Abstract
Documenting the impacts of the Pleistocene megafaunal extinctions on predator-prey interactions is a challenge because of the incomplete fossil record and depauperate extant community structure. We used a comparative ecological approach to investigate whether the existing prey preference patterns of jaguars Panthera onca were potentially affected by the Pleistocene extinctions in the Americas compared with large felids in Africa and Asia. We reviewed the literature and found 25 studies reporting 3214 jaguar kills recorded throughout the species' distribution. We found that jaguars significantly preferred capybara Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris and giant anteater Myrmecophaga tridactyla, and avoided agoutis, carnivorans, primates, black-eared opossum Didelphis marsupialis and tapirs. Generalized linear models showed that jaguars select prey primarily based on socio-ecological and behavioral traits (abundance and herd size), rather than morphological characteristics (body size). Nonetheless, their accessible prey weight range was 6–60 kg, preferred prey weight range was 45–85 kg, and mean mass of significantly preferred prey was 32 ± 13 kg leading to a predator to prey body mass ratio of 1:0.53, which is much less than that of other solitary felids (although 1:0.84 may be the relationship with the smallest jaguars). Compared with other large, solitary felids, jaguars have an unusual predator to prey body mass ratio, show limited effect of prey morphology as a driver of prey selection, lack evidence of optimal foraging beyond their preferred prey, and a lack of preferential hunting on Cetartiodactyla herbivores. These features, coupled with the reduction in jaguar body mass since the Pleistocene, suggest that the loss of larger potential prey items within the preferred and accessible weight ranges at the end-Pleistocene still affects jaguar predatory behavior. It may be that jaguars survived this mass extinction event by preferentially preying on relatively small species.
Introduction
Understanding how foraging individuals decide upon what to feed is essential for predicting links and feedbacks among individuals at the population level and amongst trophic levels (Railsback and Harvey, 2013). Morphological and behavioral characteristics of prey have previously been shown to be drivers of large predator prey selection (Hayward and Kerley, 2005). However, these elements may not contribute uniformly across all predators particularly given the different evolutionary histories of the New and Old World. Consequently, we studied the trait-mediated interactions between jaguars and their prey in the Americas. The jaguar is the largest felid in the Americas (Nowell and Jackson, 1996) and is currently listed on the IUCN Red List as Near Threatened based on a high likelihood of persistence over most of its wide (8.75 million km2) distribution (Caso et al., 2008), although they will soon qualify for Vulnerable status given current rates of habitat loss, reductions of their prey base, and human persecution (Caso et al., 2008; H. Quigley pers. comm.).
The jaguar evolved in the Old World ~2.5–3 million years before present and migrated into North America about 2 million years ago (Kurtén and Anderson, 1980). During much of the Pleistocene, its range extended much further north than at present (reaching Nebraska and Oregon in the U.S.A. (ibid) and southern England and the Netherlands in Europe also; Hemmer et al., 2001; Mol et al., 2011). Historically, the jaguar was found from the south-western U.S. to southern Argentina (Seymour, 1989), but its current distribution is considerably smaller (Figure 1). This dramatic range reduction over the last million or so years has led some to describe the jaguar today as a relictual population (Kurtén and Anderson, 1980). The decline in range since the mid-Pleistocene was accompanied by a 15–20% reduction in body mass and a change in limb proportions, such that extant jaguars have shorter metapodials, perhaps as a response to hunting in more closed habitats (Kurten, 1973).
Figure 1
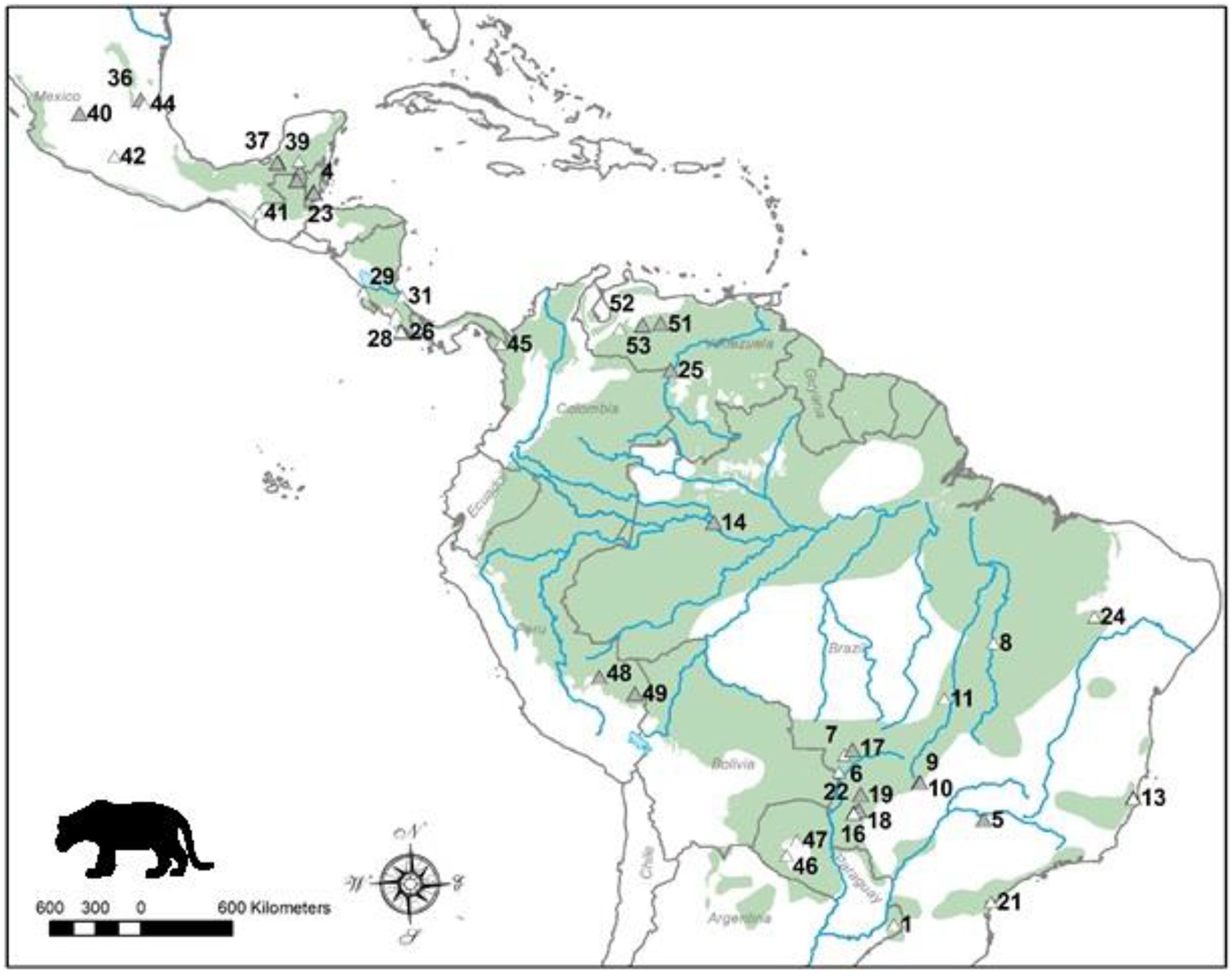
Distribution map of the jaguar and location of study sites. Current jaguar distribution is shaded and these data were obtained from the IUCN Red List. Sites where dietary studies of jaguars have been conducted are shown as triangles, and the shaded triangles represent the sites of studies that had data used in the analyses. Site numbers refer to those in Table 1. Note there are alternative maps on jaguar distribution from panthera.org and the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service that differ from that of the IUCN.
The morphology and behavior of other large predators have evolved to enable them to optimally kill a limited number of prey species within a specific prey weight range (Hayward et al., 2006b, 2014). This weight range also corresponds to the age classes of prey killed (Gervasi et al., 2015). Jaguars are solitary hunters (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2002) and so their prey preferences could be expected to be similar to those of leopards Panthera pardus (Hayward et al., 2006a), given that the two species have been considered to be ecological analogs in the New and Old Worlds, respectively (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2002). However, jaguars differ markedly from leopards in being about twice the mass with shorter, more robust limb bones, and relatively wider forepaws that are comparable in relative dimensions to those of lions Panthera leo (Gonyea, 1976; Meachen-Samuels and Van Valkenburgh, 2009b). Moreover, jaguars are more similar to lions than leopards in having both absolutely and relatively larger upper canines and lateral incisors (Meachen-Samuels and Van Valkenburgh, 2009a). In fact, jaguars appear to have the most robust canine teeth of any living felid for their body size (Meachen-Samuels and Van Valkenburgh, 2009a). These morphological characteristics indicate a specialization on strength relative to mass suggesting that jaguars should be killing larger prey than leopards, on average.
Across their range, jaguars exhibit up to 100% variation in body mass (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2002) and this is likely to impact their hunting decisions, with the smallest forms being more similar to leopards in the size of their prey. For example, Hoogesteijn and Mondolfi (1996) found that floodplain jaguars were significantly larger [body mass: Llanos = 104.5 kg (males), 66.9 kg (females) and Pantanal = 99.5 kg (males), 76.7 kg (females)] than forest jaguars [body mass: Amazon = 83.6 kg (males), no data for females and Central American = 56.1 kg (males), 41.4 kg (females)]. This variability was also reflected in the diet of the populations, with the forest jaguars having a significantly lower mean weight of vertebrate prey at 5.8 kg, compared to 89 kg (including livestock) for floodplain jaguars (Hoogesteijn and Mondolfi, 1996).
Prey is fundamental to the existence of large predators (Fuller and Sievert, 2001; Karanth et al., 2004; Hayward et al., 2007b), but in the case of the jaguar, it is not clear from existing reviews what the key prey base is or even whether they are reliant on large prey species (López Gonzalez and Miller, 2002). The currently prevailing view is that jaguars are opportunistic predators whose diet simply reflects the available prey community at a site (Mondolfi and Hoogesteijn, 1986; Rabinowitz and Nottingham, 1986; Emmons, 1987; Sunquist and Sunquist, 2002; Harmsen et al., 2010). Not surprisingly given their wide distribution and habitat tolerance, the jaguar's diet is diverse with at least 85 species listed as prey (Weckel et al., 2006b) ranging from cattle weighing more than 200 kg to small rodents (Harmsen et al., 2010). Their prey is unusually diverse and includes species such as arboreal primates (Peetz et al., 1992), ocelots (Gonzalez-Maya et al., 2010), marine and river turtles (Carrillo et al., 2009; Salera et al., 2009; Veríssimo et al., 2012), tortoises and fish (Emmons, 1989), crocodilians and their eggs (da Silveira et al., 2010) and dolphins (Castañeda et al., 2013). The diversity of aquatic prey reflects the jaguar's habitat use and ability to swim (Guggisberg, 1975). The majority of these prey are killed, but jaguars readily scavenge from carcasses for up to 17 days after death (López González and Lorenzana Piña, 2002). Despite this diversity of prey and their apparent strength, jaguars tend to kill prey slightly smaller than themselves (predator:prey ratio = 1:0.6–0.9; de Oliveira, 2002; if domestic livestock are excluded).
Hoogesteijn and Mondolfi (1996) describe the hunting technique frequently used by jaguars to kill cattle, whereby they jump on the back or side of the cattle, pull the animal's head around, unbalancing it and causing it to fall to the ground—often causing the animal to break its neck. The name jaguar is linked to their hunting technique: it comes from one of the Tupi-Guarani languages, deriving from the word “yaguara,” meaning “wild beast that overcomes its prey in a bound” (Seymour, 1989). Other hunting techniques used by jaguars include using the forepaws to hit smaller prey species (such as capybaras) to the ground and using a single bite to the nape of the neck to puncture the skull (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2002). This behavioral evidence suggests the jaguar has mechanisms by which to successfully kill large prey.
Reviews have indicated that medium and large prey are critical prey resources for jaguars (López Gonzalez and Miller, 2002), and that these vary depending on biome, competitor levels and prey availability (Sunquist, 2002). This study aimed to determine what the critical prey resources of jaguars are by determining the preferred prey of the species, and to investigate the impact of the Pleistocene extinctions on jaguar predatory ecology. There has been extensive research on the human-wildlife conflict arising from jaguar depredation on livestock (Rabinowitz, 1986; Quigley and Crawshaw, 1992; Hoogesteijn et al., 1993; Dalponte, 2002; Polisar et al., 2003; Michalski et al., 2006; Palmeira and Barrella, 2007; Hoogesteijn and Hoogesteijn, 2008; Rosas-Rosas et al., 2008; Soto-Shoender and Giuliano, 2011; Jêdrzejewski et al., 2014), so we focus predominately on wild prey in this study.
Methods
We searched Google Scholar and Web of Science for literature on the diet of jaguars, as well as gray literature (dissertations, theses) and the reference lists of any publications found. Keyword searches were for “jaguar” OR “Panthera onca” OR “onça” OR “onça-pintada” OR “onza” OR “yaguar” OR “yaguareté” OR “tigre Americano” AND “diet” OR “fezes” OR “presas” OR “heces” OR “disponibilidad” OR “alimentación” OR “dieta” OR “hábitos alimentarios” OR “depredación” OR “ecología alimentar.” Study sites that were surveyed over different years or in different treatments (hunting vs. non-hunting sections) were treated as separate data (Table 1). We included unpublished data if the raw data were obtained using standard, widely used analysis methods (scat analysis), as was done previously (Hayward et al., 2014; Lyngdoh et al., 2014).
