- China Coal Science and Technology Ecological Environment Technology Co. Ltd., China coal technology and engineering group, Beijing, China
In deep engineering, the in-situ measurement of engineering rock properties is a key issue in projects such as energy storage and resource mining. Numerous researches devoted to adopting the digital drilling methods for the in-situ application of deep rock engineering. Interdisciplinary technical means were introduced to improve the accuracy and efficiency of in-situ testing methods. In this paper, the existing progress of digital drilling technology was initially reviewed. The establishment of penetration, cutting, and rock-breaking models was discussed based on the mechanical interaction during rock drilling. Improved understanding of machine-rock interaction behavior can be achieved through solving the deep engineering problems such as detecting structural distribution, obtaining rock engineering parameters, improving drilling and rock breaking efficiency, and reducing testing costs. Importantly, the issues of current research were summarized on the digital drilling method to provide a forecast on the development in deep rock engineering. Future digital drilling technology will combine intelligence, automation and big data analysis to achieve efficient, accurate and safe drilling operations. Through digital twin and remote-control technology, the drilling process will be fully monitored and optimized to improve efficiency and reduce risks.
1 Introduction
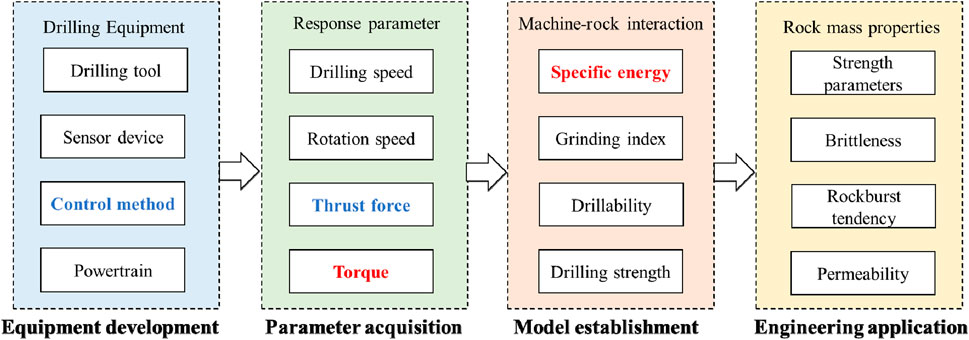
As underground space development continues to advance in depth, researchers have discovered a series of new features and phenomena in deep rock masses, which have put forward higher requirements for rock breaking technology (Qian and Li, 2008; Gao et al., 2024; Yasar et al., 2011; Song et al., 2011). In order to increase the rock breaking efficiency and detection accuracy of rock masses at deep conditions, a variety of rock breaking methods have emerged. Drilling is a conventional method in engineering exploration, in which thrust force is exerted to advance a drill bit into the rock mass, progressively inducing deformation and ultimately causing rock fragmentation, while the resulting debris is expelled from the borehole (Xie et al., 2025). This process is also referred as the mechanical response between drilling machines and rock. Understanding the mechanical interaction between the drilling system and the rock is fundamental for the characterization of rock fracture behaviors, improvement of drilling efficiency, monitoring of rock mass parameters, and optimization of drill bit design (Li et al., 2024). Inspired by this, digital drilling technology equipped with advanced rock breaking mechanisms uses digital transmission systems has emerged (Gao et al., 2024). As shown in Figure 1, this technology enables the real-time collection of drilling parameters through digital drilling equipment. The parameters of rock mass have been inversely determined through a quantitative relationship model linking drilling parameters to rock mass properties, which provides a novel approach to in-situ testing and real-time evaluation of engineering rock masses. Scholars have employed theoretical analysis, experimental studies, and numerical simulations to clarify the cutting failure characteristics of rocks and to characterize the mechanisms of machine-rock interaction (Song et al., 2011). The research concludes analysis of energy evolution (Huang et al., 2019), establishment of failure criteria, construction of drilling response models, and development of advanced monitoring equipment for real-time drilling operations (Wang Q. et al., 2020). Supported by extensive practical and theoretical advancements, these studies demonstrate promising application prospects (Qian and Li, 2008). Among them, the drilling parameters are correlated with the shape and properties of the drill bit (Sachetto et al., 2004). Meanwhile, the penetration processes using different drill bits exhibit distinct fracture characteristics. These differences in fracture behavior can bias the response between drilling characteristics and rock mass properties, affecting the characterization of drilling response.
With the advent of the information age, the rapid development of big data and the Internet of Things (IoT) has effectively addressed issues related to data storage and transmission (Wang et al., 2014), providing a new platform for the engineering application of digital drilling technology. Some researchers have applied artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to perform noise reduction on drilling data for optimizing the data acquisition. As shown in Figure 2, Yue (2014) applied time-series monitoring technology to the automatic monitoring of rotary impact drilling. He et al. (2019a) utilized a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) architecture to optimize the estimation of the rock strength based on digital drilling technology. The trained DCNN model effectively reduced the rock strength estimation error by 10%.
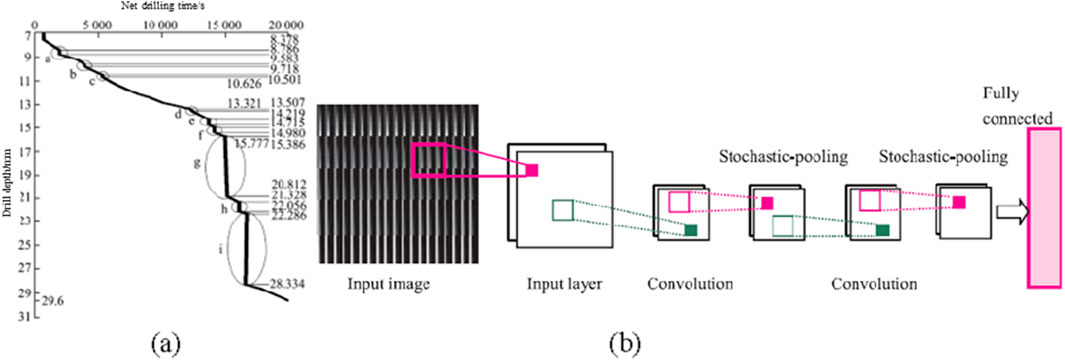
Figure 2. Optimization of digital drilling technology using artificial intelligence techniques. (a) Drilling depth-time curve (b) Convolutional neural network architecture.
Herein, this paper reviews the development of digital drilling technology and its application in deep engineering in detail, with a special focus on the following three aspects: current research progress in digital drilling technology, machine-rock interaction and rock-breaking models, and engineering application of digital drilling technology. This paper initially reviews the progress of existing digital drilling technology, then the establishment of penetration, cutting, and rock-breaking models is discussed based on the mechanical interaction between the drilling equipment and rock during the drilling process. To obtain the improved machine-rock interaction, the practical application is tried to be confirmed, such as detection of structure distribution, acquisition of rock mass engineering parameters, enhancement of drilling rock-breaking efficiency and decreasing the test costs. The issues in current research on digital drilling technology was summarized to provide an outlook on future development trends. These aspects of reviews are together to provide reference for future researches of digital drilling technology and the engineering application of such onsite testing methods.
