- 1Department of Geography, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Brussels, Belgium
- 2School of Agriculture and Environmental Sciences, Mountains of the Moon University, Fort Portal, Uganda
Efforts in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) are widely geared towards integrating indigenous knowledge and science. Several conceptual frameworks have thus evolved towards co-creating knowledge and co-designing DRR measures from the standpoint of the communities-at-risk. This is claimed to foster optimization and sustainability of measures. This study tests the effectiveness of this standpoint argument based on the case of floods in the Rwenzori, western Uganda, where a mismatch is noted between research, policy, and action. A protocol was developed to stimulate dialogue on knowledge co-creation and co-designing of DRR measures among participants from three stakeholder groups: scientists, policymakers, and communities-at-risk. Beyond convergence on some measures among participants, equitable deliberations were observed among the different stakeholders. This enabled three processes: coalescing some of the proposed measures, the emergence of hybrid worldviews, and co-design of alternative options. The co-designed options fall within the contemporary conceptualization of nature-based solutions and sustainability. This meant that they are adoptable and optimizable over time by communities-at-risk. This constructive knowledge integration and co-design of DRR options were favored by three attributes: coalescing overlaps in theorizations of processes, embracing diversity in ontological values, and self-critiques among policymakers. Lessons are drawn on how these attributes facilitate bridging gaps between science, policy, and action in DRR.
1 Introduction
International protocols, driven by the UN strategy for Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR), stress the need to integrate indigenous knowledge with science to suitably tackled disaster risk. The underlying reason is that indigenous knowledge is not only socio-culturally produced by indigenous people—or Communities-at-Risk (CAR). It also has two essential attributes. Firstly, it does provide socio-epistemic insights on the context-specificity of disaster risk (Gaillard and Mercer, 2013; UNISDR, 2015; Bwambale et al., 2021). Secondly, it ensures acceptable and suitable DRR options or interventions by giving weight to community priorities (Mathew et al., 2012; Bwambale et al., 2018). These attributes continue to underscore the indispensable role of indigenous perspectives and practices in DRR. To benefit from and integrate these attributes, scientists and DRR institutions are urged to systematically interact with indigenous people (Gaillard and Mercer, 2013; Ayeb-Karlsson et al., 2019).
The matter of interacting with indigenous people to benefit from indigenous knowledge and to integrate it with scientific DRR has long been investigated. Synthetizing earlier frameworks, Gaillard and Mercer (2013) proposed one consensual approach for integrating bottom-up and top-down actions, local and scientific knowledge, and an array of stakeholders. Re-analyzing the previous frameworks and those post Gaillard and Mercer (2013) and Bwambale et al. (2020) argue that these approaches largely focused on enabling CAR to participate at the content level: i.e., on measures developed by top-down stakeholders (i.e., scientists and policymakers). This would prompt a simplistic commentary role on the part of the CAR; yet little is considered on the salient socio-epistemic processes from the theorization of systematic or repetitive observations among CAR (see also Briggs, 2013). Bearing this gap in mind, the integrated knowledge approach has been extended under the hylomorphic framework for integrating knowledge for commensurable DRR (Bwambale et al., 2020). For consistency, this extended integrated framework is, hereafter, collectively termed the hylomorphic DRR framework.
In this hylomorphic DRR framework, the challenge with DRR is considered as socio-epistemic in the primary sense, and policy in the secondary sense: scientists continue to neglect pragmatic empiricist experiences from CAR and produce recommendations that are disconnected from the real-life context (see also Alexander, 1997; Gaillard and Mercer, 2013). It is these recommendations that are picked by policymakers and implementors. Thus, the hylomorphic DRR framework proposes that CAR are involved not only in the content, but also, in the process leading to that content. It emphasizes developing measures from the hybrid knowledge theorization as well as from the standpoint of the CAR (Bwambale et al., 2020). Moreover, debates in this line have led to the coining of the concept of interscience, i.e., integrative science (Van Opstal and Hugé, 2013): it aims to foster co-production of knowledge and a holistic approach to the understanding of—and dealing with—reality (see also Sorrell, 2013). The concept of interscience applies to the hylomorphic DRR framework since it aims at coalescing socio-epistemic processes to better understand natural hazards and tackle their consequent disasters through multi-stakeholder dialogue.
Questions remain on the effectiveness of this hylomorphic DRR framework in practice since it is yet to be operationalized in enabling the development of suitable DRR measures. This study thus attempts to test this extended knowledge integration framework in a specific context to shed light on its effectiveness. It examines the extent to and/or ways through which it can facilitate the development of suitable DRR options or compromise solutions among diverse stakes. It is based on the specific case of flood DRR in the Rwenzori.
2 Theoretical Framework
The core theoretical perspective upon which this case study is built is the hylomorphic DRR framework as proposed in Bwambale et al. (2020). Insofar as this framework emphasizes aligning science with significant others, especially culture as well as indigenous knowledge, it is a standpoint perspective. Standpoint theorists highlight the potential for indigenous perspectives to expose biases in scientific knowledge. Strong objectivity is thus possible by synthesizing partial overlaps between indigenous and scientific knowledge, weaved and grasped from the standpoint of the indigenous community (Wylie, 2003; Ludwig, 2016, Ludwig, 2017).
In the perspective of the hylomorphic DRR framework, commensurable DRR is possible if DRR strategies are developed from indigenous standpoints (Bwambale et al., 2020). Here, one of the specific arguments is the claim that the neo-rationalism of abstract scientific recommendations contrasts with the neo-empiricism of societal values. Unlike the former, the latter, being grounded in indigenous experiences, leads to pragmatic and concrete solutions that consider the sociocultural as well as livelihood needs of the CAR. Additionally, the neo-empiricist aspects are considered as drivers of action as they are part of the way of life of the CAR. In this sense, it is further argued that the sustainable implementation and continued optimization of any measures be determined by how related or distanced the CAR are from the established measure(s). Measures should thus be founded at the standpoint of the CAR through recognizing the substantial unity of lived experience and intelligible scientific understanding of disaster risk. Historical indigenous perspectives and practices should thus be vivified or systematized to expose their explanatory powers. Related global (rationalist) scientific understanding about disaster risk should be inculturated to find a relevant “receptor” to weave into the local socio-cultural context. The “receptor” would be offered by the systematized indigenous knowledge (Figure 1).
