- 1Sinopec, Northwest Oilfield Company, Urumqi, China
- 2Jiangsu Oilfield Company, No. 2 Oil Production Plant, Huaian, China
- 3Beijing Precise Energy Technology Co. Ltd., Beijing, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Exploration Technologies for Oil and Gas Resources, Ministry of Education, Yangtze University, Wuhan, China
Condensate gas reservoirs in the second area of the Shunbei Oilfield in the Tarim Basin, China have undergone multiple stages of tectonic movements, resulting in complex structural patterns and reservoir characteristics. These reservoirs face significant development challenges, including rapid production decline, limited reservoir reconstruction methods, and weak well pattern control capabilities. To enhance their stable production capacity, this study employs a comprehensive approach involving geological analysis, seismic reflection characteristics research, geological data analysis, and bottom water discrimination methods to systematically investigate the Shunbei condensate gas reservoir. The results indicate that structural characteristics significantly influence the formation of reservoirs and the distribution of oil and gas reserves. Long-term fault activity is conducive to the development of large-scale reservoirs. Reservoir connectivity and physical properties play a crucial role in production performance. Optimizing reservoir reconstruction parameters can enhance both production and stable production capacity of oil and gas wells. However, sealed water conditions during development and strong bottom water presence are unfavorable for production capacity. Based on these findings, a quantitative evaluation index system for assessing the stable production capacity of carbonate reservoirs has been successfully established. This system clarifies the importance and weight relationships of factors such as fracture activity intensity, fracture background, and water body influence. The system has been validated through its application in the No. 4 and No. 8 belts, although practical application still requires careful consideration of the complex geological conditions. The research outcomes provide a critical foundation for evaluating the stable production capacity of carbonate reservoirs and formulating effective oil and gas field development strategies. These insights contribute to improving the overall efficiency and sustainability of oil and gas field developments.
1 Introduction
In global exploration and development of oil and gas, carbonate reservoirs play a crucial role as storage spaces for hydrocarbons (Ma et al., 2019; Atmadibrata et al., 2019; Esrafili-Dizaji and Rahimpour-Bonab, 2019; Hu et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2024). However, due to their unique geological structures and complex reservoir characteristics, maintaining stable production from carbonate reservoirs faces numerous challenges. For instance, the carbonate reservoirs in the Khuff Oil Field (Rahim and Al-Qahtani et al., 2003; Khan et al., 2019; Sabouhi et al., 2024) in the Middle East suffer from low efficiency in well pattern deployment due to complex geological structures; the Yibal Oil Field (Aoudia et al., 2010) experiences a relatively low recovery rate due to high-salinity and high-temperature conditions; and the Tahe Oil Field faces a sharp production decline caused by water influx (Liu and Chen, 2010; Liao et al., 2024). The fracture-reservoir-aquifer coupling evaluation system developed in this study, compared to the production enhancement techniques used in the Khuff Oil Field, places greater emphasis on quantitative weight allocation of multi-factor interactions. It has been successfully validated in the Shunbei Oil Field, providing a novel reference for addressing the development challenges of similar reservoirs worldwide (Wu et al., 2010; Hosseini et al., 2024).
Compared with globally representative carbonate reservoirs, such as the Wolfcamp Formation (Permian Basin, USA) (Hennenfent et al., 2015; Alvarez and Schechter, 2017; Male et al., 2023; Ramiro-Ramirez et al., 2024) and the Asmari Formation (Zagros Fold Belt, Middle East) (Awdal et al., 2016; Moradi et al., 2024; Taheri et al., 2024; Tong et al., 2024; Fallah-Bagtash et al., 2025), the Shunbei Oilfield in the Tarim Basin exhibits distinct uniqueness in its ultra-deep, high-temperature, high-pressure environments and multi-phase tectonic superimposition (Yuan et al., 2021; Mou et al., 2023; Dang et al., 2024; Deng et al., 2024). Research on its sustained production mechanisms provides critical insights for global carbonate reservoir development. Consequently, the Shunbei Oilfield occupies a unique and representative position in worldwide carbonate reservoir studies. Geologically, it is located in the Shuntuoguole low uplift of the Tarim Basin. The region has undergone multiple complex tectonic movements, resulting in pronounced basement differentiation and a highly intricate tectonic pattern influenced by the interaction of various tectonic units (Deng et al., 2023). This complex tectonic setting is relatively rare among global carbonate reservoirs, making it an exceptional natural laboratory for investigating the impact of tectonic activity on reservoir formation and evolution. In terms of reservoir characteristics, the Shunbei Oilfield is classified as an ultra-deep, high-temperature, high-pressure, fault-controlled fracture-cavity carbonate reservoir with exceptionally strong heterogeneity. The reservoir types are diverse, encompassing fractured, fractured-cavity, and cavity reservoirs. The development characteristics and distribution patterns of these reservoirs are unique, differing significantly from those of most carbonate reservoirs worldwide. This makes the Shunbei Oilfield an exemplary case for studying complex reservoir characteristics. Regarding development conditions, the Shunbei Oilfield presents formidable challenges due to its high temperature, high pressure, and complex reservoir conditions. These conditions demand advanced drilling, completion, oil production, and reservoir reconstruction technologies. The specific and typical problems encountered during its development provide invaluable practical experience and research data for the development of similar reservoirs globally (Ma et al., 2022; Yun and Deng, 2022; Bu et al., 2023; Ni et al., 2023).
Although extensive research has been conducted on the stable production capacity of condensate gas reservoirs, achieving notable results (Qadir et al., 2011; Xu et al., 2019; Jiang et al., 2021), significant deficiencies remain in the current studies focusing on the Shunbei carbonate reservoirs. The existing evaluation index system is imperfect, hindering a comprehensive and accurate assessment of their stable production capacity. Moreover, the employed evaluation methodologies lack scientific rigor, complicating the formulation of precise decisions during actual development processes. These issues critically impede the efficient exploitation of the Shunbei oil and gas field, manifesting as rapid production decline, limited reservoir stimulation techniques, and insufficient well pattern control capabilities, which have become increasingly pronounced (Xiao et al., 2012; Guo et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2020). Against the backdrop of continuously growing global energy demands and the gradual depletion of conventional oil and gas resources, the efficient development of complex carbonate reservoirs such as those in the Shunbei Oilfield becomes crucial for alleviating energy pressures. Failure to address the challenges faced by the Shunbei Oilfield promptly could result not only in resource wastage but also adversely affect regional energy supply and economic development. Consequently, there is an urgent need to investigate and enhance its stable production capacity.
In recent years, advancements in petroleum exploration and development techniques have deepened the understanding of carbonate reservoirs (Wang L. Y. et al., 2024). The application of modern geophysical techniques (Wang et al., 2022; Li F. L. et al., 2024), geological modeling (Khalid et al., 2022; Xie et al., 2023), and numerical simulation techniques (Su et al., 2024) has provided robust tools for studying carbonate reservoirs. Additionally, the continuous development of reservoir stimulation (Gao et la., 2023; Li P. H. et al., 2024) and enhanced recovery techniques (Li et al., 2023) has provided technical support for efficient development. Nevertheless, challenges persist, such as unsatisfactory reservoir stimulation outcomes and the high costs of enhanced recovery technologies. Thus, further study is needed to explore more effective development techniques and management strategies for carbonate reservoirs.
In this study, we focused on the gas-condensate reservoir in Block 2 in the Shunbei Oilfield. By comprehensively analyzing the regional structural characteristics, hydrocarbon reservoir structures, controlling influence of faults on the hydrocarbon reservoirs, reservoir characteristics, effects of reservoir stimulation, and influence of bottom water on productivity, we aimed to investigate the stable production capacity of these carbonate reservoirs. The key factors affecting the stable production capacity were identified, and a scientific and rational quantitative evaluation index system was established, providing a theoretical foundation for the efficient development of the Shunbei gas-condensate reservoir.
2 Geologic background and overview of the study area
The Shunbei Oilfield is located in the Shuntuogole low uplift in the Tarim Basin, China, an area of significant tectonic importance that has undergone complex tectonic evolution (Qi, 2020; Zhang et al., 2022). During the Caledonian period, plate extrusion caused the basement to fold and fracture, forming the initial fault structures. In the Hercynian period, an extensional stress field further activated these faults, creating fault basins. Sedimentary carbonate strata formed the reservoir base, with fault activity and karstification promoting reservoir development. In the Himalayan period, plate collision led to strong tectonic deformation, reactivating fractures and forming a complex fault system. This system acted as a key pathway for oil and gas migration, influencing their direction and accumulation sites. Fold structures also facilitated the migration and entrapment of hydrocarbons into favorable reservoirs at higher structural positions. Overall, the tectonic evolution of the Shuntuoguole low uplift is closely tied to reservoir formation and hydrocarbon migration, playing a crucial role in the development and distribution of the Shunbei oil and gas field region. In this study, we focused on Block 2, specifically Zone 4 and Zone 8. As shown in Figure 1, this map illustrates the fracture network distribution in the Shunbei Oil Field region of the Tarim Basin, China, displaying the major fault zones and tectonic units (Chen et al., 2024). Zone 4, located in the core area of Block 2, contains relatively stable geological structures. The primary faults in this zone are northeast-trending, are predominantly inherited extensional-shear strike-slip faults, and exhibit a three-segment pull-apart style, making this a favorable area for reservoir development. In contrast, Zone 8, situated at the edge of Block 2, contains relatively complex geological structures. The primary faults in this zone are also northeast-trending but are predominantly inversional, compressional-shear strike-slip faults. Understanding the geological background of the Shunbei oil and gas field and the general situation of the study area provides a fundamental basis for further exploration of reservoir characteristics. Subsequently, the reservoir characteristics of Zones 4 and 8 in Shunbei will be analyzed in detail to further elucidate their relationship with stable production capacity.
