- 1School of Information and Engineering, Yancheng Teachers University, Yancheng, Jiangsu, China
- 2Academy of Engineering and Technology, Yang-En University, Quanzhou, Fujian, China
- 3Xi’an Center of Mineral Resources Survey, China Geological Survey, Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
- 4Department of Earth Sciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands
- 5Department of Geology, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman, Kerman, Iran
Effective early warning systems are crucial for mitigating the risks of landslides in vulnerable coastal areas. With the increasing frequency of coastal landslides, precise monitoring solutions are essential for timely interventions. This review addresses real-time monitoring by fiber-optic technologies, which offer high precision, rapid data acquisition, and adaptability, making them a promising solution. Fiber-optics provide continuous, real-time data for early detection of ground movements, unlike traditional methods that struggle with spatial and temporal coverage. Fiber-optic sensors cover large areas and maintain a high frequency, allowing for a detailed assessment of landslide behavior. This review highlights successful implementations of fiber-optic monitoring in both lab and field settings, showcasing their versatility and effectiveness. This review demonstrates the significant contributions of fiber-optic technologies in improving landslide monitoring and risk management. By enabling timely and accurate data collection, these sensors enhance early warning systems and trigger proactive responses to protect lives and infrastructure. Additionally, their use aids in understanding landslides, developing effective mitigation strategies, and land use planning, ultimately strengthening the resilience 22 of coastal communities.
1 Introduction
Landslides are recognized as the second most catastrophic geohazard by the United Nations Development Program. Landslides pose a significant danger to human lives, infrastructure, and the environment (Ivanov et al., 2021; Minardo et al., 2021a). The Belgium Centre for Research on Epidemiology of Disasters reports that landslides account for 17% of all fatalities caused by natural hazards worldwide (Pourkhosravani et al., 2022). Landslides include slides, falls, topples, flows, lateral spread, and complex movements, each with different failure types and scales (Longoni et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2021). Understanding the physics and triggers of landslides (Yu et al., 2022) is crucial for developing accurate models and enabling risk assessments with the aim of identifying high-risk areas and implementing precautionary measures (Wang et al., 2024). Landslides in coastal areas occur when sections of land near shorelines become unstable and move downslope into the sea or coastline (Cascini, 2008; Azarafza et al., 2018). Coastal landslides can result in the destruction of infrastructure, property loss, and even loss of lives. The complex interplay of geological, hydrological, and climatic factors drives these events, making them challenging to study (Chae et al., 2017). Understanding the causes, monitoring techniques, and mitigation strategies for coastal landslides is essential to protect lives and fragile coastal ecosystems. Efforts to enhance resilience and provide early warning systems are crucial as coastal populations continue to grow in these vulnerable areas (Nikoobakht et al., 2022; Mao et al., 2021; 2022).
In tectonically active coastal regions, such as the Makran Subduction Zone, the interplay between tectonic uplift and steep coastal slopes poses a significant geohazard risk. Historical evidence indicates that both submarine and terrestrial landslides have triggered devastating tsunamis in these areas (Hoffmann et al., 2014; Mokhtari, 2015). Tectonically active regions and deformed mountain ranges—such as Northern Chile (Mather et al., 2014) the Zagros (Ghanbarian et al., 2021; Ghanbarian and Derakhshani, 2022), the Apennines (Carlini et al., 2016), and the Daguangbao area (Cui et al., 2018) —where fault interactions and transpressional stress regimes contribute to surface instabilities and mass movements (Quintana et al., 2006; Rashidi et al., 2020), should also be considered as potentially landslide-prone zones. In such geodynamically complex settings, detailed monitoring and hazard assessment—supported by high-resolution technologies such as fiber-optic sensing systems—are essential for identifying failure-prone areas and effectively mitigating disaster risks.
Monitoring methods are crucial for studying mass movements and ground deformations (deformation in the context of landslides refers to the change in shape or structure of the slope or ground mass as it responds to stresses such as gravity, water infiltration, or seismic activity. It indicates how the earth’s surface or materials bend, twist, or fracture under the influence of these forces, which is crucial in assessing landslide risks), especially in developing early warning systems (EWS). Examples of monitoring instruments that record axial deformations and landslides include extensometers, inclinometers, and LiDAR (Chae et al., 2017). An upcoming monitoring technique is fiber-optic technology. This technology benefits seamless data transfer and real-time monitoring and has emerged as a valuable tool for landslide monitoring. Its ability to detect potential landslide events in real-time enables early warning and offers valuable insights into mass movement behavior (Aulakh et al., 2004). Fiber-optic technology is robust and resistant to weather and usage conditions, making it a reliable solution for monitoring landslides in various environmental conditions (Johnson et al., 2023). As research in fiber-optic technology advances, its potential for revolutionizing geohazard monitoring and improving landslide risk management becomes more apparent. Integrating fiber-optic monitoring systems with other advanced techniques will enhance landslide analysis and ultimately contribute to the protection of lives and infrastructure in landslide-prone areas (Zhu et al., 2014). EWS for landslides in coastal areas are crucial because they provide real-time monitoring of slope stability, rainfall, and seismic activity, allowing authorities to issue timely evacuation orders and mitigate damage. Coastal regions are highly vulnerable due to steep terrain, heavy rainfall, and erosion from waves, increasing the risk of rapid slope failure. Advanced sensors, remote sensing, and predictive models help detect warning signs, reducing casualties and infrastructure loss. Effective systems integrate geotechnical data with weather forecasts, ensuring precise risk assessment and faster response to potential disasters.
In landslide monitoring applications within geoengineering, two main types of fiber-optic cables are used for their specific capabilities: multi-mode fibers, suitable for higher data rates over shorter distances, and single-mode fibers, ideal for long-distance precise signal transmission (Zeni et al., 2015). Multi-mode fibers carry multiple light rays simultaneously, making them suitable for higher data rates over shorter distances, such as in campus networks, data centers, and laboratory settings, where multiple light modes are beneficial for efficient data transmission across relatively compact areas. Multi-mode fibers come in two variants: graded-index, where the refractive index gradually decreases from the center to the edge of the core, reducing modal dispersion and allowing for higher bandwidth over longer distances; and step-index, which has a uniform refractive index in the core and an abrupt change at the cladding, making it more suitable for shorter-distance, lower-bandwidth applications. In contrast, single-mode fibers are designed for precise signal transmission over long distances due to their smaller core size (Minardo et al., 2021a). Fiber-optic technology can detect subtle ground movements along their entire length, with resolutions often reaching millimeters per day or even finer, depending on the specific sensor type and environmental conditions (Papini et al., 2020). Fiber-optic therefore can provide detailed spatial data, enhancing understanding of landslide dynamics and improving hazard management strategies (Zhu et al., 2015). Due to their resilience against environmental challenges and immunity to electromagnetic interference, fiber-optic sensors offer a distinct advantage for long-term monitoring in unstable or remote terrains where traditional sensors may fail (Acharya and Kogure, 2024). However, fiber-optic systems entail initial setup costs and require specialized expertise for installation and maintenance (Johnson et al., 2023). Additionally, while fiber-optic sensors can be adapted to measure groundwater pressure, their primary effectiveness lies in strain monitoring (Yang et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2025); they may require specialized configurations to accurately monitor other parameters, such as soil moisture (Kelam et al., 2022) or pore pressure, depending on the specific application (Zhu et al., 2014).
Fiber-optic technology significantly advances coastal landslide monitoring by providing real-time, precise data on critical parameters like strain (strain in landslide studies is the measure of the internal deformation that occurs within the soil, rock, or slope materials due to the forces acting upon them. This strain, which includes stretching or compressing of the material, can help identify early signs of slope instability or failure, providing valuable information for monitoring and predicting landslide events) and deformation. Its durability in harsh coastal conditions, such as saltwater and moisture, ensures reliable long-term data collection, supporting EWS and automated alerts for timely evacuation. Additionally, the continuous data aids researchers in studying landslide dynamics, informing land-use planning and mitigation strategies to protect vulnerable areas (Zhu et al., 2015; Zeni et al., 2015; Sasi et al., 2020; Yimin et al., 2021; Mao et al., 2024). Although a structured review of studies on the application of fiber-optic technology in landslide and early warning systems is presented in the following sections, a brief overview of prior efforts by researchers who have attempted to address this gap is provided here. Therefore, this review aims to bridge that gap by providing a structured study of the existing body of work. We begin with an overview of conventional landslide EWS components and limitations, followed by a detailed examination of fiber-optic technologies, their principles of operation, and their application in geohazard monitoring.
The primary objective of this study is to offer a thorough and all-encompassing overview of the vital components and diverse applications of fiber-optic technology in landslide hazard monitoring. Through a comprehensive exploration of the latest advancements and the immense potential of fiber-optic monitoring systems, this paper aims to significantly contribute to the advancement and enhancement of landslide risk management strategies. By delving into the intricacies of fiber-optic technology and its integration in landslide monitoring, this study seeks to shed light on its unique capabilities, benefits, and suitability for geohazard assessments. The findings presented herein will serve as a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and policymakers, providing them with an in-depth understanding of how fiber-optic systems can revolutionize the monitoring and management of landslide-prone areas. Moreover, this study strives to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical applications, offering insights into the successful implementation of fiber-optic monitoring in real-world scenarios. By showcasing case studies and success stories, we aim to inspire further innovation and adoption of this cutting-edge technology in landslide hazard monitoring worldwide. Through collaboration with experts and stakeholders in the field, this research seeks to stimulate a productive dialogue and encourage the development of interdisciplinary approaches to address the challenges posed by landslides. By fostering collaboration and knowledge exchange, we aim to create a more resilient and proactive approach to landslide risk management, where fiber-optic technology plays a crucial role in safeguarding communities and critical infrastructure from potential geohazard events.
2 Principles of fiber-optic sensing
Fiber-optic sensing is a rapidly emerging technology that utilizes the transmission of light through optical fibers to measure changes in environmental conditions such as strain, temperature, and acoustic signals (Culshaw and Kersey, 2008). These sensors operate based on light scattering phenomena within the fiber, such as Rayleigh, Raman, and Brillouin scattering, which are sensitive to physical perturbations along the fiber’s length (Udd, 1995). When external stimuli alter the optical properties of the fiber, these changes can be measured and interpreted, enabling the detection of environmental changes across long distances with high spatial resolution (Grattan and Sun, 2000). The primary advantage of fiber-optic sensing lies in its ability to provide distributed measurements—meaning data can be gathered continuously along the entire length of the fiber rather than at discrete points (Culshaw and Kersey, 2008). This makes it especially suitable for monitoring large-scale or inaccessible areas, such as landslide-prone coastal zones (Grattan and Sun, 2000). Additionally, optical fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, chemically inert, lightweight, and capable of withstanding harsh environmental conditions, which makes them ideal for long-term monitoring in challenging engineering settings (Sabri et al., 2015).
Despite these advantages, fiber-optic systems face several limitations that must be addressed for broader application (Udd, 1995). One of the major challenges is the complexity and cost of installation, particularly in remote or rugged terrains (Culshaw and Kersey, 2008). Moreover, the data generated are often high in volume and require sophisticated signal processing algorithms for accurate interpretation (Bao and Chen, 2012). Environmental noise, temperature fluctuations, and installation-related mechanical strain can introduce measurement errors or false alarms, complicating real-time monitoring and early warning efforts (Venketeswaran et al., 2022). The main purpose of applying fiber-optic sensing in geotechnical engineering—particularly for landslide monitoring—is to detect early signs of slope instability (Wu et al., 2020). By capturing subtle strain or vibration changes, fiber-optic systems can provide valuable information that supports early warning decision-making and hazard mitigation (Mao et al., 2021). This is particularly critical in densely populated or infrastructure-sensitive coastal regions, where early detection can prevent loss of life and reduce economic damage (Sabri et al., 2015). Given the increasing frequency and severity of natural hazards due to climate change and land-use pressures, the necessity of advanced and reliable monitoring systems has never been greater (Bao and Chen, 2012). Fiber-optic sensing, with its unique combination of precision, resilience, and scalability, offers a promising solution to fill existing gaps in conventional monitoring technologies (Yimin et al., 2021). Continued development and adaptation of these systems for site-specific applications are essential to enhance their effectiveness and integration into modern EWS frameworks.
The application of fiber-optic sensing in geohazards, particularly in landslide monitoring, has shown significant promise due to the technology’s ability to detect minute changes in strain, temperature, and vibration over large spatial extents (Sasi et al., 2020). These parameters are critical in identifying early signs of slope instability, such as ground movement, water infiltration, or seismic activity, all of which often precede landslide events. Unlike traditional point sensors, fiber-optic systems provide distributed sensing along the entire length of the cable, enabling continuous, real-time monitoring of vast or remote terrain with minimal maintenance. This is especially advantageous in coastal areas where terrain is often inaccessible and exposed to harsh environmental conditions. In landslide-prone regions, early detection is essential for risk mitigation and timely evacuation (Johnson et al., 2023). Fiber-optic technologies (e.g., ground vibrations) and long-term deformations (e.g., slope creep) with high spatial resolution (Zhu et al., 2021). Their ability to operate continuously and autonomously makes them ideal components of early warning systems. As climate change increases the frequency and intensity of rainfall-triggered landslides, deploying fiber-optic monitoring systems offers a proactive approach to hazard management, improving the safety and resilience of vulnerable communities and infrastructure (Zhu et al., 2014).
Fiber-optic systems have been deployed globally for diverse geohazard applications (Pei et al., 2020). In landslide contexts, they have been used to detect precursory ground movement, monitor slope deformation, and assess infrastructure stability near unstable terrain (Zheng et al., 2018). Coastal regions benefit from fiber-optic cables’ ability to operate in harsh environments, including saltwater exposure and strong winds (Zhu et al., 2021). Field implementations have demonstrated successful detection of slope instabilities in real-time, enabling EWS to issue alerts before catastrophic failure occurs (Arslan et al., 2015). The effectiveness of EWSs depends not only on accurate detection but also on timely decision-making (Mao et al., 2021). Fiber-optic sensing can serve as a critical data source within EWS frameworks by offering continuous, high-density monitoring (Zhu et al., 2015). These sensors can be integrated with thresholds, alert algorithms, and external communication systems to trigger warnings based on real-time deformation or vibration data. However, the real benefit lies in multi-sensor integration—fiber-optic data must be combined with GNSS, satellite observations, and hydrological data for a comprehensive risk assessment (Zhu et al., 2021).
