- 1Department of Agricultural Economics and Agribusiness, Yaşar University, Izmir, Türkiye
- 2Department of Agricultural Economics, Ege University, Izmir, Türkiye
- 3Department of Agricultural Economics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
- 4Capacity Development in Nutrition, CAPNUTRA, Belgrade, Serbia
- 5Centre of Research Excellence in Nutrition and Metabolism, Institute for Medical Research, National Institute of Republic of Serbia Belgrade, University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia
In recent years, there has been a notable trend toward a global demand for sustainable nutrition, coupled with increasing concerns regarding biodiversity. Consequently, this has prompted the reintroduction of underutilized and neglected species (NUS) into the agri-food market. NUS refers to previously cultivated species no longer grown due to economic, cultural, agronomic, or genetic factors. The primary reason for their neglect often lies in widespread agricultural practices such as monoculture and the intense competition inherent in the current global trade environment. These crops often embody cultural heritage and possess a diverse genetic profile specific to their region, thereby contributing to efforts aimed at preserving biodiversity. However, the revitalization of NUS faces various hindrances, including behavioral barriers that influence their inclusion into mainstream diets. This review aims to identify the behavioral factors that restrict or limit the inclusion of NUS in mainstream diets, utilizing the principles of the Prospect Theory. Peer-reviewed studies focusing on the consumer perspective of NUS were analyzed using an inductive approach. Given the limited number of studies conducted to date, the findings reveal a significant gap in our understanding of NUS consumption. As a practical contribution, we propose a design that reinterprets the MINDSPACE tool through the lens of the Fogg Behavioral Model, offering guidance for policy interventions and marketing strategies.
1 Introduction
Global agricultural production today relies heavily on just a few crops, despite the 5,000 food crops estimated to exist worldwide (Royal Botanical Gardens, 2016). Four staple crops (wheat, rice, maize, and potatoes) represent more than 50% of the human energy supply (FAO, 2023). The interaction between urbanization, globalization, social transformations, expanding market sectors, and technological advancements has precipitated shifts in dietary patterns. Contemporary diets are characterized by an increased consumption of energy-dense, protein-rich, and fat-rich foods, which have contributed to rising obesity and overweight prevalence. According to the World Obesity Federation, an estimated 3 billion people worldwide are classified as overweight or obese (World Obesity Federation, 2024). The World Health Organization emphasizes the gravity of this issue, noting that at least 2.7 million deaths occur each year directly due to being overweight or obese (WHO, 2021). This is largely because carrying excess weight significantly increases the risk of developing non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and cardiovascular diseases (Knez et al., 2023a). This dietary shift has coincided with a decline in agricultural biodiversity. Agricultural biodiversity is crucial for building resilient food systems, yet its decline increases the vulnerability of food systems to disease outbreaks, extreme climatic events, and market fluctuations (FAO, 2019; van der Sluis et al., 2022). The relationship between dietary patterns and biodiversity is becoming increasingly clear, highlighting the urgent need for a transition to sustainable diets that promote agrobiodiversity, alternative food sources, and more efficient resource use in food production.
In response, global efforts are not only focused on promoting more sustainable farming systems but also on exploring innovative food solutions. There is a growing interest in so-called “novel foods,” including lab-cultivated meat, insect protein, and fortified food products, which offer alternative sources of nutrition with potentially lower environmental footprints (Calabrese and Ferranti, 2018). In parallel with these technological innovations, attention is also turning to strategies that actively contribute to the conservation of agricultural biodiversity. One such example is revitalizing forgotten and genetically diverse crops, known as Neglected and Underutilized Species (NUS). NUS are “useful plant species which are marginalized, if not entirely ignored, by researchers, breeders and policy makers” (Padulosi et al., 2013). The term NUS encompass a wide array of plants, ranging from domesticated, semi-domesticated minor crops, and wild species. NUS is a fluid concept because it is based primarily on their limited or localized use, referring to cases where a crop is a prominent major crop in one country but an overlooked minor crop in another (Padulosi et al., 2013). Although predominantly used for plant species, the term can also be used for animal species (Padulosi et al., 2013).
In light of the rising prevalence of obesity, overweight, and other non-communicable diseases, alongside growing economic and environmental challenges, it is imperative to promote the increased consumption of NUS in dietary regimens. The inclusion of NUS in the diet has been associated with a reduced risk of developing major diseases prevalent in industrialized nations, including diabetes, celiac disease, cardiovascular diseases, and various forms of cancer (Pereira, 2011). They also have considerable potential to enhance overall nutritional status over the course of a lifetime, from pregnancy to old age (Knez et al., 2023a).
Beyond their health benefits, NUS hold considerable potential to enhance human wellbeing in myriad ways. These include providing additional food sources, protecting the environment, maintaining local knowledge, ensuring sustainable use of soil and water, preserving biodiversity, and supporting local economies (Knez et al., 2023a). Furthermore, they exhibit a high degree of resilience to climate change, demonstrating a remarkable capacity to thrive within agroecological niches and marginal areas (Casanova-Pérez et al., 2024; Godlove et al., 2025; Knez et al., 2023a; Padulosi et al., 2013).
Despite the benefits mentioned above, some disadvantageous factors that hinder the inclusion of NUS into consumers' dietary behaviors. One major obstacle is the lack of knowledge surrounding NUS. These food products often have unfamiliar flavor profiles, and there is limited culinary knowledge regarding their preparation. Additionally, there is also a shortage of trained culinary professionals capable of preparing food products from these sources (Knez et al., 2023a). Furthermore, there is currently a significant gap in our understanding of the conservation, cultivation, genetic profile, post-harvest handling, and marketability of these plants (Knez et al., 2023a; Mondo et al., 2025; Padulosi et al., 2021). Additionally, there is insufficient baseline knowledge and awareness of NUS's nutritional, health-protective, and health-promoting properties (Knez et al., 2023a). This shortfall is attributed to the limited scope of existing research, neglect of policymakers and marginalization by the Green Revolution (Padulosi et al., 2021). Another key factor limiting the inclusion of NUS in diets is their limited cultivation due to lower yields compared to major commercial crops (Padulosi et al., 2021). In addition to these knowledge-related and technical barriers, there is also a social aspect that influences NUS consumption. NUS are often perceived as symbols of rural poverty and underdevelopment, which can discourage people from including them in their diets (Knez et al., 2023a).
Promoting a change in food choice and eating behavior to facilitate the inclusion of NUS into mainstream diets requires a comprehensive understanding of consumer behavior. This understanding, which can be illuminated through a behavioral approach, serves as the foundation for this endeavor. It is essential to explore not only the distinct benefits, knowledge-related, socio-economic and technical barriers, but also the behavioral barriers associated with the inclusion of NUS into mainstream diets. Additionally, it is crucial to identify and analyze current food products, mainstream diets, and nutritional practices as they represent competing behaviors that may limit the inclusion of NUS. Beyond identifying the barriers, the subsequent step involves the formulation of actionable strategies that facilitate NUS's inclusion in mainstream diets. The existing literature on NUS, however, does not adequately address the behavioral barriers to their inclusion in diets, limiting the development of effective policy interventions. In contrast to structural or sociocultural barriers, which are influenced by economic factors such as income and price, and political factors such as food policy and regulation (Chen and Antonelli, 2020), behavioral barriers are more intrinsically driven. These encompass psychological, social, cognitive, emotional and situational aspects that influence consumer decisions (Sayess et al., 2024). The present study seeks to identify behavioral barriers to the inclusion of NUS in mainstream diets and to explore ways to overcome them. It reviews the existing literature to examine how behavioral factors may hinder or limit their inclusion into everyday food practices. To better understand these barriers, the study will utilize the core principles of Prospect Theory (Kahneman and Tversky, 1979). The goal is to gain a comprehensive understanding of NUS consumption. Additionally, the present study will utilize the MINDSPACE Framework (Dolan et al., 2010) and Fogg Behavior Model (Fogg, 2009, 2020) to develop a design for tailoring policy interventions, offering a novel and pragmatic approach to addressing the behavioral barriers to NUS inclusion in mainstream diets. This work is a part of the BioValue Project, an EU-funded project within the framework of Horizon 2020. The project's aim is to encourage the inclusion of NUS into food value chains to improve biodiversity.
2 Reintroducing NUS as a strategy for healthy diets
As defined in the 2024 State of the Food Security and Nutrition in the World, a healthy diet includes the following four components: diversity (within and across food groups), adequacy (sufficiency of all essential nutrients compared to requirements), moderation (foods and nutrients that are related to poor health outcomes) and balance (energy and macronutrient intake) (FAO et al., 2024). Overall, the nutritional quality food intake has been overlooked for a long time in favor of increasing crop yields to meet the calorie needs of the growing global population. By 2030, an estimated 582 million individuals are projected to suffer from chronic undernourishment, highlighting the significant challenge of meeting Sustainable Development Goal 2 (Zero Hunger). This represents an increase of ~130 million undernourished people compared to a scenario based on the global economy prior to the COVID-19 pandemic (FAO et al., 2024). In addition, the world is not on course to meet the 2030 goal of stopping the increase in obesity. The projections indicate that over 1.2 billion adults will be obese by 2030 (FAO et al., 2024).
Malnutrition encompasses both undernutrition, such as micronutrient deficiencies, and overnutrition, including overweight and obesity (FAO et al., 2024). It significantly increases the risk of various diseases, particularly non-communicable ones like type II diabetes, certain cancers, and cardiovascular diseases (Eckhardt, 2006). Malnutrition is not solely a matter of access to food; it is primarily a problem of insufficient dietary diversity within global food systems (Miller and Welch, 2013). One promising strategy for enhancing dietary diversity, improving diet quality and reducing malnutrition is the inclusion of NUS into regular diets. NUS are often abundant in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals, which are critical for maintaining good health and providing a broad spectrum of health benefits. For instance, NUS such as green leafy greens, fruits, and legumes, serve as exemplary sources of micronutrients, including iron, zinc, calcium, and vitamins A and C (Ayilara et al., 2022; Scarano et al., 2021; Singh et al., 2023). These species provide alternative nutritional sources, thereby diminishing reliance on a limited selection of staple crops and fostering a more comprehensive dietary framework (Segal and Opie, 2015). As an illustration, wild edible flora such as moringa and nightshade are abundant in vitamins A and C, potassium, and dietary fiber (Sultanbawa and Sivakumar, 2022). Similarly, underutilized legumes like wattle seeds exhibit high protein content and have been evidenced to confer potential health benefits, encompassing anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects (Odeku et al., 2024). The Kakadu plum, an underappreciated fruit endemic to Australia, ranks among the most abundant natural sources of vitamin C, rendering it an excellent supplement for alleviating scurvy and enhancing immune function (Sultanbawa and Sivakumar, 2022). Additionally, NUS are rich in phytochemicals and antioxidants, which are crucial for protecting against chronic ailments, including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain malignancies (Knez et al., 2023a). As an example, the Natal plum, another underutilized fruit, possesses elevated levels of antioxidants that have been documented to exhibit anti-inflammatory characteristics (Sultanbawa and Sivakumar, 2022).
