Abstract
We review the occurrence of biogenic amines and their potential role as neurotransmitters in the nervous system of three groups of invertebrate deuterostomes: tunicates, cephalochordates, and echinoderms. In addition to an overview of biogenic amines in each subphylum, we focus on a few species, including the sea squirts Ciona intestinalis, C. robusta, C. savignyi, and Phallusia mammillata (tunicates), the lancelets Branchiostoma lanceolatum and Branchiostoma floridae (cephalochordates), and the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (echinoderms). We chose these species as they are the most studied invertebrate deuterostomes in the field of evolutionary developmental biology (EvoDevo). Providing a comparative picture of the expression and role of neurotransmitters in deuterostomes will contribute to understanding the evolution of these neural signaling systems. Such an approach represents a new frontier of comparative neuroanatomy and neurobiology, and a prerequisite to uncover the homology of neuronal structures and circuits in deuterostomes with such diverse body plan organization and complexity.
Introduction
Chemical signaling arose during the earliest evolution of living forms and, consequently, cell communication in multicellular animals occurs through signaling mechanisms via either intercellular contact or diffusible mediators acting at a distance (Gallo et al., 2016). Many signaling systems originate from primitive, even unicellular, organisms, like protists (Janakidevi et al., 1966). It has been proposed that the evolution of signaling molecules required a dynamic process in which neurotransmitters and their corresponding receptors evolved in parallel, following gene duplications and losses early in the Deuterostome lineage (reviewed by Hoyle, 2011). As organisms evolved greater complexity, certain classes of molecules were requisitioned as intercellular signaling devices. The autonomic nervous system represents the most well-known case of signaling cooption, in which chemical transmission is guaranteed by a ligand molecule and its specific receptor or receptors (Hoyle, 2011).
Neurotransmitters originate from unicellular organisms functioning in chemotaxis and chemo-signaling and are responsible for intercellular communication – for example, regulating the growth of other unicellular organisms (Rochchina, 2010). These molecules could influence (as hormones) others unicellular organism life and be attractants or repellent for them. These molecules could hereby serve a secondary role as biomediators (Rochchina, 2010).
Compounds such as acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, serotonin, and histamine (collectively known as neurotransmitters) have been found not only in animals (Boron and Boulpaep, 2005) but also in plants and microorganisms lacking a true nervous system (Rochchina, 2001). Animals produce a myriad of active molecules, probably sharing a common origin. Interestingly, these molecules are also produced by protists, sponges, and placozoans, suggesting that the endocrine system predates a centralized nervous system (Gallo et al., 2016).
While numerous review articles focus on the role of biogenic amines in single organisms, none compare the expression pattern and anatomical distribution of neurotransmitter activity in non-vertebrate deuterostomes (such as tunicates, cephalochordates, and echinoderms). Tunicates (appendicularians, salps, and sea squirts) are the sister group to vertebrates (Delsuc et al., 2006; Vienne and Pontarotti, 2006), which together comprise the recently-classified olfactores; olfactores, alongside cephalochordates, constitute the chordate phylum. Echinoderms, on the other hand, belong to Ambulacraria, the non-chordate clade within deuterostomes. We briefly review the distribution of catecholamines (dopamine, adrenalin, and noradrenalin), indolamines (serotonin), and histamine in phylogenetically-significant deuterostomes and, then, discuss common features, divergent functions and species-specific roles during embryonic development.
Catecholamines
Dopamine
Dopamine represents a major neuromodulator synthesized by various cell populations in the vertebrate forebrain and midbrain, which predates the divergence of deuterostomes (Yamamoto and Vernier, 2011). In mammals, dopamine has been widely studied for its key role in sensorimotor programming, learning, reward, and memory, as well as in many vegetative, autonomous and cognitive functions (Baudonnat et al., 2013).
Tunicates
The first evidence of dopamine in Ciona robusta was the distribution of the mRNA precursor of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), the limiting enzyme of dopamine biosynthesis, in addition to transgenic assays of its enhancer activity (Moret et al., 2005). These studies found TH in the left portion of the larval sensory vesicle, in some of the ‘coronet cells’ (Figure 1A and Table 1). Other research groups confirmed the presence of dopamine in the sensory vesicle in the same species (Razy-Krajka et al., 2012). However, since TH marks both dopaminergic and noradrenergic cells, the identity of dopamine cells in C. robusta was confirmed using a specific anti-dopamine antibody, which revealed a strong immunoreactivity in the sensory vesicle during the larval stage and early metamorphosis (Moret et al., 2005). Furthermore, the immunoreactivity shown by posterior sensory vesicle neurons (Figure 1A and Table 1) supports the hypothesis that these dopamine neurons are responsible for larval swimming (Moret et al., 2005).
FIGURE 1
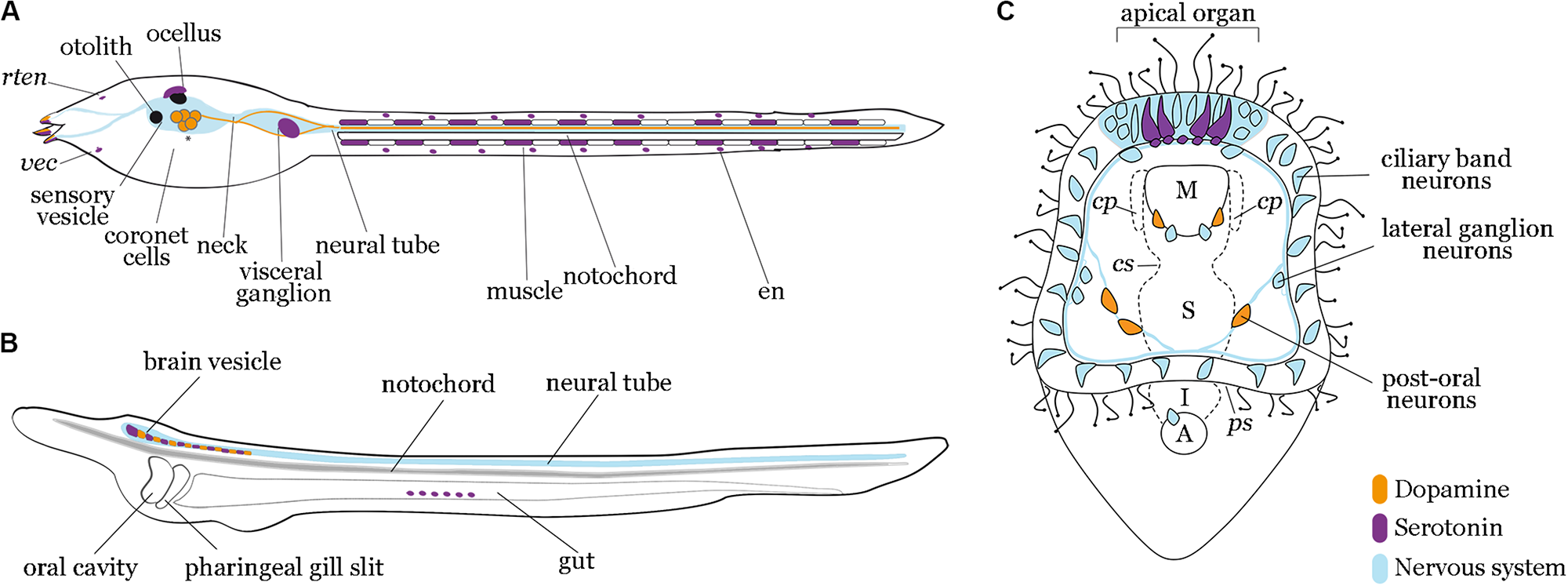
Localization of dopamine and serotonin expressing cells in tunicates, cephalochordates and echinoderms. Diagrams of tunicate (A), lancelet (B), and sea urchin (C) larvae depict dopaminergic (orange) and serotonergic (purple) neurons relative to nervous system (light blue). (A) Tunicate tadpole larva model showing signals reported in C. robusta and P. mammillata, with asterisks highlighting conserved dopaminergic neurons in both species. Dopamine is present in the coronet cells of the sensory vesicle in both species. Moreover, in P. mammillata, dopamine has been shown in the adhesive papillae, in the whole dorsal neural tube and in some fibers of the visceral ganglion extending to the tail. Serotonin is present in the visceral ganglion and muscle cells along the tail in C. robusta, while in P. mammillata it occurs in the sensory vesicle, adhesive papillae, visceral ganglion and epidermal neuron. rten, rostral trunk epidermal neuron; vec, ventral endodermal cell; en, epidermal neuron. (B) Lancelet larva model showing signals reported in B. lanceolatum and B. floridae. Dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons have been described for both species in the cerebral vesicle and the anterior part of the nerve cord. Additionally, in B. floridae serotonin has been observed in frontal eye and gut epithelium. (C) Sea urchin early pluteus larva model (S. purpuratus) showing serotonergic neurons localized in the most anterior part of the nervous system, the apical organ domain; two dopaminergic neurons are localized in the lower lip near the esophageal domain and three dopaminergic neurons approach the post-oral arms of the larva. M, mouth; cp, coelomic pouches; cs, cardiac sphincter; S, stomach; ps: pyloric sphincter; I, intestine; A, anus.