2 Advances in digital drilling technology
Since the late 20th century, geological engineers have discovered a potential correlation between the mechanical properties of rock mass and the drilling parameters (Yasar et al., 2011). Engineers utilized this conventional geological exploration method to preliminarily determine stratigraphic distribution and obtain geological information (Li et al., 2014). Subsequently, this empirical method was refined and evolved into digital drilling technology (Wang Y. et al., 2020), which has been applied to identifying structural stratified rock mass (Cao et al., 2021) and conducting preliminary assessments of tunnel surrounding rock stability (Chen et al., 2020).
In the 1970s, the goal of measurement while drilling was initially achieved through modifications to drilling equipment. However, the huge amount of drilling data, the inability to record and analyze data simultaneously, and the increase in equipment failures caused by modifications ultimately reduced the efficiency of drilling monitoring (Nishimatsu, 1972). Recently, digital drilling technology has undergone significant advancements through continuous iterations and optimization, including updates in data processing and analysis methods, as well as new insights into machine-rock interaction mechanisms. Regarding laboratory-scale digital drilling equipment, Yasar et al. (2011) developed an indoor drilling rig capable of monitoring load and drilling speed and conducted the tests by using conventional core drill bits. Zhao et al. (2009) added a drilling system to a rock triaxial compression testing machine and performed cutting tests on granite under extreme geo-environmental conditions (temperature, geostress and water). Song et al. (2011) developed the “WCS-50″indoor rotary cutting penetrometer, which was used to conduct rotary cutting tests on soft rock-like materials (e.g., building blocks, gypsum) and loess with triangular drill bits. Wang Y. et al. (2020) manufactured a true triaxial rock mass digital drilling system capable of providing an axial thrust of up to 50 kN and a torque of up to 400 Nm. However, field drilling operations are subject to numerous interference factors, such as noise, mud, heat transfer, and friction. Effectively monitoring drilling data and optimizing machine-rock interaction evaluation impose more comprehensive requirements on field while-drilling monitoring equipment. In terms of field while-drilling monitoring equipment, Sacchetto et al. (2004) pioneered the integration of while-drilling rock mass detection technology with penetration tests, conducting field tests for obtaining on hard soil layers where sampling is difficult. Rai et al. (2015) successfully extracted effective data during drilling operations in mining and tunneling projects for analyzing machine-rock interaction mechanisms without compromising operational efficiency. Additionally, Reijonen (2011) found a high correlation among critical petroleum engineering parameters evaluated by while-drilling monitoring technology, such as resistivity and porosity. The drilling process monitoring (DPM) instrument modified by Yue et al. (2004), Yu (2014) obtains drilling parameters through pneumatic down-the-hole hammers and hydraulic rotary exploration rigs. Moreover, it provides specific calculation methods for rock mass quality evaluation indices such as RQD, Q, and RMR, and conducts a series of drilling experiments on weathered granite slopes. Based on the DPM instrument, Feng and Wang (2022) added a real-time monitoring system, including a laser displacement sensor, loading sensors, and a data transmission and processing system. The XCY-type rotary cutting probe developed by Li et al. (2014), Li et al. (2024) has a maximum overall size of 5 m and a maximum drilling inclination of 90°. The XCY-2 peeling machine consists of a drilling tower, a power unit, an electronic control box, a hydraulic system and a supporting structure. By conducting a series of field borehole tests on different types of surrounding rocks at the Sanhekou Hydraulic project, it accurately estimates rock mass quality, surrounding rock classification, and rock mechanical parameters. These digital drilling devices enable the measurement of key indices in various engineering environments, such as slopes, dam foundations, and tunnel surrounding rocks. However, the adaptability of the testing equipment to different working conditions is limited: for deep rock mass engineering, the equipment’s explosion-proof performance is a concern. Due to its large size, it is difficult to apply in narrow construction spaces. Therefore, in future research and development, down-the-hole monitoring equipment will be optimized and adapted for specific fields to improve operational efficiency.
Factors influencing the mechanical rock-drilling response in digital drilling can be summarized into three main categories: rock mass properties, equipment performance, and drill bit selection (Zhang and Gao, 2005). Rock mass properties primarily include mineral composition and mechanical parameters. Taking an example, quartz content in minerals directly affects the drill bit wear, while the compressive and tensile strength of the rock determines its characteristics during penetration or cutting failure in the drilling process. The equipment performance and drill bit selection are critical for analyzing rock-drilling interaction, improving drilling efficiency, reducing mechanical wear, and accurately obtaining rock mass information. According to the differences in rock breaking methods of geological drill bits and lithology, rock breaking methods can be divided into impact rock breaking, cutting rock breaking, grinding rock breaking and mixed rock breaking. Impact rock-breaking occurs under dynamic loading, where the drill bit invades the rock at high speed, causing instantaneous failure. This is commonly applied in hard rock drilling. Cutting rock-breaking is categorized into rolling cutting and crushing cutting, depending on the shape and motion of the cutting machine (Zhou and Lin, 2013). This cutting method is suitable for medium-hard rocks. Rolling cutting utilizes roller cone bits, where the teeth penetrate the rock surface under thrust and then crush the rock along the indentation under torque. This method is widely applied in resource extraction and exploration. Crushing cutting involves rotary rolling cutters that uniformly penetrate the rock along the axis, making it the primary rock-breaking method for tunnel boring machines (TBM) used in full-section hard rock construction such as tunnel faces. Grinding rock-breaking is often employed for soft rock excavation. The drill bit applies thrust to compress the rock into elastic state (Cheng et al., 2019), followed by continuous rotation of the cutting machine to achieve material removal (Liu et al., 2018). Due to their superior wear resistance, polycrystalline diamond compact (PDC) bits and alloy drill bits have become the mainstream choices for this method. Hybrid rock-breaking combines the advantages of PDC bits and roller cutters, promoting adaptability across various application scenarios. Table 1 summarizes the key features of major drilling monitoring devices currently used domestically and internationally.
3 Machine-rock interaction and rock-breaking models
The process of drill bit penetration into rock is typically analyzed in two stages: circumferential cutting and axial compression, which are corresponding to the radial and axial components of the rock-breaking force. Under the axial force, the drilling bit contacts with the rock surface and rotary penetrates into the rock mass. Subsequently, the rock is cut under the influence of the radial force. Numerous studies have shown that the rate of penetration (ROP) is a crucial parameter of drilling efficiency (Rostamsowlat et al., 2018) and is also used to reflect tool wear, the shape of the cutting surface, and critical cutting forces (Amri et al., 2016). To provide predictions and assessments for engineering practices, researchers have analyzed the fracture modes in drilling processes for different rock types through field observations and laboratory experiments. These attempts can identify the impact of fracture modes under various rock types and drill bit structures on tool lifespan. The results indicate that rock breaking during drilling exhibits in shear failure, tensile failure, and spalling failure. Therefore, studying the stress distribution, the formation and propagation mechanisms of fracture surfaces during drilling is crucial for optimizing drill bit design, reducing damage and wear, and predicting rock properties. Based on the transformation of the dominant rock-breaking force during drilling, rock failure behavior can be categorized into compaction failure and cutting failure. The following section summarizes the research progress on different rock-breaking methods.
