- 1CCTEG Xi’an Research Institute (Group) Co., Ltd., Xi’an, Shaanxi, China
- 2Hebei State Key Laboratory of Mine Disaster Prevention, North China Institute of Science and Technology, Beijing, China
- 3College of Construction Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun, China
The electrical characteristics of cement-based grouting materials are the foundation for implementing geophysical electrical exploration in coal mine grouting engineering. However, the preparation methods for high-resistivity grouting materials, which act as “contrast agents” in geophysical surveys, remain unclear due to the multiple influencing factors of resistivity. To address this, resistivity experiments were conducted using a self-developed apparatus to investigate the effects of curing age, admixture type, and dosage on the resistivity characteristics of grouting materials. This led to identifying optimal mix proportions for conventional cement-based high-resistivity grouting materials. Concurrently, mechanical strength tests were performed to analyze the impact of admixture dosage and curing age on compressive strength. The results indicate that the resistivity enhancement effects of four common cement additives can be ranked as follows: pyrophyllite powder >polyvinyl alcohol > air-entraining agent > fly ash. Considering both resistivity increase and mechanical strength, talc powder and polyvinyl alcohol emerge as viable candidates for use as additives in cement-based high-resistivity grouting materials. Specifically, with a talc powder dosage of 15%, the electrical resistivity of the grouted body after 28 days reached 4,966.7 Ω m, which is 119.1 times that of the control group (41.7 Ω m). Similarly, with a polyvinyl alcohol dosage of 1%, the resistivity reached 7,070.6 Ω m, which is 169.6 times that of the control group. These findings provide critical insights for developing high resistivity grouting materials with dual functionality as geophysical contrast agents and structural reinforcements.
1 Introduction
Cement is widely used in engineering projects. To ensure the quality of engineering works, many national governments have explicitly proposed encouraging enterprises, universities, and research institutes to develop new cement-based materials that can meet the specific needs of industrial and mining enterprises. Cement-based grouting materials, as specialized geotechnical composites, have become prevalent in mine water hazard mitigation projects owing to their safety advantages, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. It is mainly used for grouting reinforcement and grouting water blocking (Xu et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2022). The diffusion range of grout and the mechanical strength of grouted rock mass constitute two pivotal parameters for evaluating grouting effectiveness (Xu and Huang, 2006). The former parameter determines void filling completeness in target zones, while the latter governs structural integrity compliance with design specifications. These dual criteria must simultaneously satisfy design specifications, forming necessary and sufficient conditions for engineering quality assurance. The inherent concealment of underground grouting operations impedes precise monitoring of grout diffusion patterns and distribution states within rock-soil matrices, often leading to suboptimal grouting volumes (Zhou et al., 2015).
The primary electrical exploration technique for assessing grouting effectiveness relies on resistivity contrast analysis between pre-grouting and post-grouting stages to delineate grout distribution geometry. According to established petrophysical principles, water-saturated porous media demonstrate characteristic low-resistivity anomalies ranging from 45–130 Ω m (Yang et al., 2014; Song et al., 2013; Yu and Li, 1998; Zhang et al., 2025). The subsequent attenuation or elimination of these characteristic anomalies serves as a key indicator for evaluating grouting effectiveness. However, experimental evidence demonstrates that conventional pure cement slurry fails to manifest significant resistivity enhancement upon injection into aqueous media, maintaining resistivity values within 93–130 Ω m (Peng et al., 2011; Peng et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2019). Notably, in certain scenarios, post-grouting resistivity measurements may even register below groundwater background levels, thereby compromising the reliability of grouting effectiveness assessments. To enhance electrical contrast between grouted formations and water-bearing media, current research focuses on developing cement-based grouting materials with contrast-enhancing properties (characterized by resistivity values exceeding twice those of conventional cement slurry and significantly surpassing low-resistivity background values). The resistivity contrast between grouting materials and surrounding rock formations serves as a pivotal factor in determining grouting effectiveness in electrical prospecting. Enhancing this contrast pre- and post-grouting significantly improves the detection resolution of grout dispersion patterns through geophysical instrumentation (Gong et al., 2018; Liu and Zhang, 2024). The high-resistivity grouting material developed in this study demonstrates substantial scientific merit and extensive application potential, thereby providing theoretical foundations for optimizing grout propagation monitoring in electrical prospecting and enabling non-destructive quality evaluation of grouting operations.
Contemporary methodologies for formulating high-resistivity concrete materials typically incorporate mineral additives including slag, fly ash, natural zeolite, silica fume, and talc powder, alongside chemical additives such as sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), epoxy resin (EP), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and polypropylene fibers. Experimental investigations have substantiated that the addition of 25% fly ash induces a marked improvement in concrete resistivity across diverse water-cement ratios. This enhancement becomes particularly pronounced in low water-cement environments, exhibiting a fivefold resistivity amplification relative to standard concrete formulations (Gastaldini et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2024). Comparative studies on mineral admixtures have demonstrated that the application of silica fume significantly enhances electrical resistivity compared to slag, with synergistic effects observed in silica fume-fly ash composite systems (Liu, 2023; Yang and Wei, 2022). Through hierarchical analysis, the efficacy hierarchy for resistivity enhancement was established as follows: polymeric additives (e.g., polyvinyl alcohol) demonstrated superior performance, followed by mineral admixtures (including fly ash and ground slag), while lightweight aggregates (such as shale ceramsite and clay ceramsite) exhibited the lowest enhancement capacity (Ding, 2008; Simón et al., 2025). Innovative cement-based functional composites were developed through optimization of the talc/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) ratio, resulting in significant enhancement of electrical resistivity performance (Long, 2011; Guo et al., 2024). The hierarchical effectiveness of supplementary cementitious materials in resistivity enhancement was quantitatively established through characterization of high-resistivity concrete systems, demonstrating the efficacy sequence: silica fume > fly ash > zeolite powder > polypropylene fibers (You, 2018; Li et al., 2024). The existing body of research, encompassing both domestic and international investigations into high-resistivity grouting materials, has predominantly focused on experimental conditions with low water-cement (W/C) ratios ranging from 0.38 to 0.6. According to cement hydration theory, the critical thresholds defining high W/C ratios are established as follows: >0.45 for Portland cement (PC), >0.78 for calcium sulfoaluminate cement (CSA), and >0.6 for slag calcium sulfoaluminate (GSAC) cement (Liu, 2023). In practical coal mine grouting operations, PC-based formulations dominate technical applications, typically employing W/C ratios between 0.6 and 3 (Che et al., 2025), significantly exceeding the 0.45 threshold and thereby categorizing these slurries as high-W/C systems. Current research paradigms demonstrate two notable limitations: First, investigations into high-resistivity materials remain predominantly concentrated on conventional concrete applications. Second, systematic studies specifically targeting mining-optimized high-resistivity grouting materials remain notably scarce. This research gap becomes particularly critical when considering grouting materials with W/C ratios ≥0.8, where comprehensive experimental data regarding their resistivity characteristics and associated physicochemical properties are urgently required to establish reliable material design parameters.
