- 1Geological Exploration Technology Institute of Jiangsu Province, Nanjing, China
- 2Jiangsu Province Engineering Research Center of Airborne Detecting and Intelligent Perceptive Technology, Nanjing, China
- 3School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Hohai University, Nanjing, China
The Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit, situated in the Sulu ultra-high pressure metamorphic belt, has received limited research attention. In this study, geochemical characteristics of this deposit were investigated to determine original rocks, sedimentary environments, carbon sources, and metallogenic processes. SiO2 (56.94%–72.84%) and Al2O3 (9.7%–13.29%) are enriched in graphite quartzite and granulite while CaO (21.89%–42.56%) and MgO (5.56%–18.4%) are enriched in (graphite-bearing) marbles. Ba and Nb are depleted to varying degrees in all rocks. In graphite quartzite and granulite, the Rb/Sr ratios are higher than the Sr/Ba ratios. All rocks are characterized by LREE enrichment and HREE depletion with negative Eu and Ce anomalies. The δ13C value of graphite in graphite quartzite (−31.2‰ to −30.2‰) is more negative than in graphite-bearing marble (−24.4‰ to −23.2‰) while the δ13C values of carbonates in (graphite-bearing) marbles approximate 0‰. The integrated geochemical data indicate initial deposition of this deposit occurred in coastal-neritic environments under oxygen-deficient conditions, with original rocks comprising argillaceous-sandy clastic rocks and carbonates. Carbon isotopic signatures suggest quartzite graphite originated solely from organic matter, whereas marble graphite resulted from a mixture of organic and minor carbonate-derived carbon. A three-stage metallogenic model for the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit was proposed: (1) late Proterozoic organic deposition, (2) Triassic metamorphic mineralization, (3) post-200 Ma tectonic activation. These findings enhance understanding of graphite genesis in the Sulu orogen and provides guidance for regional exploration strategies.
1 Introduction
Graphite’s exceptional properties, including chemical stability, high thermal resistance, and electrical conductivity, have established its critical role across nuclear, mechanical, and metallurgical industries (Singh et al., 2011; Luque et al., 2014). The in-depth application of graphite in emerging industries such as solar power, lithium-ion batteries, and electronic devices (smartphones, electrical cars) has greatly enhanced its economic value and strategic position. In recent years, many countries, including China and the United States, have classified graphite as a critical mineral (Luque et al., 2014). Global demand for well-crystallized graphite is projected to grow at an annual rate of nearly 4% for both military and civilian applications (Lazzeri and Barreiro, 2014). In this context, it is necessary to study the formation of graphite deposits for exploration to balance the supply and demand of graphite resources.
Geological studies document graphite mineralization in diverse rock types including marble, paragneiss, iron formations, quartzite, pegmatite, and syenite (Simandl, 1992). Three primary genetic mechanisms are currently recognized: (1) metamorphism of organic-rich sediments, (2) metasedimentary decarbonation, and (3) precipitation from carbon-bearing magmatic fluids (Lowenstern, 2001; Luque et al., 2014; Buseck and Beyssac, 2014; Galvez et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2024). As well as in other countries, graphite deposits are widely distributed with three types of graphite in China: (1) valuable but rare hydrothermal lump graphite, (2) metamorphic flake graphite (dominant in production), and (3) coal-derived amorphous graphite (Sanyal et al., 2009; Luque et al., 2014; Cui et al., 2017; Touret et al., 2019). Flake graphite exhibits crystallinity positively correlated with metamorphic grade (Wopenka and Pasteris, 1993; Beyssac et al., 2002; Cui et al., 2017), commanding a four-fold premium over amorphous varieties due to its wider applicability (Luque et al., 2014; Cui et al., 2017). Recent investigations combining petrographic analysis, geochemistry, and zircon U-Pb geochronology have revealed that most Chinese crystalline graphite deposits occur in Phanerozoic orogens bordering the North China Craton and the Cathaysia Block (Zhong et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023a; Li et al., 2023). Notable examples include the Jixi (Heilongjiang), Zhahanmuhulu (Inner Mongolia), and Wuligou (Liaoning) deposits (Li et al., 2015; Cui et al., 2017; Zhu et al., 2021). These deposits typically form through intermediate-to high-grade metamorphism of carbonaceous sedimentary sequences (Condie et al., 1992; Zhong et al., 2019), with graphite occurring in gneissic, schistose, and diopside-bearing lithologies. Stable carbon isotope signatures consistently point to biological carbon sources (Zhao et al., 2002; Eguchi et al., 2020; Parnell et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022). However, significant knowledge gaps remain regarding deposit formation along the boundary between the North China-Yangtze Blocks.
The Sulu Orogen Belt, a Triassic (ca. 240–220 Ma) continental collision belt between the North China and Yangtze Blocks, contains the Earth’s largest preserved ultra-high pressure (UHP) metamorphic terrane (Wallis et al., 1999; Zheng et al., 2003). Graphite mineralization in this belt was considered to primarily develop through UHP metamorphic recrystallization of carbonaceous precursors in metasedimentary protoliths during subduction and retrograde amphibolite-facies overprinting (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Although direct isotopic constraints are lacking, tectonic correlations suggest mineralization timing corresponds with orogenic evolution (Yu et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2023b). Orogenic graphite deposits seem to exhibit unique metallogenic characteristics in age, carbon sources, and mineralization processes compared to Chinese counterparts (Cui et al., 2017; Zhong et al., 2019; Yan et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). As a whole, systematic studies of crystalline graphite deposits in this belt remain limited despite their tectonic significance. Jiangsu Province’s exploration initiatives since 2016 have identified new graphite occurrences in northern Jiangsu which is located in the Sulu Orogen Belt, including the Shuanghu and Chenggang deposits in the Donghai Group’s marble-amphibolite sequences (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023b; Wang et al., 2023). Regarding the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit in northern Jiangsu, Liu et al. (2020) described the deposit characteristics and ore types and preliminarily explored the prospecting potential. Zhang et al. (2021), Zhang et al. (2023b) further elaborated on the induced polarization anomalies of this deposit and established prospecting prediction models. However, critical gaps persist in sedimentary environment, carbon source, and mineralization process. While preliminary studies have characterized these deposits’ geological features and geophysical signatures (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023b), critical uncertainties persist regarding sedimentary environments, carbon sources, and mineralization processes of the Shuanghu deposit.
In this study, petrographic and geochemical characteristics of the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit were investigated to determine the nature and sedimentary environments of source rocks, and trace the carbon source. This study is expected to refine metallogenic models for crystalline graphite deposits in collisional orogens and guide regional exploration strategies.
2 Geological setting
2.1 Regional geology
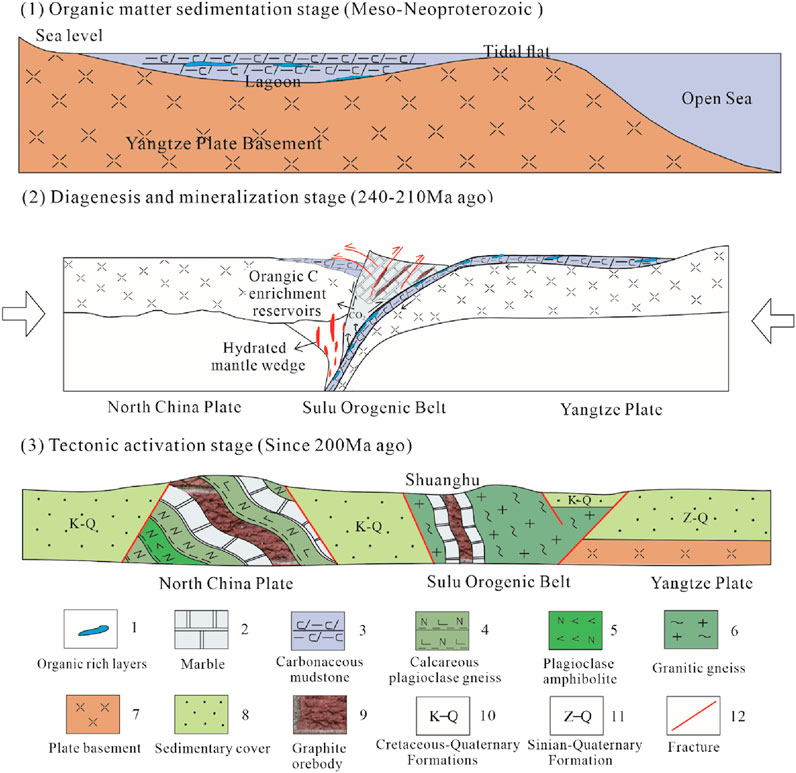
The Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit is geographically located in western Donghai County, the northern part of Jiangsu Province, China, and tectonically sits within the Sulu Orogenic Belt east of the Tanlu Fault Zone (Figure 1a). This tectonic belt originated from the Triassic continental collision between the Yangtze and North China plates, representing a typical ultra-high pressure (UHP) metamorphic belt. Researchers have recognized three distinct metamorphic episodes (Zheng et al., 2003; Liu and Liou, 2011): (1) prograde metamorphism of quartz-eclogite facies during deep subduction (246–244 Ma; 570°C–690°C; 1.7–2.1 GPa), (2) UHP peak metamorphism (233–225 Ma; 750°C–850°C; 3.0–4.0 GPa), and (3) retrograde metamorphism of amphibolite facies during tectonic exhumation (215–208 Ma; 550°C–650°C; 0.7–1.1 GPa). The belt primarily comprises granitic gneiss and metamorphic supracrustal sequences (Figure 1b), hosting multiple crystalline graphite occurrences within marble-amphibolite units of the Donghai Group (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). Geochronological studies have been conducted on the ultra-high pressure metamorphic rocks in the Sulu Orogenic Belt (Zheng et al., 2003; Liu and Liou, 2011; Yu et al., 2011). The U-Pb ages of inherited zircons in orthogneiss, eclogite, quartzite, paragneiss, and amphibolite were reported to be between 850 and 680 Ma with a peak value of around 750 Ma, indicating that the formation ages of their original rocks were the Neoproterozoic and were associated with the Rodinia Supercontinent Breakup Event occurring on the northern margin of the Yangtze Plate (Xu et al., 2006; Qiang et al., 2018; Yuan et al., 2024).
