- 1Department of Agronomy, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
- 2Department of Environmental Sciences, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
- 3International Rice Research Institute South Asia Regional Centre, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India
- 4Centre for Agricultural Nanotechnology, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
- 5Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
- 6Department of Soil Science and Agricultural Chemistry, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India
Agriculture faces significant challenges including climate change, resource inefficiency, environmental degradation, and necessitating sustainable solutions. Silica nanoparticles (SiNPs), with their unique physio-chemical properties, have emerged as a promising tool to enhance agricultural productivity while reducing ecological impact. This review article explores the potential of SiNPs to revolutionize modern farming by addressing critical inefficiencies in traditional methods. The overreliance on synthetic inputs has led to soil degradation, water contamination, and declining crop resilience. SiNPs offer an innovative alternative by improving nutrient delivery systems, enhancing stress tolerance, and reducing the environmental footprint of agricultural practices. SiNPs significantly enhance nutrient use efficiency (NUE) through controlled and sustained release mechanisms, minimizing losses and ensuring consistent crop uptake. Their application also bolsters plant resilience against abiotic stresses such as drought and salinity, as well as biotic threats from pests and pathogens. Mechanistically, SiNPs improve photosynthetic efficiency, regulate stress-responsive genes, and fortify plant cell walls, creating both biochemical and mechanical defenses. Moreover, SiNPs are biocompatible and environmentally safe, degrading into bioavailable monosilicic acid that enriches soil health and supports beneficial microbial communities. They mitigate heavy metal toxicity and reduce dependency on conventional agrochemicals, aligning with global sustainability goals. This assessment explores the functional properties, application and mechanism of SiNPs for management of biotic and abiotic stress controlling and paves the way for sustainable agriculture.
1 Introduction
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in ensuring global food security and economic stability, yet it faces mounting challenges from climate change, soil degradation, water scarcity, and the ever-increasing demand for higher yields (Selvan et al., 2021). Conventional agriculture, often characterized by the use of synthetic chemical inputs, currently produces 98.9% of the world's food. However, as global demands for food continue to grow alongside the need for sustainable practices, these methods face challenges in addressing long-term environmental and resource concerns (Willer and Lernoud, 2017). The overuse of fertilizers, pesticides, and other agrochemicals has led to environmental pollution, declining soil health, and reduced long-term agricultural productivity (Zhang et al., 2018). As the global population continues to rise, there is an urgent need for innovative solutions that can transform agricultural systems to become more resilient, efficient, and environmentally sustainable.
Silicon, a beneficial element for plants has gained attention for its critical role in improving crop resilience against both biotic and abiotic stresses (Coskun et al., 2019; Liang et al., 2007). It enhances plant structural integrity, optimizes nutrient uptake, and fortifies crops against pests, diseases, and environmental extremes such as drought and salinity (Adebisi et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2018). The silicon content in plants has been observed to range between 0.1% and 10%, influenced by various mechanisms of silicon uptake (Liang et al., 2007). Plants take up dissolved silicon primarily as monosilicic acid, and in certain plant species with a high ability to accumulate metalloids, specific silicon transporter genes such as LSi1, LSi2, and LSi6, have been identified as playing a role in its transport (Rao and Susmitha, 2017). Although silicon's potential has been extensively studied, the efficiency of its application in conventional forms is often limited by factors such as poor bioavailability and uneven distribution in soil (Schaller et al., 2022). This is where the integration of nanotechnology into agriculture presents a groundbreaking opportunity (Tubana et al., 2016). Nanotechnology, characterized by the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale, offers numerous advantages over traditional agricultural practices (Kuzma, 2007). Nanoparticles often display unique characteristics compared to their bulk counterparts due to their reduced size, increased surface area relative to their weight, and varied structural geometries (Roduner, 2006). Among the emerging innovations, SiNPs have demonstrated exceptional promise in revolutionizing farming systems (Fraceto et al., 2016; Saha et al., 2024). SiNPs, nanoscale particles of silicon dioxide, exhibit distinctive attributes such as nanoscale dimensions, nutritional benefits, surface characteristics, and porous structures, making them highly versatile in nano-enabled agriculture. These unique physicochemical properties enhance their reactivity and enable controlled release, allowing SiNPs to function effectively as plant growth stimulators, nanocarriers, and soil conditioners (Ji et al., 2018; Mahawar et al., 2023; Rastogi et al., 2019). Their applications extend to targeted nutrient delivery, stress mitigation, and sustainable pest management, underscoring their potential to improve agricultural efficiency and resilience (Adebisi et al., 2018; Goswami et al., 2022; Rai-Kalal et al., 2021; Tripathi et al., 2015).
The incorporation of SiNPs in agriculture aligns seamlessly with the principles of sustainable development, supporting Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) such as Goal 2 (Zero Hunger), Goal 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production), and Goal 13 (Climate Action). By enhancing nutrient efficiency, reducing environmental contamination, and mitigating plant stress, SiNPs promote resource conservation, climate resilience, and sustainable agricultural practices (Bhat et al., 2021; Yan et al., 2024). SiNPs can significantly reduce the dependence on excessive agrochemical inputs, thereby minimizing their environmental footprint. Their ability to improve NUE and bolster plant resilience contributes to conserving natural resources such as water and soil (Alsaeedi et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2025). Additionally, SiNPs can enhance plant growth under stress conditions, ensuring stable yields even in adverse environments (Kukarram et al., 2023; Raza et al., 2023). These benefits position SiNPs as a critical tool for addressing the pressing challenges of modern agriculture. This review aims to explore the advancements, applications, and potential of SiNPs in promoting sustainable agricultural practices. By analyzing their role in enhancing crop productivity, reducing environmental impacts, and addressing resource inefficiencies, this article underscores the transformative potential of SiNPs in shaping next-generation farming systems. The discussion seeks to bridge the gap between emerging nanotechnologies and practical agricultural applications, providing insights into how SiNPs can lead to a more sustainable and resilient agricultural future.
2 Properties of SiNPs relevant to agriculture
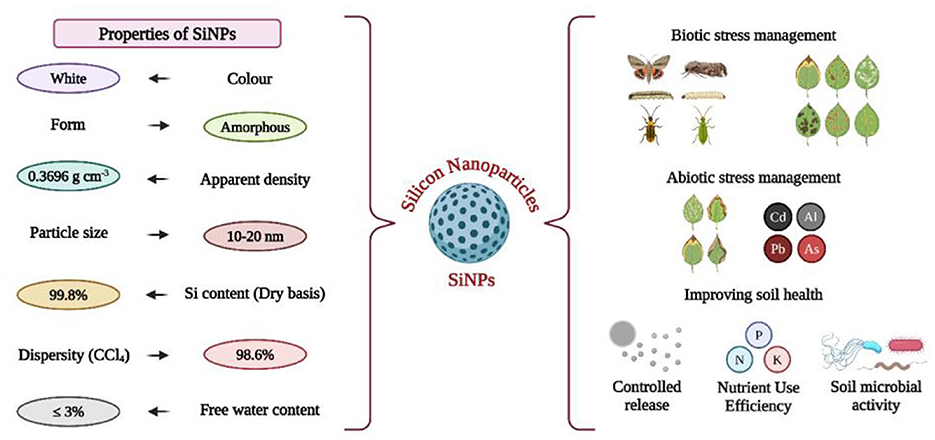
Application of SiNPs in agriculture is gaining increasing attention due to their unique properties that enhance efficiency and sustainability. These nanoparticles exhibit remarkable structural, chemical, and physical characteristics that enable innovative applications in crop management (Rastogi et al., 2017). SiNPs have been found to possess distinct physical and chemical properties compared to their bulk counterparts (O'Farrell et al., 2006). Recent research has demonstrated that SiNPs can directly interact with plants, influencing their morphology and physiology in several ways, such as enhancing the structural color of plants and promoting improved growth and yield (Siddiqui and Al-Whaibi, 2014; Strout et al., 2013; Suriyaprabha et al., 2014). However, some studies have also reported negative effects of SiNPs on plants (Le et al., 2014; Slomberg and Schoenfisch, 2012). SiNPs offer a wide array of applications due to their cost-effective large scale production, hydrophobicity, high surface area, substantial pore volume, and biocompatibility. Their exceptional adsorption capacity and non-toxic characteristics make them particularly useful for addressing various challenges in agriculture (Goswami et al., 2022). The biocompatibility and environmental safety of SiNPs make them an eco-friendly alternative to conventional agrochemicals. Functional properties such as controlled release, stability, and solubility further contribute to their utility in agriculture, allowing for precision delivery of nutrients and other agrochemicals (Yuvaraj et al., 2023). This section delves into the key properties of SiNPs that are relevant to agriculture, providing a detailed discussion of their structural, chemical, and physical attributes; their compatibility with biological systems; and their functional advantages in agricultural contexts.
2.1 Structural and physicochemical characteristics of SiNPs
SiNPs are engineered silicon particles at the nanoscale, typically ranging from 1 to 100 nm. Based on their structures, SiNPs are classified into various types including spherical, hollow, shaped (e.g., rod, cube), and porous forms (Mathur and Roy, 2020). Their nanoscale size provides a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, distinct charge properties, and improved plant bioavailability, offering significant advantages over bulk silicon sources (Yan et al., 2024). These features enhance their reactivity and enable efficient interactions with plants, soil, and agricultural systems. This high surface area also allows SiNPs to carry and deliver nutrients or agrochemicals more effectively. However, the shape, size, and other properties of SiNPs are reported to directly or indirectly affect plant responses to their application (Rastogi et al., 2019). Additionally, it has been observed that SiNPs applied to the soil are more effective than those applied to foliage (Suriyaprabha et al., 2014). Additionally, their porosity and tailor ability are key advantages; SiNPs can be engineered with specific pore sizes, volumes, and surface functionalities. Mesoporous SiNPs (MSiNPs) are highly versatile, offering tunable porosity that facilitates the encapsulation and controlled release of active compounds like fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring they cater to diverse agricultural needs (Adams et al., 2020). MSNPs exhibit considerable variation in their physical and chemical properties, but they are generally hydrophilic solid materials with a high surface area and numerous pores or channels (Gogos et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2016). The size, surface charge, and other chemical and physical characteristics of MSNPs make them ideal for immobilizing nutrients and harmful elements, as well as for carrying and releasing plant nutrients in a controlled manner. They also chemically stabilize nutrients to enhance their availability for plant uptake and facilitate the efficient transfer of nutrients into plant cells (Le et al., 2014; Luyckx et al., 2017; Naderi and Danesh-Shahraki, 2013).
Moreover, SiNPs have the ability to penetrate plant cells efficiently (Verma et al., 2021). These nanoparticles have demonstrated the potential to improve various plant functions, such as growth, photosynthesis, nutrient absorption, water use efficiency, and stress resilience in crops like rice, wheat, tomato, and lettuce (Verma et al., 2021; David et al., 2024). This stability ensures their efficacy in soils with varying pH levels and prevents the premature breakdown of encapsulated materials. Their thermal and mechanical stability further enhances their suitability for agriculture, as SiNPs can maintain structural integrity under extreme temperatures and mechanical stress (Ma et al., 2010; Tripathi et al., 2017). These combined properties make SiNPs robust and reliable tool for improving agricultural efficiency, even in challenging environments.
2.2 Biocompatibility and environmental safety
Integration of SiNPs into agricultural practices is underpinned by their biocompatibility and environmental sustainability, making them a viable alternative to conventional agrochemicals. Upon degradation, silica from all sources converts into monosilicic acid, a non-toxic compound that poses no significant ecological risks (Mahawar et al., 2023). These characteristic underscores the safety of using SiNPs in various agricultural applications to enhance crop yield and productivity. Agricultural and plant wastes serve as valuable precursors for synthesizing SiNPs. The use of such waste materials offers several advantages, including accessibility, cost-effectiveness, biodegradability, and reduced toxicity compared to chemically synthesized nanoparticles. Notably, rice husk has been extensively reported as a source for SiNPs production (Jansomboon et al., 2017). Similarly, sugarcane bagasse, a byproduct of the sugar manufacturing industry, is another commonly utilized waste material for SiNPs synthesis (Lu and Hsieh, 2012; Mohd et al., 2017). Nonetheless, some studies have highlighted the potential phytotoxic effects of SiNPs, which are influenced by factors such as particle size, surface area, concentration, pH, and plant species (Slomberg and Schoenfisch, 2012). For instance, concentrations between 540 and 1,820 mg/L caused phytotoxicity in Allium cepa, affecting germination and root elongation, with size ranges of 7, 12, and 22 nm (Slomberg and Schoenfisch, 2012). From a toxicological standpoint, the size and surface area of SiNPs are particularly significant. Smaller SiNPs, due to their larger surface area, exhibit higher reactivity and can penetrate cellular compartments more efficiently, potentially leading to greater toxicity compared to their larger counterparts. SiNPs exhibit minimal toxicity to plants when applied within appropriate concentration ranges, facilitating their uptake and translocation to plant tissues (Wei et al., 2010).
Foliar application allows NPs to enter through the cuticle or stomata, with stomatal pores (20–500 nm) serving as the primary pathway since most NPs exceed the maximum size (~5 nm) that can pass through the cuticle (Eichert et al., 2008; Yeats and Rose, 2013). In root applications, uptake predominantly occurs in immature regions such as root tips, root hairs, and lateral root junctions, where physical barriers like the Casparian strip and suberin lamella are less developed (Wang et al., 2012). This promotes enhanced stress tolerance against abiotic factors such as drought and salinity, as well as biotic stress from pathogens, ultimately improving crop productivity (De Sousa et al., 2019; Khan et al., 2022; Saw et al., 2023). Unlike some agrochemicals that disrupt soil microbial communities, SiNPs preserve the functionality of beneficial microorganisms essential for nutrient cycling and soil fertility (Rastogi et al., 2019). Furthermore, SiNPs degrade naturally into monosilicic acid, a bioavailable silicon form, thus preventing environmental accumulation and ensuring compatibility with plant and soil systems (Mahawar et al., 2023; Rao and Susmitha, 2017). Their application also reduces dependency on excessive fertilizers and pesticides by improving the efficacy of these inputs, thereby lowering the risks of nutrient leaching and contamination of soil and water resources. Collectively, the physicochemical properties and environmental degradability of SiNPs position them as a scientifically sound and sustainable strategy for advancing modern agriculture.
2.3 Functional properties: controlled release, stability, and solubility
The functional attributes of SiNPs, including controlled release, stability, and enhanced solubility, are integral to their efficacy in precision agriculture, contributing to optimized resource utilization and reduced environmental impact. One of the most significant advantages of SiNPs is their capacity for controlled release of encapsulated substances. By integrating agrochemicals such as fertilizers and pesticides within their porous architecture, SiNPs facilitate a sustained and gradual release of these compounds. This mechanism minimizes nutrient losses through leaching and volatilization, providing plants with a consistent supply of inputs over extended periods (Beig et al., 2022). The nitrogen-based fertilizers encapsulated in SiNPs have demonstrated a marked improvement in nitrogen use efficiency, significantly reducing the environmental footprint of agricultural practices (Alsaeedi et al., 2019; Mohanty et al., 2020; Rastogi et al., 2019). SiNPs also offer exceptional stability to bioactive compounds prone to degradation. Environmental factors such as UV radiation, temperature extremes, and microbial activity can compromise the efficacy of conventional agrochemicals (Quelé et al., 2024; Yang et al., 2018). Encapsulation within the SiNPs matrix safeguards these compounds, prolonging their functional lifespan and ensuring steady efficacy, thereby reducing the need for frequent reapplications. Moreover, SiNPs address challenges associated with the poor solubility of many agrochemicals, enhancing their bioavailability (Prado et al., 2011). The ability of SiNPs to increase the dissolution rate of micronutrients like zinc and iron ensures their efficient absorption by plants, effectively mitigating micronutrient deficiencies and promoting overall plant vigor (Arshad et al., 2021).
