- College of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu, China
Subduction zones constitute a fundamental element of plate tectonic theory, with the initial subduction phase representing a critical but poorly constrained transitional stage in the development of mature subduction systems. Using CiteSpace and VOSviewer knowledge mapping tools, we conducted a systematic bibliometric analysis of 6,728 peer-reviewed publications (1995–2024) to assess recent advancements in initial subduction research. This investigation reveals distinct patterns in authorship, geographical distribution, institutional productivity, and evolving research priorities within initial subduction studies. Four principal investigators emerge as dominant contributors through seminal publications: Robert J. Stern (University of Texas) established foundational models for slab dehydration processes, Julian A. Pearce (Cardiff University) pioneered geochemical discriminants of subduction-related magmatism, Sun S. Shen (Chinese Academy of Sciences) advanced isotopic tracing methodologies for mantle wedge processes, and Yildirim Dilek (Miami University) redefined ophiolite classification frameworks in subduction initiation contexts. Geographically, Chinese researchers lead in publication output (28% of total studies). Institutional productivity analysis identifies the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences as the predominant contributor (313 publications, centrality = 0.53). Four journals dominate disciplinary discourse: EARTH PLANET SC LETT (1,942 relevant publications) leads in high-resolution geochemical studies, followed by Geology (1,792) focusing on field-based tectonic reconstructions, Tectonophysics (1,696) specializing in geodynamic modeling, and J GEOPHYS RES-SOL EA (1,552) publishing numerical simulations of slab nucleation. Current research converges on two primary domains: (1) characterization of proto-subduction signatures through forearc basalts, suprasubduction zone ophiolites, and metamorphic sole assemblages, and (2) mechanical modeling of spontaneous versus induced subduction initiation mechanisms. Emerging methodologies integrate high-precision zircon geochronology (±0.1 Myr resolution), multi-isotopic (B-Li-Sr-Nd) tracer systems, and 3D numerical simulations using platforms like ASPECT and Underworld.
1 Introduction
The plate tectonics theory was one of the crucial theories in the natural science domain in the last century, offering a fundamental framework for exploring the evolution process of the Earth’s structure (Wilson, 1965; Mckenzie and Parker, 1967). Subduction zones constitute a core element of the plate tectonics theory, where oceanic plates subduct beneath another oceanic/continental plate and penetrate into the mantle. The subducting slabs convey surface substances of the Earth to the deep interior. During the subduction process, these surface substances interact with the surrounding mantle, giving rise to a series of tectonic-magmatic-metamorphic events and forming orogenic belts that contain abundant metal mineral resources (Stern, 2004; Ding et al., 2024). The research on subduction zones has always been a core aspect of plate tectonics theory studies, and the initial stage of plate subduction (initial subduction or subduction initiation) is one of the weakest links in plate tectonics research. Currently, research on initial subduction mainly pertains to two aspects, namely, the timing of initial subduction and the dynamic mechanism of subduction initiation (Schellart et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2022; Ozbey et al., 2022; Zeng et al., 2016).
To systematically assess the latest advancements in initial subduction research, we implemented a comprehensive bibliometric analysis by employing CiteSpace and VOSviewer knowledge mapping tools (Chen, 2006; Xie, 2015). Our research encompassed 2,107 peer-reviewed articles within the Web of Science Core Collection (1995–2024), using “initial subduction” as the main search term and falling within the domain of plate tectonics research. Through quantitative analysis of publication metrics, we identified the major contributing countries, research institutions, and core author networks, while establishing the disciplinary distribution within significant earth science journals (Chen, 2004; Freeman, 1979). The co-occurrence analysis of title terms and author keywords allowed for the extraction of high-frequency concept nodes, uncovering the current research foci and emerging trends, providing valuable insights for future research on the initial subduction of subduction zones.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Data description
In this study, the Web of Science Core Collection was employed as the primary data source, and an advanced retrieval strategy was adopted. The search parameters were as follows: TS = “subduction initiation” (topic search), spanning the period from 1995 to 2024 (data obtained on 14 December 2024). The initial search yielded 2,138 records. Subsequently, through rigorous screening of the literature types, only peer-reviewed articles and review articles were incorporated (Chen et al., 2012). This meticulous screening process ultimately yielded 2,107 high-quality publications that met the inclusion criteria and were utilized for a systematic bibliometric study.
2.2 Citespace and Vosviewer methodology
This study primarily utilizes CiteSpace (version 6.3. R1) and Vosviewer with the aim of conducting an in-depth analysis of the latent knowledge within scientific research and comprehensively presenting the structural framework, intrinsic laws, and distribution characteristics of scientific knowledge from multiple perspectives, including scientometrics, data, and information visualization. This tool is capable of precisely capturing the complex relationship matrices among diverse research objects and concretizing abstract information through intuitive visual images, significantly enhancing people’s understanding and cognition of scientific knowledge (Kim et al., 2016). Centrality and burstiness constitute two critical indicators. Centrality is employed to identify and measure the core significance of terms, with key nodes conspicuously marked with purple circles to form a knowledge map (Kim and Chen, 2015). The term “burst” refers to the sharp increase in citation information of nodes such as terms, publications, authors, and journals within a short period. These bursty nodes are prominently marked in red within the graph. Additionally, timelines and time zones, as key indicators reflecting research frontiers and trends, offer robust support for in-depth analyses. During the data analysis process, to ensure the clarity of the network graph and the accuracy of the centrality analysis, thresholds and parameters are selectively set based on actual requirements (Chen et al., 2014).
Furthermore, this study undertakes a comprehensive and profound analysis from multiple facets such as the annual quantity of publications, the number of authors, disciplinary distribution, national contributions, journal influence, and keyword frequencies. The total number of publications, that is, the overall number of academic papers, serves as a vital metric for assessing the research status, level, and development pace within a specific domain. Particularly, the number of publications related to the initial subduction of plates within a unit of time directly reflects the activity level and research progress within this field (Yu et al., 2017). The examination of author productivity and contributions is conducive to uncovering the narrative characteristics and academic influence of researchers within this domain. High-productivity authors, especially those with significant influence, often serve as the supporters and leaders of the research development trends within the discipline. Through setting parameters for the co-occurrence and co-citation analysis of authors, the number of publications and the degree of collaboration among authors can be intuitively determined based on the thickness of nodes and connection lines (Xiao et al., 2017). Simultaneously, we also conduct social network analysis (SNA) on countries with a substantial number of published documents to deeply analyze the publication situations, the years of initial collaboration, and the degrees of collaboration among each country. The analysis results of research institutions can clearly delineate the composition and academic strength of institutions at the forefront of a specific research field (Zhang et al., 2017). By comparing the timelines and intermediate centrality indicators of different disciplines, we can further analyze the evolutionary dynamics and development trends of specific disciplinary fields. Finally, through the analysis of common keywords, term bursts, and frequently cited documents, the foci and future development trends of initial subduction research are determined (Fu et al., 2013; Gao et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2014).
3 Analysis results
3.1 Variation characteristics of annual quantity of publications
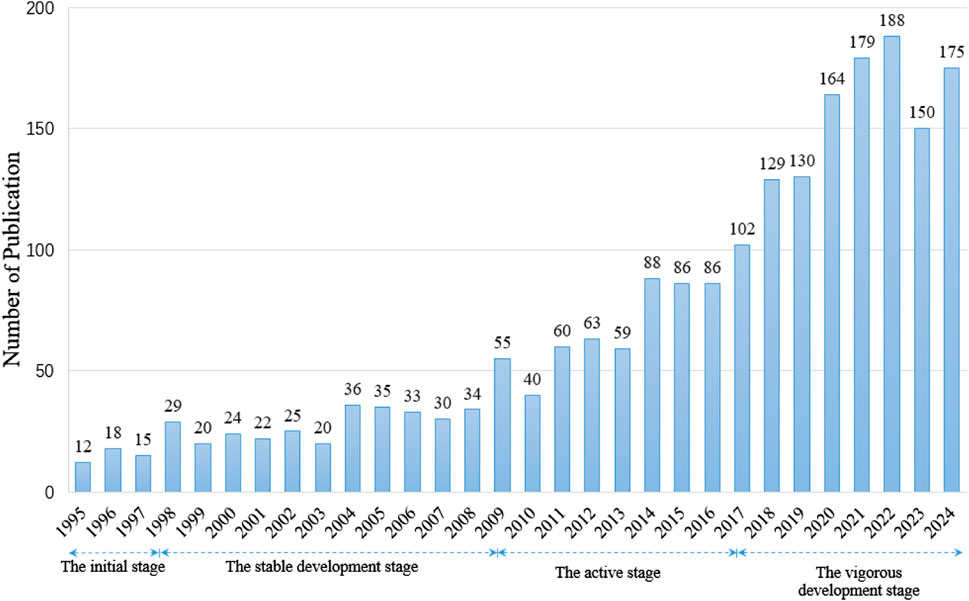
Based on the distribution of publications, the number of literature publications related to initial subduction in the Web of Science Core Collection database was 12 in 1995. During the 14-year period from 1995 to 2008, the annual number of publications exhibited a steady upward trend, rising from approximately 10 to over 30 per year. Starting from 2009, research in this field became increasingly vigorous, and the number of publications increased rapidly. It rose from 55 in 2009 to 86 in 2016. By 2017, the number of publications exceeded 100, indicating a highly active research phase (Figure 1). Beginning in 1995, the publications can be categorized into four periods: the initial stage (1995–1997), the stable development stage (1998–2008), the active stage (2009–2016), and the vigorous development stage (2017–2024).
3.2 Co-occurrence and co-citation analysis of initiation subduction
3.2.1 Author co-occurrence networks analysis
The quantity of publications and the number of collaborative networks can effectively manifest a researcher’s relative contribution within a specific research domain. When conducting the nonlinear network analysis of core authors, the time interval was set as 1 year and trimmed to a pathfinder. A total of 143 nodes and 82 links were identified, with a network density of 0.0081. The colors employed indicate the time when scholars published their first research paper on subduction zone initiation, with darker colors denoting earlier publication dates.