3.1 Compaction rock failure
Scholars have conducted numerous experiments on drill bit compaction into rock under simulated drilling conditions and collected data on the compaction breaking characteristics of rock. Currently, theoretical analysis and experimental methods are the mainstream method to reveal the mechanisms of the drill bit compaction breaking process. Due to the complex mechanism of compaction rock breaking, the elastic-plastic theory is widely employed to establish an analytical model under the limit equilibrium conditions. Based on Griffith’s fracture criterion, fractures always occur at the tips of microcracks triggered by tensile stress concentration. Marshall (1983) conducted compaction experiments on zinc sulfide with conical and spherical indenters and derived a stress intensity factor G. Based on that, the effect of the indenters on rock compaction characteristics was analyzed and found that the rock’s drillability K is directly proportional to the stress intensity factor G in Equation 1:
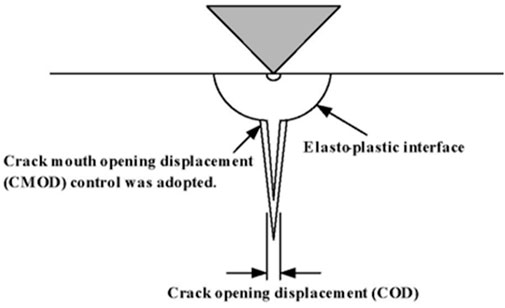
where, E is elastic modulus of rock, H is hardness of rock, C is the radial crack length (seen in Figure 3).
The indentation test results show that the rock drilling process is similar to the rock indentation tests (Sachetto et al., 2004). As shown in Figure 3, the compaction rock failure process contains three regions: the core crushing zone, the plastic deformation zone, and the crack propagation zone. Once the drill bit penetrates the rock surface completely, the rapidly increasing axial load exceeds the uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) of rock mass. Due to the confinement effect between the rock mass sidewall and the cutter tip, the generated debris continues to fracture and forms smaller particles, which constitute the core crushing zone.
Based on fracture mechanics theory, Huang et al. (2019) proposed a spatial expansion model to describe rock compaction fracturing. The model allowed for the derivation of rock strength based on the size of the plastic deformation zone and crack length during the rock compaction process. Building upon the spatial expansion model, Chen and Labuz (2006) introduced the effects of lateral confinement and indenter shape. Through theoretical analysis and experimental validation, they obtained an indentation stress field that shows good consistency with the damage zone size. However, the spatial expansion model has many parameters, which limits its integration with the cutting part of rock breaking for a comprehensive study.
From the experimental prospectives, Fan et al. (2019) compared the indentation test results of different materials (silicon dioxide, ceramics, and shale) and obtained the crack propagation characteristics of indentation fractures for each material. To simplify the characterization parameters of compaction rock-breaking, Chiaia et al. (2013) conducted experiments to test the correlations between the parameters in the model and derived a linear function of drilling pressure and ROP. Although the spatial expansion model is applied to characterize the deformation behaviors of rock compaction fracturing, two issues remain. First, rock is a type of quasi-brittle material with discontinuous fracture characteristics, the application of elastoplastic theory for analyzing rock compaction failure is questionable. Second, the practicability of the parameters of the model is uncertain.
3.2 Cutting rock failure
Since 1950, the mechanism of cutting rock failure has been a key focus of research (Merchant, 1945a; Merchant, 1945b). Based on the shear force equilibrium equation, Merchant et al. (1945a), Merchant (1945b) established the first semi-empirical model for metal cutting. Nishimatsu (1972) proposed a cutting rock model that explains the formation of rock chips. The degree of rock fragmentation was characterized by the rock shear strength. However, the limitation of Nishimatsu’s model is that it cannot describe the ductile failure that occurs during rock cutting. According to the deformation characteristics of rock shear failure, the rock cutting process can be roughly classified into three stages: elastic shear deformation, micro-crack initiation and propagation, and the formation of macro-fractures (Nishimatsu, 1972). The cutting force decreases suddenly corresponding to the formation of macro-fractures. Under the action of axial thrust, the cutting rock failure enters the next complete cycle (Verhoef et al., 1996). Based on these three stages, researchers have summarized three rock failure modes: brittle tensile fracture, ideal plastic shear fracture, and brittle tensile-shear fracture (see Figure 4).
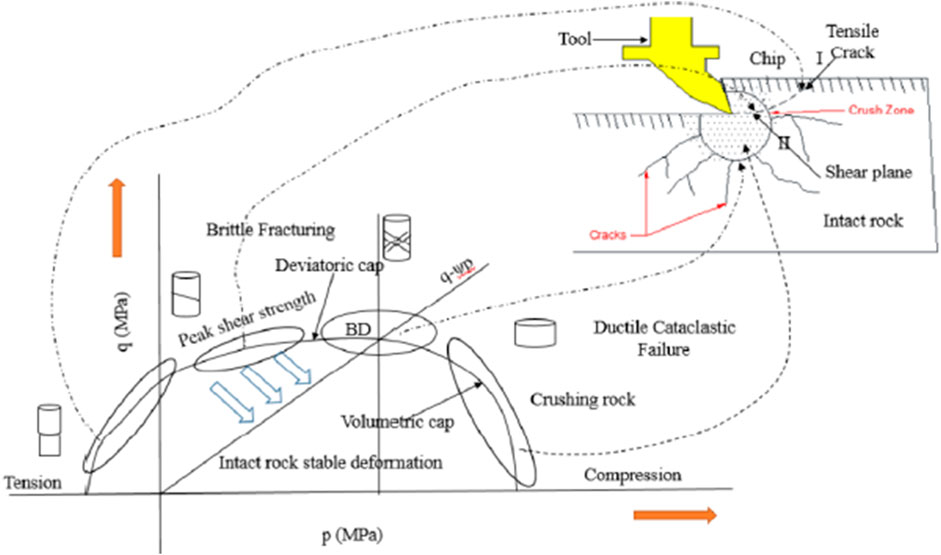
Figure 4. Typical failure modes of rock cutting and corresponding relationship between tension and compression stresses.
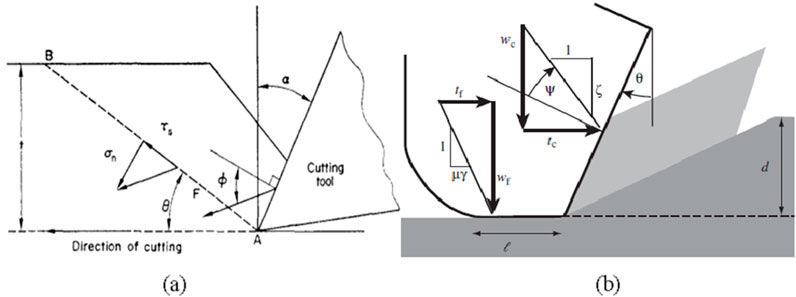
As shown in Figure 4, the initiation and propagation of cracks reveal the core of rock cutting fracture (Verhoef et al., 1996). However, the explanation of crack initiation and propagation is not unified. The factors controlling crack propagation are considered to be tensile and shear failure of the rock. The rock in front of the tool first undergoes shear failure during the cutting process. Then, tensile cracks initiate and propagate to form macro fractures eventually. The thrust force and cutting force exhibit periodic variations. The peaks of these forces correspond to the moment when cracks form. Based on this, Evans (1962) built a rock cutting fracture model (see Figure 5) by incorporating tensile strength into the metal cutting theory proposed by Merchant et al. (1945a), Merchant et al. (1945b). The cutting force Fc is defined as in Equation 2,
where d is the penetration depth per tool revolution, σt is the tensile strength, w is the tool width; θ is a shape parameter of the tool.
