- Department of Pediatrics, Medical University of Innsbruck, Innsbruck, Austria
Pertussis, caused by Bordetella (B.) pertussis, a Gram-negative bacterium, is a highly contagious airway infection. Especially in infants, pertussis remains a major health concern. Acute infection with B. pertussis can cause severe illness characterized by severe respiratory failure, pulmonary hypertension, leucocytosis, and death. Over the past years, rising incidence rates of intensive care treatment in young infants were described. Due to several virulence factors (pertussis toxin, tracheal cytotoxin, adenylate cyclase toxin, filamentous hemagglutinin, and lipooligosaccharide) that promote bacterial adhesion and invasion, B. pertussis creates a unique niche for colonization within the human respiratory tract. The resulting long-term infection is mainly caused by the ability of B. pertussis to interfere with the host’s innate and adaptive immune system. Although pertussis is a vaccine-preventable disease, it has persisted in vaccinated populations. Epidemiological data reported a worldwide increase in pertussis incidence among children during the past years. Either acellular pertussis (aP) vaccines or whole-cell vaccines are worldwide used. Recent studies did not detect any differences according to pertussis incidence when comparing the different vaccines used. Most of the currently used aP vaccines protect against acute infections for a period of 6–8 years. The resurgence of pertussis may be due to the lack of herd immunity caused by missing booster immunizations among adolescents and adults, low vaccine coverages in some geographic areas, and genetic changes of different B. pertussis strains. Due to the rising incidence of pertussis, probable solution strategies are discussed. Cocooning strategies (vaccination of close contact persons) and immunizations during pregnancy appear to be an approach to reduce neonatal contagiousness. During the past years, studies focused on the pathway of the immune modulation done by B. pertussis to provide a basis for the identification of new therapeutic targets to enhance the host’s immune response and to probably modulate certain virulence factors.
“I have a faint cold fear thrills through my veins” (1)
Bordetella spp.
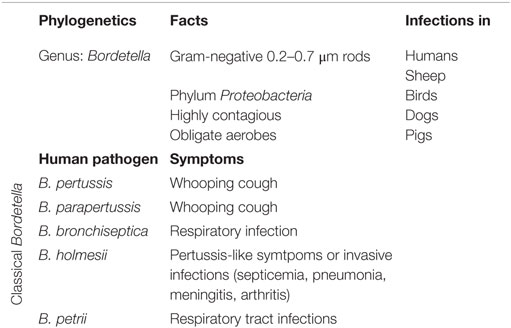
Bordetella (B.) pertussis is a fimbriated Gram-negative, aerobic coccobacillus. B. pertussis ranks to the genus Bordetella (2–5). Phylogenetic analysis revealed nine different Bordetella species. Five of them are known to cause respiratory tract infections in humans: B. pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis, Bordetella bronchiseptica, Bordetella holmesii, and Bordetella petrii (2, 3, 6). Within the species Bordetella, B. pertussis, B. bronchiseptica, and B. parapertussis are closely related pathogens that infect mammalians. B. bronchiseptica causes a mild or chronic respiratory infection in a large range of mammalian hosts (2, 7). In humans, it causes respiratory tract infections mostly in immunocompromised hosts (7, 8). Regarding B. parapertussis, two distinct hosts have been identified: humans (B. parapertussis HU) and sheep (B. parapertussis SH) (2, 9). B. holmesii is part of a different genetic lineage within the B. genus. B. holmesii causes either pertussis-like symptoms or invasive infections (e.g., septicemia, pneumonia, meningitis, arthritis, etc.) (10, 11). B. petrii was isolated in patients with cystic fibrosis and in come cases of long-lasting respiratory tract infections (Table 1) (12).
During the past years, B. pertussis, the causative agent of whooping cough, resurged as cause for upper airway infections in humans.
B. pertussis – Clinical Course
Infection by B. pertussis is acquired via droplet route (5, 13). In the susceptible child, the classical pre-vaccination textbook symptom trias is defined as: catarrhal stage with unspecific symptoms (e.g., fever, rhinitis, mild cough) which typically lasts for 1–2 weeks, followed by the paroxysmal stage where the cough evolves in the typical paroxysmal coughing spells followed by posttussive whooping and vomiting and duration of cough lasting 1–3 months. During the third stage, also known as convalescent stage, the intensity of coughing spells deceases during 1–2 weeks (14). Pertussis is at least unpleasant for the patient, as these symptoms frequently interfere with daily activities and can cause significant sleep disturbances (5, 14).
In reality, B. pertussis is a chameleon. Infection by B. pertussis nowadays often causes unspecific mild symptoms, such as rhinitis and unspecific mild cough often not leading to a physician visit (5). Even asymptomatic infections can occur in children and adults with strong residual immunity (13, 15). Life-threatening disease manifestation is often seen in newborns and young infants. Newborns and young infants often first present with apnea or respiratory distress syndromes (5, 13, 16). In <20%, fever is detected (5). The first presentation of an acute infection is affected by several parameters: patient age, previous exposure (vaccination or prior infection), first-line antibiotic administration, concomitant infections with other agents, and the presence of cross-reacting antibodies (13, 16–19).
After introduction of routine vaccination in young infants, pertussis incidence first decreased. However, B. pertussis nowadays accounts for a significant morbidity and mortality worldwide. Increasing incidence resulted from an increased awareness of the reservoir of B. pertussis infections in adolescents and adults (20–22).
Type and frequency of complications depend on host-specific age and immunity. They most commonly present as bronchoalveolar pneumonia (any age) or apnea (newborns and young infants) and more rarely as respiratory distress syndrome, seizures, and other signs of encephalopathy (2, 5).
B. pertussis – Underestimated Cases?
Since the introduction of a worldwide available vaccination in the 1950s, a significant reduction in mortality rates was detected worldwide (2, 20–22). However, pertussis still poses a significant health burden. The worldwide estimated immunization coverage among infants receiving three doses of the diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine (DTP3) increased still till 2012 and reaches about 86% of the population in 2014 (23, 24). Data on booster vaccinations are missing. Thus, the number of worldwide recognized cases of pertussis was stable, many regions reporteted a resurgence (13, 21, 23, 24). In countries with high vaccination coverage, pertussis experiences a second springtide among adolescents and adults (13, 22, 24–29). Several studies in adults revealed prolonged cough illness as a result of an infection by B. pertussis (13, 24–29). The United States (US) and the United Kingdom have seen a rise in B. pertussis cases during the past years (23, 29). The rising incidence in B. pertussis cases may be influenced by an either too low vaccination coverage especially booster vaccination coverage, or the possibility of a vaccination-breaktrough infection (29–32). During the past decades, improved surveillance and diagnostics has led to an increased incidence worldwide. However, in the US, a steady rise of reported pertussis cases was detected over the last 30 years (29, 30). In 2010 and 2012, pertussis outbreaks were reported in California and Washington with case counts similar to the 1940s (30). An increase across all ages also in infants less than 1 year of age has been reported in the US (33).
Recent studies tried to elucidate possible explanations for the increase of disease burden (29–32, 34–36): (1) the evolution of B. pertussis to escape vaccine antigens; (2) low vaccination or wild-type infection rates; (3) a changed efficacy of vaccine protection due to the use of the acellular vaccine or even a lower vaccine efficacy; and (4) an increase of reporting systems and surveillance analysis.
B. pertussis – Diagnostics
For accurate diagnosis of infection due to B. pertussis, different diagnostic procedures are available: direct fluorescent-antibody assay (DFA), culture, PCR, and serodiagnostic.
Direct fluorescent-antibody assay is performed using nasopharyngeal swabs of patients. Via microscopy fluorescent antibodies directed against B. pertussis are visualized. Due to the low sensitivity and specificity of this assay, DFA diagnosis always needs a second method for proof (22, 37) Culture is the gold standard for pertussis diagnosis. Despite its low sensitivity compared to PCR, it is still used (22, 37). Nasopharyngeal samples obtained by deep aspiration or swabs can be used (22, 37–39). Collection of oral fluids is less stressful for the patient, but it should not be used for culturing due to the probable contamination with resident oral pathogens (22). In ace of culturing B. pertussis, addition of cephalexin to the medium is recommended to inhibit growth of contaminant bacteria (22). Agar plates are incubated at 35–37°C in a high-humidity environment with low levels of carbon dioxide for up to 12 days to reach optimal sensitivity (22). After growth on the agar plate, bordetellae can be further characterized by biochemical reactions, agglutination with specific sera or PCR (22, 37). During the past years, PCR assays have become a well-established method for the detection of bordetellae (22, 37, 40–42). Dry swabs can be used for PCR (22, 42, 43).
