- 1Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Connecticut Children’s Medical Center, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Hartford, CT, USA
- 2Division of Pediatric Critical Care Medicine, Connecticut Children’s Medical Center, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Hartford, CT, USA
- 3Section of Neonatology, St. Christopher’s Hospital for Children, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA
It has been suggested that pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PARDS) may be a different entity, vis-à-vis adult acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), based on its epidemiology and outcomes. A more pediatric-specific definition of PARDS to include the subgroup of patients with underlying lung (and heart) disease has been proposed. Epidemiological data suggest that up to 13% of the children with ARDS have a history of prematurity and/or underlying chronic lung disease. However, the specific contribution of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), the most common chronic lung disease in infants, to the development of PARDS is not known. BPD leads to damaged lungs with long-term consequences secondary to disordered growth and immune function. These damaged lungs could potentially act as a substrate, which given the appropriate noxious stimuli, can predispose a child to PARDS. Interestingly, similar biomarkers [KL-6, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, sICAM-1, angiopoietin-2, and matrix metalloproteinase-8 and -9] of pulmonary injury have been associated both with BPD and ARDS. Recognition of a unique pattern of clinical symptomatology and/or outcomes of PARDS, if present, could potentially be useful for investigating targeted therapeutic interventions.
Introduction
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most common chronic respiratory disease in infants and is a devastating condition that disrupts the developmental program of the lung secondary to preterm birth. In 2013, one in nine (11.4% of all live births) babies was born at <37 weeks gestation (1). Babies born at <32 weeks gestation account for 1.9% of live births, resulting in more than 75,000 babies admitted to neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) each year (1). Of all births in the US, 1.4% (55,548/year) are of very low birth weight (VLBW; <1500 g) infants annually (1), of whom 15,000 develop BPD (2). In the US, BPD is the leading cause of chronic lung disease in babies and the third leading cause in children (2, 3).
Despite many advances in neonatal ventilation techniques, widespread use of surfactant and antenatal corticosteroids, the incidence of BPD has remained the same (4) or even increased slightly (5, 6). The emotional and financial burden of caring for babies with BPD is significant. Babies with BPD require intensive hospital care for an average of 120 days. In 2009, the presence of BPD in an infant increased mean direct hospital costs (not including physician fees) in the NICU by ~$60,000 (7). Management of BPD takes a considerable toll on health services. Among preterm infants, the single costliest complication of hospitalization during infancy is BPD, with an average cost per discharge of $116,000 (8). Additionally, BPD is associated with significant pulmonary and neurodevelopmental sequelae that continue to have health ramifications into adulthood (5, 9, 10). Home oxygen therapy, when required, averages 92 days. Up to 50% of babies with BPD require readmission to the hospital for lower respiratory tract illness in the first year of life. Median medical costs for home care after discharge is $8100 per child; if the child requires hospitalization, the cost increases up to $50,000. The overall costs of treating babies with BPD in the US are estimated to be $2.4 billion. This amount is second only to the costs for treating asthma and far exceeds the costs for treating cystic fibrosis.
Pathogenesis of BPD
There are five distinct stages in lung development, namely, embryonic, pseudoglandular, canalicular, saccular, and alveolar (11, 12). Preterm infants who are predisposed to developing BPD are born in the late canalicular or early saccular stage of lung development. In the late canalicular stage, there is development of the primitive alveoli and the alveolar capillary barrier, and the differentiation of Type I and Type II pneumocytes (13). In the early saccular stage, surfactant production starts along with pulmonary vascularization and enlargement of terminal airways (11, 12, 14, 15). The lungs complete their development after birth, which continues up to 8 years of age (16). Alveolar sacs are formed by secondary septation of alveolar ducts (13). BPD is caused due to an interaction between genetic and environmental factors (hyperoxia, invasive mechanical ventilation, and sepsis) (5, 17–19).
The foundation of BPD is the immature lung, which may or may not be surfactant deficient. Genetic predisposition probably accounts for 50–80% of the susceptibility to BPD (20, 21). The genetically predisposed immature lung is exposed to noxious external factors: pre- and postnatal infections, hyperoxia, and ventilator-induced barotrauma, volutrauma, or atelectotrauma, which initiates an inflammatory cascade involving inflammatory cells and signaling via various cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. This, in turn, activates the cell death pathways. Damage to the developing lung is followed by resolution of injury to close to normal lung architecture or repair (19). The “old” or “classical” BPD occurred in the pre-surfactant days where invasive ventilation practices led to significant lung injury characterized by a severe fibroproliferative response along with airway injury and alveolar growth abnormalities (22). In the post-surfactant, “gentler” ventilation era in the more immature lung, this reparative state of the lung is characterized by fewer and larger simplified alveoli, along with dysmorphic vasculature, leading to the description of impaired alveolarization and dysregulated vascularization – the pulmonary phenotype of “new” BPD (5, 18, 22–24).