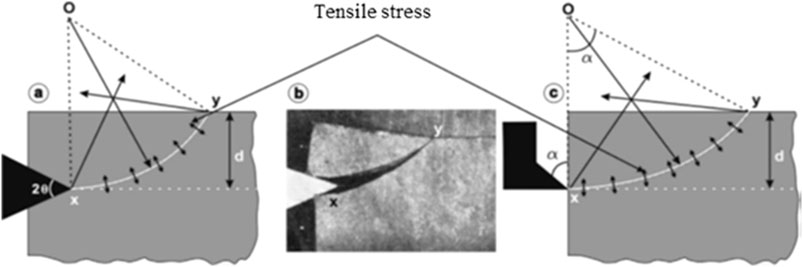
Figure 5. Determining the cutting crack path based on the improved Evans model. (a) Initial stage (b) Fracture generation (c) Mechanics diagram.
The equation of stress state in rock of the cutting process was calculated based on the maximum shear stress theory. An analytical model was developed to analyze the cutting force and rock failure surface (Cheng et al., 2019). The crack path is obtained as a curve. Liu et al. (2018) conducted a study on crack propagation behavior during rock cutting using the discrete element software PFC 2D (see Figure 6). When the penetration per revolution (d) is 11R, powder-like debris is formed. When d reaches 32R, a crushing zone is formed. Subsequently, based on the trend of the mechanical specific energy μb with cutting depth, the critical state of ductile-brittle failure in cutting rock was determined. At shallow cutting depths, the rock undergoes ductile failure, and μb remains constant. As the cutting depth increases, brittle failure occurs, and μb decreases. The transition model related to the μb can be expressed as,
where η is a constant which affected by the rake angle of cutter; Kb is influence coefficient which related to the geometry and properties of cutter material; Kp represents the cutting energy dissipated in the rock drilling process.
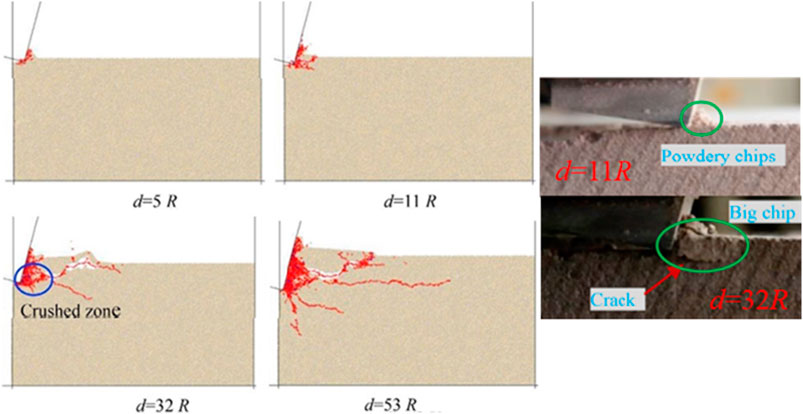
Figure 6. Validation of the crack propagation model and explanation of brittle-ductile failure characteristics.
When the cutting rock-breaking model considers few environmental factors, the rock mechanics parameters obtained from field experiments may have significant errors compared to actual parameters (Ouyang et al., 2021), so that the model necessitates modification by empirical coefficients. Rostami (1997) conducted rock cutting experiments and established the CSM (Colorado School of Mine) model to characterize the tool wear. Yagiz (2002) improved the CSM model to enhance its accuracy in describing hard rock cutting behavior. Subsequently, many researchers developed numerous cutting rock-breaking models and optimized them using advanced data processing techniques such as convolutional neural networks, discretization, and fuzzy mathematics (Yagiz, 2002).
3.3 Drilling rock failure
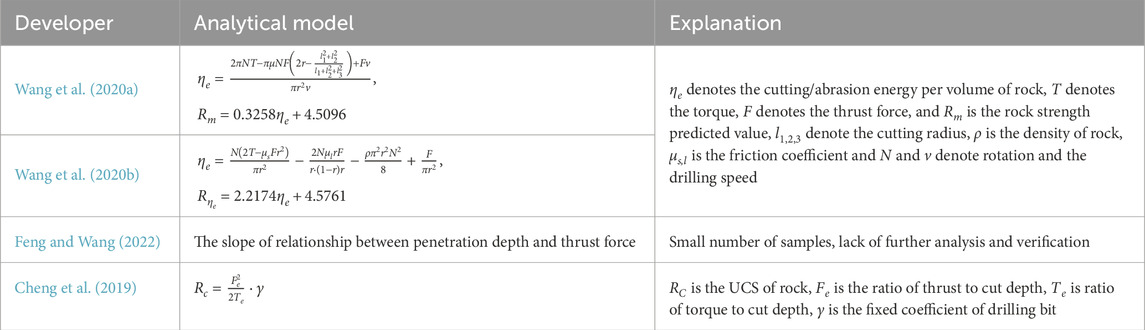
A drilling response model was established based on drilling balance conditions to evaluate the rock drillability (Detournay and Defourny, 1992). In fact, the output energy of the borehole machinery is not entirely used for breaking rock. Similarly, it is consumed by the complex frictional energy and the kinetic energy of the drilling fluid in the drilling process. As a result, the energy consumption for rock cutting is overestimated due to the ignoring of the in-situ factors (Wang et al., 2023). The influence of environmental factors is eliminated on the specific energy to establish accurate rock evaluation indicators. The models generally simplify the rock cutting stress state to a linear elastic state, which is not consistent with that during drilling process. Moreover, the rotary cutting process involves both penetration fracture and rotary crushing, accompanied by minor damage such as friction and grinding. The key mechanical parameters associated with these processes are still unclear. In conclusion, current research on rock fragmentation during drilling is necessary to focus on machine-rock interaction and rock-breaking mechanism (Rai et al., 2015; Reijonen, 2011; Yue et al., 2004). Moreover, the mainstream theoretical models of digital drilling process were listed in a summarized Table 2. These models provide the strength estimation of deep rock mass in accordance with the drilling process analysis through an index related to the rock-breaking behaviors during drilling process.
Based on the prospectives of energy release, physical mechanisms, and experimental experience. Teale (1965) first developed the energy evolution model, which defines the parameter MSE to describe the energy transfer as a drill bit penetrates rock. The model is often used to analyze the interaction between the drill bit and rock and to evaluate wellbore stability. The empirical model is constructed by summarizing existing data to provide qualitative or quantitative guidance, although their application might be limited by the scope and reliability of the data. The limit equilibrium model, based on stress field analysis, considers micro-damage and fracture processes within rock. The model accurately reflects the inelastic behavior, fracture processes of rock, stress distribution and steady behavior during drilling (Richard et al., 2012). On this basis, the classification of drilling rock-breaking models is determined by the researcher’s needs, and the combination of different model types can yield more comprehensive and accurate predictions.
As shown in Figure 7a, Nishimatsu (1972) established the first rock cutting model, which considered the formation of rock chips and the discontinuity of the rock mass. The model inspired subsequent scholars to develop cutting models based on various concepts of rock failure characteristics. However, the Nishimatsu model is unable to describe ductile failure and overlook the effects of the wear surface. Detournay and Defourny, 1992 introduced new assumptions into the model proposed by Nishimatsu (1972), which suggest that the rock-breaking processes of all cutter teeth on the drill bit are independent (see Figure 7b). The assumptions include pure cutting actions (affecting the front of the cutting face) and frictional contact (acting on the sliding surface), which have been validated by the results of rock cutting experiments conducted by many scholars (Liu et al., 2018; Teale, 1965). Rostamsowlat et al. (2018) confirmed that this typical cutting mode corresponds to ductile fracture through the analysis of drill cuttings of shallow sedimentary rocks. Kalantari et al. (2018) also analyzed the rock-cutting mechanisms of PDC drill bits. The concept of the tip crushing zone is defined to present the evolution of rock failure process and to establish a correlation between rock properties and tool wear.