Serodiagnosis is often used to confirm the clinical diagnosis of pertussis. Early serodiagnostic methods required a significant (greater than fourfold) increase of titers in serum samples 2–4 weeks after the first diagnosis (22). Nowadays, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) are used to differentiate IgM, IgA, and IgG antibodies against pertussis. ELISAs use specific cut-off values for detection of pertussis (22, 37, 43).
Taken together, the optimal diagnostic method always depends on the age of the patient, the stage of disease, and the primary vaccination status of the patient.
B. pertussis – Virulence Factors
The primary side of infection with B. pertussis is the respiratory tract. Infection is initiated via contact of respiratory droplets from an infected individual (2, 3, 5, 13, 20–22). After inhalation, B. pertussis enters the upper respiratory tract and adheres to the epithelia of the nasopharynx and the trachea (2, 3, 5, 13, 14). After attachment, B. pertussis produces a cascade of virulence factors: adhesins, immune-modulators, and toxins. The interaction and teamwork of these factors prevents B. pertussis from a rapid clearance and enable its dissemination to the lower areas of the respiratory tract (2, 3, 5, 13, 14). B. pertussis produces a number of toxins: pertussis toxin (PT), tracheal cytotoxin (TCT), adenylate cyclase toxin (ACT), heat-labile toxin, type III secretion system (TTSS), and endotoxin or lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Further on receptor-binding, virulence factors, such as filamentous hemagglutinin (FHA) and pertactin (PRN), are expressed. To complete the wall of protection B. pertussis is protected by fimbriae, which act as antigenic targets for antibodies and T cells (Figure 1) (3, 5, 14).
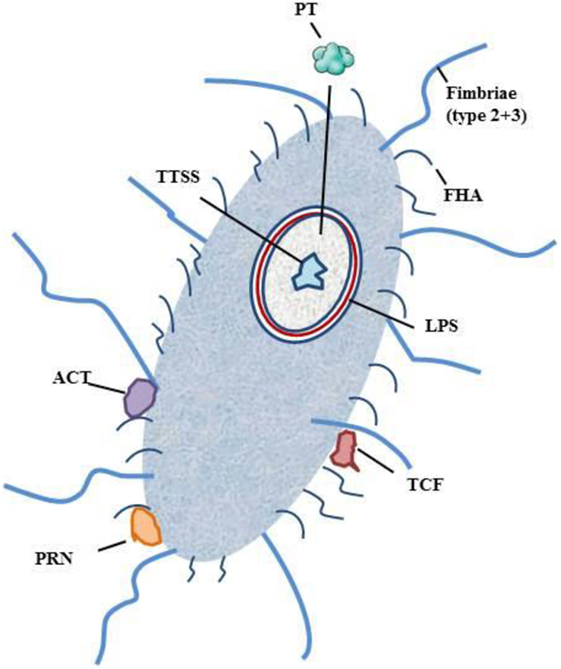
Figure 1. Schematic figure of B. pertussis and its virulence factors. Notation: PT, pertussis toxin; TCT, trachel cytotoxin; ACT, adenylate cyclase toxin; TTSS, type III secretion system; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; FHA, filamentous hemagglutinin; PRN, pertactin.
Pertussis toxin is one of the dangerous players of B. pertussis. It promotes system effects, such as lymphocytosis and histamine sensitization, and promotes T-cell response by bystander antigens. After primary adherence by fimbriae, PT facilitates FHA-mediated adhesion to macrophages (44–46). FHA has been shown to have an immunosuppressive function during infection (3, 47). PT consists of different subunits that contribute to the immunomodulatory effects, which either suppress or promote the hosts immune response (3, 46, 48, 49). PT inhibits phagocytosis by antigen-presenting cells (APC), antigen processing and presentation, and trafficking of APC to lymph nodes (3, 46, 48, 49). TCT acts as an activator of the immune deficiency pathway (3). ACT plays several roles in the invasion of the human body by B. pertussis. It binds to the complement receptor 3 and intoxicates complement receptor 3-negative cells. ATC induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest and inhibits phagocytosis, chemotaxis, and superoxide generation. Furthermore, it modulates APCs and induces a T-cell response (50–52). ACT suppresses the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-12p70) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) (53–55). FHA is the main agent for the adhesion of B. pertussis to the mucosal surface of respiratory tract. It promotes bacterial adherence to ciliated respiratory epithelial cells and promotes phagocytosis by macrophages and polymorphonuclear leukocytes (3, 56–60). TTSS stimulates innate and adaptive immune response (3). LPS is one of the main components for colonization survival. LPS acts pyrogenic, toxic, and can activate proinflammatory cytokine production (61, 62). PRN is an auto-transporter protein of the outer membrane that enables the adherence of B. pertussis to monocytes and epithelial cells (3, 63). LPS and TCT have been shown to induce NOS and NO and to inhibit DNA synthesis in epithelial cells (64) TCT and PT have been shown to inhibit the immune cell trafficking within the respiratory tract (2).
B. pertussis – Immune Modulation?
After early studies on B. pertussis-induced immune reactions in humans, studies in mouse completed the experimental settings (65–69).
The ciliated epithelium of the respiratory tract ensures that pathogens are cleared mechanically (2). Successful infection of the host, therefore, depends on the ability of B. pertussis to produce a number of adhesins and toxins, which alter immune response of the host (3). After binding to the cilia of the respiratory tract, macrophages and immature dendritic cells (DCs) are the first cells responding to the invador (3, 70, 71) In addition, many toxins and virulence factors of B. pertussis promote bacterial survival in the host by remodulating the immune system. FHA induces proinflammatory interleukin(IL)-6 and IL-10 and supresses IL-12 production (2, 72). The generation of IL-10-producing regulatory T cells (Treg cells) suppresses interferon (IFN)-gamma production and inhibits the generation and function of Th1 effector cells (2, 72). PT promotes immunosuppression via activation of T-cell receptor-associated signaling molecules in lymphocytes (3). A recent study even implicates that PT can either work pro- or anti-inflammatory depending on single versus repetitive exposure of the host, which might be linked to enhanced severity of autoimmune diseases (73). In synergy with IL-10, ACT leads to the development of Treg cells, which delays the clearance of B. pertussis (53–55). Taken together all this cellular and humoral alterations, B. pertussis acts as a very potent immune modulator.
Murine infection models showed rapid cell recruitment to the lungs (74). After the initial influx of DCs and macrophages, neutrophils, natural killer (NK) cells, and T cells follow the proinflammatory signals (75, 76).
In infants with confirmed pneumonia due to B. pertussis infection, bordetellae have been found in pulmonary alveolar macrophages (71). B. pertussis can replicate in macrophages and, therefore, evade destruction (3, 70). As a consequence, depletion of resident macrophages enhances infection (70). Controversely, former studies revealed that macrophages can harbor B. pertussis intracellularly and then be activated by IFN-gamma and IL-17 to kill the intracellular B. pertussis particles (77, 78). The second first-line immune cells activated are DCs. DCs present antigens to T cells and stimulate innate cytokines that promote further differentiation of naive T cells. After recognition of B. pertussis, proinflammatory signals (Il-12, IFN-gamma) trigger activation of T-cell response (79). In human DC cells, infection by B. pertussis enhances IL-1 and IL-23 production, which is required for maturation of Th17 cells (80).
In mouse models, neutrophils, which help to kill phagocytosed bacteria, infiltrate the lungs in around day 5 after infection (3, 81). Due to its unique structure, B. pertussis can survive in neutrophils that undergo lysosomal maturation (58). During the early time of infection, PT delays the early infiltration of neutrophils (82) and ACT inhibits neutrophil functions like phagocytosis, superoxide generation, and chemotaxis (83). Another early player of the defense against B. pertussis is NK cells. NK cells produce IFN-gamma in response to infection and lead to a Th1-guided immune response (76, 84).
