- School of Economics, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law, Wuhan, China
Enhancing the resilience of the agricultural industrial chain (RAIC) is crucial for ensuring food security and promoting rural development, and developing the digital economy is a key path in this regard. This paper focuses on the policy practice of the National Digital Economy Innovation and Development Pilot Zone (DEPZ), regarding it as a quasi-natural experiment. Based on the panel data of 30 provinces in China from 2012 to 2022, using PSM-DID, it empirically examines the impact of the DEPZ policy on RAIC and its internal mechanism. The research found that the DEPZ policy significantly increased RAIC within the region. Its mechanism of action is mainly reflected in: enhancing resilience through two intermediary paths, namely alleviating the financing constraints (FC) of agricultural business entities and promoting agricultural technological innovation (ATI). Further analysis reveals that the level of urban-rural integration (URI) has played a positive moderating role in the mediation process of alleviating the above-mentioned FC and promoting ATI. This study provides empirical evidence for understanding the specific mechanisms by which the digital economy empowers agricultural modernization and indicates that the precise application of industrial policies, especially the coordinated promotion of the development of the digital economy and the integration of urban and rural areas, is an important strategic direction for effectively enhancing the resilience of the agricultural industrial chain.
1 Introduction
Agriculture, as a fundamental industry of the national economy, not only shoulders the responsibility of ensuring national food security and stabilizing farmers' income, but also serves as a crucial support for achieving rural revitalization and common prosperity. At present, China is promoting agricultural transformation and upgrading. Its industrial chain is increasingly complete, constantly extending vertically and expanding horizontally, which has improved the production efficiency and economic benefits of agriculture (Zhou et al., 2023). However, with the in-depth advancement of agricultural industrialization, China's agricultural industrial chain still faces many development bottlenecks, including structural fragility, weak resistance, and insufficient recovery and adaptation capabilities (Wang et al., 2022). The report of the 20th National Congress of the Communist Party of China proposed that efforts should be made to enhance the resilience and security of industrial and supply chains. This represents a significant policy determination and implementation by the Central Committee of the CPC, based on a profound analysis of the domestic and international situation and a comprehensive consideration of the national development strategy, which has guided the modernization of China's agricultural industrial chain. Enhancing the RAIC is not only a key measure to maintain the overall stable operation of China's agricultural industry and promote the process of agricultural modernization, but also a realistic choice for China to deal with complex domestic and international situations.
“Resilience” was originally a physical concept, referring to the ability of an object to rebound when subjected to external force compression. Later, it was gradually applied to fields such as engineering, ecology, and psychology, during which its connotation has been continuously expanded. Briguglio (2004) innovatively proposed the theoretical framework of economic resilience in economic research, defining it as the resistance and recovery capacity demonstrated by the economic system in the face of external shocks. In recent years, with the profound transformation of the global industrial structure and the frequent occurrence of extreme events, governments around the world have increasingly emphasized the security of industrial chains. Ensuring the stable operation of industrial chains during emergencies has become the focus of policy attention. As a result, the research on resilience has gradually expanded to the field of industrial economics (Zhao et al., 2025). Many scholars have conducted in-depth analyses on the connotation of industrial chain resilience and generally believe that industrial chain resilience is mainly reflected in the ability of various industrial entities and links to withstand external shocks, disturbances, pressures or uncertain risks, quickly return to normal, and on this basis, make adaptive adjustments, achieve reconstruction and upgrading (Wang and Qian, 2025; Chao et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2023; Xiao and Li, 2022; Li, 2024).
The agricultural industrial chain is a special type of industrial chain (Zhao and Wang, 2004). Its concept was first proposed by the German economist Hirschmann, emphasizing all activities of agricultural products from raw materials, processing, production to sales, and explaining the importance of close coordination among all departments and links in agricultural production. Many domestic scholars have also conducted in-depth analyses of the agricultural industrial chain and generally believe that the agricultural industrial chain is a complex system composed of multiple links and main bodies (Feng and Wang, 2021). Its core covers the entire process of agricultural product production, processing, circulation, sales and service, including the upstream production of input materials, the midstream planting, breeding and product processing, as well as the downstream product circulation and channel sales (Cheng et al., 2017). At the same time, it also involves the industrial organization chain composed of farmers, cooperatives and enterprises related to the production, supply and sales activities of agricultural products (Shan et al., 2025). The agricultural industrial chain is not only a multi-link and multi-level dynamic system, but also features a long chain and complex links, which makes it simultaneously exposed to natural disasters and market risks, and its vulnerability far exceeds that of other industrial chains.
Given the complexity, multi-link nature and vulnerability of the agricultural industrial chain, scholars have begun to focus on how to enhance its ability to cope with internal and external shocks. Against this backdrop, the concept of “resilience” was gradually introduced into the agricultural sector, thus giving rise to the important concept of the RAIC. The RAIC refers to its ability to effectively resist external shocks such as war, natural disasters, uncertain policies, and market fluctuations, as well as internal and external changes, quickly recover and reconstruct its resilience (Zeng et al., 2025). The core lies in the fact that as an organic system, the agricultural industrial chain demonstrates its comprehensive response capabilities in the face of internal and external risks. Specifically, all links in the industrial chain (production, processing, circulation, sales, etc.) and related entities (farmers, enterprises, governments, etc.) need to work together to achieve stable operation, rapid recovery and sustainable development under risk conditions, demonstrating a mechanism of collaborative cooperation. This resilient system not only ensures the steady development of agriculture, but also provides strong support for food security and sustainable agricultural development. Therefore, exploring the influencing factors and improvement paths of the RAIC can effectively meet the actual needs of the country in strategic deployments such as promoting agricultural modernization and ensuring national food security.
With the in-depth evolution of the new round of technological revolution, the digital economy has permeated every link of China's agricultural industry, creating important development opportunities for enhancing agricultural risk management and strengthening the resilience of the industrial chain. The digital economy, based on digital elements, technologies and other resources, enhances the dynamic adaptability of agriculture in crisis situations by penetrating every link of the agricultural industrial chain (Wang S. S. et al., 2025). From the perspective of financial services, digital inclusive finance helps to reduce the financing costs and thresholds of all entities in the industrial chain, and demonstrates significant value in terms of capital support and risk management (Zeng et al., 2025). From the perspective of supply and demand matching, the construction of digital villages, through digital platforms, helps to reduce the information communication costs of each link in the agricultural industrial chain and enhance the cooperation efficiency among various entities in the industrial chain (Zhang et al., 2025). However, a prominent issue in the digital transformation process of China's agricultural industry is the digital fragmentation of each link in the agricultural industrial chain, which leads to low operational efficiency and weak risk resistance throughout the entire chain. Obviously, this characteristic is contrary to the long-term goal of further promoting the development of the digital economy and also makes it difficult for the application of digital technology in the agricultural sector to achieve a scale effect. Against this backdrop, the government of Digital China has successively issued a series of policies to guide and promote the development of the digital economy.
As a key strategic platform facilitating the integration of China's digital economy with the real economy, the DEPZ policy shoulders the significant mission of promoting the digitalization of industries and the industrialization of digitalization. In October 2019, the National Development and Reform Commission teamed up with the Cyberspace Administration of China to roll out the “Implementation Plan for DEPZ,” effectively designating it as a key vehicle for advancing policies within the digital economy. It has chosen to carry out pilot demonstrations in six provinces and municipalities including Hebei (Xiongan New Area), Zhejiang Province, Fujian Province, Guangdong Province, Chongqing Municipality and Sichuan Province. After the policy of the experimental zone was proposed, it immediately attracted extensive attention and in-depth research from all sectors of society. At the heart of the DEPZ policy is the commitment to weaving cutting-edge digital technologies into established industries, driving their digital transformation and smart modernization. This approach aims to boost industry competitiveness and elevate the overall quality and resilience of the economy (Guo et al., 2025). The establishment of policies in this pilot zone can promote technological innovations and drive digital transformation and upgrading. This provides strong technical support and a digital solution for the entire industrial chain for industrial development, optimizes each link in the industrial chain, and further enhances the resilience of the industrial chain. Therefore, an in-depth exploration of how the DEPZ can enhance the RAIC is of great significance for the sustainable development of the agricultural industry and the realization of China's construction as a modern power.
While previous research has explored the RAIC within the context of the digital economy, most studies have overlooked the crucial role of digital economy policies in shaping RAIC. This gap in the literature fails to account for how macroeconomic policy frameworks systematically influence RAIC. Especially against the backdrop of the country's vigorous promotion of the construction of DEPZ, these pilot zones, as important carriers for the pioneering and experimental implementation of digital economy policies, aim to explore effective paths for the deep integration of the digital economy and the real economy through policy guidance, mechanism innovation, and platform construction. Therefore, when studying the driving factors of the RAIC, it is particularly necessary to incorporate the policy impact of the DEPZ into the scope of investigation. However, in the research on the policy effects of the experimental zone, most of the literature focuses on the policy's impact on the level of new quality productivity (Xia et al., 2024) and the level of innovation (Li J. et al., 2024), enterprise risk-taking (Zhou and Zhou, 2025), enterprise digital transformation (Zeng, 2023), enterprise brand value (Guo et al., 2025), urban entrepreneurial activity (Yang and Liu, 2024), urban carbon emissions (Guo et al., 2025), and other aspects. Although these research results provide us with rich perspectives to understand the policy effects of the experimental zone, in summary, the current research results mainly focus on the above aspects, while the impact on the resilience of the agricultural industrial chain has not received sufficient attention and systematic research.
Given this context, utilizing panel data from 30 Chinese provinces between 2012 and 2022, this study conducts a comprehensive assessment of the RAIC. It further employs a difference-in-differences model to analyze how the DEPZ policy influences RAIC, exploring its mechanisms and moderating effects in depth. This article's potential contributions include the following points:
First, it supplements the relevant research on the policy effect evaluation of the DEPZ policy. Unlike the existing literature that mainly focuses on how policies affect the development of economic entities such as enterprises and cities, this paper extends the logical chain to the agricultural industry field and reveals the enhancing effect of the policies in the experimental zone on the RAIC. Second, the relevant literature on the influencing factors of the RAIC has been expanded. This study, from the perspective of the establishment of the experimental zone, explores its impact on the RAIC at both theoretical and empirical levels, and at the same time provides new evidence for policy empowerment of the RAIC. Thirdly, from the perspectives of FC and ATI, the mechanism by which the policies of the experimental zone affect the RAIC was explored, and a comprehensive analysis was conducted on how the experimental zone contributes to the improvement of the resilience level of the agricultural industrial chain. Fourth, the moderating role of URI is examined using a moderated mediation framework, offering theoretical insights for advancing urban-rural integration, breaking through financing bottlenecks, and promoting technological innovation.
2 Hypothesis
2.1 The direct impact of the DEPZ on the RAIC
The DEPZ policy aims to integrate the digital economy into the real economy. The DEPZ policy implementation involves five aspects: market-based allocation of data elements, digital infrastructure, digital innovation, industrial digitalization, and digital regulation. These measures have effectively promoted the digital transformation of agriculture.