In summary, the mechanical-rock response during drilling is described as an analytical relationship between the horizontal force and the axial thrust (Nishimatsu, 1972; Kalantari et al., 2018). Specifically, Detournay and Defourny (1992) defined the cutting force and thrust per unit area as drilling energy E and cutting strength S, respectively to eliminate the size influence of drill tool on characterizing the relationship between E and S. The mechanical-rock response is defined as,
where μ is the friction coefficient between cutting tool and rock, ε is the cutting energy required for a unit volume; ζ is the ratio of cutting force to thrust force.
Kalantari et al. (2018) calculated ζ as the tangent value of the relative contact angle tanθ between the drill bit and rock considering the crushed zone at the rake angle of the drilling bit. As shown in Figure 8a, a critical state exists to divide the drilling response into two independent stages: cutting and friction. The critical state is caused by the increased relative friction corresponding to chip accumulation during the drilling process. An increasing number of researchers have interpreted this critical state based on different drilling phenomena and characteristics. Fen and Wang (2022) described the critical point as the transition between normal drilling and bit jamming based on real-time monitoring data from resource extraction projects (see Figure 8b). Liu et al. (2018) interpreted the critical state of MSE variation with penetration depth as the turning point between brittle and ductile failure (see Figure 8c). The previous mainstream drilling-rock failure (response) models characterize the tool-rock interaction based on the force characteristics of rock drilling (Kalantari et al., 2018), which shows a certain applicability in representing rock failure for different cutting tools. However, the stress-based models tend to overlook tool wear and its underlying causes.
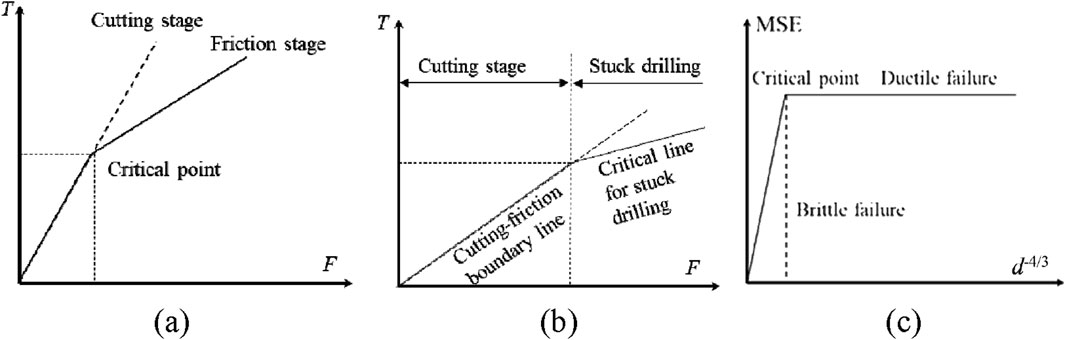
Figure 8. Different explanations of the critical state in drilling response. (a) Cutting-friction transition (b) Critical stuck-drilling state (c) Brittle-ductile failure.
In summary, the study of rock failure characteristics during drilling is in a phase of continuous advancement and development. Existing research focuses on accurately characterizing the rock-breaking process, including analyzing the evolution of rock fracture and cutting-induced failure characteristics. By integrating experimental studies, numerical simulations, and field observations, researchers are steadily improving the understanding of rock failure mechanisms during drilling, thereby driving progress in rock engineering and drilling technologies.
4 The engineering application of digital drilling technology
Significant progress has been made in laboratory experiment, theoretical and numerical studies on drilling-based rock-breaking methods, which demonstrates the great potential for addressing practical engineering challenges. These advances are particularly beneficial in enhancing engineering efficiency, optimizing design, improving decision-making support, increasing safety and reliability, and promoting innovation and sustainability. The application of digital drilling technology provides critical support for the successful implementation of projects.
4.1 Detection of structure distribution
Typically, geological surveys are performed by using core drilling and theoretical methods to detect structural plane distribution and to evaluate rock mass quality. Since drilling parameters exhibit a specific fluctuation to the properties of subsurface rock, geologists can realize the integrity of the rock mass based on variations of the parameters. To obtain the characteristics of subsurface structures, a geophysical exploration technique has garnered significant attention in the field of geotechnical engineering (Shi et al., 2020). The technique enables the rapid acquisition of abnormal physical characteristics in the target area, even under the harsh environmental condition. Some researchers have conducted detailed stratigraphic division and boundary identification by analyzing formation data using methods such as gamma-ray spectrometry (Zhang, 2003), acoustic transmission time difference (Cao et al., 2003) and resistivity measurement (Chen et al., 2005). However, geophysical exploration face challenges such as low detection accuracy and susceptibility to geomagnetic interference. These issues require extensive noise reduction processing of the data, which can lead to data distortion in turn.
Tan et al. (2007) conducted borehole drilling tests by using an impact drill equipped with a real-time monitoring system. The relationship between the degree of weathering in granite and drilling energy consumption was investigated through the analysis of axial pressure, rotational speed, and penetration rate, thereby providing a basis for rock strata identification. Yan et al. (2008) established a drilling rock-breaking model based on fractal theory by analyzing the relationship between the particle size of cuttings and the mechanical work of the drilling machine. Based on the analytical relationship between uniaxial compressive strength, ultimate cutting strength and friction angle of rock, He et al. (2021) established the residual elastic energy index to evaluate rock burst proneness. Yang et al. (2019) employed a while drilling monitoring system to rapidly and quantitatively evaluate the rock block index (RBI) of core samples, which provides a basis for assessing the integrity of engineering rock masses. Leung and Scheding (2015) developed a neural network model for formation identification based a large amount of while drilling data. The model can significantly improve the operational efficiency of coal recovery. Based on the drilling response, the digital drilling method shows potentials in detection of rock structural characteristics, where exists some issues related to the detection accuracy and environmental adaptability.
4.2 Prediction of rock engineering performances
In geotechnical engineering, conventional testing methods obtain the physical and mechanical parameters of rock masses through field sampling and laboratory experiments. However, laboratory tests often fail to accurately replicate the in-situ stress and environmental conditions of rock masses. Digital drilling technology offers a solution to this issue. Researchers have used this technology to establish models relating rock strength to drilling parameters, enabling the evaluation of rock mass properties. Some studies have introduced rock strength criteria (Kalantari et al., 2018) and energy dissipation principles to describe rock cutting and fracturing characteristics during drilling, which provides a basis for assessing engineering parameters (Wang et al., 2023). However, such research limits in the combination of drilling response and failure criterion of rock. The discussion for the failure patterns and rock cutting debris generation is lack.