3 Applications of SiNPs in sustainable agriculture
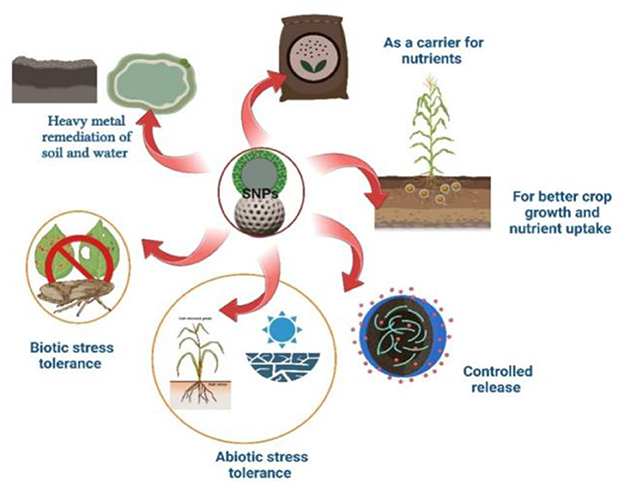
SiNPs are emerging as a promising tool in sustainable agriculture due to their unique physicochemical properties. They enhance crop resilience by improving stress tolerance, nutrient uptake, and disease resistance. SiNPs also play a crucial role in soil health by influencing microbial activity and nutrient availability. Their controlled release capabilities reduce fertilizer losses, promoting eco-friendly farming practices. The overall role of SiNPs in agriculture was illustrated in Figure 1 and Table 1.
3.1 Crop growth enhancement
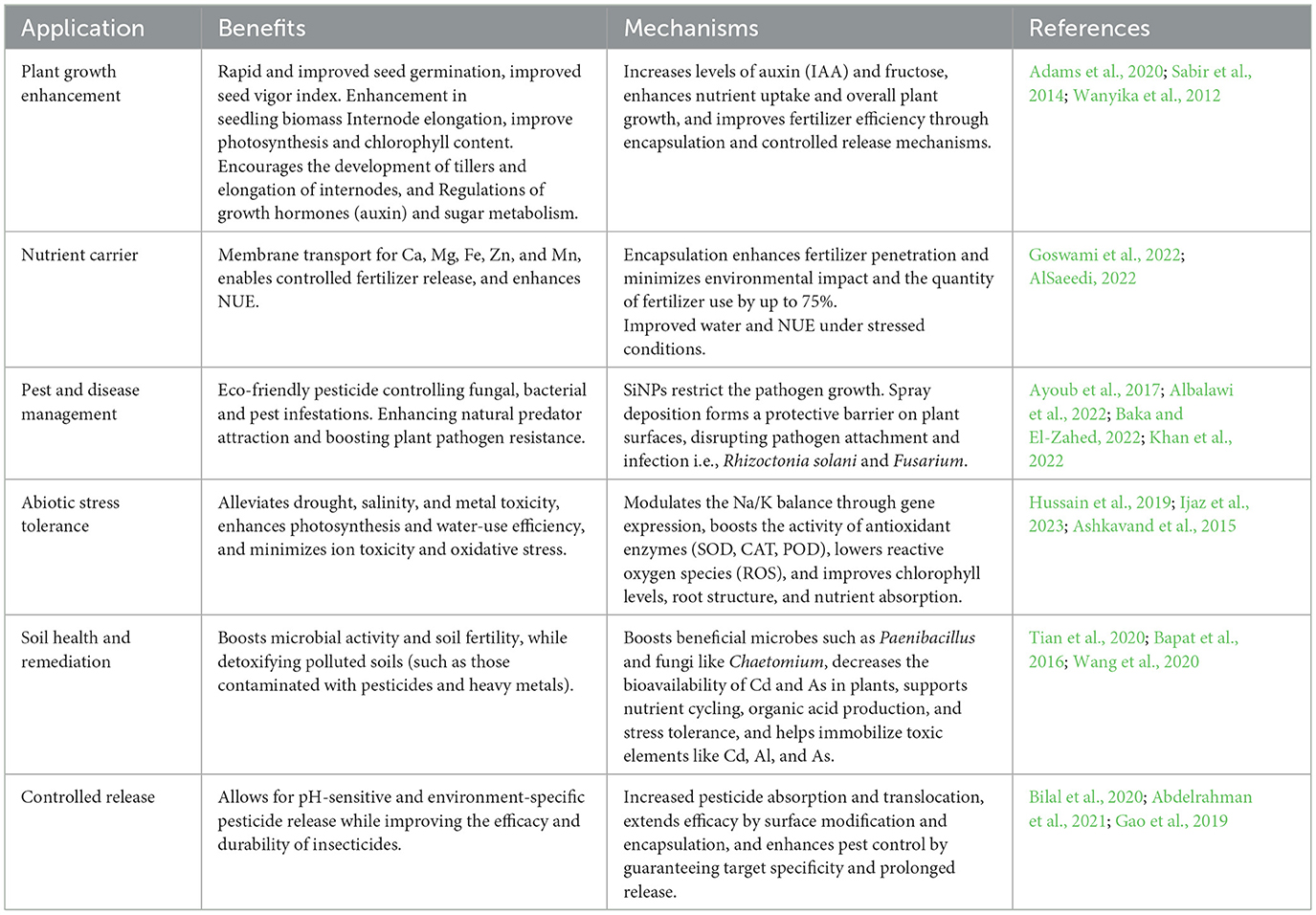
SiNPs increased tiller growth and internode elongation by 66.7% and 27.4%, respectively, resulting in increased biomass of wheat. Furthermore, SiNPs can boost net photosynthetic rate by increasing total chlorophyll content. It was hypothesized that SiNPs could influence leaf and stem growth by regulating plant hormone and soluble sugar metabolism. SiNPs can directly or indirectly promote wheat growth by increasing auxin (IAA) and fructose levels (Li et al., 2023). Researchers discovered that priming seeds of species such as Triticum aestivum and Pisum sativum with SiNPs improved seed germination and seedling growth parameters (Tripathi et al., 2017; Ali et al., 2019).
3.2 Carriers of plant nutrients
Rice husk, hull, and straw, as well as industrial residues like sugarcane bagasse, have all been identified as excellent silicon sources. Using nanocalcite, which contained 40% CaCO3, 4% nano SiO2, 1% MgO, and 1% Fe2O3, increased not only Ca, Mg, and Fe absorption but also P intake, as well as micronutrients Zn and Mn (Sabir et al., 2014). Mesoporous SiNPs, approximately 150 nm in diameter and with pores around 2.5 nm in size, were synthesized using liquid crystal templating, followed by urea incorporation within the mesopores via immersion in urea solutions. Urea loading was achieved at a concentration of 15.5% (w/w) through physisorption, with an overall adsorption capacity of up to 80% (w/w), which was increased by high-concentration urea solutions due to their steeper concentration gradients (Wanyika et al., 2012).
3.3 Improving water use efficiency (WUE) and NUE
Plant growth and development are heavily reliant on the use of fertilizers. The excessive use of fertilizers has a negative impact on the environment, including water contamination and soil deterioration. Silicon is an essential nutrient for cell growth and development, and a lack of it can lead to lower crop production and increased susceptibility to both biotic and abiotic stressors. To address this, researchers developed a fertilizer delivery system using mesoporous SiNPs, in which a thin layer of SiNPs was coated onto urea granules to enhance the controlled release of nutrients and improve crop resilience (Wanyika et al., 2012; Zargar et al., 2019; Surya et al., 2022).
The study found that urea treated with SiNPs had a slower release rate and lasted five folds longer than untreated urea. SiNPs have gained prominence as a potential delivery system for fertilizers owing to their minute size, extensive surface area, and capacity to penetrate plant cells (Goswami et al., 2022). Various approaches, including coating, encapsulation, and functionalization have been employed to develop SiNPs delivery systems for fertilizers. SiNPs delivery systems have been studied for their potential to improve fertilizer effectiveness. In safflower, Janmohammadi et al. (2016) found that combining the use of organic fertilizers with a foliar spray containing SiNPs had a significant positive effect on yields, and proposed it as a suitable agricultural practice. Generally, SiNPs additives have been demonstrated to boost the efficiency of fertilizer delivery to plants, leading to higher crop yields and decreased environmental effects. Mesoporous SiNPs improved fertilizer assimilation by boosting nutrient use effectiveness and facilitating a controlled nutrient discharge due to their high surface area and porosity. According to a study by Adams et al. (2020), the use of MSNPs resulted in enhanced zoysia grass establishment under low fertility conditions, utilizing 75% less fertilizer, while exhibiting a growth reduction of only 7.6% compared to high fertility conditions without nanoparticles. The delivery of essential nutrients like calcium, zinc, potassium, magnesium and manganese was more successful, resulting in improved growth rates. This implies that MSNPs facilitate turfgrass establishment at fertilizer levels significantly lower.
In cucumber, SiNPs application increased drought resilience through the promotion of plant development and enhancement of nutrient acquisition under conditions of water scarcity. In this study, AlSaeedi (2022) revealed that 100 ppm of nano silica led to a notable increase in chlorophyll content, a decrease in proline levels, and an improvement in nutrient status, particularly in iron and zinc. SiNPs increased water use efficiency (WUE) through improvements in soil water characteristics, including field capacity (FC), wilting point (WP), available water content (AW), and saturation moisture content (θs). The research showed that raising SiNPs rates substantially increased soluble Si4+ levels in the soil, resulting in enhanced properties and increased cucumber production. A 178% increase in WUE was most notable with the Si-NP400 treatment, which surpassed the control (Si-NP0). The Si-NP400 treatment also produced the best combined soil and yield outcomes (AlSaeedi, 2022).
3.4 Pest and disease management and its mechanisms
SiNPs are an environmentally benign pesticide that prevents diseases and insect pests from growing and becoming aggressive, shielding plants from bacterial, fungal, and pest attacks in agricultural production (Goswami et al., 2022). Regarding insect pests, Ayoub et al. (2017) discovered that SiNPs had exceptional pesticidal effects in leafworms (Spodoptera littoralis) in a surface contact and feeding experiment. These effects were also impacted by the size and surface properties of the particles. In the incubation tests, Albalawi et al. (2022) demonstrated that SiNPs significantly reduced the growth of Rhizoctonia solani and Alternaria solani. Furthermore, complex NPs of Si and Ag, or Si/AgNPs, showed exceptional fungicidal and bactericidal properties against many plant diseases, including Xanthomonas campestris, Rhizoctonia solani, and Botrytis cinerea (Baka and El-Zahed, 2022). Additionally, SiNPs and titanium nanoparticles (TiNPs) both suppressed the development of Phomopsis vexans and Ralstonia solanacearum, although SiNPs caused a more noticeable reduction in pathogen growth than TiNPs (Khan et al., 2022). Notably, SiNPs exhibit a specific advantage over conventional pesticides in that their physical effects determine their pesticidal effects, suggesting that diseases and insect pests are unlikely to evolve physiological resistance to SiNPs.
In protected maize, Wang et al. (2021) discovered that the application of SiNPs reduced damage caused by oriental armyworms (Mythimna separata), while simultaneously enhancing the metabolism of defense-related compounds such as total phenolics and chlorogenic acid. In a field test, SiNPs treatment reduced the population of three common pests in faba beans and soybeans by attracting pest predators. This could be because they regulate the metabolism of volatile chemicals (Thabet et al., 2021). Maize treated with nanosilica showed increased resistance to Fusarium and Aspergillus due to higher phenolic compound expression (2,056 and 743 mg/ml), stronger hydrophobic potential (86.18°), and silica accumulation (19.14%) when compared to bulk silica. Suriyaprabha et al. (2014), suggest that nanosilica is an effective antifungal agent against phytopathogens. In addition to their direct pesticidal activity, SiNPs serve as nanocarriers for pesticide delivery, offering controlled and site-specific release to increase efficacy (Magda and Hussein, 2016). Mesoporous SiNPs (MSiNPs) have been used to deliver commercial pesticides with improved precision and efficiency (Chen et al., 2011). SiO2NPs were reported to kill Callosobruchus maculatus (cowpea weevil; Rouhani et al., 2013), while surface-modified hydrophobic nanosilica (3–5 nm) effectively eliminated a wide range of crop insect pests, veterinary pests, and ectoparasites (Rai and Ingle, 2012). The mechanism is thought to involve adsorption onto the protective lipid-water barrier of the target organisms, leading to dehydration and mortality.
3.4.1 Antimicrobial and antifungal properties
Under various biotic stresses, SiNPs treatment combined with seed priming and foliar spray can improve plant growth specifically yield as well as seed germination (Saw et al., 2023). An efficient agronomic strategy for improving seed germination and plant growth even in presence of pathogens is seed priming with SiNPs. For instance, using SiNPs through seed priming greatly increased seed germination and seedling growth in watermelon infected with Fusariumoxysporum (Buchman et al., 2019) and wheat infected with Rhizoctoniasolani (Abdelrhim et al., 2021). Additionally, foliar treatment of SiNPs is more frequently utilized in agricultural activities to shield plants from pests and diseases. SiNPs foliar spray shown reduce disease symptoms and pathogen induced growth inhibition in plants infected with a variety of pathogens and insect pests, including Plasmoparaviticola (Rashad et al., 2021), Fusariumoxysporum (Kang et al., 2021), Mythimnaseparata (Wang et al., 2021), Aphiscraccivora, Alternariasolani (Albalawi et al., 2022), Ralstonia solanacearum (Khan et al., 2022), and Aphis craccivora (Thabet et al., 2021). According to Suriyaprabha et al. (2014), SiNPs improved maize resistance to fungus diseases such as Fusarium oxysporum and Aspergillus niger by controlling the metabolism of phenolic compounds more efficiently than bulk Si.
3.4.2 Controlled release and target specified character
Because of porous nature of SiNPs, they can be employed as a vehicle for the delivery of pesticides, and SiNPs loaded with pesticides have several benefits over direct pesticide application. SiNPs can be used to apply pesticides directly or after being modified for agricultural purposes. When loaded into SiNPs, pesticides longevity and absorption efficiency in plants will be improved, enhancing their pesticidal effects. For instance, Bilal et al. (2020) and Abdelrahman et al. (2021) found that when the chemicals are applied at the same dose, indoxacarb-loaded SiNPs shown superior insecticidal action compared to commercial indoxacarb in suppressing Plutella xylostella. Prochloras uptake, translocation, duration, and antifungal activity in rice were all enhanced using pectin-coated SiNPs as a carrier. Furthermore, it has been proposed that α cyclodextrin-anchored SiNPs improved avermectin's capacity to protect against light and heat after loading, extending its duration of action against Plutella xylostellla (Kaziem et al., 2018). Additionally, SiNPs translocation in plants was improved and the duration of azoxystrobin's release was prolonged by surface modification with copper (Cu) or carboxymethyl chitosan (Xu et al., 2020). To enable prolonged pesticide release, Chen et al. (2016) created a pH-sensitive SiNPs-based chlorpyrifos release system with salicylaldehyde or Cu alteration. Using 3-(trimethoxysilyl) propyl methacrylate. Similarly, Gao et al. (2019) developed a pH-sensitive SiNPs-based abamectin system that demonstrated more toxicity to Cnaphalocrocis medinalis larvae, longer persistence, and improved rice leaf affinity. Liang et al. (2020) enhanced the pesticidal effects of SiNPs by functionalizing them with biodegradable starch to regulate the release of avermectin in response to glutathione and a-amylase. Bapat et al. (2020) successfully inhibited Helicoverpa armigera development by delivering a trypsin inhibitor via triethoxysilane-functionalized SiNPs.
3.5 Stress tolerance in plants and mechanisms
Plants have developed various mechanisms to tolerate abiotic stresses such as drought, salinity, and heat. These mechanisms include osmotic adjustment through proline and soluble sugars, antioxidant defense systems to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS), and improved root architecture for enhanced water uptake. Additionally, plants activate stress-responsive genes and signaling pathways involving abscisic acid (ABA) to regulate their stress responses. SiNPs have emerged as a promising tool for enhancing plant stress tolerance. SiNPs improve WUE, strengthen cell walls, and regulate ROS scavenging to minimize oxidative damage. They also enhance photosynthetic efficiency and nutrient uptake, making plants more resilient under stress conditions. Furthermore, SiNPs can activate stress-responsive genes, promoting better adaptation to environmental challenges. The major interactive mechanisms of SiNP's with plant and soil is illustrated in Figure 2.