Anticarcinogenic, antidiabetic, and cholesterol-lowering properties, along with anti-inflammatory, prebiotic, and antioxidative effects of NUS have been reported by many over the years (Knez et al., 2023a; Li et al., 2020; María Ruiz-Rodríguez et al., 2014). For instance, buckwheat effectively lowers the glycaemic index serving as a great option for managing blood sugar levels (Sofi et al., 2023). Lentils are packed with essential micronutrients and can effectively supply sufficient dietary levels, particularly iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), and selenium (Se) (Migliozzi et al., 2015). Sow thistle is very rich in antioxidant properties and boasts antimicrobial effects along with the ability to promote wound healing (Li and Yang, 2018). Tomatoes and white eggplants are rich in bioactive compounds that contribute to their medicinal properties, including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects (Basudan, 2018; Bin-Jumah et al., 2022). Grass pea is high in protein and can be a valuable food source in regions with limited access to other protein-rich foods (Lambein et al., 2019). All of these examples highlight the benefits of NUS and their potential to support healthier diets, making them a valuable yet often overlooked resource in the fight against malnutrition and in efforts to create more inclusive, sustainable food systems.
In addition to their nutritional benefits, NUS can contribute to broader food system resilience and social equity. By promoting agrobiodiversity and supporting local food cultures NUS has the potential to improve food security, especially in marginalized and resource-limited settings. Urban populations frequently encounter restricted access to a diverse range of nutritious food options, particularly within low-income environments (Ziso et al., 2022). NUS can facilitate dietary diversification by introducing novel and nutrient-dense food items that are often more economically viable and accessible compared to exotic alternatives. For example, in Indonesia, wild edible plants, such as various leaves and fruits, are often consumed as a cost-effective strategy to enhance dietary diversity (Rahayu et al., 2024). NUS can effectively combat malnutrition by supplying essential nutrients that are frequently lacking in staple-based diets. As an example, in Kenya, the incorporation of NUS into school meal programs has been demonstrated to augment the nutritional quality of meals while concurrently mitigating costs (Proietti et al., 2025).
To summarize, the reintroduction of NUS offers a promising avenue to ensure healthier diets, improve dietary diversity and sustainability, ultimately fostering healthier populations and ecosystems. This initiative could catalyze a transformative transition in agricultural methodologies and dietary practices, enabling a more sustainable future in which diverse food sources flourish alongside conventional crops. Such a transition not only strengthens food security but also preserves local cultures and traditions, ensuring that future generations can enjoy the rich array of flavors, nutritional benefits, and long-term health benefits associated with more balanced, diverse, nutrient-rich diets.
3 Behavioral barriers to changing dietary behavior
The selection of food is the result of a complex interplay of interconnected factors. These factors include individual preferences and aversions to foods, influenced by sensory attributes such as taste, familiarity, and the emotional aspect of food. Beliefs, attitudes, norms, knowledge, and skills also play a significant role in shaping dietary choices. These factors are influenced by motivation, self-efficacy, and the presence of social networks. Additionally, social and environmental influences, such as resource availability, price, time, food availability, cultural practices, and media influences, also impact dietary decisions (Contento, 2011).
Changing dietary behavior is a complicated process that demands long-term and flexible methods and strategies. There isn't a single theory that is superior in predicting dietary behavior; predictiveness increases when narrower categories of behavior (such as milk consumption) are examined (Baranowski et al., 1999). Enhancing dietary behavior has become a key concern for nutritionists, health practitioners, and policymakers. The intention varies from tackling diseases such as obesity and diabetes to promoting healthier lifestyles. Many policies with this intention assume that people make poor food choices primarily due to a lack of sufficient information. Therefore, enhancing information is suggested as a policy-making strategy to help people make better choices. However, research indicates that policies found upon the premise of rational choice exert a limited influence on dietary behavior (Liu et al., 2014). This is because food choices, like many other decisions, are not driven solely by utility maximization, which can be achieved through solid cognitive and motivational capacity. They are often habitual, tend to be resistant to change, show minimal responsiveness to new information, and are more strongly influenced by situational and environmental factors than by intentions (Baranowski and Wansink, 2008; van't Riet et al., 2011). In this context, understanding how behavioral factors encompassing psychosocial factors and cognitive biases influence dietary habits can improve the design of dietary change interventions (Baranowski et al., 1999; Liu et al., 2014; Melo et al., 2025; Robinson-O'Brien et al., 2009; Shaikh et al., 2008; Story et al., 2008).
A substantial body of research consistently reports that familiarization with food is strongly associated with food choice (Günden et al., 2024; Tuorila and Hartmann, 2020). Being familiar with food builds confidence in what to expect, which can provide a benefit when compared to new or unfamiliar food items (Tuorila and Hartmann, 2020). Individuals often experience discomfort when confronted with unfamiliar food, manifesting as neophobia and/or disgust (Pliner and Hobden, 1992). Increased familiarity with a food item has been demonstrated to enhance the probability of selection in subsequent circumstances, thereby fostering the development of habitual consumption patterns that are integrated into one's dietary habits (Aldridge et al., 2009). The concept of familiarity also provides a framework for understanding how an individual's current eating habits can serve as a predictor of their level of acceptance of unfamiliar food items (BIOVALUE, 2025; Tuorila et al., 1998). This aligns with two fundamental concepts proposed by Prospect Theory, which influence choices: reference point and loss aversion. According to Prospect Theory (Kahneman and Tversky, 1979), people evaluate outcomes relative to a reference point. The reference point may be associated with individuals' present food consumption patterns, as well as with their expectations, attitudes, preferences, habits, experiences, personality, beliefs, values, norms, knowledge and skills (Chen and Antonelli, 2020; Contento, 2011). It serves as a baseline for evaluating outcomes and classifying them as gains or losses. Individuals tend to exhibit heightened sensitivity to potential losses. Categorizing an outcome as loss triggers a tendency to avoid them, known as loss aversion. Loss aversion refers to the preference for avoiding losses rather than acquiring equivalent gains; losses have a more significant psychological impact than gains of the same size (Kahneman and Tversky, 1979). In the context of eating behavior, this implies that the comfort of familiar foods establishes a reference point that makes deviations feel like losses. Consequently, individuals may be reluctant to try new alternatives because doing so is perceived as a loss relative to their established dietary behavior (Günden et al., 2024). This pattern is known as status quo bias, which is the tendency to maintain the current situation even when better options are available (Kahneman et al., 2018), such as when superior NUS alternatives exist. An important implication of status quo bias is sticking with the default option (Liu et al., 2014). For instance, it is difficult to choose a healthier option when French fries served as the default side dish (Roberto and Kawachi, 2014). Defaults often signal what is typical or acceptable, shaping our perceptions of what is acceptable or normal. It can seem reasonable to finish a large portion served as the default at a restaurant, even if it exceeds what one can eat (Roberto and Kawachi, 2014). Another behavioral barrier that may impact the mainstreaming of the NUS is the endowment effect, which is an example of the status quo and is explained by loss aversion (Kahneman et al., 1990, 1991). This phenomenon occurs when consumers assign greater value to staple foods like rice or wheat simply because they have traditionally consumed them, despite the potential benefits of NUS. To summarize, consumers are reluctant to deviate from their established routines or eating habits. Consumers perceive the inclusion of novel food, including NUS, into dietary routines as a relinquishment of their established dietary habits (Fischer and Reinders, 2016; Günden et al., 2024).
A further barrier to inclusion NUS into diets is priming. This is the effect of the consumer's initial information on perception, which is more influential than subsequent learning (Sayess et al., 2024). Therefore, consumers who strongly believe that unhealthy foods are tasty are less likely to consume healthy food, as they assume that a healthy diet is generally unpalatable. Consequently, consumers are anchored on “unhealthy = tasty” (Mai and Hoffmann, 2015; Paakki et al., 2022).
Another behavioral barrier is rooted in present bias, defined as the tendency of individuals to prioritize immediate convenience or gratification instead of long-term benefits (O'Donoghue and Rabin, 1999). Present bias, alternatively denoted as myopia or short-sightedness, makes it more difficult to choose sustainable or healthier options, especially when the consequences of those choices are unclear or only become evident in the distant future (Aibana et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2014). This is why consumers find themselves compromising between the short-term hedonic goal of eating tasty food and the long-term utilitarian goal of eating healthy food (Mai and Hoffmann, 2015; Paakki et al., 2022). Lowe and Butryn (2007) advanced the notion that consumer food consumption is predominantly driven by pleasure rather than caloric needs alone (Lowe and Butryn, 2007). Moreover, it is contended that the majority of food intake in contemporary society is driven by factors other than energy deprivation, leading to the emergence of pleasure hunger (Mankad and Gokhale, 2023). This explains the concept of “hedonic hunger,” which refers to an individual's excessive preoccupation or desire to consume food for the sole purpose of pleasure, regardless of physical hunger (Espel-Huynh et al., 2018). Hedonic hunger may lead consumers to eat more unhealthy foods rather than include NUS in their dietary habits. Additionally, seeking short-term gratification from food can easily trap individuals in a “hedonic treadmill.” When familiar, high-calorie options are readily available, it can create a cycle of dependence, causing people to associate food with comfort rather than nourishment, especially in anxiety-inducing consumer environments (Carlisle and Hanlon, 2014; Sayess et al., 2024). This means that while indulgent meals or novel food experiences may bring momentary pleasure, the satisfaction quickly fades, leading individuals to seek more. This constant pursuit encourages overconsumption and mindless eating, forming a habit that is difficult to break. Hedonic hunger can be considered in conjunction with scarcity. Scarcity, as defined by Mullainathan and Shafir (2013), refers to the state of having fewer resources than one perceives as necessary (Mullainathan and Shafir, 2013). This concept is influenced by both the available resources and individual tastes. Furthermore, the feeling of scarcity in food consumption may depend on not only on what is physically available but also on what others are perceived to be eating (van Rongen et al., 2022; Walker and Pettigrew, 1984). The feeling of scarcity is distinct from its physical reality. Therefore, the feeling of scarcity can trigger the fear of missing out. The phenomenon of “Fear of Missing Out (FoMO)” is a prevalent concern that individuals experience when they believe that others are enjoying rewarding experiences in their absence (Przybylski et al., 2013). In the context of food consumption, individuals persist in the consumption of unhealthy foods due to the apprehension of forgoing the gratification and enjoyment derived by others from food. Consumers may be inclined to consume tasty foods so as not to deprive others of the pleasure they get from eating, and when offered alternative foods such as NUS, they may fear missing out on the tasty, high-calorie, sugary foods that others consume.
Many people find it difficult to resist tempting foods in today's food environment, where high-calorie, unhealthy foods are cheap and easily available (Stok et al., 2014b). Moreover, food consumption often holds significant social meaning for individuals, further shaping their dietary choices. The impact of the social environment on dietary habits has been extensively documented (see Higgs, 2015; Higgs and Thomas, 2016). Specifically, the food choices of others and the amounts that those in the surrounding environment consume have a strong influence on food consumption decisions (Higgs, 2015). The presence of other individuals in the environment during food decision-making, when eating, or when making food choices has a significant impact on behavior (Higgs, 2015). On the other hand, it is important to note that social influences operate in both directions. The presence of others reliably increases eating, a so-called social facilitation effect, or decreases eating, an impression management effect depending on the situation (Herman et al., 2003). Previous research shows that people make more choices and eat more when they eat with friends than when they eat alone. This effect does not apply when people eat with those they are not acquainted with (Ruddock et al., 2019). On the other hand, some evidence suggests that an unhealthy eating partner may have a negative impact on the selection and consumption of healthier low-energy-dense foods (Robinson et al., 2014a). The acknowledgement of these significant influences on intake is crucial for the maintenance of a healthy diet (Vartanian et al., 2008).