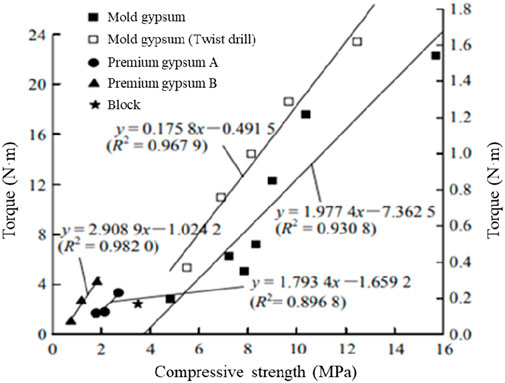
Wang Q. et al. (2020) conducted drilling tests on rocks and rock-like materials with different strength grades using a self-developed digital drilling system and derived a model linking drilling parameters to energy consumption per unit volume of rock grinding. Wang et al. (2022) incorporated the Hoek-Brown strength criterion into the drilling response model to analyze rock fracturing, where the material constant mi was expressed as a function of the internal friction angle of the rock. He et al. (2023) found anisotropic consistency between rock strength and drilling characteristics through digital drilling experiments. He et al. (2020) further evaluated rock mass quality based on energy evolution trends in engineering boreholes and their response to fracture distribution, as shown in Figure 9. Moreover, the rock anisotropy was assessed according to the drilling response by proposal of an index calculated as the ratio of different drilling direction (Wu et al., 2022). This discovery confirms the potential of digital drilling in application of deep rock engineering. Song et al. (2011) conducted rotary penetration, compression, and shear tests on masonry and gypsum samples by using blade and twist drill bits and identified the correlation between mechanical parameters and the drilling parameters of soft rock during the volumetric failure and grinding stages, as shown in Figure 10. Over the past 2 decades, many researchers have explored the relationship between rock engineering parameters and drilling parameters. However, further studies are needed to accurately determine rock mass engineering performance based on drilling-induced rock fragmentation.
4.3 Evaluation of drilling efficiency
To enhance rock-breaking efficiency, drilling engineers meticulously analyze the rock-breaking mechanism during drilling to optimize tool selection, determine the optimal drilling path, and avoid operational risks. Wear resistance, as a critical factor in cutter design, plays a crucial role in reducing mechanical wear during excavation. Alloy materials effectively improve drill bit wear resistance and extends its service life. However, the heterogeneous characteristics of rock masse become increasingly pronounced with excavation depth, posing significant challenges to tool durability. Maintaining high rock-breaking efficiency remains a core issue in improving drilling engineering designs. Engineers monitor key parameters during the drilling process, such as mechanical parameters, vibration frequency, and motor input power, in real time during the process. Based on the monitoring results, the control models are developed to quantitatively characterize bit deformation throughout the drilling cycle.
Glowka (1989) is the first to incorporate the effect of tool wear into rock-breaking models for drilling, observing a significant thermally accelerated wear effect. This wear effect arises from mechanical abrasion caused by crack propagation at the interfaces of abrasive minerals in hard rock, influenced by temperature, humidity, and stress conditions. Supported by theoretical derivation and experimental data, the relationship between motion parameters and load indicators was studied during the drilling process. Babaei and Hall (2016) discussed the monitoring information extracted from rotary blasthole drills, such as penetration rate, rotary speed, rotary torque, and pulldown force. The results indicated that specific energy of drilling can be accurately estimated using the electrical responses of the drill’s main drive system, compared to values determined based on mechanical inputs. Shankar et al. (2020) monitored the wear rate of tungsten carbide drill bits and its relationship with temperature using a fully instrumented laboratory CNC drilling setup. A linear regression analysis was employed to establish the correlation between temperature and wear rate. The results showed that the wear rate of drill bits increases with rising temperature, and the heat generated by machine-rock friction is the primary cause of tool wear. Liang et al. (2012) conducted numerical simulations of rock-breaking processes using tools of different shapes and identified a critical state in the effect of tool arrangement on specific energy consumption, which indicates that selecting appropriate drilling tools and setting optimal mechanical parameters based on varying formation properties is key to improving rock-breaking efficiency. For characterizing formation properties, intelligent data analysis models are necessary to process and summarize extensive drilling monitoring data. Therefore, developing accurate drilling process monitoring systems integrated with efficient intelligent data analysis capabilities is essential for enhancing the effectiveness of rock-breaking through real-time monitoring technology.
5 Conclusions and outlook
5.1 Problems in existing research
By summarizing relevant studies, the challenges in current research on digital drilling technologies can be outlined as follows:
(1) Mechanism of rotary cutting and characterization of rock-machine interaction
Current research primarily focuses on analyzing the influencing factors of rotary cutting rock-breaking characteristics, but the underlying mechanisms are not well explored. Destruction criteria tailored to different lithological features should be established, analytical models of rotary cutting rock-breaking should be derived, and evaluation parameters should be proposed. Combining micro- and macro-level approaches can provide a detailed explanation of the rock-breaking evolution process. Additionally, the characterization of rock-machine interaction suffers from low accuracy and unclear mechanisms.
(2) Development and improvement of rotary cutting monitoring equipment
Traditional testing equipment generally involves a simple assembly of sensor devices with standard drilling tools, which can lead to measurement errors. Many responses of drilling signals to rock structure features, such as joints, faults, tool wear, and drilling blockages or drops, manifest as changes in drilling parameters. These effective signals can be misinterpreted as measurement errors and overlooked, thereby reducing the practical effectiveness of rotary cutting detection technologies. Establishing corresponding testing standards and standardized procedures is necessary, including requirements for equipment maintenance, management, and operation.
(3) Feedback control based on digital technology
During the drilling process, the massive volume of data makes it critical to extract useful information related to rotary cutting rock-breaking characteristics. Leveraging digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize data processing can help build precise rock parameter inversion models. Using the evolution trends of drilling parameters for feedback control in the drilling process is beneficial for reducing drill bit wear and saving costs.
5.2 Challenges and issues in engineering practice
Notably, the digital drilling and logging while drilling have something in common in terms of equipment, but their application scenarios and technical focuses make them play an indispensable role in their respective professional fields. High-precision sensors are used to collect rock mechanics information such as pressure and stress during the drilling process in real time. Basically, analytical models are used to analyze data and infer the mechanical properties of rocks (such as hardness, toughness, etc.). The advantage is that the data is real-time and accurate, and can reflect the dynamic changes in the drilling process in a timely manner. Therefore, digital drilling technology focuses on deep rock engineering, ensuring accuracy and safety by precisely controlling the drilling process. Real-time rock mechanical information helps to avoid well deviation and collapse and improve construction quality. Nevertheless, digital drilling technology still faces many challenges and problems in engineering practice, including:
(1) Integration and compatibility issues: The lack of unified technical standards and platforms between different manufacturers and equipment leads to poor integration and compatibility of digital drilling systems, affecting their collaborative operation and data sharing.
(2) Complex data processing and analysis: The massive amount of real-time data collected requires powerful computing power and advanced algorithms. However, in practice, data processing and real-time analysis are often delayed or inaccurate, affecting the accuracy and efficiency of decision-making.
(3) Equipment maintenance and fault diagnosis: Although digital drilling technology can monitor equipment status in real time, the diagnosis and maintenance of complex faults are still challenging, especially in extreme environments where equipment is prone to failure, resulting in increased downtime.
(4) High initial investment and technical investment: The implementation of digital drilling technology requires a large initial investment in hardware, software and personnel training, which is a challenge for small and medium-sized mining companies.
(5) Security and data privacy issues: With the use of remote operation and cloud computing, data transmission and storage security have become a major concern. Problems such as cyber attacks and data leaks may pose a threat to operational safety and corporate interests.
