- 1Food Technology Department, Faculty of Engineering, Bina Nusantara University, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 2Laboratory of Postharvest Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan
- 3Research Center for Applied Microbiology, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), Bogor, Indonesia
Postharvest losses of fresh produce remain a persistent challenge. Application of coatings/films have been extensively investigated as sustainable preservation strategies. This review highlights the role of chitosan nanoparticle (ChiNP)-stabilized Pickering emulsions in enhancing the functional performance of such coatings for maintaining fruit and vegetable quality. The findings indicated that ChiNP offer some advantages, including antimicrobial properties due to their cationic nature, while their nanoscale size contributes to emulsion stability by improving interfacial adsorption. Their incorporation enhances gas and water vapor barrier properties through a dense structural configuration at the oil–water interface, effectively suppressing ethylene biosynthesis and delaying cell wall degradation, thereby slowing ripening. Moreover, ChiNP demonstrate synergism with essential oils (EO), significantly improving the antimicrobial efficacy. However, further research is needed to improve stability, understand interactions with biopolymer matrices, assess wettability, ensure safety, and optimize delivery performance. In industrial context, the optimization of formulation parameters and sensory evaluations should be prioritized, thereby supporting the potential implementation of ChiNP as an effective and sustainable approach for fresh postharvest commodities preservation.
1 Introduction
Fruits and vegetables are valued globally for their nutrients but are highly perishable, even under cold storage (Ding et al., 2024). Postharvest losses, caused mainly by respiration, transpiration, and poor handling, account for about 14% of global food waste (FAO, 2019; Punia Bangar et al., 2022; Udayanga et al., 2013). To reduce deterioration and contamination, coatings/films have been developed for various fresh fruits and vegetables. Made from edible polymers like polysaccharides, proteins, and lipids, these films offer protection against mechanical and microbial damage, maintain biochemical quality, antioxidant capacity, and storage life of the fresh produces (Jung et al., 2020; Wardana et al., 2021; Lin et al., 2017). However, ongoing research aims to enhance their functional properties due to current limitations.
Pickering emulsion is an emulsion that utilizes solid particles for stabilization rather than traditional surfactants (Tan et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2024). It has recently emerged as a promising alternative to conventional surfactants like Tween 20, Tween 80, and sodium dodecyl sulfate for food applications due to its potential to enhance the functional properties of edible films and coatings (Wang et al., 2013; Murray, 2019; Sarkar and Dickinson, 2020). These emulsions offer several advantages, including safety, biodegradability, stability, and cost-effectiveness, which make them particularly appealing for use in packaging systems (Ortiz et al., 2020). Furthermore, the overuse of synthetic surfactants can cause allergic reactions and may carry potential carcinogenic risks (Jiang et al., 2020a; Shah et al., 2021). Pickering emulsions are stabilized by solid particles or nanofibers that adsorb at the interface between water and oil phases (Lou et al., 2023). Functionalized polysaccharide, particularly ChiNP, have been used as stabilizers in the preparation of Pickering emulsions, which can then be incorporated into polymer matrices to produce food packaging films or coatings (Naji-Tabasi et al., 2024). Among polysaccharide-based particles, ChiNP demonstrated strong functional characteristics, serving effectively in antimicrobial roles and enhancing functional attributes as a nanofiller (Wardana et al., 2023a; Wardana et al., 2023b).