Social norms are defined as behavioral expectations or rules that are in a society or group (Dolan et al., 2010). Descriptive social norms represent one of two primary classifications of social norms, offering insight into the behaviors that are considered typical or acceptable within a given social context. In essence, descriptive norms articulate the behaviors exhibited by members of a given group. The other type of social norms is known as injunctive norms. In contrast to descriptive norms, injunctive norms prescribe behavior by indicating what behaviors are approved or disapproved of by fellow group members (Stok et al., 2014b). In the context of eating behavior, descriptive norms refer to what one's peers, friends, colleagues, and family typically eat, while injunctive norms relate to what one believes they should eat. Together, these norms shape what is considered acceptable or desirable within a social group. In this regard, the concept of social eating norms can be understood as a set of perceived standards concerning the amount of food or specific food choices for members of a social group. Deviating from these norms can lead to discomfort, embarrassment, or fear of disapproval from others (Higgs, 2015), making individuals reluctant to include certain foods in their diets (Stremmel et al., 2021). Social norms can also signal which dietary practices are viewed as healthy or unhealthy, further influencing food-related decision-making (Robinson et al., 2014b).
Despite behavioral and structural challenges, some NUS have been successfully reintroduced into contemporary diets. One well-known example is quinoa. A crop native to the Andes, quinoa has become commercially cultivated in over 90 countries, including many in Europe, due to its adaptability and recognized nutritional value (Bedoya-Perales et al., 2018; Chevarria-Lazo et al., n.d.; Costanzo, 2021). Its global success illustrates how underutilized species can gain mainstream attention when supported by research and favorable traits like genetic diversity. Another example is spelt. Spelt's recent rise in popularity has been attributed not only to its suitability for low-input, particularly organic, farming and high market value (Winnicki and Żuk-Gołaszewska, 2017), but also to its association with gourmet cuisine and the broader revival of traditional food practices, as seen for example in Spain (Alvarez, 2021). Additionally, its versatility in baked goods and widespread availability as flour have contributed to its integration into diets (Alvarez, 2021). The idea that spelt's popularity reflects its nutritional superiority remains an open question, as current evidence does not clearly differentiate it from common wheat (Alvarez, 2021; Kandić et al., 2023; Sugár et al., 2019).
4 Methodology
We conducted a narrative literature review using peer-reviewed studies from the Web of Science and Scopus databases. Grey literature was excluded to maintain a focus on peer-reviewed sources, ensuring a higher level of methodological rigor and credibility. The search was limited to studies published in English to ensure consistency in interpretation and to align with the language proficiency of the research team. Our search focused on studies published between 2014 and 2024. To capture the broadest range of relevant studies, we used multiple keyword combinations related to NUS. The initial search results were then refined using a list of terms associated with consumer research on NUS. A third filtering step involved incorporating the terms “barrier” and “obstacle” to focus specifically on constraints in this context. This stepwise process resulted in the following screening query: TITLE-ABS- KEY (“underutilized crop” OR “undervalued crop” OR “neglected crop” OR “neglected and underutilized crop” OR “underutilized plant” OR “undervalued plant” OR “neglected plant” OR “neglected and underutilized plant” OR “underutilized species” OR “undervalued species” OR “neglected species” OR “neglected and underutilized species”) AND (consumer OR market OR demand OR consumption OR “value chain” OR “supply chain”) AND (barrier OR obstacle). The initial query yielded 19 studies after removing duplicates. We excluded studies that focused solely on characterization, cultivation, sensory, or nutritional aspects and lacked content related to consumer research. The remaining 7 studies were included in the review and examined in detail. An inductive approach was used to identify the factors from each study that contribute to the formation of behavioral barriers to the consumption of NUS. Utilizing the core ideas of the Prospect Theory, the extracted information was analyzed and organized considering informational and cognitive constraints, as well as contextual factors, including social influences and situational factors, all of which play a role in shaping barriers to the inclusion of NUS in mainstream diets.
5 Results and discussion
The main objective of this review was to uncover the behavioral factors that hinder or constrain NUS consumption, aiming to provide insights into the design of policy interventions or marketing strategies that encourage their inclusion into mainstream diets. This serves the ultimate goal of encouraging NUS cultivation by stimulating demand for NUS. This section presents the findings of a detailed review of 7 peer-reviewed studies focusing on NUS and highlights the factors related to their consumption. The next subsection summarizes the main characteristics of NUS as depicted in the reviewed studies. The subsequent subsections present and discuss the NUS consumption-related behavioral factors mentioned or evaluated in these studies. Suggested strategies to address the related barriers are briefly introduced at the end of each subsection and further elaborated in the practical implications section.
5.1 Characteristics of the studied NUS
The reviewed studies address a wide range of neglected and underutilized species (NUS), considering their sources and reasons for being considered “underutilized” or “neglected” (Table 1). Five out of seven studies addressed plant species. Among them, the works of Van Loon et al. (2021), Knez et al. (2023b), Sanders et al. (2015), and Pieterse et al. (2023) have all highlighted the environmental, cultural, nutritional, and livelihood benefits of NUS they investigated. They have brought attention to a wide variety of plant species, from fruit trees in Latin America to indigenous vegetables in several African countries. All of them stress the potential for preserving biodiversity by reintroducing these species as food sources. On the other hand, Verner et al. (2023) focus on the potential contribution of traditional food products derived from underutilized plant species to development and, from this perspective, extend the understanding of tourist demand for these food products.
Two of the studies focused on animal species, namely silkworms and oysters. From a circular economy perspective, Dhakal et al. (2024) discuss waste silkworm pupae as underutilized source of protein for the food and feed industries, which demand less resources, especially water. In their 2016 study, Lawley and Birch investigated the potential of oysters in Australia, highlighting the contrast between their limited consumption and high popularity. Their primary focus was on devising effective point-of-sale marketing strategies to increase oyster consumption.
5.2 Behavioral barriers to the consumption of NUS in the reviewed studies
5.2.1 Limited degree of familiarity, awareness and knowledge
Familiarity emerges as a consistently identified factor in research focused NUS consumption. Our findings expose several factors related to limited degree of familiarity with a NUS product that hinder its consumption. Key barriers include a lack of awareness about the nutritional benefits (Dhakal et al., 2024; Pieterse et al., 2023; Van Loon et al., 2021) and concerns about potential health risks associated with the product (Verner et al., 2023). Van Loon et al. (2021) further suggest that products familiar to consumers may dominate the market, even when unfamiliar alternatives offer the potential for significant income generation. Another barrier involves strong psychological responses, such as food neophobia (fear of new experiences) and disgust, particularly in the case of insects like silkworms, across various cultural contexts (Dhakal et al., 2024). These reactions are considered evolutionary defense mechanisms that lead individuals to avoid unfamiliar foods perceived as potentially harmful (Alley, 2018). Their influence tends to diminish when individuals are provided with information on environmental and health benefits, experience positive sensory attributes, or are exposed to insect-based foods in less visually recognizable forms (Günden et al., 2024).
Accordingly, the reviewed studies emphasize the influence of increased familiarity on the acceptance of NUS. Dhakal et al. (2024) suggests incorporating insects into processed foods, such as snacks, to enhance consumer acceptance, while also noting that increasing knowledge alone is insufficient without creating positive sensory experiences through tasting opportunities. Similarly, Verner et al. (2023) highlights that familiarity positively correlates with the willingness to buy NUS among tourists in their study. However, this relationship may not be consistent across all tourism contexts. While everyday consumption is typically driven by convenience and habits, certain types of tourist behavior reflect a stronger inclination toward new experiences (Chang, 2011). Some studies report that, in such contexts, low familiarity may not act as a deterrent but rather as an appealing factor, as stepping away from one's “reference point” of comfort no longer constitutes a perceived loss. On the contrary, not engaging in the experience may be perceived as a missed opportunity or loss (Xu and Zeng, 2022). This implies that while familiarity-enhancing strategies may be effective in promoting NUS in everyday diets, alternative strategies that highlight unfamiliarity of NUS as a missed opportunity could also be considered.
5.2.2 Cultural biases
The reviewed studies point to a specific cultural bias, namely, the perception of NUS as culturally inferior foods associated with poverty or underdeveloped societies (Knez et al., 2023b; Sanders et al., 2015; Van Loon et al., 2021). This bias is commonly identified in the previous research as an obstacle to the consumption of NUS (Durst and Bayasgalanbat, 2014; Padulosi et al., 2019). Knez et al. (2023b) and Sanders et al. (2015), in particular, emphasize that negative assumptions such as “poor people's food” particularly among urban residents. As a result, these products are often excluded not on the basis of taste or nutritional value, but because of the symbolic associations they carry. Van Loon et al. (2021) further underline that this common belief results in a disadvantage for NUS fruits in the market compared to more “prestigious” fruits. These findings underscore the importance of recognizing that food choices are not merely individual decisions, but are deeply embedded in the decision-making environment, often shaped by social norms. In line with this, Van Loon et al. (2021) suggest using public campaigns and marketing tools, such as endorsements by socially respected figures, as a strategy to enhance NUS consumption, influencing social norms surrounding these foods.
Previous research suggests that individuals tend to avoid food choices that diverge from social expectations, as such behavior can be perceived as a form of social risk-taking (Stremmel et al., 2021). When NUS are culturally constructed as “inferior,” the perceived social risk may outweigh the potential environmental or nutritional benefits, further discouraging their consumption. This implies that this cultural bias may represent a barrier that familiarity or information campaigns alone are unlikely to overcome. Therefore, addressing it requires strategies that construct the consumption of NUS as socially acceptable and desirable practices.
5.2.3 Availability, convenience, habits
Alongside cultural biases, situational factors also contribute to shaping the decision-making environment surrounding NUS consumption. These factors include product availability and accessibility, eating habits and perceived convenience.
The limited availability of products in the market has been identified as a barrier to consumption due to seasonal or locational factors (Lawley and Birch, 2016; Pieterse et al., 2023; Van Loon et al., 2021). Additionally, the point of sale plays a significant role in shaping consumer trust. Lawley and Birch (2016) highlight that consumers associate trusted local vendors with higher food safety standards and quality, which can reduce the perceived need for formal regulation. They also observe that certain consumers express distrust toward supermarkets. In contrast, Pieterse et al. (2023) identify the lack of clear quality standards and regulatory frameworks as a significant barrier to NUS consumption. This difference suggests that both institutional and interpersonal trust across the supply chain may need to be addressed to ensure broader consumer confidence.
Price can function as an attribute that exerts influence on consumer behavior. Both Lawley and Birch (2016) and Pieterse et al. (2023) highlight that consumers are likely to compare the prices of NUS to similar, more familiar products and expect them to be reasonable in this comparison. If NUS are perceived as too expensive relative to conventional alternatives, this can undermine their appeal.