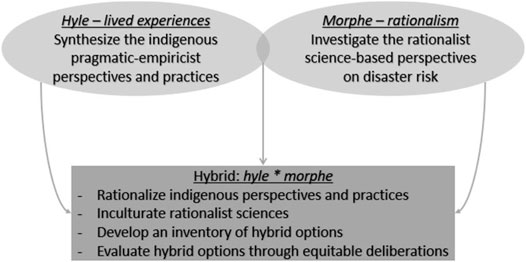
FIGURE 1. Graphic summary of the hylomorphic DRR framework—Adapted from Bwambale et al. (2020).
At the hybrid level, overlapping ontologies can be coalesced for a specific context as highlighted in related literature (Van Opstal and Hugé, 2013; Ludwig, 2016, Ludwig, 2017; Ludwig and El-Hani, 2020). It is thus possible to identify lived experiences upon which specific scientific logic can be applied to provide an intelligible explanation of disaster risk. In the perspective of the hylomorphic DRR framework, providing intelligibility to lived experiences individuates the disaster risk science to specific contexts. Doing so, the substantial unity of the rational and the lived reality is achieved, leading to hybrid (context-specific) knowledge theorization that can lead to suitable or adapted DRR options. Over time, this can erase the line between science and indigenous knowledge as well as CAR, thus enabling tacit optimization of the developed DRR options (Bwambale et al., 2020).
With these arguments, the hylomorphic DRR framework contributes to three key principles of the suitability of DRR measures (see Bwambale et al., 2020): sustainability, adaptability, and compatibility. Sustainability is viewed in the sense that a measure is designed in such a way that it can locally be maintained and optimized over time to sustainably reduce the recurring disaster. This is possible insofar as the measures align with the culture and worldviews as well as the livelihood of the CAR. Adaptability and compatibility are jointly considered in the sense that a measure can be adjusted to fit into the local culture: measures are most likely to be optimized if they fit within the historical worldviews of the CAR (see also Van Opstal and Hugé, 2013). These elements are possible to mobilize and advocate to negotiate and reach consensus among key stakeholders without any dominating the integration or the process itself. These stakeholders are the top-down actors (scientists and politicians or policymakers) who propel the (neo-)rationalist discourse and CAR who hold discourses based on lived experiences (see also Gaillard and Mercer, 2013).
The assumption in this study is that suitable or compromise DRR solutions will be co-created when lived experiences and rationalist science are hybridized and deliberated on by various stakeholders. Attention is thus paid to what can be learnt, i.e., co-creation or interweaving of knowledge and co-design of DRR options from the interactions of top-down stakeholders with CAR (Figure 1). This allows for analysis of several elements: who influences who in the dialogue, how and what informs the influences as well as the context-specific hybrid knowledge and DRR options or strategies that result. The arguments used by different actors in the dialogue are crucial for optimizing this framework and propose ways in which it can best pave the way to develop commensurable DRR strategies.
3 Methodology: A Case Study Approach
3.1 Study Setting in the Rwenzori Region
This study focuses on the case of flood DRR in the Rwenzori region, Western Uganda. A detailed description of the Rwenzori regarding natural hazards and flood disasters can be found in Jacobs et al. (2016a)—see also Eggermont et al. (2009). The Rwenzori is a relevant case study as it is a region where multiple natural hazards co-occur, leading to small but frequent disasters (Jacobs et al., 2016b). Yet there is a mismatch between science and practice that detracts effective DRR (Maes et al., 2018). The Rwenzori is also a region with an established cultural approach and indigenous practices to disaster, which generates resistance to DRR measures imposed by top-down policymakers without consideration for the local context. Moreover, the cultural and indigenous practices, as well as perspectives, are not incorporated in the disaster policy and interventions (Bwambale et al., 2018, Bwambale et al., 2021).
Two additional factors make the Rwenzori interesting for this study. First, it is a region where a recent study highlights the perceived importance of the acceptability of DRR measures by the CAR (Maes et al., 2019). Second, it is also a region in a context of a least developed economy, with limited resources to implement and sustain highly specialized technologies for DRR. Hence, the conceptualization of the hylomorphic DRR framework is relevant, to identify what determines the design and consensus-building about the suitable DRR options.
3.2 Synthesizing the Inventory
The point of departure of the implementation of the hylomorphic DRR framework is an in-depth investigation of the existing indigenous and scientific knowledge in the study area. This enabled the development of a composite inventory of potential DRR measures recommended by the different ontologies as a basis for deliberations. Based on extensive ethnographic field surveys, indigenous knowledge was investigated in terms of its epistemic nature as well as its understanding and tackling of disaster risk. Attention was paid to reconstructing the historical trajectory of the indigenous perspectives and practices as recommended in Bwambale et al. (2020). In parallel, the state-of-the-art scientific DRR strategies recommended in the study area were also inventoried based on a critical review of secondary data and FGDs. These studies were conducted between late 2018 and 2020 along the three most flood-prone watersheds of South-West Rwenzori (Figure 2).

FIGURE 2. Study area and characteristics in Kasese district, southwestern Rwenzori region. All highlighted are sub-county level administrative areas.
These studies led to a synthesis of 16 key DRR measures. To highlight the factors influencing negotiations, some high-tech DRR measures used in other regions of the globe but known to not be suitable to the Rwenzori context were also included in the inventory: flood-tolerant bridges, weather monitoring system, and dredging. This led to a total of 19 measures, touching areas of Ecological and Hydrological (Eco-hydrological) System Wellbeing, Livelihoods, and Economic Standards, Vulnerability and Exposure Reduction, and Sociopolitical Stability and Responsibility (Supplementary Appendix SA).
3.3 Defining and Administration of the Protocol
A protocol was defined to enable evaluations of as well as test co-development of convergence around the 19 different DRR measures by different stakeholders. Notably, only the measures (and not their themes nor their sources) were presented in the protocol.
Participants in this evaluation exercise were drawn from three groups of stakeholders framed along the lines of Circles of Dialogue. Circles of Dialogue offshoot from the Socratic dialogue which is acknowledged as a method of inquiry. This method is a systematic examination into participants’ assumptions, preconceived opinions, principles, and values enabling them to become aware of, and communicate about, “underlying” values. Through this method, participants can arrive at a better understanding of their own values as well as the values of the “Others” (Wortel and Verweij, 2008; Candiotto, 2017; Thomas and Goering, 2018).