According to neoclassical economic theory, production factors such as technology, labor force and capital are the decisive factors of production. During the digital transformation of agriculture, the sharing of data elements and digital technologies can optimize the combination mode and utilization degree of production factors. First of all, the essence of data elements is a kind of information. Data information can help predict the risks of agricultural natural disasters and their probabilities of occurrence, thereby enhancing the risk resistance capacity of the agricultural industrial chain. Meanwhile, data can alleviate the problem of information asymmetry. Through the transmission and analysis of data, farmers and agricultural enterprises can have a more comprehensive grasp of market information, achieve precise supply and demand matching, and promote the integration of the industrial chain. This is conducive not only to improving the quality of the industrial chain, but also to the recovery of the agricultural industry after being impacted. Secondly, digital technologies such as remote sensing and intelligent monitoring can directly help farmers accurately grasp the growth dynamics of crops, achieve automated management, and improve agricultural production efficiency. The management process that applies digital technology will continue to generate massive amounts of data, thereby generating a cumulative effect and promoting the integration of the industrial chain. Finally, agriculture relies on data and digital technologies to develop new production methods, business models, development platforms, etc., enhancing agricultural production efficiency and thereby improving the RAIC.
The RAIC is essentially the self-organizing result of multiple entities such as the government, enterprises, farmers and cooperatives pursuing survival and development under the constraints of cost and risk, which is manifested as the ability to resist risks, adapt and recover. The DEPZ policy has significantly improved the understanding of production information and each other's behaviors among various entities by promoting the integration of digital technology into the industrial chain. Agricultural production is highly influenced by natural conditions, and the related data on climate, soil, etc. are unique and complex. Digital technologies (Internet of Things, remote sensing) collect unique and complex soil and meteorological data in real time, build a risk early warning system, and enhance the ability to resist and adapt. Meanwhile, compared with industry, agricultural production is decentralized, which is not conducive to information transmission and breaking through organizational boundaries. Digital technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence record information throughout the entire industrial chain and predict related risks.
The DEPZ policy can also enhance the synergy among the entities in each link of the industrial chain. The vulnerabilities of each link in the agricultural industrial chain are different. The DEPZ policy can systematically promote the coordination of the roles of all subjects. The production end is rigidly constrained by natural risks and production cycles. However, digital technology can provide low-cost climate information services, enabling farmers to act as the first risk-bearers and promptly adopt adaptive strategies such as planting stress-resistant varieties and cooperative collaborative production. The processing, storage and transportation end relies on the stability of raw materials and the smoothness of logistics. Digital industrialization supports enterprises in establishing flexible production systems and enhancing the risk buffering capacity of the supply chain. The consumption end of circulation is vulnerable to sudden changes in demand, while digital channels can quickly reconstruct the connection between supply and demand. Driven by digital reform, the synergy among the business entities in the industrial chain has been enhanced. Small-scale farmers can take on risks first and act as the end users by adopting stress-resistant varieties and participating in the collective actions of cooperatives. Cooperatives can organize the sharing of agricultural machinery, connect with market information, and uniformly purchase agricultural supplies, thereby achieving resource integration. Agricultural enterprises can invest in smart agriculture, lay out diversified supply chains, and become drivers of technological innovation and chain leaders. The government can build a cold chain at the origin, open up an agricultural data platform, and improve the insurance system to provide public goods and institutional supplies for other entities.
The above-mentioned influences can effectively enhance the RAIC. First of all, the risk prediction ability of natural disasters can prevent the disruption of industrial chains and avoid impacts in advance. Secondly, as the level of integration increases, the RAIC strengthens. Finally, when agricultural production efficiency improves and new management platforms develop, the structure of the agricultural industry chain will upgrade and evolve into a higher form. Drawing from the preceding discourse, the study advances Hypothesis 1:
H1: The DEPZ policy can enhance the RAIC.
2.2 The indirect impact of the DEPZ on the RAIC
Based on the above analysis, the enhancement of industrial chain resilience benefits from the innovative allocation of production factors in different links of the industrial chain. Moreover, the optimization of the utilization degree and combination mode of production factors is closely related to technological innovation and capital financing. Therefore, the DEPZ policy enhances the RAIC through the following two approaches.
The DEPZ policy enhances the RAIC by promoting ATI. According to Schumpeter's theory of innovation, technological innovations can not only directly enhance production efficiency but also lead to changes in the allocation of production factors. Based on the above analysis, the DEPZ policy can generate massive amounts of data information by promoting the digital transformation of agriculture. This information can provide analytical basis for agricultural science and technology research and development. Moreover, with the help of digital technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence, information coupling and knowledge can be achieved at a low cost, broadening the channels for agricultural science and technology innovation. The application of digital technologies such as the Internet of Things and AI can effectively enhance the total factor productivity of agriculture and break through rigid constraints such as land and labor. Meanwhile, the DEPZ policy can promote agricultural technological innovation by strengthening data transmission and building an innovation consortium of “government, enterprises, farmers and research institutions.” These changes will strongly promote technological progress in key links such as seed research and development and agricultural product processing, enhance production efficiency, optimize factor allocation, strengthen weak links, and ultimately increase the resilience of the industrial chain.
The DEPZ policy enhances the resilience of the agricultural industrial chain by effectively alleviating the financing constraints faced by various entities and their key links in the agricultural industrial chain. On the one hand, the DEPZ policy can reduce the information asymmetry between financial institutions and agricultural business entities through data elements. Specifically, through the application of big data and information flow in agricultural production, financial institutions can more accurately assess the actual operating conditions, repayment capabilities and risk levels of farmers and small and micro agricultural-related enterprises, thereby reducing their perception of credit risks. This has greatly enhanced the willingness and efficiency of financial institutions to provide credit to the agricultural sector, especially to the weak links in the industrial chain and small and micro entities that were previously difficult to cover due to information scarcity. As a result, these entities have obtained more stable and convenient credit support, enhanced their ability to withstand short-term shocks, ensured the stable operation of basic production and supply links, and consolidated the micro foundation of RAIC. On the other hand, the DEPZ policy has enhanced agricultural productivity and operational efficiency through digital technologies. According to neoclassical economic theory, the improvement of agricultural production efficiency directly enhances the expected return on capital of related links in the agricultural industrial chain. This not only attracted a broader range of market capital to actively flow into the agricultural sector, but also broadened the overall financing channels. With sufficient financial support, the time for adjusting the allocation of factors can be reduced, and factors such as talents and funds can be guided to key links in the agricultural industrial chain such as research and development and consumption.
Drawing from the preceding discourse, the study advances Hypothesis 2 and Hypothesis 3:
H2: ATI plays a mediating role in the process in which the DEPZ policy affect the RAIC.
H3: Alleviating FC plays a mediating role in the process in which the DEPZ policy affect the RAIC.
2.3 The moderating effect of the URI on the RAIC
Based on the above analysis, the DEPZ policy can optimize the allocation of factors and ultimately enhance the RAIC. URI can eliminate the barriers to the flow of factors between urban and rural areas, thereby optimizing the paths of technological innovations and capital financing.
In terms of technological innovations, the integration of urban and rural areas promotes the deep integration of urban industry and rural agriculture, guiding the upgrading of agricultural technology. First of all, the technology-intensive advantage of urban industries provides support for agricultural mechanization and intelligence, accelerating the research and development and diffusion process of agricultural technological innovation. Secondly, the integration of industries between cities and rural areas promotes the integration of intelligent control systems, e-commerce platforms, etc. into agricultural production. The integration of urban and rural industries has also extended the agricultural industrial chain and enhanced the ability to resist and recover from risks. Finally, the integration of urban and rural areas has promoted the flow of talents and technologies to rural areas. This provides a guarantee for technological innovation in the agricultural industry.
In terms of capital circulation, URI helps break down the barriers to agricultural financing. Agricultural production is not only affected by market fluctuations, but also by risks such as climate, pests and diseases. These agricultural investments have a long payback period and unstable returns. Industry can promote the large-scale production of agriculture and increase the industry's profits. The integration of urban and rural areas can promote the construction of agricultural infrastructure, which enhances agricultural security and reduces the operating costs and risks of financing projects. Drawing from the preceding discourse, the study advances Hypothesis 4 and Hypothesis 5:
H4: URI can regulate the technological innovation path by which the DEPZ policy affect the RAIC.
H5: URI can regulate the financing path through which the DEPZ policy affect the RAIC.
Based on the above analysis, a theoretical mechanism diagram of the impact of DEPZ policy on RAIC is constructed (Figure 1)
3 Models and materials
3.1 Data source
China officially released the DEPZ policy in 2019. For validating the accuracy and reliability of the data, the study employs the provincial panel dataset from China spanning 2012 through 2022. The data used in this study were primarily obtained from the “China Rural Statistical Yearbook,” the “China Statistical Yearbook,” statistical data released by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, public data from the official website of the National Bureau of Statistics, and the EPS database.
3.2 Empirical models
To alleviate the pre-existing characteristic differences between the treatment group and the control group, this paper first obtains new research samples based on the PSM method (Zhao et al., 2023; Ammar Zahid et al., 2025; Du and Li, 2022). Then, an empirical analysis was conducted through DID.
The benchmark model of this paper is as follows:
Where: RAICit represents the RAIC, DIDit represents the difference-in-differences variable of the DEPZ policy, Xitencompasses various control variables, λt is the year fixed effect, δisignifies the individual fixed effect, and εitit accounts for the random error term. The coefficient β1 captures the direct effect of the DEPZ policy on RAIC. A statistically significant positive value would demonstrate that this policy initiative effectively strengthens the RAIC adaptive capacity.
To examine how FC and ATI mediate effects, this study establishes the following model:
Mediatorit is a mediating variable, representing FC and ATI. Other variables retain their prior definitions. The analysis centers on the sign and significance of coefficient α1 in Equation (2) and coefficients γ1 and γ2 in Equation (3).
To delve into how the degree of URI may moderate the aforementioned mediating impacts, we‘re relying on the research framework laid out by Wen and Ye, 2014. Based on this, we've crafted a mediating model that incorporates these moderating effects.
Where: URIit represents the level of URI, and other variables retain their prior definitions. Equation (4) represents the overall moderating effect of the URI level, mainly focusing on the direction and significance of coefficient c3. Equations (5) and (6) respectively study the moderating effects of the level of URI on the first and second half paths in the mediating effect, with a focus on the directions and significance of coefficients a3 and b2.
3.3 Variables
3.3.1 Dependent variable
The dependent variable measures RAIC. Drawing on existing research (Li, 2009; Song et al., 2022; He and Yang, 2021; Zhang and Long, 2023), this paper defines the RAIC as the ability of a complex agricultural industrial chain system composed of multiple entities (such as farmers, family farms, cooperatives, agricultural enterprises, etc.) and multiple links (production, processing, circulation, sales, etc.) to effectively resist external shocks or internal changes, quickly recover and reconstruct resilience. The core lies in that as an organic system, it requires all links and related entities in the industrial chain to cooperate under risk conditions, achieve stable operation, rapid recovery and sustainable development, and ensure the steady development of agriculture as well as food security and sustainable agricultural development.
