- 1School of Hydraulic and Civil Engineering, Ludong University, Yantai, China
- 2College of Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, Shandong, China
- 3China Construction Infrastructure Corp., Ltd., Beijing, China
- 4Shandong Hi-Speed Construction Management Group Co., Ltd., Jinan, China
Huangfan District silt exhibits discontinuous grading, low structural integrity, and insufficient binder content, failing to meet traffic subgrade specifications. This study employs alkali-activated basalt powder and slag (solid wastes) to form geopolymers for silt stabilization, analyzing stabilized soil subgrade slope stability. Key findings: (1) Alkali-activated basalt-slag synergy enhances mutual hydration, producing N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H cementitious gels. (2) Geopolymer content positively correlates with compressive strength, peaking at 20% dosage (2.74 MPa) - a 30.4-fold increase over natural silt, exceeding specification requirements by 10.96-fold. (3) Shear strength increases with vertical pressure and additives (NaOH, Na2SiO3, slag), showing significantly improved internal friction angle and cohesion versus natural silt. (4) With the increase of the content of geopolymer in solidified soil, the maximum vertical displacement of the roadbed surface and the displacement of the slope gradually decrease. The stress is mainly concentrated in the tire grounding area and gradually decays along the depth direction. The vertical stress values at other positions of the road slope are maintained at a low level.
1 Introduction
Loess-like soils are widely distributed within Shandong Province, China, with loess from the Yellow River floodplain being predominant, accounting for approximately one-third of the province’s total land area. This type of loess exhibits inherent deficiencies such as poor gradation continuity, weak structural stability, and a lack of binding materials, leading to inadequate compaction performance and poor moisture stability. These characteristics make it challenging to meet the engineering performance requirements for road base slopes, severely limiting its direct application in road construction projects. Currently, lime-based stabilization techniques are commonly used to improve loess for slope stabilization (Liu et al., 2020). However, this method has significant environmental drawbacks: the cement industry contributes to about 8% of global CO2 emissions and releases pollutants like dust, SO2, and fluorides. The negative impacts of cement use are fundamentally at odds with the green development requirements of the Yellow River Basin Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development Strategy (Tan et al., 2023). Therefore, developing environmentally friendly soil stabilization materials has become a critical technological challenge in geotechnical engineering.
Domestic and international scholars have conducted relevant research (Hasan et al., 2021). Cristelo et al. (2011) and Liu et al. (2016) used alkali-activated fly ash to stabilize loess and soft soil, demonstrating that alkali activation significantly enhances soil strength and improves its microstructure. Cui et al. (2022) utilized steel slag as a substitute for cement to effectively increase the compressive strength of clay. Syahril et al. (2020) employed volcanic ash and tailings to stabilize subgrade soil, resulting in a bearing strength far greater than that of the native soil. Rehma and Khalid (2021) developed a composite stabilization technique using waste face masks (FM) and silica powder materials. Waste face masks (FM) can effectively regulate soil plastic deformation capacity. Through the hydration reaction of the silicate phase, C-S-H gel is generated, which, in conjunction with the three-dimensional constraint network formed by FM fibers, achieves dual optimization of dynamic strength enhancement and ductility control. Sumesh and Sing (2020) systematically studied the engineering properties of fly ash-soil composite materials, evaluating the mechanical response mechanisms of the improved materials, with the maximum CBR corresponding to a 20% fly ash content. Dassekpo et al. (2021) used a NaOH + Na2SiO3 composite solution to activate loess, significantly increasing its compressive strength (17.26–27.26 MPa), with the addition of Na2SiO3 promoting the synthesis of the cementitious phase.
During the development of basalt mineral resources in China, a significant amount of waste material, including offcuts and debris, has accumulated over time, resulting in a stockpile of hundreds of millions of tons. Traditional landfill disposal methods not only occupy large areas of land but also pose environmental risks. Basalt, a typical silicate mineral, primarily consists of SiO2(45%–55%)、Al2O3(12%–18%), and is rich in active components such as Fe2O3, CaO, and MgO. The long-term use of landfill disposal for basalt solid waste leads to the wastage of silicon and aluminum resources and potential environmental hazards. Given its high content of silicon and aluminum oxides, developing geopolymer conversion technology for basalt can produce high-strength geopolymer cementitious materials under alkaline activation (Mohsin and Ana, 2023).
This paper innovatively proposes a technical pathway for preparing geopolymer-based base improvement materials by synergistically utilizing basalt waste and slag. By stabilizing loess with basalt waste and slag geopolymer, it enhances soil properties while achieving the reuse of industrial solid waste, aligning with the strategic needs of sustainable development.
2 Experimental studies
2.1 Test materials
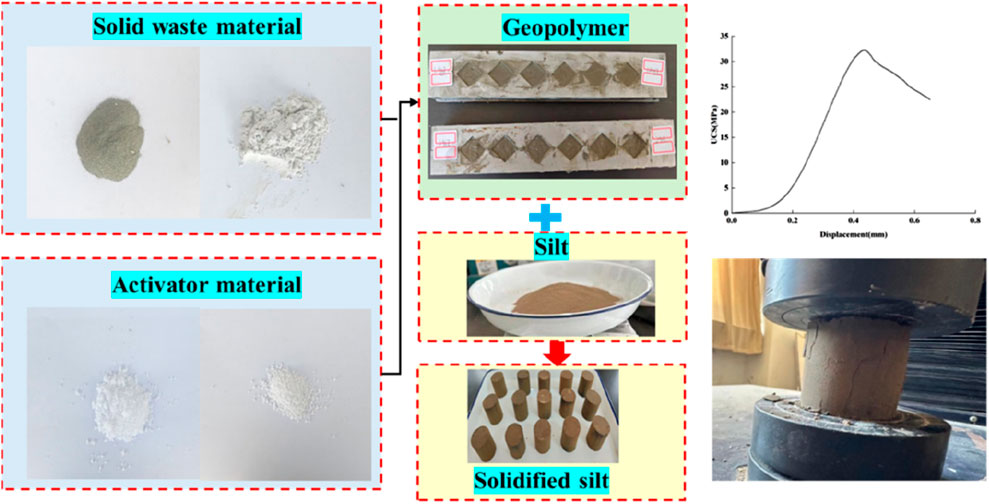
The tested silty soil specimen, representative of the Yellow River alluvial plain (Huangfan area) in Jiyang District, Jinan, was processed in strict compliance with the technical protocol specified in Code for Geotechnical Testing of Highway Engineering (JTG 3430-2020). The pretreatment chain consists of:(i) fragmentation of natural soil clods using a planetary grinder; (ii) sequential dehydration in a forced-air oven maintained at 105°C ± 2°C until mass stabilization (<0.1% weight variation in 24 h); (iii) grading preprocessed materials through electrodynamic vibration sieves (mesh aperture = 2 mm; UMS-750 model) achieving 95% undersize benefit. Based on indoor geotechnical test data analysis, the basic physical properties of the soil sample and the mineral composition of solid waste were determined, as shown in Table 1, 2.
