- 1International College Beijing, China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
- 2Jiyang College, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, Zhuji, China
In recent years, the rapid development of digital technologies and the promotion of rural digitization have profoundly reshaped the development of rural areas and provided new ideas for resolving income disparities between urban and rural residents. This study uses panel data from counties in China between 2018 and 2021 and a two-way fixed effects model to empirically test the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap and determine the underlying mechanism. The findings suggest that rural digitization effectively reduces the urban–rural income gap, with more pronounced effects in southern regions, eastern regions, central regions, and areas with better agricultural development. Mechanistically, rural digitization narrows the income gap mainly by promoting technological innovation. Rural digitization does not cause more capital to flow into rural areas. Further spatial econometric analysis indicates that the role of rural digitization in narrowing the urban-rural income gap has a significant spatial spillover effect, and this spillover is more likely to occur between counties with similar levels of economic development.
1 Introduction
The urban–rural income gap is a crucial indicator used to assess the balanced economic development of a country or region; it directly influences social equity and harmony (Zhang et al., 2022). In many countries, the income gap between urban and rural areas has widened alongside rapid economic development and accelerated urbanization (Rogers and Williamson, 1982). A large income gap may lead to the unfair distribution of social resources, exacerbate social class conflicts, and undermine long-term social stability. The urban–rural income gap also impacts the quality of life and wellbeing of residents. Differences in income levels affect residents' purchasing power, education, and healthcare, which in turn influence their health and development potential (Requena, 2016). Furthermore, the urban–rural income gap is related to the balance and sustainability of economic development. Narrowing the income gap between urban and rural areas would promote an increase in consumption demand, expand the domestic demand market, and drive balanced economic growth (Tang et al., 2022; Carter, 1997). It also would facilitate the rational flow and optimal allocation of human resources, thus improving overall economic efficiency and competitiveness (Yu and Lu, 2021).
All countries have made significant efforts to promote rural development and eliminate the urban–rural income gap. In the United States, policies such as the Rural Electrification Act, Federal Highway Act, and Morrell Act have been implemented to strengthen rural infrastructure, support agricultural technology and vocational education, and promote farmers' income and agricultural development (Hu and Tian, 2019). In South Korea, the “New Village Movement,” which was initiated in the late 1970s, invested a total of 2.8 trillion Korean won over 10 years to build infrastructure in rural areas, improve farmers' living conditions, and enhance residents' quality of life (Sun, 2016). The Indian government also has introduced a series of policies to promote rural information and reduce the urban–rural income gap, such as tax exemptions for farmers purchasing computers and software and the use of buses to provide agricultural and meteorological information to farmers in rural areas (Guo et al., 2022). In China, the income gap between urban and rural areas continues to widen (Figure 1). China recognizes this problem and has taken various measures to address it, such as implementing a rural revitalization strategy to promote rural industrial upgrading and transformation, developing characteristic agriculture and rural tourism to increase rural employment opportunities, and improving the rural social security system to promote social equity and harmony (Yu and Lu, 2021; Su et al., 2015; Yao and Jiang, 2021).
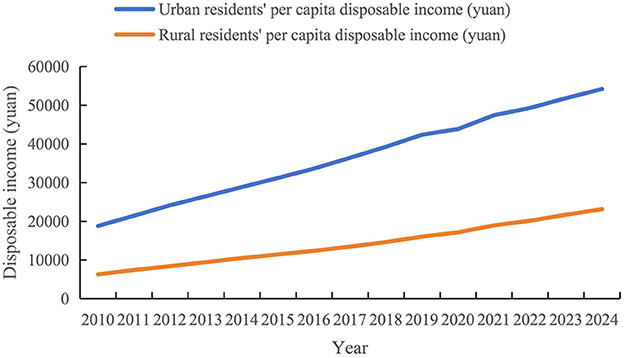
Figure 1. Trends in per capita disposable income of Chinese residents from 2010 to 2024. Data source: National Bureau of Statistics of China.
In recent years, the rapid development of digital technology and promotion of rural digitization have profoundly changed development in rural areas, offering new solutions to the urban–rural income gap problem. Briefly, rural digitization involves using advanced digital technologies to strengthen the economic and social fabric of rural populations and ultimately provide them with more opportunities to lead connected lives. Rural digitization has overcome the limitations of traditional economic models and is significantly reshaping rural development (Huang and Huang, 2018). In May 2019, the General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the General Office of the State Council issued the “Outline of the Digital Rural Development Strategy,” which clearly defines the objectives and tasks of rural digitization. The “Key Points for Digital Rural Development in 2020” clearly define the objectives for digital rural development, namely to accelerate both the construction of rural information infrastructure and the digital transformation of agriculture and rural areas. In agriculture, the application of digital technology has greatly improved the precision of agricultural production and efficiency of management (Erickson and Fausti, 2021), increased agricultural output (Deichmann et al., 2016), and enhanced the quality of agricultural products, thereby raising farmers' income levels (Zhang and Fan, 2024). E-commerce platforms have effectively shortened the distance from farm to fork and reduced intermediaries, thus increasing the selling prices of agricultural products and farmers' sales incomes (Liu et al., 2024a). Rural digitization promotes the flow and sharing of resources such as information, technology, and talent between urban and rural areas, thus increasing economic vitality and creating employment opportunities in rural areas (Leng, 2022). Taking China's rural e-commerce as an example, data from the China Digital Village Development Report (2023) show that as of November 2023, the number of rural e-commerce stores in China had reached 18.396 million, and 1,489 counties nationwide had established public service and logistics systems for e-commerce. In 2023, China's rural online retail sales amounted to 2.5 trillion yuan, with online agricultural product sales reaching 587.03 billion yuan.
Importantly, the development of digital technology and the advancement of rural digitization may hinder efforts to narrow the urban–rural income gap in new ways. Differences in the level of digital infrastructure development across regions and in digital skills between segments of the population may lead to social division and a digital divide (Leng, 2022). Due to an uneven layout of digital infrastructure and lack of digital skills, some segments of the population, especially rural and low-income groups, may not be able to take full advantage of the economic dividends of digital technologies (Salemink et al., 2017). This may not only exacerbate the economic gap between urban and rural areas but also lead to greater social division, thus hindering comprehensive poverty alleviation and urban–rural integration. These possibilities warrant a discussion of the impact of current digital village construction on the urban–rural income gap and how it can be reduced, and how balanced urban–rural development can be promoted while also promoting the application of digital technology and the construction of digital villages. This paper explores the above issues and presents two main innovations. First, it explores the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap using county-level panel data. Second, it investigates the roles of capital flow and technology flow in the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap.
2 Literature review
The development of digital technology has led to an increase in studies on how the digital economy affects the urban–rural income gap, as represented by Internet use, e-commerce, and digital inclusive finance. The conclusions of these studies can be broadly classified into three categories: first, the development of digital technology and the digital economy has widened the urban–rural income gap. Second, the development of digital technology and the digital economy has narrowed the urban–rural income gap. Third, the relationship between the development of digital technology and the income gap is non-linear. The following three paragraphs explain the relevant literature pertaining to these three categories in detail.
Some scholars have argued that the development of the digital economy, represented by Internet usage, e-commerce, and digital inclusive finance, is narrowing the urban–rural income gap. Distance and a lack of economies of scale are important factors hindering rural development, while the Internet and broadband digital communications exert a certain scale effect by providing development opportunities to rural areas while shortening the spatial and temporal distance, thus disrupting the imbalance of development between urban and rural areas (Parker, 2000; He et al., 2025, 2024). Digital technology can strengthen inter-industry connections, thereby increasing rural income levels and narrowing the urban–rural income gap (Ahvenniemi et al., 2017). Using data from 2014 to 2018, (Ji et al. 2021) explored the positive impact of digital inclusive finance on rural employment and incomes in China, finding that it narrowed the urban–rural income gap through mechanisms such as alleviating financial exclusion, expanding financing channels, and supporting entrepreneurship. (Khan et al. 2022) analyzed the impact of the digital economy on rural development in Pakistan and found that Internet technology could reshape the rural economy, promote agricultural industrial upgrading, and increase farmers' incomes, thus narrowing the urban–rural income gap. Indian scholars have argued that the Internet has improved rural agricultural markets by helping farmers obtain market information and increasing the selling prices of agricultural products, thus increasing their incomes and narrowing the urban–rural income gap (Jensen, 2007). (Goyal 2010) found that establishing Internet information libraries significantly improved the incomes of local soybean farmers in India. In China, the development of the digital economy also has narrowed the urban–rural income gap. (Yin and Choi 2022) found that the development of e-commerce in China significantly narrowed this gap.