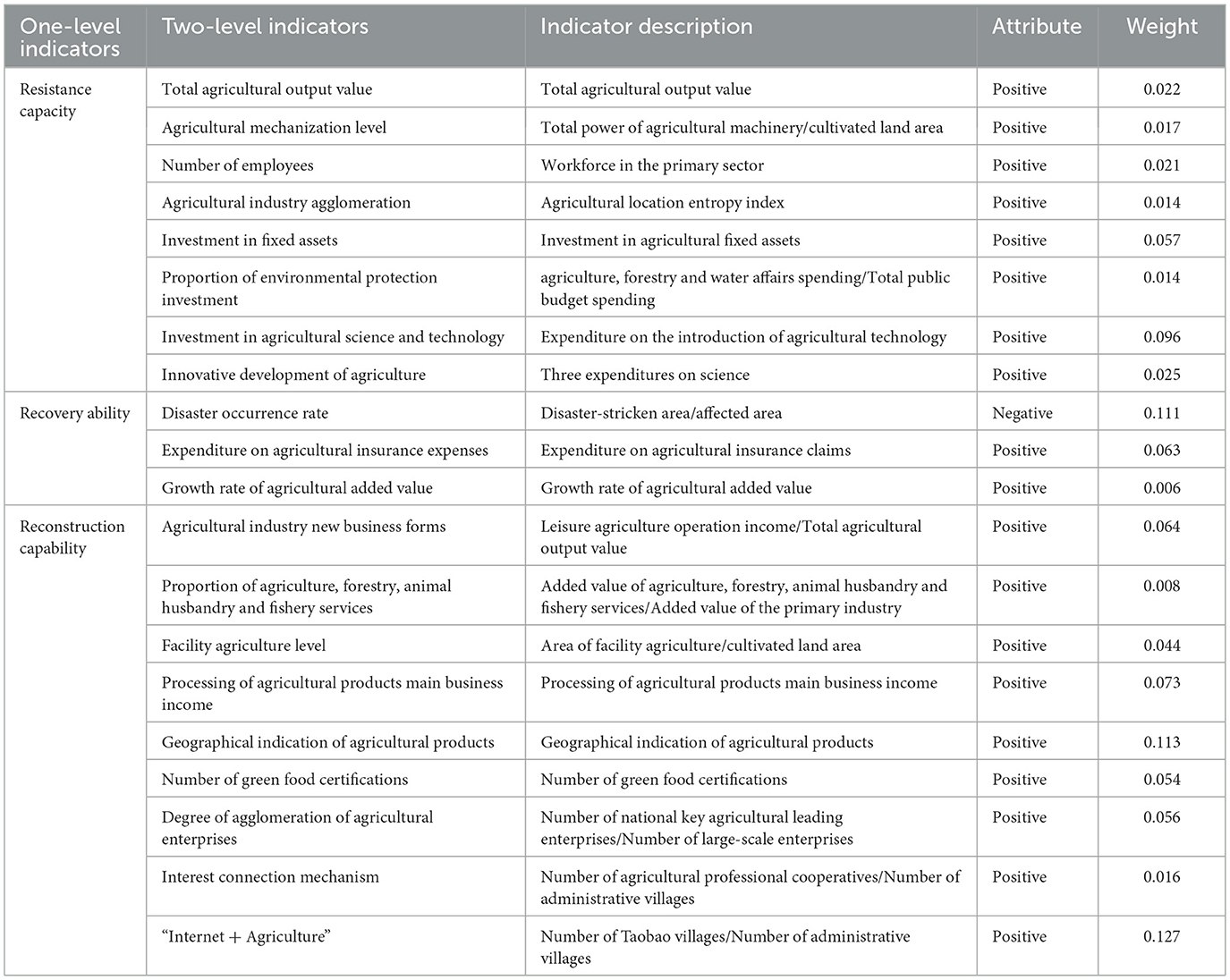
Based on the connotation of the RAIC and drawing on existing research (Lv et al., 2025; Hao et al., 2024; Wang L. S. et al., 2025; Zeng et al., 2025; Hao and Tan, 2023; Luo and Wang, 2024; Dong et al., 2021; Yu et al., 2021; Gao and Gao, 2024), an index system is constructed from three perspectives: resistance capacity, recovery capacity, and reconstruction capacity.
Resistance capacity. The resilience capacity reflects the fundamental ability of the agricultural industrial chain to resist and mitigate the damage caused by various internal and external shocks, prevent the interruption of the industrial chain and maintain overall stability. The scale and efficiency of the agricultural industry, the guarantee of resource elements, and the capacity of technological support directly affect the overall stable operation of the agricultural industrial chain, providing strong support and guarantee. Therefore, this paper selects the evaluation indicators for the resilience of the agricultural industrial chain from three perspectives: industrial foundation, resource elements, and technological innovation. Specifically, they include eight indicators: total agricultural output value, agricultural mechanization level, employment in the primary industry, agricultural industrial agglomeration, agricultural fixed asset investment, proportion of environmental protection investment, agricultural science and technology investment, and agricultural innovative development.
Recovery ability. Recovery capacity mainly refers to the ability of the agricultural industrial chain to quickly return to a normal or near-normal state after being impacted, involving the self-repair, self-regulation and adaptability of the agricultural industrial chain after being disturbed. The degree of damage suffered by the agricultural industrial chain, the resource support relied upon for its recovery, and the effectiveness are interrelated and complementary, jointly constituting a representation of the recovery capacity of the agricultural industrial chain. Therefore, this paper mainly characterizes the evaluation indicators of the recovery capacity of the agricultural industrial chain from aspects such as the degree of damage after the shock, economic security support, and the effectiveness of economic recovery, including three indicators: disaster rate, agricultural insurance expense expenditure, and the growth rate of agricultural added value.
Reconstruction capability. The ability to restructure refers to the capacity of the agricultural industrial chain to achieve transformation and upgrading as well as sustainable development after experiencing shocks by adjusting its own structure, optimizing resource allocation, and innovating production methods. This mainly involves the key aspects of structural adjustment, functional optimization and transformation and upgrading of the agricultural industrial chain after it has been impacted. Therefore, this paper mainly selects the evaluation indicators for the reconstruction capacity of the agricultural industrial chain from three perspectives: the integrated development of the agricultural industry, brand building, and organizational capacity. It includes nine indicators: new forms of agricultural industry, the proportion of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery services, the level of facility agriculture, the main business income of agricultural product processing, the number of geographical indications of agricultural products, the number of green food certifications, the concentration degree of agricultural enterprises, the interest connection mechanism, and Internet + agriculture.
In terms of determining the weights of indicators, this study adopts a combined subjective and objective weighting method. Specifically, the subjective weighting method -AHP method and the objective weighting method—entropy weighting method are organically combined to achieve complementary advantages of both, which can effectively avoid the limitations of a single weighting method in weight distribution. The specific results are shown in Table 1.
It can be found from Table 1 that “Internet + Agriculture” (0.127), “Geographical indications of Agricultural products” (0.113), and “disaster rate” (0.111) are key indicators for enhancing the RAIC. Among them, the core of “Internet + Agriculture” lies in systematically transforming and upgrading the links of agricultural production, circulation and sales by applying digital technology. In response to the current challenge of connecting “small-scale farmers with large markets” in China's agriculture, this model, relying on e-commerce platforms, effectively breaks through geographical restrictions, significantly expands the sales channels and market boundaries of agricultural products, and provides an important path for resolving structural contradictions. The “Geographical indication of Agricultural Products” centrally reflects the risk-resistance capacity of regional characteristic agriculture. Its core advantages lie in brand premium and the degree of organization. On the one hand, the strict standardized production system of geographical indication products ensures the stability of product quality, and their brand premium capacity can absorb shocks and buffer risks during market fluctuations. On the other hand, geographical indication certification promotes the formation of producer consortia, incorporates scattered farmers into a unified management system, and builds an efficient connection mechanism featuring information sharing, risk sharing, and benefit sharing. Furthermore, the “disaster rate” directly reflects the actual extent of losses suffered by the agricultural production system after being hit by major natural disasters such as droughts, floods, hailstorms, and pests and diseases. It is a core result-oriented indicator for measuring the resilience of the industrial chain and a key shortcoming that needs to be urgently addressed. In conclusion, these findings provide important empirical evidence for specifically enhancing the RAIC.
3.3.2 Independent variable
The difference-in-differences variable (DIDit) of the DEPZ policy is represented by the interaction term between the dummy variable (treatedit) of the experimental group and the policy implementation time (timeit). When the province belongs to the DEPZ policy, take 1 for treatedit; otherwise, take 0. For the year when the DEPZ policy was released (2019) or later, timei takes 1; otherwise, it takes 0. When the area belongs to the experimental zone and the time is in 2019 or later, DIDit takes 1; otherwise, it takes 0.
3.3.3 Mediator variables
(1) FC
The FC discussed by the intermediary mechanism in this article focus on the financing constraints faced by various business entities in the agricultural industrial chain. Specifically, this constraint refers to the systemic difficulties that business entities engaged in different links in the entire agricultural industrial chain encounter when obtaining the funds needed for production and operation. The core lies in the mismatch or unsmooth flow between the supply and demand of funds. In terms of manifestation, it mainly includes problems such as the difficulty for business entities to obtain any external resources, the funds obtained being far lower than the actual demand, and excessively high financing costs. Based on this, referring to existing research (Meng and Ren, 2023; Wei and Luo, 2023; Sun and Sun, 2022; Cheng and Wang, 2024; Wang et al., 2024) and data availability, this paper adopts the per capita amount of agricultural-related loans (amount of agricultural-related loans/rural population) for measurement. This indicator can reflect the actual scale of credit resources obtained by agricultural business entities, directly indicating the coverage density and accessibility of financial resources in the agricultural and rural sectors. The lower the per capita agricultural loan amount, the fewer credit resources available per capita, which can be understood as the relatively higher degree of FC on agricultural entities in the region. Conversely, if this indicator rises, it can be regarded as a certain degree of relief from FC.
(2) ATI
The existing literature on the measurement of ATI mainly includes the following three types of methods: input, output and efficiency. Specifically, the first category involves using input as an indicator to measure agricultural technological innovation, including funds, personnel input, etc (Li et al., 2021); The second category is to use output as an indicator of ATI, including various patents (Li and Wan, 2025); The third category represents agricultural technological innovation by using the total factor productivity of agriculture calculated by methods such as DEA and SFA (Yang et al., 2024). Based on the theory of endogenous growth, the most direct manifestation of ATI is agricultural patents, especially agricultural invention patents. Therefore, this paper draws on the research results of Li and Wan (2025), uses the number of authorized agricultural invention patents to measure ATI.
3.3.4 Moderator variable
URI signifies a novel phase in the evolution of urban-rural dynamics during China's modernization journey. This mission aims to break the urban-rural dichotomy and foster holistic, balanced, and enduring growth in both economic and social spheres of urban and rural areas. The realization of this goal involves various processes of regional spatial, economic, social, cultural and ecological development. Essentially, this translates to enhancing resource distribution between urban and rural areas while facilitating the seamless movement and efficient allocation of key assets—including skilled labor, capital, and technological innovation—across these interconnected zones. Accordingly, this paper draws on the evaluation index system of URI constructed by Niu and Xu (2024) to conduct a quantitative assessment of the level of URI.