In the perspective of DRR, Circles of Dialogue are basically the three key categories that are recognized to have a stake in DRR as well as a mismatch: the CAR, policymakers, and scientists (Gaillard and Mercer, 2013). These categories are, in this case study, respectively represented by: the indigenous practitioners and specialists on flood DRR, representing CAR; the policymakers, i.e., politicians charged with the responsibility of developing and approving policies on DRR under the governmental platform called Disaster Management Committee; and the scientists as well as technocrats or scientific advisers, who inform the policy development and DRR implementation (Maes et al., 2017). The selection targeting representatives knowledgeable of the DRR perspectives within their circles was conducted through a triangulated institutional stakeholder analysis following the methods described in Maes et al. (2019). For the scientists, attention was paid to identifying researchers familiar with the Rwenzori as well as scientists holding technical positions in the district local government. Researchers involved in scientific projects on disasters in Uganda were included. Policymakers and CAR participants were drawn from the cultural and political jurisdictions along the three frequently flooding rivers (Figure 2). The protocol described hereafter was administered to the participants in February 2021 through workshops along these watersheds: Nyamughasana (Workshop 1), Mubuku (Workshop 2), and Nyamwamba (Workshop 3).
For exhaustive deliberations, participants were limited to 15, with equal representation from each of the three Circles of Dialogue per watershed. In each workshop, the participants first individually scored each item of the 19 measures. A DRR measure was defined as suitable (+1) if it would be efficient, adapted, feasible: one that can easily be implemented and will be supported and maintained by the community; otherwise, it was scored with a −1 to show that it was unsuitable (Supplementary Appendix SB). This evaluation through scoring was not intended to generate quantitative data (for quantitative analysis); but rather, to facilitate the probing of the thought processes leading to the co-creation of knowledge and suitable options among participants during deliberations. Then, participants split into their circles (CAR, policymakers, and scientists) where they deliberated on each item. Each group elected a person to chair the discussions and a secretary to take notes. Each group deliberated on each item based on the definition of a suitable DRR measure but could point out any news views. Thereafter, the circles merged for a discussion between all participants. This formed the phase to observe the negotiation and co-creation process. Here, notes from discussions in the circles were presented to allow for open and constructive debate among all participants regarding the best measures and strategies. After extensive deliberations, the individual scoring of each measure was redone. This was done to check whether participants changed their opinion following the deliberations and co-creation exercise as a basis for follow-up discussions. Follow-up discussions enabled an exhaustive viewpoint on themes that emerged.
3.4 Data Analysis
The NVivo 12 software was used to structure and analyze the collected data. Data were synthesized through analytical induction. This involved identifying and coding recurrent patterns that enable the building of logical categories among stakeholders in the entire process of deliberations. In the context of the hylomorphic DRR framework, attention was paid to elements that favored the process of co-creation of knowledge around the proposed measures or new worldviews and co-development of suitable options. Enabling factors in this process were noted as indicators of interscience in understanding and tackling disaster risk. Recommendations on the analysis of qualitative data as proposed in Baxter and Eyles (1997) were followed. These results of this analysis were contrasted with the theoretical framework developed in Section 2 to highlight the added value of the hylomorphic framework. These results are presented in accordance with the format followed in deliberations, i.e., the analysis start with the experiences in the specific Circles of Dialogues, then the deliberation on the knowledge co-creation and co-adapting of the proposed measures.
4 Integrating Knowledge Perspectives in Practice
4.1 Participant Experiences With the Proposed Options
Based on the individual evaluation of DRR measures before interactions between participants, a convergence of positive opinion is observed towards nonstructural and/or less high-tech measures; but also, those that are geared towards social stability and wellbeing. This explains, accordingly, the relatively high scores for measures in the category of Eco-hydrological System Wellbeing as well as Sociopolitical Stability and Responsibility. On the opposite, sharp contrasts between opinions of participants are noted on measures that are not context-specific, i.e., not considering the local socio-ecological conditions of the CAR and/or focusing on high-tech engineering (Supplementary Appendix SC).
Additionally, observations and transcripts from workshops revealed the relative position and attitude of groups of actors to each other regarding the proposed measures. For instance, in several cases, scientists not only found the proposed measures interesting; they also discovered that several initial worldviews of the CAR are intelligible. Moreover, when asked to identify the best measures to prioritize and new ones to add, some convergence is suggested in the responses of the different circles (e.g., Table 1). These became the point of departure, not only for (re-)rationalization and (re-)contextualization of hybrid disaster risk knowledge; but also, for the re-politicization and negotiation towards the best ways for implementing DRR options among the participants.

TABLE 1. Sample viewpoints of participants when asked to prioritize measures among the inventory and add more.
4.2 (Re-)rationalization and (Re-)contextualization Foster Hybridization
The recognition of similar as well as new insights from the Circles of Dialogue was observed to spark off equitable contributions to adapt the proposed measures and co-create several new options. This can be illustrated by three key examples. First, while regional weather monitoring and gauging systems were considered unsuitable due to limited budget, the need for an early warning system or a system detecting flood onset was still much desired. Policymakers reported that a system of discharge sensors was installed in the river channel starting in 2015, following the 2013 damaging floods. This was a multibillion investment, funded by the government of Egypt (see Atef, 2017). But these devices were devastated by the subsequent floods, especially the floods of 2020. Besides that, CAR criticize the fact that the sensors only informed about the flood when it was too late. CAR elaborated on how they rather follow the behavior of the rainfall upstream with visual observations, the type of clouds, and duration of rainfall:
“There is that sort of black clouds. Once we see that and followed by rains for more than 2 hours, you know, we will experience floods. Then communications pass, telling people to move from the valley. You see, we do not even have to wait to see river levels” (Workshop 1, CAR, 2021).
The explanations of the CAR suggested that the timing of the scientific alert based on sensors was less suitable compared to that of their indigenous system to safe crucial property. Borrowing from this, participants theorized the potential to calibrate something that can be used as an early warning system, i.e., based on timing and duration of observed rainfall as well as other local parameters that have been observed through time by the indigenous people to consistently indicate the potential for floods locally. Moreover, as scientists (influenced by the CAR) frequently cited, “indeed, if we wait for the water to be high in the river to [detect and] send an alert, this is already way too late” (Workshop 2, Scientists, 2021).
The second example stems from that of dredging of the river channel being perceived as an unsuitable measure. According to participants, even local government has hardly successfully conducted it due to limited prioritization in budget. The proposal from the CAR was to rather train and support gravel and sand miners to conduct their activities in a conservation manner. This, according to the CAR, is an alternative to dredging as it would be sustained since it is also a source of livelihood. Several scientists found this interesting. For instance,
“…if they are organized, something could be done to build their capacity in contributing to desilting as they get the sand. We can, for instance, train them how to pick sand above the bridge and tell them to [avoid] the sand above the bridge. They just need to be organized, trained and monitored. We are no longer in the protectionism era, now it is conservation” (Workshop 2, Scientists, 2021).
