- 1China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources, Beijing, China
- 2School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China
Introduction: The Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt (YMB) hosts extensive Mesozoic iron oxide-apatite (IOA) and skarn iron-copper deposits, with significant high-grade iron ore potential. However, the lack of systematic understanding of mineralization types, distribution controls, and metallogenic mechanisms limits exploration efficiency, particularly due to widespread alluvium cover.
Methods: We integrated aeromagnetic data with reduction-to-pole (RTP) transformation, upward continuation, and Curie point isothermal surface calculations. A novel robust principal component analysis (RPCA) based on the inexact augmented Lagrangian method (IALM) was applied to discriminate mineralization zones. Structural controls on deposits were analyzed using updated aeromagnetic and gravity datasets.
Results: Prospective zones for iron oxide-apatite (IOA) and skarn mineralization were systematically delineated, demonstrating a robust spatial correlation between ore-bearing magmatic systems and iron deposit localization. The study further highlights the dominance of deep-seated structural frameworks and magmatic conduits in governing the distribution of mineralization, emphasizing their role as primary controls on ore formation.
1 Introduction
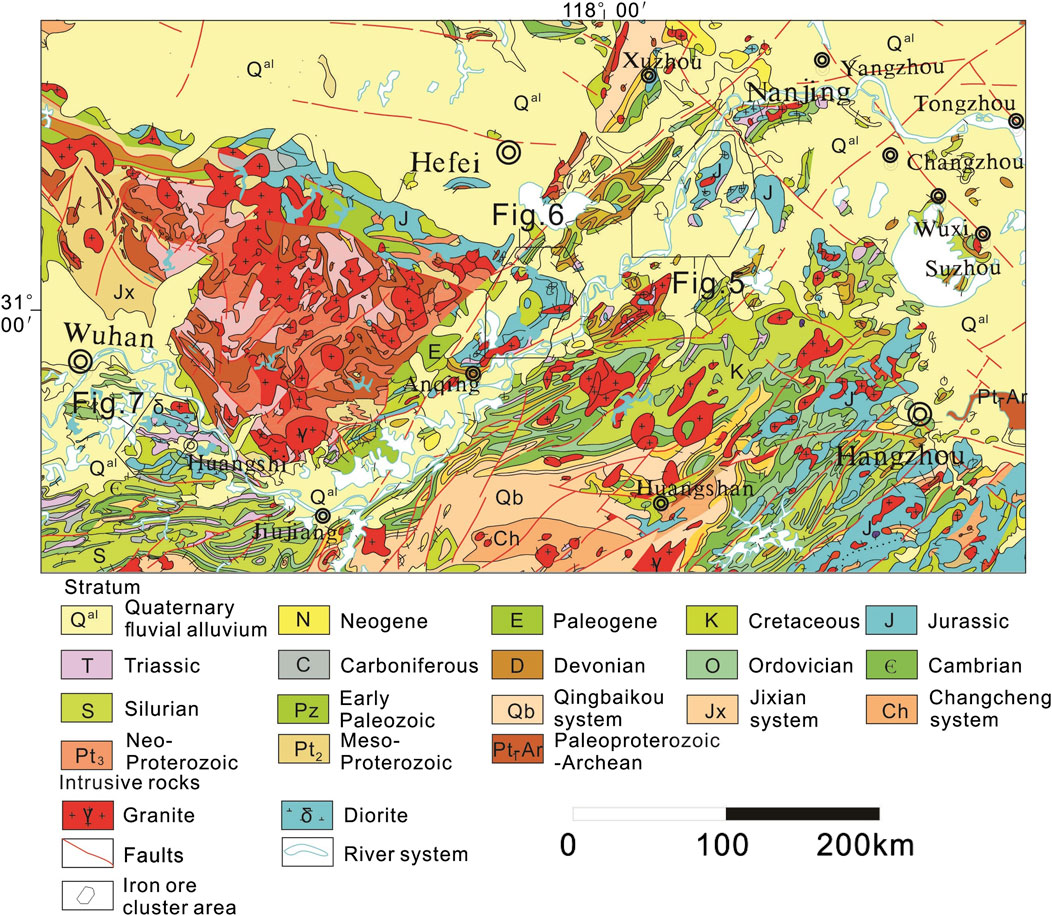
The YMB, located in eastern China, spans four provinces: Hubei, Jiangxi, Anhui, and Jiangsu. As an important polymetallic metallogenic belt in China, the YMB hosts minerals dominated by iron, copper, cobalt, nickel, gold, silver, lead, and zinc. In addition, the YMB constitutes a significant part of the Pacific Rim metallogenic domain (Lü et al., 2014; Lü et al., 2015; Lü et al., 2021). Structurally, it forms a “V”-shaped tectono-magmatic belt that is narrow in the southwest and widens toward the northeast (Figure 1).