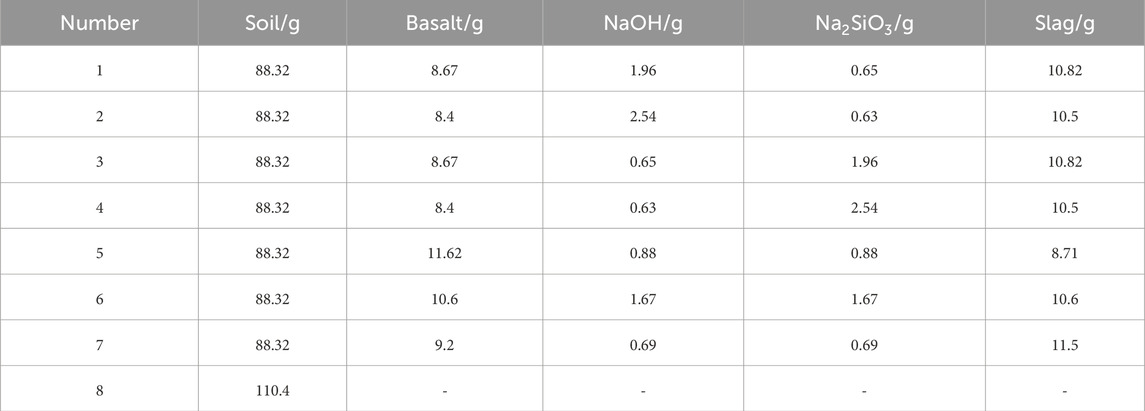
The solid waste materials used in this experiment are slag powder and basalt powder, and the exciters are sodium silicate and sodium hydroxide, as shown in Figure 1. According to the previous test, the optimal ratio of geopolymer materials is determined. The content of slag powder and basalt powder is 52% and 42% of the mass of the geopolymer, the content of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate is 3% of the mass of the geopolymer, and the unconfined compressive strength of the geopolymer is 31.02 MPa.
2.2 Compaction characteristics of solidified silt
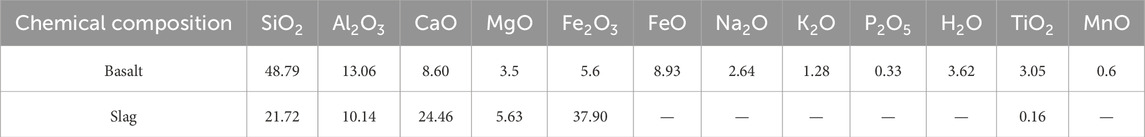
Fixed the comprehensive mass base of silt soil and geopolymer, set the content of geopolymer to 20%, 18%, 16% and 14% of the total mass respectively, and established four groups of control models to systematically explore the effect of step change of content on the stability of solidified silt subgrade slope. The compaction test is a light compaction test. Different moisture content solidified soil samples are prepared to obtain the density data of solidified soil with different moisture content, and the solidified soil compaction curve is obtained, as shown in Figure 2.
As shown in Figure 2, the increasing trend of the optimal moisture content of the solidified silt is strictly positively correlated with the increase in the content of the geopolymer, while the decreasing correlation with the maximum dry density is attributed to the chain polymerization of the geopolymer under alkali excitation-which accelerates the localized immobilization process of chemically bound water, forces the external water replenishment demand to increase to meet the double effect (liquid phase pore lubrication maintenance and Si-O copolymer structure growth), synchronously induces the encapsulation and replacement of the dense mineral phase by the gel network, and drives the dry density to a layer convergence state with the increase of the content through the looseness of the phase distribution topology.
2.3 Analysis of mineral composition of solidified silt
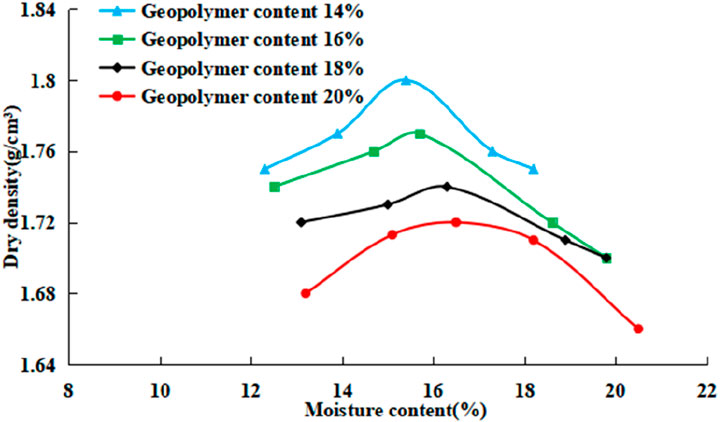
This research carried out X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis on silty soil as well as solidified soils with two distinct geopolymer ratios, specifically 14% and 20%. As depicted in Figure 3, the mineral composition of the untreated silty soil encompasses typical aluminosilicate minerals. These include quartz, accounting for 65.2%, plagioclase at 19.2%, pyroxene with 11.9%, and kaolinite at 2.1%. Subsequent to geopolymer solidification, the solidified soil continues to have quartz as its principal crystal phase. However, the intensity of its characteristic diffraction peak, for instance, the one at 2θ = 26.6°, experiences a marked weakening. Simultaneously, broadened diffraction peaks emerge in the low - angle region (2θ ≈ 10°–30°). This phenomenon verifies the formation of an amorphous gel phase during the depolymerization - recombination process of the aluminosilicate network. Notably, compared to the 14% - dosage sample, the 20% - dosage sample exhibits a more extensive range of broad-peak characteristics and an augmentation in peak intensity. This indicates that the high - dosage system promotes the topological polycondensation of the three - dimensional network structure via the synergistic coordination of multivalent cations, namely, Ca2+ and Na+.