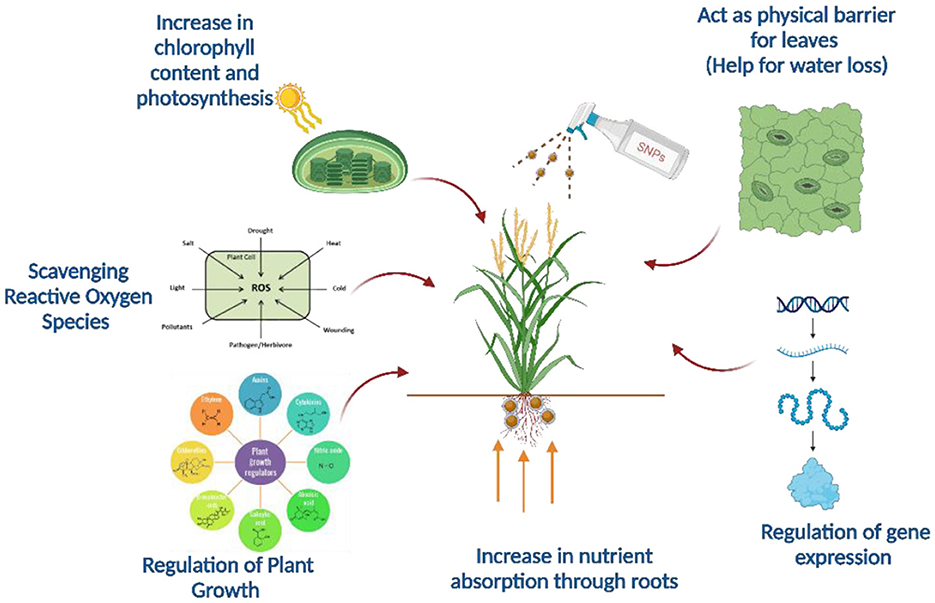
Figure 2. Mechanisms of SiNPs in enhancing plant growth and stress tolerance. SiNPs increase chlorophyll content and photosynthesis, scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS), regulate plant hormones, and boost nutrient absorption through roots. They also act as a physical barrier to reduce water loss and influence gene expression to improve plant resilience.
3.5.1 Metal stress
SiNPs aid in lowering the buildup of harmful metals in contaminated plants, particularly in the edible portions. SiNPs given through soil treatments, foliar spray or seed priming, for example, dramatically reduced Cd levels in wheat grains and enhanced plant growth (Hussain et al., 2019; Ali et al., 2019). SiNPs in rice suggested selective absorption and translocation by increasing as accumulation in the husks and shoots while decreasing its amount in the grain. According to Tripathi et al. (2017) SiNPs also decreased the buildup of Cr in the roots and shoots of pea seedlings subjected to Cr stress. SiNPs promote cell wall retention and boost polysaccharide metabolism, which lowers the absorption and translocation of metals like Cd and As in plants (Riaz et al., 2022). By increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes like peroxidase (POD), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT). SiNPs also lessen oxidative stress by lowering reactive oxygen species (ROS) and enhanced plant growth and yield in the presence of metal contamination (Yan et al., 2023; Ahmed et al., 2023).
3.5.2 Salt stress
Salt stress causes ion toxicity and osmotic limitation in plants cultivated in saline conditions, which impacts plant growth, production, and quality (Munns and Tester, 2008). With the application of SiNPs regulated the Na/K balance in rice and sweet orange by controlling the expression of Na/K transporter genes such as HKT (High-affinity Potassium Transporter), SOS (Salt Overly Sensitive), and NHX (Na+/H+ Exchanger), the homeostasis of Na/K is the primary factor in plant resistance to salt stress (Ijaz et al., 2023). Additionally, SiNPs were discovered to help squash (Cucurbita pepo L.) and peas (Ismail et al., 2022) by enhancing antioxidant enzymes like glutathione reductase (GR), APX, CAT, POD, and SOD. This helped to reduce the accumulation of MDA (malondialdehyde) and H2O2 produced by salt stress. SiNPs can enhance photosynthetic rate, mesophyll conductance, and photosynthetic water usage efficiency in hydroponically grown tomatoes, consequently fostering plant development and resilience to salt stress. Furthermore, SiNPs improved tomato growth, mineral nutrient accumulation (e.g., Mg, K, Fe, Mn, Zn), and photosynthetic performance. According to Alam et al. (2022) foliar treatment found to be more efficient than root dipping in reducing salt stress in tomatoes. In maize and faba bean plants, foliar treatment with 300 mg/L nano-silica effectively reduced salt stress. Under salinity conditions, 2.45 dS/m significantly reduced straw yield (38.84% maize and 78.06% faba bean) and grain yield (39.28% maize and 80.13% faba bean). In contrast, 1.36 dSm−1 and nano-silica produced the highest yields (4.22 Mg/fed for maize grain and 5.32 Mg fed−1 for maize straw; Amer and El-Emary, 2018). Additionally, nano silica improved root architecture and nitrogen utilization efficiency (22.75% for maize and 15.54% for faba beans; Amer and El-Emary, 2018).
3.5.3 Drought stress
There are numerous pathways involved in SiNPs demonstrated drought stress alleviation effects. SiNPs were used to improve cucumber plant development and fruit yield by increasing leaf area, chlorophyll content, and nitrogen assimilation (Alsaeedi et al., 2019). Similarly, Aqaei et al. (2020) discovered that foliar application of SiNPs to maize increased crop weight and reduced mineral nutrient imbalances caused by drought stress. According to Namjoyan et al. (2020) 1 mM SiNP treatment improved shoot water status, increased photosynthetic rate and glycine betaine metabolism, and controlled antioxidant enzyme activities such as SOD, CAT, and GPX in sugar beet. Silica nanoparticles (SiO2NPs) help wheat withstands drought stress by increasing relative water content (RWC) and leaf greenness (SPAD). Applying SiO2NPs to the soil improved RWC by 84.04% and leaf greenness by 12.54% when compared to control during drought. Applications of SiNPs to soil and leaves increased wheat production by 17.81% and 25.35%, respectively. Plant biomass and height were greatly increased by applying 30 and 60 ppm SiO2NPs, which also helped the plants withstand drought (Behboudi et al., 2018). By increasing photosynthetic rate and stomatal conductance under water deficit, SiNPs improved drought tolerance in hawthorn seedlings. Particularly in cases of extreme drought, SiNPs pre-treatment decreased the amount of proline and carbohydrates while increasing plant biomass and xylem water potential. The most notable effects were observed with SiNP treatment at 50 mg/L. SiNPs mostly supported physiological processes without changing pigment levels, as evidenced by the fact that total chlorophyll and carotenoid content stayed constant (Ashkavand et al., 2015).
3.6 Soil health and its fertility maintenance
SiNPs could enhance soil microbial activity by increasing populations of beneficial bacteria such as Paenibacillus and Rhodobacteraceae, as well as fungi like Chaetomium in rhizosphere (Tian et al., 2020). Specifically, the genus Paenibacillus, part of the Firmicutes phylum, was found to be 16% more abundant in soil treated with SiO2NPs compared to the control. Paenibacillus includes plant growth promoting bacteria that improve plant growth through mechanisms such as nitrogen fixation, nutrient solubilization, and the production of plant growth regulators and organic acids (Liu et al., 2019). The study also showed foliar application of SiO2NPs significantly altered the rhizosphere's metabolite profile (Tian et al., 2020). Furthermore, SiO2NPs enhance microbial biomass (1,508:178 μg/g) and enhance the availability of silica in soil, with registered a silica content of 14.75 mg/ml, compared to traditional silica sources. This promotes nutrient cycling, soil fertility, and root nutrient uptake, thus supporting maize growth and overall soil health (Rangaraj et al., 2014).
Beyond microbial stimulation, SiNPs significantly improve the physicochemical properties of soil. Their application enhances soil structure by promoting aggregation, which improves porosity, water infiltration, and aeration, while reducing erosion and surface crusting (Suriyaprabha et al., 2014). This improved physical environment facilitates stronger root development and enhances the soil's water-holding capacity, making water more available to plants during critical growth stages (Adrees et al., 2020). Furthermore, SiNPs contribute to soil chemistry by increasing the cation exchange capacity (CEC), thereby improving the soil's ability to retain and slowly release essential cationic nutrients like ammonium (), potassium (K+), and calcium (Ca2+), which reduces leaching losses and increases nutrient use efficiency (Rastogi et al., 2019). SiNPs also play a crucial role in mitigating soil abiotic stresses. They have been shown to reduce the bioavailability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals in contaminated soils through adsorption and complexation mechanisms, effectively immobilizing them and reducing their uptake by plants (Cui et al., 2017). Additionally, in saline soils, SiNPs help alleviate salinity stress by reducing sodium (Na+) uptake in plants and improving the K+/Na+ ratio, thereby enhancing plant tolerance and protecting soil microbial life from osmotic stress (Haghighi and Pessarakli, 2013). SiNPs improve soil by supporting microbes, strengthening soil structure, holding more nutrients, and cleaning harmful substances. In this way, they act as a soil conditioner that makes farming systems healthier, more fertile, and productive.
3.7 Remediation of contaminated soils
SiNPs can help reduce pesticide residues in edible crops and also used for extracting and degrading pesticides in environmental remediation (Bapat et al., 2016). For example, SiNPs used as carriers for prochloraz and spirotetramat reduced pesticide residues and metabolites in cucumbers (Zhao et al., 2018). SiNPs also effectively extract organic phosphorus pesticides like dicrotophos, chlorpyrifos, and diazinon from water due to mesoporous structure and high surface area (Korrani et al., 2016). Additionally, SiNPs modified with propyl methacrylate improve pesticide removal efficiency (Amani et al., 2018), and can enhance the degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol by immobilizing laccase (Yang et al., 2016). In acidic soils, SiNPs mitigate aluminum (Al) toxicity by boosting antioxidant systems, reducing ROS, and promoting organic acid accumulation, which improves plant growth and stress tolerance (De Sousa et al., 2019). Mercapto-functionalized SiNPs reduce cadmium (Cd) toxicity by lowering Cd leachability and bioavailability, resulting in a 54% reduction in Cd content in wheat grains and a 33.5% increase in grain yield (Wang et al., 2020). SiNPs also reduce arsenic (As) toxicity by immobilizing As, inducing root exudates for as sequestration, and enhancing antioxidant defenses, leading to a 40–50% growth increase and tripled yield weights in maize (David et al., 2024).
4 SiNPs interaction responses
4.1 Plant physiological and biochemical pathways
SiNPs interact with plant physiological and biochemical pathways by enhancing nutrient uptake, photosynthesis, and stress tolerance. They act as carriers for nutrients, improve bioavailability, and promote silica deposition in cell walls, strengthening structural integrity. SiNPs modulate stress response pathways by generating ROS, activating defense signaling, and regulating stress-related genes. These interactions enhance plant resilience to abiotic stresses like drought and salinity while improving growth and metabolism, offering a promising tool for sustainable agriculture when applied judiciously (Surya et al., 2025).
4.2 Enrichment of photosynthesis
Chlorophyll is vital for capturing light energy in photosynthesis, and SiNPs enhance chlorophyll a and b content, thereby increasing light absorption and photosynthetic efficiency. Silicon indirectly improves photosynthesis by strengthening stems and leaves, optimizing their structure for light capture, regulating transpiration, and balancing shoot growth (Liang et al., 2003; Samuels et al., 1993). SiNPs significantly enhance photosynthesis by boosting chlorophyll levels, improving water status, and regulating antioxidant activity. In wheat, chlorophyll a and b increased 1.17- and 1.52-fold at the jointing stage (Li et al., 2023), while in sugar beet, 1 mM SiNPs improved photosynthesis through better shoot water status and antioxidant regulation (Namjoyan et al., 2020). SiNPs enhanced the photosynthetic capacity, photochemical efficiency of photosystem II and photosynthetic pigments in Triticum aestivum under heat stress (Younis et al., 2020). In tomato seedlings, the application of SiNPs through both root and leaf treatments resulted in a 42% and 48% increase in the chlorophyll index, as well as a 35% and 39% improvement in chlorophyll fluorescence at 45 days after sowing (Alam et al., 2022).
4.3 Regulation of hormonal pathways
SiNPs regulate plant hormones and enzyme activity, influencing growth and stress responses. At 200 mg/L, SiNPs increased auxin and ABA in leaves while reducing cytokinin and GA3, whereas in stems, cytokinin and auxin rose but GA3 and ABA declined, reflecting tissue-specific effects on growth regulation (Li et al., 2023). SiNPs enhance plant resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses by modulating hormone signaling (Salicyclic acid-SA, jasmonic acid-JA, ethylene), balancing ROS for pathogen defense, and alleviating oxidative damage (Yan et al., 2024). They regulate hormone metabolism during seed germination under salt stress, improving the K/Na ratio and ROS homeostasis in crops like cucumber, lentil, and maize (Alsaeedi et al., 2018; Naguib and Abdalla, 2019). In strawberry, Si and SiNPs improve drought tolerance by influencing photosynthesis, carbon metabolism, and hormone regulation (Zahedi et al., 2023). SiNPs also synergize with plant growth regulators like PGPR, other NPs, and growth-promoting chemicals, further boosting plant resistance to abiotic stress through hormonal modulation. Nano-fertilizers containing antioxidant enzymes can help reduce oxidative damage and improve crop tolerance to environmental stress (Tripathy and Oelmüller, 2012; Zhu et al., 2016; Etesami and Jeong, 2018). Zhao et al. (2020) indicate that TiO2 nano-fertilizers regulate enzyme production, provide protection against both enzyme and non-enzyme stress, enhance nutrient uptake, and improve crop nutritional quality. Similarly, silica nano fertilizers boost seedling growth and enhance their resilience to abiotic stress by promoting antioxidant enzyme activity (Ahmad et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020; Reynolds et al., 2009).
4.4 Upgrading of nutrient uptake
Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) enhance nutrient availability, supporting plant growth and stress tolerance (Liu et al., 2015; Zhu et al., 2016). In rice, Si application improves nutrient uptake in seeds and shoots, while SiO2 nanoparticles and hydroxyapatite (HAP) nanorods alleviate salinity stress, enhance nutrient uptake, and promote growth. SiO2 nano-fertilizers increase N and P while reducing Na levels, thereby improving yields under saline conditions, though their effectiveness depends on soil texture and pH (Yassen et al., 2017). Foliar sprays of SiNPs also enhance rice growth and micronutrient (Zn, Fe, Mn) absorption (Wang et al., 2015), and combining nano-silicon dioxide with organic fertilizers further boosts productivity (Janmohammadi et al., 2016). MSiNPs, with a pore size ranging from 2 to 10 nm, have proven to be effective in delivering fertilizers such as urea, boron, and nitrogen-based compounds (Torney et al., 2007; Wanyika et al., 2012). SiNPs along with chitosan and zeolite, serve as carriers for nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, enabling their controlled and sustained release. SiNPs have also been shown to improve nutrient absorption and reduce salt stress in crops. SiNPs enhance nutrient uptake by influencing soil nutrient content and promoting beneficial microbial populations. Similarly, SiNPs were found to boost nutrient availability and soil health, significantly enhancing Zea mays growth (Suriyaprabha et al., 2014). Applying SiO2 nanoparticles at 250 and 1,000 mg/L significantly improved K uptake, increasing root K by 46.1%−68.2% and leaf K by 23.5%−33.3%, respectively (González-Moscoso et al., 2021). Ahmadian et al. (2021) reported that nano-chelated silicon fertilizer improved wheat growth under deficit irrigation, highlighting the potential of SiNPs as both nutrient sources and carriers for fertilizers and herbicides.
4.5 Induction of biochemical pathways
Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) regulate genes linked to sugar metabolism, increasing soluble sugar levels that provide energy for plant growth and development (Li et al., 2023). They also trigger key biochemical pathways that enhance growth, nutrient uptake, and stress resilience (Hajizadeh et al., 2021). A major mechanism involves activating the antioxidant defense system, where enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and POD are upregulated to balance ROS and reduce oxidative damage under stress. SiNPs at 400–600 mg/L enhanced phenol degradation (86.29 to 100%) and enzymatic activity while reducing protein (PN) and polysaccharide (PS) in extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). However, at concentrations above 600 mg/L, oxidative stress occurred, marked by increased ROS and lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) levels, reversing the positive effects (Hou et al., 2022). In wheat, Aljeddani et al. (2024) reported that application of 600 ppm SiO2NPs and Trichoderma harzianum improved drought-stressed wheat physiological traits, including chlorophyll a, carotenoids, total pigments, osmolytes, and antioxidants.