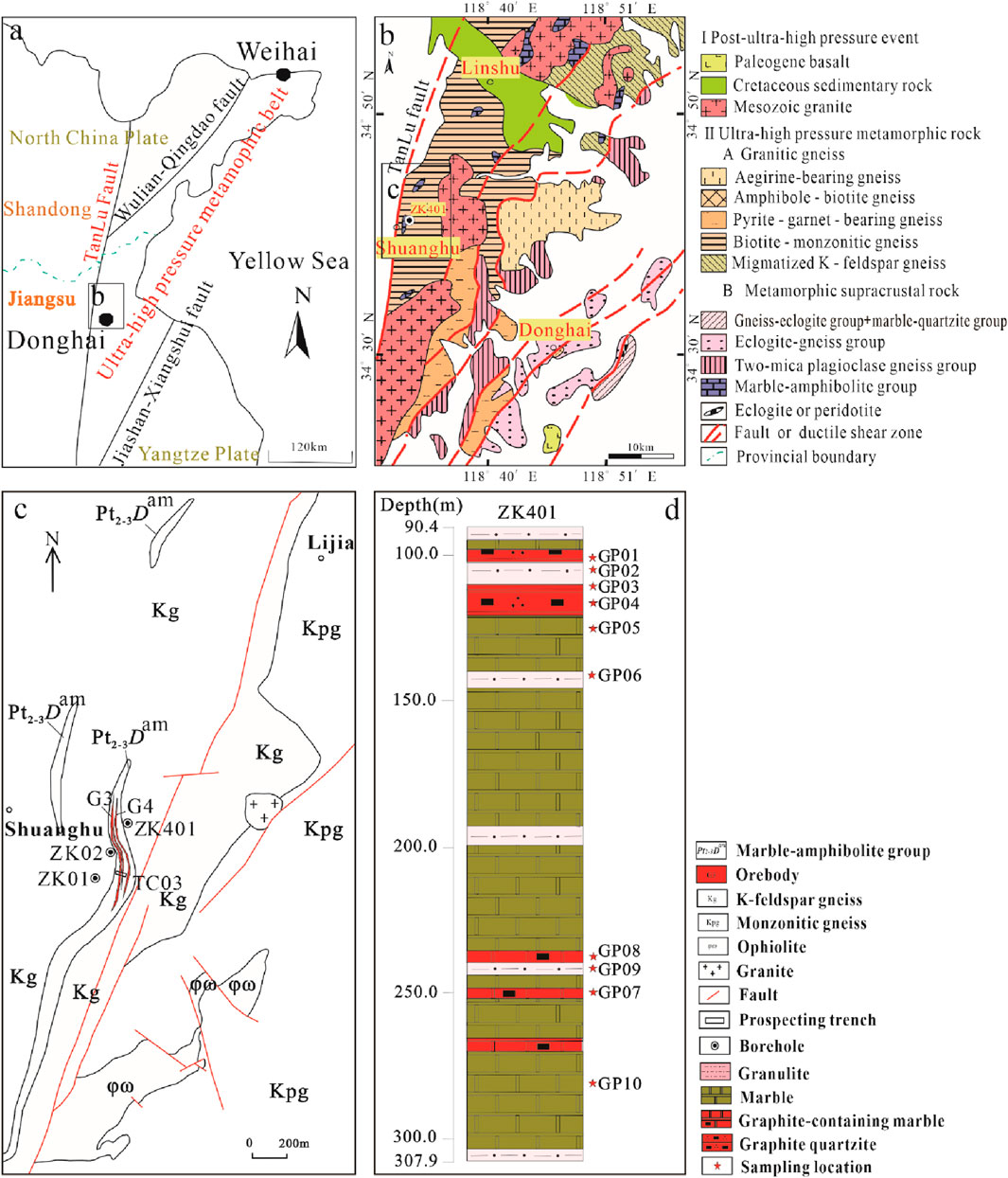
Figure 1. Geological map with four sections. (a) Regional map showing plates and faults. (b) Detailed geological features including various rock types, faults, and boundaries. (c) Local geological section highlighting faults and rock units. (d) Stratigraphic column for borehole ZK401.
Metamorphic supracrustal rocks in northern Jiangsu are little concerned until now. Since this area is located in the Sulu Orogenic Belt, its metamorphic temperature could also fluctuate within the range of 550°C–850°C. In early regional geological surveys, their ages were determined as Neoproterozoic to Paleoproterozoic by comparison with neighboring strata (Pan et al., 2002). In the subsequent survey, the rock suite was divided into five formations (Maobei Formation, Yanmachang Formation, Wuqiangshan Formation, Hushan formation and Motianling Formation) and its age was adjusted to the Meso-Neoproterozoic (Zhang et al., 2002). Liu et al. (2006) and Liu and Liou (2011) obtained 14 inherited detrital zircons with ages ranging from 2,696 to 1,386 Ma in the marble-amphibolite formation of the Sulu Orogenic Belt (one of the mentioned-above five formations). They considered that the northern margin of the Yangtze Plate experienced multiple tectonic thermal events from the late Archaean to the Mesoproterozoic. Yu et al. (2011) obtained 11 detrital zircons with ages ranging from 2,210 to 1,182 Ma with a peak age around 1,300 Ma in the marble of this formation within the southern Sulu Orogenic Belt. Although direct dating of the Shuanghu graphite deposit remains unstudied, this deposit was considered to be closely related to the marble-amphibolite formation through stratigraphic comparison (Pan et al., 2002; Zhang et al., 2002).
2.2 Ore geology
The Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit exhibits distinct lithological zonation, with K-feldspar gneiss dominating the western sector and monzonitic gneiss prevailing in the eastern portion of the mining area (Figure 1c). The ore-bearing sequence, represented by the Donghai Group’s marble-amphibolite formation, occurs as stratabound layers and lenses within K-feldspar gneiss. This metasedimentary package, reaching several hundred meters in total thickness, comprises an intercalated sequence of diopside marble, monzonitic granulite, amphibolite, graphite-bearing marble, and graphite quartzite. Drill core ZK401 reveals five mineralized horizons within this rhythmically interbedded marble-granulite sequence (Figure 1d). The area features minimal Quaternary cover (<3 m), predominantly consisting of alluvial and eluvial silty clays.
The gently S-shaped graphite orebody displays thickness variations controlled by post-depositional ductile shearing and crystal-plastic flow mechanisms (Figure 1c). Structural controls are manifested through two fault systems: NNE-NE trending secondary faults of the Tanlu Fault system, and crosscutting NW-oriented late-stage faults. Igneous intrusions in the southeastern sector consist primarily of Neoproterozoic basic-ultrabasic complexes dominated by serpentinite. Limited Yanshanian intrusives occur as NE/NEE-trending dikes within metamorphic rocks of the Donghai Group. Mesozoic magmatism is sparsely developed, represented by monzonitic granite with subordinate diorite-porphyry and lamprophyre dikes.
Five stratabound graphite orebodies occur as layered to lensoidal units within the marble-amphibolite sequence, demonstrating strong lithological control (Figure 1d). Principal orebodies G3 and G4 exhibit N-S orientations, extending 400–890 m along strike with average thicknesses of 2–5 m. Graphite quartzite and graphite-bearing marble constitute the dominant ore types, containing 5%–15% and 2%–8% graphite, respectively. Graphite morphology shows lithology-dependent variations: submillimeter (0.005–0.05 mm) aligned flakes in quartzite versus randomly oriented 0.05–0.3 mm flakes in marble. Gangue minerals comprise quartz, calcite, dolomite, and diopside. The host rocks transition from marble (principal) to granulite and K-feldspar gneiss, with corresponding alteration assemblages: (1) kaolinization-serpentinization-pyritization in marble contact zones and (2) pyrite-actinolite metasomatism at gneiss/granulite contacts.
3 Samples and methods
3.1 Sample collection
A total of 10 samples were collected from borehole ZK401 for elemental analyses (Figures 1b,d), including 3 graphite quartzite samples (GP01, GP03, GP04), 2 graphite-bearing marble samples (GP07, GP08), 2 marble samples (GP05, GP10), and 3 granulite samples (GP02, GP06, GP09). Among these samples, 3 graphite quartzite samples were selected for graphite carbon isotope analysis. In addition, from TC03 (prospecting trench) and ZK02 (borehole), samples were also collected for graphite carbon isotope analysis. Specifically, 3 graphite quartzite samples (T301 at a depth of 30.5–31.5 m, T302 at a depth of 31.5–32.5 m, T303 at a depth of 32.5–33.5 m) were collected from TC03, and four graphite-bearing marble samples (Z201 at a depth of 32.68–33.68 m, Z202 at a depth of 33.68–34.68 m, Z203 at a depth of 34.68–35.68 m, Z205 at a depth of 36.92–37.61 m) were collected from ZK02 (Figure 1c). For carbonate carbon isotope analysis, four graphite-bearing marble samples (Z101 at a depth of 71.95–72.95 m, Z102 at a depth of 72.95–73.95 m, Z103 at a depth of 73.95–74.83 m, Z104 at a depth of 74.83–75.83 m) were collected from ZK01 (borehole), and five graphite-bearing marble samples (Z204 at a depth of 35.68–36.92 m, Z201, Z202, Z203, and ZK205) were collected from ZK02 (Figure 1c).
3.2 Analytical methods
Before being used for elemental and isotopic measurements, the samples were ground to 200 mesh in an agate mortar. The measurements of elemental concentrations were completed at Shenyang Geotechnical Engineering Technology Testing and Development Co., Ltd. The concentrations of major elements were measured using an X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (ARL AdvantXP+/413) with an uncertainty of less than 1%. For the gravimetric determination of the loss on ignition, 0.2 g of the sample was weighed and burned at a high temperature of 1,000°Cfor 3 h. FeO concentration was determined using the titration method with the potassium dichromate standard solution after the sample was dissolved in hydrofluoric acid and sulfuric acid, and the analytical error was less than 5%. Regarding the concentrations of rare earth elements and other trace elements, after 0.1 g of the sample was dissolved with nitric and hydrofluoric acids through two high-pressure digestion processes, they were measured using an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICPS - 7510) with an uncertainty of better than 10%.
