-00196-2
Charatsari, C., Lioutas, E. D., De Rosa, M., and Vecchio, Y. (2022). Technological innovation and agrifood systems resilience: The potential and perils of three different strategies. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6:872706. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.872706
Chaudhary, S., and Suri, P. K. (2024). Agri-tech: experiential learning from the Agri-tech growth leaders. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 36, 1524–1537. doi: 10.1080/09537325.2022.2100755
Choruma, D. J., Dirwai, T. L., Mutenje, M. J., Mustafa, M., Chimonyo, V. G. P., Jacobs-Mata, I., et al. (2024). Digitalisation in agriculture: a scoping review of technologies in practice, challenges, and opportunities for smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Agric. Food Res. 18:101286. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101286
Devaux, A., Goffart, J.-P., Kromann, P., Andrade-Piedra, J., Polar, V., and Hareau, G. (2022). The potato of the future: opportunities and challenges in sustainable agri-food systems. Potato Res. 65:211. doi: 10.1007/s11540-021-09523-y
Dora, M., Kumar, A., Mangla, S. K., Pant, A., and Kamal, M. M. (2022). Critical success factors influencing artificial intelligence adoption in food supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 60, 4621–4640.
Eliseu Benz, L. A. (2022). Critical success factors for circular business model innovation from the perspective of the sustainable development goals. Sustain. 14:5816.
Falcone, G., Stillitano, T., Iofrida, N., Spada, E., Bernardi, B., Gulisano, G., et al. (2022). Life cycle and circularity metrics to measure the sustainability of closed-loop Agri-food pathways. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6:1014228. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.1014228
Fehlings, S., Karrar, H. H., and Rudaz, P. (2025). Small businesses and new adaptation capacities in Georgia and Kazakhstan. World Dev. 191, 106993
Garrity, K., Krzyzanowski Guerra, K., Hart, H., Al-Muhanna, K., Kunkler, E. C., Braun, A., et al. (2024). Local food system approaches to address food and nutrition security among low-income populations: a systematic review. Adv. Nutr. (Bethesda, Md.) 15:100156. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.100156
Glaros, A., Thomas, D., Nost, E., Nelson, E., and Schumilas, T. (2023). Digital technologies in local Agri-food systems: opportunities for a more interoperable digital farmgate sector. Front. Sustain. 4:3873. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2023.1073873
Govindan, K., and Hasanagic, M. (2018). A systematic review on drivers, barriers, and practices towards circular economy: a supply chain perspective. Int. J. Prod. Res. 56, 278–311. doi: 10.1080/00207543.2017.1402141
Govindan, K., Nasr, A. K., Karimi, F., and Mina, H. (2022). Circular economy adoption barriers: an extended fuzzy best–worst method using fuzzy DEMATEL and supermatrix structure. Bus. Strat. Environ. 31, 1566–1586. doi: 10.1002/bse.2970
Hartley, K., Schülzchen, S., Bakker, C. A., and Kirchherr, J. (2023). A policy framework for the circular economy: lessons from the EU. J. Clean. Prod. 412:137176. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137176
Hokmabadi, H., Rezvani, S. M., and de Matos, C. A. (2024). Business resilience for small and medium enterprises and startups by digital transformation and the role of marketing capabilities—a systematic review. Systems 12:220. doi: 10.3390/systems12060220
Horst, M., Mcclintock, N., and Hoey, L. (2024). The intersection of planning, urban agriculture, and food justice: a review of the literature. In: Raja, S., Caton Campbell, M., Judelsohn, A., Born, B., Morales, A. (eds) Planning for Equitable Urban Agriculture in the United States. Urban Agriculture. Cham: Springer. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-32076-7_6
Huang, J., Zhang, M., Mujumdar, A. S., and Ma, Y. (2024). Technological innovations enhance postharvest fresh food resilience from a supply chain perspective. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 11044–11066. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2232464
Isher, A. K., and Gangwar, V. P. (2025). Can innovation cultivate growth? A quantitative exploration of Agri-tech startups and incubation impact. J. Innov. Entrep. 14:87. doi: 10.1186/s13731-025-00499-4
Isher, A. K., Gangwar, V. P., and Sharma, S. (2024). “Green shoots of agriculture: nurturing agri start-ups in Jammu and Kashmir and Punjab – an incubation center perspective” in Innovative technologies for increasing service productivity (Hershey, Pennsylvania, USA: IGI Global Scientific Publishing), 304–323.
