- 1Sustainability and Health Initiative (SHINE), Department of Environmental Health, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, United States
- 2Human Flourishing Program, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Institute for Quantitative Social Science, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, United States
- 3Department of Humanities, IULM University Milan, Milan, Italy
- 4metaLAB (at) Harvard, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, United States
- 5Fondazione Bruno Kessler, Trento, Italy
- 6Berkman-Klein Center for Internet & Society, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, United States
- 7Department of Epidemiology, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, MA, United States
Understanding reciprocal relationships between specific arenas in life and at work is critical for designing interventions to improve workplace health and safety. Most studies about the links between dimensions of well-being in life and at work have been cross-sectional and usually narrowly focused on one of the dimensions of the work-life well-being link. The issues of causality and feedback between life and work well-being have often not been addressed. We overcome these issues by measuring six aspects of well-being for both the work arena and life in general, using longitudinal data with a clear temporal sequence of cause and effect, and by explicitly accounting for feedback with potential effects in both directions. Nine hundred and fifty-four Mexican apparel factory workers at a major global brand participated in two waves of the Worker Well-Being Survey. Data on life satisfaction and job satisfaction, happiness and positive affect, meaning and purpose, health, and social relationships in life and at work were used. Lagged regression controlling for confounders and prior outcomes was employed. Sensitivity analysis was used to assess the robustness of the results to potential unmeasured confounding. For the relationships between life satisfaction and job satisfaction and between happiness in life and happiness at work effects in both directions were found. Nevertheless, indication of a larger effect of life satisfaction on job satisfaction than the reverse was obtained. For depression and meaning in life, there was evidence for an effect of life well-being on work-related well-being, but not for the reverse. For social relationships and purpose, there was evidence for an effect of work-related well-being on life well-being, but not the reverse. Relationships based on the longitudinal data were considerably weaker than their respective cross-sectional associations. This study contributes to our understanding of the nature of the relationship between aspects of well-being in the arenas of life and work. Findings from this study may facilitate the development of novel workplace programs promoting working conditions that enable lifelong flourishing in life and at work.
Introduction
Although the influence of work on occupational health and safety has been long recognized (1), importance of work for well-being has been gaining scientific attention only recently (2–6). The impact of employee health on work has been traditionally examined through the lenses of physical and mental disabilities that limit chances for performing certain jobs (7–9). Recently the topic of worker well-being has been gaining attention in the field of occupational health. The United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (CDC/NIOSH) launched in 2011 the Total Worker Health® program that integrates protection against work-related and health hazards with promotion of injury avoidance and illness prevention to advance worker well-being (10–12). The World Health Organization introduced the Model for Action, which advocates for workers' health, safety and well-being on and off the job (13). Similar conceptual idea, highlighting the importance of achieving living and working conditions that enable people to engage and thrive at work over their lives, lies behind the concept of sustainable work over the life course which was introduced in the European Union to help people maintain health, develop skills and achieve financial security, work–life balance, meaningful work, and sense of self-fulfillment in the workplace (14). These worker well-being promoting initiatives emerge in labor market policies (14) and are subsequently integrated into companies' strategies (12, 15).
We argue that understanding the reciprocal relationships between well-being aspects at work and in life is critical to design policies to improve not only workplace health and safety but also employee satisfaction and well-being. Unfortunately, studies about the links between dimensions of well-being in life and at work have been usually narrowly focused on one of the dimensions of the work-life well-being link and additionally—have been mostly cross-sectional making causal inference implausible. The aim of this paper is to offer a more holistic outlook of the relationships between well-being at work and well-being in life by evaluating reciprocal relationships between six dimensions of well-being (such as life satisfaction, happiness, meaning, purpose, mental health, and social relationships) and their work-related counterparts while considering the bi-directional effects between work and life for each of the dimensions over time. This perspective contrasts with numerous well-being studies that not only limit well-being to a single life-related measure but also conceal the role of work as a driver for human flourishing and disregard the value of promoting flourishing in life to enhance flourishing at work. Consequently, in this article we hypothesize that for each of the six dimensions, significant reciprocal relationship between well-being in life and well-being at work can be established. In other words, we test a hypothesis that well-being while at work positively influences well-being in life and well-being in life is beneficial for well-being while at work.
Literature Review
One of the most examined relationships between well-being and work has been the one between subjective well-being (SWB)1 and job satisfaction (16–19). This relationship has been subject to scrutiny over the past decades, with early contributions dating back to the 1950's (20). Previous studies, however, identified only a modest to moderate association between SWB and job satisfaction (16, 19). Limited evidence, however, is available for the relationship between other dimensions of well-being in life and their counterparts related to well-being at work.
Many existing studies are also hardly conclusive due to serious methodological limitations. Most of the studies have been based on cross-sectional study designs (18, 21), which rendered it impossible to establish any causal link. Limited longitudinal research carried out so far mainly focused on the relationship between the broad concepts of life satisfaction and job satisfaction without delving into its constituents [see (16) for a review] or work-life conflict (22, 23), avoiding a scrutinized study of other aspects of well-being in the arena of life and work.
Theoretical and empirical lack of agreement on the directionality of the relationship between well-being and work further complicates the interpretation and assessment of the findings (16). For instance, the part-whole theory (24, 25) posits that specific aspects of life (e.g., work) influence well-being, whereas the dispositional approach (26, 27) claims that it is well-being that has a causal effect on specific aspects of life (e.g., work).
Additionally, regarding the directionality of the relationship, a heated dispute arose between proponents of the spillover approach, advocating for a reciprocal, positive relationship between specific aspects of life (e.g., work) and well-being (16, 28), the compensation approach, assuming that dissatisfaction in one sphere is compensated by search for enrichment in the other (thus envisaging a negative relationship), and the segmentalist approach, making a case for a lack of relationships between the two areas (29). Current evidence is thus inconclusive and thus all hypotheses about the cause and the effect remain plausible.
The conceptual and operational definitions of well-being in life and well-being at work have been refined more recently as well. The definitions shifted from early characterizations in broad affective terms to more articulate, conceptually sharper ones (30), which provide relatively robust and consistent frameworks necessary for a scientific analysis (16). For example, consideration of job and life satisfaction is now combined in notions of employee well-being (31–33) and more well-being interventions are proposed to ensure that workers are both happy (or high in well-being) and productive (have high performance) (34, 35).
However, the nature of the work-life link is still unclear. Despite strong evidence provided by Bowling et al. (16) that the effects are bi-directional and life satisfaction affects job satisfaction more than job satisfaction affects life satisfaction, the issue of the direction of causality and strength of bi-directional relations between dimensions of well-being at work and well-being in life remains fundamentally open and unexplored. Although recent research has extended our contextual knowledge about the possible effects on the job-life satisfaction relationship [for example the effects of: burnout (36, 37), positive affect or negative affect (19, 28), job importance (38), work-family conflict (19, 28), work-life balance (39, 40), workplace friendship (41, 42), job insecurity (43), and even geographical remoteness (44)], a more comprehensive approach—as advocated also by Neve et al. (2) is needed. However, it is worth noting that a distinction between workplace well-being from general well-being has been recently recognized (33). Still, limited evidence on how particular aspects of general well-being affect their counterparts while at work and vice versa is available.
Consequently, this paper offers the following contributions in this relatively under-explored direction. First, by carrying out a longitudinal analysis it provides more robust evidence on the causal relationships between job and life satisfaction. Second, by studying in depth other aspects of well-being in the work and life sphere, such as happiness (45), meaning (46), purpose (47), mental health (48) and social relationships (49), our results provide an innovative framework for the analysis of the job vs. life dimensions of well-being studied in the literature as well as evidence for their causal directionality.