The use of Chi-based stabilizers in the development of emulsified biomaterials is rapidly increasing, as evidenced by 470 published studies on the topic referring to the Scopus-indexed database (Figure 1). In addition to being renewable and sustainable, Chi can be easily chemically functionalized to customize its properties for specific applications in the food systems (Pandey and Mathur, 2024), including aminoethyl Chi (Tamer et al., 2024), carboxymethyl Chi (Nicolle et al., 2021), quaternized Chi (Nicolle et al., 2021), and thiolated Chi (Sacco et al., 2020). Significant progress has been made in bio-based food packaging films, driven by the development of biopolymer nanomaterial-stabilized Pickering emulsions. This article reviews recent advancements in Pickering emulsions stabilized by ChiNP, which can be incorporated into polymer matrices to produce packaging materials aimed at preserving the freshness of postharvest commodities. The antimicrobial properties, barrier performance, and overall effectiveness of these ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsion films are also discussed.
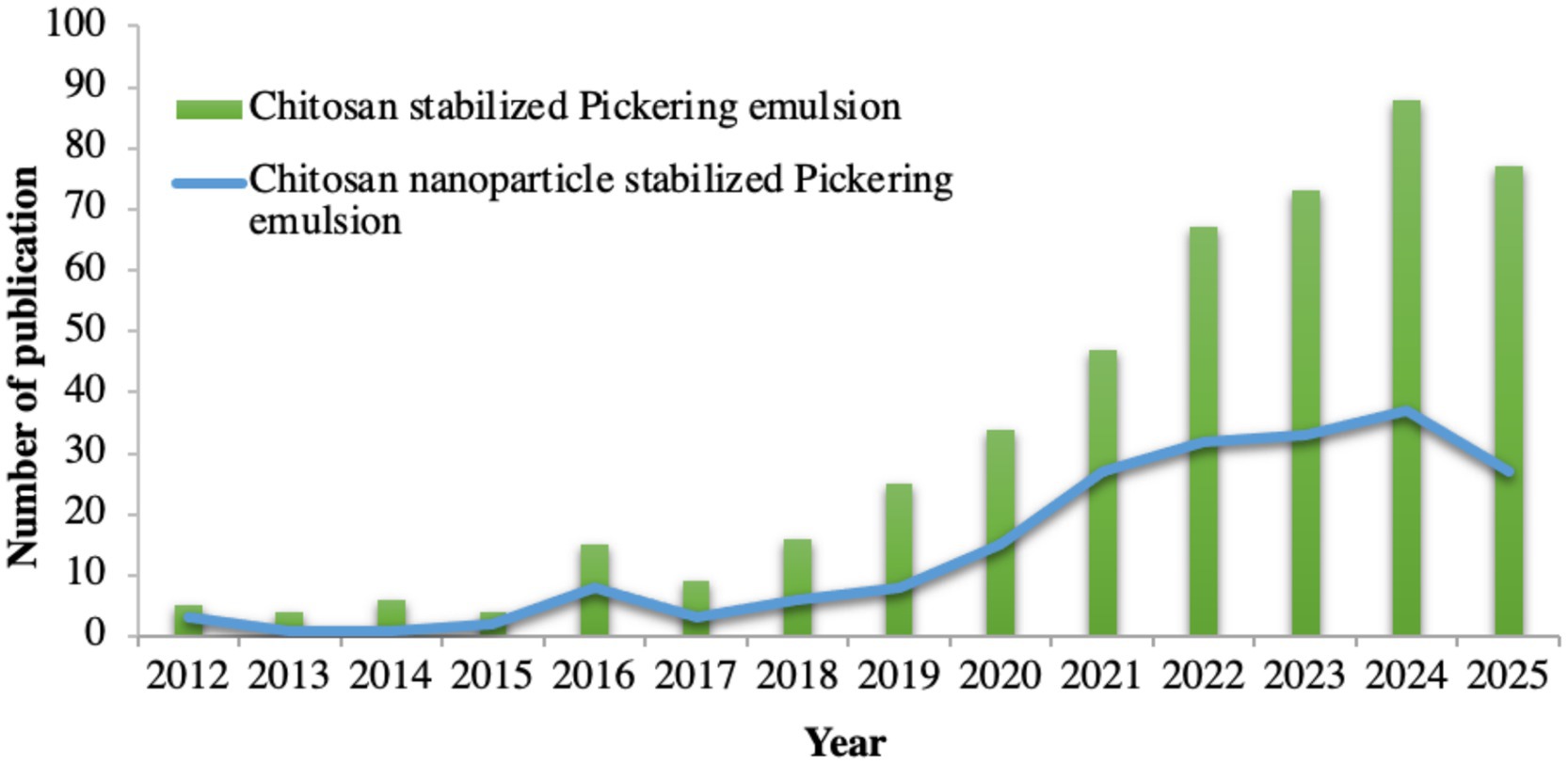
Figure 1. Annual publications (2009–2025) on “chitosan Pickering emulsion” and “chitosan nanoparticle Pickering emulsion” (Scopus, May 2025).
2 ChiNP as stabilizer agent of Pickering emulsion
Pickering emulsions are stabilized by solid colloidal particles instead of traditional emulsifiers like surfactants or proteins (Tan et al., 2022), as shown in Figure 2A. First described by Ramsden (1903) and Pickering (1907), they offer enhanced stability, reduced health risks, and eco-friendly components (Albert et al., 2019). These emulsions are increasingly used in edible films and coatings that carry functional lipids (Deng et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2020). Their stability is explained by two main theories: (1) solid particles forming a barrier at the oil–water interface to prevent coalescence (Aveyard et al., 2003), and (2) particle networks creating viscoelastic structures that increase viscosity (Chen et al., 2020). Key influencing factors include particle type, concentration, pH, and temperature. Polysaccharide-based particles, in natural or modified forms, are among the most studied stabilizers. They are often integrated into polymer matrices for edible coatings. Their use improves emulsion resistance to environmental stressors such as heat and ionic strength, enhancing performance as barriers to light, water, and gases (Qiao et al., 2020). Moreover, the incorporation of nanomaterials allows controlled release of bioactive compounds, offering functional benefits for preserving food quality during storage (De Farias et al., 2025).
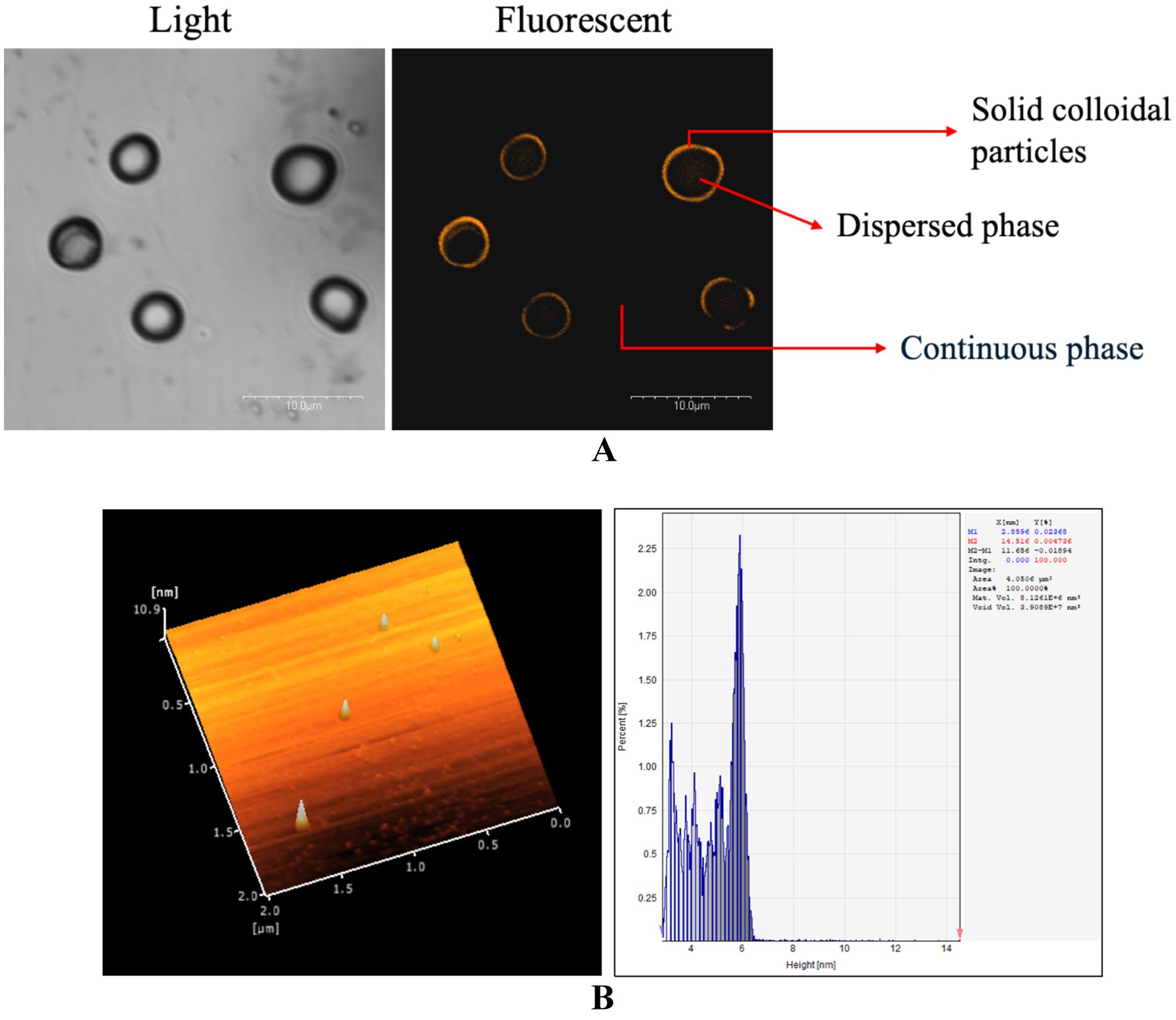
Figure 2. (A) Polysaccharide-based Pickering emulsion stained with acridine orange under confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM); (B) 3D ChiNP image and height profile observed with atomic force microscopy.