TABLE 1
| Neurotransmitter Catecholamine | Group | Species | Expression (embryos and larva) | Adult | References |
| Dopamine | Tunicates | Ciona robusta | Sensory vesicle; coronet cells   |
Moret et al., 2005; Zega et al., 2010; Razy-Krajka et al., 2012 | |
| Phallusia mammillata | Sensory vesicle; visceral ganglion; neural tube; adhesive papillae  |
Zega et al., 2005 | |||
| Cephalochordates | Branchiostoma lanceolatum | Cerebral vesicle; anterior nerve cord   |
✓ | Moret et al., 2004; Candiani et al., 2005, 2012; Burman et al., 2009; Zieger et al., 2017 | |
| Branchiostoma floridae | Anterior nerve cord | ✓ | Burman et al., 2007, 2009; Nordström et al., 2008; Burman and Evans, 2010; Bayliss and Evans, 2013; Zieger et al., 2017 | ||
| Echinoderms | Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | Apical organ; post-oral neurons   |
Adams et al., 2011 | ||
| Pseudocentrotus depressus | Ciliary band  |
Wada et al., 1997 | |||
| Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus | Lower lip cells; ciliary band; post-oral neurons  |
Katow et al., 2010 | |||
| Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis | Lower lip cells; ciliary band; post-oral neurons  |
Bisgrove and Burke, 1987 | |||
| Lytechinus variegatus | Post-oral neurons  |
Slota and McClay, 2018 | |||
| Adrenaline and noradrenaline | Tunicates | Ciona robusta | ✓ | Scudder et al., 1963; Akers, 1969; Keefner and Akers, 1971 | |
| Ciona savignyi | Sensory vesicle; visceral ganglion  |
Kimura et al., 2003 | |||
| Cephalochordates | Branchiostoma floridae | ✓ | Bayliss and Evans, 2013 |
Catecholamines: dopamine, adrenaline, noradrenaline distribution in embryos or adult tunicates, cephalochordates, and echinoderms.
Color code:  Neurotransmitters (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).
Neurotransmitters (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).  Metabolizing Enzymes or receptors (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).
Metabolizing Enzymes or receptors (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).  Enhancer activity.
Enhancer activity.  Other methods.
Other methods.
Interestingly, a recent study suggested a strong similarity between dopaminergic cells of the C. robusta sensory vesicle and the amacrine cells of the vertebrate retina, as both territories express the genes necessary to synthetize, store, and release dopamine (Razy-Krajka et al., 2012). This cellular homology is supported by the expression of transcription factors, such as Ptf1a, Rx, Six3/6, Pax6 and Meis, thereby defining a dopaminergic-specific regulatory signature (Oliver et al., 1995; D’Aniello et al., 2006, 2011; Heine et al., 2008; Irvine et al., 2008; Razy-Krajka et al., 2012).
In adult C. robusta, components of the catecholaminergic pathway, such as tyrosine hydroxylase, occur in coronal cells within the oral siphon tentacles (Rigon et al., 2018). Dopamine localization in coronal cells could play a protective role on the nerve synapse, given the homology of these cells to mammalian hair cells, for which it acts likewise (Lendvai et al., 2011).
Dopaminergic neurons have also been detected in Phallusia mammillata. Specifically, dopamine immunoreactivity was found in the adhesive papillae, the sensory vesicle (coronet cells), the entire dorsal neural tube, and in some fibers of the visceral ganglion extending to the tail (Zega et al., 2005, 2010). Interestingly, these investigations show that inhibiting dopamine signaling promotes metamorphosis, which implies a key role for dopamine in this fundamental developmental transition.
Cephalochordates
Dopamine occurs in the nervous system of the cephalochordate lancelet; three distinct dopaminergic neuronal populations were found in adult Branchiostoma lanceolatum by anti-dopamine and anti-TH immunohistochemical experiments. The most anterior dopamine domains are represented by a compact group of neurons in the cerebral vesicle (population 1) and a second group in primary motor center region, corresponding to interneurons (population 2). A third dopamine cell population is represented by dorsal commissural neurons that cross the midline of the neural tube (population 3) (Figure 1B and Table 1) (Moret et al., 2004). At the larva stage, the expression of genes for biosynthetic dopaminergic enzymes and receptors occurs in specific regions of the cerebral vesicle and hindbrain (Figure 1B), probably corresponding to the dopamine population 1 observed in the adult (Candiani et al., 2005, 2012; Zieger et al., 2017). The formation of the anterior-most dopamine neurons appears to be regulated by retinoic acid (Zieger and Schubert, 2017; Zieger et al., 2018b).
Interestingly, gene cloning and functional assays show that the lancelet Branchiostoma floridae possesses at least four dopamine D1 receptors (Burman et al., 2007, 2009; Burman and Evans, 2010). The pharmacological characterization of an lancelet dopamine D2 receptor in exogenous cell lines (Bayliss and Evans, 2013) and the identification of other two D2 receptors (Nordström et al., 2008) support the existence of D2 receptors in lancelets, contradicting the hypothesis that D2 dopamine receptors have been secondarily lost in the protochordate lineage (Yamamoto and Vernier, 2011).
Echinoderms
In echinoderms, and more specifically in sea urchins, dopamine is produced throughout most of the embryonic and larval development. In the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis, dopamine is detected throughout the apical surface of the ectoderm at the hatching blastula, prior to neurogenesis. At the pluteus stage, dopamine is detected in neurons of the post-oral ciliary band and in neurons around the mouth of the larva (Bisgrove and Burke, 1987). In the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, whole mount in situ hybridization experiments of the dopamine decarboxylase (Ddc) and TH immunofluorescent staining showed expression in the ciliary band post-oral neurons and mouth neurons (Figure 1C and Table 1) (Adams et al., 2011). Similar expression patterns were detected in the sea urchins Pseudocentrotus depressus and Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus (Wada et al., 1997; Katow et al., 2010). In the sea urchin Lytechinus variegatus, TH was detected in neurons located in the post-oral arms of the larva (Slota and McClay, 2018). Dopamine regulates the swimming of sea urchin larvae and their response to food availability. Embryos and larvae of H. pulcherrimus treated with carbidopa, a dopamine decarboxylase inhibitor, swam less than controls (Katow et al., 2010). Adams and colleagues found that dopamine signaling instigated a phenotypic response of larvae to food availability (Adams et al., 2011). When food is plentiful, they develop shorter arms than otherwise. Adams et al. (2011) showed that spatial and temporal expression of dopamine and its signaling pathway components accord with the feeding behavior of the larva and that algae-induced dopamine signaling inhibits arm elongation. In addition, externally-provided dopamine induced metamorphosis in larvae of the sand dollar Dendraster excentricus, suggesting that the dopaminergic system also plays an important role in echinoderm metamorphosis (Burke, 1983).
Adrenalin and Noradrenalin
Among monoamines, adrenalin (AD) and noradrenalin (NA) are synthetized through the catecholamine synthetic pathway, starting with the amino acid tyrosine (Daubner et al., 2011). In vertebrates, adrenalin and noradrenalin represent the main neurotransmitters of the sympathetic nervous system with specific functions in the regulation of cardiac tone and in metabolic homeostasis and emotional distress (Goldstein, 2010).
Tunicates
A first evidence of adrenalin presence and function in tunicates comes from a study in C. robusta showing that adrenalin markedly accelerates heart contraction (Scudder et al., 1963). A few years later, it was shown that adrenalin and noradrenalin also accelerate contraction of smooth muscle in this species (Akers, 1969; Keefner and Akers, 1971). However, although a detailed study of the C. robusta genome found a homolog of dopamine ß-hydroxylase (DβH), the enzyme converting dopamine in noradrenalin, this animal appears to lack phenyl ethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PNMT): the enzyme that synthetizes adrenalin from noradrenalin (Dehal et al., 2002). Nevertheless, another survey of C. robusta genome reported the existence of 10 genes encoding putative adrenergic receptors (6α and 4β type) (Sherwood et al., 2006).
In addition, the distribution of adrenalin and noradrenalin were characterized in detail in the sister species, C. savignyi. Immunohistochemistry with a DβH antibody showed a specific adrenalin and noradrenalin signal in the larva brain vesicle and visceral ganglion and in competent larvae 6 h after hatching (Kimura et al., 2003). Interestingly, immunohistochemical staining with a β1-Adrenergic receptor (β1-AR) began at the tailbud stage; this was followed by increased immunoreactivity at 6 h after hatching in (i) the brain vesicle (which envelopes the sense organs), (ii) the adhesive papillae, and (iii) the fibers along the notochord protruding from the tail. Interestingly, interactions between adrenalin, noradrenalin and β1-Adrenergic receptor in C. savignyi nervous system promote metamorphosis (Kimura et al., 2001, 2003).
Cephalochordates
No evidence of an adrenergic system has been found in a cephalochordate larva. High performance liquid chromatography and electrochemical detection assays performed on the adult lancelet head (Moret et al., 2004) support the contention that cephalochordates lack these neurotransmitters altogether. However, the lancelet B. floridae adult boasts an adrenaline/noradrenaline receptor (AmR4) that has been pharmacologically characterized by expression in mammalian cell lines (Bayliss and Evans, 2013). Moreover, DBH-like genes occur in the genomes of B. floridae (XP_002596363) and B. lanceolatum (BL17368; Marlétaz et al., 2018). Therefore, lacking dedicated investigation, we cannot rule out the possibility that adrenalin or noradrenalin occur in the larval or adult lancelet.
Echinoderms
The only evidence of putative noradrenalin synthesis in echinoderms is the existence of a DβH-like gene in the sea urchin S. purpuratus genome (XP_030854058), although we lack expression and functional studies. Interestingly, adrenalin and enzymes involved in its biosynthesis seem to have been lost in echinoderms (Burke et al., 2006).
Indolamines
Serotonin
Serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] is a key neurotransmitter throughout metazoans, suggesting that it has served this role since the inception of the nervous system (Hay-Schmidt, 2000). In vertebrates, serotonin regulates many neuronal functions, such as sleeping, feeding, and mood.