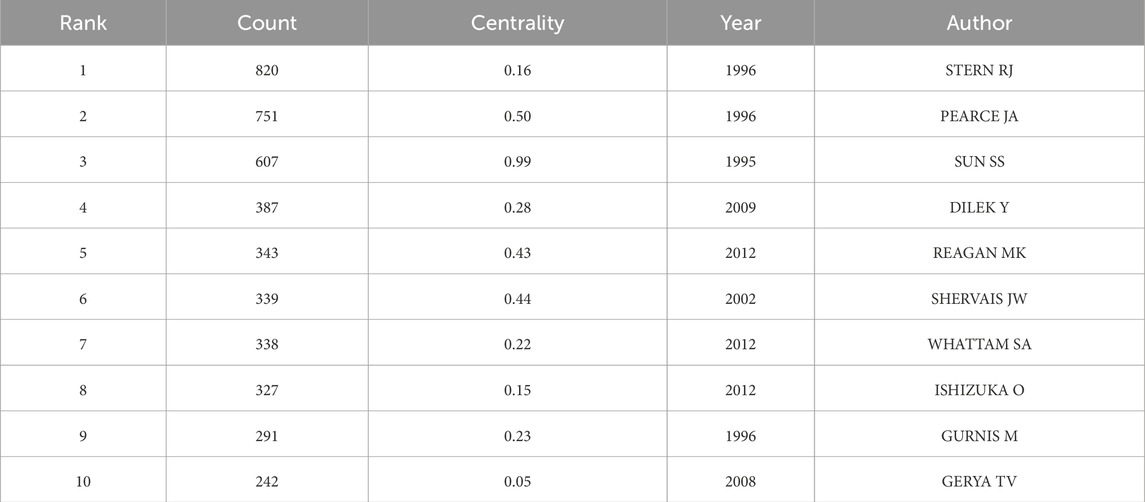
As depicted in Figure 2, the co-citation analysis of subduction zone initiation research discloses four major contributors with significant influence in this field (refer to Table 1). STERN RJ (ranked 1st, cited 820 times, centrality 0.16) and PEARCE JA (ranked 2nd, cited 751 times, centrality 0.50) both published pioneering studies in 1996, establishing the fundamental framework for the initiation mechanism of subduction zones. Their achievements still hold crucial influence up to the present, with PEARCE JA demonstrating an especially high centrality, indicating a key role in the integration of interdisciplinary research clusters. SUN SS (ranked 3rd, cited 607 times, centrality 0.99) published a paper in 1995 with an extremely high centrality (0.99), serving as a key reference for connecting different theories and methodologies. This unprecedented centrality score highlights the cross-disciplinary relevance of SUN SS’s contribution. DILEK Y (ranked 4th, cited 387 times, centrality 0.28) emerged in 2009 during the accelerated development stage of this field (Figure 2), reflecting the evolution of subduction zone initiation research towards geodynamic modeling and tectonic applications. His moderate centrality score is consistent with his specialized focus on the ophiolite-driven initiation paradigm. These four scholars collectively delineated key development stages: the theoretical foundation in the 1990s (STERN RJ, PEARCE JA, SUN SS) and the technological advancements from 2009 to 2016 (DILEK Y), which are in alignment with the publication trends identified in Figure 2 and Table 1.
3.2.2 Institutions and countries/regions co-occurrence network analysis
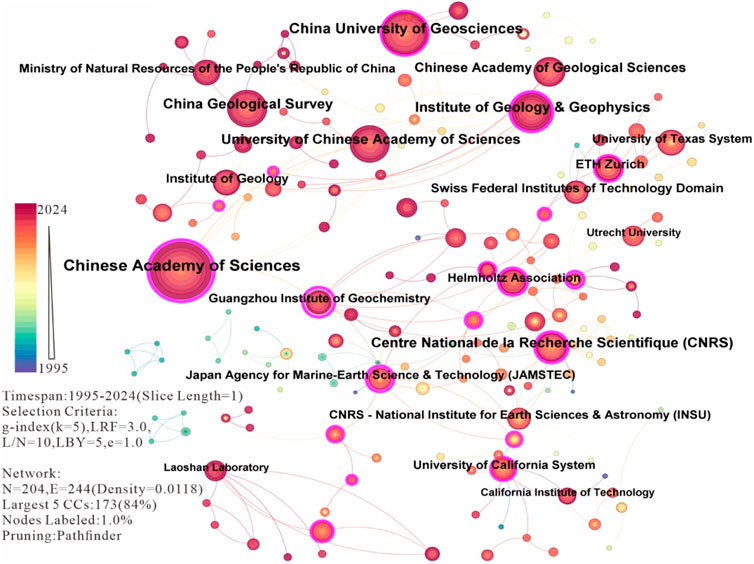
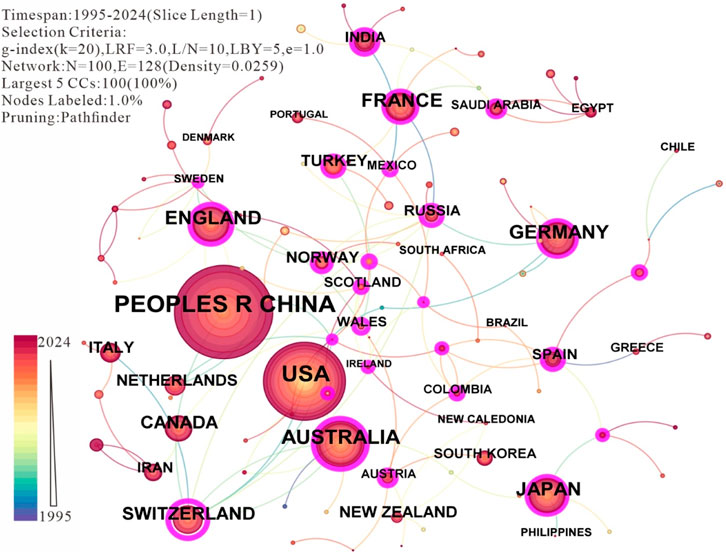
The number of articles published by countries, regions, and research institutions can be employed to determine the centers of excellence in specific research domains. Figure 3 and Table 2 present the top 20 collaborating institutions with the largest number of publications in the research on subduction zone initiation. The network map of collaborating institutions reveals 204 nodes and 244 links, with a network density of 0.0118. The top 20 institutions are largely in cooperative relationships with one another. Based on the data analysis, the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (with 313 published papers and a centrality value of 0.53) leads in terms of the number of published papers. Following the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, the institutions with a considerable number of publications are, in sequence (second to fourth), China University of Geosciences, the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS), and the China Geological Survey. Although the Institute of Geology and Geophysics ranks fifth in terms of the number of published papers (n = 139), its centrality value (centrality value = 0.38) ranks second, indicating its extensive collaboration with other institutions. The institutions ranked sixth to 20th are, in order: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, ETH Zurich, Institute of Geology, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, University of Texas System, Helmholtz Association, Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC), University of California System, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China, French National Centre for Scientific Research - National Institute of Earth Sciences and Astronomy (INSU), California Institute of Technology, and Utrecht University. The network map of the top 20 collaborating countries with the largest number of publications on subduction zone initiation research is depicted in Figure 4. Table 3 details the top 20 collaborating countries in terms of the number of publications on subduction zone initiation research.
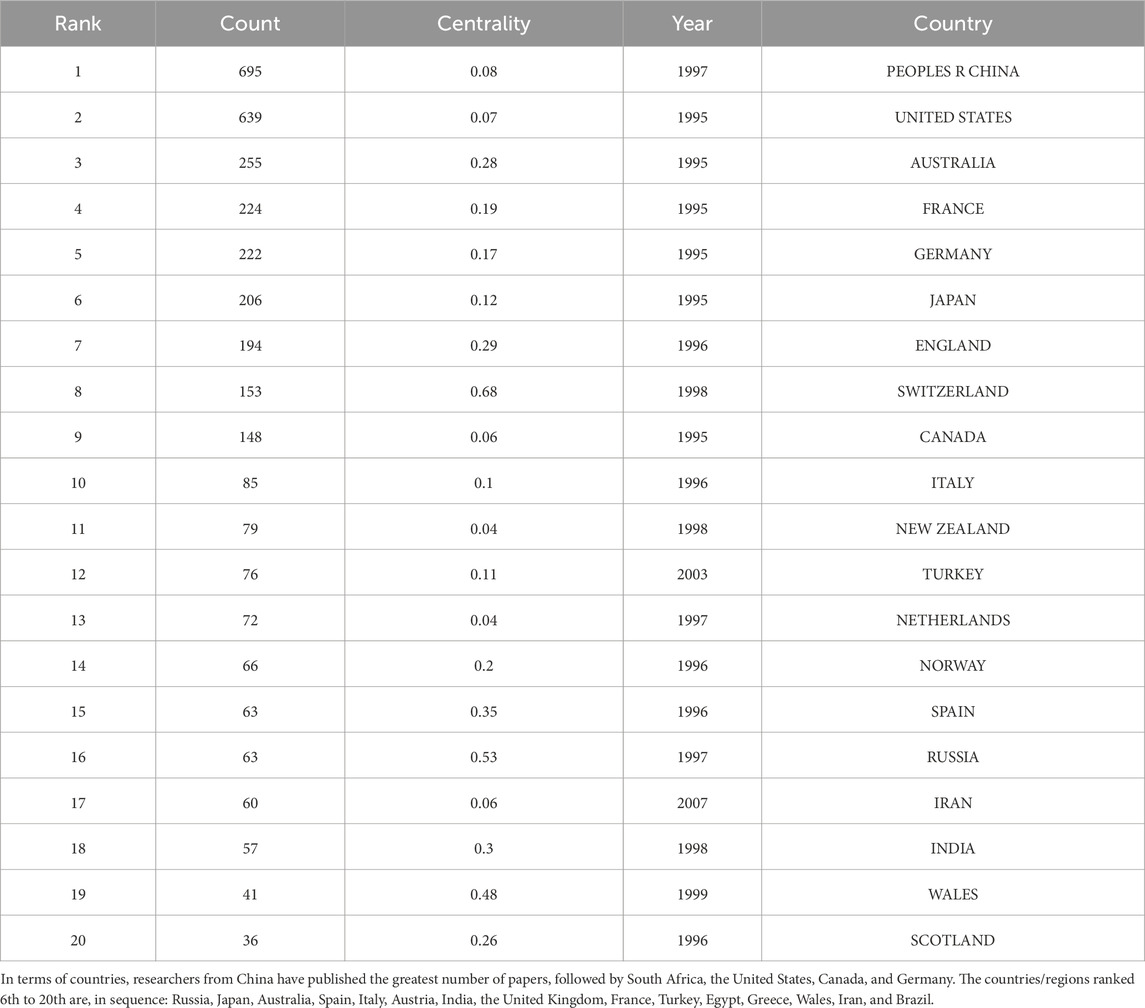
Table 3. Top 20 countries ranked by the number of publications with a focus on subduction initiation.