Other scholars, however, have argued that the development of the digital economy is exacerbating the urban–rural income gap. (Prieger 2012) suggested that in areas with significant gaps in broadband coverage, the spread of information technology in rural areas or among certain minority groups remains slow, which further widens the urban–rural income gap. (Jackson and Kanik 2019) argued that the development of digital technology has led to labor substitution and, in turn, reduced wages for replaceable workers relative to those for non-replaceable workers. The wage growth rate of high-skilled workers exceeds that of low-skilled workers; furthermore, most of China's high-skilled workers are concentrated in urban areas while low-skilled workers are concentrated in rural areas, which are exacerbating the urban–rural income gap. (Zeng et al. 2022) analyzed panel data from 287 prefecture-level cities in China from 2001 to 2019 and found that the construction of smart cities significantly widened the urban–rural income gap. (Qiu et al. 2023) conducted an empirical study based on panel data from 202 cities in China from 2011 to 2019 to examine the impact of the digital economy on the urban–rural income gap. The results of the study show that although the digital economy improved the absolute income levels of both urban and rural residents, it significantly promoted urban residents' incomes to a greater extent, thus widening the urban–rural income gap.
Some scholars have found that the relationship between digital economic development and the urban–rural income gap exhibits a U-shaped curve. (Jiang et al. 2022) conducted an empirical study using panel data from 30 provinces in China between 2009 and 2019 and found that the digital economy had a U-shaped relationship with the urban–rural income gap. The gap narrowed in early stages but widened in the medium-to-long term. Li et al. (2021) found that e-commerce development significantly enhanced the urban–rural income gap, first expanding and then narrowing it. Using panel data from 194 cities in China from 2011 to 2018, (Peng and Dan 2023) constructed a digital economic development index using the entropy method. They applied non-linear and threshold models to analyze the impact of digital economic development on the urban–rural income gap, finding that this relationship was U-shaped. (Deng et al. 2023) conducted a similar empirical study using panel data from 202 cities in China between 2011 and 2019, confirming that the relationship between the digital economy and the urban–rural income gap followed a U-shaped pattern that narrowed in the early stages but widened as the digital economy further developed. (Yao and Ma 2022) found that digital finance had a so-called Kuznets effect on income distribution: the income gap widened in the early stages of development but began to narrow as the economic development level increased and digital finance matured. However, most regions have not yet reached the turning point, and rapid digital economic development continues to exacerbate regional income inequality.
Several scholars have explored the impact of digital village construction on the urban–rural income gap. Using provincial panel data from 2011 to 2020, (Li and Chen 2023) found that rural digitization significantly narrowed the urban–rural income gap. (Lin et al. 2023) analyzed rural digitization data from 2,997 county-level administrative areas during 2012–2021 to determine the impact of digital rural development on common prosperity in revolutionary old areas. They found that digital infrastructure drove income growth in rural areas but also widened the urban–rural income gap, resulting in a digital divide. Digital rural governance significantly reduced the digital divide and led to the achievement of common prosperity. Using cross-sectional data from 865 counties in China in 2020, (Liu et al. 2024b) found that digital rural development narrowed the urban–rural income gap and that this effect was driven mainly by industrial structure transformation. (Liu and Liu 2024) used provincial panel data from China during 2011–2020 and also found that digital rural development narrowed the urban–rural income gap.
To date, research on the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap remains insufficient. There is no clear consensus on whether rural digitization promotes or inhibits this gap, and most studies have focused on the provincial or county level and thus cannot fully reflect regional differences in the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap. Moreover, the mechanism of analyzing the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap from the perspective of factor flow is not yet clear. Therefore, this paper presents an empirical test of the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap using unbalanced panel data from Chinese counties during 2018–2021 and a two-way fixed effects model. The paper also explores the influence of capital and technology flows in rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap.
3 Theoretical framework
Reducing the urban–rural income gap is a crucial aspect of achieving common prosperity. In recent years, rural digitization or digital rural construction, which focuses on broadband expansion, rural e-commerce development, digital agriculture, and digital inclusive finance, has significantly affected rural development (Deng et al., 2023). According to the Digital Rural Development Action Plan (2022–2025), the key tasks of digital rural construction include actions for upgrading digital infrastructure, the innovation and development of smart agriculture, the development of new business models, and the improvement of digital governance capacity (Jiang et al., 2022). Digital rural construction strengthens rural information infrastructure, promotes the integration of traditional infrastructure with data elements, and facilitates the flow of capital, technology, and materials into rural areas. It also significantly improves the efficiency of factor allocation in rural regions and thus is an important driver of efforts to narrow the urban–rural income gap (Jiang et al., 2022).
The extensive application of digital technologies has greatly optimized the allocation of rural capital, land, and labor and enhanced the flexibility and precision of rural industrial development. The cluster effect of digital technologies has promoted the efficient integration and utilization of rural factors. Specifically, the cluster effect of e-commerce platforms enables farmers to sell their products more conveniently and thus increases the added value (Li, 2024). Simultaneously, the development of related industries, such as logistics, processing, and finance, further enhances the efficiency of factor allocation and drives the transformation and upgrading of rural industries. The timeliness and transparency of information flow allow rural resources to be allocated more flexibly and efficiently to various production and service activities, thereby increasing the vitality and competitiveness of the rural economy. These changes driven by digital technologies have effectively promoted the interaction of factors between urban and rural areas and coordinated economic development, ultimately helping reduce the urban–rural income gap. Based on this, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 1: Rural digitization narrows the urban–rural income gap.
Rural digitization can influence the urban–rural income gap by accelerating the flow of capital to rural areas. It accelerates the construction of rural digital infrastructure and provides a foundation for the development of digital inclusive finance, thereby substantially supporting efforts to narrow the urban–rural income gap (Wang and Cheng, 2022). Rural areas have long been constrained by weak financial infrastructure and insufficient capital flow, leading to a one-way flow of capital to urban areas that has hindered the sustainable development of rural economies (Li et al., 2021a). Advances in rural digitization have enabled the state to increase investment in and continuously improve rural digital infrastructure and supporting services. The widespread adoption of digital inclusive finance in rural areas has increased the efficiency of capital flows. Rural farmers and small enterprises can more easily access credit and financial support, alleviating the long-standing issue of capital scarcity in rural areas. This acceleration of capital flow has increasingly attracted social capital and investment into rural markets to promote the economic integration of urban and rural areas and thus narrow the urban–rural income gap. Based on this, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 2: Rural digitization accelerates the flow of capital to rural areas, thereby reducing the urban–rural income gap.
The efficiency of agricultural factor allocation and technological efficiency levels have significantly improved with increasing rural digitization and are now an important driver of efforts to narrow the urban–rural income gap. In the context of digitization, advanced agricultural technologies, information technologies, and e-commerce are gradually penetrating rural areas and providing farmers with advanced production techniques and methods (Liu et al., 2023). The widespread application of digital technologies has greatly optimized the mobility of rural capital, land, and labor and enhanced the flexibility and precision of agricultural industrial development. Assisted by e-commerce, digital financial platforms, and big data technologies, farmers can more effectively access market information, optimize production decisions, and thereby improve their production efficiency and resource allocation precision (Wu and Bai, 2023). Improvements in agricultural production efficiency have enhanced the competitiveness of agricultural development, leading to increases in farmers' incomes and a decrease in the urban–rural income gap. Based on this, we propose the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 3: Rural digitization accelerates the improvement of agricultural production efficiency, thereby narrowing the urban–rural income gap.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Model construction
In this study, unbalanced panel data from counties in China during 2018–2021 are used, and a two-way fixed effects model is applied to examine the impact of digital rural development on the urban–rural income gap. The model is specified as follows:
where GAPit represents the urban–rural income gap in county i at year t, DVIit is the digital rural index for county i in year t, and Cit is a vector of other control variables, including the GDP growth rate (GDPGH), development of the primary industry (FIRIN), government expenditure (GEXP), loan conditions from financial institutions (LOAN), and education level in the county (EDU). The model also includes county fixed effects (μi), time fixed effects (δt), and an error term (εit). The standard errors of the estimated coefficients are clustered at the county level for robustness.