The third example is the conservation approach co-created around several measures: soil and water conservation, riverbank fortification through the water-tolerant trees as well as vegetating buffer zones in the alluvial plain, and reforestation of steeper parts of the catchment. These were frequently considered in the broader sense of land-use planning and as measures affecting livelihoods. For example, scientists argued that soil and water conservation is a good agronomic practice that improves soil fertility and is easy to implement considering that the CAR are largely agrarian communities. CAR concurred with this viewpoint and elaborated that they would have several benefits from it. For instance, “we get high yields when the soil and water are conserved in the gardens” (Workshop 1, CAR, 2021). Reforestation was also considered by participants as part of the broader soil and water conservation to support stabilizing soil in the riparian areas and along the watershed. Besides, trees are harvested for livelihood. The same holds for buffer vegetation across the alluvial plain. For instance,
“Some natural vegetation is culturally planted, e.g., water reeds and bamboo, along the downstream of Nyamughasana river. They are harvested in a conservation manner to ensure that the river is conserved against floods, and the CAR derive their livelihoods. However, this is conducted at a very small scale” (Workshop 1, CAR, 2021).
Moreover, it was convergently agreed that most non-degrading farm Income Generating Activities (IGAs), such as apiculture, would fit within the greened buffers and forested slopes. All these measures are, additionally, considered as crucial to limit silting of the river channel. Here, dredging was perceived to be required in the early stages of implementing such a conservation approach and/or occasionally. Participants indeed jointly theorized that the conservation-based sand mining coupled with conservation-based land use would accomplish the same outcome, thereby preventing the costly dredging. Similarly, the conservation-based land use approach was considered to also replace the need for stabilizing riverbanks with gabions. Gabion construction was several times proposed by CAR but considered unsuitable on technical grounds during the deliberations. Besides, as cited by scientists working in government, the recent gabions constructed by DMCs were funded by the Egyptian donation; there was no plan how to maintain them.
It can be noticed that the co-created solutions are geared towards both nature conservation and the improvement of the socioeconomic conditions or livelihoods of the CAR. Other observations indicate that the extent to which a measure contributes to livelihoods could be influential. For instance, formalizing and supporting Savings and Internal Lending Communities (SILCs) were evaluated as unsuitable. Experience of the CAR revealed that SILCs often have insufficient capital to lend to members for recovery and/or reconstruction in the aftermath of a flood disaster. This is a bit surprising since SILCS are known to support farmers in this region. In a related study, loan portfolios in SILCs groups were found insufficient: some groups could not function properly in the aftermath of a disaster due to the vulnerabilities associated with the disaster, disabling the capacities of farmers to pay back their loans (Maes et al., 2017). Follow-up discussions suggest that SILCs and their element of saving against risk are still at initial stages; they are yet to be studied for their potential to build a financial contingency plan for CAR. Interestingly, scientists viewed SILCS as crucial, e.g., “…they contribute to livelihood diversification, enabling CAR to engage in non-farm income generations and non-degrading farm incomes generation” (Workshop 1, Scientists, 2021).
In addition to livelihoods, culture and indigenous knowledge came out frequently. Scientists and policymakers, surprisingly, acknowledged that culture and indigenous knowledge have conservation considerations, e.g., planting of indigenous water-tolerant trees. These observations, coupled with the views extracted from the deliberations among participants, can be summarized into four thematic elements: enhancing ecological and hydrological Integrity (across the watershed), diversifying livelihoods, limiting exposure and vulnerability, and social well-being. The elaborations of these themes by participants resonate with that of the measures initially proposed in the protocol as illustrated in Table 2 (see also Supplementary Appendix SA).

TABLE 2. Sample key measures linked with the views from the participants regarding key criteria for prioritization.
4.3 Re-Politization and Negotiations Towards Best Ways for Implementation
The resultant question from the preceding sections is: why are (some of) these options not (yet) being implemented? Results of the workshops’ discussions revealed that some (such as reforestation, buffer greening, non-degrading farming) are implemented, but haphazardly at a small scale due to limited resources. Moreover, the situation is compounded by limited extension services: it was evidenced in the workshop that farmers sometimes lack facilitators to train them on the appropriate riparian farming practices specific to tackling floods.
Policymakers and CAR generally concurred on another obvious factor: the local population generally live a subsistence (hand-to-mouth) lifestyle. Moreover, as evidenced in the workshops, this subsistence life largely depends on rainfed (and riparian) moisture smallholder farming. This owes to the historical sociopolitical pressures that have left the local population largely disenfranchised and vulnerable (see also Syahuka-Muhindo, 2008). This prevents the large-scale implementation of conservation interventions (e.g., tree farming, apiculture) which take a long time to bring food to the table and fulfill other financial needs at the household level. Hence, scientists emphasized that implementing some measures (e.g., buffering and wetlands as well as non-degrading farm IGAs) might require compensating for the immediate livelihood foregone by CAR. Another alternative is to “implement these measures in phases or ways that enable meeting the immediate need in the process…” (Workshop 2, Scientists, 2021).
A debate was centered around watershed management including land-use planning to manage floods. Starting from a sort of blame game, policymakers argue that the problem is disrespect of policy; for instance, “…in the 1990s, we used to see the environmental policies implemented and respected. What has happened that this is not the case these days? Are environmental officers still relevant to us?” (Workshop 1, Policymaker, 2021). CAR respond to this question, indicating that the problem is not the environmental officers, but the politics. For instance, the mismatch is noted between the politicians’ desire for votes and community priorities: “today, when the chief wants to implement [environmental policies], say evicting tycoons defying buffer policy, the politician says, leave those ones. We shall talk to them. He is in fact saying: do not disturb my voters” (Workshop 1, CAR, 2021). Policymakers confirm these viewpoints, citing issues related to corruption and embezzlement of public funds meant to economically empower the local population, but also lip service politics.
More specific to DRR, questions were raised by CAR on the political motivation of urbanizing floodplains without any flood management practices. Scientists working in the technical division of the local government think that the problem is that evidence-based planning is not yet a central part of governance. This is clearly illustrated in workshop 3:
“…this is not [yet] a knowledge-driven community. All scientific knowledge is for scientists. Often, planning [of infrastructural and social services] is based on political opinions or motivations. In Uganda, scientists are largely involved or used to actualize politically motivated interventions” (Workshop 3, Technical Scientists, 2021).