In a second defense line of the human body, proteins are secreted by the mucosa of the airways and by innate immune cells: lysozyme, lactoferrin, and secretory leukoproteinase inhibitor, and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), e.g., cathelicidin (LL-37) and defensins (85, 86). B. pertussis fights against these agents by blocking certain molecules. For example, TTSS inhibits the expression of defensins and, therefore, promotes survial of B. pertussis. Consequentely, B. pertussis is enabled to colonize the lower airways (87). B. pertussis also has mechanisms protecting more or less against another soluble factor of the innate immune system: the complement. Susceptibility to complement remains highly variable (88).
On the cellular level, certain players are involved. Recent studies detected that cellular components of the immune system are needed to effectively clear a primary infection by B. pertussis. CD4− T cells, Treg, and Th17 cells seem to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of pertussis (89, 90). Early work focusing on the T-cell immune system evaluated that PT, FHA, and PRN stimulate CD4+ T cells in children with whooping cough (65–67). In vitro proliferation of T cells negatively correlates with clinical symptoms of pertussis (68). In murine models, high levels of CD25−Foxp3+ Treg cells have been detected in the lungs of infected animals (91). Recent studies showed that T-cell response plays a major role in protection against B. pertussis (89). It is assumed that the high amount of Treg cells may be a benefit to the infected patient by limiting pathological alterations (78).
More recent studies showed an induction of Th17 cells by B. pertussis (78, 80). Pulmonary hypertension is one possible lethal complication of pertussis infection in infants and young children. Interestingly, Th17 cells are discussed to contribute to the pathomechanisms of pulmonary hypertension in severe pertussis cases (92). By the induction of Treg cells, pertussis subverts the protective immune response (72, 93). During infection, protective Th1 and Th17 response can be detected locally and systemically (94). However, the exact role of Th17 cells in protection against B. pertussis has to be more precisely studied in humans.
Despite all achievments, the first priority for the improvement of a long-lasting protection after vaccination is to study the exact immunological responses to infection and identify new targets that improve the robustness of pertussis vaccination. Furthermore, the highest mortality rates are known in infants. The infantile immune system is difficult to treat and protect. Considering these challenges, future studies should focus on new priorities irrespective of the socioeconomic status of the patients.
B. pertussis – Vaccinations
Up to date, two differenct vaccines can be used: an acellular pertussis (aP) vaccine and a whole-cell pertussis (wP) vaccine. Early studies in murine models and humans have revealed that wP and aP vaccine induce distinct Th1 versus Th2 responses (44, 45, 95). In case of the aP vaccine, the T-cell immune responses to pertussis were assessed during the safety and efficacy trials conducted in Sweden and Italy in the 1990s (96, 97). In these early studies, a “robust” T-cell immune response to the pertussis vaccine was detected in infants and young children (96, 97). Following studies showed that T-cell immunity persisted over a long time period even after the decline of antibodies (98, 99). Furthermore, T-cell immunity could be boostered by wild virus infection (99). By contrast, T-cell response after wP vaccine was compareable to natural infection, inducing a Th1 response (98, 100, 101). After primary vaccination with wP vaccine, an aP booster dose induces a mixed Th1/Th2 response (44, 45).
Several studies emphazised the importance of booster vaccinations to enhance the T-cell response to pertussis antigen. In a study in adolescents, Rieber et al. pointed out that T-cell parameters to PT, FHA, PRN, and fimbriae increase after booster vaccination with a five-component Tdap booster vaccine (102). Due to lacking immunity more recently, a more complicated understanding of immunity after pertussis aP vaccination occurred. An aP booster vaccination in preterm infants between 13 and 16 months of age did not induce a significant immune response after vaccination, when compared to values before the booster vaccination (103). Similarly, another study showed that in children who were first vaccinated with aP vaccine an increase in cytokine production was missed after booster vaccination, whereas children who were first immunized with wP vaccine did show an increase in cytokine production (104). In children at 9 years of age, a second aP vaccine booster dose did not increase T-cell respose (105). One possible explanation might be that the enhancement of T-cell immunity during the 5 years following the booster at 4 years of age is probably caused by natural boosting (104). Early studies also proofed that vaccination-induced T-cell response could wane by 4 years of age and can be naturally boosted by symptomless wild-type infection (98). Another possible explanation for the differing results might be the differences in study design. While the early studies took blood samples to measure immune responses from the same subject before and after vaccination (102, 106), more recent studies had different subjects in the boostered and non-boostered study group (104, 105).
Nowadays, it is discussed if the duration of immunity of aP vaccines in the 1990s was overestimated due to an natural booster because of high wild-type pertussis infections. It is speculated that wild-type infection and subclincal pertussis infection may induce a long-term immunity in previously infected or immunized individuals (3, 89).
Immunization of children with wP induced a CD4+ and CD17+ T-cell respone (3, 107). wP vaccines include pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) (e.g., LPS) that induce a IL-1, -6, -12, and -23 production by macrophages and DCs (3). By contrast, vaccination with aP was shown to induce a TH2 or Th1/Th2 response (3, 107). aP vaccines consist of the adjuvant alum, which stimulates IL-1, IL-4, or IL-17 (3). When wP and aP are compared, different cytokines are stimulated after vaccination promoting the induction of different T cells and B cells (3) (Figure 2). Recent data showed that after primary aP vaccination, CCR7+CD45RA− (central memory 328 T cells) and CCR7−CD45RA− (effector memory T cells) T-cell subsets are induced (108, 109). It is discussed that, after vaccination, a greater amount of central memory T cells is associated with greater amount of Th1 cytokines after infection, whereas a greater amount of effector memory T cells is more likely associated with a Th2 response (110). Former studies showed that pertussis-specific CD8+ memory T cells are induced after vaccination (111), but booster vaccination had no effect on the total number of these specific T-cell subsets (109).
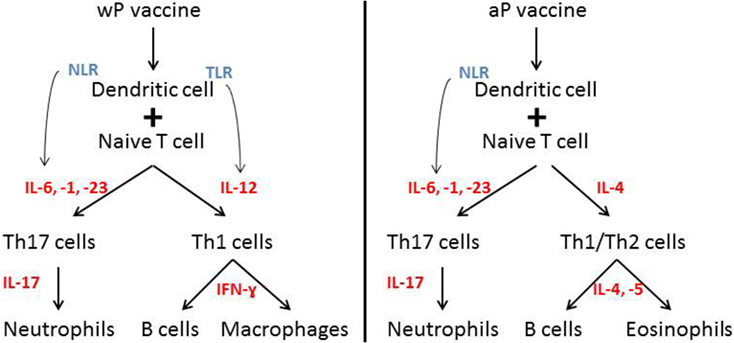
Figure 2. Immue response after wP versus aP vaccination. Different immune responses after wP versus aP vaccination. Distinct cytokine induction leads to the induction of different immune cells. Notation: IL, interleukin; NLR, NOD-like receptor; TLR, Toll-like receptor.
According to vaccine-specific long-term protection against pertussis, the available studies are problematic to compare. Data from different geographic areas with specific pertussis epidemiology and differences in the methodology used are hard to compare. Second, the determination of an asymptomatic natural booser is hard to predict. As a consequence, many studies on different vaccines and vaccination schedules in a variety of countries exit. A study in a pre-adolescent cohort showed that wP vaccination during infancy induced a longer lasting T-cell immunity than aP vaccination (109). This study showed that in vivo cytokine response to antigenic stimulation was higher in subjects who received wP vaccination even if the time from the last booster dose was significantly longer than in aP vaccinated subjects (109). Controversially, other studies showed that the antigen-specific cytokine response improved after shift from wP to aP vaccination (104, 105). Interestingly, studies of the past years unveiled that protective immunity obtained after aP vaccination wanes more rapidly than after wP vaccination (112). To overcome these deficiencies, many efforts are in progress, e.g., the inclusion of additional antigens in aP vaccines, the reformulation with adjuvants that more favor Th1 and Th17 cell response, and the development of live-attenuated vaccines (113). The development of a live attenuated vaccine has several advantages, including the generation of a mucosal immunity. However, it remains unclear if a brought public acceptance will be reached. Therefore, it should be considered to retain the immunogenicity of wP vaccines. One has to keep in mind that the development and approval of a new vaccine will be a long-lasting process.