To address these challenges, dynamic resistivity monitoring was performed using a custom-built long-term electrical resistivity monitoring system with automated data acquisition capabilities. A systematic investigation was conducted to evaluate the influence of additive types (fly ash, shale powder, polyvinyl alcohol, air entraining agent), dosage levels, and curing ages (3–28 days) on both electrical resistivity development and compressive strength evolution in Portland cement matrices. Through statistical correlation analysis of resistivity-strength relationships combined with multi-criteria optimization, the formulation demonstrating optimal balance between enhanced resistivity and maintained mechanical integrity was identified. This systematic characterization establishes fundamental correlations between compositional variables and functional properties, offering critical insights for developing advanced cementitious composites with tailored electrical characteristics.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental objectives
This study systematically examines the influence of supplementary additives on the volume resistivity and mechanical characteristics of cement-based grouting materials for mining applications under a fixed water-to-solid (W/S) ratio of 0.8. The primary objectives include optimizing high-resistance cementitious composites and establishing predictive regression models describing three fundamental relationships: (1) temporal evolution of electrical resistivity, (2) age-dependent compressive strength development, and (3) quantitative correlation between resistivity and mechanical strength. The W/S ratio is operationally defined as the mass ratio of water to total solid constituents (cement + additives), while additive dosage represents the mass percentage of supplementary materials - including fly ash (FA), pyrophyllite (PY), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and air-entraining agent (AEA) - relative to total solid content. All resistivity measurements refer to volume resistivity of standardized specimens determined through a custom-built long-term resistivity monitoring system.
2.2 Experimental materials
The materials studied in this experiment are cement, pyrophyllite powder, polyvinyl alcohol, fly ash, and air entraining agent. The performance indicators are as follows.
2.2.1 Cement
This experiment utilizes drilling plate slag silicate cement P O 32.5. The quality of the cement conforms to the Chinese national standards specified in General Portland Cement (GB 175–2007), as well as the amendments outlined in Chinese national standards for General Portland Concrete Amendment No. 2 (GB 175–2007/XG2-2014).
2.2.2 Pyrophyllite powder (PP)
Pyrophyllite exhibits excellent electrical insulation properties. This experiment uses 38 μ m pyrophyllite powder with uniform particle distribution, mainly composed of silicon dioxide (SiO2), magnesium oxide (MgO), iron oxide (Fe2O3), etc.
2.2.3 Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)
Polyvinyl alcohol has good insulation properties. The polyvinyl alcohol particle size selected for this experiment is 100 mesh, model 1788, mainly composed of polyvinyl alcohol groups (-CH2-CHOH-).
2.2.4 Fly ash (FA)
In a dry state, the electrical resistivity of fly ash is relatively high. In this experiment, fly ash from the Xingtai mining area power plant in Hebei Province was selected.
2.2.5 Air-entraining agents (AEA)
After dissolving the air entraining agent in water and adding it to the grouting material, a large number of uniform small bubbles can be generated during the mixing process, which can improve the electrical resistivity of the grouting material. In this experiment, the Dashengshi D-YQJ type was selected.
2.3 Experimental methods
2.3.1 Electrical resistivity test
Currently, there are three commonly used methods for testing concrete resistance (You, 2018; Wu et al., 2025): the two-electrode method, the four-electrode method, and the electrodeless method (Liu, 2023). The two-electrode method features a simple circuit and straightforward data processing; however, it is prone to testing errors due to electrode polarization. In contrast, the four-electrode method separates the power supply electrode from the test electrode, thereby reducing resistance testing errors associated with electrode polarization. Nonetheless, most current testing devices are manual and designed for single measurements (Xu et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2020), which limits their capability for automatic monitoring. Furthermore, the testing slot typically accommodates only a single sample, and the sample size often does not conform to the standard dimensions required for mechanical testing.
The electrodeless method eliminates contact and polarization errors caused by electrodes, but it is primarily suitable for assessing the early resistivity of concrete. The induced current generated by the 5V voltage supplied by the electrodeless method is often too small for accurate measurement. Additionally, the circular model of the specimen complicates sample preparation and poses challenges in controlling measurement conditions, such as saturation.
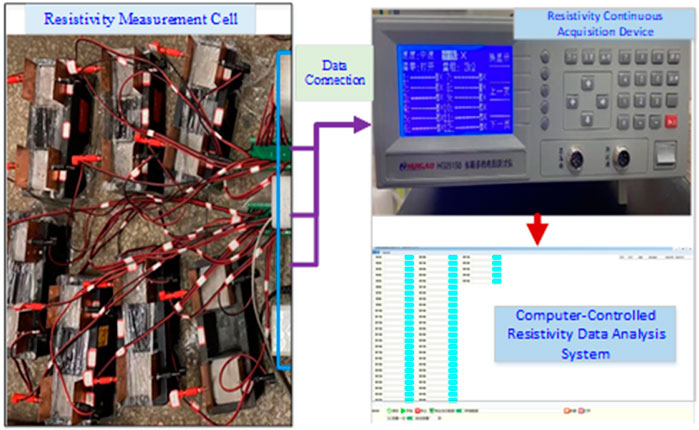
To overcome these technical limitations, a dedicated resistivity measurement system was designed and implemented in this study. The core component is a novel long-term online resistivity monitoring apparatus, which integrates a multi-channel thermistor-based resistance measurement module as its primary sensing unit. This integrated system facilitates continuous resistivity tracking with automated feedback regulation capabilities, as depicted in Figure 1. Physical diagram of the 'long-period' resistivity online automatic monitoring instrument, as depicted in Figures 1, 2.
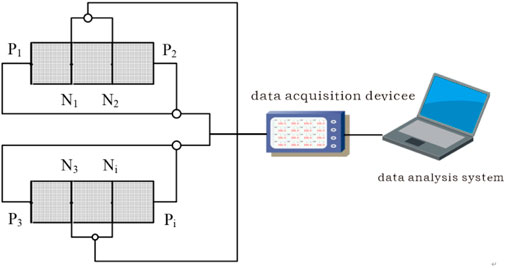
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the “long-period” electrical resistivity online automatic monitoring system.
The custom-developed resistivity monitoring system demonstrates four distinctive features for grouting material characterization.
2.3.1.1 Intelligent temporal control
The system implements programmable temporal parameters including single-cycle duration (13.3 Hz sampling frequency), interval period, and total monitoring duration through automated control algorithms. This design effectively mitigates electrode polarization effects during prolonged measurements.
2.3.1.2 Dynamic hydration process tracking
Through integrated data acquisition hardware and dedicated monitoring software, the system enables continuous resistivity tracking during cementitious material hydration, capturing real-time phase transformation characteristics.
2.3.1.3 Multi-specimen parallel monitoring
Featuring modular expansion capability, the apparatus supports simultaneous monitoring of ≥2 specimens (16 channels implemented in current experiments). This addresses the limitation of conventional concrete resistivity devices restricted to single-specimen measurements.
2.3.1.4 Dual-purpose specimen configuration
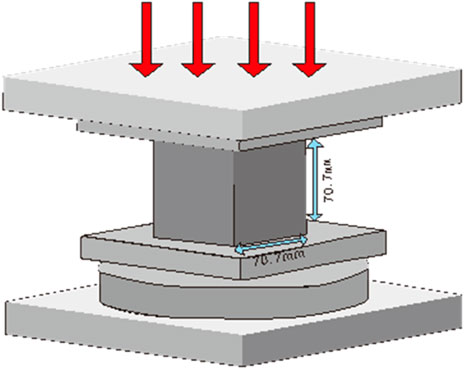
The tripartite specimen chamber incorporates standardized cubic molds (70.7 × 70.7 × 70.7 mm3, compliant with GB/T 50,082 concrete testing specifications). Post-curing specimens remain intact for subsequent 28-day mechanical property evaluation, optimizing material utilization efficiency in sequential testing protocols.
