- School of Economics and Management, China JiLiang University, Hangzhou, China
Introduction: Exploring the synergistic development of water resources, energy, and carbon dioxide (CO₂)—the WEC nexus—is essential for promoting regional sustainable development.
Methods: Using an obstacle degree model, this study identifies key barriers affecting the WEC nexus in China and predicts the future trend of its coupling coordination degree.
Results: The findings reveal: (1) From 2008 to 2022, the integrated development level of the WEC nexus in China exhibited a fluctuating upward trend, led by the carbon system and hindered by the energy system. (2) The coupling coordination degree improved from 0.47 in 2008 to 0.53 in 2022, shifting from near imbalance to marginal coordination. Spatially, the southeast outperformed the northwest, and the overall pattern displayed inertial dependence. (3) The main obstacle factors remained relatively stable over time. Specifically, water development was limited by per capita water resources and groundwater proportion; energy by per capita energy production and self-sufficiency; and carbon by investment in environmental governance and green space availability. (4) Projections for 2026–2035 indicate continued improvement in coupling coordination, although enhanced integration policies in water management, energy transition, and carbon reduction are required.
Discussion: This study contributes actionable insights for policy-making and supports ecological-economic synergies through spatial and obstacle-based analysis.
1 Introduction
In recent years, with the continuous development of industrialization, urbanization, and informatization, the problems of water scarcity, frequent occurrence of extreme weather events, and tight energy supply have become increasingly prominent. These issues are directly related to the core goals of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): ensuring clean drinking water and sanitation, providing affordable and clean energy, and taking climate action. With the exponential growth of the global population and the continuous advancement of urbanization, the demand for water and energy continues to rise. Global water consumption is expected to increase by 85% and energy consumption by 35% by 2035 (Li et al., 2024). For China, which utilizes 6% of the global freshwater resources to support the water needs of 20% of the global population, the problem of water scarcity is even more significant. Meanwhile, the carbon emissions associated with energy production cannot be neglected. It is expected that by 2050, carbon emissions related to energy production will increase by 70% in China, and greenhouse gas emissions by 50% (Zhang et al., 2022). The continued high level of carbon emissions not only exacerbates climate instability but also poses a serious threat to the sustainable development of ecosystems and economic systems. Therefore, to effectively reduce carbon emissions and construct an integrated framework system covering water security, energy security, and ecological environment security, it is essential to consider water recourses, energy, and carbon emissions as a complex coupled system. From the perspective of multi-objective optimization, the synergistic and cooperative development of the system internally and externally should be realized in an all-around way.
The water-energy-carbon (WEC) nexus is defined as a complex relationship of interactions and constraints between water resources management, energy utilization, and carbon reduction. As depicted in Figure 1, the processes of water resource development, transportation, and wastewater treatment are highly energy-intensive. For example, in urban water supply systems, the various stages of resource development, transportation, treatment, and distribution require significant energy inputs (Zhao et al., 2020). Given that the majority of this energy is derived from fossil fuel combustion, these processes indirectly contribute to increased carbon emissions. Moreover, energy production, especially electricity production, also requires the involvement of large amounts of water resources (Liao et al., 2021). This is because the entire energy production chain, from coal mining to electricity generation, requires water for cleaning and cooling. As a result, increased energy consumption is accompanied by increased water demand in urbanization. Additionally, wastewater treatment processes is a significant sources of urban carbon emissions (Singh et al., 2016). As cities expand, water and energy consumption increase significantly, thereby further contributing to the dramatic increase in carbon emissions. Overall, understanding the WEC nexus is important for further understanding ecosystem evolution, economic and social development, and the impact of climate change.
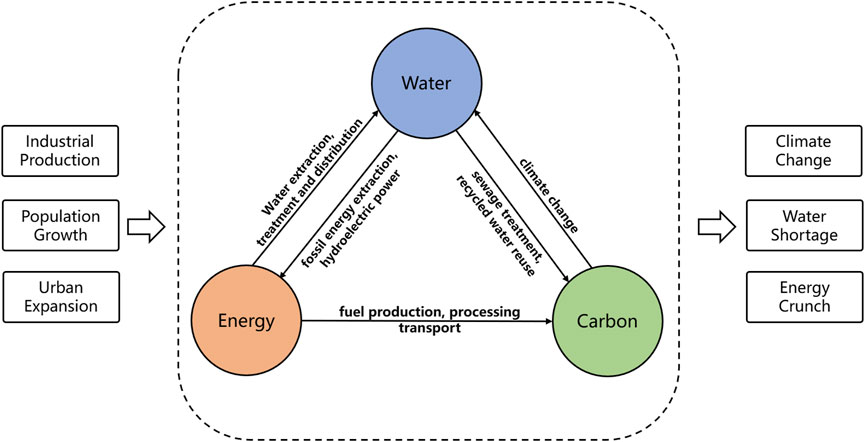
Figure 1. Schematic diagram illustrating the interactions within the Water-Energy-Carbon (WEC) nexus.
The concept of nexus, also known as the coupling or linkage, was first explicitly proposed at the conference on the Water-Food-Energy Security Nexus held in Bonn, Germany, in 2011 (Hao et al., 2023; Lin et al., 2021). The essence of this concept is rooted in the framework of the SDGs, which aims to seek synergistic strategies between two or more systems and incorporate them into the macro decision-making perspective. This approach is designed to mitigate conflicts both internal and external to the system and to realize the co-development of the economy, society, and the ecological environment (Li et al., 2016). The nexus relationship is proposed to break the siloed nature of different elements and further explore the interaction between them (Bleischwitz et al., 2018). Currently, research on nexus relationships is not limited to the water-food-energy field but extends to several aspects of sustainable development, including water-energy (Zhang et al., 2021), water-energy-carbon (Tian et al., 2022), water-energy-land (Pulighe and Pirelli, 2023), and water-energy-relationships with other elements (François et al., 2023; Silva-Afonso and Pimentel-Rodrigues, 2024).
The water-energy (WE) nexus is a complex system that involves multi-sectoral production, transportation, and usage, taking into account the coupling between water and energy resources (Yong et al., 2023). From the perspective of water-energy synergistic research, Peng et al. (2022) used an input-output model to explore the water-energy system linkage relationship and its drivers and to quantify its synergistic benefits, which provided a theoretical basis for regional synergistic development. Qiu et al. (2022) further detailed the research object, focusing on the urban water system, and quantitatively analyzed the energy intensity of water-related residential use and its main influencing factors. They pointed out that household water use is mainly influenced by income, whereas electric energy use is mainly influenced by education level. Building on this, Hao and Sun (2023) analyzed the spatial-temporal evolution patterns and spatial flow patterns of coal water footprints in China based on the top-down approach and ecological network analysis, respectively. Their research clarified the flow patterns of coal water footprints in the country and provided theoretical support for reducing coal consumption. In addition, from the perspective of policy effect assessment, Sun et al. (2021) considered the role of environmental tax policy and simulated the impacts of environmental tax mechanisms on the WE nexus under different tax rates and time horizons by using dynamic computable general equilibrium model (CGE). The study concluded that energy tax policies are more conducive to energy conservation, while carbon tax policies are more effective in promoting water resource conservation. Werner and Lazaro (2023) investigated the impacts of energy transition policies on the WE system. Their results showed that the relevant policies can not only promote the optimization of the energy structure, market competition, and technological innovation but also effectively reduce the negative impacts of energy production on water resources and ecosystems.
