- 1School of Economics and Management, Qingdao Agricultural University, Qingdao, China
- 2School of Business, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, China
Introduction: The stable and secure supply of food and important agricultural products is related to the foundation of people’s livelihoods and is a top priority for the country’s economy. The construction of a robust supply chain system for agricultural products can help to effectively cope with the impact of international political conflicts, natural disasters, emergencies, and other uncertainties. Currently, problems of chain breakage and blockage in the agricultural products supply chain occur frequently, affecting food security. It has become a pressing task to improve the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain by utilizing smart technology and other emerging forms.
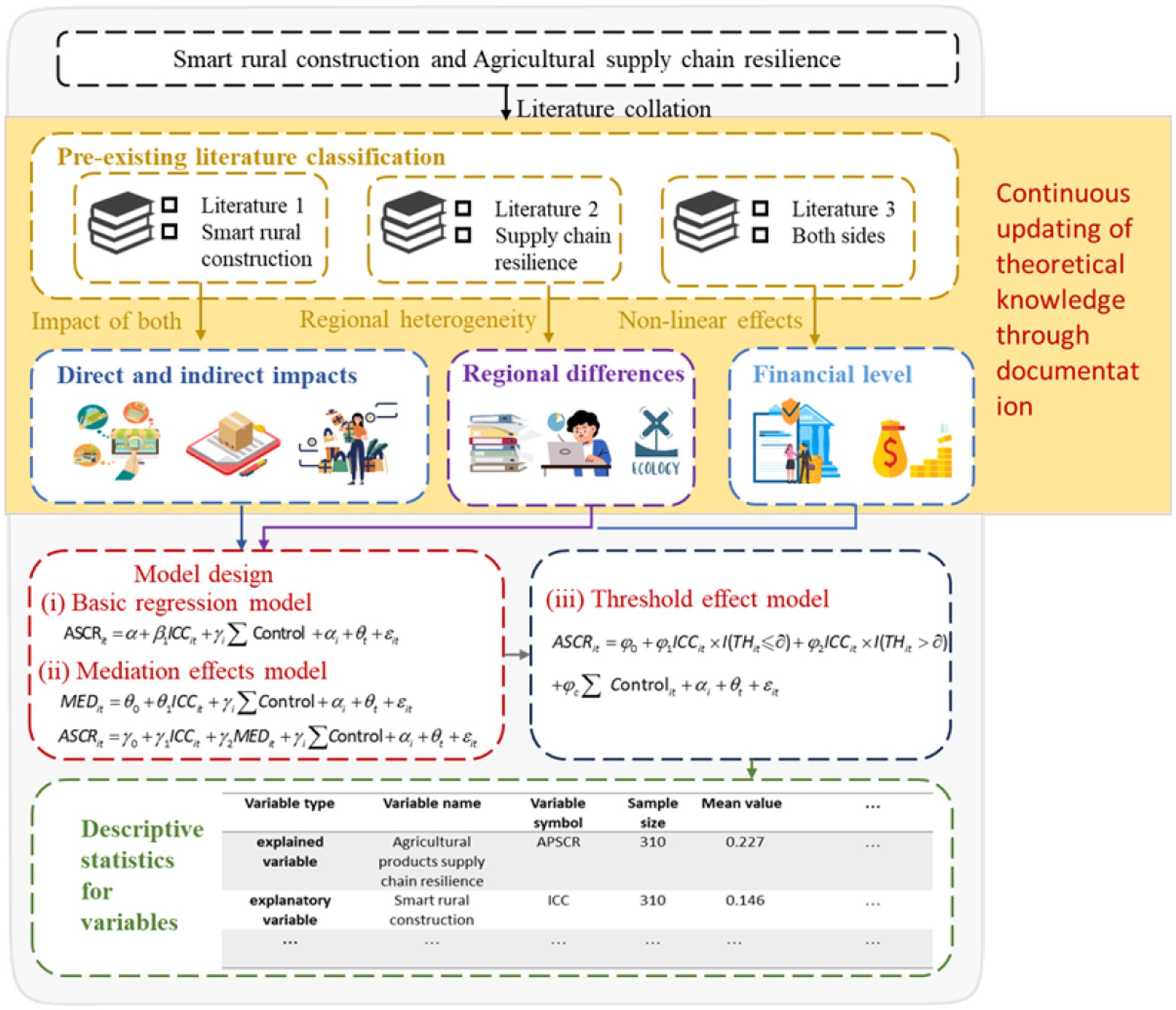
Methods: Based on panel data from 31 Chinese provinces (2013–2022), this study employs a two-way fixed effects model and a panel threshold model to analyze the impact mechanism of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain. Composite indices for smart rural construction and the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain were constructed using the entropy weight method. The robustness of these indices was rigorously tested through sensitivity analyses and by recalculating the smart rural construction index using the coefficient of variation method.
Results and discussion: Ultimately, the results of the study show that smart rural construction can enhance the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain and improve it by promoting the upgrading of industrial structure. The effect of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain is regionally heterogeneous, with a more significant positive effect in the central and western regions. Additionally, there is a threshold effect associated with the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain. The conclusions of this paper show that the smart rural construction gives new momentum for improving agricultural products supply chain resilience in China and provides theoretical and practical guidance for the modernization of China’s agriculture and rural areas, as well as the construction of a strong agricultural products country.
1 Introduction
The report of the Twentieth Party Congress emphasizes that efforts should be made to improve the resilience and security level of the industrial supply chain. As a fundamental industry of the national economy, improving the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain plays an important role in guaranteeing China’s food security, contributing to the construction of a strong agricultural products country, and realizing agricultural products modernization. The main operations of the agricultural products supply chain, such as production, processing, storage, and transportation, mainly take place in rural areas due to the fact that most of China’s rural areas are currently characterized by inadequate logistics infrastructure and a low level of information technology. Once affected by sudden and uncertain factors, real-life problems such as broken and blocked chains in the agricultural supply chain will occur, directly affecting our food security. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen its top-level design and system construction, seize the key subjects of the supply chain to enhance the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, which is an important task to promote the transformation and upgrading of the supply chain of the agricultural products industry chain and enhance the modernization of the rural industry in the long-term future (Zhang, 2024). As smart technology accelerates its extension and penetration into the agricultural products and rural sectors, smart technology innovation and application create favorable conditions for enhancing the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain. The Outline of the Smart Rural Development Strategy, which was introduced in 2019, comprehensively deploys the construction of smart rural areas. The release of the Smart Agriculture and Rural Development Plan 2019–2025 in 2020 marked the transition of smart rural development from strategic planning to a new stage of solid advancement. China’s no. 1 central document for 2024 proposed the continuous implementation of smart rural development actions, further highlighting the importance the state attaches to the construction of smart rural areas. Thus, clarifying the logical relationship and influence mechanism between smart rural construction and agricultural products supply chain resilience is one of the important topics in the study of food security and agricultural products industrial security, as well as the focus of high-quality development of agriculture, which has important theoretical significance and policy guidance value. It is important to note that China’s vast territory encompasses significant regional disparities in natural endowments, economic development levels, and agricultural production models. Consequently, the composition of major agricultural products (e.g., staple grains, commercial crops, livestock, aquaculture), the primary vulnerabilities faced by agricultural supply chains (e.g., logistical inefficiencies, market access barriers, climate risks), and the strategic focus of Smart Rural Construction (e.g., prioritizing smart logistics, e-commerce platforms, or precision agriculture) vary considerably from province to province. This study employs provincial-level panel data to capture these macro-level regional heterogeneities. While the composite indices for APSCR and SRC are designed to be comparable across provinces, we acknowledge that the specific manifestations of resilience and smart construction are context-dependent.
Recent studies have further explored various dimensions of supply chain resilience and smart rural development (Chang and Jiang, 2023; Coluccia et al., 2021; Sobczak-Malitka and Drejerska, 2024; Zhang and Zhang, 2020). To explore the relationship between smart rural construction and agricultural supply chain resilience, this paper attempts to utilize various models, and threshold effects, to construct an evaluation index system of smart rural construction and agricultural supply chain resilience based on the panel data of 31 provinces in China from 2013 to 2022 to empirically test the impact mechanism of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural supply chain, thereby filling gaps in the existing research.
Firstly, smart rural areas and their practices have received late attention compared to smart cities (Gong and Shan, 2023). However, as the application of the concept of “smart” development in rural areas has gradually received more attention, the construction of smart rural areas has become a hot issue in academic research (Zeng et al., 2022). The theoretical level of existing research mainly covers from the basic concepts of smart rural construction, development trends, other aspects of smart rural construction, how to build a smart rural area, and other basic issues for interpretation (Park and Cha, 2019; Fernández and Peek, 2023). The empirical level is mainly based on the analysis of the impact and realization path of smart rural construction. First, regarding the impact of smart rural construction, Chen et al. (2022) used the 2SLS instrumental variable approach to analyze the impact of smart rural construction on farmers’ income growth and its potential mechanisms, and the results showed that smart rural construction can significantly increase the level of farmers’ income. Zhao et al. (2022) constructed a theoretical framework for smart rural construction with the help of smart empowerment theory and verified the theoretical framework through case analysis to provide reference and guidance for smart rural construction. Mei et al. (2022) used the entropy weight TOPSIS method to evaluate the current status of rural smartization and high-quality economic development and empirically examined the impact of smart countryside construction on the high-quality development of the rural economy based on the fixed-effects model and mediated-effects model. Liu et al. (2024) empirically analyzed the impact of smart rural construction on the urban–rural income gap. Wang et al. (2023) empirically examined the impact of smart rural construction on county-level economic growth in China, and the results of the study showed that smart rural construction significantly increased county-level economic growth. Second, concerning the realization path of smart rural construction, Wang et al. (2022) described smart rural construction based on quantitative analysis and intuitive visualization. Adamowicz and Zwolińska-Ligaj (2020) assessed the potential for smart growth in rural areas in Poland and presented the results of an empirical study on the potential in the eastern region of Poland, suggesting that smart countryside development contributes to the promotion of sustainable development in rural areas. Chen and Li (Chen et al., 2024) discussed the influencing factors of China’s smart community construction and its effective path by taking 52 national-level community governance and service innovation pilot zones in China as examples. Zhang et al. (2023a) proposed a theoretical framework for smart rural systems based on general systems theory and analyzed China’s smart rural strategic planning and smart rural practice based on the theoretical framework of smart rural systems.
Secondly, the concept of supply chain resilience is multidimensional and multi-layered in its complexity (Stone and Rahimifard, 2018). In conjunction with previous literature, this paper defines agricultural products supply chain resilience as the ability of a supply chain to recover to its original state or a more optimal state after disruption (Christopher, 2004). In the face of unprecedented changes, the agricultural products supply chain may face huge adjustments, and the supply chain shows instability, uncertainty, and complexity. Based on this, scholars at home and abroad are committed to researching agricultural products supply chain resilience. Hobbs (2021) discussed agricultural products supply chain resilience and the differences that exist by reviewing the changes that have occurred in the Canadian and U. S. agri-food supply chains in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Belhadi et al. (2024) (Belhadi et al., 2024) used smart technology to design resilience strategies to manage uncertainty arising from an external environment disrupted by geopolitical events. Yuan et al. (2024) employed the BP-DEMATEL-ISM and PLS-SEM methods to conduct causal analysis and factor-level evaluation, aiming at key strategies for building resilience in agricultural products supply chains under climate change impacts. Risk management is extremely important in the agricultural products supply chain due to the seasonal and perishable nature of agricultural products (Behzadi et al., 2018). Meuwissen et al. (2019) assessed the resilience of agricultural product systems by developing a framework aimed at assessing the ability to adapt to specific challenges (specific resilience) and the ability of agricultural product systems to deal with unknowns, uncertainties, and surprises. Ali et al. (2021) promoted the intertwined impact of knowledge management, risk management culture, and resilience by integrating them for resilience in agricultural product supply chains. In recent years, research on supply chain resilience has increasingly emphasized the pivotal role of smartization and emerging technologies as strategic enablers. Recent advancements highlight that smart capabilities are not merely supportive but fundamental to building resilience against compounding disruptions, particularly in agri-food systems (Belhadi et al., 2024). Furthermore, the discourse has evolved to adopt a more systemic perspective, viewing resilience through the lens of complex adaptive systems. This systemic approach argues that resilience emerges from the dynamic interactions and information flows between multiple actors within the supply chain network, rather than from the strength of individual components alone (Zhang et al., 2024). Concurrently, the application of smart technologies in rural contexts has shown significant potential to enhance resilience. Specifically, empirical evidence from China suggests that smart rural construction, by integrating technologies like the Internet of Things and big data, can directly mitigate operational risks and strengthen the adaptive capacity of agricultural supply chains (Zhang et al., 2023b).
Despite the growing academic interest in agricultural supply chain resilience, there are fewer studies on the relationship between smart rural construction and agricultural supply chain resilience. Many studies have focused mainly on the impact of smart rural construction on agricultural resilience and food system resilience. For example, Zhao and Zhao (2024) predicted that tracer models were used to calculate scores for smart rural-level and agricultural products’ resilience, and instrumental variable methods and mediated effects models were applied to analyze the impacts and mechanisms of smart rural development on agricultural products’ resilience in ecologically fragile ethnic areas. Alam et al. (2023) used the PRISMA methodology to conduct a systematic evaluation of the existing literature, which showed that ICTs can enhance the resilience of agri-food systems in developing countries. Cai et al. (2023) empirically examined the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of rural households and the underlying mechanisms of action. Singh et al. (2023) empirically analyzed the role of smart platforms in enhancing rural resilience using a multi-case study approach. Guo et al. (2024) empirically tested the impact of smartization on agricultural products’ economic resilience by constructing a comprehensive system of agricultural products smartization and agricultural products’ economic resilience and adopting two-way fixed effect, adjustment effect, and threshold effect models. In addition, traditional statistical models usually assume linear relationships, which makes it difficult to capture complex nonlinear interactions or threshold effects among the influencing variables, thus limiting their multifactor explanatory power in agricultural supply chain resilience.