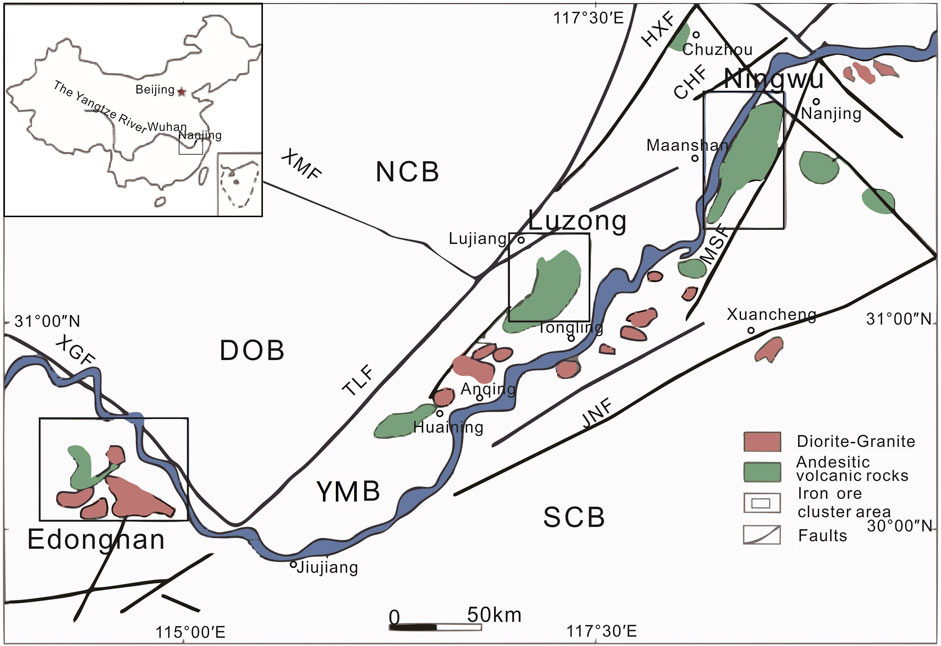
Figure 1. Tectonic maps with major igneous rocks in the study area (modified after Zhou et al., 2017) NCB: North China Block; SCB: South China Block; YMB: Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze Metallogenic Belt; DOB: Dabie Orogenic Belt; TLF: Tanlu Fault; XGF: Xiangfan-guangji Faulth; HXF:Huaiyin-XIangshui fault; CHF: Changjiang fault; JNF: Jiangnan fault; HPF: Huanglishu-Poliangting Fault; XMF: Xintian-Mozitan fault; MSF: Maoshan fault.
Previous studies have shown that metallogenic explosion occurred in the YMB during the Mesozoic, leading to the formation of numerous large- and medium-sized IOA iron deposits, skarn iron-copper deposits, and hydrothermal-porphyry copper polymetallic deposits (Chang et al., 1991; Lü et al., 2014; Lü et al., 2015; Lü et al., 2021). Among these, primary IOA iron deposits include Luohe, Nihe, Gaocun, Heshangqiao, Meishan, and Gushan, which are located in the Luzong and Ningwu ore cluster areas. IOA deposits are characterized by magnetite-apatite-actinolite/diopside assemblages, typically linked to intermediate-felsic magmatism (e.g., andesitic intrusives). Notably, high-grade iron ores are primarily found in the Meishan, Gushan, and Baixiangshan deposits. The major skarn iron deposits include Longqiao, Zhuchong, Baixiangshan, Chengchao, Tieshan, and Jinshandian, which are largely distributed in the Edongnan ore cluster area; all these deposits contain significant high-grade iron ores. Skarn deposits form through metasomatic processes at contact zones between silicate intrusives (e.g., granites) and carbonate rocks (limestone/dolomite), resulting in calcium/magnesium/iron-rich silicate minerals like garnet, pyroxene, and epidote. In addition, the YMB hosts a large number of copper polymetallic deposits, which are mainly of skarn and IOA types.
Previous geological studies on the ore-prospecting potential of the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt are abundant (Zhai et al., 1992; Lü et al., 1998; Mao et al., 2011); however, research utilizing geophysical methods to delineate exploration targets remains insufficient. Additionally, although seismic and electrical profiling has been conducted to investigate deep structures in this region, and hypotheses regarding deep ore-forming material migration have been proposed, these lack support from regional geophysical data such as gravity and magnetic surveys (Dong et al., 2011; Lü et al., 2014; Lü et al., 2020; Lü et al., 2021; Gao B., 2021). Given the extensive coverage of fluvial alluvium (Figures 2, 3), geophysical prospecting can play an important role in mineral exploration in the YMB, especially for IOA and skarn deposits. The magma and hydrothermal systems associated with such deposits are generally characterized by distinctive density and magnetic affinity (Tweto and Case, 1972; Lü et al., 1998; Shahabpour, 1999; De Oliveira et al., 2008; Lü et al., 2020). The host rocks of these deposits frequently exhibit characteristic magnetic and density features, establishing gravity and magnetic surveys as important methods for exploring these deposits. Therefore, this study employs a primarily high-precision aeromagnetic dataset supplemented by gravity data to address these research gaps.
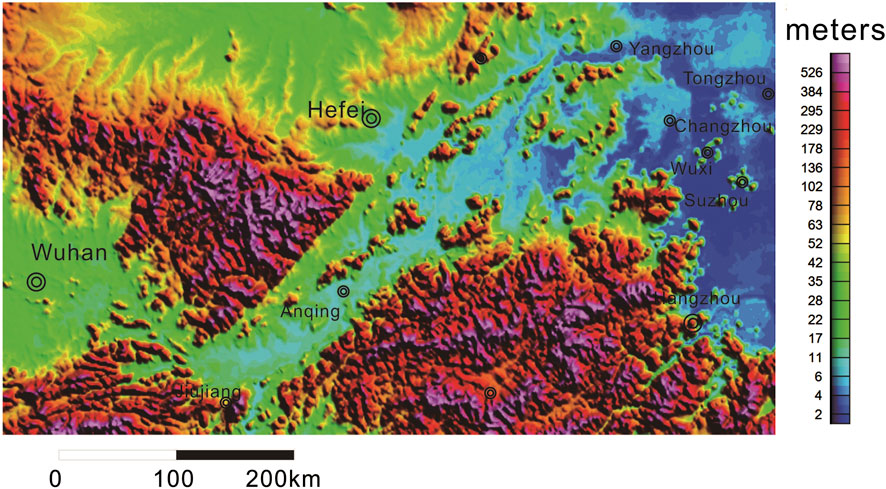
Figure 3. Topographic map in the study area [The terrain data was downloaded from (https://www.gscloud.cn/)].