Tunicates
The first evidence of serotonin occurrence in different organs of the adult C. robusta comes from a spectrofluorometric analysis (Welsh and Loveland, 1968; Nilsson et al., 1988). At the late larval stage, during the onset of metamorphosis, serotonin has been immunolocalized to the visceral ganglion (De Bernardi et al., 2006). Interestingly, in situ hybridization experiments revealed that tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH), the rate limiting enzyme in serotonin biosynthesis, is expressed in both the visceral ganglion and in some muscle cells, probably at neuro-muscular junctions (Figure 1A and Table 2A); this suggests that serotonin regulates the left-right alternate tail contraction during larval swimming (Pennati et al., 2007a). In P. mammillata swimming larvae, serotonin has been detected in the sensory vesicle, papillae, epidermal trunk neurons, and epidermal tail neurons (Figure 1A), whilst juveniles showed serotonin in the peripharyngeal band, along the endostyle and in the gut (Pennati et al., 2001). That serotonin patterns differ between C. robusta and P. mammillata can be due to the distinct experimental methods used: TPH expression and serotonin immunofluorescence, respectively. Furthermore, embryos treated with various pharmacological serotonin inhibitors exhibited impaired development of the anterior nervous system and metamorphosis (Pennati et al., 2001). Ultimately, P. mammillata juveniles treated with a specific serotonin receptor 2B (5HT2b) antagonist developed an abnormal cardiovascular system, confirming the key role of this neurotransmitter in development and morphogenesis (Pennati et al., 2001, 2003; Zega et al., 2005). Interestingly, by analyzing TPH expression in adult C. robusta, serotonergic neurons have also been found in the tentacle of coronal cells in the oral siphon. These cells are homologous to vertebrate hair cells (Rigon et al., 2018).
TABLE 2A
| Group | Species | Expression (embryos and larva) | A | References | |
| Tunicates | Ascidians | Ciona robusta | Visceral ganglion, neural tube floor, muscle cells   |
✓ | Welsh and Loveland, 1968; Nilsson et al., 1988; De Bernardi et al., 2006; Pennati et al., 2007a; Razy-Krajka et al., 2012; Braun and Stach, 2016 |
| Phallusia mammillata | Sensory vesicle, papillae, epidermal neurons  |
Pennati et al., 2001, 2003; Zega et al., 2005 | |||
| Styela plicata | Adhesive papillae, brain, photolith  |
De Bernardi et al., 2006 | |||
| Diplosoma listerianum | Everted papillae, posterior brain region  |
✓ | De Bernardi et al., 2006 | ||
| Microcosmus vulgaris | Otolith  |
De Bernardi et al., 2006 | |||
| Botrylloides leachi | Peripheral nervous system- papillae  |
Pennati et al., 2007b | |||
| Herdmania momus | Larval trunk  |
Stach, 2005 | |||
| Ascidia interrupta | Larval trunk  |
Stach, 2005 | |||
| Clavelina oblonga | Statocyte, dorsal epithelium  |
✓ | Stach, 2005 | ||
| Botryllus schlosseri | ✓ | Tiozzo et al., 2009; Braun and Stach, 2016 | |||
| Clavelina lepadiformis | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2016 | |||
| Perophora japonica | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2016, 2018 | |||
| Ascidiella scabra | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2016 | |||
| Ascidia mentula | ✓ | Nilsson et al., 1988 | |||
| Corella parallelogramma | ✓ | Nilsson et al., 1988; Braun and Stach, 2016 | |||
| Thalacians | Thalia democratica | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2016, 2018; Valero-Gracia et al., 2016 | ||
| Pyrosoma atlanticum | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2018 | |||
| Doliolum nationalis | ✓ | Stach, 2005; Braun and Stach, 2018 | |||
| Doliolina muelleri | ✓ | Valero-Gracia et al., 2016 | |||
| Pyrostremma agassizi | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2018 | |||
| Pyrosomella verticillata | ✓ | Valero-Gracia et al., 2016; Braun and Stach, 2018 | |||
| Salpa fusiformis | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2018 | |||
| Iasis cylindrica | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2018 | |||
| Ihlea punctata | ✓ | Valero-Gracia et al., 2016 | |||
| Appendicularians | Oikopleura fusiformis | ✓ | Braun and Stach, 2016 | ||
| Cephalochordates | Branchiostoma floridae | Anterior nerve cord, frontal eye complex, gut epithelium  |
✓ | Candiani et al., 2001, 2012; Morikawa et al., 2001; Moret et al., 2004; Vopalensky et al., 2012 | |
| Echinoderms | Echinoids | Temnopleurus reevesii | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Yaguchi et al., 2015 | |
| Lytechinus variegatus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Buznikov et al., 2005; Piacentino et al., 2016; Slota and McClay, 2018 | |||
| Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ    |
Yaguchi et al., 2000, 2011, 2014; Yaguchi and Katow, 2003; Katow et al., 2004, Katow et al., 2007; Katow, 2008; Yao et al., 2010 | |||
| Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ   |
✓ | Bisgrove and Burke, 1986; Burke et al., 2006, 2014; Yaguchi et al., 2006, 2010; Materna and Cameron, 2008; Wei et al., 2009, 2016; Squires et al., 2010; Range et al., 2013; Garner et al., 2016; Anishchenko et al., 2018; Perillo et al., 2018; Wood et al., 2018 | ||
| Paracentrotus lividus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ   |
Toneby, 1977 | |||
| Arbacia punctulata |

|
Brown and Shaver, 1989 | |||
| Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Bisgrove and Burke, 1987 | |||
| Psammechinus miliaris | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ; lower lip  |
Beer et al., 2001 | |||
| Heliocidaris erythrogramma | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Byrne et al., 2007 | |||
| Heliocidaris tuberculata | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Bisgrove and Raff, 1989 | |||
| Dendraster excentricus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Hay-Schmidt, 2000 | |||
| Eucidaris tribuloides | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Bishop et al., 2013 | |||
| Asteroids | Patiriella regularis | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ; ciliary band  |
Chee and Byrne, 1999 | ||
| Pisaster ochraceus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Moss et al., 1994 | |||
| Asterias rubens | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Moss et al., 1994 | |||
| Patiria miniata | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Jarvela et al., 2016 | |||
| Ophiuroids | Amphiura filiformis | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Dupont et al., 2009 | ||
| Holothurians | Stichopus japonicus | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Nakano et al., 2006 | ||
| Holothuria atra | Anterior neuroectoderm; apical organ  |
Bishop and Burke, 2007 | |||
(A) Indolamines (Serotonin) distribution in embryos or adult tunicates, cephalochordates, and echinoderms.
Color code:  Neurotransmitters (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence);
Neurotransmitters (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence); Metabolizing Enzymes or receptors (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).
Metabolizing Enzymes or receptors (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).  Enhancer activity.
Enhancer activity.  Other methods. A, adult.
Other methods. A, adult.
Serotonin in Other Tunicates
In the larva of the tunicate Styela plicata, serotonin was detected in some cells of the brain surrounding the sole sense organ, the photolith (which is considered homologous to the two separate sense organs of other tunicate species: the ocellus and the otolith), and in the single fused adhesive papillae (De Bernardi et al., 2006). The larva of Diplosoma listenarium retains serotonin in the everted papillae and in the posterior region of the brain, while differentiating zooids display adult-like localization of serotonin in the esophagus, endostyle and the peripharyngeal band (De Bernardi et al., 2006). However, in the larva of Microcosmus vulgaris, serotonin has been detected exclusively in a few brain cells, close to the otolith (De Bernardi et al., 2006). Serotonin occurs in the larvae of Botrylloides leachi, where immunohistochemical analyses found serotonin in peripheral neurons of the papillae, suggesting that serotonin released by these neurons may act as an endogenous signal inducing metamorphosis (Pennati et al., 2007b).
Other tunicates showing positive serotonin immunostaining in the larvae are Herdmania momus and Ascidia interrupta. These have a serotonergic nervous system consisting of two parts: an anterior aggregation of cell bodies (in the case of H. momus adjoining the larval statocyte complex), and a second group of serotonergic neurons projecting posteriorly (Stach, 2005). This study also found positive serotonin immunoreactivity in the larva of Clavelina oblonga at the statocyte complex and along the dorsal epithelium (Stach, 2005).
Several other studies have sought serotonin in in diverse adult tunicates and among them positive immunoreactivity has been found in the Ascidiacea: Botryllus schlosseri (Tiozzo et al., 2009; Braun and Stach, 2016), Clavelina lepadiformis (Braun and Stach, 2016), Perophora japonica (Braun and Stach, 2016), Ascidiella scabra (Braun and Stach, 2016), Ascidia mentula (Nilsson et al., 1988), and Corella parallelogramma (Nilsson et al., 1988; Braun and Stach, 2016).
In adult thaliaceas, serotonin-positive cells have been found in Thalia democratica (Braun and Stach, 2016; Valero-Gracia et al., 2016; Braun and Stach, 2018), Pyrosoma atlanticum (Braun and Stach, 2018), Doliolum nationalis (Stach, 2005; Braun and Stach, 2018), Doliolina muelleri (Valero-Gracia et al., 2016), Pyrostremma agassizi (Braun and Stach, 2018), Pyrosomella verticillata (Valero-Gracia et al., 2016; Braun and Stach, 2018), Salpa fusiformis (Braun and Stach, 2018), Iasis cylindrica (Braun and Stach, 2018), and Ihlea punctate (Valero-Gracia et al., 2016). Concerning appendicularians, only two cells in the posterior part of the neural ganglion are positively stained in Oikopleura fusiformis (Stach, 2005). However, no serotonin-like cells have been found in Oikopleura dioica (Braun and Stach, 2016).
Cephalochordates
During lancelet development (B. floridae), serotonin has been first detected at neurula stage in the forming neural tube (Candiani et al., 2001). Later in 2/3-day old larva, it has been found in two populations of cells, one in the cerebral vesicle including frontal eye complex, and another in the inner epithelium of the gut (Figure 1B and Table 2A) (Holland and Holland, 1993; Candiani et al., 2001; Vopalensky et al., 2012). In 6-day old larvae, the rostral serotonin-positive cells differentiate into dorsal serotonergic neurons and are segmentally repeated along the spinal cord (Candiani et al., 2001). During metamorphosis and in young juveniles, serotonin progressively disappears from the anterior brain and can still be detected in the visceral area (Holland and Holland, 1993; Morikawa et al., 2001).