3.2.3 Analysis of reference co-citation
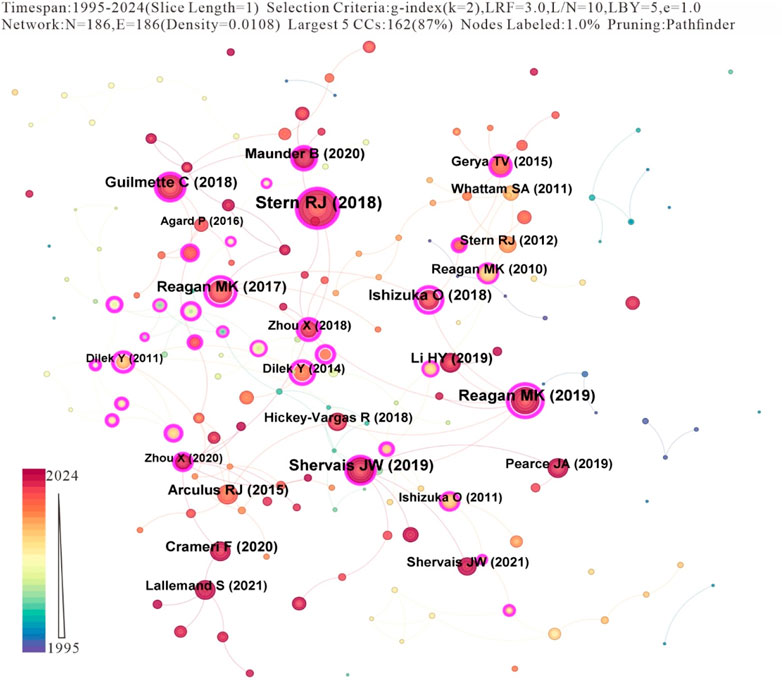
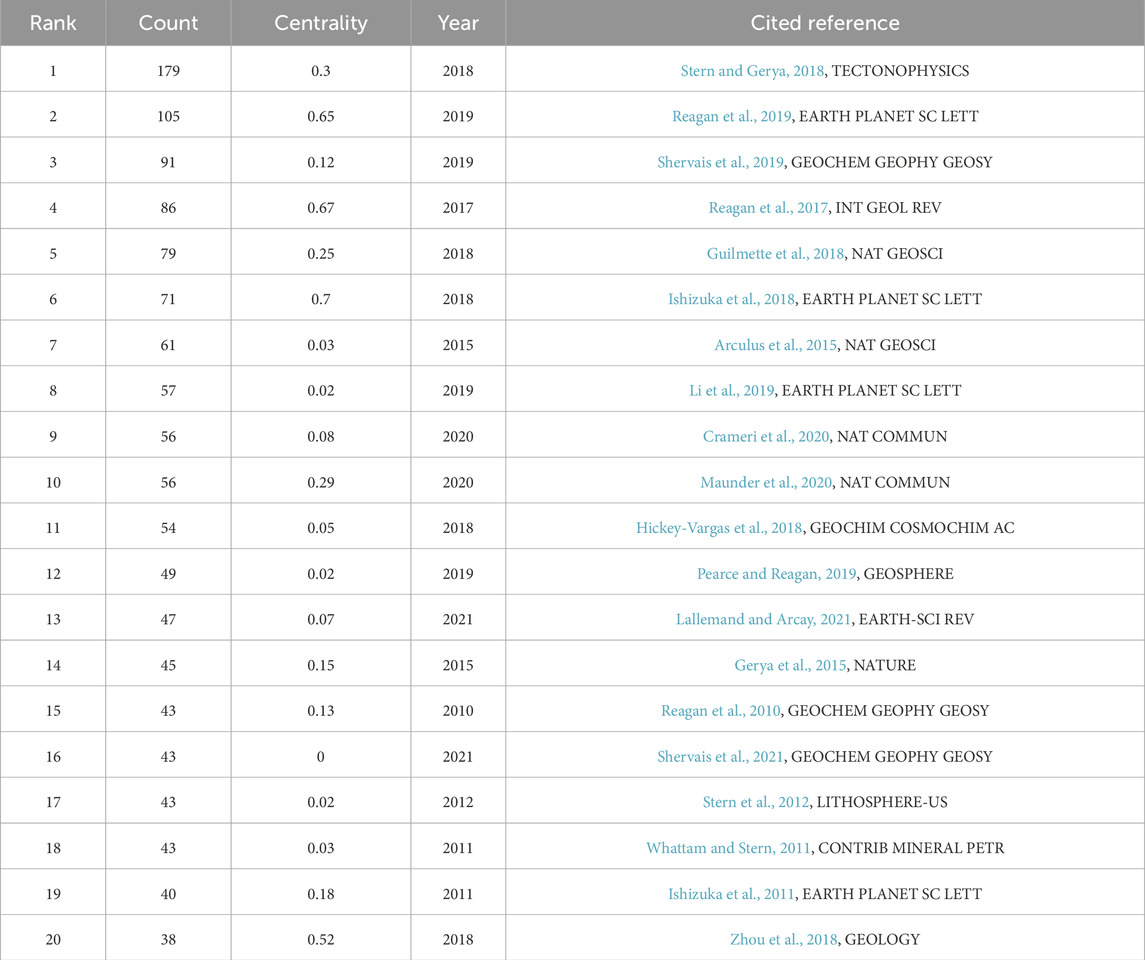
The co-citation network analysis of subduction zone initiation research reveals a structured knowledge framework encompassing at least 186 publications that have been cited at least once, with their citation frequencies systematically quantified. Of particular note is that 72% of the highly cited literature (with citation counts ≥ 25) was published after 2010, which is consistent with the accelerated development stage of this field determined in our temporal distribution analysis (Figure 5). The top 20 most-cited references (Table 4) demonstrate diverse citation dynamics and network centrality, reflecting their influence within the discipline and their role as conceptual bridges. Key contributors have dominated the citation pattern: Stern and Gerya, 2018, Tectonophysics) ranks first with 179 citations (centrality 0.30), having constructed a crucial theoretical framework for the plate rheology during subduction zone nucleation. Its moderate centrality indicates its broad interdisciplinary relevance in geodynamics and petrology; Reagan et al., 2019, EARTH PLANET SC LETT), despite having a relatively lower citation count (105), exhibits strong network connectivity (centrality 0.65), suggesting its critical bridging role between experimental petrology and numerical simulation communities; Shervais et al., 2019, Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems) combines a high citation frequency (91) with a low centrality (0.12), which reflects its specialized contribution to ophiolite-based initiation models; and Reagan et al., 2017, International Geology Review) achieves the highest centrality (0.67) among the highly cited literature, acting as a knowledge hub connecting the reconstructions of ancient subduction zones with modern analog studies.
Key patterns emerge from the dataset: temporal clustering, with 65% (13/20) of the top 20 highly cited papers being published during the mature stage of the field (2017–2021, see Figure 1), which is associated with advancements in computational models and high-resolution geochemical techniques. Decoupling of centrality and citation: highly central literature (e.g., Reagan et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2018) often serves as an intermediary for interdisciplinary concepts despite having moderate citation counts. Journal specialization: EARTH PLANET SC LETT and Nature Communications jointly host 35% of the highly cited articles, highlighting their dominance in publishing interdisciplinary breakthrough research.
This analytical framework quantitatively validates the evolutionary trajectory of subduction zone initiation research, where methodological innovations after 2010 (e.g., Guilmette et al., 2018 in Nature Geoscience; Crameri et al., 2020 in Nature Communications) have gradually complemented the early theoretical foundations (e.g., Gerya et al., 2015 in Nature; Stern et al., 2012 in Lithosphere). Centrality metrics particularly spotlight the transitional key works that facilitated the shift from descriptive geology to process-oriented numerical modeling.