The carbon isotope analysis was performed at Beijing Zirconia Navigation Technology Co., Ltd. using the 253plus Flash EA analyzer. For the carbon isotope measurement of carbonates, the powder sample was reacted with 100% phosphoric acid and the generated CO2 gas was introduced to the mass spectrometer. For the carbon isotope measurement of graphite, after the powder sample was soaked in a 1 mol/L HCl solution for 24 h to remove carbonates, it was wrapped with a tin capsule and sent to an oxidation furnace at 1,020°C for incineration, and the generated CO2 gas was introduced into the mass spectrometer. Carbon isotopic values were expressed per mil (‰) relative to the V-PDB: δ13C = [(13C/12Csample)/(13C/12Cstandard)-1] × 1000. Two international standard materials (B2151 and B2153) were used to monitor the analytical quality and the measurement accuracy was less than 0.1‰.
The selected samples were made into thin sections at the Laboratory of Hebei Provincial Institute of Regional Geological and Mineral Resources Survey and petrographic observations were made with a polarizing and reflecting microscope (OLYMPUS BX51).
3.3 Petrographic descriptions
Three representative samples (GP02, GP04 and GP07) were selected for petrographic analysis through field observation and laboratory microscopy.
Graphite quartzite displays a black coloration with mineralogical composition dominated by quartz (70%–80%), followed by sericite (10%–15%) and graphite (5%–15%), accompanied by minor biotite, diopside, and garnet (Figure 2a). It exhibits characteristic micro-flake crystalloblastic textures superimposed by mylonitic and gneissic fabrics. The ore rock shows pronounced ductile deformation features, manifesting as (1) heteromorphic quartz aggregates in granuloblastic arrangements, and (2) sericitic matrix with preferred orientation forming mylonitic foliation, (3) The ores exhibited ductile deformation features. Elliptical graphite inclusions either interstitially distributed among quartz grains or encapsulated within them (Figure 2b), occasionally coexisting with diopside-garnet assemblages (Figure 2c).
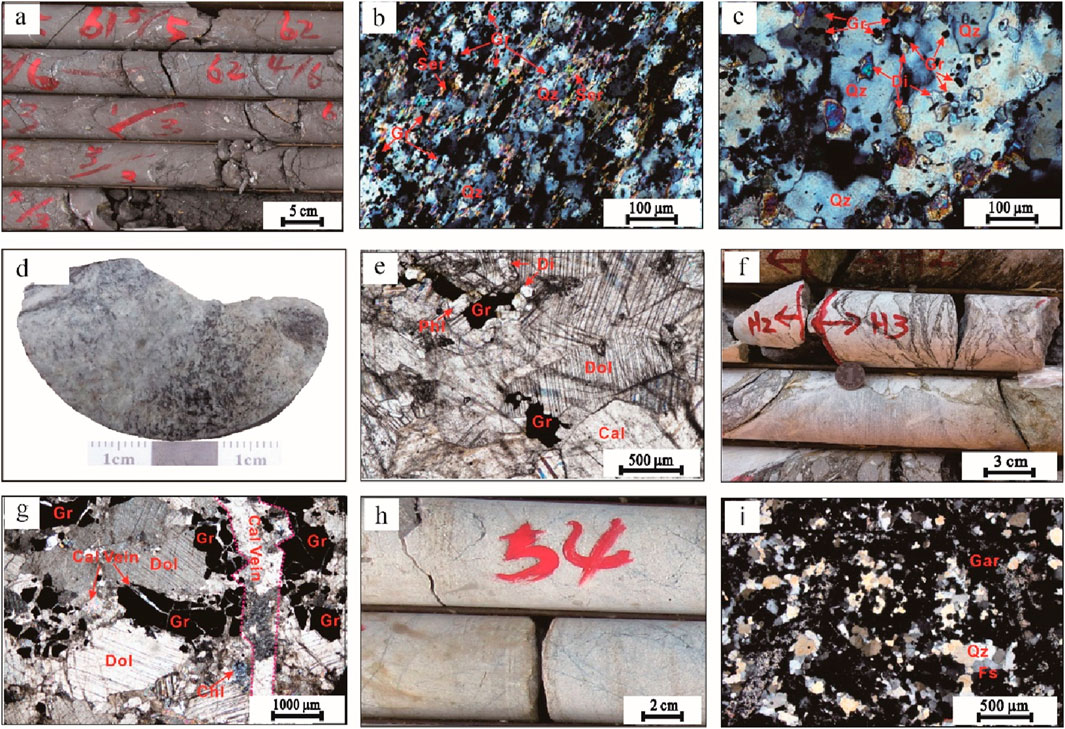

Figure 2. Petrographic features of rocks in the Shuanghu graphite deposit. (a) Graphite quartzite core; (b) Graphite is distributed between or encapsulated within quartz particles in graphite quartzite where sericite is directionally distributed and enriched to form a mylonitic foliation; (c) Graphite is distributed in a mosaic pattern with diopside and quartz or wrapped within them in graphite quartzite; (d) Graphite-bearing marble; (e) Graphite is embedded with minerals such as dolomite, calcite, and phlogopite in graphite-bearing marble; (f) Graphite is enriched along the cracks in graphite-bearing marble; (g) Large-sized graphite is fragmented and penetrated by late calcite veins in graphite-bearing marble; (h) Granulite rock core; (i) Microscopic feature of granulite rocks; Gr, graphite; Dol, dolomite; Di, diopside; Phl, phlogopite; Cal, calcite; Qz, quartz; Chl, chlorite; Ser, sericite; Cal Vein, Calcite vein body; Gar, garnet; Fs, feldspar.
Graphite-bearing marble, which appears grayish-white or gray, comprises dolomite (50%–60%), calcite (15%–25%), diopside (5%–10%), phlogopite (3%–8%), graphite (2%–6%) and a small amount of chlorite, with a granular crystalloblastic or blocky texture (Figure 2d). Dolomite mineral is distributed in the form of irregular granular inlay, while calcite fills the gaps between dolomite particles in an irregular granular pattern and is locally interspersed in a mesh pattern (Figure 2g). Two distinct graphite occurrences can be observed: (1) disseminated bladed/elliptical crystals enclosed in carbonate matrix, showing sutured boundaries with host minerals (Figure 2e), and (2) fracture-filling assemblages coexisting with phlogopite-chlorite-calcite veinlets (Figures 2f,g).
The gray to red dioritic granulite exhibits fine-grained granoblastic textures with local cataclastic overprints and transitional gneissic-xenoblastic structures (Figure 2h). The mineral composition includes K-feldspar (30%–40%), plagioclase (30%–40%), quartz (20%–30%), and accessory minerals (biotite, amphibole and pyrite, each <5%) (Figure 2i).
4 Results
4.1 Major elements
Major element compositions of ores and host rocks in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit exhibit distinct lithological characteristics (Table 1; Figure 3). Graphite quartzite shows chemical homogeneity across stratigraphic layers, characterized by high concentrations of SiO2 (56.94%–68.54%) and Al2O3 (9.7%–12.35%) and low concentrations of CaO, Na2O, TiO2, P2O5, and MnO (Table 1). The loss on ignition is high with the range from 9.16% to 21.04%, reflecting the effect of graphite (Table 1). Compared with those of the Upper Continental Crust (UCC), TiO2, P2O5 and K2O are overall enriched in graphite quartzite with similar SiO2 concentrations but other major elements are depleted (Figure 3). This rock type shows the aluminum saturation index (A/CNK) ranging between 1.53 and 2.65 with an average of 2.05, the aluminum index (A/NK) between 3.50 and 4.40 with an average of 3.61, the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio between 5.26 and 7.07 with an average of 5.91, and the K2O/Na2O ratio between 34 and 43 with an average of 37.67 (Table 1). Granulite samples collected from three different layers show similar geochemical compositions with high concentrations of SiO2 (63.08%–72.84%) and Al2O3 (10.65%–13.29%) and low concentrations of TiO2, P2O5 and MnO (Table 1). The loss on ignition of granulite varies from 1.52% to 6.03%, significantly lower than that of graphite quartzite (Table 1). Compared with UCC values, CaO, MgO and K2O are overall enriched with the similar SiO2 concentration but other major elements are depleted in granulite (Figure 3). For this rock type, the ratios of A/CNK, A/NK, SiO2/Al2O3 and K2O/Na2O are significantly lower than those of graphite quartzite (Table 1). As well as marble samples, graphite-bearing marble samples from different layers are characterized by high concentrations of CaO and MgO and low concentrations of Al2O3, Na2O, K2O and Fe2O3 with the high loss on ignition (Table 1). Compared with UCC values, CaO and MgO are enriched but other major elements are depleted in the two rock types (Figure 3). For the two rock types, the A/CNK ratio is lower than 0.08, the A/NK ratio varies from 1.83 to 4.12 with an average of 2.74, the SiO2/Al2O3 ratio is basically more than 13 except that (3.87) of GP10, and the K2O/Na2O ratio is about1 except that (6.00) of GP10 (Table 1). These geochemical characteristics of marble and graphite-bearing marble reflect the nature of carbonate rocks significantly differing from those of other rock types.