Based on the above issues, this study examines the relationship between smart rural construction and agricultural supply chain resilience under the research framework of supply chain resilience and constructs a double fixed effect model, which has revealed the mechanism of the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural supply chain. This study aims to answer the following key questions:
Q1: How does smart countryside building affect agricultural supply chain resilience?
Q2: Is there regional heterogeneity in the impact of smart rural development on agricultural supply chain resilience?
Q3: Does smart rural development have a nonlinear impact on agricultural supply chain resilience?
Based on this, this paper utilizes a variety of models such as two-way fixed effects, mediation effects, and threshold effects, and constructs an evaluation index system for smart rural construction and the agricultural products supply chain resilience based on the panel data of 31 provinces in China from 2013 to 2022 to empirically test the impact mechanism of smart rural construction on the resilience of agricultural products supply chain. The results of the study show that smart rural construction can enhance the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain and can improve the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain by promoting industrial structure upgrading. The heterogeneity test shows that the positive effect of smart rural construction on agricultural products supply chain resilience is more significant in the central and western regions.
Compared with the previous literature, the marginal contributions of this paper may be: (1) Including smart rural construction in the research framework of agricultural products supply chain resilience and, for the first time, exploring the influence mechanism of agricultural products supply chain resilience based on the empowerment perspective of smart rural construction, further deepening the understanding of the relationship between the two. (2) Most of the existing studies summarize agricultural products scientific and technological talents into the dimension of smart infrastructure, but this paper innovatively incorporates “farmers’ smart literacy,” which includes smart technologies and talents, into the scope of the indicator construction of the level of smart countryside construction, to further improve the quantitative evaluation index system of the level of smart countryside construction, and to construct an evaluation index system of agricultural products supply chain resilience with Chinese characteristics. The evaluation index system of resilience of the agricultural products supply chain is also constructed with Chinese characteristics. (3) Utilizing the panel data of 31 provinces in China from 2013 to 2022, we use the double fixed effects model and the mediation effects model to empirically test the impact and path of smart rural construction in enhancing the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, providing empirical evidence that smart rural construction enhances the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain in China.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 presents the theoretical analysis and research hypothesis. Section 3 presents the materials and methods. Section 4 provides the results and analysis. Section 5 presents the discussion. Section 6 presents the conclusions. The research framework of this paper is shown in Figure 1.
2 Theoretical analysis and research hypothesis
2.1 Theoretical framework and foundation
To clarify the intrinsic mechanism through which smart rural construction affects agricultural product supply chain resilience (APSCR), this study adopts dynamic capability theory as its core theoretical framework. This theory posits that enterprises (or organizations/systems) gain and sustain competitive advantages by integrating, building, and reconfiguring internal and external resources and capabilities to adapt to rapidly changing environments. Smart rural construction is essentially a process of deeply integrating smart technologies into the socioeconomic systems of rural areas. Its core objective is to enhance the dynamic capabilities of rural regions to cope with uncertainties and disruptions both within and beyond supply chains. Specifically, smart rural construction significantly strengthens the ability of supply chain node enterprises to sense internal and external information—such as market demand, price fluctuations, natural disasters, and geopolitical risks—enabling earlier and more accurate identification of opportunities and threats. By optimizing resource allocation, facilitating knowledge flow, and promoting collaborative cooperation, it empowers supply chain actors to swiftly seize opportunities or effectively mobilize resources to counter threats. Furthermore, by driving industrial structure upgrading, innovating business models, and optimizing organizational forms, it supports the agricultural product supply chain system in carrying out necessary reconfiguration and transformation. As a result, the system is not only able to recover from disruptions but also adapt to new environments and advance to a more optimal state.
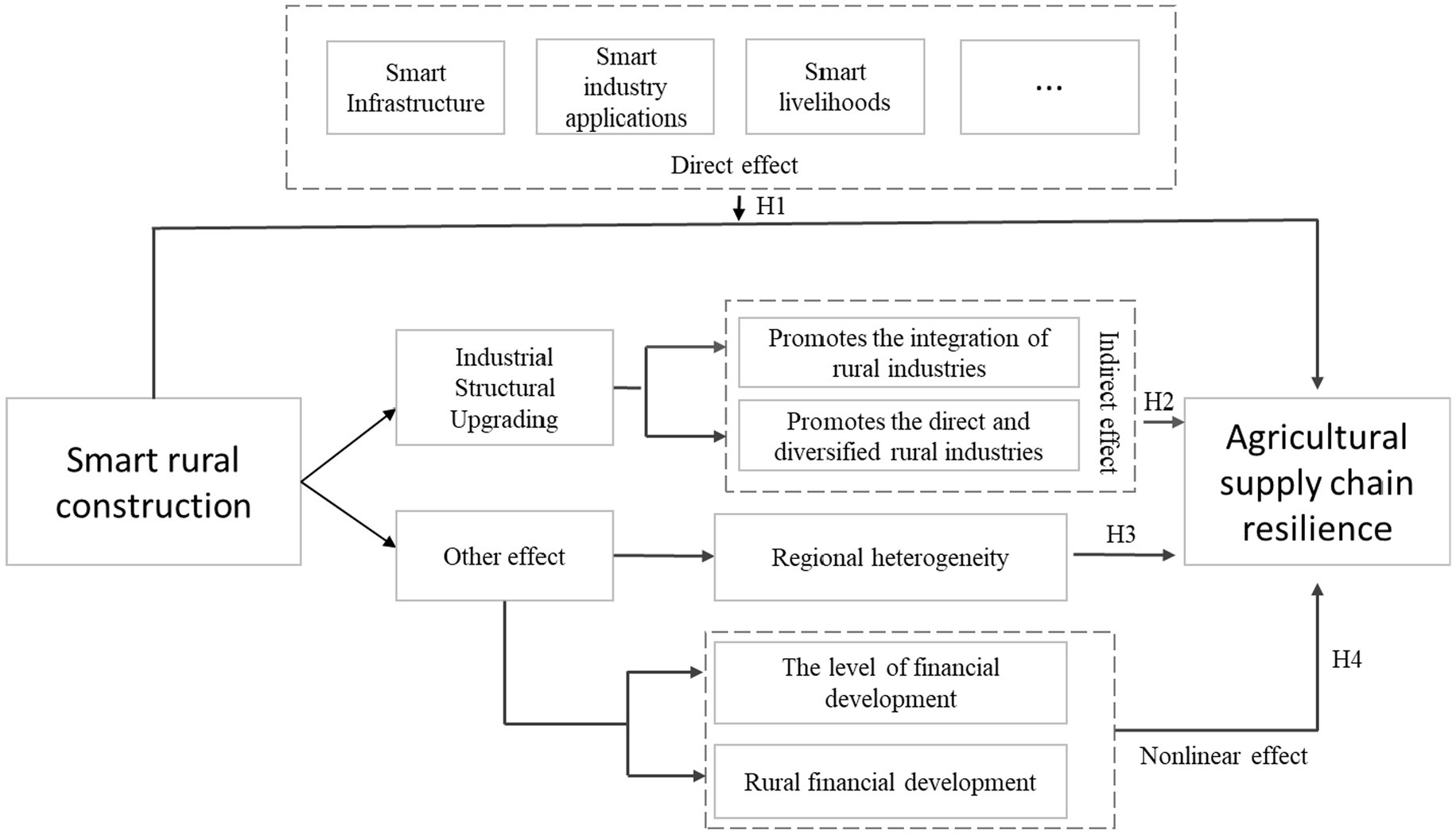
Therefore, grounded in dynamic capability theory, smart rural construction can be viewed as a strategic intervention that empowers the agricultural product supply chain by enhancing its sensing, seizing, and transforming capabilities, thereby systematically improving its resilience—the ability to withstand disruptions, adapt to changes, and achieve transformation. The subsequent hypotheses of this study are developed within this theoretical framework. The causal relationship frameworks for the four hypotheses in this paper are illustrated in Figure 2.
2.2 The direct impact of smart rural development on the resilience of agricultural product supply chains
The impact of Smart Rural Construction (SRC) on Agricultural Product Supply Chain Resilience (APSCR) is not monolithic but operates through a multidimensional framework. Smart infrastructure provides the physical backbone for resistance. This is measured by indicators such as rural mobile network coverage and Internet infrastructure construction, which enable real-time monitoring of storage conditions (e.g., via IoT sensors) and GPS-tracked logistics. This directly mitigates losses from operational shocks by preventing spoilage and reducing transit times. Concurrently, smart industry applications, captured by metrics like smart trading of agricultural products and rural e-commerce, are pivotal for competitiveness. They diversify market access, reduce monopsony power, and enable premium product positioning (e.g., for traceable, organic goods), thereby enhancing the chain’s long-term economic sustainability—a core aspect of resilience (Stone and Rahimifard, 2018). Smart livelihoods, proxied by the level of smart financial development and mobile phone penetration rate, alongside farmer smart literacy (measured by the size of the smart talent service workforce), empower individual actors. This is crucial for adaptability. When producers access real-time market prices via mobile apps, they gain the informational capacity to make swift decisions, such as switching sales channels in response to demand shocks. Smart finance provides the liquidity to execute these decisions. This micro-level behavioral agility, enabled by our measured indicators, aggregates to enhance the entire chain’s adaptive capacity. Smart governance, measured by funding for smart rural governance, strengthens the institutional capability for recovery. This investment facilitates the development of smart emergency response systems and e-platforms for swift permit approvals. During a disruption, these platforms facilitate coordinated responses among stakeholders. Streamlined e-governance processes can fast-track aid distribution, significantly reducing downtime and accelerating the return to normal operations, thus directly strengthening the recovery dimension measured in our index (Belhadi et al., 2024). Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes hypothesis H1:
H1: Smart rural construction has a positive direct impact on agricultural products supply chain resilience.
2.3 Indirect impacts of smart rural construction on agricultural products supply chain resilience through rural industrial structural upgrading
Smart rural construction improves the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain by promoting the transformation and upgrading of rural industries (Cen et al., 2022). First, the construction of smart rural areas promotes the integration of rural industries. The traditional supply chain network is relatively closed, and when a certain agricultural product suffers a shock, problems such as chain breakage will occur. This leads to other subjects in the supply chain being implicated. Therefore, the impact of any one of the chains will affect the other chain nodes and network structure; that is, there is an obvious “whip effect.” The smart rural construction will integrate the rural industry, relying on scientific and technological progress and collaborative division of labor, to realize the efficient operation of production, processing, sales, and other links, so that the trust relationship between the supply chain subjects is closer, breaking the rural industry island and enhancing the resilience of the supply chain. Second, the construction of smart rural areas promotes the direct and diversified rural industries. The traditional supply chain of agricultural products may exhibit redundancy, requiring multiple links of conduction from the origin to the intermediary and then to the market, which increases the risk of agricultural products supply chain shocks. With the construction of smart countryside to realize the transformation and upgrading of the rural industrial structure through the establishment of a smart countryside e-commerce platform, farmers, agricultural product cooperatives, and agricultural products enterprises in the country of origin can directly contact the customers through the smart platform, thereby promoting the “directness” of the agricultural products supply chain. At the same time, it explores new modes of agricultural product online marketing. Fully exploring the rural characteristics of resources and the development of special agriculture, rural culture, rural tourism, and other industries leads to the formation of a diversified rural industrial system. The transformation and upgrading of rural industries may improve the market access of agricultural products and promote information sharing and collaborative work among supply chain participants to improve the overall synergy and efficiency of the supply chain. Based on the above analysis, this paper proposes hypothesis H2:
H2: Smart rural construction improves the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain by promoting the upgrading of the rural industrial structure.
2.4 Regional heterogeneity in the effectiveness of smart rural construction to enable supply chain resilience of agricultural products
Different regions have different basic conditions in terms of economic development, resource endowment, and agricultural product production. Therefore, there may be regional differences in the promotion of the resilience of the supply chain of agricultural products by smart rural construction (Li et al., 2022). First, the penetration rate of smart rural construction in the agricultural products industry is different across regions, and the proportion of the agricultural products industry in each region also varies. Therefore, the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain is bound to have regional differences. Second, the construction of smart countryside in each region relies on the local level of science and technology innovation, policy, and other advantages, which leads to regional differences. Finally, the countryside infrastructure construction is updated at different speeds, resulting in inconsistent development of smart infrastructure across various regions. Overall, smart infrastructure in the eastern region has become well-developed, while the central and western regions are more capable of releasing smart dividends. Thus, the potential for enhancing the resilience of agricultural products supply chain is greater in these regions. Therefore, this study proposes hypothesis H3:
H3: There is regional heterogeneity in the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of agricultural products supply chains.
2.5 The nonlinear impact of smart rural development on the resilience of agricultural products supply chains
The process of smart rural construction to enhance the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain will be affected by many factors and uncertainties, and the level and speed of financial development vary in different regions, which leads to differences in regional economic development, infrastructure, and urbanization. This, in turn, has a differentiated impact on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain (Wensheng, 2020). First of all, the higher the level of financial development, the easier it is to provide sound and complete infrastructure and strong consumer demand for the construction of smart rural areas, which can promote the construction of smart rural and simultaneously empower the resilience of agricultural products supply chains. In regions with a relatively low level of financial development, on the other hand, the construction of smart rural areas is limited by the constraints of lagging supporting mechanisms, weak smart infrastructure, and limited consumer demand, which results in the resilience of agricultural products supply chains not being enhanced. Secondly, the level of financial development promotes technological innovation and talent mobility; regions with a high level of financial development usually gather more innovative and talent resources, and technological innovation alongside high-quality talent promotes the upgrading of agriculture and enhances the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain. Conversely, in regions with a low level of financial development, technological lag and a lack of talent may constrain the development of agriculture. Overall, factors such as infrastructure, consumer demand, technological innovation, and talent make agricultural products supply chains more resilient in regions with higher levels of financial development. The level of financial development as a threshold variable causes smart rural construction to have a nonlinear impact on agricultural products supply chain resilience. Based on this, this paper proposes the following hypothesis H4:
H4: When the level of financial development is used as the threshold variable, the construction of smart rural areas will have a certain nonlinear effect on the resilience of agricultural products supply chains.