4.6 Impact on metabolic functions and gene expression
SiNPs regulate gene expression and metabolic activities, enhancing plant growth, stress tolerance, and productivity. Their nanoscale size allows efficient cell penetration, activating molecular and biochemical responses. SiNP200 treatment upregulated genes for sucrose metabolism (sucrose-phosphate synthase, sucrose synthase, α-glucosidase) and chlorophyll synthesis (magnesium-chelatase, protochlorophyllide oxido-reductase, chlorophyllide a oxygenase), promoting sucrose production and photosynthesis (Li et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2016). However, the expression of Isopentenyl transferases, a gene involved in cytokinin biosynthesis was down-regulated, indicating potential modulation of plant hormonal regulation (Song et al., 2012). SiNP200 treatment up-regulated the expression of the TIR1 (Transport Inhibitor Response) gene in leaves, enhancing the auxin signaling pathway (Li et al., 2023; Yin et al., 2020). SiNPs treatment led to up-regulation of several drought-responsive genes in plants under drought stress conditions. ABC1 (ATP Binding Cassette) gene expression was up-regulated by 3.08-fold under drought stress and 1.50-fold under well-watered conditions, indicating its role in enhancing drought tolerance through the transport of ABA, which helps neutralize stress effects. Wdhn13 (Wheat Dehydration-Responsive Element Binding Protein 13) gene expression increased 2.85-fold in well-watered and 1.78-fold in drought-stressed conditions, contributing to drought tolerance via ABA-dependent pathways. CHP (Chitinase-like Protein) and EXP2 (Expansin A2 a gene involved in cell wall loosening and stress response) genes showed a 2.17–1.78-fold increase, respectively, under drought conditions, indicating their involvement in drought and salinity tolerance (Boora et al., 2023). The adaptive strategies in drought-stressed wheat improved physiological traits including chlorophyll a, carotenoids, total pigments, osmolytes, and antioxidants, while enhancing the expression of key genes (TaP5CS1, TaZFP34, TaWRKY1, TaMPK3, TaLEA, and TaActin), significantly boosting drought tolerance (Aljeddani et al., 2024).
5 Environmental impacts and safety considerations
5.1 Bioaccumulation and biodegradability of SiNPs in ecosystems
In 2020, Jeelani et al. (2020) reported the positive impacts of SiNPs on plant growth, especially in the presence of biotic or abiotic stressors. For example, studies have shown that supplementing horticultural and field crops with SiNPs enhances their resistance to abiotic stress (Ali et al., 2019; Bapat et al., 2020; Banerjee et al., 2021). However, a comprehensive evaluation of the diverse roles of SiNPs in sustainable agriculture, such as their applications as nanopesticides and nanofertilizers have remained necessary (Kah et al., 2019). The mechanisms of SiNP absorption and transport in plants have been comprehensively reviewed only once, by Mathur and Roy (2020). This scarcity of studies highlights the existing knowledge gap, as even after decades of research on cell–nanoparticle interactions, there is still no consensus on how the unique physicochemical properties of SiNPs such as size, surface charge, and morphology which influence their uptake and bioaccumulation (Avellan et al., 2021).
5.1.1 Plant gathering of SiNPs
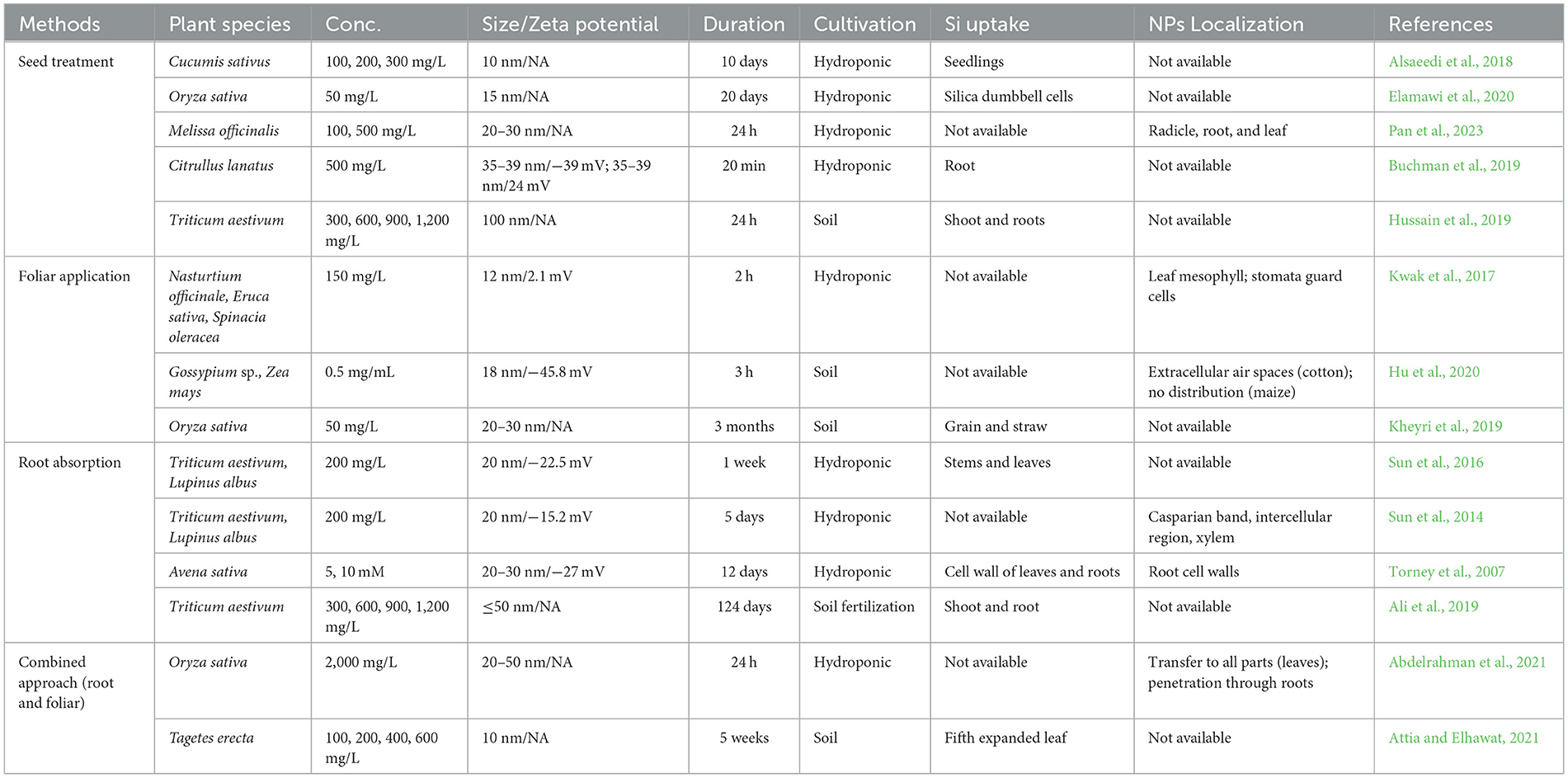
Research by Rastogi et al. (2019), investigates the way SiNPs affect plant growth, especially in plants exposed to biotic or abiotic stressors. However, despite being a significant factor in determining their biological effects, the bioaccumulation of SiNPs has received less attention. An overview of the research on SiNPs bioaccumulation in plants is shown in Table 2.
5.1.2 Seed accumulation of SiNPs
A pre-sowing method called seed priming can improve the metabolic activity of seeds and speed up germination (Paparella et al., 2015). By increasing the thickness of the silicon-cellulose layer in the epidermis and encouraging seed germination, recent field tests have demonstrated that adding SiNPs to soil can improve the mechanical stability of plants, enabling them to withstand lodging (Suriyaprabha et al., 2014). An essential factor in determining the amount of Si buildup in plant tissues is the concentration of SiNPs in the surrounding environment. When plants were exposed to increasing concentrations of SiNPs during seed soaking, higher accumulations of Si were detected in their roots and shoots (Adhikari et al., 2013). It is still to be determined, nevertheless, if the Si found in plant roots and shoots came from the SiNPs themselves or from the silicic acid release from the SiNPs.
According to recent research by Hatami et al. (2021), SiO2NPs may physically scarify the seed coat of several plant species, including Melissa officinalis, creating an opening for NP entrance into the seeds. SiNPs may enter seeds as a suspension in the imbibed water during the process of water absorption (imbibition), which also starts seed germination through tiny pores in the seed coat (Pan et al., 2023). It is possible for SiNPs that have penetrated seeds to go from the roots to the buds as the plant grows. SiNPs have been shown to penetrate and relocate within the radicle, root, and leaf tissues of SiO2NP-primed seedlings through the use of SEM (Hatami et al., 2021). To find out if SiNPs could build up in fruits and enable their transfer to the seeds of the following generation, more research is required.
5.1.3 SiNPs build-up in the roots
Through adsorption on the root surface or on root hairs, stress-induced lesions, and the thinner cuticle and wall, SiNPs can enter plants (Schwab et al., 2016). The ensuing processes have not been fully clarified, although TEM has revealed adsorption on the root surface (Slomberg and Schoenfisch, 2012). Root hairs are more receptive to NP uptake because their cell walls and cuticles are thinner, more porous, and devoid of Si reinforcement when compared to other plant cell types. Lateral roots grow and trichomes are lost as the root grows and the root hairs eventually fall off and the trichoblasts die (Schwab et al., 2016). Usually emerging from the pericycle, lateral roots pierce the parent root's cortex and, after the outer epidermal layer breaks through, form a wound around the base of the root (Huang et al., 2010). Even while the mucilage of the ruptured cells quickly seals the incision, its creation allows NP accumulation and provides an extra pathway for SiO2NPs entrance. Following their arrival at the xylem and phloem, SiO2NPs may proceed via apoplastic and symplastic pathways to the upper portions of the plant (Bhat et al., 2021).
5.1.4 SiNPs shift in plants
Although it has been suggested that apoplastic and symplastic pathways are responsible for the translocation of NPs in plants, the fundamental processes of each channel remain unclear (Mathur and Roy, 2020). Synchrotron radiation revealed that the amount of Si in the soybean root epidermis and pericycle increased following exposure to SiO2NPs. It absorbed by roots can travel through either route to enter the cortex and epidermis before reaching the upper portions of the plant system via the xylem vessels (Li et al., 2020). When exposed to 50 nm fluorescent SiO2NPs, Cheng et al. (2021) observed the enhanced fluorescence in rice roots. Sprayed on leaf surfaces, SiO2NPs (in suspension) either directly absorbs through the stomata and eventually reach vascular tissues, or they pass through the cuticle and enter the leaf epidermal cells (Bapat et al., 2020; Kwak et al., 2017). The movement of SiO2NPs from leaf to leaf or from leaf to stem has only been documented in one study, by Gao et al. (2021).
The transport and translocation of ZnO@SiO2NPs from the dosed leaf to the higher leaves and to the stem, potentially via the xylem or phloem, was demonstrated by the authors using single-particle ICP-MS. Whereas, the phloem carries photosynthates like sugar, amino acids, and peptides to their destinations, such as downward to the roots or upward to the shoot apical meristem, fruits, and newly formed leaves, the xylem mainly carries water and nutrients from roots to shoots (Avellan et al., 2021). Uncertainty surrounds the mechanism of SiO2NP transfer in plant xylem and phloem. The long-distance transport of SiO2NPs to younger shoots, older leaves, or mature roots in plants is yet unknown, despite the numerous studies showing the promise of SiO2NPs as a slow-release fertilizer under foliar spray conditions.
5.2 SiNPs degradability, dispersal and its environmental effects
SiNPs could potentially be discharged into the environment throughout their entire life cycle due to their widespread use in many different areas. The release mechanism of SiNPs is still mostly unknown, though. SiNPs can be utilized as a generic nanomaterial in a variety of disciplines in addition to the specific application. SiNPs were among the nanomaterials whose release was assessed. They stated that SiNPs may be released through the weathering process if they were included as nanocomposites to paints and varnishes (Mackevica and Foss Hansen, 2016). The pigment volume concentration should be a key element influencing the release of SiNPs, as around 1.7 weight percent of SiNPs might be released from the paint particles into the water. About 0.2% of the raw material (180 g per day) was released into the environment every day throughout the production process, according to a risk assessment of SiNPs in glass cleaners. This could have happened as a result of routine equipment cleaning (Michel et al., 2013). Additionally, Wang et al. (2022) assessed the predicted-no effect concentrations (PNEC) and expected environmental concentrations (PEC) of four typical nanomaterials, including SiNPs.
According to their report, SiNPs had a greater PNEC than the other four nanomaterials, suggesting that they should pose less of a risk to the environment. But according to a risk evaluation of these nanoparticles, SiNPs posed the second highest danger, after nano-Al2O3 (Wang and Nowack, 2018). The destiny of SiNPs in the water environment has caused a lot of concern because they may be released into the water in significant amounts. However, based on what is now known about SiO2, the environmental fate of SiNPs is frequently predicted. Under natural circumstances, SiO2 particles are incredibly stable and don't breakdown into any known compounds, because silica and silicates have inorganic structures and stable Si-O chemical connections, scientists believe they are immune to chemical and photodegradation. When SiNPs are kept in aquatic environments, their morphology won't change, even though their particle size may vary because of aggregation (Fruijtier-Pölloth, 2012).
Conferring to Otero-González et al. (2015) activated sludge was unable to successfully remove fluorescent core-shell SiNPs during stimulated secondary wastewater treatment. This was most likely because of the particles high colloid stability and restricted propensity for bioabsorption. Furthermore, Zhang et al. (2018) observed that SiNPs did not assemble quickly in tap water, in contrast to other nanoparticles. This is likely due to their low Hamaker constant. The fate of SiNPs in the environment during wastewater treatment has been examined in recent studies. The flocculation and sedimentation behavior of SiNPs in wastewater may be influenced by surface functioning. Jarvie et al. (2009) discovered that tween-coated SiNPs could be swiftly flocculated and eliminated during wastewater treatment, but that there was no discernible aggregation of unfunctionalized SiNPs throughout the primary treatment procedure.