5.3 Outlook
The continuous development of digital drilling technology promises more precise and comprehensive data acquisition capabilities for the construction engineering field. Future research directions include, but are not limited to:
(1) Development of high-performance sensors and equipment
Future studies can focus on designing smaller, more sensitive sensors to enhance the resolution and accuracy of monitoring data. Innovations in nanotechnology and advanced material science may provide significant opportunities for developing cutting-edge monitoring equipment.
(2) Comprehensive multi-parameter monitoring
To address the complex and dynamic environments in rock engineering, research can aim to develop monitoring devices capable of integrating multiple parameters, such as temperature, humidity, strain, and vibration, to gain a more holistic understanding of rock behavior.
(3) Artificial intelligence and big data analysis
By combining artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, intelligent analysis of large-scale monitoring data can uncover deeper and subtler patterns, enhancing the prediction and identification of rock behavior.
(4) Real-time monitoring and feedback systems
The construction of real-time monitoring and feedback systems can allow the timely detection of potential issues during rock engineering projects and facilitate immediate adjustments. This will significantly improve the efficiency and safety of engineering operations.
(5) Integration of rock engineering and geological exploration
Strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration with fields such as geology and geophysics can maximize the utilization of data obtained through digital drilling monitoring. This can lead to a deeper understanding of rock structures and geological features, laying a more robust foundation for accurately identifying rock mass parameters.
Advancing these research directions will drive breakthroughs in rotary cutting monitoring technology, enabling more reliable, efficient, and sustainable solutions for geotechnical engineering applications.
Author contributions
KF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is financially supported by the Study on the Spatiotemporal Evolution Law and Connectivity Characteristics of Void (Fracture) Spaces in Fully Mechanized Goafs of Shenfu Mining Area (0206KGST0026).
Conflict of interest
Author KF was employed by China Coal Science and Technology Ecological Environment Technology Co. Ltd.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Amri, M., Pelfrene, G., Gerbaud, L., Sellami, H., and Tijani, M. (2016). Experimental investigations of rate effects on drilling forces under bottomhole pressure. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 147, 585–592. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2016.09.025
Babaei, K., and Hall, R. (2016). Processing of measurement while drilling data for rock mass characterization. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 26, 989–994. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2016.09.005
Cao, R., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Wang, X., He, S., and Peng, L. (2021). In-situ tests on quantitative evaluation of rock mass integrity based on drilling process index. Chin. J. Geotech. 43 (4), 679–687. doi:10.11779/CJGE202104010
Cao, Y., Jiang, Z., Xia, B., Yang, L., and Zhang, J. (2003). Method, principle and example of identifying sequence stratigraphical boundary using sonic logging. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 21 (2), 318–323.
Chen, B., Wang, L., He, W., and Tan, J. (2020). CBM cluster wells wireless MWD technology rapid drilling operation technology in Baode block. Coal Geol. China 32 (4), 67–71. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2020.04.15
Chen, G., Sun, Z., and Geng, S. (2005). Application of logging curves to the Mesozoic stratum zonation in Jiyang Depression. Well Logging Technol. 29 (1), 40–43. doi:10.16489/j.issn.1004-1338.2005.01.012
Chen, L., and Labuz, J. (2006). Indentation of rock by wedge-shaped tools. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 43 (7), 1023–1033. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2006.03.005
Cheng, Z., Li, G., Huang, Z., Sheng, M., Wu, X., and Yang, J. (2019). Analytical modelling of rock cutting force and failure surface in linear cutting test by single PDC cutter. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 177, 306–316. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.023
Chiaia, B., Borri-Brunetto, M., and Carpinteri, A. (2013). Mathematical modelling of the mechanics of core drilling in geomaterials. Mach. Sci. Technol. 17, 1–25. doi:10.1080/10910344.2012.747881
Detournay, E., and Defourny, P. (1992). A phenomenological model for the drilling action of drag bits. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 29, 13–23. doi:10.1016/0148-9062(92)91041-3
Evans, I. (1962). A theory of the basic mechanics of coal ploughing. Min. Res., 761–798. doi:10.1016/b978-1-4832-8307-4.50053-2
Fan, M., Jin, Y., Chen, M., and Geng, Z. (2019). Mechanical characterization of shale through instrumented indentation test. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 174, 607–616. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.083
Feng, S., and Wang, S. (2022). Experimental study of rock-bit interaction mechanism for rock drillability assessment in rotary drilling. J. China Coal Soc. 47 (03), 1395–1404. doi:10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.xr21.1459
Gao, H., Wu, W., Jiang, B., and Liu, G. (2024). Research on rockburst proneness evaluation based on interpretation of drilling parameters. Eng. Fail. Anal. 163, 108421. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2024.108421
Glowka, D. (1989). Use of single-cutter data in the analysis of PDC bit designs: Part 1—development of a PDC cutting force model. J. Pet. Technol. 41 (8), 797–849. doi:10.2118/15619-pa
He, M., Li, N., Yao, X., and Chen, Y. S. (2020). A new method for prediction of rock quality designation in borehole using energy of rotary drilling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 53 (7), 3383–3394. doi:10.1007/s00603-020-02091-6
He, M., Li, N., Zhang, Z., Yao, X., Chen, Y., and Zhu, C. (2019a). An empirical method for determining the mechanical properties of jointed rock mass using drilling energy. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 116, 64–74. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.03.010
He, M., Wang, H., Ma, C., and Zhang, Z. (2023). Evaluating the anisotropy of drilling mechanical characteristics of rock in the process of digital drilling. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 56 (5), 3659–3677. doi:10.1007/s00603-023-03242-1
He, M., Zhang, Z., Ren, J., Huan, J., Li, G., Chen, Y., et al. (2019b). Deep convolutional neural network for fast determination of the rock strength parameters using drilling data. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 123, 104084. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104084
He, M., Zhang, Z., Zhu, J., Li, G., and Chen, Y. (2021). Correlation between the rockburst proneness and friction characteristics of rock materials and a new method for rockburst proneness prediction: field demonstration. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 205, 108997. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108997
Huang, K., Ai, Z., Yang, Y., and Xie, Z. (2019). The improved rock breaking efficiency of an annular-groove PDC bit. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 172, 425–435. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.079
Kalantari, S., Hashemolhosseini, H., and Baghbanan, A. (2018). Estimating rock strength parameters using drilling data. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 104, 45–52. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.02.013
Leung, R., and Scheding, S. (2015). Automated coal seam detection using a modulated specific energy measure in a monitor-while-drilling context. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 75, 196–209. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.10.012
Li, S., Liu, B., Sun, H., Nie, L., Zhong, S., Su, M., et al. (2014). State of art and trends of advanced geological prediction in tunnel construction. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 33 (006), 1090–1113. doi:10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.06.003
Li, Y., Li, J., Wu, Y., and Zhao, G. F. (2024). Extracting rock parameters through digital drilling test. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 57, 8215–8241. doi:10.1007/s00603-024-03951-1
Liang, Z., Yu, Y., Tang, S., Liu, H., and Tang, C. (2012). Numerical modeling of rock fracture mechanism under disc cutters and associated cutter spacing optimization. J. Min. Saf. Eng. 29 (01), 84–89.