To ensure the robustness of the results and mitigate potential endogeneity issues due to reverse causality, all the dependent variables are lagged by one period. Additionally, alternative measures of the urban–rural income gap, instrumental variable methods, and regressions that exclude regions with more advanced digital rural development are used to validate the results.
In the mechanism analysis, capital flow and technology flow are the dependent variables, and regressions are performed using the digital rural index. The specific model is as follows:
where Yit represents the capital flow (CAPIit) and technology flow (TFPit) in county i in year t, and Xit includes factors such as economic growth, industrial structure, and government expenditure. The other variables are the same as in model (1).
4.2 Variable selection
Dependent variable: The dependent variable in this study is the urban–rural income gap (GAPit). Referring to (Chen et al. 2023), the urban–rural income gap is defined as the difference between the per capita disposable income of urban residents and that of rural residents. To eliminate the impact of price fluctuations, both urban and rural disposable incomes are adjusted based on the 2017 price index. To mitigate heteroscedasticity, the natural logarithm of the difference between urban and rural disposable income is used. Furthermore, the urban–rural income gap is recalculated using the log difference between urban and rural residents' per capita disposable income at the county level, and the effect of digital rural development on the income gap is re-examined.
Core independent variable: The core independent variable is the Digital Village Index (DVI), developed jointly by the Rural Development Institute of Peking University and the Ali Research Institute. This index establishes a digital rural indicator system that better fits the reality of the “three rural areas” in four aspects: rural digital infrastructure (DVI1), rural economic digitization (DVI2), rural governance digitization (DVI3), and rural life digitization (DVI4). The index, which integrates national macro-statistical data, industry data, and Internet big data, reflects the status of county-level digital rural development. Empirical evaluation of this index for counties in China in the years 2018, 2019, and 2020 provides an important reference for improving the top-level design and implementation of digital rural development plans and accelerating the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy, which is a more authoritative index reflecting the current level of rural digitization in China (Wang et al., 2023).
Instrumental variables: To address endogeneity issues due to reverse causality and omitted variable bias, this study uses the average DVI of other counties in the same province (IV1) and the distance from the county government to Hangzhou (IV2) as instrumental variables for the DVI. Given the economic spillover effects between regions, the level of digital rural development in other counties within the same province should positively influence digital development in the focal county without directly affecting the urban–rural income gap (Li, 2024). Therefore, using the average DVI of other counties in the province as an instrumental variable is valid. The use of the distance from the county government to Hangzhou is justified by two factors: first, the development of digital finance (represented by Alipay) originated in Hangzhou, a region with a high level of development with respect to China's digital economy and digital countryside; as this development radiates outward, the county's spherical distance from Hangzhou should be strongly correlated with the level of development of its digital countryside (Xiao et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2024). Second, Hangzhou is only one important city in eastern China, and the distance to Hangzhou does not determine the county-level urban–rural income gap; therefore, the instrumental variable has satisfactory exogeneity. As panel data are used in this study and the distances from county governments to Hangzhou are fixed values, in this paper the distance from each county to Hangzhou is cross-multiplied with time as an instrumental variable to increase the heterogeneity of the instrumental variable in the time dimension.
Mechanism variables: According to the previous theoretical framework, the impact of digital rural development on county economic growth may be transmitted through capital flow (CAPI) and technology flow (TFP). Following (Chen et al. 2023), capital flow is measured as the difference between the ratio of year-end financial institution deposits to GDP and the ratio of loan balance to GDP. The total factor productivity (TFP) in agriculture is used as the indicator of technology flow in this study. TFP is calculated as described by (Shi 2024), using the total cultivated area, agricultural workforce, and total agricultural machinery power as inputs and the value-added of the primary sector as the output to measure changes in county-level agricultural TFP. Additionally, TFP is further decomposed into technical efficiency and scale efficiency.
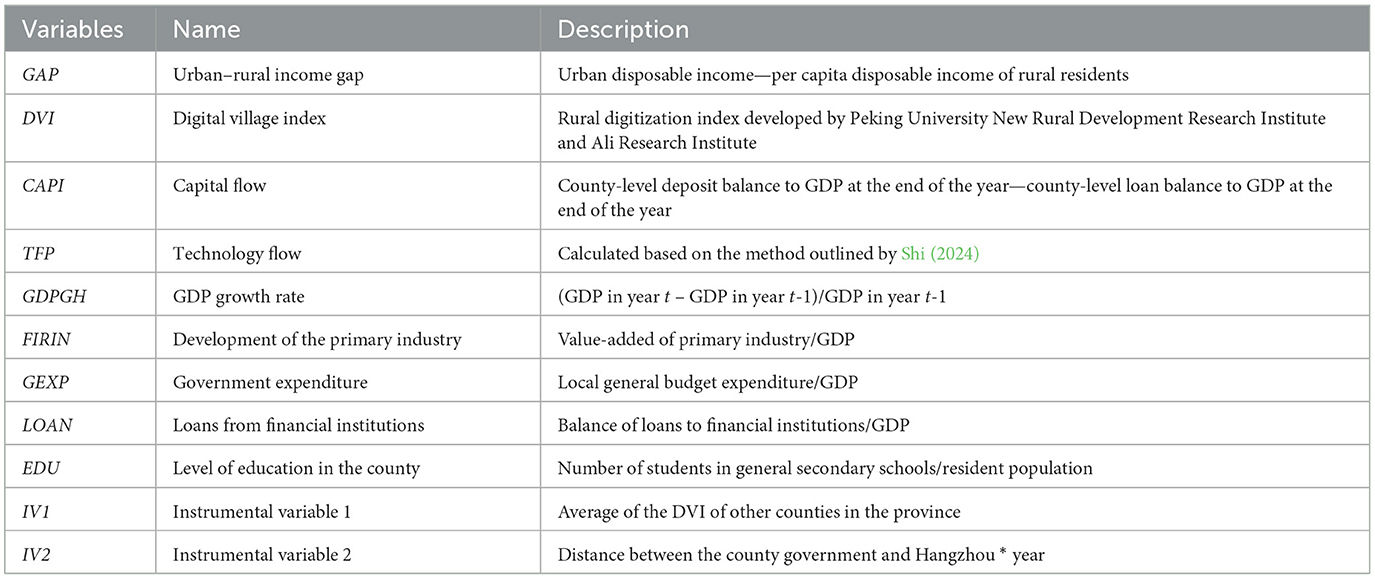
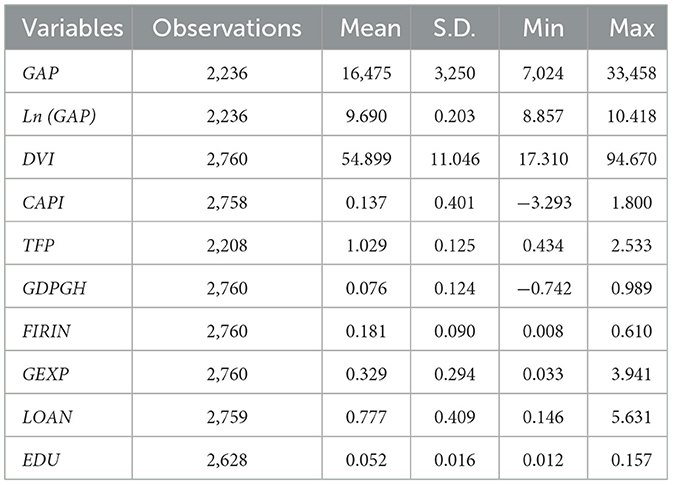
Other control variables: To control for county-level heterogeneity, this study uses the GDP growth rate (GDPGH), primary industry development (FIRIN), government expenditure (GEXP), loan conditions from financial institutions (LOAN), and education level (EDU) as control variables based on research by (Zhong et al. 2022); (Li et al. 2021b); (Chen et al. 2024), and (Munshi and Rosenzweig 2016). The GDPGH is calculated based on the previous year's figures, while FIRIN is calculated as the ratio of value-added in the primary sector to GDP. GEXP is calculated as the ratio of local fiscal budget expenditure to GDP. LOAN is calculated as the ratio of loans from financial institutions to GDP, and EDU at the county level is calculated as the ratio of students in general secondary schools to the total resident population. Table 1 summarizes the variable names, full names, and descriptions in more detail, while Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics of the sample data.