It is important to highlight the fact that for BPD to occur, it requires the known environmental factors to be exposed to the immature lung for a sustained duration, resulting in persistent inflammation (13). While markers of the early inflammatory response (cells, cytokines) may not be detectable after the prolonged exposure to the damaging environmental agents, the initial cascade of the signaling pathways of the inflammatory process/immune response does eventually lead to permanent defects of structure and function in the BPD lungs (13). Anatomical and functional pulmonary deficits in children and adults who had BPD during infancy have been well documented (25–27).
Epidemiology of Pulmonary Outcomes up to Childhood
High resolution chest CT scans (HRCT) in survivors of old BPD and new BPD both show persistent radiological abnormalities with structural changes (28–33). The extent of the structural abnormality has been found to be associated with abnormal pulmonary function tests (28, 30, 31). In younger patients with new BPD, Mahut et al. have reported that the extent of structural abnormalities is correlated with duration of mechanical ventilation and supplemental oxygen (32).
Structural changes in lungs of BPD survivors based on HRCT are more marked in the peripheral lung in both old and new BPD survivors (34).
As one would expect, a stormy perinatal period leads to lasting effects. Survivors of BPD continue to have a greater respiratory morbidity and need for respiratory medications into young adulthood. They are also more likely to have chest wall deformities and a diagnosis of asthma during childhood (35). They have greater rates of hospitalization especially in the first 2 years of life as compared with infants born full term (36, 37). Although rates of hospitalization decrease as these children get older, long-term lung function abnormalities persist. Patients with old BPD had markedly abnormal lung function during late adolescence and 68% of which had evidence of airway obstruction. There was a marked decrease in forced expiratory volume in 1 s (FEV1), forced vital capacity (FVC), and the average forced expiratory flow during the mid (25–75%) portion of the FVC (FEF 25–75%) with evidence of gas trapping in survivors of BPD, as compared with age matched controls who were term and preterm infants without BPD (38). In adolescent patients (mean age 17.7 years) who were born preterm, Halvorsen et al. reported a lower FEV1 when compared those born at term (39). Doyle et al. also reported lung function tests of BPD survivors at a mean age of 18.9 years. They found a significant decrease in FEV1 and FEV1/FVC ratios in patients with a history of BPD, compared with those with no BPD (40). Patterns of lung function abnormalities were similar in survivors of old and new BPD. In patients with new BPD, Fawke et al. found that in over half of the cohort of children born at <26 weeks of gestation that they followed had abnormal spirometry at 11 years of age (35). Others too have reported small airway abnormalities and diffusion abnormalities in infants and young children with BPD (41–43) and persistent abnormalities into late childhood (40, 44–47). BPD survivors with persistent airflow obstruction are less likely to respond to bronchodilators as compared with patients with asthma with a similar degree of obstruction, suggesting that some of the small airway dysfunction seen in BPD survivors may be related to structural change rather than eosinophilic inflammation (48). It is difficult to directly compare outcomes in patients with old BPD with new BPD due to the lack of conformity in the definition of BPD between the two eras since relatively more immature babies are surviving in the post-surfactant era as compared with the pre-surfactant era. It is important to mention here that, while not the focus of this article, significant abnormalities in pulmonary function tests in infants with BPD extend well into late adolescence and adulthood (31, 38–40, 49–52). On the other hand, in adult survivors of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (median age 44 years), pulmonary function has been shown to improve over 5 years with the majority of patients having normal and near normal lung function (53).
Thus, a damaged lung with disordered growth and immune function could potentially act as a substrate, given the appropriate noxious stimuli, to predispose a child to ARDS. However, until recently, the definitions for ARDS were not well suited for children. This may have led to an under diagnosis of ARDS in children with underlying lung disease.
Epidemiology of ARDS/PARDS
When first described by Ashbaugh et al. in the year 1967 (54), adult respiratory distress syndrome was defined as respiratory failure with the following three criteria, such as (1) PaO2/FiO2 ratio of <300 mm of Hg, (2) diffuse bilateral infiltrates on chest radiograph, and (3) an identifiable insult within 7 days of developing a compromise in oxygenation and a well preserved left ventricular function. The terminology of “respiratory distress syndrome” was coined as a reference to a similar neonatal condition. In 1994, recognizing that the adult respiratory distress syndrome occurs in both children and adults, the American-European Consensus Conference (AECC) changed the nomenclature from adult respiratory distress syndrome to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and defined it as a syndrome of inflammation and increased permeability in the lungs that is associated with a constellation of clinical, radiological, and physiological abnormalities that cannot explain but coexist with left atrial or pulmonary capillary hypertension (55).
In clinical practice, the adult criteria were used for more than a decade in the pediatric population. However, there were limitations in the use of this definition in children, including differences in triggering disease states, epidemiology, and outcomes, and technical problems of assessing oxygenation in children without arterial blood gas measurements. The Berlin definition has addressed some of the limitations of the AECC definition (56) better, in terms of validity, for predicting mortality with ARDS, but still lacked pediatric perspective. Pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PARDS) may be a different entity specifically based on its epidemiology and outcomes. A group of experts have proposed a more pediatric-specific definition of PARDS to account for differences in adults and children (57). Authors propose the following changes in the (a) simplification of chest imaging criteria to eliminate presence of bilateral infiltrates, (b) use of pulse oximetry-based criteria when PaO2 is not available, and (c) inclusion of oxygenation index instead of PaO2/FiO2 with a minimum positive end expiratory pressure for invasively ventilated patients and specific inclusion of children with underlying lung and heart disease.
Pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome is less common as compared with ARDS with an incidence of 2.0–12.8 children per 100,000 patient years with a lower morality in PARDS as compared with ARDS (58–62). The incidence of PARDS is likely underestimated, especially in patients with a preexisting lung disease. In a child with underlying lung disease (such as BPD), it can be difficult to make a diagnosis of ARDS given the Berlin definition. An acutely ill child with underlying lung disease is often diagnosed with an exacerbation of their underlying disease rather than ARDS, possibly leading to an under diagnosis and underestimation of PARDS (59). The revised definition of PARDS to specifically include the subgroup of pediatric patients with underlying lung and heart disease in the definition of PARDS may improve the recognition of this condition.
Pathogenesis of ARDS/PARDS
Similar to adults, the most common causes of ARDS in the pediatric age group are underlying pneumonia or viral illness (58, 63). Sepsis, aspiration, and trauma can also cause ARDS in children, but occur less frequently in children compared with adults. A significant proportion of patients of PARDS have underlying chronic comorbidities. Of these, underlying chronic lung disease is one of the commonest comorbidity reported in pediatric patients who develop ARDS/acute lung injury (ALI) (62). Prematurity has been reported in 13% of the children with ARDS (45), and underlying chronic lung disease has been reported to occur in 11–13% (62, 63). However, in some studies of ARDS in children, patients with underlying hypoxic lung disease were excluded (58). Nevertheless, children with BPD are at risk for developing ARDS, especially if they have a history of severe BPD that is often associated with other comorbidities. These include swallow dysfunction and neurodevelopmental delay, which puts them at risk for impaired airway clearance and aspiration pneumonia, increasing the risk of recurrent pulmonary infections. Therefore, it becomes difficult to determine if patients with BPD have a flare up of their underlying condition or have ARDS triggered by infection, aspiration, or other pulmonary insults. This may also affect the management of a patient with acute exacerbation of underlying BPD, which may be significantly different from a patient with ARDS with underlying BPD; for example, the use of corticosteroids would probably be more likely in the former category of patients. In addition, pulmonary vascular disease and coexistent pulmonary hypertension play a role in the morbidity of infants with BPD presenting with respiratory failure. Pulmonary vasodilatory therapies, such as inhaled nitric oxide (iNO), may help in these circumstances (2). This variability in reported data presents challenges in sorting out whether past history of BPD increases the risk of development of ARDS or affects outcomes in this population.
Despite multiple chronic comorbidities in those with PARDS, presence of underlying immunodeficiency is the only comorbidity associated with poor outcome (64, 65). Others have reported that non-pulmonary sepsis is associated with increased mortality in patients with ALI (62, 65). However, most epidemiological studies of ARDS do not list specific diagnoses as comorbidities or underlying conditions and, instead, describe organ system involvement more broadly. Since BPD is one of the commonest forms of preexisting lung disease, it may be reasonable to extrapolate that there is no clear associated increase in risk of death with PARDS in patients with BPD. However, it is important to clarify that there is no specific data to support or refute the extrapolated statement.
Some studies have suggested a predominance of Caucasian infants being predisposed to BPD (66); this finding has not been consistent (67). Given the significant genetic susceptibility to BPD, it very likely that if specific single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occur more commonly in a particular race/ethnic group, that would be more important for predisposing a particular race/ethnic group towards developing BPD (68, 69). It is important to mention here that race/ethnicity has been noted to impact on lung function and utilization of respiratory medications in infants born preterm and/or with BPD (70–72). African-American adults are more likely to have a more severe disease and greater mortality with ARDS. Hispanic adults also have higher mortality rates independent of severity of disease (73). There is no reported race bias in terms of mortality in PARDS. Male gender has also been shown to increase the risk of developing BPD (74, 75). However, similar to the data reported in adults with ARDS, in PARDS, there is no difference in mortality rates based on gender (58, 62, 63, 76, 77).
Outcomes of PARDS
There is significant mortality associated with PARDS; however, these mortality rates appear to be lower than that in adults, ranging from 15 to 50% mortality in children compared with 35 to 45% mortality in adults (60, 62). There is, however, a wide range in the mortality range of the cohorts of children with ARDS (47). This wide range in mortality assessment may be due to differences in the comorbid or underlying conditions in the children in these relatively small cohorts or may be due to improvements in care over time (47).
Biomarkers in BPD and ARDS
Theoretically, biomarkers can be used to identify at risk population, predict severity of illness, target therapy, and predict prognosis.
Various biomarkers detected in different biological fluids have been proposed for early identification of infants predisposed to BPD (3, 78). The majority of the studies have been conducted using blood, urine, or tracheal aspirate (TA) samples (3, 78). Among these that have been implicated both in BPD and ARDS (vide infra) are the following.