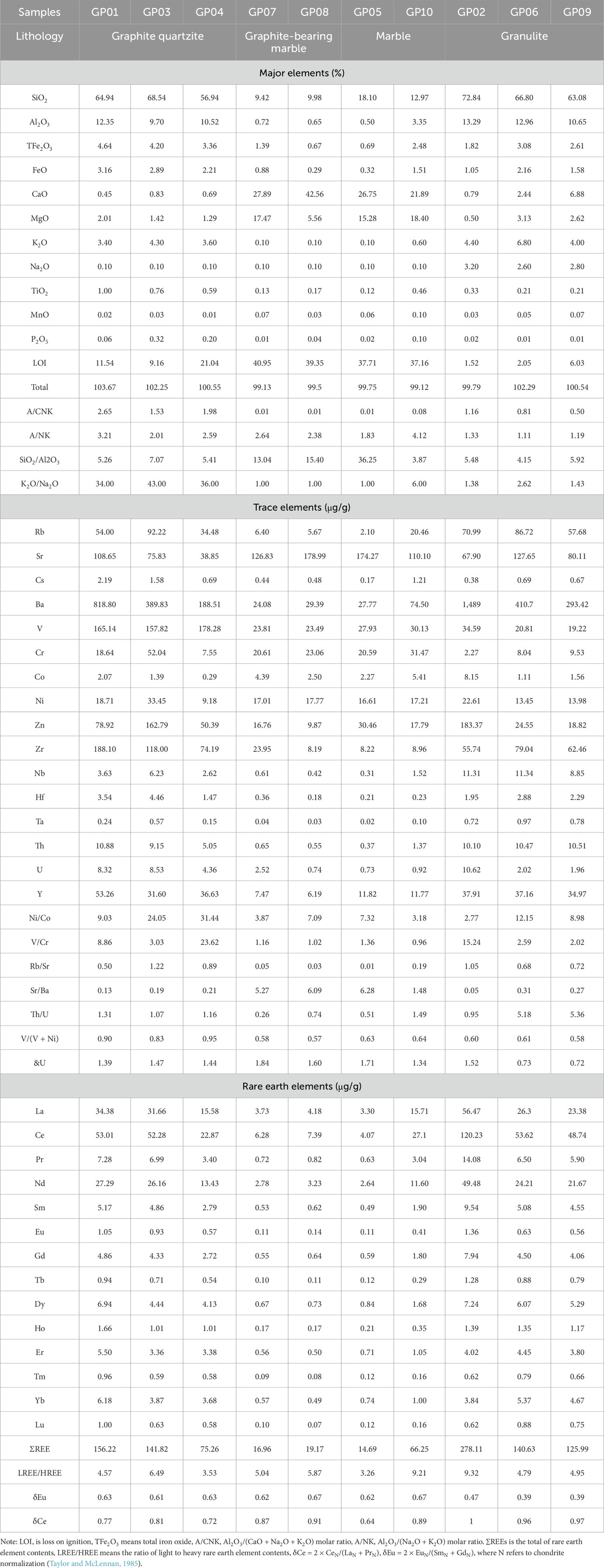
Table 1. Geochemical characteristics of mineral ores and surrounding rocks in the Shuanghu graphite deposit.
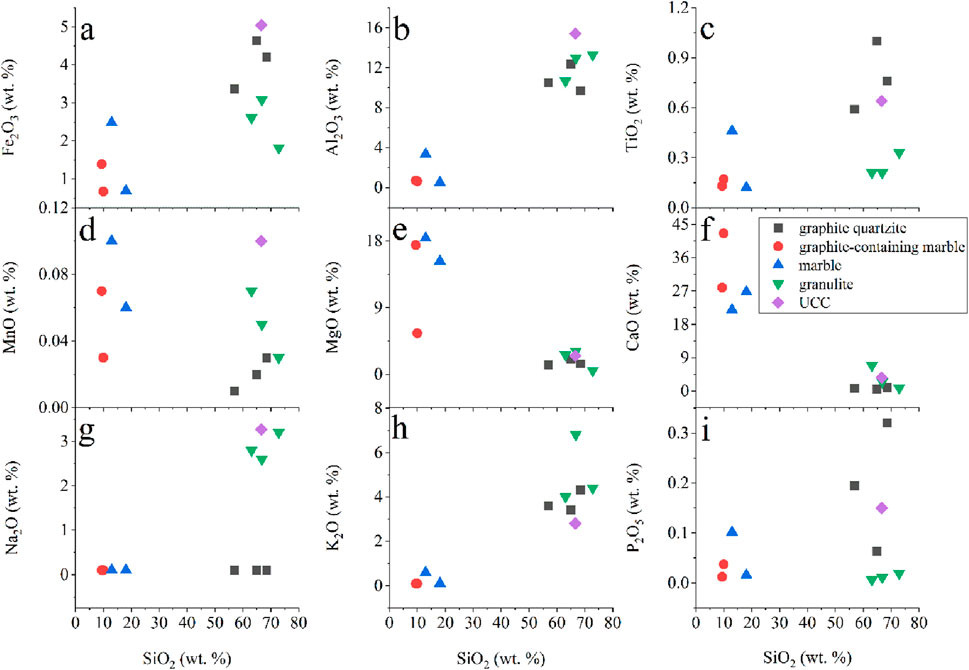
Figure 3. Nine scatter plots labeled (a–i) which compare the weight percentages of different oxides against SiO2. In each plot, different rock types and UCC are indicated by distinct shapes and colors. The UCC data are from Rudnick and Gao (2003).
4.2 Trace elements
Trace element distributions in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit reveal distinct geochemical patterns (Table 1). Among large-ion lithophile elements (LILEs), Cs exhibits a notably low concentration (<2.2 μg/g), contrasting with other LILEs that mostly exceed 5 μg/g. Among transitional metal elements, Co shows a lower concentration (<8.5 μg/g) while the concentrations of other elements are mostly >8.5 μg/g. The concentration of Ta is as low as <1 μg/g while those of Zr and Y are high among high field strength elements (HFSEs). In addition, the Sr concentration are higher in marble and graphite-bearing marble than in graphite quartzite and granulite, which is inverse to other trace elements (Table 1). For the same rock type, the concentrations of trace elements also differ to some extent between different layers (Table 1). For example, the concentrations of trace elements except Sr are higher in the lower layer (GP10) than in upper layer (GP05) for graphite-bearing marble. Nevertheless, the concentrations of most trace elements do not show consistent changes from one to another layer for other rock types. The primitive mantle-normalized patterns of trace elements showed high-low-high trends (Figure 4a). In detail, compared to the primitive mantle, all large-ion lithophile elements are significantly enriched for all types of rocks, transitional metal elements are depleted, and high-field strength elements are also enriched except that some high-field strength elements such as Zr, Nb, Hf and Ta are slightly depleted in marble and graphite-bearing marble. Overall, geochemical characteristics of trace elements in rocks of the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit show the nature of mature continental crust (Taylor and McLennan, 1985).
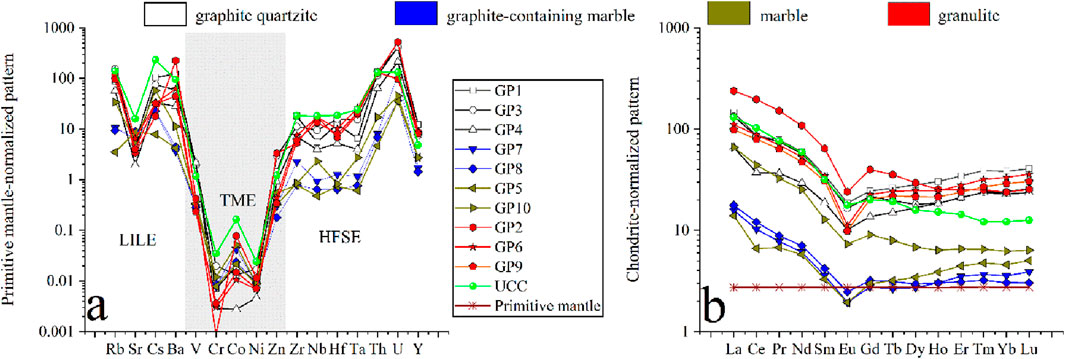
Figure 4. Spider diagrams showing primitive mantle-normalized patterns of trace elements (a) and chondrite-normalized patterns of rare earth elements (b). The data of the primitive mantle were from McDonough and Sun (1995). The rare earth element data of chondrite are from Taylor and McLennan (1985). LILE means large-ion lithophile element, TME indicates transitional metal element, HFSE refers to high-field strength element.
4.3 Rare earth elements
The Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit exhibits total rare earth element (REEs) concentrations ranging from 14.69 to 278.11 μg/g (Table 1), with lower concentrations (<70 μg/g) observed in graphite-bearing marbles and marbles compared to other lithologies. The concentrations of light rare earth elements (LREEs) are significantly higher than those of heavy rare earth elements (HREEs) for all rocks with the LREE/HREE values of 3.26–9.32 (Table 1). The chondrite-normalized REE patterns are characterized by steep LREE enrichment and flat HREE depletion with significantly negative Eu anomalies (δEu) and weakly negative Ce anomalies (δCe) for all rock samples except GP10 (Figure 4b). Notably, sample GP10 exhibits a distinct right-leaning curve, comparable to the UCC standard (Figure 4b). In addition, key parameters of REEs such as δEu and δCe vary with rock types to some degree but change little with depth for the same rock type (Table 1; Figure 4b). For example, the δEu value varies from 0.61 to 0.63 in graphite quartzite, being close to those of marble and graphite-bearing marble, while granulite shows a stronger negative Eu anomaly from 0.39 to 0.47 (Table 1; Figure 4b). The δCe value varies from 0.72 to 0.81 in graphite quartzite, and from 0.64 to 0.91 in marble and graphite-bearing marble, while granulite shows a weaker Ce anomaly from 0.96 to 1 (Table 1; Figure 4b).
4.4 Carbon isotopes
As shown in Figure 5, the δ13C value varies from −31.2‰ to −23.2‰ with an average of −28‰ for graphite mineral but has a narrow range of −0.8‰ to 0.2‰ with an average of −0.14‰ for carbonate minerals in the Shuanghu crystalline deposit. For graphite quartzite and graphite-bearing marble, the δ13C value of graphite falls in the biogenic field but is different (Yan et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2021) (Figure 5). The δ13C value of carbonate mineral in graphite-bearing marble falls in the field of marine carbonate (Yan et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2021). In addition, for each borehole, the carbon isotope value of graphite or carbonate is not significantly different in different layers (Figure 5).
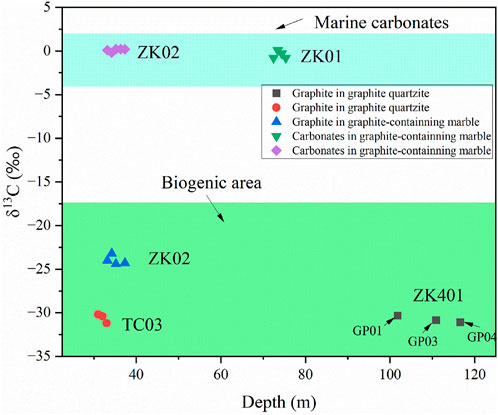
Figure 5. The carbon isotope compositions of graphite and carbonate in the rocks of the Shuanghu graphite deposit.