Table 2 shows that the average urban–rural income gap between 2018 and 2020 was 16,475 yuan, with a range of 7,024–33,458 yuan. In other words, the urban–rural income gap in Chinese counties remained substantial, requiring urgent attention. The core explanatory variable of this study is the level of rural digitization. The average DVI is 55, suggesting that rural digitization in China remains in the early stages, with an overall low development level. The DVI range of 17–95 reveals the considerable disparity in rural digitization across counties in China.
4.3 Data sources
The data for this study were collected from diverse sources. First, county-level statistical data were collected and compiled from the China County Statistical Yearbook, various county and city statistical bulletins, and government work reports. Second, the county-level DVI was computed by the New Rural Development Research Institute of Peking University and the Ali Research Institute. Third, the spherical distance between each county government location and Hangzhou city was calculated based on the latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates of the county and Hangzhou city governments. After excluding counties with significant missing data, the final research sample consisted of 1,183 counties with unbalanced panel data for the years 2018–2020. These data are limited to this period because the core independent variable of this paper, the DVI, is only available for these 3 years.
5 Results analysis
5.1 Main conclusions
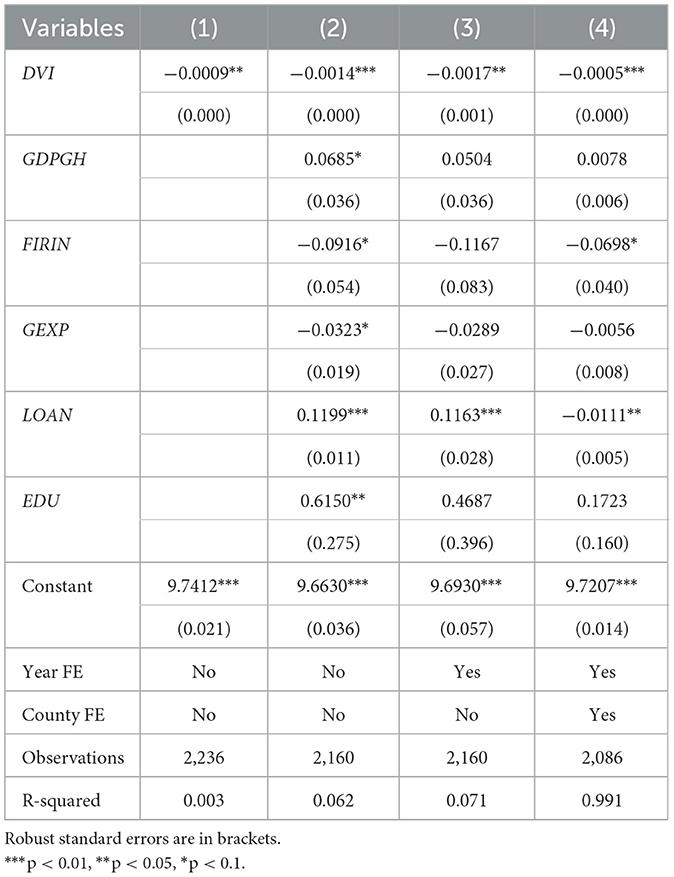
Table 3 presents the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap. Column (1) does not include any control variables or fixed effects. Column (2) includes control variables, Column (3) further controls for the year fixed effect, and Column (4) additionally controls for county fixed effects. To reduce bias from potential auto-correlation, robust standard errors are clustered at the county level. The results show that the estimated coefficient of the core explanatory variable, DVI, is positive and significant at the 1% level, indicating that rural digitization can significantly reduce the urban–rural income gap. From the perspective of economic significance, a one-standard-deviation change in DVI leads to a 2.7% reduction in the urban–rural income gap, suggesting that rural digitization plays both a statistically and economically significant role in promoting rural income growth.
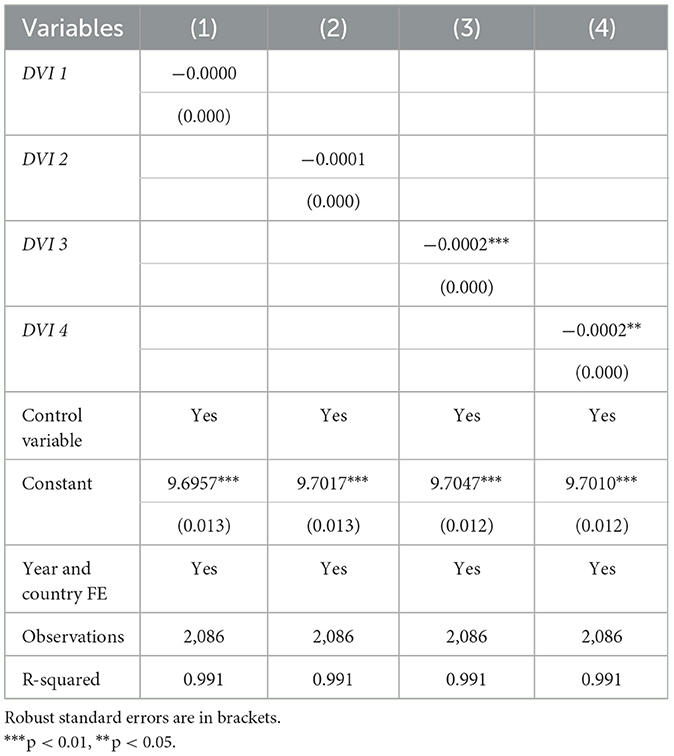
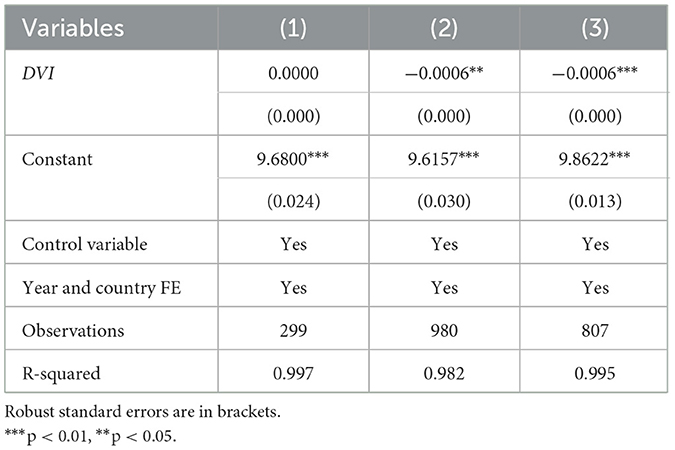
As mentioned in Section 4.2, the DVI includes four dimensions. To test differences in the impacts of different dimensions of digital countryside on the urban–rural income gap, the core explanatory variables are replaced in turn with DVI1–DVI4, and respective re-regressions are run (Table 4). The results show that DVI3 (rural governance digitization) and DVI4 (rural life digitization) both significantly reduce the urban–rural income gap, whereas DVI1 (rural digital infrastructure) and DVI2 (rural economic digitization) do not. This finding is similar to that of (Zhao et al. 2023). The integration of the digital economy and rural industries may still be at a low level in this stage, and the construction of digital infrastructure is in an early stage. Therefore, the application of digital infrastructure and the interactions and connections between digital rural new industries, new models, and rural livelihoods remain limited (Sun et al., 2023).