3.3.5 PSM covariate and control variables
PSM Covariate. The key conditions for DEPZ's selection are whether the local area has a unique economic foundation, market environment, governance capacity, and digital infrastructure, among other elements. Therefore, this paper selects the level of economic development (EDL), the level of technology market development (DLTM), the degree of government intervention (GIL), the level of informatization (LI), and the Internet penetration rate (IPR) as key covariates, and constructs a Logit model to obtain their probability values for matching.
Control Variable. Combined with relevant literature (Yang et al., 2019; Zhang and Zhang, 2024), in order to objectively and effectively study the impact of the DEPZ policy on the RAIC, this study includes the following control factors: (1) The agricultural fiscal expenditure (AFE) is calculated as the proportion of spending on agrarian, forestry, and water conservation undertakings relative to the overall agricultural, forestry, livestock, and aquatic products production value. (2) The crop cultivation structure (CCS) is defined by the ratio of the planted food crops to the total crop area. (3) The agricultural industrial structure (AIS) reflects the ratio of primary industry's added value to the region's overall output. (4) The agricultural trade openness (ATO) is defined by the proportion of combined agricultural import and export trade volumes relative to the primary industry's added value.
3.4 Descriptive statistics of variables
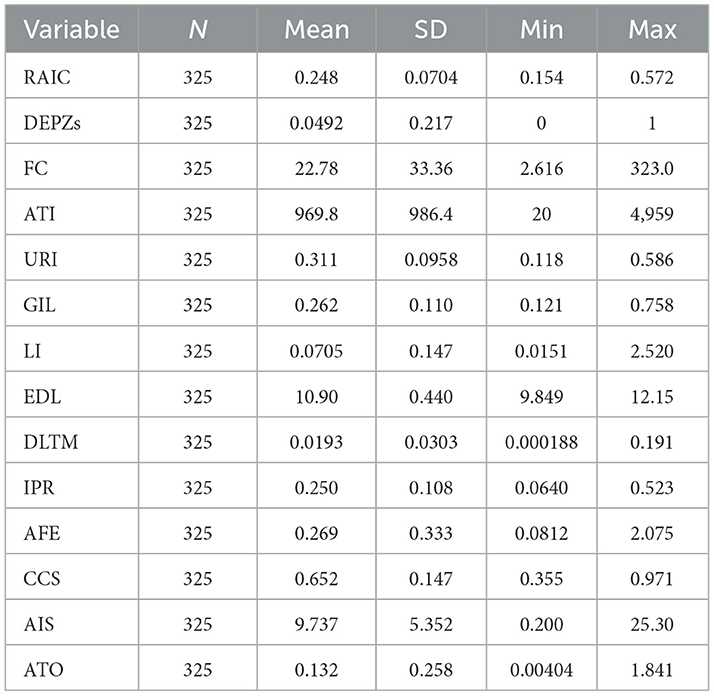
Table 2 outlines the descriptive statistics of the key variables investigated in the research. The standard deviation of the DEPZ policy is 0.217, indicating significant differences among various provinces, which highlights the necessity of evaluating the effectiveness of the policies. With regard to the analysis of the RAIC, a significant gap is observed between the minimum (0.154) and maximum (0.572) values. The mean value of this variable is 0.248, which is much lower than the maximum value. This not only reflects the significant differences regarding their resilience of the agricultural industrial chain among various provinces, but also indicates that there is still scope for enhancement with regard to the overall level.
4 Empirical results
4.1 PSM matching result
This paper adopts the PSM method. The propensity score is calculated based on the average values of variables such as GIL, LI, EDL, DLTM, IPR, and a control group with provincial characteristics similar to those of the treatment group is obtained. To verify the reliability of the PSM matching results, a balance test was conducted on the matching results, as shown in Table 3. The results show that the standard bias of all covariates after matching is < 10%, indicating that both the selected covariates and the matching method are reliable. Meanwhile, the t-test results after matching all variables do not reject the null hypothesis, that is, the control group samples matched by the PSM method have similar endowment characteristics to the treatment group samples, and the matching effect is good.
4.2 Baseline regression
Based on the samples processed by PSM, this paper regards the DEPZ policy as a quasi-natural experiment and uses the DID method to evaluate the impact of the policy on RAIC. The regression results are shown in Table 4. In Table 4, the results shown in Column (1) come from regressions run without factoring in control variable. Column (2) shows the regression results including the PSM covariate, and column (3) shows the regression results including both the covariate and the control variable. Irrespective of the inclusion of control variables, the coefficient for the DEPZ policy estimate remains notably positive, with a statistical significance at the 1% mark. This suggests that the implementation of the DEPZ policy has a pronounced positive impact on the RAIC.
4.3 Robustness test
4.3.1 Parallel test
The benchmark regression results show that compared with the provinces that have not established experimental zones, the RAIC in the provinces that have established experimental zones has been significantly enhanced. However, such differences might have existed before the establishment of the experimental area. However, to evaluate the policy effects of the establishment of the pilot zones using the difference-differences model, a prerequisite must be met, that is, the changes in the RAIC in the provinces (treatment group) that have built the DEPZ and the provinces that have not built the DEPZ (control group) before the policy implementation are parallel. This paper tests the parallel trend hypothesis. It can be seen from Figure 2 that before the policy of the experimental zone was implemented, the differences among various regions were not significant. Following the policy's introduction, the difference coefficient showed a consistently positive and statistically significant value, and the parallel trends assumption was upheld.
4.3.2 Placebo test
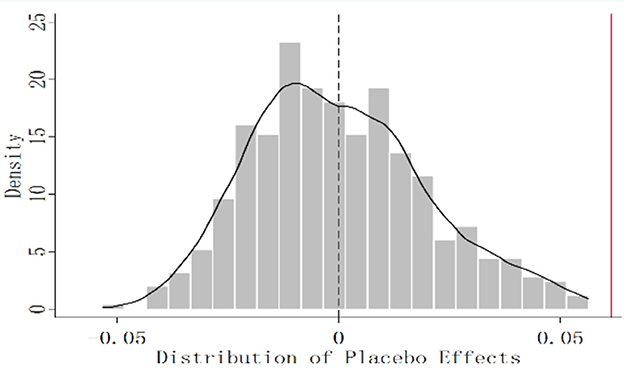
To ensure that the empirical results are not disturbed by omitted variables and random factors, this paper conducts random experiments on the experimental data. By randomly “screening” regions as the experimental areas and randomly generating the policy shock time of the experimental areas, a two-layer random model of individuals and time is constructed, and the false regression coefficient is calculated. After repeating the above-mentioned false experiment 500 times, this paper plots the experimental results as the density distribution map of the false regression coefficients, and the findings are displayed in Figure 3. It can be found that the false regression coefficients are all around the 0 value and follow a normal distribution, and the true difference coefficient is greater than the placebo effect of 96%. This indicates that the model used in this paper is reasonable, no important variables are omitted, and the outcomes of the benchmark regression model demonstrate strong robustness.
4.3.3 Other robustness test
To verify the reliability of these findings, two approaches are employed, namely changing the evaluation method (Li X. et al., 2024) and changing the scope of the experimental group (Chen et al., 2025), for robustness tests. Specifically, first, on the basis of the entropy method, the TOPSIS method is further introduced to conduct a comprehensive calculation of the resilience index system of the agricultural industrial chain again; Second, in addition to the five provinces in the experimental group mentioned earlier, Xiongan New Area has also been included in the scope of the DEPZ. To avoid any deviation in the experimental results caused by the omission of this experimental zone, Hebei Province, to which Xiongan New Area belongs, is now divided into the experimental group for a new regression analysis. Table 5 presents the test outcomes. They are similar to the results in the previous text, except that the coefficient size has changed. The overall significance and direction have not changed. Thus, the study's findings demonstrate substantial stability.
4.4 Heterogeneity test
Previous studies have shown that the implementation of the DEPZ policy has significantly promoted the improvement of RAIC. However, this positive impact may vary or be heterogeneous in different regions. The policy effect may vary due to factors such as the development level, industrial foundation, factor endowment and policy implementation of the region. Therefore, this paper examines the heterogeneity of the impact of DEPZ policy implementation on RAIC from aspects such as regional heterogeneity, industrial agglomeration level, agricultural labor productivity, and policy intensity.
4.4.1 Regional heterogeneity
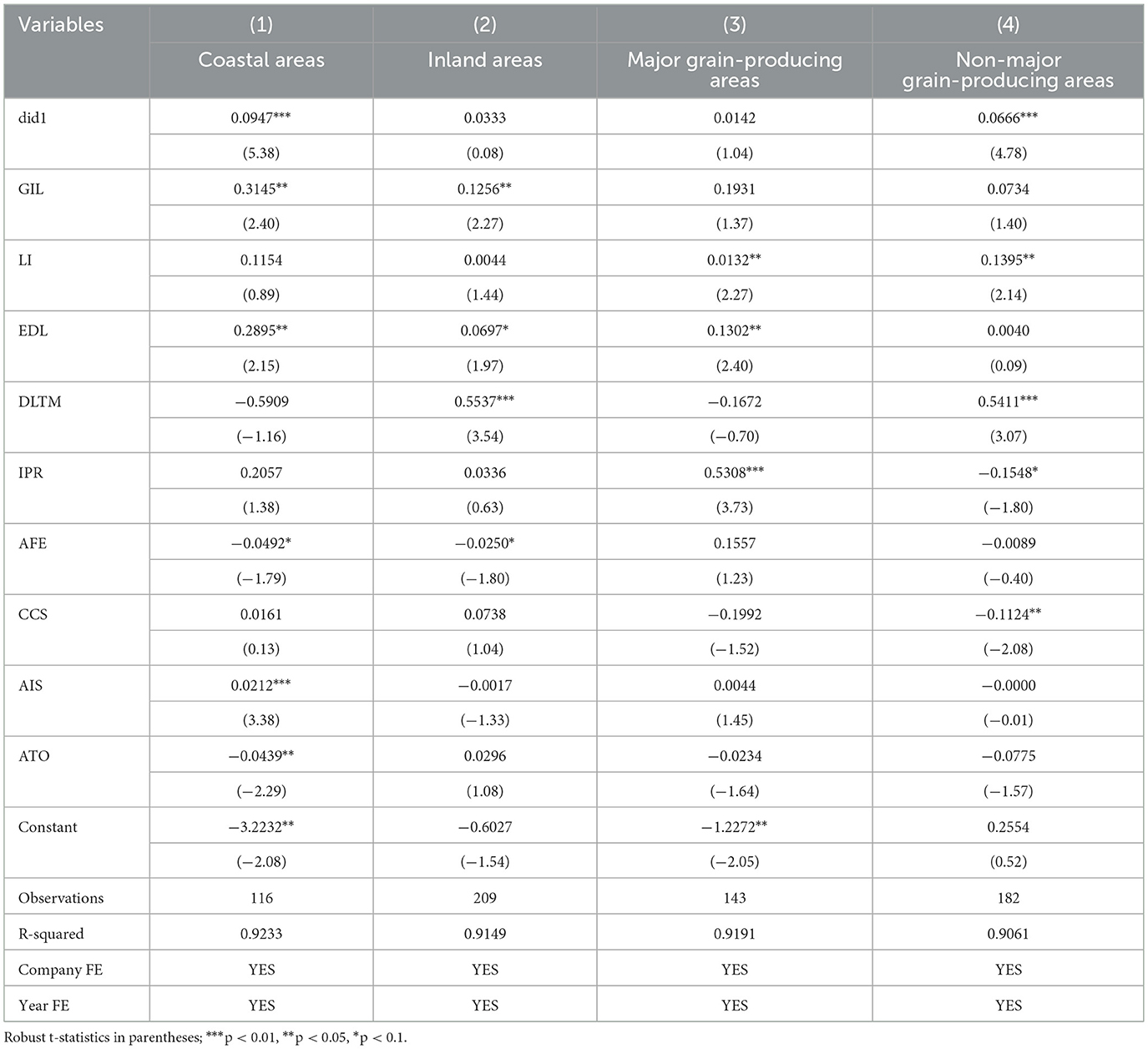
China has a vast territory. In many aspects such as geographical location, economic development and industrial structure, there are significant differences among various provinces. Considering the possible differences in policy effects between coastal and inland areas, as well as between major grain-producing areas and non-major grain-producing areas, this paper conducts a regional heterogeneity analysis.