This study suggests that regional-scale Bouguer gravity and aeromagnetic data help reveal IOA and skarn deposit-associated geological structures, which include deep-seated magmatic rocks and related structural features. These rocks and structures are genetically related to iron-copper hydrothermal mineralization systems. By applying upward continuation filtering and a fast discrimination method based on the IALM-RPCA algorithm, the distribution of igneous rocks associated with IOA and skarn deposits can be delineated. These methods also allow for the identification of areas that show gravity and magnetic anomaly patterns similar to those of IOA and skarn deposits, thus assisting in targeting magnetic iron deposits and associated magmatic rocks.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Regional geology
The study area can be divided into four major tectonic units: the North China Plate, the Dabie orogenic belt, the YMB, and the South China Plate. These units are separated by regional-scale deep-seated faults such as the Tanlu, Xiangfan-Guangji, Jiangnan, and Xiaotian-Mozitan faults (Figure 1).
To the west of the Tanlu fault zone lie the North China Craton and the Dabie orogenic belt, which are also bounded by the Xiaotian-Mozitan fault. The main body of the North China Craton consists of Archean-Paleoproterozoic strong metamorphic basement overlain by a Mesoproterozoic-Early Permian marine sedimentary cover, with many terrestrial basins formed during the Mesozoic. The Dabie orogenic belt (also known as the Dabie ultra-high-pressure metamorphic belt) was formed by the collision of the southern margin of the North China Block and the Yangtze Plate during the Middle Triassic. Within this orogenic belt, rocks of different degrees of metamorphism and Early Cretaceous magmatic rocks (Figure 2) are exposed. The deep subduction and folding of the continental crust led to the formation of the well-known ultra-high-pressure metamorphic belt in this area (Zhu et al., 2009).
The YMB is recognized as a collisional belt between the South China and the North China blocks. Its northwestern and southeastern boundaries are defined by the Tanlu fault and the Jiangnan fault (also known as the Yangxin-Changzhou fault), respectively. Previous studies have shown that this belt was formed under complex continental dynamic processes and magmatic activity backgrounds, including a Mesozoic tectonic system subjected to transformation and recombination, as well as strong crust-mantle interactions. The stratigraphy of this region is relatively complete, primarily comprising high-grade metamorphic rocks from the Archean–Lower Proterozoic, Cambrian-Ordovician marine sediments of the Paleozoic, and Triassic-Jurassic terrestrial pyroclastic rocks, with a minor distribution of Proterozoic low-grade metamorphic rocks (Figure 2). To the southeast of the Jiangnan fault lies the South China Plate, which consists primarily of a series of epimetamorphic and strongly deformed Neoproterozoic sedimentary-volcanic rocks and coeval intrusions, which form a structural belt.
The study area primarily experienced two periods of tectono-magmatic activity: the Indosinian and the Yanshanian (Yin and Nie, 1993; Li, 1994; Wu et al., 2003; Dong et al., 2011), with a peak occurring between 150 and 110 Ma. The Indosinian movement was mainly characterized by the collision between the North China and South China blocks, leading to the formation of the Dabie ultra-high-pressure metamorphic belt and the large-scale Tanlu strike-slip fault system (Yin and Nie, 1993; Li, 1994). In contrast, the Yanshanian movement was dominated by intra-continental compression caused by the subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate, resulting in large-scale uplift in eastern China and subsequent lithospheric extension and thinning (Wu et al., 2003; Dong et al., 2011). These active tectonic movements facilitated the widespread emplacement of intermediate-acidic intrusions and volcanic-subvolcanic rocks.
2.2 Iron deposits in the YMB
The YMB ranks among the most extensively explored and researched polymetallic metallogenic belts in China, with geological exploration and scientific research dating back to the early 20th century (Chang et al., 1991; Zhai et al., 1992; Zhou et al., 2011). This region exhibits abundant mineral resources, including 22 large deposits, 46 medium-sized deposits, and 109 small deposits (Figure 4). Specifically, the Ningwu and Luzong basins of volcanic origin contain numerous IOA iron deposits related to Early Cretaceous (about 130 Ma) terrestrial volcanic-subvolcanic rocks, while the Edongnan ore cluster area hosts abundant skarn iron deposits related to Early Cretaceous (about 130 Ma) high-K, calc-alkaline, intermediate-acidic intrusions (composed primarily of quartz diorite).