5.2 Robustness check
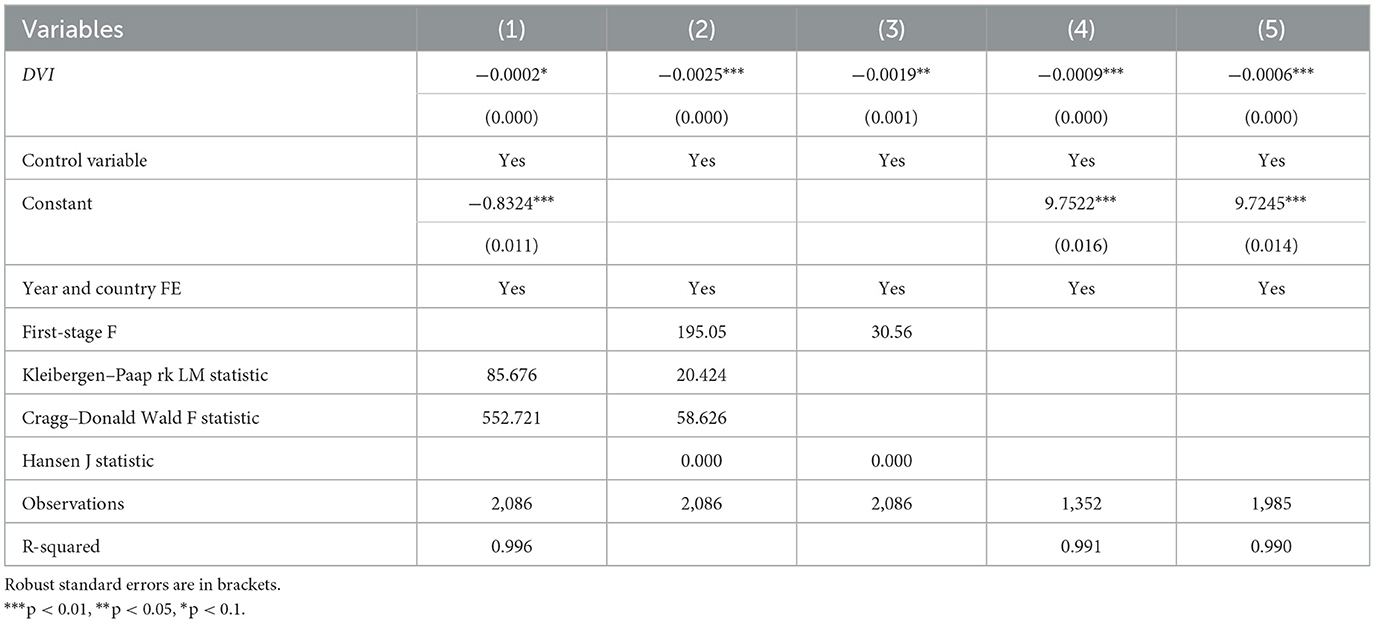
Several methods are used to examine the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap, aiming to ensure the robustness of the empirical results and address potential endogeneity issues. Column (1) in Table 5 shows the regression results when the ratio of the disposable income of rural residents to that of urban residents is used as the explanatory variable. The results indicate that rural digitization significantly increases this ratio, thus significantly reducing the urban–rural income gap. Columns (2) and (3) use IV1 and IV2 as the instrumental variables. The first-stage F-statistics are greater than 10, and the Cragg-Donald Wald F-statistics are 552.721 and 58.626, which comfortably rule out concerns about weak instruments (Stock and Yogo, 2005). In the Hansen J test, the p-value is 0.00, indicating the exogeneity of the instrumental variables. Moreover, several previous studies have adopted the same IVs, further supporting their validity (Bai et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). The results suggest that rural digitization can significantly reduce the urban–rural income gap. Column (4) presents the regression results obtained using a one-period-lagged DVI as the core explanatory variable. The results show that rural digitization can significantly reduce the urban–rural income gap. Considering the regional disparities in digital rural development, these results might be largely driven by regions with higher levels of digital rural development. Therefore, Column (5) shows the results after excluding samples from Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Guangdong. These results are similar to those in Table 3, indicating that the study findings are robust.
5.3 Heterogeneity testing
Given its vast geographic size, China exhibits significant differences in resource endowments, economic development, and social culture across regions. To further analyze regional differences in the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap, this study divides China into southern and northern regions according to the classification standards of the National Bureau of Statistics of China. Table 6, Columns (1) and (2), represent the northern and southern regions, respectively. The results indicate that the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap is mainly evident in the southern regions and is not significant in the northern regions. This may be due to the relatively high overall level of digital economic development in southern China. The levels of digital infrastructure, rural economic digitization, governance digitization, and digital living have reached a point where they can effectively promote rural development and reduce the urban–rural income gap.
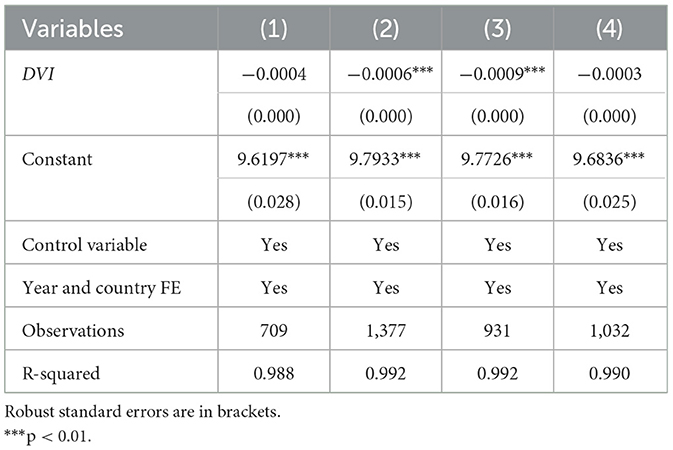
Table 6. Heterogeneity test for northern vs. southern regions and agricultural vs. non-agricultural strong counties.
Additionally, this study analyzes differences in the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap between agricultural and non-agricultural strong counties. Column (3) represents agricultural strong counties, and Column (4) represents non-agricultural strong counties. The results suggest that rural digitization has a more significant impact on the urban–rural income gap in agricultural strong counties. A possible explanation for this result is that rural digitization has driven advances in agricultural technology and improvements in agricultural production efficiency, thereby increasing farmers' incomes and narrowing the urban–rural income gap.
Columns (1), (2), and (3) of Table 7, respectively show the effects of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap in China's western, central, and eastern regions. Rural digitization is shown to significantly reduce the urban–rural income gap in the central and eastern regions but not in the western region. The eastern and central regions may have more developed economies and higher levels of rural digitization than the western region, and the effects of rural digitization in terms of narrowing the urban–rural income gap may be manifesting.
5.4 Mechanism testing
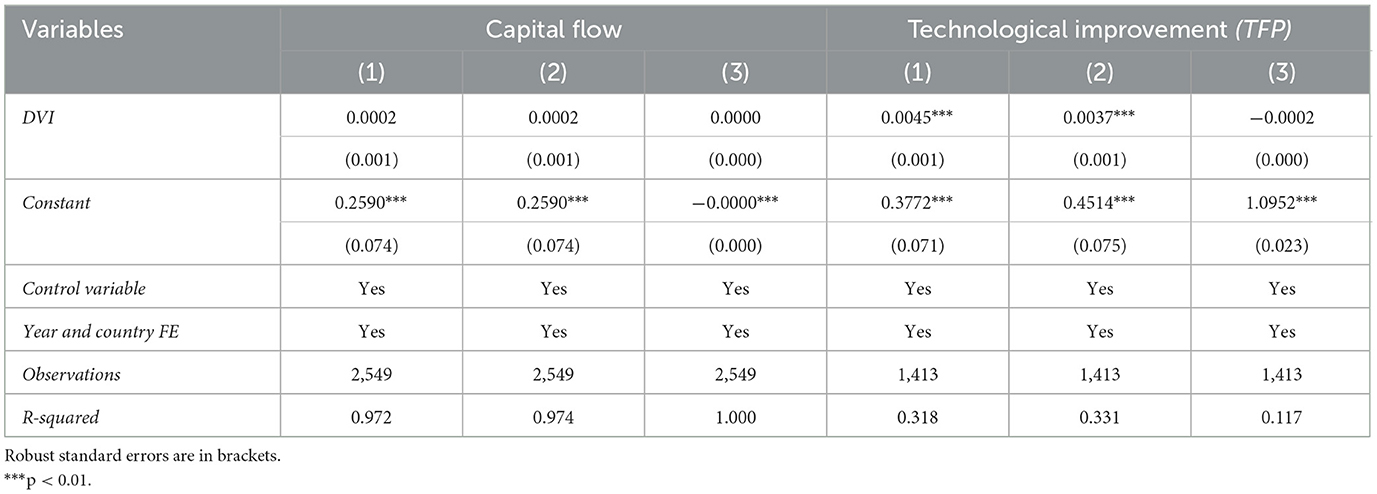
Table 8 presents the results of regression to determine the mechanism through which rural digitization affects the urban–rural income gap. The columns under the heading Capital Flow examine the roles of capital flow, while those under Technological Improvement examine the roles of technological improvement.