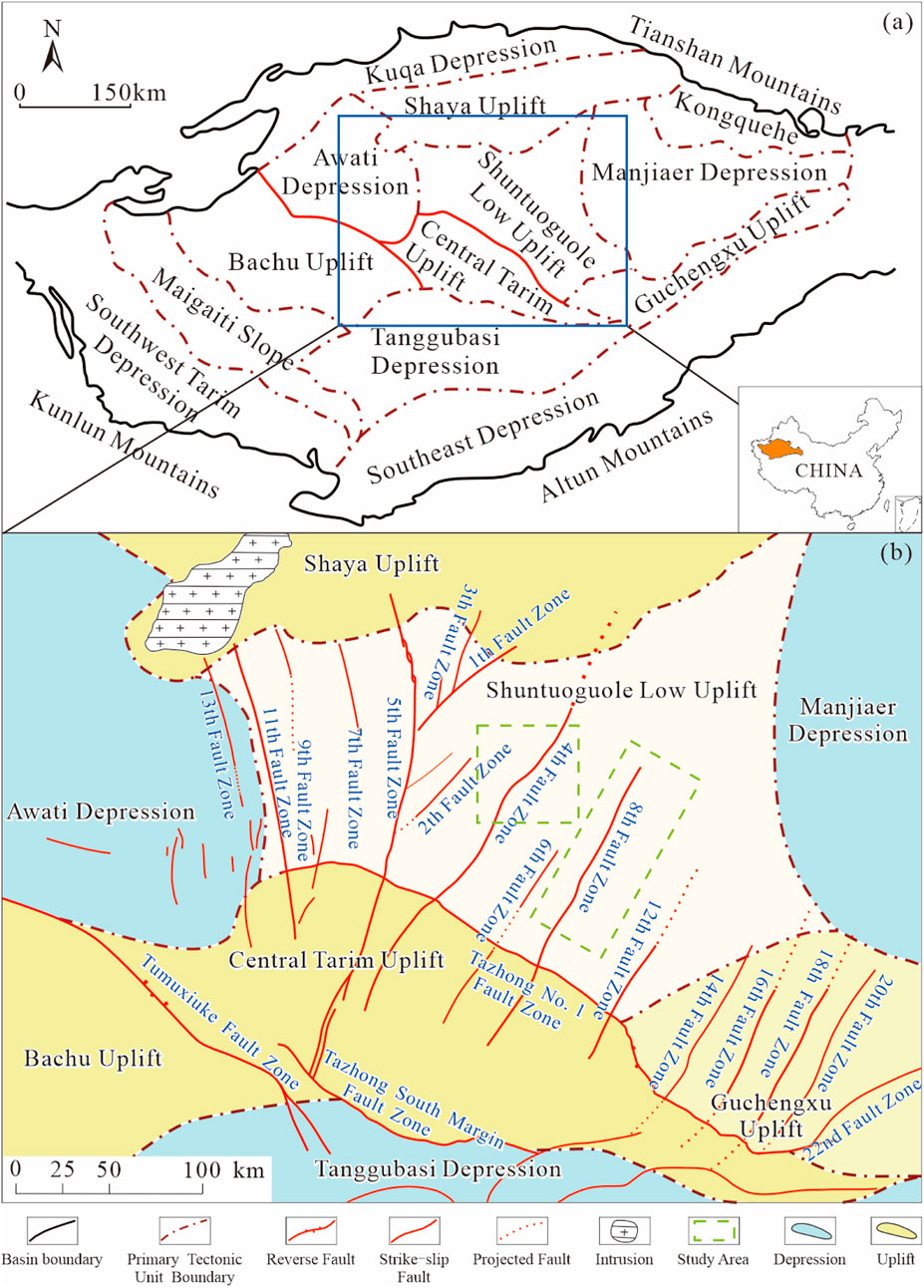
Figure 1. (a) Structural Division of Tarim Basin, China, and (b) Regional tectonic map, illustrating the distribution of the various fault systems (modified from Chen et al., 2024).
3 Analysis of reservoir characteristics
3.1 Reservoir types and distribution
The stable production capacity of the carbonate reservoirs is closely related to their unique reservoir characteristics. In Zone 4 and Zone 8 in the Shunbei area, the reservoir types are diverse, primarily including fracture-type, fracture-cavity type, and karst-cave type reservoirs. As shown in Figure 2, different reservoir types exhibit distinct seismic expressions on seismic sections, which can be characterized through various seismic attribute volumes (Wang Z. et al., 2024). The fracture-type reservoirs are characterized by high-angle fractures serving as the main storage space, limited pore development, and a relatively small storage capacity, but the fracture network provides good flow channels. Zone 4 has a higher degree of fracture development and better reservoir connectivity compared to Zone 8. The fracture-cavity type reservoirs include both fractures and cavities, and the fractures and cavities are interconnected, forming a complex storage space, with a high storage capacity and good flow performance. Data indicate that the fracture-cavity reservoirs in Zone 4 are better developed than those in Zone 8. The karst-cave type reservoirs are mainly composed of karst caves and are characterized by large storage spaces and poor connectivity, making extraction more difficult. They are distributed in both Zone 4 and Zone 8, but their scale is relatively small.
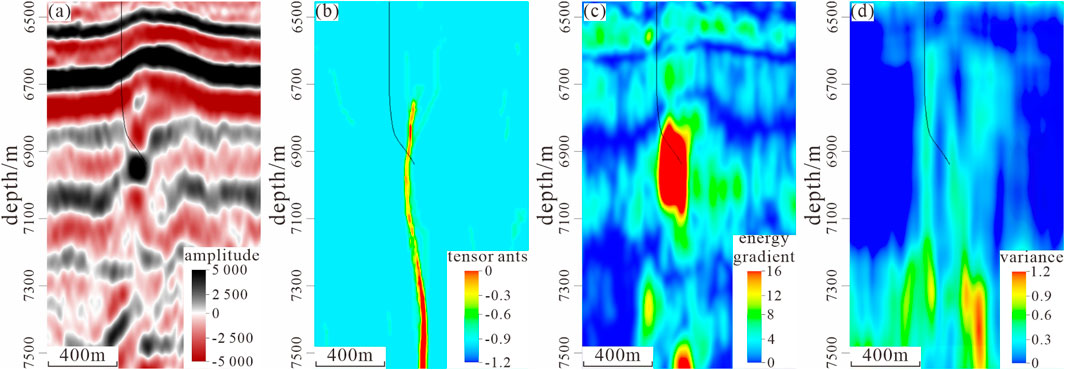
Figure 2. Types of Ordovician reservoirs in Well SHB43X, Shunbei 2nd Block: (a) Seismic profile, (b) tensor ants seismic attributes, (c) energy gradient seismic attributes, and (d) variance seismic attributes.
The reservoir distribution characteristics are critical for achieving a stable production capacity. Laterally, the reservoir development conditions vary significantly across the different areas. The reservoirs in Zone 4 are relatively concentrated and continuous and are controlled by the northeast-trending faults, and the reservoirs near the fault zones are well-developed. The reservoirs in Zone 8 are more scattered and are influenced by multiple fault interactions (As shown in Figure 3, Fault Zone 4 exhibits high continuity, while Fault Zone 8 shows poor continuity. Vertically, the reservoirs are mainly developed in the Ordovician strata, and the reservoir physical properties and storage space differ across the layers. The upper layers generally have better physical properties and more developed fractures and cavities.

Figure 3. Schematic illustration of fault trends in Zones 4 and 8 in the Shunbei area: (a) Belt 4 fracture model, and (b) belt 8 fracture model.
3.2 Reservoir physical properties and pore structure
The reservoir physical property parameters are important indicators for evaluating the stable production capacity. The porosity is a key parameter that reflects the storage capacity, and its magnitude directly impacts the hydrocarbon storage volume. The porosities of the carbonate reservoirs vary widely. The fracture-type reservoirs generally have low porosities, ranging from 1% to 5%, while the fracture-cavity and karst-cave type reservoirs have porosities ranging from 5% to 20%. The permeability reflects the reservoir’s permeability characteristics, and the permeabilities of the different reservoir types are significantly different. The fracture-type reservoirs typically have low permeabilities, usually between 1 and 10 mD, while the fracture-cavity reservoirs have permeabilities of 10–1,000 mD. In the study area, the reservoirs in Zone 4 in Shunbei have relatively higher porosities and permeabilities, with average porosities of 8%–17.6% and permeabilities of generally several hundred millidarcies. In contrast, the reservoirs in Zone 8 have lower porosities and permeabilities, with average porosities of 2%–3%, and permeabilities typically ranging from 10 to 200 mD. As shown in Table 1, the statistical results demonstrate that Zone 4 exhibits higher average permeability and porosity compared to Zone 8. Additionally, Zone 4 has a larger maximum detection radius, reflecting superior reservoir connectivity.

Table 1. Comparison of well test interpretation detection radius and fracture-cavity volume in Zones 4 and 8 in the Shunbei area.
3.3 Fracture characteristics of reservoirs
The characteristics of the fractures in a reservoir play a decisive role in its stable production capacity. The degree of fracture development is reflected by the fracture density and fracture length. Higher fracture densities and longer fracture lengths can effectively improve the conditions for hydrocarbon migration and storage (Ding et al., 2021). In Zone 4 in Shunbei, the fracture density is relatively high, with an average of 1–2 fractures per meter, and the fracture lengths reach tens to hundreds of meters. In contrast, in Zone 8, the fracture density is lower, with an average of 0.5–1 fracture per meter, and the fracture lengths range from a few meters to several tens of meters. As shown in Table 2, the fracture development characteristics of typical wells in Zones 4 and 8 were statistically analyzed. A direct correlation between fracture development intensity and productivity was established, validating the effectiveness of the fault activity intensity index. The fracture types mainly include structural fractures and non-structural fractures. Structural fractures, such as tensile fractures, compressive fractures, and shear fractures, are formed by tectonic movement. These fractures are closely related to changes in the tectonic stress field and played a significant role in the reservoir modification and hydrocarbon migration. Non-structural fractures, such as shrinkage fractures, interlayer fractures, and pressure-solutional fractures, are associated with the physical and chemical changes in rocks as well as stratigraphic subsidence. The fracture connectivity is also an important indicator for evaluating the stable production capacity of reservoirs. Parameters such as the fracture density, fracture length, and fracture aperture are typically used to assess connectivity. Reservoirs with good connectivity have densely distributed fractures, longer fracture lengths, and larger fracture apertures. In Zone 4 in Shunbei, the fractures exhibit good connectivity, and the fractures are interconnected, forming effective flow pathways. However, in Zone 8, the fracture connectivity is relatively poor, which hinders hydrocarbon flow and extraction.
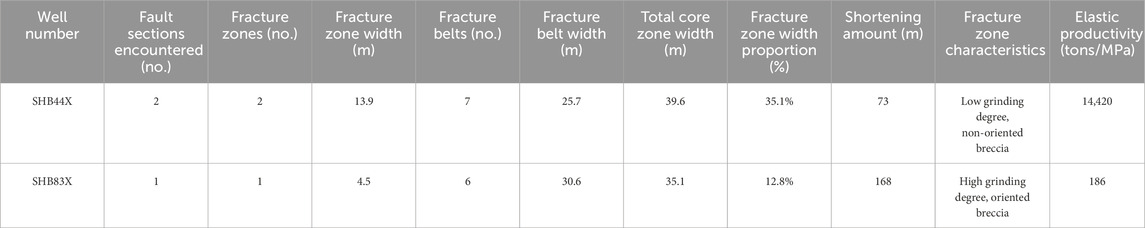
Table 2. Statistics of reservoir and fracture zones encountered in typical wells in Zone 4 and Zone 8 in the Shunbei area.
4 Analysis of fault control
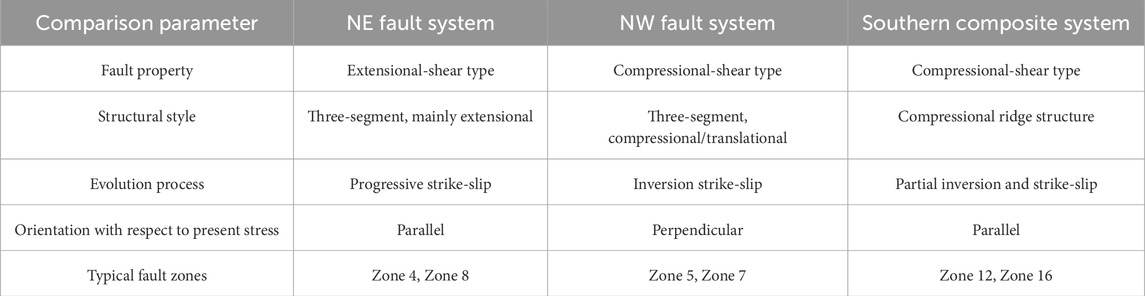
The fault activity in the Shunbei oil and gas field has evolved through the Caledonian, Hercynian, and Himalayan periods. Fault activities during these different periods have significantly influenced the formation and evolution of oil and gas reservoirs (Wang et al., 2021; Dou et al., 2024). The fault systems are primarily strike-slip faults, including northeast-trending, northwest-trending, and southern composite systems. On the plane, these fault systems exhibit a north-south junction and east-west zoning pattern. As shown in Table 3, a comparative analysis of parameters across different fault systems was conducted. This study compares the geometric and kinematic characteristics of the NE-trending, NW-trending, and southern composite fault systems, providing a basis for the classification of fault activity intensity. Based on parameters such as the fault displacement and slip rate, the intensity of the fault activity can be categorized into four levels: strong, relatively strong, moderate, and weak. The intensity of the fault activity varies among the different fault systems, with the northeast-trending fault system exhibiting stronger activity and the northwest-trending fault system exhibiting weaker activity. The fault types mainly include extensional-shear, compressional-shear, and compressional-ridge faults. The different types of faults have varying controlling effects on the hydrocarbon reservoirs. As shown in Figure 4, the structural styles of different fault systems in the Shunbei Block 2 are illustrated. This includes a comparative analysis of the NE-trending, NW-trending, and composite fault assemblages, highlighting their geometric configurations (e.g., fault spacing, segmentation) and kinematic patterns (e.g., displacement gradients, linkage mechanisms). The extensional-shear faults facilitate hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. The compressional-shear faults have relatively weaker control over the hydrocarbon reservoirs, and the compressional-ridge faults hinder hydrocarbon migration and accumulation.