Despite their advantages, several technical challenges limit the widespread use of fiber-optic systems in landslide monitoring (Wang et al., 2015). First, the initial installation cost—particularly in rugged or remote terrains—can be significant. Second, interpreting massive volumes of high-frequency data requires advanced signal-processing tools and expert knowledge (Lv et al., 2023). Environmental noise, temperature fluctuations, and non-geohazard-related vibrations can also produce false positives (Anjana et al., 2024). Furthermore, the robustness and long-term durability of sensors in saline or erosive coastal conditions remain critical concerns for large-scale deployment (Arslan et al., 2015). The geotechnical variability of landslide-prone regions adds another layer of complexity. Fiber installation must be adapted to the specific characteristics of each site, including soil type, slope angle, groundwater presence, and vegetation covers (Yu et al., 2022). Shallow landslides may require near-surface cable embedding, while deep-seated movements demand borehole installations or integration with geotechnical instruments. This heterogeneity demands flexible and site-specific sensor layout designs, which can significantly affect the cost, installation time, and data interpretation complexity (Zheng et al., 2018). Future developments must focus on improving the real-time processing of fiber-optic data. With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), new algorithms are being developed to classify signals, detect anomalies, and reduce false alarms. These tools can extract meaningful patterns from noisy data and identify the onset of geohazard events more effectively. Such approaches not only improve system responsiveness but also enable predictive capabilities based on historical patterns and environmental conditions.
To facilitate broader adoption, research should aim to lower deployment costs through modular and reusable components. Innovations in wireless backhaul systems, solar-powered nodes, and portable interrogation units can enhance the accessibility of fiber-optic systems in developing regions or hard-to-reach coastal zones. Moreover, leveraging existing telecommunication fiber networks for sensing purposes—known as “dark fiber” sensing—offers a cost-efficient alternative that reuses infrastructure already in place. So, future research in this field should target several critical areas: (1) enhancing sensor durability and signal clarity in marine/coastal environments, (2) developing integrated multi-hazard monitoring platforms, (3) improving real-time data interpretation using AI and ML, and (4) reducing overall system costs through innovation in installation and maintenance. Collaborative research between geotechnical engineers, optical physicists, and data scientists is essential to fully realize the potential of fiber-optic sensing technologies in landslide EWS applications. A more systematic, multi-disciplinary approach will not only advance technical capabilities but also improve societal resilience to geohazards.
3 Early warning systems on landslides
EWS for landslides are designed to provide timely alerts to reduce the impact on human lives, infrastructure, and the environment (Mao et al., 2021). These systems use a network of strategically placed sensors to continuously monitor ground conditions in landslide-prone areas. Sensors such as inclinometers, extensometers, piezometers, GPS receivers, accelerometers, tiltmeters, and fiber optics measure various parameters like ground movement, strain, slope stability, and rainfall intensity (Yimin et al., 2021). Data from these sensors is transmitted in real-time to a centralized processing center using wireless networks or satellite links, allowing for immediate analysis and interpretation (Wang et al., 2015). Advanced algorithms and models process this data, incorporating historical, meteorological, and geological information to predict potential landslide activities accurately (Zhu et al., 2015).
EWS enhances emergency preparedness by enabling authorities to execute evacuation plans, protect infrastructure, and allocate resources efficiently. The successful implementation of an EWS requires collaboration among geologists, meteorologists, engineers, and data analysts (Minardo et al., 2021b). Continuous monitoring, precise data interpretation, and effective communication are critical for safeguarding communities and minimizing landslide damage (Zheng et al., 2018). EWS components include sensors, databases, analysis cores, telecommunication equipment, automated decision centers, and expert controllers (Sasi et al., 2020). Sensors capture various ground movements and environmental parameters, with data stored for analysis. Analysis cores use advanced algorithms to detect anomalies, while telecommunication equipment ensures real-time data transmission (Zhang et al., 2020). Automated decision centers interpret the analyzed data, triggering alerts for critical movements (Johnson et al., 2023). Expert controllers, typically geo-engineers, verify the accuracy of warnings and make informed decisions. Despite challenges in establishing universal standards for EWS, each system is tailored to local conditions and available technologies (Pei et al., 2020). Fiber optic sensors in EWS offer high precision and durability, continuously monitoring ground movements and environmental conditions. Their resilience against harsh coastal conditions ensures reliable long-term data collection (Papini et al., 2020).
Timely warnings empower stakeholders to implement proactive measures like evacuation plans, infrastructure closures, and risk mitigation strategies, reducing the impact of landslides on vulnerable areas and minimizing casualties and property damage (Anjana et al., 2024). Integrating EWS with fiber optic sensors enhances landslide risk management by continuously collecting and analyzing data (Han et al., 2021). This information is invaluable for researchers and geologists, aiding in the development of refined predictive models and comprehensive risk assessments. Understanding landslide mechanisms, triggers, and behaviors over time helps create more effective risk management strategies, informing land-use planning and infrastructure development to improve resilience in landslide-prone regions (Zhu et al., 2021). Deploying fiber optic sensors in EWS provides high-precision, real-time monitoring of ground movements, offering detailed data that helps researchers analyze landslide dynamics and interactions with environmental factors (Zheng et al., 2020). This contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge and improves the accuracy of predictive models and risk assessments (Murray et al., 2022). Fiber optic sensors are robust and reliable, even in harsh terrains and adverse conditions, enhancing our understanding of landslide processes (Pei et al., 2020; Minardo et al., 2021b). To ensure the effective implementation of EWS, developing comprehensive standards is essential (Li et al., 2021; Minardo et al., 2021a). Advances in computational intelligence and fiber optic technology have significantly improved EWS, enabling more accurate predictions and precise monitoring. As these technologies evolve, they promise to enhance landslide monitoring efficiency and reliability, contributing to better risk management and increased resilience in landslide-prone areas.
It should be noted that strain processing in geotechnical monitoring, particularly in landslide studies, plays an important role in distinguishing between endogenic (internal) and exogenic (external) source mechanisms (Olabode et al., 2022). Endogenic sources refer to forces originating from within the Earth, such as tectonic movements, volcanic activity, or deep-seated rock stress changes, while exogenic sources are related to surface processes, such as weathering, erosion, and human activities (Liu et al., 2023). To accurately attribute strain data to either of these sources, advanced processing techniques are employed that can isolate the different causes of strain based on their temporal and spatial characteristics (Thirugnanam et al., 2022).
One key method of strain processing involves the use of time-series data from fiber-optic sensors, which continuously measure strain over long periods (Xu et al., 2024). By analyzing the rate and pattern of strain accumulation, researchers can distinguish between slow, progressive strain that results from exogenic factors like rainfall-induced soil saturation or temperature fluctuations, and abrupt, large-scale strain shifts that are typically linked to endogenic mechanisms like seismic activity or fault movements (Hussain et al., 2022). Additionally, changes in strain patterns over different depths or along specific fault lines can provide insights into the origin of the stress causing the deformation, helping to isolate whether the strain is due to surface or subsurface processes (Longoni et al., 2022). Another technique involves using multi-sensor networks that combine fiber-optic strain measurements with geophysical data, such as seismic data from seismometers or ground motion data from geophones (Liu et al., 2020). This multi-disciplinary approach allows for cross-validation of strain measurements, helping to separate exogenic sources like surface erosion or construction activities from endogenic sources such as deep seismic events (Henninges and Masoudi, 2021). Advanced signal processing algorithms also play a significant role in isolating the two types of sources. Techniques like wavelet transform, Fourier analysis, and machine learning algorithms can be applied to strain data to filter out high-frequency noise typically associated with exogenic processes, leaving the low-frequency components associated with deeper, endogenic events (Chen et al., 2020). By using these techniques, it becomes possible to identify subtle but important differences in how strain develops in response to each source mechanism (Liu et al., 2024). This enables more accurate modeling of landslide dynamics, leading to better risk assessments and more targeted mitigation strategies based on the root causes of strain accumulation.
Figure 1 illustrates the integration of various components within an EWS for landslides, emphasizing the role of fiber-optic sensors among other monitoring technologies, outlining the four key components: Risk Knowledge, Monitoring and Warning, Response Capability, and Dissemination and Communication. This diagram highlights the data flow from sensor input, through processing units, to the automated alert mechanisms, showcasing the comprehensive approach EWS takes to monitor, analyze, and respond to potential landslide threats in real-time. By capturing this entire process, Figure 1 demonstrates the interconnected structure that enables quick and coordinated responses to detected ground movement (Papini et al., 2020).
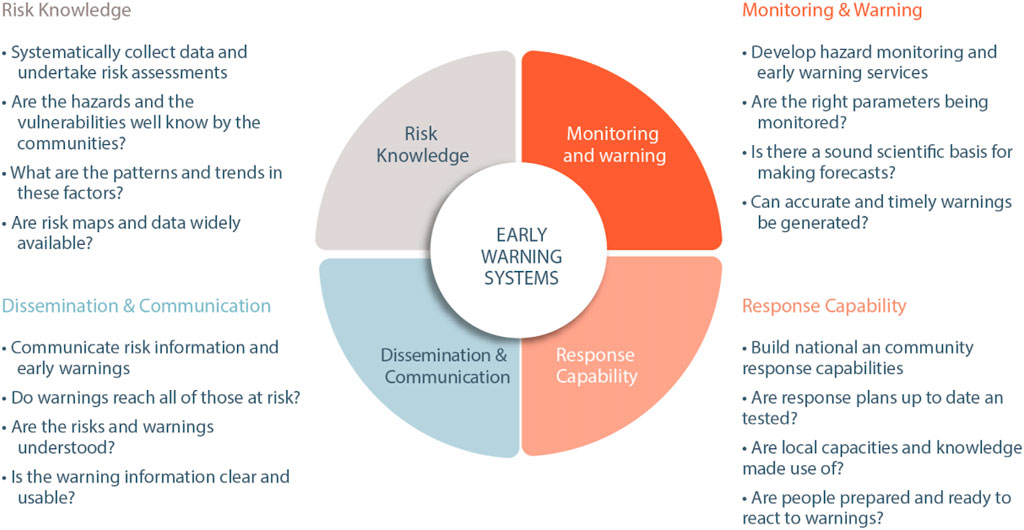
Figure 1. Topical integrated EWS (Papini et al., 2020).
Figure 2 illustrates the primary components and structures of EWS for landslides, highlighting how different sensor types—including fiber-optic technology—integrate to monitor various environmental and geophysical parameters. This setup includes data acquisition, processing, and alert mechanisms, allowing for comprehensive monitoring of landslide-prone areas. By organizing these elements systematically, the figure demonstrates the framework through which EWS can detect early signs of instability, process real-time data, and generate timely alerts for effective risk management (Zhu et al., 2014).
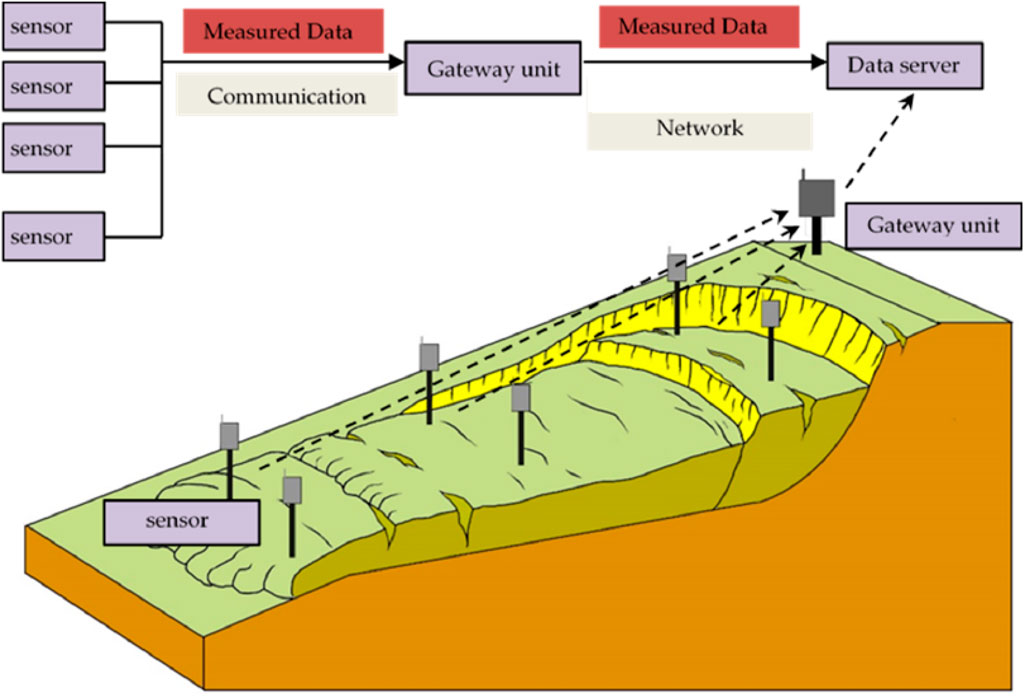
Figure 2. Topical structures of EWS for landslides (Zhu et al., 2014).
4 Fiber-optic applications in landslides
The advantages of fiber-optic technologies include fast and easy data transfer, continuous real-time data recording, high sensitivity, durability, lightweight design, ease of installation and transportation, immunity to electrical and magnetic noise, resistance to environmental impacts, and the ability to multiplex and extract time-dependent data (Zheng et al., 2018). Although fiber-optic technology has been used since the 1800s, its application in geosciences, particularly for landslides, is relatively new (Anjana et al., 2024). The ability to record data in real-time has led to the creation of comprehensive databases that track spatial variations, sliding behavior (both shallow and deep), and strain-displacement measurements from geo-sensors. This data helps describe creep status and mass movement at various slope locations. By using artificial intelligence techniques, especially deep learning, researchers can analyze this data to gain predictive insights into slope conditions and landslide behavior (Arslan et al., 2015). On the other hand, Fiber-optic technology offers significant advantages over traditional methods in landslide monitoring due to its high sensitivity and real-time data transmission capabilities. Unlike conventional sensors, fiber-optic systems can detect minute strain, temperature, and pressure changes over long distances with high precision. This allows for continuous and distributed monitoring of large and remote areas, reducing the need for multiple discrete sensors and frequent manual inspections (Zhu et al., 2015). Additionally, fiber-optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, ensuring reliable performance in harsh environmental conditions. Another key advantage is durability and low maintenance. Traditional sensors, such as inclinometers and piezometers, often require frequent calibration and are susceptible to mechanical failure over time. In contrast, fiber-optic cables have a long lifespan and can function effectively in extreme weather, soil movement, and corrosive environments without significant degradation. Their passive nature also eliminates the need for external power sources along the sensing line, making them ideal for deployment in difficult-to-access regions (Zhu et al., 2014). Furthermore, fiber-optic technology enables EWS with rapid response capabilities. By providing real-time and continuous data, authorities can detect early signs of ground movement and assess potential risks before a landslide occurs. This proactive approach enhances disaster preparedness, minimizes infrastructure damage, and improves public safety (Pei et al., 2020). As a result, fiber-optic-based monitoring is increasingly preferred for large-scale, long-term landslide hazard assessment and mitigation.