3.2.4 Keywords and hotspot
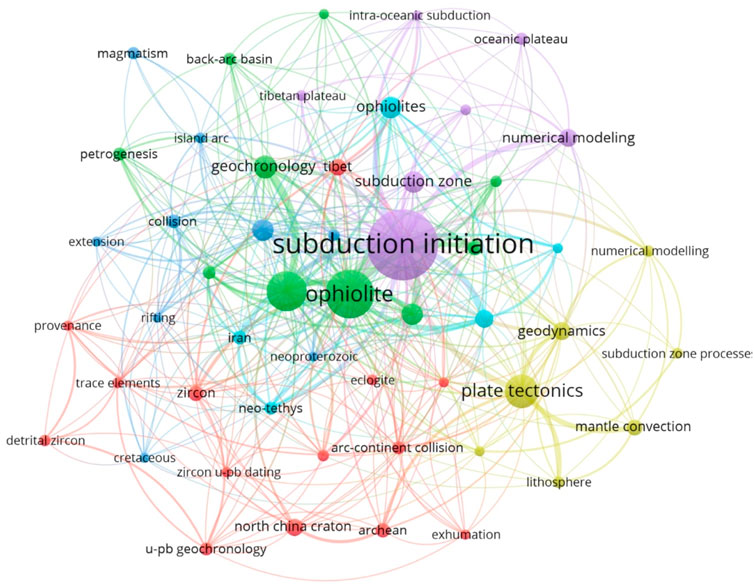
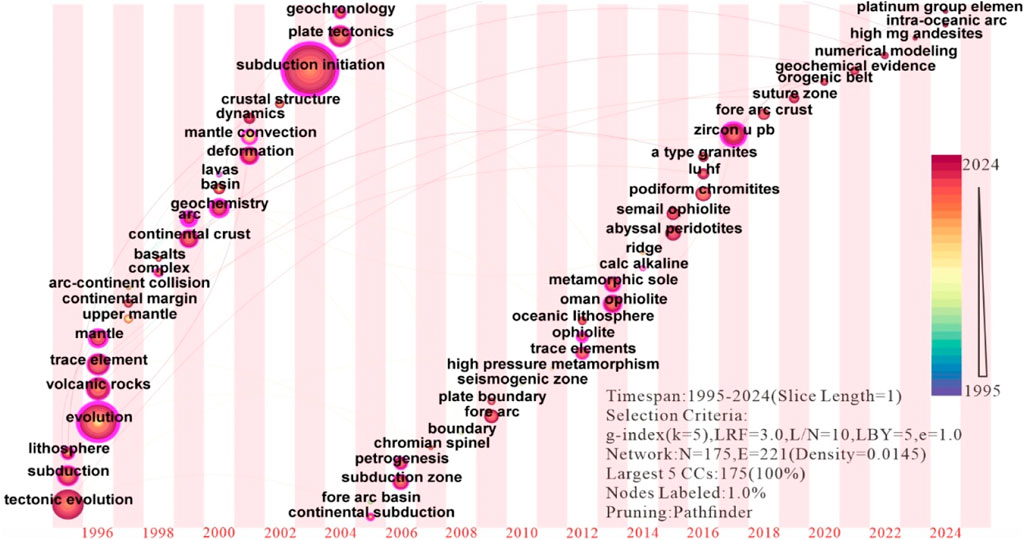
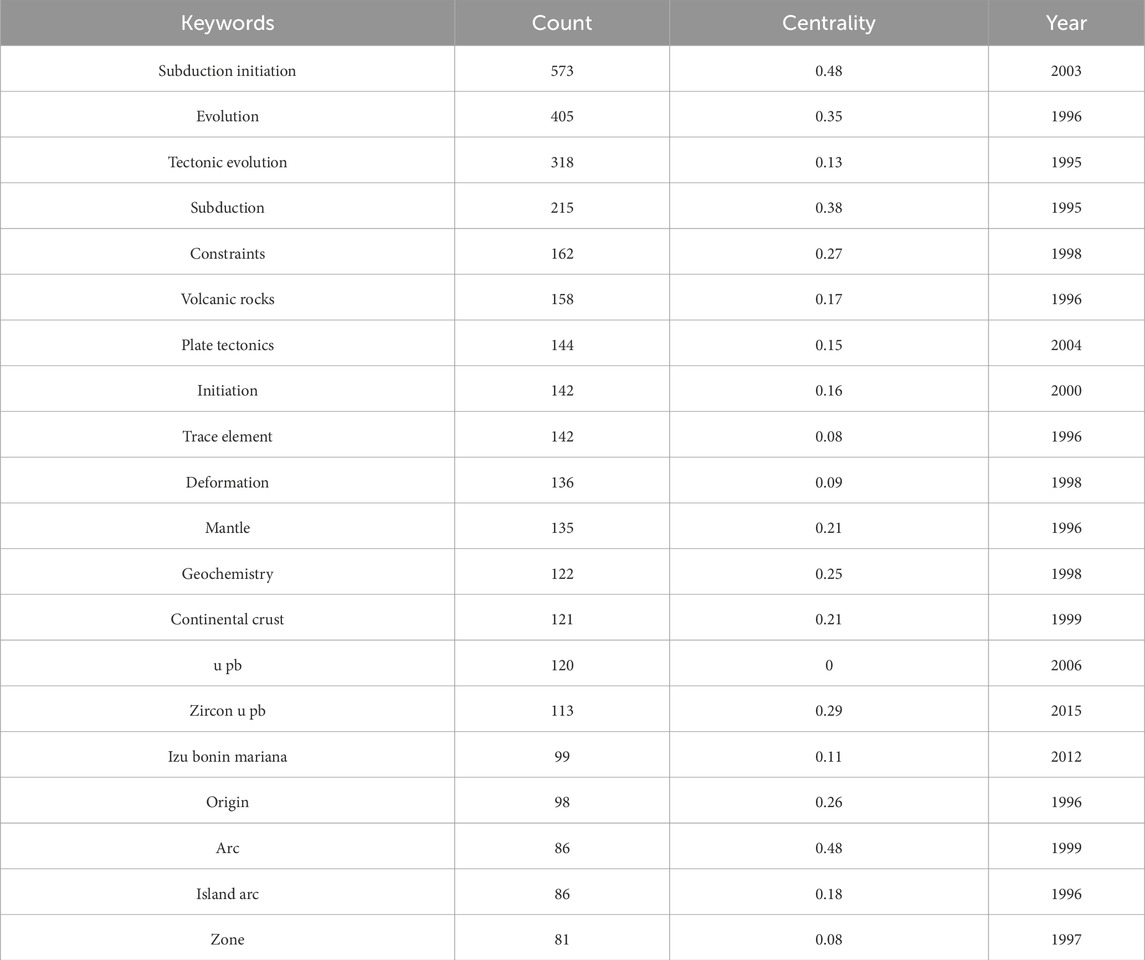
The temporal evolution of research hotspots discloses a distinct chronological pattern in the study of subduction zone initiation. The early fundamental endeavors in the mid-1990s concentrated on basic tectonic processes, as attested by the high centrality of “tectonic evolution” (centrality 0.13, 1995) and “subduction” (centrality 0.38, 1995). The emergence of “volcanic rocks” (frequency 158, 1996) and “mantle” (centrality 0.21, 1996) in 1996 was consonant with the advancement in the research of the genesis of arc magmatism (Figure 6).
In the late 1990s, a notable methodological transformation emerged, with the ascendancy of “geochemistry” (centrality 0.25, 1998) and “deformation” (frequency 136, 1998) mirroring the integration of geochemical tracers and structural analysis. Entering the 21st century, breakthroughs in geochronological methodologies were achieved, with the appearance of “U-Pb” (frequency 120, 2006) and its refined application in “zircon U-Pb” (centrality 0.29, 2015), enabling more precise temporal constraints on the subduction process.
The momentum of regional tectonic research was enhanced through studies of specific systems such as the “Izu-Bonin-Mariana” (frequency 99, 2012) arc, and the research on “continental crust” (centrality 0.21, 1999) elucidated the crust-mantle interaction mechanism. The concurrent appearance of “arc” (centrality 0.48, 1999) and “island arc” (frequency 86, 1996) accentuated the significance of modern and ancient arc systems as natural laboratories for subduction research.
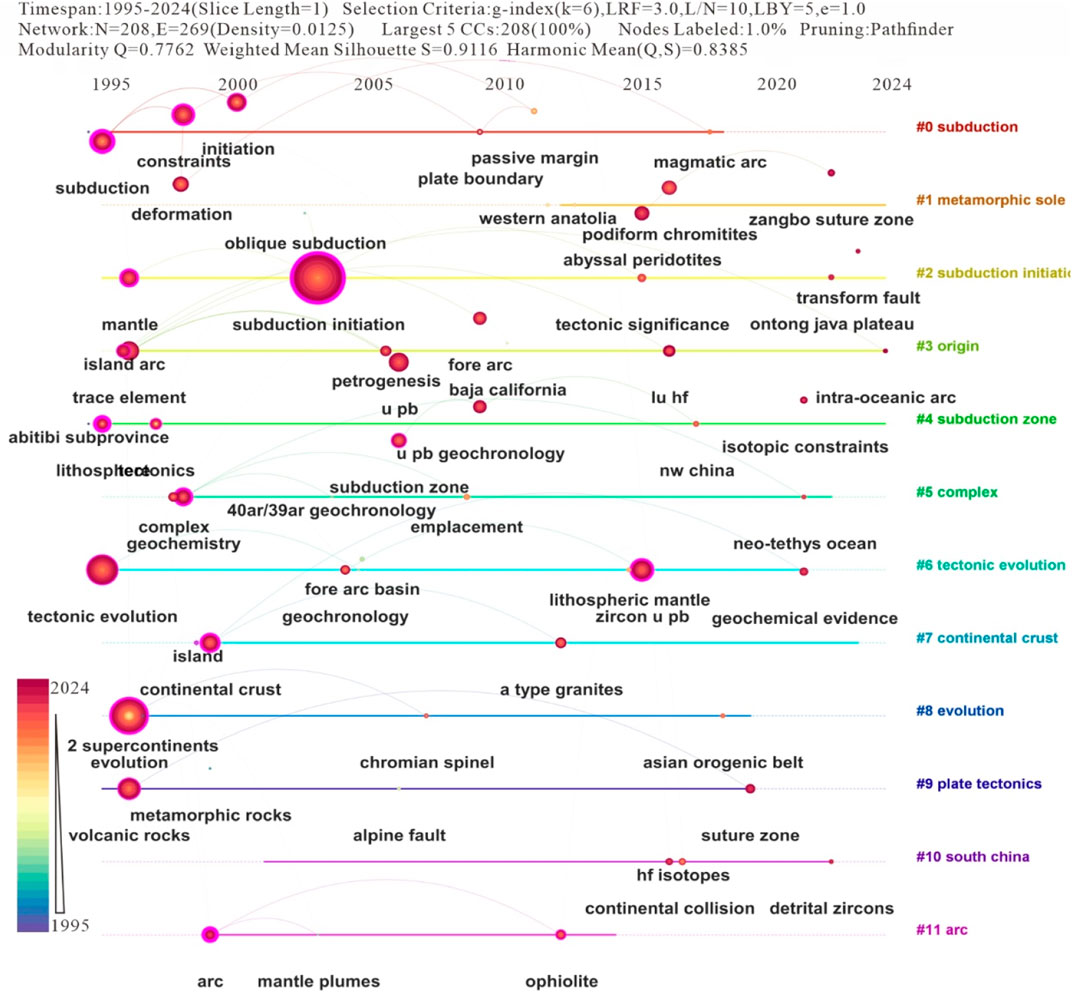
Centrality indicators unveil three core conceptual frameworks: process-oriented research (“subduction zone initiation” 0.48, “evolution” 0.35); geochemical constraints (“trace elements” 0.08, “geochemistry” 0.25) and tectonic architecture (“continental crust” 0.21, “regional” 0.08). Notably, both “subduction zone initiation” and “arc” have a centrality score of 0.48, suggesting that these two concepts act as key nodes interconnecting diverse research strands. The time interval between “initiation” (2000) and “zircon U-Pb” (2015) reveals a 15-year development course from conceptual models to quantitative geochronological validation (Figure 7; Table 5).