In the Capital Flow section of Table 8, Columns (1), (2), and (3), respectively use capital flow (CAPI), the ratio of the county-level year-end financial institution deposit balance to GDP, and the ratio of the county-level year-end financial institution loan balance to GDP as the dependent variables. The results indicate that rural digitization has no significant effect on these three variables. Rural digitization has not led to a significant flow of capital into rural areas. The possible reason is that, although rural digitization has helped remove barriers to the flow of production factors between urban and rural areas, and digital inclusive finance contributes to alleviating financial exclusion, the strong “siphon effect” of cities on various factors remains prevalent in China. As a result, the trend of net outflow of resources from rural to urban areas has yet to be reversed (Wang and Wang, 2024). In addition, compared to cities, rural areas still lag behind in network infrastructure and have relatively low penetration rates of digital devices. Financial institutions find it difficult to effectively reach rural households and enterprises, thereby reducing the feasibility of urban capital investing in rural areas through digital channels (Xiao et al., 2022).
In the Technological Improvement (TFP) section of Table 8, Columns (1), (2), and (3) examine the dependent variables of agricultural TFP, technical efficiency, and scale efficiency, respectively. The results show that rural digitization promotes an increase in agricultural TFP at the county level, which is mainly realized through increased technical efficiency. Rural digitization enhances scale efficiency, technical efficiency, and agricultural TFP because it is accompanied by the adoption of precision agriculture software and IoT sensor devices, which enable more scientific management of agricultural production, thereby improving technical efficiency (Yin et al., 2021). Moreover, the use of digital devices generally requires large-scale operations. The advancement of rural digitization promotes agricultural scale operations, which improves scale efficiency (Mondejar et al., 2021), and consequently, agricultural TFP continues to rise (Gao et al., 2022; Li et al., 2025).
5.5 Spatial effects
Due to the significant networked characteristics of the digital economy, it enhances the connectivity of economic activities between regions, thereby generating spatial spillover effects. Therefore, the impact of rural digitization on the urban-rural income gap may be influenced not only by local effects but also by spatial spillover effects from other regions. This not only involves understanding the relationship between rural digitization and the urban-rural income gap but also concerns the selection of the appropriate regression model. If rural digitization exhibits spatial spillover effects and spatial agglomeration characteristics, spatial econometric models should be introduced; otherwise, biased conclusions may result. In this context, this paper adopts spatial econometric methods to further explore the relationship between rural digitization and the urban-rural income gap.
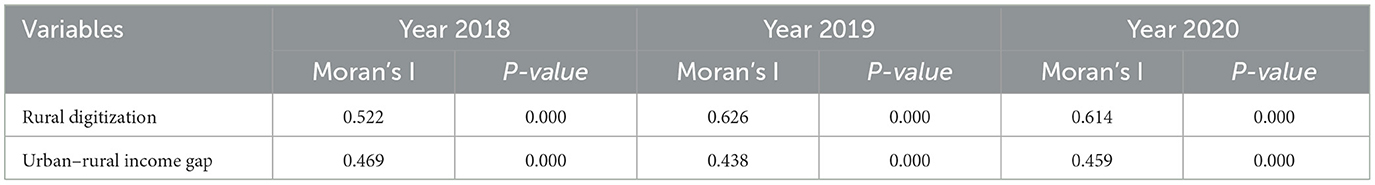
To ensure the effective application of spatial econometric models, the sample in this study was transformed into balanced panel data, resulting in a balanced panel dataset covering 514 counties from 2018 to 2020. Furthermore, the core explanatory variable, “Rural digitization,” and the dependent variable, “Urban-rural income gap,” were subjected to Moran's I-test. Table 9 presents the results of the Global Moran's I-test using a regional adjacency matrix as the spatial weight matrix. The results show that the Global Moran index for both the rural digitization index and the urban-rural income gap is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating a high level of agglomeration and low-level clustering between rural digitization and the urban-rural income gap. Therefore, it is necessary to further investigate the relationship between these two factors from a spatial perspective.
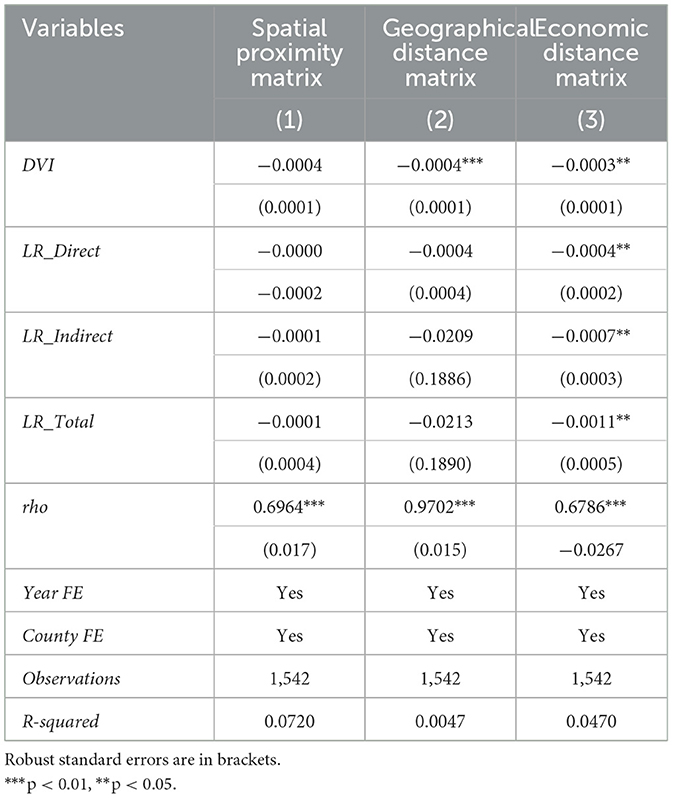
Table 10 presents the spatial econometric regression results on the impact of rural digitization on the urban-rural income gap. Three different spatial weight matrices were defined: spatial proximity (based on whether geographical areas are adjacent), Geographical distance (based on the inverse distance between county governments), and Economic distance (based on the inverse of the per capita GDP difference between counties in 2018). The SAR model was applied to study the impact of rural digitization on the urban-rural income gap. The results indicate that, under the economic distance spatial weight matrix, the direct effect, indirect effect, and total effect coefficients of rural digitization are all significantly negative at the 1% level. This confirms that rural digitization not only significantly promotes the narrowing of the urban-rural income gap within the county but also reduces the urban-rural income gap in neighboring counties through spatial spillover effects. A comparison of the different spatial weight matrices reveals that the economic distance matrix exhibits spillover effects, while the spatial proximity and geographical distance matrices do not. This suggests that spatial spillover effects of rural digitization on the urban-rural income gap are more likely to occur between counties with similar economic development levels (Shi, 2023).
6 Conclusion
The conclusion of this paper is drawn from a study that uses panel data from Chinese counties during 2018–2021 and a two-way fixed effects model to empirically examine the impact of rural digitization on the urban–rural income gap, as well as the underlying mechanisms. The findings indicate that rural digitization can effectively reduce this income gap, and the effect is more pronounced in southern regions, eastern regions, central regions, and areas with better agricultural development. Mechanistically, rural digitization reduces the income gap mainly by promoting technological innovation. Rural digitization does not cause more capital to flow into rural areas.