Table 1
| Country | Site | Number | Data collection years | Scats/Gut contents | Kills | Assumption/Comments | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Argentina | Colileuga National Park | 1 | 1991–1995 | 246 | No prey | Perovic, 2002 | |
| Belize | Cockscomb Basin | 2 | 1983–1984 | 189 | Rabinowitz and Nottingham, 1986 | ||
| 3 | 2002 | 23 | Weckel et al., 2006a,b | ||||
| 4 | 2003–2006 | 364 | Abundance from Weckel et al. (2006a) | Foster et al., 2010 | |||
| Brazil | Acurizal Ranch | 5 | 1977–1978 | 25 | Schaller, 1983 | ||
| Area de Jofre | 6 | 1988–1994 | 13 | Sample size | Dalponte, 2002 | ||
| Area de Paraguaizinho | 7 | 1988–1994 | 15 | 30 | No prey | Dalponte, 2002 | |
| Área de Proteção Ambiental do Lajeado e na do Rio Tocantins | 8 | 2000–2001 | 18 | Sample size | Trovati et al., 2008 | ||
| Emas National Park | 9 | 2000–2003 | 18 | 20 | Silveira, 2004 | ||
| 10 | 2004–2009 | 35 | Sollmann, 2011; Sollmann et al., 2013 | ||||
| Goiás | 11 | 1998–2003 | 242 | Cattle only | Palmeira et al., 2008 | ||
| Iguaçu NP | 12 | 1997–2001 | 51 | Cattle only | de Azevedo, 2008 | ||
| Linhares | 13 | 1996 | 101 | Prey availability from Chiarello (1999, 2000) | Garla et al., 2001 | ||
| Mamirauá Ecological Reserve | 14 | 2004–2005 | 29 | 10 | Ramalho, 2006 | ||
| Miranda Ranch, Pantanal | 15 | 1980–1984 | 48 | 59 | No prey | Crawshaw and Quigley, 2002 | |
| Pantanal | 16 | 2003–2004 | 149 | 114 | de Azevedo and Murray, 2007 | ||
| 17 | 2001–2006 | 160 | 431 | Perili, 2009 | |||
| 18 | 2007–2008 | 134 | 50 | Porfirio, 2009 | |||
| 19 | 2001–2004 | 438 | Cavalcanti and Gese, 2010 | ||||
| 20 | 2003–2008 | 114 | Crocodilians only | Azevedo and Verdade, 2012 | |||
| Superagui National Park | 21 | 1995–1997 | 32 | No prey | Leite and Galvão, 2002 | ||
| Pantanal Matogrossense National Park | 22 | 1988–1994 | 7 | 14 | No prey | Dalponte, 2002 | |
| Reserva Florestal da Companhia Vale do Rio Doce | 23 | 1993–1994 | 13 | Sample size | Facure and Giaretta, 1996 | ||
| Serra da Capivara National Park | 24 | 1990 | 7 | Sample size | Olmos, 1993 | ||
| Colombia | Llanos Orientales | 25 | 2005–2007 | 60 | Garrote, 2012 | ||
| Costa Rica | Corcovado National Park | 26 | 1993–1994 | 22 | Chinchilla, 1997 | ||
| 27 | 1996–1998 | 18 | Sample size | Carrillo et al., 2009 | |||
| Finca Las Alturas | 28 | 2008 | 13 | Sample size | Gutierrez and Porras, 2008 | ||
| Santa Rosa National Park | 29 | 2001–2011 | 5 | 0 | Sample size | Guadamuz, 2012 | |
| Talamanca | 30 | 2007 | 15 | Sample size | Gonzalez-Maya et al., 2010 | ||
| Tortuguero National Park | 31 | 2005–2010 | 676 | Turtles only | Veríssimo et al., 2012 | ||
| Guatemala | Laguna del Tigre National Park | 32 | 2005–2008 | 73 | No prey | Márquez, 2009 | |
| La Selva Maya | 33 | 1994–2005 | 206 | Hernandez, 2006 | |||
| Maya Biosphere Reserve (hunted section) | 34 | 2000–2001 | 23 | Novack et al., 2005 | |||
| Maya Biosphere Reserve (unhunted section) | 35 | 2000–2001 | 53 | As above | |||
| Mexico | Sierra del Abra-Tanchipa Biosphere Reserve | 36 | 2010–2012 | 43 | Hernández-SaintMartín et al., 2015 | ||
| Calakmul Biosphere Reserve | 37 | 1989–1993 | 38 | Aranda, 1994; Aranda and Sanchez-Cordero, 1996 | |||
| 38 | 1998–2000 | 84 | Same data as Ceballos et al. (2005) | Amin, 2004 | |||
| 39 | 1997–2005 | 84 | Ceballos et al., 2005 | ||||
| Chamela-Cuixmala Biosphere Reserve | 40 | 1995–1998 | 50 | Núñez et al., 2000 | |||
| Sierra Madre de Chiapas | 41 | 1995–2002 | 45 | No prey | Cruz et al., 2007 | ||
| Sierra Nanchititla Natural Park | 42 | 2002–2009 | 13 | Sample size | Gómez-Ortiz and Monroy-Vilchis, 2013 | ||
| Sonora | 43 | 1999–2005 | 28 | Cattle only | Rosas-Rosas et al., 2008 | ||
| Tamasopo | 44 | 2011 | 11 | Sample size | Rueda et al., 2013 | ||
| Panama | Darien National Park | 45 | 2004–2007 | 9 | 5 | Sample size | Moreno et al., 2006; Moreno Ruiz, 2006 |
| Paraguay | Chaco | 46 | 1987–1989 | 106 | No prey | Taber et al., 1997 | |
| 47 | 2002 | 41 | No prey | McBride et al., 2010 | |||
| Peru | Manu National Park | 48 | 1982–1985 | 25 | Emmons, 1987 | ||
| Tambopata-Candamo Reserve | 49 | 1997–1998 | 21 | Kuriowa and Ascorra, 2002 | |||
| Venezuela | Hato Piñero | 50 | 1996 | 3 | Sample size | Farrell et al., 2000 | |
| 51 | 1996–2002 | 122 | 30 | Polisar et al., 2003 | |||
| 52 | 1996–1998 | 42 | 30 | Scognamillo et al., 2003 | |||
| Los Llanos | 53 | 2002–2006 | 608 | Cattle only | Hoogesteijn and Hoogesteijn, 2008 |
Details on studies found and used in this meta-analysis including location, sample sizes, diet analysis method, and any assumptions made.
Sites in italics were excluded (see Assumption/Comments column).
Due to the cryptic nature of jaguars (Harmsen et al., 2010), scat analysis is the primary method researchers have used to determine diet (Table 1). Scat analysis may under-represent turtles in jaguar diet as only the meat is eaten while the carapace remains intact yielding no evidence of the prey source within the scat (Carrillo et al., 2009), but over-represent reptiles, rodents and mesocarnivores (Martínez-Gutiérrez et al., 2015). However, scats were invariably collected from throughout the study sites, so problems associated with patchily distributed local prey are minimized (Steenweg et al., 2015). Distinguishing jaguar scat from sympatric puma Puma concolor scat based on size and other physical characteristics can lead to mis-diagnosis of the depositor (Farrell et al., 2000; Martínez-Gutiérrez et al., 2015), which will reduce the chances of obtaining significant preferences/avoidance in our analyses by broadening the dietary niche to include puma prey (hence our results are conservative). In the jaguar's case, DNA confirmation of the diet indicated that larger prey species are more likely to be present in scats than small prey species (Farrell et al., 2000), counteracting the traditional bias toward detecting smaller prey species from scat analysis (Mills, 1992). Prey availability was obtained from each study site from information presented in the literature (Table 1).
We used Jacobs' (1974) index to determine wild prey selectivity of jaguars following previous prey preference studies (Hayward et al., 2012, 2014; Lyngdoh et al., 2014). Where domestic livestock were killed alongside wild prey, we included both, but otherwise excluded studies solely focused on domestic livestock. Positive values of Jacobs' index indicate preference and negative values indicate avoidance (Jacobs, 1974). We calculated a Jacobs' index value for each prey species at each study site and then tested these using t-tests against a mean of zero, where data were normally distributed or a sign test where it was not, to determine significant preferences or avoidance (Hayward and Kerley, 2005). We also plotted Jacobs' index values with error bars to illustrate where a larger sample size was likely to lead to significant preference or avoidance, assuming the existing trend continued. We conducted these analyses for individual species and groups of related species (e.g. primates or Agouti spp.).
We developed a set of testable covariates that could potentially influence jaguar prey preferences from our literature review. A generalized linear model with a Gaussian distribution and an identity link function was conducted on these non-correlated variables. The independent variables used were socio-ecological/behavioral (prey relative abundance, habitat type and herd size at a site, and morphological (prey body mass and potential threat to a hunting jaguar; Table 2). Prior to model fitting, we standardized all covariates. We evaluated all possible combinations of models derived from the covariates. Model selection occurred using Akaike's information criterion (AIC) in a maximum likelihood framework (Akaike, 1973, 1974). We used model averaging to derive parameter estimates (Burnham and Anderson, 1998). Strongly supported relationships among individual variables were plotted using linear or loess best fit models.
Table 2
| Species | Scientific name | P/A | n p | n a | Jacobs' index (± S.E.) | Abundance | Kills (%) | Body mass (kg) | Herd size | Habitat | Threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acouchi, green | Myoprocta pratti | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.07 | 0 | |||||
| Agouti | Dasyprocta sp. | – | 18 | 13 | −0.47±0.12 | ||||||
| Agouti, Azara's | Dasyprocta azarae | 2 | 2 | −0.42±0.55 | 0.22 | 0.14 ± 0.14 | 3 | 2 | 2.5 | 0 | |
| Agouti, black | Dasyprocta fuliginosa | 2 | 2 | 0.24 ± 0.22 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.00 | 2.6 | 2 | 2.5 | 0 | |
| Agouti, Central American | Dasyprocta punctata | ~ | 11 | 7 | −0.52±0.14 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 4 | 2 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Agouti, red-rumped | Dasyprocta leporina | 2 | 1 | −0.99±0.00 | 0.43 ± 0.42 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 2 | 2 | 2.5 | 0 | |
| Anteater, giant | Myrmecophaga tridactyla | + | 9 | 8 | 0.33 ± 0.20 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.17 ± 0.08 | 18 | 1 | 1.5 | 1 |
| Armadillos | ~ | 17 | 11 | −0.11±0.18 | |||||||
| Armadillo, nine-banded | Dasypus novemcinctus | ~ | 12 | 9 | 0.02 ± 0.21 | 0.14 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 3 | 1 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Armadillo, southern three-banded | Tolypeutes matacus | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.11 | 0 | |||||
| Armadillo, yellow | Euphractus sexcinctus | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.15 | 0 | |||||
| Caiman | ~ | 6 | 5 | −0.62±0.26 | |||||||
| Caiman, black | Melanosuchus niger | 1 | 1 | −0.92 | 0.39 | 0.03 | |||||
| Caiman, common | Caiman crocodilus | ~ | 3 | 3 | −0.32±0.49 | 0.43 ± 0.18 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 17 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Caiman, yacare | Caiman yacare | 1 | 1 | −0.82 | 0.67 | 0.16 | |||||
| Canidae | ~ | 6 | 4 | −0.43 | |||||||
| Capybara | Hydrochaeris hydrochaeris | + | 8 | 8 | 0.46 ± 0.13 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 46 | 5 | 3 | 0 |
| Carnivora | – | −0.26±0.11 | |||||||||
| Cattle | Bos indicus/taurus | 2 | 2 | −0.88±0.10 | 0.73 ± 0.06 | 0.17 ± 0.15 | 340 | 5 | 1 | 1 | |
| Chachalaca, plains | Ortalis vetula | 1 | 1 | −0.63 | 0.08 | 0.02 | |||||
| Coati | Nasua sp. | ~ | 14 | 13 | −0.11±0.14 | ||||||
| Coati, South American | Nasua nasua | ~ | 7 | 6 | −0.13±0.21 | 0.15 ± 0.09 | 0.10 ± 0.04 | 3.5 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| Coati, white-nosed | Nasua narica | ~ | 6 | 6 | −0.26±0.16 | 0.32 ± 0.10 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 3.5 | 4 | 2 | 0 |
| Coyote | Canis latrans | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.01 | 0 | |||||
| Deer | Cervidae | ~ | 30 | 25 | −0.02±0.11 | ||||||
| Deer, brocket | Mazama spp. | ~ | 15 | 11 | −0.25±0.16 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | ||||
| Deer, Central American red brocket | Mazama temama | 1 | 1 | 0.30 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |||||
| Deer, gray brocket | Mazama gouazoubira | 1 | 1 | −1 | 0.05 | 0 | |||||
| Deer, marsh | Blastocerus dichotomus | ~ | 3 | 3 | 0.56 ± 0.29 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | 60 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Deer, pampas | Ozotoceros bezoarticus | 2 | 1 | −0.32±0.68 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.05 | 30 | 3 | 1 | 0.5 | |
| Deer, red brocket | Mazama americana | ~ | 9 | 8 | −0.08±0.19 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | 24 | 1 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Deer, white-tailed | Odocoileus virginianus | ~ | 7 | 7 | 0.07 ± 0.18 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 0.12 ± 0.06 | 41 | 3 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Dog | Canis familiaris | 1 | 1 | −0.21 | 0.03 | 0.02 | |||||
| Fox, crab-eating | Cerdocyon thous | ~ | 3 | 3 | −0.41±0.47 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 5 | 2 | 1.5 | 0 |
| Fox, gray | Urocyon cinereoargenteus | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.04 | 0 | |||||
| Fox, hoary | Pseudalopex vetulus | 1 | 1 | 0.39 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |||||
| Horse | Equus spp | 2 | 2 | −0.07±0.45 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.03 | 300 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |
| Livestock | ~ | −0.48±0.3 | |||||||||
| Monkey, black-and-gold howler | Alouatta caraya | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.07 | 0 | |||||
| Monkey, Geoffroy's spider | Ateles geoffroyi | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.47 | 0 | |||||
| Monkey, golden-white bare-ear marmoset | Callithrix argentata | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.02 | 0 | |||||
| Monkey, Guianan red howler | Alouatta macconnelli | 1 | 1 | −0.03 | 0.08 | 0.08 | |||||
| Monkey, Guinean brown capuchin | Sapajus apella | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.09 | 0 | |||||
| Monkey, mantled howler | Alouatta palliata | 1 | 1 | −0.10 | 0.07 | 0.06 | |||||
| Monkey, northern night | Aotus trivirgatus | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.01 | 0 | |||||
| Monkey, red-bellied titi | Callicebus moloch | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.03 | 0 | |||||
| Monkey, white-throated capuchin | Cebus capucinus | 1 | 1 | −0.18 | 0.14 | 0.10 | |||||
| Monkey, Yucatan black howler | Alouatta pigra | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.05 | 0 | |||||
| Ocelot | Felis pardalis | 1 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.04 | 0.06 | |||||
| Opossum | Didelphis sp. | ~ | 7 | 4 | −0.71±0.18 | ||||||
| Opossum, black-eared | Didelphis marsupialis | – | 4 | 2 | −0.95±0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.16 | 0.02 ± 0.02 | 4 | 1 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Opossum, Virginia | Didelphis virginiana | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 0.02 | |||||
| Paca, spotted | Cuniculus paca | ~ | 11 | 10 | −0.12±0.16 | 0.12 ± 0.03 | 0.10 ± 0.03 | 6 | 1 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Suids | ~ | 0.18 ± 0.1 | |||||||||
| Peccary spp. | ~ | 35 | 32 | 0.19 ± 0.11 | |||||||
| Peccary, collared | Pecari tajacu | ~ | 18 | 17 | 0.24 ± 0.13 | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 0.18 ± 0.03 | 22 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
| Peccary, white-lipped | Tayassu pecari | ~ | 15 | 13 | 0.07 ± 0.20 | 0.13 ± 0.05 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | 35 | 5 | 2.5 | 1 |
| Pig, wild | Sus scrofa | ~ | 5 | 5 | 0.04 ± 0.37 | 0.09 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.18 | 47 | 5 | 3 | 1 |
| Primates | – | 11 | 4 | −0.75±0.13 | |||||||
| Lagomorphs | ~ | 11 | 7 | −0.45±0.25 | |||||||
| Rabbit, tapeti | Sylvilagus brasiliensis | ~ | 4 | 3 | −0.48±0.30 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Raccoons | ~ | −0.36±0.33 | |||||||||
| Raccoon, crab-eating | Procyon cancrivorus | ~ | 3 | 3 | 0.07 ± 0.37 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Raccoon, northern | Procyon lotor | 2 | 0 | −1 ± 0 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 0 ± 0 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | |
| Rhea | Rhea americana | 1 | 1 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.7 | |||||
| Rodents | – | −0.2±0.1 | |||||||||
| Skunk, striped hog-nosed | Conepatus semistriatus | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.00 | 0 | |||||
| Sloth, brown-throated | Bradypus variegatus | 1 | 1 | −0.30 | 0.44 | 0.3 | |||||
| Squirrel | Sciurus langsdorffi | 1 | 0 | −1 | 0.01 | 0 | |||||
| Tamandua | ~ | 5 | 5 | 0.27 ± 0.28 | |||||||
| Tamandua, northern | Tamandua mexicana | ~ | 3 | 3 | 0.10 ± 0.47 | 0.03 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Tamandua, southern | Tamandua tetradactyla | 2 | 2 | 0.54 ± 0.10 | 0.02 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 0 | |
| Tapir, Baird's | Tapirus bairdii | –* | 4 | 0 | −1 ± 0 | 0.06 ± 0.03 | 0 ± 0 | 221 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Tapir, lowland | Tapirus terrestris | − | 7 | 4 | −0.55±0.24 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.03 ± 0.03 | 130 | 1 | 2 | 0.5 |
Preference status (P/A; where –, denotes significantly avoided; +, significantly preferred; and ~, killed in accordance with relative abundance), mean Jacobs's index value of each jaguar prey species, number of studies recording it as potential prey (np) and actual prey (na), mean percentage abundance and kills of each prey species, body mass (three-quarters of adult female), and categories of herd size, main habitat and potential threat to a jaguar, based on Nowak (1999).