ChiNP is nanoscale particle derived from Chi, a biopolymer obtained from chitin primarily sourced from the shells of crustaceans such as shrimp and crabs (Abere et al., 2022; Ali et al., 2022), as seen in Figure 2B. It can be formed through various methods, including ionic gelation, emulsification, nanoprecipitation, and ionotropic gelation. In most cases, the synthesis of ChiNP was carried out using a Chi solution or using chitin directly from seafood sources via cross-linking by tripolyphosphate anions at room temperature (Sawtarie et al., 2017; Sreekumar et al., 2018; Ali et al., 2022). This method, which is commonly called ionic gelation, allowed the preparation of ChiNP with range from 50 nm to 100 nm in diameter. It is not water soluble, hindering its direct application in aqueous systems, requiring dispersion aids, or emulsifiers to ensure uniform distribution and it often require acid solubilization to improve its solubility. Most methods based on ionic gelation involve the presence of 1% acetic acid to dissolve Chi. This nanoparticle has been gaining significant interest in various fields, including food science, due to their unique properties and potential applications. In the food field, ChiNP have been explored for several purposes, including use as a food additive (Stefanowska et al., 2023), food packaging material (Stefanowska et al., 2023; Wardana et al., 2024; Hamid et al., 2025) and solid stabilizer for Pickering emulsion (Wardana et al., 2023a).
ChiNP are effective stabilizers in Pickering emulsions, offering enhanced barrier and antimicrobial properties for preserving postharvest commodities (Ngo et al., 2021; Ren et al., 2020). Their role as nanofillers improves functional performances, such as antimicrobial (Wardana et al., 2023b), barrier (Ashraf et al., 2025a) and mechanical properties (Ashraf et al., 2025b), especially when the coating solution’s pH remains above their pKa (~6.3), ensuring insolubility and stability (Lim and Hudson, 2004; Ahmed et al., 2021). While Chi’s antimicrobial action is often linked to its positive charge in acidic conditions, studies have shown increased activity at higher pH. For example, N-alkylated Chi derivatives exhibited stronger effects against E. coli from pH 5 to 7.5 (Yang et al., 2005), suggesting that factors beyond charge contribute to its activity, which remains unclear under neutral or alkaline conditions (Kong et al., 2010).
3 Antimicrobial features
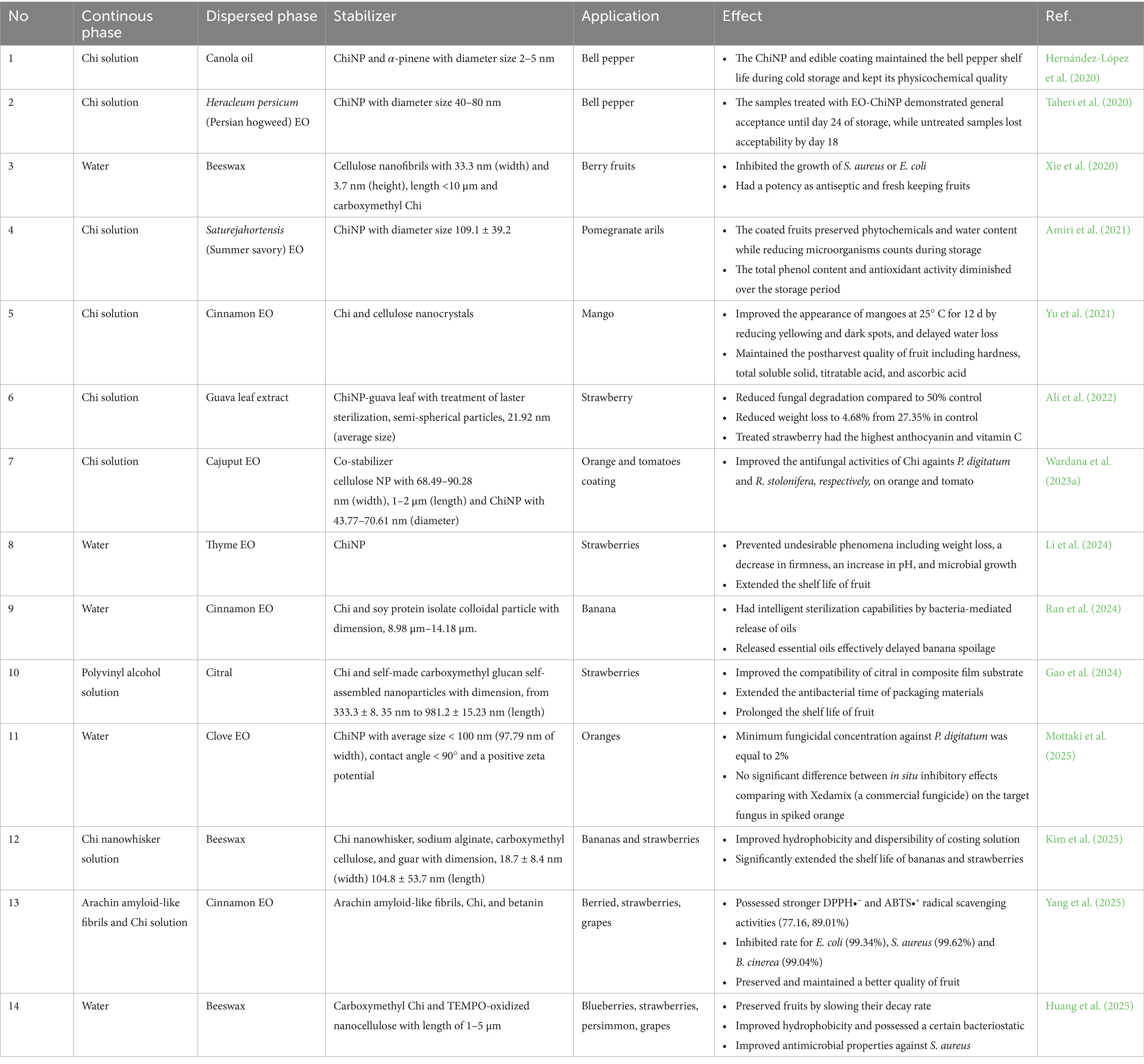
Microbial spoilage of fresh postharvest produce poses global challenges, affecting quality and safety. While synthetic antimicrobials have long been used, concerns over toxicity have shifted interest toward natural alternatives. Biodegradable antimicrobial coatings, especially Pickering emulsions, offer stability, controlled release, and bioactive compatibility. The ChiNP are particularly effective as emulsion stabilizers and antimicrobial carriers. The ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsions have shown promise as coating systems for postharvest preservation (Ahmed and Ikram, 2016; Wardana et al., 2023a; Thungphotrakul and Prapainainar, 2024). Their performance in microbial control supports continued research into their application for maintaining the postharvest quality of fresh commodities, as illustrated in Table 1.