Materials and Methods
Data Source and Sample Size
The analysis builds on the first two waves of the Worker Well-Being Survey (WWBS), a tool designed to track workers' well-being, administered in the Levi Strauss & Co.'s supplier in Mexico. The first wave of the WWBS was administered in February 2017, and the second one in March 2018.
Workers completed surveys in a private space inside the factory on tablets either connected directly to secure servers via the internet or using an offline app. In this way, all information was kept confidential. During survey administration, groups of workers were released from their line positions (e.g., one production line at a time) to come to the survey stations. A communication campaign took place prior to survey activities to invite workers to participate in the survey. The results were reported in aggregate to workers and the factory after tabulation and analysis. The workers' decision to participate in the survey was voluntary and was not disclosed to management. All workers signed an informed consent. The study was approved by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Institutional Review Board.
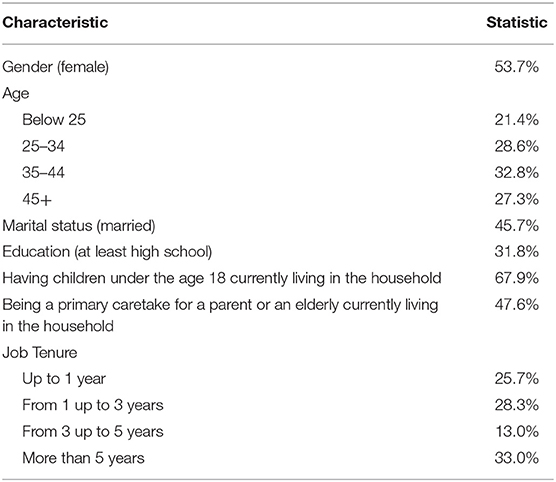
Nine hundred fifty-four apparel workers participated in both waves of the WWBS. Descriptive statistics of the sample are presented in Table 1. Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Measures
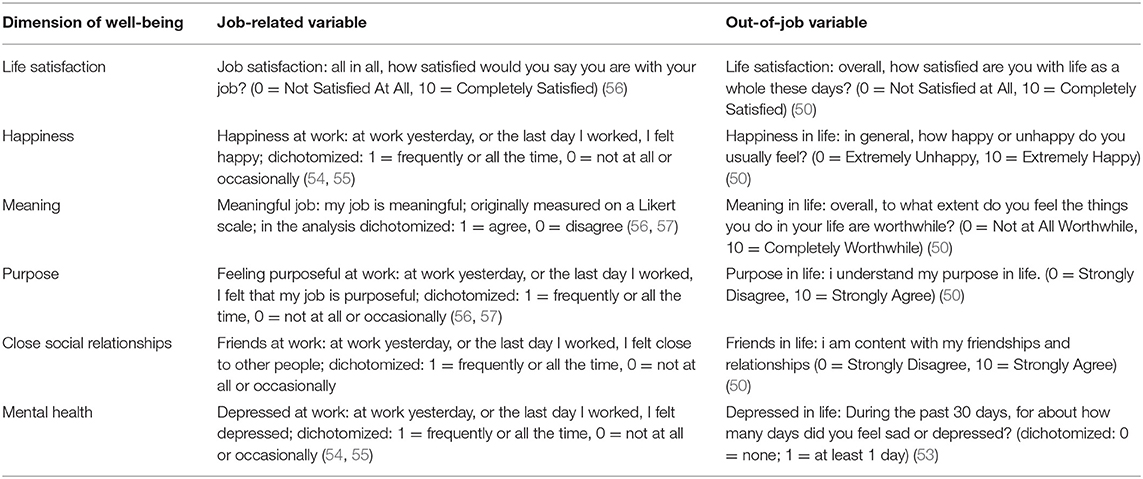
In analyzing the relationships between life-related well-being factors and their job-related counterparts, we distinguished six aspects of well-being: (1) life satisfaction and job satisfaction, (2) happiness, (3) meaning, (4) purpose, (5) social relationships, and (6) mental health. Questions measuring the first five aspects originated from the flourishing index (50–52), while the question measuring health was adopted from the set of healthy days questions of the Health-Related Quality of Life instrument (53). For each well-being question a work-related counterpart was used. Specifically, questions from an adapted version of the Positive and Negative Affect Scale (PANAS) (54) referring to work domain, i.e., from the Job-Related Affective Well-Being Scale (55) were used, as well as a question about job satisfaction and meaning and purpose at work (56, 57).
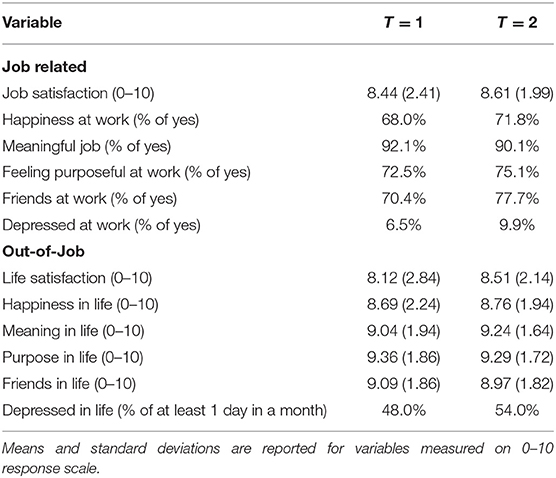
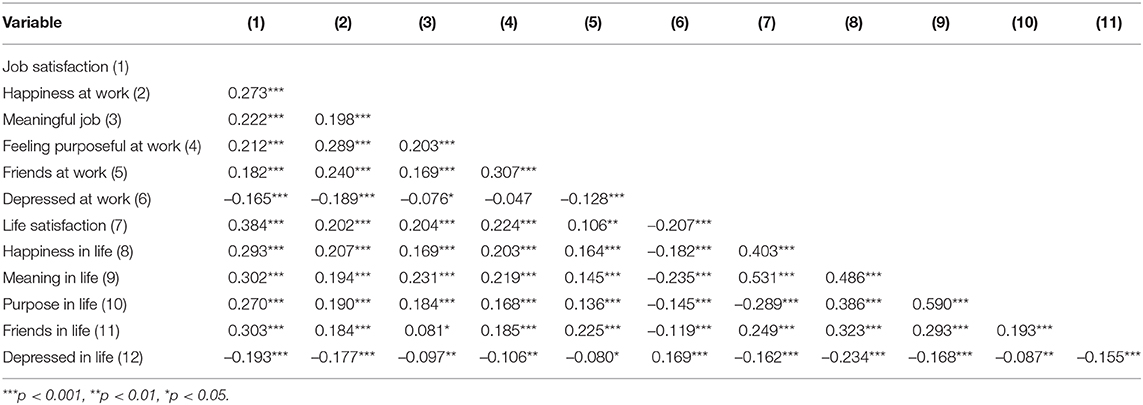
The full set of questions used to measure specific dimensions of well-being from both a life- and job-related perspective is presented in Table 2. Table 3 presents descriptive statistics of the variables in the study. Correlation matrix of the measures is provided in Table A1 in the Appendix.
Control Variables
It has been empirically shown that relationship between well-being and job attitudes may be different depending on gender, age, and education (19, 58–65) and together with job tenure, these variables are among the most commonly used as control variables in the organizational research (59). There is also evidence that marital status or having a family in general, especially in combination with a necessity of raising a child, is a discriminatory factor for happiness (66) and job attitudes (67–70). Similarly, caregiving to an elderly has a detrimental effect on well-being (71, 72), health (73), and job satisfaction and other job attitudes (74). Additionally, there are theoretical foundations and supporting empirical evidence that job demand and job control correlate with mental health and job attitudes (75, 76).