With the increasing prominence of global climate issues, the large amount of CO2 emissions has become a significant obstacle to the realization of sustainable development goals. Climate change and water scarcity have become focal points of research in the academic community (Davis et al., 2017). As a result, many scholars have further incorporated carbon emissions into the study of the water system and the energy system, respectively. Among them, the research on water-carbon (WC) systems mainly focuses on the two levels of quantitative assessment and optimization and enhancement. In terms of quantitative assessment, Molinos-Senante and Maziotis (2021) proposed a parametric methodology to estimate the carbon efficiency and total factor carbon productivity of water utilities. They suggested that environmental variables such as energy costs, water treatment complexity, and population density all play a significant role in their carbon performance. On the other hand, Battin et al. (2023) started with river ecosystems and assessed the contribution of ecosystem metabolism to the global river carbon budget using the mass balance approach. The results emphasized the complex impacts of global change on river ecosystem metabolisms and associated carbon flux, as well as the importance of establishing a global river observing system (RIOS). In addition, the concept of the carbon footprint was first derived from the ecological footprint (Rees, 1992), and has in recent years become an effective way of thinking about quantifying carbon emissions intensity. Zawartka et al. (2020) focused on the processes of wastewater collection, transportation, and treatment, and explored the carbon footprint of this complex system. They pointed out that the central wastewater treatment plant contributed the most greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, while the sewage system contributed the least. In terms of optimization and enhancement, Gui et al. (2024) took the urban water system as research object. They analyzed the relevant characteristics of the WC nexus and carbon emission intensity of different water sources and stages based on the life cycle assessment (LCA) model and then used scenario simulation to explore the carbon emission reduction potential of the urban water system. Their study proposed improving the utilization ratio of recycled water, reducing the water distribution network leakage rate, and strict water treatment process of ascension path to reach these targets. Focusing on sewage treatment systems, Donald et al. (2023) evaluated the potential of integrating hydrogen into production to reduce GHG emissions by comparatively analyzing different system configurations. Their research posed that integrating an electrowater system to produce hydrogen at a sewage treatment plant and using the produced hydrogen for local fuel cell electric buses (FCEBs) would be a useful way to reduce GHG emissions. The results indicated that the production of hydrogen in sewage treatment plants through the integration of electrowater and the use of the produced hydrogen for local FCEBs is a viable future industry with environmental benefits. Yang et al. (2024) explored the mechanisms of sewage treatment policies at 2,894 wastewater treatment plants in China on water and carbon issues from a micro perspective. They further argued that the rational expansion of urban pipelines and wastewater treatment plants, as well as the promotion of biofilm treatment technology, are feasible methods to improve water quality and implement carbon reduction.
In the context of increasing global industrialization, moreover, the continued expansion of energy demand is directly related to the growth of GHG emissions. How to enhance the utilization of clean energy technologies and reduce carbon emissions has become an urgent issue (Jin and Kim, 2019). Much of the research on energy-carbon (EC) systems has focused on improving energy use efficiency, optimizing energy structure, and developing carbon capture and storage technologies. In terms of energy utilization efficiency improvement, Karamouz et al. (2022) predicted the trends of water resources, energy, and carbon emissions under different policy contexts based on system dynamics (SD). And then illustrated that improving energy utilization efficiency plays an important role in reducing carbon emissions and sustaining economic growth, which can be achieved through carbon emission limitation policies. Belaïd and Massié (2023), conversely, evaluated the impact of energy use efficiency on Saudi Arabia’s carbon emission intensity and assessed its potential contribution to achieving the net-zero emission target. They projected that energy efficiency improvement will account for one-fifth of Saudi Arabia’s decarbonization contribution by 2060. Regarding energy mix optimization, Balsalobre-Lorente et al. (2018) introduced a renewable energy consumption variable to explore the relationship between economic growth and carbon emissions. Their research found that for every 1% increase in renewable energy consumption, there is a 0.134% reduction in carbon emissions, while for every 1% increase in renewable energy mix, there is a 1.26% reduction in carbon emissions. Despite the significant contribution of renewable energy to carbon emission reduction (Jin, 2022), through empirical research still indicated that carbon emission reduction policy tools should be rearranged in conjunction with other relevant policies, such as supply-side reforms and strengthening decarbonization of electricity production. The implementation of a single renewable energy policy is in the stage of diminishing the marginal effect. Furthermore, in terms of carbon capture technologies, Desideri et al. (2012) simulated a plant that separates carbon dioxide from the exhaust gases of a combined-heat-power plant and generates electricity. They evaluated the removal efficiency of a carbon capture system based on a molten carbonate fuel cell (MCFC) and concluded that the separation system has high performance and high economic returns. Akrami et al. (2023) proposed that low-carbon heat and electricity production can be efficiently achieved through the development and simulation of a biomass-based combined heat and power (CHP) system, which is equipped with post-combustion carbon capture and utilization (CCU) unit.
Based on the above theoretical foundation, the academic community has further conjugated and formulated a comprehensive relationship of the water-energy-carbon (WEC) nexus, including water resource utilization, energy consumption, and carbon dioxide emission reduction, aiming to promote the synergistic development among the three (Li et al., 2019). Among them, Wang et al. (2023) reviewed the research progress of the global WEC nexus and proposed four frontier topics for future research. These topics include: the study of national land spatial optimization based on the WEC bearing capacity, the decoupling analysis of resource consumption and economic growth under the WEC perspective, the quantitative analysis of the determinism and uncertainty of the complex WEC nexus, and WEC engineering measures to boost the “negative emissions”. Regarding framework improvement, Oh et al. (2021) designed a new framework for the WE system by introducing a pinch analysis and tested the framework using a case study to describe in detail how the WEC nexus can be characterized based on this system operation. Meanwhile, based on objective function expressions with explicit relationships, Gomez-Gardars et al. (2022) proposed a multi-objective approach for the WEC nexus evaluation index system. They integrated the design optimization and change of the energy system by considering its multi-cycle, multi-scenario, and multi-objective operation. In terms of urban sustainable development, Zhang et al. (2023) constructed a multi-objective dynamic optimization model based on input-output and sustainable development theories with WEC nexus as the constraints. They evaluated the economic development and sustainable development level of Hebei Province and found that there was a significant imbalance in the sustainability of various regions in Hebei Province. Similarly, Liu et al. (2022) took 15 large-scale water resource recovery facilities (WRRFs) as potential energy generation units and explored the energy recovery and scheduling strategies of WRRFs in 2030 under the renewable energy penetration scenario through simulation optimization. This approach not only improves the efficiency of water resources and energy use but also provides developmental impetus for the energy system to achieve the goal of carbon neutrality. Facing the dilemma of high energy consumption, high emission, and high cost of sewage treatment plants, Zhao X. et al. (2024) proposed incorporating carbon emission costs into the operation costs to incentivize carbon emission reduction and introducing sewage hierarchical treatment measures to promote resource utilization. Yu et al. (2020) further subdivided the carbon emissions of the sewage treatment system into direct and indirect carbon emissions and evaluated the carbon emissions of different parts of the sewage treatment process and the influencing factors through a case study. They proposed strengthening the integrated management of the resource input and circulation process of the urban sewage treatment system and further promoting the synergistic operation of water resources, energy conservation, and carbon emission reduction. In addition, Zhao R. et al. (2024) introduced the land utilization factor and emphasized the direct influence of land utilization structure, intensity, function, and layout on the association intensity and coupling characteristics of WEC elements from the perspective of “nature-society”. Then they explored the optimization strategy of land utilization pattern under WEC synergistic constraints.
To summarize, academics have conducted multi-dimensional analyses of the WEC nexus. In terms of measurement, the input-output model, CGE model, and LCA model are used to quantify the interlinkages and synergistic benefits among the three. Regarding research perspectives, the impacts on regional synergies and the decoupling of economic growth are explored at the macro level, while the potential for carbon emission reduction in urban water systems is examined at the micro level. Regarding constraints, a multi-objective dynamic optimization model is constructed with the WEC nexus to assist economic and social sustainability. However, the differentiated characteristics and targeted strategies of WEC synergistic development in different regional contexts require in-depth excavation. There is heterogeneity in resource endowment and development levels across regions, which should be analyzed and formulated in detail to achieve coordinated development. Meanwhile, in response to the complicated actual environment, a more efficient model should be chosen to improve model adaptability and forecasting capability.
As the largest developing country in the world, China possesses unique ecosystems and economic development patterns. Research related to China has both reference value for ecological protection and resource utilization, and practical significance in promoting regional economy development, optimizing industrial structures, and improving economic development quality. Therefore, this article focused on China and summarized the integrated development levels of WE, EC, WC, and WEC in the temporal dimension. This approach aimed to reveal the impacts of water resources, energy, and carbon on the overall development level over the time series. Then, by constructing a comprehensive evaluation system, the coupling coordinated development level of the China from 2008 to 2022, as well as its temporal evolution characteristics, was measured by using the coupling coordination degree model. The spatial evolution characteristics were obtained by spatial visualization analysis using ArcGIS. Finally, the key factors affecting the WEC synergistic development level were explored based on the obstacle degree model. Meanwhile, the trend of the coupling coordination level in the region from 2026 to 2035 was further predicted with the grey forecast model. This research provides new ideas to promote the synergistic development of the WEC nexus, facilitates the integrated development of the regional economy, and offers specific decision support for regional policy formulation through spatial visualization analysis and obstacle degree models.