5.2.1 SiNPs response on soil properties
Among the naturally occurring nanoscale materials in soil are silicates, phosphates, oxides, carbonates, sulfates, hydroxides, silicon, potassium, strontium, iron, rubidium, sodium, aluminum, calcium, barium (Buzea and Pacheco, 2017). According to Jilling et al. (2018) the characteristics of the soil such as its texture, pH, EC, organic matter, CEC and so on determine the destiny and actions of every element in the soil rhizosphere. According to Farooq and Dietz (2015) clay particles created by pedogenic processes involving phyllosilicates and Al-Fe oxides/hydroxides include secondary silicates, whereas sand and silt particles contain the primary mineral-bearing silicates that are naturally present in soils. There are microcrystalline and weakly crystalline forms of Si, including secondary quartz, chalcedony, and short-range ordered silicates (Farooq and Dietz, 2015). It has been reported that the solubility of crystalline and amorphous silica is almost constant between pH 2.0 and 8.5. Yet, because H4SiO4 dissociates into H3 and H+ at pH 9.0, their solubility rapidly rises when the concentration of H4SiO4 falls in the soil solution (Zellner et al., 2021). This enables the dissolution of both crystalline and amorphous silica to restore or buffer the soil solution's declining H4SiO4 concentration (Coskun et al., 2019). The range of plant available forms of Si found in soil is 10–100 mg/kg. Less than 20 mg/kg Si is regarded as a Si deficit in soil, and adding Si is advised (Zargar et al., 2019). Additionally, Figure 3 illustrates the complex interactions of SiNPs with soil components, highlighting their effects on soil structure, microbial dynamics, and nutrient availability. In the soil, the ecosystem and specific characteristics like pH, texture, and organic matter influence the mobility and behavior of Si-NPs. Additionally, soil metabolites, including enzymes, biotransformation agents, organic acids, hormones, and chelators, play a crucial role in modifying the nanoparticles' activity
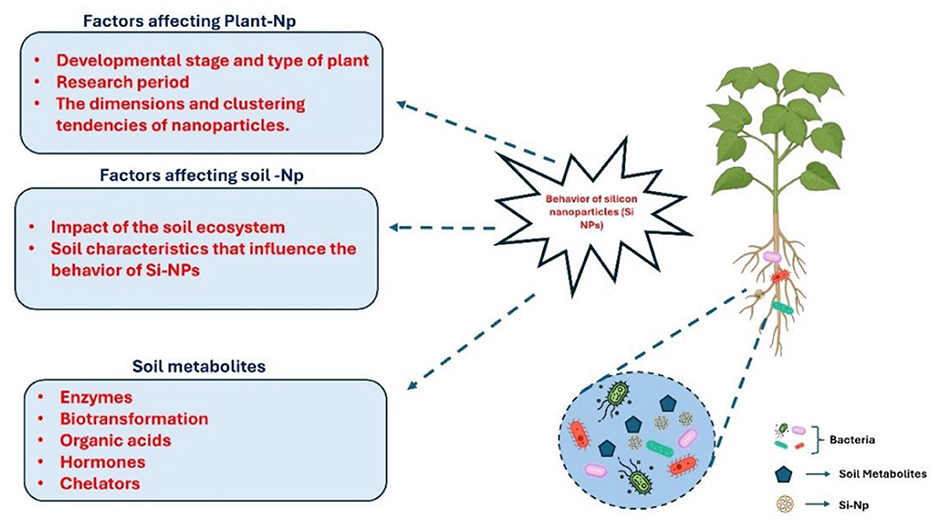
Figure 3. Behavior of silicon nanoparticles (Si-NPs) influenced by plant and soil factors. Plant-NP interactions depend on the plant's developmental stage, type, and nanoparticle dimensions, while soil-NP interactions are shaped by the soil ecosystem and characteristics.
5.2.2 Microorganisms and nano particles interaction
Crop productivity, soil health, and the soil ecology are all dependent on soil microorganisms. Both beneficial and detrimental effects of NPs on the root system and rhizosphere microbes have been confirmed. Engineered nanoparticles are known to be discharged into the environment, particularly soil. Therefore, it is crucial to consider how these NPs affect different soil phenomena and microorganisms. NPs affect soil microorganisms in three ways: (i) direct toxicity effects, (ii) changes in the bio-accessibility of toxins or essential elements, (iii) antagonistic or synergistic impact at the interface between toxic organic molecules, (iv) indirect influence on associations with organic compounds (Khanna et al., 2021).
5.2.3 SiNPs consequences for rhizhosphere microbiomes
For plants, soil serves as a storehouse of nutrients and water, making it essential to their regular functioning. The term “rhizosphere” refers to the region round a plant's roots. There are biotic and abiotic relationships within the rhizosphere complex. As a result, the rhizospheric microbiome is made up of a variety of microbial organisms that are closely associated with the roots of plants in a small area of soil such as bacteria, fungi, viruses, and archaea. Additionally, this rhizospheric unit is known to contain more than 1,000 microbial cells/g of the root, which corresponds to around 30,000 prokaryotes (Berendsen et al., 2012).
Various researchers have observed the release of a wide range of soil metabolites, including siderophores, sugars, vitamins, organic acids, inorganic acids, amino acids, purines, nucleosides, polysaccharide mucilage. According to Brolsma et al. (2017), this subset of soil microbial diversity is highly susceptible to various factors, including nanoparticle applications and other rhizosphere physicochemical changes, which can promote the selective enrichment of certain microbial communities over others. Nitrogen-fixing microbes and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria (PSB) are two beneficial microorganisms found in the rhizosphere (Kour et al., 2021). Since these microorganisms stimulate plant growth, they could modulate the biological and chemical characteristics of soils. Silicate-solubilizing bacteria (SSB) are also found in soil and have the ability to reduce the amount of Si in the soil by converting insoluble silicates into soluble Si. Therefore, the preservation of soil characteristics and plant health depends heavily on the rhizosphere (Barea et al., 2005).
Moreover, SiNPs are known to stimulate crop growth because of their significant impact on soil nutrient content and microbial biota (Theng and Yuan, 2008). The phosphate solubilizing bacteria population (3.8 × 104 CFU/g) increased in this study following SiNPs therapy, whereas the Silicate-solubilizing bacteria population was unaffected. Similarly, a study found that applying SiNPs significantly altered the microbial biota and soil nutrient content, which in turn enhanced Zea mays growth (Suriyaprabha et al., 2014). The soil with the Si addition has a large population of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. In addition to improving the rhizosphere's Chaetomium fungal species, the foliar application of SiO2NPs enhanced the bacterial communities of Paenibacillus and Rhodobacteraceae (Tian et al., 2020).
Furthermore, the genus Paenibacillus in the phylum Firmicutes was found to be almost 16% more abundant in the soil containing NPs than in the control group in this investigation. According to Liu et al. (2019) the genus Paenibacillus contains bacteria that promote plant growth through a variety of processes including nutrient solubility, biological nitrogen-fixing, induction of systemic resistance, plant growth regulators, and organic acid synthesis. A combination of copper, silver and silicon was found to decrease C and N biomass and alter the structure of the microbial community in soil (Kumar et al., 2012). The effects of some NPs such as SiNPs, showed that oversaturation of these NPs decreased dehydrogenase and urease activity as well as bacterial and archaeal amoA gene abundance in soil (McGee et al., 2017).
5.3 Response of SiNPs in agriculture
Numerous industries can benefit from the special physiochemical characteristics of nanoscale silicon particles, with the agricultural industry showing particular promise. SiNPs special qualities enable them to handle abiotic stress and climate change-related agricultural damage (Tripathi et al., 2017). By assisting in the creation of enhanced, highly productive cultivars, the use of SiNPs in agriculture may also contribute to global food security (Parisi et al., 2015). Numerous novel uses for plants are being researched, and silicon nanoparticles show promise and have consequences for agriculture. SiNPs have been used as a weapon in the agricultural sector to combat dehydration (Jullok et al., 2016), UVB stress (Tripathi et al., 2017), salt stress (Abdel-Haliem et al., 2017), and heavy metal toxicity (Cui et al., 2017).
5.3.1 Fertilizers and herbicides are transported via SiNPs
SiNPs may serve as an agent for target-specific delivery of fertilizers and herbicides in the current situation, where the goal is to remove weeds or boost agricultural productivity (Wanyika et al., 2012). Herbicides (chloroacetanilide, anilide, and benzimidazole) embedded in a diatom fistule have been shown to be transported by silicon nanocarriers, which then release the herbicide into the field in its active form. Research on fertilizer distribution indicated that using nano-silicon dioxide in conjunction with organic fertilizer increased plant yields (Janmohammadi et al., 2016). Fertilizers based on urea, boron, and nitrogen were effectively delivered using MSiNPs with a particular pore size (2–10 nm; Wanyika et al., 2012; Table 3).
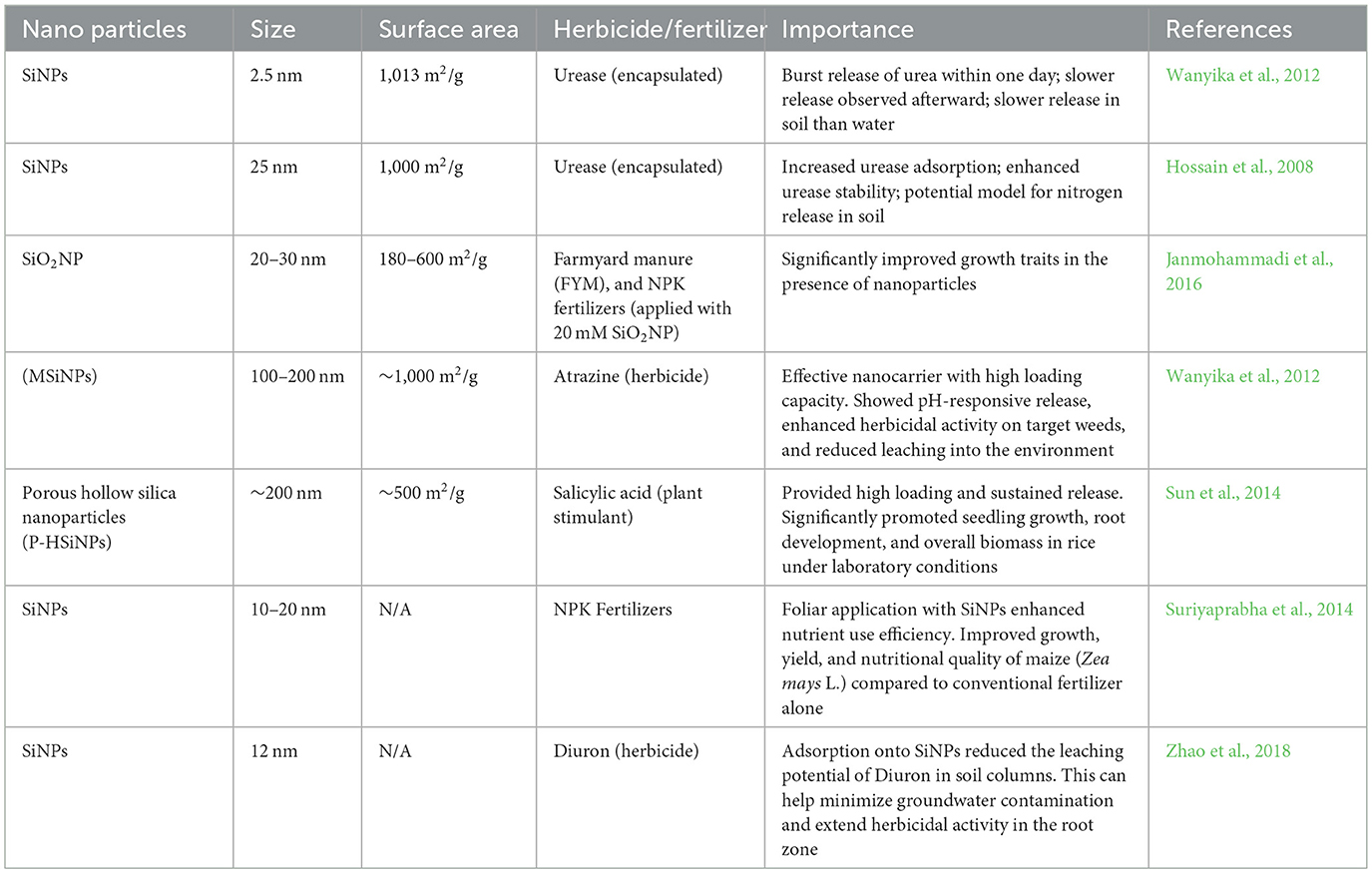
Table 3. Characteristics and agricultural significance of silica nanoparticles in nutrient and herbicide delivery.
6 Environmental safety and biocompatibility of silica nanoparticles
While the application of nanotechnology in agriculture offers immense promise, concerns regarding nanotoxicity and bioaccumulation must be thoroughly addressed to ensure sustainable deployment. A critical advantage of SiNPs over other nanomaterials lies in their superior environmental safety profile. A key mitigating factor is their inherent biodegradability; SiNPs are not persistent and undergo hydrolysis in soil and aqueous environments, dissolving into soluble silicic acid [Si(OH)4], which is the natural, plant-available form of silicon and poses negligible toxicity (Slomberg and Schoenfisch, 2012). Furthermore, the biocompatibility of SiNPs is well-established, largely due to silicon's abundance in the earth's crust and its role as a beneficial element for plants. Numerous studies have demonstrated significantly lower toxicity of amorphous SiNPs to soil microorganisms, earthworms, and plant cells compared to metal-based nanoparticles like ZnO or AgNPs (Dimkpa et al., 2013). This is primarily because their mechanism of action does not involve the release of toxic ions. Regarding bioaccumulation, evidence suggests that SiNPs have a low potential for uptake and translocation in plants compared to other nanoparticles, and they tend to aggregate and bind to soil particles, limiting their mobility and preventing leaching into groundwater (Wang et al., 2016). However, it is crucial to note that toxicity is dose-dependent and can be influenced by particle size, surface charge, and functionalization (Yang et al., 2017). Therefore, while the inherent properties of SiNPs make them a promising and potentially safer candidate, comprehensive long-term field studies remain essential to fully validate their environmental fate and effects.
7 Challenges and future perspective
One of the main problems to consider in the use of SiNPs in agriculture is their implementation, longevity and effects on the ecosystem a massive concern. Laboratory studies have been quite encouraging, but understanding the behavior of SiNPs under varied field conditions over long durations is so far not well-understood. This absence of well-rounded data further creates obstacles in the formulation of constructive risk evaluation models, and effective recommendations for practical use of agriculture on a larger scale. Another challenge is the economic feasibility and scalability of agricultural solutions based on SiNPs. Adapting present production methods, it seems impossible to make them efficient for farmers who specialize in farming, which might considerably reduce accessibility. Further improvement and consultation with scientists to create more effective and affordable technologies have to be carried out to allow farmers from different social classes access to SiNPs technologies. This appears to the author's most challenging issue since there are no sufficiently competent theoretical developments and practices that include nanoparticle agricultural policies for a specific stakeholder audience such as industry and policymakers. It is critically important to formulate recommendations that are grounded and thick with emerging evidence which will minimize environmental and human safety vulnerabilities while widening the scope of SiNPs technologies in the farming practices. In the future, the positively inclined wise impact of SiNPs on the precision agriculture technology seems encouraging. In the future, further development can be carried out in the direction of combining the applications of SiNPs with smart farming, drones, and IoT sensors in order to increase the effectiveness of resource use in crop production. Such integration could help in the efficient and effective use of SiNPs with less negative effect on the environment. However, in order to overcome these challenges and harness the complete benefits of SiNPs for sustainable agriculture, it will require a complementary approach that incorporates agronomists, nanotechnology experts, ecologists, agricultural economists as well as policy makers. In this context, future works could be directed toward:
a. Implementing a broad monitoring of agriculture with SiNPs across a diversified farming system, designed to evaluate its effect and environmental safety throughout its life cycle.
b. Creating simple and replicable procedures for the manufacture of SiNPs intended for agricultural purposes.
c. Forming international partnerships aimed at development of coordinated policies on nano materials utilization in agriculture.
d. Assessing the effect of integrating SiNPs with other precise agricultural technologies in the overall aim of providing comprehensive sustainable farming practices.
Addressing these issues would enable the agricultural sector to be able to make maximum use of the advantages of SiNPs in making agriculture more sustainable, and less harmful to future generations.
8 Conclusion
A use of SiNPs in crop production is an emerging phenomenon that could solve the world's food shortage problem without polluting the environment. SiNPs are useful in agriculture in many ways due to their particular characteristics such as having a large surface area, being of a predetermined size, and being biocompatible. Because of the properties such as targeted pest control and enhancing the ability of plants to withstand both biotic and abiotic stresses, crop production could improve even further with the utilization of SiNPs. The mechanisms of action of SiNPs in plants are complicated and numerous; there are cellular and molecular interactions. SiNPs can influence the gene, induce photosynthesis, and enhance the plant's defense system which means potential improvement in plant's productivity. But in saying so, like with any new technology, the environment and safety aspects of the SiNPs need to be taken into confederation to understand the bare minimum impact they have, when used in agriculture. The focus of recent research verticals in SiNPs research has been to look into its synthesis and specifically look for newer avenues of application. These breakthroughs are opening new avenues to conduct more effective and focused agricultural operations. However, there are still problems including the lack of harmonized guidelines, comprehensive evaluation of the environmental impacts, and legal measures governing them. Looking forward, trends of using SiNPs in promoting sustainable agricultural practices are bright but more research and development work is required. Future research may include customizing nanoparticles for specific crops and growing conditions, fashioning smart delivery devices, and using SiNPs together with other green technologies in agriculture. In the future, it is going to be very important to take a much broader perspective that looks at both the risks and benefits of integrating this technology in agriculture to fully utilize SiNPs for more sustainable agriculture systems.