3 Materials and methods
3.1 Model setup
3.1.1 Basic regression model
To test the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, this paper constructs the following two-way fixed effect model (see Equation 1):
Among them, as explanatory variables, smart rural construction, is the explained variable, agricultural products supply chain resilience, is a set of control variables, and are province and year fixed effects, respectively, and is a randomized perturbation term.
3.1.2 Mediation effects model
To further test the possible role mechanism of smart rural construction in enhancing the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, based on model (1), the mediation effect test model is constructed as follows (see Equation 2 and 3):
Included among these, is the mediating variable. If are all significant, then, it indicates that the inclusion of mediating variables changes the coefficient of the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, suggesting a partial mediating effect; If are significant, is not significant, then there is a full mediation effect.
3.1.3 Threshold effect model
In order to verify the nonlinear relationship between smart rural construction and the resilience of agricultural products supply chains, a threshold effect model is constructed with the level of financial development as the threshold variable (see Equation 4):
Among others, is the threshold variable, I (·) is the indicator function, When the threshold variable satisfies the corresponding condition, I (·) = 1, if not I (·) = 0; is the threshold value.
3.2 Description of variables
3.2.1 Explanatory variable
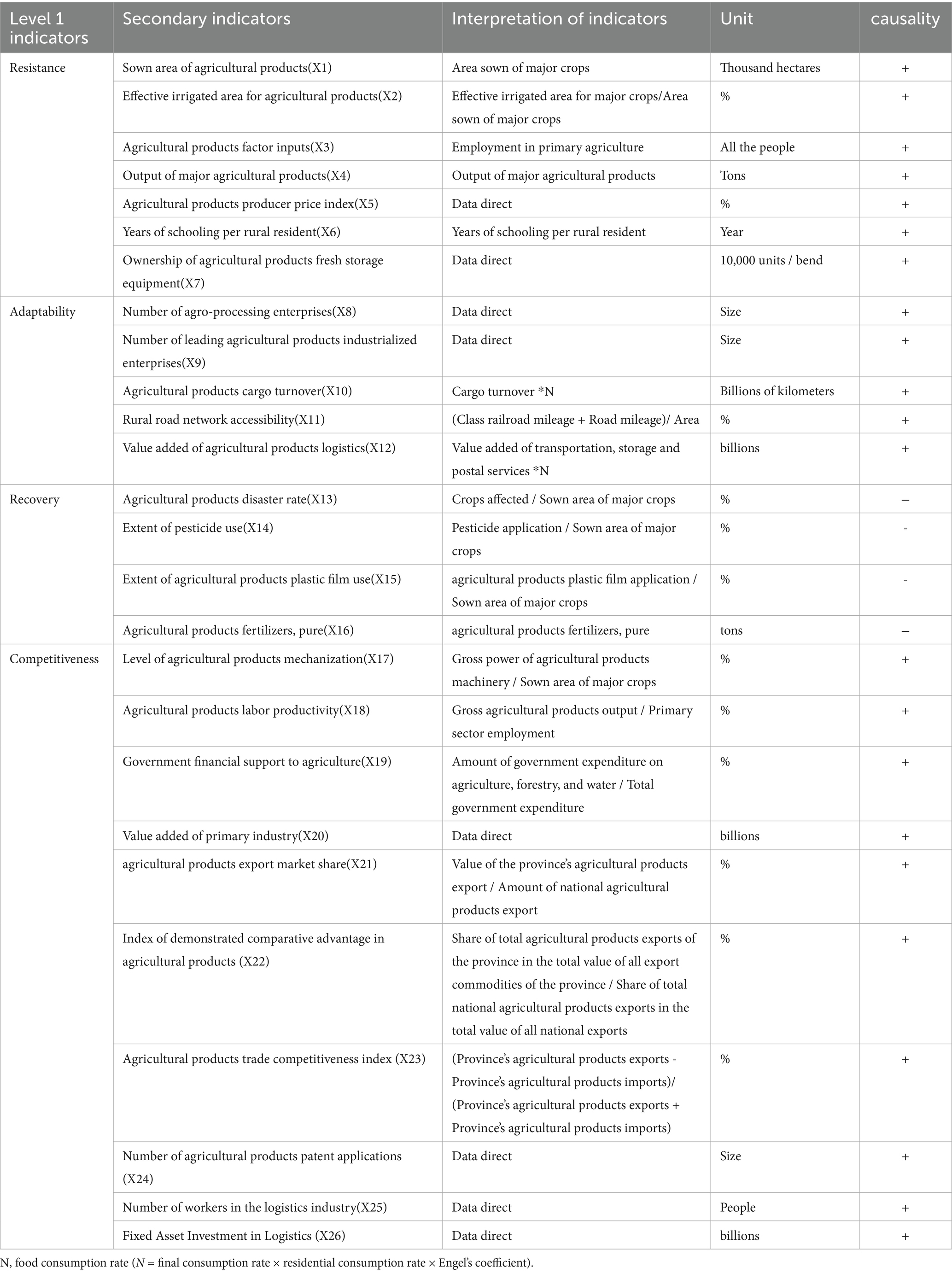
In alignment with contemporary supply chain resilience literature (Stone and Rahimifard, 2018; Belhadi et al., 2024), this study conceptualizes APSCR as a multi-dimensional construct comprising four core capacities: Resistance, Adaptability, Recovery, and Competitiveness. This framework captures not only the ability to withstand disruptions but also to adapt, recover, and sustain competitive advantage in the face of shocks (see Table 1) and uses the entropy weight method to calculate the weights. The entropy weight method assigns weights based on the degree of dispersion of each indicator value. A higher dispersion indicates a greater impact of the indicator on the overall evaluation, thus minimizing subjective influence. Among these, resistance reflects the pre-disaster buffering capacity. Indicators such as sown area (X1), effective irrigation rate (X2), and agricultural labor input (X3) represent the foundational productive capacity and resource endowment that enable the system to absorb initial shocks without immediate collapse. The producer price index (X5) and education level (X6) proxy the economic and human capital buffers that enhance stability. Adaptability captures the system’s dynamic response and reconfiguration capabilities during a disruption. The number of processing enterprises (X8) and leading enterprises (X9) indicate the flexibility and diversification of the supply chain’s nodal structure. Cargo turnover (X10) and road accessibility (X11) measure logistical agility, crucial for rerouting flows and maintaining operational continuity under stress. Recovery signifies the post-disaster bounce-back ability. The disaster rate (X13) directly measures vulnerability, while input intensity indicators like pesticide use (X14) and fertilizer application (X16) serve as inverse proxies: their overuse indicates ecological fragility and reduced long-term systemic resilience, as they compromise soil health and ecosystem self-regulating capacity. Among these, the extent of pesticide use refers to the phenomenon where over-reliance on chemical pesticides undermines soil health, reduces biodiversity (including beneficial pollinators and natural pest predators), and leads to pest resistance. This creates a “paradox” in which short-term gains in pest control compromise the long-term health and self-regulating capacity of agroecosystems, making them more vulnerable to future disruptions and weakening their ability to recover robustly (Zhang et al., 2025) (Table 2). This negative causal relationship between excessive pesticide use and systemic resilience has been widely documented in agroecological studies. Competitiveness embodies the long-term sustainability and market advantage regained after a shock. Mechanization level (X17), labor productivity (X18), and government support (X19) reflect efficiency gains and policy backing that foster robust recovery. Export share (X21), comparative advantage (X22), and patent applications (X24) indicate innovation and market repositioning capabilities, essential for transforming and thriving post-disruption. Specialized statistical data on the circulation of agricultural products only is insufficient in official yearbooks, which often report aggregate logistics data encompassing both agricultural and non-agricultural goods. Directly using these aggregate figures (e.g., total cargo turnover, total value-added of logistics) would introduce significant measurement error into our APSCR index, as it would be inflated by the circulation of industrial products, minerals, and manufactured goods, which constitute a substantial portion of logistics in a modernizing economy like China. This study adopts the methodology of Wang et al. (2023) to ensure the scientific validity and accuracy of the results by multiplying the relevant data with the food consumption rate in order to exclude the influence of non-agricultural distribution factors. The rationale behind this method lies in the fact that foodstuffs are the main component of the distribution of agricultural products, and the food consumption rate can effectively eliminate the influence of non-agricultural products in residents’ consumption. This approach aims to more precisely capture the actual proportion of agricultural products in overall circulation and enhance the accuracy and comparability of the Agricultural Products Supply Chain Resilience indicator. Therefore, using the food consumption rate to adjust the relevant circulation data can reasonably approximate the actual situation of agricultural products logistics.
3.2.2 Core explanatory variables
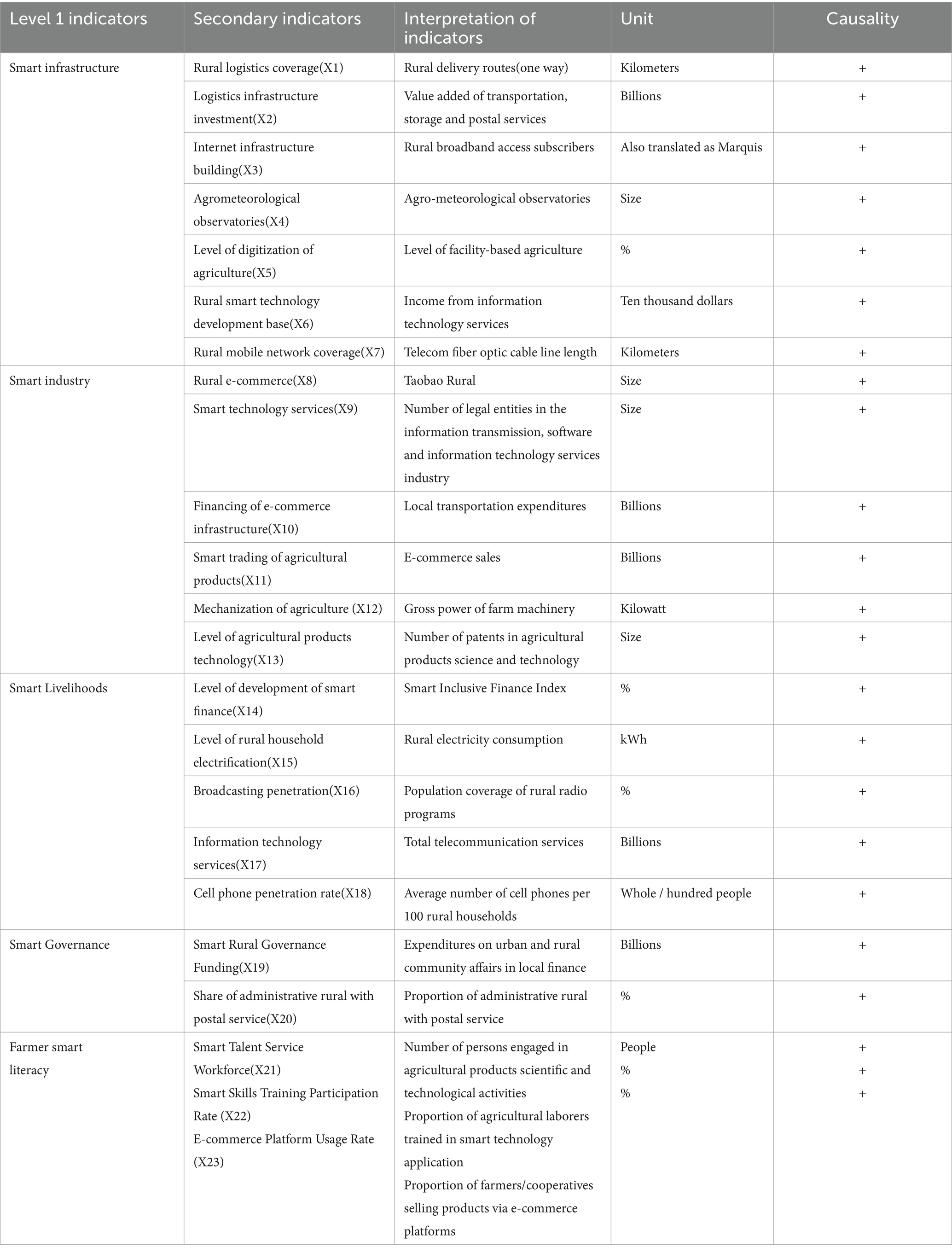
The explanatory variable in this paper is Smart Rural Construction (ICC). Moving beyond a simplistic view of digitization, we conceptualize SRC as a multidimensional systemic transformation. The evaluation indicator system is constructed from five theoretically distinct yet interconnected dimensions, each representing a critical pillar for building a smart rural ecosystem, which in turn forms the foundation for a resilient agricultural supply chain. Smart infrastructure constitutes the physical and smart backbone of the smart rural ecosystem. It is measured by indicators such as rural logistics coverage, Internet infrastructure, and mobile network coverage. The theoretical rationale is that high-speed connectivity and pervasive sensor networks (IoT) are prerequisite enabling technologies. They facilitate the real-time data acquisition and transmission that are fundamental to all other smart applications. Without this backbone, the information flows necessary for supply chain visibility, coordination, and rapid response to disruptions would be impossible (Hrustek, 2020). Smart industry captures the productive application of smart technologies in the economic sphere. Measured by e-commerce activity, smart trading, and levels of agricultural technology, it reflects the transition from traditional to smart agriculture. The theoretical contribution of this dimension lies in its direct value-creation mechanism. It enhances resilience by diversifying income sources (e.g., through e-commerce), optimizing production decisions (via data analytics), and improving resource efficiency (through precision agriculture), thereby increasing the economic robustness of the entire chain (Zhao et al., 2022). Smart livelihoods measure the integration of smart tools into daily life and the consumption side of the economy, proxied by smart finance, electrification, and IT services. Its theoretical importance is in empowering individual end-users (farmers, residents). Access to smart financial services (e.g., mobile payments, microloans) enhances their adaptive capacity to absorb financial shocks. Improved access to information and services improves human capital, which is a critical, often overlooked, component of a resilient system (Singh et al., 2023). Smart governance represents the institutional and governance modernization enabled by technology, measured by funding for smart governance and postal network coverage. Its theoretical role is to strengthen the institutional response capacity. Smart governance platforms can streamline administrative processes, enable faster policy dissemination, and facilitate coordinated crisis management during supply chain disruptions, thus directly contributing to the system’s recovery capacity (Belhadi et al., 2024). Farmer smart literacy evaluates the human capital aspect of smart transformation. Skilled farmers are more capable of adopting advanced technologies, engaging in smart markets, and responding to smart information, which is critical for sustaining supply chain adaptability and innovation.