This multi-scale analysis demonstrates how the field has evolved from descriptive studies of phenomena in the 1990s to process-oriented and geochemically constrained research in the 21st century. The coexistence of high-centrality theoretical concepts (“plate tectonics” 0.15) and nascent technical approaches (“zircon U-Pb” 0.29) exhibits the field’s maturation towards an interdisciplinary Earth system science. Future research trajectories might focus on integrating the enumerated clusters through four-dimensional modeling that combines geochemical fingerprints (Cluster #3), temporal constraints (Cluster #5), and spatial architecture (Cluster #4/10) (Figure 8).
3.2.5 Analysis of the impact of publications
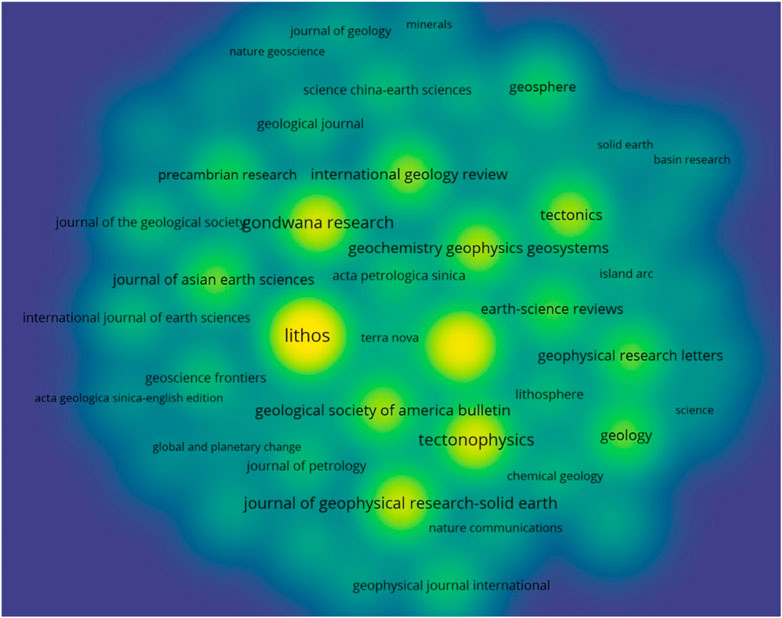
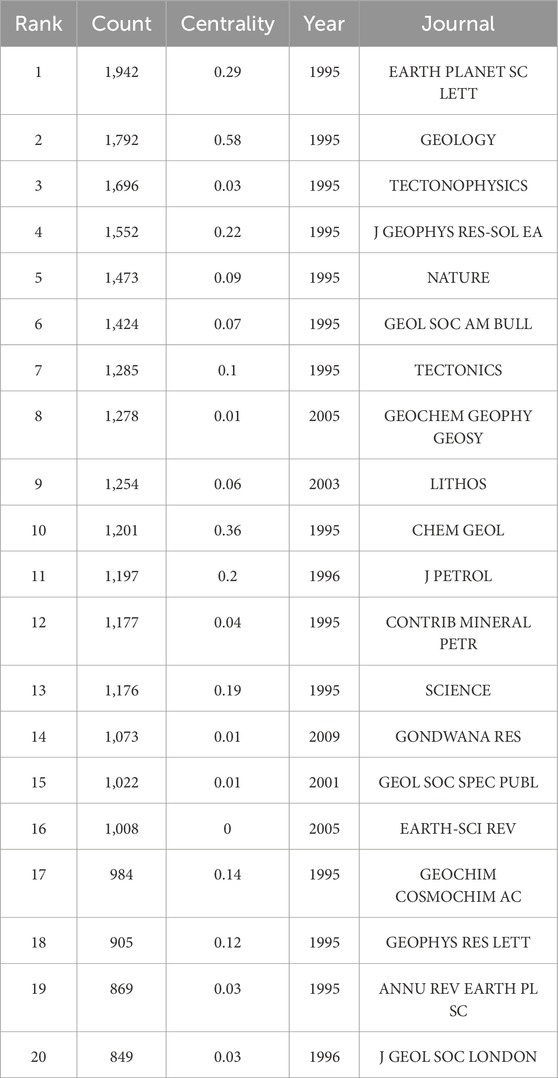
The data indicate that EARTH PLANET SC LETT, GEOLOGY, and TECTONOPHYSICS are the three journals that have made the greatest contributions in the field of initial subduction research. Their article publication frequencies are 1,942 times, 1,792 times, and 1,696 times respectively, demonstrating their significant positions in this field. Furthermore, although J GEOPHYS RES-SOL EA ranks fourth with a frequency of 1,552 times, its centrality is extremely high, suggesting that it also has a very concentrated and prominent influence in this field (Figure 9; Table 6).
3.3 The latest research advances of plate tectonics theory and subduction zones
The plate tectonics theory, as a landmark achievement in the field of Earth sciences in the 20th century (Wilson, 1965; Mckenzie and Parker, 1967), systematically unveils the movement laws of lithospheric plates and their regulatory effects on the Earth’s evolution. The Wilson Cycle, as the core paradigm of this theory, comprehensively delineates the entire dynamic process from continental rifting, ocean basin expansion, subduction and consumption to continental collision (Baes and Sobolev, 2017; Peng and Leng, 2017). Among them, the subduction zone, as a crucial tectonic unit at the convergent boundary of plates, not only serves as the core conduit for the circulation of surface materials to the deep mantle but also drives the formation of orogenic belts and the enrichment of metal mineral deposits through the coupling of tectonics, magmatism, and metamorphism (Xiao et al., 2022; Torro et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2015; Stern, 2004).
The current international cutting-edge research on subduction zones focuses on the following five dimensions: (1) Three-dimensional/four-dimensional modeling of subduction zones: Unveiling the morphology and spatio-temporal evolution of subducting slabs through seismic tomography and numerical simulation (Qin et al., 2025; Tong et al., 2024; Shuck et al., 2021; Bahadori and Holt, 2019; Kneller and van Keken, 2007); (2) Subduction zone identification techniques: Integrating geophysical inversion and rock geochemical tracing techniques to establish criteria for identifying ancient subduction zones (Nasrabady et al., 2023; Zeng et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2021; Abhishek et al., 2018); (3) Correlation with supercontinent cycles: Exploring the response of subduction zone dynamics to the rifting and aggregation processes of supercontinents such as Rodinia and Pangea (Cawood and Buchan, 2007; Cawood et al., 2016; Dal Zilio et al., 2018); (4) Initial subduction mechanisms: Analyzing the triggering conditions and dynamic processes of subduction initiation (Yang, 2022; Yang et al., 2021; Auzemery et al., 2020; Peng and Leng, 2017); (5) Sources of plate driving forces: Quantifying the contributions of plate negative buoyancy, mantle convection, and boundary forces to subduction (Candioti et al., 2020; Sun, 2019; Dal Zilio et al., 2018).
The determination of initial subduction requires the consideration of both temporal scale (global tectonic regime transition and local ocean basin initiation) and dynamic mechanism constraints (Stern, 2004; Zheng et al., 2020). Its typical geological records include: (1) Fore-arc basalts (FAB): Characterized by enriched large-ion lithophile elements (LILE) and depleted high-field-strength elements (Nb-Ta), they form due to decompression melting of the asthenospheric mantle induced by subduction fluids and are spatially adjacent to trenches (Reagan et al., 2010; Ishizuka et al., 2011; Xiao et al., 2016; Shervais et al., 2019); (2) SSZ-type ophiolite: Characterized by a mantle peridotite - cumulate - volcanic rock sequence, its formation age in an initial arc environment can constrain the initiation time of subduction (Pearce, 2003; Chen et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2024; Zhai et al., 2024; Shen et al., 2024); (3) Boninite: Rich in Si (>52 wt%), Mg (Mg# > 0.6), and poor in Ti (TiO2 < 0.5 wt%), reflecting a high degree of melting of the mantle wedge strongly metasomatized by the subducting slab (Stern et al., 2012; Shervais et al., 2021; Yang, 2023; Whattam, 2024); (4) Metamorphic basement: A high-pressure granulite-greenschist facies assemblage indicates a high thermal gradient environment at the initial stage of subduction (peak pressure > 1.5 GPa, geothermal gradient > 15°C/km), and it is in fault contact with ophiolite in the tectonic mélange (Wakabayashi and Dilek, 2003; Dewey and Casey, 2013; Shen et al., 2021; Zhong and Li, 2022; Fournier-Roy et al., 2024; Arao et al., 2025).
Based on the differences in driving force sources, the initial subduction mechanism can be divided into two types: (1) Spontaneous subduction (dominated by vertical stress): Transform fault collapse: Density differences drive the ancient plate to sink along the weak zone (such as the Izu-Bonin-Mariana subduction zone) (Stern and Bloomer, 1992; Arculus et al., 2015; Arcay et al., 2020); Passive continental margin collapse: Sedimentary load causes the young oceanic crust (<30 Ma) to rupture (supported by numerical simulation, Zhong and Li, 2019; Zhou and Wada, 2021); Mantle plume edge collapse: Plume head thermal erosion weakens the lithosphere (Caribbean case, Whattam and Stern, 2015). (2) Induced subduction (dominated by horizontal stress):Subduction migration: Continental collision causes the subduction zone to shift (Bangonghu-Nujiang Tethys Ocean, Yan and Zhang, 2020; Wang et al., 2024); Polarity reversal: The intrusion of an external block causes the subduction direction to reverse (Cooper and Taylor, 1985; Sun et al., 2021; Ning et al., 2020; Almeida et al., 2019).