Interestingly, several policymakers acknowledge these critiques and were moved to think that it is high time to have evidence-based planning. Scientists pointed out that it is however more relevant to focus on what the CAR can do within their means insofar as evidence-based planning and solving of (socio)political hindrances are yet to be achieved. Moreover, several technical scientists attested of being hampered by politics to implement. This is summarized by this quote: “implementation in this country is very complicated. You want to plan something to do, but the door is locked; you need a key to open, but you do not have the key” (Workshop 3, Technical Scientists, 2021).
To support evidence-based planning of DRR as well as proper implementation, deliberations were focused on the establishment of an independent unit (authority or committee). This unit would manage the river and flood disasters, but it would also be mandated through the national or central government. This was considered the best temporary option for the current situation. Moreover, as frequently cited, in the current situation it is “independent authorities [i.e., parastatals] like UNRA [Uganda National Roads Authority] get well funded and work better” (Workshop 3, Policymakers, 2021). This unit, according to participants, would be composed of members of the CAR, scientific advisors, and policymakers.
5 Lessons From and Implications of This Case Study
5.1 The Co-Creation Processes
In the perspective of the hylomorphic DRR framework, integrating perspectives is centered on converging different theorizations to arrive at a hybrid context-specific body of knowledge based upon which to co-design strategies. This implies integrating the pragmatic empiricist aspects from the CAR (i.e., hyle) and the abstract rationalism of science (i.e., morphe). This is possible when the two are brought into equal dialogue to cocreate knowledge and best practices as well as devise the best way to implement them (see Section 2). The first evidence for this assumption is the consensus reached on some measures proposed under the hylomorphic DRR framework (Figure 1). This is further attested by the negotiations between the participants in the workshops.
Evidence of co-creation of knowledge and co-development of DRR suitable options is observed in the adaptation of the proposed measures. Specifically, participants were observed to co-create knowledge and co-design suitable DRR options on that would work in situations where some of the proposed measures were perceived as unsuitable. Consider, for example, the elaboration around the potential for designing an alert system based on the parameters that indigenous people have over time consistently recognized as an indicator for intense floods. Interestingly, such hybrid techniques are being noted in other contexts as effective in enabling the local community to avoid damage (Balay-As et al., 2018).
Another evidence of co-creation is elaborated around dredging. While it is found unsuitable, scientists and policymakers craft a strategy based on the suggestion by CAR: sand mining could be used (together with ecosystem-based measures) as a livelihood source to do the job that the costly river dredging would do. The centralization of this co-creation around livelihood is interesting; it evidences the maneuver by CAR in this dialogue through which scientists are grounded into the local dynamics, to understand the driving pressures for certain community activities. Such dynamics are too often neglected in scientific debates.
Another neglected aspect conceptualized in the co-creation is culture at first sight, scientists revealed that they are aware of the critical role of culture through experience. Yet, that was not conceptualized in their debates in their circles. For instance, prior to the intergroup dialogues, several scientists (within their specific circle) still wondered what to do with culture and indigenous knowledge. Consider, for example, this conversation: “[what] do we with the indigenous opinion or views that have never been verified. When floods come, they will say that the gods are not happy. Maybe [they should be included] just a buy-in that they participated, so that they can easily adopt” (Workshop 1, Scientists, 2021). This is a typical exemplification of the misconceptions of indigenous knowledge to which some scientists still cling. Often, this is due to the limited awareness of the evidence of the epistemic contributions of indigenous knowledge in contemporary literature (e.g., Ludwig, 2016, Ludwig, 2017; Balay-As et al., 2018). Interestingly, during the deliberations, indigenous people demonstrate their knowledge in understanding and tackling disaster risk, including those where scientists can start from or to which they can affix their model calibrations to produce more adapted technologies. Additionally, the knowledge of the indigenous people exposes historical sociopolitical constraints and factors influencing disaster risk, fostering self-critiques among policymakers. This motivated scientists to not only propose DRR options that are considerate of livelihoods and culture; but also, those that could be optimized by the CAR themselves considering the political hindrances.
The proposal to solve the sociopolitical hindrances on DRR, e.g., through an independent (public-private partnership) unit, is also a maneuver from the CAR. This would solve the current challenges by bringing aboard key stakeholders to enable holistic negotiations and optimization of knowledge and practices that work in real life. The proposed independent unit would also give a formal representation to the CAR, enabling them to take part in negotiating and controlling the implementation of DRR strategies, with continuous attention to their culture. This agrees with what is currently emphasized among some disaster risk researchers: CAR will consider a measure seriously and support its implementation if it considers their livelihood and culture; but also if they have been involved in the design and decision process (Cannon, 2015; Maes et al., 2019).
Livelihood and culture (especially structures and attitudes) are indeed crucial aspects of DRR as found in various contexts elsewhere and other theoretical literature (Cannon, 2015; Hazarika et al., 2016; Hooli, 2016). They are also seen to largely contribute to community-based DRR in which initiatives of the local community are increasingly found indispensable (Ayeb-Karlsson et al., 2019; Shaw et al., 2021). Yet the aspect of culture should not be over-emphasized: in communities with multiple ethnicities, a cultural mindset could cause a setback related to whose culture and/or indigenous knowledge is considered. Maathai (2010) elaborates this when referring to ethnicities as micronations in various countries across Africa. Cultural structures of domination can, according to this author, create a “tribal mindset” at the expense of a nationalistic identity, especially if micronations are antagonistic. Antagonism related to cultural institutions is historical in the Rwenzori since colonial times. Moreover, until now, they are systematically used as political platforms for patronage politics and clientelism all over the post-colonial Uganda (see Sseremba, 2019; Sseremba, 2020).
Bearing this in mind, the question should be, what causes the embracement of measures when they come through culture? What is generally noted is that it is the DRR measures considered to be working on and for the common good of the (local) population that are accepted. Coupled with the viewpoints in the workshops, this can be considered as a matter related to putting local people first in the interventions and giving weight to community priorities. Giving weight to community priorities is often compromised by the capitalist and political pressures of the so-called state-building. In general, however, if these pressures were solved, giving weight to community priorities can improve community embracement (Mathew et al., 2012; Gaillard and Mercer, 2013; Shaw et al., 2021). Thus, it is not only the missing link with culture; but also, with a people-centered development. The central elements are on the needs of the people, which is consistent with the view that DRR be linked with human development (Zakour and Swager, 2018; Raikes et al., 2021).
5.2 Fundamentals of the Hylomorphic Disaster Risk Reduction Framework and Beyond
Beyond evaluation and co-creation of knowledge as well as suited DRR options, convergence is also observed on core principles and assumptions for substantial DRR. Specifically, in the perspective of the hylomorphic framework, a measure is adopted, optimized through time and lead to substantial DRR depending on how the CAR are distanced or related to it. Here, the key elements described in Section 2 are related to adaptability as well as compatibility which together are ingredients of sustainable DRR options. These are broadly evidenced not by focusing the evaluation and co-creation around the culture and livelihood; but also, with the contextualization of the (culture and livelihood) around ecosystem-based and social well-being (see also Table 2). What enabled this convergence?