To date, over 30 iron deposits have been delineated in the Ningwu area, with total reserves of about 2.7 billion tons (Zhou et al., 2011). Several large concealed iron deposits, such as Luohe and Nihe, have been discovered in the deep part of the Luzong volcanic rock basin. The IOA iron deposits in the Ningwu and Luzong basins, formed at about 130 Ma, exhibit significant characteristics of metallogenic explosion (Zhou et al., 2010; Zhou et al., 2011). Meanwhile, the Chengchao, Wangbaoshan, and Jinshandian skarn iron deposits along the western margin of the Jinniushan volcanic basin in the Edongnan ore cluster area were all formed at about 130 Ma (Zhai et al., 1992; Mao et al., 2011; Hu et al., 2020), aligning closely with the ages of the IOA iron deposits in the YMB. The IOA-type ores of the same period have been identified in the deep part of the Wangbaoshan iron deposit, indicating a genetic relationship between skarn and IOA iron deposits (Hu et al., 2020). Therefore, this expands the distribution range of IOA iron deposits in the YMB.
From a geophysical perspective, the quartz diorite and granite in the ore-bearing rocks of skarn iron deposits produce relatively low-amplitude gravity anomalies and moderate-to-high-amplitude magnetic anomalies owing to their composition of low-density felsic minerals and magnetite with high magnetic susceptibility (Shang et al., 2014; Lü et al., 2020; Zheng et al., 2022). In contrast, IOA iron deposits occur in basal-affinity volcanic rocks with relatively high density and magnetic susceptibility, resulting in high-amplitude gravity and magnetic anomalies (Figure 4) (Lü et al., 2020; Gao et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2022). Both the analysis of regional geophysical data and the geophysical investigation of iron-copper mineralization areas suggest that skarn-type mineralization tends to occur along areas with gravity-magnetic anomaly gradients (i.e., on the flanks of high-amplitude gravity-magnetic anomaly backgrounds), where gravity anomalies transition from low to moderate amplitude and magnetic anomalies from moderate to high amplitude. In contrast, IOA iron deposits are commonly found near the peaks of gravity–magnetic anomalies (Shang et al., 2014; Lü et al., 2020; Gao M. et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2022). Given the similar geological features, the characteristic gravity-magnetic anomaly patterns of IOA iron and skarn iron-copper deposits have been widely applied as models for the geophysical exploration of iron-copper deposits in the YMB. These models have proven effective in the exploration and potential assessment of similar minerals in this region (Yan et al., 2015; Lü et al., 2020; Gao M. et al., 2021).
2.3 Geophysical surveys in the study area
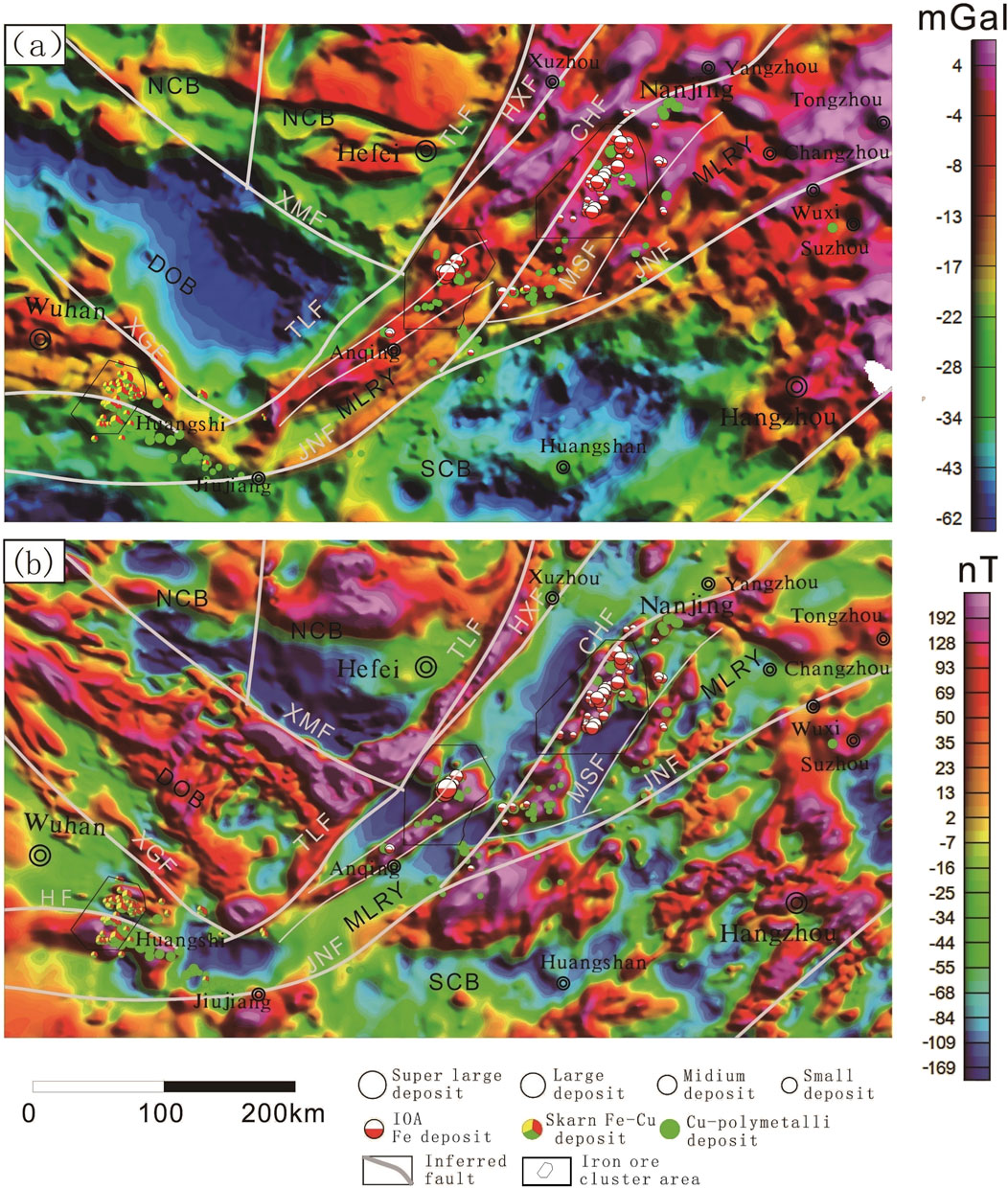
Over the past few decades, the Ministry of Natural Resources (MNR) has conducted extensive regional-scale aeromagnetic and gravity surveys across the YMB (Xiong et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2021; Yang, 2023). The most recent survey was conducted by the China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural Resources (AGRS) in 2019 (Zheng et al., 2022). Aeromagnetic and gravity surveys in the YMB were conducted along nearly north-south-striking flight lines, which were generally perpendicular to tectonic zones. The resulting data were initially gridded using a grid size of 0.5 km × 0.5 km (Figures 4–6), with a higher-resolution grid size of 0.1 km × 0.1 km (Figures 6–11) applied to specific ore cluster areas. These data were processed according to Chinese industrial standards (National Standardization Administration of China, 2019). Specifically, the Bouguer gravity data were derived from Bouguer correction, for which height, mass, and terrain effects in natural gravity measurements were considered (Ge et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 1989).