The present findings suggest that NUS consumption often entails a compromise in convenience, either by requiring adjustments to established habits or the development of new cooking skills. A lack of cooking skills for preparing NUS-based meals acts as an impediment to their consumption (Knez et al., 2023b; Pieterse et al., 2023). Another contributing factor is the lengthy preparation of NUS-based dishes, particularly when compared to ready meals or fast food (Sanders et al., 2015). Shorter storage time also disturbs the feeling of convenience, thus acting as a barrier to NUS consumption (Knez et al., 2023b; Lawley and Birch, 2016; Pieterse et al., 2023). Together, these factors contribute to a high mental load associated with NUS consumption, as individuals must navigate unfamiliar preparation processes, adjust their routines, and plan around limited storage or availability. These conditions may deter even motivated consumers, convenience often takes precedence over other factors in food-related decision-making (Günden et al., 2024). This tendency is largely due to their inherent loss aversion, a response where the pain of losing something (i.e., convenience) outweighs the pleasure of gaining something of equal value (Kahneman and Tversky, 1984). Additionally, present bias plays a role, as individuals tend to prioritize immediate rewards over future benefits (O'Donoghue and Rabin, 1999). This suggests that strategies to increase NUS consumption should not focus solely on improving cooking skills, but also on minimizing the cognitive barriers that make NUS consumption feel effortful or burdensome. Interventions that simplify preparation, offer clear guidance, or incorporate NUS into familiar formats may help lower the mental load.
5.3 Strengths and limitations of the reviewed studies
This sub-section critically examines the methodological approaches and potential sources of bias in the reviewed studies, with the aim of better contextualizing their findings and assessing their reliability and generalizability. As shown in Table 1, the studies reviewed vary considerably in terms of research design and scope. Van Loon et al. (2021), Dhakal et al. (2024), Knez et al. (2023b) and Sanders et al. (2015) adopt non-systematic literature review methodologies. These studies focus on a single NUS or a thematically selected group of species and explore strategies for their revitalization by identifying and addressing context-specific barriers. However, the search procedures employed in these reviews are often not explicitly described, making it difficult to assess the comprehensiveness or transparency of their literature selection. Their emphasis lies in highlighting the nutritional, economic, or cultural value of the selected NUS, and the barriers to their integration into value chains. A notable strength of these studies is their attention to the barriers faced by different value chain actors, including consumers, within food systems. However, while barriers are acknowledged, the studies generally do not undertake a comparative analysis of their relative weight or significance, such as which barriers are most constraining, or which would be most impactful to remove. Similarly, although various benefits are outlined, there is limited discussion on how these benefits are actually perceived or valued by different value chain actors. This approach leaves less room for a deeper understanding of the factors that may drive or impede the mainstreaming of NUS into food systems, or of the potential trade-offs that may arise in the process (see also Section 7). However, these limitations are, to some extent, understandable given the relatively small and emerging body of literature on the topic.
Pieterse et al. (2023) and Lawley and Birch (2016) employ the thematic analysis method. Their data collection processes are transparently described and demonstrate sufficient inclusiveness in scope. The former focuses on various stakeholders across the value chain. The latter develops and tests a retail strategy tailored to a specific type of retailer, drawing on consumer focus groups. The comprehensive approach of both studies contributes to a deeper understanding of the barriers and drivers of NUS mainstreaming into food systems, particularly in relation to their respective value chain contexts. The main limitation of these studies lies in the fact that their findings cannot be readily generalized beyond their specific contexts.
Verner et al. (2023) utilize quantitative methods, with data collection and analysis procedures clearly described in the study. This study is notable for its large sample size and its multidimensional approach to the topic. The main limitation of this study stems from the selection bias of the participants, which is also acknowledged by the authors.
This section was intended to support a better understanding of the reviewed studies' findings by focusing on their methodological features. Although the diversity of cases prevents strong generalizations or the identification of clear inconsistencies, the findings still provide useful context-sensitive insights into behavioral aspects of NUS integration.
6 Conclusions
Revitalizing NUS is gaining attention as a strategy to enhance agricultural resilience, improve nutrition, and reduce dependence on a narrow range of staple crops. However, despite their potential benefits, NUS remain marginalized in consumer diets due to a range of interrelated psychological, cultural, and structural factors that together constitute behavioral barriers to their inclusion in mainstream diets. This review has examined the existing literature to identify the key factors contributing to behavioral barriers that hinder the broader integration of NUS into everyday food practices.
This review highlights the complex interplay of cognitive, cultural, and situational factors that shape the behavioral barriers to NUS consumption. Familiarity consistently emerges as a central determinant of acceptance. The limited familiarity can pertain to various aspects of the products, including their taste, methods for handling and cooking, nutritional value, and their role in biodiversity conservation (Dhakal et al., 2024; Pieterse et al., 2023; Van Loon et al., 2021; Verner et al., 2023). However, the findings also indicate that increased familiarity does not necessarily lead to acceptance. When consumers have some degree of familiarity with NUS, they might perceive its consumption as “risky.” The associated risks stem from multiple factors. First, consumers often associate NUS consumption with social risks, due to the perception of products being culturally incompatible with modernized societies (Knez et al., 2023b; Sanders et al., 2015; Van Loon et al., 2021). Additionally, consumers perceive convenience-related risks, as incorporating NUS into their diets may increase mental effort that can deter even motivated individuals from adopting NUS (Knez et al., 2023b; Lawley and Birch, 2016; Pieterse et al., 2023; Sanders et al., 2015). This combination of factors underlying behavioral barriers suggests that strategies aimed solely at increasing familiarity, such as providing information about health and environmental benefits, may be insufficient. These barriers are further reinforced by market-related limitations, including the limited availability of NUS due to limited or inconsistent supply (Lawley and Birch, 2016; Pieterse et al., 2023; Van Loon et al., 2021). Additionally, the lack of clear quality standards or regulatory frameworks or interpersonal trust might undermine consumer trust (Lawley and Birch, 2016; Pieterse et al., 2023). The potential for NUS-based products to face intense competition in the marketplace further complicates their successful integration (Lawley and Birch, 2016; Pieterse et al., 2023). The market already offers a variety of convenience products that emphasize different aspects of sustainability and healthy attributes, making it more difficult for NUS to stand out.
This review offers a novel contribution by showing that lasting dietary change requires not only information, but also a restructuring of the decision-making environment to make sustainable and nutritious choices simpler and socially accepted. To successfully reintroduce NUS into mainstream diets, the food system must shift from merely informing consumers to actively reshaping behavioral environments through targeted, evidence-based interventions. Only then can we address both the nutrition crisis and the erosion of agricultural biodiversity.
7 Limitations and future research directions
While the increasing inclusion of certain NUS into everyday diets is a promising development, it should be interpreted with caution. Prioritizing the use of only a few varieties, while excluding others, may further endanger the diversity necessary for resilient farming systems (Sanders et al., 2015). As seen in the case of quinoa, the risk of turning NUS into monocrops raises sustainability concerns (Bedoya-Perales et al., 2018). On the other hand, in the case of spelt, overstated health claims may lead to misconceptions about their benefits (Alvarez, 2021). NUS should be seen as complementary to traditional alternatives rather than as substitutes; otherwise, the structural problems underlying current food systems are likely to persist. Moreover, the rapid commercialization of NUS may exacerbate existing inequalities, particularly in rural areas where communities are more vulnerable to shifts in market dynamics (Bedoya-Perales et al., 2018; McDonell, 2021). Future research is needed to examine the broader social and environmental impacts of NUS integration beyond the cultivation phase, with attention to maintaining wider crop diversity and considering the responses of consumers, farmers, and supply chain actors.
This study demonstrates that our understanding of the behavioral factors influencing NUS consumption remains incomplete and warrants further investigation. While previous studies have identified several non-structural factors limiting NUS consumption, the behavioral aspects underlying NUS adoption have yet to be thoroughly explored. This gap is further complicated by the heterogeneity of NUS consumption, as the cultural significance and local knowledge tied to these foods can differ substantially across regions and communities. Future research could concentrate on advancing our understanding of key areas, such as the role of cultural norms in reintroducing NUS into diets across different cultural contexts, strategies for promoting NUS amid competition from conventional products, and the supply chain factors that could support their successful integration to the market.
The present study is not without limitations. First, the review was based on a limited number of peer-reviewed studies, which may not fully capture the breadth of existing knowledge, particularly grey literature or locally specific studies that may offer additional perspectives. Second, the studies included in the review are diverse in their methods, geographic focus, and the context-specific factors contributing to the neglect of NUS. This limits comparability and generalizability. Third, the review focused primarily on behavioral barriers at the individual level of consumption, and thus did not examine the roles of producers, supply chain actors, or institutional stakeholders who also shape the integration of NUS into food systems. These limitations point to the need for more comprehensive and interdisciplinary research to deepen our understanding of NUS adoption across contexts.
8 Practical implications
Although the primary focus of this study is on behavioral barriers and interventions, it is important to acknowledge that structural factors, such as distribution systems, affordability, and regulatory gaps, also shape the landscape for NUS promotion. With this in mind, this section explores various behavioral intervention strategies to overcome resistance to change and foster long-term improvements in dietary habits that include NUS. The Fogg Behavior Model (FBM) will serve as the framework to elucidate the mechanisms underlying behavioral change, while the MINDSPACE Framework will be utilized as a nudge design instrument.
According to the Fogg Behavior Model (FBM), behavior manifests when three elements converge: motivation, ability, and prompt (also referred to as prompts) (Fogg, 2009, 2020). Motivation refers to the individual's desire to engage in a specific behavior. Ability (also referred to as capacity) reflects the individual's capacity to execute that behavior, influenced by factors such as time, money, physical effort, mental effort, and routine. Lastly, prompts act as cues that trigger the individual to initiate the behavior. FBM further posits a compensatory relationship between motivation and ability; a deficiency in one can be offset by a sufficient level in the other. This interplay can be illustrated as an indifference curve, with prompts positioned above the curve effectively eliciting behavior, while those situated below fail to do so (Fogg, 2009, 2020). Each of these elements can be understood through three dimensions: the individual involved, the action taken, and the context in which behavior occurs (Fogg, 2020). For example, motivation can arise from a combination of personal factors, the perceived outcomes of actions, and the decision-making environment, such as social norms. Similarly, ability is related to personal skills, the ease of the action, and the tools and resources available in the decision-making environment. Finally, prompts can be designed to target any of these elements: the person, the action, or the decision-making environment (Fogg, 2020).
A “nudge” encompasses a range of interventions designed to subtly guide individuals toward desired behaviors by modifying the surrounding environmental factors or altering the presentation of available choices (Janusch et al., 2018; Thaler and Sunstein, 2008). The primary aim of these nudges is to overcome behavioral challenges and promote improved social and individual outcomes without imposing any requirements or limitations. As a design tool, we utilize the MINDSPACE Framework, developed by Dolan et al. (2010). This framework identifies the following nine key ideas that shape human behavior:
• Messenger: people are influenced by who communicates information to them.
• Incentives: the way rewards and punishments are structured can significantly shape decision-making. People respond to both financial and non-financial incentives, such as recognition or convenience.
• Norms: social norms play a crucial role in guiding behavior. People tend to align with what others in their community or peer group are doing.
• Defaults: people often stick with the pre-set options because changing them requires effort.
• Salience: individuals focus more on information that is novel, personally relevant, or stands out.
• Priming: subtle cues in the environment can unconsciously influence behavior.
• Affect: emotions heavily influence decision-making.
• Commitment: people are more likely to follow through with an action if they have made a prior commitment.