Author contributions
KS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology. GS: Writing – original draft. MA: Writing – original draft. RI: Writing – original draft. CE: Methodology, Writing – original draft. BK: Writing – original draft. BS: Writing – original draft. VS: Writing – original draft. JN: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SR: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. EP: Writing – review & editing, Resources. JP: Resources, Writing – review & editing. KR: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
I extend my sincere gratitude to the Department of Agronomy and the Nammazhvar Organic Farming Research Centre for their invaluable support and opportunities that facilitated the writing of this manuscript. Additionally, I would like to acknowledge BioRender for providing the tools to create the illustrations used in this manuscript, which were generated using the free version of BioRender.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Haliem, M. E., Hegazy, H. S., Hassan, N. S., and Naguib, D. M. (2017). Effect of silica ions and nano silica on rice plants under salinity stress. Ecol. Eng. 99, 282–289. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.060
Abdelrahman, T. M., Qin, X., Li, D., Senosy, I. A., Mmby, M., Wan, H., et al. (2021). Pectinase-responsive carriers based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles for improving the translocation and fungicidal activity of prochloraz in rice plants. Chem. Eng. J. 404:126440. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126440
Abdelrhim, A. S., Mazrou, Y. S. A., Nehela, Y., Atallah, O. O., El-Ashmony, R. M., Dawood, M. F. A., et al. (2021). Silicon dioxide nanoparticles induce innate immune responses and activate antioxidant machinery in wheat against Rhizoctonia solani. Plants 10:2758. doi: 10.3390/plants10122758
Adams, C. B., Erickson, J. E., and Bunderson, L. (2020). A mesoporous silica nanoparticle technology applied in dilute nutrient solution accelerated establishment of zoysiagrass. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 3:e20006. doi: 10.1002/agg2.20006
Adebisi, J., Agunsoye, J., Bello, S., Haris, M., Ramakokovhu, M., Daramola, M., et al. (2018). Extraction of silica from cassava periderm using modified sol-gel method. Niger. J. Technol. Dev. 15, 57–65. doi: 10.4314/njtd.v15i2.4
Adebisi, J. A., Agunsoye, J. O., Bello, S. A., Haris, M., Ramakokovhu, M. M., Daramola, M. O., et al. (2020). Green production of silica nanoparticles from maize stalk. Part Sci. Technol. 38, 667–675. doi: 10.1080/02726351.2019.1578845
Adhikari, T., Kundu, S., and Rao, A. S. (2013). Impact of SiO2 and Mo nanoparticles on seed germination of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Int. J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 4, 809–816. Available online at: https://www.ijcmas.com/7-12-2018/Nita%20Babaso%20Patil2,%20et%20al.pdf
Adrees, M., Khan, Z. S., Ali, S., Hafeez, M., Khalid, S., Ur Rehman, M. Z., et al. (2020). Simultaneous mitigation of cadmium and drought stress in wheat by soil application of iron nanoparticles. Chemosphere 238:124681. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124681
Ahmad, B., Shabbir, A., Jaleel, H., Khan, M., and Sadiq, Y. E. (2018). Efficacy of titanium dioxide nanoparticles in modulating photosynthesis, peltate glandular trichomes and essential oil production and quality in Mentha piperita L. Curr. Plant Biol. 13, 6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.cpb.2018.04.002
Ahmadian, K., Jalilian, J., and Pirzad, A. (2021). Nano-fertilizers improved drought tolerance in wheat under deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 244:106544. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106544
Ahmed, T., Masood, H. A., Noman, M., Al-Huqail, A. A., Alghanem, S. M., Khan, M. M., et al. (2023). Biogenic silicon nanoparticles mitigate cadmium (Cd) toxicity in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by modulating the cellular oxidative stress metabolism and reducing Cd translocation. J. Hazard. Mater. 459:132070. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132070
Alam, P., Arshad, M., Al-Kheraif, A. A., Azzam, M. A., and Al Balawi, T. (2022). Silicon nanoparticle-induced regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, photosynthesis, and ROS homeostasis in Solanum lycopersicum subjected to salinity stress. ACS Omega 7, 31834–31844. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c02586
Albalawi, M. A., Abdelaziz, A. M., Attia, M. S., Saied, E., Elganzory, H. H., Hashem, A. H., et al. (2022). Mycosynthesis of silica nanoparticles using Aspergillus niger: control of Alternaria solani causing early blight disease, induction of innate immunity and reducing oxidative stress in eggplant. Antioxidants 11:20. doi: 10.3390/antiox11122323
Ali, S., Rizwan, M., Hussain, A., ur Rehman, M. Z., Ali, B., Yousaf, B., et al. (2019). Silicon nanoparticles enhanced the growth and reduced the cadmium accumulation in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 140, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.04.041
Aljeddani, G. S., Hamouda, R. A., Abdelsattar, A. M., and Heikal, Y. M. (2024). Stress-responsive gene expression, metabolic, physiological, and agronomic responses by consortium nano-silica with Trichoderma against drought stress in bread wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25:10954. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010954
Alsaeedi, A., El-Ramady, H., Alshaal, T., El-Garawani, M., Elhawat, N., Al-Otaibi, A., et al. (2018). Exogenous nanosilica improves germination and growth of cucumber by maintaining K+/Na+ ratio under elevated Na+ stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 125, 164–171. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.02.006
Alsaeedi, A., El-Ramady, H., Alshaal, T., El-Garawany, M., Elhawat, N., Al-Otaibi, A., et al. (2019). Silica nanoparticles boost growth and productivity of cucumber under water deficit and salinity stresses by balancing nutrients uptake. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 139, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.03.008
AlSaeedi, A. H. (2022). Enhancement of soil water characteristics curve (SWCC) and water use efficiency of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) in sandy soils by using silica nanoparticles. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 34:101926. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101926
Amani, M. A., Latifi, A. M., Tahvildari, K., and Karimian, R. (2018). Removal of diazinon pesticide from aqueous solutions using MCM-41 type materials: isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 15, 1301–1312. doi: 10.1007/s13762-017-1469-x
Amer, M., and El-Emary, F. A. (2018). Impact of foliar with nano-silica in mitigation of salt stress on some soil properties, crop-water productivity, and anatomical structure of maize and faba bean. Environ. Biodivers. Soil Secur. 2, 25–38. doi: 10.21608/jenvbs.2018.3753.1026
Aqaei, P., Weisany, W., Diyanat, M., Razmi, J., and Struik, P. C. (2020). Response of maize (Zea mays L.) to potassium nano-silica application under drought stress. J. Plant Nutr. 43, 1205–1216. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2020.1727508
Arshad, R., Gulshad, L., Haq, I. U., Farooq, M. A., Al-Farga, A., Siddique, R., et al. (2021). Nanotechnology: a novel tool to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients. Food Sci. Nutr. 9, 3354–3361. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2311
Ashkavand, P., Tabari, M., Zarafshar, M., Tomášková, I., and Struve, D. (2015). Effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on drought resistance in hawthorn seedlings. For. Res. Pap. Leśne Prace Badawcze 76, 350–359. doi: 10.1515/frp-2015-0034
Attia, E. A., and Elhawat, N. (2021). Combined foliar and soil application of silica nanoparticles enhances the growth, flowering period and flower characteristics of marigold (Tagetes erecta L.). Sci. Hortic. 282:110015. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110015
Avellan, A., Yun, J., Morais, B. P., Clement, E. T., Rodrigues, S. M., Lowry, G. V., et al. (2021). Critical review: role of inorganic nanoparticle properties on their foliar uptake and in planta translocation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 13417–13431. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c00178
Ayoub, H. A., Khairy, M., Rashwan, F. A., and Abdel-Hafez, H. F. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of silica nanostructures for cotton leaf worm control. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 7, 91–100. doi: 10.1007/s40097-017-0229-2
Baka, Z. A., and El-Zahed, M. M. (2022). Antifungal activity of silver/silicon dioxide nanocomposite on the response of faba bean plants (Vicia faba L.) infected by Botrytis cinerea. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 9:19. doi: 10.1186/s40643-022-00591-7
Banerjee, A., Singh, A., Sudarshan, M., and Roychoudhury, A. (2021). Silicon nanoparticle-pulsing mitigates fluoride stress in rice by fine-tuning the ionomic and metabolomic balance and refining agronomic traits. Chemosphere 262:127826. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127826
Bapat, G., Labade, C., Chaudhari, A., and Zinjarde, S. (2016). Silica nanoparticle based techniques for extraction, detection, and degradation of pesticides. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 237, 1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2016.06.001
Bapat, G., Zinjarde, S., and Tamhane, V. (2020). Evaluation of silica nanoparticle mediated delivery of protease inhibitor in tomato plants and its effect on insect pest Helicoverpa armigera. Colloids Surf. B 193:111079. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111079
Barea, J. M., Pozo, M. J., Azcon, R., and Azcon-Aguilar, C. (2005). Microbial co-operation in the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 56, 1761–1778. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri197
Behboudi, F., Tahmasebi Sarvestani, Z., Kassaee, M. Z., Modares Sanavi, S. A. M., and Sorooshzadeh, A. (2018). Improving growth and yield of wheat under drought stress via application of SiO2 nanoparticles. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 20, 1479–1492. 20.1001.1.16807073.2018.20.7.10.4
Beig, B., Khan Niazi, M. B., Sher, F., Jahan, Z., Malik, U. S., Khan, M. D., et al. (2022). Nanotechnology-based controlled release of sustainable fertilizers: a review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 20, 2709–2726. doi: 10.1007/s10311-022-01409-w
Berendsen, R. L., Pieterse, C. M., and Bakker, P. A. (2012). The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 17, 478–486. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.04.001
Bhat, J. A., Rajora, N., Raturi, G., Sharma, S., Dhiman, P., Sanand, S., et al. (2021). Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) in sustainable agriculture: major emphasis on the practicality, efficacy and concerns. Nanoscale Adv. 3, 4019–4028. doi: 10.1039/D1NA00233C
Bilal, M., Xu, C., Cao, L., Zhao, P., Cao, C., Li, F., et al. (2020). Indoxacarb-loaded fluorescent mesoporous silica nanoparticles for effective control of Plutella xylostella L. with decreased detoxification enzymes activities. Pest Manag. Sci. 76, 3749–3758. doi: 10.1002/ps.5924
Boora, R., Rani, N., Kumari, S., Yashveer, S., Kumari, N., Grewal, S., et al. (2023). Efficacious role of silica nanoparticles in improving growth and yield of wheat under drought stress through stress-gene upregulation. Plant Nano Biol. 6:100051. doi: 10.1016/j.plana.2023.100051
Brolsma, K. M., Vonk, J. A., Mommer, L., Van Ruijven, J., Hoffland, E., Goede, D., et al. (2017). RG. Microbial catabolic diversity in and beyond the rhizosphere of plant species and plant genotypes. Pedobiologia 61, 43–49. doi: 10.1016/j.pedobi.2017.01.006
Buchman, J. T., Elmer, W. H., Ma, C., Landy, K. M., White, J. C., Haynes, C. L., et al. (2019). Chitosan-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticle treatment of Citrullus lanatus (watermelon): enhanced fungal disease suppression and modulated expression of stress-related genes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 19649–19659. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04800
Buzea, C., and Pacheco, I. (2017). “Nanomaterials and their classification,” in EMR/ESR/EPR Spectroscopy for Characterization of Nanomaterials, ed. A. K. Shukla (New York, NY: Springer), 3–45. doi: 10.1007/978-81-322-3655-9_1
Chen, H. Y., Lin, Y. S., Zhou, H. J., Zhou, X. H., Gong, S., Xu, H., et al. (2016). Synthesis and characterization of chlorpyrifos/copper (II) schiff base mesoporous silica with pH sensitivity for pesticide sustained release. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 8095–8102. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b03262
Chen, J., Wang, W., Xu, Y., and Zhang, X. (2011). Slow-release formulation of a new biological pesticide, pyoluteorin, with mesoporous silica. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 307–311. doi: 10.1021/jf103640t
Cheng, B., Chen, F., Wang, C., Liu, X., Yue, L., Cao, X., et al. (2021). The molecular mechanisms of silica nanomaterials enhancing the rice (Oryza sativa L.) resistance to planthoppers (Nilaparvata lugens Stal). Sci. Total Environ. 767:144967. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.144967
Coskun, D., Deshmukh, R., Sonah, H., Menzies, J. G., Reynolds, O., Ma, J. F., et al. (2019). The controversies of silicon's role in plant biology. New Phytol. 221, 67–85. doi: 10.1111/nph.15343
Cui, J., Liu, T., Li, F., Yi, J., Liu, C., Yu, H., et al. (2017). Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: mechanisms and size effects. Environ. Pollut. 228, 363–369. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.05.014
David, O. A., Labulo, A. H., Hassan, I., Olawuni, I., Oseghale, C. O., Terna, A. D., et al. (2024). Complexation and immobilization of arsenic in maize using green synthesized silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs). Sci. Rep. 14:6176. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56924-3
De Sousa, A., Saleh, A. M., Habeeb, T. H., Hassan, Y. M., Zrieq, R., Wadaan, M. A., et al. (2019). AbdElgawad H. Silicon dioxide nanoparticles ameliorate the phytotoxic hazards of aluminum in maize grown on acidic soil. Sci. Total Environ. 693:133636. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133636
Dimkpa, C. O., McLean, J. E., Martineau, N., Britt, D. W., Haverkamp, R., Anderson, A. J., et al. (2013). Silver nanoparticles disrupt wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) growth in a sand matrix. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 1082–1090. doi: 10.1021/es302973y
Eichert, T., Kurtz, A., Steiner, U., and Goldbach, H. E. (2008). Size exclusion limits and lateral heterogeneity of the stomatal foliar uptake pathway for aqueous solutes and water-suspended nanoparticles. Physiol. Plant. 134, 151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01135.x
Elamawi, R. M., Tahoon, A. M., Elsharnoby, D. E., and El-Shafey, R. A. (2020). Bio-production of silica nanoparticles from rice husk and their impact on rice bakanae disease and grain yield. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 53, 459–478. doi: 10.1080/03235408.2020.1750824
Etesami, H., and Jeong, B. R. (2018). Silicon (Si): review and future prospects on the action mechanisms in alleviating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 147, 881–896. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.09.063
Farooq, M. A., and Dietz, K.-J. (2015). Silicon as versatile player in plant and human biology: overlooked and poorly understood. Front. Plant Sci. 6:994. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00994
Fraceto, L. F., Grillo, R., de Medeiros, G. A., Scognamiglio, V., Rea, G., Bartolucci, C., et al. (2016). Nanotechnology in agriculture: which innovation potential does it have? Front. Environ. Sci. 4:20. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2016.00020
Fruijtier-Pölloth, C. (2012). The toxicological mode of action and the safety of synthetic amorphous silica—a nanostructured material. Toxicology 294, 61–79. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.02.001
Gao, X., Kundu, A., Bueno, V., Rahim, A. A., and Ghoshal, S. (2021). Uptake and translocation of mesoporous SiO2-coated ZnO nanoparticles to Solanum lycopersicum following foliar application. Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 13551–13560. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c00447
Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., He, S., Xiao, Y., Qin, X., Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). Fabrication of a hollow mesoporous silica hybrid to improve the targeting of a pesticide. Chem. Eng. J. 364, 361–369. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.105
Gogos, A., Knauer, K., and Bucheli, T. D. (2012). Nanomaterials in plant protection and fertilization: current state, foreseen applications, and research priorities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 60, 9781–9792. doi: 10.1021/jf302154y