Kantoğlu, B., Çabaş, M., Erdem, A., Pilatin, A., Barut, A., and Radulescu, M. (2025). Impacts of agritech on sustainable agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa: a quantile regression approach towards SDG 2.4. Carbon Balance Manag. 20, 1–22. doi: 10.1186/s13021-025-00313-4
Karan, E. P., Asgari, S., and Asadi, S. (2023). Resilience assessment of centralized and distributed food systems. Food Secur. 15, 59–75. doi: 10.1007/s12571-022-01321-9
Klerkx, L., Jakku, E., and Labarthe, P. (2019). A review of social science on digital agriculture, smart farming and agriculture 4.0: New contributions and a future research agenda. NJAS Wageningen J. Life Sci. 90:100315. doi: 10.1016/j.njas.2019.100315
Kohl, R. D. (2023). Key factors for advancing innovations to scale: evidence from multiple country case studies of agricultural innovations. Front. Sustain Food Syst. 7:1053152. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1053152
Lidder, P., Cattaneo, A., and Chaya, M. (2025). Innovation and technology for achieving resilient and inclusive rural transformation. Glob. Food Sec. 44:100827. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2025.100827
Lisboa, H. M., Pasquali, M. B., Dos Anjos, A. I., Sarinho, A. M., De Melo, E. D., Andrade, R., et al. (2024). Innovative and sustainable food preservation techniques: enhancing food quality, safety, and environmental sustainability. Sustain. 16:8223.
Macready, A. L., Hieke, S., Klimczuk-Kochańska, M., Szumiał, S., Wachter, K., Arnoult, M. H., et al. (2025). Why trust is crucial-the moderating role of trust in the relationship between motivation and intention to buy healthy, sustainable and novel foods. Food Qual. Prefer. 126:105386.
Mhlanga, D., and Ndhlovu, E. (2023). Digital technology adoption in the agriculture sector: challenges and complexities in Africa. Hum. Behav. Emerging Technol. 2023:6951879. doi: 10.1155/2023/6951879
Michel, M., Eldridge, A. L., Hartmann, C., Klassen, P., Ingram, J., and Meijer, G. W. (2024). Benefits and challenges of food processing in the context of food systems, value chains and sustainable development goals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 153:104703. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104703
Mottet, A., Bicksler, A., Lucantoni, D., De Rosa, F., Scherf, B., Scopel, E., et al. (2020). Assessing transitions to sustainable agricultural and food systems: a tool for agroecology performance evaluation (TAPE). Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 4:579154. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.579154
Nxumalo, G. S., and Chauke, H. (2025). Challenges and opportunities in smallholder agriculture digitization in South Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1583224. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1583224
Ofosu-Ampong, K., Abera, W., Mesfin, T., and Abate, T. (2025). Digital agro-advisory tools in the global south: a behavioural analysis of impacts, and future directions. Discover Agric. 3, 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s44279-025-00190-y
Ogbari, M. E., Folorunso, F., Simon-Ilogho, B., Adebayo, O., Olanrewaju, K., Efegbudu, J., et al. (2024). Social empowerment and its effect on poverty alleviation for sustainable development among women entrepreneurs in the Nigerian agricultural sector. Sustainability 16:2225. doi: 10.3390/su16062225
Ogwu, M. C., Izah, S. C., Ntuli, N. R., and Odubo, T. C. (2024). “Food security complexities in the global south” in Food safety and quality in the global south. Eds. M. C. Ogwu, S. C. Izah, and N. R. Ntuli, (Singapore: Springer), 3–33. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-2428-4_1
Onukwulu, E. C., Dienagha, I. N., Digitemie, W. N., Egbumokei, P. I., and Oladipo, O. T. (2025). Enhancing sustainability through stakeholder engagement: strategies for effective circular economy practices. South Asian J. Soc. Stud. Econ. 22, 135–150. doi: 10.9734/sajsse/2025/v22i1950
Priyono, A., and Hidayat, A. (2024). Fostering innovation through learning from digital business ecosystem: a dynamic capability perspective. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 10:100196. doi: 10.1016/j.joitmc.2023.