However, it is still unclear which vaccination strategy might be the most effective. Actual studies on vaccination effectiveness and population-based vaccine coverage rates are not comparable. Therefore, it is not possible to identify a predictive value for the estimated vaccination coverage. Further studies should use comparable vaccination and testing schedules in age matched patients and controls for a more precise estimation of real duration of vaccination coverage.
B. pertussis and Aging?
Pertussis affects all people from the first hour of life to the last breath. Throughout life, the immune systems undergo several changes that might lead to age-related difference in the pertussis-specific immune response. During the past years, more insight was gained into vaccine-specific B- and T-cell memory. With ongoing age, significantly stronger waning of vaccine-induced memory B cells is detected when compared to younger age groups (66). Studies in infants detected a mature development of Th1 and Th2 response in neonates and pre-terms (114, 115). With ongoing age, the lymphoproliferative responsiveness is lost (66, 110). Taken together, studies showed an impact of immunosenescence on pertussis-specific immunity via a decreased T-cell responsiveness (66).
B. pertussis – Cocooning Versus Vaccination During Pregnancy
After the resurgence of pertussis infection, several studies showed that the main source of infection in newborns and infants were close contact persons, mostly family members (116, 117). In a first attempt to reduce pertussis incidence, indirect protection by reduction of transmission rates was favored, as the so called “cocooning strategy.” Therefore, some countries adapted their national immunization guidelines (116, 118, 119) and some studies were elicited. Another study focused on the influence of vaccination rates among siblings and vaccination rates among mothers showed that the provided protection rates are comparable (120). A recent study on the effect of cocooning infants younger than 6 months of age did not detect any reduction in pertussis cases among infants younger than 6 months of age (117). It is discussed controversially if cocoon strategies are cost-effective or even prevent infections (116, 121, 122). Taken together, it is advisable for women to know their immunization status and to identify all close contact persons (family members, non-household close contact persons), which may play a considerable role in the transmission of pertussis.
Another attempt to reduce pertussis rates among newborns and young infants was the introduction of pertussis vaccinations during pregnancy. Vaccination during pregnancy has become more important in some countries.
Up to date pertussis cocooning strategies remain deficient and vaccines are licensed for use after 6 weeks of age (116, 123–125). Due to a steady transplacental transfer of pertussis antibodies from the mother to the fetus, health authorities first recommended in 2011 the use of pertussis vaccinations for pregnant woman (126–128). The US first recommended maternal vaccination after gestational week 20 and subsequently the time window was narrowed to gestational week 27–36 (129). Switzerland and the United Kingdom adopted these recommendations (128). Early studies showed that vaccination with Tdap vaccines during gestational week 27–30 + 6 was associated with the highest values of IgG in umbilical cord blood when compared to vaccination beyond gestational week 31 (125). According to one of the most potent virulence factors of pertussis PT (44–46), it was shown that vaccination of the mother between gestational week 27–30 + 6 elicited the highest PT antibody concentrations at birth (125). A recent study supports these data because it showed that maternal Tdap vaccination in the early second-trimester significantly increases neonatal antibodies at birth when compared to third-trimester vaccinations (123). All in all the antenatal vaccination campaign in the United Kingdom achieved a vaccine coverage of 60% with >90% effectiveness (130, 131). A recent study in the United Kingdom showed that after introduction of pertussis vaccination during pregnancy a strong reduction in confirmed cases and hospital admissions because of pertussis, especially in infants younger than 3 months of age was reported (131). Furthermore, the question arose if vaccination early in pregnancy might adversely affect the infant’s immune response to vaccinations after birth. Some studies showed that antibody concentrations at birth did not interfere with the immune response to further immunizations after birth (132–134). It is known that maternally derived antibodies are able to interfere with the infant’s immune responses with the same vaccination (135), which was detected after DTaP vaccination (136). It was shown that maternal antibodies interfere with antibody responses after primary vaccination during infancy in children born to Tdap-vaccinated mothers (127). Interestingly, a mouse model showed that the vaccination of infant mice reduced the protective functions of maternally derived antibodies in vitro and in vivo (137). A study that focused on the Repevax vaccination (a combined tetanus, low-dose diphtheria, 5-component aP, inactivated polio vaccine; Repevax; Sanofi Pasteur) detected a significant attenuation of pertussis antibodies in infants whose mothers where vaccinated with Repevax during pregnancy (136).
Spotlighted by recent findings, the lack of protection by aP vaccines, the efficacy of current vaccines should be maximized by prenatal vaccination, additional boosting, and alternative vaccination strategies. In future, it is important to determine the functionality of maternal and infant antibodies to better understand a probable interference of vaccination during pregnancy and later vaccinations of the infants.
B. pertussis – Conclusion
It is irrefutable that the incidence of severe pertussis cases is rising worldwide. Nearly 90% of all cases of deaths caused by pertussis occur in infants younger than 4 months of age (113). Most of these cases are caused by fatal pertussis pneumonia caused by PT (113). Therefore, it is also imperative to conduct studies focusing on the limitation of PT activity during acute infection. During the past years, the resurgence of pertussis lead to many new studies focusing on a better understanding of transmission dynamics, virulence factors, and host immune reactions as well as the search for new vaccine targets. It was shown that the first tries to achieve herd immunity and focusing on cocooning and possible eradication failed. It is discussed if a meanwhile switch to wP vaccine as a first dose in the primary immunization schedule should be introduced (29). Frightfully by gaining more and more inside into the cellular and humoral immune response to an infection caused by B. pertussis, more and more questions arise. Efficacious vaccines need to be long-lasting, prevent transmission, and reduce disease burden. Up to date, none of the existing vaccines fulfils these criteria. Recent studies highlighted that a likely effective immune response requires the induction of a Th1/Th17 immune response, which stimulates opsonizing, toxin-neutralizing, and mucosal antibody production as well as the induction of a memory T-cell response, which recruites and activates phagocytes. Therefore, it is an urgent need to re-evaluate certain immunization routes to achieve a better vaccine. New studies on vaccinations during pregnancy showed interesting first results but long-term protection in the new borne have to be controlled over time. Furthermore, more detailed studies on the surveillance rates of symptomatic and asymptomatic infections and the examination of the genetic diversity of circulation B. pertussis strains may probably lead to a better understanding of possible prevention targets.
Although all insights into the pathogenicity of pertussis infection identified in animal models, our understanding of the human disease has to be improved. Therefore, more detailed studies on several levels, including gene expression, virulence-factor delivery, binding-specificity and activity have to be conducted. Because we should not forget, that we still do not know why infected patients cough!
Author Contributions
The author confirms being the sole contributor of this work and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. Shakespeare W. In: Geisen H, editor. Romeo and Juliet. Germany: Reclam Fremdsprachentexte (1994). Act IV, Scene 3, 2565 p.
2. de Gouw D, Diavatopoulos DA, Bootsma HJ, Hermans PW, Mooi FR. Pertussis: a matter of immune modulation. FEMS Microbiol Rev (2011) 35:441–74. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00257.x
3. Higgs R, Higgins SC, Ross PJ, Mills KH. Immunity to the respiratory pathogen Bordetella pertussis. Mucosal Immunol (2012) 5:485–500. doi:10.1038/mi.2012.54
4. Mooi FR, van Loo IH, van Gent M, He Q, Bart MJ, Heuvelman KJ, et al. Bordetella pertussis strains with increased toxin production associated with pertussis resurgence. Emerg Infect Dis (2009) 15:1206–13. doi:10.3201/eid1508.081511
5. Heininger U. Pertussis: what the pediatric infectious disease specialist should know. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2012) 31:78–9. doi:10.1097/INF.0b013e31823b034e
6. Guiso N, Hegerle N. Other Bordetellas, lessons for and from pertussis vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines (2014) 13:1125–33. doi:10.1586/14760584.2014.942221
7. Diavatopoulos DA, Cummings CA, Schouls LM, Brinig MM, Relman DA, Mooi FR. Bordetella pertussis, the causative agent of whooping cough, evolved from a distinct, human-associated lineage of B. bronchiseptica. PLoS Pathog (2005) 1:e45. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0010045
8. Woolfrey BF, Moody JA. Human infections associated with Bordetella bronchiseptica. Clin Microbiol Rev (1991) 4:243–55.