Fiber-optic techniques measure displacements (displacement refers to the movement of soil or rock in a landslide, typically measured as the shift in position from its original location. Monitoring displacement allows scientists and engineers to assess the extent of ground movement during or before a landslide, which is essential for understanding the dynamics of slope failure and for issuing early warnings to reduce risk) at shallow depths near the surface or deeper, depending on the specific movement behavior observed (Pei et al., 2020). When deformation or strain exceeds a critical limit, indicating the factor of safety equals 1, a slip occurs. This limit serves as a threshold for continuous, time-dependent failure events initiating slope movement under static conditions. Creep, influenced by triggering factors, contributes to failure conditions and landslide breakdown (Li et al., 2021). Ground-based monitoring techniques, such as fiber-optic technologies, enable continuous monitoring of creep processes within slopes, measuring various creep conditions over time, especially under risky circumstances (Wang et al., 2015). This concept is fundamental to EWS, which forecasts critical conditions related to creep behavior and mass deformation before failure (Minardo et al., 2021a). Fiber-optic systems provide extensive spatial coverage, making them valuable for monitoring large landslide-prone areas like coastlines and mountains. These sensors can be embedded in the ground, attached to structures, or placed underwater, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of landslide dynamics from surface to subsurface. Their durability ensures reliability in harsh conditions, such as moisture, saltwater, or extreme temperatures. Fiber optic sensors can be integrated with other monitoring technologies, including GPS, weather stations, and satellite imagery, enhancing landslide predictions and understanding of triggers and behavior (Cole et al., 2022). The real-time data from fiber optic sensors can trigger automated alerts when thresholds are crossed, prompting timely responses such as evacuations or infrastructure protection measures, thus reducing landslide impacts. Figure 3 illustrates the application of fiber-optic technology in landslide displacement monitoring, showcasing how sensors are strategically positioned to detect ground movements with high precision. This setup enables continuous, real-time monitoring of displacement along various points on a slope, providing detailed insights into strain distribution and deformation patterns. The data gathered from these sensors enhances early warning capabilities by identifying potential instability zones, allowing for timely intervention and risk mitigation (Zhu et al., 2021).
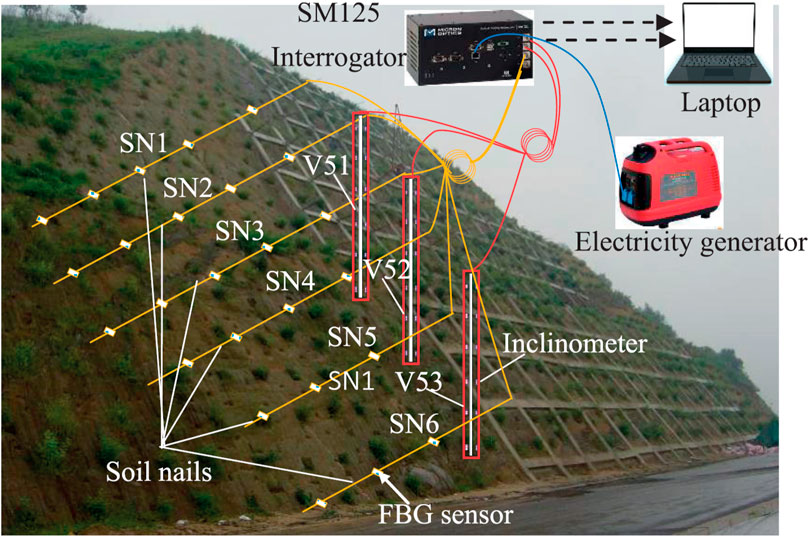
Figure 3. Application of fiber-optic technology in landslide displacement monitoring (Zhu et al., 2021).
Various researchers have made significant contributions to the field of landslide monitoring using fiber-optic technology. Aulakh et al. (2004) evaluated and monitored landslide slip until failure occurrence using optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) sensors in a laboratory setting. Higuchi et al. (2005) utilized OTDR sensors and fiber-optic technology to monitor the Takisaka landslide in Japan, measuring displacement through strain-displacement variations in the landslide mass. Ho et al. (2006) employed fiber glass Bragg grating (FBG) inclinometers for landslide monitoring. Dai et al. (2008) utilized high-resolution distributed fiber-optic stress sensors to monitor stress distribution in a landslide body and used it as an EWS. Iten et al. (2008) applied BOTDR sensors to monitor the St. Moritz landslide and employed large-scale strain gauges to estimate mass displacement. Liu et al. (2010) used POFDR and high-quality OFDR with a 5 cm resolution to examine mechanical behavior and continuously monitor landslides, enabling accurate prediction of ground movements with a low error percentage. Pei et al. (2011), following the work of Ho and colleagues, employed FBG sensors to monitor debris flows in laboratory settings and reported positive results in tracking debris flows. Zhu et al. (2014) developed a new distributed optic fiber transducer that employed electro-optic detection technology to evaluate and monitor slope stability variations. Zeni et al. (2015) developed and implemented a laboratory model for small-scale landslide behavioral analysis using BOTDA to measure mass movements during the landslide. Arslan et al. (2015) used OTDR in conjunction with fiber-optic sensors to monitor the deformation and slip behavior of the soil mass in a laboratory model. Wang et al. (2015) employed FBG sensors to investigate probable sliding surfaces in a landslide site near Wenzhou city and used limit equilibrium methods to analyze slope stability. Zheng et al. (2018) used OTDR sensors for real-time monitoring and landslide stability analysis during an experimental study. In the present work, an artificial intelligence-based approach and deep learning techniques were utilized to monitor and forecast landslide movements in real-time using field data collected by a fiber-optic system consisting of BOTDA and fiber-optic cables.
Zhang et al. (2020) utilized FBG as a real-time monitoring system to measure the displacements occurring in two sliding surfaces (shallow and deep) of the Majiagou landslide. The average displacement rate indicated that the landslide was still creeping at a rate of 0.1 mm/day, which is significant for stability evaluation and the formulation of early warning plans for the reservoir landslide. Herlin et al. (2020) employed fiber-optic-based energy demodulation to monitor deformation in soil layers, demonstrating that the IoT-based system can provide highly accurate measurements of soil shift deformation. Pei et al. (2020) used FBG-based fiber sensors to experimentally measure the displacements occurring in slopes, potentially contributing to EWS for slope monitoring. The study’s results were utilized to develop a new methodology for recording deformations in slopes experiencing different scales of creep. Papini et al. (2020) employed optical fiber strain sensors to monitor sliding conditions in lab-scale landslides under heavy precipitation in controlled laboratory conditions. The study aimed to measure the impact of precipitation in triggering landslides, and the results demonstrated the sensors’ ability to reflect developing instabilities during the experiments, encouraging further investigation of their applicability. Lanciano and Salvini (2020) explored the use of strain-based fiber-optic sensors, employing distributed acoustic sensing (DAS), unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), and distributed fiber-optic sensing (DFOS) to analyze ground deformation under static and dynamic loadings. Minardo et al. (2021b) employed distributed fiber-optic strain sensors for long-term monitoring of a railway tunnel affected by an active landslide in southern Italy. The experimental results, spanning 3 years, demonstrated the sensor’s capability to identify potentially hazardous strained regions along the tunnel walls and track their temporal evolution.
Li et al. (2021) employed FBG fiber sensors to measure strain distribution in the slope mass during erosion. Zhu et al. (2021) implemented a large-scale monitoring system for landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Han et al. (2021) focused on analyzing the error rate of OFDR sensors used for recording displacements in subsurface displacement monitoring landslides. The scholar aimed to solve the error rate issue by designing a new joint fiber-optic displacement sensor capable of achieving accurate displacement monitoring. Its measurement error was analyzed, and feasibility was demonstrated through theory and laboratory experiments. Costrada and Kemal (2021) and Costrada et al. (2021) utilized a fiber-optic sensor and CCD TSL140CL linear sensor array for real-time monitoring of landslide displacement based on micro-strain. The CCD TSL1401CL linear sensor array was specifically used to measure rain intensity, which is the main triggering factor for slope failure and initiation of sliding. The testing results showed that the measurement system, potentially used as an early warning framework, operated with a 0.59% error percentage. Minardo et al. (2021a) employed Brillouin scattering-based optical fiber strain sensors to monitor deformations in a national railway crossing the accumulation zone of an active landslide, the Varco d'Izzo earthflow, in the southern Italian Apennines. The tunnel, after stabilization and installation of a reinforced support system in 2016, was instrumented with distributed fiber-optic strain sensors to detect the onset of potentially dangerous strains in the tunnel structure. The recorded results were used for monitoring periods using inclinometers and acceleration sensors during landslide movements. Ivanov et al. (2021) utilized experimental fiber-optic sensors to simulate rainfall-induced shallow landslide models composed of non-cohesive soil slopes to monitor ground displacements. The researchers stated that the proposed sensing technique could provide a viable and cost-effective alternative to commercially available optical fiber interrogators, offering quantitative monitoring data for shallow landslide monitoring in soil-like materials. Zhao et al. (2021) applied pulse-prepump Brillouin optical time domain analysis (PPP-BOTDA) distributed optical fiber sensing technology to monitor and record the displacement of landslides along the Yangtze River in China, particularly in the Three Gorges Reservoir area. Allil et al. (2021) analyzed slope instability and landsliding using FBG-based inclinometers as long-term surface or underground monitoring methods to detect small soil displacements (Anjana et al., 2024). The errors found in all tests were less than 1%, indicating that the proposed system can serve as an alternative methodology to conventional geotechnical instrumentation techniques.
Ye et al. (2022) utilized a fiber-optic nerve system based on weak-reflection FBG to monitor a giant landslide located in the Three Gorges Reservoir region, China. Cole et al. (2022) conducted an experimental study using DAS-based fiber-optic arrays to monitor a landslide in northern England. Time-lapse analysis of passive data from different time periods revealed velocity changes that may be related to geological changes. Alongside building 2D velocity profiles for each receiver line, the study explored methods for estimating 3D velocity models. Liu and Zhou (2022) employed a distributed real-time in-situ monitoring method based on ultra-weak fiber Bragg gratings (UWFBG) for deformation measurement of a real landslide in Yibin City, Sichuan Province, China. The monitored results suggested that the landslide was in a stable state during the monitoring period. Clarkson et al. (2022a) developed a new slope stability monitoring system using distributed Rayleigh sensing (DRS). Yu et al. (2022) utilized a combined optical fiber transducer (COFT) based on the optical fiber bending loss characteristic for landslide monitoring, determining the sliding direction, magnitude, and rate of slope movement.
One of the most significant areas that overlay is used in geohazard monitoring applications of thermomechanical monitoring with fiber-optic technology (Cheng et al., 2023). Thermomechanical monitoring with fiber-optic technology is an advanced method for detecting and analyzing changes in temperature and strain within geological formations (Di Gennaro et al., 2022). Fiber-optic sensors, particularly Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) and Distributed Strain Sensing (DSS) provide continuous, real-time data over long distances with high spatial resolution (Bado and Casas, 2021; Henninges and Masoudi, 2021). These sensors are embedded in the ground or infrastructure to measure temperature fluctuations and mechanical deformations caused by subsurface movements, allowing for early detection of anomalies that may indicate instability (Miah and Potter, 2017; Soga and Luo, 2018). In the context of geohazards, fiber-optic thermomechanical monitoring is particularly valuable for assessing risks related to landslides (Shi et al., 2017; Minutolo et al., 2020; Tang et al., 2023). Changes in temperature and strain patterns within soil and rock masses (Ye et al., 2024a) can signal shifts in groundwater levels, thermal expansion (Ibrahim et al., 2024), or mechanical stress (Sun et al., 2024) buildup—factors that contribute to slope failures (Wen et al., 2025). By detecting these variations, fiber-optic systems can identify EWS signs of instability (Kashaganova et al., 2023), providing crucial information for risk mitigation and disaster prevention efforts. The integration of this technology with remote sensing and geospatial analysis enhances its effectiveness in monitoring large and inaccessible regions (Liu et al., 2022). Landslide monitoring benefits greatly from the deployment of fiber-optic networks along critical slopes, infrastructure corridors, and high-risk zones (Wang D. Y. et al., 2023). The ability of fiber optics to function in extreme environmental conditions, combined with their long-term stability (Johnson et al., 2023) and low maintenance (Ye et al., 2022), makes them an ideal solution for continuous monitoring (Zhang et al., 2024). When coupled with data analytics and machine learning algorithms, these sensors can improve prediction models, enabling authorities to take proactive measures such as reinforcing slopes or issuing early warnings. As climate change and human activities increase the frequency of landslides (Zhu et al., 2021), fiber-optic thermomechanical monitoring plays a crucial role in improving resilience and minimizing the impact of these geohazards (Ye et al., 2024a).
Fiber-optic sensors contribute to real-time monitoring and early detection of ground movements by providing continuous, high-resolution data on strain, temperature, and pressure changes along a monitored area. Unlike traditional point-based sensors, DFOS systems use optical fibers as sensing elements, enabling the detection of subtle deformations over long distances without gaps in coverage. These sensors operate based on light transmission variations caused by ground movement, allowing for precise and instantaneous detection of potential landslide triggers such as soil displacement, subsurface deformation, and water infiltration (Yu et al., 2022). One of the key advantages of fiber-optic sensors is their ability to deliver real-time alerts. Since they do not require electrical power along the sensing cable, they can be deployed in remote or hazardous locations and provide continuous data transmission to monitoring stations. By integrating fiber-optic data with advanced algorithms and machine learning models, experts can analyze trends and predict slope instability with high accuracy (Cole et al., 2022). This enables authorities to take proactive measures, such as issuing early warnings and initiating preventive actions, before a landslide occurs. Additionally, fiber-optic sensors enhance the reliability and efficiency of landslide monitoring systems. They are highly resistant to environmental factors such as electromagnetic interference, corrosion, and extreme temperatures, ensuring long-term functionality with minimal maintenance (Minardo et al., 2021b). Their scalability allows them to cover vast and geologically complex regions, making them an ideal solution for real-time landslide monitoring in both urban and remote settings. By detecting ground movement at an early stage, fiber-optic technology significantly reduces the risks associated with landslides, protecting infrastructure and human lives (Zheng et al., 2018).
