- College of Geosciences, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China
The Late Triassic Chang 7 Member lacustrine organic-rich shale in the Ordos Basin is the most significant source rock for the Mesozoic oil system in the basin. This study utilizes high-resolution source rock samples to systematically analyze the organic carbon isotopes and carbonate carbon-oxygen isotopes of the Chang 7 Member source rocks. The results indicate that the average δ13Ccarb values for the Chang 71 to Chang 73 sub-members are 0.17‰, 0.33‰, and −2.8‰, respectively, and the average δ18Ocarb values are −14.1‰, −14.3‰, and −16.0‰, respectively. The Chang 73 sub-member exhibits anomalously low δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values due to the influence of volcanic and hydrothermal activity. The carbon-oxygen isotopes, together with other element proxies, indicate that the Ordos Basin had semi-closed to semi-open hydrological conditions during the depositional periods of Chang 71 and Chang 72, with an overall warm and humid climate. The climate during the Chang 72 depositional period was relatively stable, while the Chang 71 period showed a trend towards increasing aridity. The lake during the Chang 7 depositional period had high paleo-productivity, with sedimentary organic matter being of mixed origin, primarily from aquatic organisms with some contribution from C3-type terrestrial higher plants. The findings of this study provide support and reference for research on paleoclimate, paleoenvironment, and organic matter enrichment mechanisms in the region.
1 Introduction
Paleolake sediments contain abundant and valuable records of environmental conditions, often recording local and regional responses to climate (Alonso-Zarza, 2003; Jin et al., 2004). Stable carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of lake sediments (including lacusrine authigenetic carbonate and organic matter) is one of the most widely used indicator, which can be used in paleohydrology (e.g., closed or open lake, the change of water level and the source of lake water) and paleolake hydrochemistry (e.g., salinity), paleoclimate (e.g., temperature, precipitation and their seasonal variation) and lake paleoproductivity (Wang and Zhang, 1999; Khadkikar et al., 2000; Nordt et al., 2002; Budd et al., 2002; Leng and Marshall, 2004; Retallack, 2005; Cai et al., 2009; Breecker et al., 2010; Hong and Lee, 2012; Li et al., 2013; Aref’ev et al., 2015). These paleoenvironmental and paleoclimate informations are important for understanding the abundance, biochemical degradation and preservation of organic matter in sedimentary rocks of petroliferous basins (Liu et al., 2001; 2004).
The Chang 7 lacustrine organic-rich shale of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation is the most important oil source of the Mesozoic petroleum system in the Ordos Basin, Central China (Qiu et al., 2014; Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2019b; Yuan et al., 2020). Previous studies on the stratigraphic sequence, lithofacies paleogeography, element and organic geochemistry characteristics of the Chang 7 Member have been carried out (Yang and Zhang, 2005; Qiu, 2011; Yang and Deng, 2013; Qiu et al., 2014; 2015; Yuan et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015; He et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2020), however, the characteristics of stable carbon and oxygen isotopes remain uninvestigated. Their analysis can provide potential new insights in comparison with existing studies. Therefore, it is necessary to systematically analyze the carbon and oxygen isotopic characteristics of the Chang 7 Membrer, further to reconstruct the local and regional paleoclimate during the deposition of the Chang 7 organic-rich shale and provide geochemical evidence for the correct understanding of the sedimentary evolution of the study area.
In this paper, a large number of high-resolution carbon and oxygen isotope data from bulk carbonates and organic matters in the Chang 7 Member lacustrine sediments are provided, and many data of DOPT, Corg:P, CIA and Al contents of the Chang 7 shale are collected from previously published literature (Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2020). We mainly attempt to study the stable carbon and oxygen characteristics and changes of paleoproductivity, paleoclimate and paleoenvironment during the Chang7 sedimentary period.
2 Geological setting
The Ordos Basin of central China (Figure 1) is a prolific petroliferous basin consisting of six tectonic units: Yimeng uplift, West margin thrust belt, Tianhuan depression, Yishan slope, Jinxi flexure belt, and Weibei uplift (Figure 1) (Yang and Deng, 2013; Qiu et al., 2014; Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2020). The basin formed on Paleozoic strata of the North China Craton (Figure 2) (Wan et al., 2013; Qiu et al., 2014; 2015). The tectonic evolution of the Ordos Basin during the Triassic was tied to the Indosinian Orogeny, which comprises two episodes: the Early Indosinian Orogeny corresponding with the end of Middle Triassic and the Late Triassic Late Indosinian Orogeny (Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2020). The Ordos Basin during Early-Middle Triassic time was part of the North China intracratonic depression (Qiu et al., 2014; 2015). By Late Triassic time, the Ordos Basin had evolved to an intracontinental foreland basin characterized by an asymmetric cross-section comprising of low-gradient northeastern and high-gradient southwestern flanks (Qiu et al., 2014; 2015). Rapid uplift of the Qinling Mountains bordering the basin to the south was accompanied by subsidence of the southern Ordos Basin coincident with the onset deposition of Chang 7 Member (Qiu et al., 2014; 2015; Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2020). Evidence of enhanced tectonic activity documented from the Chang 7 Member include inferred seismites (Li et al., 2008; Qiu, 2011; Xia et al., 2007; Yang et al., 2010), volcanic ash deposits (Qiu, 2011; Zhang et al., 2009; Yuan et al., 2019a), and mineral concentrations (e.g., pyrite veins, marcasite, gypsum, and manganese nodules) attributed to hydrothermal fluid movement (Qiu, 2011; Zhang et al., 2010; Yuan et al., 2017).
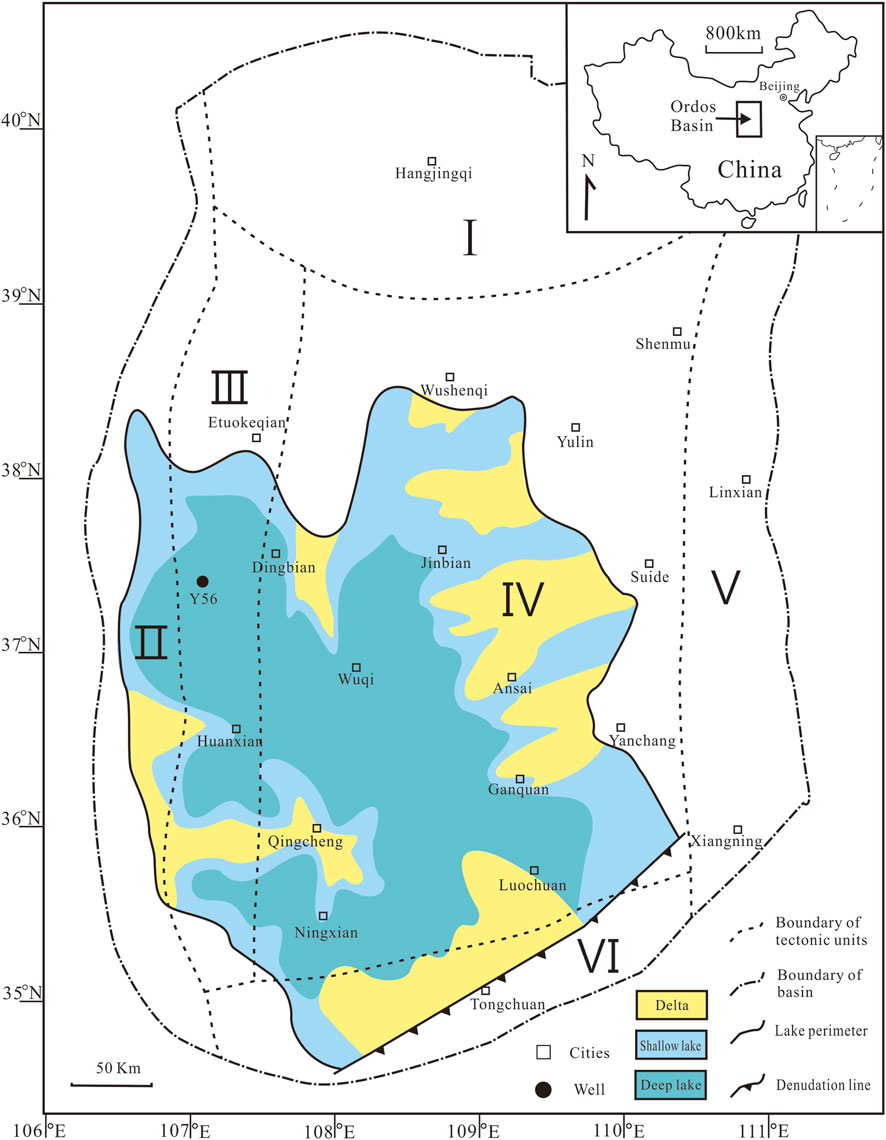
Figure 1. Location of the Ordos Basin, its tectonic division, and the location of sample well (after Yuan et al., 2017). I-Yimeng uplift; II-West margin thrust belts; III-Tianhuan depression; IV-Yishan slope; V-Jinxi flexure belts; VI-Weibei uplift.
The Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation, 1000–1300 m of terrigenous deposits (Qiu et al., 2015), comprises 10 members (Chang 10-Chang 1 from bottom to top) distinguished on the basis of marker beds, sedimentary cycles, and/or lithological association (Qiu et al., 2014; 2015). Peak lake level coincided with deposition of the Chang 7 Member (Yang and Deng, 2013), which is dominated by lacustrine and deltaic sedimentary facies (Yuan et al., 2015). The Chang 7, which includes three sub-members (Chang 71, Chang 72, and Chang 73), comprises 100–130 m of siltstone, mudstone, black shale, and tuff intervals (Figure 3). The organic-rich shale, the principal source of hydrocarbon source rock of the Mesozoic petroleum system of the Ordos Basin, is distributed over much of the southwest Yishan slope and southern portion of the Tianhuan depression (Figure 1), covering an area of more than 105 km2 (Qiu et al., 2015). The Chang 7 shale is strongly enriched in TOC content, mostly kerogens of type I or II1, indicating that the organic matter mainly came from the aquatic plants (Zhang et al., 2015).
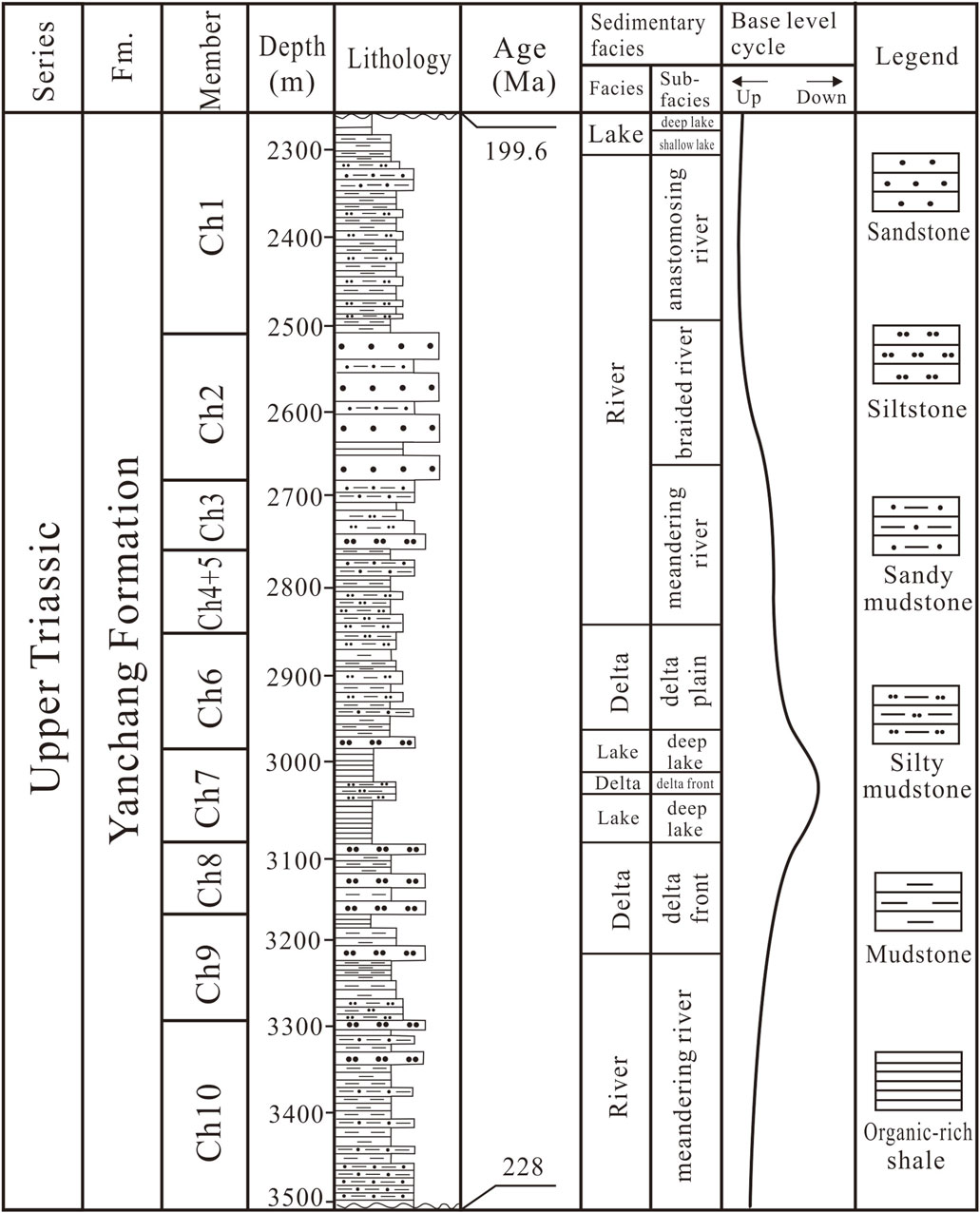
Figure 3. Integrated stratigraphic column of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin (after Yuan et al., 2017).
3 Materials and methods
Forty-eight organic-rich shale samples used in this study were collected from the Well Yan 56 core, which lies at the periphery of Ordos Basin (Figure 1), covering a thickness of ∼122 m (2956–3078 m), including 20 Chang 71 samples, 15 Chang 72 samples and 13 Chang 73 samples. Tuff intervals, pyrite veins and visible phosphate nodules were carefully avoided in the sampling. The total of 48 shale samples were powdered (<200 mesh) in an agate mortar.
The δ13C and δ18O of the bulk lacustrine carbonate in the samples were measured using an automated carbonate preparation device coupled to a Thermo Fisher MAT 253 isotope ratio mass spectrometer (IRMS) at the Analytical Laboratory of the Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology. CO2 gas liberated from the carbonate was extracted by reacting ground samples with dehydrated phosphoric acid in a vacuum. The results are presented using the delta notation referred to the VPDB standard. Repeated measurements of a homogenized sample yields a standard deviation of ±0.1‰ for δ13C and δ18O measurements. The δ13C of bulk organic matter in the samples were measured at the State Key Laboratory of Petroleum Resource and Prospecting, China University of Petroleum (Beijing). Approximately 100 mg of powder was gently leached using dilute HCl (hydrochloric acid) and rinsed with distilled water to remove inorganic carbon. After drying, the shale powders were analyzed using a Finnigan MAT 253 IRMS connecting with Flash 2000HT elemental analyzer. The results are presented using the delta notation referred to the VPDB standard. The analytical precision was better than 0.1‰.
The data of DOPT, Corg:P,CIA and Al contents of the Chang 7 shale are collected from publicly available scholarly articles (Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan et al., 2019a; Yuan et al., 2020). DOPT represents the ratio of pyrite Fe (based on total S) to total Fe, and Corg:P means the molar ratio of organic carbon to total phosphorus (Yuan et al., 2017). CIA = [Al2O3/(Al2O3 + CaO* + Na2O+ K2O) * 100] in molecular proportions, where CaO* represents CaO content of the silicate fraction (Nesbitt and Young, 1982).
4 Results
4.1 Carbon isotope values of bulk carbonate
The stable carbon isotope values of bulk carbonates (δ13Ccarb) in the Chang 7 Member shale are presented in Table 1. The δ13Ccarb values in Well Yan 56 vary between −5.7‰ and 4.5‰, with an average of −0.6‰ (n = 48). The δ13Ccarb values are relatively low and range from −5.7‰ to −0.9‰ (mean = −2.8‰) in the Chang 73 submember, showing decrease upward gradually to the middle (at ∼3051 m) and then followed by an opposite trend (Figure 4). In the Chang 72 submember, the δ13Ccarb values vary between −4.4‰ and 4.5‰ (mean = 0.3‰), higher than that in the Chang 73 submember. The values show a general upward-decreasing trend, interrupted by a sharp positive excursion to 4.5‰ at ∼3011 m. In the Chang 71 submember, the δ13Ccarb values change from −5.2‰ to 3.6‰ (mean = 0.2‰), showing twice obvious negative shifts at the bottom and middle.