It is worth noting that the agricultural product mix and smart rural development priorities vary significantly across Chinese provinces. For instance, provinces like Heilongjiang and Henan are major grain producers, where resilience may focus on yield stability and logistics efficiency. Conversely, coastal provinces such as Shandong and Zhejiang emphasize high-value products like seafood and fruits, requiring cold-chain and e-commerce capabilities. Similarly, smart rural initiatives range from IoT-based precision farming in Jiangsu to e-commerce platforms in Guangdong. These regional distinctions underline the need for context-specific resilience strategies, though our composite indicators aim to capture these variations through multidimensional measurement.
3.2.3 Other variables
In this study, the mediating variable is industrial structure upgrading (MED), measured as the ratio of the value-added of the tertiary industry to that of the secondary industry. The following control variables are also included: (1) government support level (GS), represented by the proportion of regional fiscal expenditure to regional GDP; (2) regional economic development level (RED), measured as the per capita GDP of each province, expressed in logarithmic form; (3) urbanization rate (UR), indicated by the proportion of urban permanent residents to the total population. (4) Financial development level (FDL), defined as the ratio of the loan balance of financial institutions to regional GDP. To address potential concerns that this broad macroeconomic indicator may not accurately reflect rural financial conditions, an additional rural-specific financial indicator is introduced as a robustness check in our threshold analysis: (5) Rural financial development (RFD), measured by agricultural insurance depth, calculated as the premium income of agricultural insurance divided by the value-added of the primary industry. This indicator offers distinct advantages for our analysis, as it specifically captures the penetration and development of financial services within the agricultural sector. The availability of agricultural insurance serves as a critical financial tool for farmers to mitigate production risks, such as natural disasters and price fluctuations. Higher insurance depth implies a more robust financial safety net, which can enable farmers and cooperatives to invest in and adopt smart technologies with greater confidence. Unlike the broad FDL ratio, agricultural insurance depth directly targets the financial ecosystem in which smart rural initiatives operate, providing a clearer depiction of financial constraints or empowerment at the rural level.
3.3 Data sources and descriptive statistics of variables
In this paper, the panel data of 31 provinces in China (excluding Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan) from 2013 to 2022 are selected as the research sample. The main data for the study come from the China Statistical Yearbook, China Rural Statistical Yearbook, Peking University Smart Financial Inclusion Index, as well as statistical yearbooks and statistical bulletins of each province. In addition, the interpolation method is used to fill in the missing sample data. The descriptive statistics of each variable are shown in Table 3.
4 Results and analysis
4.1 Base regression analysis
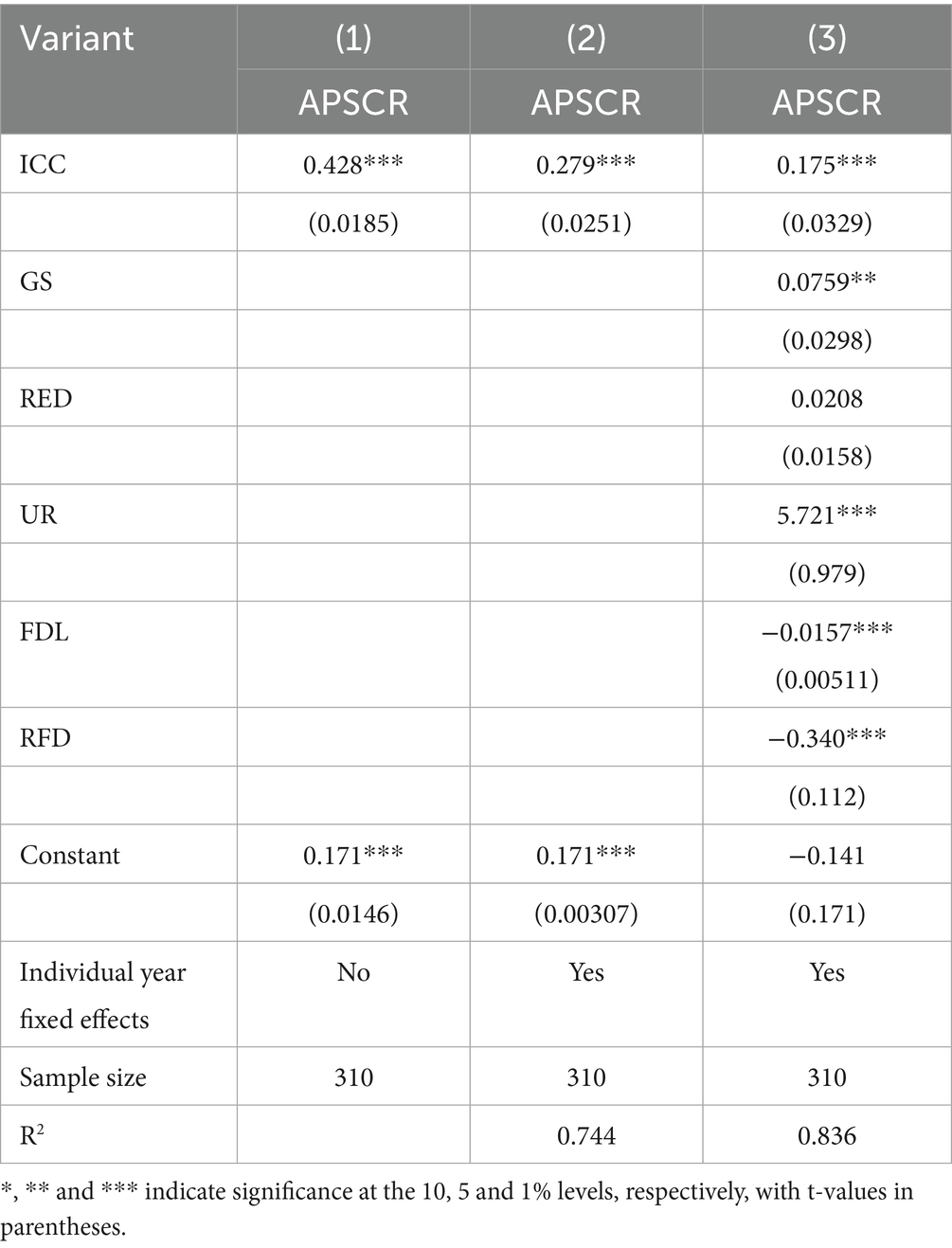
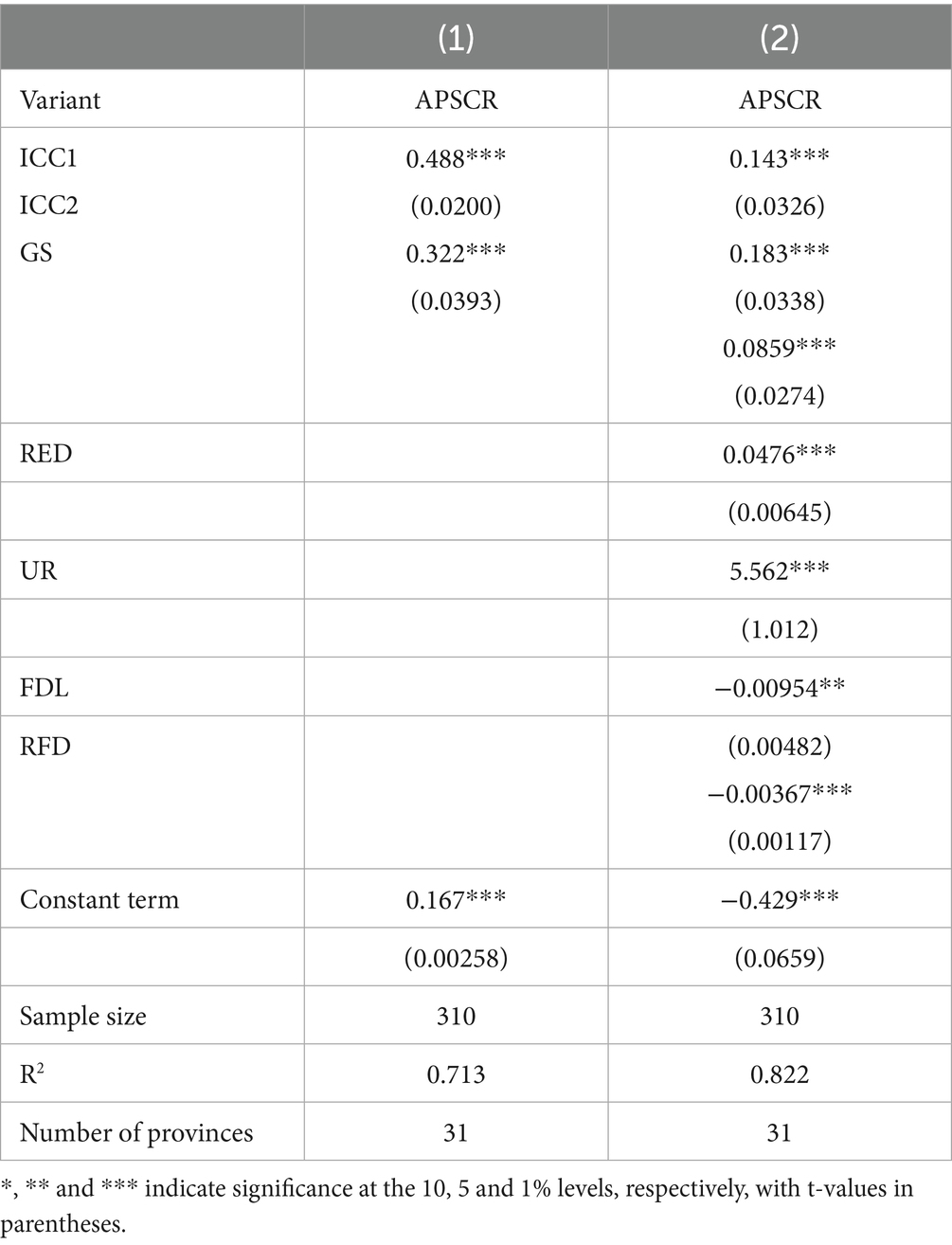
Table 4 reports the regression results of the effect of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, where column (1) shows the regression results without considering the control variables and fixed effects, and column (2) demonstrates the regression results with the inclusion of the individual year fixed effects in both directions. Column (3) examines the regression results with the inclusion of control variables fixed in both directions. The results show that the regression coefficients of smart rural construction are significantly positive regardless of whether control variables and two-way fixed effects are added, which indicates that smart rural construction significantly improves the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain and verifies Hypothesis H1. As mentioned in the previous section, the implementation and advancement of smart rural construction not only provides complete infrastructure for rural construction but also helps to improve the flow of information optimize resource allocation, and upgrade the rural industry. As mentioned above, the implementation and promotion of smart rural construction not only provides complete infrastructure for rural construction, but also helps to improve information circulation, optimize resource allocation, and provide a long-term guarantee for the upgrading of rural industries, thus promoting the enhancement of the toughness of the agricultural products supply chain.
4.2 Robustness and endogeneity tests
4.2.1 Replacement of explanatory variable measures
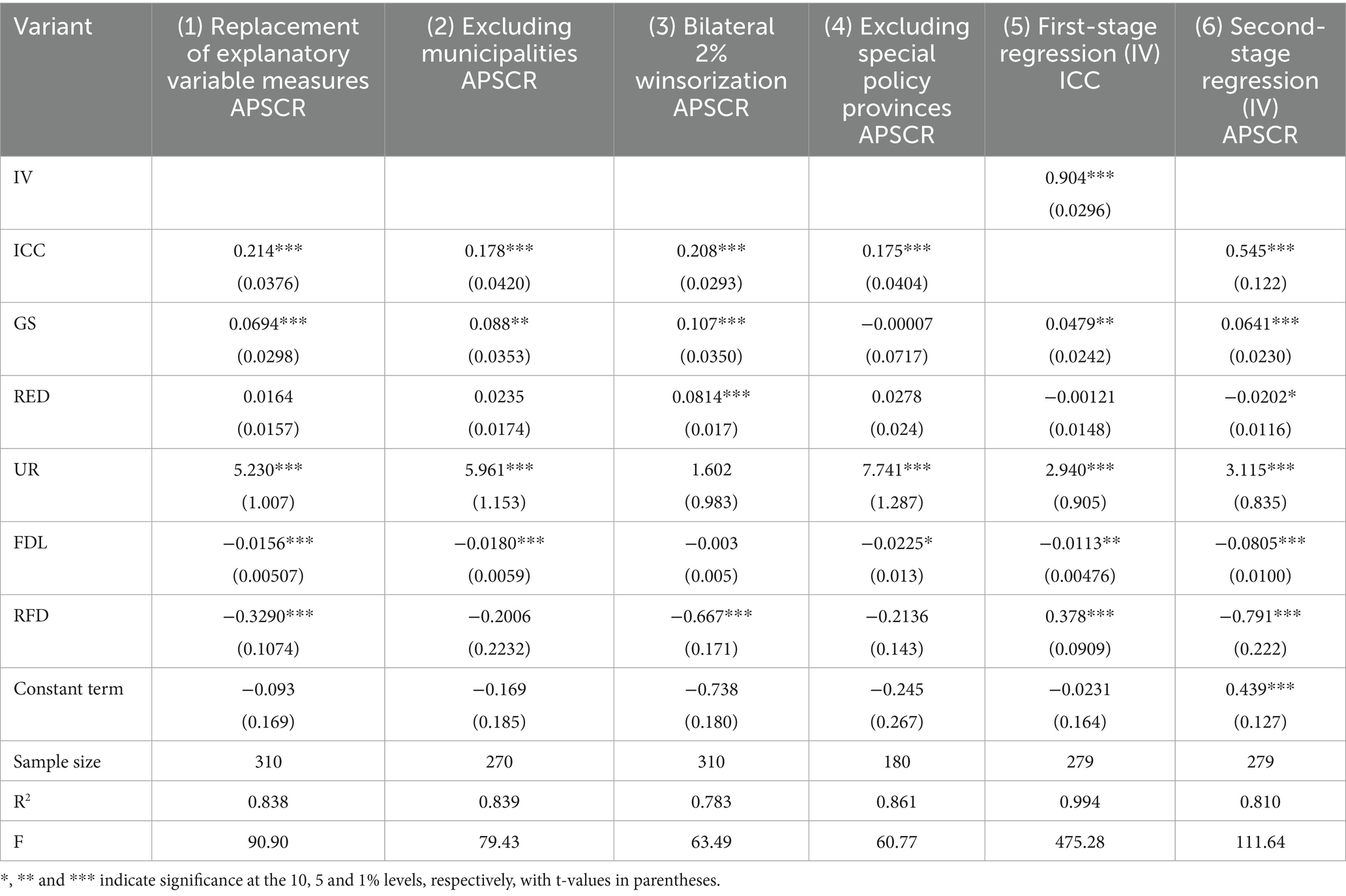
This paper uses the entropy weight method to measure the development level of smart rural construction in the benchmark regression. To avoid the error generated by a single objective assignment, this paper draws on the practice of Zhang et al. (2023a), who used the coefficient of variation method to re-measure the level of smart rural construction for robustness testing. The coefficient of variation method determines the weights by evaluating the difference between the average value of each indicator and the initial value, and the differences between the weights of the indicators are small compared to the entropy weight method of assigns weights based on the degree of discretization between the indicators. As can be seen from column (1) of Table 5, the coefficient estimates of the level of smart rural construction measured using the coefficient of variation method are all significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that the results of the study are robust. The smart rural construction index (ICC) was developed using both the entropy weight method and the coefficient of variation method. Regression analyses incorporating these indices consistently demonstrated a significant positive impact of smart rural construction on agricultural supply chain resilience, with consistent coefficient directions and significance levels (see Column 1 of Table 5). These results indicate that our index construction method exhibits strong robustness and remains insensitive to the choice of weighting approach.