4.1 Faults and reservoirs
Fault activity causes reservoir rocks to fracture, forming numerous cracks and cavities, thereby increasing the reservoir porosity and permeability. Fault activity can also modify the reservoir through processes such as dissolution and compaction, which further improve the reservoir’s physical properties (Li Y. B. et al., 2024). The fractures and cavities formed by fault activity are interconnected, enhancing the reservoir connectivity and facilitating hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. In the study area, the impacts of the different fault systems on the reservoir connectivity varies. The northeast-trending fault system significantly improves the reservoir connectivity, whereas the northwest-trending fault system has a relatively smaller impact on the connectivity. For carbonate reservoirs, the main reservoir stimulation measures include acidizing, fracturing, temporary plugging segmentation, fracture expansion, and chelating agent-based unblocking. The effectiveness of these measures varies depending on the characteristics and actual conditions of the reservoir. Therefore, it is necessary to select appropriate stimulation techniques tailored to specific reservoir features.
4.2 Faults and hydrocarbon accumulation
Fault systems serve as critical hydrocarbon migration pathways. Oil and gas can migrate through fault zones into surrounding reservoirs. The migration direction is primarily controlled by the fault systems and structural patterns, typically moving from structural highs to structural lows. The oil and gas accumulation process in carbonate reservoirs is complex, including the generation, migration, accumulation, and preservation of oil and gas. The Shunbei gas-condensate reservoir follows a fault-lithological composite trap accumulation model, in which the fault zones control the hydrocarbon migration and accumulation, and the lithological features influence the hydrocarbon storage and distribution.
4.3 Case studies
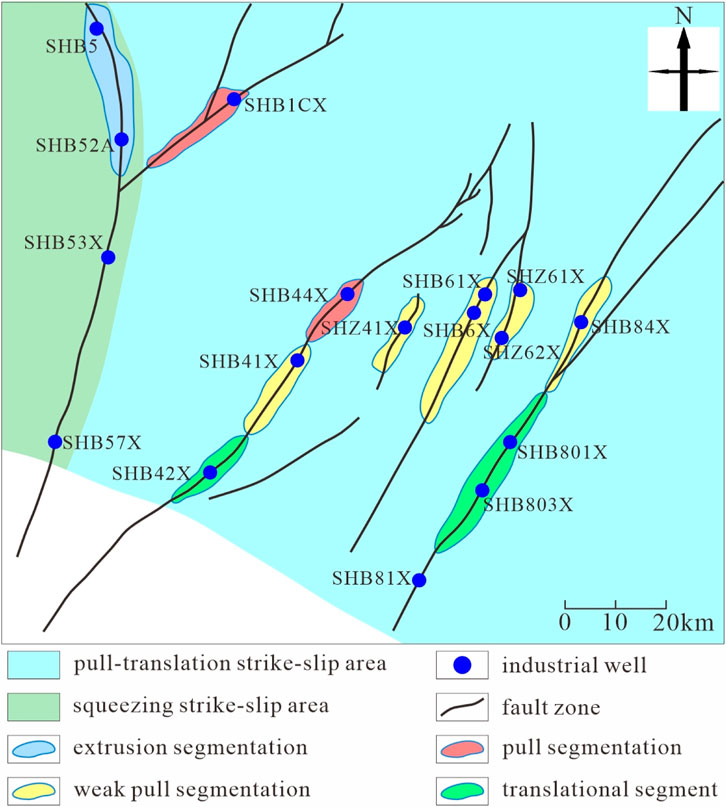
The fault activity in Zone 4 in the Shunbei area is frequent and intense, making the fault intersection zones key areas for hydrocarbon enrichment. The intersections of multiple faults result in highly fractured rocks, creating numerous interconnected fracture and pore systems. These provide superior spaces for hydrocarbon storage and migration. Such favorable reservoir conditions lead to high hydrocarbon production and a strong stable production capacity in this area. As shown in Figure 5, the spatial correlation between high-productivity well distribution and fault attributes in Zone 4 is analyzed. This demonstrates the controlling effect of fault locations on hydrocarbon productivity, thereby providing a basis for well placement optimization in structurally complex areas. For example, well SHB4-2, located near a fault intersection, exhibited an excellent initial production performance during the early stage of development, and a relatively slow decrease in production during the subsequent production. This demonstrates its strong stable production characteristics, which are attributable to the superior reservoir physical properties and efficient hydrocarbon migration pathways created by the fault activity. These factors enable sustained and effective hydrocarbon flow from the deep reservoirs to the wellhead.
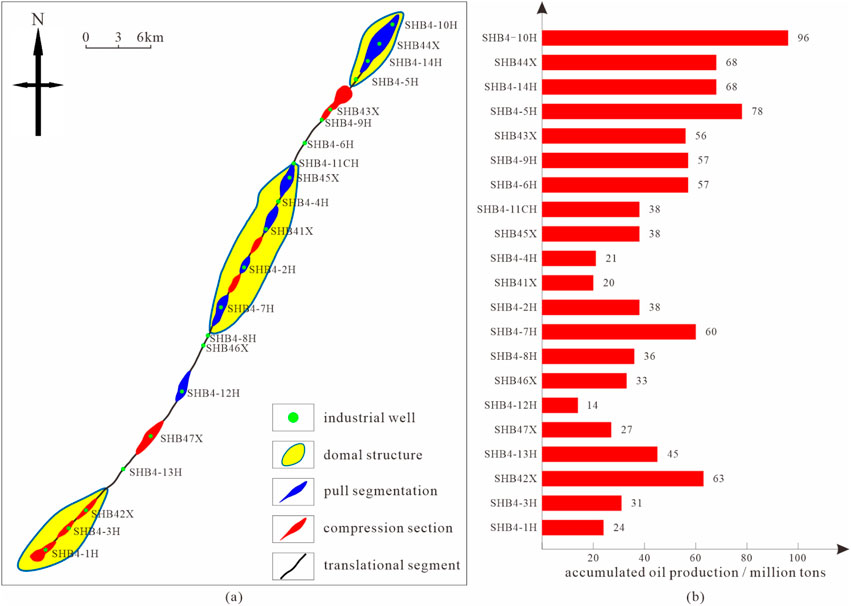
Figure 5. Relationship between fault properties and high-yield wells in Zone 4 in the Shunbei area: (a) fault characteristics of zone 4 (refer to Fault Zone No.4 in Figure 4), and (b) cumulative production from belt 4 production wells.
In contrast, the fault characteristics in Zone 8 in the Shunbei area differ. While faults are present, the intensity of their activity is weaker, and their distribution is more dispersed. This has resulted in less effective reservoir modification compared to Zone 4. In some areas in Zone 8, the poor fault connectivity restricts hydrocarbon migration, leading to a smaller scale of hydrocarbon accumulation. As shown in Figure 6, the spatial correlation between high-productivity well distribution and fault attributes in Zone 8 is analyzed. This validates the critical control of fault positioning on hydrocarbon productivity, thereby providing a geological basis for optimizing well placement strategies in fault-controlled reservoirs. For instance, in the area around well SHB8-5, the limited communication effect of the faults on the reservoir has resulted in a lower initial production and shorter stable production period. However, in certain localized areas in Zone 8, when the faults intersect with favorable reservoir lithologies, some hydrocarbon accumulations can form. In particular, in zones with well-developed limestone, the faults provide hydrocarbon migration pathways, leading to higher production in these areas. Nonetheless, the overall stable production capacity in Zone 8 remains inferior to that in Zone 4.
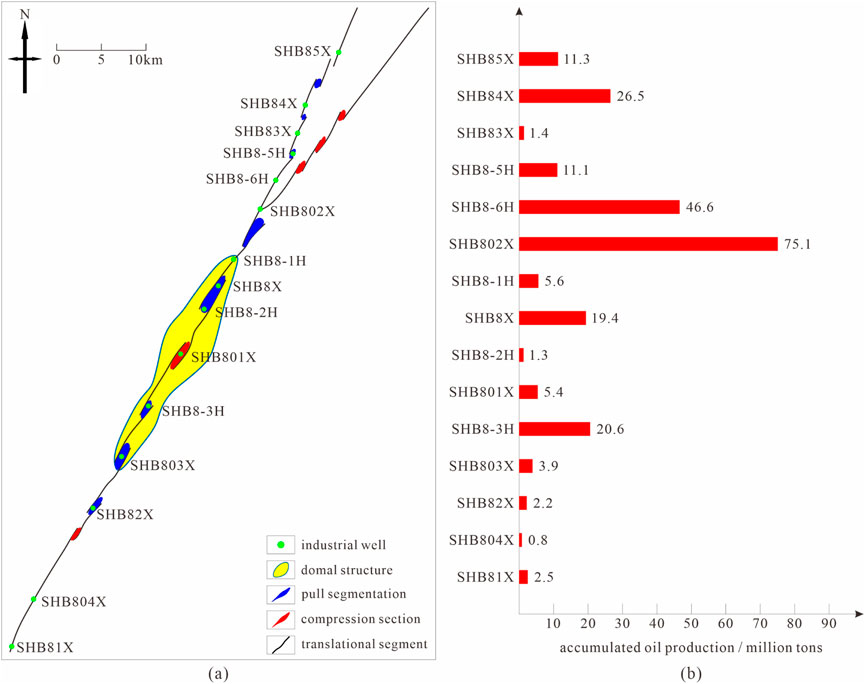
Figure 6. Relationship between fault properties and high-yield wells in Zone 8 in the Shunbei area: (a) fault characteristics of zone 8 (refer to Fault Zone No. 8 in Figure 1), and (b) cumulative production from belt 8 production wells.
5 Analysis of factors affecting stable production capacity of reservoirs
5.1 Fault properties
The fault intersection area is crucial for stable reservoir production. In these zones, strong fault activity extensively fractures the rock, creating numerous cracks and pores. This provides excellent conditions for oil and gas storage and migration. The stress concentration at the fault intersections has promoted hydrocarbon enrichment and preservation, making these areas the primary zones for high-yield well development. The reservoirs in the extensional zones have stronger stable production capacities due to their better connectivity and abundant hydrocarbon reserves. This is because the higher fault activity intensity in the extensional zones has enhanced the reservoir modification and facilitated hydrocarbon migration and accumulation. In contrast, the compressional zones have weaker stable production capacities, poorer reservoir connectivity, and smaller hydrocarbon reserves. As shown in Figure 7, the differential stress regimes within Shunbei Block 2 are characterized, explaining the controlling effect of tectonic stress on reservoir development. There is a positive correlation between the fault activity intensity and stable production capacity: the greater the fault activity intensity is, the better the reservoir modification, hydrocarbon migration, and accumulation are, leading to a stronger stable production capacity.