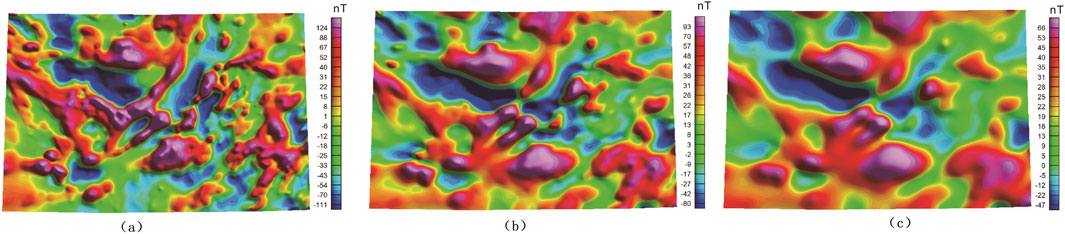
Figure 5. Map of Aeromagnetic anomalies with Upward Continuation to 5 km (a), 10 km (b) and 20 km (c).
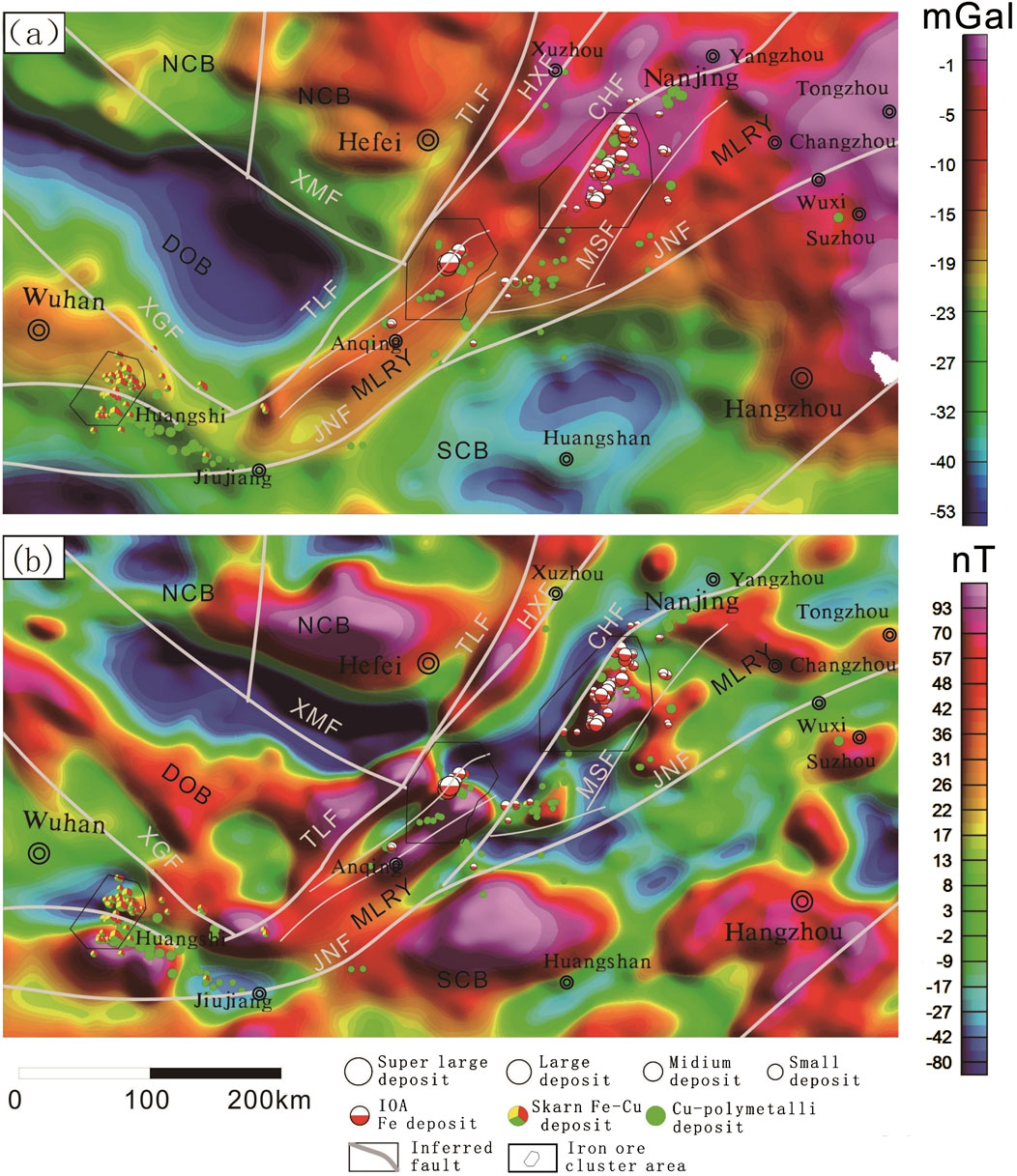
Figure 6. Map of the Bouguer Gravity (a) and Aeromagnetic (b) anomalies with Upward Continuation to 10 km in the study area.