KL-6 (a lung injury marker) was increased in infants in the umbilical cord blood samples in infants who went on to develop BPD (n = 50 vs. non-BPD n = 24) (79) and was also useful as a predictor of moderate/severe BPD at 1 week of postnatal life (80). Combining results from all models, BPD/death (n = 606 out of 1062) was associated with higher levels of interleukin (IL)-6 and -8 in blood samples collected at various timepoints during the infants’ stay in the NICU (81).
Among the cytokines, it is important to note consistent results with increased blood levels of IL-6 and -8 have been associated with BPD (3). This is supported by increased concentrations of these cytokines in TA obtained from human infants developing BPD (3). Among other pulmonary biomarkers of BPD, two independent cohorts have reported increased TA levels of angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) to be associated with increased risk of BPD and/or death (82, 83).
Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) is increased in TA samples in the first week of life in infants developing BPD (77, 84). Increased levels of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-8 and -9 have been reported in infants developing BPD (18, 77, 84).
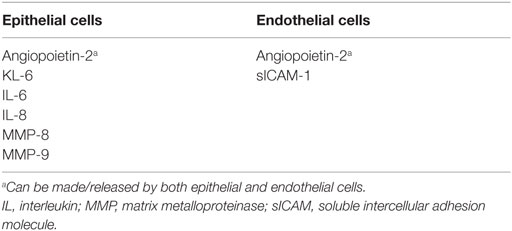
In a systematic meta-analysis of plasma-derived biomarkers associated with ARDS, Terpstra et al. reported ranking of plasma biomarkers for ARDS according to the strength of association with both diagnosis and mortality of ARDS (85). Authors found that KL-6, lactic dehydrogenase, soluble RAGE, and von Willebrand factor are strongly associated with the development of ARDS in at-risk patients. They also concluded that mortality with ARDS was most strongly associated with IL-4, IL-2, Ang-2, and KL-6. Increased plasma levels of transferrin and protein C were associated with decreased odds for both development of ARDS and mortality with ARDS (85). Studies examining the role of inflammatory biomarkers in PARDS are far fewer than in ARDS (86). Serum IL-8 and IL-6 have both been shown to be elevated in patients with PARDS (86). While elevated levels of plasma sICAM-1 on days 1 and 2 of ALI were associated with increased risk of death and prolonged mechanical ventilation, Flori et al. noted that when combined with a physiological index of oxygenation defect (PaO2/FiO2), it further strengthened the predicted value risk of death in PARDS (87). Higher TA MMP-8 and MMP-9 levels in patients with PARDS have been shown to correlate with increased risk of death and prolonged mechanical ventilation (87, 88). The biomarkers have been categorized into markers of pulmonary epithelial or endothelial ling injury and summarized in Table 1.
It is unclear what causes the difference in outcomes of pediatric patients, as compared with adults with ARDS. It has been suggested that in pediatric patients the stage of lung development at the time of the insult may be one cause of this outcome difference. This may pertain especially to younger children. It is known that alveolar development is a primarily postnatal process which starts at ~36 weeks of gestation and continues in the postnatal period. Maximal alveolar growth is completed by 24 months of age, although there may be some growth that occurs for up to 8 years. Although this has not been researched adequately, in a child where alveolar growth is still not complete, ARDS may lead to a different pathology, thus affecting not only the course of the disease but also the long-term outcome.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is primarily an inflammatory response to injury. There is evidence to suggest that children have a unique inflammatory response to injury, which confers protection from development of multi-organ failure, although underlying mechanisms are not known (89). It is fair to say that the child’s inherent immune response may have some role to play in the difference in the course and outcomes of PARDS.
Lack of Data and Need for Future Research
Pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome is less common than ARDS; furthermore, epidemiological studies of PARDS do not provide specific diagnoses as comorbidities or underlying conditions. This limits our understanding of how underlying lung disease (specifically BPD) may affect the pattern of clinical presentation and/or outcomes of PARDS. Newer criteria of PARDS have been proposed recently, which we hope will help better understand the contribution of underlying chronic lung disease to PARDS. Proper categorization and definition of ARDS in patients with underlying disease, such as BPD, are also important to guide clinical therapy. This review highlights many questions that remain unanswered and underscores the need for future multidisciplinary collaboration to study the long-term outcome of BPD and as a substrate for PARDS.
Summary and Conclusion
Chronic pulmonary disease is a commonly seen comorbidity in patients with PARDS. There is no clear data to suggest an association of BPD with increased probability of developing ARDS, neither is there any suggestion that underlying lung disease portends a worse outcome with ARDS. However, similar biomarkers (KL-6, IL-6, IL-8, sICAM-1, Ang-2, and MMP-8 and -9) of pulmonary injury have been associated both with BPD and ARDS. Current practice where pediatric patients are more likely to be diagnosed with their underlying disease rather than PARDS underestimates the true incidence of ARDS, and possibly the effect of underlying chronic lung disease. Future research incorporating listing BPD as a specific underlying diagnosis would assist in recognition of a unique pattern (if present) of clinical presentation and/or outcomes of PARDS, which, in turn, could potentially set the stage for investigating targeted therapeutic interventions.
