- 1Department of Agriculture, University of Zululand, KwaDlangezwa, South Africa
- 2Discipline of Agricultural Economics, University of KwaZulu-Natal, Pietermaritzburg, South Africa
- 3Department of Agricultural Economics and Animal Science, University of Limpopo (Turfloop Campus), Sovenga, South Africa
Livestock farming is essential for achieving sustainable livelihoods in Africa, especially among smallholder farmers. However, these farmers face challenges like limited resources, market access, and support services. Moreover, there is insufficient clarity pertaining to the factors influencing smallholder farmers' management decisions to mitigate risks. Therefore, this study aims to investigate the factors that have an impact on the livestock management practices smallholder farmers use in the Eastern Cape. This study employed a descriptive approach following a cross-sectional design using a multi-stratified sampling procedure to randomly select 160 smallholder livestock farmers to participate in this study. Findings reveal that livestock farming in the province is becoming evenly balanced, with more women participating, though challenges still prevail. Currently, middle-aged farmers lead production, but growing youth involvement offers hope for the future. Household factors like marital status, education, and employment influence the farmer's resilience. Livestock play vital roles in smallholder households, with cattle often kept as long-term assets, providing security and savings. Sheep and goats help balance income and nutrition, while pigs and chickens offer quick sales and food for families. However, environmental risks and management challenges remain. Most farmers rely on free-range grazing due to limited access to proper feeds, restricting livestock growth. Extension services and vaccination programs are limited, thus reducing animal health support. Farmers face risks from pests and diseases, market fluctuations, and a lack of credit. More frequent extension visits and targeted policies can assist farmers in maintaining healthy livestock and reducing risks, building a sustainable future for smallholder farmers. The study concludes that strengthening household resilience through education, gender inclusivity and improved access to credit, markets, and extension services is essential. These findings provide critical policy insights for promoting sustainable livestock systems and enhancing smallholder livelihoods.
1 Introduction
Livestock systems form an indispensable pillar of global food systems, playing a vital role in enhancing food and nutrition security, sustaining rural livelihoods, and supporting economic stability across both developed and developing regions. Beyond their contribution to agricultural GDP, livestock systems underpin human survival by providing diverse products such as meat, milk, eggs, hides, and draft power, while generating employment opportunities along complex value chains (Munaf et al., 2024; Alders et al., 2021). Smallholder livestock farming, in particular, remains central to global food security, local economies, and rural wellbeing. It contributes significantly to household nutrition and income generation by supplying essential animal-based foods and generating off-farm income through sales and labor. Globally, livestock production accounts for approximately 17% of daily caloric intake and 33% of global protein consumption, while directly supporting the livelihoods of nearly one billion people living in poverty (Rojas-Downing et al., 2017; Maltou and Bahta, 2019). Beyond its nutritional and economic value, livestock serves as a multifunctional asset, functioning as a store of wealth, a form of insurance, and a source of social and cultural capital, especially in rural and traditional societies. For smallholder and subsistence farmers, livestock ownership enhances resilience by providing a buffer against seasonal income fluctuations, crop failures, and market uncertainties.
Livestock systems contribute to food and nutrition security both directly and indirectly. Directly, livestock products supply essential micronutrients such as proteins, iron, and vitamin B12, which are often deficient in plant-based diets. Indirectly, livestock improves crop productivity by providing manure that enhances soil fertility, reduces dependence on chemical fertilizers, and sustains long-term soil health [Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO), 2012]. Moreover, livestock contributes to household labor productivity by balancing workloads across seasons, genders, and age groups while ensuring a steady income flow throughout the year (Bwalya et al., 2024). The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) estimates that over 1.3 billion people are engaged in livestock and poultry production worldwide, with more than 600 million smallholders depending directly on livestock for food, income, and social wellbeing (Hashem et al., 2023; Binns et al., 2021). However, the sustainability of these systems faces increasing pressure from multiple challenges, including land degradation, feed scarcity, animal diseases, and climate change. Such pressures threaten not only livestock productivity but also the broader rural livelihoods that depend on them. Strengthening livestock systems through improved management and proactive risk mitigation is therefore essential for enhancing global food system resilience and achieving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 1, 2, and 13, eradicating poverty, ending hunger, and addressing climate action.
In Africa, livestock production forms a cornerstone of agricultural development and rural economies. The continent hosts approximately 356 million cattle, 384 million sheep, 438 million goats, 40 million pigs, 2 billion poultry, and over 30 million camels (Panel, 2020). This diversity reflects the adaptability of livestock systems to varied ecological zones, from arid pastoral areas to intensive mixed crop-livestock systems (Erdaw, 2023). Livestock contributes nearly 35% of the agricultural GDP in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) and accounts for about 14% of global livestock resources (De Lange et al., 2025). It is estimated that smallholder farmers contribute up to 35% of the world's food and account for about 80% of food produced in Sub-Saharan Africa (Knight, 2022). Beyond economic contributions, livestock plays critical socio-cultural roles such as serving as dowries, symbols of wealth, and social security for households. Animal-sourced foods (such as meat, milk, and eggs) provide vital nutrients that are often unavailable or insufficient in crop-based diets, contributing to the reduction of malnutrition and stunting in children (Akasha et al., 2021; Hossain et al., 2021). Hence, livestock farming is deeply woven into the socio-economic and cultural fabric of African societies, acting as both a livelihood strategy and a safety net.
Despite its importance, livestock production in SSA remains largely underdeveloped. The sector is characterized by low productivity due to inadequate access to quality feed, veterinary services, improved breeds, and modern production technologies (Hashem et al., 2023). Moreover, climatic stressors such as droughts, floods, and temperature extremes have aggravated feed and water shortages, increased disease prevalence, and reduced overall productivity (Tirivanhu et al., 2023). Land degradation poses a further risk: approximately 60% of arable land in SSA is degraded, resulting in an estimated annual loss of USD 68 billion in agricultural productivity (Abera et al., 2020). Persistent challenges (ranging from poor infrastructure and limited market access to weak institutional support) have constrained the ability of smallholder farmers to enhance productivity and income. Without adequate risk management strategies, these vulnerabilities continue to perpetuate cycles of poverty and food insecurity. As a result, identifying the determinants of livestock management and developing effective risk mitigation strategies has become an urgent research and policy priority across SSA.
In South Africa, livestock farming constitutes the largest and most significant subsector of agriculture, contributing approximately 48% to total agricultural output and occupying over 53% of agricultural land (Blignaut et al., 2014; Bahta, 2021). The sector employs nearly 500,000 workers and supports millions indirectly through value chains involving feed manufacturing, transportation, processing, and marketing (Ali et al., 2025). Smallholder livestock farming plays a crucial role in enhancing the livelihoods of rural communities in South Africa. It not only provides a vital source of food but also holds significant potential to strengthen household economies. For resource-poor farmers, livestock production serves multiple purposes, addressing various livelihood needs and contributing to both income generation and food security (Myeki and Bahta, 2021). Recognized as a key driver for poverty alleviation, smallholder agriculture, including the livestock sector, remains essential for reducing household food insecurity and promoting resilient rural livelihoods in South Africa (Cheteni and Mokhele, 2019).
Livestock contributes to both national food security and rural economic development by providing meat, milk, hides, and draft power. According to Manyike et al. (2025), livestock farming not only contributes to income and food security but also functions as a form of savings and insurance, carries cultural importance, and provides a key adaptation strategy during periods of drought. Smallholder livestock farmers (who typically operate on plots of less than 10 hectares and rely primarily on family labor) play an especially important role in sustaining rural livelihoods. In South Africa, smallholders are largely concentrated in provinces such as the Eastern Cape, Limpopo, and KwaZulu-Natal, where livestock serves not only as a source of food and income but also as a cultural asset that defines social identity and family heritage. Despite its central role, the smallholder livestock sector in South Africa faces numerous challenges that hinder its full potential. These include limited access to quality breeding stock, inadequate extension and veterinary services, insufficient feed resources, and poor infrastructure. The smallholder sector is dominated by approximately four million black farmers located in former homeland areas, which are often characterized by degraded land, low rainfall, and limited market access (Pienaar and Traub, 2015; Carelsen et al., 2021). Furthermore, climate change has intensified the vulnerability of these systems through increased frequency of droughts and fluctuating rainfall patterns, which negatively affect pasture growth and water availability. The sustainability of the livestock sector, therefore, depends on the extent to which smallholder farmers can adopt adaptive management practices and implement effective risk mitigation measures that ensure resilience to environmental and economic shocks.
The adoption of improved livestock management practices is shaped by a combination of socio-economic, institutional, and environmental factors. Education level, farming experience, land tenure security, access to credit, and availability of extension services are key determinants influencing the adoption of sustainable practices (Danso-Abbeam et al., 2024). Similarly, environmental conditions such as pasture availability, water resources, and climatic variability influence farmers' day-to-day management decisions. Effective risk mitigation strategies, including herd diversification, supplemental feeding, vaccination, drought preparedness, and community-based insurance schemes, are essential for minimizing losses associated with disease, predation, and climatic extremes (Hänke and Barkmann, 2017). However, adoption of formal risk management strategies remains low among smallholders due to financial limitations, limited awareness, and institutional weaknesses. Understanding these determinants is crucial for designing context-specific interventions that enhance livestock resilience and household welfare.
In the Eastern Cape Province (ECP), livestock farming forms an integral part of household livelihoods and local economies. The province is predominantly rural, with agriculture serving as a key livelihood source for the majority of its population. However, the ECP faces some of the most pressing agricultural challenges in South Africa, including land degradation, water scarcity, poor infrastructure, and limited access to extension and veterinary services (Bahta, 2021). Smallholder farmers in the province depend heavily on livestock for food, income, and social capital, yet their production systems remain highly vulnerable to climatic shocks and market fluctuations. Despite the critical role of livestock in sustaining rural livelihoods, there remains limited empirical evidence on the determinants of livestock management and the risk mitigation strategies employed by smallholder farmers in the ECP. Existing studies have largely focused on livestock production systems or climate adaptation in isolation, often overlooking the socio-economic and institutional determinants that influence farmers' management decisions (Erdaw, 2023; Akasha et al., 2021).
This knowledge gap limits the ability of policymakers and development practitioners to design effective interventions aimed at improving livestock productivity, enhancing resilience, and supporting sustainable rural development. The persistent challenges faced by smallholder farmers, including poor access to markets, inadequate agricultural inputs, insufficient extension support, and weak institutional linkages, continue to hinder progress toward poverty reduction and food security goals (Chisasa, 2019; Otekunrin et al., 2019; Gwiriri et al., 2021; Mokgomo et al., 2022). Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of the factors that shape livestock management decisions and the strategies farmers employ to mitigate production and livelihood risks. This study, therefore, seeks to examine the determinants and risk mitigation practices of smallholder livestock farmers in the Eastern Cape Province. By integrating socio-economic, environmental, and institutional dimensions, the research aims to identify the key drivers influencing livestock management decisions and assess the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies adopted by farmers. The findings will provide evidence-based insights to inform policy formulation, strengthen agricultural extension programs, and support targeted interventions that promote sustainable livestock management. Ultimately, the study contributes to broader development objectives of improving rural livelihoods, enhancing food and nutrition security, and fostering resilience to climate change in South Africa.
2 Conceptual framework
This study employed a conceptual framework to generalize the link between its different factors. A conceptual framework is essentially a structured way of organizing ideas, theories, assumptions, and expectations that guide a study (Aliu et al., 2021). It can take the form of a written explanation or a visual diagram that highlights the main concepts, variables, and how they are thought to be connected. In this study, the conceptual diagram presented in Figure 1 depicts the link between the main concepts of this study, which are sources of risks, farming constraints, smallholder farmer perceptions, adoption of mitigation strategies, and the effects it has on production. Smallholder farmers' perceptions are driven by various sources of risks that come with various farming constraints. In this case, farmer perceptions rely on the impact of these constraints in all stages of the farming sector. For instance, in the production stage, farmers may face livestock production failure due to a lack of knowledge, essential farming resources, and the outbreak of livestock diseases. The experience of facing such constraints will drive smallholder farmers to come up with management strategies to reduce the vulnerability to risks. Some of the mitigation strategies may include farm diversification, the use of vaccines to treat diseases, as employing intensive and semi-intensive practices. The adoption of various risk mitigation strategies could yield better returns for smallholder farmers. In that way, their production will be high, which will generate their income and promote household consumption (meat, milk, and eggs). Therefore, smallholder farmer livelihoods can be sustained and improved.