Fiber-optic technology presents significant advantages for landslide monitoring, such as high spatial resolution and real-time data acquisition (Schenato and Pasuto, 2021). However, its implementation comes with several challenges, particularly due to the complexity of installation and maintenance in rugged and unstable terrains (Costrada and Kemal, 2021). Deploying fiber-optic cables in landslide-prone areas requires extensive groundwork (Anjana et al., 2024), including trenching or borehole drilling (Lv et al., 2023), which can be logistically difficult and costly (Pellegrini et al., 2024). Moreover, extreme weather conditions, soil erosion, and ongoing ground deformation can damage the cables, affecting long-term data reliability (Damiano et al., 2024). Another critical limitation is the issue of sensor coupling with the shifting ground (Cola et al., 2021). Landslides involve continuous movement, which can cause fiber-optic cables to lose proper contact with the surrounding soil or rock (Ravet et al., 2021). This affects the accuracy of strain and temperature measurements, leading to potential false readings or data gaps (Han et al., 2023). Ensuring strong sensor-soil coupling requires careful engineering (Clarkson et al., 2022b), but even well-embedded sensors may face issues when subjected to rapid or complex ground deformation patterns, making consistent monitoring difficult (Ye et al., 2024b).
Difficult terrain conditions further complicate data transmission and power supply to fiber-optic systems (Kelam et al., 2023). Remote or mountainous regions, where landslides are most common, often lack the necessary infrastructure to support continuous operation (Brezzi et al., 2024). Establishing a stable power source and data communication network in such areas can be expensive and technically challenging (Kelam et al., 2023). In some cases, harsh environmental conditions, such as heavy rainfall, snowfall, or seismic activity (Brezzi et al., 2024), can further hinder the accessibility and maintenance of fiber-optic installations. Additionally, the dynamic nature of landslides makes predictive modeling and data interpretation more complex (Qin, 2020). Fiber-optic sensors generate vast amounts of data, but distinguishing between natural ground variations and actual precursors of failure requires advanced analytical models (Li et al., 2021). The presence of heterogeneous soil properties, varying moisture content, and external disturbances (such as human activities or vegetation growth) can introduce noise into the collected data (Ebrahim et al., 2024). As a result, effective landslide monitoring using fiber optics requires sophisticated algorithms and cross-validation with other geotechnical and remote sensing methods. Finally, cost considerations and long-term sustainability pose additional limitations (Qin, 2020). While fiber-optic technology offers high precision, its initial installation and maintenance expenses can be prohibitive, particularly for large-scale or long-term monitoring projects (Fenta et al., 2021). Funding constraints may limit widespread deployment, especially in developing regions where landslide risks are high (Tao et al., 2024). Additionally, fiber-optic components degrade over time, requiring periodic replacements or recalibrations, which further adds to operational challenges. Addressing these limitations requires continuous innovation in sensor technology, integration with complementary monitoring techniques, and improved deployment strategies tailored to challenging landscapes (Qin, 2020).
5 Recent advances in fiber-optics in landslide monitoring
Fiber-optic technology has gained considerable attention in the field of geohazard monitoring, particularly in landslide studies. Its application has proven to be highly valuable for providing real-time, continuous, and high-resolution data over long distances. Fiber-optic sensors, such as DTS and DSS, offer a unique advantage in monitoring landslides because they can capture subtle changes in strain and temperature across the entire length of the fiber, which traditional methods struggle to do. This ability to continuously monitor deformation in the ground allows for early detection of potential landslide movements, a crucial factor for risk mitigation in vulnerable areas. Recent advancements in fiber-optic technology have significantly enhanced landslide monitoring capabilities (Johnson et al., 2023; Wang J. et al., 2023). Distributed fiber optic sensors, such as DAS and DTS, are among the notable innovations. DAS enables continuous strain measurements along the entire fiber length, providing comprehensive data on ground movements. DTS monitors temperature changes that can indicate hydrological processes potentially triggering landslides (Anjana et al., 2024). Improved sensing resolution in these fiber-optic sensors allows the detection of even the smallest displacements and strain variations, offering detailed insights into landslide dynamics and enhancing EWS’s accuracy (Zhang et al., 2024).
Previous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of fiber-optic sensors in monitoring landslides. For example, a study by Lienhart (2015) in Austria used fiber-optic strain sensors along a landslide-prone slope to monitor progressive deformations. This illustrates the significant potential of fiber-optic sensors to enhance the safety and accuracy of landslide monitoring, providing more lead time for preventive measures. Furthermore, fiber-optic technology enables the monitoring of areas that are otherwise difficult to access, such as steep or remote slopes, or locations with complex geological conditions (Arslan et al., 2015). Traditional landslide monitoring tools, such as inclinometers, piezometers, or geophones, often require manual data collection or are limited to specific points of measurement (Pei et al., 2011). In contrast, fiber-optic sensors can be deployed over long distances, providing a comprehensive view of the slope’s behavior (Iten et al., 2008). The continuous data collected from these sensors can be transmitted in real-time to monitoring stations, offering a more complete and dynamic understanding of the ongoing processes, which is vital for decision-making in landslide-prone regions (Anjana et al., 2024).
One of the primary advantages of using fiber-optic sensors in landslide monitoring is their ability to detect both slow, progressive deformations and more sudden, catastrophic events. For instance, Howe et al. (2022) conducted a study on a landslide in earth and ocean, also, Schenato (2017) conducted a study on a landslide in France, where fiber-optic sensors were used to monitor strain and temperature fluctuations. Their results revealed that the sensors could detect both gradual shifts in the soil structure due to factors like rainfall and rapid shifts caused by seismic activity or landslide triggers. The ability to distinguish between these types of events is invaluable in landslide risk management, as it allows for tailored responses to different types of ground movement. In addition to monitoring strain and temperature, fiber-optic technology can also be used in conjunction with other geotechnical tools, creating a multi-sensor network that provides a more comprehensive picture of the landslide’s behavior.
While fiber-optic sensors offer numerous advantages, challenges still exist in their application to landslide monitoring (Johnson et al., 2023). One issue is the difficulty of maintaining sensor stability in environments with high seismic activity or rapidly shifting ground (Pellegrini et al., 2024). Fiber-optic cables embedded in the ground can experience a loss of coupling with the surrounding soil or rock, which may affect data accuracy (Ma et al., 2023). To mitigate this, new advancements in sensor design are being explored, such as the use of multi-core fibers and more robust installation techniques, to improve the durability and reliability of these systems (Cola et al., 2021). Additionally, fiber-optic systems are often more expensive than traditional monitoring techniques, which can limit their widespread adoption, particularly in regions with limited funding for geohazard monitoring (Costrada and Kemal, 2021). Despite these challenges, the potential of fiber-optic technology in landslide monitoring is vast, and ongoing research continues to improve its application (Wang J. et al., 2023). Future studies should focus on enhancing sensor robustness, reducing costs, and integrating fiber-optic systems with other geohazard monitoring technologies (Li et al., 2021). There is also a need for more long-term case studies to better understand the behavior of fiber-optic sensors in real-world landslide scenarios (Herlin et al., 2020). By incorporating lessons learned from past studies and addressing existing challenges, fiber-optic technology can play an increasingly vital role in landslide monitoring and EWS, ultimately contributing to improved disaster risk reduction strategies.
Integrating multiple sensing modalities into a single fiber-optic cable allows for simultaneous measurement of various geophysical parameters, providing a more holistic understanding of conditions leading to landslides (Anjana et al., 2024). Combining data from fiber-optic sensors with remote sensing technologies like LiDAR and satellite imagery further enhances real-time monitoring and assessment of large-scale landslides over extensive areas (Pellegrini et al., 2024). The use of artificial intelligence algorithms in data fusion improves landslide predictions’ accuracy and early warning systems’ reliability (Wang J. et al., 2023). Long-term stability and reliability of fiber-optic sensors in challenging environmental conditions remain a focus of ongoing research to ensure their effectiveness for continuous monitoring over extended periods (Zhang et al., 2024). As fiber-optic technology continues to evolve, consulting up-to-date academic sources and reputable journals in geotechnical engineering and landslide monitoring is essential for the latest advancements.
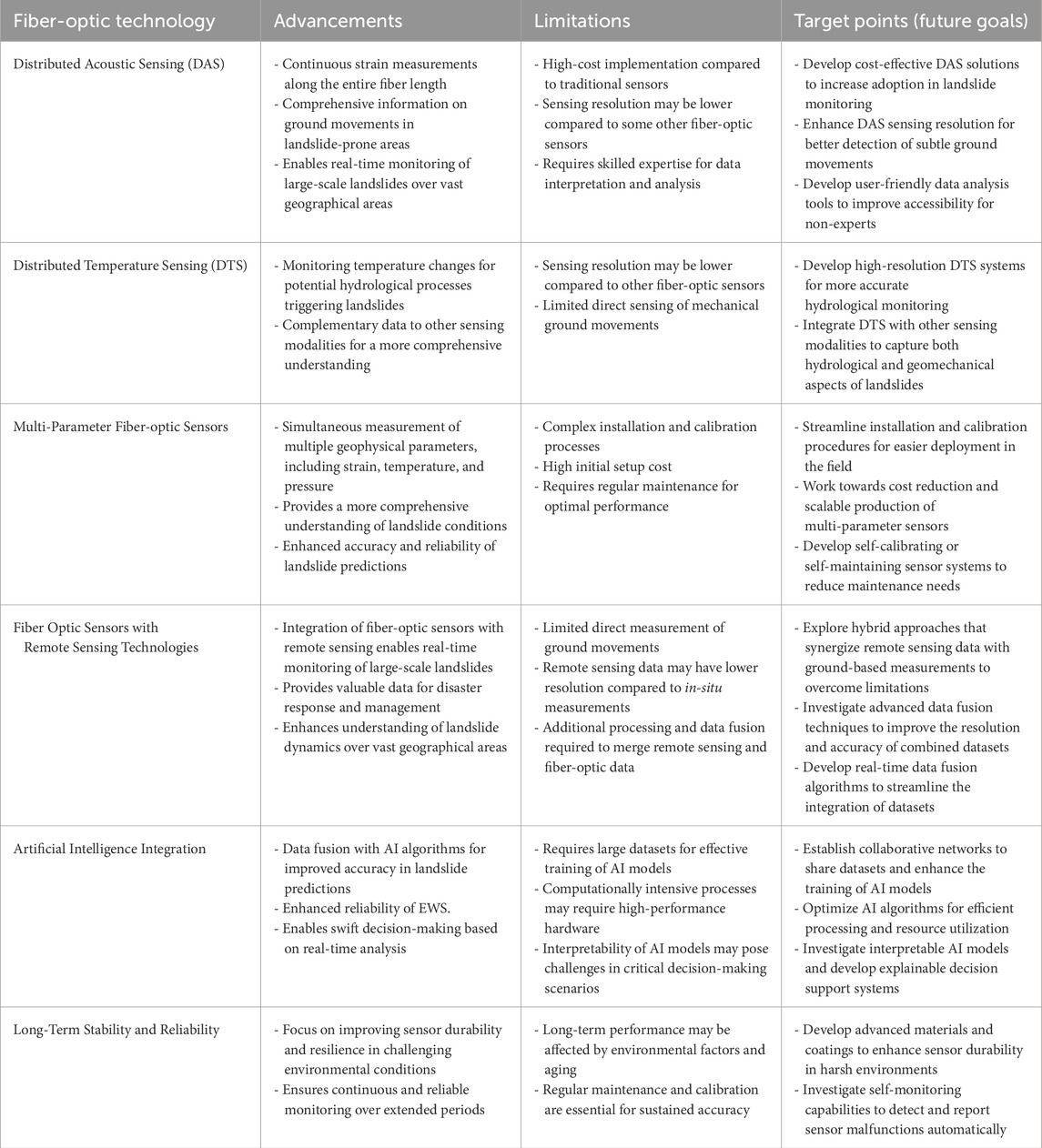
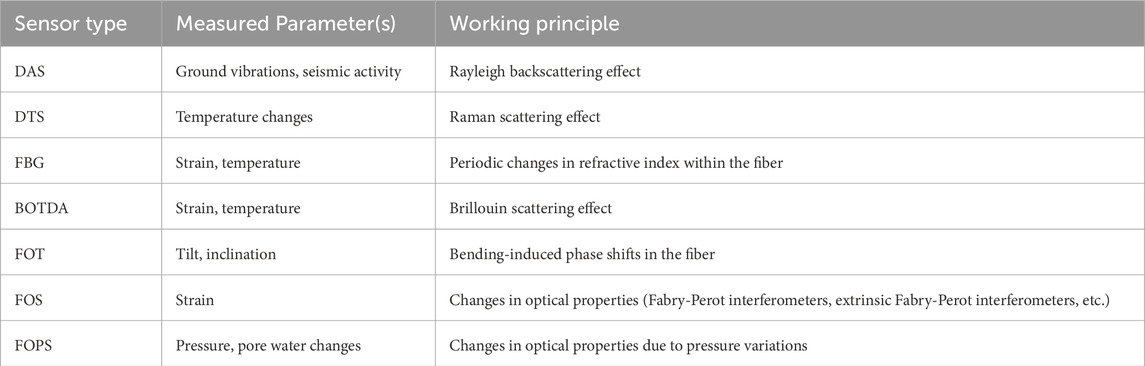
Table 1 provides an overview of various fiber-optic technologies applied in landslide monitoring, highlighting their advancements and limitations. Table 2 details different types of fiber-optic sensors, measured parameters, and working principles. The diverse capabilities of these sensors, including distributed sensing, high accuracy, and environmental resistance, make them invaluable for landslide monitoring. Integrating these sensors into EWS enables continuous, real-time data collection, supporting timely, informed decisions to enhance landslide risk management and improve safety in vulnerable regions. BOTDA and FBG sensors have specific applications in landslide monitoring (Johnson et al., 2023). BOTDA sensors offer high spatial resolution and distributed sensing capability, allowing for precise monitoring of ground movements and early detection of potential landslide activities. Their real-time data provision supports timely decision-making and EWS implementation (Ma et al., 2023). Additionally, their non-intrusive and remote sensing capabilities make them suitable for deployment in challenging terrains without disturbing the natural environment (Pellegrini et al., 2024).
Building upon the strengths and limitations outlined in Table 1, several key directions can be identified to guide future research and development in the application of fiber-optic technologies for landslide monitoring and early warning systems. Technological challenges remain a major barrier, particularly regarding sensor durability in harsh coastal environments, the need for stable long-term calibration, and the complexity of power supply and data transmission in remote or inaccessible areas. Additionally, the highly site-specific nature of landslides necessitates adaptable deployment strategies tailored to varying geological, topographical, and hydrological conditions. Cost-effectiveness also plays a critical role, especially in low-resource settings, where high installation and maintenance costs may hinder widespread adoption. Furthermore, advancing the capability of data interpretation is essential. Fiber-optic sensing systems generate vast volumes of high-resolution, continuous data, which require robust analytical frameworks for real-time processing and decision-making. Future research should prioritize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to enhance anomaly detection and risk assessment. Moreover, effective early warning depends on the seamless integration of fiber-optic data with complementary technologies, such as remote sensing (e.g., InSAR), GNSS, meteorological data, and geotechnical instrumentation. A multidisciplinary approach that synthesizes these technologies can significantly enhance the reliability, responsiveness, and coverage of landslide early warning systems.