Scientific names are based on the IUCN Red List.
Denotes a significant result is likely with a larger sample size.
We estimated prey species body size as three-quarters of adult female body mass to account for juveniles and sub-adult prey killed (Jooste et al., 2013). Body mass, herd size, habitat use, and potential threat data were taken from Nowak (1999). Herd size is assumed to be an indicator of how well prey could detect predators (Hamilton, 1971; Fitzgibbon and Lazarus, 1995) and how the attraction effect of congregating prey affects predator detection of prey (Hebblewhite and Pletscher, 2002), and was a categorical variable with 1 relating to solitary individuals, two to species existing in pairs, three to small family groups, 4 to small herds (10–19) and 5 to large herds (>20; Table 2). Habitat type may influence predation as the density of vegetation can affect detectability and catchability, and predator and prey must overlap in habitat to encounter one another (Hayward and Kerley, 2005). A categorical variable of habitat use was used with 1 relating to open environments, 2 to woodlands, and 3 to dense forests (Table 2). Threat was a categorical variable where 0 represents no threat, 1 a minor threat, and two a major threat based on body size and the possession of weaponry, such as horns or teeth (Table 2).
We identified the accessible prey weight range following the break point analysis of Clements et al. (2014). The accessible prey weight range is most likely to encompass the preferred weight range of earlier prey preference studies, which we estimated from loess smoothed plots of mean species Jacobs' index scores against body mass (Hayward et al., 2014). We calculated the ideal mass as the mean body mass of those species that were significantly preferred. We estimated the body mass of jaguars as 60 kg, which is the lower range of adult female body mass (Nowak, 1999) and used this to determine the predator to prey mass ratio by dividing the ideal mass of prey by 60. We also include 38 kg as this is the lowest reported body mass of adult jaguars in Nowak (1999). We recognize jaguar body mass varies substantially throughout their range and these ratios could be affected by site-specific variability, however, we used this as representing the body mass over the entire distribution of the species.
We tested whether jaguar preferences for individual species varied with prey abundance, rainfall or size of prey available at a site (following Kiltie, 1984) using linear regression. We could not run generalized models on these variables because of insufficient sample size for individual species (cf the global models we ran with data from all species). Climate data were obtained from details presented in individual studies or the US National Climatic Data Center (http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/). Note that the regression of Jacobs' index on prey abundance tests how jaguars respond to changes in the relative abundance of individual species, whereas the inclusion of prey abundance in the generalized linear model is looking at how a species' overall abundance affects its likelihood of being selected by jaguars.
Finally, we tested aspects of optimal foraging theory using linear regression. We hypothesized that (1) jaguars would show greater preferences at sites with higher species richness because there would be sufficient prey for them to specialize on particular species; and (2) jaguars would show greater preferences at sites with higher prey biomass for the same reason. We used total biomass, largest biomass of a single species, and body mass of the most preferred prey at a site as measures for this second hypothesis.
All analyses were conducted in R (R Core Development Team, 2008; Barton, 2013). Mean (±1 S.E.) values are presented throughout.
Results
We found 53 studies documenting the diet of jaguars collected over 176 study years and based on 5977 kill records (Table 1). These studies were conducted throughout the distribution of the jaguar (Figure 1). Twenty-five (25; 47%) of these studies, collected over 75 survey years with 3214 kill records (Table 1), had sufficient data for use in this meta-analysis. The remaining 28 studies were excluded due to inadequate prey availability data or a focus on livestock predation (Table 1). Brazil, Mexico and Costa Rica had the largest number of jaguar diet studies, while Brazil (9 useable of 20 studies), Guatemala (4 of 4) and Mexico (4 of 9) had most of the studies that could be included in this meta-analysis (Table 1). Studies that were used came from the suite of habitats used by jaguars including tropical forest, the Llanos, Cerrado, Pantanal, and Chacos. No studies from Argentina, Panama, or Paraguay could be used in this analysis (Figure 1).
Within our meta-analysis there were 111 wild species in the diet of jaguars, ranging in size from 1 kg rabbits to 130 kg lowland tapirs (these results and scientific names of species mentioned in the text are presented in Table 2). The species that appeared most frequently in their diet (16–21%) included capybara, wild pig, caiman, collared peccary, nine-banded armadillo, giant anteater and white-nosed coati. In addition, there were species that were always preyed upon if they were present, suggesting a possible preference (capybara, white-tailed deer, white-nosed coati, wild pigs, common caiman, marsh deer, crab-eating fox, crab-eating raccoon, and northern tamandua). In addition, collared peccary, red brocket deer, spotted paca, giant anteater, white-lipped peccary and South American coati were also killed by jaguars more than 85% of the time they were present in the prey community (Table 2). Conversely, Baird's tapir was never killed by jaguars in the sampled studies, and primates were killed at only four of 11 sites where they were recorded as present (Table 2).
Common caiman, white-nosed coati, Azara's agouti and black-eared opossum constituted over 20% of the available prey community where they were recorded (Table 2). Capybara, wild pigs, common caiman, nine-banded armadillo, collared peccary, white-nosed coati, giant anteater, and white-lipped peccary constituted more than 10% of the kills of jaguar where they occurred (Table 2).
When the relative abundance of prey species was accounted for, jaguars significantly preferred to prey on only two species: giant anteater [t(8) = 7.24, p < 0.001] and capybara [t(7) = 16.96, p < 0.001; Table 2; Figure 2A). Southern tamandua and marsh deer may become preferred with a larger sample size (Table 2; Figure 2A), all but two of the remaining 109 prey species were killed in accordance with their relative abundance within the prey community (Figure 2A). Both black-eared opossum [t(4) = −31.42, p < 0.001] and lowland tapir [t(6) = −2.66, p = 0.038] were significantly avoided, along with Baird's tapir if sample sizes were larger (Table 2; Figure 2A).
Figure 2
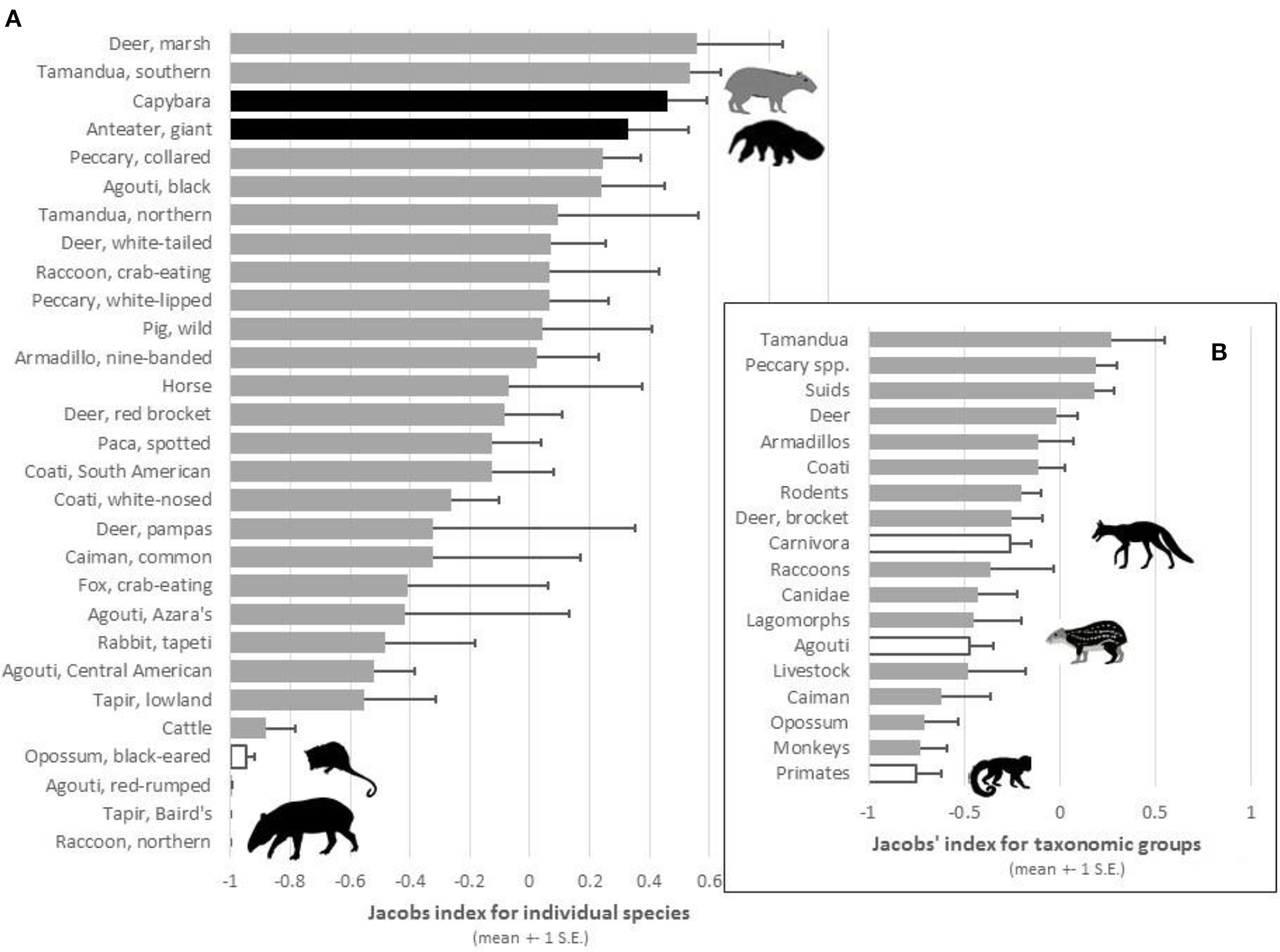
Plot of the mean Jacobs' index values (±1 S.E.) of preference for (A) prey species and (B) taxonomic groups that were reported as potential prey of jaguars in at least two study sites. Black bars represent significantly preferred species, white bars significantly avoided species, and gray bars species killed in accordance with their availability.
There was no indication that jaguars prefer a particular group of related prey, such as peccaries or armadillos, but they do significantly avoid carnivorans [t(27) = −2.86, p = 0.008], the agoutis [t(18) = −4.09, p < 0.001] and primates (binomial test 0/11, p < 0.001; Table 2; Figure 2B). All other broad taxonomic groups were killed in accordance with their abundance (Figure 2B).
Jaguars reduced their preference for white-nosed coatis as they became more abundant in the prey community (r2 = 0.92, n = 7, p < 0.001; Figure 3). No other prey species exhibited a significant relationship between their Jacobs' index value and their relative abundance (Figure 3). There was no relationship between the degree to which jaguars preferred or avoided a prey species and the mean annual rainfall at each study site where it occurred (Figure 4).