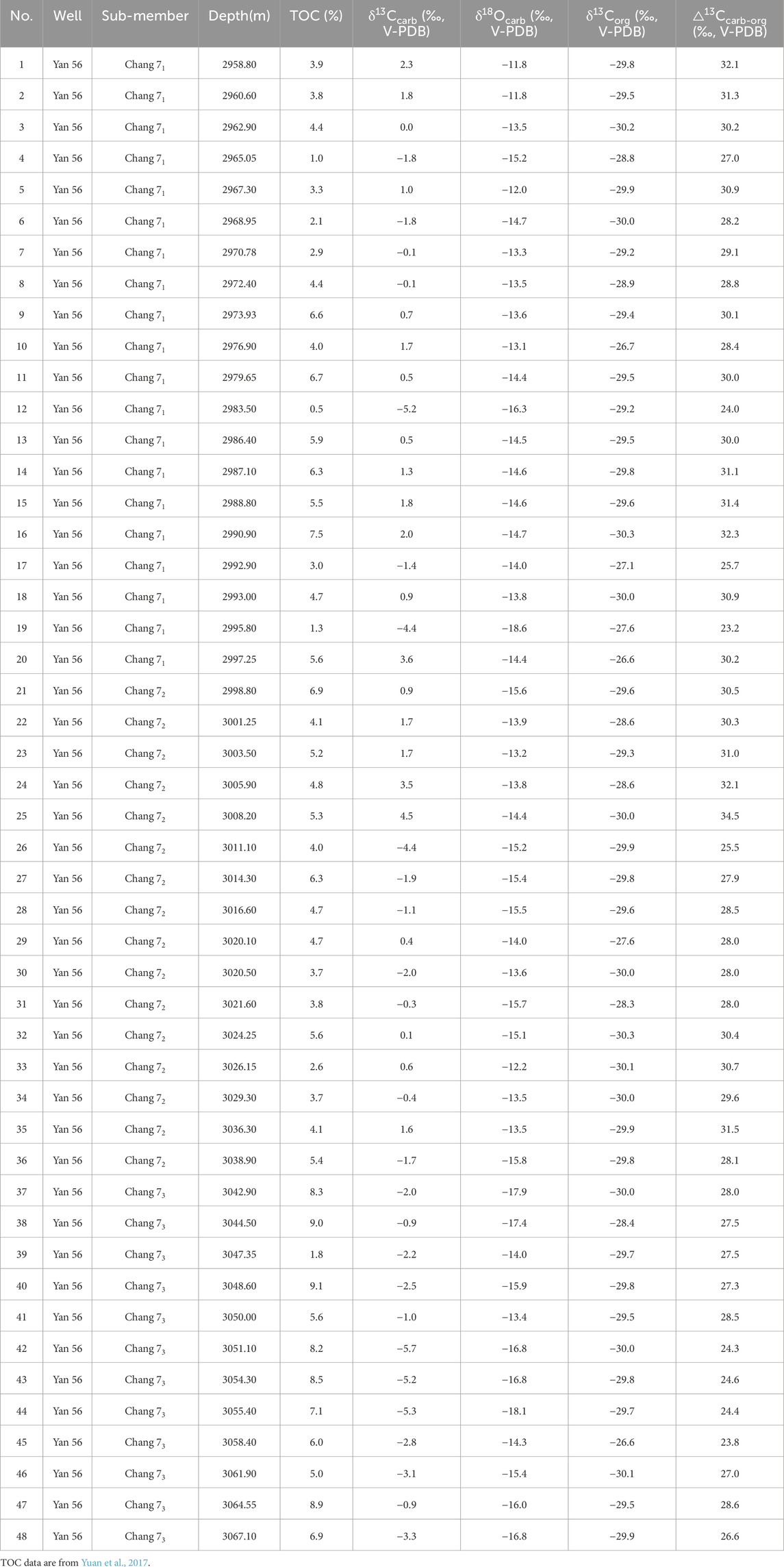
Table 1. Carbon and oxygen isotope values from bulk carbonates and organic matters in the Chang 7 source rocks of the Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin.
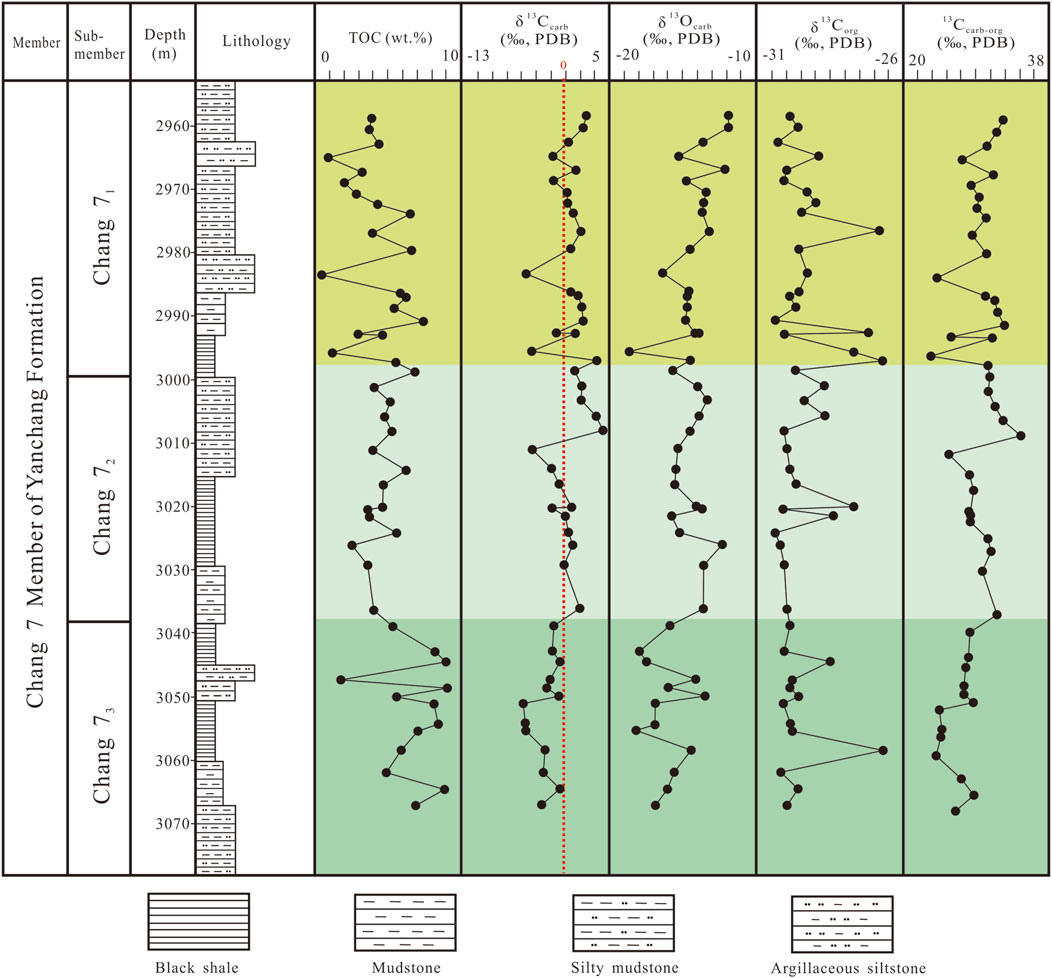
Figure 4. The δ13Ccarb, δ18Ocarb and δ13Corg records of carbonates and organic matter in the Chang 7 sediments for Well Yan 56, Ordos Basin. The data of TOC are from Yuan et al. (2017).
4.2 Oxygen isotope values of bulk carbonate
The stable oxygen isotope values of bulk carbonates (δ18Ocarb) in the Chang 7 Member shale are listed in Table 1. The δ18Ocarb values of the Chang 7 Member in Well Yan 56 range from −18.6‰ to −11.8‰, with an average of −14.7‰. Specifically, the δ18Ocarb values change from −18.1‰ to −13.4‰ (mean = −16.0‰), from −15.7‰ to −12.2‰ (mean = −14.3‰), and from −18.6‰ to −11.8‰ (mean = −14.1‰) in the Chang 73, Chang 72, Chang 71 submember, respectively. Overall, there is a trend of gradual increase from the bottom to the top (Figure 4). Throughout the Chang 7 Member, the variation trend of δ18Ocarb values shows some similarity with that of δ13Ccarb, with a moderate positive correlation between the two.