Firstly, a collaboration of overlapping knowledge theorizations on DRR was observed; for example, in the elaborated consensus around the potential to use observed flood precursors identified by CAR. Secondly, there was an embracement of difference in ontologies and attached values, e.g., embracing the cultural beliefs insofar as they are (riparian) conservation-based and/or enable implementation. These first two led to the shared (hybrid) knowledge theorizations. Thirdly, there is self-critiquing, especially among policymakers based on the political ills unearthed by CAR. This third factor further enabled equitable deliberations among participants: i.e., space was opened for debate, enabling the pointing out of real issues at hand and considering disasters as matters of concern. This, in the perspective of some recent related literature, is a requirement to create a platform for negotiations to arrive at adapted DRR options (Delima et al., 2021). Indeed, it further fostered the adaption of the developed shared knowledge and options at the overlap of science and indigenous knowledge. In other words, the deliberations in the workshops can be summarized to have moved from evaluation through the selection of relevant options to re-grounding as well as re-rationalizing each relevant option. This process, although based on the proposed measures, affirms the position that scientific DRR recommendations are but rarely a given. It is a matter of concern requiring socio-epistemic processes or negotiations to arrive at the most suited options (Figure 3).
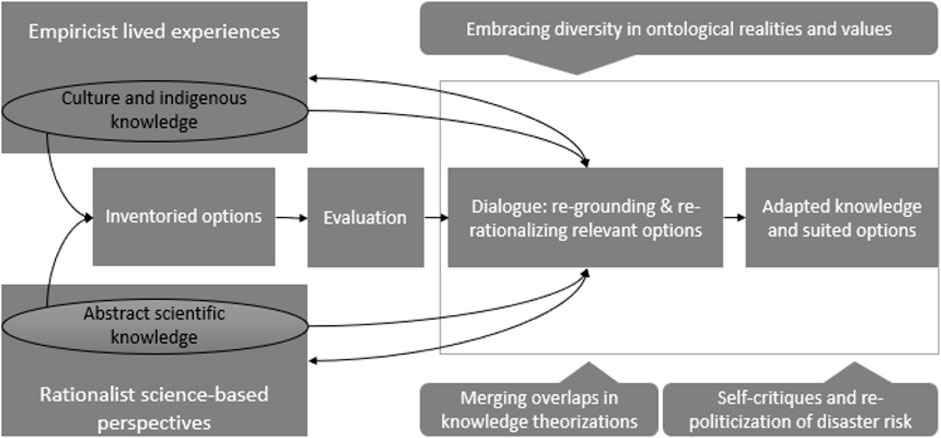
FIGURE 3. Observed process from inventorying to co-creation of knowledge and co-development of suitable DRR options.
The core options arrived at in the deliberations (i.e., the ecosystem-livelihood approaches), are in line with two contemporary conceptualizations: Nature-Based Solutions (NBS) and Sustainability. The conceptualization of NBS is aimed at a holistic approach that links social and environmental challenges and opportunities sustainably and cost-effectively. It takes into consideration the contribution of nature to people and vice versa, thereby making it possible to outcompete degradation motives (Fernandes and Guiomar, 2018). This, in the perspective of sustainability science, is possible when the primacy of a systems approach is considered. This means transcending disciplinarity, embracing the diversity of ontological aspects to derive knowledge theories that bridge the natural and social aspects of reality, thereby leading to adapted options (Van Opstal and Hugé, 2013). This, moreover, is linked with four key priorities in and/or around which the proposed measures were grounded: Ecological and Hydrological Integrity, Diversifying and Improving Livelihoods, Limiting Exposure and Vulnerabilities, and Social and Community Well-being (Table 2).
The question remaining here is: how does this NBS conceptualization and Sustainability enable or enhance optimization of measures in the perspective of this hylomorphic framework? For this case study, the focus around culture and indigenous knowledge on scientifically sound options is interesting. It means that it is possible to erase the line between the lived experiences of the CAR and science. This could favor limiting the mismatch between the rationalist and empiricist discourses. Consider, for example, the NBS cocreated around soil and water conservation, reforestation, livelihood, land use, and non-degrading income generating activities. These are scientifically sound interventions, but which meet with the aspirations of the local population apart from the means to have them started. They are avenues to foster optimization over time.
Another assumption is that if nature is continually observed as a source of livelihood and cultural nourishment, it would incessantly foster the desire for conservation (Bwambale et al., 2018). This assumption has yet met a series of criticism dating from historical debates about human capitalist motives and natural source exploitation (Maathai, 2010). Moreover, in other contexts, the nature of the incentive from nature determines which resources to conserve. For instance, one of the recent studies is on the role of trees in mitigating flood disasters (Tembata et al., 2020): coniferous trees having higher economic and wood value, yet less effective to prevent floods, tend to be preferred against broadleaf and mixed forests in afforestation by policymakers. This implies that effective implementation of the suited options can be compromised by the dynamics related to the market. Accordingly, considering the economic incapacities at the local levels, applying adapted strategies lies in the commitment of the state to provide subsidies that can enable the implementation of the suited yet less marketable options.
The self-critiquing exhibited by policymakers is a crucial part of advocacy, especially by CAR, not only for DRR measures; but also, for systematically adapting them, over time, as political pressures inhibiting them are brought to the spotlight. It helps to reconcile the priorities of all key stakeholders. Besides, CAR have influential knowledge keepers and practitioners. They were cited during field reconnaissance in the CAR: They were acquainted with the indigenous perspectives and practices as well as related to concrete historical dynamics to favorably deliberate with scientists and policymakers. This explains the observed re-rationalization as well as re-contextualization of each of the selected options during deliberations (Figure 3). This suggests that local people are likely to favorably participate if their perspectives and practices, as well as worldviews, are equitably presented among the items on the agenda of discussion. Moreover, the core criteria that DRR options be supported and/or maintained by the CAR played a key role in (re)focusing the dialogue to context-specific standpoint. Interestingly, this unearths aspects that scientists are unaware of and the co-creation of hybrid solutions by all participants. This highlights the potential for multi-stakeholder consensus on the people-centered DRR approaches. It is indeed at this stage that the priorities of local people and scientists, as well as policymakers, can be reconciled. This shows the centrality of standpoints. Several scholars had alluded to the view that meaningful engagement of indigenous people requires skewing the discourse on disaster risk reduction to the standpoint of CAR (Gaillard and Mercer, 2013; Cannon, 2015).