9. Porter JF, Connor K, Donachie W. Differentiation between human and ovine isolates of Bordetella parapertussis using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol Lett (1996) 135:131–5. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb07977.x
10. Pittet LF, Posfay-Barbe KM. Bordetella holmesii infection: current knowledge and a vision for future research. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther (2015) 13:965–71. doi:10.1586/14787210.2015.1056161
11. Fishbain JT, Riederer K, Sawaf H, Mody R. Invasive Bordetella holmesii infections. Infect Dis (Lond) (2015) 47:65–8. doi:10.3109/00365548.2014.968609
12. Le Coustumier A, Njamkepo E, Cattoir V, Guillot S, Guiso N. Bordetella petrii infection with long-lasting persistence in human. Emerg Infect Dis (2011) 17:612–8. doi:10.3201/eid1704.101480
13. Cherry JD, Grimprel E, Guiso N, Heininger U, Mertsola J. Defining pertussis epidemiology: clinical, microbiologic and serologic perspectives. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2005) 24:S25–34. doi:10.1097/01.inf.0000160926.89577.3b
14. Kliegman R, Stanton B, St. Geme J, Schor N. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 20th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier (2015). 197 p.
15. Long SS, Welkon CJ, Clark JL. Widespread silent transmission of pertussis in families: antibody correlates of infection and symptomatology. J Infect Dis (1990) 161:480–6. doi:10.1093/infdis/161.3.480
16. Nuolivirta K, Koponen P, He Q, Halkosalo A, Korppi M, Vesikari T, et al. Bordetella pertussis infection is common in nonvaccinated infants admitted for bronchiolitis. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2010) 29:1013–5.
17. Cosnes-Lambe C, Raymond J, Chalumeau M, Pons-Catalano C, Moulin F, de Suremain N, et al. Pertussis and respiratory syncytial virus infections. Eur J Pediatr (2008) 167:1017–9. doi:10.1007/s00431-007-0633-6
18. Walsh PF, Kimmel L, Feola M, Tran T, Lim C, De Salvia L, et al. Prevalence of Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella parapertussis in infants presenting to the emergency department with bronchiolitis. J Emerg Med (2011) 40:256–61. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2008.04.048
19. Siberry GK, Paquette NR, Ross TL, Perl TM, Valsamakis A. Low prevalence of pertussis among children admitted with respiratory symptoms during respiratory syncytial virus season. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol (2006) 27:95–7. doi:10.1086/499999
20. Schellekens J, von König CH, Gardner P. Pertussis sources of infection and routes of transmission in the vaccination era. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2005) 24:S19–24. doi:10.1097/01.inf.0000160909.24879.e6
21. Tan T, Trindade E, Skowronski D. Epidemiology of pertussis. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2005) 24:S10–8. doi:10.1097/01.inf.0000160708.43944.99
22. van der Zee A, Schellekens JF, Mooi FR. Laboratory diagnosis of pertussis. Clin Microbiol Rev (2015) 28:1005–26. doi:10.1128/CMR.00031-15
23. World Health Organization (WHO). Global and Regional Immunization Profile: Global. World Health Organization (2015). Available from: http://www.who.int/immunization/monitoring_surveillance/data/gs_gloprofile.pdf?ua=1
24. Tan T, Dalby T, Forsyth K, Halperin SA, Heininger U, Hozbor D, et al. Pertussis across the globe: recent epidemiologic trends from 2000-2013. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2015) 34:e222–32. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000000795
25. Cherry JD. Comparison of the epidemiology of the disease pertussis vs.the epidemiology Bordetella pertussis infection. Pediatr Res (2003) 53:324A.
26. Hodder SL, Cherry JD, Mortimer EA Jr, Ford AB, Gornbein J, Papp K. Antibody responses to Bordetella pertussis antigens and clinical correlations in elderly community residents. Clin Infect Dis (2000) 31:7–14. doi:10.1086/313913
27. Senzilet LD, Halperin SA, Spika JS, Alagaratnam M, Morris A, Smith B, et al. Pertussis is a frequent cause of prolonged cough illness in adolescents and adults. Clin Infect Dis (2001) 32:1691–7. doi:10.1086/320754
28. Wright SW, Edwards KM, Decker MD, Zeldin MH. Pertussis infection in adults with persistent cough. JAMA (1995) 273:1044–6. doi:10.1001/jama.1995.03520370086042
29. Althouse BM, Scarpino SV. Asymptomatic transmission and the resurgence of Bordetella pertussis. BMC Med (2015) 13:146. doi:10.1186/s12916-015-0382-8
30. Gambhir M, Clark TA, Cauchemez S, Tartof SY, Swerdlow DL, Ferguson NM. A change in vaccine efficacy and duration of protection explains recent rises in pertussis incidence in the United States. PLoS Comput Biol (2015) 11:e1004138. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004138
31. Jackson DW, Rohani P. Perplexities of pertussis: recent global epidemiological trends and their potential causes. Epidemiol Infect (2013) 142:1–13. doi:10.1017/S0950268812003093
32. Águas R, Gonçalves G, Gomes MGM. Pertussis: increasing disease as a consequence of reducing transmission. Lancet Infect Dis (2006) 6:112–7. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70384-X
33. Center of Disease Control (CDC). Reported Pertussis Incidence by Age Group: 1990-2014. CDC (2015). Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/pertussis/images/incidence-graph-age.jpg
34. Lavine JS, King AA, Bjornstad ON. Natural immune boosting in pertussis dynamics and the potential for long-term vaccine failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2011) 108:7259–64. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014394108
35. Wood N, McIntyre P. Pertussis: review of epidemiology, diagnosis, management and prevention. Paediatr Respir Rev (2008) 9:201–11. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2008.05.010
36. Misegades LK, Winter K, Harriman K, Talarico J, Messonnier NE, Clark TA, et al. Association of childhood pertussis with receipt of 5 doses of pertussis vaccine by time since last vaccine dose, California, 2010. JAMA (2012) 308:2126–32. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.14939
37. Miyashita N, Akaike H, Teranishi H, Kawai Y, Ouchi K, Kato T, et al. Diagnostic value of symptoms and laboratory data for pertussis in adolescent and adult patients. BMC Infect Dis (2013) 13:129. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-13-129
38. Marcon MJ, Hamoudi AC, Cannon HJ, Hribar MM. Comparison of throat and nasopharyngeal swab specimens for culture diagnosis of Bordetella pertussis infection. J Clin Microbiol (1987) 25:1109–10.
39. Hallander HO, Reizenstein E, Renemar B, Rasmuson G, Mardin L, Olin P. Comparison of nasopharyngeal aspirates with swabs for culture of Bordetella pertussis. J Clin Microbiol (1993) 31:50–2.
40. Ewanowich CA, Chui LWL, Paranchych MG, Peppler MS, Marusyk RG, Albrittons WL. Major outbreak of pertussis in northern Alberta, Canada: analysis of discrepant direct fluorescent-antibody and culture results by using polymerase chain reaction methodology. J Clin Microbiol (1993) 31:1715–25.