• Ego: individuals act in ways that support their self-image (Dolan et al., 2010).
We combined the FBM and MINDSPACE concepts to derive a design for developing nudges that specifically encourage NUS consumption. Our design is grounded in the core principles of the FBM, which suggests that behavior change prompts (nudges, in our model) must include balanced levels of motivation and ability elements and that change occurs across three behavioral dimensions (person, action, and context). The motivation and ability elements are operationalized through the nine MINDSPACE ideas. The design identifies segmentation by age groups, lifestyles, and health issues as an important design factor that should be carefully considered.
We adopted the following procedure to develop the design. First, the three dimensions of behavior change have been formulated in relation to their role in NUS consumption behavior. Then, their relationship to the behavioral barriers identified in this study was mapped. The person dimension focuses on enabling consumers to self-trigger NUS consumption, the action dimension emphasizes using existing anchors associated with NUS consumption, and the context dimension involves incorporating or tailoring the elements within the decision-making environment. Following this, each MINDSPACE idea has been systematically integrated into the design by assessing its function to alter eating behavior taking into account both the ability and motivational aspects within these three dimensions. Messenger pertains to nudge itself within our design. Incentives, norms, ego, priming and affect are related to interventions that increase motivation for NUS consumption. Defaults, salience and commitment are linked to influencing the ability to adopt new eating habits. They typically reduce the mental effort required to engage in the desired behavior or help overcome present bias. Within the person dimension, priming, affect and salient can be beneficial. Norms, ego and commitment can be particularly effective within the interventions targeting the context. Lastly, incentives and defaults may work together to simplify the action itself or to shift perceptions regarding the outcomes of consuming NUS. Accordingly, Table 2 illustrates which behavioral barriers can be addressed and how. The table should be interpreted as follows: for instance, if a behavioral barrier related to availability, convenience, or habits identified in the action dimension is targeted, the nudge (i.e., prompt) should use existing anchors associated with NUS consumption (such as routines). In this case, a combination of incentives and defaults may be used to simultaneously address both motivational and ability-related elements of behavior.
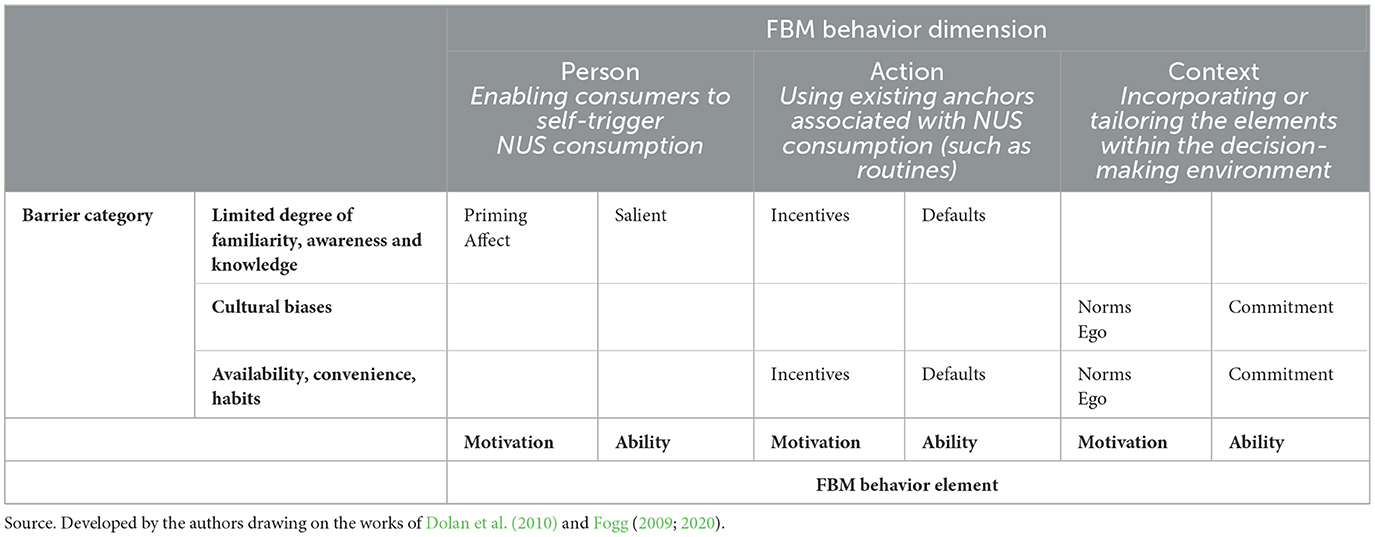
Table 2. Mapping behavioral barriers to NUS consumption with the MINDSPACE framework and the Fogg Behavior Model.
Based on Table 2 and Figure 1 provides a few examples of nudges as prompts aimed at Western urban populations, targeting the inclusion of NUS in their diets. In subsequent discussions, we will discuss some of these in detail. This will be preceded by a brief section that provides an overview of a commonly utilized design technique known as framing.
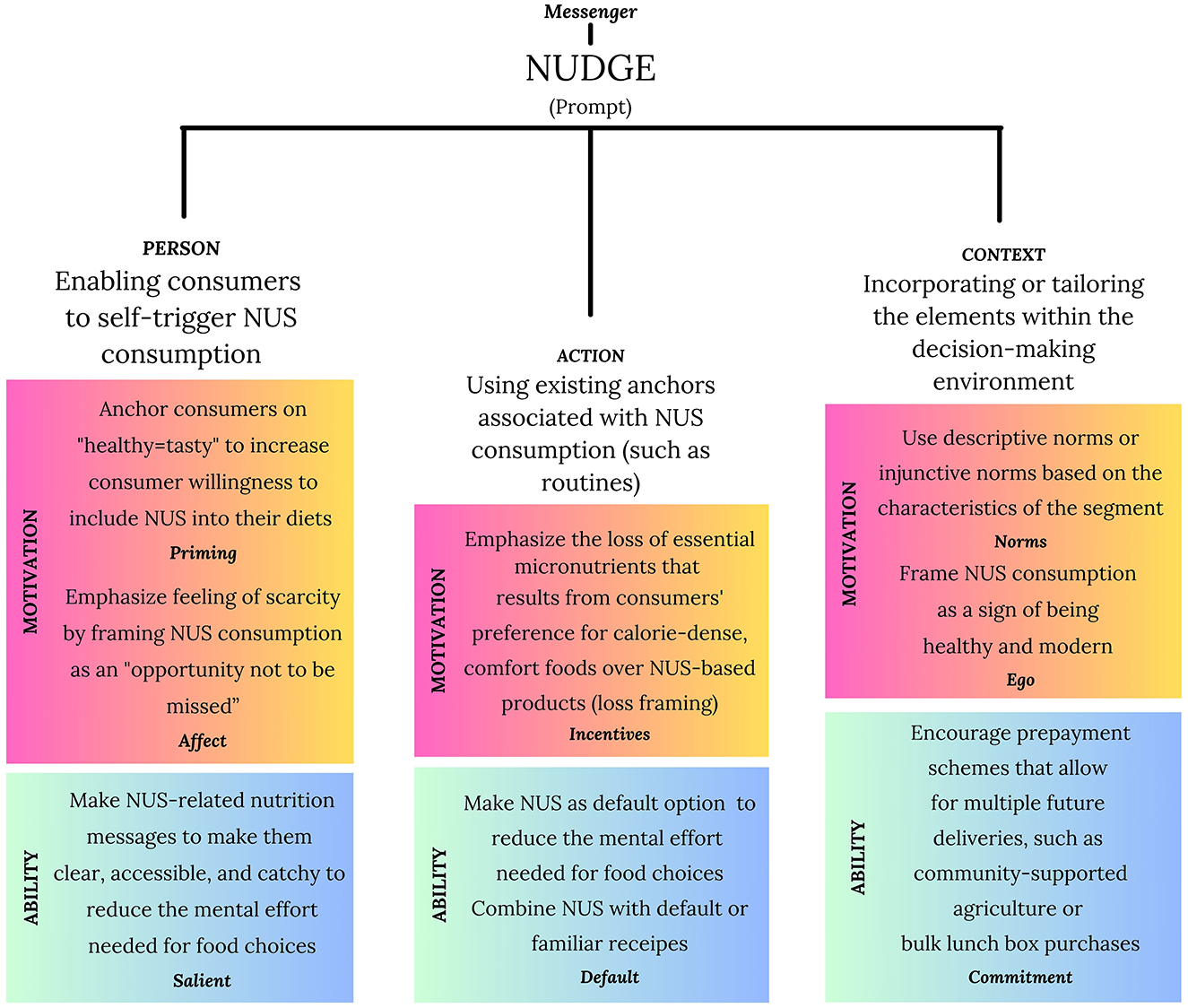
Figure 1. A design that encourages consumers to include NUS to their diet using the MINDSPACE framework and the Fogg Behavior Model (FBM), developed by authors drawing on the works of Dolan et al. (2010) and Fogg (2009; 2020). FBM's three dimensions (person, action, and context) and its elements of motivation and ability were used to structure the focus of each nudge (here defined as prompts). Accordingly, each nudge incorporates both motivational and ability-enhancing elements within at least one dimension. These elements were operationalized using corresponding MINDSPACE ideas, particularly focusing on the inclusion of NUS into the diets of Western urban populations.
8.1 Framing as a nudge design technique
Framing is a technique that strategically organizes information related to decision-making to influence how individuals perceive options and support better choices (Tversky and Kahneman, 1986). This technique can be particularly valuable in mitigating the influence of biases related to reference dependence and loss aversion, such as status quo bias, and limited attentional capacity to comprehend and process information (Buttenheim et al., 2023). Consumers typically regard NUS as a substitute for their customary dietary regimens. They then proceed to categorize the perceived benefits derived from NUS as gains, while perceiving the abandonment of familiar foods as losses. As a result, consumers are often hesitant to replace their existing mainstream foods with NUS in their diets. Within the MINDSPACE framework, incentives, norms, ego, priming and affect may particularly benefit from framing, as they target the motivational aspect of behavior change.
8.2 Enabling consumers to self-trigger NUS consumption (the person dimension)
Consumers often seek out pleasurable experiences when choosing what to eat, and when presented with healthier alternatives, such as NUS, they may experience a sense of deprivation regarding tasty foods (i.e., scarcity). This feeling of scarcity can lead to a perception of missing out on the enjoyment that others derive from unhealthy foods, commonly referred to as the “fear of missing out” (Przybylski et al., 2013). Within the person dimension, the feeling of scarcity can be utilized as an affect tool by framing NUS consumption as an “opportunity not to be missed.” This emphasizes that NUS is not always easily accessible and should be savored when it is available in the market or when a menu can create a sense of urgency. An alternative approach that focuses on the motivational aspect of the person dimension would be to use priming. This might involve conveying messages not directly related to NUS consumption, but rather presenting the idea of healthy = tasty or portraying the revitalization of forgotten cultural aspects as an eco-conscious modern lifestyle trend.
Such priming and affect tools should be complemented by a salient tool, meaning messages should be clear and actionable.