6 Conclusion
Synthesizing several prior research on integrating knowledge, Bwambale et al. (2020) argue that: “indigenous and scientific knowledge perspectives grasp partial realities of the disaster risk [at the local context], …they should [thus] be integrated.” Integration would be possible by synthesizing the (pragmatic) empiricist lived experience with the rationalist scientific perspectives through the hylomorphic DRR framework. Contrasted with standpoint theories, this framework enables developing a composite knowledge theorization that can lead to adapted options for DRR. In this case study, the implementation of the proposed framework demonstrates how to facilitate a consensus on a set of DRR options that is nearer to the local context. This is done by investigating the empiricist and rationalist DRR knowledge. Suitable DRR options are optimized through dialogue, sharing of knowledge, and co-creation of more adapted options. In the dialogue, progress is noted from simple evaluation of the proposed measures to deliberations for co-creation of those that are considerate of the specific context. The knowledge and options arrived at in the co-creation process highlight the convergence between the different stakeholders involved. This is noted to be influenced by three key aspects: the ability to merge overlapping epistemologies, accepting diversity in ontological realities and values between scientists as well as policymakers and indigenous people, and self-critiquing which opened space for negotiations on the best ways towards DRR. This process suggests that DRR options cannot be considered as a (scientific) given, but a matter requiring socio-epistemic processes or negotiations. The resultant convergences and co-creations were found to be centered around ecosystems-based management of the floods, but also considerate of livelihood and embracing the role of culture. Implementation of such DRR options will however depend on the willingness of policymakers to foster specific nature-based interventions, e.g., supporting implementation of non-market oriented DRR solutions through offering some subsidies.
These findings are largely explained by skewing the discourse to the aspirations of the CAR in accordance with the hylomorphic framework. It can thus be argued that this framework is not only crucial for arriving at suited approaches; it also evidences the viewpoint held in the vulnerability paradigm of DRR, that standpoint matters in developing measures and strategies that would be appropriate to the local context. Further studies will increase understanding of its effectiveness in integrating knowledge, identifying, and implementing substantial DRR.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
BB: Conceptualization, methodology, formal analysis, and writing—original draft. MK: Conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision, and funding acquisition
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Vrije Universiteit Brussel (VUB) for the Research Grant through Global Minds that financially supported the data collection and writing of this manuscript. The venues for the data collection workshops of this manuscript were offered by two local government departments: departments of Natural Resources and Health (Kasese district local government), and Kasese Municipality—Central Division. We are grateful to all the people that participated in the workshops. These include the politicians, technocrats as well as scientists, and representatives of the local community of Nyamughasana (Nyamugasani), Nyamwamba, and Mubuku watersheds.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2021.783264/full#supplementary-material
References
Alexander, D. (1997). The Study of Natural Disasters, 1977-97: Some Reflections on a Changing Field of Knowledge. Disasters 21, 284–304. doi:10.1111/1467-7717.00064
Ayeb‐Karlsson, S., Kniveton, D., Cannon, T., van der Geest, K., Ahmed, I., Derrington, E. M., et al. (2019). I Will Not Go, I Cannot Go: Cultural and Social Limitations of Disaster Preparedness in Asia, Africa, and Oceania. Disasters 43, 752–770. doi:10.1111/disa.12404
Balay-As, M., Marlowe, J., and Gaillard, J. C. (2018). Deconstructing the Binary between Indigenous and Scientific Knowledge in Disaster Risk Reduction: Approaches to High Impact Weather Hazards. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduction 30, 18–24. doi:10.1016/j.ijdrr.2018.03.013
Baxter, J., and Eyles, J. (1997). Evaluating Qualitative Research in Social Geography: Establishing 'Rigour' in Interview Analysis. Trans. Inst. Br. Geog 22, 505–525. doi:10.1111/j.0020-2754.1997.00505.x
Briggs, J. (2013). Indigenous Knowledge: A False Dawn for Development Theory and Practice? Prog. Dev. Stud. 13, 231–243. doi:10.1177/1464993413486549
Bwambale, B., Muhumuza, M., and Nyeko, M. (2018). Traditional Ecological Knowledge and Flood Risk Management: A Preliminary Case Study of the Rwenzori. Jàmbá 10, 536. doi:10.4102/jamba.v10i1.536
Bwambale, B., Nyeko, M., Muhumuza, M., and Kervyn, M. (2020). Questioning Knowledge Foundation: What Is the Best Way to Integrate Knowledge to Achieve Substantial Disaster Risk Reduction? Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduction 51, 101850. doi:10.1016/j.ijdrr.2020.101850
Bwambale, B., Nyeko, M., Sekajugo, J., and Kervyn, M. (2021). The Essential Contribution of Indigenous Knowledge to Understanding Natural Hazards and Disaster Risk: Historical Evidence from the Rwenzori (Uganda). Nat. Hazards. doi:10.1007/s11069-021-05015-x
Candiotto, L. (2017). “Socratic Dialogue: A Comparison between Ancient and Contemporary Method,” in Encyclopedia of Educational Philosophy and Theory. Editor M. A. Peters (Singapore: Springer), 2192–2199. doi:10.1007/978-981-287-588-4_367
Cannon, T. (2015). “Disasters, Climate Change and the Significance of “Culture,” in CULTURES and DISASTERS: Understanding Cultural Framing in Disaster Risk Reduction. Editors F. Krüer, G. Bankoff, T. Cannon, B. Orlowski, and E. L. F. Schipper (London and New York: Routledge), 87–106.