In adult lancelet, serotonin occurs in the roof of the cerebral vesicle, posterior to the frontal eye complex, and in the intestinal epithelium in several endocrine-like cells, functioning as a hormone in the latter (Candiani et al., 2001). Serotonergic neurons are near to but distinct from dopaminergic cells, and have highlighted that the dopaminergic and serotoninergic cells in the lancelet cerebral vesicle and the vertebrate hindbrain are distributed analogously; this distribution is proposed as an ancestral character of chordates (Moret et al., 2004).
Moreover, the distribution of the serotonergic system in lancelet has also been studied indirectly through the expression pattern of its biosynthesis enzymes: tryptophan hydroxylase (TpH, the limiting enzyme in serotonin synthesis) and a serotonin transporter (SERT), confirming previous immunohistochemical analyses (Candiani et al., 2012). A recent work also highlighted that the development of lancelet serotonergic cells is controlled by the retinoic acid signaling pathway, as per dopaminergic neurons (Zieger and Schubert, 2017; Zieger et al., 2018a).
Echinoderms
The development of the embryonic and larval nervous system in sea urchins is well-studied. An abundance of work on this topic demonstrates that these species mainly undergo neurogenesis during the late gastrula stage with the first neurons specified in the anterior extreme of the ectoderm: the anterior neuroectoderm. Until the larval stage, neurons proliferate and differentiate to a few 100 neurons forming the ‘central nervous system,’ the apical organ, the ‘peripheral nervous system’ (lateral ganglion cells and post-oral neurons), and the ciliary band neurons (Figure 1C). Serotoninergic neurons are among the first types to differentiate during early neurogenesis.
The presence of serotonin in echinoderms was first described by thin layer chromatography and fluorometric analysis in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. It accretes throughout embryonic development and was found to regulates cell motility (Toneby, 1977). The first stage-specific data derive from immunolocalization experiments in the sea urchin S. purpuratus, where serotonin is localized, from late gastrula to pluteus stage, in the anterior neurogenic regions of the embryo. More specifically, at gastrula stage, serotonin is detected in 2–4 bilaterally symmetric cells in the anterior neural ectoderm, which give rise to the sensory ganglion of the late larva, the apical organ (Bisgrove and Burke, 1986). Similarly, in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis, serotonin-positive cells have been detected in the apical organ from the late gastrula to the pluteus stage, together with the pan neuronal marker Synaptotagmin B (Bisgrove and Burke, 1987). This suggests that serotonin in echinoderms has a major role in neuronal communication, as in vertebrates.
Serotonin and its signaling components have also been detected in the pre-nervous embryo. Blocking the serotonergic receptors with antagonists and agonists produces embryonic malformations, as does inhibiting the serotonin transporters. These malformations appear to be serotonin-specific since the phenotype can be rescued by reverse drugs or serotonin itself. These observations suggest that serotonergic signaling also has an important role in early embryogenesis and morphogenesis (Buznikov et al., 2005).
In all echinoderms studied (with most research performed in S. purpuratus) both serotonin and tryptophan hydroxylase (the rate limiting enzyme of serotonin synthesis) are expressed specifically (i) in a population of bilaterally symmetric patches of cells in the anterior ectoderm during the early stages and (ii) in neuronal clusters in the apical organ, ciliary band and lip ganglion neurons during late larval stages (Bisgrove and Raff, 1989; Brown and Shaver, 1989; Moss et al., 1994; Chee and Byrne, 1999; Hay-Schmidt, 2000; Yaguchi et al., 2000, 2006, 2008, 2010, 2011, 2014; Yamamoto and Vernier, 2011; Beer et al., 2001; Yaguchi and Katow, 2003; Burke et al., 2006, 2014; Nakano et al., 2006; Bishop and Burke, 2007; Byrne et al., 2007; Katow et al., 2007; Katow, 2008; Materna and Cameron, 2008; Dupont et al., 2009; Wei et al., 2009, 2016; Yao et al., 2010; Bishop et al., 2013; Range et al., 2013; Garner et al., 2016; Jarvela et al., 2016; Anishchenko et al., 2018; Perillo et al., 2018; Wood et al., 2018).
In the sea urchin Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus, inhibition of serotonin synthesis reduces larval swimming (Yaguchi and Katow, 2003; Katow et al., 2007). In most echinoderms investigated, the cell bodies of the serotonergic neurons reside in the ciliary band, whereas in the echinopluteus, serotonin positive cells localize mostly in the thick epithelium of the apical organ (Byrne et al., 2007). Data are unavailable on serotonin expression in adult echinoderms, although they seem to be able to uptake and catabolize it Squires et al. (2010).
Histamine
The histamine neurotransmitter is synthetized by the histidine decarboxylase (HDC) after catalyzing the decarboxylation of histidine to histamine. It is a biogenic amine with different roles in muscle contraction, neural transmission, and regulation of gastric secretions in both invertebrates and vertebrates (Reite, 1972). In vertebrates, histamine has also a key function in the regulation of inflammatory processes (Eto et al., 2001).
Tunicates
The first evidence of the presence of histamine-like compounds was found in P. mammillata; chemical extracts from tunics, siphons, and gut of this species induce contractions of the guinea-pig ileum. This suggests that these regions contained either histamine or histamine-releasing compounds acting on histamine receptors (Costa et al., 1997). Histamine is stored inside granular hemocytes and test cells of Styela plicata (Garcia-Garcia et al., 2014; Wong et al., 2014). Interestingly, histamine injection into the tunic induces the recruitment of hemocytes that ultimately mediate the constriction of tunic hemolymph vessel (Garcia-Garcia et al., 2014); this establishes that histamine regulates inflammation and host defense in tunicates, although histamine receptors of tunic vessel constriction remain unidentified. No histamine homologous receptors has been found in the genomes of C. robusta or C. savignyi (Garcia-Garcia et al., 2014). Wong and colleagues have cloned a C. robusta histidine decarboxylase (HDC) (Wong et al., 2014). The occurrence of this enzyme was confirmed by immunohistochemical analysis in a lysate of oocytes by using a mammalian polyclonal antibody (Wong et al., 2014).
Cephalochordates
Although histamine has not been found in a lancelet, a genomic survey of the G-proteins coupled receptor family (GPCR) in B. floridae indicated several putative histamine receptors (Burman et al., 2007). However, recently HDC sequences have been found in the genome of B. lanceolatum (BL08385; Marlétaz et al., 2018) and B. floridae (XP_002597913.1) Further ad hoc studies will be necessary to determine the role of these receptors.
Echinoderms
The genome of the sea urchin S. purpuratus encodes two HDC-like genes and 3 histamine receptors (Burke et al., 2006). One of those receptors, the H1R, is expressed symmetrically on either side of the larval mouth. In the same species, histamine is detected by a specific anti-His antibody staining, at gastrula stage in the putative echinoderm immune cells, in a few cells at the apical organ and in ciliary band neurons of the late pluteus (Sutherby et al., 2012; Lutek et al., 2018). Histamine is expressed in the juvenile tube feet, where at least two opsins types are also expressed (Ullrich-Luter et al., 2011), suggesting a possible role in phototransduction (Sutherby et al., 2013). Moreover, in various sea urchin species, histamine appears to regulate larval settlement and metamorphosis (Swanson et al., 2004, 2012; Sutherby et al., 2012). In addition, histaminergic neurons were detected in the buccal tentacles, the circumoral nerve ring, and in papillae scattered across the body of juveniles and adults of the sea cucumber Leptosynapta clarki (Hoekstra et al., 2012).
Discussion
In this review, we focused on the expression pattern and role of biological amines in three deuterostome groups displaying well-established animal model systems for evolutionary and developmental biology field to shed light on their function during embryogenesis and the onset of metamorphosis.
This comparative analysis, summarized in Tables 1, 2A,B and depicted in a simplified form in Figure 1, is discussed in relation to the phylogeny of these deuterostomes (tunicates, cephalochordates, and echinoderms). Chordates are characterized by a conserved body plan with a dorsal hollow neural tube, a notochord, lateral muscle, and a cephalic nervous system that expanded enormously in vertebrate chordates (Annona et al., 2015). In tunicates and cephalochordates, the typical chordate body plan features are established during early embryogenesis and maintained in the tadpole larva. Nevertheless, most tunicate species undergo a metamorphosis that induces profound morphologial modifications, while cephalochordates undergo only a partial metamorphosis in which the mouth changes its initial position from lateral to rostral (Holland and Holland, 1999). This contrasts with echinoderms: non-chordate deuterostomes that represent an ideal deuterostome outgroup for the chordate phylum that display distinct body plan organizations and developmental strategies, yet which all undergoing a dramatic metamorphosis.
TABLE 2B
| Neurotransmitter Indolamines | Group | Species | Expression (embryos and larva) | Adult | References |
| Melatonin | Tunicates | ||||
| Cephalochordates | Branchiostoma lanceolatum | ✓ | Vernadakis et al., 1998 | ||
| Echinoderms | |||||
| Histamine | Tunicates | Ciona robusta Botryllus schlosseri | ✓ | Garcia-Garcia et al., 2014; Wong et al., 2014Cima and Franchi, 2016 | |
| Styela plicata | ✓ | Garcia-Garcia et al., 2014; Wong et al., 2014 | |||
| Phallusia nigra | ✓ | Costa et al., 1997 | |||
| Cephalochordates | Branchiostoma lanceolatum | Burman et al., 2007 | |||
| Echinoderms | Strongylocentrotus purpuratus | Post-oral neurons; ciliary band; cells around the mouth    |
Burke et al., 2006; Leguia and Wessel, 2006; Sutherby et al., 2012, 2013; Lutek et al., 2018 | ||
| Holopneustes purpurascens |

|
Swanson et al., 2004, 2012 | |||
| Holopneustes inflatus |

|
Swanson et al., 2012 | |||
| Centrostephanus rodgersii |

|
Swanson et al., 2012 | |||
| Heliocidaris erythrogramma |

|
Swanson et al., 2012 | |||
| Leptosynapta clarki |

|
✓ | Hoekstra et al., 2012 |
(B) Indolamines: melatonin and histamine distribution in embryos or adult tunicates, cephalochordates, and echinoderms.