41. Loeffelholz M. Towards improved accuracy of Bordetella pertussis nucleic acid amplification tests. J Clin Microbiol (2012) 50:2186–90. doi:10.1128/JCM.00612-12
42. Riffelmann M, Wirsing von Konig CH, Caro V, Guiso N. Nucleic acid amplification tests for diagnosis of Bordetella infections. J Clin Microbiol (2005) 43:4925–9. doi:10.1128/JCM.43.10.4925-4929.2005
43. Faulkner AE, Skoff TH, Tondella ML, Cohn A, Clark TA, Martin SW. Trends in pertussis diagnostic testing in the United States, 1990-2012. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2016) 35:39–44. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000000921
44. Ryan M, Murphy G, Ryan E, Nilsson L, Shackley F, Gothefors L, et al. Distinct T-cell subtypes induced with whole cell and acellular pertussis vaccines in children. Immunology (1998) 93:1–10. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2567.1998.00401.x
45. Ryan M, McCarthy L, Rappuoli R, Mahon BP, Mills KH. Pertussis toxin potentiates Th1 and Th2 responses to co-injected antigen: adjuvant action is associated with enhanced regulatory cytokine production and expression of the co-stimulatory molecules B7-1, B7-2 and CD28. Int Immunol (1998) 10:651–62. doi:10.1093/intimm/10.5.651
46. Carbonetti NH. Pertussis toxin and adenylate cyclase toxin: key virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis and cell biology tools. Future Microbiol (2010) 5:455–69. doi:10.2217/fmb.09.133
47. Dirix V, Verscheure V, Goetghebuer T, Hainaut M, Debrie AS, Locht C, et al. Monocyte-derived interleukin-10 depresses the Bordetella pertussis-specific gamma interferon response in vaccinated infants. Clin Vaccine Immunol (2009) 16:1816–21. doi:10.1128/CVI.00314-09
48. Shumilla JA, Lacaille V, Hornell TM, Huang J, Narasimhan S, Relman DA, et al. Bordetella pertussis infection of primary human monocytes alters HLA-DR expression. Infect Immun (2004) 72:1450–62. doi:10.1128/IAI.72.3.1450-1462.2004
49. Martino A, Volpe E, Auricchio G, Colizzi V, Baldini PM. Influence of pertussis toxin on CD1a isoform expression in human dendritic cells. J Clin Immunol (2006) 26:153–9. doi:10.1007/s10875-006-9009-3
50. Guermonprez P, Khelef N, Blouin E, Rieu P, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Guiso N, et al. The adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis binds to target cells via the alpha(M)beta(2) integrin (CD11b/CD18). J Exp Med (2001) 193:1035–44. doi:10.1084/jem.193.9.1035
51. Eby JC, Gray MC, Mangan AR, Donato GM, Hewlett EL. Role of CD11b/CD18 in the process of intoxication by the adenylate cyclase toxin of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun (2012) 80:850–9. doi:10.1128/IAI.05979-11
52. Gray MC, Hewlett EL. Cell cycle arrest induced by the bacterial adenylate cyclase toxins from Bacillus anthracis and Bordetella pertussis. Cell Microbiol (2010) 13:123–34. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2010.01525.x
53. Boyd AP, Ross PJ, Conroy H, Mahon N, Lavelle EC, Mills KH. Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin modulates innate and adaptive immune responses: distinct roles for acylation and enzymatic activity in immunomodulation and cell death. J Immunol (2005) 175:730–8. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.175.2.730
54. Nagamatsu K, Kuwae A, Konaka T, Nagai S, Yoshida S, Eguchi M, et al. Bordetella evades the host immune system by inducing IL-10 through a type III effector, BopN. J Exp Med (2009) 206:3073–88. doi:10.1084/jem.20090494
55. Skinner JA, Reissinger A, Shen H, Yuk MH. Bordetella type III secretion and adenylate cyclase toxin synergize to drive dendritic cells into a semimature state. J Immunol (2004) 173:1934–40. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.173.3.1934
56. Locht C, Bertin P, Menozzi FD, Renauld G. The filamentous haemagglutinin, a multifaceted adhesion produced by virulent Bordetella spp. Mol Microbiol (1993) 9:653–60. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01725.x
57. Perez Vidakovics ML, Lamberti Y, van der Pol WL, Yantorno O, Rodriguez ME. Adenylate cyclase infl uences fi lamentous haemagglutinin-mediated attachment of Bordetella pertussis to epithelial alveolar cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol (2006) 48:140–7. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2006.00136.x
58. Lamberti Y, Alvarez Hayes J, Perez Vidakovics ML, Rodriguez ME. Cholesterol-dependent attachment of human respiratory cells by Bordetella pertussis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol (2009) 56:143–50. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2009.00557.x
59. Ishibashi Y, Nishikawa A. Bordetella pertussis infection of human respiratory epithelial cells up-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression: role of fi lamentous hemagglutinin and pertussis toxin. Microb Pathog (2002) 33:115–25. doi:10.1006/mpat.2002.0517
60. Mobberley-Schuman PS, Connelly B, Weiss AA. Phagocytosis of Bordetella pertussis incubated with convalescent serum. J Infect Dis (2003) 187:1646–53. doi:10.1086/374741
61. Harvill ET, Preston A, Cotter PA, Allen AG, Maskell DJ, Miller JF. Multiple roles for Bordetella lipopolysaccharide molecules during respiratory tract infection. Infect Immun (2000) 68:6720–8. doi:10.1128/IAI.68.12.6720-6728.2000
62. Preston A, Maskell D. The molecular genetics and role in infection of lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in the Bordetellae. J Endotoxin Res (2001) 7:251–61. doi:10.1177/09680519010070040601
63. Everest P, Li J, Douce G, Charles I, De Azavedo J, Chatfield S, et al. Role of the Bordetella pertussis P.69/pertactin protein and the P.69/pertactin RGD motif in the adherence to and invasion of mammalian cells. Microbiology (1996) 142:3261–8. doi:10.1099/13500872-142-11-3261
64. Flak TA, Heiss LN, Engle JT, Goldman WE. Synergistic epithelial responses to endotoxin and a naturally occurring muramyl peptide. Infect Immun (2000) 68:1235–42. doi:10.1128/IAI.68.3.1235-1242.2000
65. De Magistris MT, Romano M, Bartoloni A, Rappuoli R, Tagliabue A. Human T cell clones define S1 subunit as the most immunogenic moiety of pertussis toxin and determine its epitope map. J Exp Med (1989) 169:1519–32. doi:10.1084/jem.169.5.1519
66. van Twillert I, Han WG, van Els CA. Waning and aging of cellular immunity to Bordetella pertussis. Pathog Dis (2015) 73:ftv071. doi:10.1093/femspd/ftv071
67. Hafler JP, Pohl-Koppe A. The cellular immune response to Bordetella pertussis in two children with whooping cough. Eur J Med Res (1998) 3:523–6.
68. Tran Minh NN, He Q, Edelman K, Olander RM, Viljanen MK, Arvilommi H, et al. Cell-mediated immune responses to antigens of Bordetella pertussis and protection against pertussis in school children. Pediatr Infect Dis J (1999) 18:366–70. doi:10.1097/00006454-199904000-00012
69. Dunne A, Ross PJ, Pospisilova E, Masin J, Meaney A, Sutton CE, et al. Inflammasome activation by adenylate cyclase toxin directs Th17 responses and protection against Bordetella pertussis. J Immunol (2010) 185:1711–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1000105
70. Carbonetti NH, Artamonova GV, Van Rooijen N, Ayala VI. Pertussis toxin targets airway macrophages to promote Bordetella pertussis infection of the respiratory tract. Infect Immun (2007) 75:1713–20. doi:10.1128/IAI.01578-06
71. Paddock CD, Sanden GN, Cherry JD, Gal AA, Langston C, Tatti KM, et al. Pathology and pathogenesis of fatal Bordetella pertussis infection in infants. Clin Infect Dis (2008) 47:328–38. doi:10.1086/589753
72. McGuirk P, Mills KH. Direct anti-inflammatory effect of a bacterial virulence factor: IL-10-dependent suppression of IL-12 production by filamentous hemagglutinin from Bordetella pertussis. Eur J Immunol (2000) 30:415–22. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200002)30:2<415::AID-IMMU415>3.3.CO;2-O
73. Weber MS, Benkhoucha M, Lehmann-Horn K, Hertzenberg D, Sellner J, Santiago-Raber ML, et al. Repetitive pertussis toxin promotes development of regulatory T cells and prevents central nervous system autoimmune disease. PLoS One (2010) 5:e16009. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016009
74. Mills KH, Barnard A, Watkins J, Redhead K. Cell-mediated immunity to Bordetella pertussis: role of Th1 cells in bacterial clearance in a murine respiratory infection model. Infect Immun (1993) 61:399–410.