4.2.2 Excluding municipalities
China’s municipalities have special characteristics in the level of agricultural products economic development, agricultural product policy support, and the quality of agricultural products labor force avoid the influence of other unobservable factors, and to further verify the reliability and robustness of the conclusions, this paper draws on the practice of Yao and Chen (2024) to re-test the sample by re-moving the municipality. Column (2) of Table 5 reports the regression results with the exclusion of four municipalities, from which it can be seen that the coefficient of smart rural construction after the exclusion of municipalities is 0.178, which is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that the smart rural construction enhances the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, which verifies the robustness of the benchmark regression mentioned above.
4.2.3 Bilateral indentation treatment
In order to avoid extreme values of each variable in the analysis, this paper draws on the practice of Qin and Wang (2022), shrinking 2% for each study variable. The regression results after shrinkage are shown in column (3) of Table 5, and the regression coefficient of smart rural construction is 0.208, which is significantly positive at the 1% level. This indicates that smart rural construction significantly enhances the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain, further indicating that the findings of this paper are robust.
4.2.4 Exclusion of provinces with special policies
The heterogeneity results may be confounded by the fact that central and western regions often overlap with key national strategy zones, such as the Western Development Strategy and the Rise of Central China Strategy, which entail substantial financial transfers and preferential policies. To ensure that our estimated heterogeneity is driven by smart rural construction itself rather than other concomitant regional policies, we conduct a robustness test by excluding provinces that are typically classified as national-level rural revitalization key assistance counties (a policy targeting the most underdeveloped regions). These provinces include: Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, Xinjiang, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Tibet, Guangxi, Inner Mongolia, Jilin, Heilongjiang, and Hainan.
As shown in column (4) of Table 5, after excluding these provinces, the coefficient of smart rural construction (ICC) remains positive and statistically significant at the 1% level, although the coefficient size changes. This confirms that the positive impact of smart rural construction on APSCR is robust. More importantly, it suggests that the core finding of regional heterogeneity—stronger effects in less developed regions—is not solely attributable to other special support policies but is indeed linked to the marginal utility of smart infrastructure construction.
4.2.5 Endogenous processing
Both smart rural construction and agricultural product supply chain resilience are composite indices, which may introduce endogeneity issues due to measurement bias, in addition to potential omitted variables not accounted for. To address endogeneity concerns as much as possible, an instrumental variable (IV) approach is employed to estimate the baseline model. In selecting the instrumental variable, the use of the one-period lagged explanatory variable is a common method in econometrics to mitigate endogeneity caused by reverse causality or omitted variables. The lagged value is correlated with the current explanatory variable (relevance condition) but is not influenced by the current error term (exogeneity condition), making it a suitable instrumental variable. This approach has been widely adopted in similar studies in regional and agricultural economics. For instance, Yang and Sun (2024) and Zhang et al. (2023a) used lagged variables as instruments when assessing the impact of smart transformation using smart infrastructure indicators, supporting the validity and rationality of this method. The endogeneity of the empirical analysis results was tested based on Two-Stage Least Squares (2SLS). The relevant test results are shown in the table. Column (5) of Table 5 presents the first-stage regression results, indicating that the instrumental variable L. ICC is positively correlated with ICC at the 1% significance level, suggesting a strong correlation between the selected instrumental variable and the explanatory variable. Column (6) reports the second-stage regression results, showing that smart rural construction remains significantly positively correlated with agricultural product supply chain resilience, verifying the robustness of the aforementioned conclusions.
4.3 Mechanism testing
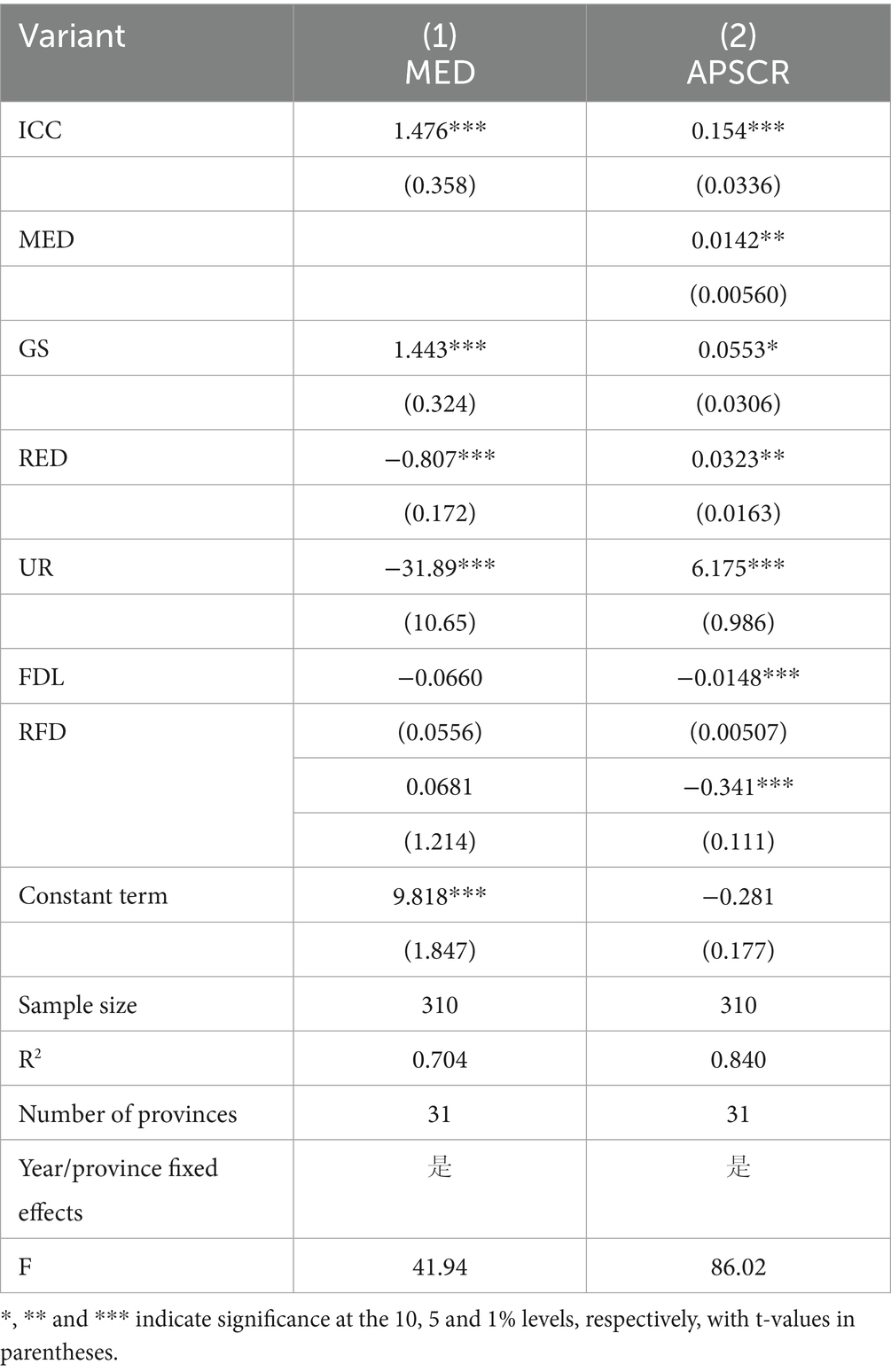
In this paper, industrial structure upgrading is selected as the mediating variable. Column (1) in Table 6 shows the regression results of smart rural construction on industrial structure upgrading, and the estimated coefficient of smart rural construction is 1.476 and significant, which indicates that smart rural construction can promote the upgrading of industrial structure. The coefficient of industrial structure upgrading in column (2) is significantly positive, indicating that the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain increases when the degree of industrial structure upgrading increases. Therefore, smart rural construction can promote regional agricultural products by promoting rural industrial structure upgrading. The coefficient of ICC in Column (2) is significantly positive, indicating that smart rural construction has a positive effect on the enhancement of the toughness of the agricultural products supply chain, thus indicating that there is a mediating effect of industrial structure upgrading in the impact of smart rural construction on the toughness of the agricultural products supply chain (Coopmans et al., 2021), and hypothesis H2 is valid.
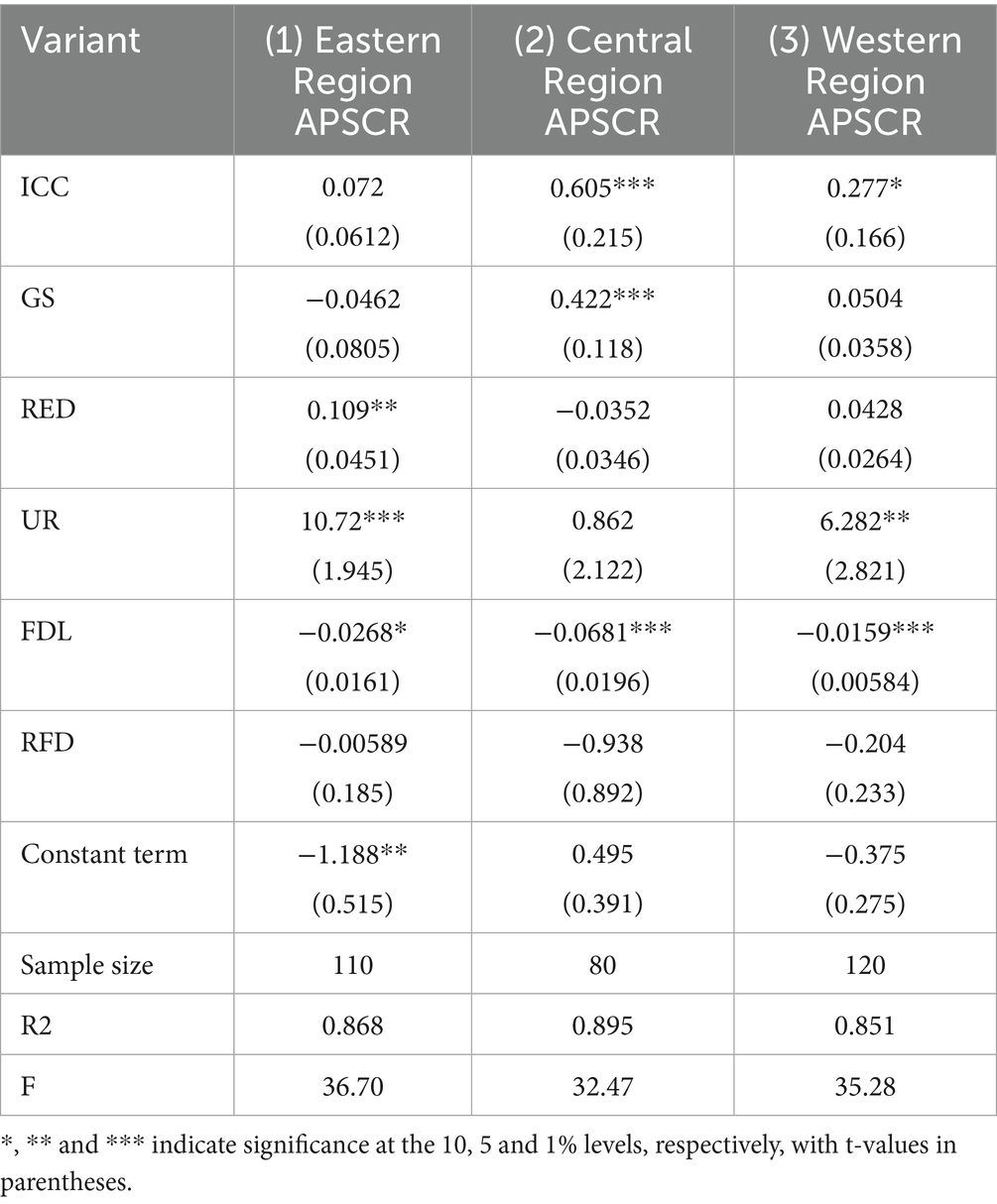
4.4 Heterogeneity test
Given the significant disparities in economic development, resource endowment, and smart infrastructure across China, this study investigates the regional heterogeneity of the impact of smart rural construction on APSCR. The regional division follows the standard classification officially adopted by the National Bureau of Statistics of China (NBSC). Specifically, Eastern region includes Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Liaoning, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Fujian, Shandong, Guangdong, and Hainan; the Central region comprises Shanxi, Jilin, Heilongjiang, Anhui, Jiangxi, Henan, Hubei, and Hunan; and the Western region consists of: Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Tibet, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang. Grouped regressions were conducted for the eastern, central, and western regions of China to further examine the regional heterogeneity in the impact of smart rural construction on agricultural product supply chain resilience. The estimation results are presented in Table 7. Columns (1) to (3) report the results for the eastern, central, and western regions, respectively. The findings indicate that the coefficients of smart rural construction on APSCR are 0.072, 0.605, and 0.277 in the eastern, central, and western regions, with the estimates for the central and western regions being statistically significant at the 10% level. This suggests that smart rural construction significantly enhances APSCR in the central and western regions. A comparison of the coefficient magnitudes reveals notable regional disparities in the effect of smart rural construction on APSCR. Specifically, the promoting effect is most substantial in the central region, followed by the western region, and weakest in the eastern region. This pattern of significant regional disparity leads us to conclude that Hypothesis H3 is supported. This pronounced regional heterogeneity can be attributed to differences in economic foundations, agricultural structures, policy environments, and their interplay with the developmental stages of smart rural initiatives across regions. The relatively weaker effect observed in the eastern region may be explained by the following factors: (1) Structural divergence in the agricultural economy: Agriculture constitutes a smaller share of the economy in the eastern region, with a greater emphasis on high-value-added sectors (e.g., urban agriculture and leisure agriculture). Enhancements in resilience in these sectors may rely more on non-smart precision management or specialized technologies, thereby reducing the marginal contribution of universal smart infrastructure. (2) Diminishing marginal returns on policy and technology investments: As an early adopter of smart agriculture, the eastern region has already capitalized on initial dividends. Further improvements necessitate addressing more complex system integration challenges, resulting in lower marginal returns from additional investments. (3) Transition to advanced smart application phases: The focus of smart transformation in the eastern region has shifted from “tool dissemination” to “value creation,” a process that inherently involves longer gestation periods for tangible outcomes.