Calculate the resistivity value of the ith sample in the experiment using the following Formula 1:
where ρi denotes the resistivity of the ith sample (Ω·m), Ri is the measured resistance of the ith sample (Ω), Li is the electrode spacing (m), Si corresponds to the effective cross-sectional contact area between electrode and concrete (m2).
2.3.2 Compressive strength test
The STD-1006W microcomputer controlled electro-hydraulic servo hydraulic universal testing machine was selected for mechanical strength testing of grouting material samples. The mechanical strength of grouting material specimens was evaluated using an STD-1006W microcomputer-controlled electro-hydraulic servo universal testing machine. To investigate the effects of common mineral additives—including fly ash (FA), pyrophyllite powder (PP), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and an air-entraining agent (AEA)—on the electrical resistivity and mechanical properties of cement-based composites, five experimental groups were established using a controlled single-variable methodology. These groups include: the control group (pure cement), the cement + pyrophyllite powder group, the cement + high polyvinyl alcohol group, the cement + fly ash group, and the cement + air-entraining agent group.
Cubic specimens (70.7 mm × 70.7 mm × 70.7 mm) were fabricated in strict compliance with Chinese National Standard GB/T 50,080–2016 (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China & State Administration for Market Regulation, 2016). Each group contained 15 specimens, with 12 allocated for mechanical parameter determination and three reserved for resistivity measurements. Considering four curing ages (3, 7, 14, and 28 days), this design resulted in a total of 390 test points. Uniaxial compressive strength was determined through displacement-controlled compression at 0.5 mm/min loading rate, while electrical resistivity measurements followed the four-probe method using a GW Instek LCR-8105G impedance analyzer. Detailed experimental parameters including additive dosage ranges, mixing proportions, and curing conditions are systematically presented in Table 1.
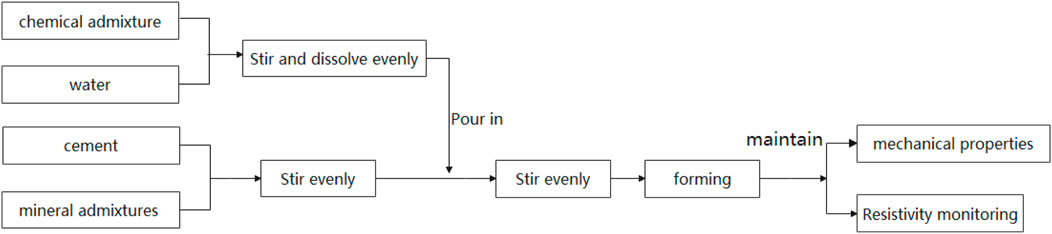
The experimental procedure consisted of the following steps (Figure 3).
2.3.2.1 Additive selection and dosage determination
High-resistivity additives (fly ash, pyrophyllite powder, polyvinyl alcohol, and air-entraining agent) were selected based on literature review. The dosage ranges were established as: pyrophyllite powder (0%–40%), polyvinyl alcohol (0%–4%), fly ash (0%–80%), and air-entraining agent (0%–0.2%).
2.3.2.2 Cement mixing
Cement and mineral admixtures were homogenized using a solid particle mixer with a water-to-solid ratio of 0.8:1 at 82 r/min for 90–100 s. The mixing parameters complied with the Chinese National Standard GB 50666–2011 for concrete structure construction.
2.3.2.3 Specimen molding
The liquid-solid mixture was poured into resistivity measurement molds after thorough stirring. Specimens for both resistivity and mechanical property testing were formed and initially cured under controlled conditions: (25 ± 2)°C temperature and (90 ± 5)% relative humidity.
2.3.2.4 Curing protocol
Molds containing specimens were transferred to a standard curing chamber for controlled hydration under predefined environmental conditions.
2.3.2.5 Parameter measurement
Resistivity evolution was monitored using a custom-built long-term resistivity monitoring system, with automated data acquisition at 5-min intervals during 1-h test sessions. Mechanical properties were assessed at 3, 7, 14, and 28 days using an electronic universal testing machine per standard mechanical testing protocols.
2.3.2.6 Data analysis
Experimental data were statistically analyzed to elucidate the impact mechanisms of additives on material resistivity. Optimal formulations were identified based on comprehensive evaluation of mechanical performance, resistivity characteristics, and cost-effectiveness.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Analysis of resistance test data
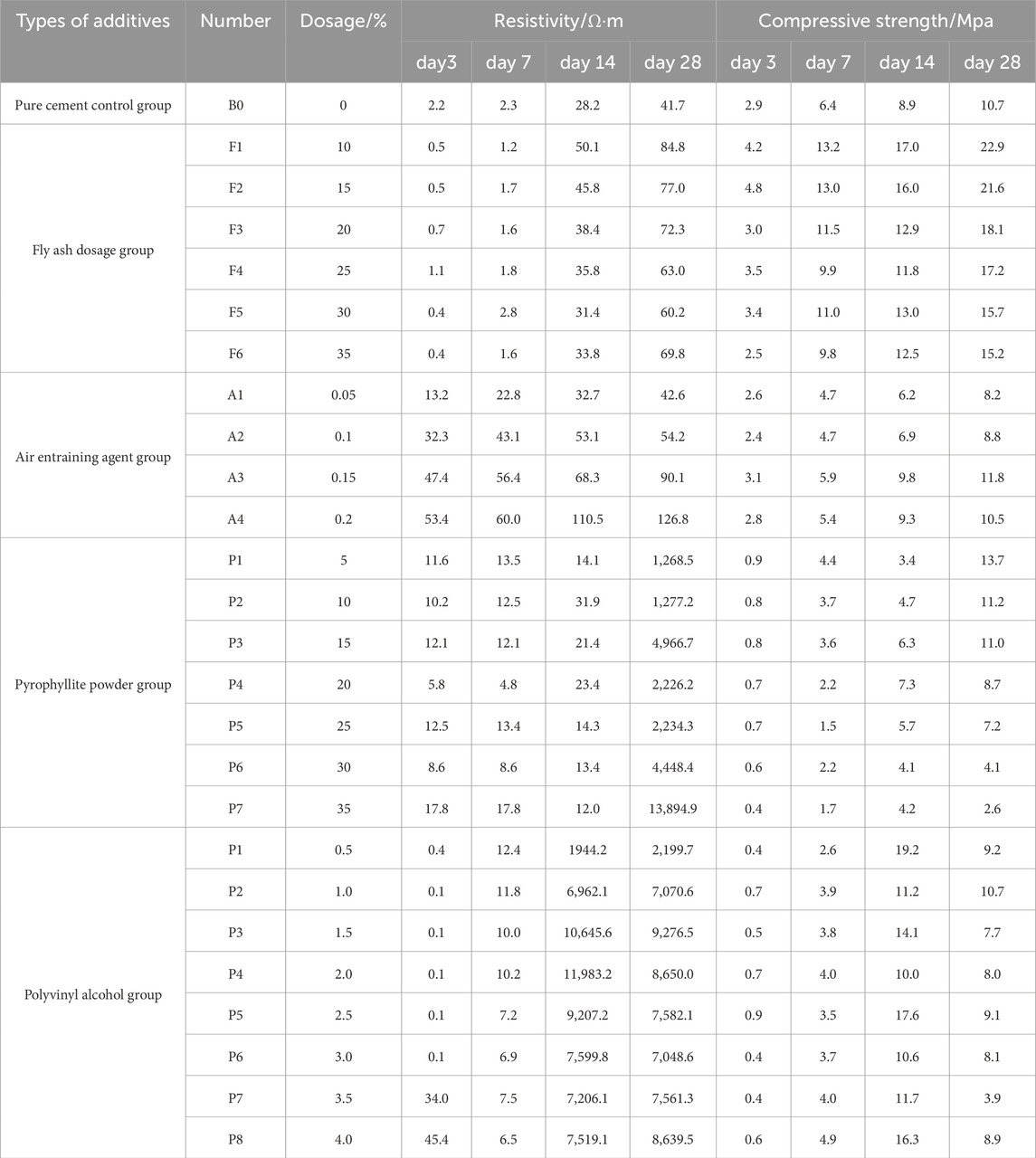
The volume resistivity values were calculated as the average of triplicate measurements. Table 2 summarizes the resistivity and tensile strength data for different additives across curing ages.