Current disputes are concentrated on: (1) The initiation time of the global plate tectonic system (whether the modern subduction mode existed in the Precambrian) (Gerya et al., 2015; Brown et al., 2020; Lu et al., 2021; Marshall, 2024); (2) The universality of the initial subduction magmatic sequence (whether the IBM model is applicable to ancient orogenic belts) (Zhou et al., 2018; Arcay et al., 2019; 2020); (3) The early Earth subduction mechanism (the explanatory power of the mantle plume collapse model for the first subduction zone) (van Hinsbergen et al., 2021; Baes et al., 2021). In the future, a unified theoretical framework for the initiation of subduction needs to be constructed through interdisciplinary integration (high-precision chronology- geochemistry-numerical simulation-deep exploration) (Stern and Gerya, 2018; Yang, 2023).
4 Results and conclusion
A bibliometric analysis conducted on 2,107 publications encompassed in the Web of Science Core Collection (1995–2024) has disclosed four prominent phases in the research of subduction zone initiation (SI) (Figure 1):
(1) The initial exploration stage (1995–1997): During this phase, the average annual output was relatively low (with an average of 12 publications per year), and the fundamental theories were established through pioneering research on plate rheology and arc magmatism.
(2) The stable development stage (1998–2008): The average annual output increased linearly from 10 to 32 publications (R2 = 0.92), mirroring the integrated application of geochemical tracers and structural analysis methods.
(3) The accelerated growth stage (2009–2016): The number of publications exhibited exponential growth (jumping from 55 to 86 per year, with a compound annual growth rate of 6.8%), which was concomitant with the advancements in high-precision geochronology (for instance, zircon U-Pb ±0.1 million years) and numerical simulation techniques.
(4) The prosperous innovation stage (2017–2024): Since 2017, the average annual output has surpassed 100 publications, benefiting from the integration and impetus of interdisciplinary fields such as deep seismic imaging, machine learning-enhanced petrological modeling, and global geodynamic simulations.
This paper conducts a comprehensive review of 139 key studies and constructs a multi-index identification system for the initiation of subduction zones: (1) Petrological characteristics: Fore-arc basalts (FABs) display significant enrichment in large-ion lithophile elements (Ba/Nb = 15–45) and depletion in Nb-Ta elements (Th/Nb > 1.2); basaltic andesites exhibit SiO2 > 52 wt%, Mg#> 0.6, and TiO2 < 0.5 wt%, indicating that they result from fluid-mediated melting dominated by subducting slabs. (2) Metamorphic records: High-pressure granulites (1.5–2.2 GPa, 700°C–850°C) and greenschist assemblages impose constraints on the early thermal gradient (15°C–25 °C/km). (3) Temporal constraints: The time interval between magmatic crystallization ages (zircon U-Pb) and metamorphic ages (muscovite Ar-Ar) is less than 5 Ma.
Two end-member mechanisms, spontaneous and induced, were derived from 67 numerical models (table): Spontaneous initiation is mainly driven by gravitational instability (Δρ > 80 kg/m3) and has a higher success rate in young oceans (<30 million years), with a replication rate of 65%–72%; while induced initiation requires lateral compressive stress (>100 MPa) and is commonly observed in continental collision zones (such as the closure process of the Neo-Tethys Ocean).
Despite certain advancements, key knowledge gaps persist: (1) Applicability of subduction zone initiation criteria in the Precambrian: Less than 40% of the criteria for subduction zone initiation in the Phanerozoic are in alignment with the characteristics of Archean greenstone belts; (2) Global model validation: The consistency between the IBM-type subduction zone initiation sequence and Paleozoic orogenic belts amounts to only 58%; (3) Multi-scale coupling: Quantitative studies on the interaction between plumes and subduction zones are limited (model parameter uncertainty > 32%).
Future developments and progress require: (1) Ultra-high-resolution chronostratigraphy (±0.05 million years) in combination with trace element zonation profiles. (2) Exascale geodynamic models capable of integrating seismic anisotropy and mantle convection patterns. (3) Standardization of a global database for subduction zone initiation (metadata conforming to ISO 19115 standards).
This study, leveraging bibliometrics, co-citation analysis, and concept network analysis, quantitatively and comprehensively examines the evolutionary course of initial subduction research for the first time. The identified stage transitions (from 1995 to 2024) are closely associated with technological breakthroughs in the fields of geochemistry and computational geodynamics. Although diagnostic criteria and numerical models for Cenozoic systems have achieved 60%–75% consistency, there are still critical disconnections when applying these frameworks to Precambrian terrains. Addressing these challenges necessitates the comprehensive application of interdisciplinary theories and methods (high-precision chronology-geochemistry- numerical simulation-deep exploration) based on existing case studies of subduction zones.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. NJ: Writing – review and editing. KL: Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (No. 41102065 and 41872110) and Chengdu University of Technology (2020ZF11407).
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to the Editorial staff of Frontiers in Earth Science and the reviewers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abhishek, S., Manikyamba, C., Ray, J., DuttaSantosh, J. M., and Sohini, G. (2018). Geochemical cycling during subduction initiation:Evidence from serpentinized mantle wedge peridotite in the south Andaman ophiolite suite. Geosci. Front. 9 (6), 1755–1775. doi:10.1016/j.gsf.2017.12.017
Almeida, J., Riel, N., Rosas, F., and Duarte, J. (2019). Numerical modelling of induced subduction initiation: thermal control exerted by plate ages in polarity reversal during plateau docking. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 21, 1.
Arao, M., Imayama, T., Sawada, Y., Yagi, K., Siddiqu, R. H., and Dutta, D. (2025). Magmatic and metamorphic evolution of the late cretaceous Muslim Bagh Ophiolite, western Pakistan: implications for ridge subduction after subduction initiation. Int. Geol. Rev. 67 (7), 950–967. doi:10.1080/00206814.2024.2417214
Arcay, D., Lallemand, S., Abecassis, S., and Garel, F. (2019). Conditions of subduction initiation at transform faults. Geophys. Res. Abstr. 21, 1.
Arcay, D., Lallemand, S., Abecassis, S., and Garel, F. (2020). Can subduction initiation at a transform fault be spontaneous? Solid Earth 11 (1), 37–62. doi:10.5194/se-11-37-2020
Arculus, R. J., Ishizuka, O., Bogus, K. A., Gurnis, M., Hickey-Vargas, R., Aljahdali, M. H., et al. (2015). A record of spontaneous subduction initiation in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana arc. Nat. Geosci. 8 (9), 728–733. doi:10.1038/NGEO2515
Auzemery, A., Willingshofer, E., Yamato, P., Duretz, T., and Sokoutis, D. (2020). Strain localization mechanisms for subduction initiation at passive margins. Glob. Planet. Change 195, 103323. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2020.103323
Baes, M., Sobolev, S., Gerya, T., Stern, R., and Brune, S. (2021). Plate motion and plume-induced subduction initiation. Gondwena Res. 98, 277–288. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2021.06.007
Baes, M., and Sobolev, S. V. (2017). Mantle flow as a trigger for subduction initiation: a missing element of the wilson cycle concept. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 18 (12), 4469–4486. doi:10.1002/2017GC006962
Bahadori, A., and Holt, W. E. (2019). Geodynamic evolution of southwestern north America since the late eocene. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 5213–5218. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-12950-8
Brown, M., Johnson, T., and Gardiner, N. J. (2020). Plate tectonics and the archean earth. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 48 (1), 291–320. doi:10.1146/annurev-earth-081619-052705
Candioti, L. G., Schmalholz, S. M., and Duretz, T. (2020). Impact of upper mantle convection on lithosphere hyperextension and subsequent horizontally forced subduction initiation. Solid Earth 11 (6), 2327–2357. doi:10.5194/se-11-2327-2020
Cawood, P. A., and Buchan, C. (2007). Linking accretionary orogenesis with supercontinent assembly. Earth-Science Rev. 82 (3-4), 217–256. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.03.003
Cawood, P. A., Strachan, R. A., Pisarevsky, S. A., Gladkochub, D. P., and Murphy, J. B. (2016). Linking collisional and accretionary orogens during Rodinia assembly and breakup: implications for models of supercontinent cycles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 449, 118–126. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2016.05.049
Chen, C., Su, B. X., Jing, J. J., Xiao, Y., Lin, W., Chu, Y., et al. (2018). Geological records of subduction initiation of Neo-Tethyan ocean: ophiolites and metamorphic soles in southern Turkey. Acta Petrol. Sin. 34 (11), 3302–3314.