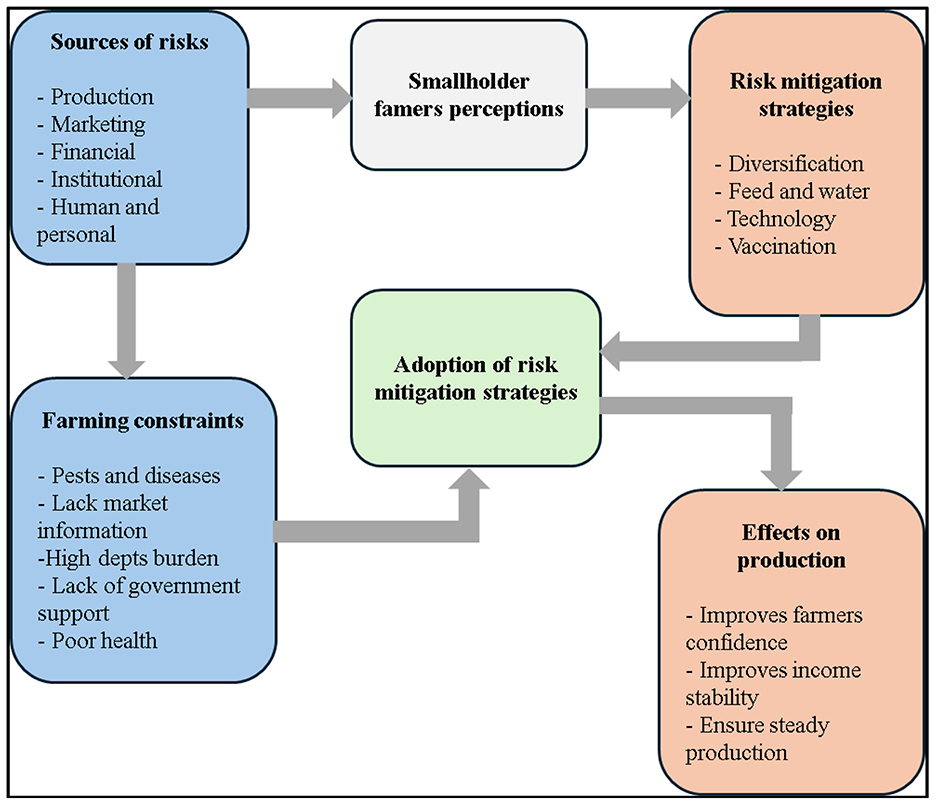
Figure 1. Conceptual framework for enhancing livestock management and risk mitigation among smallholder farmers.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Description of the study area
The study was conducted in the Eastern Cape Province (ECP) in South Africa. The ECP is one of the largest provinces (first being Northern Cape Province, then ECP) and is located in the south-central part of South Africa. ECP has 168,966 km2, which makes the province the second largest after the Northern Cape Province of South Africa. The province combined areas from the former Xhosa homelands of the Transkei and Ciskei, together with what was previously part of the Cape Province. The province is dominated by Xhosa tribes (which include AmaMpondo, AbaThembu, AmaMpondomise, AmaHlubi, AmaBhaca, AmaXesibe, AmaBomvana). The population of Eastern Cape Province is 7,230,000, of whom 86.3% are Black, 8.3% are Coloreds, 4.7% are White, and 0.4% are Indian/Asian.
The Eastern Cape becomes gradually wetter from west to east. The west of ECP is mostly the semi-arid Karoo, except in the far south, which is temperate rainforest in the Tsitsikamma region. The coast is generally rocky with scattered beaches. Most of the province is hilly to very mountainous, while the east from East London and Komani toward the KwaZulu-Natal border (a region known previously as Transkei) is luxurious grassland on rolling hills, scattered by deep valleys with alternating forest. The climate of the province is highly varied. The west is dry with thin rain during winter or summer, with frosty winters and hot summers. The area from Tsitsikamma to Makhanda receives more rainfall, which is also relatively evenly dispersed, and temperatures are mild. Further east, rainfall becomes more abundant and humidity increases, becoming more subtropical along the coast with summer rainfall. The interior can become very cold in winter, with heavy snowfalls occasionally occurring in the mountains. This makes the landscape of the province diverse and much productive land in the Eastern Cape, and agriculture remains important as people generate livelihoods from as the province is very poor and has a high unemployment rate (60%) and high food insecurity (78%) (Mdoda and Obi, 2019; Mdoda et al., 2024). The province practices citrus, crop, and vegetable farming, and livestock farming, and subsistence agriculture is the most dominant in the province. When it comes to livestock production, the province is mainly involved in the production of cattle, goats, and sheep, which forms the backbone of the rural livelihoods. These animals provide meat, milk, income, and social value, simultaneously serving as a form of financial security for smallholder farmers. The socio-economic importance of livestock in the ECP cannot be overstated as directly contributes toward livelihood. Hence the study investigates the effects of risk behavior in livestock farmers situated within the ECP. This area is suitable due to its large smallholder livestock production, climatic vulnerability and relevance to SA's rural development policies aimed at improving resilience and food security. Figure 2 illustrates the study sites.
Figure 2. Map showing study sites. Source: University of Fort Hare Department of Geography and Information Systems (2025).
3.2 Sampling procedure, frame, and sample size
The study was conducted in the Eastern Cape Province, adopting a descriptive research approach and cross-sectional research design. The study made use of a multi-stratified sampling procedure with specifically 3 stages. The unit of analysis for this study was livestock farmers. The first stage was selecting district municipalities in the province that have the potential for livestock farming and contribute to the livelihoods of households in the province. These districts were OR Tambo, Chris Hani, Amatole, and Alfred Ndzo District Municipalities. The second stage was selecting two local municipalities and wards where the study was conducted within the district. The stratified sampling was also implemented in this stage, where farmers were stratified into the type of farming they practice, which includes crops and livestock farming, with the livestock being the focal point of this study. In the last stage, random sampling was used to select the desired sample size of livestock farmers and to reduce bias.
In this case, smallholder farmers were selected based on the following criteria: (i) they owned or managed livestock as a primary or secondary livelihood activity, (ii) they operated on small plots of land (typically less than 10 hectares) using family labor and traditional production methods, and (iii) they derived part of their household income or food security directly from livestock production. Importantly, respondents were not chosen because they were already facing financial crises or risk mitigation problems; rather, they were purposively sampled within selected districts known for active livestock farming. Within these districts, random sampling ensured representation of households across different socio-economic and demographic categories, without bias toward only those experiencing problems. This approach allowed the study to capture a realistic picture of smallholder livestock practices, the risks they face, and the mitigation strategies they employ under varying conditions. Also, this ensured that the data collected reflected the experiences, perceptions and management practices of active livestock farmers in the study area.
3.2.1 Sample size
To gather the appropriate sample size, the Taro Yamane formula was used. This sample size calculation was adopted from a study by Nontu et al. (2024). This sampling technique is mathematically expressed as follows (Equation 1):
Where n = sample size (unknown); z = the z-value of a given confidence level (95% for this study, which is a z-value of 1.96); N = size of the total population of Eastern Cape (7 230 000); p = sample proportion (0.5); q = 1–p, which would be the remaining sample proportion (0.5); e = margin of error (7.75% which is 0.0775). Substituting the values in Equation 1 will then yield a sample size of 160, as expressed in Equation 2:
n = 160
Using the Taro Yamane sample size technique, the required sample size for the study was determined to be 160 smallholder livestock farmers.
3.2.2 Power analysis
To analyse the power of the sample size, the Priori Power Analysis developed by Cohen in 1988 is used (Sommet et al., 2023). The estimated rate of non-response in the Eastern Cape Province is 22.50%. The test is one-tailed since this study consists of a known parameter and follows a probability sampling approach, increasing the data's feasibility. Given the following (Equation 3):
α error probability (margin of error) = 0.0775; sample size (n) = 160; and estimated population parameter (N) = 7,230,000. Therefore,
FPC =
FPC = 0.999
AES = 0.775 × 0.999
AES = 0.775
Since Z is one-tailed, Zα = 1.645
To gain 95% desired power, Zβ = 1.645
Since Zα = Zβ, the distribution is non-central
NCP = 0.775 ×
NCP = 9.80
P = 1 – Φ (1.645 – 9.80)
P = 0.99
Given the power analysis result (P = 0.99), this means that the study has a 99% chance of detecting an effect of size d = 0.775 (or larger) at the 5% significance level.
3.3 Data collection
The study obtained ethical clearance from the institution before the commencement of data collection in the selected study areas. It adopted primary and secondary data as tools for data collection. The primary data was collected using a survey and face-to-face interviews administered by the researchers and enumerators in all district municipalities selected for this study. The survey made use of structured questionnaires for the purpose of data collection in the study. A pre-test of 10% of the sample size was carried out to standardize the survey instruments, check the relevance of questions, and time taken to respond to a platform of training enumerators, as well as the study. Enumerators asked the questions to the farmers in IsiXhosa, the home language of the province. Questionnaires were translated into IsiXhosa and then retranslated back to English to review and verify the meaning. Within districts and villages, enumerators utilized their contacts and used agricultural extensions to organize local farmers for the visits. Farmers were interviewed on a voluntary basis and screened on the condition that they practice livestock farming. While secondary data was collected from published peer-reviewed articles, books, and Departmental gazettes. The collected data were farmers' profiles, farming activities practices, perception and effect of risk in their farming, challenges they faced, and strategies adopted to minimize risk in their farming practices. Before asking questions, participants were provided an informed consent form to sign in agreement with the research conduct. Questionnaire-based face-to-face interviews were agreed upon with the heads of the farmers, but in cases where they were absent at the time of the interview, data were obtained from other senior farm members (managers or acting head of Departments).
3.4 Data analysis
Data quality was evaluated in terms of accuracy, completeness, and missing information. The data collected from livestock farmers in the study area were coded and entered into Excel for the purpose of analysis. The data was transferred from Excel to STATA 15 for analysis. The study adopted and used three types of analytical tools for analysis: Descriptive, Binary logistic, and Propensity score. Specifically, the binary logistic regression was used to estimate factors influencing the risk behavior of livestock farmers, while Propensity score matching estimated the effects of risk behavior on livestock farming.
3.4.1 Descriptive statistics
Descriptive statistics were used to estimate the profile of farmers and the farming practices used. This was done using means, frequencies, percentages, pie charts, and tables.
3.4.2 Binary logistic regression (BLR) model
The study made use of binary logistic regression to estimate the determinants of risk behavior among livestock farmers in the Eastern Cape Province. The study used this model because this objective is binary in nature and only binary models are capable of measuring such. This method was chosen because it is a standard analysis method when the outcome variable is dichotomously measured as having a value of 1 or 0, where 1 = experienced risk or 0 = otherwise. This followed the practice established by Loki and Mdoda (2023), Sigigaba et al. (2021) and Kumar et al. (2025), who used a BLR model to analyze the factors affecting smallholder farmers. The Binary logistic regression was chosen because of its capacity to better answer our main research questions, which are binary in nature. Additionally, the significant explanatory variables do not have the same level of impact on the risk behavior of farmers. The relative effect of a given quantitative explanatory variable on the risk behavior decision is measured by examining risk elasticity, which is why Logit is the most suitable model to be used (Mdoda and Obi, 2019). The variables that were assumed to influence the risk behavior decision of livestock farmers were tested for multicollinearity. According to Sigigaba et al. (2021) and Mdoda et al. (2025), the binary logit model was used as it offers the likelihood to save the projected variables used to estimate drivers of risk automatically. The general BLR model is expressed as follows (Gujarati, 2010):
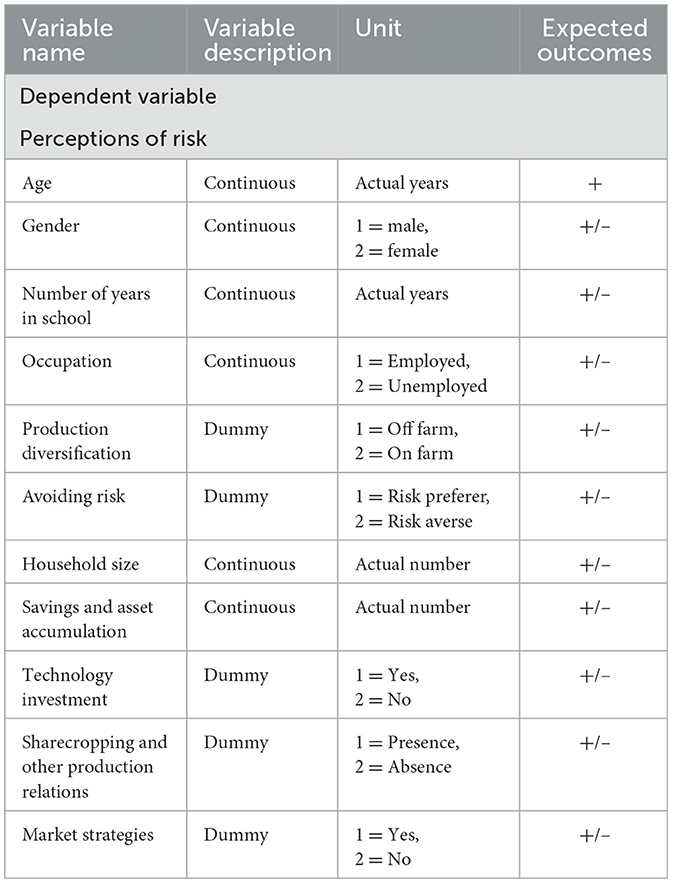
Where, Yi—dependent variable (risk experienced by livestock farmers), Pi—the probability of a farmer experiencing risk, 1–Pi—the probability of a farmer not experiencing risk, β0–intercept, β1 − βn–parameter coefficients, X1−Xn–explanatory variables and, μi–the disturbance terms. During analysis, the model employed multiple tests to strengthen the results. These tests include the Log Likelihood test and the Chi-square to check how well the model fits the data and whether the predictors are meaningful. Measures like R-squared and Adjusted R-squared help explain how much of the outcome the model can predict. When used in conjunction, these statistics give a clear picture of the reliability and strength of the model's results. Table 1 describes regression variables, unit types, and expected outcomes.