2 Data and methodology
2.1 Data source and indicators selection
2.1.1 Data source
This study selected the panel data of all 30 provinces in China from 2008 to 2022. Water resources data were obtained from the China Environmental Statistics Yearbook, China Water Resources Bulletin, and relevant provincial water resources bulletins. Energy data were derived from the China Statistical Yearbook China Energy Statistical Yearbook, National Bureau of Statistics (National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2023), and statistical yearbooks of provinces and cities. Carbon emission data came from the China Carbon Emission Accounting Database (China Carbon Emission Accounting Database, 2023), with energy carbon emissions referred to in the study by Wang and Li (2022). Additionally, the energy carbon emission coefficients were taken from the 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, and the discounted standard coal coefficients were taken from the General Principles for the Calculation of Comprehensive Energy Consumption (GBT2589-2020).
2.1.2 Evaluation indicator selection
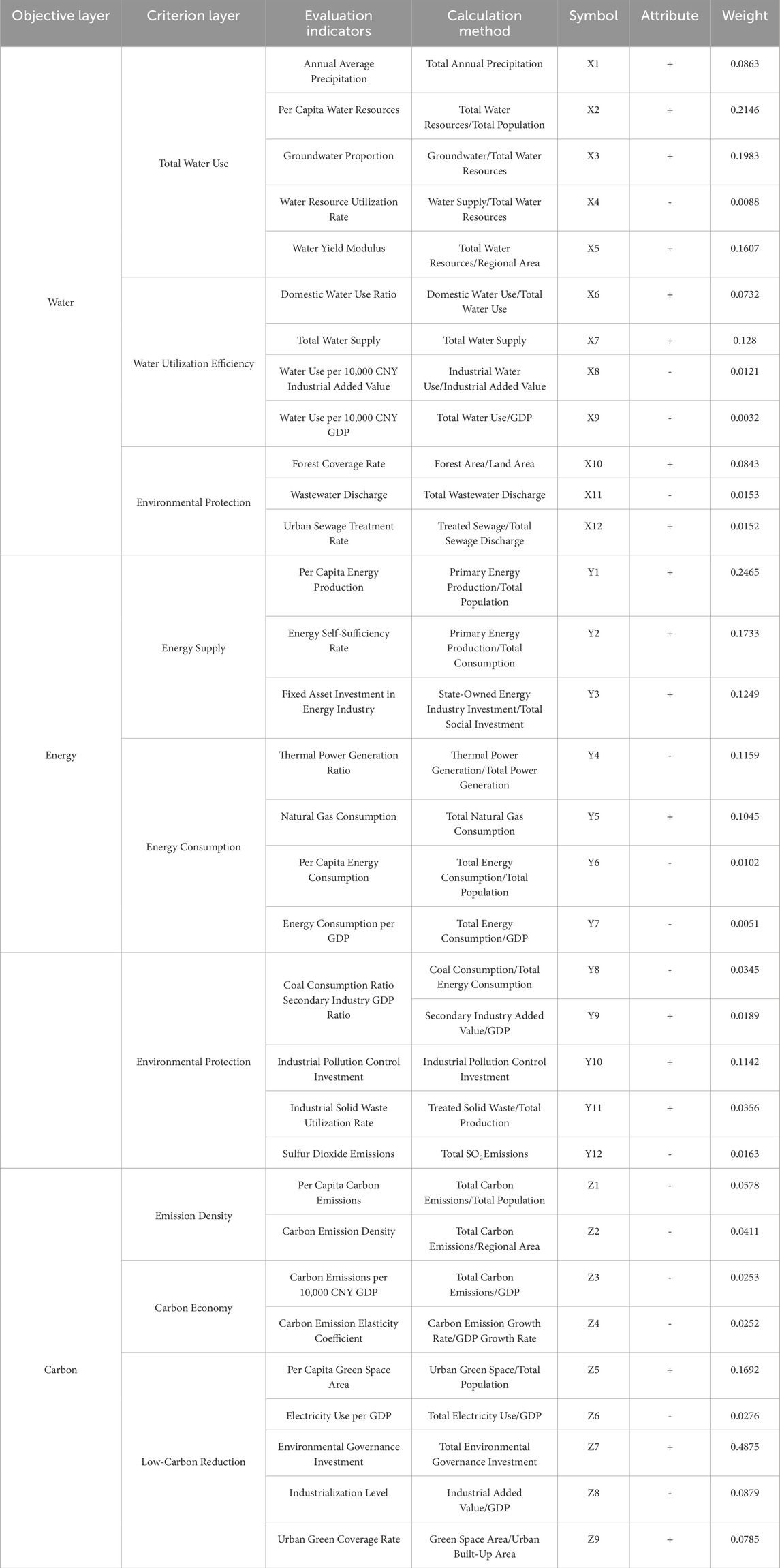
Based on the theoretical analysis of relevant literature (Li et al., 2023; Yang and Ran, 2024; Yuan et al., 2024) and the representativeness of the indicators, this research constructed a comprehensive evaluation system for the WEC nexus, as shown in Table 1. Systematically, the indicator system includes water resources, energy and carbon emission reduction elements, and builds a three-level structure (objective layer, criterion level and evaluation indicators). The indicators not only emphasize the characteristics of each element, but also reflect the interactions between them, which fully reflects the development status of the WEC nexus system. Regarding value relevance, indicators including water resource utilization rate and energy self-sufficiency rate are used to highlight the value of evaluating the sustainable utilization of resources (Li et al., 2022; Sarkodie, 2022). Meanwhile, the indicator system also emphasizes the environmental protection-oriented feature, which guides economic activities to seek environmental governance while pursuing economic growth, and realizing the economic and ecological coordinated development (Czyżewski et al., 2022). Regional adaptability considers the distributional variability of water resource endowment, economic progress and energy structure (e.g., water yield modulus, secondary industry GDP ratio) in different regions, which provides a theoretical basis for locally adapted policy formulation. Moreover, the selected indicators are relatively independent from each other, both to avoid crossover and double counting, and to represent the main aspects of the WEC nexus system, which is oriented to meet the sustainable development requirements.
2.2 Evaluation index calculation
Prior to the calculation of the evaluation index, the raw data underwent standardization to eliminate the influence of variations in scale. The standardized calculation formulas are shown below (Lv et al., 2024), where
For positive indicators:
For negative indicators:
The entropy weight method was employed to calculate the indicator weights, based on the processed panel data. A linear weighting was applied to the water, energy and carbon systems to calculate their respective comprehensive evaluation indices (Cai et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2021), which were used as a basis for assessing the composite development level of the subsystems. The expression is presented below:
2.3 Coupling coordination degree model
Coupling coordination degree model is a way to work out how two or more systems interact and synchronize with each other. With the Stata tool, the strength of the interaction between multiple systems and the consistency of subsystems is measured using the coupling degree and the coordination degree, respectively (Jiang et al., 2022). In doing so, it reveals the state of coordination. The following formulas are provided below:
The coupling degree of each water-energy-carbon system is represented by
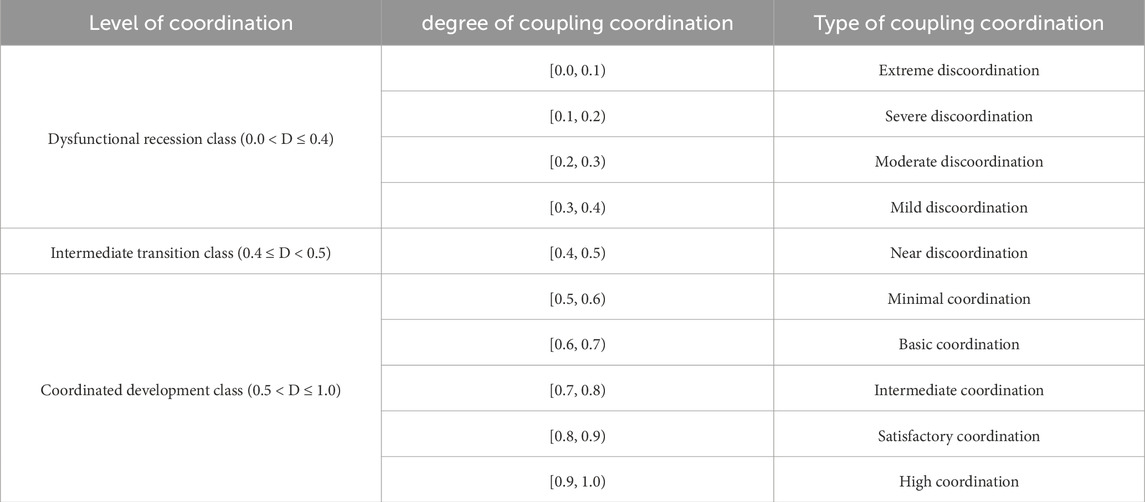
To better measure the coordination and development level of systems, this was classified into three categories and ten grades (Table 2) based on current research (Deng and Liu, 2023).