Chen, C. M. (2004). Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (101-Sup1), 5303–5310. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307513100
Chen, C. M. (2006). CiteSpace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 57 (3), 359–377. doi:10.1002/asi.20317
Chen, C. M., Dubin, R., and Kim, M. C. (2014). Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: a scientometric update (2000 - 2014). Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 14 (9), 1295–1317. doi:10.1517/14712598.2014.920813
Chen, C. M., Hu, Z. G., Liu, S. B., and Tseng, H. (2012). Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 12 (5), 593–608. doi:10.1517/14712598.2012.674507
Chen, Y. C., Zhang, J. E., Tian, Z. H., QuanRen, Y., QuanLin, H., and WenJiao, X. (2021). The structure of suture in orogenic belts and its tectonic implications. Acta Petrol. Sin. 37 (8), 2324–2338. doi:10.18654/1000-0569/2021.08.05
Cooper, P. A., and Taylor, B. (1985). Polarity reversal in the solomon-islands arc. Nature 314 (6010), 428–430. doi:10.1038/314428a0
Crameri, F., Magni, V., Domeier, M., Shephard, G. E., Chotalia, K., Cooper, G., et al. (2020). A transdisciplinary and community-driven database to unravel subduction zone initiation. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 3750. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17522-9
Dal Zilio, L., Faccenda, M., and Capitanio, F. (2018). The role of deep subduction in supercontinent breakup. Tectonophysics 746, 312–324. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2017.03.006
Dewey, J. F., and Casey, J. F. (2013). The sole of an ophiolite: the Ordovician Bay of Islands complex, Newfoundland. J. Geol. Soc. 170 (5), 715–722. doi:10.1144/jgs2013-017
Ding, B. Q., Pei, F. P., Wei, J. Y., Zhang, J. R., Guan, Z. C., Song, K., et al. (2024). Genesis of high-Al chromitites from Xiaosuihe peridotite (central Jilin Province, NE China): implication for initial subduction of the Paleo-Asian ocean. Lithos 482, 107686. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2024.107686
Fournier-Roy, F., Guilmette, C., Larson, K., Godet, A., Soret, M., van Staal, C., et al. (2024). Geochemistry and geochronology of the Bay of Islands metamorphic sole, Newfoundland, Canada: Protoliths and implications for subduction initiation. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 136 (1-2), 371–387. doi:10.1130/B36662.1
Freeman, L. C. (1979). Centrality in social networks conceptual clarification. Soc. Networds 1 (3), 215–239. doi:10.1016/0378-8733(78)90021-7
Fu, H. Z., Wang, M. H., and Ho, Y. S. (2013). Mapping of drinking water research: a bibliometric analysis of research output during 1992-2011. Sci. Total Environ. 443, 757–765. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.11.061
Gao, W., Chen, Y., Liu, Y., and Guo, H. c. (2015). Scientometric analysis of phosphorus research in eutrophic lakes. Scientometrics 102 (3), 1951–1964. doi:10.1007/s11192-014-1500-7
Gerya, T. V., Stern, R. J., Baes, M., Sobolev, S. V., and Whattam, S. A. (2015). Plate tectonics on the Earth triggered by plume-induced subduction initiation. Nature 527 (7577), 221–225. doi:10.1038/nature15752
Guilmette, C., Smit, M. A., van Hinsbergen, D. J. J., Gürer, D., Corfu, F., Charette, B., et al. (2018). Forced subduction initiation recorded in the sole and crust of the Semail Ophiolite of Oman. Nat. Geosci. 11 (9), 688–695. doi:10.1038/s41561-018-0209-2
Hickey-Vargas, R., Yogodzinski, G. M., Ishizuka, O., McCarthy, A., Bizimis, M., Kusano, Y., et al. (2018). Origin of depleted basalts during subduction initiation and early development of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana island arc: evidence from IODP expedition 351 site U1438, Amami-Sankaku basin. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 229, 85–111. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2018.03.007
Ishizuka, O., Hickey-Vargas, R., Arculus, R. J., Yogodzinski, G. M., Savov, I. P., Kusano, Y., et al. (2018). Age of Izu-Bonin-Mariana arc basement. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 481, 80–90. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.10.023
Ishizuka, O., Tani, K., Reagan, M. K., Kanayama, K., Umino, S., Harigane, Y., et al. (2011). The timescales of subduction initiation and subsequent evolution of an oceanic island arc. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 306 (3-4), 229–240. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.04.006
Kim, M. C., and Chen, C. M. (2015). A scientometric review of emerging trends and new developments in recommendation systems. Scientometrics 104 (1), 239–263. doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1595-5
Kim, M. C., Zhu, Y. J., and Chen, C. M. (2016). How are they different? A quantitative domain comparison of information visualization and data visualization (2000-2014). Scientometrics 107 (1), 123–165. doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1830-0
Kneller, E. A., and van Keken, P. E. (2007). Trench-parallel flow and seismic anisotropy in the Mariana and Andean subduction systems. Nature 450 (7173), 1222–1225. doi:10.1038/nature06429
Lallemand, S., and Arcay, D. (2021). Subduction initiation from the earliest stages to self-sustained subduction: insights from the analysis of 70 Cenozoic sites. Earth-Science Rev. 221, 103779. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103779
Li, H. Y., Taylor, R. N., Prytulak, J., Kirchenbaur, M., Shervais, J. W., Ryan, J. G., et al. (2019). Radiogenic isotopes document the start of subduction in the Western Pacific. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 518, 197–210. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2019.04.041
Lu, G., Zhao, L., Chen, L., Wan, B., and Wu, F. (2021). Reviewing subduction initiation and the origin of plate tectonics:What do we learn from present-day Earth? Earth Planet. Phys. 5 (2), 123–140. doi:10.26464/epp2021014
Marshall, M. (2024). Geology’s biggest mystery: when did plate tectonics start to reshape Earth? Nature 632 (8025), 490–492. doi:10.1038/d41586-024-02602-3
Maunder, B., Prytulak, J., Goes, S., and Reagan, M. (2020). Rapid subduction initiation and magmatism in the Western Pacific driven by internal vertical forces. Nat. Commun. 11 (1), 1874. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15737-4
McKenzie, D. P., and Parker, R. L. (1967). The North Pacific: an example of tectonics on a sphere. Nature 216 (5122), 1276–1280. doi:10.1038/2161276a0
Nasrabady, M., Shi, Y. R., Lustrino, M., and Rossetti, F. (2023). Geochemical and geochronological constraints on the origin of the Sabzevar ophiolites (NE Iran): forced far-field subduction initiation in the upper-plate of the Neo-Tethys subduction zone. Geochemistry 83 (2), 125962. doi:10.1016/j.chemer.2023.125962
Ning, W. B., Kusky, T., Wang, J. P., Wang, L., Deng, H., Polat, A., et al. (2020). From subduction initiation to arc–polarity reversal: life cycle of an Archean subduction zone from the Zunhua ophiolitic mélange, North China Craton. Precambrian Res. 350, 105868. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2020.105868
Ozbey, Z., Karslioglu, O., and Aysal, N. (2022). First evidence for the subduction initiation and boninitic magmatism from the Armutlu Peninsula (NW Turkey): geodynamic significance for the Cadomian magmatic arc system of the Gondwanan margin. Int. Geol. Rev. 64 (18), 2497–2521. doi:10.1080/00206814.2021.1986680
Pearce, J. A. (2003). Supra-subduction zone ophiolites: the search for modern analogues. Special Pap. Geol. Soc. Am. 373, 269–293. doi:10.1130/0-8137-2373-6.269
Pearce, J. A., and Reagan, M. K. (2019). Identification, classification, and interpretation of boninites from Anthropocene to Eoarchean using Si-Mg-Ti systematics. Geosphere 15 (4), 1008–1037. doi:10.1130/GES01661.1
Peng, H., and Leng, W. (2017). Progress in the study of subduction initiation. JUSTC 47 (2), 163–175. doi:10.3969/j.issn.0253-2778.2017.02.007
Qin, K., Hou, F. H., Du, Q. Z., Kai, L., Jingtao, Z., Panfeng, L., et al. (2025). Multi-channel seismic reflection study of tectonic-sedimentary features and subduction initiation in the middle Kyushu-Palau Ridge and adjacent basins. Geophys. Prospect. 73 (3), 752–762. doi:10.1111/1365-2478.13467
Reagan, M. K., Heaton, D. E., Schmitz, M. D., Pearce, J. A., Shervais, J. W., and Koppers, A. A. (2019). Forearc ages reveal extensive short-lived and rapid seafloor spreading following subduction initiation. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 506, 520–529. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2018.11.020
Reagan, M. K., Ishizuka, O., Stern, R. J., Kelley, K. A., Ohara, Y., Blichert-Toft, J., et al. (2010). Fore-arc basalts and subduction initiation in the Izu-Bonin-Mariana system. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 11 (3), Q03X12. doi:10.1029/2009GC002871
Reagan, M. K., Pearce, J. A., Petronotis, K., Almeev, R. R., Avery, A. J., Carvallo, C., et al. (2017). Subduction initiation and ophiolite crust: new insights from IODP drilling. Int. Geol. Rev. 59 (11), 1439–1450. doi:10.1080/00206814.2016.1276482
Schellart, W. P., Strak, V., Beniest, A., Duarte, J., and Rosas, F. (2023). Subduction invasion polarity switch from the Pacific to the Atlantic Ocean: a new geodynamic model of subduction initiation based on the Scotia Sea region. Earth-Science Rev. 236, 104277. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.104277
Shen, J., Dai, J. G., and Yang, K. (2021). Texture,lithofacies,age and emplacement mechanism of the metamorphic sole:Insights into oceanic subduction initiation. Chin. J. Geol. 56 (2), 533–559. doi:10.12017/dzkx.2021.028
Shen, J., Dai, J. G., Yang, K., Zhao, L., Zhang, W., Malaspina’s, N., et al. (2024). Coeval formation and exhumation of metamorphic sole and ophiolite in the Saga ophiolitic melange: insights into subduction initiation of the Neo-Tethys. J. Metamorph. Geol. 42 (6), 843–865. doi:10.1111/jmg.12776
Shervais, J. W., Reagan, M., Godard, M., Prytulak, J., Ryan, J. G., Pearce, J. A., et al. (2021). Magmatic response to subduction initiation, Part II: boninites and related rocks of the Izu-Bonin arc from IODP expedition 352. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 22 (1), e2020GC009093. doi:10.1029/2020GC009093
Shervais, J. W., Reagan, M., Haugen, E., Almeev, R. R., Pearce, J. A., Prytulak, J., et al. (2019). Magmatic response to subduction initiation: Part 1. Fore-arc basalts of the Izu-Bonin arc from IODP expedition 352. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 20 (1), 314–338. doi:10.1029/2018GC007731