Figure 3
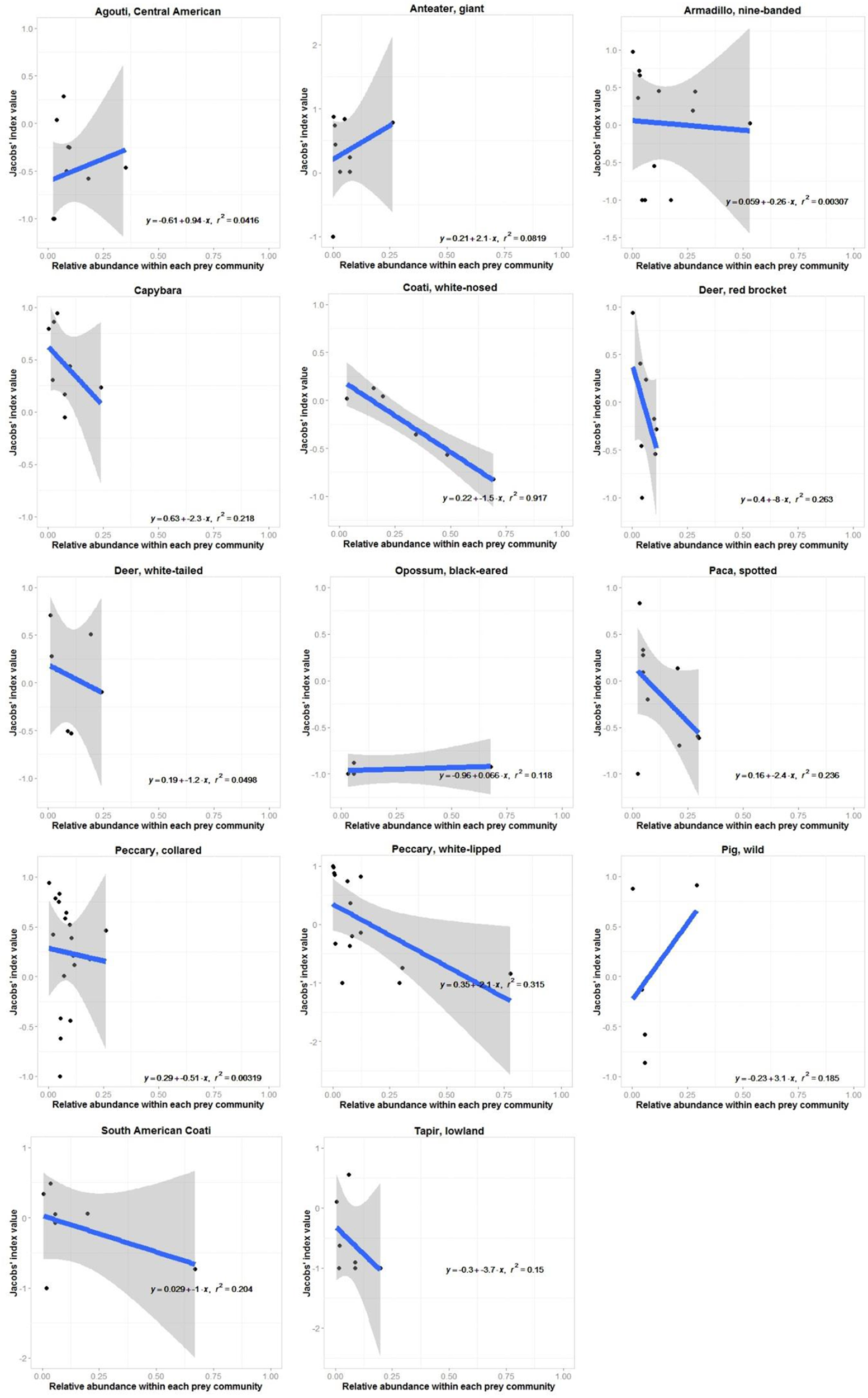
Relationship between site-specific preference (Jacobs' index value) and relative abundance for each prey species of jaguars with four or more Jacobs' index value estimates within the prey community. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals are shown unless they extend to far beyond the y-axis limits.
Figure 4
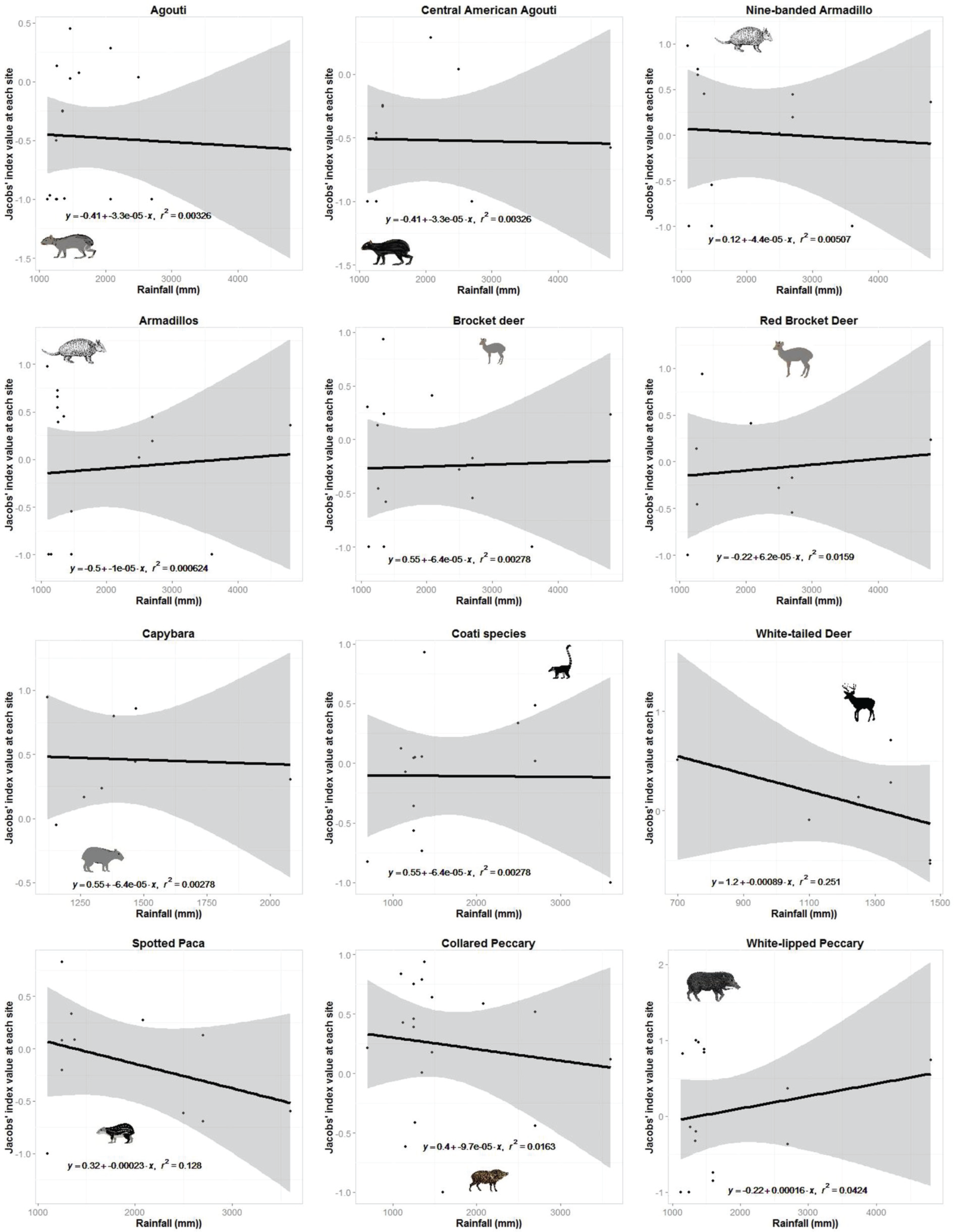
Plots of the relationship between prey preference of jaguar prey species or taxonomic groups with more than six site records and the mean annual rainfall at each site.
A generalized linear model of the drivers of jaguar prey preferences revealed that prey abundance was the most supported predictor variable (sum of Akaike's weights wi = 0.93), with prey herd size also strongly supported (wi = 0.74; Table 3). Model averaged parameter estimates from the top-ranking model showed that jaguar prey preferences were negatively associated with prey abundance (β = −1.39) and positively associated with herd size (β = 0.08; Table 3; Figure 5). Prey body mass was the next most important variable (Table 3), and a regression of Jacobs' index against prey body mass indicated that jaguars significantly preferred larger prey up until 100 kg (Figure 6). In our sample, tapirs are the only wild prey that exceed 100 kg and jaguars avoided both species.
Table 3
| Intercept | Abundance | Body mass | Habitat | Herd size | Threat | d.f. | AICc | ΔAICc | Akaike's weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.256 | −1.567 | 0.111 | 4 | 35.0 | 0 | 0.246 | |||
| −0.263 | −1.379 | −0.001 | 0.128 | 5 | 36.0 | 0.98 | 0.151 | ||
| −0.276 | −1.505 | −0.002 | 0.114 | 0.225 | 6 | 36.9 | 1.92 | 0.094 | |
| −0.263 | −1.682 | 0.098 | 0.143 | 5 | 37.0 | 2.02 | 0.089 | ||
| −0.029 | −1.289 | 3 | 37.5 | 2.46 | 0.072 | ||||
| −0.321 | −1.551 | 0.029 | 0.112 | 5 | 37.9 | 2.89 | 0.058 | ||
| −0.080 | −1.522 | 0.227 | 4 | 38.0 | 3.04 | 0.054 | |||
| −0.072 | −1.381 | −0.002 | −0.086 | 0.131 | 6 | 38.8 | 3.85 | 0.036 | |
| −0.068 | −1.364 | −0.001 | 0.299 | 5 | 39.3 | 4.29 | 0.029 | ||
| −0.014 | −1.172 | −0.001 | 4 | 39.7 | 4.72 | 0.023 | |||
| Model averaged parameter estimates | −1.386±0.618 | −0.001±0.001 | 0.001 ± 0.073 | 0.084 ± 0.067 | 0.070 ± 0.140 | ||||
| Sum of Akaike's weights | 0.93 | 0.40 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 0.34 |
Model selection statistics for the 10 most supported models of drivers of jaguar prey selection, including model averaged parameter estimates and summed Akaike's weights for each variable.
Figure 5
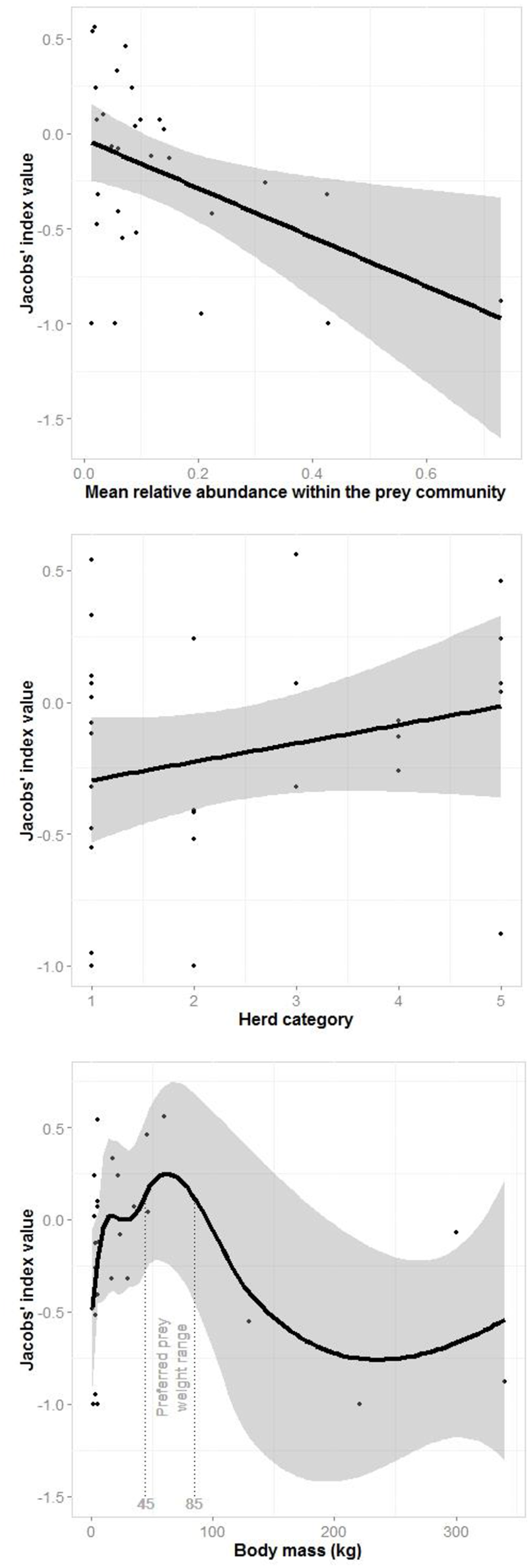
Plots of the relationship between the most important drivers of jaguar prey selection based on the generalized linear model (Table 3): mean prey abundance (linear), prey herd category (1–solitary, 2–pairs, 3–small groups, 4–groups of 5–20, and 5 large groups; linear) and prey body mass (three-quarters of adult female body mass; loess smooth).