3.4.3 Propensity score matching
The study adopted the propensity score matching to estimate the impact of risk behavior on smallholder livestock farmers. This is the most used analytical tool for impact studies, and studies such as Mdoda et al. (2025) made use of this analytical tool. PSM is a useful tool to account for the disparity in covariates between treated and comparison groups. Specifically, the study used the Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) to measure the impact, which is the average difference between expected outcome values with and without treatment for those who had experienced risk in their livestock farming (Khumalo et al., 2025; Mdoda et al., 2025). A propensity is a semi-parametric method that gives an estimate of agricultural credit access, as assumed by the binary logit regression model. The PSM uses propensity scores to match every individual observation of a treated livestock farmer with an observation with similar characteristics from the non-treated or control group. Propensity score matching estimation relies on two important assumptions, namely, the conditional independence and overlap assumptions. The conditional independence assumption, Chappa et al. (2024) states that the treatment assignment is essentially randomized when we condition on a rich set of covariates. It recommends that systematic differences in outcomes between treated and comparison livestock farmers with the same values for covariates are attributable to treatment. The CIA assumption cannot be tested and only relies on conditioning on a rich set of observed covariates. The overlap assumption, on the other hand, states that by conditioning on a set of covariates, everyone has a positive probability of receiving treatment (also known as the overlap assumption). The propensity score is the conditional probability of the task given the treatment, given a vector of observed covariates. The PSM model was expressed as follows:
Where, p are the propensity scores estimated from Equation 10 and defined as:
where, X is a vector of covariates based on observed characteristics of livestock farmers and F{.} is a normal cumulative distribution function. In the estimation of the ATT, we used the nearest neighbor and kernel-based matching algorithm.
4 Findings and discussion
4.1 Demographics of the respondents
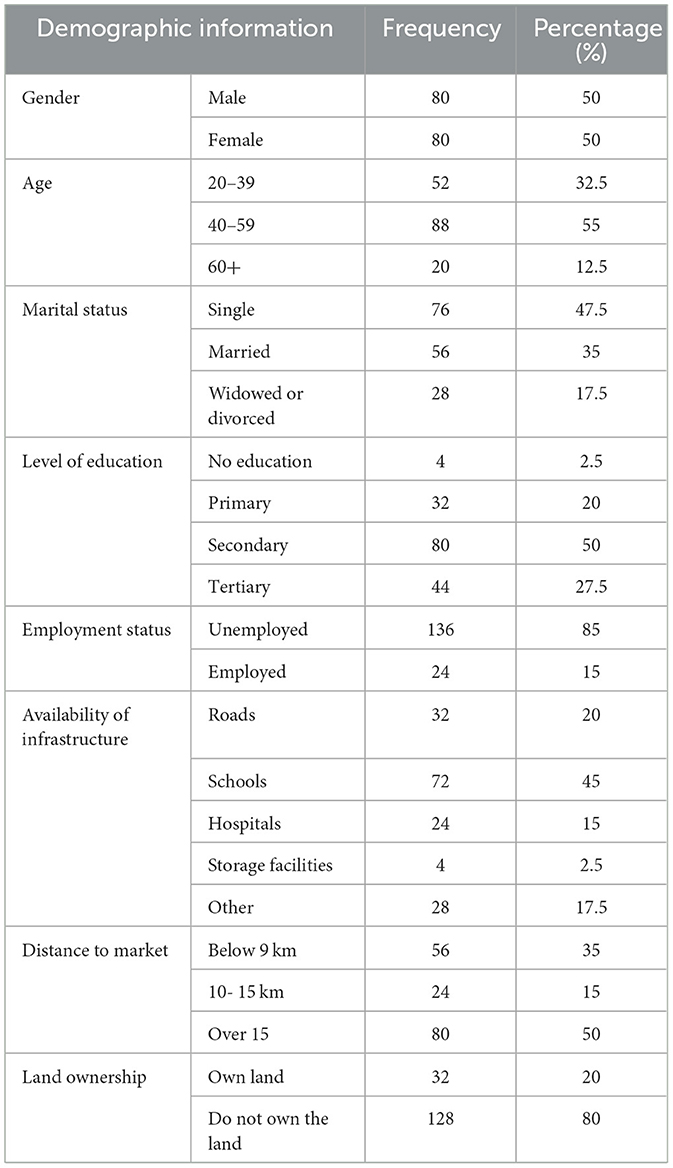
Respondents in the Eastern Cape had different socio-economic characteristics, including gender, age, marital status, level of education, employment status, availability of infrastructure, distance to market, and land ownership. These characteristics illustrate the conditions people in the chosen area live under. Findings from the study regarding the socio-economic conditions is represented in Table 2.
Gender plays a vital role in shaping individuals' participation and potential in agriculture, often influenced by societal expectations. This study found a balanced representation of both male and female respondents, highlighting the importance of both genders in agricultural practices. Research by Krishnan et al. (2023) supports the need for balanced gender involvement to foster sustainable development. Including both genders ensures diverse perspectives in agricultural decision-making (Karat and Shinoji, 2022). However, Noge (2025) notes that women still face unique challenges like unequal pay and higher injury risks. Thus, while equal participation reflects shared capabilities, it also uncovers areas where deeper gender-based inequalities remain.
Age is often linked to experience and knowledge, which are valuable in farming. This study found that the majority of participants (55%) were between 40 and 59 years old, followed by younger farmers aged 20 to 39 (32.5%), and older farmers over 60, making up 12.5%. These figures show that farming attracts a wide age range, with middle-aged individuals being the most active. Similarly, Singh and Pandey (2018) observed a strong presence of middle-aged and older farmers in Muzapir. Research also shows that middle-aged farmers tend to be the most productive (Song et al., 2024), while youth participation reflects growing interest in agribusiness (Simbeko et al., 2023). Older farmers, meanwhile, bring valuable experience and passion to the sector (Conway et al., 2022).
Marital status states the formal relationship of a person regarding the familial bond. These statuses are classified into single, married, divorced, or widowed. This study indicated that 47.5% of the population is formally single, allowing these households to maintain farming activities independently, which is crucial for their livelihoods. These findings are in line with a study conducted in Vhembe district by Mudzielwana et al. (2022). The married group, comprising 35%, benefits from shared responsibilities in farming, such as livestock management, which enhances productivity and ensures effective farming practices. The stability and support provided by marriage may encourage greater involvement in labor-intensive activities like farming. Moreover, the presence of a spouse can provide additional labor and resources, which are crucial for sustaining production (Lai-Solarin et al., 2024). The remaining 17.5% of the population includes widowed and divorced individuals, underscoring the integral role of farming in sustaining households regardless of marital status. These findings further indicate that marital stability may play a role in sustained agricultural engagement (Nontu et al., 2024).
Level of education denotes the amount of formal education the participant has obtained. Farming can be conducted with either the availability or the unavailability of formal education. In this study, the level of education was classified into no education, primary, secondary, and tertiary education. From the results, half of the study population had secondary education, followed by tertiary education holders at 27.5%, primary education at 20% and the remaining 2.5% having no formal education. These results demonstrate the profound capability of farming across all factorial levels of life, including access to formal education. These results are in line with findings by Mulugeta et al. (2024), who observed that education significantly affects knowledge of occupational hazards, with higher education correlating with better awareness and practices. Another study demonstrated that educated farmers are more likely to be early adopters of agricultural innovations (Rizzo et al., 2024). Pavlov and Pavlova (2024) further argued that the level of education is a key factor in forming human capital in agriculture, which is essential for ensuring food security. This indicates that higher education levels contribute to better agricultural practices and outcomes.
Employment status denotes the respondent's involvement in employment opportunities other than farming for themselves. This shows whether the household has another income source available apart from selling farm produce, grants, or remittances. This study discovered that 85% of the study population is unemployed and the remaining 15% is employed in various areas of specialization. This shows that most households that participate in livestock farming are unemployed, depending on the livestock they produce and other sources such as grants and remittances. Unemployment in agriculture, especially among youth and graduates, remains alarmingly high due to skill mismatches, poor sector perceptions, low profitability, and structural barriers (Rani and Sharma, 2024).
Availability of infrastructure refers to the availability of tangible assets that contribute toward the overall success or development of a society. These include roads, schools, hospitals, storage facilities, and many more. From this study, the available infrastructure includes schools being the one many (45%) have access to, roads (20%), other infrastructure (17.5%), hospitals (15%), and storage facilities (2.5%). This distribution highlights a significant disparity in infrastructure access. Schools are the most commonly available, suggesting a prioritization of basic education infrastructure (Opabola and Galasso, 2024). However, the limited access to roads and hospitals indicates challenges in transportation and healthcare, which can hinder economic development and wellbeing (Lawrence, 2024). The extremely low access to storage facilities (2.5%) is particularly concerning for agriculture, as it restricts the ability to store and preserve produce, leading to post-harvest losses and reduced income for farmers. The limited availability of storage facilities exacerbates the negative effects of long market distances by increasing post-harvest losses (Kaur and Watson, 2024).
Distance to market reveals the availability and efficiency of the product to be sold or the accessibility of certain requirements. Half of the study sample goes over 15 km to reach markets, followed by those having a distance below 9 km, accounting for 35% and the other 15% with the distance of between 10 km and 15 km. This shows that most farmers live in areas that are far from the markets. Traveling more than 15 km to reach markets presents significant challenges in market accessibility for a large proportion of smallholder farmers. Such long distances increase transportation costs, reduce the frequency of market visits, and limit farmers' ability to sell fresh produce promptly (Sennuga et al., 2024). The lack of storage facilities (available to only 2.5% of respondents) further compounds these challenges, leading to higher post-harvest losses. Farmers reported that perishable products such as milk, eggs, and chickens often spoiled or deteriorated in quality due to delays in reaching markets, with some produce lost entirely before being sold. For larger livestock such as cattle, sheep, and goats, the losses were indirect: animals lost body weight during long treks to markets or while waiting for buyers in informal trading points, reducing their sale value. These combined effects lower household incomes, limit reinvestment in critical inputs such as feed and veterinary care and discourage active market participation. Ultimately, the interaction between long market distances and weak infrastructure negatively impacts both farm profitability and rural livelihoods. The 35% traveling less than 9 km is likely to have better access to markets, which can facilitate more frequent sales and better integration into the supply chain. On the other hand, the 15% traveling between 10 km and 15 km are in an intermediate position, facing some challenges but not as severe as those traveling over 15 km. Market accessibility can therefore be noted as a critical factor in agricultural productivity and income. Farmers located farther from markets often face reduced profitability due to higher transport costs and limited access to market information. In regions with poor road infrastructure and long distances to markets, agricultural productivity and rural development tend to be delayed (Ezeudu and Fadeyi, 2024).
Land ownership is a crucial factor affecting the process of farming. This is because land is one of the most important factors of production in a business that deals with goods such as crops or livestock (Saqib et al., 2025). Findings illustrate that 80% of the farming population does not own the land they practice farming on. They either rent the land they are using or jointly own the land. The remaining 20% owns land which may have been purchased or left as an inheritance. Not owning the farmland underscores a widespread issue of land tenure insecurity that affects agricultural productivity, investment, and rural livelihoods. This is supported by global trends showing increasing land ownership concentration and a large share of farmers operating on leased or rented land (Georgieva, 2025). This may be due to the fact that historical land distribution patterns, land reforms, and policies have resulted in large landholdings concentrated in a few hands, forcing many farmers to lease or sharecrop. High land prices and limited access to credit prevent many farmers from purchasing land (Pun et al., 2024). Increasing land acquisition by investors and corporations (including foreign investors) can reduce land availability for smallholder ownership.
4.2 Livestock farmed by smallholder farmers
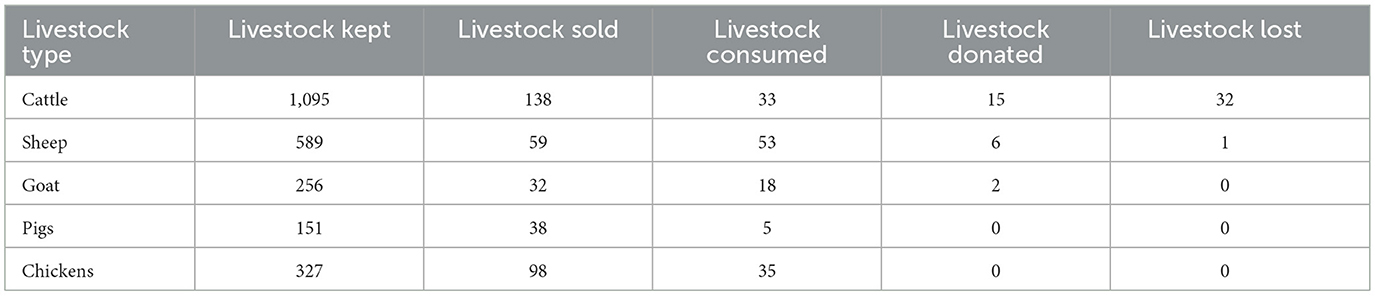
This study looked at the patterns of livestock ownership, use, and losses among farming households, focusing on five major livestock types: cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, and chickens. The findings reveal a clear trend in the multifunctional role of livestock, with most animals being retained rather than sold, consumed, donated, or lost. These findings are outlined in Table 2.
Cattle were found to be the most kept livestock, with 1,095 animals retained by households. A total of 138 cattle were sold, while 33 were consumed, 15 donated, and 32 were reported lost. This highlights the significance of cattle as long-term economic assets and symbols of wealth in rural communities (Julius and Odemero, 2024). The relatively high number of cattle kept suggests their integral role in agricultural activities such as plowing and as a form of security. The sales figures, while considerable, indicate that cattle are not typically sold frequently but are instead used as a source of income in times of financial need (Riesman, 2024). The reported losses reflect environmental challenges such as drought, disease, or theft.
Sheep followed cattle in overall importance, with 589 kept. A notable number of sheep were consumed (53) and sold (59), suggesting that sheep are more commonly used for both income generation and household nutrition. Only six sheep were donated, and one was lost. This dual function indicates a balance between the economic and subsistence roles of sheep within households (Chappa et al., 2024).
Goats also featured prominently, with 256 animals kept, 32 sold, and 18 consumed. Donations and losses were minimal. The data suggest that goats are moderately utilized for consumption and income but are primarily retained, potentially due to their resilience in harsh environmental conditions and relatively low maintenance requirements (Cooke et al., 2024).