González-Moscoso, M., Martínez-Villegas, N. V., Meza-Figueroa, D., Rivera-Cruz, M. C., Cadenas-Pliego, G., Juárez-Maldonado, A., et al. (2021). SiO2 nanoparticles improve nutrient uptake in tomato plants developed in the presence of arsenic. Revista Bio Ciencias. 8:e1084. doi: 10.15741/revbio.08.e1084
Goswami, P., Mathur, J., and Srivastava, N. (2022). Silica nanoparticles as novel sustainable approach for plant growth and crop protection. Heliyon 8:e09908. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09908
Haghighi, M., and Pessarakli, M. (2013). Influence of silicon and nano-silicon on salinity tolerance of cherry tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L.) at early growth stage. Sci. Hortic. 161, 111–117. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.06.034
Hajizadeh, H. S., Asadi, M., Zahedi, S. M., Hamzehpour, N., Rasouli, F., Helvaci, M., et al. (2021). Silicon dioxide-nanoparticle nutrition mitigates salinity in gerbera by modulating ion accumulation and antioxidants. Folia Hortic. 33, 91–105. doi: 10.2478/fhort-2021-0007
Hatami, M., Khanizadeh, P., Bovand, F., and Aghaee, A. (2021). Silicon nanoparticle-mediated seed priming and Pseudomonas spp. inoculation augment growth, physiology and antioxidant metabolic status in Melissa officinalis L. plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 162:113238. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113238
Hossain, K.-Z., Monreal, C. M., and Sayari, A. (2008). Adsorption of urease on PE-MCM-41 and its catalytic effect on hydrolysis of urea. Colloids Surf. B Biointerf. 62, 42–50. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.09.016
Hou, Y., Zeng, Q., Li, H., Wu, J., Xiang, J., Huang, H., et al. (2022). Metagenomics-based interpretation of the impacts of silica nanoparticles exposure on phenol treatment performance in sequencing batch reactor system. Chem. Eng. J. 428:132052. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.132052
Hu, P., An, J., Faulkner, M. M., Wu, H., Li, Z., Tian, X., et al. (2020). Nanoparticle charge and size control foliar delivery efficiency to plant cells and organelles. ACS Nano 14, 7970–7986. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b09178
Huang, J., Zhao, R., Wang, H., Zhao, W., and Ding, L. (2010). Immobilization of glucose oxidase on Fe3O4/SiO2 magnetic nanoparticles. Biotechnol. Lett. 32, 817–821. doi: 10.1007/s10529-010-0217-9
Hussain, A., Rizwan, M., Ali, Q., and Ali, S. (2019). Seed priming with silicon nanoparticles improved the biomass and yield while reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat grains. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26, 7579–7588. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-04210-5
Ijaz, U., Ahmed, T., Rizwan, M., Noman, M., Shah, A. A., Azeem, F., et al. (2023). Rice straw based silicon nanoparticles improve morphological and nutrient profile of rice plants under salinity stress by triggering physiological and genetic repair mechanisms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 201:107788. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107788
Ismail, L. M., Soliman, M. I., Abd El-Aziz, M. H., and Abdel-Aziz, H. M. M. (2022). Impact of silica ions and nano silica on growth and productivity of pea plants under salinity stress. Plants 11:494. doi: 10.3390/plants11040494
Janmohammadi, M., Amanzadeh, T., Sabaghnia, N., and Ion, V. (2016). Effect of nano-silicon foliar application on safflower growth under organic and inorganic fertilizer regimes. Bot. Lithuan. 22, 53–64. doi: 10.1515/botlit-2016-0005
Jansomboon, W., Boonmaloet, K., Sukaros, S., and Prapainainar, P. (2017). Rice hull micro and nanosilica: synthesis and characterization. Key Eng. Mater. 718, 77–80. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.718.77
Jarvie, H. P., Al-Obaidi, H., King, S. M., Bowes, M. J., Lawrence, M. J., Drake, A. F., et al. (2009). Fate of silica nanoparticles in simulated primary wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 43, 8622–8628. doi: 10.1021/es901399q
Jeelani, P. G., Mulay, P., Venkat, R., and Ramalingam, C. (2020). Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles: a review. Silicon 12, 1337–1354. doi: 10.1007/s12633-019-00229-y
Ji, X. Y., Wang, H. Y., Song, B., Chu, B. B., and He, Y. (2018). Silicon nanomaterials for biosensing and bioimaging analysis. Front. Chem. 6:38. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2018.00038
Jilling, A., Keiluweit, M., Contosta, A. R., Frey, S., Schimel, J., Schnecker, J., et al. (2018). Minerals in the rhizosphere: overlooked mediators of soil nitrogen availability to plants and microbes. Biogeochemistry 139, 103–122. doi: 10.1007/s10533-018-0459-5
Jullok, N., Van Hooghten, R., Luis, P., Volodin, A., Van Haesendonck, C., Vermant, J., et al. (2016). Effect of silica nanoparticles in mixed matrix membranes for pervaporation dehydration of acetic acid aqueous solution: plant-inspired dewatering systems. J. Clean. Prod. 112, 4879–4889. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.019
Kah, M., Tufenkji, N., and White, J. C. (2019). Nano-enabled strategies to enhance crop nutrition and protection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 14, 532–540. doi: 10.1038/s41565-019-0439-5
Kang, H., Elmer, W., Shen, Y., Zuverza-Mena, N., Ma, C., Botella, P., et al. (2021). Silica nanoparticle dissolution rate controls the suppression of Fusarium wilt of watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 55, 13513–13522. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c07126
Kaziem, A. E., Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., Qin, X., Xiao, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). α-Amylase triggered carriers based on cyclodextrin anchored hollow mesoporous silica for enhancing insecticidal activity of avermectin against Plutella xylostella. J. Hazard. Mater. 359, 213–221. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.07.059
Khan, M., Siddiqui, Z. A., Parveen, A., Khan, A. A., Moon, I. S., Alam, M., et al. (2022). Elucidating the role of silicon dioxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mitigating the disease of the eggplant caused by Phomopsis vexans, Ralstonia solanacearum, and root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nanotechnol. Rev. 11, 1606–1619. doi: 10.1515/ntrev-2022-0097
Khanna, K., Kohli, S. K., Handa, N., Kaur, H., Ohri, P., Bhardwaj, R., et al. (2021). Enthralling the impact of engineered nanoparticles on soil microbiome: a concentric approach towards environmental risks and cogitation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 222:112459. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112459
Kheyri, N., Norouzi, H. A., Mobasser, H. R., and Torabi, B. (2019). Effects of silicon and zinc nanoparticles on growth, yield, and biochemical characteristics of rice. Agron. J. 111, 3084–3090. doi: 10.2134/agronj2019.04.0304
Korrani, Z. S., Ibrahim, W. A., Nodeh, H. R., Aboul-Enein, H. Y., and Sanagi, M. M. (2016). Simultaneous preconcentration of polar and non-polar organophosphorus pesticides from water samples by using a new sorbent based on mesoporous silica. J. Sep. Sci. 39, 1144–1151. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201500896
Kour, D., Kaur, T., Devi, R., Yadav, A., Singh, M., Joshi, D., et al. (2021). Beneficial microbiomes for bioremediation of diverse contaminated environments for environmental sustainability: present status and future challenges. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 28, 24917–24939. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13252-7
Kukarram, M., Khan, M. M. A., Kurjak, D., Lux, A., and Corpas, F. J. (2023). Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) restore photosynthesis and essential oil content by upgrading enzymatic antioxidant metabolism in lemongrass (Cymbopogon flexuosus) under salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 14:1116769. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1116769
Kumar, N., Shah, V., and Walker, V. K. (2012). Influence of a nanoparticle mixture on an arctic soil community. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 31, 131–135. doi: 10.1002/etc.721
Kuzma, J. (2007). Moving forward responsibly: oversight for the nanotechnology-biology interface. J. Nanopart. Res. 9, 165–182. doi: 10.1007/s11051-006-9151-0
Kwak, S. Y., Giraldo, J. P., Wong, M. H., Koman, V. B., Lew, T. T., Ell, J., et al. (2017). nanobionic light-emitting plant. Nano Lett. 17, 7951–7961. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b04369
Le, V. N., Rui, Y., Gui, X., Li, X., Liu, S., Han, Y., et al. (2014). Uptake, transport, distribution, and bio-effects of SiO2 nanoparticles in Bt-transgenic cotton. J. Nanobiotechnol. 12:50. doi: 10.1186/s12951-014-0050-8
Li, Y., Xi, K., Liu, X., Han, S., Han, X., Li, G., et al. (2023). Silica nanoparticles promote wheat growth by mediating hormones and sugar metabolism. J. Nano. 21:2. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01753-7
Li, Y., Zhu, N., Liang, X., Bai, X., Zheng, L., Zhao, J., et al. (2020). Silica nanoparticles alleviate mercury toxicity via immobilization and inactivation of Hg (ii) in soybean (Glycine max). Environ. Sci. Nano. 7, 1807–1817. doi: 10.1039/D0EN00091D
Liang, Y., Chen, Q., Liu, Q., Zhang, W., and Ding, R. (2003). Exogenous silicon (Si) increases antioxidant enzyme activity and reduces lipid peroxidation in roots of salt-stressed barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Plant Physiol. 160, 1157–1164. doi: 10.1078/0176-1617-01065
Liang, Y., Gao, Y., Wang, W., Dong, H., Tang, R., Yang, J., et al. (2020). Fabrication of smart stimuli-responsive mesoporous organosilica nano-vehicles for targeted pesticide delivery. J. Hazard. Mater. 389:122075. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122075
Liang, Y., Sun, W., Zhu, Y. G., and Christie, P. (2007). Mechanisms of silicon-mediated alleviation of abiotic stresses in higher plants: a review. Environ. Pollut. 147, 422–428. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2006.06.008
Liu, P., Yin, L., Wang, S., Zhang, M., Deng, X., Zhang, S., et al. (2015). Enhanced root hydraulic conductance by aquaporin regulation accounts for silicon alleviated salt-induced osmotic stress in Sorghum bicolor L. Environ. Exp. Bot. 111, 42–51. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2014.10.006
Liu, X., Li, Q., Li, Y., Guan, G., and Chen, S. (2019). Paenibacillus strains with nitrogen fixation and multiple beneficial properties for promoting plant growth. PeerJ 7:e7445. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7445
Lu, P., and Hsieh, Y. L. (2012). Highly pure amorphous silica nano-disks from rice straw. Powder Technol. 225, 149–155. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.04.002
Luyckx, M., Hausman, J. F., Lutts, S., and Guerriero, G. (2017). Silicon and plants: current knowledge and technological perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 8:411. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00411
Ma, X., Geiser-Lee, J., Deng, Y., and Kolmakov, A. (2010). Interactions between engineered nanoparticles (ENPs) and plants: phytotoxicity, uptake, and accumulation. Sci. Total Environ. 408, 3053–3061. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.03.031
Mackevica, A., and Foss Hansen, S. (2016). Release of nanomaterials from solid nanocomposites and consumer exposure assessment - a forward-looking review. Nanotoxicology 10, 641–653. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2015.1132346
Magda, S., and Hussein, M. (2016). Determinations of the effect of using silica gel and nano-silica gel against Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in tomato fields. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 8, 506–512. Available online at: https://www.jocpr.com/articles/determinations-of-the-effect-of-using-silca-gel-and-nanosilica-gel-against-tuta-absoluta-lepidoptera-gelechiidae-in-toma.pdf
Mahawar, L., Ramasamy, K. P., Suhel, M., Prasad, S. M., Živčák, M., Brestic, M., et al. (2023). Silicon nanoparticles: comprehensive review on biogenic synthesis and applications in agriculture. Environ. Res. 232:116292. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116292
Mathur, P., and Roy, S. (2020). Nanosilica facilitates silica uptake, growth and stress tolerance in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 157, 114–127. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.10.011
McGee, C., Storey, S., Clipson, N., and Doyle, E. (2017). Soil microbial community responses to contamination with silver, aluminium oxide and silicon dioxide nanoparticles. Ecotoxicology 26, 449–458. doi: 10.1007/s10646-017-1776-5
Michel, K., Scheel, J., Karsten, S., Stelter, N., and Wind, T. (2013). Risk assessment of amorphous silicon dioxide nanoparticles in a glass cleaner formulation. Nanotoxicology 7, 974–988. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2012.689881
Mohanty, S., Nayak, A. K., Swain, C. K., Dhal, B., Kumar, A., Tripathi, R., et al. (2020). Silicon enhances yield and nitrogen use efficiency of tropical lowland rice. Agron. J. 112, 758–771. doi: 10.1002/agj2.20087
Mohd, N. K., Wee, N. N. A., and Azmi, A. A. (2017). Green synthesis of silica nanoparticles using sugarcane bagasse. AIP Conf. Proc. 1885:020123. doi: 10.1063/1.5002317
Munns, R., and Tester, M. (2008). Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 59, 651–681. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Naderi, M. R., and Danesh-Shahraki, A. (2013). Nanofertilizers and their roles in sustainable agriculture. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 19, 2229–2232. Available online at: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20133304426
Naguib, D. M., and Abdalla, H. (2019). Metabolic status during germination of nano silica primed Zea mays seeds under salinity stress. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 22, 415–423. doi: 10.1007/s12892-019-0168-0
Namjoyan, S., Sorooshzadeh, A., Rajabi, A., and Aghaalikhani, M. (2020). Nano silicon protects sugar beet plants against water deficit stress by improving the antioxidant systems and compatible solutes. Acta Physiol. Plant 42:157. doi: 10.1007/s11738-020-03137-6
O'Farrell, N., Houlton, A., and Horrocks, B. R. (2006). Silicon nanoparticles: applications in cell biology and medicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 1, 451–472. doi: 10.2147/nano.2006.1.4.451
Otero-González, L., Field, J. A., Calderon, I. A., Aspinwall, C. A., Shadman, F., Zeng, C., et al. (2015). Fate of fluorescent core-shell silica nanoparticles during simulated secondary wastewater treatment. Water Res. 77, 170–178. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2015.03.021
Pan, W., Zhang, H.-J., Zhang, Y.-F., Wang, M., Tsui, M. T.-K., Yang, L., et al. (2023). Silica nanoparticle accumulation in plants: current state and future perspectives. Nanoscale 15, 15079–15091. doi: 10.1039/D3NR02221H
Paparella, S., Araújo, S., Rossi, G., Wijayasinghe, M., Carbonera, D., Balestrazzi, A., et al. (2015). Seed priming: state of the art and new perspectives. Plant Cell Rep. 34, 1281–1293. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1784-y
Parisi, C., Vigani, M., and Rodríguez-Cerezo, E. (2015). Agricultural nanotechnologies: what are the current possibilities? Nano Today 10, 124–127. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2014.09.009
Prado, A. G. S., Moura, A. O., and Nunes, A. R. (2011). Nanosized silica modified with carboxylic acid as support for controlled release of herbicides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 59, 8847–8852. doi: 10.1021/jf202509g
Quelé, L. N. S., de Matos, M., de Lima, G. G., Brugnari, T., Ribeiro, C. S. P., Pedro, A. C., et al. (2024). Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of photodegraded amorphous curcumin on silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 8, 4384–4396. doi: 10.1021/acsanm.4c05159
Rai, M., and Ingle, A. (2012). Role of nanotechnology in agriculture with special reference to management of insect pests. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 94, 287–293. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-3969-4
Rai-Kalal, P., Tomar, R. S., and Jajoo, A. (2021). Seed nanopriming by silicon oxide improves drought stress alleviation potential in wheat plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 48, 905–915. doi: 10.1071/FP21079
Rangaraj, S., Gopalu, K., Rathinam, Y., Periasamy, P., Venkatachalam, R., Narayanasamy, K., et al. (2014). Effect of silica nanoparticles on microbial biomass and silica availability in maize rhizosphere. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 61, 668–675. doi: 10.1002/bab.1191
Rao, G. B., and Susmitha, P. (2017). Silicon uptake, transportation, and accumulation in rice. J. Pharm. Phytochem. 6, 290−293. Available online at: https://www.phytojournal.com/archives/2017.v6.i6.2091/silicon-uptake-transportation-and-accumulation-in-rice