Consequently, in the analysis, we controlled for: (1) demographic variables: gender, age, marital status, education, having children below 18 at home, taking care of an elderly; and (2) job characteristics: job tenure, job demand (“I have too much work to do, to do everything well;” yes/no), job control (“I have a lot of say about what happens on my job;” yes/no), and work shift (day vs. otherwise).
In the longitudinal analysis, these variables were controlled at baseline in Wave 1, in order to ensure that they were confounders and not mediators. In the cross-sectional analysis, they were measured simultaneously with the exposure and outcome so as to compare results with the more rigorous longitudinal analyses.
Statistical Analysis
As the goal was to investigate a causal link between well-being in life and job-related well-being (i.e., how well-being in life influences job-related well-being and vice versa), longitudinal data was used and statistical approaches for modeling longitudinal data were employed. Contrary to analyses conducted on cross-sectional data, this approach offered more reliable causal evidence by virtue of the logical temporal sequence of cause and effect. However, as most of the empirical evidence in the field is based on cross-sectional data, we also ran secondary analysis on such kind of data, with the aim of assessing the level to which the relationship is inflated by the use of cross-sectional data.
The relationship was modeled using either linear regression model (for continuous outcomes), or logistic regression model (for dichotomous outcomes). With respect to dichotomous outcomes, odds ratios were reported; with respect to continuous outcomes, standardized regression estimates were provided to report standardized effect sizes.
The relationship between work-related well-being factors and their out-of-work well-being counterparts for continuous outcomes was modeled as follows:
and for dichotomous outcomes as follows:
where i = 1,…, N, k = 1,…,6.
Subscript i represents an individual, the variable WBW indicates one out of six (k = 1,…,6) work-related well-being factors, WBL is one out of six well-being in life factors. X is a vector of control variables including the first wave (T = 1) outcomes. α1reflects effects of an out-of-work well-being factor on a well-being at work outcome and β1 shows the effects of a well-being at work factor on a well-being in life outcome. α2 shows the association between control variables and the well-being at work outcome, β2 shows the association between control variables and a well-being in life outcome. ηi and εi are disturbance terms.
Robustness of the results was ensured by performing the sensitivity analysis (77) and through the design of the study's procedure to account for the common method bias (78). Sensitivity analysis was applied to assess the extent to which an unmeasured confounder would need to be associated with both the exposure and the outcome to explain away the observed association (77, 79). To this end, the E-value, which is a continuous measure of how robust the association is to potential uncontrolled confounders, was applied. The E-value is the minimum strength of association on the risk ratio scale that an unmeasured confounder would need to have with both the outcome and the primary exposure or independent variable, above and beyond the measured covariates, in order to explain away the observed association (77).
Regarding the common method bias, we accounted for it through the design of the study procedure (78). Specifically, although it was not feasible to account for a common rater and a common measurement context (as it was of crucial importance to get data from the same persons being in the same measurement context), we proximally and methodologically separated predictor, and outcome variables. Specifically, these variables were located in different sections of the questionnaire and different response scales were used, e.g., 4-point Likert scales, number of days, intensity scales, 0–10 Likert type scales (see Table 2), with different scale endpoints, and different verbal labeling. Additionally, the research team strived to ensure anonymity of respondents and reduce evaluation apprehension by (i) providing the choice to participate in the study and (ii) ensuring that participation would affect neither the employment conditions nor the employment status. Moreover, (iii) respondent might choose to not respond to any question(s) and (iv) withdraw without penalty at any time. Appropriate information about (i–iv) was conveyed in the communication campaign and also added to the invitation letter. Finally, the follow-up visits to the factories were conducted 1, 3 and 6 months after the survey administration and the individual interviews with selected workers were conducted to make sure that the workforce was not negatively affected by the participation in the study.
Analyses were performed using Stata 15.
Results
The strength of the relationships based on the longitudinal data, controlling for prior outcome (Table 4), was found to be in each case weaker—and in the case of purpose and close social relationships also insignificant—than the strength of associations revealed from the cross-sectional analysis (Table 5). This suggests that evaluations based solely on cross-sectional data could over-estimate the actual strength of the relationships, which is consistent with previous research about job satisfaction and subjective well-being (16).

Table 4. Effect sizes (standardized estimates [std. est.] and odds ratios [OR]) and 95% confidence intervals (in parentheses) for the relationships between job-related well-being factors and their out-of-job counterparts—longitudinal results.
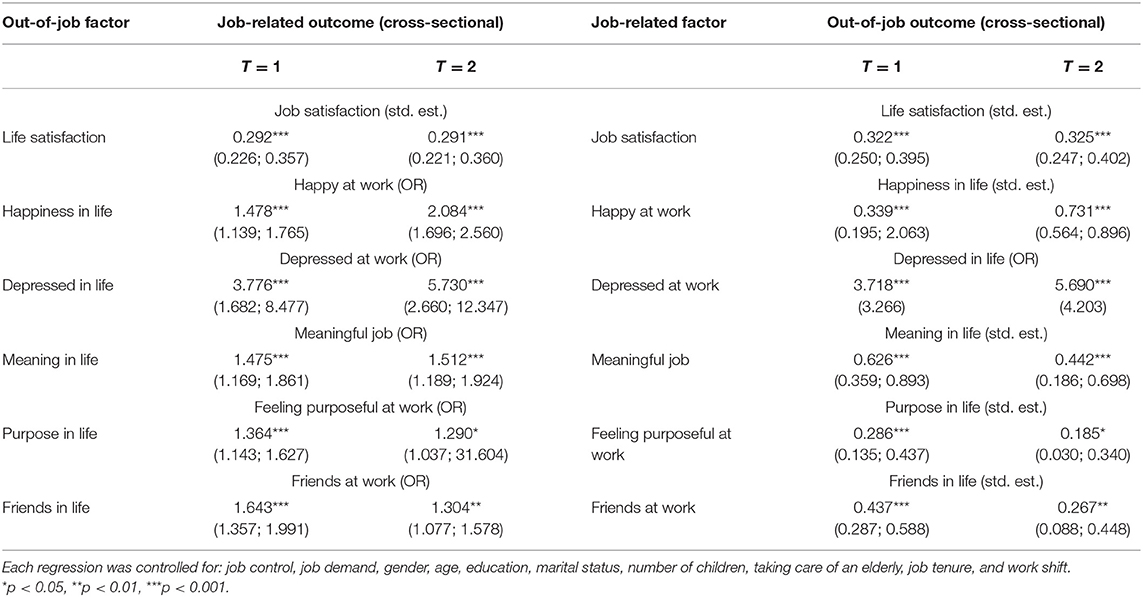

Table 5. Effect sizes (standardized estimates [std. est.] and odds ratios [OR]) and 95% confidence intervals (in parentheses) for the association between job-related factors and their out-of-job counterparts—cross-sectional results.
The effect size of the influence of life satisfaction on job satisfaction was found to be higher (0.14) than the effect size of the influence of job satisfaction on life satisfaction (0.09). Happiness in life was found to influence feelings of happiness at work and it was also the case that feelings of happiness at work influence happiness in life (effect sizes could not be directly compared as the former was assessed with an odds ratio scale and the latter with a standardized difference scale). Therefore, for both relationships—life vs. job satisfaction and happiness in life vs. at work—there is evidence that the causal relations are bi-directional, despite having different strength in the two directions. Additionally, in terms of absolute strengths, causal links in the happiness sphere turn out to be considerably stronger than those in the satisfaction sphere.