Existing literature has pointed out that there is a relatively significant regional heterogeneity in the development level of China's digital economy (Wang L. S. et al., 2025). Based on this research result, this paper divides the research samples into coastal areas and inland areas, and then conducts heterogeneity analysis. The regression results are shown in columns (1) to (2) of Table 6. The DEPZ policy has a significant promoting effect on RAIC in coastal areas, but for inland areas, its promoting effect is not significant. A deeper exploration of the underlying reasons reveals that coastal areas possess abundant data resources and an advanced information technology application environment, which helps promote the standardized collection and open sharing of agricultural data, thereby reducing information asymmetry and effectively enhancing the collaborative efficiency of each link in the agricultural industrial chain. Meanwhile, the agricultural industrial chain in coastal areas is relatively mature. From the agricultural production link to processing, sales and logistics, a complete and closely connected industrial system has been formed, and the synergy effect among each link is very significant.
Given the different functional positioning of agriculture in various provinces, the impact of DEPZ policies on RAIC also shows differences between major grain-producing areas and non-major grain-producing areas. This paper draws on existing research (Nie et al., 2025), divides the research samples into major grain-producing areas and non-major grain-producing areas, and then conducts heterogeneity analysis. The regression results are shown in columns (3) to (4) of Table 6. The DEPZ policy can significantly promote RAIC in non-major grain-producing areas, but its promoting effect on major grain-producing areas is not significant. The reason lies in the fact that non-major production areas are dominated by cash crops and face greater market uncertainties. Enhancing competitiveness is the key. The DEPZ policy has effectively enhanced the stability and competitiveness of the industrial chain by promoting the deep integration of the digital economy and agriculture, facilitating the organic integration of agriculture with tourism, culture, education, health and other industries, expanding the multi-functionality of agriculture and channels for farmers' income growth, and providing strong support for improving the resilience of non-major production areas.
4.4.2 Heterogeneity of industrial agglomeration
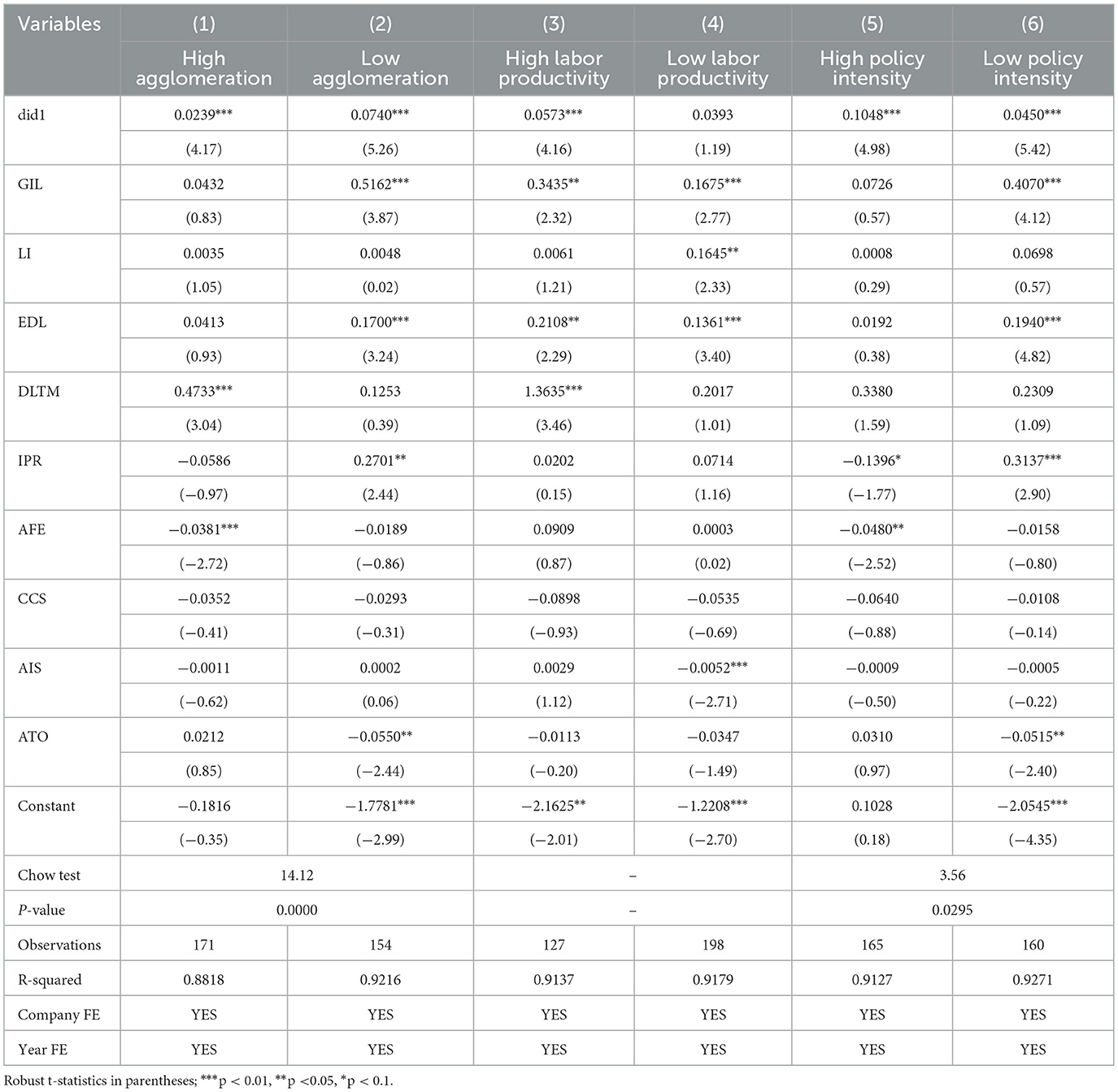
With the acceleration of China's agricultural modernization process, the distribution of agricultural industries has shown a distinct trend of agglomeration (Du et al., 2017). This kind of agglomeration reflects the development of large-scale and intensive agricultural production and operation, and has an important impact on RAIC. For this reason, this paper draws on relevant research (Wang and Zhang, 2024), divides the samples into high-agglomeration areas and low-agglomeration areas based on the level of agricultural industrial agglomeration, and analyzes the heterogeneity of the DEPZ policy on RAIC. The regression results are shown in columns (1) to (2) of Table 7.
The research found that, whether in high-concentration areas or low-concentration areas, the DEPZ policy significantly and positively promotes RAIC at the 1% level. It is worth noting that the estimated coefficient of the DEPZ policy is higher in low-agglomeration areas, indicating that its effect on enhancing RAIC in this region is stronger. The reason for this difference lies in the fact that in low-concentration areas, agricultural production and operation entities are usually scattered, industrial chains are short and weak, and the resilience foundation is relatively poor. The digital economy empowerment in the DEPZ policy can effectively break through the geographical dispersion limitations, promote information sharing and collaborative actions among business entities, enabling them to organize mutual assistance and respond uniformly more quickly in the face of shocks, thereby significantly enhancing the overall recovery capacity. In contrast, high-concentration areas themselves already have a relatively strong foundation of resilience, and the application of digital technology is more reflected in optimization and upgrading.
4.4.3 Heterogeneity of agricultural labor productivity
Agricultural labor productivity, as the core driving force for the development of modern agriculture, profoundly influences agricultural production models and efficiency. This paper draws on relevant research (Gao, 2024), taking the average level of per capita added value of the primary industry as the dividing point, divides the samples into regions with higher and lower agricultural labor productivity, and analyzes the heterogeneity of the impact of DEPZ policies on RAIC. The regression results are shown in columns (3) to (4) of Table 7.
The research found that the DEPZ policy significantly increased the RAIC in regions with high labor productivity, but its promoting effect on regions with low labor productivity was not significant. The reason lies in the fact that regions with high labor productivity have a relatively high level of scale and mechanization, and have already provided the material foundation and infrastructure conditions for the application of digital technology, which enables digital technology to play an effective role.
4.4.4 Heterogeneity in policy implementation intensity
Given the impact of the implementation effect of the DEPZ policy on the policy execution in pilot regions, this paper refers to the method of Tao and Ding (2022), and uses the word frequency of digital economy-related keywords in the provincial government work reports from 2012 to 2022 as the proxy variable for the intensity of the DEPZ policy, and conducts group regression based on the median. The regression results are shown in columns (5) to (6) of Table 7.
The research found that, whether in regions with high policy intensity or low policy intensity, the DEPZ policy significantly positively promotes at the 1% level. However, the promoting effect of the DEPZ policy is notably stronger in regions with high policy intensity. This difference mainly stems from the disparity in digital infrastructure construction. Regions with high policy intensity usually have more complete digital infrastructure, enabling all links in the agricultural industrial chain to apply digital technologies more efficiently, achieve synergy and efficiency enhancement, and thereby significantly enhance resilience. On the contrary, in regions with relatively low policy intensity, digital infrastructure lags behind, and it is difficult for all links in the industrial chain to fully achieve digital collaboration, which limits the space for enhancing resilience.
4.5 Mediating effect
The benchmark regression shows that the DEPZ policy can significantly promote RAIC. However, its specific mechanism of action still needs to be further explored. For this purpose, regression analysis was conducted on models (2) and (3), focusing on examining whether the DEPZ policy enhances the RAIC in the test area through both FC and ATI paths. The regression results are shown in Table 8.