5 Discussion
5.1 The nature of original rock
Determining the original rocks of metamorphic rocks in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit proves challenging through traditional approaches like field observations and experimental analysis alone. However, this task can be achieved by integrating geochemical analysis with geological occurrence and petrographic features (Roser and Korsch, 1986; Jones and Manning, 1994; Chen and Jahn, 2004; Plank and Langmuir, 1998; Castillo et al., 1999; Sun et al., 2021).
Parametamorphites typically show K enrichment over Na (K/Na >1), a chemical signature preserved during low-grade metamorphic processes (Han and Ma, 2003; Xia, 2018). Diagnostic geochemical indicators include: (1) siliceous protoliths (SiO2 >80%), carbonate precursors (CaO >15% and CaO + MgO >30%), and alkaline/acidic igneous origins (Na2O + K2O >10%) (Wang et al., 1987; Han and Ma, 2003). The high SiO2 concentrations (56.94%–72.84%) and the K/Na ratio of >1 in granulite and graphite quartzite of the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit indicates that the original rocks were of parametamorphite type (Table 1; Figure 3). For marbles (including graphite - containing marble), the CaO concentrations range between 21.89% and 42.56%, and the MgO plus CaO concentrations vary from 40.29% to 48.12% with significant LOI values, suggesting carbonate protoliths (Table 1; Figure 3).
Immobile elemental ratios (Zr/TiO2 versus Ni) effectively discriminate original rock types, with parametamorphites showing elevated Zr/TiO2 at constant Ni levels (Winchester et al., 1980; Bhatia, 1983; Wang et al., 1987). As illustrated in Figure 6a, all samples except for one marble sample (GP10) plot within the sedimentary rock field, indicating sedimentary dominance for various rocks in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit. Major element reconstruction, excluding mobile components (H2O, CO2, K2O, Na2O), is also an effective approach for original rock identification (Wang et al., 1987). As shown in Figure 6b, all samples are almost plotted in the sedimentary rock field, also indicating sedimentary affiliation. It can be further observed from Figure 6c that graphite quartzite clusters near argillaceous graywacke fields, while granulite is distributed across pelitic, volcanic, and quartzose domains. The marbles (including graphite-bearing marble) are geochemically plotted in the calcareous carbonate fields. Therefore, the ore-bearing metamorphic rocks in the study area originated from parametamorphic protoliths dominated by carbonates and muddy greywackes, with local intercalation of organic-rich components.
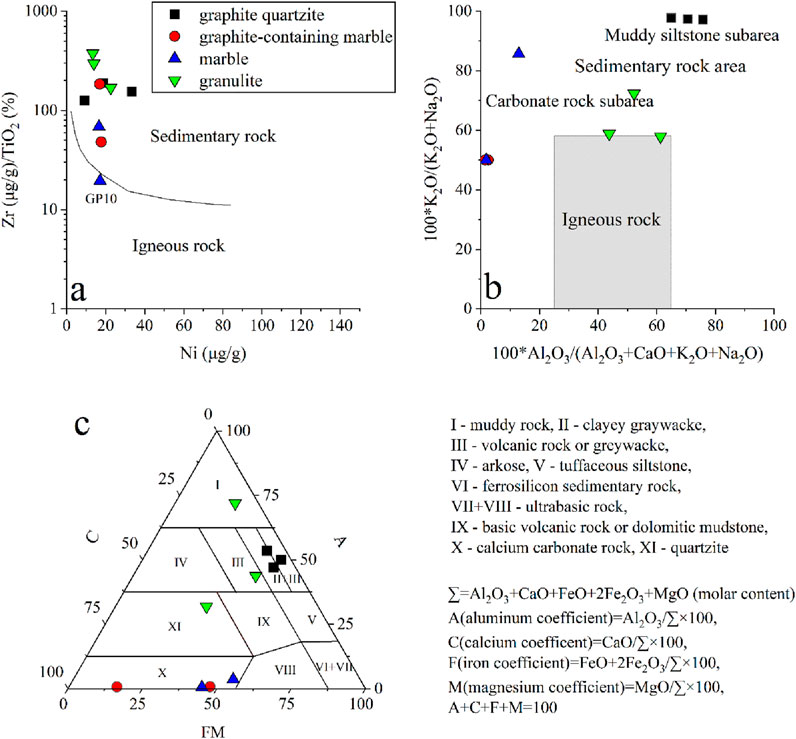
Figure 6. Three geochemical plots depicting different rock classifications. (a) a logarithmic Zr/TiO2 versus Ni chart distinguishing sedimentary and igneous rocks. (b) a K2O/(K2O + Na2O) versus Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO + K2O + Na2O) plot identifying sedimentary, igneous, and carbonate rock areas. (c) a triangular diagram categorizing rock types.
5.2 Sedimentary environment
Various sedimentary material types often form in distinct sedimentary facies with different provenances (Roser and Korsch, 1988; Wan et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2021). For instance, carbonate rocks such as limestone and dolomite typically form through shallow marine deposition. Continental shelf sediments predominantly originate from terrestrial weathering products, exhibiting K2O and Al2O3 enrichment, whereas seabed sediments mainly derive from oceanic crust erosion, characterized by FeO, MgO, Na2O, and CaO enrichment. In the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit, three principal lithologies (graphite quartzite, granulite and marble) display interbedded relationships (Figure 1d), suggesting comparable depositional settings. As listed in Table 1, both graphite quartzite and granulite are characterized by high SiO2 and Al2O3 concentrations and a higher concentration of K than that of Na, suggesting that the sources of these two rocks could be weathered debris and compounds from coastal, shallow-marine or terrestrial sources. The magnesium to aluminum ratio (m = 100 × MgO/Al2O3), due to the terrestrial affinity of Al2O3 and the marine affinity of MgO in sedimentary rocks, serves as a critical palaeosalinity proxy with a higher m value indicating a higher salinity of ancient water body in transitional sedimentary environments between land and sea (Cheng et al., 2021). In detail, a m value of less than 1 indicates a freshwater sedimentary environment, 1–10 represents transitional sedimentation between land and sea, 10–500 shows marine sedimentation with a salinity higher than 30.63%, and higher than 500 may reflect carbonate deposits in epeiric seas or lagoons. According to Table 1, the m value ranges from 12.31 to 16.25 with an average of 14.39 for graphite quartzite, from 3.80 to 24.64 with an average of 17.52 for granulite, and from 549.40 to 3,060.11 with an average of 1721.49 for marble (including graphite-bearing marble) in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit, indicating that their original rocks were associated with marine sedimentation, epicontinental sea, and lagoon carbonate deposit environments.
Barium (Ba) is depleted in seawater as it is prone to form insoluble BaSO4, while Sr is relatively enriched, thus the Sr/Ba ratio is a key indicator for distinguishing marine and continental sedimentary environments. When the Sr/Ba ratio is < 0.6, 0.6–1, and >1, it indicates a freshwater environment, a semi-saline water environment, and a saline water environment, respectively (Wang et al., 2017; Li et al., 2023). In the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit, the Sr/Ba ratios of graphite quartzite and granulite range between 0.05 and 0.31, and are plotted in the semi-saline water environment field except for sample GP2 falling in the freshwater field, indicating that their original rocks developed in a coastal or sea-land transitional environment (Figure 7a). The Sr/Ba ratios of marbles (including graphite-bearing marble) vary from 1.48 to 6.28, and fall in the saline water field (Figure 7a), showing that the original rocks of marbles were closely associated with carbonate rocks formed in shallow sea environments. As shown in Figure 7B, graphite quartzite and granulite fall in the passive continental margin field while graphite-bearing marble and marble are located in the island arc environment field, which is consistent with the results obtained from Sr/Ba.
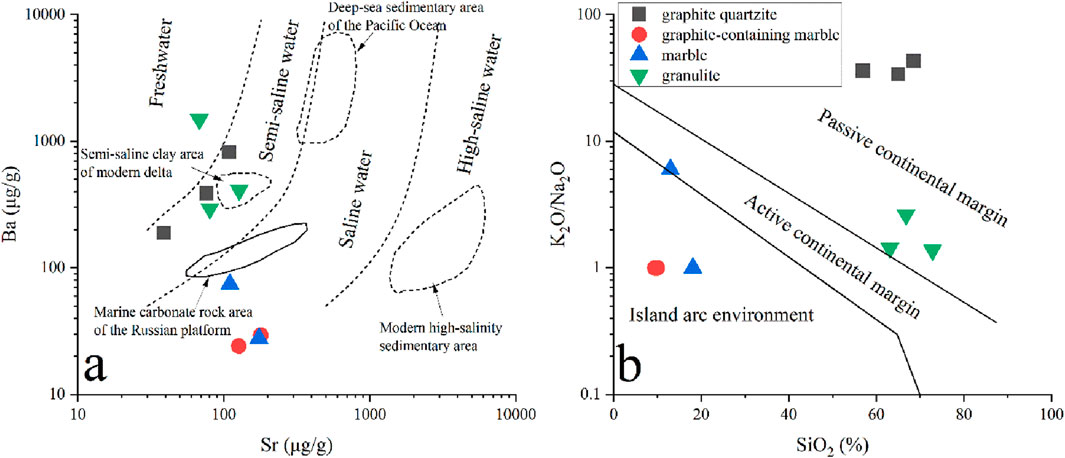
Figure 7. Cross plots of Ba versus Sr (a) and K2O/Na2O versus SiO2 (b) in the Shuanghu graphite deposit, indicating different geological environments.
Marine sedimentation is usually characterized by the enrichment of LREEs, the depletion of HREEs and negative Ce anomalies (Pipe et al., 2025). In the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit, the average δCe values are 0.77, 0.83, and 0.98 for graphite quartzite, marble (graphite-bearing marble) and granulite, respectively, suggesting that these rocks mainly formed in coastal or shallow-sea environments, consistent with the results from Sr/Ba.
The solubilities of some trace elements such as V, Co, Cr, Ni, U, and Th are greatly affected by redox conditions in water, thus their concentrations and ratios are helpful for illustrating the redox states of paleo-oceanic environments (Jones and Manning, 1994; Dean et al., 1997; Tribovillard et al., 2006; Li and Guo, 2023; Banerjee et al., 2025). In detail, the V concentration increases due to its combination with organic matter under hypoxic conditions, while the concentrations of Ni and Cr have opposite variations. Therefore, V/(V + Ni) and V/Cr can be used to determine sedimentary redox conditions. Under strong reducing conditions, U is easily enriched in the form of insoluble U4+, while U exists in the form of soluble U6+ in the oxidized state. So, Th/U and & U can also be used to distinguish redox conditions of sediments. As shown in Table 2, graphite quartzite in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit initially occurred in a hypoxic reducing environment while granulite and marble (including graphite-bearing marble) were generally developed between anaerobic and hypoxic environments.