For the remaining variables, however, the evidence suggests that the causal relations may be unidirectional, with the actual links emerging from the life to the job sphere or the other way around, depending on the specific dimension. Depression was shown to increase the probability of feeling depressed at work, but reports of feeling depressed at work were not found to increase probability of feeling depressed in general. Similarly, meaning in life was found to have an impact on meaning in job, but the reverse relationship was not found to be significant. Conversely, feeling purposeful at work was found to increase purpose in life but not the other way around. We also found evidence that feeling close to people at work contributes to a sense of improved social connections in life; however, the reverse relationship was not supported by our results. We provide some further exploration of the potential reasons for these uni-directional associations in the discussion.
Sensitivity Analysis for Unmeasured Confounding
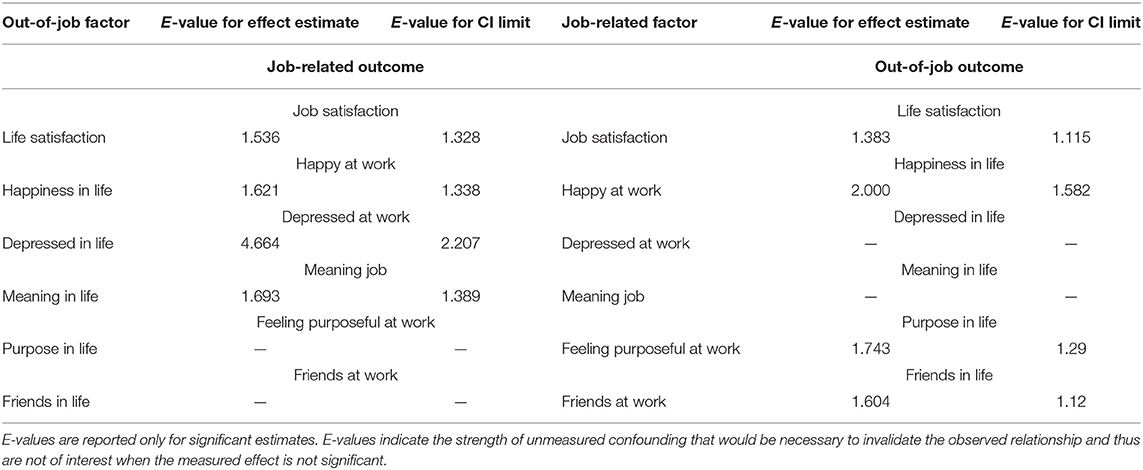
The E-values calculated for the longitudinal results (Table 6) indicate that most of the estimated associations were relatively robust to unmeasured confounding, which provides some further evidence of causality for those outcomes. The influence of job satisfaction on life satisfaction, and the relationship in the opposite direction, were moderately robust to potential unmeasured confounding. Only an unmeasured confounder that would be associated with both job satisfaction and life satisfaction by a risk ratio of 1.383 (the effect of job satisfaction on life satisfaction) and 1.536 (the effect of life satisfaction on job satisfaction), above and beyond the measured confounders, could explain away the observed association between life satisfaction and job satisfaction; weaker confounding could not. Confounders associated with both the outcome and exposure by risk ratios of 1.5-fold to 2-fold each would be required to explain the relationship between life and job: happiness, purpose, meaning, and friends, also pointing to relatively strong evidence of robustness to confounding for the link between life and job-related outcomes. An even stronger confounder would be necessary to explain away the relationship between depression in life and depression at work. The strength of association of this hypothetical confounder would have to reach at least 4.664 in terms of risk ratios, with both depression at work and depression in life in the model; and even to reduce the 95% confidence interval to include the null would require an unmeasured confounder association with both depression in life and depression at work by risk ratios of 2.2-fold each having already adjusted for all measured confounders.
Discussion and Conclusions
The results contribute to our understanding of the nature of the relationship between job satisfaction and life satisfaction, as well as between other dimensions of well-being in life and well-being at work. Generally, job satisfaction and happiness, but also purpose, and social connections while at work were found to influence their out-of-job counterparts 1 year later. With regard to the reverse direction, life satisfaction and happiness, but also depression and meaning in life were found to influence the work-related counterparts 1 year later. Thus, only for life satisfaction and happiness was there an evidence for effects running in both directions, confirming our research hypothesis about the reciprocal benefits between well-being in life and well-being at work. Other relationships were more unidirectional but not always necessarily indicative of an impact of work on life—the directionality more often acknowledged in the literature.
Our results are in some ways intuitive, but nonetheless they call for further scrutiny. Regarding happiness and life satisfaction, causal links in the happiness sphere in absolute terms turn out to be significantly stronger than those in the satisfaction sphere. This may be due to the fact that happiness, as a construct, also includes elements of coping resources and positive emotions (80), potentially eliciting more immediate connections between the work and life spheres. However, the feedback loops we found are in line with the two competing theoretical models of well-being: the bottom-up (situational) model and top-down (dispositional) model (27). The bottom-up model of well-being assumes that well-being is a sum of small pleasures. This implies, in turn, that life satisfaction and happiness may be situational and thus influenced by job satisfaction and positive affect while at work, respectively. Instead, according to the top-down model, each person tends to experience things in a particular, positive or negative way, thus well-being is dispositional (81). This is reflected in the way in which all life experiences are perceived, and in particular this implies that well-being is projected onto other variables. Specifically, the impact of life satisfaction on job satisfaction and of happiness in life on happiness while at work are anticipated. Consequently, life satisfaction and happiness may be both the cause (as in the top-down model) and the effect (as in the bottom-up model) of job satisfaction and positive affect while at work, respectively. This conclusion has been already made by other scholars, based on empirical evidence (82, 83) and on theoretical considerations conceptualized as the spillover model of well-being (18, 84, 85).
For depression, it was shown that depression in life increases the probability of feeling depressed at work, but reports of feeling depressed at work were not found to increase probability of feeling depressed in general. Depression in life is likely to manifest itself at work as its symptoms are neither temporarily limited to the periods spent out-of-work nor spatially confined to the non-working environment. However, depression at work may depend on very context-specific conditions that do not necessarily reflect a more general susceptibility to depression. In particular, the evidence on the effects of workplace stressors [e.g., prolonged job strain (86, 87), increased job demand (88, 89) and limited job control (90, 91)] on the development of depression is moderate but the level of exposure to stressors that seems to be generally needed to cause depression still requires further investigation (86, 92, 93).
Meaning in life was found to have an impact on meaning in one's job, but the reverse relationship was not corroborated. Thus, no support was found for the assertion by Steger and Dik (94), Duffy and Sedlacek (95), and Allan et al. (46) that meaning at work translates into greater meaning in life. Instead, our findings were in line with the top-down theory of subjective well-being (27) or the dispositional approach (26, 27), according to which global well-being translates into domain-specific well-being.
Specifically, meaning refers to overall relatedness in a larger sense, such as coherence and significance of one's experiences, whereas, purpose mainly refers to pursuit and aspiration of certain ends (57, 96). The one-directional causal links that we found seem to conform to intuition—with meaning, the more existential dimension, being driven by the life sphere, whereas purpose, the more goal-oriented dimension, being driven by the work sphere. This result appears to be in line with the findings of Steger and Dik (94), who report that both experiencing a calling and seeking life meaning are predictors of life meaning.