Author Contributions
AB: concept, design, interpretation, analysis, revision for critical intellectual content, and final approval of draft. CC: interpretation, analysis, revision for critical intellectual content, and final approval of draft. VB: concept, design, initial draft, interpretation, analysis, revision for critical intellectual content, and final approval of draft.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
1. National Center for Health Statistics, Final Natality Data. (2016). Available from: www.marchofdimes.org/peristats
2. Lal CV, Ambalavanan N. Pulmonary hypertension in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. In: Bhandari V, editor. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Respiratory Medicine. Switzerland: Springer (2016). p. 259–80.
3. Bhandari A, Bhandari V. Biomarkers in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Paediatr Respir Rev (2013) 14(3):173–9. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2013.02.008
4. Smith VC, Zupancic JA, McCormick MC, Croen LA, Greene J, Escobar GJ, et al. Trends in severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia rates between 1994 and 2002. J Pediatr (2005) 146(4):469–73. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2004.12.023
5. Bhandari A, Bhandari V. “New” bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a clinical review. Clin Pulm Med (2011) 18(3):137–43. doi:10.1097/CPM.0b013e318218a071
6. Trembath A, Laughon MM. Predictors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Clin Perinatol (2012) 39(3):585–601. doi:10.1016/j.clp.2012.06.014
7. Johnson TJ, Patel AL, Jegier BJ, Engstrom JL, Meier PP. Cost of morbidities in very low birth weight infants. J Pediatr (2013) 162(2):243–9.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.07.013
8. Russell RB, Green NS, Steiner CA, Meikle S, Howse JL, Poschman K, et al. Cost of hospitalization for preterm and low birth weight infants in the United States. Pediatrics (2007) 120(1):e1–9. doi:10.1542/peds.2006-2386
9. Bhandari A, Panitch HB. Pulmonary outcomes in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol (2006) 30(4):219–26. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2006.05.005
10. Anderson PJ, Doyle LW. Neurodevelopmental outcome of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol (2006) 30(4):227–32. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2006.05.010
11. Kotecha S. Lung growth: implications for the newborn infant. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed (2000) 82(1):F69–74. doi:10.1136/fn.82.1.F69
12. Maeda Y, Dave V, Whitsett JA. Transcriptional control of lung morphogenesis. Physiol Rev (2007) 87(1):219–44. doi:10.1152/physrev.00028.2006
13. Balany J, Bhandari V. Understanding the impact of infection, inflammation, and their persistence in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Front Med (2015) 2:90. doi:10.3389/fmed.2015.00090
14. Joshi S, Kotecha S. Lung growth and development. Early Hum Dev (2007) 83(12):789–94. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2007.09.007
15. Kramer EL, Deutsch GH, Sartor MA, Hardie WD, Ikegami M, Korfhagen TR, et al. Perinatal increases in TGF-{alpha} disrupt the saccular phase of lung morphogenesis and cause remodeling: microarray analysis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol (2007) 293(2):L314–27. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00354.2006
16. Berger J, Bhandari V. Animal models of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The term mouse models. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol (2014) 307(12):L936–47. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00159.2014
17. Baraldi E, Filippone M. Chronic lung disease after premature birth. N Engl J Med (2007) 357(19):1946–55. doi:10.1056/NEJMra067279
18. Bhandari A, Bhandari V. Pitfalls, problems, and progress in bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics (2009) 123(6):1562–73. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-1962
19. Bhandari V. Postnatal inflammation in the pathogenesis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol (2014) 100(3):189–201. doi:10.1002/bdra.23220
20. Bhandari V, Bizzarro MJ, Shetty A, Zhong X, Page GP, Zhang H, et al. Familial and genetic susceptibility to major neonatal morbidities in preterm twins. Pediatrics (2006) 117(6):1901–6. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-1414
21. Lavoie PM, Pham C, Jang KL. Heritability of bronchopulmonary dysplasia, defined according to the consensus statement of the national institutes of health. Pediatrics (2008) 122(3):479–85. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2313
22. de Paepe ME. Pathology of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. In: Bhandari V, editor. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Respiratory Medicine. Switzerland: Springer (2016). p. 149–64.
23. Bhandari A, Bhandari V. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: an update. Indian J Pediatr (2007) 74(1):73–7.