2.4 Obstacle degree model
The key influencing factors that restrict the further development of systems can be identified by the obstacle degree model (Bai et al., 2022). The model is primarily dependent on the weights of indicators for evaluation objects, and it assesses the level to which each indicator hinders the integration progress of the system. Thus, the SPSS tool was utilized in this section to calculate the obstacle degree and to better identify how much the key factors influence the regional WEC coupling coordination degree with SPSS tool. The calculation formula is as follows:
2.5 Grey forecast model
A grey forecast model (GM(1,1)) is an invaluable tool for addressing issues of uncertainty and incomplete information (Hamzacebi and Es, 2014). It does this by processing raw data using techniques such as interpolation and extrapolation to predict future movements. GM(1,1) possesses distinct strengths in short-term prediction and processing irregular data, and it has been widely applied in multiple fields. This article forecasted the WEC nexus coupling level in China from 2026 to 2035 by using a Python programming tool, with a view to providing a forward-looking theoretical basis for the governance behaviors of relevant authorities.
3 Results and analysis
3.1 Comprehensive development analysis of the WEC nexus
The comprehensive indices of the water, energy, and carbon systems in China from 2008 to 2022 were estimated separately, and the temporal evolution trend of the comprehensive index of each subsystem was obtained, as shown in Figure 2. In general, the carbon system displayed the highest level of development, with an average annual index of 0.36. And the energy system showed the lowest level of coordination, with an average annual index of 0.2.
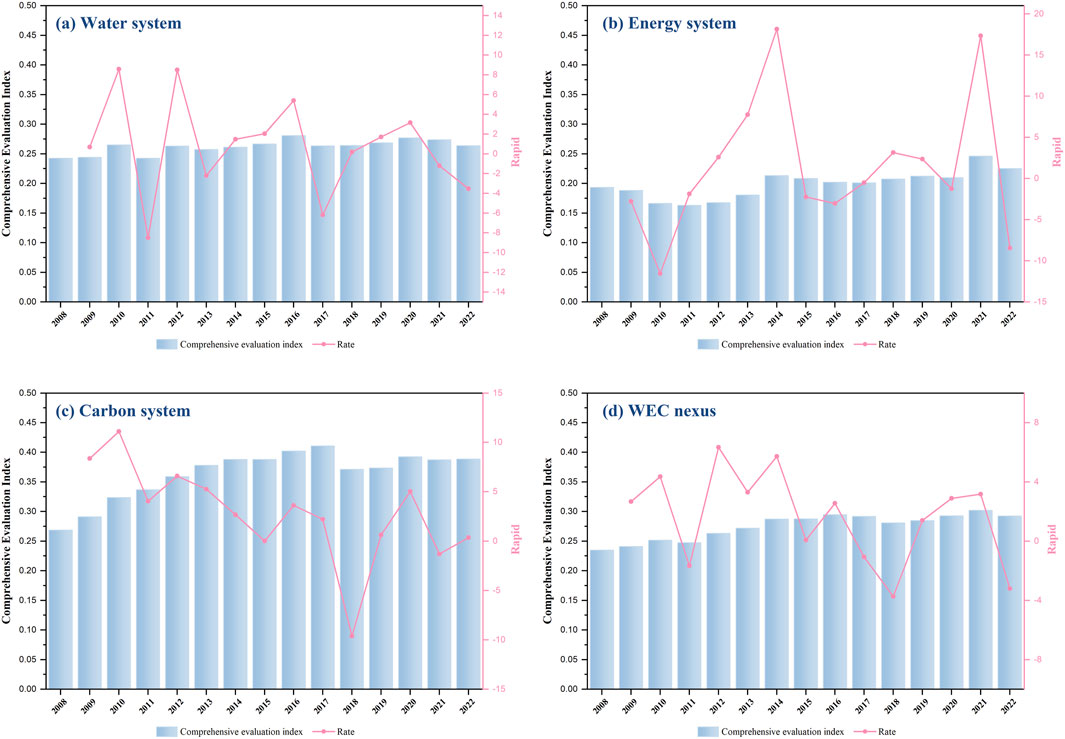
Figure 2. Temporal evolution (2008–2022) of the comprehensive evaluation indices for: (a) Water system; (b) Energy system; (c) Carbon system; (d) Overall WEC nexus in China.
Specifically, the water system comprehensive evaluation index followed a fluctuating upward trend, but its growth rate was the lowest among the four systems (with a growth rate of 8.8%). The phenomenon demonstrated that water environment management in China had gradually overcome the early wave situation and stepped into the stable progress stage under the dual effects of policy promotion and technology advancement. The growth rate curve tendency showed that the development rate of the water system fluctuated drastically around 2011. This was inextricably linked to the advancement of large-scale hydraulic projects and facilities such as the South-to-North Water Diversion in China, which resulted in damage to the regional water ecology by extent of the large-scale construction activities.
In addition, the composite index of the energy system was rising slowly from 0.19 to 0.22, and although it still displayed a growing trend, its overall developing degree was weak and its growth fluctuated significantly. This reflected the enormity that the energy system faced in the transition process: the necessity to ensure energy security supply and to strengthen control over fossil fuel usage for a low-carbon transition. According to the growth rate curve, the energy system evaluation index was in a negative growth phase in more than half of the years, which was mainly due to the effects of industrialization and urbanization, and further exacerbated the stiff growth of energy consumption. The mismatch between energy structural adjustment and economic development pattern aggravated energy security instability and dependence in China.
Furthermore, carbon system’s evaluation index increased from 0.27 to 0.39, which was the most significant growth among the four systems (with a growth rate of 45%). That was closely related to the growing international attention to global climate issues and the Paris Agreement. From the growth rate curve, the carbon system showed large up-and-downs around both 2011 and 2018, which corresponded to key points including the beginning of carbon emission rights market pilots in China and the landing of a nationwide carbon market. The growth rate stabilized after 2019, reflecting that carbon emission reduction in China had gradually stepped into an institutionalized track. An increase in clean energy shares, a greening transformation of industry and an enhanced carbon sink capacity of ecosystems had combined to drive the speedy development of the carbon system and accelerate the regional low-carbon transition.
Based on the above respective measurements of the integrated index of water, energy, and carbon systems, further integration explored the development level of the WEC nexus (as shown in Figure 2d). Overall, the evaluation index of WEC nexus presented a fluctuating upward trend (from 0.23 to 0.3), and the growth rate was the smoothest one among the four systems. The less volatile growth rate of the WEC nexus system reflected a much more stable and balanced pattern than the evolutionary trend of the separate systems. Meanwhile, this highlighted the strengths of integrating the water, energy, and carbon management to facilitate the overall synergistic level of WEC nexus improvement. With the evaluation index peaking twice, in 2016 and 2021, it reflected the remarkable achievements of green development strategies and circular economy planning in China, respectively, which promoted the economic structural shift to environmental protection while also achieving high-efficient recycling of resources.