Pigs demonstrated the highest proportion of animals sold relative to the number kept, with 38 out of 151 pigs sold. Consumption (5) and donation (0) were low, which may point to pigs being viewed more as commercial assets than sources of food or social capital. The absence of reported losses suggests pigs may be better confined to or less susceptible to loss compared to larger animals (Zeltner and Pedersen, 2024).
Chickens were also widely kept (327), with 98 sold and 35 consumed. Like pigs, no chickens were donated or reported lost. The high number sold indicates chickens are an accessible source of short-term income, while their consumption underscores their role in improving household food security (Bist et al., 2024). Their absence in the donation records may reflect cultural preferences or their lower perceived social value compared to larger livestock (Table 3).
Results reveal that livestock ownership plays a crucial role in rural livelihoods, serving various functions including income generation, food provision, social obligations, and asset accumulation. Cattle appear to be central to economic and cultural life, while species such as chickens and pigs serve more immediate financial and nutritional needs. Sheep and goats offer a hybrid model, contributing to both subsistence and market functions.
4.3 Types of feeds used by smallholder farmers
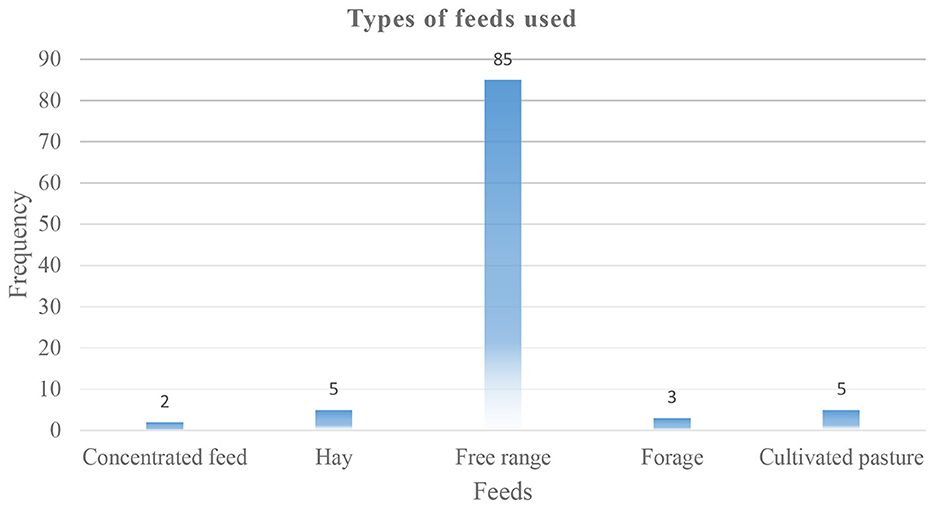
Smallholder farmers use different feeds to cater to their livestock. Figure 3 illustrates the feeding practices among farmers, showing a prevalent reliance on free-range grazing (85%), with minimal adoption of cultivated pasture (5%), hay (5%), forage (3%), and concentrated feed (2%). This distribution emphasizes a dependence on extensive grazing systems, a characteristic feature of smallholder livestock farming in Southern Africa. The preference for free-range systems is often attributed to their low input requirements and alignment with traditional farming practices (Bist et al., 2024). However, such systems are increasingly vulnerable to climatic variabilities, including prolonged droughts and erratic rainfall patterns, which adversely affect pasture availability and quality. The limited use of cultivated pastures and hay suggests constraints such as inadequate access to land, resources, and knowledge necessary for establishing and managing these feed resources (Alimi et al., 2024). Moreover, the minimal adoption of concentrated feeds may be due to their cost implications and limited availability in rural areas.
4.4 Extension visits and vaccination
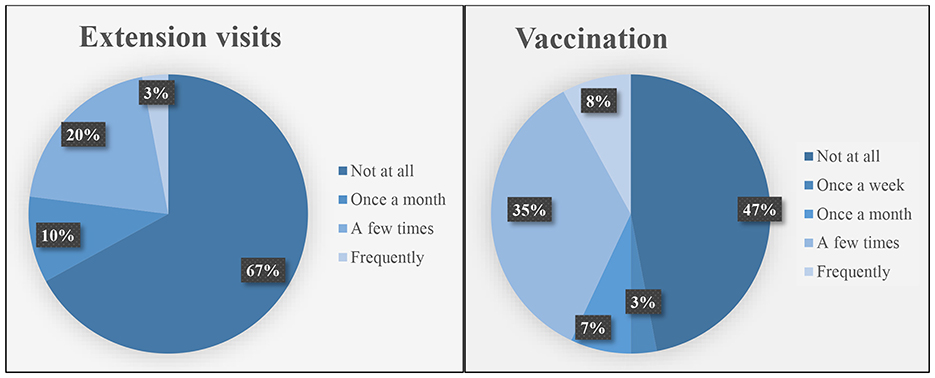
Extension visits and vaccination are the important aspects that each farmer needs to have access to. These elements assist in the upholding of the overall production. Extension visits ensure training and accumulation of more information whereas vaccination ensures that the livestock can withstand diseases and other effects associated with seasonal variations. Figure 4 illustrates the rate of these factors in terms of how much time smallholder farmers receive the visits and the frequency of vaccination for livestock.
4.4.1 Extension visits
The results presented in Figure 4 reveal a concerning gap in extension service delivery, with 67% of smallholder farmers reporting no access to agricultural extension services. This significant lack of technical support highlights a critical weakness in the livestock development framework, particularly in rural and under-resourced areas. Extension services are pivotal for disseminating up-to-date knowledge on animal health, nutrition, disease prevention, and market information (Rose et al., 2025). Only 20% of farmers reported receiving extension support “a few times,” while just 10% experienced monthly visits, and a mere 3% benefited from frequent extension contact. These findings align with previous studies emphasizing how infrequent or irregular extension services hinder the adoption of improved livestock practices (Berhanu et al., 2024). Inadequate extension outreach may also contribute to poor record-keeping, suboptimal feeding strategies, and limited disease control, ultimately impeding productivity and farm profitability (Nhokwara, 2024). Given the challenges of climate variability, emerging livestock diseases, and the need for sustainable farming methods, strengthening extension systems is critical.
4.4.2 Vaccination
Vaccination uptake among respondents shows similar concerns. About 47% of farmers reported never vaccinating their livestock, while 35% administered vaccines only occasionally. Only 8% vaccinated frequently, 7% did so once a month, and 3% once a week. These figures suggest that animal health management remains largely reactive rather than preventative, leaving livestock populations vulnerable to preventable diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease, brucellosis, and Newcastle disease (Lane et al., 2024). The low vaccination uptake may be directly linked to the limited access to extension services, as farmers without regular advisory support may lack awareness of vaccination schedules, access to vaccines, or knowledge of disease symptoms (Ogolla et al., 2024). Improving vaccination uptake is a critical component of effective livestock management, particularly in smallholder systems where disease outbreaks can devastate herds and household incomes.
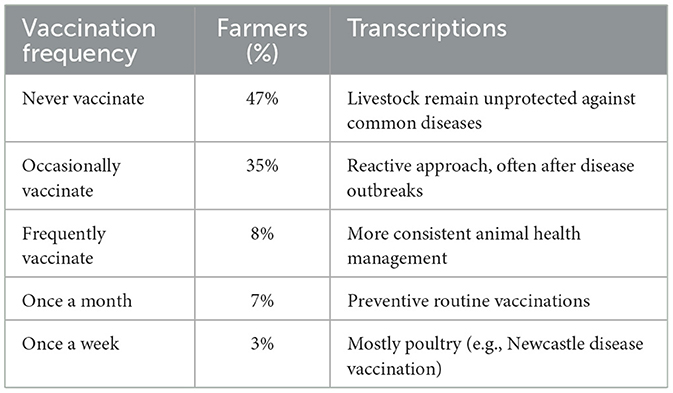
4.4.3 Vaccination frequency among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape
The results are presented in Table 4 reveal a worrying trend in vaccination uptake among smallholder livestock farmers in the Eastern Cape. Nearly half of the farmers (47%) reported that they had never vaccinated their livestock. This lack of preventive health care leaves animals highly vulnerable to recurring and preventable diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease, brucellosis, and Newcastle disease. The absence of vaccination also reflects structural challenges faced by smallholders, including poor access to veterinary services, limited extension support, and high costs of vaccines. Another 35% of farmers indicated that they only vaccinate occasionally, often in response to disease outbreaks rather than as a preventive measure. This reactive approach indicates that farmers are not benefiting from the full protective potential of vaccination, which requires consistent and scheduled application. In contrast, only 8% of farmers were vaccinated frequently, while 7% followed a monthly vaccination routine, and 3% maintained a weekly schedule. These minority groups demonstrate an awareness of the importance of regular vaccination and better integration of animal health into farm management. However, their small share highlights the broader systemic failure in ensuring effective disease prevention in rural livestock systems. Overall, the findings illustrate that vaccination practices are irregular and insufficient, undermining livestock health, productivity, and the resilience of smallholder farming households.
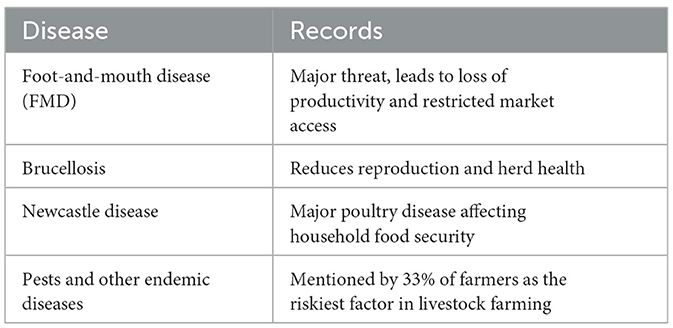
4.4.4 Common livestock diseases reported by farmers smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape
Table 5 highlights the most common livestock diseases affecting smallholder farmers in the study area, with foot-and-mouth disease (FMD), brucellosis, and Newcastle disease identified as the most pressing concerns. FMD is a highly contagious disease that causes significant production losses, reduced weight gain, and market restrictions, making it particularly devastating in rural communities where cattle serve as both an economic and social asset. Brucellosis, another major disease, undermines herd fertility, causes abortions, and reduces milk production, thereby threatening both food security and income generation. Newcastle disease is a leading cause of mortality in poultry flocks and directly impacts household nutrition and small-scale poultry trade. In addition to these, farmers reported the presence of pests and other endemic livestock diseases, with 33% of respondents identifying them as the riskiest factor in livestock production. This finding reinforces the notion that livestock health challenges remain central to the vulnerability of smallholder farmers. The presence of these diseases further underscores the importance of consistent vaccination programs, biosecurity measures, and improved extension services. Without effective control, such diseases perpetuate a cycle of economic losses, reduced household resilience, and limited market participation, keeping smallholder farmers in a state of persistent vulnerability.
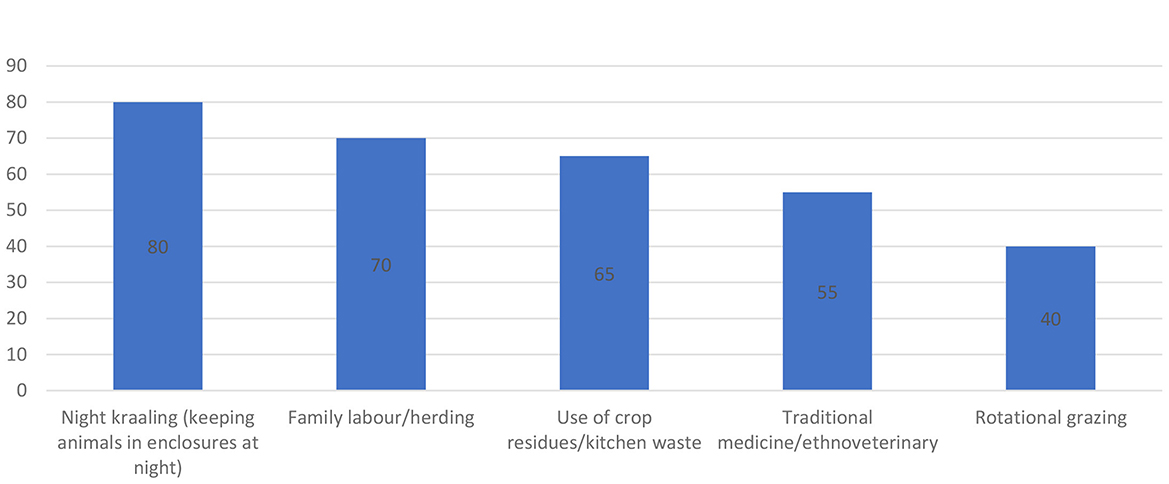
4.5 Home based practices utilized by farmers in the study area
The findings indicate that smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape continue to rely heavily on indigenous, home-based livestock management practices to sustain their herds. Night kraaling is the most dominant practice, with 80% of respondents enclosing animals overnight as a measure to prevent theft and predation. Family labor and herding remain central to livestock management, with 70% of farmers depending on household members rather than hired labor, which reflects both cost-saving strategies and cultural traditions. The use of crop residues and kitchen waste was reported by 65% of farmers, highlighting the integration of livestock and crop production systems to maximize resource use. Over half of the farmers (55%) rely on traditional medicine and ethnoveterinary practices for disease prevention and treatment, largely due to limited access to formal veterinary services. Meanwhile, 40% practice rotational grazing, an indigenous method that helps preserve pasture and reduce overgrazing. Collectively, these practices demonstrate the resilience and adaptive strategies of smallholder farmers, but they also underscore the need for complementary modern interventions to enhance productivity and reduce risks.