3.1.1 Effect of Fly Ash Content on electrical resistivity
Figure 4 illustrates the variation trends of electrical resistivity with fly ash content and curing age. The pure cement grout exhibited an age-dependent increase in resistivity, reaching 41.7 Ω m at 28 days. This value shows a minimal difference (5.2 Ω m) from the resistivity of the experimental water (46.9 Ω m), consistent with typical groundwater resistivity ranges (20–100 Ω m) reported by (Cheng et al., 2004). Such limited contrast suggests reduced efficacy of electrical contrast-based geophysical methods (Peng et al., 2011) for grouting quality assessment in similar hydrogeological environments. In fly ash-modified groups, resistivity remained low (<3 Ω m) during early curing (0–7 days), indicating negligible pozzolanic activity at this stage. A pronounced acceleration in resistivity development occurred between 14–28 days, with values significantly exceeding those of the initial curing phase.
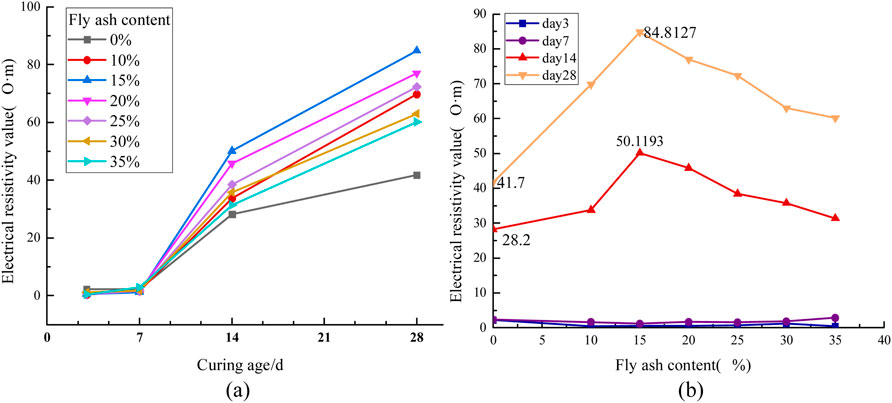
Figure 4. Effect of Fly Ash Content on the Electrical Resistivity of Grouting Materials (a) Relationship between resistivity and time variation (b) Relationship between resistivity and dosage variation.
Figure 4b demonstrates that specimens incorporating fly ash exhibited elevated electrical resistivity compared to the pure cement control group. The resistivity evolution displayed a non-linear response to incremental fly ash additions, with distinct behavioral phases observed. Specifically, electrical resistivity increased proportionally with fly ash content up to 15%, reaching maximum enhancement at this critical threshold. Beyond 15% content, an inverse correlation emerged where additional fly ash increments resulted in resistivity reduction. This transition point corresponds to the peak resistivity increase of 84.8 Ω m measured at 28 days, though the magnitude of this increase remained constrained compared to the control group.
3.1.2 Effect of air-entraining agent dosage on electrical resistivity
Figures 5a, b illustrate that the electrical resistivity of the grouting material increases as the dosage of the air-entraining agent rises. The increase in electrical resistivity from days 0–seven is relatively small, whereas from days 7–14, the increase is more pronounced. From days 14–28, the growth rate of electrical resistivity slows, which correlates with the sample’s porosity. An increase in the dosage of the air-entraining agent results in greater internal porosity of the cement-based grouting material; higher porosity corresponds to increased electrical resistivity (Yang et al., 2014; Weng et al., 2019) The rate of porosity increase is highest during the 7–14 day period, which explains the more rapid increase in electrical resistivity during this interval. While the addition of an air-entraining agent can enhance the resistivity of the grouting material, the increase remains limited. The dosage of the air-entraining agent that yields the greatest increase in resistivity is 0.2%, resulting in a maximum resistivity of 85.1 Ω m for the grouting material. In comparison to the control group, this increase is relatively modest.
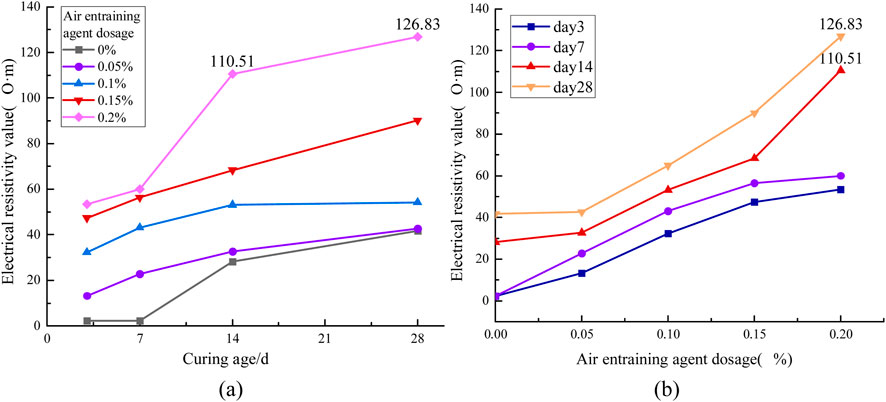
Figure 5. Effect of Air-Entraining Agent Content on the Electrical Resistivity of Grouting Materials (a) Relationship between resistivity and time variation (b) Relationship between resistivity and dosage variation.
3.1.3 Effect of pyrophyllite powder content on electrical resistivity
Figure 6 illustrates the temporal evolution of electrical resistivity in cement-based grouting materials containing varying proportions of pyrophyllite powder additive.