3.2 Spatial-temporal evolution analysis of coupling coordination degree
3.2.1 Temporal evolution characteristics
As depicted in Figure 3, from 2008 to 2022, the coupling coordination of the WEC nexus system in China exhibited a steady upward trend overall. Especially during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan period (2011–2015), the implementation of the energy conservation and emission reduction plan greatly boosted this process, and the coupling and coordination levels of the four-dimensional systems had been significantly improved. Among these, the average value of the coupling coordination degree in the WC nexus was 0.55, which was the maximum among the four-dimensional systems, with an average annual growth rate of 12.2%. This increase reflected not only the close correlation between the water resources system and the carbon system but also indicated its positive effect on resource utilization and regulation. The sustainable utilization of water resources was crucial for maintaining ecological balance and driving low-carbon development in the region, while the continual promotion of carbon reduction measures directly impacts regional environmental quality and sustainable development. In addition, the coupling and coordination levels between the WE nexus and the EC nexus had shown a steady growth trend, especially for the EC nexus, with an average annual growth rate of up to 12.6%. This growth rate reflected the interdependence between energy consumption and carbon emission reduction. In particular, the accumulation of regional carbon dioxide stocks was exacerbated by an expansion of energy demand. Effective energy policies, especially those related to renewable energy utilization, could reduce dependence on fossil energy sources as well as carbon emissions. Thereby, the optimization of the energy structure and the improvement of environmental quality will be realized.
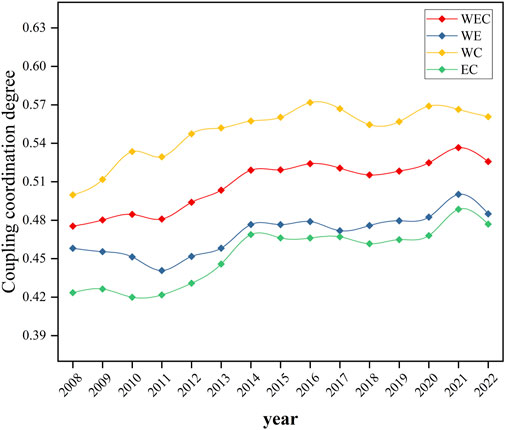
Figure 3. Temporal evolution (2008–2022) of coupling coordination degrees for the Water-Energy (WE), Water-Carbon (WC), Energy-Carbon (EC), and Water-Energy-Carbon (WEC) nexus systems in China.
Besides, taking 2008 as the benchmark year, the regional coupling coordination value of WEC nexus increased from 0.47 to 0.53, with a growth rate of 10.6%. This robust growth validated the policy synergies of the water management system, the dual-control mechanism for energy, and the carbon trading market structure. The comparison revealed that WEC nexus had the lowest average annual fluctuation, which showed significant stability characteristics, indicating that it possessed better resistance to disturbances. Meanwhile, it also indicated that the utilization of institutional innovation to address the resource-environment dilemma will achieve the transformation of regional coupling from near discoordination to minimal coordination.
3.2.2 Spatial evolution characteristics
A spatial distribution analysis was implemented using ArcGIS 10.8 on the basis of the calculated coupling coordination value to visualize the data. According to Figure 4, the coupling coordination in China gradually increased gradually from north to south and from west to east. And large variations were observed between different provinces, indicating an overall development trend of inertia dependence.

Figure 4. Spatial distribution of the WEC nexus coupling coordination degree across China’s 30 provinces in: (a) 2008; (b) 2012; (c) 2018; (d) 2022.
The trends in temporal evolution could be roughly categorized into three periods. (1) 2008–2012 was the slow-growth phase, when the percentage of regions at low coupling coordination levels (<0.5) exceeded 65%, which reflected insufficient policy attention to multi-system synergies in earlier years. (2) 2013–2018 was the rapid development period, with the high-value area gradually expanding to the central and western regions, while the regions in low coupling only accounted for less than 40% of the total. (3) 2018–2022 was the stable development period, with provinces and cities basically entering the minimal coordination stage, which indicated that the low-coupling region was gradually transitioning to the medium level, but interprovincial differences still existed.
Looking at geographical differences, the Yangtze River Delta (Zhejiang, Shanghai, Jiangsu) and Pearl River Delta (Guangdong) region played a leading role in WEC nexus and were the first regions to enter into minimal coordination. Its strengths were centered on industrial structure optimization and cross-sectoral collaboration mechanisms, which allowed them to develop innovatively on the basis of its superior geographic conditions. For example, by establishing the Yangtze River Delta Eco-Green Integrated Development Demonstration Region, it reinforced inter-provincial resource allocation efficiency and boosted the industrial greening transformation. Conversely, the development of the three northeastern provinces (Jilin, Heilongjiang, and Harbin) and part of the inland northwest (Qinghai) lagged behind, and the coupling coordination was always at the near discoordination stage. As the region was dominated by high-consumption and high-pollution industrial structure, and the new industries are relatively underdeveloped, which intensified the conflict between energy demand and low-carbon transition. Moreover, due to the influence of geomorphology and climate, water resources in Qinghai were unevenly distributed, and seasonal differences were obvious, thus hindering the water resources deployment and utilization. And although the three northeastern provinces possessed relatively abundant water resources, the water resources allocation in industry, agriculture and so forth still existed a contradiction between supply and demand owing to the heavy industry development.
3.3 Obstacle degree analysis
By averaging the obstacle degree values of all the provinces, we could obtain the stacked map of obstacle degree for water system, energy system, and carbon system in China during 2008–2022, as shown in Figure 5. According to the graph, it was observed that the obstacle factors contributions of the three systems displayed a relatively stable character and basically did not change significantly over time. This phenomenon indicated that the factors affecting the integrated development of the systems had a high stability and embodied rigid characteristics.
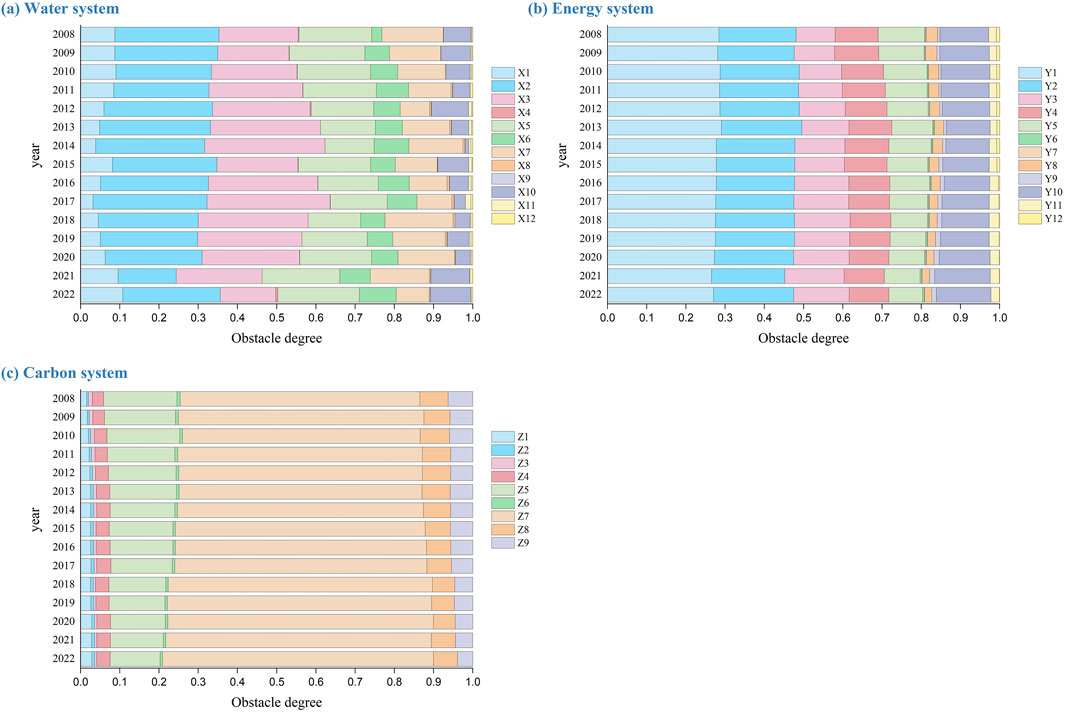
Figure 5. Average obstacle degrees (2008–2022) of key indicators hindering the development of: (a) Water system (X1-X12); (b) Energy system (Y1-Y12); (c) Carbon system (Z1-Z9) in China (30 provinces).