4.6 Factors affecting farming business
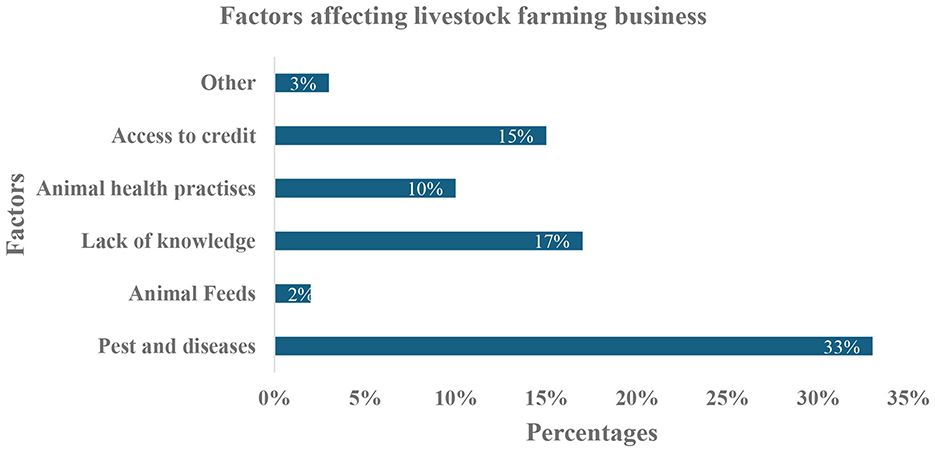
The Figure 5 displays results generated from a fieldwork survey. This field survey was conducted to find out the risks that the respondents perceive as being the riskiest.
Figure 6 presents insights into the key factors perceived by respondents as making their farming businesses risky. Particularly, pests and diseases emerged as the most significant threat, mentioned by 33% of the surveyed farmers. This aligns with broader findings in the literature, which identify livestock diseases as a major constraint to productivity and profitability, particularly among smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa (Kimeli et al., 2025). Disease outbreaks, such as foot-and-mouth disease or brucellosis, often lead to severe economic losses, reduced animal productivity, and restricted market access.
The second most noted risk was lack of knowledge, reported by 17% of respondents. This highlights the persistent information gap that limits technical capacity among small-scale farmers, which constrains informed decision-making in areas such as animal nutrition, breeding, and health management. Recent studies emphasize that improved access to farmer training and livestock extension services can substantially mitigate this risk (Kalogiannidis and Syndoukas, 2024; Prabex et al., 2024; Prajapati et al., 2025).
Access to credit was identified as a major risk factor by 15% of respondents. Financial constraints often limit farmers' ability to purchase inputs such as feed, vaccines, or improved livestock breeds. Moreover, the absence of tailored credit products for livestock farming hampers investment and innovation in rural settings. Jatto and Gambo (2025) indicate that credit access, particularly through cooperative models or government-backed schemes, is essential for enabling smallholder resilience and scale.
Animal health practices were stated by 10% of the respondents, suggesting challenges in preventive health management, including vaccination and regular veterinary services. These findings echo those discussed earlier, where limited extension visits and poor vaccination uptake were evident. Without regular veterinary input, even basic preventive care becomes difficult, compounding risks related to disease burden (Owusu and Sanad, 2025).
Also, animal feed was seen as a relatively minor risk, with only 2% of farmers identifying it as a key concern. This could be due to the high reliance on free-range systems (as seen earlier), where farmers do not incur substantial feed costs. However, this perception may overlook the long-term risks posed by climate-induced changes in natural pasture availability.
Finally, the remaining 3% of respondents selected “other” as a risk factor, indicating that while the major challenges are well-defined, there is the presence of localized or context-specific issues such as theft, water shortages, or land tenure insecurity that require further exploration. These challenges play a major role in the farming process as they determine the total production a farmer can have.
Overall, these findings underscore the multifaceted nature of risk in smallholder livestock farming. Addressing these risks requires a holistic strategy involving improved veterinary services, knowledge dissemination, financial inclusion, and institutional support to enhance farm resilience and sustainability.
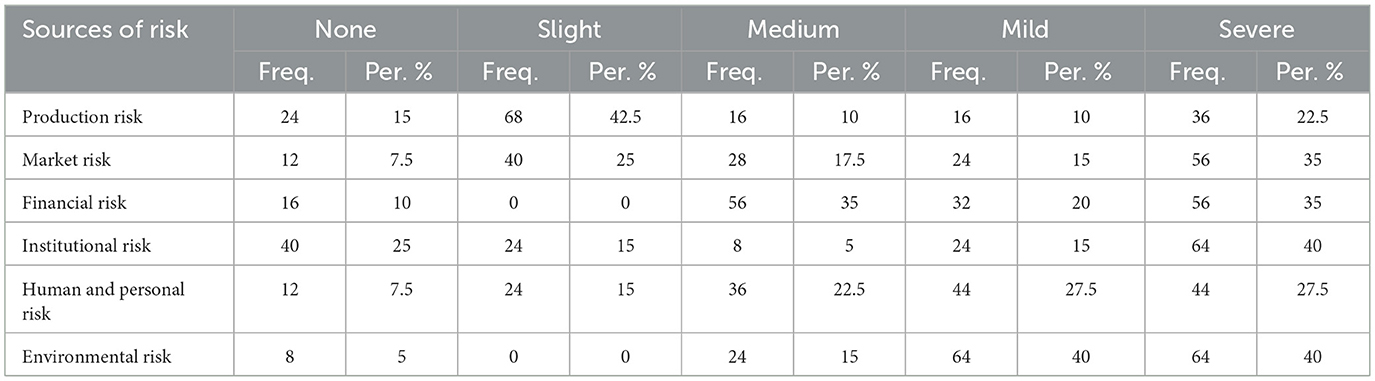
4.7 Sources of risks
The Table 6 shows field results for sources of risk. The sources of risk were ranked on a Likert scale, where the respondent was able to choose the sources of risk and further indicate the extent to which the impact is severe or slight to them.
Table 6 illustrates the perceived severity of various risk sources affecting smallholder livestock farming operations, based on a Likert scale assessment by respondents. These sources include production, market, financial, institutional, human/personal, and environmental risks. The results highlight the complex and multi-dimensional nature of risk in smallholder livestock systems, with several categories showing a high proportion of farmers experiencing moderate to severe impacts.
Production risk was identified as severe by 22.5% of respondents, while 42.5% rated it as slight. This category includes uncertainties related to animal health, feed availability, and reproductive performance. The relatively low proportion of severe ratings may reflect the adaptive capacity of farmers relying on indigenous breeds and traditional knowledge. However, it still suggests that a significant segment of farmers remains vulnerable to disruptions in inputs or biological performance. Pezo et al. (2024) emphasize that unmanaged production risks, particularly diseases, can rapidly escalate into economic shocks in smallholder systems.
Market-related risk was rated severe by 35% of respondents, with an additional 17.5% reporting mild risk. This indicates concerns over price volatility, lack of access to formal markets, and limited bargaining power. Market instability has been a persistent challenge in the Southern African livestock sector, where rural farmers often lack access to real-time pricing information or reliable buyers (Morepje et al., 2024). Unpredictable demand and seasonal fluctuations further exacerbate these risks.
Financial risk was perceived as severe by 35%, mild by 20%, and medium level by 35% of respondents. This reflects widespread challenges in accessing capital for farm operations, purchasing inputs, or scaling production. As highlighted by Mishra (2024), the absence of affordable and farmer-friendly credit facilities remains a barrier to resilience and growth among rural livestock farmers. Financial constraints also limit farmers' ability to respond effectively to other risks, such as disease outbreaks or climate-related shocks.
With 42% of respondents quoting severe institutional risk and 25% citing none, the data reveals a stark divide. Institutional risk includes limited access to extension services, ineffective local governance, and a lack of support from veterinary and marketing institutions. As seen in earlier findings, most farmers lack regular contact with extension agents, which contribute to both production and animal health challenges (Arowosegbe et al., 2024). The significant number mentioning no institutional risk may reflect reliance on informal knowledge networks rather than public services.
Human and personal risk, which includes illness, aging, family labor constraints, and household-level disruptions, was rated severe by 27.5% and medium by another 27.5%. Such risks are often underestimated in livestock development planning but are crucial in smallholder systems where operations are heavily dependent on family labor. Human risks have been shown to influence decisions around herd management, marketing, and investments (Melak et al., 2024).
Environmental risk stood out, with 40% of farmers rating it as severe, and another 40% as medium. These include risks related to drought, pasture degradation, floods, and water scarcity. The findings reinforce growing concerns about climate change impacts on livestock systems. Studies have consistently shown that increased climate variability, such as drought, threatens feed availability and water access, thereby exacerbating other production risks (Sintayehu et al., 2025).
4.8 Effect of risk management strategies and risk perceptions on livestock production
Table 7 presents results showing how various risk management strategies and socio-demographic factors influence livestock production. The results are derived from regression coefficients (β) and significance levels (p-values), indicating the strength and statistical significance of these variables in predicting livestock production outcomes.
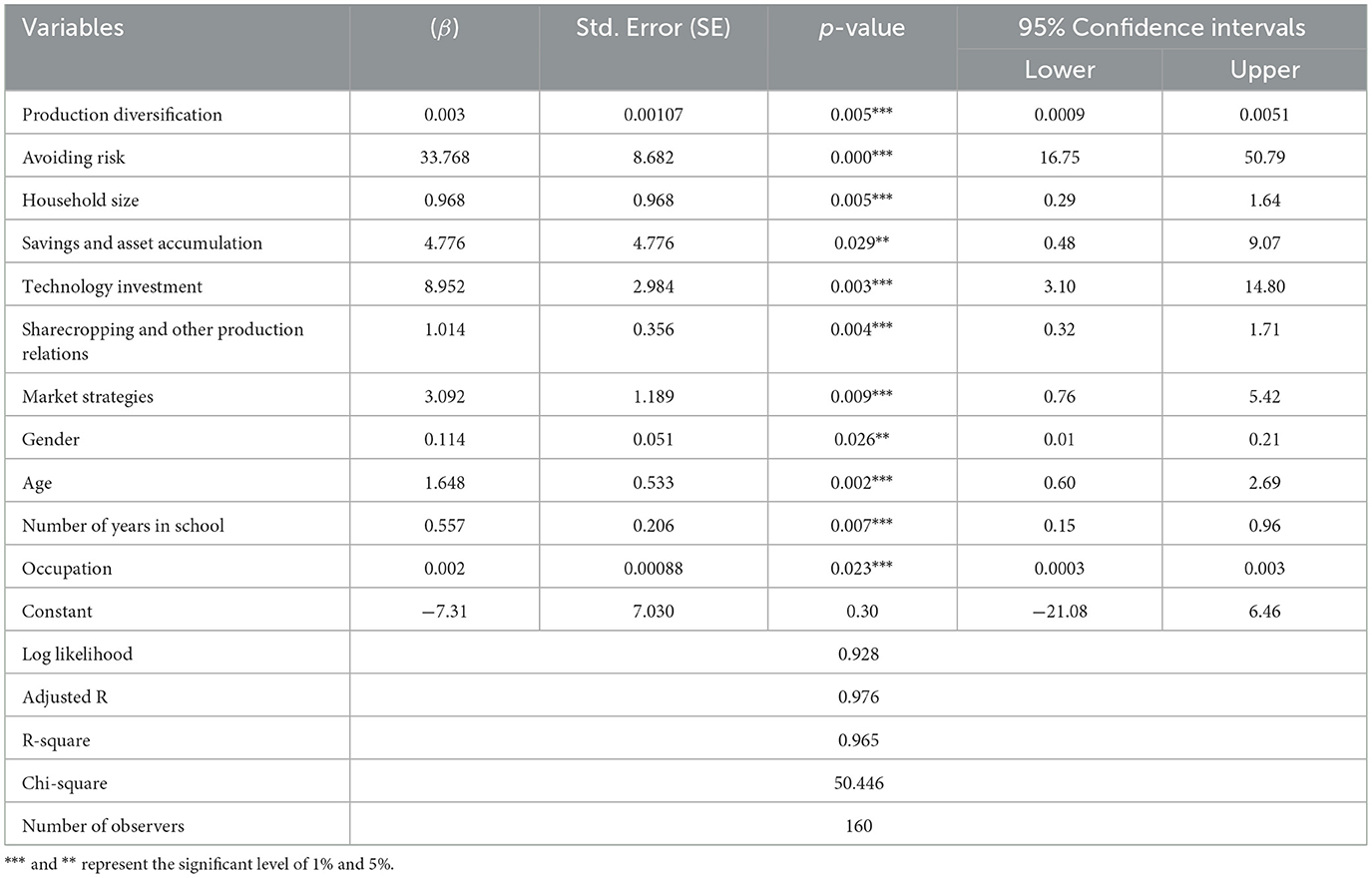
Table 7. The analysis of the effects of risk management strategies and perceptions of risk on livestock production.
The results reveal that avoiding risk exhibits the strongest positive influence on livestock production, with a very high β value of 33.768 and a highly significant p-value (p < 0.001). This suggests that farmers who actively engage in risk avoidance strategies such as diversifying income sources, adopting conservative production practices, or reducing exposure to known hazards tend to achieve better livestock production outcomes. This finding is consistent with previous studies highlighting the importance of risk-averse behaviors in improving farm stability and productivity (Patil and Veettil, 2024; Spada et al., 2025).