BOTDA and FBG sensors offer long-term stability and accurate monitoring for landslide-prone areas. FBG sensors excel at detecting small ground movements due to their high accuracy in measuring strain and temperature changes (Ma et al., 2023). Their ability to take simultaneous measurements along a single optical fiber makes them cost-effective and comprehensive. They are also immune to electromagnetic interference, making them reliable near electrical equipment. Compact and lightweight, FBG sensors are easy to install, even in challenging terrains, and their low power consumption makes them ideal for remote monitoring systems. Integrating FBG sensors into EWS helps protect communities and infrastructure by providing early alerts for potential landslides. However, BOTDA sensors have higher implementation costs due to the need for specialized equipment and expertise (Johnson et al., 2023; Pellegrini et al., 2024). While they offer high spatial resolution, they might not detect the finest ground movements. Data interpretation for BOTDA sensors is complex and requires skilled professionals (Anjana et al., 2024). They can also be affected by environmental factors like temperature changes and external disturbances. FBG sensors have a lower sensing range, which can be a limitation in areas with larger ground movements. The multiplexing capability can introduce crosstalk between sensors, affecting data accuracy, but proper design can mitigate this (Ebrahim et al., 2024). Although generally immune to electromagnetic interference, some minimal disturbances can occur near electronic devices or power lines. Regular calibration and maintenance are crucial for ensuring long-term accuracy.
Incorporating three-component strain field measurements using fiber-optic technology is an exciting prospect for improving the accuracy and comprehensiveness of geohazard monitoring, such as landslides and other subsurface deformations (Ebrahim et al., 2024). Traditionally, fiber-optic sensors have been primarily used to measure strain along a single axis, typically along the length of the fiber, which provides valuable but limited information about the state of stress in the surrounding environment (Mreyen et al., 2022). However, for a more complete understanding of the strain field, it is essential to measure the components of strain in all three spatial directions longitudinal, lateral, and vertical (Mehrabi, 2021). This is crucial in the context of complex ground movements, where deformation is not limited to a single plane but occurs in three dimensions (Calamita et al., 2023). One potential approach to incorporating three-component strain field measurements using fiber-optic technology is through the use of specialized fiber-optic sensor configurations, such as the use of multi-core fibers or 3D fiber-optic strain gauges (An et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2025). Multi-core fiber-optic cables contain multiple fibers that can be oriented in different directions along the sensor installation (Yin et al., 2022). By measuring the strain at various orientations simultaneously, these systems can provide multi-dimensional strain data (Piao et al., 2024). Additionally, advanced sensor designs using FBG sensors can be strategically placed in different directions to measure strain components in all three axes. This would allow for the capture of complex deformation patterns in real-time (Cui, 2020).
Another promising technique is to integrate DSS with other sensing modalities, such as accelerometers or piezoelectric sensors, to obtain three-component strain field measurements (Zhang et al., 2023). Fiber-optic sensors can be used to monitor continuous strain along the fiber (Anjana et al., 2024), while additional sensors placed at key points along the installation can capture dynamic motion or vertical strain components (Johnson et al., 2023). By combining these datasets through a centralized monitoring system, a more complete picture of the strain field can be obtained (Ma et al., 2023). This hybrid approach allows for enhanced monitoring of geohazards by capturing both the slow, progressive deformations detected by fiber-optic systems and the rapid, dynamic events captured by inertial sensors (Pellegrini et al., 2024). However, there are challenges to implementing three-component strain field measurements in practice (Cui, 2020). The complexity of sensor deployment and the need for accurate calibration of multi-axis measurements can increase the cost and logistical difficulty of such systems (Qin, 2020). Additionally, the effectiveness of multi-axis fiber-optic strain sensors depends on the sensor’s ability to withstand environmental factors, such as soil movement, temperature fluctuations, and moisture changes, which could affect the accuracy of measurements (Wang J. et al., 2023). Nonetheless, as fiber-optic technology continues to evolve, with advancements in sensor design and data processing techniques (Zheng et al., 2018), the integration of three-component strain field measurements is becoming increasingly feasible (Mreyen et al., 2022). This capability would significantly enhance the ability to monitor and predict geohazard events, offering more reliable EWS and improved risk management strategies (Mehrabi, 2021).
Seismometers and geophones excel at detecting high-frequency, transient ground motions, such as those caused by earthquakes, explosions, or rapid landslide movements (Indukala et al., 2024). However, they are limited in their ability to detect slower, more gradual ground deformations (Cui, 2020). Fiber-optic sensors, on the other hand, offer continuous, high-resolution measurements over long distances, making them highly effective for monitoring the subtle strain variations that often precede or accompany landslides and other geohazards (Qin, 2020). By merging these technologies, it becomes possible to monitor both fast-moving and slow-moving ground deformations, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the state of the terrain (Clare et al., 2024). One promising method for integrating fiber-optic sensors with conventional seismometers and geophones is through data fusion techniques (Chávez-García et al., 2021). Data fusion involves combining measurements from different sensor types to improve the overall accuracy, reliability, and resolution of monitoring systems (Hoffman and Eduard, 2024). In this context, the real-time strain data from fiber-optic sensors could be combined with the dynamic motion data from seismometers or geophones (Imani et al., 2021). For example, while fiber-optic sensors continuously track ground deformation, seismometers can capture sudden movements or vibrations (Wang J. et al., 2023). By correlating the data from these two systems, more precise models of ground behavior can be developed, allowing for better prediction and early detection of potential geohazards such as landslides, earthquakes, or slope failures (Yu et al., 2022).
Another approach is the use of hybrid monitoring networks, where fiber-optic sensors are deployed alongside seismometers and geophones in strategic locations. This hybrid setup allows each sensor type to complement the other (Wei and Liu, 2020). For instance, fiber-optic cables can be placed along slopes or infrastructure to monitor continuous strain, while seismometers or geophones can be positioned to detect dynamic events that might affect these same areas (Chávez-García et al., 2021). The advantage of this approach is that it provides real-time data on both gradual and rapid deformations, enabling a more nuanced understanding of the geohazard environment (Qin, 2020). The integration can also provide redundancy, improving system reliability in challenging monitoring environments. Furthermore, machine learning and advanced signal processing techniques can be applied to the integrated data from fiber-optic sensors, seismometers, and geophones (Delgado et al., 2021). These technologies can help identify patterns and anomalies in the data that might not be immediately apparent through traditional analysis (Wei and Liu, 2020). By using algorithms to process and interpret the combined data sets, the system can generate more accurate models of ground behavior and improve the prediction of geohazards (Cui, 2020). For example, in a landslide monitoring scenario, machine learning algorithms could correlate slow, progressive strain data from fiber-optic sensors with sudden, dynamic shifts detected by seismometers, offering early warnings of potential landslide events (Qin, 2020). This integration of technologies, along with sophisticated data analysis, represents a powerful tool for advancing geohazard monitoring capabilities (Zeni et al., 2015).
6 Risk management and resilience
Fiber-optic technologies play a crucial role in improving risk management and landslide mitigation by providing real-time, high-precision monitoring of ground stability over large areas. Unlike traditional sensors, fiber-optic systems enable continuous and distributed data collection, allowing for early detection of ground deformations, subsurface movements, and environmental changes that may indicate an impending landslide (Johnson et al., 2023). This real-time data helps geotechnical experts and emergency response teams assess risks more accurately and implement timely interventions, reducing potential damage to infrastructure and loss of life. Another key contribution of fiber-optic technology is its integration with predictive modeling and EWS. By analyzing data collected from fiber-optic sensors, advanced machine learning algorithms, and geospatial models can forecast landslide occurrences with greater accuracy. This predictive capability enhances decision-making processes for engineers, urban planners, and disaster management authorities, enabling them to design effective mitigation measures such as slope reinforcements, drainage improvements, and controlled evacuations. The ability to detect small changes before they escalate into major events significantly improves long-term risk assessment and disaster preparedness (Ma et al., 2023). Furthermore, fiber-optic systems enhance the resilience and sustainability of monitoring infrastructure. These systems require minimal maintenance, withstand harsh environmental conditions, and provide long-term, cost-effective solutions for landslide-prone regions. Their scalability makes them ideal for large-scale monitoring projects, including critical infrastructure such as highways, railways, and pipelines. By offering continuous and automated surveillance, fiber-optic technologies help authorities transition from reactive disaster response to proactive risk management, ultimately enhancing community safety and resilience against landslides (Arslan et al., 2015).
In other words, strain-based sensing approaches are considered superior to traditional sensing methods, due to their ability to provide distributed (Wu et al., 2020), high-resolution measurements over large areas (Magisano et al., 2022). Unlike inertial sensors, which detect ground motion at discrete points, strain-based fiber-optic sensors, such as DSS, offer continuous spatial coverage along the entire length of the fiber (Wang et al., 2025). This allows for early detection of slow deformations that precede landslides, which inertial sensors may fail to capture due to their reliance on acceleration thresholds (Liu et al., 2021). Additionally, fiber-optic strain sensors can operate in harsh environmental conditions with minimal maintenance, whereas seismometers and geophones require periodic calibration and may be affected by environmental noise (Zhu et al., 2024). Another key advantage of strain-based sensing is its ability to measure permanent ground deformation, rather than just transient motion (Wang J. et al., 2023). Inertial sensors primarily detect dynamic events such as earthquakes or sudden landslide movements, but they may not be effective in identifying gradual stress accumulation within a slope (Soga, 2024). Strain-based sensors, on the other hand, can continuously track strain evolution, offering crucial insights into progressive failure mechanisms (Silveira et al., 2025). This makes them particularly valuable for landslide EWS, where detecting precursors to failure is essential for mitigation efforts (Sun et al., 2020). Moreover, fiber-optic strain sensors are scalable and can be integrated into existing infrastructure, such as pipelines or retaining walls, providing multipurpose monitoring capabilities that traditional inertial sensors lack (Wen et al., 2024).
Fiber-optic monitoring systems can significantly strengthen the resilience of coastal communities by providing early detection of landslides, soil erosion, and other ground movements that are common in such regions. These systems offer real-time, continuous monitoring over vast and hard-to-access areas, ensuring that any signs of slope instability or geological hazards are detected well before they escalate into disasters (Anjana et al., 2024). By enabling EWS, fiber-optic sensors allow authorities to issue timely evacuations, implement protective measures, and reduce the impact of these events on vulnerable coastal infrastructure and populations. In addition to real-time detection, fiber-optic systems contribute to long-term resilience by offering detailed data on environmental changes, such as shifting water levels, soil moisture, and temperature variations. This data is essential for understanding the dynamic nature of coastal environments and for improving hazard modeling and risk assessments (Rak et al., 2021). By integrating fiber-optic data into local disaster management strategies, communities can make informed decisions about land-use planning, coastal defenses, and infrastructure development, thereby mitigating the risks posed by landslides and coastal erosion. Moreover, fiber-optic technologies are highly durable; require low maintenance, and are resistant to environmental challenges like corrosion, electromagnetic interference, and extreme weather conditions, making them particularly suitable for coastal environments (Ebrahim et al., 2024). Their ability to operate in remote, hard-to-reach locations without frequent human intervention allows for continuous monitoring, even in areas prone to frequent storms or rising sea levels. As a result, fiber-optic systems enhance the overall preparedness of coastal communities, ensuring they can respond quickly to threats and protect both lives and property.
7 Future development
The application of fiber-optic technologies for real-time coastal landslide monitoring has gained significant momentum in recent years, driven by advances in distributed sensing systems (Nie et al., 2025) and growing concerns over coastal hazards exacerbated by climate change (Chandel et al., 2025). One of the most promising developments is the enhancement of DAS, which repurposes standard telecommunication optical fibers into dense arrays of virtual sensors (Anjana et al., 2024). This innovation allows for high-resolution detection of ground vibrations, offering a non-intrusive, cost-effective method for long-term monitoring of unstable coastal slopes (Johnson et al., 2025). Recent research has demonstrated the effectiveness of combining DAS with machine learning algorithms to improve signal classification and noise filtering (Sun et al., 2025). These hybrid approaches enable the differentiation between actual geophysical signals (such as precursor microseismic activity associated with slope failure) and ambient noise (such as ocean wave action), thereby increasing the reliability of early warnings (Johnson et al., 2025). As training datasets become more comprehensive, these algorithms are expected to provide near-real-time event detection and risk assessment. Another emerging direction is the integration of FBG sensors in multi-parameter sensing arrays (Zhang et al., 2016). FBGs can simultaneously monitor strain, temperature, and pressure along coastal slopes (Gao et al., 2024). Recent developments in multiplexing techniques have allowed a higher density of FBGs along a single fiber line, significantly enhancing spatial coverage without a proportional increase in cost or complexity (Anjana et al., 2024). This advancement is particularly valuable in heterogeneous coastal terrains where localized failure zones may develop rapidly (Minardo et al., 2021b). Moreover, hybrid fiber-optic systems that combine FBG, DAS, and DTS are gaining attention for their ability to provide a comprehensive, multi-dimensional picture of slope dynamics. These systems can detect both slow-developing deformation and sudden failure events, contributing to a more nuanced understanding of landslide precursors (May-Arrioja et al., 2024). Ongoing experiments in coastal testbeds suggest that the fusion of these sensing modalities improves early detection capabilities and reduces false alarms (Anjana et al., 2024).
In parallel, the miniaturization and ruggedization of interrogation units have made fiber-optic systems more suitable for deployment in harsh marine environments (Sun et al., 2025). New waterproof housings and energy-efficient processing units now allow continuous operation under extreme coastal conditions, including salt spray, variable temperatures, and high humidity (Anjana et al., 2024). This expands the potential for long-term deployments without frequent maintenance, a critical factor for real-time hazard monitoring systems. The integration of fiber-optic sensing networks into existing Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructures has also seen considerable progress (Thirugnanam et al., 2022). Edge computing devices connected to fiber-optic arrays can now perform real-time data analysis and issue alerts without relying on centralized processing hubs. This decentralization reduces latency and improves system resilience, especially in remote or infrastructure-scarce coastal regions prone to landslides (Esposito et al., 2022). In the context of early warning systems, recent studies have emphasized the importance of data fusion between fiber-optic monitoring and satellite-based Earth Observation (EO) platforms, such as InSAR and optical remote sensing (Liang et al., 2022). The co-analysis of in-situ fiber-optic data and satellite imagery enhances the spatial and temporal resolution of landslide monitoring systems. It also provides valuable cross-validation that strengthens the robustness of risk forecasts and early warning messages (Gagliardi et al., 2023). Another promising avenue is the use of fiber-optic sensors for real-time monitoring of groundwater fluctuations in coastal slopes (Anjana et al., 2024). As pore water pressure is a critical triggering factor in landslides, monitoring its dynamics with DSS and DTS technologies offers a proactive approach to landslide prediction (Bado and Casas, 2021; Henninges and Masoudi, 2021). Field experiments have shown that integrating fiber-optic data with hydrogeological models can provide more accurate thresholds for early warning systems (Wang et al., 2024).