Regarding the water system, per capita water resources (X2) and groundwater proportion (X3) were consistently the most prominent hindering factors from 2008 to 2022 (with an average annual barrier above 0.25). These were followed by water yield modulus (X5) and total water supply (X7). Specifically, indicators X2 and X5 reflected the structural conflict between economic progress and insufficient resource endowment, and exposed the regional overloading problem arising from the rapid urbanization process in China. And indicators X3 and X7 illustrated the deeper exploitation crisis, where groundwater overexploitation was not only exacerbating the discrepancy between water supply and demand, but also posing a serious danger to its security. Therefore, the central contradiction in China’s water resources lied in “insufficient total quantity, unequal distribution and inefficient utilization.”
Regarding the energy system, the top four annual rankings were concentrated on per capita energy production (Y1), energy self-sufficiency rate (Y2), fixed asset investment in energy industry (Y3), and industrial pollution control investment (Y10). The most notable were per capita energy production (Y1) and energy self-sufficiency rate (Y2), both of which had average annual barriers above 0.2. This showed that energy security and pollution control were two principal issues that required urgent attention in China. The energy production scale had continued to expand as demand continued to grow, yet the limited nature of resources had intensified the pressure for energy self-sufficiency, which had led to an increase in the external dependence and a decrease in energy security. In addition, the accelerated pace of industrialization resulted in increased pollution, although investment in pollution control had increased, it was still not sufficient to fully offset the speed and scale of pollution.
For the carbon system, the barrier indicators mainly focused on total investment in environmental governance (Z7), and per capita green space area (Z5). The high obstacle level of indicator Z7 showed that China had insufficiently invested in environmental governance and was lagging behind in financing. Indicator Z5 also exposed the shortcomings of ecological construction, with low green space per capita weakening the self-purification of ecosystems while exacerbating the carbon pressure. This phenomenon was closely associated with economic development and resource allocation policies in China, where more resources were invested in production, contributing to the absence of ecological governance and construction. Furthermore, the conflict between urbanization and land-usage structure restricted the green space expansion.
3.4 Coupling degree prediction
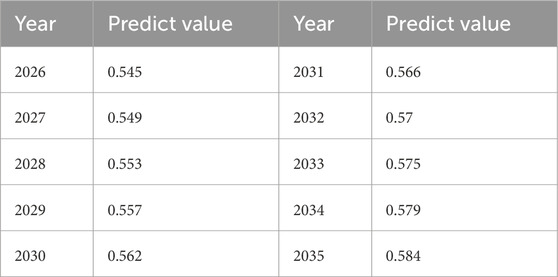
Having clarified the practical situations of the synergistic development of the system and the key obstacle factors impacting growth in the previous phases, this section adopted a reasonable forecasting method to speculate on the future trend of China in strengthening the implementation of water management, energy transition and carbon reduction requires more attention (Table 3). This analysis aimed to further determine the strategic direction and policy focus in the forthcoming evolutionary process.
As predicted by the model, the coupling coordination level in China is expected to display a steady upward trend from 2026 to 2035, basically maintaining the previous growth rate, with an average annual growth rate of 3.9%. This aligns with the objectives of the high-quality development plan. However, the numerical range of the coupling coordination level during the forecast period is expected to be between 0.545 and 0.584, which is still in the minimum coordination stage. This phenomenon indicates that under the current policy continuity, the WEC nexus coupling improvement level still exhibits poor synergy, inadequate innovation incentives and other issues.
4 Discussion
4.1 Implications
First, by measuring the comprehensive evaluation index of WEC nexus and the subsystems (water, energy, and carbon) in China, the understanding of the ecological construction achievements of the region has been deepened. Meanwhile, the results indicates that water resources management, energy use, and carbon emission reduction are a unified entity, and the WEC nexus has a certain coupling and coordination relationship. Fluctuations in any one of the subsystems will influence the overall situation. Therefore, there is a necessity to consider the synergistic development between the three subsystems, so as to not only facilitate the overall progress of the WEC nexus but also take into account the development of the subsystems themselves. This approach will drive the efficient and coordinated development of WEC in the region (Zhu et al., 2024).
Second, the coupling coordination degree of WEC nexus in China is characterized by a distribution of “high in the east and low in the west, high in the south and low in the north”. The coupling degree of the eastern coastal areas (e.g., Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta) and the provinces along the Yangtze River Economic Belt is relatively higher, while the northwestern inland (e.g., Qinghai) has long been in the low-coupling range. The formation of such pattern closely correlates with the regional economic development and resource endowment (Ren and Ni, 2025). The eastern region accounts for a higher proportion of technology-intensive and low-carbon industries, with stronger synergistic management capabilities (Liang et al., 2022). And the western region relies on a high energy resource dependence, with prominent inter-systemic contradictions. Therefore, for the promotion of regional synergistic development, interregional cooperation and linkages ought to be strengthened to facilitate the resource sharing and advantage complementarity. In addition, attention also needs to be focused on addressing regional development imbalance to narrow the regional growth gap and achieve a new situation of coordinated regional progress through differentiated policies and precise implementation of measures.
Moreover, this article identifies the key influencing elements of the water, energy and carbon systems through the obstacle degree model, and emphasizes the “problem-oriented” principle of ecological construction. In the face of global water scarcity (Wang et al., 2024), attention should be paid to the contradiction between economic balance, population development and limited resources, and to settle the groundwater exploitation issue. From a long-term perspective, it is necessary to strengthen water resources management and allocation, improve water use efficiency, and strictly control the development and utilization of water. Regarding energy security, the industrial structure needs to be optimized, the energy transition accelerated, and based on this, pollution control investment enhanced and environmental protection supervision strengthened. In addition, conflicts in developing countries are also recognized as being associated with global warming and climate change, of which the most significant greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide (72 per cent) (Sanglimsuwan, 2011; Adams and Acheampong, 2019). Therefore, as for carbon emission reduction, it is required to continuously increase the environmental governance capital investment, including financial subsidies and green finance, and to optimize the utilization of capital. Besides, concerning the contradictory relationship between urbanization and land usage, urban construction shall be reasonably planned, and ecological restoration projects shall be carried out to expand the green area thus to enhance the regional carbon sink capacity.
Finally, our findings reveal that the WEC nexus in China will remains at the minimum coordination stage during 2026–2035, which demonstrates the insufficiency of the current policy incentives for the coordinated development of water, energy, and carbon systems in China. Therefore, it is crucial to emphasize the importance of advancing the WEC nexus system by enhancing the development level of the water, energy, and carbon system. To achieve a leap from minimal coordination to intermediate or even high coordination, a deeper level of coordination and optimization in policy-making is necessary. More attention should be paid to strengthening the implementation of water management, energy transition and carbon reduction. Most notably, it is essential to focus more on the synergies between these three elements.
4.2 Limitations and future research directions
However, the study is not without limitations. First, the coupled coordination model assumes that the water, energy and carbon systems are equally important, and fails to consider the effects of regional natural conditions and resource endowments on the weights. Therefore, a dynamic weight adjustment model may be developed in future research to optimize the weight allocation of subsystems by combining the ecological differences of regions. Furthermore, based on the obstacle degree model and the grey prediction model, only critical constraints have been proposed, without exploring the impact mechanisms of the differentiated policies and lacking the feasibility assessment of specific measures. Further research should design policy scenario simulation models to assess the marginal effects of different policy combinations on WEC nexus coupling.
5 Conclusion
This article investigated the synergistic development and temporal evolution of the WEC nexus using the comprehensive evaluation method and the coupling coordination degree model from 2008 to 2022 in China. And the spatial evolution was then explored. Moreover, the key obstacle factors affecting the development of the water, energy, and carbon systems were summarized based on the obstacle degree model, and the coupling coordination tendency of the research region from 2026 to 2035 was further predicted. The major conclusions of this research are as follows:
(1) The overall trajectory of the integrated WEC development level in China from 2008 to 2022 was characterized by a fluctuating upward trend. The carbon system had the highest level of integrated development, with an average annual index of 0.36, while the energy system had the lowest level of coordination, with an average annual index of only 0.2.