In Zone 4 in the Shunbei area, there are numerous highly active fault intersections, such as the fault zone near well SHB42X. These provide efficient pathways for hydrocarbon migration and accumulation, resulting in excellent reservoir connectivity. This allows hydrocarbons to flow rapidly and smoothly within the reservoir, ensuring high production rates and strong stable production capacities. However, in Zone 8, the fault activity is weaker and more dispersed, leading to poorer reservoir connectivity. For instance, in the area around well SHB8-3, limited hydrocarbon migration has resulted in lower production and greater challenges in achieving stable production.
5.2 Reservoir characteristics
The reservoir scale is one of the key factors influencing the stable production capacity. Larger reservoirs indicate greater hydrocarbon reserves, which can ensure long-term stable production. The larger the reservoir scale is, the higher the hydrocarbon production and recovery rate are, and the stronger the stable production capacity is. The degree of reservoir filling significantly impacts the stable production capacity. Higher filling levels reduce the effective reservoir volume, decrease the hydrocarbon reserves, and weaken the stable production capacity. Additionally, the nature and distribution characteristics of the filling materials affect the reservoir physical properties and flow capacity, thereby influencing the stable production capacity. Reservoir connectivity is crucial for hydrocarbon migration and accumulation within the reservoir and is critical for achieving a stable production capacity. In reservoirs with good connectivity, hydrocarbons can migrate smoothly, improving the recovery rates Conversely, reservoirs with poor connectivity restrict hydrocarbon movement, resulting in a weaker stable production capacity.
In Zone 4 in the Shunbei area, the reservoirs are relatively large and have high porosities and permeabilities. For example, the reservoir associated with well SHB4-5 benefits from favorable physical conditions, leading to abundant hydrocarbon reserves and sustained stable production during extraction. However, in certain areas in Zone 8, the higher degrees of reservoir filling reduce the effective reservoir volume. For instance, near well SHB8-6, the reduced hydrocarbon reserves significantly impact the stable production capacity, leading to a noticeable decline.
5.3 Water body characteristics
In the geological history period, confined water was primarily formed by the rapid accumulation of sediments and the entrapment of pore water. Over extended geological periods, this water interacted with the surrounding rock, gradually altering the physical properties of the reservoir while maintaining its relative stability. Tectonic movements subsequently influenced the pressure and distribution of the confined water, modifying the reservoir pressure environment. Confined water benefits the stable production capacity of reservoirs by acting as a natural pressure support and slowing the decrease in hydrocarbon production. It also reduces the risk of water intrusion, providing a stable environment for hydrocarbon extraction (Qiu et al., 2023). Bottom water typically accumulates at the base of the reservoir and connects with the aquifer during deposition. Tectonic movements alter the formation, leading to changes in bottom water flow and distribution, which have complex effects on reservoir physical properties. Dissolution can enhance porosity and permeability, but water flooding and hydration expansion can reduce oil and gas saturation and permeability. These processes may even cause water breakthrough, increasing the difficulty of extraction (Tang et al., 2022). In contrast, bottom water negatively impacts the stable production capacity. The intrusion of bottom water causes a decrease in hydrocarbon production, increases the difficulty of extraction, and increases costs. Bottom water has strong energy, making it prone to upward intrusion into hydrocarbon reservoirs, thereby disrupting production. Water energy replenishment plays a critical role in maintaining the stable production capacity of reservoirs. Adequate replenishment of water energy helps maintain the reservoir pressure stability and extends the stable production period. Water energy replenishment mainly comes from formation water recharge and the elastic expansion of the water bodies. Changes in these factors affect the role of water bodies in maintaining the stable production capacity.
In Zone 4 in the Shunbei area, the water energy replenishment is relatively stable, and confined water provides excellent pressure support, slowing the decrease in hydrocarbon production. For instance, during the development of well SHB44X, the stable water environment helped sustain relatively stable production over an extended period of time. As presented in Table 4, the correlation between water distribution patterns and hydrocarbon productivity in Zone 4 is statistically analyzed. However, in Zone 8, certain areas exhibit active bottom water conditions. The intrusion of bottom water in wells such as well SHB8-4 caused a rapid decline in production, significantly impairing the stable production capacity of the reservoir.
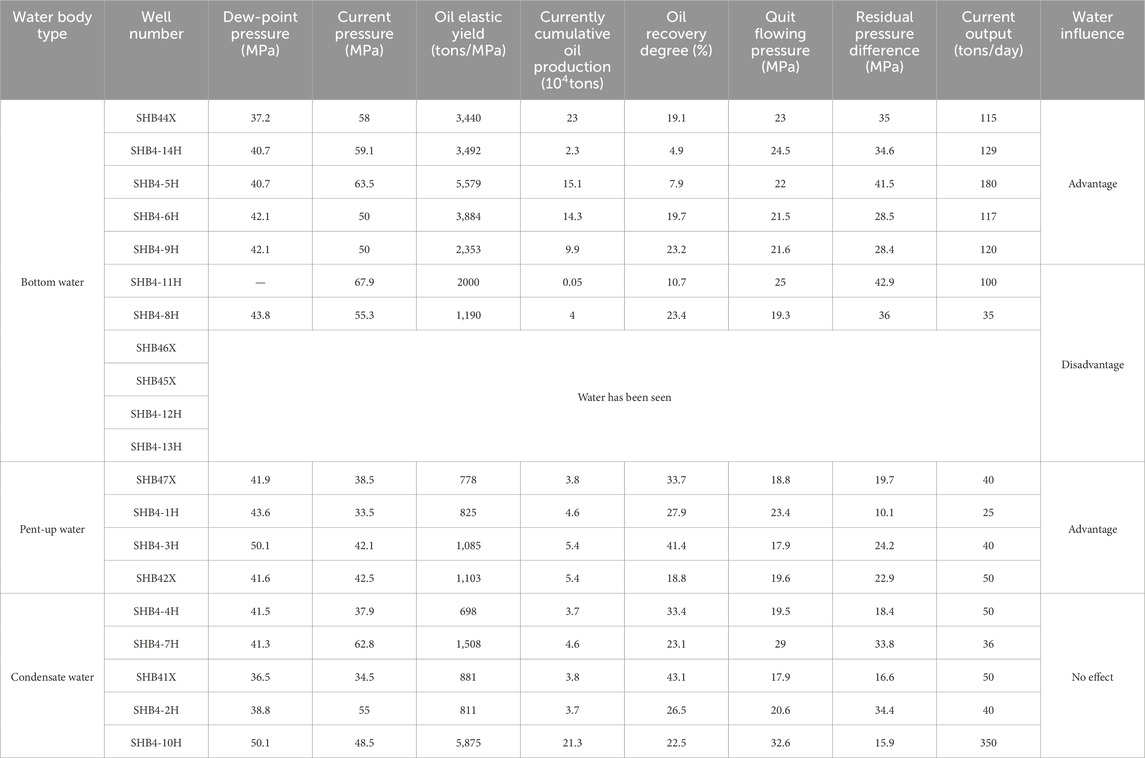
Table 4. Analysis of water body distribution and its relationship to productivity in Zone 4 in the Shunbei area.
6 Analysis of reservoir stimulation measures
For carbonate reservoirs, the primary reservoir stimulation measures include acidizing, fracturing, temporary plugging segmentation, fracture expansion, and chelating agent-based unblocking (Liu et al., 2020). Acidizing treatment involves using acid solutions to dissolve obstructions in the reservoir, such as clay and calcite, thereby improving the permeability of the reservoir. Fracturing involves injecting fracturing fluid under high pressure to create fractures in the reservoir, thereby enhancing the connectivity and permeability of the reservoir. Temporary plugging segmentation is a reservoir reconstruction technique used in oil exploitation. During fracturing, a temporary plugging agent is injected to block opened cracks or high-permeability areas temporarily. This divides the reservoir into smaller sections, allowing the fracturing fluid to target other areas for more effective stimulation and improved mining efficiency. Fracture expansion involves using specialized tools and processes to extend and widen existing fractures after reservoir fracturing. This increases the length and width of the fractures, expands the oil and gas seepage channels, and enhances production rates. By enlarging the pathways for oil and gas flow, this technique significantly boosts the reservoir’s productivity. Chelating agent-based unblocking involves the use of chelating agents that react with metal ions in the reservoir to remove obstructions and improve the reservoir permeability.
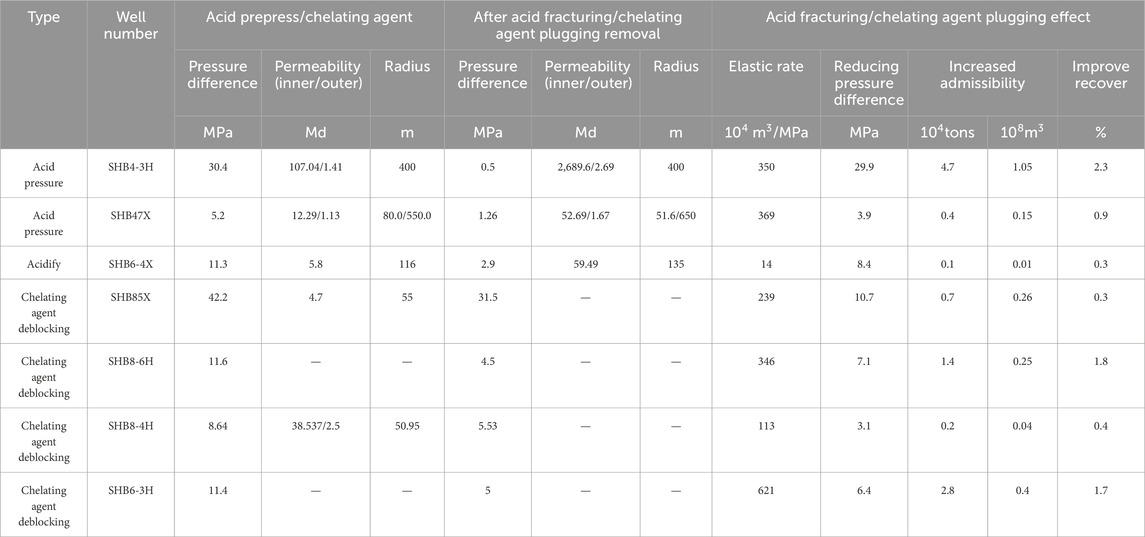
In Zone 4 in the Shunbei area, reservoir stimulation measures have achieved significant results. Acidizing treatment has played an important role. For example, after acidizing treatment, in well SHB4-3, substantial improvements in both the oil production and the duration of the stable production were achieved. In addition, fracturing measures have also had positive impacts on the reservoir development. Due to the proper fracturing design and construction parameters, the fracturing fluid effectively entered the deeper parts of the reservoir, formed an efficient fracture network, and increased the oil and gas output. In high-yield wells such as wells SHB42X and SHB44X, significant improvements in the production and stable production time were achieved through fracturing. In Zone 8, due to the differences in the reservoir characteristics compared to those in Zone 4, the reservoir stimulation measures required more specific targeting. Temporary plugging segmentation was particularly effective in this region. By using plugging agents to divide the reservoir into multiple segments, the individual segments were successfully modified, improving the overall effect of the stimulation. For example, in well SHB8X, a significant increase in oil and gas production was achieved through the application of temporary plugging segmentation. Additionally, fracture expansion techniques also yielded some improvement in the reservoir stimulation in Zone 8. By expanding the fractures along their walls, the lengths and widths of the fractures were increased, thereby improving the flow capacity of the reservoir. As presented in Table 5, the effectiveness statistics of reservoir stimulation measures are analyzed by comparing the application outcomes of various techniques (e.g., hydraulic fracturing, acidizing) in Zone 4 and Zone 8. Reservoir reconstruction measures have improved reservoir conditions to a certain extent. However, to more scientifically evaluate the stable production capacity of reservoirs and guide the development of oil and gas fields, it is essential to establish a comprehensive quantitative evaluation index system.