24. Bhandari V. Hyperoxia-derived lung damage in preterm infants. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med (2010) 15(4):223–9. doi:10.1016/j.siny.2010.03.009
25. Bhandari A, McGrath-Morrow S. Long-term pulmonary outcomes of patients with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol (2013) 37(2):132–7. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2013.01.010
26. Islam JY, Keller RL, Aschner JL, Hartert TV, Moore PE. Understanding the short- and long-term respiratory outcomes of prematurity and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2015) 192(2):134–56. doi:10.1164/rccm.201412-2142PP
27. Saarenpaa HK, Tikanmaki M, Sipola-Leppanen M, Hovi P, Wehkalampi K, Siltanen M, et al. Lung function in very low birth weight adults. Pediatrics (2015) 136(4):642–50. doi:10.1542/peds.2014-2651
28. Aquino SL, Schechter MS, Chiles C, Ablin DS, Chipps B, Webb WR. High-resolution inspiratory and expiratory CT in older children and adults with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. AJR Am J Roentgenol (1999) 173(4):963–7. doi:10.2214/ajr.173.4.10511158
29. Howling SJ, Northway WH Jr, Hansell DM, Moss RB, Ward S, Muller NL. Pulmonary sequelae of bronchopulmonary dysplasia survivors: high-resolution CT findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol (2000) 174(5):1323–6. doi:10.2214/ajr.174.5.1741323
30. Wong PM, Lees AN, Louw J, Lee FY, French N, Gain K, et al. Emphysema in young adult survivors of moderate-to-severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Eur Respir J (2008) 32(2):321–8. doi:10.1183/09031936.00127107
31. Aukland SM, Rosendahl K, Owens CM, Fosse KR, Eide GE, Halvorsen T. Neonatal bronchopulmonary dysplasia predicts abnormal pulmonary HRCT scans in long-term survivors of extreme preterm birth. Thorax (2009) 64(5):405–10. doi:10.1136/thx.2008.103739
32. Mahut B, De Blic J, Emond S, Benoist MR, Jarreau PH, Lacaze-Masmonteil T, et al. Chest computed tomography findings in bronchopulmonary dysplasia and correlation with lung function. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed (2007) 92(6):F459–64. doi:10.1136/adc.2006.111765
33. Ochiai M, Hikino S, Yabuuchi H, Nakayama H, Sato K, Ohga S, et al. A new scoring system for computed tomography of the chest for assessing the clinical status of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Pediatr (2008) 152(1): 90–5, 95.e1–3. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.05.043
34. Wilson AC. What does imaging the chest tell us about bronchopulmonary dysplasia? Paediatr Respir Rev (2010) 11(3):158–61. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2010.05.005
35. Fawke J, Lum S, Kirkby J, Hennessy E, Marlow N, Rowell V, et al. Lung function and respiratory symptoms at 11 years in children born extremely preterm: the EPICure study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2010) 182(2):237–45. doi:10.1164/rccm.200912-1806OC
36. Greenough A, Cox S, Alexander J, Lenney W, Turnbull F, Burgess S, et al. Health care utilisation of infants with chronic lung disease, related to hospitalisation for RSV infection. Arch Dis Child (2001) 85(6):463–8. doi:10.1136/adc.85.6.463
37. Doyle LW, Casalaz D; Victorian Infant Collaborative Study Group. Outcome at 14 years of extremely low birthweight infants: a regional study. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed (2001) 85(3):F159–64. doi:10.1136/fn.85.3.F159
38. Northway WH Jr, Moss RB, Carlisle KB, Parker BR, Popp RL, Pitlick PT, et al. Late pulmonary sequelae of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med (1990) 323(26):1793–9. doi:10.1056/NEJM199012273232603
39. Halvorsen T, Skadberg BT, Eide GE, Roksund OD, Carlsen KH, Bakke P. Pulmonary outcome in adolescents of extreme preterm birth: a regional cohort study. Acta Paediatr (2004) 93(10):1294–300. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2004.tb02926.x
40. Doyle LW, Faber B, Callanan C, Freezer N, Ford GW, Davis NM. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very low birth weight subjects and lung function in late adolescence. Pediatrics (2006) 118(1):108–13. doi:10.1542/peds.2005-2522
41. Filbrun AG, Popova AP, Linn MJ, McIntosh NA, Hershenson MB. Longitudinal measures of lung function in infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol (2011) 46(4):369–75. doi:10.1002/ppul.21378
42. Fakhoury KF, Sellers C, Smith EO, Rama JA, Fan LL. Serial measurements of lung function in a cohort of young children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatrics (2010) 125(6):e1441–7. doi:10.1542/peds.2009-0668
43. Korhonen P, Laitinen J, Hyodynmaa E, Tammela O. Respiratory outcome in school-aged, very-low-birth-weight children in the surfactant era. Acta Paediatr (2004) 93(3):316–21. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2004.tb02954.x
44. Lum S, Kirkby J, Welsh L, Marlow N, Hennessy E, Stocks J. Nature and severity of lung function abnormalities in extremely pre-term children at 11 years of age. Eur Respir J (2011) 37(5):1199–207. doi:10.1183/09031936.00071110
45. Balinotti JE, Chakr VC, Tiller C, Kimmel R, Coates C, Kisling J, et al. Growth of lung parenchyma in infants and toddlers with chronic lung disease of infancy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2010) 181(10):1093–7. doi:10.1164/rccm.200908-1190OC
46. Cazzato S, Ridolfi L, Bernardi F, Faldella G, Bertelli L. Lung function outcome at school age in very low birth weight children. Pediatr Pulmonol (2013) 48(8):830–7. doi:10.1002/ppul.22676
47. Landry JS, Chan T, Lands L, Menzies D. Long-term impact of bronchopulmonary dysplasia on pulmonary function. Can Respir J (2011) 18(5):265–70. doi:10.1155/2011/547948