(2) The coupling coordination level of the WEC nexus in China exhibited a trend of steady increase. Taking 2008 as the benchmark, the value of the coupling coordination degree grew from 0.47 to 0.53, with a growth rate of 10.6%, realizing the leap from near discoordination to minimal coordination. In the spatial dimension, the coupling and coordinated development had obvious geographical differences, with the southeast developing better level than the northwest. The overall development trend presented an inertial dependence.
(3) There was significant stability in the obstacles affecting the development of the water system, energy system, and carbon system from 2008 to 2022. The water system was primarily influenced by per capita water resources and groundwater proportion. The energy system was mainly affected by per capita energy production and energy self-sufficiency rate. The carbon system was mainly affected by total investment in environmental governance and per capita green space area.
(4) According to the grey prediction results, the coupling coordination degree of the WEC nexus in China will maintain a steadily increasing tendency from 2026 to 2035. However, to further increase the level of regional coupling, the implementation of water management, energy transition, and carbon reduction requires strengthening. Most notably, it is essential that more attention be paid to the synergies between the three elements.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JL: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. PP: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the MOE (Ministry of Education in China) Liberal arts and Social Sciences Foundation (20YJCZH095).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2025.1570713/full#supplementary-material
References
Adams, S., and Acheampong, A. O. (2019). Reducing carbon emissions: the role of renewable energy and democracy. J. Clean. Prod. 240, 118245. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118245
Akrami, E., Khalilarya, S., and Rocco, M. V. (2023). Techno-economic evaluation of a novel bio-energy system integrated with carbon capture and utilization technology in greenhouses. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 148, 104729. doi:10.1016/j.jtice.2023.104729
Bai, X., Jin, J., Zhou, R., Wu, C., Zhou, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2022). Coordination evaluation and obstacle factors recognition analysis of water resource spatial equilibrium system. Environ. Res. 210, 112913. doi:10.1016/j.envres.2022.112913
Balsalobre-Lorente, D., Shahbaz, M., Roubaud, D., and Farhani, S. (2018). How economic growth, renewable electricity and natural resources contribute to CO2 emissions? Energy Policy 113, 356–367. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2017.10.050
Battin, T. J., Lauerwald, R., Bernhardt, E. S., Bertuzzo, E., Gener, L. G., Hall, R. O., et al. (2023). River ecosystem metabolism and carbon biogeochemistry in a changing world. Nature 613, 449–459. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05500-8
Belaïd, F., and Massié, C. (2023). The viability of energy efficiency in facilitating Saudi Arabia's journey toward net-zero emissions. Energy Econ. 124, 106765. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106765
Bleischwitz, R., Spataru, C., VanDeveer, S. D., Obersteiner, M., van der Voet, E., Johnson, C., et al. (2018). Resource nexus perspectives towards the united Nations sustainable development goals. Nat. Sustain. 1, 737–743. doi:10.1038/s41893-018-0173-2
Cai, J., Yao, J., Zheng, J., Chen, L., Lu, T., Chen, H., et al. (2019). THU-065-Metformin reverses liver fibrosis via AMPK/PGC-1a mediated mitochondrial metabolic switch. J. Hepatology 70, e188. doi:10.1016/s0618-8278(19)30346-9
China Carbon Emission Accounting Database (2023). CEADs. Available online at: https://www.ceads.net.cn/ (Accessed December 20, 2024).
Czyżewski, B., Polcyn, J., and Brelik, A. (2022). Political orientations, economic policies, and environmental quality: multi-valued treatment effects analysis with spatial spillovers in country districts of Poland. Environ. Sci. and Policy 128, 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.envsci.2021.11.001
Davis, K. F., Rulli, M. C., Seveso, A., and D’Odorico, P. (2017). Increased food production and reduced water use through optimized crop distribution. Nat. Geosci. 10, 919–924. doi:10.1038/s41561-017-0004-5
Deng, J., and Liu, X. (2023). Evaluation of water-energy-food system coupling coordination degree in Jilin Province. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 54, 126–136. doi:10.13928/j.cnki.wrahe.2023.10.011
Desideri, U., Proietti, S., Sdringola, P., Cinti, G., and Curbis, F. (2012). MCFC-based CO2 capture system for small scale CHP plants. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 19295–19303. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.05.048
Donald, R., Boulaire, F., and Love, J. G. (2023). Contribution to net zero emissions of integrating hydrogen production in wastewater treatment plants. J. Environ. Manag. 344, 118485. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118485
François, H., Samacoïts, R., Bird, D. N., Köberl, J., Prettenthaler, F., and Morin, S. (2023). Climate change exacerbates snow-water-energy challenges for European ski tourism. Nat. Clim. Change 13, 935–942. doi:10.1038/s41558-023-01759-5
Gomez-Gardars, E. B., Rodriguez-Macias, A., Tena-Garcia, J. L., and Fuentes-Cortes, L. F. (2022). Assessment of the water-energy-carbon nexus in energy systems: a multi-objective approach. Appl. Energy 305, 117872. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.117872
Gui, Z., Qi, H., and Wang, S. (2024). Study on carbon emissions from an urban water system based on a life cycle assessment: a case study of a typical multi-water county in China’s river network plain. Sustainability 16, 1748. doi:10.3390/su16051748
Hamzacebi, C., and Es, H. A. (2014). Forecasting the annual electricity consumption of Turkey using an optimized grey model. Energy 70, 165–171. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2014.03.105
Hao, L., Yu, J., Wang, P., and Han, C. (2023). Analysis of the water-energy-food nexus system for sustainable development and its research framework. Prog. Geogr. 42, 173–184. doi:10.18306/dlkxjz.2023.01.014
Hao, S., and Sun, C. (2023). Spatial transfer characteristics of inter⁃provincial coal water footprint in China under water⁃energy nexus. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power 44, 16–25. doi:10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2023064
Jiang, L., Wu, Y., He, X., Fu, Q., Wang, Z., and Jiang, Q. (2022). Dynamic simulation and coupling coordination evaluation of water footprint sustainability system in Heilongjiang province, China: a combined system dynamics and coupled coordination degree model. J. Clean. Prod. 380, 135044. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135044
Jin, T. (2022). The evolutionary renewable energy and mitigation impact in OECD countries. Renew. Energy 189, 570–586. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2022.03.044
Jin, T., and Kim, J. (2019). A comparative study of energy and carbon efficiency for emerging countries using panel stochastic frontier analysis. Sci. Rep. 9, 6647. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-43178-7
Karamouz, M., Zare, M., and Ebrahimi, E. (2022). System dynamics based carbon footprint assessment of industrial water and energy use. Water Resour. Manag. 37, 2039–2062. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1770740/v1
Li, D., Zuo, Q., and Zhang, Z. (2022). A new assessment method of sustainable water resources utilization considering fairness-efficiency-security: a case study of 31 provinces and cities in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 81, 103839. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.103839
Li, G., Li, Y., Jia, X., Du, L., and Huang, D. (2016). Establishment and simulation study of system dynamic model on sustainable development of water-energy-food nexus in Beijing. Manag. Rev. 28, 11–26. doi:10.14120/j.cnki.cn11-5057/f.2016.10.002
Li, H., Zhao, Y., and Lin, J. (2019). A review of the energy–carbon–water nexus: concepts, research focuses, mechanisms, and methodologies. WIREs Energy Environ. 9, e358. doi:10.1002/wene.358
Li, Q., Cao, Y., Wang, f., Fan, S., and Chen, M. (2024). Study on the coupling coordination development and driving factors of water-energy-carbon system in the Haihe River Basin. J. North China Univ. Water Resour. Electr. Power 45, 20–31+40. doi:10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2024062
Li, Y., Wang, Y., and Liu, Z. (2023). Research on the coupling coordination degree of Chinese Cities' water-energy-food nexus system and influencing factors. J. Industrial Technol. Econ. 42, 97–105. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-910X.2023.06.011
Liang, M. S., Huang, G. H., Chen, J. P., and Li, Y. P. (2022). Energy-water-carbon nexus system planning: a case study of Yangtze River Delta urban agglomeration, China. Appl. Energy 308, 118144. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.118144
Liao, X., Huang, L., Xiong, S., and Ma, X. (2021). Optimizing future electric power sector considering water-carbon policies in the water-scarce North China Grid. Sci. Total Environ. 768, 144865. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144865
Lin, Z., Liu, X., Chen, Y., and fFu, B. (2021). Water-food-energy nexus: progress, challenges and prospect. Acta Geogr. Sin. 76, 1591–1604. doi:10.11821/dlxb202107002
Liu, Q., Li, R., Dereli, R. K., Flynn, D., and Casey, E. (2022). Water resource recovery facilities as potential energy generation units and their dynamic economic dispatch. Appl. Energy 318, 119199. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119199
Lv, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Z., Luo, S., Feng, X., and Chen, X. (2024). Spatio-temporal evolution pattern and obstacle factors of water-energy-food nexus coupling coordination in the Yangtze river economic belt. J. Clean. Prod. 444, 141229. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141229
Molinos-Senante, M., and Maziotis, A. (2021). Assessing the dynamic carbon performance of water companies: a parametric approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 5461–5472. doi:10.1007/s13762-021-03508-7
National Bureau of Statistics of China (2023). National Bureau of Statistics of China. Available online at: https://www.stats.gov.cn/ (Accessed December 15, 2024).