7 Establishment of a quantitative evaluation index system
7.1 Construction of the evaluation index system
Regarding the stable production capacity of carbonate reservoirs, in this paper, we develop a quantitative evaluation index system for Zones 4 and 8. First, the reservoir scale-related indicators are determined based on the fault activity intensity, fault properties, and reservoir genesis. Under the framework of geological analysis and geophysical exploration techniques, key parameters are derived to evaluate reservoir scale (S). Fault activity intensity (I), reflecting the magnitude of fault movement, exhibits a positive correlation with reservoir dimensions. Higher intensity values enhance reservoir space development through intense rock fragmentation, promoting pore-fracture networks and justifying its substantial weighting. Fault properties, quantified as extensional (F1), compressional (F2), and translational (F3) components, demonstrate differential impacts: extensional faults optimize fluid migration and reservoir formation, compressional faults impose destructive effects, while translational motions exert minimal influence, necessitating distinct weighting coefficients. Reservoir genetic mechanisms, including karstification (C1) and tectonic fracturing (C2), exhibit scale-dependent contributions, karst-dominated systems prioritize large-scale dissolution voids, whereas fracture-controlled reservoirs emphasize connectivity, requiring weighted quantification based on their respective capacity to enhance subsurface storage potential. S is expressed as follows (Equation 1):
where a1, a2, …, a6 are coefficients to be determined. For the fault activity intensity (I), quantitative assessment was conducted through three parameters: fault displacement, slip rate, and activity phases (as shown in Table 3), with values assigned using the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). The fault properties (F1, F2, F3) are mutually exclusive variables, while the reservoir genetic types (C1, C2) can coexist and were determined based on core samples and well logging data. Data from over 20 wells in the Shunbei No.4 and No.8 Zones were collected, including reservoir scale, fault parameters, and genetic types. Using reservoir scale as the dependent variable and other influencing factors as independent variables, a multiple linear regression analysis was performed to establish the coefficient of determination.
The indicators pertaining to reservoir effectiveness are derived from well logging, well testing, and core analysis data, with weighting coefficients assigned based on fault activity intensity (A), the angle between fault and principal stress (θ), and fault properties. Fault activity intensity directly governs the degree of reservoir modification and the development of fluid migration pathways. Higher activity intensity enhances reservoir permeability and connectivity, favoring hydrocarbon storage and extraction, and thus receives greater weighting. The angle between fractures and principal stress (θ) influence fault orientation and propagation, where smaller angles promote stress-driven fault initiation and extension, thereby improving reservoir effectiveness, though with a slightly lower weighting compared to fault activity intensity. Additional considerations include fault properties and other geological parameters. The reservoir effectiveness, denoted as E, is calculated as follows (Equation 2):
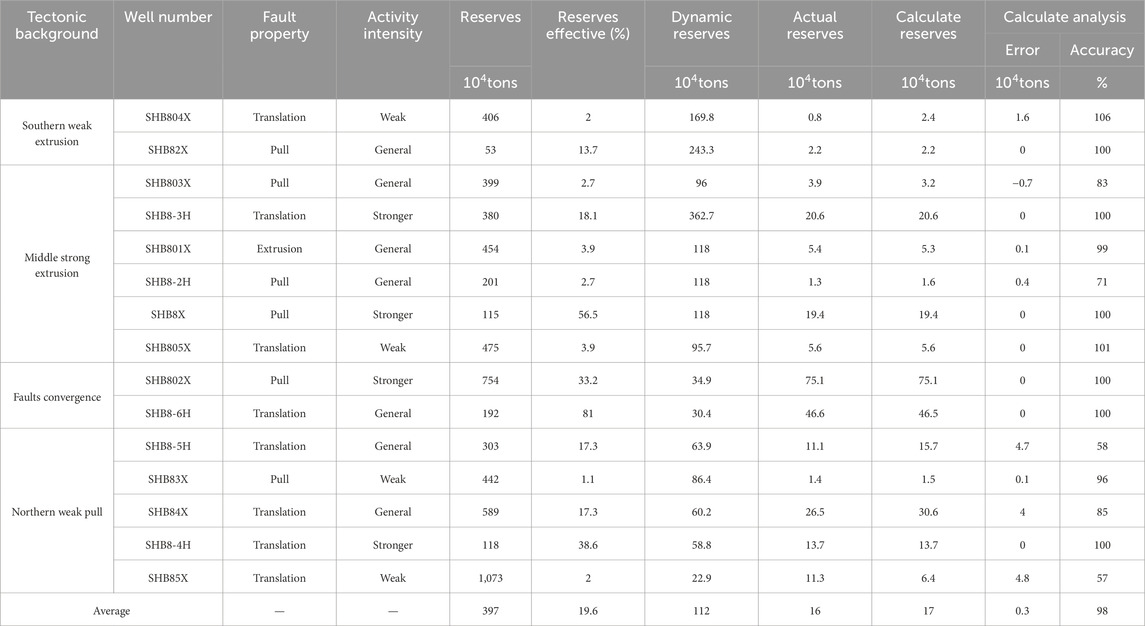
where b1, b2, and b3 are coefficients to be determined. The effectiveness ratings of reservoir units in Shunbei Zone 4 are listed in Table 6. This table establishes quantitative scoring criteria for reservoir effectiveness under different structural settings, providing a basis for parameter selection in the quantitative evaluation model. The fault activity intensity (A) is quantified into three grades (see Table 6), while the fault-stress intersection angle (θ), defined as the measured angle between the maximum principal stress orientation and fault strike, critically influences seepage efficiency. Fault properties (F) are categorized into three classes reflecting reservoir connectivity variations. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) was employed to integrate qualitative expert knowledge with quantitative data for weight assignment, ensuring logical rationality through consistency verification and alignment with hierarchical reservoir effectiveness evaluations. The entropy weight method was implemented for weight calculation based on reservoir effectiveness values assigned across diverse structural settings. The systematic weight allocation involved constructing a hierarchical framework (target layer E, criterion layer A/θ/F, and solution layer with reservoir classifications), developing averaged judgment matrices through pairwise comparisons of criteria by domain experts, computing weight vectors via the eigenroot method with consistency validation, and ultimately verifying results through Equation 2 using Table 6’s index values.
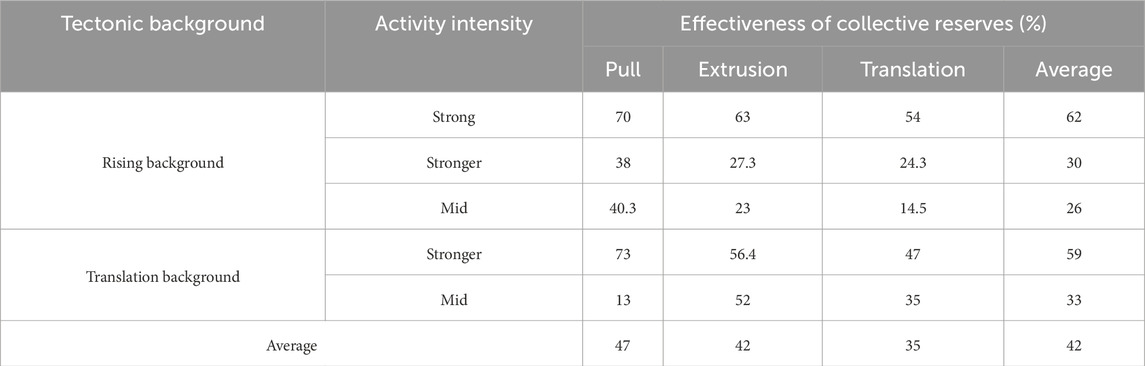
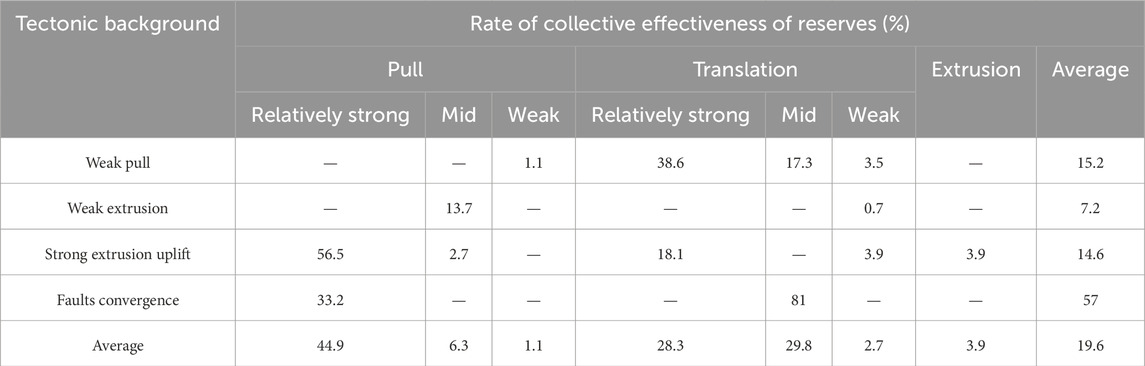
The water impact index is defined as the proportion of the water’s impact on the recovery rate. Statistical data are used to assign the water impact quantification values based on the activity intensity. Table 7 establishes quantitative scoring criteria for water body impacts under different structural settings, providing a basis for parameter selection in the quantitative evaluation model. Observations of the water distribution patterns revealed that the water bodies are primarily developed in a translational tectonic setting with poor connectivity and drainage. In the translational fault zones, the impact on the recovery rate ranges from 4% to 9%, with an average of 5%. The statistical results indicate that the compressional segments are unaffected by water, while the extensional segments in the high-activity areas are moderately affected, with an impact of approximately 5%.
The indicators related to the water impact are determined through analysis of the formation water chemistry, resistivity logging, and water production data for the wells. The water impact index (W) is calculated as follows (Equation 3):
where the parameter T (Hydrocarbon connectivity) quantifies hydraulic communication between water bodies and source rocks, with higher weighting in the model given its critical influence on hydrocarbon production. Strong connectivity with bottom water facilitates aquifer influx into reservoirs, adversely impacting hydrocarbon recovery. This parameter is categorized into three tiers based on water chemical analysis. The parameter D (Conduit efficiency) evaluates fault-mediated water migration capacity, where enhanced fault conductivity mitigates water interference during production. It receives lower weighting and is quantified using the water invasion index derived from well test interpretation combined with structural context analysis. Undetermined coefficients c1 and c2 were defined using a logistic regression model trained on water breakthrough observations and recovery data from multiple wells in Zone 4. The water body impacts (see Table 7) and a quantitative scoring standard for water impacts under varying tectonic backgrounds were established, providing parameter inputs for the quantitative evaluation model.
Reservoir scale (S) serves as a fundamental factor influencing cumulative production, where larger reservoirs typically indicate greater hydrocarbon reserves and theoretically higher cumulative yields. Reservoir effectiveness (E) quantifies production feasibility and efficiency, with highly effective reservoirs enabling easier hydrocarbon extraction and making more substantial contributions to cumulative production. The water impact index (W) represents the adverse effects of aquifer interference on productivity, higher index values correspond to stronger production suppression. In the model, this inhibitory effect is mathematically expressed through the (1-W) term to reduce predicted cumulative production values. When accounting for the water in Zone 4, the cumulative production (P) can be predicated using Equation 4:
For Zone 4, the ideal recovery factor is the average dynamic recovery factor, which is 31%. Based on the three factors, i.e., the reservoir scale, reservoir effectiveness, and water impact, we assigned values for the individual wells in Zone 4. The calculated cumulative production was compared with the elastic rate-based production predictions (Table 8), and an accuracy of 99% was achieved.