Other significant risk management strategies include technology investment (β = 8.952, p = 0.003) and market strategies (β = 3.092, p = 0.009). Investment in improved technologies such as better breeds, feeding systems, or veterinary care has been shown to enhance production efficiency and disease resistance (Dayoub et al., 2024). Meanwhile, strategic engagement with markets through better pricing information, contract farming, or cooperative marketing helps farmers mitigate price risks and access premium markets (Saroj and Paltasingh, 2024). The variable production diversification also positively influences livestock production, albeit with a smaller coefficient (β = 0.003, p = 0.005). This aligns with the concept that diversified farming systems, incorporating multiple livestock species or crop-livestock integration, enhance resilience by spreading risk across various outputs (Bilotto et al., 2024).
Socio-demographic factors further contribute significantly to livestock production. Household size (β = 0.968, p = 0.005) and age (β = 1.648, p = 0.002) indicate that larger households and older farmers tend to have higher production, possibly due to greater labor availability and accumulated experience, respectively. Education, measured by number of years in school (β = 0.557, p = 0.007), also positively impacts production, underscoring the role of formal education in improving farmers' capacity to adopt innovations and effective management practices. Other socio-economic variables, such as savings and asset accumulation (β = 4.776, p = 0.029), gender (β = 0.114, p = 0.026), occupation (β = 0.002, p = 0.023), and sharecropping and other production relations (β = 1.014, p = 0.004), also significantly affect livestock productivity. Savings and assets provide critical buffers that allow farmers to invest in inputs and recover from shocks. Gender significance points to differential access to resources and decision-making power, with implications for production efficiency (Wann et al., 2024). Occupation and production relations influence how farmers allocate resources and labor, affecting overall output.
The model fit statistics demonstrate explanatory power, with an adjusted R2 of 0.976 and R2 of 0.965, indicating that over 96% of the variation in livestock production is explained by the variables included in the model. The significant chi-square statistics (50.446) further confirm the model's strength.
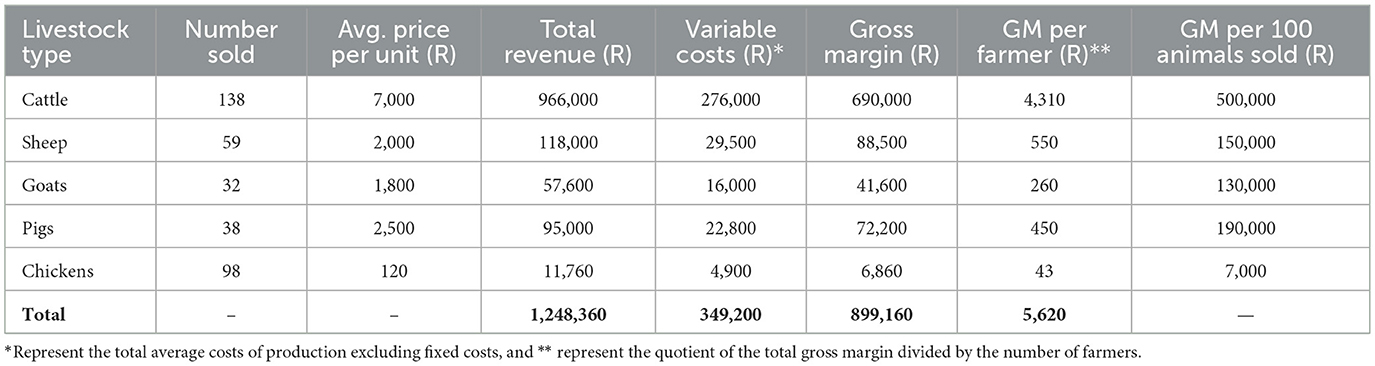
4.9 Gross margin analysis of smallholder livestock farming in the study
The gross margin analysis was undertaken to evaluate the profitability of livestock farming among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape. This approach allows for a clear understanding of the balance between income generated from livestock sales and the variable costs incurred in maintaining production. By focusing on the major livestock types (cattle, sheep, goats, pigs, and chickens), the analysis highlights which enterprises provide the greatest financial returns and how these align with household livelihood strategies. The results are particularly important given the study's finding that 85% of farmers are unemployed and depend heavily on livestock as their primary income source. Presenting gross margins both per farmer and per 100 animals sold provides a comprehensive picture of the economic contributions of different livestock species within smallholder systems. The Table 8 shows the gross margin results of smallholder livestock farming in the study area.
The gross margin analysis demonstrates that livestock farming among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape generates a positive return, though with varying contributions across species. Cattle dominate the revenue stream, contributing nearly ZAR966,000 from sales, with a gross margin of ZAR690,000, which is equivalent to about ZAR500,000 per 100 animals sold. This supports the study's observation that cattle are retained as long-term financial assets and symbols of wealth, only sold during times of financial pressure. Sheep and goats, with gross margins of ZAR150,000 and R130,000 per 100 animals respectively, provide a hybrid role by serving both income-generation and nutritional needs. Pigs, though fewer in number, yield strong margins (ZAR190,000 per 100 animals), highlighting their role as a more commercialized livestock option compared to ruminants. Chickens, on the other hand, provide the lowest gross margins (ZAR7,000 per 100 birds), but their short production cycle and accessibility make them essential for meeting immediate household needs and food security, consistent with the study's findings that pigs and poultry offer quick cash inflows.
At the household level, the average gross margin per farmer is estimated at ZAR5,620 annually. This aligns with the sociodemographic profile presented in the study, where 85% of respondents were unemployed and thus heavily reliant on livestock as a primary income source. The analysis confirms that while livestock income does cover basic operational costs (such as feed supplementation, veterinary care, and transport), it is also diverted to meet pressing household obligations like food, education, and social commitments. These results are consistent with the findings of Mdoda and Obi (2019), Manganyi et al. (2023), Mbelebele et al. (2024) and Mujuru et al. (2022), who emphasize that smallholder farming remains the most reliable and trusted source of income generation in the Eastern Cape Province, particularly in the context of high unemployment and poverty. Smallholder farming plays a critical role in sustaining livelihoods, as the income generated is not only essential for supporting household needs but also for maintaining and improving farming operations. This dual use of income underscores the vulnerability of smallholder farmers: although livestock farming is economically viable, reinvestment into herd improvement and risk mitigation remains limited (Mdoda et al., 2019; Nondzutha et al., 2020). The findings reinforce the study's argument that institutional gaps, such as inadequate extension services and poor vaccination uptake, constrain productivity, and profitability.
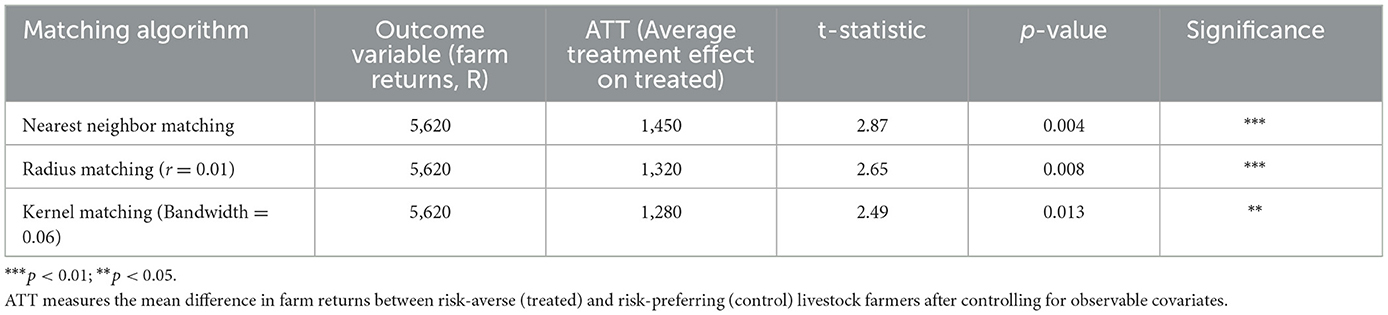
4.10 The impact of risk behavior on smallholder livestock farmers
The propensity score matching results presented above indicate that risk behavior significantly influences farm returns among smallholder livestock farmers in the Eastern Cape Province. Results are shown in Table 9. Across all matching algorithms (nearest neighbor, radius, kernel, and stratification), the Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT) is positive and statistically significant, ranging from R1,250 to R1,450. This suggests that risk-averse farmers, who actively engage in strategies such as diversification, precautionary savings, and adoption of preventive animal health measures, achieve higher farm returns compared to risk-preferring farmers. The highest ATT value observed under nearest neighbor matching (R1,450, p < 0.01) implies that risk-averse behavior yields approximately a 26% increase in net farm returns relative to the average gross margin per farmer (R5,620). These results affirm the hypothesis that risk-averse decision-making enhances financial resilience and income stability, consistent with findings by Mdoda et al. (2025) and Patil and Veettil (2024) that cautious and diversified management strategies improve profitability in uncertain agricultural contexts.
The results further emphasize the importance of behavioral and managerial choices in determining economic outcomes in smallholder systems. The significant ATT values across multiple matching methods confirm the robustness of the estimates, indicating that differences in farm returns are attributable to behavioral differences rather than sample selection bias. Risk-averse farmers tend to adopt a longer-term perspective, reinvesting profits into herd improvement, veterinary care, and market-oriented production, while risk-preferring farmers often exhibit reactive or speculative behaviors that expose them to greater financial volatility.
4.11 Strengths of the study
This study distinguishes itself through methodological innovation, conceptual depth, and contextual relevance to smallholder livestock systems in South Africa and beyond. It advances existing knowledge by integrating risk mitigation, livestock management, and economic performance within a unified analytical framework, a perspective seldom explored in African agricultural research. Through a case study strategy grounded in empirical fieldwork, the research captures the lived experiences of smallholder livestock farmers in the Eastern Cape Province, an area where evidence-based insights remain limited. The study employs a triangulated econometric approach combining descriptive statistics, binary logistic regression, and propensity score matching (PSM) to provide a rigorous and multidimensional analysis. This methodological fusion enhances internal validity and allows the research not only to identify determinants of risk behavior but also to quantify the economic effects of risk management strategies on livestock productivity. The adoption of a multi-stratified random sampling technique across diverse districts strengthens representativeness, ensuring that variations in socioeconomic and environmental contexts are captured. Additionally, the translation and back-translation of survey instruments into IsiXhosa, along with enumerator training and ethical compliance, reflect a deep commitment to research integrity, cultural sensitivity, and scientific robustness.
Beyond its analytical sophistication, the study contributes meaningfully to both theoretical and policy discourse by introducing an integrated conceptual framework that visually and empirically connects sources of risk, farmer perceptions, mitigation strategies, and production outcomes. This framework offers a transformative lens for understanding risk and resilience in smallholder systems, moving beyond deficit-based models toward an agency-centered perspective that acknowledges farmers as adaptive, strategic decision-makers. The study's methodological rigor (anchored in the triangulation of descriptive statistics, binary logistic regression, and PSM) systematically isolates and measures the influence of risk behavior on livestock-specific outcomes such as farm returns, herd productivity, and animal health management. Unlike general agricultural analyses, this research focuses explicitly on behavioral risk attitudes, institutional support systems, and indigenous management strategies as core determinants of livestock resilience. The PSM results provide robust comparative estimates of the Average Treatment Effect on the Treated (ATT), revealing that risk-averse farmers achieve higher economic returns than risk-preferring counterparts, directly linking behavioral risk management to economic stability. By bridging econometric precision with contextual empathy, the study not only deepens scholarly understanding of livestock risk management economics but also generates actionable policy insights on how targeted interventions in extension services, vaccination access, market integration, and financial inclusion can foster resilience and sustainable rural development across the Global South.
5 Conclusions and recommendations
This study reveals the key determinants and risk mitigation strategies influencing livestock management among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape. Livestock management among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape is shaped by diverse socio-economic and structural factors. This forms the basis of the conduction of this study, which was aimed at.
Gender balance reflects growing inclusivity, though women still face challenges, while middle-aged farmers lead production with youth participation promising future growth. Household characteristics such as marital status, education, and employment influence farming resilience and the adoption of improved practices. However, limited infrastructure, poor market access, and widespread land tenure insecurity hinder productivity and investment. Livestock serve multifunctional roles, providing income, nutrition, and social value. Sustainable livestock farming requires integrated support to address equity, education, infrastructure, land rights, and market connectivity toward enhancing risk mitigation and the sustainability of livelihood.
Livestock farming among smallholder farmers in this area demonstrates the importance of farming different animal types in supporting livelihoods. Cattle are primarily retained as long-term assets and sources of security, while sheep and goats balance income generation and household nutrition. Pigs and chickens serve more immediate commercial and food security roles, with high turnover in sales but minimal losses reported. These patterns reflect both the economic, cultural, and nutritional significance of livestock, alongside challenges such as environmental risks and management practices. Keeping these dynamics in check is essential when it comes to enhancing productivity and resilience in smallholder livestock systems toward sustainability.
When it comes to feed, free-range grazing leads, reflecting resource constraints that limit access to cultivated pastures and commercial feeds, thereby affecting livestock productivity. Limited extension services and insufficient vaccination coverage highlight substantial gaps in institutional support, hindering animal health management. Farmers perceive pests, diseases, market volatility, and restricted credit access as major risks, with environmental and institutional factors exerting the greatest impact on production stability. The findings underscore the complex nature of risks confronting smallholder livestock systems and the necessity for integrated mitigation methods. Importantly, practical strategies such as expansion, technology investment, and market engagement significantly enhance livestock productivity. Socio-demographic factors, including household size, education, and age, further influence outcomes, emphasizing the role of empowerment, and knowledge dissemination. This implies that fostering sustainable livestock production in the Eastern Cape requires strengthening veterinary and extension services, improving financial access, and promoting adaptive risk management. Such integrated interventions are essential to enhance resilience and support sustainable livelihoods within smallholder farming communities.