48. Baraldi E, Bonetto G, Zacchello F, Filippone M. Low exhaled nitric oxide in school-age children with bronchopulmonary dysplasia and airflow limitation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2005) 171(1):68–72. doi:10.1164/rccm.200403-298OC
49. Trachsel D, Brutsche MH, Hug-Batschelet H, Hammer J. Progressive static pulmonary hyperinflation in survivors of severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia by mid-adulthood. Thorax (2012) 67(8):747–8. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2011-200695
50. Gough A, Spence D, Linden M, Halliday HL, McGarvey LP. General and respiratory health outcomes in adult survivors of bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a systematic review. Chest (2012) 141(6):1554–67. doi:10.1378/chest.11-1306
51. Gibson AM, Reddington C, McBride L, Callanan C, Robertson C, Doyle LW. Lung function in adult survivors of very low birth weight, with and without bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Pulmonol (2015) 50(10):987–94. doi:10.1002/ppul.23093
52. Landry JS, Tremblay GM, Li PZ, Wong C, Benedetti A, Taivassalo T. Lung function and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in adults born prematurely. A cohort study. Ann Am Thorac Soc (2016) 13(1):17–24. doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201508-553OC
53. Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matte A, Tomlinson G, Diaz-Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med (2011) 364(14):1293–304. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1011802
54. Ashbaugh DG, Bigelow DB, Petty TL, Levine BE. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet (1967) 2(7511):319–23. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(67)90168-7
55. Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, et al. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (1994) 149(3 Pt 1):818–24. doi:10.1164/ajrccm.149.3.7509706
56. Force ADT, Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson BT, Ferguson ND, Caldwell E, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA (2012) 307(23):2526–33. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5669
57. Khemani RG, Smith LS, Zimmerman JJ, Erickson S; Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference Group. Pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: definition, incidence, and epidemiology: proceedings from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2015) 16(5 Suppl 1):S23–40. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000000432
58. Erickson S, Schibler A, Numa A, Nuthall G, Yung M, Pascoe E, et al. Acute lung injury in pediatric intensive care in Australia and New Zealand: a prospective, multicenter, observational study. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2007) 8(4):317–23. doi:10.1097/01.PCC.0000269408.64179.FF
59. Kneyber MC, Brouwers AG, Caris JA, Chedamni S, Plotz FB. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: is it underrecognized in the pediatric intensive care unit? Intensive Care Med (2008) 34(4):751–4. doi:10.1007/s00134-008-1029-4
60. Lopez-Fernandez Y, Azagra AM, de la Oliva P, Modesto V, Sanchez JI, Parrilla J, et al. Pediatric acute lung injury epidemiology and natural history study: incidence and outcome of the acute respiratory distress syndrome in children. Crit Care Med (2012) 40(12):3238–45. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e318260caa3
61. Bindl L, Dresbach K, Lentze MJ. Incidence of acute respiratory distress syndrome in German children and adolescents: a population-based study. Crit Care Med (2005) 33(1):209–312. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000151137.76768.08
62. Zimmerman JJ, Akhtar SR, Caldwell E, Rubenfeld GD. Incidence and outcomes of pediatric acute lung injury. Pediatrics (2009) 124(1):87–95. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2462
63. Flori HR, Glidden DV, Rutherford GW, Matthay MA. Pediatric acute lung injury: prospective evaluation of risk factors associated with mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2005) 171(9):995–1001. doi:10.1164/rccm.200404-544OC
64. Flori H, Dahmer MK, Sapru A, Quasney MW; Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference Group. Comorbidities and assessment of severity of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: proceedings from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2015) 16(5 Suppl 1):S41–50. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000000430
65. Quasney MW, Lopez-Fernandez YM, Santschi M, Watson RS; Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference Group. The outcomes of children with pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: proceedings from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2015) 16(5 Suppl 1):S118–31. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000000438
66. Akram Khan M, Kuzma-O’Reilly B, Brodsky NL, Bhandari V. Site-specific characteristics of infants developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Perinatol (2006) 26(7):428–35. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211538
67. Petrova A, Mehta R, Anwar M, Hiatt M, Hegyi T. Impact of race and ethnicity on the outcome of preterm infants below 32 weeks gestation. J Perinatol (2003) 23(5):404–8. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7210934
68. Lal CV, Ambalavanan N. Genetic predisposition to bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol (2015) 39(8):584–91. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2015.09.004
69. Bhandari V, Gruen JR. The genetics of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Perinatol (2006) 30(4):185–91. doi:10.1053/j.semperi.2006.05.005