The augmentation of amorphous scattering in the XRD pattern discloses the synergistic cementation mechanism of the basalt - slag binary system under the influence of the alkaline activator (Na2SiO3/NaOH) (Figure 3). The Ca2+ released from the slag and the [SiO4]4-/[AlO4]5- monomers leached from the basalt undergo coordination reconstruction within the OH− medium, thereby forming a composite gel phase of N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H with a spatial network configuration. As the dosage escalates, the quantity of the generated cementitious phase increases, effectively filling the voids among the silty soil particles and enhancing the density of the solidified soil. The characteristic diffuse peaks within the 2θ = 20°–40° range in the diffraction pattern and the enhanced diffraction of the zeolite phase further corroborate the cementation process of the formation of a three - dimensional network structure through the dehydroxylation condensation of the aluminosilicate tetrahedron under alkaline conditions. The evolution of this microstructure is significantly correlated with the macroscopic mechanical behavior manifested as an increase in the unconfined compressive strength of the sample.
3 Study on mechanical properties of solidified silt
3.1 Compressive strength of solidified soil
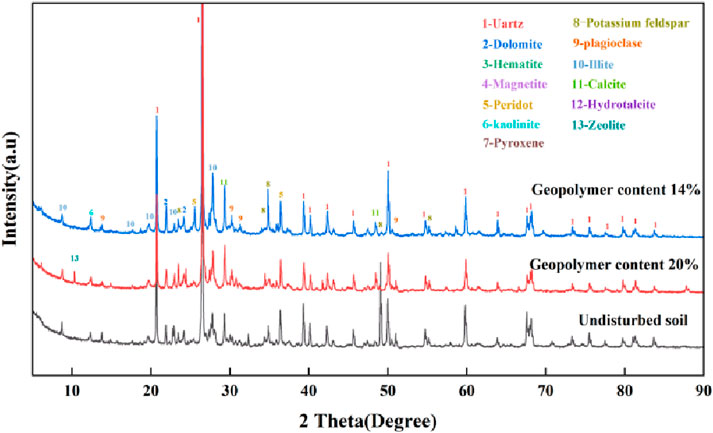
As can be seen from Figure 4, the unconfined compressive strength of solidified soil is 2.74 MPa when the mixing ratio of solidified material is 20%, 1.66 MPa when 18%, 0.91 MPa when 16%, and 0.45 MPa when 14%, while the unconfined compressive strength of undisturbed soil is 0.09 MPa. Comparing the strength data of undisturbed soil and improved soil, it is obvious that the unconfined compressive strength of undisturbed soil is extremely low. When the dosage is 14%, 16%, 18% and 20%, the unconfined compressive strength of solidified soil is increased by 400%, 911%, 1744% and 2,944%, respectively. With the continuous increase of the content of geopolymer materials, the unconfined compressive strength of solidified soil materials also increases. The main reason is that the solid waste material generates C-A-S-H gel and N-A-S-H gel and other hydration products to fill the gaps between the soils under the action of alkali excitation. The cementitious material presents a three-dimensional network structure, which effectively improves the microstructure of the soil and increases the compressive strength of the solidified silt.
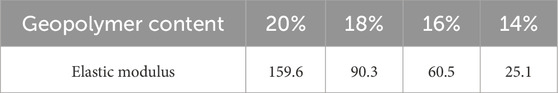
When the content of geopolymer increases from 14% to 20%, the elastic modulus of solidified silt showed a continuous increasing trend (Table 3).
3.2 Shear strength of solidified silt
Design different solid waste material ratio test plan (Table 4; Figure 5), in order to explore the different mixing ratio changes on the shear strength of solidified soil, compaction degree of 96%, the optimal moisture content modulation solidified silt samples.
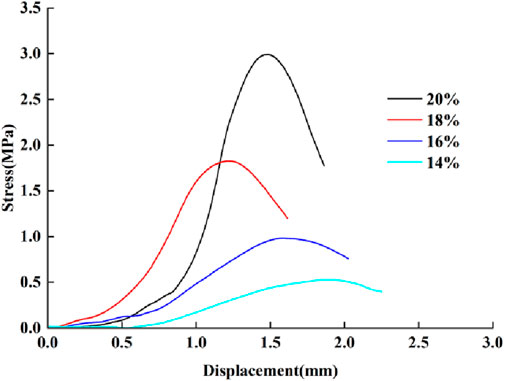
The shear strength-displacement curves of the modified geopolymer systems with different gelling ratios show significant differences, as shown in the mechanical evolution characteristics in Figure 6: Under the normal stress (sigma) layer loading conditions, the ultimate shear strength of the plain soil and the cured modified samples showed a positive correlation growth trend. However, the cured soil exhibited a sudden structural disintegration phenomenon in the strain softening stage after the peak strength - the stress concentration effect of the main slip surface induced the brittle fracture of the gel network, and the shear strength decrease rate was significantly higher than that of the plain soil, which is in line with the critical failure response characteristics of typical brittle solid materials. In contrast, the failure process of undisturbed soil is controlled by mineral grain rearrangement and viscous flow, and has the characteristics of continuous plastic flow. The stress-strain constitutive shows a typical ductile dissipation effect, and no stress drop behavior in the solidified system has been observed.