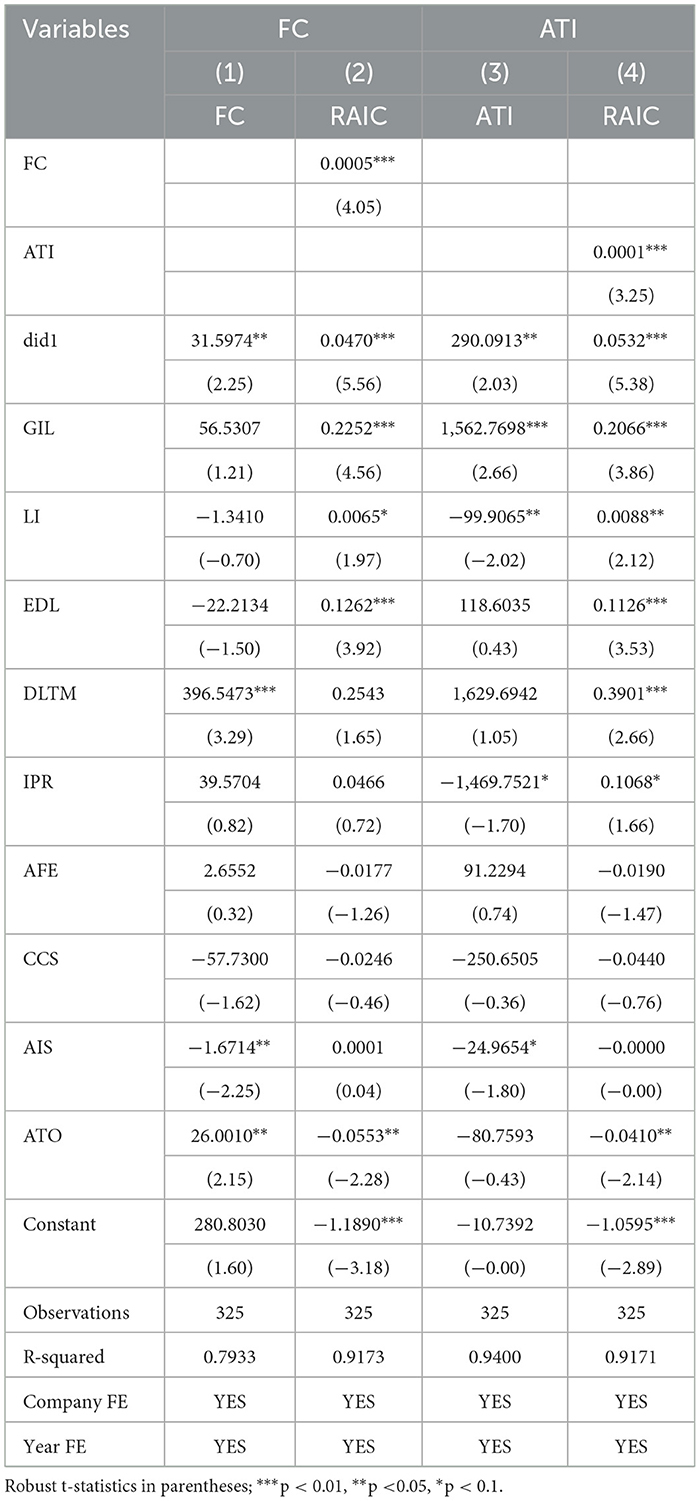
Columns (1) and (2) are the test results of the mechanism of action of FC. It can be seen from Column (1) that the coefficient of the DEPZ policy is significant at the 5% level, indicating that the implementation of the DEPZ policy has alleviated the financing constraints of the operating entities in the agricultural industrial chain. The implementation of the DEPZ policy can accurately identify the credit demands of farmers and agricultural enterprises, alleviate the information asymmetry between lenders and borrowers, thereby reducing financial discrimination and the entry threshold of the credit market, and broadening the financing channels for business entities. In Column (2), it can be seen that both the DEPZ policy and the FC coefficient are significant at the 1% level, indicating that the DEPZ policy can enhance RAIC by alleviating FC. The easing of financing constraints provides financial guarantees for the business entities in the agricultural industrial chain, enabling them to withstand risks such as natural disasters and market fluctuations, and ensuring their basic production and operation activities. Meanwhile, business entities with abundant funds are more capable of integrating resources from the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain, achieving centralized management and optimal allocation of resources, and enhancing production efficiency.
Columns (3) and (4) are the test results of the mechanism of action of ATI. It can be seen from Column (3) that the coefficient of the DEPZ policy is significant at the 5% level, indicating that the implementation of the DEPZ policy can enhance ATI. The DEPZ policy, by establishing demonstration zones for smart and digital agriculture, showcases the practical application effects of digital technologies in agricultural production, sets an example for farmers and agricultural enterprises, and encourages them to actively apply new technologies, accelerating the promotion of agricultural technological innovation. In Column (4), it can be seen that both the DEPZ policy and the ATI coefficient are significant at the 1% level, indicating that the DEPZ policy can enhance RAIC through ATI. ATI (Seed breeding, intelligent agricultural machinery, green plant Protection, cold chain Preservation) runs through all links of the agricultural industrial chain, which can effectively optimize resource allocation, improve production efficiency and accuracy, reduce losses, and enhance system stability and risk resistance.
4.6 Moderating effect
To explore how the URI influences the mediating processes discussed earlier, regression analyses were conducted on models (4) through (6). The results of these analyses are summarized in Table 9.
Firstly, discuss whether the introduction of the moderating factor of the URI has an impact on the direct effect of the DEPZ policy. As can be seen from column (1) of Table 9 the coefficient of the interaction term between DEPZ policy and URI is positively significant at the 1% level, indicating that URI significantly enhances the improvement effect of DEPZ policy on RAIC. URI can optimize the allocation of labor, capital and digital technology through the mechanism of free flow of factors, and enhance the ability of the agricultural industrial chain to cope with risks.
Secondly, it is discussed whether the introduction of URI as a moderating factor has an impact on the two mediators FC and ATI. The results are shown in columns (2) to (5) of Table 9.
It can be seen from columns (2) and (3) that the URI's regulatory effect on FC is effective in the first half of the path but fails in the second half. The URI process has significantly improved the infrastructure and public service levels in rural areas, effectively reducing the information acquisition costs and related risks for financial institutions in serving agriculture, rural areas and farmers. Meanwhile, the implementation of the DEPZ policy has further strengthened the ability to collect, integrate and verify the credit information of agricultural-related business entities. These two measures have worked in synergy, significantly alleviating the long-standing agricultural financing problem caused by information asymmetry. However, in the subsequent links of enhancing the resilience of the industrial chain, the policy effects have not been fully manifested. At its root, URI itself failed to address and solve the inherent vulnerabilities and deep-seated structural defects of the agricultural industrial chain, resulting in the injected funds being difficult to effectively translate into substantial improvements in the overall resilience of the industrial chain. In the upstream of the agricultural industrial chain, there are mainly a large number of scattered small-scale farmers. They adopt highly decentralized and small-scale business models, which makes it difficult for funds to be transformed into systematic and large-scale resilient investments.
It can be seen from columns (4) and (5) that the regulating factor of URI can have a promoting effect on both the first and second halves of the ATI mediation process. The DEPZ policy often brings in elements such as advanced technology, data resources, financial capital and high-end talents. Under the impetus of URI, barriers between urban and rural areas such as household registration, land and capital have been broken down. This enables the above-mentioned key elements to flow more smoothly from cities to rural areas and from experimental zones to the agricultural sector. Therefore, the driving effect of this DEPZ policy on ATI has been significantly enhanced. Furthermore, URI has also promoted the deep integration of the agricultural industrial chain. Under the background of URI, the agricultural industrial chain is no longer confined to the traditional planting and breeding links. It extends to the processing, circulation and sales of agricultural products. This deep integration provides a broader application space for ATI. ATI can thus exert greater efficiency.
5 Discussion
Against the backdrop of the agricultural industrial chain facing predicaments such as shortages of financial resources, risks of disruption, and insufficient resilience, the implementation of the DEPZ policy plays a significant role in the RAIC. While prior research has predominantly examined how DEPZ policies influence corporate innovation and sustainable urban development, this paper shifts focus to analyze their effect on RAIC. Based on the classification of geographical location and economic development level, heterogeneous inferences are made on the effects of policies in the pilot zones. Meanwhile, it reveals that the policies of this experimental zone mainly enhance the RAIC by alleviating financing constraints and technological innovation. Furthermore, from the perspective of URI, the moderating effects on the two intermediary paths of FC and ATI were discussed.
Studies indicate that DEPZ policies greatly benefit the RAIC. The study focuses on 30 Chinese provinces for the research domain. Based on the evaluation of RAIC data across provinces from 2012 to 2022, it can be found that the overall resilience level is relatively low, and the ability of each link to resist risks is relatively weak. However, after the implementation of the experimental zone policy, it has spurred the digital evolution in agriculture. Through the sharing of data elements and the application of digital technologies, it has reshaped the allocation model and utilization efficiency of production factors, thereby effectively enhancing the overall RAIC.
Subsequently, through the exploration of the mechanism test of the policies of the DEPZ on the RAIC in this paper, it is found that by alleviating FC and promoting ATI, the development of key links and the rational flow of factors have been facilitated, thereby enhancing the ability of the agricultural industrial chain to cope with various internal and external shocks. Therefore, this paper holds that in the policy implementation process of the DEPZ, alleviating FC and promoting ATI are important means to effectively enhance the RAIC.
Finally, from the perspective of URI, this paper discusses its moderating role in the two mediating paths of FC and ATI. It is found that the moderating effect of URI on FC is effective in the first half of the path but ineffective in the second half. Meanwhile, URI has a promoting effect on both the first and second halves of the ATI mediation process. Therefore, considering the intricate regulatory effects of URI across various stages and pathways, it is essential to capitalize on the developmental opportunities presented by URI, guaranteeing that URI genuinely enhances the efficiency of agricultural sector financing and supports the sustainable progress of agricultural technological innovation.
Of course, the research in this article still has certain limitations and is worthy of in-depth exploration in the future. In this paper, the influence of the DEPZ on the RAIC was analyzed with provincial data as the observation values. In future studies, attempts can be made to conduct the analysis at the urban or county level in order to examine the specific effects of the policies of the experimental zone at a more micro level. Secondly, this paper focuses on enhancing resilience and the application of technology, but neglects the long-term social impacts and structural changes that digital transformation may bring. In future research, the influence of digital transformation on rural livelihoods and agricultural structure can be given more attention.
6 Conclusions and policy implications
This paper theoretically explores the path through which the DEPZ policy enhances the RAIC. Utilizing panel data from 30 provinces between 2012 and 2022, a PSM-DID model was employed to empirically examine the policy's direct impact on agricultural industry chain resilience. Concurrently, drawing upon a mediation analysis framework and a mediation model incorporating moderating variables, the study thoroughly investigates the mediating mechanisms and moderating effects of the policy's impact. This comprehensive approach reveals the mechanisms by which the digital economy demonstration zone policy functions in strengthening agricultural industry chain resilience. In addition, this paper also analyzed the heterogeneity of the impact of DEPZ policies on RAIC from aspects such as geographical location, agricultural industrial agglomeration, agricultural labor productivity, and the intensity of policy implementation.