Figure 6
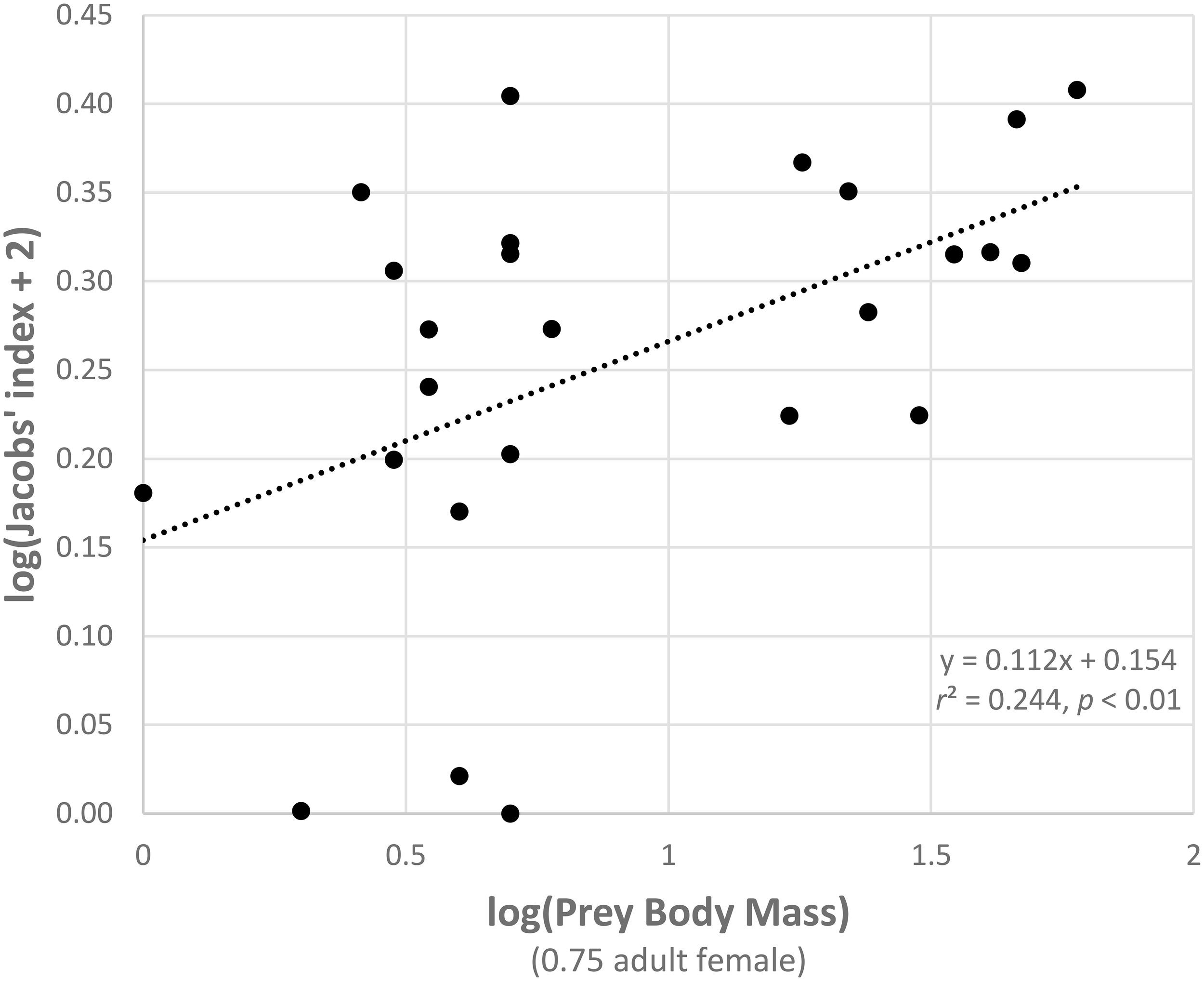
Relationship between the Jacobs' index of each prey species with three or more records and prey body mass (both log transformed).
Segmented modeling showed strong support for two and four breakpoints in jaguar prey preference and prey body mass relationships (Table 4). We use the most conservative of these and discuss the results with two breakpoints hereafter. The segmented modeling showed the accessible prey weight range was from 6 to 60 kg (Figure 7). The preferred prey weight range of jaguars is 45 to 85 kg (Figure 5). Note that the upper limit of the preferred weight range is larger than that of the accessible weight range due to the loess smoothing function. The body mass of significantly preferred prey (ideal prey; capybara and giant anteater) is 32 ± 14 kg. The predator: ideal prey ratio for jaguars is therefore 1: 0.53 based on adult female jaguar body mass of 60 kg and 1:0.84 for adult body mass of 38 kg.
Table 4
| Breakpoints | AIC | ΔAIC |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 76.82 | 0.00 |
| 4 | 76.82 | 0.00 |
| 1 | 80.93 | 4.11 |
| 5 | 89.34 | 12.52 |
| 3 | 93.38 | 16.56 |
Model selection statistics for the segmented model to identify the preferred and accessible prey of jaguars.
Figure 7
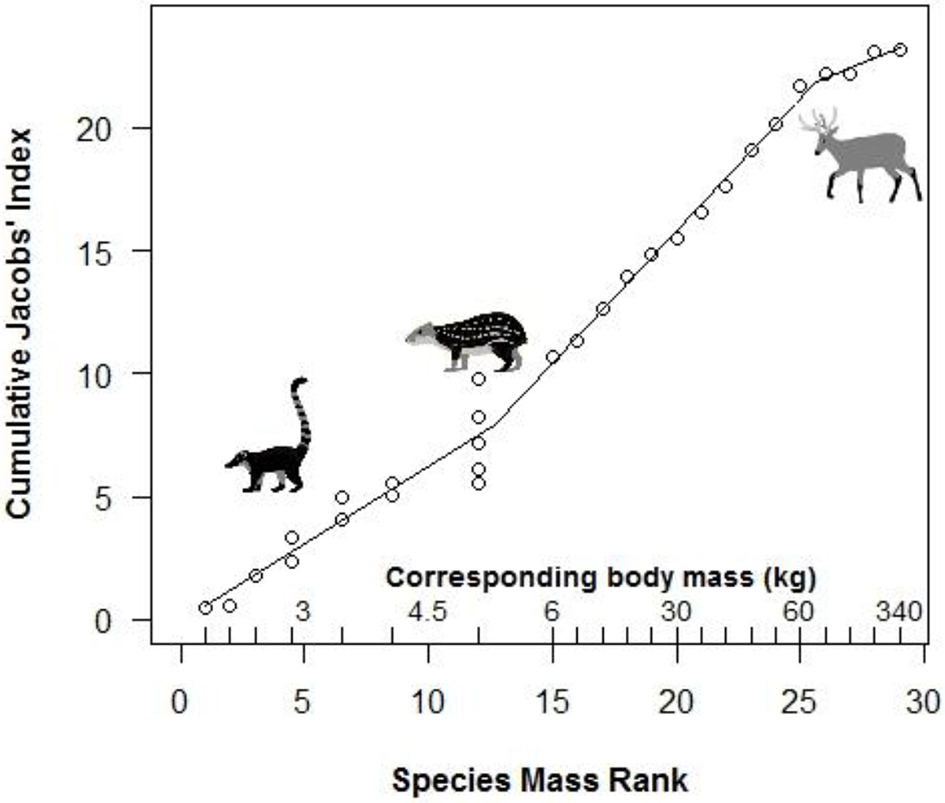
Segmented model of the relationship between the mass rank of each prey species and jaguar preference. Preference is based on cumulative Jacobs' index values (+1 for standardization) following Clements et al. (2014). Actual prey masses corresponding to mass ranks are shown above the x-axis. Representative species sitting at breakpoints are shown (coati, paca, marsh deer).
Individual prey species within the preferred and accessible weight ranges were invariably increasingly avoided as they became more abundant within the prey community (Figure 3). Significantly preferred prey species (mean b = −0.1±2.2), species within the preferred weight range (b = −7.7±8.3) and significantly avoided prey (b = −1.8±1.9) had a mean slope of this relationship with standard error bars crossing 0 (Figure 3). Conversely, accessible prey (b = −3.9±2.7) and prey outside the accessible prey weight range (b = −9.4±3.8) had a consistently negative relationship between preference and abundance (Figure 3).
There was no support for our hypotheses relating to optimal foraging theory of jaguars (Figure 8). Jaguars did not show greater preferences where there was greater prey species richness or where there was a greater biomass of potential prey.
Figure 8
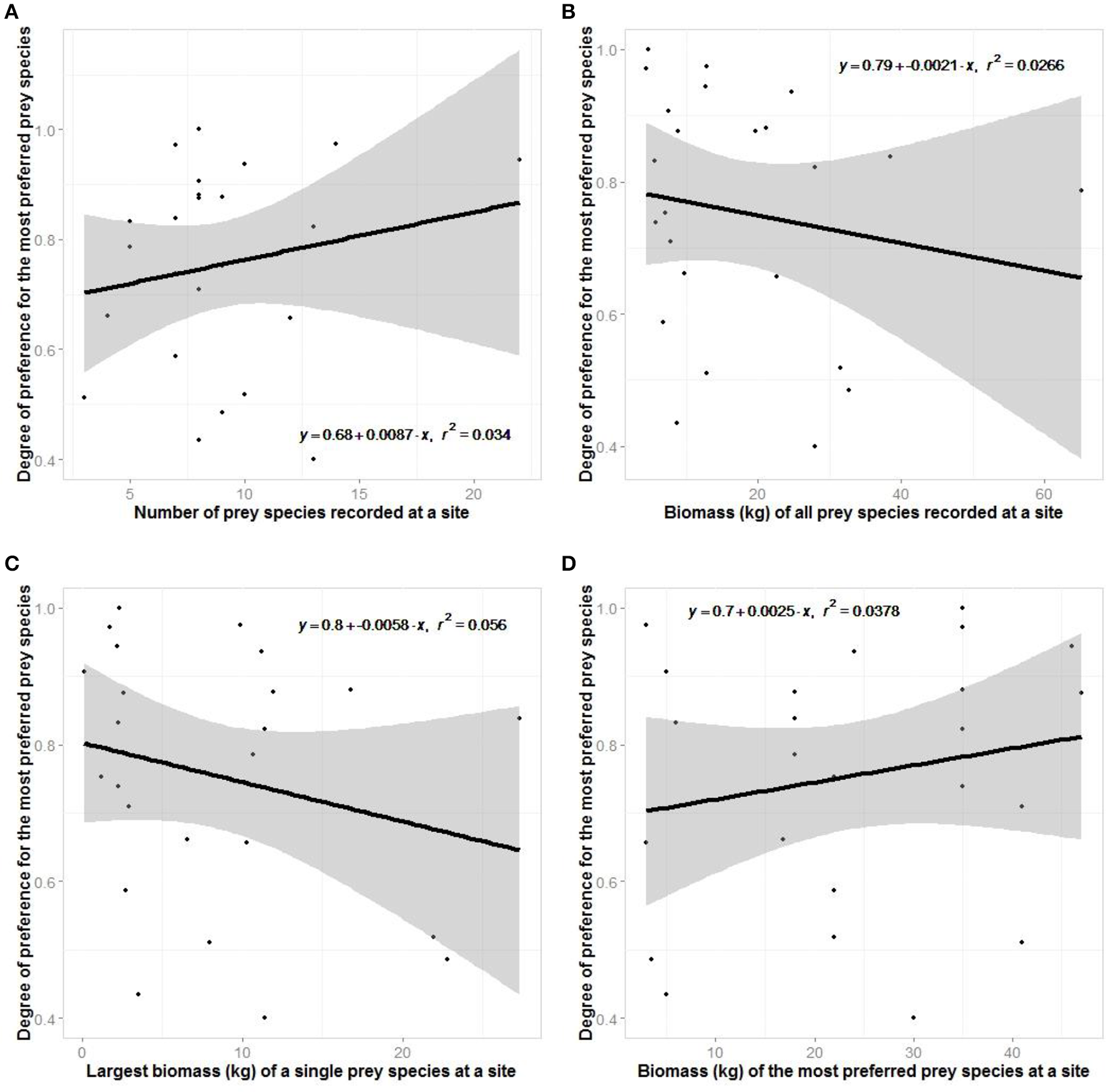
Regression plots testing aspects of optimal foraging theory where the degree of prey preference exhibited at a site is related to (A) the number of species there, (B) the biomass of all prey there, (C) the largest biomass of a species there, and (D) the body mass of the most preferred prey species there.
Discussion
Jaguars exhibit trait-mediated foraging interactions with their prey species (Railsback and Harvey, 2013) by significantly preferring capybara and giant anteater, and avoiding species outside their preferred and accessible weight ranges (Figure 2). In contrast to other large predators, the traits that mediate jaguar foraging decisions are ecological (prey abundance) and behavioral (herd size) more than morphological (body mass; Table 3). Thus, jaguars are not generalist predators as once thought, but prey specifically on particular species and according to certain prey characteristics.
During the late Pleistocene, there were more than 50 additional species of large (>40 kg) herbivores in the Americas (Kurtén and Anderson, 1980; Greenwood, 2009), and so jaguars evolved in ecosystems with a much higher diversity and availability of potential prey than found today. This is in contrast to Africa, where extant large carnivores prey upon herbivore communities that were similar in abundance, richness and diversity to those which occurred at the end of the Pleistocene (Lyons et al., 2004). This difference likely explains why the predator to prey body mass of jaguars is much smaller than other large solitary felids (Figure 9). For example, jaguars are often considered to be ecologically similar to leopards (Sunquist and Sunquist, 2002), yet jaguars preferentially prey on smaller species than leopards (Figure 9), despite jaguars having a larger body size. The lack of diverse large herbivores in the Holocene also likely explains why jaguars do not have prey selection driven by prey morphology (Figure 5), do not show any evidence of optimal foraging (Figure 8), are the only large felid not preferentially hunting Cetartiodactyla herbivores, and have reduced body mass compared to the Pleistocene (Seymour, 1989). The larger prey species that survived the Pleistocene extinctions in South America, such as tapirs, are currently above the upper limits of the accessible weight range of jaguars. Those Cetartiodactyla species that persist today are likely to have been kept at lower density than jaguars evolved with due to continual hunting pressure from humans since the Holocene. Thus, jaguars may be persisting on sub-optimal prey, as is the case for some puma (Yanez et al., 1986; Iriarte et al., 1990) and African wild dog Lycaon pictus populations (Woodroffe et al., 2007).