4.3 Bulk organic carbon isotope
The stable organic carbon isotope values of bulk rock (δ13Corg) in the Chang 7 Member shale are showed in Table 1. The δ13Corg values of the Chang 7 member in Well Yan 56 range from −30.3‰ to −26.6‰, with an average of −29.3‰. Specifically, the δ13Corg values vary from −30.1‰ to −26.6‰ (mean = −29.4‰), from −30.3‰ to −27.6‰ (mean = −29.5‰), and from −30.3‰ to −26.6‰ (mean = −29.4‰) in the Chang 73, Chang 72, Chang 71 submember, respectively. There is no significant difference among the three sub-members. Overall, most samples have δ13Corg values around −29‰, with distinct higher values observed in the middle of the Chang 73 sub-member, the middle of the Chang 72 sub-member, and the bottom and middle of the Chang 71 sub-member (Figure 4).
4.4 △13Ccarb-org
The △13Ccarb-org represents the difference between the carbon isotope values of carbonate minerals and organic matter (δ13Ccarb - δ13Corg). It primarily reflects the degree of carbon isotope fractionation between the organic and inorganic carbon reservoirs (Wang et al., 2014). A larger △13Ccarb-org indicates a stronger degree of fractionation. In the Chang 7 Member of Well Yan 56, the △13Ccarb-org values range from 23.2‰ to 34.5‰, with an average of 28.7‰. Specifically, the △13Ccarb-org values range from 23.8‰ to 28.6‰ (mean = 26.6‰), from 25.5‰ to 34.5‰ (mean = 29.8‰), and from 23.2‰ to 32.3‰ (mean = 29.2‰) in the Chang 73, Chang 72, Chang 71 submember, respectively. The lower △13Ccarb-org value in the Chang 73 sub-member is mainly related to the lower δ13Ccarb values during this period. Throughout the Chang 7 Member, the trend of △13Ccarb-org shows significant similarity to the δ13Ccarb values (Figure 4).
5 Discussion
5.1 Impact of volcanic and hydrothermal activity on carbon and oxygen isotope values
From the preceding data analysis, it is evident that the average δ13Ccarb values for the Chang 71 to Chang 73 sub-members in Well Yan 56 are 0.17‰, 0.33‰, and −2.8‰, respectively, while the average δ18Ocarb values are −14.1‰, −14.3‰, and −16.0‰. The Chang 73 sub-member exhibits relatively lower δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values compared to the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members. The carbon and oxygen isotope values of terrestrial or lacustrine carbonate rocks are primarily influenced by their sources and isotopic fractionation. Anomalies in these isotope values over short periods often reflect special geological events or changes in climatic conditions. Previous studies have shown that intense volcanic and hydrothermal activities, evidenced by diagnostic minerals (pyrite veins, marcasite, gypsum, siliceous rock, etc.) and element indicators (Al/(Fe + Mn), Al/(Al + Fe + Mn)), occurred in the Ordos Basin during the depositional period of the Chang 7 member of the Yanchang Formation, especially during the Chang 73 sub-member (Zhang et al., 2009; 2010; Qiu, 2011; Yuan et al., 2017; Yuan, 2018; Yuan et al., 2019b; Yuan et al., 2020; Yuan et al., 2022). Core observations from Well Yan 56 revealed the presence of tuff (altered volcanic ash sediments) indicative of volcanic activity and carbonate veins indicative of hydrothermal activity in the Chang 73 sub-member (Figure 5). Therefore, the anomalously low δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values in the Chang 73 sub-member may be influenced by volcanic and hydrothermal activities. Volcanic and hydrothermal activities release large amounts of CO2, which typically has a lower δ13C value (close to −5‰ to −8‰), significantly lower than the δ13C values of seawater (about 0‰) and lake water. When this CO2 dissolves in water and participates in the formation of carbonate rocks, it significantly reduces the δ13C value of the carbonate rocks. Hydrothermal fluids also generally have lower δ18O values, and under high-temperature conditions, the fractionation effect of oxygen isotopes (with heavy oxygen isotopes being largely lost in high-temperature environments) can also lead to a decrease in the δ18O value of carbonate rocks (Veizer et al., 1999; Chiodini et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2013). For example, studies in southern Italy have shown that volcanic and hydrothermal activities significantly reduce the δ13C values of carbonate rocks, with the lowest values reaching −10‰; research in Yellowstone National Park in the United States indicates that hydrothermal activities reduce the δ18O values of carbonate rocks by about 3‰–5‰ (Veizer et al., 1999; Chiodini et al., 2000). Our preliminary studies also found that the carbon and oxygen isotopes of hydrothermal carbonate laminae in the Chang 7 source rocks of Well Wu 100 in the Ordos Basin exhibit anomalously low values, with δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values of −8.2‰ and −20.0‰, respectively (Yuan, 2018).

Figure 5. Core photographs from the Chang 73 sub-member of Yan 56 Well in the Ordos Basin. (a) Tuff, Chang 73, 3044.67 m; (b) Carbonate veins in the source rock, Chang 73, 3065.24 m (after Yuan et al., 2022).
In summary, the intense volcanic and hydrothermal activities during the depositional period of the Chang 73 sub-member in the Yanchang Formation of the Ordos Basin caused the anomalously low carbon and oxygen isotope values during this period. Therefore, in subsequent analyses of other aspects, we primarily utilize the carbonate carbon and oxygen isotope data from the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members.
5.2 Is the lake open or closed?
Previous studies have analyzed the dynamic background and the bottom morphology of the lake basin during the Late Triassic Yanchang Formation depositional period in the Ordos Basin. These studies revealed that the southwestern part of the basin was relatively steeply inclined, while the northeastern part was relatively gentle, as a whole exhibited a northwest-southeast orientation, opening towards the southeast, roughly parallel to the Qinling orogenic belt (Qiu, 2011). This suggests that the lake basin during this period had a certain degree of openness. The correlation between the δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb of lacustrine carbonate minerals can also be used to identify whether a lake was open or closed (Talbot, 1990; Li and Ku, 1997; Leng and Marshall, 2004; Li et al., 2013; Hou et al., 2014). In closed lake systems, intense evaporation and/or prolonged water retention can lead to the enrichment of heavy oxygen isotopes (18O) in the lake water, while the equilibrium exchange between long-retained lake water and atmospheric CO2 can increase the δ13C value of dissolved inorganic carbon in the lake water (Leng and Marshall, 2004; Hou et al., 2014). Generally, a high correlation between δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values in lacustrine carbonate minerals is widely used as a paleohydrological indicator for closed lake systems. According to Talbot (1990), the square of the correlation coefficient (R2) between δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb in closed lakes is typically greater than 0.5, whereas open lakes show weaker correlations and a smaller range of δ18Ocarb values (Talbot, 1990; Li and Ku, 1997; Valero Garcés et al., 1997; Alonso-Zarza and Calvo, 2000; Li et al., 2013). The correlation between δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values in lacustrine carbonate minerals from the Chang 7 Member of the Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin is shown in Figure 5. The samples from Well Yan 56 reveal two characteristics. Firstly, there is a weak to moderate correlation between δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values (R2 = 0.31, p-value <0.05); Secondly, the δ18Ocarb values of the carbonate minerals are relatively dispersed (−18.6‰ to −11.8‰). These characteristics suggest that the hydrological conditions of the lake during the Late Triassic Chang 7 depositional period in the Ordos Basin were likely semi-open to semi-closed, which aligns with the findings of Qiu (2011). Furthermore, the correlation between δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values in the Chang 72 sub-member is generally poor (R2 values distributed around 0.16, p-value <0.05), while the correlation in the Chang 71 sub-member is better (R2 = 0.46, p-value <0.05) (Figure 6). This indicates that the lake during the Chang 71 depositional period was relatively more closed, possibly due to the smaller lake area and shallower water depth during this time (Yuan, 2018).