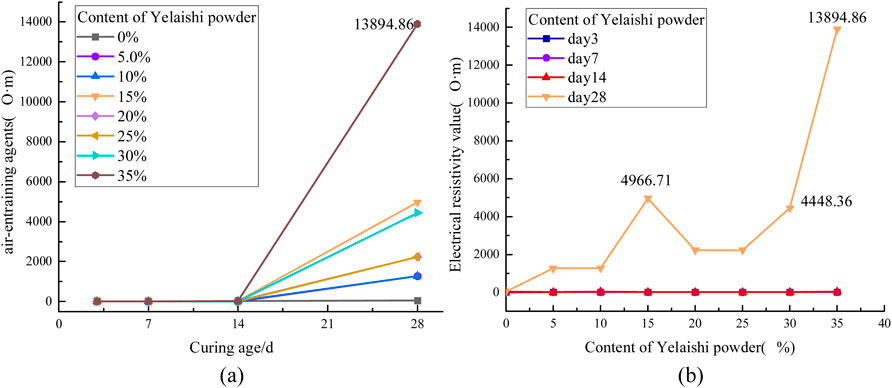
Figure 6. Influence of Talc Powder Content on the Electrical Resistivity of Grouting Materials (a) Relationship between resistivity and time variation (b) Relationship between resistivity and dosage variation.
As shown in Figure 6a, the resistivity exhibited a gradual increase during the initial 14-day curing period. A significant acceleration in resistivity growth was observed between 14 and 28 days, with all pyrophyllite-modified specimens demonstrating higher resistivity values compared to the pure cement control group. This trend aligns with findings reported by Chen in high-resistivity concrete preparation experiments (Long, 2011). Quantitative analysis revealed that specimens containing up to 45% pyrophyllite powder displayed a dosage-dependent resistivity enhancement, maintaining a positive correlation between additive content and electrical resistance.
Figure 6b demonstrates non-linear behavior in the dosage-resistivity relationship. Notably, a 15% pyrophyllite content resulted in minor resistivity fluctuations (ΔR < 5%), indicating complex interaction mechanisms between the additive and cement matrix. The most pronounced enhancement occurred at 35% dosage, achieving a resistivity of 13,895 Ω m at 28 days. These results suggest that optimized pyrophyllite powder incorporation (35%–45% range) significantly improves dielectric properties, making it a viable additive for high-resistance material engineering applications.
3.1.4 Effect of polyvinyl alcohol content on electrical resistivity
The electrical resistivity evolution of cementitious composites with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) dosage variation is systematically presented in Figure 7. The experimental data reveal three distinct curing stages: an initial slow growth phase (0–7 days) with limited resistivity enhancement, followed by an accelerated growth phase (7–14 days) characterized by rapid resistivity elevation, and ultimately reaching a stabilized growth pattern (14–28 days). Notably, at a dosage of 2%, the resistivity achieves its maximum value. As shown in Figure 7b, when the polyvinyl alcohol content is below 2%, electrical resistivity increases with higher dosage. However, when the content exceeds 2%, electrical resistivity starts to decrease. This suggests that a polyvinyl alcohol content of 2% represents a turning point in electrical resistivity and can be considered the optimal ratio for formulating high-resistance cement-based materials. Compared to the pure cement control group, the electrical resistivity of this formulation increased by 10,617.4 Ω m, significantly enhancing the material’s resistivity. This indicates that polyvinyl alcohol additives are effective for preparing high-resistance materials.
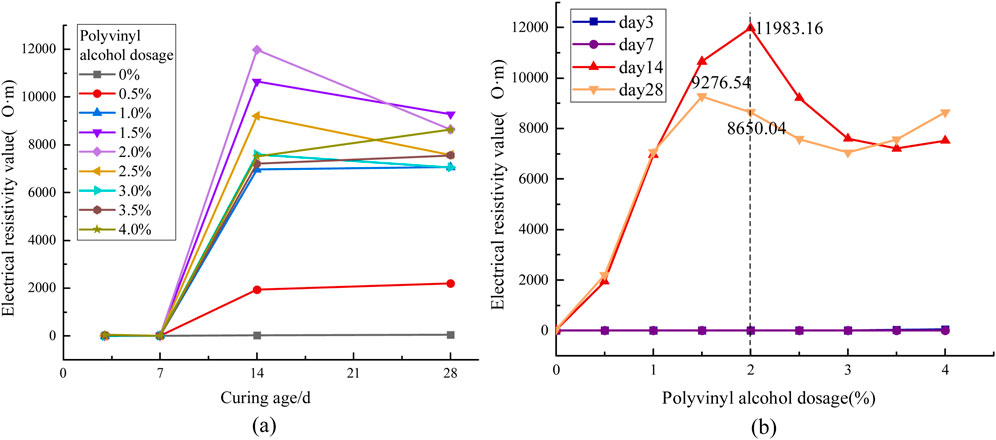
Figure 7. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on the electrical resistivity of grouting materials. (a) Relationship between resistivity and time variation (b) Relationship between resistivity and dosage variation.
3.1.5 Comparative analysis of high-resistivity grouting material formulations
The optimal ratio scheme was selected for each additive based on their respective resistivity enhancement performance. The resistivity values of selected ratios were comparatively analyzed, with the formulation demonstrating the maximum resistivity increment (Δρ) during equivalent curing periods being designated as the optimal high-resistance grouting material. The resistivity enhancement (Δρ) was calculated using the following Formula 2:
Where ρ is the measured resistivity (Ω·m), ρb is the baseline resistivity of the control group at equivalent timepoints.
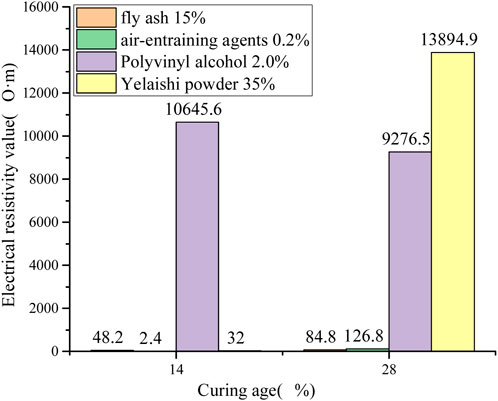
According to Table 3 and Figure 8 analysis, the overall order of the effect of the four additives on increasing the resistivity of cement-based materials in this experiment is as follows: pyrophyllite powder > polyvinyl alcohol > air entraining agent > fly ash. Optimal resistivity enhancement was achieved with 2.0% polyvinyl alcohol and 35% pyrophyllite powder additions, producing a 28-day resistivity increment of approximately 104 Ω m. Pre-grouting water-filled defects (cracks, voids, and existing cavities) exhibited marked electrical property contrasts post-grouting, establishing a robust foundation for resistivity-based evaluation of grouting effectiveness, including slurry diffusion range identification and filling completeness assessment (Song et al., 2013; Liu et al., 2011).