Analysis of the wells with significant prediction errors: For well SHB4-3, the reservoir effectiveness value was set as 46.9% according to the parameter table (Table 6), while the actual statistical value was 31.2%, likely due to the poor well-reservoir connectivity. For well SHB4-13, the calculated cumulative production is far lower than the actual prediction. The actual prediction may involve deviations in the elastic production rate or dynamic reserve estimates. For well SHB4-7, the calculated value is lower than the actual prediction. The analysis results suggest that within the central uplift zone, the fault activity intensity at the location of this well is relatively strong, meaning that the reservoir effectiveness should be higher than the average value in the parameter table (Table 6). Additionally, the influence of the adjacent water flow, which was not accounted for in the calculation, resulted in underestimation of the cumulative production.
For Zone 8, the overall reservoir effectiveness is relatively low, with an average of 19.6%. The reservoir scale and effectiveness are significantly higher in the fault intersection zones than in other areas, and they are lowest in the weak extensional zones. The reservoir effectiveness is correlated with the fault properties and activity intensity, and the extensional segments in the high-activity areas perform better. The assigned values for the reservoir effectiveness are presented in Table 9, establishes quantitative scoring criteria for reservoir effectiveness under different structural settings, providing a basis for parameter selection in the quantitative evaluation model.
Zone 8 is minimally affected by water, and the estimated cumulative production (P) was calculated using Equation 5:
For Zone 8, the ideal recovery factor is 30%. The cumulative production predictions, calculated based on the reservoir scale, filling degree, and connectivity, are compared in Table 10.
The prediction results have an accuracy of 98%. The fault intersection zones have the highest cumulative production, aligning with the distribution of the high-yield wells. Although the reservoir effectiveness is lower in the extensional segments than in the translational segments, because they have a larger scale results, they have the highest cumulative production.
Based on comprehensive analysis of the calculation results for Zones 4 and 8, we summarized four qualitative discrimination indicators for the macro-regional distribution characteristics of high-yield wells.
First, regarding the impact of the maximum principal stress direction, the smaller the angle with the fracture orientation is, the lower the compressive stress is, the better the continuity of the high-permeability fractures along the fault’s strike is, and the larger the recoverable volume and cumulative production are. The trend deteriorates toward the east, and the ranking is as follows: three-segment > three-segment + compressional ridge transition zone > compressional ridge structure. Second, regarding the impact of the fault activity intensity, within the same fault zone, the degree of reservoir development is related to the intensity of the fault activity. The middle section, which has a greater activity intensity, is more favorable for reservoir development. Third, regarding the stress background of the fault development, the extensional and weak extensional zones are the most favorable areas for high-yield well development. Lastly, the favorability of the reservoir development locations is as follows: fault intersections > turning sections > midsections of translational strike-slip faults > ends of the fault. Fault intersections are the most favorable zones for high-yield well development. In this study, a three-dimensional evaluation system encompassing six major factors for the stable production capacity of high-yield wells was established. Table 11 establishes a three-dimensional evaluation matrix based on fault location, structural settings, and water body impacts, providing a visual decision-making tool for development plan optimization.
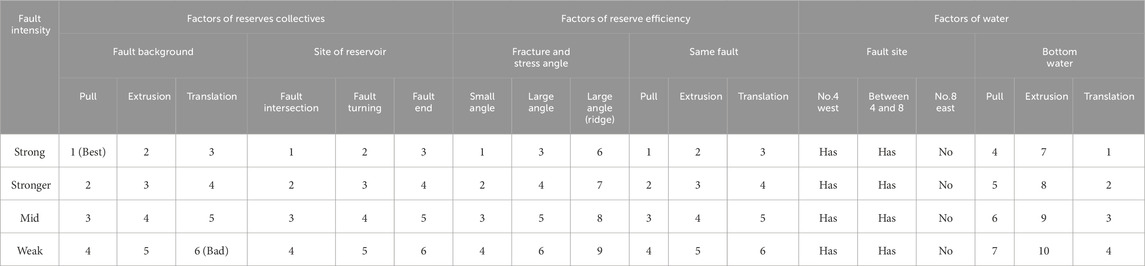
Table 11. Key factors controlling stable production capacity of high-yield wells in Block 2 in the Shunbei area.
7.2 Uncertainty analysis and sensitivity assessment
Uncertainty analysis of the model identified three primary sources: (1) Fault parameter interpretation errors caused by seismic data resolution limitations (burial depths exceeding 7,500 m in ultra-deep reservoirs), which may lead to misjudgment of fault activity intensity. This issue can be mitigated through integration of borehole image logging and core-based fault density calibration. (2) Ambiguity in water body type discrimination, where dynamic boundaries between confined water and bottom water under tectonic stress require refinement. Water chemical isotope analysis could enhance identification accuracy and reduce misclassification. (3) Reservoir heterogeneity, characterized by significant well-to-well variations in fracture-cavity connectivity. Fractal dimension analysis is proposed to quantify heterogeneity patterns, with a heterogeneity correction term added to Equation 2 to optimize effective porosity calculation models.
A single-factor sensitivity analysis was performed to assess the impact of parameter variations (±20% perturbation) on production forecasts, quantifying cumulative production response amplitudes in two case wells: SHB4-10H (Zone 4, highly fractured area) and SHB802X (Zone 8, fault intersection zone). Results indicate that a 20% increase in fault activity intensity (I) enhanced cumulative production by 18.2% (Zone 4) and 15.3% (Zone 8), consistent with the geological concept of “fault-controlled reservoirs” governing storage capacity and connectivity. For the fault-stress intersection angle (θ), a 20% increase reduced production by 12.5% (Zone 4) and 10.5% (Zone 8), attributed to elevated seepage resistance from angle widening, with Zone 4’s higher fracture density amplifying sensitivity. A 20% increase in effective reservoir effectiveness (E) boosted production by 10.5% (Zone 4) and 8.9% (Zone 8), reflecting stronger sensitivity in Zone 4’s karst reservoirs to volumetric efficiency. Conversely, a 20% increase in the aquifer influence index (W) decreased production by 7.5% (Zone 4) and 3.2% (Zone 8), confirming weaker aquifer impacts in Zone 8. The analysis highlights I as the most sensitive parameter, aligning with fault-dominated reservoir dynamics, while the inverse correlation between W and production stability validates bottom-water encroachment as a detrimental factor.
8 Discussion
Compared with the traditional single factor evaluation method, the fracture-reservoir-water coupling evaluation method constructed in this study comprehensively considers various factors such as tectonic activity, reservoir characteristics, reservoir reconstruction and water characteristics, and achieves accurate evaluation of stable production capacity through quantitative weight distribution. This system emphasizes the dynamic interaction of geological factors and provides a new paradigm for the evaluation of complex carbonate reservoirs. The proposed principle of prioritized development in fault intersection zones, as outlined in this study, exhibits theoretical consistency with the fault-block reservoir development strategies implemented in the North Sea Viking Graben region (Fossen et al., 2003; Eikeland and Hansen, 2009; Gomes et al., 2018; Underhill and Richardson, 2022). However, the parameter threshold determination for ultra-deep reservoir conditions presents significantly greater technical challenges, particularly regarding geological complexity and engineering feasibility under extreme depth constraints. The research results have direct reference value for global carbonate reservoirs. By reasonably increasing or reducing the influencing factors of reservoir stable production, the framework of reservoir stable production for a specific oilfield is established, and the influence weight of each factor is quantitatively characterized. The reservoir stable production development model is established to guide the optimization of oilfield development plan and improve economic benefits.
At the methodological level, this study integrates the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) (Lee, 2015) and Entropy Weight Method to resolve the weight allocation challenges in geological multi-factor evaluation. The Fault Activity Intensity (I) is quantified through displacement, slip rate, and active periods, with its weight assignment reflecting the cumulative modification effects of multi-phase fracture fragmentation-dissolution on reservoir porosity and permeability. The Effective Reservoir effectiveness (E) introduces the parameter of angle (θ) between fractures and stress, revealing the dynamic control of current NE-trending maximum principal stress on paleo-fracture openness, thereby addressing the oversight of current geostress field responses in traditional static reservoir evaluations. The Water Impact Index (W), through coupling water chemical isotopes with production dynamics, establishes for the first time a quantitative relationship between water types and recovery rates, challenging the conventional belief that water presence universally hinders development (Tan et al., 2022).
For this method, there are the following improvement strategies: We should further improve the geological models of carbonate reservoirs and conduct in-depth research on the formation mechanisms and evolutionary processes of reservoirs, providing a more accurate geological basis for studying the reservoir stable production capacity. We should enhance research on and application of new techniques and methods, such as three-dimensional seismic techniques (Narayan et al., 2023; Zhang G. Y. et al., 2024), numerical simulation (Tang et al., 2024; Zhang Y. et al., 2024), and artificial intelligence (Huang et al., 2023; Hu et al., 2024), to improve the accuracy of reservoir characterization and prediction, thereby offering more scientific technical support for evaluating the stable production capacity. Three-dimensional seismic technology enhances reservoir characterization and fault identification with high precision. It integrates with existing geological and geophysical methods to improve prediction accuracy. Numerical simulation uses actual data to model oil and gas migration and reservoir dynamics, predicting mining effects and optimizing development plans to boost efficiency and extend stable production. Artificial intelligence (AI) analyzes data to predict reservoir parameters and intelligently adjusts development strategies using optimization algorithms, ensuring precise decision-making.
Future research directions could focus on the following aspects: Firstly, deepening the understanding of fault-reservoir-aquifer coupling mechanisms. This should involve conducting dynamic reservoir-controlling mechanism studies of multi-phase fault activities. While current models primarily quantify static parameters of fault activity intensity, future studies could investigate the time-dependent control of multi-stage faulting on reservoir formation. Additionally, as the current aquifer influence index employs static assignments, establishing quantitative relationships between basal water breakthrough timing and reservoir dip angle/fracture aperture would strengthen dynamic water invasion prediction models. Secondly, optimizing and expanding quantitative evaluation frameworks. Research should address time-dependent effects of high temperature/pressure on reservoir properties to enhance ultra-deep reservoir prediction accuracy. Systematic validation across global carbonate reservoirs is recommended to develop regionally adaptable evaluation protocols. Lastly, advancing uncertainty analysis and risk assessment methodologies. Quantifying geological controls on reservoir development through probabilistic modeling would enable risk early-warning systems. This would inform rational development planning and contingency strategies, ultimately mitigating operational risks. Implementation of sensitivity-constrained Monte Carlo simulations could effectively characterize parameter interdependencies.
9 Conclusion
The primary factors influencing the stable production capacity of carbonate reservoirs include the fault properties, reservoir characteristics, and water body characteristics. Fault intersections, turning sections, and the midsections of translational strike-slip faults are the most favorable zones for high-yield well development. A positive correlation exists between the fault activity intensity and stable production capacity. The key factors affecting the cumulative reservoir production capacity are the reservoir scale, filling degree, and connectivity, while the reservoir physical properties and pore structure significantly impact the stable production capacity. Confined water enhances the productivity, whereas strong bottom water negatively impacts productivity. Water energy replenishment plays a crucial role in maintaining the stable production capacity.