Based on these findings, the following policy recommendations are proposed. First, it is important to adopt localized approaches and continuously promote digital rural development. Rural digitization remains at a relatively low level in China, with significant regional disparities. Efforts should be made to advance digital rural development gradually, in a manner suited to each region's unique circumstances. It is necessary to both increase the construction of digital infrastructure and thus build a foundation for digital village construction and to consolidate “digital + rural” application scenarios, thus enabling more residents to benefit from the advantages of digital rural construction. For example, attention should be paid to promoting the development of smart agriculture and how digital technology can improve agricultural TFP; additionally, efforts should promote the development of rural digital inclusive finance and rural industry and the alleviation of rural financing difficulties. Second, attention must be paid to the issue of the so-called digital divide in digital rural construction. The heterogeneity analysis shows that the varying level of rural digitization affects its degree of impact on the urban–rural income gap. As a result, efforts are needed to actively explore new models of digital rural development and accelerate the bridging of gaps in rural digitization across the central, western, and northern regions of China, thus, ensuring coordinated nationwide development. Further spatial econometric analysis indicates that the role of rural digitization in narrowing the urban-rural income gap has a significant spatial spillover effect, and this spillover is more likely to occur between counties with similar levels of economic development.
However, this study has some limitations. First, due to data constraints, the sample does not reflect the situations of all counties in China, and the DVI is available only for the 2018–2020 periods, which limits the temporal scope of the findings regarding the impact of rural digitization on the income gap. Second, digital economies often exhibit strong spatial spillover effects. This study uses non-balanced panel data; the use of balanced panel data would significantly reduce the sample size and preclude a discussion of spatial effects. Third, the Gini coefficient and Theil index are other important relative indicators of income inequality but are not considered in this study. Future studies could combine these relative indicators to conduct a more comprehensive measurement and decomposition analysis of urban–rural income inequality.
Data availability statement
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: no restriction, contact with authors if need. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to Pingping Wang, d3BwcHJpdmF0ZUAxMjYuY29t.
Author contributions
XW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YL: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. MZ: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. FF: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. PW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Social Science Foundation of Beijing, China (Grant No. 23JJC038).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahvenniemi, H., Huovila, A., Pinto-Seppä, I., and Airaksinen, M. (2017). What are the differences between sustainable and smart cities? Cities 60, 234–245. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2016.09.009
Bai, F., Huang, Y., Shang, M., and Ahmad, M. (2022). Modeling the impact of digital economy on urban environmental pollution: empirical evidence from 277 prefecture-level cities in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 10:991022. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.991022
Carter, C. A. (1997). The urban-rural income gap in China: implications for global food markets. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 79, 1410–1418. doi: 10.2307/1244354
Chen, X., Huang, Z., Luo, C., and Hu, Z. (2024). Can agricultural industry integration reduce the rural–urban income gap? Evidence from county-level data in China. Land 13:332. doi: 10.3390/land13030332
Chen, X. G., Tang, L., and Tang, Y. H. (2023). Does the rural e-commerce policy help narrow the urban-rural income gap?—From the perspective of factor flow and expenditure structure. J. Agric. Econ. 3, 89–103. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.jae.20211126.001
Deichmann, U., Goyal, A., and Mishra, D. (2016). Will digital technologies transform agriculture in developing countries? Agric. Econ. 47, 21–33. doi: 10.1111/agec.12300
Deng, X., Guo, M., and Liu, Y. (2023). Digital economy development and the urban-rural income gap: evidence from Chinese cities. PLoS ONE 18:e0280225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280225
Erickson, B., and Fausti, S. W. (2021). The role of precision agriculture in food security. Agron. J. 113, 4455–4462. doi: 10.1002/agj2.20919
Gao, Q., Cheng, C., Sun, G., and Li, J. (2022). The impact of digital inclusive finance on agricultural green total factor productivity: evidence from China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 10:905644. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2022.905644
Goyal, A. (2010). Information, direct access to farmers, and rural market performance in central India. Am. Econ. J. 2, 22–45. doi: 10.1596/1813-9450-5315
Guo, Y., Li, J. J., and Du, Z. X. (2022). The evolution trend of the income gap between urban and rural residents: international experience and its enlightenment to China. World Agric. 6, 5–17. doi: 10.13856/j.cn11-1097/s.2022.06.001
He, B., Nan, G., Xu, D., and Sun, J. (2025). Bridging or widening? The impact of the Broadband China policy on urban-rural income inequality. Humanities Soc. Sci. Commun. 12, 1–11. doi: 10.1057/s41599-025-04875-z
He, B., Xu, D., Nan, G., Zhang, X., and Yu, X. (2024). Does the cross-border e-commerce comprehensive pilot zones policy affect the urban–rural income gap in China? Am. J. Econ. Sociol. 83, 773–792. doi: 10.1111/ajes.12593
Hu, Y., and Tian, Z. H. (2019). How to achieve rural revitalization?—Experience and enlightenment from the evolution of rural development policies in the United States. Chin. Rural Econ. 128–144. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2019.03.009
Huang, Y., and Huang, Z. (2018). Digital finance development in China: present and future. Economics 17, 1489–1502. doi: 10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2018.03.09
Jackson, M. O., and Kanik, Z. (2019). How automation that substitutes for labor affects production networks, growth, and income inequality. Growth Income Inequal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3375523
Jensen, R. (2007). The digital provide: information (technology), market performance, and welfare in the South Indian fisheries sector. Q. J. Econ. 122, 879–924. doi: 10.1162/qjec.122.3.879
Ji, X., Wang, K., Xu, H., and Li, M. (2021). Has digital financial inclusion narrowed the urban-rural income gap: the role of entrepreneurship in China. Sustainability 13:8292. doi: 10.3390/su13158292
Jiang, Q., Li, Y., and Si, H. (2022). Digital economy development and the urban–rural income gap: Intensifying or reducing. Land 11:1980. doi: 10.3390/land11111980
Khan, N., Ray, R. L., Zhang, S., Osabuohien, E., and Ihtisham, M. (2022). Influence of mobile phone and internet technology on income of rural farmers: evidence from Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province, Pakistan. Technol. Soc. 68:101866. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2022.101866
Leng, X. (2022). Digital revolution and rural family income: Evidence from China. J. Rural Stud. 94, 336–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2022.07.004
Li, C., Chen, G., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Ding, W., Yu, X., et al. (2025). The impact of digital inclusive finance on agricultural carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 34, 1593–1605. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/187165
Li, L., Zeng, Y., Ye, Z., and Guo, H. (2021b). E-commerce development and urban-rural income gap: evidence from Zhejiang Province, China. Papers Reg. Sci. 100, 475–495. doi: 10.1111/pirs.12571
Li, B., and Chen, H. (2023). The mechanism and realization path of digital rural construction in narrowing the income gap. J. South-Central Univ. Natl. 43, 137–145 + 187. doi: 10.19898/j.cnki.42-1704/c.20230513.12
Li, L. L., Yu, J., and Zhang, Z. G. (2021a). Investment in rural human capital in China: policy review and prospect. J. Zhejiang Univ. 51, 36–50. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-942X.CN.33-6000/C.2020.06.083
Lin, H., Zhao, L. B., and Hu, Y. Q. (2023). Can digital rural construction promote common prosperity in revolutionary old areas? Chin. Rural Econ. 5, 81–102. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2023.05.005
Liu, M., and Liu, H. (2024). The influence and mechanism of digital village construction on the urban–rural income gap under the goal of common prosperity. Agriculture 14:775. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14050775
Liu, S., Jin, Y., and Zheng, F. (2024a). Did product certification and e-commerce benefit agricultural producers in China? Food Policy 127:102688. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2024.102688
Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Ning, M., and Wang, L. (2024b). Has digital village construction narrowed the urban–rural income gap: Evidence from Chinese counties. Sustainability 16:5330. doi: 10.3390/su16135330
Liu, H. Y., Sun, L. J., and Gao, Q. (2023). Research on the impact of digital rural construction on farmers' income increase. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. 17, 95–102. doi: 10.12371/j.ynau(s).202212048
Liu, Y., Li, J., and Lei, L. (2022). Has the development of digital finance promoted industrial structure upgrading in Chinese cities? Empirical evidence from prefecture-level and above cities. J. Southwest Univ. 48, 123–136. doi: 10.13718/j.cnki.xdsk.2022.06.011
Mondejar, M. E., Avtar, R., Diaz, H. L. B., Dubey, R. K., Esteban, J., Gómez-Morales, A., et al. (2021). Digitalization to achieve sustainable development goals: steps towards a Smart Green Planet. Sci. Total Environ. 794:148539. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148539
Munshi, K., and Rosenzweig, M. (2016). Networks and misallocation: insurance, migration, and the rural-urban wage gap. Am. Econ. Rev.106, 46–98. doi: 10.1257/aer.20131365
Parker, E. B. (2000). Closing the digital divide in rural America. Telecommun. Policy 24, 281–290. doi: 10.1016/S0308-5961(00)00018-5
Peng, Z., and Dan, T. (2023). Digital dividend or digital divide? Digital economy and urban-rural income inequality in China. Telecommun. 47:102616. doi: 10.1016/j.telpol.2023.102616
Prieger, J. (2012). The Economic Benefits of Mobile Broadband. Malibu, CA: Pepperdine University, School of Public Policy.