The antibacterial mechanisms of ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsions are not yet fully understood. Studies showed that ChiNP stabilizer alone had no inhibitory effect on E. coli or Staphylococcus aureus (Thungphotrakul and Prapainainar, 2024). ChiNP are not effective antimicrobials in neutral to alkaline pH due to reduced solubility and weaker interaction with microbial membranes (Quan et al., 2021). However, incorporating clove essential oil (EO) enhanced antibacterial activity in a dose-and species-dependent manner. For example, 2.5% clove EO inhibited E. coli but not S. aureus, while 10% EO produced the highest inhibition zones (13.33 mm for E. coli and 11.33 mm for S. aureus) (Thungphotrakul and Prapainainar, 2024). This suggests that phenolic compounds in clove EO and controlled release via ChiNP encapsulation contribute to effectiveness. Similarly, Ran et al. (2024) reported that ChiNP-based emulsions with cinnamon EO inhibited E. coli, S. aureus, Bacillus subtilis, and Pseudomonas fluorescens by disrupting ATPase activity and chitin synthesis. B. subtilis was most affected. Microscopic staining confirmed increased bacterial death, highlighting the strong antimicrobial potential of these EO-loaded Pickering emulsions for food preservation.
Rhizopus stolonifer and Penicillium digitatum are major fungal pathogens causing postharvest rot in fruits and vegetables. Wardana et al. (2023a) examined the antifungal efficacy of cajuput EO stabilized with cellulose nanofibers and ChiNP against these fungi. Tangerines and tomatoes were inoculated with fungal spores, respectively 5 and 3 μL, and treated with EO-based Pickering emulsions. By day 3, lesions were absent in coated tangerines under storage temperature ~18°C and RH ~ 48%, while controls had 2.4 mm lesions. By day 6, lesion sizes in coated fruits were significantly smaller (22.41 mm in tangerines, 4.72 mm in tomatoes) than in uncoated controls (42.15 mm and 10.21 mm). The results showed that ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsions effectively suppressed fungal growth, with differing impacts across fruit types due to synergistic effects of EO and stabilizers. Mottaki et al. (2025) evaluated clove EO/ChiNP-stabilized emulsions against P. digitatum in vitro and in vivo. Treated samples showed significantly reduced fungal growth. Oranges coated with the formulation had minimal decay after 60 days, while uncoated fruits decayed entirely. The antifungal effect was comparable to commercial agents, likely due to increased hydrogen peroxide release and activation of plant defense enzymes. Bioactive compounds in clove EO, such as punicalagin and gallic acid, contributed to fungal inhibition (Wardana et al., 2021).
4 Preservation effect on fresh postharvest commodities
4.1 Light, gas, and water vapor barrier properties
The incorporation of ChiNP into Pickering emulsions enhances barrier properties, aiding postharvest preservation. ChiNP significantly reduce oxygen and water vapor permeability compared to conventional chitosan, especially when combined with pectin (Ngo et al., 2021). These emulsions maintain fruit quality by inhibiting enzymes and creating tortuous microstructures that slow moisture transmission and extend shelf life (Yu et al., 2021; Pan et al., 2024). Stabilizer particles at the oil–water interface form dense layers, minimizing evaporation and oxidation while reducing gas permeability (Jiang et al., 2020b). Light-blocking and UV-filtering effects are enhanced by certain nanoparticles like lignin-based types, making them suitable for food and cosmetic applications (Dai et al., 2019; Wu et al., 2024). These structural and antimicrobial properties support their potential in sustainable packaging (Lu and Tian, 2021; De Farias et al., 2025). The surface characteristics and hydrophilicity of stabilizers influence emulsion stability. Greater hydrophilicity improves particle adsorption, strengthening barriers against water and gases (Chakrabarty and Teramoto, 2020). Overall, ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsions present an eco-friendly strategy for extending the freshness of perishable foods, aligning with the demand for biodegradable, high-performance packaging (Ghavidel and Fatehi, 2020).