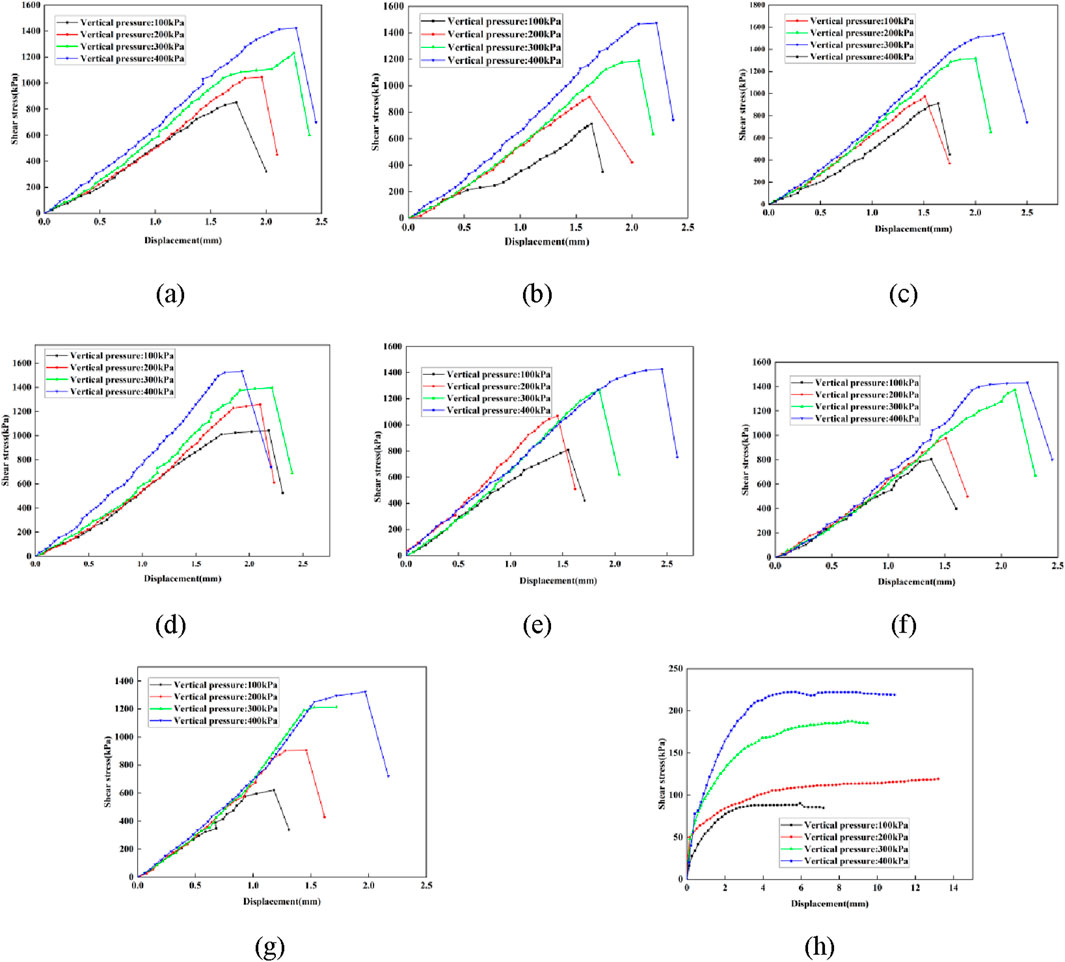
Figure 6. Shear stress curve of specimen. (A) Number 1. (B) Number 2. (C) Number 3. (D) Number 4. (E) Number 5. (F) Number 6. (G) Number 7. (H) Number 8.
Experimental data analytics based on the consolidation mechanism of geopolymer materials show that: The test results in Figure 7 show that the shear strength of the solidified silt is significantly positively correlated with the amount of alkaline activator (sodium hydroxide/sodium silicate). This is attributed to the increase in the concentration of the alkaline environment, which effectively promotes the depolymerization-condensation reaction process of the aluminosilicate phase. When the amount of activator increases, the degree of geopolymer reaction is significantly increased, and the amount of gel products is correspondingly increased. The three-dimensional network gel structure formed by solid waste materials under alkali excitation not only fills the pores as a cementing phase, but also strengthens the interfacial bonding between soil particles through chemical bonding, achieving the overall optimization of shear strength. The decrease in the content of slag powder will lead to a linear decay in the shear strength of the solidified system. This is due to the complementary effect of the components between the slag powder and the basalt solid waste: the calcium-rich components in the slag can synergistically polymerize with the active silica and aluminum in the solid waste to form a composite gel system of C- (A) -S-H and N-A-S-H. When the slag content is insufficient, the decrease in the concentration of Ca2+ in the system leads to the homogenization of the type of gel products, the decrease in the crosslinking density of the network structure, and the local discontinuity of the microstructure, which makes it difficult to form an effective stress transfer network, ultimately resulting in the deterioration of the macroscopic mechanical properties.