Standardization of protocols for fiber-optic landslide monitoring is also becoming a priority (Johnson et al., 2023). Recent international collaborative projects, such as those under Horizon Europe and GEO’s Disaster Risk Reduction initiatives, have highlighted the need for harmonized calibration techniques, data sharing frameworks, and response protocols (Solheim et al., 2022). Standardization will facilitate interoperability among monitoring systems and improve the scalability of early warning platforms across different coastal settings (Sun et al., 2025). Emerging research has also explored the potential of artificial intelligence AI-driven predictive analytics built on fiber-optic time-series data (Anjana et al., 2024). Deep learning models trained on historical deformation signals can identify subtle temporal patterns indicative of impending failure (Pamukti et al., 2024). These tools hold promise for transforming early warning systems from reactive to predictive frameworks, which is particularly valuable for densely populated or critical coastal infrastructure zones (Wu et al., 2020). From a socio-technical perspective, the successful implementation of these advanced fiber-optic technologies hinges on the development of user-centered early warning platforms (Ebrahim et al., 2024). Recent case studies stress the importance of real-time visualization dashboards, risk communication strategies, and integration with local emergency response protocols (Ma et al., 2023). The future of fiber-optic monitoring thus lies not only in technological innovation but also in the effective translation of sensor data into actionable information for decision-makers and the public.
8 Conclusion
Coastal landslides are significant geohazards with devastating consequences, affecting both coastal and marine environments. These events pose a direct threat to human lives and coastal communities, causing casualties, injuries, and displacements, especially in densely populated areas. Understanding the triggers and mechanisms of coastal landslides is crucial for implementing effective EWS and evacuation plans to protect human safety. The impact on infrastructure is substantial, with coastal landslides damaging or destroying critical assets like ports, roads, and bridges. This leads to disruptions in transportation, commerce, and daily life. Mitigating these risks is essential to preserve infrastructure and prevent economic losses.
Environmentally, coastal landslides release debris, sediments, and pollutants, harming aquatic ecosystems and water quality. They contribute to coastal erosion, threatening property, habitats, and ecosystems. Managing erosion and understanding its drivers are crucial for sustainable coastal planning. Underwater landslides can generate tsunamis, posing catastrophic risks far from the source. Accurate assessment and monitoring are vital for tsunami hazard mitigation. Climate change increases the frequency and intensity of these events, making adaptation essential. Fiber-optic technology has revolutionized landslide monitoring, providing precise, real-time data. This innovation enhances EWS and mitigates the impacts of coastal landslides, safeguarding lives, infrastructure, and the environment. Ongoing research and development will further refine these technologies, improving our ability to manage coastal landslide hazards.
Author contributions
AC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. JC: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. FT: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YN: Conceptualization, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AR: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. TS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. RD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
CRED, Centre for Research on Epidemiology of Disasters; GPS, Global Positioning System; InSAR, Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar; UAV, Unmanned Aerial Vehicle; IoT, Internet of Things; EWS, Early Warning Systems; OTDR, Optical Time Domain Reflectometry Sensors; FBG, Fiber-glass Bragg Grating Sensors; PMF, Polarization-maintaining Fiber Sensors; POTDR, Polarization-sensitive Optical Time Domain Reflectometry; OFDR, Optical Frequency Domain Reflectometry; BOTDR, Brillouin Optical Time Domain Reflectometry; ROTDR, Rayleigh Optical Time Domain Reflectometry; COFT, Combined Optical Fiber Transducer; PSCFODS, Parallel-series Connected Fiber-optic Displacement Sensors; DRS, Distributed Rayleigh Sensing; DTS, Distributed Temperature Sensing; DFOS, Distributed Fiber-optic Sensing; DAS, Distributed Acoustic Sensing; DSS, Distributed Strain Sensing; BOTDA, Brillouin Optical Time-Domain Analysis; PPP-BOTDA, Pulse-prepump Brillouin Optical Time Domain Analysis; FOPS, Fiber Optic Pressure Sensors or Fiber Optic Piezometers; UWFBG, Ultra-weak Fiber Bragg Gratings; FOT, Fiber Optic Tilt Sensors; FOS, Fiber Optic Strain Sensors.
References
Acharya, A., and Kogure, T. (2024). Advances in fibre-optic-based slope reinforcement monitoring: a review. J. Rock Mech. Geotechnical Eng. 17 (2), 1263–1284. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2024.03.022
Allil, R. C. S. B., Lima, L. A. C., Allil, A. S., and Werneck, M. M. (2021). FBG-based inclinometer for landslide monitoring in Tailings dams. IEEE Sens. J. 21, 16670–16680. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2021.3081025
An, H., Ouyang, C., and Zhou, S. (2021). Dynamic process analysis of the Baige landslide by the combination of DEM and long-period seismic waves. Landslides 18, 1625–1639. doi:10.1007/s10346-020-01595-0
Anjana, K., Herath, M., and Epaarachchi, J. (2024). Optical fibre sensors for geohazard monitoring–A review. Measurement 235, 114846. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2024.114846
Arslan, A., Kelam, M. A., Eker, A. M., Akgun, H., and Koçkar, M. K. (2015). “Optical fiber technology to monitor slope Movement,” in Engineering geology for society and territory - volume 2: landslide processes. Cham, Switzerland: Springer.
Aulakh, N. S., Chhabra, J. K., Kamar, A., and Aggarwal, A. K. (2004). Development of a fiber optic based system to monitor Landslide activity. IETE Tech. Rev. 21, 75–81. doi:10.1080/02564602.2004.11417130
Azarafza, M., Ghazifard, A., Akgün, H., and Asghari-Kaljahi, E. (2018). Landslide susceptibility assessment of south pars Special zone, Southwest Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 77 (24), 805. doi:10.1007/s12665-018-7978-1
Bado, M. F., and Casas, J. R. (2021). A review of recent distributed optical fiber sensors applications for civil engineering structural health monitoring. Sensors 21 (5), 1818. doi:10.3390/s21051818
Bao, X., and Chen, L. (2012). Recent progress in distributed fiber optic sensors. Sensors 12 (7), 8601–8639. doi:10.3390/s120708601
Brezzi, L., Fabbian, N., Schenato, L., Scala, A., and Cola, S. (2024). Distributed optical fiber-based monitoring of smart passive anchors for soil stabilization. Procedia Struct. Integr. 64, 1589–1596. doi:10.1016/j.prostr.2024.09.413
Calamita, G., Gallipoli, M. R., Gueguen, E., Sinisi, R., Summa, V., Vignola, L., et al. (2023). Integrated geophysical and geological surveys reveal new details of the large Montescaglioso (southern Italy) landslide of December 2013. Eng. Geol. 313, 106984. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.106984
Carlini, M., Chelli, A., Vescovi, P., Artoni, A., Clemenzi, L., Tellini, C., et al. (2016). Tectonic control on the development and distribution of large landslides in the Northern Apennines (Italy). Geomorphology 253, 425–437. doi:10.1016/J.GEOMORPH.2015.10.028
Cascini, L. (2008). Applicability of landslide susceptibility and hazard zoning at different scales. Eng. Geol. 102, 164–177. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.016
Chae, B. G., Park, H. J., Catani, F., Simoni, A., and Berti, M. (2017). Landslide prediction, monitoring and early warning: a Concise review of State-of-the-Art. Geosci. J. 21, 1033–1070. doi:10.1007/s12303-017-0034-4
Chandel, R. S., Rai, P. K., and Misra, R. K. (2025). Advancing sustainability: a comprehensive review of geospatial technology in monitoring climate change-driven landslide hazards. GNSS Appl. Earth Space Observations. CRC Press, 80–103.
Chávez-García, F. J., Natarajan, T., Cárdenas-Soto, M., and Rajendran, K. (2021). Landslide characterization using active and passive seismic imaging techniques: a case study from Kerala, India. Nat. Hazards 105, 1623–1642. doi:10.1007/s11069-020-04369-y
Chen, G., Ding, Y. N., and Liu, Y. (2020). A wavelet-based fiber optic sensors data processing method and its application on embankment sliding surface detection. Dam Breach Model. Risk Dispos. Proc. First Int. Conf. Embankment Dams 1, 333–339. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-46351-9_34
Cheng, G., Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Shi, B., Li, T., Wu, J., et al. (2023). Research on performance test of the optic-electric sensors for reservoir landslide temperature field monitoring. Water 15 (17), 3125. doi:10.3390/w15173125
Clare, M. A., Lintern, G., Pope, E., Baker, M., Ruffell, S., Zulkifli, M. Z., et al. (2024). Seismic and acoustic monitoring of submarine landslides: ongoing challenges, recent successes, and future opportunities. Noisy Oceans Monit. Seismic Acoust. Signals Mar. Environ., 59–82. doi:10.1002/9781119750925.ch5
Clarkson, P., Cole, S., Godfrey, A., Crickmore, R., Minto, C., Watlet, A., et al. (2022b). “Verification of a distributed fiber optic sensing slope stability monitoring solution,” in ARMA US rock mechanics/geomechanics symposium, ARMA–2022. doi:10.56952/ARMA-2022-0715
Clarkson, P., Cole, S., Godfrey, A., Crickmore, R., Minto, C., Watlet, A., et al. (2022a). Verification of a distributed fiber optic sensing slope stability monitoring solution. In: Proceedings of the 56th U.S. Rock mechan-ics/geomechanics symposium.
Cola, S., Girardi, V., Bersan, S., Simonini, P., Schenato, L., and De Polo, F. (2021). An optical fiber-based monitoring system to study the seepage flow below the landside toe of a river levee. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 11 (3), 691–705. doi:10.1007/s13349-021-00475-y
Cole, S., Karrenbach, M., Yartsev, V., and Clarkson, P. (2022). DAS fiber optic monitoring of an active landslide. EAGE GeoTech 2022 Third EAGE Workshop Distributed Fiber Opt. Sens. 2022, London, UK, 1–5. doi:10.3997/2214-4609.20224043
Costrada, A. N., Kemal, B. M., and Marzuki, (2021). Landslide monitoring system based on fiber optic sensor and CCD TSL1401CL linear sensor array. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1876 (1), 012002. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1876/1/012002
Costrada, A. N. H., Kemal, B. M., and Marzuki, M. (2021) “Landslide monitoring system based on fiber optic sensor and CCD TSL1401CL Linear sensor array,” in Proceedings of the IOP journal of physics: conference series 2021. (1876), 012002. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1876/1/012002
Cui, L. (2020). Distributed optical fibre sensing system for civil and geotechnical Infrastructures. MSc. Thesis (Quebec, Canada: Université Laval, ULaval).
Cui, S., Pei, X., and Huang, R. (2018). Effects of geological and tectonic characteristics on the earthquake-triggered Daguangbao landslide, China. Landslides 15, 649–667. doi:10.1007/s10346-017-0899-3
Culshaw, B., and Kersey, A. (2008). Fiber-optic sensing: a historical perspective. J. Light. Technol. 26 (9), 1064–1078. doi:10.1109/jlt.0082.921915
Dai, Z. Y., Liu, Y., Zhang, L. X., Ou, Z. H., Zhou, C., and Liu, Y. Z. (2008). “Landslide monitoring based on high-resolution Distributed fiber Optic stress sensor,” in Proceedings of the 2008 1st asia-pacific optical fiber sensors Conference, APOS 2008. Chengdu, China.
Damiano, E., de Cristofaro, M., Molitierno, E., and Olivares, L. (2024). DFOS-based inclinometers: challenges and potentialities in monitoring slow landslides. Procedia Struct. Integr. 64, 1628–1635. doi:10.1016/j.prostr.2024.09.418
Delgado, J., Galiana-Merino, J. J., Garcia-Tortosa, F. J., Garrido, J., Lenti, L., Martino, S., et al. (2021). Ambient noise measurements to constrain the geological structure of the güevéjar landslide (S Spain). Appl. Sci. 11 (4), 1454. doi:10.3390/app11041454
Di Gennaro, L., Damiano, E., De Cristofaro, M., Netti, N., Olivares, L., Zona, R., et al. (2022). An innovative geotechnical and structural monitoring system based on the use of NSHT. Smart Mater. Struct. 31 (6), 065022. doi:10.1088/1361-665X/ac5fc6
Ebrahim, K. M., Gomaa, S. M., Zayed, T., and Alfalah, G. (2024). Recent phenomenal and investigational subsurface landslide monitoring techniques: a mixed review. Rem. Sens. 16 (2), 385. doi:10.3390/rs16020385
Esposito, M., Palma, L., Belli, A., Sabbatini, L., and Pierleoni, P. (2022). Recent advances in internet of things solutions for early warning systems: a review. Sensors 22 (6), 2124. doi:10.3390/s22062124
Fenta, M. C., Potter, D. K., and Szanyi, J. (2021). Fibre optic methods of prospecting: a comprehensive and modern branch of geophysics. Surv. Geophys. 42 (3), 551–584. doi:10.1007/s10712-021-09634-8
Gagliardi, V., Tosti, F., Ciampoli, L. B., Battagliere, M. L., D’Amato, L., Alani, A. M., et al. (2023). Satellite remote sensing and non-destructive testing methods for transport infrastructure monitoring: advances, challenges and perspectives. Remote Sens. 15 (2), 418. doi:10.3390/rs15020418
Gao, S., Cheng, S., Jin, Q., Li, S., Jin, H., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Model test research of wave-induced submarine landslide based on Fibre Bragg Grating sensing technology. Ocean. Eng. 291, 116492. doi:10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.116492
Ghanbarian, M. A., and Derakhshani, R. (2022). The folds and faults kinematic association in Zagros. Sci. Rep. 12, 8350. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-12337-8
Ghanbarian, M. A., Yassaghi, A., and Derakhshani, R. (2021). Detecting a sinistral transpressional deformation belt in the Zagros. Geosci. (Basel) 11, 226. doi:10.3390/geosciences11060226
Grattan, K. T., and Sun, T. (2000). Fiber optic sensor technology: an overview. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 82 (1-3), 40–61. doi:10.1016/s0924-4247(99)00368-4
Han, H., Shi, B., Zhang, C. C., Sang, H., Huang, X., and Wei, G. (2023). Application of ultra-weak FBG technology in real-time monitoring of landslide shear displacement. Acta Geotech. 18 (5), 2585–2601. doi:10.1007/s11440-022-01742-y
Han, H. M., Shi, B., Zhang, L., Wei, G. Q., and Chen, Q. (2021). Error analysis and experimental research of joint Fiber-Optic displacement Sensor based on shear lag model. Measurement 186, 110106–. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110106
Henninges, J., and Masoudi, A. (2021). “Fiber-optic sensing in geophysics, temperature measurements,” in Encyclopedia of solid earth geophysics (Springer International Publishing), 384–394. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-58631-7_281
Herlin, H. S., Harmadi, F., and Muldarisnur, M. (2020). Applications of fiber optic sensor for monitoring and Early warning of soil Shift on iot-based system. Int. J. Inf. Vis. 4 (3), 117–122. doi:10.30630/joiv.3.1.219
Higuchi, K., Fujisawa, K., Asai, K., Pasuto, A., and Marcato, G. (2005). Development of landslide displacement detection Sensor using Optical fiber in the OTDR method. In: Proceedings of the 44th colloquium of Japan landslide Society, pp. 315–318.