The research results show that:
(1) The DEPZ policy has a significant positive impact on the RAIC, and this conclusion still holds true after undergoing parallel trend tests, placebo tests and a series of robustness tests. Meanwhile, for different geographical locations and economic development levels, the policy impacts of the experimental zone vary.
(2) The results of heterogeneity analysis show that the DEPZ policy has a significant promoting effect on coastal areas, non-major grain-producing areas, and regions with high agricultural labor productivity. Moreover, the promoting effect of this policy on RAIC is more pronounced in regions with low agricultural industrial clusters and high policy implementation intensity.
(3) The DEPZ policy effectively strengthened the RAIC through measures such as improving agricultural financing and accelerating technological iteration and upgrading. Specifically, FC and ATI constitute the key mechanisms through which the DEPZ policy enhance RAIC.
(4) URI shows multidimensional moderating effects in the mediating role of FC and ATI. Specifically, URI has a significant positive moderating effect on the direct interaction path between DEPZ policy and RAIC; Its regulatory effect on FC is limited to the first half of the mediating path, while the second half shows regulatory failure. For the mediating variable ATI, URI plays a positive role in promoting both the first and second halves of the path.
Drawing from these findings, the following policy recommendations are proposed:
First, to effectively enhance RAIC, efforts should be made to strengthen the construction of key links by relying on digital technology. In terms of seed industry security, digital technology can help collect and analyze a large amount of agricultural data, thereby providing a scientific basis for breeding. In terms of cold chain logistics, the Internet of Things (iot) technology is utilized to monitor and control the temperature and humidity of goods in real time during transportation, thereby maintaining the freshness and quality of agricultural products. In the market channel link, e-commerce platforms are utilized to help agricultural products expand their sales channels, promote the products to a wider market, and increase sales opportunities and income.
Second, to effectively enhance RAIC, efforts should be made to promote cooperation between small-scale farmers and new types of agricultural business entities. At present, small-scale farmers are in a disadvantaged position in the agricultural industrial chain and find it difficult to fully share the policy dividends of the national digital economy innovation and development pilot zone. To truly benefit small-scale farmers, the government should encourage e-commerce platforms, agricultural cooperatives and other entities to establish close cooperative relationships with small-scale farmers, providing services such as market information, sales channels and technical training. This will help small-scale farmers better understand market demands, improve product sales efficiency and enhance production technology levels, thereby strengthening their competitiveness in the market.
Thirdly, the decentralized operation model of small-scale farmers in the upstream of the agricultural industrial chain leads to low efficiency in the use of funds, making it difficult to form large-scale investment and restricting the improvement of industrial resilience. To this end, it is necessary to cultivate large-scale business entities and open up a transformation path from financing to enhancing resilience. Specifically, efforts should be accelerated to promote the standardized transfer of rural land, support the development of new types of business entities such as farmers' cooperatives and family farms, in order to address the issue of scattered operations, promote large-scale and organized development, and enhance industrial resilience.
Fourth, differentiated policies should be implemented in accordance with the characteristics of different regions. For inland areas, priority should be given to improving the construction of digital infrastructure and creating a favorable environment for the application of data resources and digital technologies. For major grain-producing areas, the key lies in leveraging the power of digital technology to achieve precise monitoring and scientific management of all links from storage, processing, transportation to sales after grain harvest, thereby enhancing food security and the resilience of the industrial chain in these areas. For low-agricultural industrial clusters, efforts should be made to strengthen the construction of digital infrastructure, fully leverage the advantages of digital technology, effectively break through spatial limitations, and precisely make up for the shortcomings of the industrial chain. For regions with low labor productivity, priority should be given to strengthening investment in hardware such as farmland water conservancy and mechanization to enhance the level of large-scale operation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AB: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Conceptualization. MH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Data curation. QZ: Methodology, Data curation, Writing – original draft. HG: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the General Project of the National Social Science Foundation of China: “Research on the Collaborative Governance and Optimization Path of Urban Environment under the Constraint of Biased Emission Reduction Targets” (Grant No. 23BGL222).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ammar Zahid, R. M., Maqsood, U. S., Hussain, M., and Younas, M. W. (2025). Incentivizing digitalization: CEO compensation and digitalization in China's A-share corporate landscape. Tech. Soc. 82, 102888–102888. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2025.102888
Briguglio, L. (2004). “Economic vulnerability and resilience: concepts and measurements,” in Economic Vulnerability and Resilience of Small States, eds. L. Briguglio and E. J. Kisanga (Malta; London: Islands and Small States Institute; Commonwealth Secretariat).
Chao, X. J., Lian, Y. M., Yuan, R. J., and Chen, S. Y. (2024). Digital infrastructure construction and industrial chain resilience: empirical analysis based on industrial chain recovery capability data. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 41, 112–131. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.20240812.001
Chen, Y., Li, J., Zhang, Y., and Yang, F. (2025). Pollution and carbon reduction effects of the pilot policy on clean winter heating in Northern China: evidence from the county level. Chin. J. Popul. Res. Environ. 23, 85–95. doi: 10.1016/j.cjpre.2025.01.008
Cheng, D. N., Wang, H., and Huang, Y. (2017). Transformation and upgrading of agricultural industry chain in our country under the background of “Internet + agriculture”. Rural Econ. 52–57. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjsnDRJQr1D9Ur7id_AMmsKsB4TSE2HJjGSyfZPrhXqWea9N2pgH_xP6pI_FPupQeDmvAd-j1xXtrihO0vsHCboQuxttUOZvU-0-JSV9JBzJQQZ1iQw2inf6I22nOQSU7wzUsqcW2rUyHZc9viEn7PjU4iu2TacyQwANTd_S5pco5Q==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Cheng, X. J., and Wang, M. (2024). On consumer finance and rural revitalization under the background of financial technology. Lanzhou Acad. J. 131–145. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjul7wd8Tp_oQfeedGWyjzx64GGDLE84bv_mIp88OsZYfpwPuh2hNKE0lR4juh3lvTwiKz_3s_Wxwr0C11u2CrZ1i3NGfgcCr4KwAD1I93E3txpcrBGYQYPacZ1a9pYOF9fn8DMdNyBz8GM7OahMlY9XuYq_TLj_dBi23ibcJHY1Og==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Dong, Y. N., Gu, Y., and Yang, K. Z. (2021). agricultural products brands, market integration and agricultural income growth. J. Cap. Univ. Econ. Bus. 23, 70–80. doi: 10.13504/j.cnki.issn1008-2700.2021.01.007
Du, G., and Li, W. D. (2022). Does innovative city building promote green logistics efficiency? Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment with 285 cities. Energy Econ. 114:106320. doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2022.106320
Du, J. J., Zhang, J. W., and Shao, S. (2017). Formation and development of China's agricultural industry agglomeration under the background of supply side reform. Finan. Trade Res. 28, 33–46+99. doi: 10.19337/j.cnki.34-1093/f.2017.05.004
Feng, H., and Wang, J. S. (2021). Evolution trend and reform and innovation of agricultural industry chain organization. Reform Econ. Syst. 74–80. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjvoZDhuc6lpi9gmiT8Kufqf6kZxEMlXKpf7ygLJD2UXk7cBOx7BOIJcPFdoCmRSaBK1mzDCvbRlpbO29GWdx_d7E6qoOIlFXQVjsXGtcz00LKvDNFiCBGRJg1ulZMxGJ8CEX0dDf7rHno8HkboOJyNiqm177CReItGWwNDmj6IoEA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Gao, G. X. (2024). Measurement of the construction level of digital countryside in China, its dynamic evolution and convergence characteristics. Statis Dec. 40, 119–124. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2024.20.020
Gao, X., and Gao, R. (2024). A study of the impact of digital financial inclusion on the resilience of the agricultural chain. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1448550. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1448550
Guo, F., Yang, C., and Ren, Y. (2025). How does the digital economy innovation and development pilot zone affect urban carbon emissions—Based on the perspective of digital technology innovation and industrial structure upgrading. Jianghan Tribune 46–57. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjs181_tEFmg31I5CkaXX4t3vcIwzRnKs7008I1gykRfbl1bX9sZEF1IdzY0wdeVBIyAYrdQcVzRq6L94WR3ed_a9E9ty-3H8Sd0NaJw1FC89H4WcCKMz1o_682YrlE73s1CFWzIjoQvGOOvpDOF1NCIXFN2X9szFWe6FqVskeBpTg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Hao, A. M., and Tan, J. Y. (2023). Empowering agricultural resilience by rural industrial integration: influence mechanism and effect analysis. J. Agrotech. Econ. 88–107. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.20220418.002
Hao, A. M., Xie, M. H., and Liu, Y. T. (2024). Resilience level measurement and spatio-temporal evolution of agricultural industry chain. Statis. Dec. 40, 95–100. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2024.16.017
He, Y. L., and Yang, S. C. (2021). Study on ductile forging of agricultural industry chain under the “Dual Circulation.” Iss. Agric. Econ. 78–89. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.20210714.001
Li, H. L., Zhang, J. B., Luo, S. X., and He, K. (2021). Impact and mechanism of agricultural technology innovation on agricultural development quality-empirical evidence from the spatial perspective. RandD Manag. 33, 1–15. doi: 10.13581/j.cnki.rdm.20201077
Li, J., Mai, S., and Liu, L. (2024). The innovation effect of the establishment of national digital economy innovation and development pilot zones: a study from the dual perspectives of supply side and demand side. Sci. Tech. Progress Policy 41, 45–56. doi: 10.6049/kjjbydc.2022120057
Li, J. C. (2024). The effect of industrial intelligence on the enhancement of industrial chain resilience: theoretical mechanisms and empirical evidence. Reform 80–94. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjvE4nUhaV7rvb1n7FGDb4bjVpcXVN6gM7VpLAS5rnr2-zxzMZCRn2LlbUZyXooZsEwr9Ayp8_qZj2z8I4dej9WI7hGBm5vpp4oI2gMW273WRDesjsx0lTBaWHaHEh8NFu3ZpWLTIliEbxbKfmjjAT2UebIDNI7umyUbWPIM0PUKOg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Li, J. S., and Wan, Q. (2025). Influence of agricultural technological innovation on agricultural economic resilience: based on the threshold effect analysis of financial policy supporting agriculture. J. Agrotech. Econ. 4–17. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.20250103.001