In contrast, smart rural construction demonstrates a stronger empowering effect in the central and western regions due to the following reasons: (1) Precise alignment between resources and pain points: As major production bases for bulk agricultural products, the central and western regions face critical supply chain challenges—such as information asymmetry, logistical inefficiencies, and market access barriers—that can be effectively mitigated by inclusive smart technologies like e-commerce and the Internet of Things. (2) Targeted policy support and resource allocation: As prioritized regions under national strategies such as Rural Revitalization, these areas benefit from substantial central fiscal transfers and policy resources, ensuring robust implementation and extensive coverage of smart rural projects, which amplifies policy effectiveness. (3) Pronounced late-mover advantages and leverage effects: These regions can adopt mature technological solutions directly, avoiding trial-and-error costs. Moreover, their initially underdeveloped infrastructure allows new smart investments to yield significant leverage and “catch-up effects.” It is important to note that the central and western regions are also the main beneficiaries of national policies like the Western Development and Rural Revitalization strategies. While our robustness test in section 4.2.4 helps to mitigate this concern, we cannot fully rule out the possibility that some of the observed effect are amplified by these broader policy environments. Future research could employ more granular data or quasi-experimental designs to better disentangle the pure effect of smart rural construction from confounding regional policies.
4.5 Threshold effect analysis
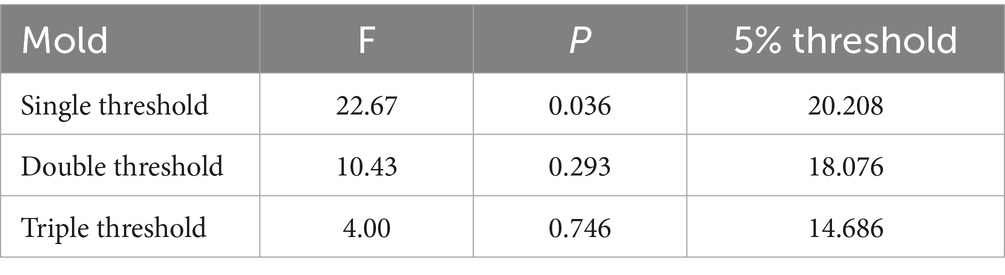
The level of financial development is selected as the threshold variable. After determining the existence of threshold effects in the model, the number of thresholds is tested. The results are shown in Table 8. The single threshold of smart rural construction passed the test of significance at the 5% level, and the corresponding self-sampling p-value was 0.036. The double threshold and triple threshold tests were not significant. Therefore, the single threshold model was analyzed.
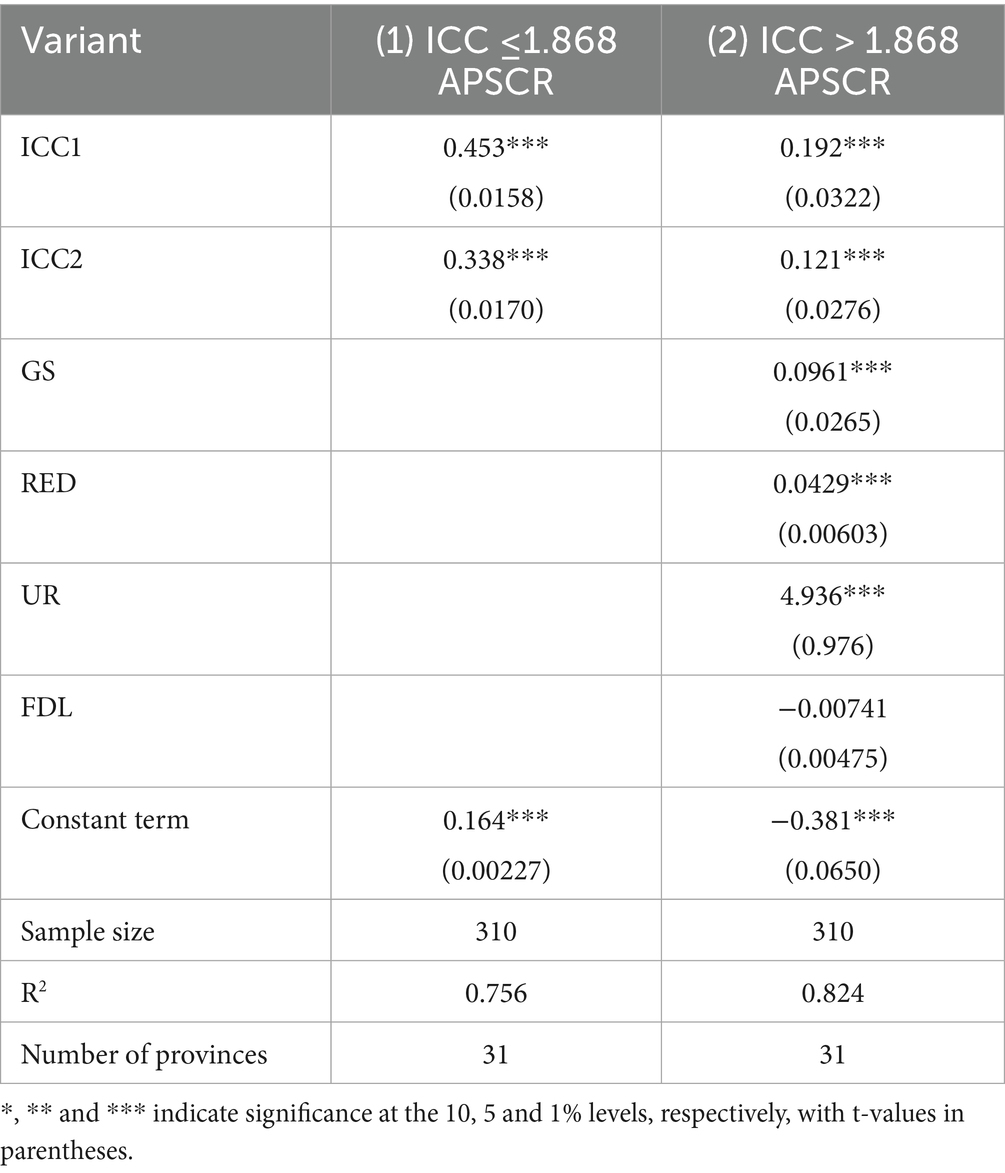
The estimate of the threshold parameter γ in a single threshold is 1.868, the confidence interval is [1.848, 1.884]. According to the single threshold value, China’s provinces are categorized into two types: provinces with a low level of smart countryside construction (ICC ≤ 1.868) and provinces with a high level of smart countryside construction (ICC > 1.868). As shown in Table 9, when ICC ≤ 1.868, the estimated coefficient of the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain is 0.453, which passes the 1% significance test; when ICC > 1.868, the estimated coefficient of the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of the agricultural products supply chain is 0.338 and is more significant. This non-linear relationship, where the effect diminishes after financial development reaches a certain high level, provides clear evidence to support Hypothesis H4. This finding reveals a nonlinear characteristic of the empowering effect of smart rural construction on supply chain resilience, consistent with the concept of diminishing marginal returns. We provide the following theoretical explanation for this pattern: In the initial construction phase, the proliferation of smart infrastructure and general-purpose technologies can rapidly break down information barriers and optimize resource allocation, yielding significant marginal gains. However, at higher development levels, further growth becomes increasingly dependent on building complex, agriculture-specific smart capabilities (e.g., precision agriculture, predictive analytics). Cultivating such capabilities requires more specialized knowledge, substantial complementary investments (e.g., in high-skilled talent, organizational process redesign), and might encounter coordination bottlenecks (e.g., data standards, benefit sharing), resulting in higher marginal costs and slower realization of benefits, thus leading to a slowdown in the rate of marginal return (Hrustek, 2020; Stone and Rahimifard, 2018). Furthermore, the results using the level of financial development (FDL) as the threshold variable indicate that the financial system plays a critical moderating role in the aforementioned relationship. In the high FDL regime, well-developed credit and insurance markets can effectively alleviate the financing constraints faced by agricultural entities and provide a buffer against the risks associated with adopting smart technologies, thereby “activating” and amplifying the empowering effect of smart rural construction (Wensheng, 2020). Conversely, under low financial development, even where smart infrastructure exists, capital shortage and risk aversion significantly constrain the depth and breadth of practical technology adoption by entities. This prevents the investments in smart rural construction from being fully translated into resilience enhancement, attenuating the observed effect. Therefore, financial development acts as a vital complementary asset for smart rural construction to exert its empowering effect, and its level determines the strength of this effect.
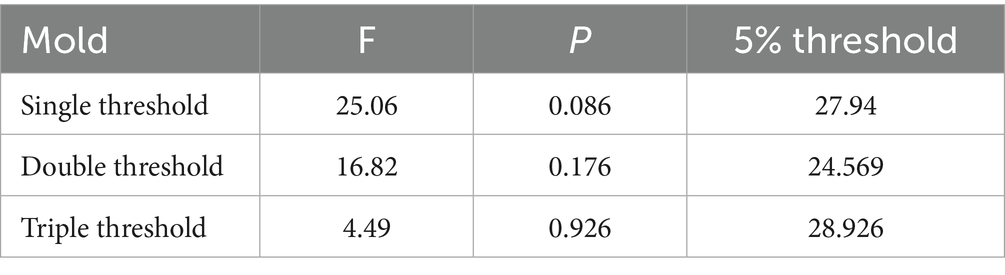
To enhance the practical relevance of our findings, we further employ the rural-specific financial indicator (RFD - Agricultural Insurance Depth) as a new threshold variable. The threshold effect test results for RFD are presented in Table 10. A single threshold is identified and is statistically significant at the 5% level (F = 25.06, p = 0.096).
The estimate of the threshold parameter γ for RFD is 0.839, with a confidence interval of [0.796, 0.852]. This threshold value meaningfully categorizes provinces into those with a lower level of rural financial development (RFD ≤ 0.839) and those with a higher level (RFD > 0.839). As shown in Table 11, when rural financial development is below the threshold (RFD ≤ 0.839), the estimated coefficient of smart rural construction on APSCR is 0.488 and significant at the 1% level. When rural financial development exceeds the threshold (RFD > 0.839), the empowering effect becomes even stronger, with a coefficient of 0.322 (significant at the 1% level). This result reveals a more nuanced story than the one using the macro FDL indicator: The positive and significant coefficient in the low RFD regime confirms that financial development is indeed a constraint. In regions where the agricultural financial safety net is weak, smart rural construction still has a positive effect, but it is somewhat limited. Crucially, when rural financial development (proxied by insurance depth) reaches a certain threshold, it does not exhibit diminishing returns but instead becomes a powerful enabler. A robust rural financial system amplifies the positive impact of smart rural construction. This is likely because better risk mitigation through insurance encourages greater adoption of smart technologies and investments in smart agriculture, leading to a multiplicative effect on supply chain resilience. Therefore, we conclude that the development of rural-specific financial instruments is not merely a complementary factor but a critical amplifier that unlocks the full potential of smart rural initiatives in enhancing agricultural supply chain resilience.
4.6 Sensitivity analysis
To further assess the robustness of our Agricultural Products Supply Chain Resilience (APSCR) index and identify which underlying indicators exert the most substantial influence on the composite measure, we conducted a sensitivity analysis. This analysis helps to determine how variations in individual input indicators affect the overall APSCR score, thereby providing insights into the relative importance and stability of each component within our multidimensional index framework. We employed a standardized linear regression approach, normalizing the values of each indicator and then regressing the APSCR index against these normalized inputs to derive sensitivity coefficients.