Qiu, Y., He, N., Yan, C., and Rao, Q. (2023). Whether the digital divide widens the income gap between China's regions? PLoS ONE 18:e0273334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273334
Requena, F. (2016). Rural–urban living and level of economic development as factors in subjective well-being. Soc. Indic. Res. 128, 693–708. doi: 10.1007/s11205-015-1051-1
Rogers, A., and Williamson, J. G. (1982). Migration, urbanization, and third world development: an overview. Econ. Dev. Cult. Change 30, 463–482. doi: 10.1086/452572
Salemink, K., Strijker, D., and Bosworth, G. (2017). Rural development in the digital age: a systematic literature review on unequal ICT availability, adoption, and use in rural areas. J. Rural Stud. 54, 360–371. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2015.09.001
Shi, C. (2023). Rural digitalization empowers farmer income growth: direct effects and spatial spillovers. Hunan Soc. Sci. 1, 67–76.
Shi, C. L. (2024). Digital economy empowering the growth of total factor productivity in agriculture: effects and mechanisms. J. South Chin. Agric. Univ. 3, 94–109.
Stock, J. H., and Yogo, M. (2005). “Testing for weak instruments in Linear Iv regression,” in Identification and Inference for Econometric Models: Essays in Honor of Thomas Rothenberg, eds. D. W. K. Andrews and J. H. Stock (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press), 80–108.
Su, C. W., Liu, T. Y., Chang, H. L., and Jiang, X. Z. (2015). Is urbanization narrowing the urban-rural income gap? A cross-regional study of China. Habit. Int. 48, 79–86. doi: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2015.03.002
Sun, J. N., Hu, W. T., and Wang, S. G. (2023). Digital technology empowering farmers' income increase: mechanism of action, theoretical explanation, and promotion strategy. Reform 6, 73–82.
Sun, T. (2016). The governance models of new rural communities abroad and their implications for China. J. Jinling Inst. Technol. 30, 63–67. doi: 10.16515/j.cnki.32-1745/c.2016.03.014
Tang, J., Gong, J., and Ma, W. (2022). Narrowing urban–rural income gap in China: the role of the targeted poverty alleviation program. Econ. Anal. Policy 75, 74–90. doi: 10.1016/j.eap.2022.05.004
Wang, P., Li, C., and Huang, C. (2023). The impact of digital village construction on county-level economic growth and its driving mechanisms: evidence from China. Agriculture 13:1917. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13101917
Wang, S., and Wang, R. (2024). Has digital inclusive finance facilitated the integration of urban and rural development? - An examination from the perspective of labor mismatch. J. Shanghai Bus. Coll. 25, 23–37. doi: 10.19941/j.cnki.CN31-1957/F.2024.03.002
Wang, X. H., and Cheng, L. (2022). Digital inclusive finance and the urban-rural income gap: opportunity or chasm? J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. 58, 127–146. doi: 10.16088/j.issn.1001-6597.2022.05.011
Wang, X., Sun, X., Zhang, H., and Xue, C. (2022). Digital economy development and urban green innovation CA-pability: based on panel data of 274 prefecture-level cities in China. Sustainability 14:2921. doi: 10.3390/su14052921
Wu, C. Z., and Bai, Y. X. (2023). Research on the mechanism of digital technology empowering the integrated development of urban and rural areas - From the perspective of Marx's theory of social reproduction. Mod. Econ. Sci. 45, 123–134. doi: 10.20069/j.cnki.DJKX.202306010
Xiao, Y., Wu, S., Liu, Z. Q., and Lin, H. J. (2023). Digital economy and green development: empirical evidence from China's cities. Front. Environ. Sci. 11:1124680. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1124680
Xiao, Y., Li, B., and Tian, K. (2022). Research on the mechanism and pathways of digital inclusive finance in promoting common prosperity for farmers and rural areas. Rural Finance Res. 3–12. doi: 10.16127/j.cnki.issn1003-1812.2022.10.006
Yao, L., and Ma, X. (2022). Has digital finance widened the income gap? PLoS ONE 17:e0263915. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263915
Yao, Y., and Jiang, L. (2021). Urbanization forces driving rural urban income disparity: evidence from metropolitan areas in China. J. Clean. Prod. 312:127748. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127748
Yin, H., Cao, Y., Marelli, B., Zeng, X., Mason, A. J., and Cao, C. (2021). Soil sensors and plant wearables for smart and precision agriculture. Adv. Mater. 33:2007764. doi: 10.1002/adma.202007764
Yin, Z. H., and Choi, C. H. (2022). Does e-commerce narrow the urban–rural income gap? Evidence from Chinese provinces. Internet Res. 32, 1427–1452. doi: 10.1108/INTR-04-2021-0227
Yu, G., and Lu, Z. (2021). Rural credit input, labor transfer and urban–rural income gap: evidence from China. Chin. Agric. Econ. Rev.13, 872–893. doi: 10.1108/CAER-09-2020-0229
Zeng, Y. W., Sun, W. C., Li, L. L., and Fu, C. L. (2022). New coordinates of the digital divide: the impact of smart city construction on the urban-rural income gap. Chin. Rural Surv. 3, 165–182. Available online at: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=wOuTVkq58NkJGSxRprh8cpZUC94wOOdt-OtwhFk4WZD0S7InGIr1img3wDCSy2X1tmtLyBu7LcoXRE8WQIR9iWuZI92qT87zWKyHqRZqJXtnEFBOqEilMQ-wCNHAGswR-YBYvEpm6ME3Iw51XyQETWKKTRdzzu9bcqv1oll26-k=&uniplatform=NZKPT
Zhang, H., Qi, R., Liu, Y., Wang, T., Zhong, F., Zhou, Q., et al. (2024). The spatial impact of digital economy on carbon emissions reduction: evidence from 215 cities in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1370938. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1370938
Zhang, M., Wang, L., Ma, P., and Wang, W. (2022). Urban-rural income gap and air pollution: a stumbling block or stepping stone. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 94:106758. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2022.106758
Zhang, X., and Fan, D. (2024). Can agricultural digital transformation help farmers increase income? An empirical study based on thousands of farmers in Hubei Province. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 26, 14405–14431. doi: 10.1007/s10668-023-03200-5
Zhao, J. J., Wei, J., and Liu, T. J. (2023). Research on the impact and mechanism of digital rural development on farmers' entrepreneurship. Chin. Rural Econ. 5, 61–80. doi: 10.20077/j.cnki.11-1262/f.2023.05.004
Keywords: China, rural digitization, urban-rural income gap, factor flow, economics
Citation: Wen X, Li Y, Zhou M, Feng F and Wang P (2025) Rural digitization and the urban–rural income gap: a perspective of factor flow. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1647632. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1647632
Received: 16 June 2025; Accepted: 04 August 2025;
Published: 25 August 2025.
Edited by:
Stefano Rinaldi, University of Brescia, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Wen, Li, Zhou, Feng and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fengcun Feng, ZmVuZ2ZjMjAyNEAxNjMuY29t; Pingping Wang, d3BwcHJpdmF0ZUAxMjYuY29t
 Xiaoai Wen
Xiaoai Wen Yiran Li
Yiran Li Minxi Zhou
Minxi Zhou Fengcun Feng2*
Fengcun Feng2* Pingping Wang
Pingping Wang