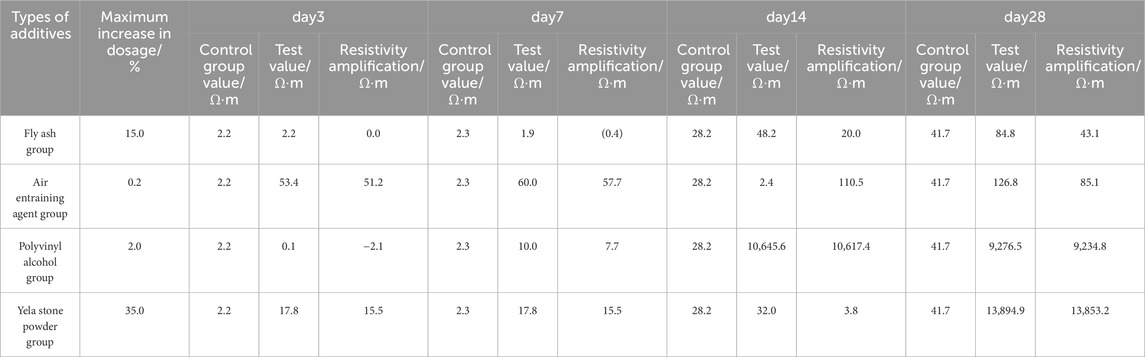
Table 3. Comparative analysis of the increase in electrical resistivity of grouting materials induced by additives.
3.2 Compressive strength evaluation of cementitious grouts
To enable effective resistivity monitoring while ensuring adequate mechanical performance, the compressive strength characteristics of four admixture formulations were systematically investigated.
In the experiment, standard cubes measuring 70.7 mm × 70.7 mm × 70.7 mm were utilized. A pressure testing machine was employed to cure the high-resistance grouting material specimens in a constant temperature and humidity chamber until they reached the predetermined design age. Upon reaching the specified curing age, the specimens were transferred to the compressive strength testing bench for evaluation. This process is illustrated in Figure 9. To ensure uniform force distribution during testing, a pressure strip was placed on both the upper and lower surfaces of each specimen. During the loading phase, a constant loading rate of 1 mm/min was maintained while recording real-time stress changes on the specimen. Upon failure of the specimen, the maximum pressure applied was recorded for further analysis. The compressive strength was calculated using the following Formula 3:
where f represents the compressive strength of the standard cement-based grout specimen.,The unit is MPa,.F denotes the ultimate load of the cube test block, The unit is N. And A indicates the cross-sectional area of the test block. The unit is mm2.
3.2.1 Effect of fly ash content on compressive strength development
Figure 10 illustrates the relationship between compressive strength development and both fly ash content (%) and curing period (days) under controlled material composition. As demonstrated in Figure 10, specimens containing fly ash exhibit higher mechanical strength than the pure cement control group. This indicates that the hydration products of fly ash enhance the compressive strength of cement-based materials. Compressive strength increases with curing time, with a critical transition observed at 10% fly ash content. Below 10% fly ash content, compressive strength exhibits a positive correlation with additive dosage. However, exceeding 10% fly ash content results in a gradual decline in compressive strength. As discussed in Section 2.1 regarding fly ash’s resistivity characteristics, a 15% fly ash dosage is recommended when utilizing this additive as a resistivity modifier for cement-based materials. This formulation achieves maximum resistivity enhancement while maintaining satisfactory mechanical performance.
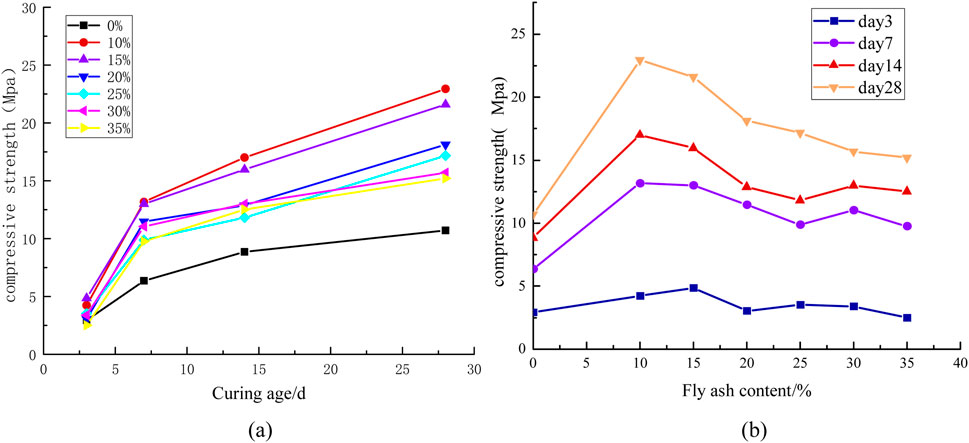
Figure 10. Effect of Fly Ash Content on Compressive Strength (a) Relationship between compressive strength and time variation (b) Relationship between compressive strength and dosage variation.
3.2.2 Effect of Air-entraining agent dosage on compressive strength
As evidenced by Figures 11a, b, increasing air-entraining agent dosage adversely affects compressive strength. Notably, a 0.15% dosage demonstrates exceptional behavior, with 28-day compressive strength exceeding that of the pure cement control group. This specific dosage represents a critical threshold for mechanical performance. Beyond this optimal value, compressive strength exhibits an inverse relationship with additive content. The strength reduction correlates with microstructural modifications, where higher dosages induce increased porosity and pore size within the grout matrix. This pore structure evolution ultimately degrades load-bearing capacity. This observation aligns with previous findings on pore structure-compressive strength relationships in cementitious materials (Liu, 2021; Weng et al., 2019).
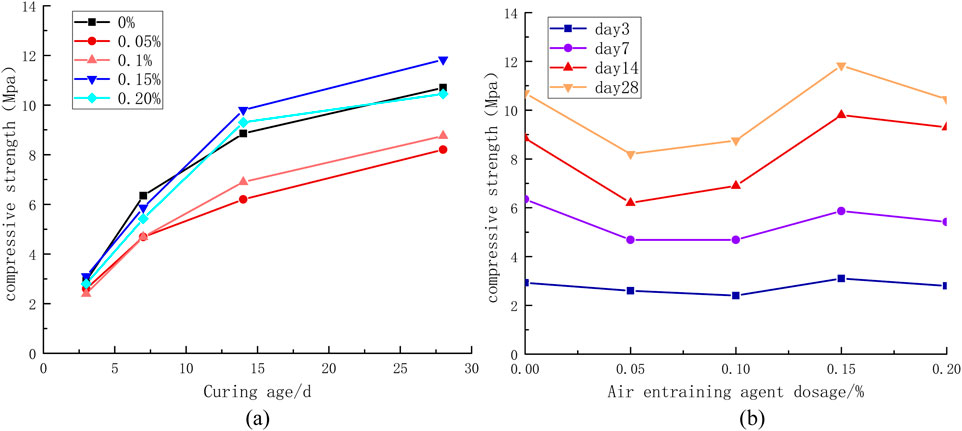
Figure 11. Effect of Air-entraining Agent on Compressive Strength (a) Relationship between compressive strength and time variation (b) Relationship between compressive strength and dosage variation.
3.2.3 Effect of pyrophyllite powder dosage on compressive strength
As revealed in Figures 12a, b, compressive strength exhibited progressive reduction with increasing pyrophyllite content during early curing stages (3–14 days). Notably, at 28-day maturation, specimens containing ≤15% pyrophyllite demonstrated 10.7 MPa strength enhancement over the pure cement group. Beyond this threshold, strength degradation occurred proportionally with additive content, ultimately underperforming the control group. Based on the analysis of the electrical resistivity characteristics with the addition of pyrophyllite powder, if pyrophyllite powder is used as a resistivity modifying additive for cement-based materials, it is recommended to choose a dosage of 15%. At this dosage, the electrical resistivity reaches 4,966.7 Ω m after 28 days, which is 119.1 times higher than the control group’s 4,925 Ω m. These findings establish technical basis for grouting diffusion monitoring via resistivity tomography.