Ho, Y., Te, H., Bin, A., and Lee, J. T. (2006). Development of a fiber Bragg grating sensored ground movement Monitoring system. In Proceedings of the measurement science and technology, 17.
Hoffman, M., and Eduard, K. (2024). Comparison of anomalies in the VLF spectrum of the natural electromagnetic field with data from the seismometer in a landslide-affected area. Contributions Geophys. Geodesy 54 (1), 67–84. doi:10.31577/congeo.2024.54.1.4
Hoffmann, G., Al-Yahyai, S., Naeem, G., Kociok, M., and Grützner, C. (2014). An Indian Ocean tsunami triggered remotely by an onshore earthquake in Balochistan, Pakistan. Geology 42, 883–886. doi:10.1130/G35756.1
Howe, B. M., Angove, M., Aucan, J., Barnes, C. R., Barros, J. S., Bayliff, N., et al. (2022). SMART subsea cables for observing the earth and ocean, mitigating environmental hazards, and supporting the blue economy. Front. Earth Sci. 9, 775544. doi:10.3389/feart.2021.775544
Hussain, Y., Schlögel, R., Innocenti, A., Hamza, O., Iannucci, R., Martino, S., et al. (2022). Review on the geophysical and UAV-based methods applied to landslides. Remote Sens. 14 (18), 4564. doi:10.3390/rs14184564
Ibrahim, A., Meguid, M. A., Dang, K., and Yacoub, T. (2024). Thermal modeling of geosynthetics and earth structures in a changing climate: overview and future challenges. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 10 (2), 24. doi:10.1007/s40891-024-00536-4
Imani, P., Abd EL-Raouf, A., and Tian, G. (2021). Landslide investigation using Seismic Refraction Tomography method: a review. Ann. Geophys. 64 (6), SE657. doi:10.4401/ag-8633
Indukala, P. K., Gosh, U. G., and Ramesh, M. V. (2024). IoT-driven microseismic sensing system and monitoring platform for landslide detection. IEEE Access 12, 97787–97805. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3427386
Iten, M., Puzrin, A. M., and Schmid, A. (2008). “Landslide monitoring using a road-embedded optical fiber sensor,” in Proceedings of the SPIE smart Sensor phenomena, technology, networks, and systems. San Diego, California, USA. 6933, 328–336. doi:10.1117/12.774515
Ivanov, V., Longoni, L., Ferrario, M., Brunero, M., Arosio, D., and Papini, M. (2021). Applicability of an interferometric optical fibre sensor for shallow landslide monitoring–Experimental tests. Eng. Geol. 288, 106128. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106128
Johnson, M. A. M., Phang, S. K., Wong, W., Chew, W. J. E. N., Mun, H. K. I. T., and Hoon, Y. (2023). Distributed fiber optic sensing landslide monitoring–a comparative review. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 18 (1), 406–423.
Johnson, M. A. M., Phang, S. K., Wong, W. R., and Happonen, A. (2025). A novel quad-core double-steel optical fiber solution for landslide monitoring. IEEE Access 13, 55416–55430. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3555734
Kashaganova, G., Kozbakova, A., Kartbayev, T., Balbayev, G., Togzhanova, K., Alimseitova, Z., et al. (2023). Research of a fiber sensor based on fiber Bragg grating for road surface monitoring. Electronics 12 (11), 2491. doi:10.3390/electronics12112491
Kelam, A. A., Akgün, H., and Koçkar, M. K. (2022). Application of an optical fiber-based system for mass movement monitoring. Environ. Earth Sci. 81 (5), 170. doi:10.1007/s12665-022-10289-w
Kelam, A. A., Koçkar, M. K., and Akgün, H. (2023). “Monitoring of an Unstable slope in kocaeli (türkiye) by an optical fiber based system,” in ARMA US rock mechanics/geomechanics symposium, ARMA–2023. doi:10.56952/ARMA-2023-0698
Lanciano, C., and Salvini, R. (2020). Monitoring of strain and temperature in an open pit using Brillouin distributed Optical fiber sensors. Sensors 20 (7), 1924. doi:10.3390/s20071924
Li, H. J., Zhu, H. H., Li, Y. H., Hu, W., and Shi, B. (2021). Fiber Bragg grating–based flume test to study the initiation of landslide-debris flows induced by concentrated runoff. Geotechnical Test. J. 44 (4), 986–999. doi:10.1520/GTJ20190290
Liang, Y., Gu, K., Shi, B., Liu, S., Wu, J., Lu, Y., et al. (2022). Estimation of land subsidence potential via distributed fiber optic sensing. Eng. Geol. 298, 106540. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106540
Lienhart, W. (2015). Case studies of high-sensitivity monitoring of natural and engineered slopes. J. Rock Mech. Geotechnical Eng. 7 (4), 379–384. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.04.002
Liu, L., Nie, Y., and Lei, Y. (2020). A Novel Sensor Prototype with enhanced and adaptive sensitivity based on negative stiffness mechanism. Sensors 20 (16), 4644. doi:10.3390/s20164644
Liu, P., Liu, Z., and Zhou, C. (2022). Measurement and region identification in deep displacement of slopes based on rod-fiber coupling structure. Sensors 22 (10), 3623. doi:10.3390/s22103623
Liu, S. P., Shi, B., Gu, K., Zhang, C. C., He, J. H., Wu, J. H., et al. (2021). Fiber-optic wireless sensor network using ultra-weak fiber Bragg gratings for vertical subsurface deformation monitoring. Nat. Hazards 109, 2557–2573. doi:10.1007/s11069-021-04932-1
Liu, W., and Zhou, W. (2022). Real-time monitoring of soil moisture field using ultra-weak fiber Bragg gratings. Eighth Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications 12169, 2179–2185. doi:10.1117/12.26251950
Liu, Y., Dai, Z., Zhang, X., Peng, Z., Li, J., Ou, Z., et al. (2010). Optical fiber sensors for landslide monitoring. In: Proceedings of the SPIE semiconductor lasers and applications IV 7844, 41–46.
Liu, Y., Teza, G., Nava, L., Chang, Z., Shang, M., Xiong, D., et al. (2024). Deformation evaluation and displacement forecasting of baishuihe landslide after stabilization based on continuous wavelet transform and deep learning. Nat. Hazards 120 (11), 9649–9673. doi:10.1007/s11069-024-06580-7
Liu, Z., Cai, G., Wang, J., Liu, L., and Zhuang, H. (2023). Evaluation of mechanical and electrical properties of a new sensor-enabled piezoelectric geocable for landslide monitoring. Measurement 211, 112667. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2023.112667
Longoni, L., Ivanov, V., Ferrario, M., Brunero, M., Papini, M., and Arosio, D. (2022). Laboratory tests with interferometric optical fibre sensors to monitor shallow landslides triggered by rainfalls. Landslides 19 (3), 761–772. doi:10.1007/s10346-021-01803-5
Lv, Z., Zhang, X., Wang, C., and Yang, X. (2023). Application of weak fiber grating sensing technology in landslide monitoring. SPIE AOPC 2023 Opt. Fiber Gyro. Beijing, China. 12968, 210–218. doi:10.1117/12.3004066
Ma, J., Pei, H., Zhu, H., Shi, B., and Yin, J. (2023). A review of previous studies on the applications of fiber optic sensing technologies in geotechnical monitoring. Rock Mech. Bull. 2 (1), 100021. doi:10.1016/j.rockmb.2022.100021
Magisano, D., Mastroianni, M., Leonetti, L., Madeo, A., Garcea, G., Gagliardi, G., et al. (2022). A finite element model for monitoring the displacement of pipelines in landslide regions by discrete FBG strain sensors. Appl. Sci. 12 (15), 7510. doi:10.3390/app12157510
Mao, Y., Li, Y., Teng, F., Sabonchi, A. K., Azarafza, M., and Zhang, M. (2024). Utilizing hybrid machine learning and soft computing techniques for landslide susceptibility mapping in a drainage basin. Water 16 (3), 380. doi:10.3390/w16030380
Mao, Y., Mwakapesa, D. S., Li, Y. C., Xu, K. B., Nanehkaran, Y. A., and Zhang, M. S. (2022). Assessment of landslide susceptibility using DBSCAN-AHD and LD-EV methods. J. Mt. Sci. 19 (1), 184–197. doi:10.1007/s11629-020-6491-7
Mao, Y., Mwakapesa, D. S., Wang, G., Nanehkaran, Y. A., and Zhang, M. (2021). Landslide susceptibility modelling based on AHC-OLID clustering algorithm. Adv. Space Res. 68 (1), 301–316. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2021.03.014
Mather, A. E., Hartley, A. J., and Griffiths, J. S. (2014). The giant coastal landslides of Northern Chile: tectonic and climate interactions on a classic convergent plate margin. Earth Planet Sci. Lett. 388, 249–256. doi:10.1016/J.EPSL.2013.10.019
May-Arrioja, D. A., Cuando-Espitia, N., Velázquez-Benítez, A. M., and Hernández-Cordero, J. (2024). Fiber optic sensors for environmental applications. IOP Glass-based Materials. Adv. Energy, Environ. Health. Bristol, England: IOP Publishing., 5–38.
Mehrabi, H. (2021). Three-dimensional strain descriptors at the Earth’s surface through 3D retrieved co-event displacement fields of differential interferometric synthetic aperture radar. J. Geodesy 95 (4), 39. doi:10.1007/s00190-021-01489-6
Miah, K., and Potter, D. K. (2017). A review of hybrid fiber-optic distributed simultaneous vibration and temperature sensing technology and its geophysical applications. Sensors 17 (11), 2511. doi:10.3390/s17112511
Minardo, A., Catalano, E., Coscetta, A., Zeni, G., Di Maio, C., Vassallo, R., et al. (2021a). Long-term monitoring of a tunnel in a landslide prone area by brillouin-based distributed optical Fiber sensors. Sensors 21 21, 7032–. doi:10.3390/s21217032
Minardo, A., Zeni, L., Coscetta, A., Catalano, E., Zeni, G., Damiano, E., et al. (2021b). Distributed optical fiber sensor applications in geotechnical monitoring. Sensors 21 (22), 7514. doi:10.3390/s21227514
Minutolo, V., Cerri, E., Coscetta, A., Damiano, E., De Cristofaro, M., Di Gennaro, L., et al. (2020). NSHT: new smart hybrid transducer for structural and geotechnical applications. Appl. Sci. 10 (13), 4498. doi:10.3390/app10134498
Mokhtari, M. (2015). The role of splay faulting in increasing the devastation effect of tsunami hazard in Makran, Oman Sea. Arabian J. Geosciences 8, 4291–4298. doi:10.1007/s12517-014-1375-1
Mreyen, A. S., Donati, D., Elmo, D., Donze, F. V., and Havenith, H. B. (2022). Dynamic numerical modelling of co-seismic landslides using the 3D distinct element method: insights from the Balta rockslide (Romania). Eng. Geol. 307, 106774. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106774
Murray, C., Jalilian, E., Najeeb, A., Toms, S., and Hossain, T. (2022). High fidelity distributed fiber optic sensing for landslide detection. Int. Pipeline Conf. 86588, V003T04A017. doi:10.1115/IPC2022-87809
Nie, W., Tian, C., Song, D., Liu, X., and Wang, E. (2025). Disaster process and multisource information monitoring and warning method for rainfall-triggered landslide: a case study in the southeastern coastal area of China. Nat. Hazards 121 (3), 2535–2564. doi:10.1007/s11069-024-06897-3
Nikoobakht, S., Azarafza, M., Akgün, H., and Derakhshani, R. (2022). Landslide susceptibility assessment by using Convolutional neural Network. Appl. Sci. 12, 5992. doi:10.3390/app12125992
Olabode, O. P., Lim, H. S., and Ramli, M. H. (2022). Geophysical and geotechnical evaluation of landslide slip surface in a residual soil for monitoring of slope instability. Earth Space Sci. 9 (12), e2022EA002248. doi:10.1029/2022EA002248
Pamukti, B., Wang, Z., Pradipta, M. F. F., Liaw, S. K., Yeh, C. H., and Yang, F. L. (2024). Deep learning and time series signal processing for bending detection in mining environment using optical fiber sensor. Opt. Fiber Technol. 88, 103819. doi:10.1016/j.yofte.2024.103819
Papini, M., Ivanov, V. I., Brambilla, D., Ferrario, M., Brunero, M., Cazzulani, G., et al. (2020). First steps for the Development of an Optical fiber strain sensor for shallow landslide stability monitoring through Laboratory experiments. Appl. Geol., 197–208. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-43953-8_12
Pei, H., Cui, P., Yin, J., Zhu, H., Chen, X., Pei, L., et al. (2011). Monitoring and warning of landslides and debris Flows using an optical Fiber sensor technology. J. Mt. Sci. 8, 728–738. doi:10.1007/s11629-011-2038-2
Pei, H., Jing, J., and Zhang, S. (2020). Experimental study on a new FBG-based and terfenol-D inclinometer for slope Displacement Monitoring. Measurement 151, 107172. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107172
Pellegrini, S., Rizzelli, G., Barla, M., and Gaudino, R. (2024). Polarization-based fiber optic system for debris flow early warning: on-field demonstration. IEEE Photonics J. 16 (3), 1–8. doi:10.1109/JPHOT.2024.3403159
Piao, C., Yin, Y., He, Z., Du, W., and Wei, G. (2024). Research on transparency of coal mine geological conditions based on distributed fiber-optic sensing technology. Deep Undergr. Sci. Eng. doi:10.1002/dug2.12134
Pourkhosravani, M., Mehrabi, A., Pirasteh, S., and Derakhshani, R. (2022). Monitoring of maskun landslide and Determining its quantitative Relationship to different climatic conditions using D-InSAR and PSI Techniques. Geomatics, Nat. Hazards Risk 13, 1134–1153. doi:10.1080/19475705.2022.2065939
Qin, J. Q. (2020). Development and evaluation of new fiber optic sensors for geotechnical applications. MSc. Thesis (Hong Kong: Hong Kong Polytechnic University).