Quayson, M., Bai, C., Sarkis, J., and Hossin, M. A. (2024). Evaluating barriers to blockchain technology for sustainable agricultural supply chain: a fuzzy hierarchical group DEMATEL approach. Oper. Manag. Res. 17, 728–753. doi: 10.1007/s12063-024-00443-x
Raihan, A., Ridwan, M., and Rahman, M. S. (2024). An exploration of the latest developments, obstacles, and potential future pathways for climate-smart agriculture. Climate Smart Agric. 1:100020. doi: 10.1016/j.csag.2024.100020
Rialti, R., Marrucci, A., Zollo, L., and Ciappei, C. (2022). Digital technologies, sustainable open innovation and shared value creation: evidence from an Italian agritech business. Br. Food J. (Croydon, England) 124, 1838–1856. doi: 10.1108/bfj-03-2021-0327
Rijswijk, K., Klerkx, L., Bacco, M., Bartolini, F., Bulten, E., Debruyne, L., et al. (2021). Digital transformation of agriculture and rural areas: a socio-cyber-physical system framework to support responsibilisation. J. Rural Stud 85, 79–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2021.05.003
Ruben, R., Cavatassi, R., Lipper, L., Smaling, E., and Winters, P. (2021). Towards food systems transformation-five paradigm shifts for healthy, inclusive and sustainable food systems. Food Secur. 13, 1423–1430. doi: 10.1007/s12571-021-01221-4
Sarku, R., and Ayamga, M. (2025). Is the right going wrong? Analysing digital platformization, data extractivism and surveillance practices in smallholder farming in Ghana. Inf. Technol. Dev., 1–27. doi: 10.1080/02681102.2024.2447596
Sharma, C., Pathak, P., Kumar, A., and Gautam, S. (2024). Sustainable regenerative agriculture allied with digital Agri-technologies and future perspectives for transforming Indian agriculture. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 26, 30409–30444. doi: 10.1007/s10668-024-05231-y
Sharma, K., and Shivandu, S. K. (2024). Integrating artificial intelligence and internet of things (IoT) for enhanced crop monitoring and management in precision agriculture. Sensors Int. 5:100292. doi: 10.1016/j.sintl.2024.100292
Sharma, S. K., Routroy, S., Singh, R. K., and Nag, U. (2024). Analysis of supply chain vulnerability factors in manufacturing enterprises: a fuzzy DEMATEL approach. Int J Log Res Appl. 27, 814–841. doi: 10.1080/13675567.2022.2083590
Sindakis, S., and Showkat, G. (2024). The digital revolution in India: bridging the gap in rural technology adoption. J. Innov. Entrep. 13:29. doi: 10.1186/s13731-024-00380-w
Singh, A. K., and Kumar, V. R. P. (2024). Integrating blockchain technology success factors in the supply chain of circular economy-driven construction materials: an environmentally sustainable paradigm. J. Clean. Prod. 460:142577. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.142577
Suresh, D., Choudhury, A., and Shaw, R. (2024). “Future of agritech startups: perspectives from India and Japan” in India, Japan and beyond. Eds. R. Shaw and S. R. Choudhury, (Singapore: Springer), 193–210. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-3282-1_12
Tornatzky, L. G., and Fleischer, M. (1990). The processes of technological innovation. Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
Touch, V., Tan, D. K. Y., Cook, B. R., Liu, D. L., Cross, R., Tran, T. A., et al. (2024). Smallholder farmers’ challenges and opportunities: implications for agricultural production, environment and food security. J. Environ. Manag. 370:122536. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122536
Tripoli, M., and Schmidhuber, J. (2018). Emerging Opportunities for the Application of Blockchain in the agri-food Industry. Geneva, Switzerland: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and International Centre for Trade and Sustainable Development (ICTSD) International Environment.
Vishnu, C. R., Chatterjee, P., Maddali, S. P., and Akenroye, T. O. (2025). Characterizing the critical success factors influencing blockchain technology adoption in Indian public distribution system: an exploratory approach. Benchmarking. 32, 1410–1433. doi: 10.1108/BIJ-07-2023-0466
Wielopolski, M., and Bulthuis, W. (2023). The better building initiative-a collaborative ecosystem involving all stakeholders as catalyst to accelerate the adoption of circular economy innovations in the construction sector. Circ. Econ. Sustain. 3, 719–733. doi: 10.1007/s43615-022-00205-6
Yontar, E. (2023). Critical success factor analysis of blockchain technology in Agri-food supply chain management: a circular economy perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 330:117173. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117173
Zafar, O., Namazi, M., Xu, Y., Yoo, Y., and Ayday, E. (2025). A user-centric, privacy-preserving, and verifiable ecosystem for personal data management and utilization. arXiv.
Zhao, G., Chen, X., Jones, P., Liu, S., Lopez, C., Leoni, L., et al. (2024). Understanding the drivers of industry 4.0 technologies to enhance supply chain sustainability: insights from the agri-food industry. Inf. Syst. Front., 1–31. doi: 10.1007/s10796-024-10539-1
Zhao, G., Liu, S., Wang, Y., Lopez, C., Zubairu, N., Chen, X., et al. (2022). Modelling enablers for building agri-food supply chain resilience: insights from a comparative analysis of Argentina and France. Prod. Plan. Control, 1–25. doi: 10.1080/09537287.2022.2078246
Zhao, Y., Yang, C., and Khan, S. (2025). The impact of new digital infrastructure on agriculture green development: evidence from China. Front. Environ. Econ. 4:1525531. doi: 10.3389/frevc.2025.1525531
Keywords: sustainable food systems, agri-tech startups, technology-organization-environment, waste minimization, fuzzy DEMATEL
Citation: Sharma M, Gupta P and Joshi S (2025) Strengthening sustainable food systems through agri-tech startups: a fuzzy DEMATEL analysis of critical success factors. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1621741. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1621741
Edited by:
Marcello De Rosa, University of Cassino, ItalyReviewed by:
Mohammad Aslam Ansari, G. B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, IndiaRashmi Singh, Indian Agricultural Research Institute (ICAR), India
Copyright © 2025 Sharma, Gupta and Joshi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Manu Sharma, bWFudS5zaGFybWFAZ2V1LmFj
 Manu Sharma
Manu Sharma Priyanka Gupta
Priyanka Gupta Sudhanshu Joshi
Sudhanshu Joshi