Rashad, Y. M., El-Sharkawy, H. H. A., Belal, B. E. A., Abdel Razik, E. S., and Galilah, D. A. (2021). Silica nanoparticles as a probable anti-oomycete compound against downy mildew, and yield and quality enhancer in grapevines: field evaluation, molecular, physiological, ultrastructural, and toxicity investigations. Front. Plant Sci. 12:763365. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.763365
Rastogi, A., Zivcak, M., Sytar, O., Kalaji, H. M., He, X., Mbarki, S., et al. (2017). Impact of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on plants: a critical review. Front. Chem. 5:78. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2017.00078
Rastogi, R., Tripathi, D. K., Yadav, S., Chauhan, D. K., Živčák, M., Ghorbanpour, M., et al. (2019). Application of silicon nanoparticles in agriculture. 3 Biotech 9, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1626-7
Raza, M. A. S., Zulfiqar, B., Iqbal, R., Muzamil, M. N., Aslam, M. U., Muhammad, F., et al. (2023). Habib-ur-Rahman M. Morpho-physiological and biochemical response of wheat to various treatments of silicon nanoparticles under drought stress conditions. Sci. Rep. 13:2700. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29784-6
Reynolds, O. L., Keeping, M. G., and Meyer, J. H. (2009). Silicon-augmented resistance of plants to herbivorous insects: a review. Ann. Appl. Biol. 155, 171–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7348.2009.00348.x
Riaz, M., Kamran, M., Fahad, S., and Wang, X. (2022). Nano-silicon mediated alleviation of Cd toxicity by cell wall adsorption and antioxidant defence system in rice seedlings. Plant Soil. 486, 103–117. doi: 10.1007/s11104-022-05588-x
Roduner, E. (2006). Size matters: why nanomaterials are different. Chem. Soc. Rev. 35, 583–592. doi: 10.1039/b502142c
Rouhani, M., Samih, M., and Kalantari, S. (2013). Insecticidal effect of silica and silver nanoparticles on the cowpea seed beetle, Callosobruchus maculatus F. (Col.: Bruchidae). J. Entomol. Res. 4, 297–305. Available online at: https://share.google/F8sWcuCs8NUSwCj5X
Sabir, A., Yazar, K., Sabir, F., Kara, Z., Yazici, M. A., Goksu, N., et al. (2014). Vine growth, yield, berry quality attributes, and leaf nutrient content of grapevines as influenced by seaweed extract (Ascophyllum nodosum) and nanosize fertilizer pulverizations. Sci. Hortic. 175, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2014.05.021
Saha, A., Mishra, P., Biswas, G., and Bhakta, S. (2024). Greening the pathways: a comprehensive review of sustainable synthesis strategies for silica nanoparticles and their diverse applications. RSC Adv. 14, 11197–11216. doi: 10.1039/D4RA01047G
Samuels, A. L., Glass, A. D. M., Ehret, D. L., and Menzies, J. G. (1993). The effects of silicon supplementation on cucumber fruit: changes in surface characteristics. Ann. Bot. 72, 433–440. doi: 10.1006/anbo.1993.1129
Saw, G., Nagdev, P., Jeer, M., and Murali-Baskaran, R. K. (2023). Silica nanoparticles mediated insect pest management. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 194:105524. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2023.105524
Schaller, J., Wu, B., Amelung, W., Hu, Z., Stein, M., Lehndorff, E., et al. (2022). Silicon as a potential limiting factor for phosphorus availability in paddy soils. Sci. Rep. 12:16329. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-20805-4
Schwab, F., Zhai, G., Kern, M., Turner, A., Schnoor, J. L., Wiesner, M. R., et al. (2016). Barriers, pathways and processes for uptake, translocation and accumulation of nanomaterials in plants–critical review. Nanotoxicology 10, 257–278. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2015.1048326
Selvan, S. S., Wahid, A., Patel, A., Kumar, V., and Sahu, P. (2021). Challenges in Indian agriculture. Agric. Rev. 42, 465–469. doi: 10.18805/ag.R-2103
Siddiqui, M. H., and Al-Whaibi, M. H. (2014). Role of nano-SiO2 in germination of tomato (Lycopersicum esculentum seeds Mill.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 21, 13–17. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2013.04.005
Slomberg, D. L., and Schoenfisch, M. H. (2012). Silica nanoparticle phytotoxicity to Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 10247–10254. doi: 10.1021/es300949f
Song, J. C., Jiang, L. J., and Jameson, P. E. (2012). Co-ordinate regulation of cytokinin gene family members during fag leaf and reproductive development in wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 12:78. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-78
Strout, G., Russell, S. D., Pulsifer, D. P., Erten, S., Lakhtakia, A., Lee, D. W., et al. (2013). Silica nanoparticles aid in structural leaf coloration in the Malaysian tropical rainforest understorey herb Mapania caudata. Ann. Bot. 112, 1141–1148. doi: 10.1093/aob/mct172
Sun, D., Hussain, H. I., Yi, Z., Rookes, J. E., Kong, L., Cahill, D. M., et al. (2016). Mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhance seedling growth and photosynthesis in wheat and lupin. Chemosphere 152, 81–91. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.096
Sun, D., Hussain, H. I., Yi, Z., Siegele, R., Cresswell, T., Kong, L., et al. (2014). Uptake and cellular distribution, in four plant species, of fluorescently labeled mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Plant Cell Rep. 33, 1389–1402. doi: 10.1007/s00299-014-1624-5
Suriyaprabha, R., Karunakaran, G., Yuvakkumar, R., Rajendran, V., and Kannan, N. (2014). Foliar application of silica nanoparticles on the phytochemical responses of maize (Zea mays L.) and its toxicological behavior. Synthesis Reactivity Inorg. Metal Org. Nano Metal Chem. 44, 1128–1131. doi: 10.1080/15533174.2013.799197
Surya, K., Ramanujam, K., Saitheja, V., Sanbagavalli, S., Senthil Kumar, G., Parameswari, E., et al. (2025). Polyhalite as a next generation chloride free multi-nutrient fertilizer for sustainable agriculture – review. J. Plant Nutr. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2025.2523539
Surya, K., Sanbagavalli, S., Somasundaram, E., Renukadevi, A., and Panneerselvam, S. (2022). Effect of potassium and foliar nutrition on yield and economics of kodo millet under irrigated condition. Biol. Forum Int. J. 14, 42–46. Available online at: https://shorturl.at/RRRSX
Thabet, A. F., Boraei, H. A., Galal, O. A., El-Samahy, M. F. M., Mousa, K. M., Zhang, Y. Z., et al. (2021). Silica nanoparticles as pesticide against insects of different feeding types and their non-target attraction of predators. Sci. Rep. 11:14484. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93518-9
Theng, B. K., and Yuan, G. (2008). Nanoparticles in the soil environment. Elements 4, 395–399. doi: 10.2113/gselements.4.6.395
Tian, L., Shen, J., Sun, G., Wang, B., Ji, R., Zhao, L., et al. (2020). Foliar application of SiO2 nanoparticles alters soil metabolite profiles and microbial community composition in the Pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) rhizosphere grown in contaminated mine soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 54, 13137–13146. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c03767
Torney, F., Trewyn, B. G., Lin, V. S. Y., and Wang, K. (2007). Mesoporous silica nanoparticles deliver DNA and chemicals into plants. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 295–300. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.108
Tripathi, D. K., Singh, S., Singh, V. P., Prasad, S. M., Dubey, N. K., Chauhan, D. K., et al. (2017). Silicon nanoparticles more effectively alleviated UV-B stress than silicon in wheat (Triticum aestivum) seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 110, 70–81. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.06.026
Tripathi, D. K., Singh, V. P., Prasad, S. M., Chauhan, D. K., and Dubey, N. K. (2015). Silicon nanoparticles (SiNp) alleviate chromium (VI) phytotoxicity in Pisum sativum (L.) seedlings. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 96, 189–198. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.07.026
Tripathy, B. C., and Oelmüller, R. (2012). Reactive oxygen species generation and signaling in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 7, 1621–1633. doi: 10.4161/psb.22455
Tubana, B. S., Babu, T., and Datnoff, L. E. (2016). A review of silicon in soils and plants and its role in US agriculture: history and future perspectives. Soil Sci. 181, 393–411. doi: 10.1097/SS.0000000000000179
Verma, D., Patel, S., and Kushwah, K. (2021). Effects of nanoparticles on seed germination, growth, phytotoxicity, and crop improvement. Agric. Rev. 42, 1–11. doi: 10.18805/ag.R-1964
Wang, L., Ning, C., Pan, T., and Cai, K. (2022). Role of silica nanoparticles in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:1947. doi: 10.3390/ijms23041947
Wang, L., Pan, T., Li, S., Wang, Y., White, J. C., Xing, B., et al. (2025). Silica nanoparticles enhance plant disease resistance by modulating the endophyte community structure in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) roots. Environ. Sci. Nano. 12, 1401–1413. doi: 10.1039/D4EN00511B
Wang, P., Lombi, E., Zhao, F. J., and Kopittke, P. M. (2016). Nanotechnology: a new opportunity in plant sciences. Trends Plant Sci. 21, 699–712. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2016.04.005
Wang, S., Wang, F., and Gao, S. (2015). Foliar application with nano-silicon alleviates Cd toxicity in rice seedlings. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 22, 2837–2845. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3525-0
Wang, W. X., Martin, J. C., Fan, X. T., Han, A. J., Luo, Z. P., Sun, L. Y., et al. (2012). Silica nanoparticles and frameworks from rice husk biomass. ACS Appl. Mater. Interf. 4, 977–981. doi: 10.1021/am201619u
Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Zhan, W., Zheng, K., Lian, M., Zhang, C., et al. (2020). Long-term stabilization of Cd in agricultural soil using mercapto-functionalized nano-silica (MPTS/nano-silica): a three-year field study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 197:110600. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110600
Wang, Y., and Nowack, B. (2018). Environmental risk assessment of engineered nano-SiO2, nano iron oxides, nano-CeO2, nano-Al2O3, and quantum dots. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 37, 1387–1395. doi: 10.1002/etc.4080
Wang, Z., Zhu, W., Chen, F., Yue, L., Ding, Y., Xu, H., et al. (2021). Nanosilicon enhances maize resistance against oriental armyworm (Mythimna separata) by activating the biosynthesis of chemical defences. Sci. Total Environ. 778:146378. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146378
Wanyika, H., Gatebe, E., Kioni, P., Tang, Z., and Gao, Y. (2012). Mesoporous silica nanoparticles carrier for urea: potential applications in agrochemical delivery systems. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 12, 2221–2228. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2012.5801
Wei, C., Zhang, Y., Guo, J., Han, B., Yang, X., Yuan, J., et al. (2010). Effects of silica nanoparticles on growth and photosynthetic pigment contents of Scenedesmus obliquus. J. Environ. Sci. 22, 155–160. doi: 10.1016/S1001-0742(09)60087-5
Willer, H., and Lernoud, J. (2017). Organic Agriculture Worldwide 2017: Current Statistics. Research Institute of Organic Agriculture (FiBL). Available online at: www.fibl.org (accessed December 1, 2024).
Xu, C. L., Shan, Y. P., Bilal, M., Xu, B., Cao, L. D., Huang, Q. L., et al. (2020). Copper ions chelated mesoporous silica nanoparticles via dopamine chemistry for controlled pesticide release regulated by coordination bonding. Chem. Eng. J. 395:13. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125093
Yan, G., Huang, Q., Zhao, S., Xu, Y., He, Y., Nikolic, M., et al. (2024). Silicon nanoparticles in sustainable agriculture: synthesis, absorption, and plant stress alleviation. Front. Plant Sci. 15:1393458. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1393458
Yan, G., Jin, H., Yin, C., Hua, Y., Huang, Q., Zhou, G., et al. (2023). Comparative effects of silicon and silicon nanoparticles on the antioxidant system and cadmium uptake in tomato under cadmium stress. Sci. Total Environ. 904:166819. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166819
Yan, G. C., Nikolic, M., Ye, M. J., Xiao, Z. X., and Liang, Y. C. (2018). Silicon acquisition and accumulation in plants and its significance for agriculture. J. Integr. Agric. 17, 2138–2150. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(18)62037-4
Yang, S. A., Choi, S., Jeon, S. M., and Yu, J. (2018). Silica nanoparticle stability in biological media revisited. Sci. Rep. 8:185. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18502-8
Yang, X., Pan, H., Wang, P., and Zhao, F. J. (2017). Particle-specific toxicity and bioavailability of cerium oxide (CeO2) nanoparticles to Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Hazard. Mater. 322, 292–300. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.03.054
Yang, Y., Xu, Y., Yang, Y., Yang, H., Yuan, H., Huang, Y., et al. (2016). Laccase immobilized on mesoporous SiO2 and its use for degradation of chlorophenol pesticides. Russ J. Phys. Chem. A 90, 2044–2054. doi: 10.1134/S0036024416100307
Yassen, A., Abdallah, E., Gaballah, M., and Zaghloul, S. (2017). Role of silicon dioxide nano fertilizer in mitigating salt stress on growth, yield, and chemical composition of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Int. J. Agric. Res. 22, 130–135. doi: 10.3923/ijar.2017.130.135
Yeats, T. H., and Rose, J. K. C. (2013). The formation and function of plant cuticles. Plant Physiol. 163, 5–20. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.222737
Yin, J., Tian, J., Li, G., et al. (2020). Carbohydrate, phytohormone, and associated transcriptome changes during storage root formation in alligatorweed (Alternanthera philoxeroides). Weed Sci. 68, 382–395. doi: 10.1017/wsc.2020.37
Younis, A., Khattab, H., and Emam, M. (2020). Impacts of silicon and silicon nanoparticles on leaf ultrastructure and TaPIP1 and TaNIP2 gene expressions in heat stressed wheat seedlings. Biol. Plant 64, 343–352. doi: 10.32615/bp.2020.030
Yuvaraj, M., Cyriac, J., Priya, R. S., Anitha, R., Jagathjothi, N., Subramanian, K. S., et al. (2023). Silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs): challenges and perspectives for sustainable agriculture. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 128:102161. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2023.102161
Zahedi, S. M., Hosseini, M. S., Fahadi Hoveizeh, N., Kadkhodaei, S., and Vaculík, M. (2023). Comparative morphological, physiological and molecular analyses of drought stressed strawberry plants affected by SiO2 and SiO2-NPs foliar spray. Sci. Hortic. 309:111686. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111686
Zargar, S. M., Mahajan, R., Bhat, J. A., Nazir, M., and Deshmukh, R. (2019). Role of silicon in plant stress tolerance: opportunities to achieve a sustainable cropping system. 3 Biotech 9:73. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1613-z
Zellner, W., Tubaña, B., Rodrigues, F. A., and Datnoff, L. E. (2021). Silicon's role in plant stress reduction and why this element is not used routinely for managing plant health. Plant Dis. 105, 2033–2049. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-20-1797-FE
Zhang, L., Yan, C., Guo, Q., Zhang, J., and Ruiz-Menjivar, J. (2018). The impact of agricultural chemical inputs on environment: global evidence from informetrics analysis and visualization. Int. J. Low Carbon Technol. 13, 338–352. doi: 10.1093/ijlct/cty039
Zhao, L., Lu, L., Wang, A., Zhang, H., Huang, M., Wu, H., et al. (2020). Nano-biotechnology in agriculture: use of nanomaterials to promote plant growth and stress tolerance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 68, 1935–1947. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b06615
Zhao, P. Y., Yuan, W. L., Xu, C. L., Li, F. M., Cao, L. D., Huang, Q. L., et al. (2018). Enhancement of spirotetramat transfer in cucumber plant using mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 11592–11600. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04415
Keywords: SiNPs, biotic and abiotic stresses, nutrient use efficiency (NUE), environmental safety, sustainable agriculture
Citation: Surya K, Sornam G, Asritha M, Paul RAI, Easwaran C, Sri BK, Sathasivam B, Saitheja V, Narayanan J, Ramalingam SP, Parameswari E, Ponnusamy J and Ramanujam K (2025) Unraveling approaches of silica nanoparticles for next-generation in agricultural sustainability. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 9:1677788. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2025.1677788
Received: 01 August 2025; Accepted: 07 October 2025;
Published: 22 October 2025.
Edited by:
Amitava Rakshit, Banaras Hindu University, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Surya, Sornam, Asritha, Paul, Easwaran, Sri, Sathasivam, Saitheja, Narayanan, Ramalingam, Parameswari, Ponnusamy and Ramanujam. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Krishnan Ramanujam, YWdyaWtyaXNoQHRuYXUuYWMuaW4=
 Konappan Surya
Konappan Surya Gowtham Sornam2
Gowtham Sornam2 Ratchagar Arockia Infant Paul
Ratchagar Arockia Infant Paul Vaddi Saitheja
Vaddi Saitheja Ettiyagounder Parameswari
Ettiyagounder Parameswari Janaki Ponnusamy
Janaki Ponnusamy Krishnan Ramanujam
Krishnan Ramanujam