5.3 Carbon source
Graphite formation in crustal environments derives carbon from three primary reservoirs: organic matter (−40‰ to −17‰ δ13C, avg. −25‰), marine carbonates (−2‰ to +4‰), and mantle sources (∼-7‰), each exhibiting distinct isotopic fingerprints (Weis et al., 1981; Kehelpannala, 1999; Luque et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2018) (Figure 8). Carbon isotopes of graphite depend on both the carbon sources and the degree of isotope fractionation (Luque et al., 2012). Numerous studies have demonstrated that carbon isotopic ratios serve as robust tracers for identifying carbon sources and understanding metamorphic processes of graphite deposits (Sanyal et al., 2009; Luque et al., 2014; Yan et al., 2020; Zhu et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2023b; Barrenechea et al., 2009; Huff and Nabelek, 2007; Maibam et al., 2015; Touzain et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2014; Luque et al., 2009).
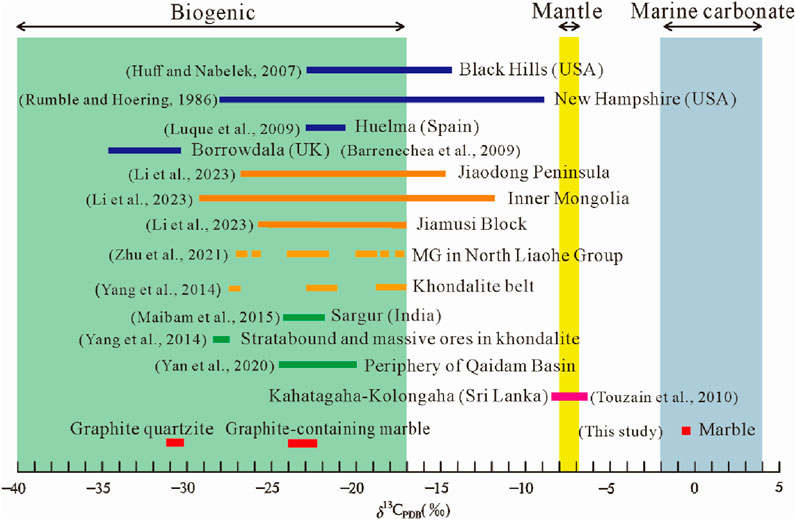
Figure 8. Carbon isotope comparison of graphite deposits between Shuanghu and other regions in the world.
In the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit, graphite-bearing quartzite records δ13C values (−31.2‰ to −30.2‰) comparable to organic precursors, aligning with global biogenic graphite signatures (Figures 4, 8). In contrast, carbonates in marble and graphite-bearing marble preserve δ13C values (−0.8‰ to +0.2‰) typical of marine carbonates. Graphite within graphite-bearing marble displays the δ13C value (−24.4‰ to −23.2‰), significantly lower than that of carbonate but close to those of most graphite deposits in the world, showing a predominance of biogenic carbon (Figures 4, 8). Notably, the δ13C value of graphite in graphite-bearing marble is slightly higher than that of quartzite-hosted graphite (Figures 4, 8). As proposed by some authors such as Luque et al. (2014), Yan et al. (2020) and Zhang et al. (2023a), biogenic graphite isotopes can be enriched (heavier) relative to original organic matter through isotopic exchange with carbonates or CO2-rich fluids derived from decarbonation reactions or mantle sources during high-temperature metamorphism. Higher grade metamorphism also results in an increasing δ13C value of residual carbon (Rumble and Hoering, 1986). Given the presence of graphite in marble in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit (Figure 1d), the slightly higher δ13C value of graphite relative to quartzite-hosted graphite reflects incorporation of minor abiogenic carbon from carbonate rock decarbonation during regional metamorphism (Zhang et al., 2023b; Guo et al., 2024).
In summary, carbon in graphite quartzite derived entirely from biogenic sources, while graphite in graphite-bearing marble predominantly originated from organic matter with minor contributions from abiogenic sources such as CO2-rich fluids during metamorphism at Shuanghu (Guo et al., 2024).
5.4 Metallogenic model
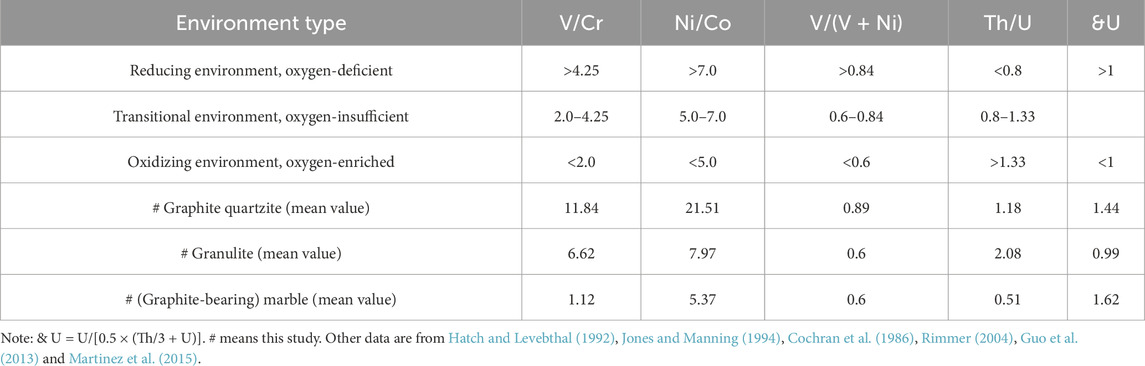
All metamorphic rock types (including lower amphibolite-facies rocks) within the Sulu UHP metamorphic belt experienced Triassic ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and retrogressive amphibolite-facies metamorphism during exhumation (Zheng et al., 2003; Yu et al., 2011; Zhao et al., 2024). As the Shuanghu graphite deposit occurs in this orogenic belt, its ore-hosting strata likely underwent analogous metamorphic processes. Despite possible attainment of upper mantle depths by the UHP metamorphism (Zheng et al., 2003), rapid deep subduction could have prevented timely carbon isotope exchange between graphite-bearing strata and mantle carbon reservoirs. This interpretation is supported by the distinctly negative δ13C values of graphite quartzites (Figure 8). Mesozoic tectonic reactivation primarily induced brittle deformation and ore fragmentation (Zhao et al., 2024). Integration of regional geology, petrographic constraints, and geochemical analyses suggests three key metallogenic stages for the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit (Figure 9).
(1) Organic matter deposition in the Middle Neoproterozoic
The original rocks of the graphite-bearing rock series in the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit likely formed during the Middle Neoproterozoic, coinciding with the Rodinia Continent Aggregation Event (Xu et al., 2006; Yuan et al., 2024). During this period, the Shuanghu area occupied a subsiding lagoonal basin characterized by rhythmic sedimentation (submillimeter-scale layering) comprising mudstone-sandstone alternations, organic-rich marl, and Mg-enriched carbonates. The graphite deposit accumulated under warm-humid climatic conditions favorable for algal proliferation.
(2) Metamorphic diagenesis and mineralization in the Triassic
During the Triassic continental collision between the Yangtze and North China plates, the ore-bearing rocks underwent deep subduction-related UHP metamorphism followed by retrograde amphibolite-facies metamorphism during exhumation. Progressive breakdown of organic matter during prograde metamorphism and dynamic recrystallization under shear stress facilitated the growth of large flake crystalline graphite, ultimately forming the graphite deposit.
(3) Tectonic activation since 200 Ma
Cenozoic Pacific Plate subduction initiated at 200 Ma led to the development of the NE-striking Tan-Lu fault system in East China (Deng et al., 2013). Subsequent multistage tectonic activity subjected UHP metamorphic rocks to dynamic metamorphism (Luo and Yao, 2021), generating greenschist-facies minerals (e.g., sericite, chlorite) and refining graphite crystal sizes. This complex tectonic regime ultimately generated the current three-dimensional distribution pattern of graphite ores through spatial redistribution.
6 Conclusion
Elemental and isotopic characteristics of the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit were investigated in detail in this study. Graphite quartzite is represented by SiO2-Al2O3-K2O enrichment and Na2O depletion, contrasting with the CaO-MgO dominated graphite-bearing marble. The two ore-bearing rocks show the consistent trace element patterns marked by Ba-Nb depletion and display light REE enrichment (LREE/HREE = 3.26–9.32) with negative Eu and Ce anomalies (δEu = 0.39 to 0.67, δCe = 0.64–1). Their original rocks could develop under coastal-neritic conditions with moderate detrital input, including organic-rich greywackes, argillaceous siltstones, and bioclastic limestones. Graphite in quartzite could be purely of biogenic origin (δ13C-graphite: −31.2‰ to −30.2‰), whereas graphite in marble could be a mixture of organic and inorganic sources (δ13C-graphite: −24.4‰ to −23.2‰). Matrix carbonates in (graphite-bearing) marbles display the δ13C values near zero (avg. −0.14‰), showing marine inorganic carbon sources. It is further inferred that the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit could develop through the following stages: (1) the Middle Neoproterozoic deposition of algal-rich sediments under warm coastal conditions, (2) the Triassic collisional metamorphism (North China-Yangtze convergence) facilitating organic carbon graphitization, and (3) tectonic activation since 200 Ma generating the current graphite distribution pattern. In future research geochronometric dating and Raman spectroscopy will be required to precisely constrain metamorphic ages and thermal pathways of this deposit.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
FL: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – original draft. WR: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. WY: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. LS: Writing – review and editing. MX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. SR: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. XL: Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZL: Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the Special fund project for natural resources development in Jiangsu Province (SCZH2020-20, SCZH2021-46, SCZH2023-30).