Color code:  Neurotransmitters (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).
Neurotransmitters (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).  Metabolizing Enzymes or receptors (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).
Metabolizing Enzymes or receptors (whole mount in situ hybridization or immunofluorescence).  Enhancer activity.
Enhancer activity.  Other methods.
Other methods.
The Dopamine Prominent Role in Controlling Metamorphosis of Invertebrate Deuterostomes
The evidence that dopaminergic cells occur in the tunicate sensory vesicle and cephalochordate cerebral vesicle and that dopamine occurs in cells near photoreceptor cells in both groups, suggest that a dopamine neurotransmission system predates the emergence of chordates (Moret et al., 2004, 2005; Candiani et al., 2005, 2012; Zega et al., 2010; Razy-Krajka et al., 2012; Zieger et al., 2017). Furthermore, genome duplications in the vertebrate lineage (but not basal chordates) generated multiple orthologs of the suite of protein factors necessary to synthetize, store and release dopamine; this probably facilitated most dopamine machinery genes acquiring new expression territories and additional functions (Yamamoto and Vernier, 2011).
In tunicates, dopaminergic neurons occurring at late larval stages in proximity to photoreceptor cells and in the posterior part of the sensory vesicle appear to modulate the neural network involved in age-dependent swimming behavior of the larva (Moret et al., 2005): a physiological condition necessary before metamorphosis. Similarly, in P. mammillata dopaminergic neurons likely regulate metamorphosis (Zega et al., 2005). No evidence yet exists of crosstalk between photoreceptor cells and dopaminergic neurons in sea urchin larvae or adults. The only evidence of dopamine signaling implicated in metamorphosis comes from the sand dollar D. excentricus, in which externally-provided dopamine induced metamorphosis in competent larvae (Burke, 1983).
In the sea urchin early larva, dopaminergic neurons are localized in the posterior part of the ciliary band and around the mouth. As the larva grows and the nervous system becomes increasingly complex, additional dopaminergic neurons arise in the same regions. The dopaminergic system in sea urchin larvae regulates swimming behavior (Katow et al., 2010), and initiates a phenotypic response to food availability (Yaguchi and Katow, 2003). The dopaminergic system seems to function similarly in tunicates, given that dopamine regulates swimming, making it a key neuromodulator of locomotory circuits throughout the deuterostomes.
In the lancelet (assuming that TH + neurons in larvae use dopamine) the TH system probably regulates the larval escape response as per other locomotor functions throughout the catecholaminergic system. Specifically, transmission electron microscopy and TH + expression indicate that the large pain neuron (LPN) represents a source of excitatory input, targeting the motoneurons (Zieger et al., 2017).
The modulation of locomotor circuits via dopamine appear to be ancient and conserved among both vertebrates (Ryczko and Dubuc, 2017) and invertebrates (Harris-Warrick et al., 1998), which is further supported by tunicates, sea urchins, and lancelets all retaining dopamine. However, we lack experimental data on the role of dopamine in regulating swimming behavior of lancelets or phenotypic responses to food availability in either Ciona or lancelets.
Serotonin Conserved Role in the Nervous System
In all taxa analyzed in this study, serotonergic neurons are predominantly localized in the anterior part of the organism and enable patterning of the anterior nervous system, development, and morphogenesis. In tunicates, serotonergic neurons reside mostly in the visceral ganglion of the larva with minor differences that are species-specific. In sea urchin embryos, serotonergic neurons arise from the most dorsal part of the anterior neuroectoderm (Bisgrove and Burke, 1987), whereas in lancelet embryos they are first detected at neurula stage in the developing neural tube (Candiani et al., 2001) and at the 2/3-day old larva they are localized to the anterior nerve cord.
During the development of tunicates, lancelet, and sea urchins, the expression pattern of the serotonergic pathway components expands from the anterior part of the larva to gut and muscle structures – progression that is conserved in these clades. In P. mammillata juveniles, serotonergic neurons reside in the peripharyngeal band, along the endostyle and in the gut (Pennati et al., 2001), suggesting that the peripharyngeal and gut expression pattern of serotonin could also be conserved. In the 2/3-day old lancelet larva, serotonin is also detected in gut epithelium structures, while in adult lancelet, serotoninergic neurons are detected in the digestive tract (Candiani et al., 2001). In late sea urchin larvae, serotonin is detected in neurons surrounding the mouth near the esophageal muscles (Burke et al., 2006), which correlates with C. robusta TPH expression adjoining muscle cells (Pennati et al., 2007a); this suggests that serotonin could have an ancestral role regulating muscle contraction.
Pharmacological treatment with serotonin inhibitors during C. robusta embryogenesis impairs metamorphosis and the development of the anterior nervous system (Pennati et al., 2001), whereas in P. mammillata blocking the serotonergic pathway impaired the cardiovascular system (Pennati et al., 2001, 2003; Zega et al., 2005). Similarly, serotonergic signaling inhibition during early embryogenesis in sea urchin leads to developmentally-arrested or malformed larvae (Buznikov et al., 2005); when applied after gastrulation, larvae swim less (Yaguchi and Katow, 2003; Katow et al., 2007).
Histamine Conserved Role in Immune Response in Echinoderms and Tunicates
In both echinoderms and tunicates, histamine is detected in the immune and nervous systems, suggesting that the role of histamine in regulating inflammatory processes in vertebrates is a general characteristic of deuterostomes (Eto et al., 2001). Injections of histamine in tunicates induce a rapid immune response by recruiting hemocytes (Garcia-Garcia et al., 2014). Histamine is essential for sea urchin competent larvae to settle and metamorphose; pharmacological blocking of the histamine receptors at the competent 8 arm S. purpuratus larval stage led to spontaneous settlement and metamorphosis, showing that in normal conditions histamine signaling prevents apoptosis and promotes healthy development of larvae (Swanson et al., 2004, 2012; Sutherby et al., 2012). No evidence exists that lancelets synthesize histamine, apart from putative histamine receptors reported in B. floridae (Burman et al., 2007).
Conclusion
Summarizing almost 60 years of research in this field exceeds the scope of this review. Our main goal has been to highlight common features and major differences in localization and function of the biological amines within deuterostomes.
Biogenic amines are ancient and, therefore, it is difficult to decipher a common role or a meaningfully conserved expression pattern, especially considering the dearth of deuterostome species for which data exist. Recently, the single cell RNA sequencing approach has been applied in C. robusta to determine the regulatory network governing the successful development of dopaminergic neurons in the central nervous system. A combination of classical embryologic approaches manipulating the expression of the ptf1 gene (considered a key factor for dopamine expression in coronet cells) together with single cell sequencing, allowed the authors of this study to demonstrate that in C. robusta the protein Meis is a key co-factor of Ptf1, necessary to specify dopaminergic neurons (Horie et al., 2018). This exemplifies the power of single cell transcriptomics approach to identify cell types and clarify their ontogeny and function (cf. Butler et al., 2018; Zeisel et al., 2018; Cao et al., 2019; Sladitschek et al., 2020), and laying the ground for future studies reconstructing the evolutionary history of the aminergic system in animals.
Statements
Author contributions
ED’A, SD’A, and MA conceived and designed the review. ED’A, PP, SD’A, and MA contributed to drafting and revising the manuscript. EA contributed to design and edit Figure 1. All authors contributed to review the literature and conceived the figure and tables.
Funding
PP has been supported by the Marie Curie ITN EvoCELL (grant number: 766053, H2020 PEOPLE Work Programme of the European Commission, PI: MA).
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to John D. Kirwan (Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn) for a critical reading of the manuscript and for the final English revision of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1
Adams D. K. Sewell M. A. Angerer R. C. Angerer L. M. (2011). Rapid adaptation to food availability by a dopamine-mediated morphogenetic response.Nat. Commun.2:592.
2
Akers T. K. (1969). Effects of epinephrine, norepinephrine and some blocking agents on tunicate smooth muscle.Comp. Biochem. Physiol.29813–819. 10.1016/0010-406x(69)91632-6
3
Anishchenko E. Arnone M. I. D’Aniello S. (2018). SoxB2 in sea urchin development: implications in neurogenesis, ciliogenesis and skeletal patterning.Evodevo9:5.
4
Annona G. Holland N. D. D’Aniello S. (2015). Evolution of the notochord.Evodevo6:30.
5
Baudonnat M. Huber A. David V. Walton M. E. (2013). Heads for learning, tails for memory: reward, reinforcement and a role of dopamine in determining behavioral relevance across multiple timescales.Front. Neurosci.7:175. 10.3389/fnins.2013.00175
6
Bayliss A. L. Evans P. D. (2013). Characterisation of AmphiAmR11, an amphioxus (Branchiostoma floridae) D2-dopamine-like G protein-coupled receptor.PLoS One8:e80833. 10.1371/journal.pone.0080833
7
Beer M. Heavens R. Handford E. Mcallister G. (2001). Edg receptors as therapeutic targets in the nervous system.Fund. Clin. Pharmacol.1559–59.