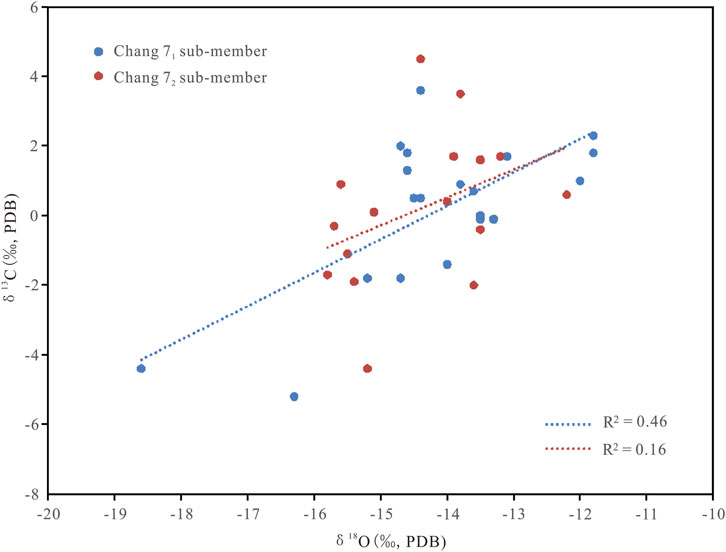
Figure 6. Correlation between δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb values of the Chang 7 carbonates in Well Yan 56, Ordos Basin.
5.3 Source of organic matter
The carbon isotope values of organic matter in sediments or sedimentary rocks are primarily influenced by the source of the organic matter, the depositional environment, and the degree of thermal evolution (Yu et al., 2001). During the Late Triassic Chang 7 depositional period in the Ordos Basin, the water bodies were mainly freshwater, and the overall thermal evolution degree of the Chang 7 source rocks did not vary significantly (with an average vitrinite reflectance of about 8.5%) (Yuan, 2018). Therefore, the δ13Corg values of the shale in the Chang 7 section of Well Yan 56 are closely related to the source of the organic matter. Previous studies have shown that the δ13Corg values of aquatic organic matter (Type I) are typically less than −28‰, those of mixed organic matter (Type II) are usually between −28‰ and −25‰, and those of terrestrial higher plant organic matter (Type III) are generally above −26‰ (Schoell, 1984). In subsequent research, Huang (1988) proposed a more detailed classification standard: Type I organic matter has δ13Corg values < −30‰, Type II1 organic matter has δ13Corg values between −30‰ and −28‰, Type II2 organic matter has δ13Corg values between −28‰ and −26‰, and Type III organic matter has δ13Corg values > −26‰. The δ13Corg values of the source rock in the Chang 7 section of Well Yan 56 in the Ordos Basin range from −30.3‰ to −26.6‰, with an average of −29.3‰. As can be seen from Figure 7, the organic matter types in the Chang 7 section of the Yanchang Formation in the study area are mainly Type I and Type II1, indicating that the organic matter during the Chang 7 depositional period was primarily aquatic, with some contribution from terrestrial higher plant organic matter. This is consistent with previous research findings (Yang and Zhang, 2005; Zhang et al., 2008; 2015).
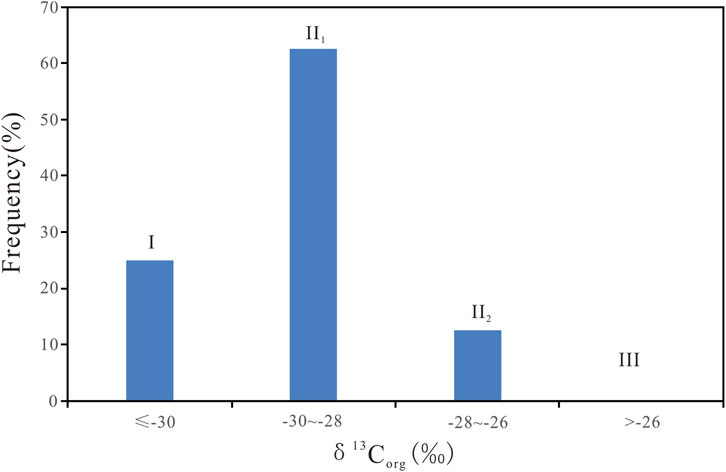
Figure 7. Frequency distribution diagram of organic carbon isotopes in the Chang 7 Member of Well Yan 56, Ordos Basin.
Terrestrial plants can be classified into three major categories: C3, C4, and CAM plants, based on the number of carbon atoms in the primary products of photosynthesis (Liu et al., 2005). Due to significant differences in photosynthetic pathways, leaf structure, photorespiration, ecological adaptability, water use efficiency, and photosynthetic efficiency between C3 and C4 plants, their living environments and carbon isotope compositions also differ (Liu et al., 2005). C3 plants have lower photosynthetic efficiency and lower water use efficiency, typically thriving in warm and humid environments, with carbon isotope compositions ranging from −22‰ to −34‰, averaging −27‰ (Liu et al., 2005). In contrast, C4 plants exhibit higher photosynthetic efficiency and higher water use efficiency, usually found in hot and arid environments, with carbon isotope compositions ranging from −9‰ to −19‰, averaging −13‰ (Liu et al., 2005). The δ13Corg values from the Chang 7 section of Well Yan 56 indicate that the terrestrial plants contributing to the sedimentary organic matter during that period were likely C3 plants. This further suggests that the climate conditions at that time were probably warm and humid, which aligns with the findings from paleomagnetic studies, pollen analysis, and elemental indicators (Yuan et al., 2019b).
5.4 Lake paleoproductivity
The carbon isotopic composition of lacustrine carbonate rocks is primarily controlled by the carbon isotopic fractionation during carbonate formation and the carbon isotopic composition of dissolved inorganic carbon (DIC) in the lake water (Chen et al., 2010). The carbon isotopic composition of lake water DIC is influenced by various factors, including the carbon isotopic composition of inflowing lake water, CO2 exchange between the atmosphere and lake water DIC, the magnitude of lake palaeoproductivity, and the degradation of organic matter (Chen et al., 2010). However, significant positive shifts in the δ13C values of freshwater lacustrine carbonate rocks can only be attributed to the intense degradation of sedimentary organic matter by methanogenic bacteria during the diagenetic stage and the increase in lake palaeoproductivity (Zhang et al., 2013). Among these, the increase in δ13C values caused by the degradation of sedimentary organic matter by methanogenic bacteria is quite significant, often showing a positive shift of >4‰ (Garzione et al., 2004). In the study area, except for one sample from the Chang 72 sub-member (4.5‰), the δ13Ccarb values in Well Yan 56 are mostly below 4‰, indicating that the variation in δ13Ccarb values is not influenced by methanogenic bacteria. Redox conditions have been demonstrated to exert a significant influence on isotopic signatures, owing to the capacity of redox conditions to modify the isotopic fractionation of carbon, predominantly through the process of bacterial sulfate reduction. DOPT and Corg:P suggest that the water column during the Chang 71 and Chang 72 depositional period was dominately oxic-suboxic (Figure 8), suggesting that redox conditions had a limited influence on isotopic fractionation during this period. So, the δ13Ccarb values of Chang 7 samples may be closely related to lake palaeoproductivity. When lake palaeoproductivity is high, aquatic organisms thrive and preferentially absorb 12C from the DIC in the water through photosynthesis, leading to a relative increase in the 13C content in the inorganic carbon pool (Liu, 1998). This increases the degree of carbon isotopic fractionation between the inorganic carbon pool and organic matter, thereby increasing the δ13Ccarb and △13Ccarb-org values. Therefore, the δ13Ccarb and △13Ccarb-org values can be used to analyze changes in lake palaeoproductivity.