75. Dunne PJ, Moran B, Cummins RC, Mills KH. CD11c+CD8alpha+ dendritic cells promote protective immunity to respiratory infection with Bordetella pertussis. J Immunol (2009) 183:400–10. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900169
76. Byrne P, McGuirk P, Todryk S, Mills KH. Depletion of NK cells results in disseminating lethal infection with Bordetella pertussis associated with a reduction of antigen-specific Th1 and enhancement of Th2, but not Tr1 cells. Eur J Immunol (2004) 34:2579–88. doi:10.1002/eji.200425092
77. Mahon BP, Mills KH. Interferon-gamma mediated immune effector mechanisms against Bordetella pertussis. Immunol Lett (1999) 68:213–7. doi:10.1016/S0165-2478(99)00070-X
78. Higgins SC, Jarnicki AG, Lavelle EC, Mills KH. TLR4 mediates vaccine-induced protective cellular immunity to Bordetella pertussis: role of IL-17-producing T cells. J Immunol (2006) 177:7980–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.11.7980
79. Higgins SC, Lavelle EC, McCann C, Keogh B, McNeela E, Byrne P, et al. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated innate IL-10 activates antigen-specific regulatory T cells and confers resistance to Bordetella pertussis by inhibiting inflammatory pathology. J Immunol (2003) 171:3119–27. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3119
80. Fedele G, Spensieri F, Palazzo R, Nasso M, Cheung GY, Coote JG, et al. Bordetella pertussis commits human dendritic cells to promote a Th1/Th17 response through the activity of adenylate cyclase toxin and MAPK-pathways. PLoS One (2010) 5:e8734. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008734
81. McGuirk P, Mahon BP, Griffin F, Mills KH. Compartmentalization of T cell responses following respiratory infection with Bordetella pertussis: hyporesponsiveness of lung T cells is associated with modulated expression of the co-stimulatory molecule CD28. Eur J Immunol (1998) 28:153–63. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199801)28:01<153::AID-IMMU153>3.0.CO;2-#
82. Andreasen C, Carbonetti NH. Role of neutrophils in response to Bordetella pertussis infection in mice. Infect Immun (2009) 77:1182–8. doi:10.1128/IAI.01150-08
83. Ahuja N, Kumar P, Bhatnagar R. The adenylate cyclase toxins. Crit Rev Microbiol (2004) 30:187–96. doi:10.1080/10408410490468795
84. Barbic J, Leef MF, Burns DL, Shahin RD. Role of gamma interferon in natural clearance of Bordetella pertussis infection. Infect Immun (1997) 65:4904–8.
85. Travis SM, Singh PK, Welsh MJ. Antimicrobial peptides and proteins in the innate defense of the airway surface. Curr Opin Immunol (2001) 13:89–95. doi:10.1016/S0952-7915(00)00187-4
86. Fernandez RC, Weiss AA. Susceptibilities of Bordetella pertussis strains to antimicrobial peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (1996) 40:1041–3.
87. Legarda D, Klein-Patel ME, Yim S, Yuk MH, Diamond G. Suppression of NF-kappaB-mediated beta-defensin gene expression in the mammalian airway by the Bordetella type III secretion system. Cell Microbiol (2005) 7:489–97. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2004.00473.x
88. Weiss AA, Mobberley PS, Fernandez RC, Mink CM. Characterization of human bactericidal antibodies to Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun (1999) 67:1424–31.
89. Fedele G, Cassone A, Ausiello CM. T-cell immune responses to Bordetella pertussis infection and vaccination. Pathog Dis (2015) 73:7. doi:10.1093/femspd/ftv051
90. Ross PJ, Sutton CE, Higgins S, Allen AC, Walsh K, Misiak A, et al. Relative contribution of Th1 and Th17 cells in adaptive immunity to Bordetella pertussis: towards the rational design of an improved acellular pertussis vaccine. PLoS Pathog (2013) 9:e1003264. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003264
91. Coleman MM, Finlay CM, Moran B, Keane J, Dunne PJ, Mills KH. The immunoregulatory role of CD4+ FoxP3+ CD25- regulatory T cells in lungs of mice infected with Bordetella pertussis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol (2012) 64:413–24. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2011.00927.x
92. Agarwal SK, Gourh P, Shete S, Paz G, Divecha D, Reveille JD, et al. Association of interleukin 23 receptor polymorphisms with anti-topoisomerase-I positivity and pulmonary hypertension in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol (2009) 36:2715–23. doi:10.3899/jrheum.090421
93. McGuirk P, Mills KH. Pathogen-specific regulatory T cells provoke a shift in the Th1/Th2 paradigm in immunity to infectious diseases. Trends Immunol (2002) 2002(23):450–5. doi:10.1016/S1471-4906(02)02288-3
94. McGuirk P, McCann C, Mills KH. Pathogen-specific T regulatory 1 cells induced in the respiratory tract by a bacterial molecule that stimulates interleukin 10 production by dendritic cells: a novel strategy for evasion of protective T helper type 1 responses by Bordetella pertussis. J Exp Med (2002) 195:221–31. doi:10.1084/jem.20011288
95. Ausiello CM, Urbani F, la Sala A, Lande R, Cassone A. Vaccine and antigen-dependent type 1 and type 2 cytokine induction after primary vaccination of infants with whole-cell or acellular pertussis vaccines. Infect Immun (1997) 65:2168–74.
96. Greco D, Salmaso S, Mastrantonio P, Giuliano M, Tozzi AE, Anemona A, et al. A controlled trial of two acellular vaccines and one whole-cell vaccine against pertussis. Progetto Pertosse Working Group. N Engl J Med (1996) 334:341–8. doi:10.1056/NEJM199602083340601
97. Gustafsson L, Hallander HO, Olin P, Reizenstein E, Storsaeter J. A controlled trial of a two-component acellular, a five-component acellular, and a whole-cell pertussis vaccine. N Engl J Med (1996) 1996(334):349–55. doi:10.1056/NEJM199602083340602
98. Ausiello CM, Lande R, Urbani F, la Sala A, Stefanelli P, Salmaso S, et al. Cell-mediated immune responses in four-year-old children after primary immunization with acellular pertussis vaccines. Infect Immun (1999) 67:4064–71.
99. Meyer CU, Zepp F, Decker M, Lee M, Chang SJ, Ward J, et al. Cellular immunity in adolescents and adults following acellular pertussis vaccine administration. Clin Vaccine Immunol (2007) 14:288–92. doi:10.1128/CVI.00364-06
100. Zepp F, Knuf M, Habermehl P, Schmitt JH, Rebsch C, Schmidtke P, et al. Pertussis-specific cellmediated immunity in infants after vaccination with a tricomponent acellular pertussis vaccine. Infect Immun (1996) 64:4078–84.