Similar to other studies (41, 42), we also found evidence that feeling close to people at work contributes to improved social connection in life. This finding corroborates Rumens' [(97), p. 1149] assertion that “workplace friendships contribute to human flourishing.” However, the reverse relationship was not supported by our results. This is again a result that conforms to intuition, as social connection at work will contribute to one's overall social well-being, but relationships outside of the workplace do not necessarily make workplace friendships any more likely. Additionally, social connection in the workplace may call for a more demanding social adaptation compared to the life sphere since, in the work environment, people have less control over the choice to associate with certain people or not, compared to their own out-of-work social environment, and the emotional control tasks in the former case are consequently more demanding (98). Additionally, it is natural that social relationships from work can spread (spill-over) into the life domain, while relationships from life are confined in the life domain. Despite recognition and effectiveness of word-of-mouth as a recruitment source (99, 100), one cannot expect to be able to often influence the hiring decisions of one's employer based on non-work-related friendship.
In contrast to the majority of other studies, we used longitudinal data thus making a substantial adjustment for confounding and control for work and life characteristics, which are known to correlate with aspects of both well-being at work and well-being in life. Although cross-sectional analyses [both ours and those of other authors; see e.g., (19)] suggest presence of moderate to strong bidirectional relationships, our longitudinal results provide evidence for potential effects in both directions, with effect sizes of roughly equal magnitude only for the relationships of life satisfaction-job satisfaction, and happiness at work-happiness in general/life. This confirms the findings of the meta-analysis of the relationship between job and life satisfaction conducted by Bowling et al. (16) on 11 (eight published and three unpublished) longitudinal studies, which may be more valid as they account for the logical and temporal sequence of cause and effect and for prior levels of outcomes. Moreover, our results here also suggest that only unidirectional effects exist concerning meaning, purpose, mental health, and social connectedness. Although the Worker Well-Being Survey was designed to target working adults and examine worker well-being, it must be also noted that our sample of Mexican manufacturing workers may reflect specific social conditions and cultural inclinations. Different samples, covering jobs with different characteristics and professional profiles, or taken in different geographical and socio-cultural contexts, might yield different results. The literature shows that cross-country variation in the dimensions, which are the object of this study, should be expected, with a possibly prominent role played by the local level of social capital (101–103). Likewise, work-related stress varies significantly across occupations (104, 105), and therefore—although we controlled for job demand and job control, which are well-known correlates of work-related stress and burnout (75, 76)—one can expect this source of variation to affect the relationship between well-being at work and in life. Consequently, there should be caution as to the generalizability of our results, and more research for different job profiles and in different geographical contexts should be carried out to gain a deeper insight. To this end, in particular, relatively more research effort should be directed toward longitudinal rather than cross-sectional studies, in order to improve our understanding of the structure of the causal relations between the work and life spheres of the other related variables of interest.
Our study made use of observational data. Most of the results presented in this study proved to be relatively robust to potential unmeasured confounding beyond a considerable number of measured potential confounders already included in the analyses. Thus, the evidence for causality was further strengthened. However, the results may still be subject to unmeasured confounding by personality, core self-evaluations, such as self-esteem, self-efficacy, locus of control and emotional stability (106, 107), as well as goal self-concordance (108). However, our sensitivity analysis indicates that, for an unmeasured confounder to explain the effect of the observed associations, it would have to be associated with both job-related and out-of-job well-being factors by a risk ratio equal in magnitude to at least 1.383, while in order to explain away the relationship between general depression and work-related depression an unmeasured confounder related to both measures of depression by more than four on the risk-ratio scale would be required.
We used two waves of data, which let us control for the baseline outcomes. However, future research should consider replicating the results using more waves of data to control also for the baseline exposure. Such analysis will provide further evidence for the robustness of our results.
Finally, in the analyses we relied on single item measures of well-being dimensions. Although it is a common practice to use multi-item measures in such a case, we argue that long instruments—despite the advantages of conceptual richness—are inferior to short instruments in studies focusing on a vast array of topics. Workers' well-being study measures well-being along with physical and psycho-social working conditions, work safety and occupational health, job burden, job autonomy, job resources, work-family conflict, and others. In such a setting, a less time-consuming instrument may be beneficial. By being short enough for practical use in the workplace, it facilitates company's efforts to improve the worker well-being (32). Criticism of short instruments—especially those with one item per domain—relates to elevated Type 1 and Type 2 error probabilities [see (109)] for evidence in the personality studies). Yet, such instruments can still be found in psychology (110, 111), educational psychology (112) and organizational behavior (113), among others. In the well-being field, it is worth noting that the United Kingdom Office for National Statistics—to avoid excessive costs and to enable widespread use—since 2011 includes a set of only four well-being questions in the UK National Survey (114).
In sum, we concede that work is just one arena to enhance well-being, however, given the amount of time spent at work across our lifetimes, seemingly a powerful one. Therefore, understanding the well-being ecosystem for impact areas and reciprocal relationships in life and at work is important to finding ways to intervene. Without this holistic view, the leverage points for optimizing well-being may be invisible or inadequate by an overemphasis or attribution to one sphere of influence only.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health Institutional Review Board. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
DW-B developed the study concept, contributed to data analysis and interpretation of the result, drafted the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript. PB contributed to data analysis and interpretation of the result, drafted the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript. PS contributed to interpretation of the results, drafted the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript. TV contributed to interpretation of the results, revised the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript. EM developed the study design, revised the manuscript and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation under the grant No. 74275 Building a Culture of Health: A Business Leadership Imperative and by the Levi Strauss Foundation under the grant Follow up of Well-being measures in Mexico, China, Cambodia, and Sri Lanka.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Footnotes
1. ^SWB is defined as either a cognitive or affective evaluation of life, and is usually assessed for life as a whole, or for specific facets (e.g., life at work).
References
1. Rosner D, Markowitz GE. Dying for Work: Workers' Safety and Health in Twentieth-Century America. Bloomington, Indianapolis, IN: Indiana University Press (1989).
2. Neve J, Krekel C, Ward G. Work and well-being: a global perspective. In: Global Happiness Council, editor. Global Happiness Policy Report. Dubai: Global Happiness Council (2018). p. 74–128.
3. Litchfield P, Cooper C, Hancock C, Watt P. Work and wellbeing in the 21st century. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2016) 13:1–11. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13111065
4. Sorensen G, Sparer E, Williams JAR, Gundersen D, Boden LI, Dennerlein JT, et al. Measuring best practices for workplace safety, health and wellbeing: the workplace integrated safety and health assessment. J Occup Environ Med. (2018) 60:430–9. doi: 10.1097/JOM.0000000000001286
5. Sorensen G, Peters S, Nielsen K, Nagler E, Karapanos M, Wallace L, et al. Improving working conditions to promote worker safety, health, and well-being for low-wage workers: the workplace organizational health study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:1–16. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16081449
6. Schulte PA, Guerin RJ, Schill AL, Bhattacharya A, Cunningham TR, Pandalai SP, et al. Considerations for incorporating “well-being” in public policy for workers and workplaces. Am J Public Health. (2015) 105:e31–44. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302616
7. Tate DG. Workers' disability and return to work. Am J Phys Med Rehab. (1992) 71:92–6. doi: 10.1097/00002060-199204000-00006
8. Turner JA, Franklin G, Fulton-Kehoe D, Egan K, Wickizer TM, Lymp JF, et al. Prediction of chronic disability in work-related musculoskeletal disorders: a prospective, population-based study. BMC Musculoskeletal Disord. (2004) 5:1–7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-5-14
9. Chin-Lung C, Tzu-Yu L. Risk for occupational injury of handicapped workers in Taiwan. Percept Motor Skills. (2001) 93:89–94. doi: 10.2466/pms.2001.93.1.89
10. Tamers SL, Chosewood LC, Childress A, Hudson H, Nigam J, Chang CC. Total worker health® 2014–2018: the novel approach to worker safety, health, and well-being evolves. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:e321. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16030321
11. Schill AL. Advancing well-being through total worker health®. Workplace Health Safety. (2017) 65:158–63. doi: 10.1177/2165079917701140
12. Hudson HL, Nigam JAS, Sauter SL, Casey Chosewood L, Schill AL, Howard J. Total Worker Health. Washington DC: American Psychological Association (2019). doi: 10.1037/0000149-000
13. WHO. Healthy Workplaces: A Model for Action. For Employers, Workers, Policy-Makers and Practitioners. Geneva: World Health Organization (2010).