Figure 9
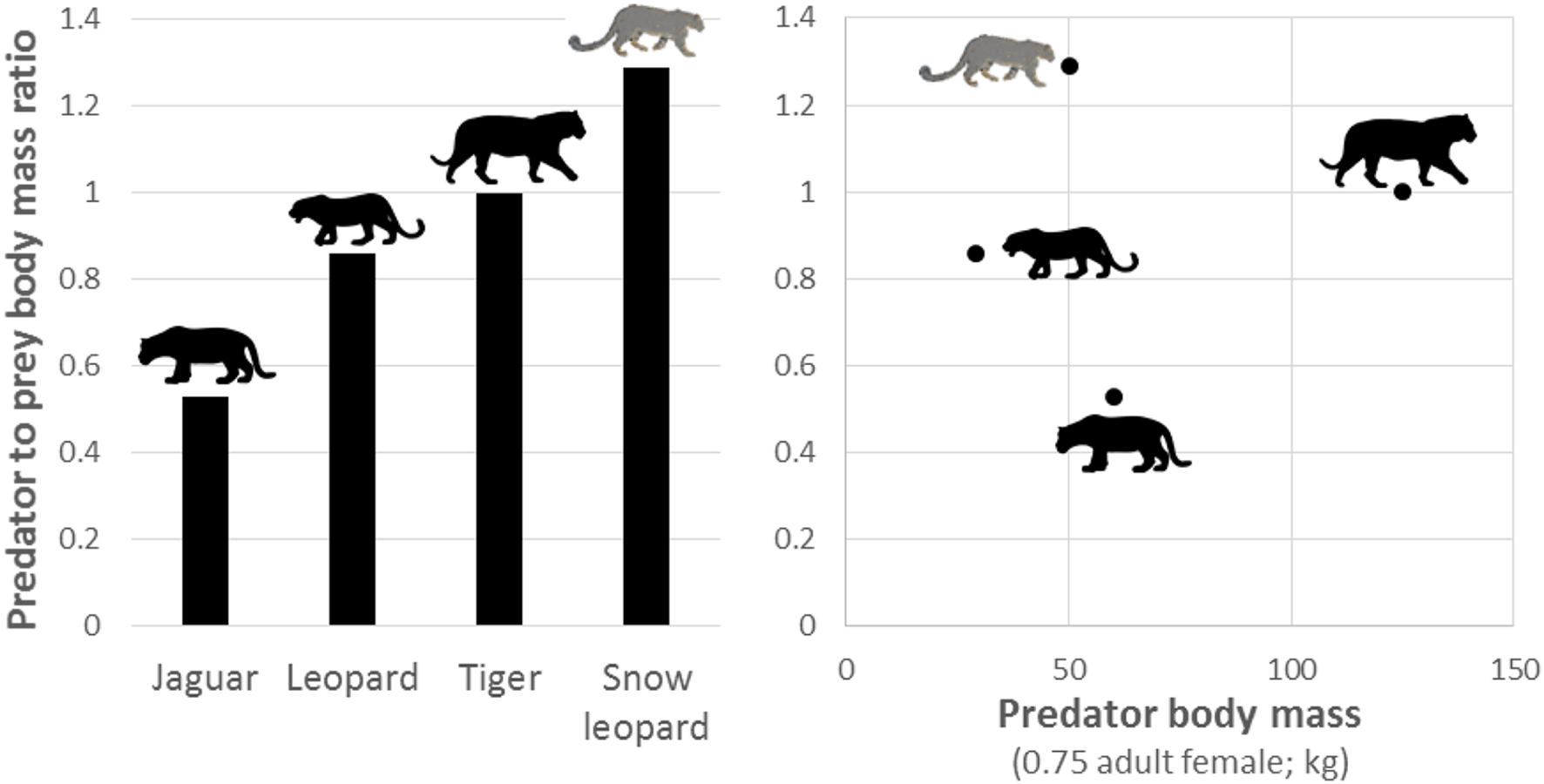
Plot of the predator to prey body mass ratio of solitary members of the genus Panthera and how this relates to the body mass of each species (Hayward et al., 2006a, 2012; Lyngdoh et al., 2014).
Additionally, even though the jaguar is regarded today as the largest and most dominant apex predator in the Americas, it has only occupied that role for the past 10,000 years. Near the end of the Pleistocene, the jaguar in the Americas was sympatric with a least ten carnivore species that were larger than itself (Cione et al., 2009). Thus, similar to that reported for the gray wolf (Canis lupus; Tedford et al., 2004), the jaguar was somewhat of a mesocarnivore rather than an apex carnivore for most of its evolutionary existence, so its predatory behavior should be viewed in that context. Indeed, the jaguar's ability to function as a mesopredator by preying on a wide range of different-sized species, particularly smaller species, is probably why this large felid species, together with the puma (P. concolor), survived the end-Pleistocene extinction in the Americas, whereas the other five sympatric large felid species went extinct (Van Valkenburgh and Hertel, 1998). The effects of the end-Pleistocene megafaunal extinctions, together with the “ghosts” of more dominant extinct carnivores (Connell, 1980), may explain why jaguars continue to preferentially prey upon species smaller than expected given their body size, especially in comparison to African large carnivores, which continuously had a high diversity of large herbivores on which to prey.
It is unclear if jaguars also preferentially preyed upon relatively small prey during the Pleistocene, or simply reduced their preferred prey size in the Holocene as a strategy to survive the end-Pleistocene extinctions. Given the high diversity of potential prey species during the Pleistocene in the Americas (higher diversity than contemporary African savannah ecosystems; Lyons et al., 2004), it seems unlikely that jaguars would have restricted themselves to such small prey. In fact, their larger body size in the Pleistocene would have allowed jaguars accessible prey between 30 and 150 kg, with preferred prey around 90 kg (based on the equations in Van Valkenburgh et al., 2015). Interestingly, other carnivore species, ranging from black-footed ferrets Mustela nigripes to coyotes Canis latrans, appear to have significantly different diets and ecological niches between the Pleistocene and Holocene (Owen et al., 2000; Meachen et al., 2014), probably as an adaptation to survive the end-Pleistocene extinctions, and the same is likely true for jaguars. For the coyotes, the switch to smaller prey species in Holocene coincided with a reduction in body size (Meachen et al., 2014). This suggests that jaguars also could have exhibited adaptive behavioral changes during the Holocene to preferentially prey upon smaller species. Similar to the coyote, this possible behavioral adaptation coincided with a decrease in body size of the jaguar during the Holocene. Furthermore, there is no evidence that canids in North America expanded their dietary niche following the Pleistocene extinctions, possibly because competition with humans outweighed the advantages of niche expansion (Pardi and Smith, 2015).
Adding further pressure to a predator with a limited or reduced abundance of suitably sized prey, previous research has highlighted the importance of areas with no human hunting as jaguar prey refugia (Harmsen et al., 2010). For example, important jaguar prey species, such as peccaries, spotted paca and nine-banded armadillo are heavily hunted by humans (Redford, 1992; Jorgenson and Redford, 1993). Given the importance of prey in determining predator densities (Fuller and Sievert, 2001; Karanth et al., 2004; Hayward et al., 2007b), reduced prey abundance has been, and probably still is, keeping jaguar populations below densities at which they evolved. Thus we reiterate that the “empty forests syndrome” (Redford, 1992; Wilkie et al., 2011) can have cascading impacts on all trophic levels, including apex predators (Steinmetz et al., 2013).
Both peccary species are within the accessible and preferred weight ranges of jaguars, however neither is preferred. Although frequently killed by jaguars, there is no evidence that the predator-prey relationship between jaguars and peccaries is a coevolutionary predator-prey “arms race” given that existing evidence suggests the species evolved at separate times and places (Mayer and Wetzel, 1987). This lack of preference may be because peccaries are formidable opponents that can seriously injure jaguars (Perry, 1970). Furthermore, severe population reductions of peccaries during the late-Pleistocene may have prevented jaguars from optimally foraging on them. In fact, several peccary species did not survive these extinctions (Kurtén and Anderson, 1980; Greenwood, 2009), and those that did likely suffered severe population bottlenecks, similar to that found for other Pleistocene ungulate survivors such as bison Bison bison and musk ox Ovibos moschatus (Cione et al., 2009) and their loss is likely to have led to a chain of extinction for large scavenging birds such as condors, vultures and teratorns (Van Valkenburgh and Hertel, 1998). Consequently, the surviving jaguars may have been those that preferentially preyed upon species smaller than peccaries, and thus the non-preference for peccaries by modern jaguars could be an artifact from the end-Pleistocene extinctions. Despite this, jaguars can have significant impacts on peccary populations, such as in Iguaçu National Park, Brazil, where half the peccary population was killed by jaguars annually (Crawshaw, 1995). Elsewhere, white-lipped peccaries were found in 89% of jaguar scats along beaches in Corcovado National Park (Carrillo et al., 2009) and collared peccaries were killed almost three-times more frequently than any other prey species in the Sierra Madre de Chiapas of Mexico (Cruz et al., 2007). Our results also support hypotheses that the expanding wild boar population in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest will enable jaguars to recolonize the region (Verdade et al., 2015), because wild boars are killed in accordance with their abundance (Table 2) and are expected to function as buffer prey facilitating this expansion.
Jaguars prefer capybara and giant anteaters throughout their range and we assume this is based on optimal foraging of high energy meat yield for minimal investment in handling and processing, and limited injury risk. They are unselective in their predation on capybara age classes, but can kill a substantial proportion of a population over short periods of time (30% of a population within 2 months; Schaller and Vasconcelos, 1978). Just as the heavy predation by leopards Panthera pardus on baboons Papio spp. does not indicate preferential predation (Hayward et al., 2006a), the high levels of predation on caiman (over 62% of all caiman mortalities; Azevedo and Verdade, 2012) do not mean jaguars preferentially prey on them (Table 2). Although previous studies have shown reptiles can constitute up to 54% of a jaguars diet (Ramalho, 2006), a broader review of 19 studies showed that this is closer to 21 ± 3% (although this drops to 0.9 ± 0.1% when means weighted by sample size are used; calculated from da Silveira et al., 2010).
Although we focus this study on wild prey, jaguars are well known predators of livestock (Hoogesteijn et al., 1993; Quigley et al., 2015). Data from Polisar et al. (2003) show that jaguars prefer to kill cattle less than 1 year of age weighing less than 120 kg (D = 0.60) and avoid adult cattle (D = −0.78). Garrote (2012) showed that jaguars preferred pigs (D = 0.91) over horses (D = 0.38) and avoided cattle (D = −0.98). These results serve to reinforce our prey preference results, but also suggest that the predator naiveté that livestock have evolved through the domestication process allows predators to kill larger individuals than is possible with wild prey.
Other large predators we have studied exhibited reduced preferences for preferred prey species as they became more abundant within the prey community (Hayward, 2011). Conversely, they show increasing preference for non-preferred prey within the preferred weight range as they became more abundant (Hayward, 2011). Jaguars show no such relationship, with non-preferred species also being less preferred as they become more abundant (Figure 3). We contend that this is further evidence that jaguar predatory ecology has been substantially altered since the late-Pleistocene extinctions. This is in addition to the unusually small predator to prey body mass ratio of jaguars compared to other solitary felids, the limited effect of prey morphology as a driver of jaguar prey selection, the absence of evidence of optimal foraging by jaguars, the reduction in jaguar body mass since the Pleistocene, and the absence of preferentially hunting on Cetartiodactyla herbivores.
While this meta-analysis highlights the number of studies conducted on jaguar foraging ecology, it illustrates that research exhibits substantial spatial variation across the Americas, being dominated by work in Brazil and Mexico (Table 1; Figure 1) and data from these sites may be influencing our results. It also concurs with earlier reviews that concluded that research on this species has been limited by small sample sizes and a corresponding lack of information on prey abundance (Sunquist, 2002). In previous research on Africa's large predator guild, we were able to use trait-based aspects of their foraging to predict the number of large predators that could be sustained at a site, the home range sizes, and the diet using the results of prey preference studies similar to this one (Hayward et al., 2007a,b, 2009; Jooste et al., 2013). This was not possible here because jaguar prey abundance data is invariably presented as a relative measure rather than actual densities, which is satisfactory for determining prey preferences (Hayward et al., 2006a) but inadequate for these other purposes. The frequent use of camera traps to monitor prey communities in jaguar territories offers the opportunity to derive population density estimates via entropy modeling (Rowcliffe et al., 2008, 2011) and these would assist predictive ecology for these species.
This research highlights the important prey species and weight ranges of prey that are necessary for the conservation of jaguars and will be useful if plans for reintroduction come to fruition (Galetti et al., 2013). It also highlights areas for focus in future research programmes. Most importantly, however, this study illustrates the predatory response of an apex predator to the Pleistocene extinctions and more recent overhunting in which jaguars exhibit a diverse prey spectrum with minimal evidence of adhering to optimal foraging rules and, where they do, preferentially killing smaller than predicted prey (Figure 9).
Statements
Author contributions
MH designed, analyzed and wrote up this study. JK collected data and wrote-up this study. RM wrote-up this study. AN collected data and wrote-up this study. SR collected data and wrote-up this study. LS collected data and wrote-up this study. BV wrote-up this study.
Acknowledgments
We thank Howard Quigley, Adrian Schiavini and Carlos Alberto Lopez Gonzalez for their substantial assistance in improving this manuscript and the IUCN Red List for providing spatial distribution data for the jaguar for Figure 1.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1
Akaike H. (1973). Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. Budapest: Akademiai Kiado.
2
Akaike H. (1974). A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. AC19, 716–723. 10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705
3
Amin M. (2004). Patrones de Alimentación y Disponibilidad de Presas del Jaguar (Panthera onca) y del Puma (Puma concolor) en la Reserva de la Biosfera Calakmul, Campeche, México. México: Universidad Nacional Autonoma de México.
4
Aranda M. (1994). Importancia de los pacaries (Tayassu spp.) en la alimentacion del jaguar (Panthera onca). Acta Zool. Mex.62, 11–22.
5
Aranda M. Sanchez-Cordero V. (1996). Prey spectra of jaguar (Panthera onca) and puma (Puma concolor) in tropical forests of Mexico. Stud. Neotrop. Environ.31, 65–67. 10.1076/snfe.31.2.65.13334
6
Azevedo F. C. C. Verdade L. M. (2012). Predator-prey interactions: jaguar predation on caiman in a floodplain forest. J. Zool.286, 200–207. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2011.00867.x
7
Barton K. (2013). Package ‘MuMIn’. R package version 1.5. Aberdeen.
8
Burnham K. P. Anderson D. R. (1998). Model Selection and Multimodel Inference: A Practical Information-Theoretic Approach. New York, NY: Springer.
9
Carrillo E. Fuller T. K. Saenz J. C. (2009). Jaguar (Panthera onca) hunting activity: effects of prey distribution and availability. J. Trop. Ecol.25, 563–567. 10.1017/S0266467409990137
10
Caso A. Lopez-Gonzalez C. Payan E. Eizirik E. de Oliveira T. (2008). Panthera onca.Gland: IUCN. Available online at: http://www.iucnredlist.org/details/15953/0 Accessed 03 June 2015
11
Castañeda F. Herrera L. Pereira S. (2013). Behaviour of two male jaguars scavenging on a marine dolphin in Honduras. Cat News58, 3–12.
12
Cavalcanti S. M. C. Gese E. M. (2010). Kill rates and predation patterns of jaguars (Panthera onca) in the southern Pantanal, Brazil. J. Mammal.91, 722–736. 10.1644/09-MAMM-A-171.1
13
Ceballos G. Chávez C. Zarza H. Manterola C. (2005). Ecología y conservación del jaguar en la región de Calakmul. Biodiversitas62, 1–7.