8
Bisgrove B. W. Burke R. D. (1986). Development of serotonergic neurons in embryos of the sea-urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus.Dev. Growth Diff.28569–574. 10.1111/j.1440-169x.1986.00569.x
9
Bisgrove B. W. Burke R. D. (1987). Development of the nervous-system of the pluteus larva of Strongylocentrotus droebachiensis.Cell Tissue Res.248335–343.
10
Bisgrove B. W. Raff R. A. (1989). Evolutionary conservation of the larval serotonergic nervous-system in a direct developing sea-urchin.Dev. Growth Differ.31363–370. 10.1111/j.1440-169x.1989.00363.x
11
Bishop C. D. Burke R. D. (2007). Ontogeny of the holothurian larval nervous system: evolution of larval forms.Dev. Genes Evol.217585–592. 10.1007/s00427-007-0169-9
12
Bishop C. D. Macneil K. E. A. Patel D. Taylor V. J. Burke R. D. (2013). Neural development in Eucidaris tribuloides and the evolutionary history of the echinoid larval nervous system.Dev. Biol.377236–244. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.03.006
13
Boron W. F. Boulpaep E. L. (2005). A Cellular and Molecular Approach.Philadelphia, PA: Elsievier/Saunderrs.
14
Braun K. Stach T. (2016). Comparative study of serotonin-like immunoreactivity in the branchial basket, digestive tract, and nervous system in tunicates.Zoomorphology135351–366. 10.1007/s00435-016-0317-8
15
Braun K. Stach T. (2018). Distribuition and evolution of serotonin-like immunoreactivity cells in Thaliacea (Tunicata).Zoomorphology137565–578. 10.1007/s00435-018-0416-9
16
Brown K. M. Shaver J. R. (1989). [H-3] Serotonin binding to blastula, gastrula, prism, and Pluteus sea-urchin embryo cells.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol.93281–285. 10.1016/0742-8413(89)90234-x
17
Burke R. D. (1983). Neural control of metamorphosis in dendraster excentricus.Biol. Bull.164176–188. 10.2307/1541137
18
Burke R. D. Angerer L. M. Elphick M. R. Humphrey G. W. Yaguchi S. Kiyama T. et al (2006). A genomic view of the sea urchin nervous system.Dev. Biol.300434–460. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.007
19
Burke R. D. Moller D. J. Krupke O. A. Taylor V. J. (2014). Sea urchin neural development and the metazoan paradigm of neurogenesis.Genesis52208–221. 10.1002/dvg.22750
20
Burman C. Evans P. D. (2010). Amphioxus expresses both vertebrate-type and invertebrate-type dopamine D(1) receptors.Invert Neurosci.1093–105. 10.1007/s10158-010-0111-0
21
Burman C. Maqueira B. Coadwell J. Evans P. D. (2007). Eleven new putative aminergic G-protein coupled receptors from Amphioxus (Branchiostoma floridae): identification, sequence analysis and phylogenetic relationship.Invert Neurosci.787–98. 10.1007/s10158-006-0041-z
22
Burman C. Reale V. Srivastava D. P. Evans P. D. (2009). Identification and characterization of a novel amphioxus dopamine D-like receptor.J. Neurochem.11126–36. 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06295.x
23
Butler A. Hoffman P. Smibert P. Papalexi E. Satija R. (2018). Integrating single-cell transcriptomic data across different conditions, technologies, and species.Nat. Biotechnol.36411–420. 10.1038/nbt.4096
24
Buznikov G. A. Peterson R. E. Nikitina L. A. Bezuglov V. V. Lauder J. M. (2005). The pre-nervous serotonergic system of developing sea urchin embryos and larvae: pharmacologic and immunocytochemical evidence.Neurochem. Res.30825–837. 10.1007/s11064-005-6876-6
25
Byrne M. Nakajima Y. Chee F. C. Burke R. D. (2007). Apical organs in echinoderm larvae: insights into larval evolution in the Ambulacraria.Evol. Dev.9432–445. 10.1111/j.1525-142x.2007.00189.x
26
Candiani S. Augello A. Oliveri D. Passalacqua M. Pennati R. De Bernardi F. et al (2001). Immunocytochemical localization of serotonin in embryos, larvae and adults of the lancelet. Branchiostoma floridae.Histochem. J.33413–420.
27
Candiani S. Moronti L. Ramoino P. Schubert M. Pestarino M. (2012). A neurochemical map of the developing amphioxus nervous system.BMC Neurosci.13:59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-13-59
28
Candiani S. Oliveri D. Parodi M. Castagnola P. Pestarino M. (2005). AmphiD1/beta, a dopamine D1/beta-adrenergic receptor from the amphioxus Branchiostoma floridae: evolutionary aspects of the catecholaminergic system during development.Dev. Genes Evol.215631–638. 10.1007/s00427-005-0019-6
29
Cao C. Lemaire L. A. Wang W. Yoon P. H. Choi Y. A. Parsons L. R. et al (2019). Comprehensive single-cell transcriptome lineages of a proto-vertebrate.Nature571349–354. 10.1038/s41586-019-1385-y
30
Chee F. Byrne M. (1999). Development of the larval serotonergic nervous system in the sea star Patiriella regularis as revealed by confocal imaging.Biol. Bull.197123–131. 10.2307/1542609
31
Cima F. Franchi N. (2016). Histamine stimulates ciliary beat frequency via the H2 receptor in the protochordateBotryllusschlosseri.J. Exp. Zool. B Mol. Dev. Evol.326176–192. 10.1002/jez.b.22675
32
Costa L. V. Malpezzi E. L. A. Berlinck R. G. S. Rowan E. G. Defreitas J. C. (1997). This histamine-like effects of Phallusia nigra extract: Evidences for direct activity at H1 receptors.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol.117111–115. 10.1016/s0742-8413(96)00228-9
33
D’Aniello E. Pezzotti M. R. Locascio A. Branno M. (2011). Onecut is a direct neural-specific transcriptional activator of Rx in Ciona intestinalis.Dev. Biol.355358–371. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.05.584
34
D’Aniello S. D’Aniello E. Locascio A. Memoli A. Corrado M. Russo M. T. et al (2006). The ascidian homolog of the vertebrate homeobox gene Rx is essential for ocellus development and function.Differentiation74222–234. 10.1111/j.1432-0436.2006.00071.x
35
Daubner S. C. Le T. Wang S. Z. (2011). Tyrosine hydroxylase and regulation of dopamine synthesis.Arch. Biochem. Biophys.5081–12. 10.1016/j.abb.2010.12.017
36
De Bernardi F. Pennati R. Candiani S. Zega G. Groppelli S. Pestarino M. (2006). Serotonin in the morphogenesis of ascidian nervous system.Caryologia59375–379.
37
Dehal P. Satou Y. Campbell R. K. Chapman J. Degnan B. De Tomaso A. et al (2002). The draft genome of Ciona intestinalis: insights into chordate and vertebrate origins.Science2982157–2167. 10.1126/science.1080049
38
Delsuc F. Brinkmann H. Chourrout D. Philippe H. (2006). Tunicates and not cephalochordates are the closest living relatives of vertebrates.Nature439965–968. 10.1038/nature04336
39
Dupont S. Thorndyke W. Thorndyke M. C. Burke R. D. (2009). Neural development of the brittlestar Amphiura filiformis.Dev. Genes Evol.219159–166. 10.1007/s00427-009-0277-9
40
Eto M. Kitazawa T. Yazawa M. Mukai H. Ono Y. Brautigan D. L. (2001). Histamine-induced vasoconstriction involves phosphorylation of a specific inhibitor protein for myosin phosphatase by protein kinase C alpha and delta isoforms.J. Biol. Chem.27629072–29078. 10.1074/jbc.m103206200
41
Gallo V. P. Accordi F. Chimenti C. Civinini A. Crivellato E. (2016). Catecholaminergic system of invertebrates: comparative and evolutionary aspects in comparison with the octopaminergic system.Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol.322363–394. 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2015.12.006
42
Garcia-Garcia E. Gomez-Gonzalez N. E. Meseguer J. Garcia-Ayala A. Mulero V. (2014). Histamine regulates the inflammatory response of the tunicate Styela plicata.Dev. Comp. Immunol.46382–391. 10.1016/j.dci.2014.05.017
43
Garner S. Zysk I. Byrne G. Kramer M. Moller D. Taylor V. et al (2016). Neurogenesis in sea urchin embryos and the diversity of deuterostome neurogenic mechanisms.Development143286–297. 10.1242/dev.124503
44
Goldstein D. S. (2010). Adrenaline and Noradrenaline. Encyclopedia of Life Sciences.Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
45
Harris-Warrick R. M. Johnson B. R. Peck J. H. Kloppenburg P. Ayali A. Skarbinski J. (1998). Distributed effects of dopamine modulation in the crustacean pyloric network.Neuronal Mech. Gen. Locomot. Act.860155–167. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09046.x
46
Hay-Schmidt A. (2000). The evolution of the serotonergic nervous system.Proc. Biol. Sci.2671071–1079. 10.1098/rspb.2000.1111
47
Heine P. Dohle E. Bumsted-O’brien K. Engelkamp D. Schulte D. (2008). Evidence for an evolutionary conserved role of homothorax/Meis1/2 during vertebrate retina development.Development135805–811. 10.1242/dev.012088
48
Hoekstra L. A. Moroz L. L. Heyland A. (2012). Novel insights into the Echinoderm nervous system from histaminergic and FMRFaminergic-like cells in the sea cucumber Leptosynapta clarki.PLoS One7:e44220. 10.1371/journal.pone.0044220
49
Holland L. Z. Holland N. D. (1999). Chordate origins of the vertebrate central nervous system.Curr. Opin. Neurobiol.9596–602. 10.1016/s0959-4388(99)00003-3
50
Holland N. D. Holland L. Z. (1993). Serotonin-containing cells in the nervous-system and other tissues during ontogeny of a lancelet, Branchiostoma-Floridae.Acta Zool.74195–204. 10.1111/j.1463-6395.1993.tb01234.x
51
Horie T. Horie R. Chen K. Cao C. Nakagawa M. Kusakabe T. G. et al (2018). Regulatory cocktail for dopaminergic neurons in a protovertebrate identified by whole-embryo single-cell transcriptomics.Genes Dev.321297–1302. 10.1101/gad.317669.118
52
Hoyle C. H. V. (2011). Evolution of neuronal signalling: Transmitters and receptors.Autonomic Neurosci. Basic Clin.16528–53. 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.05.007
53
Irvine S. Q. Fonseca V. C. Zompa M. A. Antony R. (2008). Cis-regulatory organization of the Pax6 gene in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis.Dev. Biol.317649–659. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.036
54
Janakidevi K. Dewey V. C. Kidder G. W. (1966). Serotonin in protozoa.Arch. Biochem. Biophys.113758–759. 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90259-1
55
Jarvela A. M. C. Yankura K. A. Hinman V. F. (2016). A gene regulatory network for apical organ neurogenesis and its spatial control in sea star embryos.Development1434214–4223. 10.1242/dev.134999
56
Katow H. (2008). Spatio-temporal expression of a Netrin homolog in the sea urchin Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus (HpNetrin) during serotonergic axon extension.Int. J. Dev. Biol.521077–1088. 10.1387/ijdb.082684hk
57
Katow H. Suyemitsu T. Ooka S. Yaguchi J. Jin-Nai T. Kuwahara I. et al (2010). Development of a dopaminergic system in sea urchin embryos and larvae.Journal of Experimental Biology2132808–2819. 10.1242/jeb.042150
58
Katow H. Yaguchi S. Kiyomoto M. Washio M. (2004). The 5-HT receptor cell is a new member of secondary mesenchyme cell descendants and forms a major blastocoelar network in sea urchin larvae.Mech. Dev.121325–337. 10.1016/j.mod.2004.03.005
59
Katow H. Yaguchi S. Kyozuka K. (2007). Serotonin stimulates [Ca2+](i) elevation in ciliary ectodermal cells of echinoplutei through a serotonin receptor cell network in the blastocoel.J. Exp. Biol.210403–412. 10.1242/jeb.02666
60
Keefner K. R. Akers T. K. (1971). Sodium localization in digitalis- and epinephrine-treated tunicate myocardium.Comp. Gen. Pharmacol.2415–422. 10.1016/0010-4035(71)90038-3
61
Kimura Y. Yoshida M. Morisawa M. (2001). Participation of Neurotransmitters and Adrenergic Receptor in the Metamorphosis of Ascidian Larvae.Tokyo: Springer.