101. Edwards KM, Berbers GAM. Immune responses to pertussis vaccines and disease. J Infect Dis (2014) 209:10–5. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit560
102. Rieber N, Graf A, Belohradsky BH, Hartl D, Urschel S, Riffelmann M, et al. Differences of humoral and cellular immune response to an acellular pertussis booster in adolescents with a whole cell or acellular primary vaccination. Vaccine (2008) 26:6929–35. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.064
103. Vermeulen F, Dirix V, Verscheure V, Damis E, Vermeylen D, Locht C, et al. Persistence at one year of age of antigen-induced cellular immune responses in preterm infants vaccinated against whooping cough: compareson of three different vaccines and effect of a booster dose. Vaccine (2013) 31:1981–6. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.02.004
104. Schure RM, Hendrikx LH, de Rond LG, Oztürk K, Sanders EA, Berbers GA, et al. T-cell responses before and after the fifth consecutive acellular pertussis vaccination in 4-year-old Dutch children. Clin Vaccine Immunol (2012) 19:1879–86. doi:10.1128/CVI.00277-12
105. Schure RM, de Rond L, Oztürk K, Hendrikx L, Sanders E, Berbers G, et al. Pertussis circulation has increased T-cell immunity during childhood more than a second acellular booster vaccination in Dutch children 9 years of age. PLoS One (2012) 7:e41928. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041928
106. Edelman KJ, He Q, Makinen JP, Haanpera MS, Tran Minh NN, Schuerman L, et al. Pertussis-specific cellmediated and humoral immunity in adolescents 3 years after booster immunization with acellular pertussis vaccine. Clin Infect Dis (2004) 39:179–85. doi:10.1086/421943
107. Carollo M, Palazzo R, Bianco M, Smits K, Mascart F. Antigen-specific responses assessment for the evaluation of Bordetella pertussis T cell immunity in humans. Vaccine (2012) 30:1667–74. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.104
108. Sharma SK, Pichichero ME. Functional deficits of pertussisspecific CD4+ T cells in infants compared to adults following DTaP vaccination. Clin Exp Immunol (2012) 169:281–91. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04613.x
109. Smits K, Pottier G, Smet J, Dirix V, Vermeulen F, De Schutter I, et al. Different T cell memory in preadolescents after whole-cell or acellular pertussis vaccination. Vaccine (2013) 32:111–8. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.10.056
110. Han WG, Helm K, Poelen MM, Otten HG, van Els CA. Ex vivo peptide-MHC II tetramer analysis reveals distinct end-differentiation patterns of human pertussis-specific CD4(+) T cells following clinical infection. Clin Immunol (2015) 157:205–15. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2015.02.009
111. Rieber N, Graf A, Hartl D, Urschel S, Belohradsky BH, Liese J. Acellular pertussis booster in adolescents induces Th1 and memory CD8+ T cell immune response. PLoS One (2011) 6:e17271. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017271
112. Acosta AM, DeBolt C, Tasslimi A, Lewis M, Stewart LK, Misegades LK, et al. Tdap vaccine effectiveness in adolescents during the 2012 Washington state pertussis epidemic. Pediatrics (2015) 135:981–9. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-3358
113. Melvin JA, Scheller EV, Miller JF, Cotter PA. Bordetella pertussis pathogenesis: current and future challenges. Nat Rev Microbiol (2014) 12:274–88. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3235
114. Mascart F, Verscheure V, Malfroot A, Hainaut M, Piérard D, Temerman S, et al. Bordetella pertussis infection in 2-month-old infants promotes type 1 T cell responses. J Immunol (2003) 170:1504–9. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.170.3.1504
115. Knuf M, Schmitt HJ, Wolter J, Schuerman L, Jacquet JM, Kieninger D, et al. Neonatal vaccination with an acellular pertussis vaccine accelerates the acquisition of pertussis antibodies in infants. J Pediatr (2008) 152:655–60. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.09.034
116. Urwyler P, Heininger U. Protecting newborns from pertussis – the challenge of complete cocooning. BMC Infect Dis (2014) 14:397. doi:10.1186/1471-2334-14-397
117. Healy CM, Rench MA, Wootton SH, Sastagnini LA. Evaluation of the impact of a pertussis cocooning program on infant pertussis infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2015) 34:22–6. doi:10.1097/INF.0000000000000486
118. Frère J, De Wals P, Ovetchkine P, Coïc L, Audibert F, Tapiero B. Evaluation of several approaches to immunize parents of neonates against B. pertussis. Vaccine (2013) 31:6087–91. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.09.043
119. Donnan EJ, Fielding JE, Rowe SL, Franklin LJ, Vally H. A cross sectional survey of attitudes, awareness and uptake of the parental pertussis booster vaccine as part of a cocooning strategy, Victoria, Australia. BMC Public Health (2013) 13:676. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-13-676
120. De Greeff SC, de Melker HE, Westerhof A, Schellekens JF, Mooi FR, van Boven M. Estimation of household transmission rates of pertussis and the effect of cocooning vaccination strategies on infant pertussis. Epidemiology (2012) 23:852–60. doi:10.1097/EDE.0b013e31826c2b9e
121. Rivero-Santana A, Cuéllar-Pompa L, Sánchez-Gómez LM, Perestelo-Pérez L, Serrano-Aguilar P. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of different immunization strategies against whooping cough to reduce child morbidity and mortality. Health Policy (2014) 115:82–91. doi:10.1016/j.healthpol.2013.12.007
122. Swamy GK, Wheeler SM. Neonatal pertussis, cocooning and maternal immunization. Expert Rev Vaccines (2014) 13:1107–14. doi:10.1586/14760584.2014.944509
123. Eberhardt CS, Blanchard-Rohner G, Lemaître B, Boukrid M, Combescure C, Othenin-Girard V, et al. Maternal immunization earlier in pregnancy maximizes antibody transfer and expected infant seropositivity against pertussis. Clin Infect Dis (2016) 62:829–36. doi:10.1093/cid/ciw027
124. Tiwari TS, Baughman AL, Clark TA. First pertussis vaccine dose and prevention of infant mortality. Pediatrics (2015) 135:990–9. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-2291
125. Abu Raya B, Srugo I, Kessel A, Peterman M, Bader D, Gonen R, et al. The effect of timing of maternal tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) immunization during pregnancy on newborn pertussis antibody levels – a prospective study. Vaccine (2014) 32:5787–93. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.08.038
126. Gall SA, Myers J, Pichichero M. Maternal immunization with tetanus-diphtheriapertussis vaccine: effect on maternal and neonatal serum antibody levels. Am J Obstet Gynecol (2011) 204:.e1–5. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2010.11.024
127. Hardy-Fairbanks AJ, Pan SJ, Decker MD, Johnson DR, Greenberg DP, Kirkland KB, et al. Immune responses in infantswhose mothers received Tdap vaccine during pregnancy. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2013) 32:1257–60. doi:10.1097/INF.0b013e3182a09b6a
128. UK Department of Health. Pregnant Women to be Offered Whooping Cough Vaccination. (2015). Available from: http://www.dh.gov.uk/health/2012/09/whooping-cough/
129. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated recommendations for use of tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis vaccine (Tdap) in pregnant women – Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep (2013) 62:131–5.
130. Dabrera G, Amirthalingam G, Andrews N, Campbell H, Ribeiro S, Kara E, et al. A case-control study to estimate the effectiveness of maternal pertussis vaccination in protecting newborn infants in England and Wales, 2012–2013. Clin Infect Dis (2015) 60:333–7. doi:10.1093/cid/ciu821
131. Amirthalingam G, Andrews N, Campbell H, Ribeiro S, Kara E, Donegan K, et al. Effectiveness of maternal pertussis vaccination in England: an observationalstudy. Lancet (2014) 384:1521–8. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60686-3
132. Heininger U, Riffelmann M, Bär G, Rudin C, von König CH. The protective role of maternally derived antibodies against Bordetella pertussis in young infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J (2013) 32:695–8. doi:10.1097/INF.0b013e318288b610
133. Jones C, Pollock L, Barnett SM, Battersby A, Kampmann B. The relationship between concentration of specific antibody at birth and subsequent response to primary immunization. Vaccine (2014) 32:996–1002. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.11.104
134. Munoz FM, Bond NH, Maccato M, Pinell P, Hammill HA, Swamy GK, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of tetanus diphtheria and acellular pertussis (Tdap) immunization during pregnancy in mothers and infants: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA (2014) 311:1760–9. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3633
135. Niewiesk S. Maternal antibodies: clinical significance, mechanism of interference with immune responses, and possible vaccination strategies. Front Immunol (2014) 5:446. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00446
136. Ladhani SN, Andrews NJ, Southern J, Jones CE, Amirthalingam G, Waight PA, et al. Antibody responses after primary immunization in infants born to women receiving a pertussis-containing vaccine during pregnancy: single arm observational study with a historical comparator. Clin Infect Dis (2015) 61:1637–44. doi:10.1093/cid/civ695
Keywords: pertussis, whooping cough, vaccine-preventable disease, vaccination, herd immunity
Citation: Zlamy M (2016) Rediscovering Pertussis. Front. Pediatr. 4:52. doi: 10.3389/fped.2016.00052
Received: 25 February 2016; Accepted: 02 May 2016;
Published: 08 June 2016
Edited by:
Andreas Schwingshackl, University of California in Los Angeles (UCLA), USAReviewed by:
Stasa Veroukis, University of Manitoba, CanadaMyke Drayer Federman, Mattel Children’s Hospital, USA
Copyright: © 2016 Zlamy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Manuela Zlamy, bWFudWVsYS56bGFteUBpLW1lZC5hYy5hdA==
 Manuela Zlamy
Manuela Zlamy