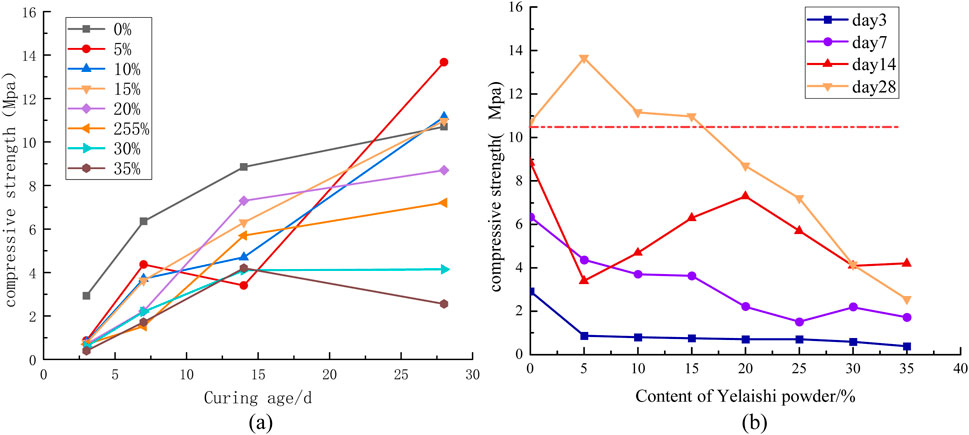
Figure 12. Effect of Talc Powder Content on Compressive Strength (a) Relationship between compressive strength and time variation (b) Relationship between compressive strength and dosage variation.
3.2.4 Effect of polyvinyl alcohol content on compressive strength
As shown in Figure 13a, the compressive strength on the 14th day significantly increases with PVA addition, likely due to PVA’s earlier crystallization compared to other cement components. This crystallization property explains the frequent use of PVA fibers in enhancing cement-based composites (Layssi et al., 2015; Chen, 2004; Wang et al., 2005). Figure 13b illustrates that the influence of PVA content on mechanical strength fluctuates across varying concentrations. At a PVA content of 1%, the compressive strength reaches 10.7 MPa, comparable to that of the control group. However, when PVA content exceeds 1%, the compressive strength decreases on the 28th day in correlation with the increased dosage. Based on the analysis of electrical resistivity characteristics, a PVA dosage of 1% is recommended when used as a resistivity modifier in cement-based materials. Although this dosage does not yield the highest resistivity increase, on the 28th day, the resistivity of the modified cement reaches 7,070.6 Ω m, which is 169.6 times greater than the control group’s resistivity of 41.7 Ω m. Concurrently, its compressive strength remains comparable to that of the pure cement control group.

Figure 13. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol content on compressive strength. (a) Relationship between compressive strength and time variation (b) Relationship between compressive strength and dosage variation.
4 Conclusion
1) The experimental results indicate that among the four common cement additives, their effectiveness in enhancing the resistivity of cement-based materials is ranked as follows: pyrophyllite powder > polyvinyl alcohol > air-entraining agent > fly ash. The optimal dosages for enhancing resistivity for each additive are as follows: fly ash at 15.0%, air-entraining agent at 0.2%, polyvinyl alcohol at 2.0%, and pyrophyllite powder at 35.0%. The inclusion of fly ash and air-entraining agent has a limited impact on resistivity enhancement and is therefore not recommended for use in high-resistance cement-based materials.
2) When the fly ash content is less than 10%, the compressive strength at 28 days increases with the addition of fly ash. However, when the fly ash content exceeds 10%, a decreasing trend in compressive strength is observed. Notably, when the fly ash content is less than 35%, its mechanical strength surpasses that of the pure cement control group. The compressive strength at 28 days is higher than that of the pure cement control group when the air-entraining agent dosage is 0.15%. Additionally, when the pyrophyllite powder content is below 15%, the compressive strength at 28 days exceeds that of the pure cement control group. Conversely, when the polyvinyl alcohol content exceeds 1%, the compressive strength at 28 days declines as the content increases. At a PVA content of 1%, the compressive strength is comparable to that of the control group, measuring approximately 10.7 MPa.
3) Considering the dual factors of enhanced electrical resistivity and mechanical strength, pyrophyllite powder and polyvinyl alcohol are identified as suitable additives for cement-based high-resistance grouting materials. At a dosage of 15% pyrophyllite powder, the electrical resistivity of the grouted stone body at 28 days is measured at 4,966.7 Ω m, representing a 119.1-fold increase compared to the control group (41.7 Ω m). Similarly, at a 1% dosage of polyvinyl alcohol, the electrical resistivity of the grouted stone body at 28 days reaches 7,070.6 Ω m, which is 169.6 times greater than that of the control group (41.7 Ω m). These ratios significantly enhance the reliability of the resistivity method for evaluating grouting effectiveness.
4) This experiment focuses solely on the variations in electrical resistivity and mechanical strength of cement-based materials with common additives at a water-to-solid ratio (W:C) of 0.8:1. However, the water-to-solid ratio in mine grouting often exceeds 0.8, necessitating further investigation into its impact on electrical resistivity and mechanical strength in subsequent studies. Additionally, this study examines the mechanisms underlying the effects of additives on the variations in electrical resistivity and mechanical strength. In future research, it will be essential to characterize the microstructure of the samples (e.g., pores, mineral composition) and investigate the hydration mechanisms of cement-based materials influenced by these additives.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
BX: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Data curation. RQ: Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SD: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. ZD: Validation, Writing – review and editing, Supervision. SY: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. HM: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. CZ: Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 3142020002, No. 3 142021004), National Natural Science Foundation of China (42202291), the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC3005701-04, 2024YFC3013802) during the 14th Five-Year Plan Period.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers of this paper for their constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
Authors BX, SD, and HM were employed by CCTEG Xi’an Research Institute (Group) Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Che, Z., Wang, T. L., Zhou, Z. G., Wang, S. W., and Ma, X. W. (2025). Research on cement-free grouting material for shield tunneling in water-rich karst regions. Materials 18 (6), 1192. doi:10.3390/MA18061192
Chen, J. M., Xia, H. Y., Lin, Z. W., Guo, R. X., Suo, Y. X., Wu, Y. C., et al. (2020). Investigation on mechanical properties of graphene nanoplatelets reinforced cement-based composite with different curing ages and water-cement ratios. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 39 (6), 1703–1708. doi:10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2020.06.002
Cheng, Y. X., Liu, H. S., and Zhao, Z. Y. (2004). Investigation of urban landfill contamination using geophysical methods. Chin. J. Eng. Geophys. (01), 26–30.
Ding, H. T. (2008). Research on high impedance and high impermeability concrete for subway applications. Wuhan Univ. Technol.