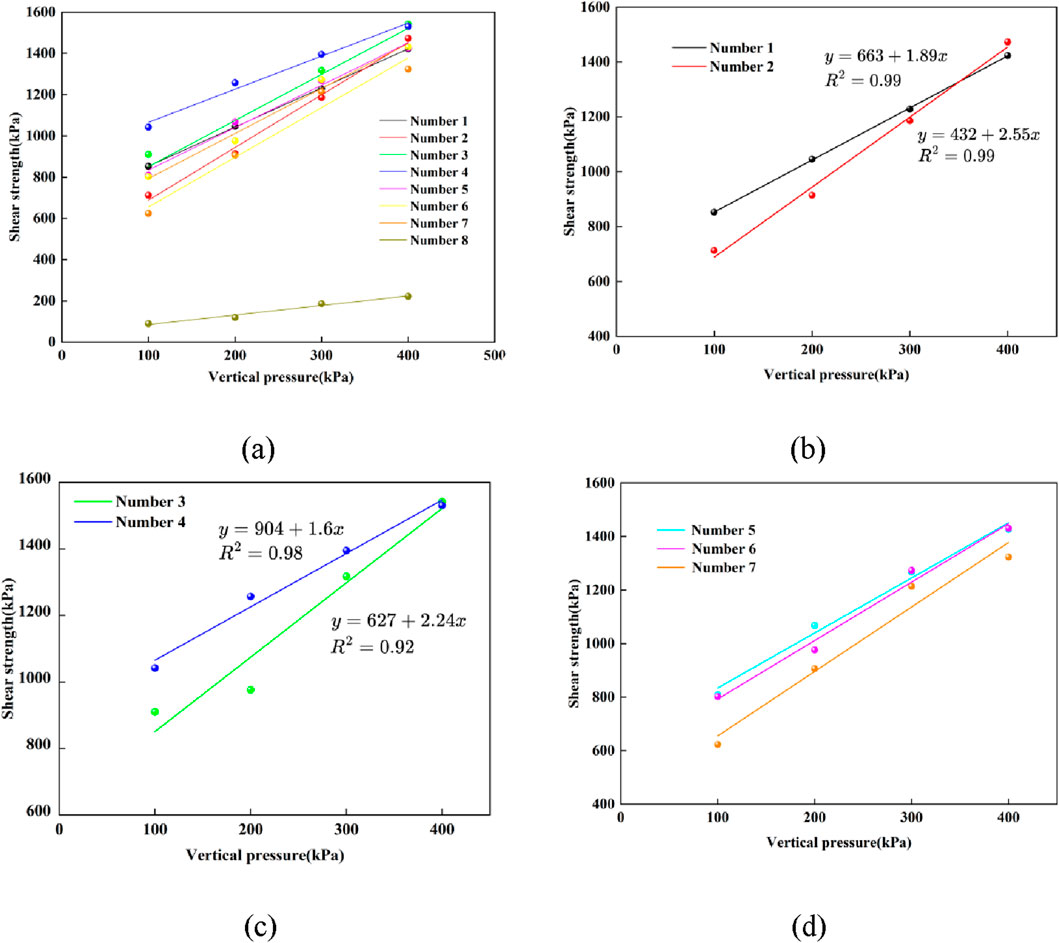
Figure 7. Shear strength curve of soil sample. (a) Shear Strength Curve of Different Content and Undisturbed Soil Specimen. (b) Effect of sodium hydroxide Content on Shear Strength of Improved Soil. (c) Effect of Sodium Silicate Content on Shear Strength of Improved Soil. (d) Effect of Slag Content on Shear Strength of Improved Soil.
3.3 Solidification mechanism of silt in huangfan area
The shear strength of the sample consists of two parts, one is the frictional resistance generated by the internal friction angle, and the other is the initial resistance formed by the cohesion. According to the above test results, the different doses of cured materials are closely related to the shear strength of the cured soil.
It can be seen from Figures 8, 9 that with the increase of sodium hydroxide content, the size of the cohesion and internal friction angle of the solidified soil show a gradual decrease. This is because too high sodium hydroxide content will increase the pH value of the alkaline environment, reduce the modulus of sodium silicate, weaken the excitation reaction, reduce the generated cementitious material, and loosen the connection between the soil particles, thereby reducing the cohesion and internal friction angle.
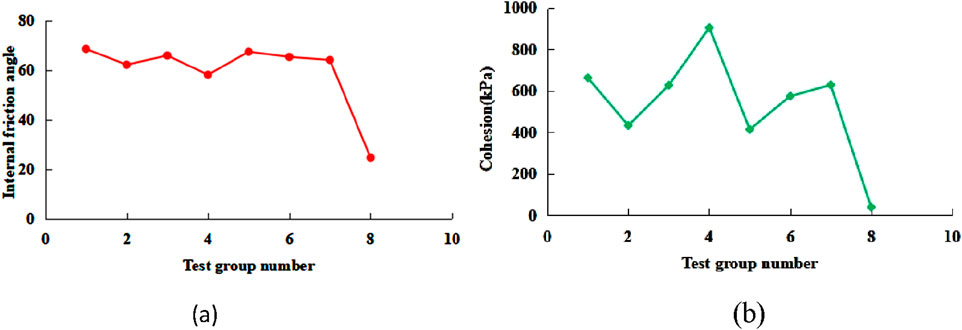
Figure 8. Cohesion and internal friction angle of solidified soil and undisturbed soil (a) Internal friction angle. (b) Cohesion.
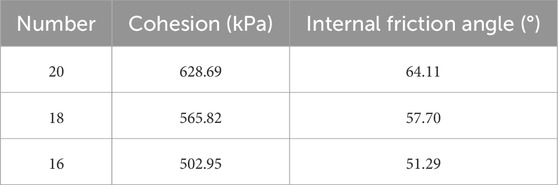
With the increase of sodium silicate content, the cohesion of solidified soil gradually increases while the internal friction angle gradually changes. This is due to the increase of sodium silicate content, the increase of SiO2 content, the increase of sodium silicate modulus, and the increase of the number of geopolymer gels generated by the reaction, which can better fill the pores between soil particles. This not only reduces the pore size and number between soil particles, but also makes the contact between soil particles closer, further enhances the interaction force between particles and improves the cohesion. Excessive sodium silicate may cause uneven distribution of gel substances around soil particles, resulting in changes in the arrangement of soil particles. The soil particles may originally have a relatively rough surface and intersecting morphology, with a larger internal friction angle, but under the action of excess sodium silicate, the intersecting effect between the particles is weakened, the arrangement becomes relatively loose and disordered, and the particles are more likely to slide with each other, reducing the internal friction angle (Table 5).
With the increase of slag content, the cohesion of the solidified soil increases first and then decreases, and the internal friction angle decreases first and then increases. This is mainly due to the fact that when the content is low, the active ingredients in the slag (such as aluminosilicate) generate gelling substances under the action of basic exciters, which effectively fill the pores of the soil and enhance the chemical bonding between the particles, significantly improve the cohesion. The initially generated gelling substances wrap the surface of the particles, reduce the roughness of direct contact between the particles, and temporarily reduce the friction resistance. When the slag content increases, some unreacted coarse particles have a negative impact on the original cementation network, and the structural integrity of the soil decreases, resulting in a decrease in cohesion. However, the accumulation of unreacted slag particles increases the surface roughness and the internal friction angle increases.