This study therefore recommends that smallholder farmers adopt resilient livestock breeds, diversify livestock production, and supplement fodder crops supported by veterinary services and practical training to mitigate production risks. To mitigate market risks, cooperative marketing, efficient information access, and investment in storage and transportation are recommended. Financial resilience can be strengthened through access to credit, savings groups, and budgeting training. Institutional support must also not be disregarded, as consistent policies, coordination, and collaboration between farmers and stakeholders are crucial for the expansion of production. Human and personal risks can be addressed through safety training, mentorships and community labor sharing. On the other hand, environmental sustainability can be promoted through climate-smart grazing, water management, and sustainable fodder management, ensuring livestock productivity and long-term resilience of smallholder livestock farming systems.
Future studies could investigate the determinants and impact of sources of risks on the overall production and livelihood of farmers. These findings have vital policy implications, suggesting that strengthening farmers' risk management capacity, through financial literacy, insurance access, and extension support, can substantially improve livestock productivity and household income.
Data availability statement
The data for this study will be made available upon a reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Humanities and Social Sciences Research Ethics Committee, University of KwaZulu Natal. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YN: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. LM: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. BD: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Writing – original draft. NN: Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. LG: Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MX: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the smallholder farmers and enumerators who availed themselves of this research. The authors are very thankful for the job done.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abera, W., Assen, M., and Budds, J. (2020). Determinants of agricultural land management practices among smallholder farmers in the Wanka watershed, northwestern highlands of Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 99:104841. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104841
Akasha, M. H., Mondalb, S., and Adusumillic, S. (2021). “Sustainable livestock production and food security,” in Emerging Issues in Climate Smart Livestock Production: Biological Tools Techniques, 71. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-822265-2.00011-9
Alders, R. G., Campbell, A., Costa, R., Guèye, E. F., Ahasanul Hoque, M., Perezgrovas-Garza, R., et al. (2021). Livestock across the world: diverse animal species with complex roles in human societies and ecosystem services. Anim. Front. 11, 20–29. doi: 10.1093/af/vfab047
Ali, Z., Siddiqui, M. S., Khan, S., and Ali, R. (2025). A multi-method analysis of risk mitigation strategies for the livestock supply chain. Sustainability 17:6741. doi: 10.3390/su17156741
Alimi, N., Assani, A. S., Sanni Worogo, H., Baco, N. M., and Traoré, I. A. (2024). Livestock feed resources used as alternatives during feed shortages and their impact on the environment and ruminant performance in West Africa: a systematic review. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1352235. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1352235
Aliu, J., Aigbavboa, C., and Thwala, W. (2021). A 21st Century Employability Skills Improvement Framework for the Construction Industry. London: Routledge.
Arowosegbe, O. B., Alomaja, O. A., and Tiamiyu, B. B. (2024). The role of agricultural extension workers in transforming agricultural supply chains: enhancing innovation, technology adoption, and ethical practices in Nigeria. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 23, 2585–2602. doi: 10.30574/wjarr.2024.23.3.2962
Bahta, Y. T. (2021). Perception of agricultural drought resilience in South Africa: a case of smallholder livestock farmers. Jàmbá J. Disaster Risk Stud. 13, 1–11. doi: 10.4102/jamba.v13i1.984
Berhanu, A. A., Ayele, Z. B., Dagnew, D. C., Fenta, A. B., and Kassie, K. E. (2024). Smallholder farmers' coping strategies to climate change and variability: evidence from Ethiopia. Clim. Serv. 35:100509. doi: 10.1016/j.cliser.2024.100509
Bilotto, F., Harrison, M. T., Vibart, R., Mackay, A., Christie-Whitehead, K. M., Ferreira, C. S., et al. (2024). Towards resilient, inclusive, sustainable livestock farming systems. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 152:104668. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2024.104668
Binns, C. W., Lee, M. K., Maycock, B., Torheim, L. E., and Nanishi, K. Duong, D. T. T. (2021). Climate change, food supply, and dietary guidelines. Annu. Rev. Public Health 42, 233–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev-publhealth-012420-105044
Bist, R. B., Bist, K., Poudel, S., Subedi, D., Yang, X., Paneru, B., et al. (2024). Sustainable poultry farming practices: a critical review of current strategies and future prospects. Poult. Sci. 103:104295. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104295
Blignaut, J., De Wit, M., Knot, J., Midgley, S., Crookes, D., Drimie, S., et al. (2014). Sustainable Agriculture: A Viable Option for Enhanced Food and Nutritional Security and a Sustainable Productive Resource Base in South Africa: An Investigation. Pretoria: Green Fund.
Bwalya, B., Chiluba, B. C., and Mwanza, K. (2024). Livestock ownership among smallholder farming households in Eastern Zambia: a gendered pathway for enhancing climate resilience? Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1487798. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1487798
Carelsen, C., Ncube, B., and Fanadzo, M. (2021). Classification and characterisation of smallholder farmers in South Africa: a brief review. South Afr. J. Agric. Ext. 49, 97–106. doi: 10.17159/2413-3221/2021/v49n2a12821
Chappa, L. R., Nungula, E. Z., Makwinja, Y. H., Ranjan, S., Sow, S., Alnemari, A. M., et al. (2024). “Outlooks on major agroforestry systems,” in Agroforestry, eds. A. Raj, M. K. Jhariya, A. Banerjee, R. K. Jha, and K. P. Singh (Scrivener Publishing LLC), 21–48. doi: 10.1002/9781394231164.ch2
Cheteni, P., and Mokhele, X. (2019). Small-scale livestock farmers' participation in markets: evidence from the land reform beneficiaries in the central Karoo, Western Cape, South Africa. South. Afr. J. Agric. Exten. 47, 118–136. doi: 10.17159/2413-3221/2019/v47n1a494
Chisasa, J. (2019). Determinants of access to bank credit by smallholder farmers: evidence from South Africa. Acad. Account. Finan. Stud. J. 23, 1–10. Available online at: https://www.abacademies.org/articles/Determinants-of-Access-to-Bank-Credit-by-Smallholder-Farmers-1528-2635-23-4-444.pdf (Accessed April 20, 2025).
Conway, S. F., Farrell, M., Mcdonagh, J., and Kinsella, A. (2022). ‘Farmers don't retire': re-evaluating how we engage with and understand the ‘older' farmer's perspective. Sustainability 14:2533. doi: 10.3390/su14052533
Cooke, A. S., Machekano, H., Gwiriri, L. C., Tinsley, J. H., Silva, G. M., Nyamukondiwa, C., et al. (2024). The nutritional feed gap: Seasonal variations in ruminant nutrition and knowledge gaps in relation to food security in Southern Africa. Food Sec. 17, 73–100. doi: 10.1007/s12571-024-01509-1
Danso-Abbeam, G., Okolie, C. C., Ojo, T. O., and Ogundeji, A. A. (2024). Understanding drought impacts on livelihoods and risk management strategies: South African smallholder farmers' perspectives. Nat. Hazard. 120, 8931–8951. doi: 10.1007/s11069-024-06561-w
Dayoub, M., Shnaigat, S., Tarawneh, R. A., Al-Yacoub, A. N., Al-Barakeh, F., and Al-Najjar, K. (2024). Enhancing animal production through smart agriculture: possibilities, hurdles, resolutions, and advantages. Ruminants 4, 22–46. doi: 10.3390/ruminants4010003
De Lange, E., Du Toit, L., Fletcher, A., Iliushyk, T., Kalinovska, B., Lupton, N., et al. (2025). Shifting the focus from animal species to livestock production systems: an interactive tool for evaluating food contributions relative to environmental impacts. Anim. Front. 15, 72–79. doi: 10.1093/af/vfaf008
Erdaw, M. M. (2023). Contribution, prospects and trends of livestock production in sub-Saharan Africa: a review. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 21:2247776. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2023.2247776
Ezeudu, T. S., and Fadeyi, T. J. (2024). Examining the influence of infrastructure deficit on economic activities, education, and healthcare in rural areas of Nigeria. Nnamdi Azikiwe J. Polit. Sci. 9, 155–176. Available online at: https://najops.org.ng/index.php/najops/article/view/229 (Accessed March 10, 2025).
Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) (2012). Livestock sector development for poverty reduction: An economic and policy perspective– Livestock's many virtues. Rome: Food and Agricultural Organization.
Georgieva, V. (2025). Agricultural land: balancing ownership and leasing and its impact on the economic performance of agricultural farms. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 31, 3–12. Available online at: https://www.agrojournal.org/31/01-01.pdf (Accessed March 18, 2025).
Gujarati, J. (2010). Portraits of early career elementary teachers: Examining beliefs about mathematics in the midst of classroom practices. [Dissertation]. Teachers College, Columbia University, New York, NY, United States.
Gwiriri, L. C., Bennett, J., Mapiye, C., and Burbi, S. (2021). Emerging from below? Understanding the livelihood trajectories of smallholder livestock farmers in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Land 10:226. doi: 10.3390/land10020226
Hänke, H., and Barkmann, J. (2017). Insurance function of livestock, farmers' coping capacity with crop failure in southwestern Madagascar. World Dev. 96, 264–275. doi: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2017.03.011
Hashem, N. M., Martinez-Ros, P., Gonzalez-Bulnes, A., and El-Raghi, A. A. (2023). Case studies on impacts of climate change on smallholder livestock production in Egypt and Spain. Sustainability 15:13975. doi: 10.3390/su151813975
Hossain, M. E., Hoque, M. A., Giorgi, E., Fournié, G., Das, G. B., and Henning, J. (2021). Impact of improved small-scale livestock farming on human nutrition. Sci. Rep. 11:191. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80387-x
Jatto, Y., and Gambo, S. (2025). Effect of conventional agriculture financing on development of small-scale farming in Nigeria. Kashere J. Polit. Int. Relat. 3, 397–403. Available online at: https://journals.fukashere.edu.ng/index.php/kjpir/article/view/529 (Accessed March 28, 2025).
Julius, I. U., and Odemero, A. F. (2024). Effects of banditry security risk on livelihood of cattle herders in Katsina State, Nigeria. Magna Sci. Adv. Res. Rev. 10, 223–242. doi: 10.30574/msarr.2024.10.1.0010
Kalogiannidis, S., and Syndoukas, D. (2024). The impact of agricultural extension services on farm output: a worldwide viewpoint. Res. World Agric. Econ. 5, 96–114. doi: 10.36956/rwae.v5i1.999
Karat, S., and Shinoji, K. (2022). “Gender in agriculture research: trends over the years,” in Engendering Agricultural Development (Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press), 81–94.
Kaur, R., and Watson, J.A. (2024). A scoping review of postharvest losses, supply chain management, and technology: implications for produce quality in developing countries. J. ASABE 67, 1103–1131. doi: 10.13031/ja.15660
Khumalo, N. Z., Sibanda, M., and Mdoda, L. (2025). The effect of heterogeneous adoption of climate-smart agriculture practices on household food and nutrition security of small-scale urban crop farmers in eThekwini Municipality. PLoS Clim. 4:e0000551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pclm.0000551
Kimeli, P., Mwacalimba, K., Tiernan, R., Mijten, E., Miroshnychenko, T., and Nautrup, B. P. (2025). Important diseases of small ruminants in sub-Saharan Africa: a review with a focus on current strategies for treatment and control in smallholder systems. Anim. Open Access J. MDPI 15:706. doi: 10.3390/ani15050706
Knight, A. (2022). What is a smallholder farmer? Heifer Int. 14. Available online at: http://www.heifer.org/blog/what-is-a-smallholder-farmer.html (Accessed December 10, 2024).
Krishnan, S., Gupta, S., Adusumili, R., Barooah, P., Maliappan, S., Singh, S., et al. (2023). Assessment of Agroecological Principles in the Context of Community-Based Natural Farming in Andhra Pradesh.