Acknowledgments
Lin Shi is appreciated for his help during field work and Prof. Changping Mao is also thanked for his guidance in preparing this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Banerjee, M., Bhattacharya, B., Bhattacharya, A., Pathak, A., and Banerjee, P. P. (2025). Geochemistry of shales of middle permian barren measures formation, west bokaro basin, India: implications on provenance, paleodepositional and paleoclimatic conditions. J. Palaeogeogr. 14 (1), 40–65. doi:10.1016/j.jop.2024.08.011
Barrenechea, J. F., Luque, F. J., Millward, D., Ortega, L., Beyssac, O., and Rodas, M. (2009). Graphite morphologies from the Borrowdale deposit (NW England, UK): Raman and SIMS data. Contrib. Min. Petrol. 158, 37–51. doi:10.1007/s00410-008-0369-y
Beyssac, O., Goffé, B., Chopin, C., and Rouzaud, J. N. (2002). Raman spectrum of carbonaceous material in metasediments: a new geothermometer. J. Metamorph. Geol. 20, 859–871. doi:10.1046/j.1525-1314.2002.00408.x
Bhatia, M. R. (1983). Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones. Geology 91, 611–627. doi:10.1086/628815
Buseck, P. R., and Beyssac, O. (2014). From organic matter to graphite: graphitization. Elements 10 (6), 421–426. doi:10.2113/gselements.10.6.421
Castillo, P. R., Janney, P. E., and Solidum, R. U. (1999). Petrology and geochemistry of Camiguin island, southern Philippines: insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting. Contrib. Min. Petrol. 134, 33–51. doi:10.1007/s004100050467
Chen, B., and Jahn, B. M. (2004). Genesis of post-collisional granitoids and basement nature of the Junggar Terrane, NW China: Nd–Sr isotope and trace element evidence. J. Asian Earth Sci. 23 (5), 691–703. doi:10.1016/s1367-9120(03)00118-4
Cheng, S. J., Kang, W., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y. S., Wang, G. H., Liu, Y. H., et al. (2021). Genesis of the Bolinping graphite deposit in Nanjiang of Sichuan by constraints of lithological and C-O isotopic geochemistry. J. Guilin Univ. Technol. 41 (4), 733–742. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2021.04.002
Cochran, J. K., Carey, A. E., Sholkovitz, E. R., and Surprenant, L. D. (1986). The geochemistry of uranium and thorium in coastal marine sediments and sediment pore waters. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50 (5), 663–680. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(86)90344-3
Condie, K. C., Boryta, M. D., Liu, J. Z., and Qian, J. (1992). The origin of khondalites: geochemical evidence from the Archean to Early Proterozoic granulite belt in the North China craton. Precambrian Res. 59, 207–223. doi:10.1016/0301-9268(92)90057-u
Cui, N., Sun, L., Bagas, L., Xiao, K. Y., and Xia, J. S. (2017). Geological characteristics and analysis of known and undiscovered graphite resources of China. Ore Geol. Rev. 91, 1119–1129. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.09.023
Dean, W. E., Gardner, J. V., and Piper, D. Z. (1997). Inorganic geochemical indicators of glacial-interglacial changes in productivity and anoxia on the California continental margin. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 61 (21), 4507–4518. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(97)00237-8
Deng, Y. F., Fan, W. M., Zhang, Z. J., and Badal, J. (2013). Geophysical evidence on segmentation of the Tancheng-Lujiang fault and its implications on the lithosphere evolution in East China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 78, 263–276. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.006
Eguchi, J., Seales, J., and Dasgupta, R. (2020). Great oxidation and Lomagundi events linked by deep cycling and enhanced degassing of carbon. Nat. Geosci. 13, 71–76. doi:10.1038/s41561-019-0492-6
Galvez, M. E., Fischer, W. W., Jaccard, S. L., and Eglinton, T. I. (2020). Materials and pathways of the organic carbon cycle through time. Nat. Geosci. 13, 535–546. doi:10.1038/s41561-020-0563-8
Guo, H., Du, Y. S., Zhou, L., and Yang, J. H. (2013). Trace and rare earth elemental geochemistry of carbonate succession in the Middle Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Pingquan Section: implications for Early Mesoproterozoic ocean redox conditions. J. Palaeogeogr. 2 (2), 209–221. doi:10.3724/SP.J.1261.2013.00027
Guo, Z. X., Papineau, D., O’Neil, J., Rizo, H., Chen, Z. Q., Qiu, X. C., et al. (2024). Abiotic synthesis of graphitic carbons in the Eoarchean Saglek-Hebron metasedimentary rocks. Nat. Commun. 15, 5679. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-50134-1
Han, Y. W., and Ma, Z. D. (2003). Geochemistry. Beijing, China: Geological Press, 1–370. (in Chinese).
Hatch, J. R., and Levebthal, J. S. (1992). Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark shale member of the Dennis Limestone, Wahaunsee County, Kansas, USA. Chem. Geol. 99, 65–82. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-y
Huff, T. A., and Nabelek, P. I. (2007). Production of carbonic fluids during metamorphism of graphitic pelites in a collisional orogendan assessment from fluid inclusions. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 71, 4997–5017. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2007.08.001
Jones, B., and Manning, D. A. (1994). Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 111 (1-4), 111–129. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-x
Kehelpannala, K. V. W. (1999). Epigenetic vein graphite mineralization in the granulite terrain of Sri Lanka. Gondwana Res. 2, 654–657. doi:10.1016/s1342-937x(05)70231-8
Lazzeri, M., and Barreiro, A. (2014). Carbon-based nanoscience. Elements 10, 447–452. doi:10.2113/gselements.10.6.447
Li, C., Wang, D. H., Zhao, H., Pei, H. X., Li, X. W., Zhou, L. M., et al. (2015). Minerogenetic regularity of graphite deposits in China. Min. Deposits 34 (6), 1223–1236. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.16111/j.0258-7106.2015.06.010
Li, H., Hong, T., Liu, S. K., Ke, Q., Yang, Z. Q., Ma, Y. C., et al. (2023). Genesis of the graphite from the Tugeman graphite deposit, Xinjiang, China: evidence for carbon isotope refining by fluids associated with the ductile shear zone. Minerals 13, 1328. doi:10.3390/min13101328
Li, Y. H., Satish-Kumar, M., Kiran, S., Wan, C. H., and Zheng, J. P. (2022). 2.0 Ga orogenic graphite deposits and associated 13C-enriched meta-carbonate rocks from South China Craton: implications for global Lomagundi event. Geosci. Front. 13, 101409. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2022.101409
Li, Y. Y., and Guo, S. B. (2023). Sedimentary response and restoration of paleoshoreline of Taiyuan-Shanxi Formations in North China basin. Pet. Geol. 152, 106218. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106218
Liu, F., Zhang, Y. Y., Yao, W. J., Shi, L., Pan, G., and Shen, R. (2020). Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit in the ultra-high pressure metamorphic belt in northern Jiangsu Province. J. Geol. 44 (1/2), 76–84. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2020.h1.008
Liu, F. L., Gerdes, A., Liou, J. G., Xue, H. M., and Liang, F. H. (2006). SHRIMP U–Pb zircon dating from Sulu–Dabie dolomitic marble, eastern China: constraints on prograde, ultrahigh-pressure and retrograde metamorphic ages. J. Metamorph. Geol. 24, 569–589. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2006.00655.x
Liu, F. L., and Liou, J. G. (2011). Zircon as the best mineral for P-T time history of UHP metamorphism: a review on mineral inclusions and U-Pb SHRIMP ages of zircons from the Dabie-Sulu UHP rocks. J. Asian Earth Sci. 40 (1), 1–39. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.08.007
Lowenstern, J. B. (2001). Carbon dioxide in magmas and implications for hydrothermal systems. Min. Deposita 36, 490–502. doi:10.1007/s001260100185
Luo, S., and Yao, H. J. (2021). Multistage tectonic evolution of the Tanlu fault: insights from upper crustal azimuthal anisotropy of the Chao Lake segment. Tectonophysics 806, 228795. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2021.228795
Luque, F., Crespo-Feo, E., Barrenechea, J., and Ortega, L. (2012). Carbon isotopes of graphite: implications on fluid history. Geosci. Front. 3, 197–207. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2011.11.006
Luque, F., Huizenga, J., Crespo Feo, E., Wada, H., Ortega, L., and Barrenechea, J. (2014). Vein graphite deposits: geological settings, origin, and economic significance. Min. Deposita 49, 261–277. doi:10.1007/s00126-013-0489-9
Luque, F. J., Ortega, L., Barrenechea, J. F., Millward, D., Beyssac, O., and Huizenga, J. M. (2009). Deposition of highly crystalline graphite from moderate-temperature fluids. Geology 37, 275–278. doi:10.1130/g25284a.1
Maibam, B., Sanyal, P., and Bhattacharya, S. (2015). Geochronological study of metasediments and carbon isotopes in associated graphites from the Sargur area, Dharwar craton: constraints on the age and nature of the protoliths. J. Geol. Soc. India 85, 577–585. doi:10.1007/s12594-015-0252-1
Martinez, R. F., Kastner, M., Gallego, T. D., Rodrigo, G. M., Nieto, M. V., and Ortega, H. M. (2015). Paleoclimate and paleoceanography over the past 20,000 yr in the Mediterranean Sea Basins as indicated by sediment elemental proxies. Quat. Sci. Rev. 107, 25–46. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.09.018
McDonough, W. F., and Sun, S. S. (1995). The composition of the Earth. Chem. Geol. 120, 223–253. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
Pan, M. B., Zhang, Q. L., Chen, H. G., Wang, H., and Guo, L. Z. (2002). Lithostratigraphic framework on the southern margin of the Sulu orogen. Geol. Bull. China 21 (12), 848–854. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.12.007
Parnell, J., Brolly, C., and Boyce, A. J. (2021). Graphite from Palaeoproterozoic enhanced carbon burial, and its metallogenic legacy. Geol. Mag. 158 (9), 1711–1718. doi:10.1017/s0016756821000583
Pipe, A. B., Leybourne, M. I., Johannesson, K. H., Hannigan, R. E., and Layton-Matthews, D. (2025). Trace and rare earth element geochemistry of black shales from the Upper Ordovician Utica Shale magnafacies. Chem. Geol. 672, 122507. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2024.122507
Plank, T., and Langmuir, C. H. (1998). The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chem. Geol. 145, 325–394. doi:10.1016/s0009-2541(97)00150-2
Qiang, H., Zhang, S. B., and Zheng, Y. F. (2018). Evidence for regional metamorphism in a continental rift during the Rodinia breakup. Precambrian Res. 314, 414–427. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.06.009
Rimmer, S. M. (2004). Geochemical paleoredox indicators in devonian–mississippian black shales, central appalachian basin (USA). Chem. Geol. 206 (3/4), 373–391. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.029
Roser, B. P., and Korsch, R. J. (1986). Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suite using SiO2 content and K2O/Na2O ratio. J. Geol. 94 (5), 635–650. doi:10.1086/629071
Roser, B. P., and Korsch, R. J. (1988). Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discriminant function analysis of major element data. Chem. Geol. 67, 119–139. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(88)90010-1
Rudnick, R. L., and Gao, S. (2003). “Composition of the continental crust,”. The crust. Editor R. L. Rudnick (Oxford, United Kingdom: Elsevier), 3, 1–64. doi:10.1016/b0-08-043751-6/03016-4
Rumble, D., and Hoering, T. C. (1986). Carbon isotope geochemistry of graphite vein deposits from New Hampshire, U.S.A. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 50, 1239–1247. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(86)90407-2
Sanyal, P., Acharya, B. C., Bhattacharya, S. K., Sarkar, A., Agrawal, S., and Bera, M. K. (2009). Origin of graphite, and temperature of metamorphism in Precambrian Eastern Ghats Mobile Belt, Orissa, India: A carbon isotope approach. J. Asian Earth Sci. 36, 252–260. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2009.06.008
Simandl, G. J. (1992). Gîtes de graphite de la region de la Gatineau. Montreal, QC: University of Montréal, Doctoral Dissertation, 1–351.