4.2 Postharvest physiology
Climacteric fruits continue to respire after harvest, releasing ethylene gas that drives ripening. Ethylene stimulates enzymes that break down pectin in the cell wall, leading to reduced firmness and increased soluble solids (Zhu et al., 2019). Chi has been reported to suppress ethylene accumulation, potentially through downregulating the expression or enzymatic activity of ACS (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase) and ACO (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase). Edible coatings using Pickering emulsions stabilized by ChiNP have shown effectiveness in slowing respiration, as presented in Table 1. One of mechanisms is the inhibition of pectin-degrading enzymes like polygalacturonase (PLG) and pectate lyase (PLY), which normally break down the colloidal layer of the cell wall (Wantat et al., 2021). Research confirms ChiNP’s enzyme-inhibiting effect. Yu et al. (2021) found that ChiNP-based coatings on mangoes suppressed PLG and PLY activity for up to 9 days, especially on day 6. This helped maintain fruit firmness, reducing the loss by only 47% in coated samples versus 87% in uncoated ones over 12 days. Similarly, Yang et al. (2025) reported that ChiNP-coated strawberries had better firmness and lower total soluble solids (TSS), indicating slower polysaccharide hydrolysis. The effectiveness of ChiNP is largely due to its function as a gas exchange barrier. The emulsion creates a dense, stable, and hydrophobic layer that limits the diffusion of water vapor and gases. This restricts ethylene biosynthesis and pectin-degrading enzyme activity, thereby slowing ripening and reducing TSS accumulation. Moreover, ChiNP coatings helped preserve fruit color and prevent browning by minimizing moisture loss (Ali et al., 2022). Hence, ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsions are a promising postharvest strategy to delay ripening by inhibiting enzyme activity and enhancing the fruit’s barrier properties against gas and moisture exchange.
5 Challenges and limitations
There have been growing interest in Pickering emulsions stabilized by ChiNP for fresh fruit and vegetable applications, as stated in previous section, due to their biofunctionality and ability to replace synthetic surfactants harmful to health and the environment. Incorporating edible polymers such as gelatin, alginate, or starch can enhance the mechanical and flexible properties of ChiNP-based systems, especially in hydrogels and films (Luo et al., 2022). Despite their potential, challenges still remain, particularly in improving emulsion stability under varying environmental conditions such as temperature, pH, ionic strength (Gonzalez Ortiz et al., 2020; Meng et al., 2023). Limited research exists on how ChiNP-based emulsions interact with complex film/coating biomatrices. Furthermore, limited data are available regarding the contact angle measurements of ChiNP-based materials proposed as novel Pickering stabilizers (Sharkawy et al., 2020). Gaining deeper infromation into their wettability would clearly support the enhancement of stability and barrier properties in chitosan-based Pickering emulsion systems. As a pH-sensitive cationic polysaccharide, ChiNP is ideal for stimuli-responsive delivery of bioactive compounds (Zhao et al., 2022), however more studies are needed to understand its dynamic behavior and bioavailability in both in vitro and in vivo models. Toxicological assessments are also necessary to ensure food safety (Meng et al., 2023). Finally, further exploration is essential to fully harness the functional potential of ChiNP-based Pickering emulsions.
6 Conclusion and future perspective
The use of ChiNP-stabilized Pickering emulsion shows promising potential in extending fruit shelf life by preserving quality and preventing microbial contamination. Its nanoparticle size offers effective stabilization and compatibility, enabling the encapsulation and controlled release of bioactive compounds. It is important to note that although ChiNP holds promise in various food applications, further research is ongoing to fully explore their potential and ensure their safety and regulatory compliance. Several mechanisms of action of ChiNP as an antimicrobial agent and barrier properties also need to be investigated thoroughly. This allows further understanding for future research on the formulation and development process (e.g., encapsulation efficiency, in vivo release kinetics) in allowing the modification of emulsion to combat specific microbial contamination (Ashraf et al., 2025b). Concerns related to allergenicity, and sustainability arise from the sourcing of Chi from crustaceans, prompting researchers to explore alternative sources, such as fungi and insects, for Chi production (Peng et al., 2022). Moreover, sensory evaluations play a vital role in determining consumer acceptance, yet this aspect remains insufficiently investigated in recent research. For food applications, higher concentrations of EO are often required, leading to undesirable tastes and odors. Encapsulating EO in ChiNP could offer a potential approach for achieving sustained release (Bakr et al., 2024). Overall, ChiNP-based stabilization of Pickering emulsion offers a wide range of possibilities for improving food quality, safety, and sustainability.