Liu, W., Zhu, X. H., and Jing, J. (2018). The analysis of ductile-brittle failure mode transition in rock cutting. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 163, 311–319. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2017.12.067
Marshall, D. (1983). Geometrical effects in elastic/plastic indentation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 66 (8), 57–60. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1984.tb19148.x
Merchant, M. (1945). Mechanics of the metal cutting process. I. Orthogonal cutting and a type 2 chip. J. Appl. Phys. 16, 267–275. doi:10.1063/1.1707586
Merchant, M. (1945). Mechanics of the metal cutting process. II. Plasticity conditions in orthogonal cutting. J. Appl. Phys. 16, 318–324. doi:10.1063/1.1707596
Nishimatsu, Y. (1972). The mechanics of rock cutting. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 9, 261–270. doi:10.1016/0148-9062(72)90027-7
Ouyang, Y., Chen, X., Yang, Q., Xu, Y., and Qiu, Y. (2021). Experimental study on sandstone rock cutting with chisel picks. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 54, 1609–1619. doi:10.1007/s00603-020-02331-9
Qian, Q., and Li, S. (2008). A review of research on zonal disintegration phenomenon in deep rock mass engineering. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 199 (06), 1278–1284.
Rai, P., Schunesson, H., Lindqvist, P., and Kumar, U. (2015). An overview on measurement-while-drilling technique and its scope in excavation industry. J. Inst. Eng. (India) Ser. D. 96 (1), 57–66. doi:10.1007/s40033-014-0054-4
Reijonen, J., McDaniel, F. D., and Doyle, B. L. (2011). Nuclear tools for oilfield logging-while-drilling applications. Am. Inst. Phys. 1336 (1), 433–436. doi:10.1063/1.3586136
Richard, T., Dagrain, F., Poyol, E., and Detournay, E. (2012). Rock strength determination from scratch tests. Eng. Geol. 147, 91–100. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.07.011
Rostami, J. (1997). Development of a force estimation model for rock fragmentation with disc cutters through theoretical modeling and physical measurement of crushed zone pressure. Colorado School of Mines. PhD dissertation.
Rostamsowlat, I., Akbarib, B., and Evans, B. (2018). Analysis of rock cutting process with a blunt PDC cutter under different wear flat inclination angles. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 171, 771–783. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2018.06.003
Sachetto, M., Elmgren, K., and Trevisian, A. (2004). CPTWD (Cone Penetration Test while Drilling) a new method for deep geotechnical surveys. Proc. ISC-2 Geotechnical Geophys. Site Charact. Viana da Fonseca and Mayne 1, 787–794.
Shankar, V., Kunar, B., Murthy, C., and Ramesh, M. R. (2020). Measurement of bit-rock interface temperature and wear rate of the tungsten carbide drill bit during rotary drilling. Friction 8, 1073–1082. doi:10.1007/s40544-019-0330-2
Shi, X., Cui, Y., Xun, W., Zhang, J., and Guan, Y. (2020). Formation permeability evaluation and productivity prediction based on mobility from pressure measurement while drilling. Petrol. explor. Dev. 47 (01), 146–153. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(20)60013-1
Song, L., Li, N., and Li, Q. (2011). Study of intrinsic relationship between mechanical parameters and parameters of rotary penetration test of soft rock. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 30 (06), 1274–1282.
Tan, Z., Yue, Z., and Cai, M. (2007). Analysis of energy for rotary drilling in weathered granite formation. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 182 (03), 478–483.
Teale, R. (1965). The concept of specific energy in rock drilling. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 2, 245–273. doi:10.1016/0148-9062(65)90016-1
Verhoef, P., Ockeloen, J., and Kesteren, W. (1996). The significance of rock ductility for mechanical rock cutting. Rock Mech. Tools Tech. 1, 709–716.
Wang, H., He, M., Zhang, Z., and Zhu, J. (2022). Determination of the constant m(i) in the Hoek-Brown criterion of rock based on drilling parameters. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 25, 615–621. doi:10.1016/j.ijmst.2022.06.002
Wang, H., He, M., Zhao, J., Zhang, Y., and Yang, B. (2023). Cutting energy characteristics for brittleness evaluation of rock using digital drilling method. Eng. Geol. 319, 107099. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107099
Wang, H., Qin, W., Jiao, Y., and He, Z. (2014). Transitions and opportunities of geotechnical engineering monitoring in coming big data era. Rock Soil Mech. 35 (09), 2634–2641.
Wang, Q., Gao, H., Jiang, Z., Li, S., and Jiang, B. (2020a). Development and application of a surrounding rock digital drilling test system for underground engineering. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 39 (02), 301–310.
Wang, Y., She, L., Zhao, Y., and Cao, R. (2020b). Experimental study on measurement of rock strength parameters based on digital drilling technology. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 42 (09), 1669–1678.
Wu, K. Q., He, M., Liu, X., Lu, B., Ma, X., and Ma, C. (2022). Characterizing rock transverse anisotropic spatial variations using digital drilling. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 232, 212451. doi:10.1016/j.geoen.2023.212451
Xie, H., Lin, P., Xu, Z., Kang, J., and Zhang, Q. (2025). Drilling response law for PDC bit cutting and breaking rock: governing equation and experiment validation. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. doi:10.1007/s00603-025-04532-6
Yagiz, S. (2002). Development of rock fracture and brittleness indices to quantify the effects of rock mass features and toughness in the CSM model basic penetration for hard rock tunneling machines. Colorado School of Mines.
Yan, T., Li, W., Bi, X., and Li, S. (2008). Fractal analysis of energy consumption of rock fragmentation in rotary drilling. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 27 (2), 3649–3654.
Yang, G., Li, T., Tang, H., Xing, D., Hu, Y., and Li, S. (2019). Evaluation method for the intactness of tunnel face surrounding rock based on tunnel face images. Q. J. Eng. Geol. Hydrogeology 57 (3), 2024018. doi:10.1144/qjegh2024-018
Yasar, E., Ranjith, P., and Viete, D. (2011). An experimental investigation into the drilling and physico-mechanical properties of a rock-like brittle material. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 76 (3-4), 185–193. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2011.01.011
Yue, Z. (2014). Drilling process monitoring for refining and upgrading rock mass quality classification method. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 33 (10), 1977–1996. doi:10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.10.005
Yue, Z., Lee, C., Law, K., and Tham, L. (2004). Automatic monitoring of rotary-percussive drilling for ground characterization-illustrated by a case example in Hong Kong. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. 41 (4), 573–612. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2003.12.151
Zhang, H., and Gao, D. (2005). Review on drill bit selection methods. Oil Drill. Prod. Technol. 027 (004), 1–5. doi:10.13639/j.odpt.2005.04.001
Zhang, W. (2003). Application of interval transit time to formation zonation in Zhoukou sag. Well Logging Technol. 27 (4), 317–319. doi:10.16489/j.issn.1004-1338.2003.04.014
Zhao, J., Wan, Z., Li, Y., Zhao, Y., Dong, F., Feng, Z., et al. (2009). Research on granite cutting and breaking test under conditions of high temperature and high pressure. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 28 (07), 1432–1438.
Keywords: digital drilling, rock breaking theory, mechanical parameters, machine-rock interaction, deep engineering
Citation: Fan K (2025) Advancements in digital drilling technology for deep engineering: a review. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1604584. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1604584
Received: 02 April 2025; Accepted: 28 April 2025;
Published: 22 May 2025.
Edited by:
Xin Yin, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaReviewed by:
Yonghui Zhang, Chang’an University, ChinaKaiqiang Wu, Xi’an University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Fan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Keqi Fan, ZmFua2VxaUAxMjYuY29t
 Keqi Fan
Keqi Fan