8.3 Using existing anchors associated with NUS consumption (the action dimension)
Incentives and defaults may work together to simplify the action itself or to shift perceptions regarding the outcomes of consuming NUS. When crafting incentives to promote NUS, a key focus could be on emphasizing the loss of essential micronutrients that results from consumers' preference for calorie-dense, comfort foods over NUS-based products. Highlighting the nutritional benefits that are missed by not choosing NUS can effectively showcase the value these foods provide. Another approach may be to focus on the consequences of the associated biodiversity loss resulting from non-consumption of NUS today, rather than focusing solely on their environmental or health benefits (Günden et al., 2024). This helps reorient the emphasis toward the pressing need for action today and the role of NUS in mitigating these biodiversity losses. In doing so, it addresses the issues of loss aversion and present bias concurrently. Moreover, referring to neglected crops as “forgotten” can facilitate a deeper understanding of consumer food purchasing decisions by highlighting their significance as neglected yet valuable resources (Günden et al., 2024). This terminology reinforces the perception of these crops as lost treasures that merit greater recognition and re-inclusion in the food system. These loss framing techniques can be used as an incentive. An incentive can form the motivational part of the nudge and thus should be combined with a default to be complete.
Given the significant emphasis on the role of familiarity in NUS consumption that emerged in the findings of this study, we included familiarity as a lever across the various instruments of our design. Nearly all tools benefit at some level from increased familiarity with NUS. However, the effect of familiarity is most pronounced when considered in conjunction with the default effect. Increased familiarity may serve the purpose of increasing NUS consumption capacity by reducing the mental effort required for food selection. For example, listing buckwheat pasta as the default on restaurant menus can effectively encourage consumers to choose it over standard pasta. Another strategy could be blending NUS with familiar dishes as an ingredient. This strategy not only helps in familiarizing consumers with new ingredients but also reduces the perceived risk associated with trying something completely unfamiliar. For example, adding boiled buckwheat to salads, an example of a common side dish in most Mediterranean diets, can increase its consumption without requiring significant changes to established routines or requiring individuals to learn new recipes. This initial integration may subsequently facilitate the increased consumption of other buckwheat-based products or encourage the adoption of novel recipes centered around buckwheat over time. This approach is often used to incorporate novel foods, such as edible insects or worms, as ingredients in familiar dishes (Grahl et al., 2018; Tan et al., 2016).
8.4 Incorporating or tailoring the elements within the decision-making environment (the context dimension)
Making small changes in the decision-making environment can encourage healthy food choices. Consequently, the implementation of social nudges, which harness the pervasive influence of social context, may be a promising approach to policy design aimed at promoting healthy behaviors (Prinsen et al., 2013). Research indicates that descriptive norms, that is, what other people do, are often more effective than injunctive norms, especially when individuals feel a connection to the social group in question or when that group is in the majority (Robinson et al., 2014a; Salmivaara et al., 2021; Stok et al., 2014a). A descriptive norm message, which suggests that the average student consumes more than three servings of vegetables daily, can be more effective in encouraging healthy eating behaviors than messages based on injunctive norms or health-related advice (Robinson et al., 2014a). This may be due to the possibility that injunctive norms may trigger feelings of resistance or reactance (Stok et al., 2014a) or be perceived as irrelevant by individuals (Salmivaara et al., 2021). Building on the findings of these studies, instead of sharing information about the nutritional benefits of NUS, it would be more effective to convey a message about the common NUS consumption habits of an urban citizen. On the other hand, for younger generations like Gen Z, injunctive norms may be effective. Young generations link global sustainability issues, such as climate change, to their food choices (Jürkenbeck et al., 2021). However, despite having similar or even higher levels of knowledge and awareness about sustainability than other generations, Generation Z does not exhibit a high rate of sustainable purchasing behavior (Makowska et al., 2024; Moisés et al., 2024). Several factors may contribute to this gap, including price considerations (Makowska et al., 2024; Pradeep and Pradeep, 2023) and a reluctance to view tackling sustainability challenges as a personal responsibility (Wray-Lake et al., 2010). Ham et al. (2021) suggest that the purchase decision of younger generations are influenced by social norms as well as utilitarian considerations (Ham et al., 2021). Additionally, Swim et al. (2022) argue that younger individuals experience heightened negative emotions such as worry, anger, and guilt related to climate change more than other generations. These emotions may prompt a desire to connect with others as a coping mechanism for their climate concerns (Swim et al., 2022). In light of these insights, we propose that messages highlighting injunctive norms can tap into the younger generations' desire to connect with others and could effectively promote their engagement in NUS consumption. One strategy could be framing NUS consumption as an eco-friendly behavior that is both socially approved within their peer groups and aligned with the expectations of Mother Nature.
Previous research shows that one of the most prevalent biases is the association of NUS with underdevelopment, labelled as “foods of the poor” (Knez et al., 2023a). To tackle this bias, an effective approach could involve creating environments that communicate social acceptance (Hartmann et al., 2015). From a policy design perspective, any public event that serves food can be transformed into an event that promotes NUS. This can be achieved by hosting tasting events and workshops focusing on NUS-based recipes and their preparation techniques or simply serving dishes made with NUS-based products. Another potential can be the provision of NUS-based dishes in schools, public institutions or workspaces. This strategy exploits both the default option effect and the ability of the default option effect to shape norms (Roberto and Kawachi, 2014). Establishing social contexts not only enhances familiarity with NUS products but also helps create self-communicating descriptive norms around NUS consumption. These strategies can effectively trigger the first interaction between individuals and NUS.
These social norm strategies form the motivational part of a nudge and should be complemented by a commitment tool to reach their full potential. Commitment tools might include bulk-purchase schemes such as community supported agriculture or food communities (i.e., membership-based communities offering seasonal shares or subscriptions) or prepaid meal plans in university/school canteens.
In this article, we approached a re-examination of the nine MINDSPACE tools (Dolan et al., 2010) through the lens of the FBM (Fogg, 2009, 2020) with the objective of developing practical applications for our findings. A structured design was proposed for implementation in policy interventions and marketing strategies. Our design conceptualizes FBM's prompts as nudges that encourage healthier choices and support the formation of lasting habits. It aims to address two key behavioral components (i.e., motivation and ability) while also accounting for the three dimensions of behavior change (i.e., person, action, and context). Future research could evaluate the effectiveness of this design, explore which population segments benefit most or least, and conduct targeted analyses of the barriers to NUS consumption. By bridging two established approaches, our design offers an innovative foundation for developing more targeted and effective policy interventions that can be utilized by policymakers, marketers, and civil society professionals. To ensure the effectiveness of behavioral interventions aimed at including NUS into mainstream diets, future efforts should incorporate robust evaluation mechanisms. These could include choice tracking to monitor purchasing behavior over time, longitudinal surveys to assess changes in attitudes and habits, or randomized controlled trials implemented in real-world settings such as cafeterias or retail environments. Such approaches would provide empirical evidence on what works, for whom, and under what conditions.
Author contributions
PA: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Visualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. CG: Writing – original draft, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Project administration, Methodology, Conceptualization. MY: Funding acquisition, Data curation, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Investigation. KM: Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. MK: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by BIOVALUE PROJECT: Fork-to-farm agent-based simulation tool augmenting BIOdiversity in the agri-food VALUE chain, supported by European Commission Grant Agreement No: 101000499. This research was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation, Republic of Serbia, for M.K. (Grant No. 451-03-136/2025-03/200015).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the European Commission for granting support for the BIOVALUE project. This research was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation, Republic of Serbia, for M.K. (Grant No. 451-03-136/2025-03/200015). We thank the reviewers for their constructive and helpful comments, which have significantly improved the quality and clarity of our manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsufs.2025.1623138/full#supplementary-material
References
Aibana, K., Kimmel, J., and Welch, S. (2017). Consuming differently, consuming sustainably: Behavioural insights for policymaking.
Aldridge, V., Dovey, T. M., and Halford, J. C. G. (2009). The role of familiarity in dietary development. Developmental Rev. 29, 32–44. doi: 10.1016/j.dr.2008.11.001
Alley, T. R. (2018). Conceptualization and Measurement of Human Food Neophobia. Food Neophobia: Behavioral and Biological Influences. Amsterdam: Elsevier (169–192). doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-101931-3.00009-4
Alvarez, J. B. (2021). Spanish spelt wheat: From an endangered genetic resource to a trendy crop. In Plants 10:2748. doi: 10.3390/plants10122748
Ayilara, M. S., Abberton, M., Oyatomi, O. A., Odeyemi, O., and Babalola, O. O. (2022). Potentials of underutilized legumes in food security. Front. Soil Sci. 2. doi: 10.3389/fsoil.2022.1020193
Baranowski, T., Cullen, K. W., and Baranowski, J. (1999). Psychosocial correlates of dietary intake: advancing dietary intervention. Ann. Rev. Nutr. 19, 17–40. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.19.1.17
Baranowski, T., and Wansink, B. (2008). Mindless eating: why we eat more than we think. American J. Clin. Nutr. 87:795. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.3.795
Basudan, N. (2018). Antioxidant, total phenolic content as well as antimicrobial potentiality effect of peel white and black eggplant extracts. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 11, 161–167. doi: 10.20902/IJCTR.2018.110817
Bedoya-Perales, N. S., Pumi, G., Talamini, E., and Padula, A. D. (2018). The quinoa boom in Peru: Will land competition threaten sustainability in one of the cradles of agriculture? Land Use Policy 79, 475–480. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2018.08.039
Bin-Jumah, M. N., Nadeem, M. S., Gilani, S. J., Mubeen, B., Ullah, I., Alzarea, S. I., et al. (2022). Lycopene: a natural arsenal in the war against oxidative stress and cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants 11:232. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020232
BIOVALUE Project Consortium (2025). Handbook on Fagopyron spp. (Deliverable No. D7.4.3). BIOVALUE Project. Available online at: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101000499/
Buttenheim, A., Moffitt, R., and Beatty, A. (2023). Behavioral Economics: Policy Impact and Future Directions. Behavioral Economics: Policy Impact and Future Directions. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. doi: 10.17226/26874
Calabrese, M. G., and Ferranti, P. (2018). Novel Foods: New Food Sources. Encyclopedia of Food Security and Sustainability. Heidelberg: EMBO Press. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-08-100596-5.22128-8
Carlisle, S., and Hanlon, P. (2014). Connecting food, well-being and environmental sustainability: towards an integrative public health nutrition. Critical Public Health 24, 405–417. doi: 10.1080/09581596.2013.877580
Casanova-Pérez, L., Cruz-Bautista, P., San Juan-Martínez, A., García-Alonso, F., and Barrios, F. (2024). Underutilized food plants and their potential contribution to food security: lessons learned from the local context. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 48, 1265–1288. doi: 10.1080/21683565.2024.2388687
Chang, S.-Y. (2011). The influence of novelty-seeking and risk-perception behavior on holiday decisions and food preferences. Int. J. Hospital. Tour. Admin. 12, 305–329. doi: 10.1080/15256480.2011.614553
Chen, P. J., and Antonelli, M. (2020). Conceptual models of food choice: influential factors related to foods, individual differences, and society. Foods 9:1898. doi: 10.3390/foods9121898
Chevarria-Lazo, M., Bazile, D., Dessauw, D., Louafi, S., Trommetter, M., and Hocdé, H. (n.d.). “Quinoa and the exchange of genetic resources: improving the regulation systems,” in State of the art report on quinoa around the world in 2013, eds. D. Bazile, H. D. Bertero, and C. Nieto, (Rome: FAO and CIRAD), 83–105.