Author contributions
AAW: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Validation, Methodology, Conceptualization. VM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. LPW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. FNN: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. FuminT: Resources, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. FumihT: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Resources. RHBS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Research and Technology Transfer Office – Bina Nusantara University.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical, resource, and financial support from Bina Nusantara University, Indonesia and Kyushu University, Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The author(s) verify and take full responsibility for the use of generative AI in the preparation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abere, D. V., Ojo, S. A., Paredes-Epinosa, M. B., and Hakami, A. (2022). Derivation of composites of chitosan-nanoparticles from crustaceans source for nanomedicine: a mini review. Biomed. Eng. Adv. 4:100058. doi: 10.1016/j.bea.2022.100058
Ahmed, S., and Ikram, S. (2016). Chitosan based scaffolds and their applications in wound healing. Achievements Life Sci. 11, 27–37. doi: 10.1016/j.als.2016.04.001
Ahmed, R., Wang, M., Qi, Z., Hira, N. U. A., Jiang, J., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Pickering emulsions based on the pH-responsive assembly of food-grade chitosan. ACS Omega 6, 17915–17922. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01166
Albert, C., Beladjine, M., Tsapis, N., Fattal, E., Agnely, F., and Huang, N. (2019). Pickering emulsions: preparation processes, key parameters governing their properties and potential for pharmaceutical applications. J. Control. Release 309, 302–332. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.07.003
Ali, L. M., Ahmed, A. E. A. E., Hasan, H. E., Suliman, A. E. E., and Saleh, S. S. (2022). Quality characteristics of strawberry fruit following a combined treatment of laser sterilization and guava leaf-based chitosan nanoparticle coating. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 9:80. doi: 10.1186/s40538-022-00343-x
Ali, E. F., Fahmy, A. S., Hassan, M. S., Al-Harbi, O. H. M., Ibrahim, E. Y., and Moussa, M. M. A.-H. (2022). Impact of chitosan nanoparticles edible coating on shelf-life extension and postharvest quality of coriander herb. J. Food Process. Preserv. 46:e16238. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.16238
Amiri, A., Ramezanian, A., Mortazavi, S. M. H., Hosseini, S. M. H., and Yahia, E. (2021). Shelf-life extension of pomegranate arils using chitosan nanoparticles loaded with Satureja hortensis essential oil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 101, 3778–3786. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11010
Ashraf, J., Ismail, N., Tufail, T., Zhang, J., Awais, M., Zhang, Q., et al. (2025a). Fabrication of novel pullulan/carboxymethyl chitosan-based edible film incorporated with ultrasonically equipped aqueous zein/turmeric essential oil nanoemulsion for effective preservation of mango fruits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 294:139330. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.139330
Ashraf, J., Ismail, N., Tufail, T., Zhang, J., Chen, J., Rehman, A., et al. (2025b). Technological advancements in zein-based nano-colloids: current emerging trends in sustainable packaging and their potential in enhancing shelf-life of fresh fruits. Food Packag. Shelf Life 49:101523. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2025.101523
Aveyard, R., Binks, B. P., and Clint, J. H. (2003). Emulsions stabilised solely by colloidal particles. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 100, 503–546. doi: 10.1016/S0001-8686(02)00069-6
Bakr, J. G., Khalid, S. A., Khafaga, N. I. M., Yassien, N. A., Hamdy, M. B., and Zak, A. (2024). Impact of using cinnamon (Cinnamomum verum) essential oil and its pectin-chitosan nano-emulsion on survival of aspergillus flavus and total aflatoxin inhibition in beef burger patties. Food Control 159:110294. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2024.110294
Chakrabarty, A., and Teramoto, Y. (2020). Scalable Pickering stabilization to design cellulose nanofiber-wrapped block copolymer microspheres for thermal energy storage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 8, 4623–4632. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00687
Chen, L., Ao, F., Ge, X., and Shen, W. (2020). Food-grade Pickering emulsions: preparation, stabilization and applications. Molecules 25:3202. doi: 10.3390/molecules25143202
Dai, L., Li, Y., Kong, F., Liu, K., Si, C., and Ni, Y. (2019). Lignin-based nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsion for stability improvement and thermal-controlled release of trans-resveratrol. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 13497–13504. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b02966
De Farias, P. M., De Sousa, R. V., Maniglia, B. C., Pascall, M., Matthes, J., Sadzik, A., et al. (2025). Biobased food packaging systems functionalized with essential oil via Pickering emulsion: advantages, challenges, and current applications. ACS Omega 10, 4173–4186. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c09320
Deng, Z., Jung, J., Simonsen, J., and Zhao, Y. (2018). Cellulose nanocrystals Pickering emulsion incorporated chitosan coatings for improving storability of postharvest Bartlett pears (Pyrus communis) during long-term cold storage. Food Hydrocoll. 84, 229–237. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.06.012
Ding, F., Long, S., Huang, X., Shi, J., Povey, M., and Zou, X. (2024). Emerging Pickering emulsion films for bio-based food packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 42:101242. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2024.101242
FAO. (2019). Redução de perdas e desperdícios alimentares é essencial para alcançar metas globais. Available online at: http://www.fao.org/brasil/noticias/detail-events/pt/c/1199506/ (Accessed 14 March 2025).
Gao, T.-H., Yan, L.-J., Chen, M.-Q., Dong, W.-F., and Shi, D.-J. (2024). Preparation and properties of antibacterial composite films with high loading of citral. Chin. J. Appl. Chem. 41, 1284–1296. doi: 10.19894/j.issn.1000-0518.240033
Ghavidel, N., and Fatehi, P. (2020). Pickering/non-Pickering emulsions of nanostructured sulfonated lignin derivatives. Chem. Sus. Chem. 13, 4567–4578. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202000965
Hamid, K. H. A., Fauzi, M. A., Ajit, A., Arzmi, M. H., and Azman, N. A. M. (2025). Eugenol Pickering emulsion stabilized by chitosan self-assembled nanoparticles: fabrication, emulsion stability, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. doi: 10.1002/jctb.7905
Hernández-López, G., Ventura-Aguilar, R. I., Correa-Pacheco, Z. N., Bautista-Baños, S., and Barrera-Necha, L. L. (2020). Nanostructured chitosan edible coating loaded with α-pinene for the preservation of the postharvest quality of Capsicum annuum L. and Alternaria alternata control. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 165, 1881–1888. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.094