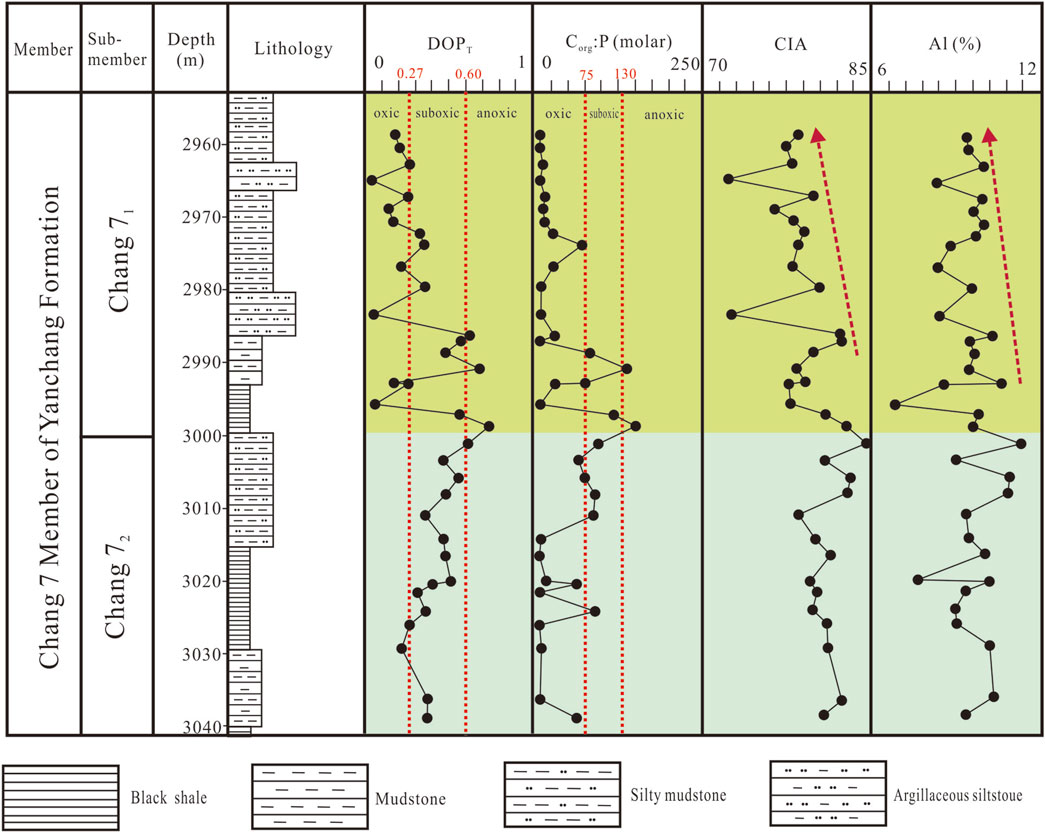
Figure 8. Vertical variation of redox and paleoclimate indicators in Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members of Well Yan 56. The data of DOPT and Corg:P are from Yuan et al. (2017). The data of CIA and Al are from Yuan et al. (2019a) and Yuan et al. (2020), respectively.
The mean δ13Ccarb values for the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members in Well Yan 56 are 0.17‰ and 0.33‰, respectively, and the mean △13Ccarb-org values are 29.2‰ and 29.8‰, respectively, indicating that the lake palaeoproductivity during the Chang 72 depositional period was generally relatively high. From the vertical changes in δ13Ccarb and △13Ccarb-org values (Figure 4), the trends of both are very consistent, indicating that the palaeoproductivity of the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members had periodic fluctuations. In the Chang 72 sub-member, two obvious cycles from large to small can be seen, and the δ13Ccarb and △13Ccarb-org values in the upper cycle of the Chang 72 sub-member are larger than those in the lower cycle (Figure 4), indicating that the late Chang 72 depositional period had higher lake palaeoproductivity. The lake palaeoproductivity in the Chang 71 sub-member shows two cycles from large to small and then to large in the middle and lower parts, while in the upper part, it shows a gradually increasing trend (Figure 4).
In addition, as can be seen from Figure 9, except for the Chang 73 sub-member, which is affected by volcanic and hydrothermal activity, the TOC content in the Chang 7 Member of Well Yan 56 in the Ordos Basin has a good positive correlation with the δ13Ccarb and △13Ccarb-org values, indicating that the enrichment of organic matter during the Chang 71 and Chang 72 depositional periods in the Ordos Basin was mainly controlled by lake palaeoproductivity. This can provide support for studying the enrichment of sedimentary organic matter or the formation of source rocks during this period.
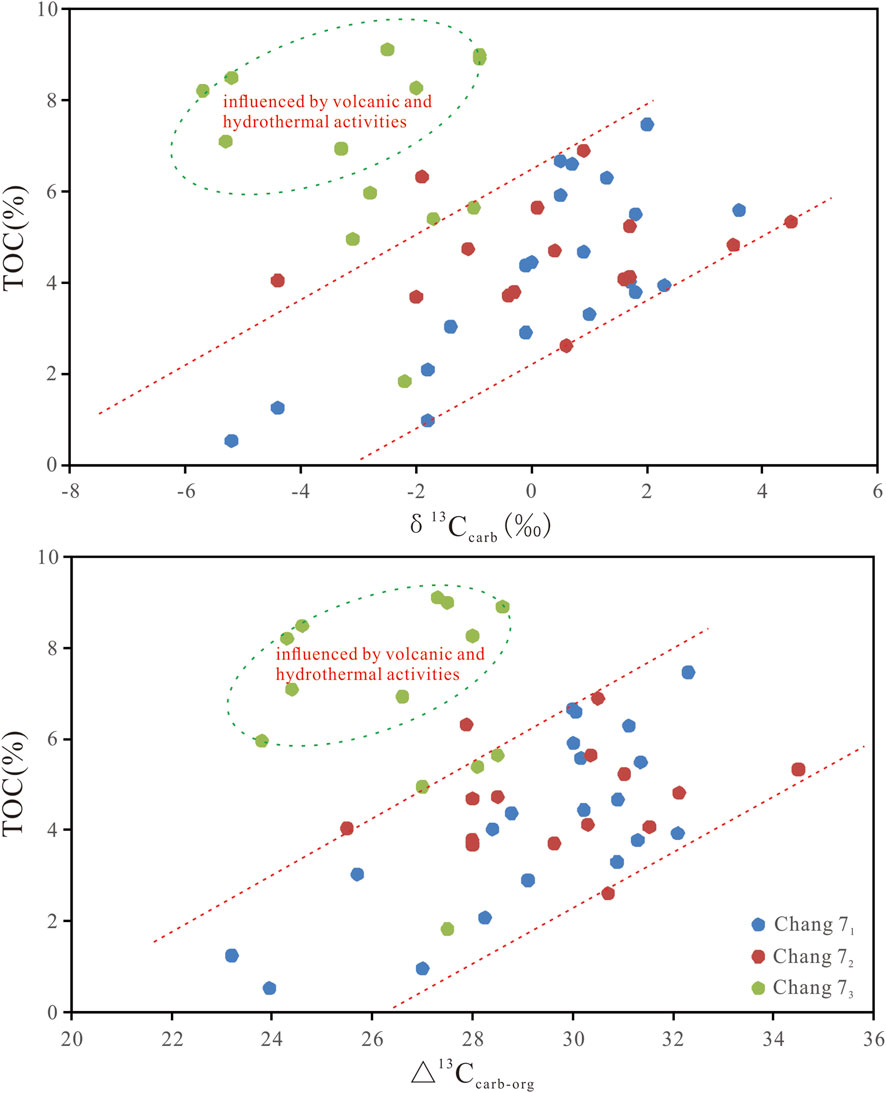
Figure 9. Relationship diagram of TOC content with δ13Ccarb and △13Ccarb-org values in the Chang 7 Member of Well Yan 56, Ordos Basin.
5.5 Paleoclimate
The oxygen isotope composition of lacustrine carbonates is closely related to the oxygen isotope composition of dissolved oxygen in the water body at the time of carbonate formation. The oxygen isotope composition of the water body, in turn, is influenced by various factors such as the oxygen isotope composition of atmospheric precipitation and inflow runoff, evaporation intensity, and hydrological conditions of the lake (Chen et al., 2010). Therefore, the oxygen isotopes in lacustrine carbonates can often be used to qualitatively indicate paleoclimate information from the time of their formation. The size of the lake area, whether the lake is open or closed, the residence time of lake water, and the intensity of evaporation are the most important factors controlling the oxygen isotope composition of lake water (Liu, 1998). During the Chang 7 depositional period, the Ordos Basin was a large lake (Qiu, 2011). Even during the depositional periods of the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members, when the hydrology was semi-closed to semi-open, the residence time of the lake water would still be relatively long, and the δ18O of the lake water was mainly influenced by the precipitation/evaporation ratio (P/E) (Leng and Marshall, 2004). Therefore, δ18Ocarb can, to some extent, indicate the wet and dry changes in the lake area. Enriched δ18O signatures (positive values) in climate archives typically reflect aridification, whereas depleted δ18O (negative values) correlates with increased humidity (Leng and Marshall, 2004).
The mean δ18Ocarb values for the Chang 71 and Chang 72 sub-members in the Yanchang Formation of Well Yan 56 in the Ordos Basin are −14.1‰ and −14.3‰, respectively, characterized by negative excursions, indicating that the overall climatic conditions during these two depositional periods were both humid, which aligns with the findings from paleomagnetic studies, pollen analysis, and C-value (Yuan et al., 2019b). From the vertical variation of δ18Ocarb values in Well Yan 56 (Figure 4), the δ18Ocarb values during the depositional period of the Chang 72 sub-member show two cycles of first increasing and then decreasing, indicating periodic changes in climate during this period. In contrast, the δ18Ocarb values during the depositional period of the Chang 71 sub-member show an overall increasing trend from bottom to top, indicating a gradual drying trend in the climate during this period. In addition, both the CIA (chemical index of alteration) values and Al contents of the Chang 71 samples exhibit a consistent downward trend from the base to the top of the section, indicating a progressive decline in chemical weathering intensity over time (Figure 8). The lithology of the Chang 71 sub-member also coarsens from bottom to top (Figure 4), and from the Chang 72 to the Chang 71 depositional period, the lake underwent a gradual shrinking process (Yuan, 2018), which aligns well with the climatic changes observed during this period.