Kumar, P., Sarda, R., Yadav, A., Ashwani, Gonencgil, B., and Rai, A. (2025). Farmer's perception of climate change and factors determining the adaptation strategies to ensure sustainable agriculture in the cold desert region of Himachal Himalayas, India. Sustainability 17:2548. doi: 10.3390/su17062548
Lai-Solarin, W. I., Bamidele, J., Joel, O. J., Mohammed, A. U., Olaitan, M. A., Joel, A. F., et al. (2024). Factors limiting rural women participation in dairy value chain activities in Zaria Local Government, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Res. 10, 1–16. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.13858933
Lane, J. K., Kelly, T., Bird, B., Chenais, E., Roug, A., Vidal, G., et al. (2024). A one health approach to reducing livestock disease prevalence in developing countries: advances, challenges, and prospects. Ann. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 13, 277–302. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-111523-102133
Lawrence, A. (2024). Impact of healthcare cost on the health and well-being of rural dwellers in Nigeria. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 55, 47494–47501. doi: 10.26717/BJSTR.2024.55.008772
Loki, O., and Mdoda, L. (2023). Assessing the contribution and impact of access to extension services toward sustainable livelihoods and self-reliance in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. African J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. (AJFAND) 23, 23000–23025. doi: 10.18697/ajfand.119.22990
Maltou, R., and Bahta, Y. T. (2019). Factors influencing theresilience of smallholder livestock farmers to agricultural drought in South Africa: implication for adaptive capabilities. Jàmbá J. Disaster Risk Stud. 11:a805. doi: 10.4102/jamba.v11i1.805
Manganyi, B., Lubinga, M. H., Zondo, B., and Tempia, N. (2023). Factors influencing cassava sales and income generation among cassava producers in South Africa. Sustainability 15:14366. doi: 10.3390/su151914366
Manyike, J. Z., Taruvinga, A., and Zhou, L. (2025). Factors influencing livestock ownership and herd intensity among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape, South Africa. Heliyon 11:e41787. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41787
Mbelebele, Z., Mdoda, L., and Ntlanga, S. S. (2024). Growing wealth from nature: analyzing the profitability and determinants of high-value medicinal plants in smallholder production systems. Cogent Econ. Financ. 12:2426536. doi: 10.1080/23322039.2024.2426536
Mdoda, L., Loki, O., and Sikwela, M. M. (2025). Evaluating the economic effect of sustainable agricultural practices on small-scale farmers in the Eastern Cape Province: a propensity score matching analysis. Int. J. Agric. Sustain. 23:2478733. doi: 10.1080/14735903.2025.2478733
Mdoda, L., Meleni, S., Mujuru, N., and Alaka, K. O. (2019). Agricultural credit effects on smallholder crop farmers input utilisation in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. J. Hum. Ecol. 66, 45–55. doi: 10.31901/24566608.2019/66.1-3.3151
Mdoda, L., Naidoo, D., Ncoyini-Manciya, Z., Nontu, Y., Govender, L., Tamako, N., et al. (2024). Adaptation measures to drought risk perceived by smallholder crop farmers in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa: implications for food and nutrition security. Sustainability 16:11154. doi: 10.3390/su162411154
Mdoda, L., and Obi, A. (2019). Analysis of profitability of smallholder Irrigated food plots in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. J. Agribus. Rural Dev. 53, 225–232. doi: 10.17306/J.JARD.2019.01265
Melak, A., Aseged, T., and Shitaw, T. (2024). The influence of artificial intelligence technology on the management of livestock farms. Int. J. Distrib. Sensor Netw. 2024:8929748. doi: 10.1155/2024/8929748
Mishra, A. (2024). Government investment in agriculture and policy recommendations. SP Swag 1, 1–10. Available online at: https://www.nepjol.info/index.php/spswag/article/view/69406
Mokgomo, M. N., Chagwiza, C., and Tshilowa, P. F. (2022). The impact of government agricultural development support on agricultural income, production and food security of beneficiary small-scale farmers in South Africa. Agriculture 12:1760. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12111760
Morepje, M. T., Sithole, M. Z., Msweli, N. S., and Agholor, A. I. (2024). The influence of E-commerce platforms on sustainable agriculture practices among smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa. Sustainability 16:6496. doi: 10.3390/su16156496
Mudzielwana, R. V. A., Mafongoya, P., and Mudhara, M. (2022). An analysis of livelihood-diversification strategies among farmworker households: a case study of the Tshiombo irrigation scheme, Vhembe district, South Africa. Agriculture 12:1866. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12111866
Mujuru, N., Obi, A., Mishi, S., and Mdoda, L. (2022). Profit efficiency in family-owned crop farms in Eastern Cape Province of South Africa: a translog profit function approach. Agric. Food Secur. 11:20. doi: 10.1186/s40066-021-00345-2
Mulugeta, T., Ilomo, M., Mueke, A., Onyango, C., Matsaunyane, L., Kritzinger, Q., et al. (2024). Smallholder farmers' knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) regarding agricultural inputs with a focus on agricultural biologicals. Heliyon 10:e26719. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26719
Munaf, S., Swingler, K., Brulisauer, F., O'Hare, A., Gunn, G., and Reeves, A. (2024). Social media network analysis of Smallholder livestock farming communities in the United Kingdom. Heliyon 10:e23265. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23265
Myeki, V. A., and Bahta, Y. T. (2021). Determinants of smallholder livestock farmers' household resilience to food insecurity in South Africa. Climate 9:117. doi: 10.3390/cli9070117
Nhokwara, S. M. (2024). Farmer knowledge and behavior towards the prevention, control and eradication of bovine theileriosis in Zimbabwe Principal agent problem and animal health management.
Noge, G. (2025). The role of African feminist philanthropy in effecting change in the working conditions of women in the South African mining industry: a literature review. Int. Rev. Philanthr. Soc. Invest. 4, 46–65. doi: 10.47019/IRPSI.2025/v4n1a4
Nondzutha, T., Mdoda, L., and Qange, S. (2020). The profitability and contribution of indigenous chicken production towards improving household well-being in Lusikisiki. J. Hum. Ecol. 71, 212–221. doi: 10.31901/24566608.2020/71.1-3.3257
Nontu, Y., Mdoda, L., Dumisa, B. M., Mujuru, N. M., Ndwandwe, N., Gidi, L. S., et al. (2024). Empowering rural food security in the Eastern Cape Province: exploring the role and determinants of family food gardens. Sustainability 16:6780. doi: 10.3390/su16166780
Ogolla, K. O., Anyona, D. N., Chemuliti, J. K., Kimani, W. W., King'oo, F. M., Waweru, K. M., et al. (2024). Effectiveness of a community-centered Newcastle disease vaccine delivery model under paid and free vaccination frameworks in southeastern Kenya. PLoS ONE 19:e0308088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308088
Opabola, E. A., and Galasso, C. (2024). Informing disaster-risk management policies for education infrastructure using scenario-based recovery analyses. Nat. Commun. 15:325. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42407-y
Otekunrin, O. A., Momoh, S., and Ayinde, I. A. (2019). Smallholder farmers' market participation: concepts and methodological approach from Sub-Saharan Africa. Curr. Agric. Res. J. 7:139. doi: 10.12944/CARJ.7.2.02
Owusu, H., and Sanad, Y. M. (2025). Comprehensive Insights into Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza H5N1 in Dairy Cattle: Transmission Dynamics, Milk-Borne Risks, Public Health Implications, Biosecurity Recommendations, and One Health Strategies for Outbreak Control. Pathogens 14:278. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030278
Panel, M. M. (2020). Meat, milk and more: policy innovations to shepherd inclusive and sustainable livestock systems in Africa. Intl. Food Policy Res. Inst. doi: 10.2499/9780896293861
Patil, V., and Veettil, P. C. (2024). Farmers' risk attitude, agricultural technology adoption and impacts in Eastern India. Agric. Food Secur. 13:50. doi: 10.1186/s40066-024-00497-x
Pavlov, K., and Pavlova, O. (2024). Human capital and productive forces of rural areas: aspects of economic security of the state and its regions. Herald Khmelnytskyi Natl. Univ. Econ. Sci. 334, 397–403. doi: 10.31891/2307-5740-2024-334-60
Pezo, D., Ávalos, I., Pulido, A., Villanueva, C., Peguero, F., Sepúlveda, C., et al. (2024). Key drivers of change that affect livestock systems and their impact on sustainability and resilience. Serie Técn. Inform. Técn. 46.
Pienaar, L., and Traub, L. (2015). Understanding the smallholder farmer in South Africa: Towards a sustainable livelihoods classification.
Prabex, S., Meena, H. R., Chander, M., Srikanth, V., and Saran, V. (2024). Extension approaches and advisory services for climate smart livestock (CSL): an overview. Indian J. Vet. Sci. Biotechnol. 20:2. doi: 10.48165/ijvsbt.20.6.01
Prajapati, C. S., Priya, N. K., Bishnoi, S., Vishwakarma, S. K., Buvaneswari, K., Shastri, S., et al. (2025). The role of participatory approaches in modern agricultural extension: bridging knowledge gaps for sustainable farming practices. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 47, 204–222. doi: 10.9734/jeai/2025/v47i23281
Pun, R., Joshi, N. P., and Pun, S. (2024). Factors influencing farmers' preference for farmland consolidation in Nepal: Evidence from randomized conjoint experiment. Agric. Syst. 219:104038. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2024.104038
Rani, S., and Sharma, S. (2024). Understanding unemployment among tertiary educated youth. Arch. Curr. Res. Int. 24, 241–249. doi: 10.9734/acri/2024/v24i121015
Riesman, P. (2024). “The Fulani in a development context: the relevance of cultural traditions for coping with change and crisis,” in Life Before the Drought (London: Routledge), 171–191.
Rizzo, G., Migliore, G., Schifani, G., and Vecchio, R. (2024). Key factors influencing farmers' adoption of sustainable innovations: a systematic literature review and research agenda. Organ. Agric. 14, 57–84. doi: 10.1007/s13165-023-00440-7
Rojas-Downing, M. M., Nejadhashemi, A. P., Harrigan, T., and Woznicki, S. A. (2017). Climate change and livestock: impacts, adaptation, and mitigation. Clim. Risk Manag. 16, 145–163. doi: 10.1016/j.crm.2017.02.001
Rose, D. C., Schillings, J., Breen, J., and Morrison, R. (2025). A RESET of dairy farmer animal health planning behaviour: symbiotic advisory relationships and knowledge brokering in HerdAdvance. J. Agric. Educ. Ext. 31, 285–308. doi: 10.1080/1389224X.2024.2371295
Saqib, S. E., Yaseen, M., Ali, S., and Visetnoi, S. (2025). Agricultural land conversion and challenges for tenant farmers: empirical evidence from Pakistan. Land Degrad. Dev. 36, 802–815. doi: 10.1002/ldr.5395
Saroj, V., and Paltasingh, K. R. (2024). What promotes production contract in Indian agriculture? Managing market risk versus profit orientation. Agric. Econ. 55, 140–153. doi: 10.1111/agec.12791
Sennuga, S. O., Isola, E. O., Bamidele, J., Ameh, D., and Olaitan, M. (2024). Impact of fuel subsidy removal on agricultural production among Smallholder Farmers in Niger State, Nigeria. J. Econ. Bus. Manage. Admin. 5, 7–17. Availavble online at: http://Impact-of-Fuel-Subsidy-Removal-on-Agricultural-Production-among-Smallholder-Farmers-in-Niger-State-Nigeria.pdf (Accessed January 16, 2024).
Sigigaba, M., Mdoda, L., and Mditshwa, A. (2021). Adoption drivers of improved Open-Pollinated (OPVs) maize varieties by smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. Sustainability 13:13644. doi: 10.3390/su132413644
Simbeko, G., Nguezet, P.-M. D., Sekabira, H., Yami, M., Masirika, S.A., Bheenick, K., et al. (2023). Entrepreneurial potential and agribusiness desirability among youths in South Kivu, Democratic Republic of the Congo. Sustainability 15:873. doi: 10.3390/su15010873
Singh, B., and Pandey, R. K. (2018). Cattle and Buffalo Management Practices in Etawah District of Uttar Pradesh. Environ Ecol. 36:425–9.
Sintayehu, D. W., Alemayehu, S., Terefe, T., Tegegne, G., Engdaw, M. M., Gebre, L., et al. (2025). Effects of drought on livestock production, market dynamics, and pastoralists' adaptation strategies in semi-arid Ethiopia. Climate 13:65. doi: 10.3390/cli13040065
Sommet, N., Weissman, D. L., Cheutin, N., and Elliot, A. J. (2023). How many participants do I need to test an interaction? Conducting an appropriate power analysis and achieving sufficient power to detect an interaction. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 6:25152459231178728. doi: 10.1177/25152459231178728
Song, M., Wu, Q., and Zhu, H. (2024). Could the aging of the rural population boost green agricultural total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Sustainability 16:6117. doi: 10.3390/su16146117
Spada, R., Moritz, L., Rommel, J., Cerroni, S., Meuwissen, M. P., and Dalhaus, T. (2025). Behavioral Preferences Affecting the Adoption of Financial Price Risk Management Tools in Agriculture: A Systematic Literature Review.
Tirivanhu, N., Freddy Ruzhani, F., and Newettie Jambo, N. (2023). Determinants of effective cattle disease management among smallholder farmers in light of rapid theileriosis outbreaks and economic losses: the case of Mutare rural district, Manicaland province, Zimbabwe. Cogent Food Agric. 9:2275419. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2023.2275419
Wann, T., Khongtim, J., and Chyne, R. C. (2024). Assessing the impact of information literacy on farmers' decision-making processes: a mixed-methods approach. IFLA J. 50, 463–478. doi: 10.1177/03400352241261730
Keywords: livestock practices, challenges, risk management, smallholder farmers, Eastern Cape Province
Citation: Nontu Y, Mbelebele Z, Mdoda L, Dumisa BM, Ndwandwe N, Gidi LS and Xaba M (2025) Determinants and risk mitigation in livestock management practices among smallholder farmers in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1636417. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1636417
Received: 27 May 2025; Accepted: 30 October 2025;
Published: 28 November 2025.
Edited by:
Monika Thakur, Amity University, IndiaReviewed by:
Juliet Angom, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham University, IndiaEnock Siankwilimba, University of Zambia, Zambia
Dhananjay S. Gaikwad, Amity University, India
Sunayan Sharma, Amity University, India
Copyright © 2025 Nontu, Mbelebele, Mdoda, Dumisa, Ndwandwe, Gidi and Xaba. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanga Nontu, bm9udHV5QHVuaXp1bHUuYWMuemE=
†ORCID: Yanga Nontu orcid.org/0000-0003-4843-9437
Lelethu Mdoda orcid.org/0000-0002-5402-1304
Bonguyise Mzwandile Dumisa orcid.org/0000-0001-8993-5846
Nkosingimele Ndwandwe orcid.org/0009-0006-4672-3556
Majezwa Xaba orcid.org/0000-0002-5600-5850
 Yanga Nontu
Yanga Nontu Zusiphe Mbelebele
Zusiphe Mbelebele Lelethu Mdoda
Lelethu Mdoda Bonguyise Mzwandile Dumisa
Bonguyise Mzwandile Dumisa Nkosingimele Ndwandwe
Nkosingimele Ndwandwe Lungile Sivuyile Gidi
Lungile Sivuyile Gidi Majezwa Xaba1†
Majezwa Xaba1†