Shuck, B., Van, A. H., Gulick, S. P. S., Gurnis, M., Sutherland, R., Stock, J., et al. (2021). Strike-slip enables subduction initiation beneath a failed rift: new seismic constraints from puysegur margin, New Zealand. Tectonics 40 (5), e2020TC006436. doi:10.1029/2020TC006436
Stern, R. J. (2004). Subduction initiation: spontaneous and induced. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 226 (3-4), 275–292. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.08.007
Stern, R. J., and Bloomer, S. H. (1992). Subduction zone infancy-examples from the eocene Izu-Bonin-Mariana and Jurassic California arcs. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 104 (12), 1621–1636. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1992)104<1621:SZIEFT>2.3.CO;2
Stern, R. J., and Gerya, T. (2018). Subduction initiation in nature and models: a review. Tectonophysics 746, 173–198. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2017.10.014
Stern, R. J., Reagan, M., Ishizuka, O., Ohara, Y., and Whattam, S. (2012). To understand subduction initiation, study forearc crust: to understand forearc crust, study ophiolites. Lithosphere 4 (6), 469–483. doi:10.1130/L183.1
Sun, B. L., Kaus, B. J. P., Yang, J. F., Lu, G., Wang, X., Wang, K., et al. (2021). Subduction polarity reversal triggered by oceanic plateau accretion: implications for induced subduction initiation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 48 (24), e2021GL095299. doi:10.1029/2021GL095299
Sun, W. D. (2019). The Magma Engine and subduction initiation. Acta Geochim. 38 (5), 611–612. doi:10.1007/s11631-019-00366-6
Tong, Z. Y., Ding, W. W., Wang, C. Y., and Li, C. F. (2024). Analogue modelling of subduction initiation: a review and perspectives. Int. Geol. Rev. 66 (11), 2123–2165. doi:10.1080/00206814.2023.2272273
Torro, L., Proenza, J. A., Melgarejo, J. C., Alfonso, P., Farré de Pablo, J., Colomer, J., et al. (2016). Mineralogy, geochemistry and sulfur isotope characterization of Cerro de Maimon (Dominican Republic), San Fernando and Antonio (Cuba) lower cretaceous VMS deposits: formation during subduction initiation of the proto-caribbean lithosphere within a fore-arc. Ore Geol. Rev. 72 (Part1), 794–817. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.09.017
van Hinsbergen, D. J. J., Steinberger, B., Guilmette, C., Maffione, M., Gürer, D., Peters, K., et al. (2021). A record of plume-induced plate rotation triggering subduction initiation. Nat. Geosci. 14 (8), 626–630. doi:10.1038/s41561-021-00780-7
Wakabayashi, J., and Dilek, Y. (2003). What constitutes \“emplacement\” of an ophiolite? Mechanisms and relationship to subduction initiation and formation of metamorphic soles. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 218 (1), 427–447. doi:10.1144/gsl.sp.2003.218.01.22
Wang, C. Y., Ding, W. W., Schellart, W. P., Tong, Z., Dong, C., Fang, Y., et al. (2024). Effects of along-trench asymmetric subduction initiation on plate rotation and trench migration: a laboratory modeling perspective. Tectonics 43 (1), e2023TC007941. doi:10.1029/2023TC007941
Wang, Q., Yang, Z. G., Yang, Y., Long, C., and Li, H. (2014). A bibliometric analysis of research on the risk of engineering nanomaterials during 1999-2012. Sci. Total Environ. 473, 483–489. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.066
Whattam, S. A. (2024). Subduction initiation ophiolites of the SW Pacific II: second-stage melts of boninites, high-Mg andesites, and related rocks. Int. Geol. Rev. 66 (12), 2167–2194. doi:10.1080/00206814.2023.2273374
Whattam, S. A., and Stern, R. J. (2011). The ‘subduction initiation rule’: a key for linking ophiolites, intra-oceanic forearcs, and subduction initiation. Contributions Mineralogy Petrology 162 (5), 1031–1045. doi:10.1007/s00410-011-0638-z
Whattam, S. A., and Stern, R. J. (2015). Late Cretaceous plume-induced subduction initiation along the southern margin of the Caribbean and NW South America: the first documented example with implications for the onset of plate tectonics. Gondwana Res. 27 (1), 38–63. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2014.07.011
Wilson, J. T. (1965). A new class of faults and their bearing on continental drift. Nature 207 (4995), 343–347. doi:10.1038/207343a0
Xiao, F. J., Li, C. Z., Sun, J. M., and Zhang, L. (2017). Knowledge domain and emerging trends in organic photovoltaic Technology: a scientometric review based on CiteSpace analysis. Front. Chem. 5 (Sep), 67. doi:10.3389/fchem.2017.00067
Xiao, Q. H., Li, T. D., Pan, G. T., Lu, S. N., Ding, X. Z., Deng, J. F., et al. (2016). Petrologic ideas for identification of ocean-continent transition: recognition of intra-oceanic arc and initial subduction. Geol. China 43 (3), 721–737. doi:10.12029/gc20160303
Xiao, W. J., Song, D. F., Zhang, J. E., Mao, Q. G., Ao, S. J., Han, C. M., et al. (2022). Anatomy of the structure and evolution of subduction zones and research prospects. Earth Sci. 47 (9), 3073–3106. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2022.380
Xie, P. (2015). Study of international anticancer research trends via co-word and document co-citation visualization analysis. Scientometrics 105 (1), 611–622. doi:10.1007/s11192-015-1689-0
Yan, L. L., and Zhang, K. J. (2020). Infant intra-oceanic arc magmatism due to initial subduction induced by oceanic plateau accretion: a case study of the Bangong Meso-Tethys, central Tibet, western China. Gondwana Res. 79, 110–124. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2019.08.008
Yang, G. X. (2022). Subduction initiation triggered by collision: a review based on examples and models. Earth-Science Rev. 232, 104129. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.104129
Yang, G. X. (2023). Mechanism,Geological record and significance of subduction initiation. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 45 (2), 194–207. doi:10.19814/j.jese.2022.09011
Yang, G. X., Li, Y. J., Si, G. H., Li, H., Tong, L. L., and Wang, Z. P. (2021). Discussion on time and mechanism of subduction initiation in the western central asian orogenic belt. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 43 (2), 244–261. doi:10.19814/j.jese.2020.11023
Yang, G. X., Li, Y. J., Tong, L. L., Wang, Z., Si, G., Lindagato, P., et al. (2022). Natural observations of subduction initiation: implications for the geodynamic evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean. Geosystems Geoenvironment 1 (1), 100009. doi:10.1016/j.geogeo.2021.10.004
Yu, D. J., Xu, Z. S., Pedrycz, W., and Wang, W. (2017). Information sciences 1968-2016: a retrospective analysis with text mining and bibliometric. Inf. Sci. 418, 619–634. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2017.08.031
Zeng, M., Zhang, X., Cao, H., Ettensohn, F. R., Cheng, W., and Lang, X. (2016). Late triassic initial subduction of the bangong-nujiang ocean beneath Qiangtang revealed: stratigraphic and geochronological evidence from gaize, Tibet. Basin Res. 28 (1), 147–157. doi:10.1111/bre.12105
Zeng, X. W., Wang, M., Li, H., Chi, P., and Shen, D. (2022). Early Jurassic intra-oceanic subduction initiation along the Bangong Meso-Tethys: geochemical and geochronological evidence from the Shiquanhe ophiolitic complex, western Tibet. Lithos 416, 106657. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2022.106657
Zhai, Q. G., Tang, Y., Hu, P. Y., Liu, Y., and Wang, W. (2024). Induced subduction initiation near an ultra-slow spreading ridge: a case study from the Beila ophiolite in the north-central Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Res. 135, 1–16. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2024.07.019
Zhang, Q. H., Chen, Y., Chen, S., Su, B., Li, Y. B., Shi, K. H., et al. (2024). Intra-Neo-Tethyan subduction initiation inferred from the Indawgyi mafic rocks in the Central Ophiolite Belt, Myanmar. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 136 (7-8), 2753–2766. doi:10.1130/B37076.1
Zhang, S., Mao, G. Z., Crittenden, J., Liu, X., and Du, H. (2017). Groundwater remediation from the past to the future: a bibliometric analysis. Water Res. 119, 114–125. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.029
Zhao, M. S., Chen, Y. X., and Zheng, Y. F. (2021). Geochemical evidence for forearc metasomatism of peridotite in the Xigaze ophiolite during subduction initiation in Neo-Tethyan Ocean, south to Tibet. Lithos 380, 105896. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105896
Zheng, R. G., Li, J. Y., Zhang, J., Xiao, W., and Wang, Q. (2020). Permian oceanic slab subduction in the southmost of Central Asian Orogenic Belt: evidence from adakite and high-Mg diorite in the southern Beishan. Lithos 358 (0), 105406. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105406
Zhong, X. Y., and Li, Z. H. (2019). Forced subduction initiation at passive continental margins: velocity-driven versus stress-driven. Geophys. Res. Lett. 46 (20), 11054–11064. doi:10.1029/2019GL084022
Zhong, X. Y., and Li, Z. H. (2022). Formation of metamorphic soles underlying ophiolites during subduction initiation: a systematic numerical study. J. Geophys. Research-Solid Earth 127 (1), e2021JB023431. doi:10.1029/2021JB023431
Zhou, M. F., Robinson, P. T., Su, B., Gao, J., Li, J., Yang, J., et al. (2015). “Subduction initiation” for the genesis of podiform chromite deposits. Acta Geol. Sin. Ed. 89 (A02), 122–123. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12308_73
Zhou, X., and Wada, I. (2021). Differentiating induced versus spontaneous subduction initiation using thermomechanical models and metamorphic soles. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 4632. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24896-x
Zhou, X. L., Zhong, H., Gerya, T. V., Stern, R. J., Xu, Z., and Zhang, J. (2018). Subduction initiation dynamics along a transform fault control trench curvature and ophiolite ages. Geology 46 (7), 607–610. doi:10.1130/G40154.1
Keywords: initial subduction, subduction zone, bibliometric analysis, citespace, VOSviewer
Citation: Zhang Y, Jiang N and Liu K (2025) An analytical study of initial subduction of the plate based on a bibliometric analysis method spanning 1995–2024. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1585148. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1585148
Received: 28 February 2025; Accepted: 30 April 2025;
Published: 22 May 2025.
Edited by:
Huan Li, Central South University, ChinaReviewed by:
Gaoxue Yang, Chang’an University, ChinaAnlin Ma, Nanjing University, China
Chuanyang Lei, Sichuan Provincial Geological Big Date Center, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Jiang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongqiang Zhang, Mjc2NDg1MjAyQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Yongqiang Zhang
Yongqiang Zhang Nan Jiang
Nan Jiang Kexin Liu
Kexin Liu