4.6.1 Sensitivity analysis of agricultural products cargo turnover
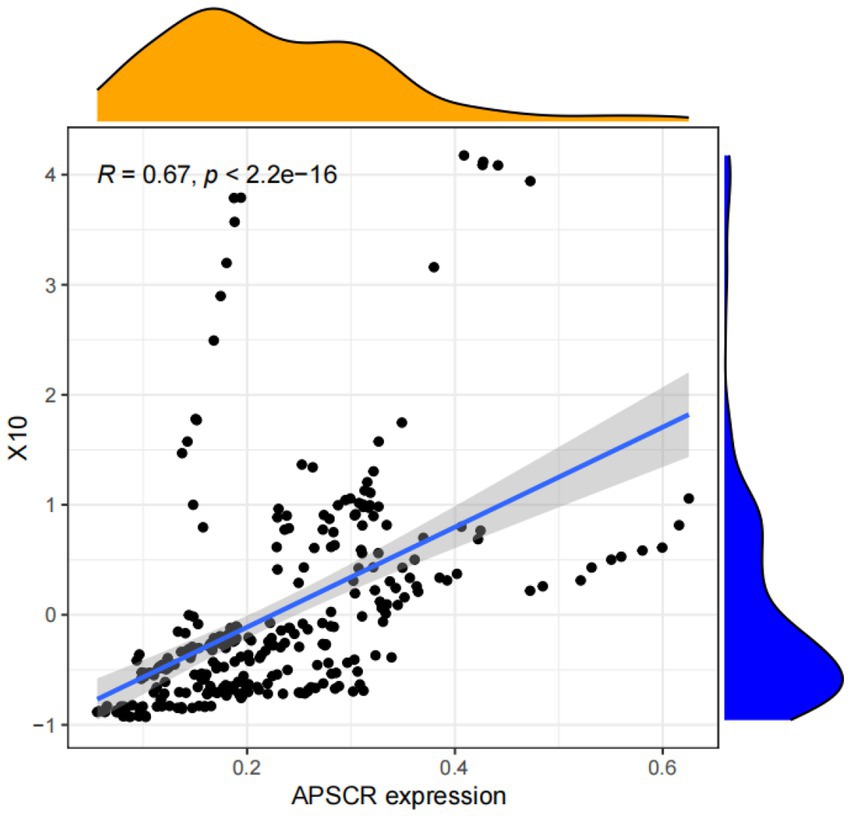
We selected Agricultural Products Cargo Turnover (X10) for sensitivity analysis due to its critical role in capturing the logistical efficiency and fluidity of the agricultural supply chain. This indicator, adjusted by the food consumption rate to isolate agricultural product movement, reflects the volume-distance of goods transported and is a direct measure of the supply chain’s operational throughput and connectivity. Efficient cargo turnover is essential for maintaining supply chain continuity, reducing time lags, and mitigating disruptions caused by logistical bottlenecks.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the scatter plot displays a clear positive linear relationship between the normalized values of Agricultural Products Cargo Turnover (X10) and the APSCR index. The sensitivity coefficient, derived from the linear regression slope, is positive and statistically significant, indicating that enhancements in logistical efficiency—proxied by cargo turnover—contribute substantially to overall supply chain resilience. This finding underscores the importance of investing in and optimizing transportation infrastructure and logistics management as a key strategy to bolster the resilience of agricultural supply chains, particularly in mitigating risks associated with delays and distribution inefficiencies.
4.6.2 Sensitivity analysis of agricultural products disaster rate
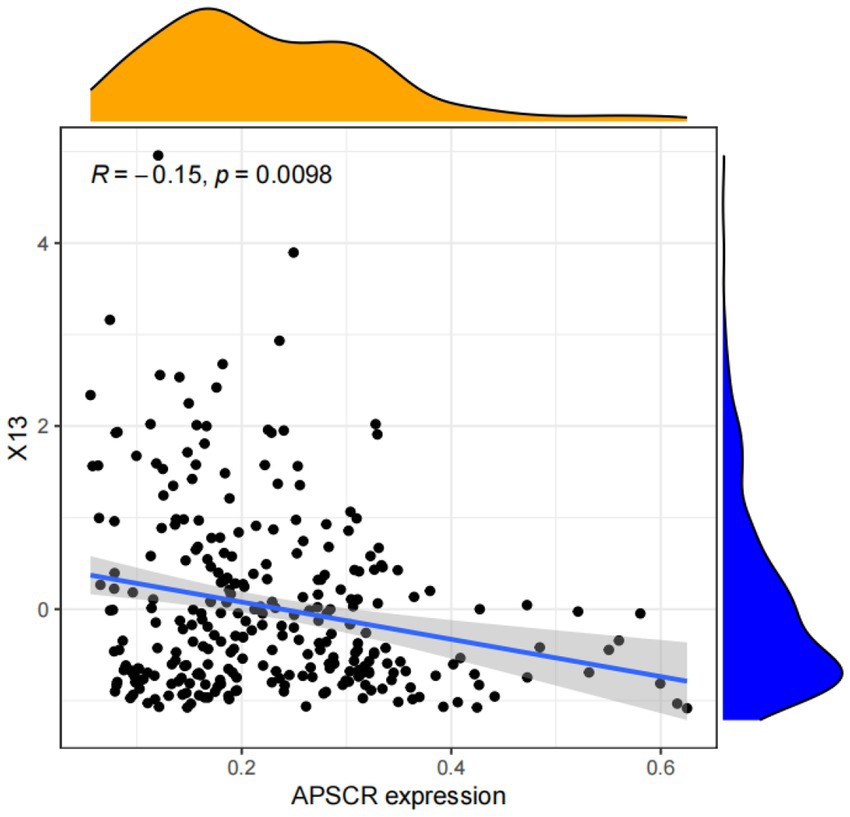
The Agricultural Products Disaster Rate (X13) was chosen for sensitivity analysis because it directly measures the vulnerability of agricultural production to natural shocks and adverse events. This indicator, calculated as the ratio of affected crop area to total sown area, serves as a critical inverse proxy for the buffering capacity and pre-disaster resistance of the supply chain. A high disaster rate signifies heightened exposure to environmental risks, which can severely compromise production stability and supply chain continuity.
Figure 4 presents the scatter plot of the normalized Agricultural Products Disaster Rate (X13) against the APSCR index. The regression analysis reveals a significant negative sensitivity coefficient, confirming that an increase in the disaster rate corresponds to a decrease in overall supply chain resilience. This strong inverse relationship highlights the detrimental impact of production vulnerabilities on the system’s ability to withstand and recover from disruptions. It emphasizes the necessity of integrating robust risk management strategies—such as improved irrigation, disaster forecasting systems, and climate-resilient agricultural practices—to enhance the defensive capacity of the supply chain against environmental uncertainties.
Together, these sensitivity analyses validate the construction of the APSCR index by demonstrating that its composite score is meaningfully and intuitively responsive to changes in both enabling (e.g., logistics efficiency) and constraining (e.g., disaster exposure) factors. The results reinforce the importance of addressing both operational efficiencies and environmental risks in policies aimed at enhancing the resilience of agricultural product supply chains.
5 Discussion
5.1 Primary causal link
Our findings underscore that the effectiveness of smart rural construction in enhancing agricultural supply chain resilience is highly context-dependent, influenced by regional economic structures, product types, and local policy emphases. For example, western provinces with extensive farming systems may benefit most from smart logistics and disaster early-warning systems, whereas eastern regions with high-value products might prioritize smart traceability and e-commerce integration. Future policy-making should therefore adopt a differentiated approach, aligning smart technologies with local agricultural profiles and resilience needs. This study empirically analyzes the direct impact of smart rural construction on agricultural supply chain resilience through a two-way fixed effects model and a panel threshold model. The results show that smart rural construction significantly enhances agricultural supply chain resilience (the coefficient is 0.175, significant at a 1% level). This causal relationship is mainly reflected in the following aspects: breaking down of information barriers: smart rural construction reduces information asymmetry in the supply chain through smart technology (e.g., e-commerce platforms, Internet of Things, etc.) and improves the efficiency of information transfer, thus enhancing the transparency and coordination of the supply chain. Improvement of infrastructure: Improvement of smart infrastructure (e.g., logistics network and Internet coverage) reduces the cost of agricultural product circulation and improves the supply chain’s risk-resistant ability to cope with emergencies. Optimized allocation of re-sources: the construction of smart rural promotes the efficient flow of production factors, optimizes the allocation of resources in agricultural production and circulation, and thus enhances the overall resilience of the supply chain. Our findings robustly demonstrate a significant positive direct impact of smart rural construction on agricultural supply chain resilience (ASCR). This aligns with and extends the growing body of literature that underscores the role of digitalization in enhancing agri-food system robustness. For instance, Belhadi et al. (2024) conceptually argued that smart capabilities are fundamental to building resilience against compounding disruptions, particularly in agri-food systems. Our empirical results from the Chinese context provide strong quantitative support for their theoretical proposition, moving from conceptual framing to measurable evidence. Furthermore, our results resonate with the findings of Guo et al. (2024), who identified a positive impact of agricultural digitization on economic resilience. However, our study diverges by focusing specifically on multi-dimensional supply chain resilience rather than broader economic resilience, thereby offering a more granular understanding of the mechanisms within the agricultural product flow. The positive impact we observe can be primarily attributed to three mechanisms derived from our analysis: the breaking down of information barriers, the improvement of infrastructure, and the optimized allocation of resources. This multi-pathway explanation addresses the call by Stone and Rahimifard (2018) for a more nuanced understanding of how resilience is built in agri-food supply chains, moving beyond a monolithic view.
5.2 Mechanical effect
The study further examined the role path of smart rural construction affecting the resilience of the agricultural supply chain through the mediation effect model and found that industrial structure upgrading is an important mediating variable. The results of the mediated effect test show that smart rural construction indirectly improves the resilience of the agricultural supply chain by promoting industrial structure upgrading (the mediated effect coefficient is 0.0142, which is significant at the 5% level), which verifies hypothesis H2. The specific mechanisms can be elucidated by integrating insights from recent literature on the broader impacts of smartization: First, the foundational element of smart rural construction is the deployment of smart infrastructure, such as broadband internet. Evidence from the “Broadband China” policy (a key component of smart rural initiatives) shows that while its primary aim was to reduce the urban–rural smart divide, its effect on income inequality is nuanced (He et al., 2025). Crucially, this infrastructure “bridges” information gaps for rural entrepreneurs and enterprises, providing them with unprecedented access to market information, online marketplaces, and knowledge resources. This access is a critical prerequisite for industrial upgrading. It enables rural producers to move beyond traditional cultivation by facilitating engagement in e-commerce, brand building, and the development of value-added products (e.g., processed foods, organic goods), thereby driving the vertical upgrading of the local industrial structure from primary towards secondary and tertiary sectors. Second, smart rural construction fosters the development of Smart Inclusive Finance (DIF), which directly alleviates a critical constraint on industrial upgrading: capital. The study by Li et al. (2025) demonstrates that DIF impacts agricultural outcomes by altering production and investment behaviors. Improved access to credit through mobile platforms and fintech solutions allows farmers and agricultural cooperatives to invest in productivity-enhancing technologies (e.g., advanced machinery, smart irrigation systems, green technologies) that they were previously unable to afford. This investment not only has environmental implications but also fundamentally changes the mode of production. It enables capital-for-labor substitution and a shift towards more efficient, scale-oriented, and technology-intensive operations. This transition is the essence of industrial structure upgrading within the agricultural sector itself, enhancing its competitiveness and reducing its vulnerability to disruptions. In summary, smart rural construction drives industrial structure upgrading through two intertwined channels: (1) by providing the informational bridge (via infrastructure like broadband) that enables market participation and value chain extension, and (2) by providing the financial tools (via smart inclusive finance) that enable investment in technological modernization and efficient production practices. This upgraded industrial structure, characterized by higher value-added activities and more efficient operations, subsequently enhances the overall resilience of the agricultural supply chain.
5.3 Policy recommendations
Based on the mechanisms, heterogeneity, and threshold effects identified in this study, we propose the following region-specific and technology-focused policy recommendations to deepen the application of smart technologies in smart rural construction and enhance the agricultural supply chain resilience:(1) The significant regional heterogeneity observed in our findings indicates that a “one-size-fits-all” policy approach is inefficient. In the eastern region, policies should move beyond universal smart infrastructure coverage and instead focus on supporting advanced, industry-integrated smart innovations—such as AI-driven decision-making and blockchain-based traceability—to overcome diminishing returns. In contrast, policy priorities in the central and western regions should continue to emphasize expanding smart infrastructure coverage and reducing the cost of technology adoption to unlock their significant “catch-up dividends” and “leverage effects.”(2) The threshold effect suggests that financial development acts as a critical “complementary asset” and “enabler” for the effectiveness of smart rural initiatives. Policymaking must therefore synergize smart infrastructure investment with the development of the rural financial system. In regions with lower levels of financial development, priority should be given to promoting inclusive finance and agricultural insurance to alleviate financing constraints and mitigate smart transformation risks for farmers and agribusinesses, thereby removing barriers to the effective implementation of smart rural projects.(3) While smart rural construction enhances resilience by promoting industrial structure upgrading, this process may also lead to agricultural labor reallocation and potential technological unemployment—particularly among low-skilled workers. Policies must be forward-looking and incorporate smart skills training, occupational transition support, and social safety nets as essential components of smart rural initiatives. This will ensure an inclusive transition process and prevent the exacerbation of social inequality. (4) As smart rural construction advances, data silos and coordination bottlenecks are likely to emerge as major constraints. Governments should take a leading role in establishing standards and protocols for agricultural data sharing and interoperability to facilitate data flow and operational collaboration among supply chain actors. This will fully unlock the potential of smart rural development at more advanced stages.