Oh, X. B., Rozali, N. E. M., Liew, P. Y., and Klemes, J. J. (2021). Design of integrated energy-water systems using Pinch Analysis: a nexus study of energy-water-carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 322, 129092. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129092
Peng, H., Xu, P., Shao, L., Pan, Y., He, G., Guo, M., et al. (2022). Water-energy nexus and co-benefits in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Resour. Sci. 44, 2330–2340. doi:10.18402/resci.2022.11.13
Pulighe, G., and Pirelli, T. (2023). Assessing the sustainability of bioenergy pathways through a land-water-energy nexus approach. Renew. and Sustain. Energy Rev. 184, 113539. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2023.113539
Qiu, G. Y., Zou, Z., Li, W., Li, L., and Yan, C. (2022). A quantitative study on the water-related energy use in the urban water system of Shenzhen. Sustain. Cities Soc. 80, 103786. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2022.103786
Rees, W. E. (1992). Ecological footprints and appropriated carrying capacity: what urban economics leaves out. Environ. Urbanization 4, 121–130. doi:10.1177/095624789200400212
Ren, X., and Ni, T. (2025). National shared responsibility mechanism for carbon reduction: addressing resource imbalances from interprovincial flows of virtual water-energy-carbon. Appl. Geogr. 177, 103576. doi:10.1016/j.apgeog.2025.103576
Sanglimsuwan, K. (2011). Carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth: an econometric analysis. Int. Res. J. Finance Econ. 67, 97–102.
Sarkodie, S. A. (2022). Winners and losers of energy sustainability—global assessment of the sustainable development goals. Sci. Total Environ. 831, 154945. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154945
Silva-Afonso, A., and Pimentel-Rodrigues, C. (2024). Water–energy–nutrients nexus of urban environments. Water 16, 904. doi:10.3390/w16060904
Singh, P., Kansal, A., and Carliell-Marquet, C. (2016). Energy and carbon footprints of sewage treatment methods. J. Environ. Manag. 165, 22–30. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.09.017
Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Mao, X., Yin, X., Liu, G., Zhao, Y., et al. (2021). Effects of different types of environmental taxes on energy–water nexus. J. Clean. Prod. 289, 125763. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.125763
Tian, P., Lu, H., Reinout, H., Li, D., Zhang, K., and Yang, Y. (2022). Water-energy-carbon nexus in China's intra and inter-regional trade. Sci. Total Environ. 806, 150666. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150666
Wang, H., Li, X., Zhang, L., Wang, L., and Jiang, X. (2023). Research progress and the prospect of a complex relationship between water-energy-carbon emission. South-to-North Water Transfers Water Sci. and Technol. 21, 13–21. doi:10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2023.0002
Wang, M., Bodirsky, B. L., Rijneveld, R., Beier, F., Bak, M. P., Batool, M., et al. (2024). A triple increase in global river basins with water scarcity due to future pollution. Nat. Commun. 15, 880. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-44947-3
Wang, X., and Li, T. (2022). Has the development of green finance reduced the energy consumption intensity? J. Jiangnan Univ. Humanit. and Soc. Sci. 21, 54–70. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6973.2022.06.005
Wang, Y., Wu, Y., and Jiang, L. (2021). Application of interval information comprehensive ranking model based on entropy weight in river water quality evaluation. J. Coast. Res. 105, 137–140. doi:10.2112/JCR-SI105-029.1
Werner, D., and Lazaro, L. L. B. (2023). The policy dimension of energy transition: the Brazilian case in promoting renewable energies (2000–2022). Energy Policy 175, 113480. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2023.113480
Yang, X., Duan, C., Chen, B., and Wang, S. (2024). Does stricter sewage treatment targets policy exacerbate the contradiction between effluent water quality improvement and carbon emissions mitigation? An evidence from China. Glob. Environ. Change 87, 102881. doi:10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2024.102881
Yang, X., and Ran, G. (2024). Factors influencing the coupled and coordinated development of cities in the Yangtze River Economic Belt: a focus on carbon reduction, pollution control, greening, and growth. J. Environ. Manag. 370, 122499. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2024.122499
Yong, W., Wang, J., Xue, L., and Bie, Z. (2023). Water-energy collaborative optimization for regional energy internet: review and prospect. Automation Electr. Power Syst. 47, 185–199. doi:10.7500/AEPS20220726003
Yu, J., Zhao, R., Xiao, L., Zhang, L., Wang, S., Chuai, X., et al. (2020). Carbon emissions of urban wastewater treatment system based on the “water-energy-carbon” nexus. Resour. Sci. 42, 1052–1062. doi:10.18402/resci.2020.06.04
Yuan, L., Cheng, J., He, W., and Xu, S. (2024). Evaluation of ‘water-energy-carbon’ system adaptability and characterization of spatial correlation in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. China Population, Resources Environ. 34, 187–199. doi:10.12062/cpre.20240510
Zawartka, P., Burchart-Korol, D., and Blaut, A. (2020). Model of carbon footprint assessment for the life cycle of the system of wastewater collection, transport and treatment. Sci. Rep. 10, 5799. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-62798-y
Zhang, G., Wang, R., and Liu, M. (2023). Empirical research on imputation method for sparse air quality functional data. J. Hebei Univ. Environ. Eng. doi:10.13358/j.issn.2096-9309.2023.0614.01
Zhang, K., Tian, M., and Zhang, L. (2022). Carbon peaking and carbon neutrality goals and reflections on China′s energy transition Part I. Sino-Global Energy 27, 1–6.
Zhang, Y., Fu, Z., Xie, Y., Li, Z., Liu, Y., Zhang, B., et al. (2021). Dynamic metabolism network simulation for energy-water nexus analysis: a case study of Liaoning Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 779, 146440. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146440
Zhao, R., Ji, Y., Feng, W., Xie, Z., Xiao, L., and Li, H. (2024). Research on water-energy-carbon nexus of land use: theoretical framework and key issues. China Land Sci. 38, 97–108. doi:10.11994/zgtdkx.20240722.084418
Zhao, S., Liu, Y., Liang, S., Wang, C., Smith, K., Jia, N., et al. (2020). Effects of urban forms on energy consumption of water supply in China. J. Clean. Prod. 253, 119960. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.119960
Zhao, X., Shi, S., Mao, Y., and Wu, Z. (2024). Coordinated “water-energy-carbon” dispatching in urban wastewater treatment plants. Power Syst. Technol. 48, 1918–1928. doi:10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2023.1160
Keywords: WEC nexus, coupling coordination degree, obstacle degree model, China, implications
Citation: Liu J and Pan P (2025) Water-energy-carbon coupling relationships and barrier analysis: an empirical study based on China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1570713. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1570713
Received: 11 February 2025; Accepted: 04 June 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Marcelo Cohen, Federal University of Pará, BrazilReviewed by:
Medani Bhandari, Akamai University, United StatesVladyslav Zakharovskyi, Massey University, New Zealand
Copyright © 2025 Liu and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinhua Liu, bGl1amluaHVhMjAxOEAxMjYuY29t
 Jinhua Liu*
Jinhua Liu* Pei Pan
Pei Pan