Delima, G., Jacobs, L., Loopmans, M., Ekyaligonza, M., Kabaseke, C., Kervyn, M., et al. (2021). DisCoord: Co-creating DRR Knowledge in Uganda through Interaction in a Serious Game. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduction 60, 102303. doi:10.1016/j.ijdrr.2021.102303
Eggermont, H., Damme, K. V., and Russell, J. M. (2009). “Rwenzori Mountains (Mountains of the Moon): Headwaters of the White Nile,” in The Nile: Origin, Environments, Limnology and Human Use, Monographiae Biologicae (Dordrecht, Netherlands: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9726-3_13
Fernandes, J. P., and Guiomar, N. (2018). Nature-based Solutions: The Need to Increase the Knowledge on Their Potentialities and Limits. Land Degrad. Dev. 29, 1925–1939. doi:10.1002/ldr.2935
Gaillard, J. C., and Mercer, J. (2013). From Knowledge to Action. Prog. Hum. Geogr. 37, 93–114. doi:10.1177/0309132512446717
Hazarika, N., Tayeng, T., and Das, A. K. (2016). Living in Troubled Waters: Stakeholders' Perception, Susceptibility and Adaptations to Flooding in the Upper Brahmaputra plain. Nat. Hazards 83, 1157–1176. doi:10.1007/s11069-016-2366-1
Hooli, L. J. (2016). Resilience of the Poorest: Coping Strategies and Indigenous Knowledge of Living with the Floods in Northern Namibia. Reg. Environ. Change 16, 695–707. doi:10.1007/s10113-015-0782-5
Jacobs, L., Dewitte, O., Poesen, J., Delvaux, D., Thiery, W., and Kervyn, M. (2016a). The Rwenzori Mountains, a Landslide-Prone Region? Landslides 13, 519–536. doi:10.1007/s10346-015-0582-5
Jacobs, L., Maes, J., Mertens, K., Sekajugo, J., Thiery, W., van Lipzig, N., et al. (2016b). Reconstruction of a Flash Flood Event through a Multi-hazard Approach: Focus on the Rwenzori Mountains, Uganda. Nat. Hazards 84, 851–876. doi:10.1007/s11069-016-2458-y
Ludwig, D., and El-Hani, C. N. (2020). Philosophy of Ethnobiology: Understanding Knowledge Integration and its Limitations. J. Ethnobiol. 40, 3. doi:10.2993/0278-0771-40.1.3
Ludwig, D. (2016). Overlapping Ontologies and Indigenous Knowledge. From Integration to Ontological Self-Determination. Stud. Hist. Philos. Sci. A 59, 36–45. doi:10.1016/j.shpsa.2016.06.002
Ludwig, D. (2017). The Objectivity of Local Knowledge. Lessons from Ethnobiology. Synthese 194, 4705–4720. doi:10.1007/s11229-016-1210-1
Maes, J., Mertens, K., Jacobs, L., Bwambale, B., Vranken, L., Dewitte, O., et al. (2019). Social Multi-Criteria Evaluation to Identify Appropriate Disaster Risk Reduction Measures: Application to Landslides in the Rwenzori Mountains, Uganda. Landslides 16, 1793–1807. doi:10.1007/s10346-018-1030-0
Maes, J., Parra, C., Mertens, K., Bwambale, B., Jacobs, L., Poesen, J., et al. (2018). Questioning Network Governance for Disaster Risk Management: Lessons Learnt from Landslide Risk Management in Uganda. Environ. Sci. Pol. 85, 163–171. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2018.04.002
Maes, J., Poesen, J., Parra, C., Kabaseke, C., Bwambale, B., Mertens, K., et al. (2017). “Landslide Risk Management in Uganda: A Multi-Level Policy Approach,” in Advancing Culture of Living with Landslides. Editors M. Mikoš, Ž. Arbanas, Y. Yin, and K. Sassa (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 395–403. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-53487-9_46
Mathew, S., Trück, S., and Henderson-Sellers, A. (2012). Kochi, India Case Study of Climate Adaptation to Floods: Ranking Local Government Investment Options. Glob. Environ. Change 22, 308–319. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2011.11.005
Raikes, J., Smith, T. F., Baldwin, C., and Henstra, D. (2021). Linking Disaster Risk Reduction and Human Development. Clim. Risk Manag. 32, 100291. doi:10.1016/j.crm.2021.100291
Shaw, R., Pulhin, J. M., and Inoue, M. (2021). “Disaster Risk Reduction, Climate Change Adaptation, and Human Security: A Historical Perspective under the Hyogo Framework and beyond,” in Climate Change, Disaster Risks, and Human Security, Disaster Risk Reduction. Editors J. M. Pulhin, M. Inoue, and R. Shaw (Singapore: Springer Singapore), 21–36. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-8852-5_2
Sorrell, K. (2013). Pragmatism and Moral Progress. Philos. Soc. Criticism 39, 809–824. doi:10.1177/0191453713494967
Sseremba, Y. (2020). Ethnic Emancipation and Conflict Escalation in Uganda. Third World Q. 41, 2030–2047. doi:10.1080/01436597.2020.1803059
Sseremba, Y. (2019). The Making and Remaking of "Native Tribes" in Uganda's Toro Kingdom. Nationalism Ethnic Polit. 25, 311–328. doi:10.1080/13537113.2019.1639429
Syahuka-Muhindo, A. (2008). “Migrations and Social Formation in the Rwenzori Region,” in Rwenzori: Histories and Cultures of an African Mountain. Editors C. Pennacini, and H. Wittenberg (Kampala: Fountain Publishers), 18–58.
Tembata, K., Yamamoto, Y., Yamamoto, M., and Matsumoto, K. i. (2020). Don't Rely Too Much on Trees: Evidence from Flood Mitigation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 732, 138410. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138410
Thomas, C., and Goering, C. Z. (2018). Socratic Circles in World History: Reflections on a Year in Dialogue. The Clearing House: A J. Educ. Strateg. Issues Ideas 91, 103–110. doi:10.1080/00098655.2017.1411132
Van Opstal, M., and Hugé, J. (2013). Knowledge for Sustainable Development: a Worldviews Perspective. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 15, 687–709. doi:10.1007/s10668-012-9401-5
Wortel, E., and Verweij, D. (2008). Inquiry, Criticism and Reasonableness: Socratic Dialogue as a Research Method? Pract. Philos 9, 54–72.
Wylie, A. (2003). “Why Standpoint Matters,” in Science and Other Cultures: Issues in Philosophies of Science and Technology. Editors R. Figueroa, and S. G. Harding, 26–48.
Keywords: disaster risk governance, disaster risk reduction philosophy, disaster risk interscience, hylomorphic framework, standpoint disaster theory
Citation: Bwambale B and Kervyn M (2021) Testing Interscience in Understanding and Tackling Disaster Risk. Front. Earth Sci. 9:783264. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.783264
Received: 25 September 2021; Accepted: 30 November 2021;
Published: 20 December 2021.
Edited by:
Irasema Alcántara-Ayala, National Autonomous University of Mexico, MexicoReviewed by:
Jussara Rowland, Instituto de Ciências Sociais da Universidade de Lisboa, PortugalPriya Namrata Topno, Tata Institute of Social Sciences, India
Copyright © 2021 Bwambale and Kervyn. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bosco Bwambale, Qm9zY28uQndhbWJhbGVAdnViLmJl
 Bosco Bwambale
Bosco Bwambale Matthieu Kervyn1
Matthieu Kervyn1