Gastaldini, A. L. G., Isaia, G. C., Hoppe, T. F., Missau, F., and Saciloto, A. (2009). Influence of the use of rice husk ash on the electrical resistivity of concrete: a technical and economic feasibility study. Constr. Build. Mater. 23 (11), 3411–3419. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2009.06.039
Gong, Y. F., Yang, T. C., Dong, S. Y., and Jiang, K. (2018). High density resistivity method for detecting grouting reinforcement quality of pipe jacking. Geophys. and Geochem. Explor. 42 (06), 1317–1320. doi:10.11720/wtyht.2018.0011
Guo, Y. H., Li, P. F., Sun, Q., and Liu, J. P. (2024). Characteristics of physico-mechanical evolution of cement-fly ash slurry agglomerates with different ratios. J. Xi' Univ. Sci. Technol. 44 (5), 846–856. doi:10.13800/j.enki.xakjdxxb.2024.0505
Li, X. L., Du, X. J., Feng, G. R., Ju, F., Wang, J. W., Liu, W. H., et al. (2024). Failurecharacteristics and strength formation mechanism of cement-fly ash based cemented gangue backfill. Coal Sci. Technol. 52 (5), 36–45.
Liu, G., Xu, J., Wang, M., and Sun, S. (2011). The application of high-density resistivity method to landfill leakage detection. Geochemical and Geophysical Exploration 35 (5), 680–683+691. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2024.03.010
Liu, J., and Zhang, Y. M. (2024). Effect of air entraining agent on properties of lightweight plastering gypsum mortar. J. Build. Mater. 27 (03), 1–11. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2024.03.010
Liu, Q. (2021). Study on air voids formation mechanism and influencing factors of air-entrained concrete. Doctoral dissertation, Harbin Institute of Technology. doi:10.27061/d.cnki.ghgdu.2021.000090
Liu, W. J. (2023). Study on mechanical properties and application of slag calcium sulphoaluminate cement under high water cement ratio. Hebei Univ. Technol.
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China (MOHURD) and State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) (2017). Standard for test methods of performance of ordinary concrete mixtures (GB/T 50080-2016). Beijing, China: China Architecture and Building Press.
Peng, Y. L., Hu, X. W., and Song, D. G. (2013). Inspection method for grouting effect in treating large complicated cavities due to mining. J. Eng. Geol. 21 (04), 664–671.
Peng, Y. L., Hu, X. W., Song, D. G., Zhang, L., Zheng, Y. X., and Sun, M. H. (2011). Test study of geophysical method on grouting quality evaluationin complicated cavities. Hydrogeology and Eng. Geol. 38 (05), 38–42+48. doi:10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2011.05.004
Simón, P., Lizarazo, J. M., Camilo, H. F., and Alejandro, U. (2025). Fly ash blended cement resistivity monitoring using carbon screen-printed electrodes. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 44 (2), 34. doi:10.1007/s10921-025-01167-z
Song, D. G., Hu, X. W., Peng, Y. L., Zheng, Y. X., and He, X. (2013). Comprehensive geophysical prospecting methods for the detection of grouting quality in complex mined-out areas. Geotechnical Investigation and Surv. 41 (05), 85–89.
Weng, Y. B., Zhao, R. H., Xu, A., Zhou, X. Y., and Mei, C. (2019). Influence of different air-ent raining agent on the porosity and conductivity of ionically conductive mortar. Concrete (04), 91–96. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2019.04.021
Wu, G. Z., Qiao, Z., Song, L., Zhang, J., Li, W. B., Yang, T. T., et al. (2025). Research on preparation and performance of new composite cement-based weakly consolidated soil grouting material. New Build. Mater., 44–50.
Xu, B., Dong, S. N., Xu, L. L., Zhou, Y., Chen, J. J., Dai, Z. X., et al. (2019). Stability of cement-based grouting slurry and test of its bleeding law. Coal Geology&Exploeration 47 (05), 24–31. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2019.05.004
Xu, H. G., and Huang, M. L. (2006). Overview of grouting effect detection methods. Proc. 15th Natl. Symposium Geotechnical Anchoring Eng. Organ. by China Assoc. Geotechnical Anchoring Eng. Guilin, 224–231.
Yang, J. M., Wei, Z. Z., and Gao, X. W. (2014). The application of the methods of high density resistivity method and transient electromagnetic to detecting coal mining goaf and to inspect grouting effeet. Prog. Geophys. (in Chinese) 29 (1), 0362–0369. doi:10.6038/pg20140151
Yang, L. W., Wei, H., He, W., Meng, X., Shen, Y., Du, T., et al. (2022). Influence of dolomite rock powder and iron tailings powder on the electrical resistivity, strength and microstructure of cement pastes and concrete. Coatings 12 (1), 95. doi:10.3390/coatings12010095
You, C. (2018). Study on the preparation and properties of high resistivity concrete. AnHui University of Science and Technology.
Yu, J. C., and Li, Z. D. (1998). The high density resistivity method used for detecting foundation grouting. Geology and Prospecting 1998 (05), 50–53.
Zhang, K. K., Guo, X. J., and Li, N. (2019). Progress on electrical resistivity method to monitoring submarine groundwater discharge from 1998 to 2018. Progress in Geophysics(in Chinese) 34 (04), 1700–1706. doi:10.6038/pg2019CC0284
Zhang, L. X., Guo, Y. Q., and Wang, N. F. (2025). Study on microstructure evolution law of steel slag modified cement-based material under CO2 curing condition. Shandong Coal Science and Technology 02, 185–190. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-2801.2025.02.037
Zhang, R. Q., Xu, B., Yin, S. S., Li, S. X., Chang, Y. W., Lian, H. Q., et al. (2022). Quantitative experimental study on time-varying characteristics of bleeding of cement-based grouting materials. Coal Geology and Exploration 50 (11), 153–161. doi:10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.04.0224
Zhang, Y. D., Zhang, F. Y., Xie, L., Gao, Y. Z., Wang, Y. X., and Wang, S. L. (2024). Research on correlation between microstructure and mechanical properties of low strength recycled concrete. WaterResourcesandPower 42 (4), 111–114. doi:10.20040/j.cnki.1000-7709.2024.20230773
Zhao, Z., Meng, Q. S., Han, K., Liu, S. B., and Xiao, Z. G. (2017). Rock mass velocity ima-ging based on high density resistivity method in near surface engineering. Computing techniques forgeophysical and geochemical exploration 39 (06), 742–747. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2017.06.05
Keywords: coal mine grouting, cement-based materials, admixtures, high-resistivity ratio formulation, compressive strength
Citation: Xu B, Qi R, Dong S, Dai Z, Yin S, Ma H and Zhong C (2025) Experimental investigation on the resistivity and mechanical properties of high-resistance cement-based grouting materials for mining. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1604681. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1604681
Received: 02 April 2025; Accepted: 05 May 2025;
Published: 12 June 2025.
Edited by:
Binbin Yang, Xuchang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Mu Wenping, China University of Geosciences, ChinaHongfu Sun, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing, China
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Qi, Dong, Dai, Yin, Ma and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bin Xu, amluemlnYW9mZW5nQDEyNi5jb20=; Shuning Dong, ZG9uZ3NodW5pbmdAY2N0ZWd4aWFuLmNvbQ==
 Bin Xu
Bin Xu Rongrong Qi2
Rongrong Qi2 Zhenxue Dai
Zhenxue Dai Shangxian Yin
Shangxian Yin Hewen Ma
Hewen Ma