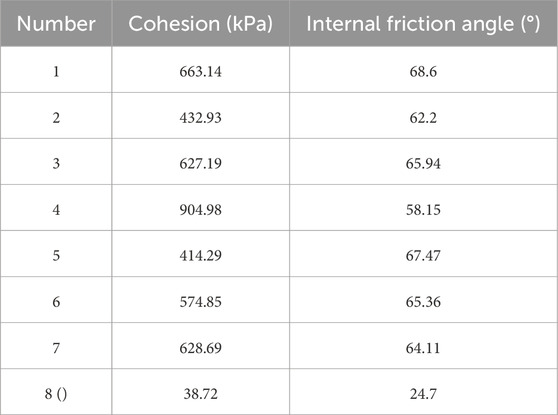
Through the shear test, the cohesion of the original silt is 38.72 kPa, the internal friction angle is 24.7°, and the cohesion of the seventh group of reinforced silt is 628.69 kPa, and the internal friction angle is 64.11°. The solidification effect of basalt-slag geopolymer significantly improves the internal friction angle and cohesion of the soil. The improvement of cohesion may be due to the solidified material (basalt-slag geopolymer) cementing the soil particles together, enhancing the structural strength. The increase of internal friction angle is the improvement of the friction characteristics between the soil particles and the enhancement of the occlusal effect between the particles.
Direct shear tests were conducted on stabilized soil with different dosages based on the optimal mix ratio, cohesion (c) and internal friction angle (φ) as shown in Table 6.
4 Stability analysis of subgrade slope
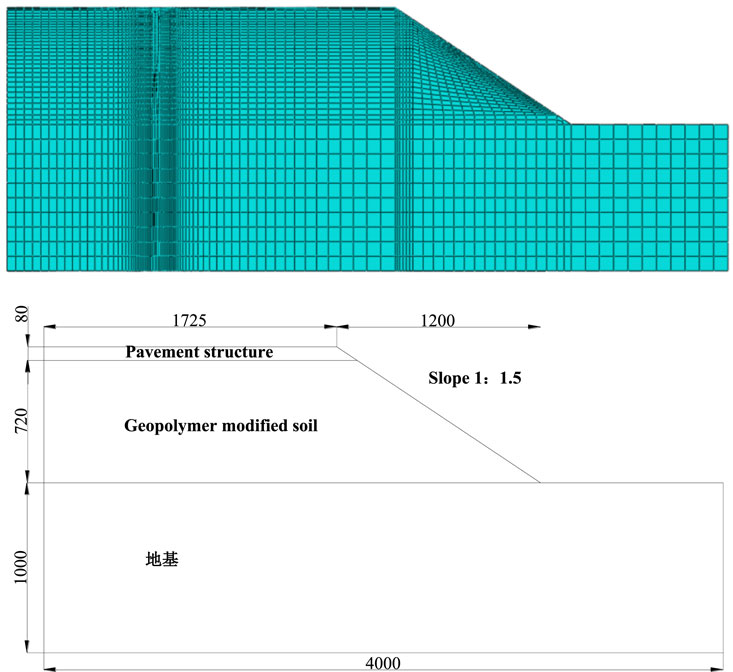
4.1 Establishment of subgrade slope models and parameter settings
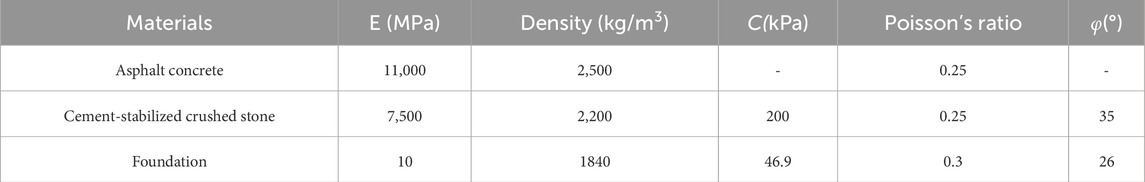
Based on the parameters of a certain highway embankment, the numerical calculation model parameters were determined. Considering the symmetric characteristics of the road structure, this study employed a half-section for numerical simulation analysis. The embankment height was set at 8 m, with a top width of 17.25 m and a base width of 29.25 m, resulting in a slope ratio of 1:1.5 (Figure 10). The embankment material used was geopolymer-stabilized soil. The model foundation dimensions were set to a depth of 10 m and a width of 40 m, with model parameters as shown in Table 7. The cohesion (c) value of the geopolymer-stabilized soil was determined through experiments. For subsequent analyses, considering the contact width between the tire and the road surface to be 0.16 m, the model length in the direction of travel was taken as 0.23 m.
During the finite element modeling process, C3D8R type hexahedral elements are used for mesh generation. The boundary conditions are set as follows: the lower boundary is fixed, and the left and right boundaries are constrained in the horizontal direction. A half-wave sinusoidal distribution is used to simulate the dynamic load of the vehicle, with an axle load of 0.7 MPa and an application time of 10 s.
4.2 Analysis of experimental results
4.2.1 Vertical settlement analysis of roadbed slopes
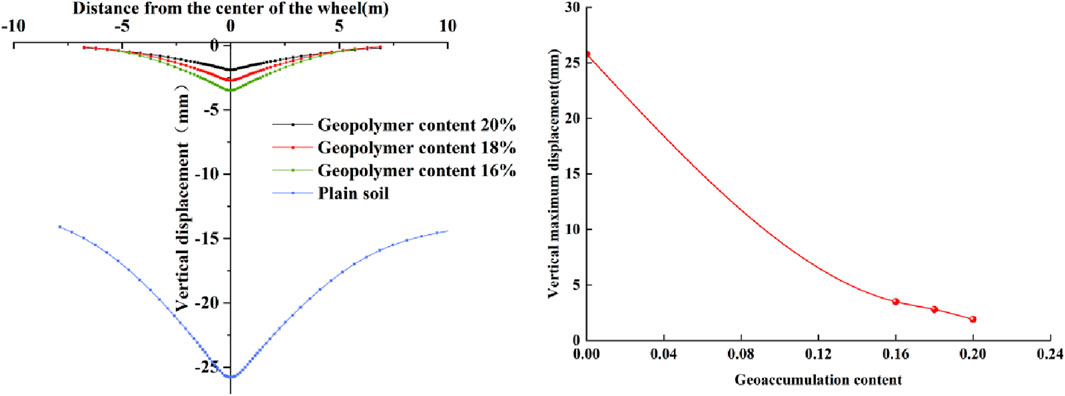
The maximum vertical displacement of all geopolymer admixture proportioned subgrade structures is concentrated in the area subjected to vehicular loads and exhibits a decay trend along the horizontal direction of the subgrade. As shown in Figure 11 of the experimental data, with the increase of geopolymer admixture from 0% (plain soil) to 20%, the maximum vertical displacement at the surface of the subgrade significantly decreases from 25.8 mm to 1.9 mm. Specifically, the maximum vertical settlement for plain soil, 16%, 18%, and 20% admixture samples were recorded as 25.8 mm, 3.5 mm, 2.8 mm, and 1.9 mm, respectively. Compared to plain soil, the settlement reduction rates for 16%, 18%, and 20% admixture stabilized subgrades are 86%, 89%, and 93%, respectively, indicating a pronounced dose-effect relationship in settlement control. Mechanism analysis reveals that the formation of geopolymer cementitious products enhances the stiffness of the improved soil, effectively increasing its dynamic modulus of elasticity and resistance to plastic deformation.