Singh, A. P., Mishra, M., Chandra, A., and Dhawan, S. (2011). Graphene oxide/ferrofluid/cement composites for electromagnetic interference shielding application. Nanotechnology 22, 465701. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/22/46/465701
Sun, X. H., Ren, Y. S., Sun, Z. J., Wang, C. Y., and Li, Z. W. (2021). Geochronology and geochemical properties of the large-scale graphite mineralization associated with the Huangyangshan alkaline pluton, Eastern Junggar, Xinjiang, NW China. Geochemistry 81, 125820. doi:10.1016/j.chemer.2021.125820
Taylor, S. R., and McLennan, S. M. (1985). The continental crust: its composition and evolution. Blackwell, United Kingdom: Oxford, 1–312.
Touret, J. L. R., Huizenga, J. M., Kehelpannala, K. V. W., and Piccoli, F. (2019). Vein-type graphite deposits in Sri Lanka: The ultimate fate of granulite fluids. Chem. Geol. 508, 167–181. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.03.001
Touzain, P., Balasooriya, N., Bandaranayake, K., and Descolas-Gros, C. (2010). Vein graphite from the Bogala and Kahatagaha-Kolongaha mines, Sri-Lanka: a possible origin. Can. Mineral. 48, 1373–1384. doi:10.3749/canmin.48.5.1373
Tribovillard, N., Algeo, T. J., Lyons, T., and Riboulleau, A. (2006). Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update. Chem. Geol. 232, 12–32. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
Wallis, S., Enami, M., and Banno, S. (1999). The Sulu UHP terrane: A review of the petrology and structural geology. Int. Geol. Rev. 41 (10), 906–920. doi:10.1080/00206819909465178
Wan, Y., Wilde, S. A., Liu, D. Y., Yang, C. X., Song, B., and Yin, X. Y. (2006). Further evidence for ∼1.85 Ga metamorphism in the Central Zone of the North China Craton: SHRIMP U–Pb dating of zircon from metamorphic rocks in the Lushan area, Henan Province. Gondwana Res. 9, 189–197. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2005.06.010
Wang, R. M., He, G. P., Chen, Z. Z., Zheng, S. Y., and Gen, Y. S. (1987). Graphic discrimination of metamorphic rocks. Beijing, China: Geological Press, 1–199. (in Chinese).
Wang, X., Wang, L. C., Zhang, K., Wang, L., Zhao, S. B., and Hong, L. M. (2023). Geological characteristics and genesis of Xinji graphite deposit in ultra-high pressure metamorphic belt of northern Jiangsu. Contrib. Geol. Min. Resour. Res. 38 (1), 37–43. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.6053/j.issn.1001.1412.2023.01.005
Wang, Z., Fu, X., Feng, X., Song, C., Wang, D., Chen, W., et al. (2017). Geochemical features of the black shales from the Wuyu Basin, southern Tibet: implications for palaeoenvironment and palaeoclimate. Geol. J. 52, 282–297. doi:10.1002/gj.2756
Weis, P. L., Friedman, I., and Gleason, J. P. (1981). The origin of epigenetic graphite: evidence from isotopes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 45, 2325–2332. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90086-7
Winchester, J. A., Park, R. G., and Holland, J. G. (1980). The geochemistry of Lewisian semipelitic schists from the Gairloch District, Wester Ross. J. Geol. 16 (2), 165–179. doi:10.1144/sjg16020165
Wopenka, B., and Pasteris, J. D. (1993). Structural characterization of kerogens to granulite facies graphite: applicability of Raman microprobe spectroscopy. Am. Min. 78, 533–557.
Xia, J. S. (2018). Geological and geochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of graphite deposit in Nanjing County, Sichuang Province. Master thesis. Xi’an, China: University of Geosciences, 1–106.
Xu, Z. Q., Liu, F. L., Zhang, Z. M., Yang, J. S., Zeng, L. S., and Liang, F. H. (2006). Record for Rodinia supercontinent breakup event in the south Sulu ultra-high pressure metamorphic terrane[J]. Acta Petrol. Sin. 22 (7), 1745–1760.
Yan, M. Q., Zhang, D. H., Huizenga, J. M., Wei, J. H., Li, H., Li, G. M., et al. (2020). Mineralogical and isotopic characterization of graphite deposits in the western part of the North Qaidam Orogen and East Kunlun Orogen, northeast Tibetan Plateau, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 126, 103788. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103788
Yang, Q. Y., Santosh, M., and Wada, H. (2014). Graphite mineralization in Paleoproterozoic khondalites of the North China Craton: a carbon isotope study. Precambrian Res. 255, 641–652. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.04.005
Yu, F., Zhang, Z. M., Wang, W., Liu, F., Dong, X., and Liou, J. G. (2011). Zircon U-Pb constraints on the origin of UHP meta-supracrustal rocks in the Southern Sulu orogen, eastern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 42, 740–751. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.05.010
Yuan, X. Y., Niu, M. L., Cai, Q. R., and Zhu, G. (2024). The nature of Neoproterozoic magmatism in the northeastern Yangtze Craton: Implications for breakup of Rodinia supercontinent. Precambrian Res. 405, 107353. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2024.107353
Zhang, C., He, X. F., Sun, L. X., Santosh, M., Chi, J., Yu, X. Y., et al. (2023a). Graphitization in Paleoproterozoic granulites from the Taihua Complex, North China Craton: Constraints from laser Raman spectroscopy, carbon isotopes and geochronology. Lithos 454/455, 107266. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2023.107266
Zhang, Y. Y., Liu, F., Shi, L., Gao, S. I., Tao, K., and Xu, S. W. (2021). Application of induced polarization to exploration of Shuanghu graphite deposit in the ultra-high pressure belt in northern Jiangsu Province. J. Geol. 45 (1), 65–68. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2021.01.010
Zhang, Y. Y., Yao, W. J., Liu, F., Shi, L., Pan, G., and Xu, S. W. (2023b). Prospecting prediction model of Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit in northern Jiangsu. Sci. Technol. Eng. 23 (21), 8959–8965. (in Chinese with English abstract). doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.21.007
Zhang, Z. M., Xu, Z. Q., Liu, F. L., Meng, F. C., Yang, T. N., Li, T. F., et al. (2002). Composition and metamorphism of the root of the southern Sulu orogen. Geol. Bull. China 21 (10), 609–616. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao, G. C., Cawood, P. A., Wilde, S. A., and Sun, M. (2002). Review of global 2.1-1.8 Ga orogens: Implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent. Earth Sci. Rev. 59, 125–162. doi:10.1016/s0012-8252(02)00073-9
Zhao, Y. J., Zhou, G. Y., Chang, H., Zhuang, Y. D., Hu, P., and Wu, Y. B. (2024). Zircon petrochronological evidences for diachronous tectonic switch and orogenic keel collapse of the Tongbai-Dabie-Sulu orogens. Lithos 480/481, 107639. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2024.107639
Zheng, Y. F., Fu, B., Gong, B., and Li, L. (2003). Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie-Sulu orogen in China: Implications for geodynamics and fluid regime. Earth Sci. Rev. 62 (1/2), 105–161. doi:10.1016/s0012-8252(02)00133-2
Zhong, Y., Ma, X. D., Li, H. K., and Zhai, M. G. (2019). Revisit and comparative analysis of the typical graphite deposits in the Paleoproterozoic khondalite series, western North China Craton: Implications for genesis, depositional environment and prospecting potential. Ore Geol. Rev. 109, 370–380. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.04.023
Zhu, J. J., Liu, F. L., Wang, F., Xu, W. T., Liu, F. X., and Shi, C. (2021). Carbon isotope and geochemical characteristics of the Paleoproterozoic graphite deposits in the Jiao-Liao-Ji belt, North China Craton: Implications for genesis and depositional environment. Precambrian Res. 362, 106320. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2021.106320
Keywords: Sulu orogenic zone, graphite-bearing rocks, geochemical characteristics, original rocks, ore genesis, carbon source, Northern Jiangsu
Citation: Liu F, Rao W, Zhang Y, Yao W, Shi L, Xu M, Ren S, Li X and Li Z (2025) Geochemical characteristics of the Shuanghu crystalline graphite deposit in East China: implications for original rocks, sedimentary environments and carbon sources. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1576709. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1576709
Received: 14 February 2025; Accepted: 12 June 2025;
Published: 07 July 2025.
Edited by:
Ramanathan Alagappan, Independent Researcher, Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu, IndiaReviewed by:
Cun Zhang, Qilu University of Technology, ChinaAnjali Vijayan, Central University of Tamil Nadu, India
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Rao, Zhang, Yao, Shi, Xu, Ren, Li and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenbo Rao, cmFvd2VuYm9AMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Feng Liu1,2
Feng Liu1,2 Wenbo Rao
Wenbo Rao