Contento, I. R. (2011). Overview of determinants of food choice and dietary change: Implications for nutrition education. Nutrition Education: Linking Research, Theory and Practice.
Costanzo, A. (2021). Underutilized Genetic Resources and Crop Diversification in Europe. Orphan Crops for Sustainable Food and Nutrition Security. New York: Routledge (pp. 138–146). doi: 10.4324/9781003044802-12
Dhakal, R., Sahu, R. K., Das Gupta, D., Saikia, M., Borthakur, S., Majumder, M., et al. (2024). Recycling of protein rich silk industry waste for potential food and therapeutic application. Food Biosci. 60:104461. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104461
Dolan, P., Hallsworth, M., Halpern, D., King, D., and Vlaev, I. (2010). MINDSPACE: Influencing Behaviour Through Public Policy. Cabinet Office.
Durst, P., and Bayasgalanbat, N. (2014). Promotion of underutilized indigenous food resources for food and nutrition in Asia and in the Pacific (RAP Publication 2014/07).
Eckhardt, C. L. (2006). Micronutrient Malnutrition, Obesity, and Chronic Disease in Countries Undergoing the Nutrition Transition: Potential Links and Program/Policy Implications. FCND Discussion Paper 213, November 2006.
Espel-Huynh, H. M., Muratore, A. F., and Lowe, M. R. (2018). A narrative review of the construct of hedonic hunger and its measurement by the Power of Food Scale. Obesity Sci. Pract. 4, 238–249. doi: 10.1002/osp4.161
FAO (2019). The State of the World's Biodiversity for Food and Agriculture, eds. J. Bélanger and D. Pilling. FAOCommission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture Assessments. Available online at: https://www.fao.org/3/CA3129EN/CA3129EN.pdf
FAO IFAD, UNICEF„ WFP, and WHO. (2024). The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2024. FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO.
Fischer, A. R. H., and Reinders, M. J. (2016). Consumer Acceptance of Novel Foods. Innovation Strategies in the Food Industry. Amsterdam: Elsevier (271–292). doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-803751-5.00014-3
Fogg (2009). A behavior model for persuasive design. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series 350. doi: 10.1145/1541948.1541999
Godlove, J., Lyimo, L. D., Tryphone, G. M., Hamisy, W., van Zonneveld, M., and N'Danikou, S. (2025). Traditional knowledge and use of wild cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata) in selected communities of Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1562474
Grahl, S., Strack, M., Weinrich, R., and Mörlein, D. (2018). Consumer-oriented product development: the conceptualization of novel food products based on spirulina (arthrospira platensis) and resulting consumer expectations. J. Food Qual. 2018. doi: 10.1155/2018/1919482
Günden, C., Atakan, P., Yercan, M., Mattas, K., and Knez, M. (2024). Consumer response to novel foods: a review of behavioral barriers and drivers. Foods 13:2051. doi: 10.3390/foods13132051
Ham, C.-D., Chung, U. C., Kim, W. J., Lee, S. Y., and Oh, S.-H. (2021). Greener than others? Exploring generational differences in green purchase intent. Int. J. Market Res. 64, 376–396. doi: 10.1177/14707853211034108
Hartmann, C., Shi, J., Giusto, A., and Siegrist, M. (2015). The psychology of eating insects: a cross-cultural comparison between Germany and China. Food Qual. Prefer. 44, 148–156. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2015.04.013
Herman, C. P., Roth, D. A., and Polivy, J. (2003). Effects of the presence of others on food intake: a normative interpretation. Psychol. Bull. 129, 873–886. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.129.6.873
Higgs, S. (2015). Social norms and their influence on eating behaviours. Appetite 86, 38–44. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2014.10.021
Higgs, S., and Thomas, J. (2016). Social influences on eating. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 9, 1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2015.10.005
Janusch, N., Palm-Forster, L. H., Messer, K. D., and Ferraro, P. J. (2018). Behavioral Insights for Agri-Environmental Program and Policy Design. 2018 Allied Social Sciences Association (ASSA) Annual Meeting, January 5-7, 2018, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Jürkenbeck, K., Spiller, A., and Schulze, M. (2021). Climate change awareness of the young generation and its impact on their diet. Clean. Respons. Consum. 3:100041. doi: 10.1016/j.clrc.2021.100041
Kahneman, D., Knetsch, J. L., and Thaler, R. H. (1990). Experimental tests of the endowment effect and the coase theorem. J. Polit. Econ. 98, 1325–1348. doi: 10.1086/261737
Kahneman, D., Knetsch, J. L., and Thaler, R. H. (1991). Anomalies: the endowment effect, loss aversion, and status quo bias. J. Econ. Perspect. 5, 193–206. doi: 10.1257/jep.5.1.193
Kahneman, D., Knetsch, J. L., and Thaler, R. H. (2018). The endowment effect, loss aversion, and status quo bias. Exp. Environ. Econ. 5, 193–206.
Kahneman, D., and Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: an analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 47, 263–292. doi: 10.2307/1914185
Kahneman, D., and Tversky, A. (1984). Choices, values, and frames. Am. Psychol. 39, 341–350. doi: 10.1037/0003-066X.39.4.341
Kandić, V., Nikolić, V., Simić, M., Žilić, S., Stevanović, M., Mandić, D., et al. (2023). Spelt wheat (Triticum spelta) and common bread wheat compared for nutritional contents and functional-technological properties. Chile. J. Agri. Res. 83, 146–158. doi: 10.4067/s0718-58392023000200146
Knez, M., Ranić, M., and Gurinović, M. (2023a). Underutilized plants increase biodiversity, improve food and nutrition security, reduce malnutrition, and enhance human health and well-being. Let's put them back on the plate! Nutr. Rev. 82, 1111–1124. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuad103
Knez, M., Ranic, M., Gurinovic, M., Glibetic, M., Savic, J., Mattas, K., et al. (2023b). Causes and conditions for reduced cultivation and consumption of underutilized crops: is there a solution? Sustainability 15:3076. doi: 10.3390/su15043076
Lambein, F., Travella, S., Kuo, Y. H., Van Montagu, M., and Heijde, M. (2019). Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.): orphan crop, nutraceutical or just plain food? Planta 250, 821–838. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-03084-0
Lawley, M., and Birch, D. (2016). Exploring point of sale strategies for improving seafood retailing: the case of the australian oyster industry. J. Food Prod. Market. 22, 792–808. doi: 10.1080/10454446.2015.1121430
Li, X., Yadav, R., and Siddique, K. H. M. (2020). Neglected and underutilized crop species: the key to improving dietary diversity and fighting hunger and malnutrition in Asia and the Pacific. Front. Nutr. 7:593711. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.593711
Li, X.-M., and Yang, P.-L. (2018). Research progress of Sonchus species. Int. J. Food Propert. 21, 147–157. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2017.1415931
Liu, P. J., Wisdom, J., Roberto, C. A., Liu, L. J., and Ubel, P. A. (2014). Using behavioral economics to design more effective food policies to address obesity. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 36, 6–24. doi: 10.1093/aepp/ppt027
Lowe, M. R., and Butryn, M. L. (2007). Hedonic hunger: a new dimension of appetite? Physiol. Behav. 91. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.04.006
Mai, R., and Hoffmann, S. (2015). How to combat the unhealthy = tasty intuition: the influencing role of health consciousness. J. Public Policy Market. 34, 63–83. doi: 10.1509/jppm.14.006
Makowska, M., Boguszewski, R., and Hrehorowicz, A. (2024). Generational differences in food choices and consumer behaviors in the context of sustainable development. Foods 13:521. doi: 10.3390/foods13040521
Mankad, M., and Gokhale, D. (2023). Not Hungry, but still snacking: the association between hedonic hunger and snacking behaviour among young adults in Vadodara, Gujarat. Cureus. 13:e18414. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44814
María Ruiz-Rodríguez, B., de Ancos, B., Sánchez-Moreno, C., Fernández-Ruiz, V., de Cortes Sánchez-Mata, M., Cámara, M., et al. (2014). Wild blackthorn (Prunus spinosa L.) and hawthorn (Crataegus monogyna Jacq.) fruits as valuable sources of antioxidants. Fruits 69, 61–73. doi: 10.1051/fruits/2013102
McDonell, E. (2021). Commercializing the “Lost Crop of the Inca”: Quinoa and the Politics of Agrobiodiversity in “Traditional” Crop Commercialization, in Andean Foodways (New York, NY: Springer) 383–406. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51629-1_15
Melo, G. L. R., Santo, R. E., Mas Clavel, E., Bosque Prous, M., Koehler, K., Vidal-Alaball, J., et al. (2025). Digital dietary interventions for healthy adolescents: a systematic review of behavior change techniques, engagement strategies, and adherence. Clin. Nutr. 45, 176–192. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2025.01.012
Migliozzi, M., Thavarajah, D., Thavarajah, P., and Smith, P. (2015). Lentil and kale: complementary nutrient-rich whole food sources to combat micronutrient and calorie malnutrition. Nutrients 7, 9285–98. doi: 10.3390/nu7115471
Miller, B. D. D., and Welch, R. M. (2013). Food system strategies for preventing micronutrient malnutrition. Food Policy 42, 115–128. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2013.06.008
Moisés, C. M. C., Tomazini, C. E. G., Fernandes, A., and Ribeiro, M. I. (2024). From X to Z: Examining generational differences in sustainable food consumption in Portugal. IBIMA Business Review.
Mondo, J. M., Mugisho, G. M., Chuma, G. B., Agre, P. A., Banda, V. R., Adebola, P., et al. (2025). Yam urban market characteristics and consumer preferences in Bukavu City, eastern D.R. Congo. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1553876. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1553876
Mullainathan, S., and Shafir, E. (2013). Scarcity: Why Having Too Little Means so Much. Times Books.
Odeku, O. A., Ogunniyi, Q. A., Ogbole, O. O., and Fettke, J. (2024). Forgotten gems: exploring the untapped benefits of underutilized legumes in agriculture, nutrition, and environmental sustainability. Plants 13:1208. doi: 10.3390/plants13091208
O'Donoghue, T., and Rabin, M. (1999). Doing it now or later. Am. Econ. Rev. 89, 103–124. doi: 10.1257/aer.89.1.103
Paakki, M., Kantola, M., Junkkari, T., Arjanne, L., Luomala, H., and Hopia, A. (2022). “Unhealthy = Tasty”: how does it affect consumers' (Un)Healthy food expectations? Foods 11:3139. doi: 10.3390/foods11193139
Padulosi, S., Meldrum, G., King, E. O., and Hunter, D. (2021). “NUS: What They are and Why We Need Them More Than Ever,” in Orphan Crops for Sustainable Food and Nutrition Security (New York: Routledge), pp. 3–18. doi: 10.4324/9781003044802-2
Padulosi, S., Roy, P., and Rosado-May, F. J. (2019). Supporting nutrition sensitive agriculture through neglected and underutilized species – operational framework. Bioversity International and IFAD.
Padulosi, S., Thompson, J., and Rudebjer, P. (2013). Fighting poverty, hunger and malnutrition with neglected and underutilized species: needs, challenges and the way forward. Biovers. Int. Available online at: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/items/30d45d24-eeac-49d5-93cb-3d3188143dbb
Pereira, L. (2011). “A review of the nutrient composition of selected edible seaweeds,” in Seaweed: Ecology, Nutrient Composition and Medicinal Uses, eds. Vitor H. Pomin (Hauppauge: Nova Science Publishers, Inc) 15–47.