62
Kimura Y. Yoshida M. Morisawa M. (2003). Interaction between noradrenaline or adrenaline and the beta 1-adrenergic receptor in the nervous system triggers early metamorphosis of larvae in the ascidian, Ciona savignyi.Dev. Biol.258129–140. 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00118-0
63
Leguia M. Wessel G. M. (2006). The histamine H1 receptor activates the nitric oxide pathway at fertilization.Mol. Reprod. Dev.731550–1563. 10.1002/mrd.20586
64
Lendvai B. Halmos G. B. Polony G. Kapocsi J. Horvath T. Aller M. et al (2011). Chemical neuroprotection in the cochlea: the modulation of dopamine release from lateral olivocochlear efferents.Neurochem. Int.59150–158. 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.05.015
65
Lutek K. Dhaliwal R. S. Van Raay T. J. Heyland A. (2018). Sea urchin histamine receptor 1 regulates programmed cell death in larval Strongylocentrotus purpuratus.Sci. Rep.8:4002.
66
Marlétaz F. Firbas P. N. Maeso I. Tena J. J. Bogdanovic O. Perry M. et al (2018). Amphioxus functional genomics and the origins of vertebrate gene regulation.Nature56464–70.
67
Materna S. C. Cameron R. A. (2008). The sea urchin genome as a window on function.Biol. Bull.214266–273. 10.2307/25470668
68
Moret F. Christiaen L. Deyts C. Blin M. Joly J. S. Vernier P. (2005). The dopamine-synthesizing cells in the swimming larva of the tunicate Ciona intestinalis are located only in the hypothalamus-related domain of the sensory vesicle.Eur. J. Neurosci.213043–3055. 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04147.x
69
Moret F. Guilland J. C. Coudouel S. Rochette L. Vernier P. (2004). Distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase, dopamine, and serotonin in the central nervous system of amphioxus (Branchiostoma lanceolatum): implications for the evolution of catecholamine systems in vertebrates.J. Comp. Neurol.468135–150. 10.1002/cne.10965
70
Morikawa K. Tsuneki K. Ito K. (2001). Expression patterns of HNK-1 carbohydrate and serotonin in sea urchin, amphioxus, and lamprey, with reference to the possible evolutionary origin of the neural crest.Zool. Anal. Comp. Syst.10481–90. 10.1078/0944-2006-00011
71
Moss C. Burke R. D. Thorndyke M. C. (1994). Immunocytochemical localization of the neuropeptide-S1 and serotonin in larvae of the starfish Pisaster ochraceus and asterias-rubens.J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U.K.7461–71. 10.1017/s0025315400035669
72
Nakano H. Murabe N. Amemiya S. Nakajima Y. (2006). Nervous system development of the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus.Dev. Biol.292205–212. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2005.12.038
73
Nilsson O. Fredriksson G. Ofverholm T. Ericson L. E. (1988). Electron-microscopic immunocytochemistry of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the ascidian endostyle.Cell Tissue Res.253137–143.
74
Nordström K. J. Fredriksson R. Schioth H. B. (2008). The amphioxus (Branchiostoma floridae) genome contains a highly diversified set of G protein-coupled receptors.BMC Evol Biol8:9. 10.1186/1471-2148-8-9
75
Oliver G. Mailhos A. Wehr R. Copeland N. G. Jenkins N. A. Gruss P. (1995). Six3, a murine homologue of the sine oculis gene, demarcates the most anterior border of the developing neural plate and is expressed during eye development.Development1214045–4055.
76
Pennati R. Candiani S. Biggiogero M. Zega G. Groppelli S. Oliveri D. et al (2007a). Developmental expression of tryptophan hydroxylase gene in Ciona intestinalis.Dev. Genes Evol.217307–313. 10.1007/s00427-007-0138-3
77
Pennati R. Groppelli S. Sotgia C. Candiani S. Pestarino M. De Bernardi F. (2001). Serotonin localization in Phallusia mammillata larvae and effects of 5-HT antagonists during larval development.Dev. Growth Differ.43647–656. 10.1046/j.1440-169x.2001.00608.x
78
Pennati R. Groppelli S. Sotgia C. Zega G. Pestarino M. De Bernardi F. (2003). WAY-100635, an antagonist of 5-HT(1A) receptor, causes malformations of the CNS in ascidian embryos.Dev. Genes Evol.213187–192. 10.1007/s00427-003-0311-2
79
Pennati R. Zega G. Groppelli S. De Bernardi F. (2007b). Immunohistochemical analysis of the adhesive papillae of Botrylloides leachi (Chordates, Tunicata, Ascidiacea): implications for their sensory function.Ital. J. Zool.74325–329. 10.1080/11250000701562229
80
Perillo M. Paganos P. Mattiello T. Cocurullo M. Oliveri P. Arnone M. I. (2018). New neuronal subtypes with a “Pre-Pancreatic” signature in the sea Urchin Stongylocentrotus purpuratus.Front. Endocrinol.9:650. 10.3389/fendo.2018.00650
81
Piacentino M. L. Chunga O. Ramachandrana J. Zuch D. T. Yua J. Conawaya E. A. et al (2016). Zygotic LvBMP5-8 is required for skeletal patterning and for left–right but not dorsal–ventral specification in the sea urchin embryo.Dev. Biol.41244–56. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.02.015
82
Range R. C. Angerer R. C. Angerer L. M. (2013). Integration of canonical and noncanonical Wnt signaling pathways patterns the neuroectoderm along the anterior-posterior axis of sea Urchin embryos.PLoS Biol.11:e1001467. 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001467
83
Razy-Krajka F. Brown E. R. Horie T. Callebert J. Sasakura Y. Joly J. S. et al (2012). Monoaminergic modulation of photoreception in ascidian: evidence for a proto-hypothalamo-retinal territory.BMC Biol10:45. 10.1186/1741-7007-10-45
84
Reite O. B. (1972). Comparative physiology of histamine.Physiol Rev52778–819.
85
Rigon F. Gasparini F. Shimeld S. M. Candiani S. Manni L. (2018). Developmental signature, synaptic connectivity and neurotransmission are conserved between vertebrate hair cells and tunicate coronal cells.J Comp Neurol526957–971. 10.1002/cne.24382
86
Rochchina V. V. (2001). Neurotrasmitters in Plant Life.Plymouth: Science Publ.
87
Rochchina V. V. (2010). Evolutionary Considerations of Neurotransmitters in Microbial, Plant, and Animal Cells.New York, NY: Springer.
88
Ryczko D. Dubuc R. (2017). Dopamine and the brainstem locomotor networks: from lamprey to human.Front. Neurosci.11:295. 10.3389/fnins.2017.00295
89
Scudder C. L. Akers T. K. Karczmar A. G. (1963). Effects of drugs on the tunicate electrocardiogram.Comp. Biochem. Physiol.9307–312. 10.1016/0010-406x(63)90005-7
90
Sherwood N. M. Tello J. A. Roch G. J. (2006). Neuroendocrinology of protochordates: insights from Ciona genomics.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol.144254–271. 10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.11.013
91
Sladitschek H. L. Fiuza U. M. Pavlinic D. Benes V. Hufnagel L. Neveu P. A. (2020). MorphoSeq: full single-cell transcriptome dynamics up to gastrulation in a chordate.Cell181e921.