14. Eurofound. Sustainable Work throughout the Life Course: National Policies and Strategies. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union (2016).
15. Schulte PA, Delclos G, Felknor SA, Chosewood LC. Toward an expanded focus for occupational safety and health: a commentary. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:44946. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16244946
16. Bowling NA, Eschleman KJ, Wang Q. A meta-analytic examination of the relationship between job satisfaction and subjective well-being. J Occup Organ Psychol. (2010) 83:915–34. doi: 10.1348/096317909X478557
17. Judge TA, Watanabe S. Another look at the job satisfaction-life satisfaction relationship. J Appl Psychol. (1993) 78:939–48. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.78.6.939
18. Rain JS, Lane IM, Steiner DD. A current look at the job satisfaction/life satisfaction relationship: review and future considerations. Hum Relations. (1991) 44:287–307. doi: 10.1177/001872679104400305
19. Tenney ER, Poole JM, Diener E. Does positivity enhance work performance?: why, when, and what we don't know. Res Organ Behav. (2016) 36:27–46. doi: 10.1016/j.riob.2016.11.002
20. Weitz J. A neglected concept in the study of job satisfaction. Person Psychol. (1952) 5:201–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.1952.tb01012.x
21. Erdogan B, Bauer TN, Truxillo DM, Mansfield LR. Whistle while you work: a review of the life satisfaction literature. J Manage. (2012) 38:1038–83. doi: 10.1177/0149206311429379
22. Nohe C, Meier LL, Sonntag K, Michel A. The chicken or the egg? a meta-analysis of panel studies of the relationship between work – family conflict and strain. J Appl Psychol. (2014) 102:522–36. doi: 10.1037/a0038012
23. Nohe C, Sonntag K. Work-family conflict, social support, and turnover intentions: a longitudinal study. J Vocation Behav. (2014) 85:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2014.03.007
24. Near JP, Sorcinelli MD. Work and life away from work: predictors of faculty satisfaction. Res Higher Edu. (1986) 25:377–94. doi: 10.1007/BF00992133
25. Rice RW, Near JP, Hunt RG. The job-satisfaction/life-satisfaction relationship: a review of empirical research. Basic Appl Soc Psychol. (1980) 1:37–64. doi: 10.1207/s15324834basp0101_4
26. Staw BM, Bell E, John A. The dispositional approach to job attitudes: a lifetime longitudinal test. Admin Sci Quart. (1986) 31:56–77. doi: 10.2307/2392766
27. Diener E. Subjective well-being. Psychol Bulletin. (1984) 95:542–75. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.95.3.542
28. Judge TA, Thoresen CJ, Bono JE, Patton GK. The job satisfaction—job performance relationship: a qualitative and quantitative review. Psychol Bulletin. (2001) 127:376–407. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.127.3.376
29. Steiner DD, Truxillo DM. Another look at the job satisfaction-life satisfaction relationship: a test of the disaggregation hypothesis. J Occup Behav. (1987) 8:71–7. doi: 10.1002/job.4030080109
30. Weiss HM. Deconstructing job satisfaction separating evaluations, beliefs and affective experiences. Hum Resour Manage Rev. (2002) 12:173–94. doi: 10.1016/S1053-4822(02)00045-1
31. Zheng X, Zhu W, Zhao H, Zhang CHI. Employee well-being in organizations: theoretical model, scale development, and cross-cultural validation. J Organ Behav. (2015) 36:621–44. doi: 10.1002/job.1990
32. Weziak-Bialowolska D, McNeely E, VanderWeele TJ. Flourish index and secure flourish index—validation in workplace settings. Cogent Psychol. (2019) 6:1–10. doi: 10.1080/23311908.2019.1598926
33. Bartels AL, Peterson SJ, Reina CS. Understanding well-being at work: development and validation of the eudaimonic workplace well-being scale. PLoS ONE. (2019) 14:1–21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215957
34. Nielsen K, Nielsen MB, Ogbonnaya C, Känsälä M, Saari E, Isaksson K. Workplace resources to improve both employee well-being and performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Work Stress. (2017) 31:101–20. doi: 10.1080/02678373.2017.1304463
35. Keeman A, Näswall K, Malinen S, Kuntz J. Employee wellbeing: evaluating a wellbeing intervention in two settings. Front Psychol. (2017) 8:505. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00505
36. Chiron B, Michinov E, Olivier-Chiron E, Laffon M, Rusch E. Job satisfaction, life satisfaction and burnout in French. J Health Psychol. (2010) 15:948–58. doi: 10.1177/1359105309360072
37. Hombrados-Mendieta I, Cosano-Rivas F. Burnout, workplace support, job satisfaction and life satisfaction among social workers in Spain: a structural equaltion model. Int Soc Work. (2011) 56:228–46. doi: 10.1177/0020872811421620
38. Iris B, Barrett GV. Some relations between job and life satisfaction and job importance. J Appl Psychol. (1972) 56:301–4. doi: 10.1037/h0033095
39. Haar JM, Russo M, Suñe A, Ollier-Malaterre A. Outcomes of work—life balance on job satisfaction, life satisfaction and mental health : a study across seven cultures. J Vocation Behav. (2014) 85:361–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2014.08.010
40. Reynolds J, McKinzie AE. Riding the waves of work and life: explaining long-term experiences with work hour mismatches. Soc Forces. (2019) 98:427–60. doi: 10.1093/sf/soy112
41. Sias PM, Cahill DJ. From coworkers to friends: the development of peer friendships in the workplace. Western J Commun. (1998) 62:273–99. doi: 10.1080/10570319809374611
42. Morrison RL, Cooper-Thomas HD. Friendship among coworkers. In: Hojjat M, Moyer A, editor. The Psychology of Friendship. New York, NY: Oxford University Press (2016). p. 123–40. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780190222024.003.0008
43. Sjoberg O. Social insurance as a collective resource: unemployment benefits, job insecurity and subjective well-being in a comparative perspective. Soc Forces. (2010) 88:1281–304. doi: 10.1353/sof.0.0293
44. Iverson RD, Maguire C. The relationship between job and life satisfaction: evidence from a remote mining community. Hum Relations. (2000) 53:807–39. doi: 10.1177/0018726700536003
45. Michalos AC. Satisfaction and happiness. Soc Indicat Res. (1980) 8:385–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00461152
46. Allan BA, Duffy RD, Douglass R. Meaning in life and work: a developmental perspective. J Positive Psychol. (2015) 10:323–31. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2014.950180
47. Bronk KC. The Role of Purpose in Optimal Human Functioning. Purpose in Life. A Critical Component of Optimal Youth Development. Dordrecht: Springer (2014). doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-7491-9_3
48. Warr P. A conceptual framework for the study of work and mental health. Work Stress. (1994) 8:84–97. doi: 10.1080/02678379408259982
49. Ambrey C, Ulichny J, Fleming C. The social connectedness and life satisfaction nexus: a panel data analysis of women in Australia. Feminist Econ. (2017) 23:1032. doi: 10.1080/13545701.2016.1222077