Based on the three key elements of fault-reservoir-aquifer, this study establishes a stable production capacity evaluation system integrating six core indicators: fault activity intensity, fault nature, effective reservoir volume, reservoir scale, aquifer type, and stimulation parameters. The Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) was employed to determine indicator weights, achieving a breakthrough from qualitative description to quantitative prediction, with successful applications in Zone 4 and Zone 8. Compared with traditional methods, the system innovatively incorporates dynamic structural parameters (including fault activation stages and stress intersection angles) into reservoir effectiveness calculations, addressing evaluation challenges in ultra-deep heterogeneous reservoirs. It precisely differentiates development effects between confined water and bottom water through coupled water chemical isotope analysis and production dynamics, while establishing a three-dimensional evaluation matrix encompassing fracture location, structural context, and aquifer influence, providing an intuitive decision-making tool for development optimization.
Reservoir stimulation measures are vital for enhancing the stable production capacity. Techniques such as acidizing, fracturing, temporary plugging segmentation, fracture expansion, and chelating agent-based unblocking effectively improve reservoir connectivity, permeability, and stability. Further optimization of these measures is needed to enhance their effectiveness.
This study elucidates the stable production mechanisms of ultra-deep fault-controlled carbonate reservoirs, advancing the structural-reservoir-fluid coupling theory for reservoir characterization. By identifying fracture intersections, extensional segments, and central strike-slip zones as sweet spot criteria, it challenges the conventional structural high-zone reservoir control paradigm and offers valuable insights for global exploration and development of analogous reservoirs. From an economic perspective, this study offers significant benefits for actual oil and gas field development. In terms of production improvement, identifying the qualitative discriminant index for high-yield well distribution allows for precise targeting of favorable mining areas, enhancing extraction efficiency. For example, optimizing mining layouts in Shunbei’s No. 4 and No. 8 belts based on this research increased production by 1%–9% in certain areas. Regarding cost control, optimizing reservoir stimulation schemes has reduced unnecessary operations and material waste, cutting single-well stimulation costs by 3%–12%. Furthermore, detailed analysis of reservoir and water properties enables more rational extraction methods, improving recovery rates by an anticipated 1%–3%. These findings contribute to both enhanced productivity and cost efficiency, making a substantial impact on the economic viability of oil and gas field developments. The comprehensive improvements in production and cost management underscore the practical value of this research, supporting sustainable and economically viable operations in challenging reservoir environments.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SC: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. CH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft. WC: Conceptualization, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. LZ: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. HS: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. PX: Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank LetPub (www.letpub.com.cn) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Authors SC, SM, and CH were employed by Sinopec, Northwest Oilfield Company. Author WC was employed by Jiangsu Oilfield Company. Author LZ was employed by Beijing Precise Energy Technology Co. Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alvarez, J. O., and Schechter, D. S. (2017). Improving oil recovery in the Wolfcamp unconventional liquid reservoir using surfactants in completion fluids. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 157, 806–815. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2017.08.004
Aoudia, M., Al-Maamari, R. S., Nabipour, M., Al-Bemani, A. S., and Ayatollahi, S. (2010). Laboratory study of alkyl ether sulfonates for improved oil recovery in high-salinity carbonate reservoirs: a case study. Energy and Fuels 24, 3655–3660. doi:10.1021/ef100266p
Atmadibrata, R. M. R., Muslim, D., Hirnawan, R. F., and Abdurrokhim, A. (2019). Characteristics of arun carbonate reservoir and its implication to optimize the most potential gas resource zone in arun gas field, aceh, Indonesia. Indonesian J. Geoscience 6, 209–222. doi:10.17014/ijog.6.2.209-222
Awdal, A., Healy, D., and Alsop, G. (2016). Fracture patterns and petrophysical properties of carbonates undergoing regional folding: a case study from Kurdistan, N Iraq. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 71, 149–167. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.12.017
Bu, X. Q., Wang, L. Y., Zhu, L. H., Huang, C., and Zhu, X. X. (2023). Characteristics and reservoir accumulation model of Ordovician fault-controlled fractured-vuggy reservoirs in Shunbei oil and gas field, Tarim Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 35, 152–160. doi:10.12108/yxyqc.20230313
Chen, S. Y., He, Y. F., Wang, L. X., Shang, H. J., Yang, X. R., and Yin, Y. S. (2024). Architecture characterization and 3D geological modeling of Ordovician carbonate reservoirs in Shunbei No. 1 fault zone, Tarim Basins. Lithol. Reserv. 36, 124–135. doi:10.12108/yxyqc.20240212
Dang, Z. G., Chen, X. P., Yao, X. Z., Xu, Z. M., Zhou, M. M., Yang, W. X., et al. (2024). Wellbore temperature prediction model and influence law of ultra-deep wells in Shunbei field, China. Processes 12, 1715. doi:10.3390/pr12081715
Deng, X. L., Chen, J. J., Cao, P., Zhang, Y. T., Luo, X., Chang, S. Y., et al. (2023). Segmentation and lateral growth of intracratonic strike-slip faults in the northern Tarim Basin, NW China: influences on Ordovician fault-controlled carbonate reservoirs. Front. earth Sci. 11. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1255162
Deng, Z. Y., Zhou, D. S., Dong, H. Z., Huang, X. W., Wei, S. P., and Kang, Z. J. (2024). Deep learning for predicting porosity in ultra-deep fractured vuggy reservoirs from the Shunbei oilfield in Tarim Basin, China. Sci. Rep. 14, 29605. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-81051-4
Ding, Y. Y., Xiang, Z. P., Ao, X., Li, Z. Q., Yang, W., Wang, Z. Y., et al. (2021). Influence of artificial fracture on stable production capacity of deep shale gas reservoir. J. Chongqing Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 23, 6–11. doi:10.19406/j.cnki.cqkjxyxbzkb.2021.02.003
Dou, Z. Y., Yang, Z. M., Dong, C. C., Li, H. B., Wang, Y. M., and Hou, H. T. (2024). Rock physical evolution and microscopic flow mechanism of massive energy replenishment in tight oil reservoirs. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 14, 49–63. doi:10.46690/ager.2024.10.07
Eikeland, K. M., and Hansen, H. (2009). Dry gas reinjection in a strong waterdrive gas/condensate field increases condensate recovery - case study: the sleipner ost ty field, south viking graben, Norwegian North Sea. Spe Reserv. Eval. and Eng. 12, 281–296. doi:10.2118/110309-PA
Esrafili-Dizaji, B., and Rahimpour-Bonab, H. (2019). Carbonate reservoir rocks at giant oil and gas fields in SW Iran and the adjacent offshore: a review of stratigraphic occurrence and Poro-perm characteristics. J. petroleum Geol. 42, 343–370. doi:10.1111/jpg.12741
Fallah-Bagtash, R., Bayet-Goll, A., Omidpour, A., and Kakemem, U. (2025). Reservoir quality drivers in the oligo-miocene Asmari Formation, dezful embayment, Iran: facies, diagenesis, and tectonic controls. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 173, 107279. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2024.107279
Fossen, H., Hesthammer, J., Johansen, T. E. S., and Sygnabere, T. O. (2003). Structural geology of the Huldra Field, northern North Sea - a major tilted fault block at the eastern edge of the Horda Platform. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 20, 1105–1118. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.07.003
Gao, X. P., Yang, J., Han, H. F., Peng, J. L., Peng, H., and Yang, Z. F. (2023). Experimental research on the effect caused by effective stress change in injection production capacity of carbonate reservoir. Front. Earth Sci. 11, 1101056. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1101056
Gomes, C. P., Fossen, H., Almeida, R. P. D., and Salmoni, B. (2018). Subseismic deformation in the vaza-barris transfer zone in the cretaceous recôncavo-tucano-jatobá rift system, NE Brazil. J. Struct. Geol. 117, 81–95. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2018.09.007
Guo, P., Tu, H. M., Wang, Z. H., Ren, Y. M., and Qiu, Y. L. (2016). Discussion about the exploitation rate of gas condensate reservoirs. Sci. Technol. Eng. 16, 31–35.
Hennenfent, G., Hegmann, M., Harris, C., and Schwartz, K. (2015). From core analysis to log-based pay identification in the Delaware Basin Wolfcamp Formation. Interpretation-A J. Subsurf. Charact. 3, SV35–SV44. doi:10.1190/INT-2014-0267.1
Hosseini, M., Ali, M., Fahimpour, J., Keshavarz, A., and Iglauer, S. (2024). Energy storage in carbonate and basalt reservoirs: investigating secondary imbibition in H2 and CO2 systems. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 11, 132–140. doi:10.46690/ager.2024.02.05
Hu, S. Y., Li, J. Z., Wang, T. S., Wang, Z. C., Yang, T., Li, X., et al. (2020). CNPC oil and gas resource potential and exploration target selection. Petroleum Geol. Exp. 42, 813–823. doi:10.11781/sysydz202005813
Hu, X., Hou, J. G., and Liu, Y. M. (2024). Construction of a multi-source fault-controlled karst cave training dataset and application in three-dimensional modelling using generative adversarial networks. Petroleum Sci. Bull. 03, 422–433. doi:10.3969/j.issn.2096-1693.2024.03.031
Huang, J. P., Huang, Y. B., Ma, Y. Y., and Liu, B. W. (2023). Automatic karst cave detection from seismic images via a convolutional neural network and transfer learning. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 1043218. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.1043218
Jiang, T. W., Sun, L. D., Xie, W., Xiao, X. J., Wang, Y., and Xia, J. (2021). Three-element development mechanism of cyclic gas injection in condensate gas reservoirs and a new technique of enhancing condensate oil recovery. Acta Pet. Sin. 42, 1654–1664. doi:10.7623/syxb202112010
Khalid, P., Ehsan, M. I., Khurram, S., Ullah, I., and Ahmad, Q. A. (2022). Reservoir quality and facies modeling of the early Eocene carbonate stratigraphic unit of the Middle Indus Basin, Pakistan. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 1063877. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.1063877
Khan, S., Khulief, Y., and Al-Shuhail, A. (2019). “Reservoir geomechanical modeling and ground uplift during CO2 injection into Khuff reservoir,” in Proceedings of the ASME-JSME-KSME 2019. doi:10.1115/AJKFluids2019-4809
Lee, S. (2015). Determination of priority weights under multiattribute decision-making situations: AHP versus fuzzy AHP. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 141. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)CO.1943-7862.0000897
Li, F. L., Lin, C. Y., Zhang, G. Y., Ren, L. H., Zhu, Y. F., Zhang, Y. T., et al. (2024c). Characteristics of geophysical response and fine identification of multistage strike-slip fault in Tabei area. J. China Univ. Petroleum Ed. Nat. Sci. 48, 1–14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2024.03.001
Li, P. H., Liu, Z. W., Cai, L., and Chen, Y. (2024a). The research on high efficiency water injection development of carbonate rock reservoir in the middle east. Front. Energy Res. 12, 1396480. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2024.1396480
Li, R. X., Deng, H. C., Fu, M. Y., Hu, L. X., Xie, X. H., Zhang, L. Y., et al. (2023). Identification method of thief zones in carbonate reservoirs based on the combination of static and dynamic data: a case study from the Cretaceous Mishrif Formation in the H oilfield, Iraq. Front. Energy Res. 10, 1043231. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2022.1043231
Li, Y. B., Xu, T. F., Xin, X., Xia, Y. L., Zhu, H. X., and Yuan, Y. L. (2024b). Multi-scale comprehensive study of the dynamic evolution of permeability during hydrate dissociation in clayey silt hydrate-bearing sediments. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 12, 127–140. doi:10.46690/ager.2024.05.05
Liao, H. Y., Xu, T., and Yu, H. M. (2024). Progress and prospects of EOR technology in deep, massive sandstone reservoirs with a strong bottom-water drive. Energy Geosci. 5, 100164. doi:10.1016/j.engeos.2023.100164
Liu, C. H., and Chen, Z. H. (2010). Analysis of production decline and influence factors in the carbonate reservoirs of Tahe oilfield. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs 17, 72–74+116+127.