Based on the experimental data from Figure 12, as the dosage of geopolymer increases, the slope displacement response shows a significant attenuation trend. The peak slope displacement decreases from 15.1 mm in the untreated soil condition to 0.2 mm at a geopolymer dosage of 20%. This improvement in slope stability confirms that geopolymer-modified soil exhibits a dose-dependent enhancement in shear strength.
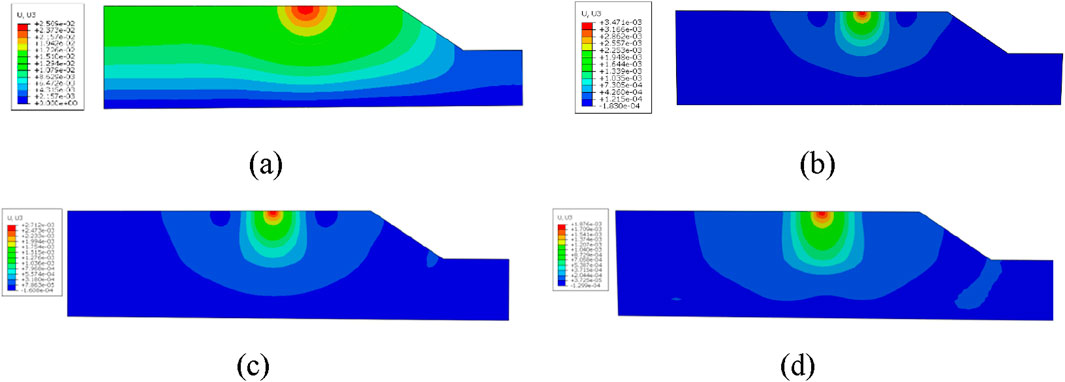
Figure 12. (a) Plain soil. (b) Geopolymer content 16%. (c) Geopolymer content 18%. (d) Geopolymer content 20%.
4.2.2 Vertical profitability analysis of roadbed slopes
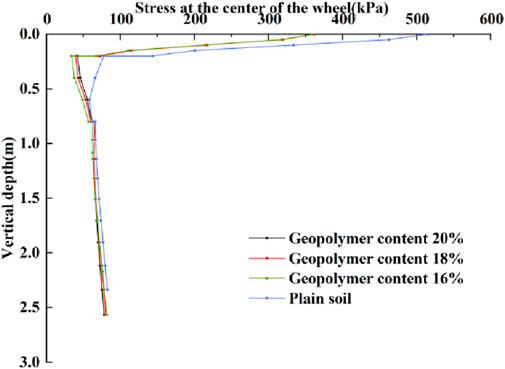
Figure 13 illustrates the variation of stress at the load center along the depth direction. It can be observed that the additional stress at the load center decreases rapidly from a depth of 0m–1 m and then increases slowly. The primary reason for this trend is the stratification of the subgrade, which results in differences in stiffness and abrupt changes in stress at the stratification points. Due to the high stiffness of asphalt material used on the road surface, the stress decreases rapidly within the asphalt layer. In contrast, the lower layers consisting of cement-stabilized crushed stone and stabilized soil have relatively lower stiffness, leading to a rebound in stress. Compared to the stress on the surface of a plain soil subgrade, the stress on the surface of a stabilized soil subgrade is significantly reduced. As the proportion of stabilized soil in the subgrade increases, the additional stress on the road surface decreases further, and the rebound stress in the lower layer of the composite subgrade remains less than that of the plain soil subgrade (Figure 13).
The vertical stress at the top surface changes regularly over time. When the half-wave sinusoidal load reaches its maximum value, the compressive stress at the top surface also peaks. Throughout the loading process, the stress changes tend to stabilize. Figure 14 shows the stress distribution characteristics of the road base slope under load. The results indicate that the stress is mainly concentrated in the tire contact area and gradually decreases with depth. In areas other than the load application zone, the vertical stress values remain at low levels.
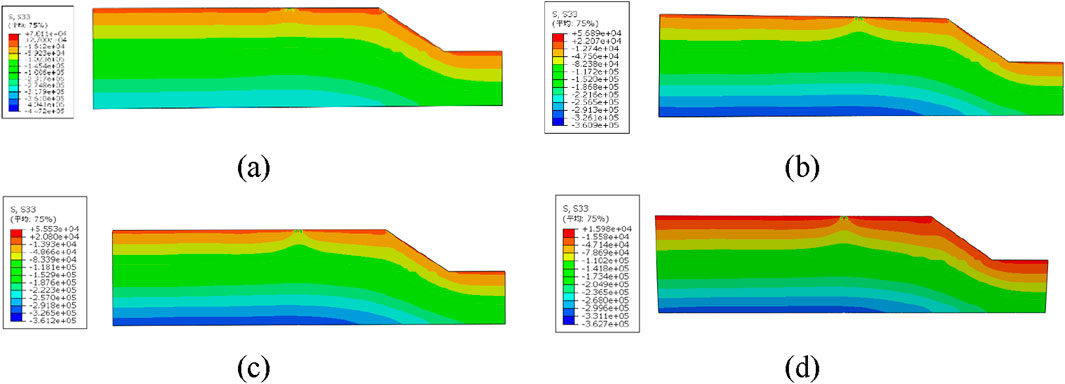
Figure 14. (a) Plain soil. (b) Geopolymer content 16%. (c) Geopolymer content 18%. (d) Geopolymer content 20%.