50. VanderWeele TJ. On the promotion of human flourishing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2017) 114:8148–56. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1702996114
51. VanderWeele TJ, McNeely E, Koh HK. Reimagining health—flourishing. JAMA. (2019) 321:1667–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.3035
52. Weziak-Bialowolska D, McNeely E, VanderWeele TJ. Human flourishing in cross cultural settings evidence from the US, China, Sri Lanka, Cambodia, and Mexico. Front Psychol. (2019) 10:e1269. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01269
53. Moriarty DG, Zack MM, Kobau R. The centers for disease control and prevention's healthy days measures—population tracking of perceived physical and mental health over time. Health Qual Life Outcome. (2003) 1:1–8. doi: 10.1186/1477-7525-1-37
54. Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A. Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS scales. J Personal Soc Psychol. (1988) 54:1063–70. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063
55. Katwyk PTV, Fox S, Specter PE, Kelloway EK. Using the job-related affective well-being scale (JAWS) to investigate affective responses to work stressors. J Occup Health Psychol. (2000) 5:219–30. doi: 10.1037/1076-8998.5.2.219
56. Daley DM. Humanistic management and organizational success: the effect of job and work environment on organizationa effectiveness, public responsiveness, and job satisfaction. Publ Person Manage. (1986) 15:131–42. doi: 10.1177/009102608601500204
57. George LS, Park CL. Are meaning and purpose distinct? an examination of correlates and predictors. J Positive Psychol. (2013) 8:365–75. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2013.805801
58. Chow A, Galambos NL, Krahn HJ. Work values during the transition to adulthood and mid-life satisfaction: cascading effects across 25 years. Int J Behav Dev. (2017) 41:105–14. doi: 10.1177/0165025415608518
59. Bernerth JB, Aguinis H. A critical review and best-practice recommendations for control variable usage. Personnel Psychol. (2016) 69:229–83. doi: 10.1111/peps.12103
60. Batz-Barbarich C, Tay L, Kuykendall L, Cheung HK. A meta-analysis of gender differences in subjective well-being: estimating effect sizes and associations with gender inequality. Psychol Sci. (2018) 29:1491–503. doi: 10.1177/0956797618774796
61. Kaiser LC. Gender-job satisfaction differences across Europe. Int J Manpower. (2007) 28:75–94. doi: 10.1108/01437720710733483
62. Westover JH. The job satisfaction-gender paradox revisited. J Glob Responsibil. (2012) 3:263–77. doi: 10.1108/20412561211260557
63. Sousa-Poza A, Sousa-Poza AA. Taking another look at the gender/job-satisfaction paradox. Kyklos. (2000) 53:135–52. doi: 10.1111/1467-6435.00114
64. Grönlund A, Öun I. The gender-job satisfaction paradox and the dual-earner society: are women (still) making work-family trade-offs? Work. (2018) 59:535–45. doi: 10.3233/WOR-182708
65. Clark AE. Job satisfaction and gender: why are women so happy at work? Lab Econ. (1997) 1:341–72. doi: 10.1016/S0927-5371(97)00010-9
66. Baranowska-Rataj A, Matysiak A, Mynarska M. Does lone motherhood decrease women's happiness? evidence from qualitative and quantitative research. J Happiness Stud. (2013) 15:1457–77. doi: 10.1007/s10902-013-9486-z
67. Booth AL, van Ours JC. Job satisfaction and family happiness: the part-time work puzzle. Econ J. (2008) 118:F77–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0297.2007.02117.x
68. Scandura TA, Lankau MJ. Relationships of gender family responsibility and flexible work hours. J Organ Behav. (1997) 18:377–91. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1379(199707)18:4<377::AID-JOB807>3.0.CO;2-1
69. Grandey AA, Cordeiro BL, Crouter AC. A longitudinal and multi-source test of the work–family conflict and job satisfaction relationship. J Occup Organ Psychol. (2005) 78:305–23. doi: 10.1348/096317905X26769
70. Saltzstein AL, Ting Y, Saltzstein GH. Work-family balance and job satisfaction: the impact of family-friendly policies on attitudes of federal government employees. Publ Admin Rev. (2003) 61:452–67. doi: 10.1111/0033-3352.00049
71. Pinquart M, Sörensen S. Associations of caregiver stressors and uplifts with subjective well-being and depressive mood: a meta-analytic comparison. Aging Mental Health. (2004) 8:438–49. doi: 10.1080/13607860410001725036
72. Haley WE, LaMonde LA, Han B, Burton AM, Schonwetter R. Predictors of depression and life satisfaction among spousal caregivers in hospice: application of a stress process model. J Palliative Med. (2004) 6:215–24. doi: 10.1089/109662103764978461
73. Beach SR, Schulz R, Yee JL, Jackson S. Negative and positive health effects of caring for a disabled spouse: longitudinal findings from the caregiver health effects study. Psychol Aging. (2000) 15:259–71. doi: 10.1037/0882-7974.15.2.259
74. Engström M, Wadensten B, Häggström E. Caregivers' job satisfaction and empowerment before and after an intervention focused on caregiver empowerment. J Nurs Manage. (2010) 18:14–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2834.2009.01047.x
75. Karasek R, Brisson C, Kawakami N, Houtman I, Bongers P, Amick B. The job content questionnaire (JCQ): an instrument for internationally comparative assessments of psychosocial job characteristics. J Occup Health Psychol. (1998) 3:322–55. doi: 10.1037/1076-8998.3.4.322
76. Karasek RA. Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job redesign. Admin Sci Quart. (1979) 24:285–308. doi: 10.2307/2392498
77. VanderWeele TJ, Ding P. Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the E-value. Ann Intern Med. (2017) 167:268–74. doi: 10.7326/M16-2607
78. Podsakoff PM, MacKenzie SB, Yeon Lee J, Podsakoff NP. Common method biases in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. J Appl Psychol. (2003) 88:879–903. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.88.5.879
79. Ding P, Vanderweele V. Sensitivity analysis without assumptions. Epidemiology. (2016) 27:368–77. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000457
80. Cohn MA, Fredrickson BL, Brown SL, Conway AM. Happines unpacked: positive emotions increase life satisfaction by building resilience. Emotions. (2009) 9:361–8. doi: 10.1037/a0015952
81. Judge TA, Hulin CL. Job satisfaction as a reflection of disposition: a multiple source causal analysis. Organ Behav Hum Decision Processes. (1993) 56:388–421. doi: 10.1006/obhd.1993.1061
82. Headey B, Muffel R. Two-Way Causation in Life Satisfaction Research: Structural Equation Models With Granger-Causation. IZA Discussion Paper, no. 8665. (2014). Available online at: https://www.iza.org/publications/dp/8665/two-way-causation-in-life-satisfaction-research-structural-equation-models-with-granger-causation (accessed April 01, 2020).