Li, J. Y. (2009). The connotation, type and regional economic effect of agricultural industry chain. Theory and Reform 143–146. doi: 10.13553/j.cnki.llygg.2009.05.033
Li, X., Zhang, S., Ren, R., and Wang, Y. (2024). Comprehensive evaluation and spatial-temporal evolution characteristics of urban resilience in Chengdu-Chongqing Economic Circle. Chin. J. Populat. Res. Environ. 22, 58–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cjpre.2024.03.007
Luo, Z. H., and Wang, Y. M. (2024). The influence and mechanism of agricultural industry chain extension on rural economic development. Statis. Dec. 40, 117–121. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2024.24.020
Lv, Y. H., Yuan, J. W., Zhang, S. Q., and Shi, J. N. (2025). Agricultural industry chain resilience, regional differences and dynamic evolution. Statis. Dec. 41, 87–93. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2025.03.015
Meng, W. F., and Ren, B. Y. (2023). Influence mechanism and spatial effect of digital finance on rural industrial integration. J. Southwest Minzu Univ. 44, 96–106. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjvxKeLAcDXrVzE_AbaZPyFcPlfV2zpYg4SJw_QbUyta_qD2EqdQCX1ZPaxo6FcxAN4wCD0xQrvGPr5pTC2lK97epBIfOrVu0hEtYCZ1uEqnJ1rFlHhNsleN7oMrw-RovLpOPhuTgJx7cC9MuJ-0k-BRrsyakjU8DJMyuSMViTkfJg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Nie, S. C., Wang, G. X., and Zhong, F. Y. (2025). New infrastructure driving agricultural economic resilience: theoretical mechanism and empirical test. J. Agric. Forest. Econ. Manag. 24, 65–74. doi: 10.16195/j.cnki.cn36-1328/f.2025.01.07
Niu, K., and Xu, H. (2024). Does urban–rural integration reduce rural poverty? Agribusiness 1–16. doi: 10.1002/agr.21935
Shan, P. X., Chen, J., and He, E. M. (2025). Digital inclusive finance, extension of the agricultural industry chain and increase farmer' income. Chin. J. Agric. Res. Reg. Plann. 1–14. Available online at: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.3513.s.20250328.1533.022
Song, H., Chen, F., Bao, D., and Chen, H. H. (2022). Fintech's assistance in the Innovation and Development of Supply Chain Finance. Exploration of Financial Theory. 41–48. doi: 10.16620/j.cnki.jrjy.2022.04.004
Sun, J. G., and Sun, Y. (2022). Does FinTech promote rural industry revitalization in pursuing the goal of common prosperity. Collect. Essays Fin. Econ. 51–60. doi: 10.13762/j.cnki.cjlc.2022.11.009
Tao, C. Q., and Ding, Y. (2022). How data elements become innovation dividends?–Evidence from human capital matching. Chin. Soft Sci. 45–56. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjtQ7-QyeGbGHE6_1dnzM1u_ureRj7bjRHu8wpTTTDC_E8Y3jsQvjxocqmGPQCcDMUNr1JcENaYiSMpdRdqF_rQGxJRYWmwq6cZg_9-1oMPbfStBGdbzLiZ5UOziOkn_yWJG520ellxU0Qhk4Hl3blfIjROlh5edvzx6Ae5rDbtkgw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Wang, L. S., Fu, X. H., Wang, Z. H., and Yang, J. X. (2025). Study on the spatial-temporal evolution and influencing factors of rural digital economy in China. Agric. Econ. Manag. 27–39. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjsr64oYeQ4R7-pvF0eFFBeYAa3tNeZFH5eQDCp4SXBc6rQD2AqCSs3UL7aqkjh0yFpp6U5d2HN4AVGwfiKdVLlRlYdWXEu9aFLNQbCJbHXipAQx5LF7Iqt08hRZ_kEZJxtNHwKgBvtKWEypr2mROSjv6jo2BnbCwcQkg84b84w0BQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Wang, P., Luo, F., and Fang, Y. (2022). Research on resilience governance models of rural biomass energy eco-industrial chain. Energy Rep. 8, 1508–1517. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2022.02.041
Wang, S. S., Gao, M. Y., and Lü, J. (2025). Digital economy, industrial integration and agricultural industrial chain resilience: index measurement and effect test. Statis. Dec. 41,11–16. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2025.02.002
Wang, W. C., and Zhang, S. F. (2024). An empirical test of modernization of agricultural industry chain driven by digital economy. Statis. Dec-Making 40, 22–27. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2024.05.004
Wang, W. J., and Qian, X. X. (2025). Research on the measurement of industrial chain resilience in china: based on the perspective of external shock risk and efficiency drive. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 42, 115–135. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.20250402.004
Wang, W. X., Yin, X. K., Wang, C. G., and Fang, S. L. (2024). Farmland property rights stability and low-carbon agricultural development: evidence from a new-round land certification in China. Chin. Land Sci. 38, 49–59+71. doi: 10.11994/zgtdkx.20240723.143649
Wei, B. H., and Luo, M. Z. (2023). The effect of digital financial inclusion on agricultural services: empirical evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. Finan. Econ. Res. 38, 61–74. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjtw6lsSqLqBj3j5oCAMAmzzp10A2FEZ-YvEHTHJAPA22ugMRTrXL0E5keYp0bK89SG0rb4Bs37cg_-orLoxqwawj-EbUjs30f1HcAb44xNUWD5PNn0auNlKhUPLkFLQ3nJlgk6YxMJFaSPa4L25ZHxtAkniE5nsY2hVrwwhdyU4xg==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Wen, Z. L., and Ye, B. J. (2014). Different methods for testing moderated mediation models: competitors or backups? Acta Psychol. Sin. 46, 714–726.
Xia, W., Zhang, J., and Cao, Z. (2024). Point “count” becomes “gold”: the effectiveness test of the National Digital Economy Innovation and Development Pilot Zone in empowering new quality productivity. Journal of Chongqing University (Social Science Edition). doi: 10.11835/j.issn.1008-5831.jg.2024.11.008
Xiao, X. Z., and Li, S. L. (2022). Resilience of industrial chain under the great change: generation logic, practical concerns and policy orientation. Reform 1–14. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjuobN0OqAZBLM5UXtGvTcK3O5qztBzBIeHdwTOUn-9DJwzGBTT66CRL8TZKG9stAHOvau-wZgUMIlpjQnbZjD98p19iBSvSdjJywyZDgbtCZ1kSrFr0IdOB0tnBZWc-sjh0mNDcWAGsxz6kzDlQB_3ervgrEZhwiK1U5ma7TRZaEA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CH
Yang, C. Y., Li, H. Y., and Sun, Z. Y. (2024).The impact of agricultural specialization agglomeration on agricultural carbon productivity from the perspective of technological innovation: an analysis based on mediating effect and threshold effect. Ecol. Econ. 40, 97–103+111. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjsImjNqdG0cuVOEVIWigHPCVBp_uX3rhLie2OuTQMmcuvR0HyvPN2pdOIqieGiPqAG55EXUpGh27_jxisBARmAmAjz5Zp_1P8bTCJ37yuejxhzyS_i1p7h1j70cs001sPTrYFNTFtkgM68NiIqCIcTQwPNHaffeGvhPYcS8GzyJIA==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Yang, Q., Wang, J., Li, C., and Liu, X. (2019). The spatial differentiation of agricultural green total factor productivity and its driving factor recognition in China. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 36, 21–37. doi: 10.13653/j.cnki.jqte.2019.10.002
Yang, Y., and Liu, X. (2024). Can the Initiative of Digital China Promote Entrepreneurial Activity of Cities-Empirical Evidence Based on the National Pilot Zone for Innovative development of Digital Economy. The World of Survey and Research. 74–85. doi: 10.13778/j.cnki.11-3705/c.2024.10.007
Yu, X., Su, Q., Gong, Y. Y., and Li, D. M. (2021). Research on the spatial effect of agricultural product quality certification on agricultural economic growth. Sci. Technol. Manage. Res. 41, 93–99.
Zeng, H. (2023). Does the policy promote the digital transformation of enterprises? Quasi natural experiment based on national digital economy innovation and development pilot area. Collect. Essays Finan. Econ. 3–13. doi: 10.13762/j.cnki.cjlc.20221009.001
Zeng, X. W., Zhang, X. Q., Li, Z. S., Yang, Y. M., and Yang, W. T. (2025). Spatial effect of digital inclusive finance on the resilience of agricultural industry chain. Econ. Geograph. 45, 183–191. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2025.02.018
Zhang, M., and Zhang, H. (2024). Effects of black soil protection policy instruments on agricultural green total factor productivity and its spatial differences. Econ. Geograph. 44, 165–174. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2024.07.017
Zhang, Q., Li, Y., Li, M. L., and Shan, N. N. (2025). Research on the impact of digital rural construction on the resilience of agricultural industry Chain. J. Southw. Univ. 47, 129–140.
Zhang, W., Li, H. Y., and Zhang, T. (2023). Measuring the resilience of china's manufacturing industry chain and its spatial-temporal differentiation. Econ. Geograph. 43, 134–143. doi: 10.15957/j.cnki.jjdl.2023.04.014
Zhang, Y. M., and Long, W. J. (2023). Challenges and countermeasures for improving the resilience of agricultural industry chain under the great food outlook. Acad. J. Zhongzhou 54–61. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjvgX3ECxuUzLNGZiirMrio63g4LaatmqyIjjG0CMbexnFSiEyzbmtUJtFlEkK7VTqxzruWspuMNZUmB0a_hFlL3TyXo1kfOlmfoOM3-PwUyspOKo9hzXGGhbo9c9z6IiID3GzpI8dLt-VRXjM_YBA93GY91cQyCrNE6-0Q1OmPQFQ==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Zhao, S., Zhang, L. Q., An, H. Y., Peng, L., Zhou, H. Y., and Hu, F. (2023). Has China's low-carbon strategy pushed forward the digital transformation of manufacturing enterprises? Evidence from the low-carbon city pilot policy. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 102:107184. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2023.107184
Zhao, X. F., and Wang, Y. P. (2004). The difference and connection of agricultural industry chain, industrialization and industrial system. Rural Econ. 44–45. Available online at: https://knshtbprolcnkihtbprolnet-s.libvpn.zuel.edu.cn/kcms2/article/abstract?v=hx6LgM6qJjsH0fPjXhmavnqknFT-0HIuyUThM0D8JIci7SoiFi6MRlrIu2dFa80hWf3qJgxTGUlnmdzichtaYpDErulZ6itsjIFttTtHjg83qkBCVt3HNZr7pxxVWCAEj36k0wK6EFSFLseT4DCgvknAi0ivXd4bgMjP3D5M37rIumdhTtKXKw==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Zhao, Y., Ye, S. Q., Yang, C. H., and Hong, Y. M. (2025). Measurement, connectedness and attribution of China's industrial chain resilience from the perspective of big Data. China Industr. Econ. 61–79. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2025.02.008
Zhou, J., Chen, H., Bai, Q., Liu, L., Li, G., and Shen, Q. (2023). Can the integration of rural industries help strengthen China's agricultural economic resilience? Agriculture 13:1813. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13091813
Keywords: DEPZ policy, RAIC, digital economy, industrial policy, PSM-DID
Citation: Bao A, He M, Zhou Q and Gao H (2025) The impact of industrial policies oriented toward the digital economy on the resilience of the agricultural industrial chain. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1634474. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1634474
Received: 24 May 2025; Accepted: 23 July 2025;
Published: 01 September 2025.
Edited by:
Dingde Xu, Sichuan Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ismail Suardi Wekke, Institut Agama Islam Negeri Sorong, IndonesiaMaogang Gong, Shandong University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Bao, He, Zhou and Gao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meixuan He, MTQxNjkzNzUwN0BxcS5jb20=
 Aruna Bao
Aruna Bao Meixuan He*
Meixuan He* Quan Zhou
Quan Zhou