14
Chiarello A. G. (1999). Effects of fragmentation of the atlantic forest on mammal communities in south-eastern Brazil. Biol. Conserv.89, 71–82. 10.1016/S0006-3207(98)00130-X
15
Chiarello A. G. (2000). Density and population size of mammals in remnants of brazilian atlantic forest. Conserv. Biol.14, 1649–1657. 10.1046/j.1523-1739.2000.99071.x
16
Chinchilla F. A. (1997). La dieta del jaguar (Panthera onca), el puma (Felis concolor) y el manigordo (Felis pardalis)(Carnivora; Felidae) en el parque nacional corcovado, costa rica. Rev. Biol. Trop.45, 1223–1230.
17
Cione A. L. Tonni E. P. Soibelzon L. (2009). Did Humans Cause the Late Pleistocene-Early Holocene Mammalian Extinctions in South America in a Context of Shrinking Open Areas?Amsterdam: Springer.
18
Clements H. S. Tambling C. J. Hayward M. W. Kerley G. I. H. (2014). An objective approach to determining the weight ranges of prey preferred by and accessible to the five large African carnivores. PLoS ONE9:e101054. 10.1371/journal.pone.0101054
19
Connell J. H. (1980). Diversity and the coevolution of competitors, or the ghost of competition past. Oikos35, 131–138. 10.2307/3544421
20
Crawshaw P. G. Jr. (1995). Comparative Ecology of Ocelot (Felis pardalis) and Jaguar (Panthera onca) in a Protected Subtropical Forest in Brazil and Argentina. Unpublished PhD thesis, Gainesville, FL: University of Florida.
21
Crawshaw P. G. Jr. Quigley H. B. (2002). Hábitos Alimentarios del Jaguar y el Puma en el Pantanal, Brasil, con Implicaciones Para su Manejo y Conservación. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society y Fondo de Cultura Económica.
22
Cruz E. Palacios G. Guiris M. (2007). Situación Actual del Jaguar en Chiapas. México: Conabio-Alianza WWF/Telcel-Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México.
23
da Silveira R. Ramalho E. E. Thorbjarnarson J. B. Magnusson W. E. (2010). Depredation by jaguars on caimans and importance of reptiles in the diet of jaguar. J. Herpetol.44, 418–424. 10.1670/08-340.1
24
Dalponte J. (2002). Dieta del Jaguar y Depredación de Ganado en el Norte del Pantanal, Brasil. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society y Fondo de Cultura Económica.
25
de Azevedo F. C. C. (2008). Food habits and livestock depredation of sympatric jaguars and pumas in the Iguaçu national park area, south brazil. Biotropica40, 494–500. 10.1111/j.1744-7429.2008.00404.x
26
de Azevedo F. C. C. Murray D. L. (2007). Spatial organization and food habits of jaguars (Panthera onca) in a floodplain forest. Biol. Conserv.137, 391–402. 10.1016/j.biocon.2007.02.022
27
de Oliveira T. G. (2002). Ecologia Comparativa de la Alimentación del Jaguar y del Puma en el Neotrópico. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society y Fondo de Cultura Económica.
28
Emmons L. H. (1987). Comparative feeding ecology of felids in a neotropical rainforest. Behav. Ecol. Sociob.20, 271–283. 10.1007/BF00292180
29
Emmons L. H. (1989). Jaguar predation on chelonians. J. Herpetol.23, 311–314. 10.2307/1564460
30
Facure K. G. Giaretta A. A. (1996). Food habits of carnivores in a coastal Atlantic forest of southeastern Brazil. Mammalia60, 499–502. 10.1515/mamm-1996-0319
31
Farrell L. E. Roman J. Sunquist M. E. (2000). Dietary separation of sympatric carnivores identified by molecular analysis of scats. Mol. Ecol.9, 1583–1590. 10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.01037.x
32
Fitzgibbon C. D. Lazarus J. (1995). Antipredator Behaviour of Serengeti Ungulates: Individual Differences and Population Consequences. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
33
Foster R. J. Harmsen B. J. Valdes B. Pomilla C. Doncaster C. P. (2010). Food habits of sympatric jaguars and pumas across a gradient of human disturbance. J. Zool.280, 309–318. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2009.00663.x
34
Fuller T. K. Sievert P. R. (2001). Carnivore Demography and the Consequences of Changes in Prey Availability. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press and the Zoological Society of London.
35
Galetti M. Eizirik E. Beisiegel B. Ferraz K. Cavalcanti S. Srbek-Araujo A. C. et al . (2013). Atlantic rainforest's jaguars in decline. Science342:930. 10.1126/science.342.6161.930-a
36
Garla R. C. Setz E. Z. F. Gobbi N. (2001). Jaguar (Panthera onca) food habits in atlantic rain forest of southeastern brazil. Biotropica33, 691–696. 10.1111/j.1744-7429.2001.tb00226.x
37
Garrote G. (2012). Depredación del jaguar (Panthera onca) sobre el ganado en los llanos orientales de Colombia. Mastozoología Neotrop.19, 139–145.
38
Gervasi V. Nilsen E. B. Linnell J. D. C. (2015). Body mass relationships affect the age structure of predation across carnivore–ungulate systems: a review and synthesis. Mammal. Rev.45, 253–266. 10.1111/mam.12047
39
Gómez-Ortiz Y. Monroy-Vilchis O. (2013). Feeding ecology of puma Puma concolor in Mexican montane forests with comments about jaguar Panthera onca. Wildl. Biol.19, 179–187. 10.2981/12-092
40
Gonyea W. J. (1976). Adaptive differences in the body proportions of large felids. Acta Anat.96, 81–96. 10.1159/000144663
41
Gonzalez-Maya J. F. Navarro-Arquez E. Schipper J. (2010). Ocelots as prey items of jaguars: a case from Talamanca, Costa Rica. Rev. Biol. Trop.45, 1223–1229.
42
Greenwood A. D. (2009). Ancient D. N. A., and the genetic consequences of late pleistocene extinctions, in American Megafaunal Extinctions at the End of the Pleistocene (Amsterdam: Springer), 107–123.
43
Guadamuz V. H. M. (2012). Cambios en la Abundancia, Actividad Temporal y Dieta de Jaguar (Panthera onca), Otros Felinos y Sus Presas en el Parque Nacional Santa Rosa, Área de Conservación Guanacaste, Costa Rica, Unpublished thesis, Heredia: Universidad Nacional de Costa Rica.
44
Guggisberg C. A. W. (1975). Wild Cats of the World. New York, NY: Taplinger Publishing Co.
45
Gutierrez D. C. Porras J. C. (2008). Ecología Poblacional de Jaguar (Panthera onca) y Puma (Puma concolor) y Dieta de Jaguar, en el Sector Pacífico de la Cordillera de Talamanca. Costa Rica. San Jose, CA: Universidad Latina de Costa Rica.
46
Hamilton W. D. (1971). Geometry of the selfish herd. J. Theor. Biol.31, 295–311. 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90189-5
47
Harmsen B. J. Foster R. J. Silver S. C. Ostro L. Doncaster C. P. (2010). The ecology of jaguars in the cockscomb basin wildlife sanctuary, belize, in The Biology and Conservation of Wild Felids, eds MacdonaldD. W.LoveridgeA. (Oxford: Oxford University Press), 403–416.
48
Hayward M. W. (2011). Scarcity in the prey community yields anti-predator benefits. Acta Oecol.37, 314–320. 10.1016/j.actao.2011.03.003
49
Hayward M. W. Hayward G. J. Druce D. Kerley G. I. H. (2009). Do fences constrain predator movements on an evolutionary scale? home range, food intake and movement patterns of large predators reintroduced to addo elephant national park, south africa. Biodiv. Conserv.18, 887–899. 10.1007/s10531-008-9452-y
50
Hayward M. W. Henschel P. O'Brien J. Hofmeyr M. Balme G. A. Kerley G. I. H. (2006a). Prey preferences of the leopard (Panthera pardus). J. Zool.270, 298–313. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00139.x
51
Hayward M. W. Hofmeyr M. O'Brien J. Kerley G. I. H. (2006b). Prey preferences of the cheetah Acinonyx jubatus: morphological limitations or the need to capture rapidly consumable prey before kleptoparasites arrive?J. Zool.270, 615–627. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00184.x
52
Hayward M. W. Hofmeyr M. O'Brien J. Kerley G. I. H. (2007a). Testing predictions of the prey of the lion (Panthera leo) derived from modelled prey preferences. J. Wildl. Manage.71, 1567–1575. 10.2193/2006-264
53
Hayward M. W. Jedrzejewski W. Jedrzejewska B. (2012). Prey preferences of the tiger Panthera tigris. J. Zool.286, 221–231. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2011.00871.x
54
Hayward M. W. Kerley G. I. H. (2005). Prey preferences of the lion (Panthera leo). J. Zool.267, 309–322. 10.1017/S0952836905007508
55
Hayward M. W. Lyngdoh S. Habib B. (2014). Diet and prey preferences of dholes (Cuon alpinus): dietary competition within Asia's apex predator guild. J. Zool.294, 255–266. 10.1111/jzo.12171
56
Hayward M. W. O'Brien J. Kerley G. I. H. (2007b). Carrying capacity of large African predators: predictions and tests. Biol. Conserv.139, 219–229. 10.1016/j.biocon.2007.06.018
57
Hebblewhite M. Pletscher D. H. (2002). Effects of elk group size on predation by wolves. Can. J. Zool.80, 800–809. 10.1139/z02-059
58
Hemmer H. Kahlke R.-D. Vekua A. K. (2001). The Jaguar-Panthera onca gombaszoegensis (Kretzoi, 1938)(Carnivora: Felidae) in the late lower pleistocene of Akhalkalaki (south Georgia; Transcaucasia) and its evolutionary and ecological significance. Geobios34, 475–486. 10.1016/S0016-6995(01)80011-5
59
Hernandez C. G. E. (2006). Dieta, uso de Hábitat y Patrones de Activdad del Puma (Puma concolor) y el Jaguar (Panthera onca) en La Selva. Guatemala: Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala.
60
Hernández-SaintMartín A. D. Rosas-Rosas O. C. Palacio-Núñez J. Tarango-Arambula L. A. Clemente-Sanchez F. Hoogesteijn A. L. et al . (2015). Food habits of jaguar and puma in a protected area and adjacent fragmented landscape of northeastern Mexico. Nat. Areas J.35, 308–317. 10.3375/043.035.0213
61
Hoogesteijn A. L. Mondolfi E. (1996). Body mass and skull measurements in four jaguar populations and observations on their prey base. Bull. Fla. Mus. Nat. Hist.39, 1952–1219.
62
Hoogesteijn R. Hoogesteijn A. (2008). Conflicts between cattle ranching and large predators in Venezuela: could use of water buffalo facilitate felid conservation?Oryx42, 132–138. 10.1017/S0030605308001105
63
Hoogesteijn R. Hoogesteijn A. Mondolfi E. (1993). Jaguar predation and conservation: cattle mortality caused by felines on three ranches in the Venezuelan Llanos. Symp. Zool. Soc. Lond.65, 391–407.
64
Iriarte J. A. Franklin W. L. Johnson W. E. Redford K. H. (1990). Biogeographic variation of food habits and body size of the american puma. Oecologia85, 185–190. 10.1007/BF00319400
65
Jacobs J. (1974). Quantitative measurement of food selection - a modification of the forage ratio and Ivlev's electivity index. Oecologia14, 413–417. 10.1007/BF00384581
66
Jêdrzejewski W. Cerda H. Viloria A. Schmidt K. (2014). Predatory behavior and kill rate of a female jaguar (Panthera onca) on cattle. Mammalia78, 235–238. 10.1515/mammalia-2012-0113
67
Jooste E. Hayward M. Pitman R. Swanepoel L. H. (2013). Effect of prey mass and selection on predator carrying capacity estimates. Eur. J. Wildl. Res.59, 487–494. 10.1007/s10344-013-0696-9
68
Jorgenson J. P. Redford K. H. (1993). Humans and big cats as predators in the Neotropics. Symp. Zool. Soc. Lond.65, 367–390.
69
Karanth K. U. Nichols J. D. Kumar N. S. Link W. A. Hines J. E. (2004). Tigers and their prey: predicting carnivore densities from prey abundance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.101, 4854–4858. 10.1073/pnas.0306210101
70
Kiltie R. A. (1984). Size ratios among sympatric neotropical cats. Oecologia61, 411–416. 10.1007/BF00379644
71
Kuriowa A. Ascorra C. (2002). Dieta y Densidad de Posibles Presas de Jaguar en las Inmediaciones de la Zona de Reserva Tambopata-Candamo, Perú. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society y Fondo de Cultura Económica.
72
Kurten B. (1973). Pleistocene jaguars of North America. Comment. Biol. Soc. Sri. Fennica62, 1–23.
73
Kurtén B. Anderson E. (1980). Pleistocene Mammals of North America. New York, NY: Columbia University Press.
74
Leite M. R. P. Galvão F. (2002). El Jaguar, el Puma y el Hombre en Tres Áreas Protegidas del Bosque Atlántico Costero de Paraná, Brasil. México: Fondo de Cultura Económica, Universidad Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society.
75
López González C. A. Lorenzana Piña G. (2002). Carrion use by jaguars (Panthera onca) in Sonora, Mexico. Mammalia66, 603–605.
76
López Gonzalez C. A. Miller B. J. (2002). Do jaguars (Panthera onca) depend on large prey?West. North Am. Nat.62, 218–222.
77
Lyngdoh S. Shrotriya S. Goyal S. P. Clements H. Hayward M. W. Habib B. (2014). Prey preferences of the snow leopard (Panthera uncia): regional diet specificity holds global significance for conservation. PLoS ONE9:e88349. 10.1371/journal.pone.0088349
78
Lyons S. K. Smith F. A. Brown J. H. (2004). Of mice, mastodons and men: human-mediated extinctions on four continents. Evol. Ecol. Res.6, 339–358.
79
Martínez-Gutiérrez P. G. Palomares F. Fernández N. (2015). Predator identification methods in diet studies: uncertain assignment produces biased results?Ecography38, 922–929. 10.1111/ecog.01040
80
Márquez I. J. (2009). Disponibilidad, Uso de Habitat y Estado de Salud del Jaguar (Panthera onca) en Los Parques Nacionales Laguna del Tigre y Sierra de Lacandón. Consejo Nocioal de Ciencia y Tecnologia, Guatemala.
81
Mayer J. J. Wetzel R. M. (1987). Tayassu pecari. Mamm. Species12, 1–7. 10.2307/3503865
82
McBride R. Giordano A. Ballard W. B. (2010). Note on the winter diet of jaguars Panthera onca in the paraguyan transitional chaco. Bellbird4, 1–4.