Pieterse, E., Millan, E., and Schönfeldt, H. C. (2023). Consumption of edible flowers in South Africa: nutritional benefits, stakeholders' views, policy and practice implications. Br. Food J. 125, 2099–2122. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-10-2021-1091
Pliner, P., and Hobden, K. (1992). Development of a scale to measure the trait of food neophobia in humans. Appetite 19, 105–120. doi: 10.1016/0195-6663(92)90014-W
Pradeep, S., and Pradeep, M. (2023). Awareness of sustainability, climate emergency, and generation Z's consumer behaviour in UAE. Clean. Respons. Consumpt. 11:100137. doi: 10.1016/j.clrc.2023.100137
Prinsen, S., De Ridder, D. T. D., and De Vet, E. (2013). Eating by example. Effects of environmental cues on dietary decisions. Appetite 70, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2013.05.023
Proietti, I., Jordan, I., and Borelli, T. (2025). Enhancing nutrition and cost efficiency in kenyan school meals using neglected and underutilized species and linear programming: a case study from an informal settlement. doi: 10.20944/preprints202501.1692.v1
Przybylski, A. K., Murayama, K., Dehaan, C. R., and Gladwell, V. (2013). Motivational, emotional, and behavioral correlates of fear of missing out. Comput. Human Behav. 29, 1841–1848. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.02.014
Rahayu, Y. Y. S., Dwiartama, A., Sujarwo, W., Rosleine, D., and Irsyam, A. S. D. (2024). Exploring wild edible plants in West Java, Indonesia: ethnobotanical assessment, use trends, and potential for improved nutrition. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4327834/v1
Roberto, C. A., and Kawachi, I. (2014). Use of psychology and behavioral economics to promote healthy eating. Am. J. Prevent. Med. 47, 832–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2014.08.002
Robinson, E., Fleming, A., and Higgs, S. (2014a). Prompting healthier eating: testing the use of health and social norm based messages. Health Psychol. 33, 1057–64. doi: 10.1037/a0034213
Robinson, E., Thomas, J., Aveyard, P., and Higgs, S. (2014b). What everyone else is eating: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of informational eating norms on eating behavior. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 114, 414–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2013.11.009
Robinson-O'Brien, R., Story, M., and Heim, S. (2009). Impact of garden-based youth nutrition intervention programs: a review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 109, 273–80. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2008.10.051
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. (2016). State of the World's Plants Report – 2016, 80. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew.
Ruddock, H. K., Brunstrom, J. M., Vartanian, L. R., and Higgs, S. (2019). A systematic review and meta-analysis of the social facilitation of eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 110, 842–861. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqz155
Salmivaara, L., Lombardini, C., and Lankoski, L. (2021). Examining social norms among other motives for sustainable food choice: the promise of descriptive norms. J. Clean. Prod. 311:127508. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127508
Sanders, H. L., Hollington, P. A., Pasquini, M. W., and Carpena, P. C. (2015). How can we remove barriers to increased usage of indigenous crops? Acta Horticulturae 1102, 127–134. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1102.15
Sayess, D., Koaik, F., Schnider, R., and Saraf, S. (2024). “From Mindless Consumer to Mindful Citizen: A Behavioral Lens Approach,” in The Behavioral Economics Guide 2024, ed. A. Samson (Amsterdam: Altiorem).
Scarano, A., Semeraro, T., Chieppa, M., and Santino, A. (2021). Neglected and underutilized plant species (NUS) from the Apulia Region worthy of being rescued and re-included in daily diet. Horticulturae 7:177. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7070177
Segal, L., and Opie, R. S. (2015). A nutrition strategy to reduce the burden of diet related disease: access to dietician services must complement population health approaches. Front. Pharmacol. 6:160. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00160
Shaikh, A. R., Yaroch, A. L., Nebeling, L., Yeh, M. C., and Resnicow, K. (2008). Psychosocial predictors of fruit and vegetable consumption in adults. A review of the literature. Am. J. Prevent. Med. 34, 535–543. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.12.028
Singh, A., Bundela, A. K., and Abhilash, P. C. (2023). Nutritional, ethnomedicinal, and agricultural significance of neglected and underutilized crops from Eastern Uttar Pradesh, North India. Agronomy 13:2318. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13092318
Sofi, S. A., Ahmed, N., Farooq, A., Rafiq, S., Zargar, S. M., Kamran, F., et al. (2023). Nutritional and bioactive characteristics of buckwheat, and its potential for developing gluten-free products: an updated overview. Food Sci. Nutr. 11, 2256–2276. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3166
Stok, F. M., De Ridder, D. T. D., De Vet, E., and De Wit, J. B. F. (2014a). Don't tell me what i should do, but what others do: the influence of descriptive and injunctive peer norms on fruit consumption in adolescents. Br. J. Health Psychol. 19, 52–64. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12030
Stok, F. M., Verkooijen, K. T., de Ridder, D. T. D., de Wit, J. B. F., and de Vet, E. (2014b). How norms work: self-identification, attitude, and self-efficacy mediate the relation between descriptive social norms and vegetable intake. Appl. Psychol. Health Well-Being 6, 230–250. doi: 10.1111/aphw.12026
Story, M., Kaphingst, K. M., Robinson-O'Brien, R., and Glanz, K. (2008). Creating healthy food and eating environments: policy and environmental approaches. Ann. Rev. Public Health 29, 253–72. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.29.020907.090926
Stremmel, G., Elshiewy, O., and Boztug, Y. (2021). When insect consumption is socially risky: Social norms as a major barrier to widespread acceptance of non-normative food. Urbana: Association for Consumer Research.
Sugár, E., Fodor, N., Sándor, R., Bónis, P., Vida, G., and Árendás, T. (2019). Spelt wheat: an alternative for sustainable plant production at low N-Levels. Sustainability 11:6726. doi: 10.3390/su11236726
Sultanbawa, Y., and Sivakumar, D. (2022). Enhanced nutritional and phytochemical profiles of selected underutilized fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 46:100853. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2022.100853
Swim, J. K., Aviste, R., Lengieza, M. L., and Fasano, C. J. (2022). OK boomer: a decade of generational differences in feelings about climate change. Global Environ. Change 73:102479. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2022.102479
Tan, H. S. G., van den Berg, E., and Stieger, M. (2016). The influence of product preparation, familiarity and individual traits on the consumer acceptance of insects as food. Food Qual. Prefer. 52, 222–231. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2016.05.003
Thaler, R. H., and Sunstein, C. R. (2008). Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness. Yale University Press.
Tuorila, H., and Hartmann, C. (2020). Consumer responses to novel and unfamiliar foods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 33, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.09.004
Tuorila, H. M., Meiselman, H. L., Cardello, A. V., and Lesher, L. L. (1998). Effect of expectations and the definition of product category on the acceptance of unfamiliar foods. Food Qual. Prefer. 9, 421–430. doi: 10.1016/S0950-3293(98)00012-3
Tversky, A., and Kahneman, D. (1986). The framing of decisions and the evaluation of prospects. Stud. Logic Found. Math. 114, 503–520. doi: 10.1016/S0049-237X(09)70710-4
van der Sluis, M., Anten, N., van Asselt, E., Bonekamp, G., van Hintum, T., Michels, R., et al. (2022). The need to enhance crop, livestock and aquatic genetic diversity in food systems. (No. 1385). Wageningen Livestock Research. doi: 10.18174/575252
Van Loon, R., Lagneaux, E., Guerra, G. W., Chiriboga-Arroyo, F., Thomas, E., Gamarra, B., et al. (2021). Barriers to adopting a diversity of NUS fruit trees in Latin American food systems. Orphan Crops for Sustainable Food and Nutrition Security. Milton Park: Routledge (88–108). doi: 10.4324/9781003044802-8
van Rongen, S., Handgraaf, M., Benoist, M., and de Vet, E. (2022). The effect of personal relative deprivation on food choice: an experimental approach. PLoS ONE 17:e0261317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0261317
van't Riet, J., Sijtsema, S. J., Dagevos, H., and de Bruijn, G. J. (2011). The importance of habits in eating behaviour. An overview and recommendations for future research. Appetite 57, 585–596. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2011.07.010
Vartanian, L. R., Herman, C. P., and Wansink, B. (2008). Are we aware of the external factors that influence our food intake? Health Psychol. 27, 533–538. doi: 10.1037/0278-6133.27.5.533
Verner, V., Kosova, M., Chaloupkova, P., Nguon, S., Van Damme, P., and Kokoska, L. (2023). Tourists' preferences for traditional food products as indicators of the market potential of underutilised species in Cambodia. Agriculture 13:1599. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13081599
Walker, I., and Pettigrew, T. F. (1984). Relative deprivation theory: an overview and conceptual critique. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 23, 301–310. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8309.1984.tb00645.x
WHO (2021). Obesity and Overweight. Available online at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (Accessed February 5, 2025).
Winnicki, T., and Żuk-Gołaszewska, K. (2017). Agronomic and economic characteristics of common wheat and spelt production in an organic farming system. Acta Sci. Pol. Agri. 16, 247–254.
World Obesity Federation (2024). Prevalence of Obesity. Available online at: https://www.worldobesity.org/about/about-obesity/prevalence-of-obesity (Accessed February 5, 2025).
Wray-Lake, L., Flanagan, C. A., and Osgood, D. W. (2010). Examining trends in adolescent environmental attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors across three decades. Environ. Behav. 42, 61–85. doi: 10.1177/0013916509335163
Xu, Y., and Zeng, G. (2022). Not eating is a loss: how familiarity influences local food consumption. Tour. Manag. 90:104479. doi: 10.1016/j.tourman.2021.104479
Keywords: underutilized and neglected species, Prospect Theory, sustainable diets, behavioral barriers, MINDSPACE, Fogg Behavior Model, orphan crops
Citation: Atakan P, Günden C, Yercan M, Mattas K and Knez M (2025) Behavioral barriers in the inclusion of neglected and underutilized species into mainstream diets. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1623138. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1623138
Received: 05 May 2025; Accepted: 28 July 2025;
Published: 14 August 2025.
Edited by:
Elliot Berry, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, IsraelReviewed by:
Subhasree Ray, TVS Motor Company (India), IndiaAnisa Dwi Utami, IPB University, Indonesia
Bissola Bankole, Alliance of Bioversity International and the International Center for Tropical Agriculture Benin, Benin
Copyright © 2025 Atakan, Günden, Yercan, Mattas and Knez. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pelin Atakan, cGVsaW4uYXRha2FuQHlhc2FyLmVkdS50cg==
†ORCID: Pelin Atakan orcid.org/0000-0001-8998-7179
Cihat Günden orcid.org/0000-0003-0353-5054
Murat Yercan orcid.org/0000-0002-8061-0882
Konstadinos Mattas orcid.org/0000-0001-8304-4292
Marija Knez orcid.org/0000-0003-2773-0137
 Pelin Atakan
Pelin Atakan Cihat Günden2†
Cihat Günden2† Konstadinos Mattas
Konstadinos Mattas Marija Knez
Marija Knez