5.4 Limitations and future research directions
Although this study empirically examines the impact and pathways of smart rural construction on agricultural supply chain resilience, several limitations inherent to the research design and data availability should be acknowledged. These limitations, however, pave the way for fruitful future research:(1) Measurement of Smart Infrastructure and Literacy: Our study, like many in this field, measures smart infrastructure using proxy indicators like network coverage and logistics investment. However, this approach fails to capture critical qualitative aspects such as network stability, broadband speed, and the affordability of data plans—factors that ultimately determine the usability and impact of smart tools. Similarly, while we innovatively incorporated “farmers’ smart literacy,” it was measured by the number of technical personnel, which does not directly assess farmers’ actual skills in using smartphones, e-commerce platforms, or agricultural apps. Future research should prioritize developing more nuanced metrics, perhaps through large-scale farmer surveys, to directly gauge usage frequency, competency levels, and the perceived usefulness of smart technologies. This will provide a more accurate understanding of the human capital constraints on smart transformation. (2) Potential Data and Omitted Variable Biases: Our reliance on provincial-level panel data, while necessary for macro-analysis, masks significant intra-provincial heterogeneity. The benefits of smart rural construction likely vary greatly between rich and poor counties within the same province, leading to aggregation bias. Furthermore, despite our efforts to include a comprehensive set of control variables, unobserved factors such as local governance quality, the social capital of rural communities, and the presence of pioneering smart entrepreneurs could confound our results. Future studies should employ more granular (county- or rural-level) data and adopt quasi-experimental designs, such as difference-in-differences (DID) models leveraging the phased rollout of smart rural pilot policies, to better establish causality and uncover micro-level mechanisms. (3) Evolving Nature of Smart Technology: This study treats smart rural construction as a relatively static investment. However, technologies like generative AI, blockchain, and autonomous drones are rapidly evolving and their integration into agriculture is still in its infancy. Our findings capture the first-order effects of foundational smartization but may not predict the second-order transformative effects of these next-generation technologies. Therefore, we strongly encourage longitudinal case studies and continuous monitoring to explore how emerging technologies disrupt traditional supply chain models and create new pathways for building resilience. This study proposes several promising research directions aimed at prioritizing the resilience of agricultural supply chains while systematically aligning them with the development of a green economy. Specifically, future research should focus on digital-environment synergies, exploring how smart technologies can simultaneously enhance supply chain resilience and promote green practices—such as optimizing logistics to reduce carbon emissions, adopting precision agriculture to minimize chemical inputs, or leveraging blockchain for sustainable traceability. Concurrently, behavioral and skills-based research should be advanced, utilizing primary survey data and structural equation modeling to examine how farmers’ digital literacy and behavioral adoption patterns influence the effectiveness of intelligent supply chain interventions. Furthermore, attention must be paid to resilience under compound shocks, investigating the performance of digitally enhanced supply chains in concurrent disruptions such as climate events and market breakdowns, and whether green resilience strategies yield synergistic benefits. Lastly, research on policy integration is critical, particularly in developing regions, to assess comprehensive policy designs that incorporate digitalization, resilience, and sustainability objectives within agri-food systems, thereby bridging theoretical insights and practical innovation.
6 Conclusion
This study empirically analyzes the mechanism of the impact of smart rural construction on the resilience of agricultural supply chain based on panel data from 31 provinces in China from 2013 to 2022 through a two-way fixed effects model and panel threshold model. The main conclusions of this study directly support and fulfill the proposed marginal contributions: First, the baseline regression and a series of robustness tests confirm a significant direct enhancing effect of smart rural construction on APSCR, filling the theoretical and empirical gap of incorporating smart rural construction into the APSCR research framework. Second, the mediation effect analysis reveals that industrial structure upgrading is a key pathway, and the innovative inclusion of “farmers’ smart literacy” in the evaluation index system provides a more scientific measurement tool to accurately capture its multidimensional nature, addressing a deficiency in existing index system construction. Finally, the heterogeneity test and threshold effect analysis reveal that the empowering effect varies by region and financial development level, providing new evidence from Chinese provincial panel data for understanding its nonlinear impact mechanisms and emphasizing that policy intervention must consider regional development stages and complementary asset conditions. This study underscores smart rural construction as a catalyst for agricultural supply chain resilience, mediated by industrial upgrading and moderated by regional disparities. Policymakers should leverage smart technologies to build adaptive, efficient, and sustainable agricultural systems, ensuring food security in an era of global uncertainties.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HW: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HR: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Humanities and Social Science Research Project of Ministry of Education of China (Grant no. 22YJA790057), Sponsor (HW) and 2024 Qingdao Social Science Planning Project (Grant no. QDSKL2401186), Sponsor (HW).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the editors and reviewers for their hard work in the course of this research work.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adamowicz, M., and Zwolińska-Ligaj, M. (2020). The “smart rural” as a way to achieve sustainable development in rural areas of Poland. Sustainability 12:503. doi: 10.3390/su12166503
Alam, G. M. M., Khatun, M. N., Sarker, M. N. I., Joshi, N. P., and Bhandari, H. (2023). Promoting Agri-food systems resilience through ICT in developing countries amid COVID-19. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6:972667. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.972667
Ali, I., Golgeci, I., and Arslan, A. (2021). Achieving resilience through knowledge management practices and risk management culture in Agri-food supply chains. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 28, 284–299. doi: 10.1108/scm-02-2021-0059
Behzadi, G., O’Sullivan, M. J., Olsen, T. L., and Zhang, A. (2018). Agribusiness supply chain risk management: a review of quantitative decision models. Omega 79, 21–42. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2017.07.005
Belhadi, A., Kamble, S., Subramanian, N., Singh, R. K., and Venkatesh, M. (2024). Smart capabilities to manage Agri-food supply chain uncertainties and build supply chain resilience during compounding geopolitical disruptions. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 44, 1914–1950. doi: 10.1108/ijopm-11-2022-0737
Cai, Z., Li, S., and Cheng, D. (2023). Has smart rural construction improved rural family resilience in China? Evidence based on China household finance survey. Sustainability 15:704. doi: 10.3390/su15118704
Cen, T., Lin, S., and Wu, Q. (2022). How does smart economy affect rural revitalization? The mediating effect of industrial upgrading. Sustainability 14::987. doi: 10.3390/su142416987
Chang, J., and Jiang, H. (2023). Spatio-temporal differentiations and influence factors in China’s grain supply chain resilience. Sustainability 15:8074. doi: 10.3390/su15108074
Chen, T., Li, W., and Zhang, L. (2024). Influencing factors and realization paths for smart community construction in China. PLoS One 19:303687. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303687
Chen, W., Wang, Q., and Zhou, H. (2022). Smart rural construction and farmers’ income growth: theoretical mechanism and Micro experience based on data from China. Sustainability 14:679. doi: 10.3390/su141811679
Christopher, H. P. (2004). Building the resilient supply chain. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2, 1–13. doi: 10.1108/09574090410700275
Coluccia, B., Agnusdei, G. P., Miglietta, P. P., and De Leo, F. (2021). Effects of COVID-19 on the Italian Agri-food supply and value chains. Food Control 123:107839. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107839
Coopmans, I., Bijttebier, J., Marchand, F., Mathijs, E., Messely, L., Rogge, E., et al. (2021). COVID-19 impacts on Flemish food supply chains and lessons for Agri-food system resilience. Agric. Syst. 190:103136. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2021.103136
Fernández, C., and Peek, D. (2023). Connecting the smart rural: a switch towards smart and sustainable rural-urban linkages in Spain. Land 12:822. doi: 10.3390/land12040822
Gong, D., and Shan, X. (2023). How does smart city construction affect urban–rural collaborative development? A quasi-natural experiment from Chinese cities. Land 12:1571. doi: 10.3390/land12081571
Guo, N., Lyu, T., and Zong, H. (2024). Impact of agricultural digitization on agricultural economic resilience. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 22:607. doi: 10.12357/cjea.20240607
He, B., Nan, G., Xu, D., and Sun, J. (2025). Bridging or widening? The impact of the broadband China policy on urban-rural income inequality. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 12, 1–11. doi: 10.1057/s41599-025-04875-z
Hobbs, J. (2021). Food supply chain resilience and the COVID-19 pandemic: what have we learned? Can. J. Agric. Econ. 69, 189–196. doi: 10.1111/cjag.12279
Hrustek, L. (2020). Sustainability driven by agriculture through smart transformation. Sustainability 12:596. doi: 10.3390/su12208596
Li, C., Chen, G., Zhang, X., Li, Y., Ding, W., Yu, X., et al. (2025). The impact of smart inclusive finance on agricultural carbon emissions: evidence from China. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 34::165. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/187165
Li, X., Singh Chandel, R. B., and Xia, X. (2022). Analysis on regional differences and spatial convergence of smart rural development level: theory and evidence from China. Agriculture 12:164. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12020164
Liu, Y., Zhang, H., Ning, M., and Wang, L. (2024). Has smart rural construction narrowed the urban–rural income gap: evidence from Chinese counties. Sustainability 16:330. doi: 10.3390/su16135330
Mei, Y., Miao, J., and Lu, Y. (2022). Smart rurals construction accelerates high-quality economic development in rural China through promoting smart entrepreneurship. Sustainability 14:4224. doi: 10.3390/su142114224
Meuwissen, M., Feindt, P., Spiegel, A., Meuwissen, M. P. M., Feindt, P. H., Termeer, C. J. A. M., et al. (2019). A framework to assess the resilience of farming systems. Agric. Syst. 176:102656. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2019.102656
Park, C., and Cha, J. (2019). A trend on smart rural and implementation of smart rural platform. Int. J. Adv. Smart Convergence 8, 177–183. doi: 10.7236/IJASC.2019.8.3.177
Qin, J. Z., and Wang, W. (2022). Mediating effect of smart economy on industrial structure upgrading and empirical evidence. Statist. Decis. 38, 99–103. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2022.11.020
Singh, N., Kumar, A., and Dey, K. (2023). Unlocking the potential of knowledge economy for rural resilience: the role of smart platforms. J. Rural. Stud. 104:103164. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2023.103164
Sobczak-Malitka, W., and Drejerska, N. (2024). Integrating short supply chains and smart rural initiatives: strategies for sustainable rural development. Sustainability 16:529. doi: 10.3390/su162310529
Stone, J., and Rahimifard, S. (2018). Resilience in Agri-food supply chains: a critical analysis of the literature and synthesis of a novel framework. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 23, 207–238. doi: 10.1108/scm-06-2017-0201
Wang, P., Li, C., and Huang, C. (2023). The impact of smart rural construction on county-level economic growth and its driving mechanisms: evidence from China. Agriculture 13:1917. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13101917
Wang, Q., Luo, S., Zhang, J., and Furuya, K. (2022). Increased attention to smart development in rural areas: a scientometric analysis of smart rural research. Land 11:362. doi: 10.3390/land11081362
Wang, L., Qi, C., Tang, L., and Xiang, S. (2023). Evaluation and Spatio-temporal analysis of agricultural products circulation efficiency in the context of unified domestic market: from the “three dimensional” perspective of modern circulation theory. Issues Agric. Econ. 8, 127–143. doi: 10.13246/j.cnki.iae.2023.08.005
Wensheng, D. (2020). Rural financial information service platform under smart financial environment. IEEE Access 8, 199944–199952. doi: 10.1109/access.2020.3033279
Yang, J., and Sun, J. (2024). Research on the impact of smart economy on agricultural green total factor productivity. Dongyue Tribune 45, 139–148. doi: 10.15981/j.cnki.dongyueluncong.2024.11.016
Yao, S. C., and Chen, K. (2024). Can the development of the smart economy improve ecological environment quality? Finance Economy. 10, 77–88. doi: 10.19622/j.cnki.cn36-1005/f.2024.10.007
Yuan, M., Hu, H., Xue, M., and Li, J. (2024). Framework for resilience strategies in agricultural supply chain: assessment in the era of climate change. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 8:1444910. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2024.1444910
Zeng, Y., Sun, W., Li, L., and Fu, C. (2022). A new coordinate of smart divide: the impact of smart city construction on urban-rural income gap 22, 165–184. doi: 10.1080/14765284.2022.2059055
Zhang, X. (2024). The evolution mechanism, development challenges, and coping strategies of China's agricultural product supply chain. Foods 5, 118–128. doi: 10.16158/j.cnki.51-1312/f.2024.05.010
Zhang, D., Jiang, D., and He, B. (2025). Empowering agricultural economic resilience with smart supply chain: theoretical mechanism and action path. Sustainability 17:2930. doi: 10.3390/su17072930
Zhang, J., Yang, Z., and He, B. (2023a). Does smart infrastructure improve urban economic resilience? Evidence from the Yangtze River Economic Belt in China. Sustainability 15:4289. doi: 10.3390/su151914289
Zhang, J., Yang, Z., and He, B. (2024). Empowerment of smart technology for the resilience of the logistics industry: mechanisms and paths. Systems 12:278. doi: 10.3390/systems12080278
Zhang, X., and Zhang, Z. (2020). How do smart rurals become a way to achieve sustainable development in rural areas? Smart rural planning and practices in China. Sustainability 12:510. doi: 10.3390/su122410510
Zhang, S. G., Zhang, P., and Dong, X. (2023b). Intelligent logistics empowers supply chain resilience: theory and empirical evidence. China Soft Sci. 11, 54–65.
Zhao, W., Liang, Z., and Li, B. (2022). Realizing a rural sustainable development through a smart rural construction: experiences from China. Sustainability 14:4199. doi: 10.3390/su142114199
Keywords: smart rural construction, food security, agricultural products, supply chain resilience, threshold effect
Citation: Wang H, Zheng J and Ran H (2025) Can smart rural construction improve agricultural products supply chain resilience? Empirical evidence from 31 provinces in China. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1659012. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1659012
Edited by:
Afiya John, The University of the West Indies St. Augustine, Trinidad and TobagoCopyright © 2025 Wang, Zheng and Ran. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiaojiao Zheng, MjAyMzIxNTMwNTFAc3R1LnFhdS5lZHUuY24=
 Hongzhi Wang1
Hongzhi Wang1 Jiaojiao Zheng
Jiaojiao Zheng