5 Conclusion
The experimental data of solidified soil under different content of geopolymer is tested by geotechnical test, and the solidification mechanism of basalt-slag geopolymer solidified soil is analyzed by electron microscope scanning and X-ray diffraction. At the same time, the solidified soil subgrade slope model is established, and the influence of different content of geopolymer on the stability of subgrade slope is analyzed. The following conclusions are drawn.
(1) Through XRD composition and SEM structure analysis, it was found that under alkaline activation, basalt and slag produced a synergistic effect, promoting each other’s hydration reaction, generating N-A-S-H, C-A-S-H cementitious substances, filling the pores in the silt soil particles, making the solidified soil microstructure more compact, thereby improving the mechanical properties.
(2) With the increase of content, the compressive strength of solidified soil increases. When the content of geopolymer is 20%, 18%, 16% and 14%, the compressive strength of solidified soil is 2.74MPa, 1.66MPa, 0.91 MPa and 0.45MPa, respectively, which is 2,610%, 1,560%, 811% and 350% higher than that of silt. The compressive strength of solidified soil reaches the maximum when the content of geopolymer is 20%, which is much higher than the requirement of 0.25 MPa in the specification.
(3) The shear stress of the solidified soil is positively correlated with the vertical pressure. With the increase of sodium hydroxide, sodium silicate and slag, the shear strength of the solidified soil is increasing. The internal friction angle and cohesion of the solidified soil are significantly higher than that of the silt. The geopolymer can not only improve the mechanical properties of the solidified soil, but also conform to the concept of green environmental protection and economic rationality.
(4)With the increase of the content of geopolymer in the solidified soil, the maximum vertical displacement of the subgrade surface and the displacement of the slope gradually decrease, and the stress at the center of the load shows a trend of decreasing rapidly and then slowly increasing from the depth of 0 m to the depth of 1 m. The stress is mainly concentrated in the tire grounding area and gradually decays along the depth direction. Except for the load area, the vertical stress values at other positions of the pavement slope are maintained at a low level.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
LW: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. WLu: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. JC: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. JL: Investigation, Writing – review and editing. CT: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. WLi: Software, Writing – original draft. LM: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Software, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to show sincere thanks to all the technicians who have helped this research.
Conflict of interest
Authors JC, CT, and LM were employed by China Construction Infrastructure Corp., Ltd.
Author JL was employed by Shandong Hi-Speed Construction Management Group Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Cristelo, N., Glendinning, S., and Teixeira, P. A. (2011). Deep soft soil improvement by alkaline activation. Proc. Institution Civ. Engineers-Ground Improv. 164, 73–82. doi:10.1680/grim.900032
Cui, C. Y., Yu, C. Y., Zhao, J. Y., and Zheng, J. (2022). Steel slag/precarbonated steel slag as a partial substitute for Portland cement:effect on the mechanical properties and microstructure of stabilized soils. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 26, 3803–3814. doi:10.1007/s12205-022-1762-1
Dassekpo, J. B. M., Feng, W., Li, Y., Miao, L., Dong, Z., and Ye, J. (2021). Synthesis and characterization of alkali-activated loess and its application as protective coating. Constr. Build. Mater. 282, 122631. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.122631
Hasan, M., Imran Zaini, M. S., Yie, L. S., Masri, K. A., Putra Jaya, R., Hyodo, M., et al. (2021). Effect of optimum utilization of silica fume and eggshell ash to the engineering properties of expansive soil. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 14, 1401–1418. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.07.023
Liu, H., Sun, S., Wang, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, J., Luo, G., et al. (2020). Microscopic mechanism of the macroscopic mechanical properties of cement modified subgrade silty soil subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Appl. Sci. 10, 2182. doi:10.3390/app10062182
Liu, Z., Cai, C. S., Liu, F. Y., and Fan, F. (2016). Feasibility study of loess stabilization with fly ash-based geopolymer. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 28, 04016003. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001490
Mohsin, N., and Ana, H. (2023). Muttucumaru S. Triaxial stress-strain behavior of a novel basalt rock waste and ground granulated blast furnace slag geopolymer. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 35, 04023054. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0004717
Rehman, Z. U., and Khalid, U. (2021). Reuse of COVID-19 face mask for the amelioration of mechanical properties of fat clay: a novel solution to an emerging waste problem. Sci. Total Environ. 794, 148746. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.148746
Sumesh, M., and Singh, B. (2020). Vigneshwaran K. Effect of coal ash on strength characteristics of clayey silt soil treated with cement. Mater. Today Proc. 2020. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2020.10.247
Syahril, S., Somantri, A. K., and Haziri, A. A. (2020). Study of stabilized soil clay soil characteristics using vulcanic ash and tailing as subgrade layers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 830, 022043. doi:10.1088/1757-899X/830/2/022043
Keywords: subgrade slope, geopolymer, slope stability, solidified silt, reinforced silt
Citation: Wang L, Lu W, Cheng J, Li J, Tian C, Lin W, Meng L and Zhang Y (2025) Study on mechanical properties of solidified silt from waste rock powder and stability of subgrade slope. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1608064. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1608064
Received: 08 April 2025; Accepted: 26 May 2025;
Published: 15 July 2025.
Edited by:
Wen Nie, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Huibin Sun, Shandong Jianzhu University, ChinaRui Pan, Anhui Jianzhu University, ChinaYingcheng Luan, China University of Mining and Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Wang, Lu, Cheng, Li, Tian, Lin, Meng and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lu Wei, bHV3ZWlAb3VjLmVkdS5jbg==
 Lei Wang
Lei Wang Wei Lu2*
Wei Lu2*