70. Hoo AF, Gupta A, Lum S, Costeloe KL, Huertas-Ceballos A, Marlow N, et al. Impact of ethnicity and extreme prematurity on infant pulmonary function. Pediatr Pulmonol (2014) 49(7):679–87. doi:10.1002/ppul.22882
71. Collaco JM, Choi SJ, Riekert KA, Eakin MN, McGrath-Morrow SA, Okelo SO. Socio-economic factors and outcomes in chronic lung disease of prematurity. Pediatr Pulmonol (2011) 46(7):709–16. doi:10.1002/ppul.21422
72. Lorch SA, Wade KC, Bakewell-Sachs S, Medoff-Cooper B, Escobar GJ, Silber JH. Racial differences in the use of respiratory medications in premature infants after discharge from the neonatal intensive care unit. J Pediatr (2007) 151(6): 604–10, 610.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2007.04.052
73. Erickson SE, Shlipak MG, Martin GS, Wheeler AP, Ancukiewicz M, Matthay MA, et al. Racial and ethnic disparities in mortality from acute lung injury. Crit Care Med (2009) 37(1):1–6. doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819292ea
74. Klinger G, Sokolover N, Boyko V, Sirota L, Lerner-Geva L, Reichman B, et al. Perinatal risk factors for bronchopulmonary dysplasia in a national cohort of very-low-birthweight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol (2013) 208(2):115.e1–9. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2012.11.026
75. Laughon MM, Langer JC, Bose CL, Smith PB, Ambalavanan N, Kennedy KA, et al. Prediction of bronchopulmonary dysplasia by postnatal age in extremely premature infants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2011) 183(12):1715–22. doi:10.1164/rccm.201101-0055OC
76. Ghuman AK, Newth CJ, Khemani RG. The association between the end tidal alveolar dead space fraction and mortality in pediatric acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2012) 13(1):11–5. doi:10.1097/PCC.0b013e3182192c42
77. Dahlem P, van Aalderen WM, Hamaker ME, Dijkgraaf MG, Bos AP. Incidence and short-term outcome of acute lung injury in mechanically ventilated children. Eur Respir J (2003) 22(6):980–5. doi:10.1183/09031936.03.00003303
78. Thompson A, Bhandari V. Pulmonary biomarkers of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Biomark Insights (2008) 3:361–73.
79. Kim DH, Kim HS, Shim SY, Lee JA, Choi CW, Kim EK, et al. Cord blood KL-6, a specific lung injury marker, correlates with the subsequent development and severity of atypical bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Neonatology (2008) 93(4):223–9. doi:10.1159/000111100
80. Ogihara T, Hirano K, Morinobu T, Kim HS, Ogawa S, Hiroi M, et al. Plasma KL-6 predicts the development and outcome of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res (2006) 60(5):613–8. doi:10.1203/01.pdr.0000242361.47408.51
81. Ambalavanan N, Carlo WA, D’Angio CT, McDonald SA, Das A, Schendel D, et al. Cytokines associated with bronchopulmonary dysplasia or death in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics (2009) 123(4):1132–41. doi:10.1542/peds.2008-0526
82. Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z, Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL, et al. Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death. Nat Med (2006) 12(11):1286–93. doi:10.1038/nm1494
83. Aghai ZH, Faqiri S, Saslow JG, Nakhla T, Farhath S, Kumar A, et al. Angiopoietin 2 concentrations in infants developing bronchopulmonary dysplasia: attenuation by dexamethasone. J Perinatol (2008) 28(2):149–55. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211886
84. Bose CL, Dammann CE, Laughon MM. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia and inflammatory biomarkers in the premature neonate. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed (2008) 93(6):F455–61. doi:10.1136/adc.2007.121327
85. Terpstra ML, Aman J, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Groeneveld AB. Plasma biomarkers for acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis*. Crit Care Med (2014) 42(3):691–700. doi:10.1097/01.ccm.0000435669.60811.24
86. Sapru A, Flori H, Quasney MW, Dahmer MK; Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference Group. Pathobiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2015) 16(5 Suppl 1):S6–22. doi:10.1097/PCC.0000000000000431
87. Flori HR, Ware LB, Glidden D, Matthay MA. Early elevation of plasma soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in pediatric acute lung injury identifies patients at increased risk of death and prolonged mechanical ventilation. Pediatr Crit Care Med (2003) 4(3):315–21. doi:10.1097/01.PCC.0000074583.27727.8E
88. Kong MY, Li Y, Oster R, Gaggar A, Clancy JP. Early elevation of matrix metalloproteinase-8 and -9 in pediatric ARDS is associated with an increased risk of prolonged mechanical ventilation. PLoS One (2011) 6(8):e22596. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022596
Keywords: BPD, pediatric ARDS, lung diseases, biomarkers, lung development
Citation: Bhandari A, Carroll C and Bhandari V (2016) BPD Following Preterm Birth: A Model for Chronic Lung Disease and a Substrate for ARDS in Childhood. Front. Pediatr. 4:60. doi: 10.3389/fped.2016.00060
Received: 04 April 2016; Accepted: 26 May 2016;
Published: 15 June 2016
Edited by:
Kanwaljeet J. S. Anand, Stanford University School of Medicine, USAReviewed by:
Maroun Jean Mhanna, Case Western Reserve University, USANarendra Reddy Dereddy, Maria Fareri Children’s Hospital at Westchester Medical Center, USA
Copyright: © 2016 Bhandari, Carroll and Bhandari. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vineet Bhandari, dmluZWV0LmJoYW5kYXJpQGRyZXhlbG1lZC5lZHU=
 Anita Bhandari
Anita Bhandari Christopher Carroll
Christopher Carroll Vineet Bhandari
Vineet Bhandari