92
Slota L. A. McClay D. R. (2018). Identification of neural transcription factors required for the differentiation of three neuronal subtypes in the sea urchin embryo.Dev. Biol.435138–149. 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.12.015
93
Squires L. N. Rubakhin S. S. Wadhams A. A. Talbot K. N. Nakano H. Moroz L. L. et al (2010). Serotonin and its metabolism in basal deuterostomes: insights from Strongylocentrotus purpuratus and Xenoturbella bocki.J. Exp. Biol.2132647–2654. 10.1242/jeb.042374
94
Stach T. (2005). Comparison of the serotonergic nervous system among Tunicata: implications for its evolution within Chordata.Org. Div. Evol.515–24. 10.1016/j.ode.2004.05.004
95
Sutherby J. Giardini J. L. Nguyen J. Wessel G. Leguia M. Heyland A. (2012). Histamine is a modulator of metamorphic competence in Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea).BMC Dev. Biol.12:14. 10.1186/1471-213X-12-14
96
Sutherby J. Giardini J. L. Nguyen J. Wessel G. Leguia M. Heyland A. (2013). Histamine is a modulator of metamorphic competence in Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea).BMC Dev. Biol.30:14. 10.1186/1471-213X-12-14
97
Swanson R. L. Byrne M. Prowse T. A. A. Mos B. Dworjanyn S. A. Steinberg P. D. (2012). Dissolved histamine: a potential habitat marker promoting settlement and metamorphosis in sea urchin larvae.Mar. Biol.159915–925. 10.1007/s00227-011-1869-2
98
Swanson R. L. Williamson J. E. De Nys R. Kumar N. Bucknall M. P. Steinberg P. D. (2004). Induction of settlement of larvae of the sea urchin Holopneustes purpurascens by histamine from a host alga.Biol. Bull.206161–172. 10.2307/1543640
99
Tiozzo S. Murray M. Degnan B. M. De Tomaso A. W. Croll R. P. (2009). Development of the neuromuscular system during asexual propagation in an invertebrate chordate.Dev. Dyn.2382081–2094. 10.1002/dvdy.22023
100
Toneby M. (1977). Functional aspects of 5-Hydroxytryptamine in early embryogenesis of sea-Urchin Paracentrotus lividus.Wilhelm Rouxs Arch. Dev. Biol.181247–259. 10.1007/bf00848424
101
Ullrich-Luter E. M. Dupont S. Arboleda E. Hausen H. Arnone M. I. (2011). Unique system of photoreceptors in sea urchin tube feet.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.1088367–8372. 10.1073/pnas.1018495108
102
Valero-Gracia A. Marino R. Crocetta F. Nittoli V. Tiozzo S. Sordino P. (2016). Comparative localization of serotonin-like immunoreactive cells in Thaliacea informs tunicate phylogeny.Front. Zool.13:45. 10.1186/s12983-016-0177-6
103
Vernadakis A. J. Bemis W. E. Bittman E. L. (1998). Localization and partial characterization of melatonin receptors in amphioxus, hagfish, lamprey, and skate.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol.11067–78. 10.1006/gcen.1997.7042
104
Vienne A. Pontarotti P. (2006). Metaphylogeny of 82 gene families sheds a new light on chordate evolution.Int J Biol Sci232–37. 10.7150/ijbs.2.32
105
Vopalensky P. Pergner J. Liegertova M. Benito-Gutierrez E. Arendt D. Kozmik Z. (2012). Molecular analysis of the amphioxus frontal eye unravels the evolutionary origin of the retina and pigment cells of the vertebrate eye.Proc. Natil. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.10915383–15388. 10.1073/pnas.1207580109
106
Wada Y. Mogami Y. Baba S. A. (1997). Modification of ciliary beating in sea urchin larvae induced by neurotransmitters: beat-plane rotation and control of frequency fluctuation.J. Exp. Biol.2009–18.
107
Wei Z. Angerer L. M. Angerer R. C. (2016). Neurogenic gene regulatory pathways in the sea urchin embryo.Development143298–305. 10.1242/dev.125989
108
Wei Z. Yaguchi J. Yaguchi S. Angerer R. C. Angerer L. M. (2009). The sea urchin animal pole domain is a Six3-dependent neurogenic patterning center (vol 136, pg 1179, 2007).Development1361583–1583. 10.1242/dev.037002
109
Welsh J. H. Loveland R. E. (1968). 5-hydroxytryptamine in the ascidian, ciona intestinaslis l.∗.Comp. Biochem. Physiol.27719–722. 10.1016/0010-406x(68)90613-0
110
Wong G. W. Zhuo L. S. Kimata K. Lam B. K. Satoh N. Stevens R. L. (2014). Ancient origin of mast cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.451314–318. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.07.124
111
Wood N. J. Mattiello T. Rowe M. L. Ward L. Perillo M. Arnone M. I. et al (2018). Neuropeptidergic systems in pluteus larvae of the sea Urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus: neurochemical complexity in a “Simple” nervous system.Front. Endocrinol.9:628. 10.3389/fendo.2018.00628
112
Yaguchi S. Kanoh K. Amemiya S. Katow H. (2000). Initial analysis of immunochemical cell surface properties, location and formation of the serotonergic apical ganglion in sea urchin embryos.Dev. Growth Diff.42479–488.
113
Yaguchi S. Katow H. (2003). Expression of Tryptophan 5-hydroxylase gene during sea urchin neurogenesis and role of serotonergic nervous system in larval behavior.J. Comp. Neurol.466219–229.
114
Yaguchi S. Yaguchi J. Angerer R. C. Angerer L. M. (2008). A Wnt-FoxQ2-nodal pathway links primary and secondary axis specification in sea urchin embryos.Dev. Cell1497–107.
115
Yaguchi S. Yaguchi J. Angerer R. C. Angerer L. M. Burke R. D. (2010). TGF beta signaling positions the ciliary band and patterns neurons in the sea urchin embryo.Dev. Biol.34771–81.
116
Yaguchi S. Yaguchi J. Burke R. D. (2006). Specification of ectoderm restricts the size of the animal plate and patterns neurogenesis in sea urchin embryos.Development1332337–2346.
117
Yaguchi S. Yaguchi J. Inaba K. (2014). Bicaudal-C is required for the formation of anterior neurogenic ectoderm in the sea urchin embryo.Sci. Rep.4:6852.
118
Yaguchi S. Yaguchi J. Wei Z. Jin Y. H. Angerer L. M. Inaba K. (2011). Fez function is required to maintain the size of the animal plate in the sea urchin embryo.Development1384233–4243.
119
Yaguchi S. Yamazaki A. Wada W. Tsuchiya Y. Sato T. Shinagawa H. et al (2015). Early development and neurogenesis of Temnopleurus reevesii.Dev. Growth Differ.57242–250. 10.1111/dgd.12202
120
Yamamoto K. Vernier P. (2011). The evolution of dopamine systems in chordates.Front. Neuroanat.5:21. 10.3389/fnana.2011.00021
121
Yao D. Ru S. G. Katow H. (2010). The neurotoxic effects of monocrotophos on the formation of the serotonergic nervous system and swimming activity in the larvae of the sea urchin Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus.Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol.30181–187.
122
Zega G. Candiani S. Groppelli S. De Bernardi F. Pennati R. (2010). Neurotoxic effect of the herbicide paraquat on ascidian larvae.Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol.2924–31.
123
Zega G. Pennati R. Groppelli S. Sotgia C. De Bernardi F. (2005). Dopamine and serotonin modulate the onset of metamorphosis in the ascidian Phallusia mammillata.Dev. Biol.282246–256.
124
Zeisel A. Hochgerner H. Lonnerberg P. Johnsson A. Memic F. Van Der Zwan J. et al (2018). Molecular architecture of the mouse nervous system.Cell174:e1022.
125
Zieger E. Candiani S. Garbarino G. Croce J. C. Schubert M. (2018a). Correction to: roles of retinoic acid signaling in shaping the neuronal architecture of the developing amphioxus nervous system.Mol. Neurobiol.555230–5231.
126
Zieger E. Garbarino G. Robert N. S. M. Yu J. K. Croce J. C. Candiani S. et al (2018b). Retinoic acid signaling and neurogenic niche regulation in the developing peripheral nervous system of the cephalochordate amphioxus.Cell Mol. Life Sci.752407–2429.
127
Zieger E. Lacalli T. C. Pestarino M. Schubert M. Candiani S. (2017). The origin of dopaminergic systems in chordate brains: insights from amphioxus.Int. J. Dev. Biol.61749–761.
128
Zieger E. Schubert M. (2017). New insights into the roles of retinoic acid signaling in nervous system development and the establishment of neurotransmitter systems.Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol.3301–84.
Summary
Keywords
nervous system, non-vertebrate chordate, echinoderms, dopamine, serotonin, histamine, tunicates, cephalochordates
Citation
D’Aniello E, Paganos P, Anishchenko E, D’Aniello S and Arnone MI (2020) Comparative Neurobiology of Biogenic Amines in Animal Models in Deuterostomes. Front. Ecol. Evol. 8:587036. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2020.587036
Received
24 July 2020
Accepted
04 September 2020
Published
25 September 2020
Volume
8 - 2020
Edited by
Alessandro Minelli, University of Padua, Italy
Reviewed by
Honoo Satake, Suntory Foundation for Life Sciences, Japan; Simona Candiani, Università degli Studi di Genova, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2020 D’Aniello, Paganos, Anishchenko, D’Aniello and Arnone.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Enrico D’Aniello, enrico.daniello@szn.itMaria Ina Arnone, miarnone@szn.it
This article was submitted to Evolutionary Developmental Biology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.