6 Conclusion
1. The average values of δ13Ccarb in the Chang 71-Chang 73 sub-sections of Well Yan 56 in the Ordos Basin are 0.17‰, 0.33‰, and −2.8‰, respectively, and the average values of δ18Ocarb are −14.1‰, −14.3‰, and −16.0‰, respectively. The Chang 73 sub-section exhibits anomalously low values of δ13Ccarb and δ18Ocarb due to the influence of volcanic and hydrothermal activity.
2. During the depositional periods of Chang 71 and Chang 72, the Ordos Basin had semi-closed to semi-open hydrological conditions. The overall climate during these periods was warm and humid supported by carbon-oxygen isotopes and other element proxies (CIA and Al), with relatively stable climatic conditions during the Chang 72 depositional period, while the Chang 71 depositional period showed a gradual trend towards drier conditions.
3. The lake palaeoproductivity during the Chang 7 depositional period in the Ordos Basin was relatively high. The sedimentary organic matter was of mixed origin, primarily from aquatic organisms, with some contribution from C3-type terrestrial higher plants.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42102125).
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Associate Professor Wei Yuan for his assistance during the research process.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Alonso-Zarza, A. M. (2003). Palaeoenvironmental significance of palustrine carbonates and calcretes in the geological record. Earth-Science Rev. 60, 261–298. doi:10.1016/s0012-8252(02)00106-x
Alonso-Zarza, A. M., and Calvo, J. P. (2000). Palustrine sedimentation in an episodically subsiding basin: the Miocene of the northern Teruel graben (spain). Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 160, 1–21. doi:10.1016/s0031-0182(00)00041-9
Aref’ev, M. P., Kuleshov, V. N., and Pokrovskii, B. G. (2015). Carbon and oxygen isotope composition in upper permian-lower Triassic terrestrial carbonates of the east european platform: a global ecological crisis against the background of an unstable climate. Dokl. Earth Sci. 460, 11–15. doi:10.1134/s1028334x15010109
Breecker, D. O., Sharp, Z. D., and McFadden, L. D. (2010). “Atmospheric CO2 concentrations during ancient greenhouse climates were similar to those predicted for A.D. 2100,” in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 576–580. doi:10.1073/pnas.0902323106
Budd, D. A., Pack, S. M., and Fogel, M. L. (2002). The destruction of paleoclimatic isotopic signals in Pleistocene carbonate soil nodules of Western Australia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 188, 249–273. doi:10.1016/s0031-0182(02)00588-6
Cai, G. Q., Guo, F., Liu, X. T., and Sui, S. L. (2009). Carbon and oxygen isotope characteristics and palaeoenvironmental implications of lacustrine carbonate rocks from the shahejie formation in the dongying sag. Earth Environ. 37 (4), 347–354. doi:10.14050/j.cnki.1672-9250.2009.04.003
Chen, G., Zhu, Z. J., and Zhou, B. (2010). Advances in research into carbon and oxygen isotopes of lacustrine carbonate. Sichuan Geol. J. 30 (1), 75–78. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2010.01.020
Chiodini, G., Allard, P., Caliro, S., and Parello, F. (2000). 18O exchange between steam and carbon dioxide in volcanic and hydrothermal gases: implications for the source of water. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 64, 2479–2488. doi:10.1016/s0016-7037(99)00445-7
Garzione, C. N., Dettman, D. L., and Horton, B. K. (2004). Carbonate oxygen isotope paleoaltimetry: evaluating the effect of diagenesis on paleoelevation estimates for the Tibetan plateau. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 212 (1-2), 119–140. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2004.05.020
He, C., Ji, L. M., Wu, Y. D., Su, A., and Zhang, M. Z. (2016). Characteristics of hydrothermal sedimentation process in the yanchang formation, south ordos basin, China: evidence from element geochemistry. Sediment. Geol. 345, 33–41. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.09.001
Hong, S. K., and Lee, Y. I. (2012). Evaluation of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations during the Cretaceous. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 327-328, 23–28. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.01.014
Hou, Z. F., Li, J. J., Song, C. H., Zhang, J., Hui, Z. C., Chen, S. Y., et al. (2014). Understanding Miocene climate evolution in northeastern Tibet: stable carbon and oxygen isotope records from the Western tianshui basin, China. J. Earth Sci. 25 (2), 357–365. doi:10.1007/s12583-014-0416-8
Huang, J. Z. (1988). Classification criteria for stable carbon isotopes of kerogen. Geol. Geochem. 16 (3), 66–68.
Jin, Z. D., Wang, S. M., Shen, J., and Song, J. F. (2004). Watershed chemical weathering and its response to climate events in daihai area during Holocene. Geochimica 33 (1), 29–36. doi:10.19700/j.0379-1726.2004.01.004
Khadkikar, A. S., Chamyal, L. S., and Ramesh, R. (2000). The character and genesis of calcrete in late Quaternary alluvial deposits, Gujarat, western India, and its bearing on the interpretation of ancient climates. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 162, 239–261. doi:10.1016/s0031-0182(00)00130-9
Leng, M. J., and Marshall, J. D. (2004). Palaeoclimate interpretation of stable isotope data from lake sediment archives. Quat. Sci. Rev. 23, 811–831. doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2003.06.012
Li, H. C., and Ku, T. L. (1997). δ13C - δ18O covariance as a paleohydrological indicator for closed basin lakes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 133, 69–80. doi:10.1016/s0031-0182(96)00153-8
Li, Y. H., Liu, C. Y., and Wang, X. J. (2008). Discovery and significance of seismites in Late Triassic yanchang formation of ordos basin. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 26 (5), 772–778. doi:10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2008.05.004
Li, X. H., Xu, W. L., Liu, W. H., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., et al. (2013). Climatic and environmental indications of carbon and oxygen isotopes from the Lower Cretaceous calcrete and lacustrine carbonates in southeast and northwest China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 385, 171–189. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.03.011
Li, D. L., Li, R. X., Zhu, Z. W., Wu, X. L., Zhao, B. S., Chen, J. H., et al. (2017). Rare earth elements geochemistry characteristics and their geological implications of lacustrine oil shale from chang 7 oil layer in southern ordos basin, China. Geol. J. 52 (S1), 119–131. doi:10.1002/gj.2980
Liu, C. L. (1998). Carbon and oxygen isotopic compositions of lacustrine carbonates of the shahejie formation in the dongying depression and their paleolimnological significance. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 16 (3), 109–114. doi:10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.1998.03.019
Liu, C. L., Zhao, Q. H., and Wang, P. X. (2001). Correlation between carbon and oxygen isotope ratios of lacustrine carbonates and types of oil-producing paleo-lakes. Geoscience 30 (4), 363–367. doi:10.19700/j.0379-1726.2001.04.009
Liu, C. L., Fursich, F. T., Bai, Y., Yang, X. Q., and Li, G. Q. (2004). Palaeogene environmental changes deduced from stable isotopic data from bulk carbonates in the sanshui basin, south China. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 22 (1), 36–40. doi:10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2004.01.006
Liu, Q., Gu, Z. Y., Liu, J. Q., and You, H. T. (2005). Bulk organic carbon isotope records of huguangyan maar Lake, southeastern China and its paleoclimatic and paleoenvironmental significance of sediments since 62 kaBP. Mar. Geol. and Quat. Geol. 25 (2), 115–125. doi:10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2005.02.018
Nesbitt, H. W., and Young, G. M. (1982). Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 299, 715–717. doi:10.1038/299715a0
Nordt, L., Atchley, S., and Dworkin, S. (2002). Paleosol barometer indicates extreme fluctuations in atmospheric CO2 across the cretaceous-tertiary boundary. Geology 30, 703–706. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0703:pbiefi>2.0.co;2
Qiu, X. W. (2011). Characteristics and dynamic settings of yanchang period hydrocarbon-rich depression in ordos basin, China. Xi’an, China: Northwestern University. Ph.D. Dissertation.