Huang, S., Lv, J., Liu, X., Yuan, H., Wang, Y., Huan, S., et al. (2025). Sustainable and green design of beeswax-based Pickering emulsion coating for food packaging. J. Clean. Prod. 495:145096. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2025.145096
Jiang, H., Sheng, Y., and Ngai, T. (2020a). Pickering emulsions: versatility of colloidal particles and recent applications. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 49, 1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2020.04.010
Jiang, Y., Zhu, Y., Li, F., Du, J., Huang, Q., Sun-Waterhouse, D., et al. (2020b). Antioxidative pectin from hawthorn wine pomace stabilizes and protects Pickering emulsions via forming zein-pectin gel-like shell structure. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 151, 193–203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.164
Jung, J., Deng, Z., and Zhao, Y. (2020). Mechanisms and performance of cellulose nanocrystals Pickering emulsion chitosan coatings for reducing ethylene production and physiological disorders in postharvest 'Bartlett' pears (Pyrus communis L.) during cold storage. Food Chem. 309:125693. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125693
Kim, J., Seo, J., Kim, H. J., Jeong, Y., Lee, H., Park, C., et al. (2025). Synergistic design of Pickering emulsion inks of nanochitosan-alginate-beeswax for edible coating in fruit preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 167:111462. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2025.111462
Kong, M., Chen, X. G., Xing, K., and Park, H. J. (2010). Antimicrobial properties of chitosan and mode of action: a state of the art review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 144, 51–63. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.09.012
Li, H., Liu, M., Han, S., Hua, S., Zhang, H., Wang, J., et al. (2024). Edible chitosan-based Pickering emulsion coatings: preparation, characteristics, and application in strawberry preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 264:130672. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130672
Lim, S. H., and Hudson, S. M. (2004). Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of a water-soluble chitosan derivative with a fiber-reactive group. Carbohydr. Res. 339, 313–319. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2003.10.024
Lin, M. G., Lasekan, O., Saari, N., and Khairunniza-Bejo, S. (2017). The effect of the application of edible coatings on or before ultraviolet treatment on postharvested longan fruits. J. Food Qual. 2017, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2017/5454263
Lou, S., Wen, M., Wang, Y., and Ni, X. (2023). Recent progress in the application of nanoparticle-stabilized Pickering emulsion in food packaging. Food Sci. 44, 344–352. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20220414-164
Lu, H., and Tian, Y. (2021). Nanostarch: preparation, modification, and application in Pickering emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 69, 6929–6942. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01244
Luo, Q., Hossen, M. A., Zeng, Y., Dai, J., Li, S., Qin, W., et al. (2022). Gelatin-based composite films and their application in food packaging: a review. J. Food Eng. 313:110762. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2021.110762
Meng, W., Sun, H., Mu, T., and Garcia-Vaquero, M. (2023). Chitosan-based Pickering emulsion: a comprehensive review on their stabilizers, bioavailability, applications and regulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 304:120491. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2022.120491
Mottaki, M., Jafari, S. M., Hosseini, S. M., Sadeghi, A., and Heydari-Delfard, F. (2025). Pickering emulsions stabilized by chitosan nanoparticles and loaded with clove essential oil as a green biopesticide: a case study on controlling fungal growth in oranges. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 219:113234. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2024.113234
Murray, B. S. (2019). Pickering emulsions for food and drinks. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 27, 57–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.05.004
Naji-Tabasi, S., Shakeri, M.-S., Modiri-Dovom, A., and Shahbazizadeh, S. (2024). Application of Pistacia atlantica Pickering emulsion-filled chitosan gel for targeted delivery of curcumin. Food Sci. Nutr. 12, 2809–2817. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3962
Ngo, T. M. P., Nguyen, T. H., Dang, T. M. Q., Do, T. V. T., Reungsang, A., Chaiwong, N., et al. (2021). Effect of pectin/nanochitosan-based coatings and storage temperature on shelf-life extension of “elephant” mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit. Polymers 13:19. doi: 10.3390/polym13193430
Nicolle, L., Journot, C. M. A., and Gerber-Lemaire, S. (2021). Chitosan functionalization: covalent and non-covalent interactions and their characterization. Polymers 13:4118. doi: 10.3390/polym13234118
Ortiz, G. D., Pochat-Bohatier, C., Cambedouzou, J., Bechelany, M., and Miele, P. (2020). Current trends in Pickering emulsions: particle morphology and applications. Eng 6, 468–482. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.08.017
Pan, Z., Zhong, W., Xu, J., Li, D., Lin, J., Wu, W., et al. (2024). Effects of oregano essential oil Pickering emulsion and ZnO nanoparticles on the properties and antibacterial activity of konjac glucomannan/carboxymethyl chitosan nanocomposite films. RSC Adv. 14, 6548–6556. doi: 10.1039/D3RA07845K
Pandey, R., and Mathur, G. (2024). Current trends in chitosan functionalization methods and their applications. Starch 77:2300248. doi: 10.1002/star.202300248
Peng, S., Liang, Y., Xiao, W., Liu, Y., Yu, M., and Liu, L. (2022). Anaphylaxis induced by intra-articular injection of chitosan: a case report and literature review. Clin. Case Rep. 10:e6596. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.6596
Punia Bangar, S., Whiteside, W. S., Ozogul, F., Dunno, K. D., Cavender, G. A., and Dawson, P. (2022). Development of starch-based films reinforced with cellulosic nanocrystals and essential oil to extend the shelf life of red grapes. Food Biosci. 47:101621. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2022.101621
Qiao, M., Yang, X., Zhu, Y., Guerin, G., and Zhang, S. (2020). Ultralight aerogels with hierarchical porous structures prepared from cellulose nanocrystal stabilized Pickering high internal phase emulsions. Langmuir 36, 6421–6428. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00646
Quan, Z., Luo, C., Zhu, B., Zhao, C., Yang, M., Bjørås, M., et al. (2021). Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of chitosan/polypropylene carbonate-based nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 11, 10121–10129. doi: 10.1039/D0RA09257F
Ramsden, W. (1903). Separation of solids in the surface-layers of solutions and suspensions (observations on surface-membranes, bubbles, emulsions, and mechanical coagulation). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 72, 156–164.