83
Meachen-Samuels J. Van Valkenburgh B. (2009a). Craniodental indicators of prey size preference in the Felidae. Biol. J. Linn. Soc.96, 784–799. 10.1111/j.1095-8312.2008.01169.x
84
Meachen-Samuels J. Van Valkenburgh B. (2009b). Forelimb indicators of prey-size preference in the Felidae. J. Morphol.270, 729–744. 10.1002/jmor.10712
85
Meachen J. A. Janowicz A. C. Avery J. E. Sadlier R. W. (2014). Ecological changes in coyotes (canis latrans) in response to the Ice Age megafaunal extinctions. PLoS ONE9:e116041. 10.1371/journal.pone.0116041
86
Michalski F. Boulhosa R. L. P. Peres C. A. (2006). Human-wildlife conflicts in a fragmented Amazonian forest landscape: determinants of large felid depredation on livestock. Anim. Conserv.9, 179–190. 10.1111/j.1469-1795.2006.00025.x
87
Mills M. G. L. (1992). A Comparison of Methods Used to Study Food Habits of Large African Carnivores. London: Elsevier.
88
Mol D. Logchem W. V. Vos J. D. (2011). New record of the european jaguar, Panthera onca gombaszoegensis (Kretzoi, 1938), from the Plio-Pleistocene of Langenboom (The Netherlands). Cainozoic Res.8, 35–40.
89
Mondolfi E. Hoogesteijn R. (1986). Notes on the Biology and Status of the Jaguar in Venezuela. Washington, DC.: National Wildlife Federation.
90
Moreno R. S. Kays R. W. Samudio R. (2006). Competitive release in diets of ocelot (Leopardus pardalis) and puma (Puma concolor) after jaguar (Panthera onca) decline. J. Mammal.87, 808–816. 10.1644/05-MAMM-A-360R2.1
91
Moreno Ruiz R. S. (2006). Parámetros Poblacionales y Aspectos Ecológicos de los Felinos y sus Presas en Cana, Parque Nacional Darien, Panamá. Panamá: Universidad Nacional de Panamá.
92
Novack A. J. Main M. B. Sunquist M. E. Labisky R. F. (2005). Foraging ecology of jaguar (Panthera onca) and puma (Puma concolor) in hunted and non-hunted sites within the maya biosphere reserve, Guatemala. J. Zool.267, 167–178. 10.1017/S0952836905007338
93
Nowak R. M. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. Baltimore, MD: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
94
Nowell K. Jackson P. (1996). Wild Cats: Status, Survey and Conservation Action Plan. Gland: IUCN/Species Survival Commission Cat Specialist Group.
95
Núñez R. Miller B. Lindzey F. (2000). Food habits of jaguars and pumas in Jalisco, Mexico. J. Zool.252, 373–379. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2000.tb00632.x
96
Olmos F. (1993). Notes on the food habits of Brazilian “Caatinga” carnivores. Mammalia57, 126–130.
97
Owen P. R. Bell C. J. Mead E. M. (2000). Fossils, diet, and conservation of black-footed ferrets (Mustela nigripes). J. Mammal.81, 422–433. 10.1093/jmammal/81.2.422
98
Palmeira F. B. L. Barrella W. (2007). Conflitos causados pela predação de rebanhos domésticos por grandes felinos em comunidades quilombolas na Mata Atlântica. Biota Neotrop.7, 119–128. 10.1590/S1676-06032007000100017
99
Palmeira F. B. L. Crawshaw P. G. Haddad C. M. Ferraz K. M. P. M. B. Verdade L. M. (2008). Cattle depredation by puma (Puma concolor) and jaguar (Panthera onca) in central-western Brazil. Biol. Conserv.141, 118–125. 10.1016/j.biocon.2007.09.015
100
Pardi M. I. Smith F. A. (2015). Biotic responses of canids to the terminal Pleistocene megafauna extinction. Ecography. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1111/ecog.01596
101
Peetz A. Norconk M. A. Kinzey W. G. (1992). Predation by jaguar on howler monkeys (Alouatta seniculus) in Venezuela. Am. J. Primat.28, 223–228. 10.1002/ajp.1350280307
102
Perili M. L. L. (2009). Ecologia Alimentar da Onça-pintada (Panthera onca) na Região sul do Pantanal Utilizando Análise de Fezes – uma Comparação com o Método Direto de Rádio-telemetria GPS. Campo Grande: Federal University of Mato Grosso do Sul.
103
Perovic P. G. (2002). Conservación del Jaguar en el Noroeste de Argentina. Conservación del jaguar en el noroeste de Argentina. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society y Fondo de Cultura Económica.
104
Perry R. (1970). The World of the Jaguar. New York, NY: Taplinger Publishing Company.
105
Polisar J. Maxit I. Scognamillo D. Farrell L. Sunquist M. E. Eisenberg J. F. (2003). Jaguars, pumas, their prey base, and cattle ranching: ecological interpretations of a management problem. Biol. Conserv.109, 297–310. 10.1016/S0006-3207(02)00157-X
106
Porfirio G. E. O. (2009). Ecologia Alimentar da Onça-Pintada (Panthera onca) na Sub-Regiao do Pantanal de Miranda, M. S. Brazil.Matto Grosso.
107
Quigley H. Hoogesteijn R. Hoogesteijn A. Foster R. Payan E. Corrales D. et al . (2015). Observations and preliminary testing of jaguar depredation reduction techniques in and between core jaguar populations. Parks21, 1–10. 10.2305/IUCN.CH.2014.PARKS-21-1HQ.en
108
Quigley H. B. Crawshaw P. G. (1992). A conservation plan for the jaguar Panthera onca in the Pantanal region of Brazil. Biol. Conserv.61, 149–157. 10.1016/0006-3207(92)91111-5
109
R Core Development Team (2008). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing.
110
Rabinowitz A. (1986). Jaguar predation on domestic livestock in Belize. Wildl. Soc. Bull.14, 170–174.
111
Rabinowitz A. Nottingham B. G. (1986). Ecology and behaviour of the jaguar (Panthera onca) in Belize, Central America. J. Zool.210, 149–159. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.1986.tb03627.x
112
Railsback S. F. Harvey B. C. (2013). Trait-mediated trophic interactions: is foraging theory keeping up?TREE28, 119–125. 10.1016/j.tree.2012.08.023
113
Ramalho E. (2006). Uso do Habitat e Dieta da Onça-Pintada (Panthera onca) em Uma Area de Várzea, Reserva de Desenvolvimento Sustentável Mamirauá, Amazônia Central, Brasil. Manaus: Instituto Nacional de Pesquisa da Amazônia.
114
Redford K. H. (1992). The empty forest. Bioscience42, 412–422. 10.2307/1311860
115
Rosas-Rosas O. C. Bender L. C. Valdez R. (2008). Jaguar and puma predation on cattle calves in northeastern Sonora, Mexico. Rangeland Ecol. Manag.61, 554–560. 10.2111/08-038.1
116
Rowcliffe J. M. Carbone C. Jansen P. A. Kays R. Kranstauber B. (2011). Quantifying the sensitivity of camera traps: an adapted distance sampling approach. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2, 464–476. 10.1111/j.2041-210x.2011.00094.x
117
Rowcliffe J. M. Field J. Turvey S. T. Carbone C. (2008). Estimating animal density using camera traps without the need for individual recognition. J. Appl. Ecol.45, 1228–1236. 10.1111/j.1365-2664.2008.01473.x
118
Rueda P. Mendoza G. Martínez D. Rosas-Rosas O. C. (2013). Determination of the jaguar (Panthera onca) and puma (Puma concolor) diet in a tropical forest in San Luis Potosi, Mexico. J. Appl. Anim. Res.41, 484–489. 10.1080/09712119.2013.787362
119
Salera G. Portelinha T. C. G. Malvasio A. (2009). Predation on Adult Females of Podocnemis Expansa Schweigger (Testudines, Podocnemididae) by Panthera onca Linnaeus (Carnivora, Felidae), in Tocantins State. Biota Neotropica 9. Available online at: http://www.biotaneotropica.org.br/v9n3/en/abstract?short-communication+bn00709032009
120
Schaller G. B. (1983). Mammals and their biomass on a Brazilian ranch. Arq. Zool.31, 1–36. 10.11606/issn.2176-7793.v31i1p1-36
121
Schaller G. B. Vasconcelos J. (1978). Jaguar predation on capybara. Z. Saugetierkd.43, 296–301.
122
Scognamillo D. Maxit I. Sunquist M. E. Polisar J. (2003). Coexistence of jaguar (Panthera onca) and puma (Puma concolor) in a mosaic landscape in the Venezuelan llanos. J. Zool.259, 269–279. 10.1017/S0952836902003230
123
Seymour K. L. (1989). Panthera onca. Mamm. Species340, 1–9. 10.2307/3504096
124
Silveira L. (2004). Ecologia Comparada e Conservação da Onça-Pintada (Panthera onca) e Onça-parda (Puma concolor), no Cerrado e Pantanal. Unpublished PhD thesis, Universidade de Brasilia.
125
Sollmann R. (2011). Ecology and Conservation of the Jaguar (Panthera onca) in the Cerrado Grasslands of Central Brazil. Unpublished PhD thesis, Berlin, Freie Universität Berlin.
126
Sollmann R. Betsch J. Furtado M. Hofer H. Jacomo A. T. A. Palomares F. et al . (2013). Note on the diet of the jaguar in central Brazil. Eur. J. Wildl. Res.59, 445–448. 10.1007/s10344-013-0708-9
127
Soto-Shoender J. R. Giuliano W. M. (2011). Predation on livestock by large carnivores in the tropical lowlands of Guatemala. Oryx45, 561–568. 10.1017/S0030605310001845
128
Steenweg R. Gillingham M. Parker K. Heard D. C. (2015). Considering sampling approaches when determining carnivore diets: the importance of where, how, and when scats are collected. Mamm. Res.60, 207–216. 10.1007/s13364-015-0222-4
129
Steinmetz R. Seuaturien N. Chutipong W. (2013). Tigers, leopards, and dholes in a half-empty forest: assessing species interactions in a guild of threatened carnivores. Biol. Conserv.163, 68–78. 10.1016/j.biocon.2012.12.016
130
Sunquist M. (2002). Historia de la Investigación Sobre el Jaguar en el Continente Americano. México: Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Wildlife Conservation Society y Fondo de Cultura Económica.
131
Sunquist M. Sunquist F. (2002). Wild Cats of the World. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
132
Taber A. B. Novaro A. J. Neris N. Colman F. H. (1997). The food habits of sympatric jaguar and puma in the Paraguayan Chaco. Biotropica29, 204–213. 10.1111/j.1744-7429.1997.tb00025.x
133
Tedford R. H. Wang X. Van Valkenburgh B. Wayne R. K. (2004). Evolutarionary history, molecular systematics and evolutionary ecology of wild canids, in Biology and Conservation of Wild Canids, eds MacdonaldD. W.Sillero-ZubiriC. (Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press).
134
Trovati R. G. Campos C. Brito B. (2008). Nota sobre convergência e divergência alimentar de canídeos e felídeos (Mamalia: Carnivora) simpátricos no Cerrado brasileiro. Neotrop. Biol. Conserv.3, 95–100.
135
Van Valkenburgh B. Hayward M. W. Ripple W. J. Meloro C. Roth V. L. (2015). The impact of large terrestrial carnivores on Pleistocene ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1073/pnas.1502554112
136
Van Valkenburgh B. Hertel F. (1998). The decline of North American Predators during the Late Pleistocene. The decline of North American Predators during the Late Pleistocene. Springfield, IL: Illinois State Museum Scientific Papers.
137
Verdade L. M. Palomares F. do Couto H. T. Z. Polizel J. L. (2015). Recent land-use changes and the expansion of an exotic potential prey: a possible redemption for Atlantic forest jaguars?Anim. Conserv. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1111/acv.12221
138
Veríssimo D. Jones D. Chaverri R. Meyer S. R. (2012). Jaguar Panthera onca predation of marine turtles: conflict between flagship species in Tortuguero, Costa Rica. Oryx46, 340–347. 10.1017/S0030605311001487
139
Weckel M. Giuliano W. M. Silver S. C. (2006a). Cockscomb revisited: jaguar diet in the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, Belize. Biotropica38, 687–690. 10.1111/j.1744-7429.2006.00190.x
140
Weckel M. Giuliano W. M. Silver S. C. (2006b). Jaguar (Panthera onca) feeding ecology: distribution of predator and prey through time and space. J. Zool.270, 25–30. 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2006.00106.x
141
Wilkie D. S. Bennett E. L. Peres C. A. Cunningham A. A. (2011). The empty forest revisited. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci.1223, 120–128. 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05908.x
142
Woodroffe R. Lindsey P. A. Romanach S. S. ole Ranah S. M. K. (2007). African wild dogs (Lycaon pictus) can subsist on small prey: implications for conservation. J. Mammal.88, 181–193. 10.1644/05-MAMM-A-405R1.1
143
Yanez J. L. Crdenas J. C. Gezelle P. Jaksic F. M. (1986). Food habits of the southermost mountain lions (Felis concolor) in South America: natural versus livestocked ranges. J. Mammal.67, 604–606. 10.2307/1381301
Summary
Keywords
predator-prey interactions, apex predator, optimal foraging theory, Pleistocene megafaunal extinction, capybara, giant anteater, accessible prey, preferred prey weight range
Citation
Hayward MW, Kamler JF, Montgomery RA, Newlove A, Rostro-García S, Sales LP and Van Valkenburgh B (2016) Prey Preferences of the Jaguar Panthera onca Reflect the Post-Pleistocene Demise of Large Prey. Front. Ecol. Evol. 3:148. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2015.00148
Received
07 October 2015
Accepted
11 December 2015
Published
25 January 2016
Volume
3 - 2015
Edited by
Ricardo Baldi, Centro Nacional Patagónico (CENPAT - CONICET), Argentina
Reviewed by
Adrian Schiavini, Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas, Argentina; Carlos Alberto Lopez Gonzalez, Universidad Autonoma de Queretaro, Mexico
Updates
Copyright
© 2016 Hayward, Kamler, Montgomery, Newlove, Rostro-García, Sales and Van Valkenburgh.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Matt W. Hayward m.hayward@bangor.ac.uk
This article was submitted to Conservation, a section of the journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.