Qiu, X. W., Liu, C. Y., Mao, G. Z., Deng, Y., Wang, F. F., and Wang, J. Q. (2014). Late Triassic tuff intervals in the ordos basin, central China: their depositional, petrographic, geochemical characteristics and regional implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 80, 148–160. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.11.004
Qiu, X. W., Liu, C. Y., Mao, G. Z., Deng, Y., Wang, F. F., and Wang, J. Q. (2015). Major, trace and platinum-group element geochemistry of the Upper Triassic nonmarine hot shales in the ordos Basin, Central China. Appl. Geochem. 53, 42–52. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.028
Retallack, G. J. (2005). Pedogenic carbonate proxies for amount and seasonality of precipitation in paleosols. Geology 33, 333–336. doi:10.1130/g21263.1
Schoell, M. (1984). Recent advances in petroleum isotope geochemistry. Org. Geochem. 84 (6), 645–663. doi:10.1016/0146-6380(84)90086-x
Talbot, M. R. (1990). A review of the palaeohydrological interpretation of carbon and oxygen isotopic ratios in primary lacustrine carbonates. Chem. Geol. Isot. Geosci. Sect. 80, 261–279. doi:10.1016/0168-9622(90)90009-2
Valero Garcés, B. L., Gierlowski-Kordesch, E., and Bragonier, W. A. (1997). Pennsylvanian continental cyclothem development: no evidence of direct climatic control in the Upper freeport formation (allegheny group) of Pennsylvania (northern appalachian basin). Sediment. Geol. 109, 305–319. doi:10.1016/s0037-0738(96)00071-1
Veizer, J., Ala, D., Azmy, K., Bruckschen, P., Buhl, D., Bruhn, F., et al. (1999). 87Sr/86Sr, δ13C and δ18O evolution of Phanerozoic seawater. Chem. Geol. 161, 59–88. doi:10.1016/s0009-2541(99)00081-9
Wan, Y. S., Xie, H. Q., Yang, H., Wang, A. J., Liu, D. Y., Kröner, A., et al. (2013). Is the ordos block Archean or Paleoproterozoic in age? Implications for the Precambrian evolution of the north China craton. Am. J. Sci. 313, 683–711. doi:10.2475/07.2013.03
Wang, S. M., and Zhang, Z. K. (1999). New progress in the study of Lake sedimentation and environmental evolution in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 44 (6), 579–587. doi:10.1007/BF02886151
Wang, Q. C., Zhang, Y., and Xiao, L. (2013). Characteristics of carbon and oxygen stable isotopes in diagenetic facies of Ordovician carbonate rocks in the ordos basin. Oil Gas Geol. 34 (5), 652–658. doi:10.11743/ogg20130511
Wang, W., Zhou, C. M., Guan, C. G., Yuan, X. L., Chen, Z., and Wan, B. (2014). An integrated carbon, oxygen, and strontium isotopic studies of the lantian formation in south China with implications for the shuram anomaly. Chem. Geol. 373, 10–26. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.02.023
Wang, C., Wang, Q. X., Chen, G. J., He, L., Xu, Y., Chen, L. Y., et al. (2017). Petrographic and geochemical characteristics of the lacustrine Black shales from the Upper Triassic yanchang formation of the Ordos basin, China: implications for the organic matter accumulation. Mar. Petroleum Geol. 86, 52–65. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.05.016
Xia, Q. S., Tian, J. C., and Huang, C. W. (2007). Study on the recognition marks of seismites in Upper Triassic yanchang formation, ordos basin, China. J. Chengdu Univ. Technol. Sci. and Technol. Ed. 34 (3), 312–316. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2007.03.015
Yang, H., and Deng, X. Q. (2013). Deposition of yanchang formation deep-water sandstone under the control of tectonic events, ordos basin. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 40 (5), 513–520. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(13)60072-5
Yang, H., and Zhang, W. Z. (2005). Leading effect of the seventh member high-quality source rock of yanchang formation in ordos basin during the enrichment of low-penetrating oil-gas accumulation: geology and geochemistry. Geochemica 34 (2), 147–153. doi:10.19700/j.0379-1726.2005.02.007
Yang, H., Zhang, W. Z., Wu, K., Li, S. P., Peng, P. A., and Qin, Y. (2010). Uranium enrichment in lacustrine oil source rocks of the chang 7 member of the yanchang formation, erdos basin, China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 39, 285–293. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.013
Yu, J. Q., Wang, X. Y., Jun, L., and An, Z. S. (2001). Paleoenvironmental interpretations on organic carbon isotopic records from Lake sediments: a critique. J. Lake Sci. 13 (1), 72–78. doi:10.18307/20010111
Yuan, W. (2018). Formation mechanism of the organic-rich shales in the 7th member of yanchang formation, ordos basin. Beijing: China Petroleum of University. Ph.D. Dissertation.
Yuan, X. J., Lin, S. H., Liu, Q., Wang, L., Guo, H., Yao, J. L., et al. (2015). Lacustrine fine-grained sedimentary features and organic-rich shale distribution pattern: a case study of chang 7 member of Triassic yanchang formation in ordos basin, NW China. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 42 (1), 37–47. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(15)60004-0
Yuan, W., Liu, G. D., Stebbins, A., Xu, L. M., Niu, X. B., Luo, W. B., et al. (2017). Reconstruction of redox conditions during deposition of organic-rich shales of the Upper Triassic yanchang formation, ordos basin, China. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 486, 158–170. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.12.020
Yuan, W., Liu, G. D., Xu, L. M., Niu, X. B., and Li, C. Z. (2019a). Petrographic and geochemical characteristics of organic-rich shale and tuff of the Upper Triassic yanchang formation, ordos basin, China: implications for lacustrine fertilization by volcanic ash. Can. J. Earth Sci. 56, 47–59. doi:10.1139/cjes-2018-0123
Yuan, W., Liu, G. D., Xu, L. M., and Niu, X. B. (2019b). Main controlling factors for organic matter enrichment in chang member of the yanchang formation,Ordos Basin. Oil Gas Geol. 40 (2), 326–334. doi:10.11743/og20190211
Yuan, W., Liu, G. D., Zhou, X. X., Xu, L. M., and Li, C. Z. (2020). Palaeoproductivity and organic matter accumulation during the deposition of the Chang 7 organic-rich shale of the Upper Triassic Yanchang formation, ordos basin, China. Geol. J. 55, 3139–3156. doi:10.1002/gj.3578
Yuan, W., Liu, G. D., Zhou, X. X., and Bulseco, A. (2022). Linking hydrothermal activity with organic matter accumulation in the chang 7 black shale of yanchang formation, ordos basin, China. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 786634. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.786634
Zhang, W. Z., Yang, H., Yang, Y. H., Kong, Q. F., and Wu, K. (2008). Chang-7 high quality source rocks in ordos basin petrology and element geochemistry and development environment of yanchang formation. Geochemica 37 (1), 59–64. doi:10.19700/j.0379-1726.2008.01.008
Zhang, W. Z., Yang, H., and Peng, P. A. (2009). The influence of Late Triassic volcanism on the development of chang 7 high grade hydrocarbon source rock in ordos basin. Geochemica 38 (6), 573–582. doi:10.19700/j.0379-1726.2009.06.007
Zhang, W. Z., Yang, H., Xie, L. Q., and Yang, Y. H. (2010). Lake-bottom hydrothermal activities and their influences on the high-quality source rock development: a case from Chang7source rocks in ordos basin. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 37 (4), 424–428. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60043-2
Zhang, W., Li, Z. W., Feng, F., and Zhai, Z. H. (2013). Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of lacustrine carbonate rocks of the lower-middle Jurassic in NE part of central Sichuan Province and their palaeoenvironmental significance. J. Palaeogeogr. 15 (2), 247–259. doi:10.7605/gdlxb.2013.02.021
Keywords: triassic, carbon and oxygen isotope, organic matter, paleoproductivity, paleoclimate, source rocks
Citation: Deng H (2025) High-resolution carbon and oxygen isotope records in the Chang 7 organic-rich shale of the Yanchang formation, Ordos Basin, China and their geological significance. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1591514. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1591514
Received: 11 March 2025; Accepted: 05 September 2025;
Published: 19 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ramanathan Alagappan, Independent Researcher, Tiruchirapalli, IndiaReviewed by:
Arif Husain Ansari, Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences (BSIP), IndiaIgor Hamid, Federal University of Ceara, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haowen Deng, aGFvd2VuZGVuZzIwMjVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Haowen Deng
Haowen Deng