Ran, R., Zhang, X., Guo, X., Yang, C., Zhang, F., and Li, G. (2024). An “intelligent-sensing and targeted release” antimicrobial Pickering emulsion for banana preservation. Food Hydrocoll. 156:110325. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2024.110325
Ren, X., He, S., Liu, D., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Multistimuli-responsive Pickering emulsion stabilized by se-containing surfactant-modified chitosan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 3986–3994. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00010
Sacco, P., Cok, M., Scognamiglio, F., Pizzolitto, C., Vecchies, F., Marfoglia, A., et al. (2020). Glycosylated-chitosan derivatives: a systematic review. Molecules 25:1534. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071534
Sarkar, A., and Dickinson, E. (2020). Sustainable food-grade Pickering emulsions stabilized by plant-based particles. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 49, 69–81. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2020.04.004
Sawtarie, N., Cai, Y., and Lapitsky, Y. (2017). Preparation of chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles with highly tunable size and low polydispersity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 157, 110–117. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.055
Shah, B. R., Dvořák, P., Velíšek, J., and Mráz, J. (2021). Opening a new gateway towards the applications of chitosan nanoparticles stabilized Pickering emulsion in the realm of aquaculture. Carbohydr. Polym. 265:118096. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118096
Sharkawy, A., Barreiro, M. F., and Rodrigues, A. E. (2020). Chitosan-based Pickering emulsions and their applications: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 250:116885. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116885
Sreekumar, S., Goycoolea, F. M., Moerschbacher, B. M., and Rivera-Rodriguez, G. R. (2018). Parameters influencing the size of chitosan-TPP nano-and microparticles. Sci. Rep. 8:4695. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23064-4
Stefanowska, K., Woźniak, M., Dobrucka, R., and Ratajczak, I. (2023). Chitosan with natural additives as a potential food packaging. Materials 16:1579. doi: 10.3390/ma16041579
Taheri, A., Behnamian, M., Dezhsetan, S., and Karimirad, R. (2020). Shelf life extension of bell pepper by application of chitosan nanoparticles containing Heracleum persicum fruit essential oil. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 170:111313. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111313
Tamer, T. M., Abbas, R., Sadik, W. A., and El-Naggar, M. E. (2024). Development of novel amino-ethyl chitosan hydrogel for the removal of methyl orange azo dye model. Sci. Rep. 14:1284. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51538-1
Tan, H., Zhang, R., Han, L., Zhang, T., and Ngai, T. (2022). Pickering emulsions stabilized by aminated gelatin nanoparticles: are gelatin nanoparticles acting as genuine Pickering stabilizers or structuring agents? Food Hydrocoll. 123:107151. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.107151
Thungphotrakul, N., and Prapainainar, P. (2024). Development of polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethylcellulose-based bio-packaging film with citric acid crosslinking and clove essential oil encapsulated chitosan nanoparticle Pickering emulsion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 282:137223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137223
Udayanga, D., Manamgoda, D. S., Liu, X., Chukeatirote, E., and Hyde, K. D. (2013). What are the common anthracnose pathogens of tropical fruits? Fungal Divers. 61, 165–179. doi: 10.1007/s13225-013-0257-2
Wang, L., Yin, Y. C., Yin, S. W., Yang, X. Q., Shi, W. J., Tang, C. H., et al. (2013). Development of novel zein–sodium caseinate nanoparticle-stabilized emulsion films for improved water barrier properties via emulsion/solvent evaporation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 61, 11089–11097. doi: 10.1021/jf4029943
Wantat, A., Rojsitthisak, P., and Seraypheap, K. (2021). Inhibitory effects of high molecular weight chitosan coating on ‘Hom thong’ banana fruit softening. Food Packag. Shelf Life 29:100731. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2021.100731
Wardana, A. A., Wigati, L. P., Marcellino, V., Kusuma, G., Yan, X. R., Nkede, F. N., et al. (2024). The incorporation of chitosan nanoparticles enhances the barrier properties and antifungal activity of chitosan-based nanocomposite coating films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 280:135840. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135840
Wardana, A. A., Wigati, L. P., Tanaka, F., and Tanaka, F. (2021). Inhibition of Botrytis cinerea by alginate/cajuput essential oil and the composite’s surface properties as potential antifungal coating. Mater Today Proc 45, 5263–5268. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.830
Wardana, A. A., Wigati, L. P., Tanaka, F., and Tanaka, F. (2023a). Incorporation of co-stabilizer cellulose nanofibers/chitosan nanoparticles into cajuput oil-emulsified chitosan coating film for fruit application. Food Control 148:109633. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.109633
Wardana, A. A., Wigati, L. P., Tanaka, F., and Tanaka, F. (2023b). Functional enhancement of hydroxypropyl cellulose-based bionanocomposite films incorporating chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 58, 907–920. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.16071
Wu, X., Lian, H., Yuan, Y., Hong, S., and Deng, J. (2024). Evaluation of Pickering emulsions stabilized with nano-cellulose and nano-chitin treated with deep eutectic solvent. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 141:e54787. doi: 10.1002/app.54787
Xie, B., Zhang, X., Luo, X., Wang, Y., Li, Y., Li, B., et al. (2020). Edible coating based on beeswax-in-water Pickering emulsion stabilized by cellulose nanofibrils and carboxymethyl chitosan. Food Chem. 331:127108. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127108
Yang, T. C., Chou, C. C., and Li, C. F. (2005). Antibacterial activity of N-alkylated disaccharide chitosan derivatives. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 97, 237–245. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.04.014
Yang, Q., Ren, W.-J., Yu, X.-H., Zhang, J.-W., and Chen, H.-Q. (2025). Arachin amyloid-like fibrils and chitosan composite coatings with antimicrobial and antioxidant activities for effective preservation of perishable fruits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 308:142704. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00083-7
Yu, K., Xu, J., Zhou, L., Zou, L., and Liu, W. (2021). Effect of chitosan coatings with cinnamon essential oil on postharvest quality of mangoes. Food Secur. 10:3003. doi: 10.3390/foods10123003
Zhang, Q., Kong, B., Liu, H., Du, X., Sun, F., and Xia, X. (2024). Nanoscale Pickering emulsion food preservative films/coatings: compositions, preparations, influencing factors, and applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 23:e13279. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.13279
Zhao, Q., Fan, L., Liu, Y., and Li, J. (2022). Recent advances on formation mechanism and functionality of chitosan-based conjugates and their application in o/w emulsion systems: a review. Food Chem. 380:131838. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131838
Keywords: packaging, shelf life, postharvest, edible, quality
Citation: Wardana AA, Marcellino V, Wigati LP, Nkede FN, Tanaka F, Tanaka F and Setiarto RHB (2025) Application of Pickering emulsion-based coatings/films stabilized with chitosan nanoparticles for the preservation of fresh postharvest commodities. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1646457. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1646457
Edited by:
Raul Avila-Sosa, Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, MexicoReviewed by:
Jawad Ashraf, Jiangsu University, ChinaMaolin Liu, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, China
Copyright © 2025 Wardana, Marcellino, Wigati, Nkede, Tanaka, Tanaka and Setiarto. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ata Aditya Wardana, YXRhLndhcmRhbmFAYmludXMuYWMuaWQ=
 Ata Aditya Wardana
Ata Aditya Wardana Vincensius Marcellino
Vincensius Marcellino Laras Putri Wigati2
Laras Putri Wigati2 Fumihiko Tanaka
Fumihiko Tanaka