Liu, H. T., Liu, J., Liu, H. F., Qiu, J. P., Cai, B., Liu, J. Y., et al. (2020). Progress and development direction of production test and reservoir stimulation technologies for ultra-deep oil and gas reservoirs in Tarim Basin. Nat. Gas. Ind. 40, 76–88. doi:10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.11.009
Ma, Y. S., Cai, X. Y., Yun, L., Li, Z. J., Li, H. L., Deng, S., et al. (2022). Practice and theoretical and technical progress in exploration and development of Shunbei ultra-deep carbonate oil and gas field, Tarim Basin, NW China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 49, 1–20. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(22)60001-6
Ma, Y. S., He, Z. L., Zhao, P. R., Zhu, H. Q., Han, J., You, D. H., et al. (2019). A new progress in formation mechanism of deep and ultra-deep carbonate reservoir. Acta Pet. Sin. 12, 1415–1425. doi:10.7623/syxb201912001
Male, F., Dommisse, R., Sivila, L. J., Hamlin, S., and Goodman, E. D. (2023). Properties of high-performing horizontal wells in the Midland Basin. Interpretation-A J. Subsurf. Charact. 11, T697–T706. doi:10.1190/INT-2022-0105.1
Moradi, M., Kadkhodaie, A., Taheri, M. R., and Chenani, A. (2024). Estimation of porosity distribution from formation image logs and comparing the results with NMR log analysis: implications for the heterogeneity analysis of carbonate reservoirs with an example from the Asmari reservoir, southwest Iran. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 218, 105366. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2024.105366
Mou, J. Y., He, J. Y., Zheng, H. Q., Zhang, R. S., Zhang, L. F., and Gao, B. D. (2023). A new model of temperature field accounting for acid-rock reaction in acid fracturing in Shunbei oilfield. Processes 11, 294. doi:10.3390/pr11010294
Narayan, S., Konka, S., Chandra, A., Abdelrahman, K., Andráš, P., and Eldosouky, A. M. (2023). Accuracy assessment of various supervised machine learning algorithms in litho-facies classification from seismic data in the Penobscot field, Scotian Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 11, 1150954. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1150954
Ni, X. F., Shen, A. J., Qiao, Z. F., Zheng, J. F., Zheng, X. P., and Yang, Z. (2023). Genesis and exploration enlightenment of Ordovician fracture-vuggy carbonate karst reservoirs in Tarim Basin. Lithol. Reserv. 35, 144–158. doi:10.12108/yxyqc.20230214
Qadir, S., Haque, A., Ahmed, N., and Mohamed, Z. (2011). Comparison of different enhanced oil recovery techniques for better oil productivity. Int. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 1, 143–153.
Qi, L. X. (2020). Characteristics and inspiration of ultra-deep fault-karst reservoir in the Shunbei area of the Tarim Basin. China Pet. Explor. 25, 102–111. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.01.010
Qiu, H., Wen, M., Wu, Y., Xing, X. S., Ma, N., Li, Z. D., et al. (2023). Water control experiments in huizhou buried-hill fractured condensate reservoirs in nanhai oilfield. Xinjiang Pet. Geol. 44, 84–92. doi:10.7657/XJPG20230112
Rahim, Z., and Al-Qahtani, M. Y. (2003). Selecting perforation intervals and stimulation technique in the Khuff reservoir for improved and economic gas recovery. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 37, 113–122. doi:10.1016/S0920-4105(02)00314-5
Ramiro-Ramirez, S., Bhandari, A. R., Reed, R. M., and Flemings, P. B. (2024). Permeability of upper Wolfcamp lithofacies in the Delaware Basin: the role of stratigraphic heterogeneity in the production of unconventional reservoirs. AAPG Bull. 108, 293–326. doi:10.1306/12202222033
Sabouhi, M., Wood, D. A., Mollajan, A., and Azad, M. N. (2024). Tectono-sedimentary evolution of prolific Permo-Triassic petroleum reservoirs offshore Iran: insights from seismic stratigraphy. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 242, 213217. doi:10.1016/j.geoen.2024.213217
Su, H., Guo, Y. D., Cao, L. Y., Yu, C., Cui, S. Y., Lu, T., et al. (2024). Natural depletion characteristics and pressure maintenance strategies of fault-controlled fracture-cavity condensate gas reservoirs in Shunbei Oilfield. Lithol. Reserv. 36, 178–188. doi:10.12108/yxyqc.20240517
Taheri, K., Alizadeh, H., Askari, R., Kadkhodaie, A., and Hosseini, S. (2024). Quantifying fracture density within the Asmari reservoir: an integrated analysis of borehole images, cores, and mud loss data to assess fracture-induced effects on oil production in the Southwestern Iranian Region. Carbonates Evaporites 39, 8. doi:10.1007/s13146-023-00916-3
Tan, J., Cai, H., Li, Y. L., Liu, C. Y., Miao, F. F., and Liu, C. Z. (2022). Physical simulation of residual oil displacement production in offshore strong bottom water reservoir. J. petroleum Explor. Prod. Technol. 12, 521–546. doi:10.1007/s13202-021-01297-w
Tang, H. X., Jia, C. S., Lu, H., Deng, Y. H., and Zhu, B. Y. (2024). Numerical simulation of residual oil distribution characteristic of carbonate reservoir after water flooding. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1395483. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1395483
Tang, M. R., Wang, C. W., Deng, X. A., Yang, H. F., Lu, J., and Yu, H. Y. (2022). Experimental investigation on plugging performance of nanospheres in low-permeability reservoir with bottom water. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 6, 95–103. doi:10.46690/ager.2022.02.02
Tong, K. J., He, J., Chen, P. Y., Li, C. Y., Dai, W. H., Sun, F. T., et al. (2024). Key technologies for the efficient development of thick and complex carbonate reservoirs in the Middle East. Energies 17, 4566. doi:10.3390/en17184566
Underhill, J. R., and Richardson, N. (2022). Geological controls on petroleum plays and future opportunities in the North Sea rift super basin. AAPG Bull. 106, 573–631. doi:10.1306/07132120084
Wang, L. Y., Gong, W., and Li, H. Y. (2024a). Seismic prediction and well trajectory design for ultra-deep fault-controlled carbonate fractured cave reservoirs: taking the north-central part of fault zone No. 4 in the Shunbei Oilfield as an example. Complex Hydrocarb. Reserv. 17, 288–295. doi:10.16181/j.cnki.fzyqc.2024.03.006
Wang, Q. H., Yang, H. J., Wang, R. J., Li, S. Y., Deng, X. L., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Discovery and exploration technology of fault-controlled large oil and gas fields of ultra-deep formation in strike slip fault zone in Tarim Basin. China Pet. Explor. 26, 58–71. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.04.005
Wang, Y. J., Xu, G. S., Zhou, W., Liang, J. J., Xu, F. H., and He, S. (2022). Predicting granitic buried-hill reservoirs using seismic reflection data—a case study from the bongor basin, southwestern Chad. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 949660. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.949660
Wang, Z., Zhang, Y. Q., Wang, X. K., Lin, Y. P., Jiang, L., and Zhang, X. Z. (2024b). Meteoric water effect of diagenesis processes in deep carbonate reservoirs. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1292104. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1292104
Wu, G. H., Wang, H., Chen, Z. Y., Liu, J. L., Zhao, K. Z., Gao, L., et al. (2010). Characteristics of the complex ordovician carbonate reservoirs in the Tarim Basin. Oil and Gas Geol. 31, 763–769.
Xiao, Y., Kang, B., Deng, X. L., Shi, Y., and Guo, P. (2012). The physical simulation research of full diameter core for different development way of fractured-vuggy carbonate gas condensate reservoir. Xinjiang Oil and Gas 8, 58–61. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2012.01.013
Xie, P. F., Hou, J. G., Wang, Y., Zhang, H. T., Lv, X. R., Li, H. K., et al. (2023). Application of multi-information fusion modeling of fracture-vuggy reservoir in Ordovician reservoir of 12th block in Tahe Oilfield. J. China Univ. Petroleum Ed. Nat. Sci. 47, 1–14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2023.03.001
Xu, C. G., Yu, H. B., Wang, J., and Liu, X. J. (2019). Formation conditions and accumulation characteristics of Bozhong 19-6 large condensate gas field in offshore Bohai Bay Basin. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 46, 27–40. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(19)30003-5
Yang, H. J., Deng, X. L., Zhang, Y. T., Xie, Z., Li, Y., Li, S. Y., et al. (2020). Great discovery and its significance of exploration for Ordovician ultradeep fault-controlled carbonate reservoirs of Well Manshen 1 in Tarim Basin. China Pet. Explor. 25, 13–23. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2020.03.002
Yuan, H. W., Chen, S. P., Neng, Y., Zhao, H. B., Xu, S. D., Wang, X. P., et al. (2021). Composite strike-slip deformation belts and their control on oil and gas reservoirs: a case study of the northern part of the Shunbei 5 strike-slip deformation belt in Tarim Basin, northwestern China. Front. Earth Sci. 9. doi:10.3389/feart.2021.755050
Yun, L., and Deng, S. (2022). Structural styles of deep strike-slip faults in Tarim Basin and the characteristics of their control on reservoir formation and hydrocarbon accumulation: a case study of Shunbei oil and gas field. Acta Pet. Sin. 43, 770–787. doi:10.7623/syxb202206003
Zhang, G. Y., Huang, X. R., Xu, Y. G., Tang, S. H., Chen, K., and Peng, D. (2024a). Deep carbonate gas reservoir sweet spot identification with seismic data based on dual-factor control of sedimentary facies and fault system. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1427426. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1427426
Zhang, X., Wang, X. Z., Guo, T. K., Zhao, H. Y., Li, Z. M., Yang, B., et al. (2020). Experiment on evaluation of temporary plugging agent for in-fracture steering fracturing in Shunbei oilfield. Lithol. Reserv. 32, 170–176. doi:10.12108/yxyqc.20200518
Zhang, Y., Li, H. Y., Chen, X. P., Bu, X. Q., and Han, Y. (2022). Practice and effect of geology-engineering integration in the development of ultra-deep fault-controlled fractured-vuggy oil/gas reservoirs,Shunbei area, Tarim Basin. Oil and Gas Geol. 43, 1466–1480. doi:10.11743/ogg20220615
Zhang, Y., Xu, K., Zhang, H., Lai, S. J., Liang, J. R., and Qian, Z. W. (2024b). Numerical simulation and application of ground stress field in ultra-deep strike-slip faults—taking the FI12 fault zone in the Fuman Oilfield as an example. Front. Energy Res. 12, 1361247. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2024.1361247
Keywords: carbonate reservoirs, stable production capacity, geological structure, reservoir characteristics, water body characteristics
Citation: Chen S, Mei S, Huang C, Chen W, Zhang L, Shang H and Xie P (2025) Main factors controlling stable production from gas-condensate reservoirs in block 2 of the Shunbei Oilfield, Tarim Basin. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1559057. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1559057
Received: 11 January 2025; Accepted: 16 May 2025;
Published: 26 May 2025.
Edited by:
Yuming Liu, China University of Petroleum, ChinaReviewed by:
Muming Wang, University of Calgary, CanadaBo Liao, China University of Petroleum (East China), China
Iman Nowrouzi, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Mei, Huang, Chen, Zhang, Shang and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Pengfei Xie, cGVuZ2ZlaS54aWVAeWFuZ3R6ZXUuZWR1LmNu
 Shuyang Chen1
Shuyang Chen1 Haojie Shang
Haojie Shang Pengfei Xie
Pengfei Xie