Quintana, L., Alonso, J. L., Pulgar, J. A., and Rodríguez-Fernández, L. R. (2006). Transpressional inversion in an extensional transfer zone (the Saltacaballos fault, northern Spain). J. Struct. Geol. 28, 2038–2048. doi:10.1016/J.JSG.2006.06.013
Rak, J., Girão-Silva, R., Gomes, T., Ellinas, G., Kantarci, B., and Tornatore, M. (2021). Disaster resilience of optical networks: state of the art, challenges, and opportunities. Opt. Switch. Netw. 42, 100619. doi:10.1016/j.osn.2021.100619
Rashidi, A., Abbassi, M.-R., Nilfouroushan, F., Shafiei, S., Derakhshani, R., and Nemati, M. (2020). Morphotectonic and earthquake data analysis of interactional faults in Sabzevaran Area, SE Iran. J. Struct. Geol. 139, 104147. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2020.104147
Ravet, F., Briffod, F., Goy, A., and Rochat, E. (2021). Mitigation of geohazard risk along transportation infrastructures with optical fiber distributed sensing. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 11 (4), 967–988. doi:10.1007/s13349-021-00492-x
Sabri, N., Aljunid, S. A., Salim, M. S., and Fouad, S. (2015). Fiber optic sensors: short review and applications. Rec. Tren. Phys. Mater. Sci. Technol., 299–311. doi:10.1007/978-981-287-128-2_19
Sasi, D., Philip, S., David, R., and Swathi, J. (2020). A review on structural health monitoring of railroad track structures Using fiber optic Sensors. Proc. Mater. Today 33 (7), 3787–3793. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.06.217
Schenato, L. (2017). A review of distributed fibre optic sensors for geo-hydrological applications. Appl. Sci. 7 (9), 896. doi:10.3390/app7090896
Schenato, L., and Pasuto, A. (2021). On the use of optical fiber sensors for debris flow monitoring: a review of recent achievements. Energy Environ., 60–70. doi:10.1007/978-981-16-9963-4_5
Shi, B., Jiang, H., and Sun, Y. (2017). DFOS technology-based landslide monitoring: the Majiagou landslide case study (China). Adv. Cult. Living Landslides Volume 3 Adv. Landslide Technol. 317, 317–324. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-53487-9_36
Silveira, R. M. D., Buras, M., Pereira Filho, A. L. D., Fernandes, J. F., and Futai, M. M. (2025). Laboratory tests using distributed fiber optical sensors for strain monitoring. Sensors 25 (2), 324. doi:10.3390/s25020324
Soga, K. (2024). CAAP final report: distributed strain sensing for pipeline safety against fault moving and landslide. Berkeley: University of California.
Soga, K., and Luo, L. (2018). Distributed fiber optics sensors for civil engineering infrastructure sensing. J. Struct. Integr. Maintenance 3 (1), 1–21. doi:10.1080/24705314.2018.1426138
Solheim, A., Kalsnes, B., Strout, J., Piciullo, L., Heyerdahl, H., Eidsvig, U., et al. (2022). Landslide risk reduction through close partnership between research, industry, and public entities in Norway: pilots and case studies. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 855506. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.855506
Sun, M., Liu, Y., Zhao, L., Xie, W., and Mao, W. (2025). Advances and challenges in assessing submarine landslide risks to marine infrastructure. Nat. Hazards 121, 7811–7837. doi:10.1007/s11069-025-07113-6
Sun, M., Wu, S., Wang, T., Xie, Y., Xu, M., Dong, Y., et al. (2024). Thermo-mechanical coupling load transfer method of energy pile based on hyperbolic tangent model. Buildings 14 (10), 3190. doi:10.3390/buildings14103190
Sun, Y., Cao, S., Xu, H., and Zhou, X. (2020). Application of distributed fiber optic sensing technique to monitor stability of a geogrid-reinforced model slope. Int. J. Geosynth. Ground Eng. 6, 29–11. doi:10.1007/s40891-020-00209-y
Tang, Y., Cao, M., Li, B., Chen, X., and Wang, Z. (2023). Horizontal deformation monitoring of concrete pile with FRP-packaged distributed optical-fibre sensors. Buildings 13 (10), 2454. doi:10.3390/buildings13102454
Tao, Z., Feng, Y., Zhang, X., and Yu, Z. (2024). Experimental study on joint sensing and early warning method of landslide disaster based on NPR-OFST. Geomechanics Geophys. Geo-Energy Geo-Resources 10 (1), 108. doi:10.1007/s40948-024-00823-4
Thirugnanam, H., Uhlemann, S., Reghunadh, R., Ramesh, M. V., and Rangan, V. P. (2022). Review of landslide monitoring techniques with IoT integration opportunities. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sens. 15, 5317–5338. doi:10.1109/JSTARS.2022.3183684
Udd, E. (1995). An overview of fiber-optic sensors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 66 (8), 4015–4030. doi:10.1063/1.1145411
Venketeswaran, A., Lalam, N., Wuenschell, J., Ohodnicki Jr, P. R., Badar, M., Chen, K. P., et al. (2022). Recent advances in machine learning for fiber optic sensor applications. Adv. Intell. Syst. 4 (1), 2100067. doi:10.1002/aisy.202100067
Wang, D. Y., Zhu, H. H., Wang, J., Sun, Y. J., Schenato, L., Pasuto, A., et al. (2023). Characterization of sliding surface deformation and stability evaluation of landslides with fiber–optic strain sensing nerves. Eng. Geol. 314, 107011. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107011
Wang, D. Y., Zhu, H. H., Wu, B., Ye, X., Wang, J., Tan, D. Y., et al. (2024). Performance evaluation of underground pipelines subjected to landslide thrust with fiber optic strain sensing nerves. Acta Geotech. 19 (10), 6993–7009. doi:10.1007/s11440-024-02311-1
Wang, J., Zhu, H. H., Ye, X., Tian, F., Zhang, W., Li, H. Z., et al. (2025). Shear strain prediction of reservoir landslide based on FBG monitoring and bagging-MLP algorithm. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 84 (2), 67–18. doi:10.1007/s10064-024-04076-z
Wang, Y. L., Shi, B., Zhang, T. L., Zhu, H. H., Jie, Q., and Sun, Q. (2015). Introduction to an FBG-based inclinometer and its Application to Landslide monitoring. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 5, 645–653. doi:10.1007/s13349-015-0129-4
Wang J., J., Dong, W., Yu, W., Zhang, C., and Zhu, H. (2023). Numerical and experimental investigation of slope deformation under stepped excavation equipped with fiber optic sensors. Photonics 10 (6), 692. doi:10.3390/photonics10060692
Wei, S. C., and Liu, K. F. (2020). Automatic debris flow detection using geophones. Landslides 17 (2), 349–359. doi:10.1007/s10346-019-01258-9
Wen, C., Hu, S., Wang, J., Fang, H., and Xue, X. (2024). Fiber optic sensing technology in underground pipeline health monitoring: a comprehensive review. Struct. Health Monit., 14759217241280904. doi:10.1177/14759217241280904
Wen, Z., Xu, W., Yuan, B., Zhang, L., and Liang, Z. (2025). Numerical analysis of anti-slide pile reinforcement for slope stability under rainfall conditions. Buildings 15 (4), 638. doi:10.3390/buildings15040638
Wu, H., Zhu, H. H., Zhang, C. C., Zhou, G. Y., Zhu, B., Zhang, W., et al. (2020). Strain integration-based soil shear displacement measurement using high-resolution strain sensing technology. Measurement 166, 108210. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108210
Xu, Q., Song, K., Liu, H., Zheng, W., Dong, S., and Zhang, L. (2024). Remote real-time monitoring and early warning of pipeline status under landslide conditions based on stress–strain analysis. ASCE-ASME J. Risk Uncertain. Eng. Syst. Part A Civ. Eng. 10 (1), 04023060. doi:10.1061/AJRUA6.RUENG-1078
Yang, C., Lizheng, D., Huang, L., Tao, C., Jianguo, C., and Hongyong, Y. (2022). Landslide early warning model based on acoustic emission monitoring. J. Tsinghua Univ. 62 (6), 1052–1058. doi:10.16511/j.cnki.qhdxxb.2022.22.030
Yang, Y., Cai, W., Wang, Y., Kong, L., Xu, J., Yang, J., et al. (2025). Omnidirectional optic fiber shape sensor for submarine landslide monitoring. Measurement 239, 115429. doi:10.1016/j.measurement.2024.115429
Ye, X., Zhu, H., Wang, J., Zheng, W., Zhang, W., Schenato, L., et al. (2024b). Towards hydrometeorological thresholds of reservoir-induced landslide from subsurface strain observations. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 67 (6), 1907–1922. doi:10.1007/s11431-023-2657-3
Ye, X., Zhu, H. H., Cheng, G., Pei, H. F., Shi, B., Schenato, L., et al. (2024a). Thermo-hydro-poro-mechanical responses of a reservoir-induced landslide tracked by high-resolution fiber optic sensing nerves. J. Rock Mech. Geotechnical Eng. 16 (3), 1018–1032. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.004
Ye, X., Zhu, H. H., Wang, J., Zhang, Q., Shi, B., Schenato, L., et al. (2022). Subsurface multi-physical monitoring of a reservoir landslide with the fiber-optic nerve system. Geophys. Res. Lett. 49 (11), e2022GL098211. doi:10.1029/2022GL098211
Yimin, M., Yican, L., Mwakapesa, D. S., Genglong, W., Nanehkaran, Y. A., Khan, M. A., et al. (2021). Innovative landslide susceptibility mapping portrayed by CA-AQD and K-means clustering algorithms. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 1–17. doi:10.1155/2021/8846779
Yin, J., Li, Z. W., Liu, Y., Liu, K., Chen, J. S., Xie, T., et al. (2022). Toward establishing a multiparameter approach for monitoring pipeline geohazards via accompanying telecommunications dark fiber. Opt. Fiber Technol. 68, 102765. doi:10.1016/j.yofte.2021.102765
Yu, J., Zheng, Y., Chen, B. L., Yang, C., and Guo, D. P. (2022). Experimental investigation on performance monitoring of the combined optical fiber transducer in landslide. Opt. Eng. 61 (2), 024101. doi:10.1117/1.OE.61.2.024101
Zeni, L., Picarelli, L., Avolio, B., Coscetta, A., Papa, R., Zeni, G., et al. (2015). Brillouin Optical Time-Domain analysis for geotechnical monitoring. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 7 (4), 458–462. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2015.01.008
Zhang, L., Cui, Y., Zhu, H., Wu, H., Han, H., Yan, Y., et al. (2023). Shear deformation calculation of landslide using distributed strain sensing technology considering the coupling effect. Landslides 20 (8), 1583–1597. doi:10.1007/s10346-023-02051-5
Zhang, L., Shi, B., Zhang, D., Sun, Y., and Inyang, H. I. (2020). Kinematics, triggers and mechanism of Majiagou landslide Based on FBG Real-Time monitoring. Environ. Earth Sci. 79, 200. doi:10.1007/s12665-020-08940-5
Zhang, L., Zhu, H., Han, H., and Shi, B. (2024). Fiber optic monitoring of an anti-slide pile in a retrogressive landslide. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 16 (1), 333–343. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.011
Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Gao, L., Zhang, Z., Zhang, W., et al. (2016). Using custom fiber Bragg grating-based sensors to monitor artificial landslides. Sensors 16 (9), 1417. doi:10.3390/s16091417
Zhao, J., Huang, Q., Peng, J., Wang, Z., Ma, P., Leng, Y., et al. (2025). Typical characteristics and causes of giant landslides in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, China. Landslides 22 (2), 313–334. doi:10.1007/s10346-024-02363-0
Zhao, M., Yi, X., Zhang, J., and Lin, C. (2021). PPP-BOTDA distributed optical fiber sensing technology and its Application to the baishuihe Landslide. Front. Earth Sci. 9. doi:10.3389/feart.2021.660918
Zheng, Y., Huang, D., Zhu, Z., and Li, W. (2018). Experimental study on a parallel-series connected fiber-optic Displacement sensor for Landslide monitoring. Opt. Lasers Eng. 111, 236–245. doi:10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.08.017
Zheng, Y., Zhu, Z. W., Xiao, W., and Deng, Q. X. (2020). Review of fiber optic sensors in geotechnical health monitoring. Opt. Fiber Technol. 54, 102127. doi:10.1016/j.yofte.2019.102127
Zhu, H. H., Gao, Y. X., Chen, D. D., and Cheng, G. (2024). Interfacial behavior of soil-embedded fiber optic cables with micro-anchors for distributed strain sensing. Acta Geotech. 19 (4), 1787–1798. doi:10.1007/s11440-023-01956-8
Zhu, H. H., Shi, B., Yan, J. F., Zhang, J., and Wang, J. (2015). Investigation of the evolutionary process of a reinforced model Slope using a Fiber-Optic monitoring network. Eng. Geol. 186, 34–43. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.10.012
Zhu, H. H., Ye, X., Pei, H. F., Cheng, G., Zhang, W., Wang, J., et al. (2021). Real-time and multi-physics fiber optic monitoring of landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 861 (4), 042044. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/861/4/042044
Keywords: landslides, fiber-optic technology, early warning system, real-time monitoring, coastal mass movement
Citation: Cemiloglu A, Chengyong J, Teng F, Nanehkaran YA, Raoof A, Sweijen T and Derakhshani R (2025) Fiber-optic technologies for real-time monitoring of coastal landslides: a review of their role in early warning systems. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1570413. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1570413
Received: 03 February 2025; Accepted: 30 May 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Hans-Balder Havenith, University of Liège, BelgiumReviewed by:
Chong Xu, Ministry of Emergency Management, ChinaYawar Hussain, The University of Texas at Dallas, United States
Mohammad Azarafza, University of Tabriz, Iran
Copyright © 2025 Cemiloglu, Chengyong, Teng, Nanehkaran, Raoof, Sweijen and Derakhshani. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Reza Derakhshani, ci5kZXJha2hzaGFuaUB1dS5ubA==, ZGVyYWtoc2hhbmlAdWsuYWMuaXI=; Thomas Sweijen, dC5zd2VpamVuQHV1Lm5s
 Ahmed Cemiloglu
Ahmed Cemiloglu Jin Chengyong2
Jin Chengyong2 Fei Teng
Fei Teng Yaser A. Nanehkaran
Yaser A. Nanehkaran Amir Raoof
Amir Raoof Reza Derakhshani
Reza Derakhshani