83. Headey B, Veenhoven R, Wearing A. Top-down versus bottom-up theories of subjective well-being. Soc Indicat Res. (1991) 24:81–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00292652
84. Heller D, Judge TA, Watson D. The confounding role of personality and trait affectivity in the relationship between job and life satisfaction. J Organ Behav. (2002) 23:815–35. doi: 10.1002/job.168
85. Champoux JE. A sociological perspective on work involvement. Appl Psychol. (1981) 30:65–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-0597.1981.tb00980.x
86. Madsen IEH, Nyberg ST, Magnusson Hanson LL, Ferrie JE, Ahola K, Alfredsson L, et al. Job strain as a risk factor for clinical depression: systematic review and meta-analysis with additional individual participant data. Psychol Med. (2017) 47:1342–56. doi: 10.1017/S003329171600355X
87. Stansfeld SA, Shipley MJ, Head J, Fuhrer R. Repeated job strain and the risk of depression: longitudinal analyses from the Whitehall Ii Study. Am J Public Health. (2012) 102:2360–6. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2011.300589
88. Sanne B, Mykletun A, Dahl AA, Moen BE, Tell GS. Testing the job demand-control-support model with anxiety and depression as outcomes: the Hordaland Health Study. Occup Med. (2005) 55:463–73. doi: 10.1093/occmed/kqi071
89. Muntaner C, Li Y, Xue X, Thompson T, O'Campo P, Chung H, et al. County level socioeconomic position, work organization and depression disorder: a repeated measures cross-classified multilevel analysis of low-income nursing home workers. Health Place. (2006) 12:688–700. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2005.09.004
90. Saijo Y, Chiba S, Yoshioka E, Nakagi Y, Ito T, Kitaoka-Higashiguchi K, et al. Synergistic interaction between job control and social support at work on depression, burnout, and insomnia among Japanese Civil Servants. Int Archiv Occup Environ Health. (2015) 88:143–52. doi: 10.1007/s00420-014-0945-6
91. Bentley RJ, Kavanagh A, Krnjacki L, LaMontagne AD. A longitudinal analysis of changes in job control and mental health. Am J Epidemiol. (2015) 182:328–34. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwv046
92. Netterstrøm B, Conrad N, Bech P, Fink P, Olsen O, Rugulies R, et al. The relation between work-related psychosocial factors and the development of depression. Epidemiol Rev. (2008) 30:118–32. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxn004
93. Theorell T, Hammarström A, Aronsson G, Bendz LT, Grape T, Hogstedt C, et al. A systematic review including meta-analysis of work environment and depressive symptoms. BMC Public Health. (2015) 15:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-1954-4
94. Steger MF, Dik BJ. If one is looking for meaning in life, does it help to find meaning in work? Appl Psychol. (2009) 1:303–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-0854.2009.01018.x
95. Duffy RD, Sedlacek WE. The presence of and search for a calling: connections to career development. J Vocation Behav. (2007) 70:590–601. doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2007.03.007
96. King LA, Hicks JA, Krull JL, Del Gaiso AK. Positive affect and the experience of meaning in life. J Personal Soc Psychol. (2006) 90:179–96. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.90.1.179
97. Rumens N. Researching workplace friendships: drawing insights from the sociology of friendship. J Soc Person Relationships. (2017) 34:1149–67. doi: 10.1177/0265407516670276
98. James N. Emotional labour: skill and work in the social regulation of feelings. Sociol Rev. (1989) 37:15–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-954X.1989.tb00019.x
99. Hoye GV, Weijters B, Lievens F, Stockman S. Social influences in recruitment: when is word-of-mouth most effective? Int J Select Assessment. (2016) 24:42–52. doi: 10.1111/ijsa.12128
100. Hoye GV, Lievens F. Tapping the grapevine: a closer look at word-of-mouth as a recruitment source. J Appl Psychol. (2009) 94:341–52. doi: 10.1037/a0014066
101. Bjørnskov C. The happy few: cross-country evidence on social capital and life satisfaction. Kyklos. (2003) 56:3–16. doi: 10.1111/1467-6435.00207
102. Huang X, Van de Vliert E. Where intrinsic job satisfaction fails to work: national moderators of intrinsic motivation. J Organ Behav. (2003) 24:159–79. doi: 10.1002/job.186
103. Gundelach P, Kreiner S. Happiness and life satisfaction in advanced European countries. Cross-Cultural Res. (2004) 38:359–86. doi: 10.1177/1069397104267483
104. Shin JC, Jung J. Academics job satisfaction and job stress across countries in the changing academic environments. Higher Edu. (2014) 67:603–20. doi: 10.1007/s10734-013-9668-y
105. Johnson S, Cooper C, Cartwright S, Donald I, Taylor P, Millet C. The experience of work-related stress across occupations. J Manag Psychol. (2005) 20:178–87. doi: 10.1108/02683940510579803
106. Judge TA, Bono JE. Relationship of core self-evaluations traits—self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control, and emotional stability—with job satisfaction and job performance: a meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol. (2001) 86:80–92. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.86.1.80
107. Judge TA, Locke EA, Durham CC, Kluger AN. Dispositional effects on job and life satisfaction: the role of core evaluations. J Appl Psychol. (1998) 83:17–34. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.83.1.17
108. Judge TA, Bono JE, Erez A, Locke EA. Core self-evaluations and job and life satisfaction: the role of self-concordance and goal attainment. J Appl Psychol. (2005) 90:257–68. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.90.2.257
109. Credé M, Harms P, Niehorster S, Gaye-Valentine A. An evaluation of the consequences of using short measures of the big five personality traits. J Personal Soc Psychol. (2012) 102:874–88. doi: 10.1037/a0027403
110. Maples JL, Lamkin J, Miller JD. A test of two brief measures of the dark triad: the dirty dozen and short dark triad. Psychol Assess. (2014) 26:326–31. doi: 10.1037/a0035084
111. Jonason PK, Webster GD. The dirty dozen: a concise measure of the dark triad. Psychol Assess. (2010) 22:420–32. doi: 10.1037/a0019265
112. Ugen S, Keller U, Preckel F, Martin R, Fischbach A, Gogol K, et al. ‘My questionnaire is too long!' the assessments of motivational-affective constructs with three-item and single-item measures. Contemp Edu Psychol. (2014) 39:188–205. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2014.04.002
113. Liden RC, Wayne SJ, Meuser JD, Hu J, Wu J, Liao C. Servant leadership: validation of a short form of the SL-28. Lead Quart. (2015) 26:254–69. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2014.12.002
114. Allin P, Hand DJ. New statistics for old?—measuring the wellbeing of the UK. J Royal Statist Soc A. (2017) 180:3–43. doi: 10.1111/rssa.12188
Appendix
Keywords: well-being in life, well-being at work, health, job and life satisfaction, happiness, meaning and purpose in life and at work, social relationships
Citation: Weziak-Bialowolska D, Bialowolski P, Sacco PL, VanderWeele TJ and McNeely E (2020) Well-Being in Life and Well-Being at Work: Which Comes First? Evidence From a Longitudinal Study. Front. Public Health 8:103. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00103
Received: 11 January 2020; Accepted: 16 March 2020;
Published: 09 April 2020.
Edited by:
Marissa G. Baker, University of Washington, United StatesReviewed by:
Trevor K. Peckham, University of Washington, United StatesKyoung-Mu Lee, Korea National Open University, South Korea
Copyright © 2020 Weziak-Bialowolska, Bialowolski, Sacco, VanderWeele and McNeely. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dorota Weziak-Bialowolska, ZG93ZXppYWtAaHNwaC5oYXJ2YXJkLmVkdQ==
 Dorota Weziak-Bialowolska
Dorota Weziak-Bialowolska Piotr Bialowolski1
Piotr Bialowolski1 Pier Luigi Sacco
Pier Luigi Sacco