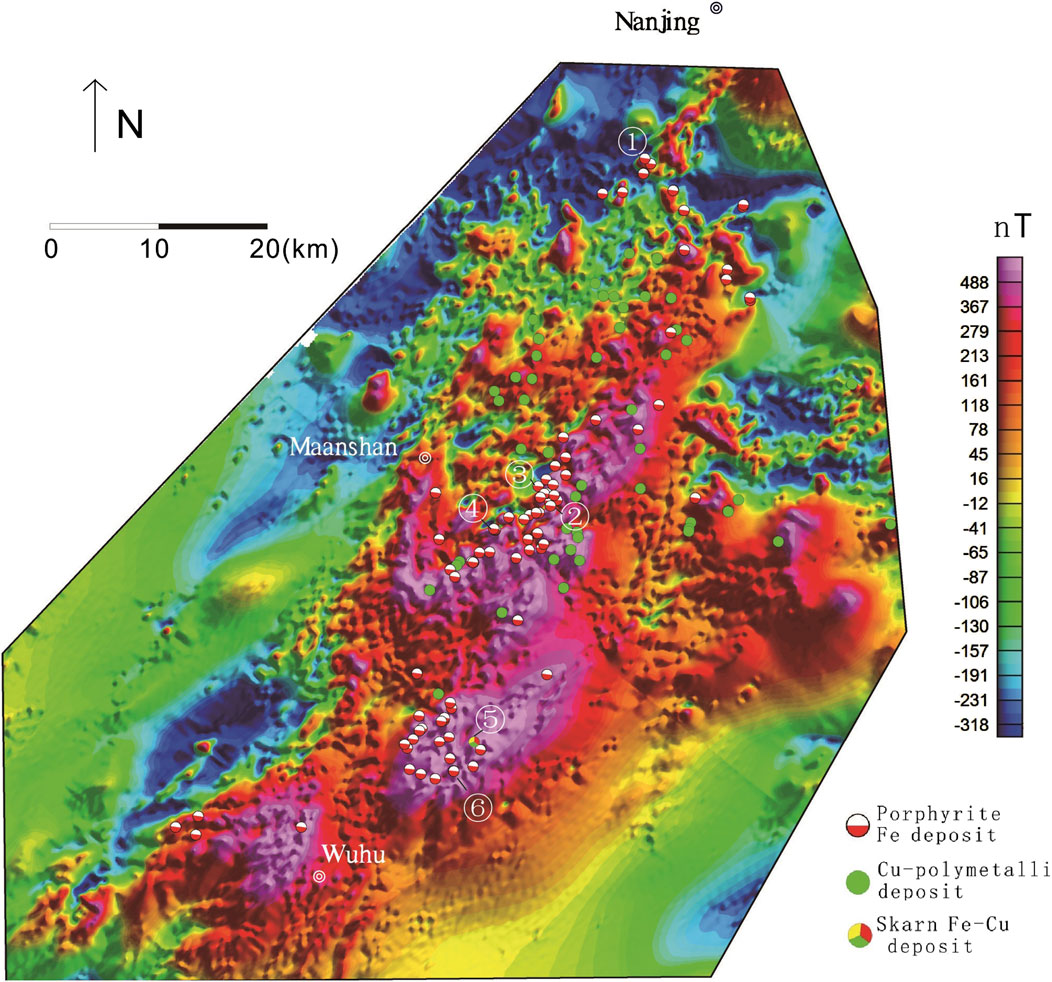
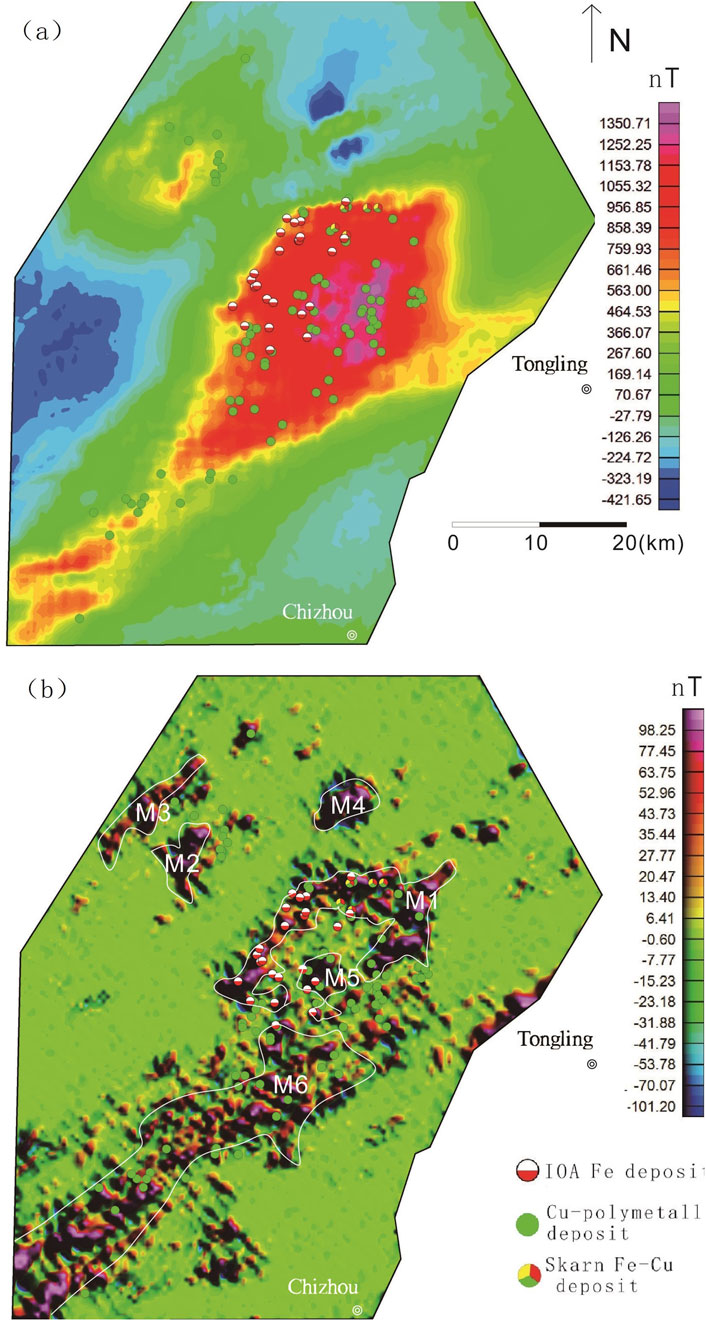
Figure 7. Map showing the magnetic data of Ningwu area Deposits: ①Meishan, ②Washan, ③Gaocun, ④Heshangqiao, ⑤Baixiangshan, ⑥Gushan.
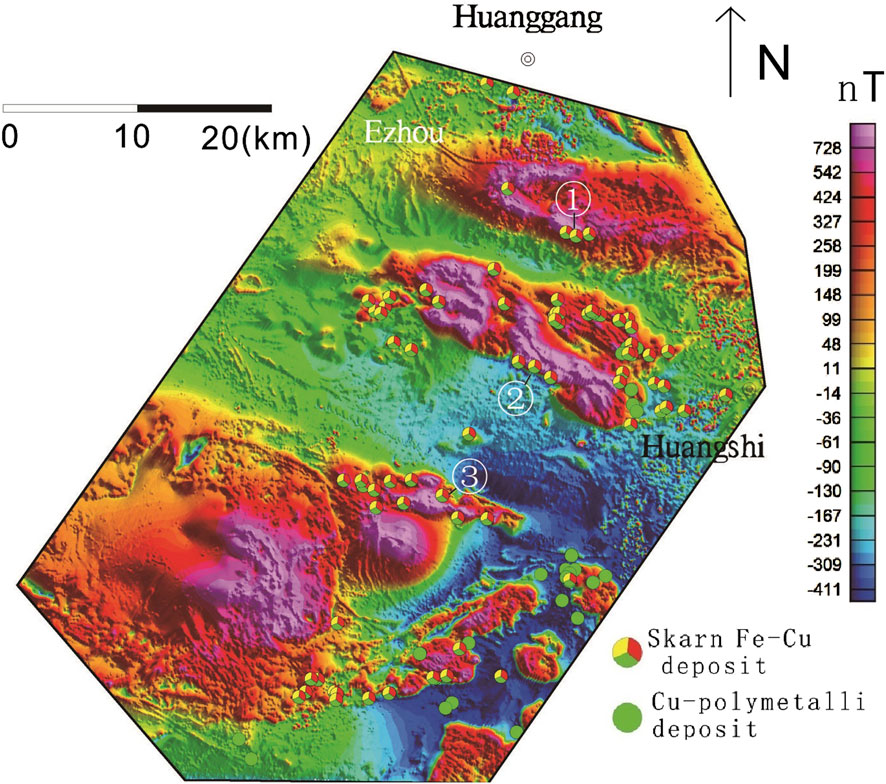
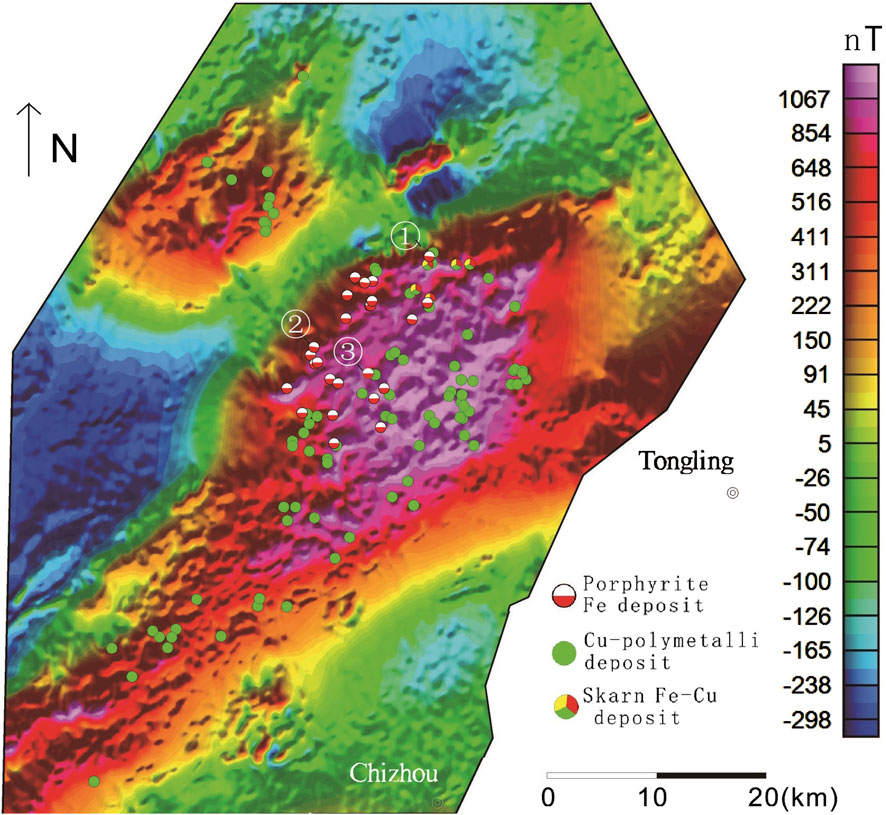
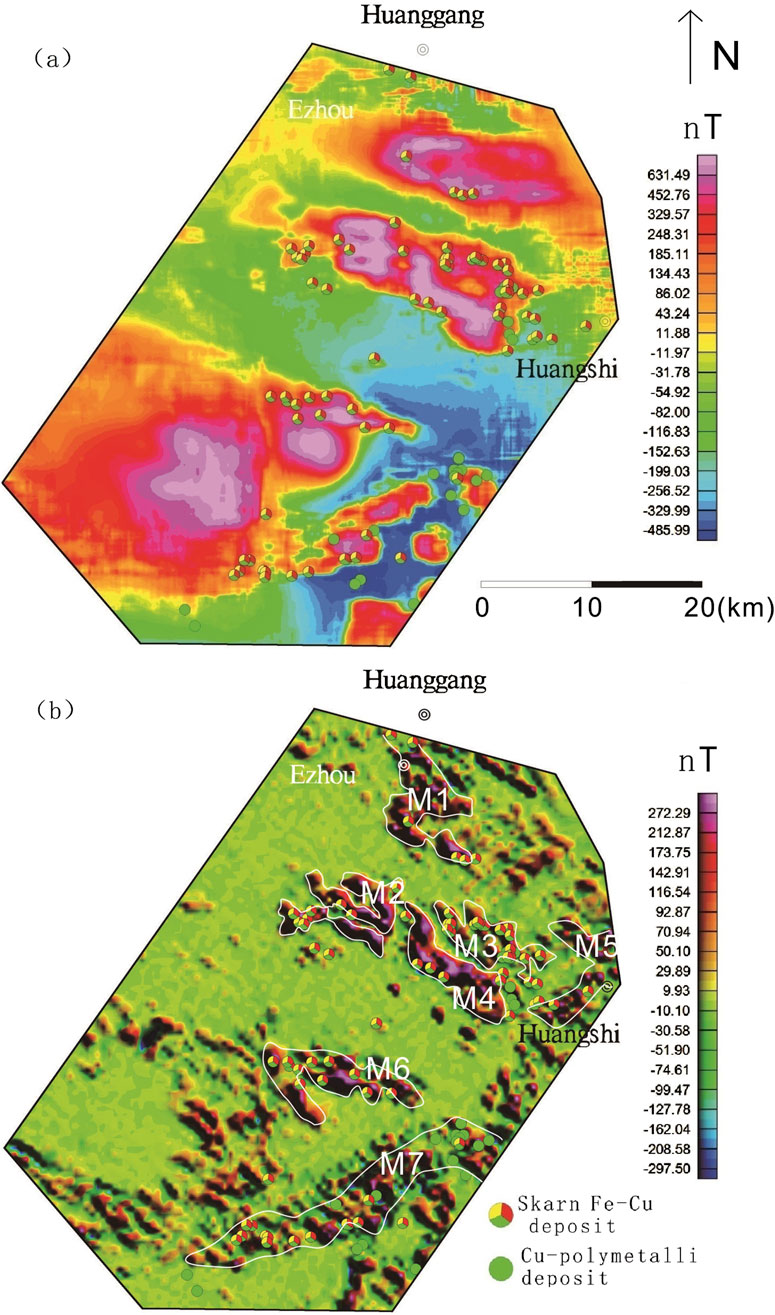
Figure 9. Map showing the magnetic data of Edongnan area Deposits: ①Chengchao, ②Tieshan, ③Jinshandian.
2.4 Magnetic and density properties of rocks
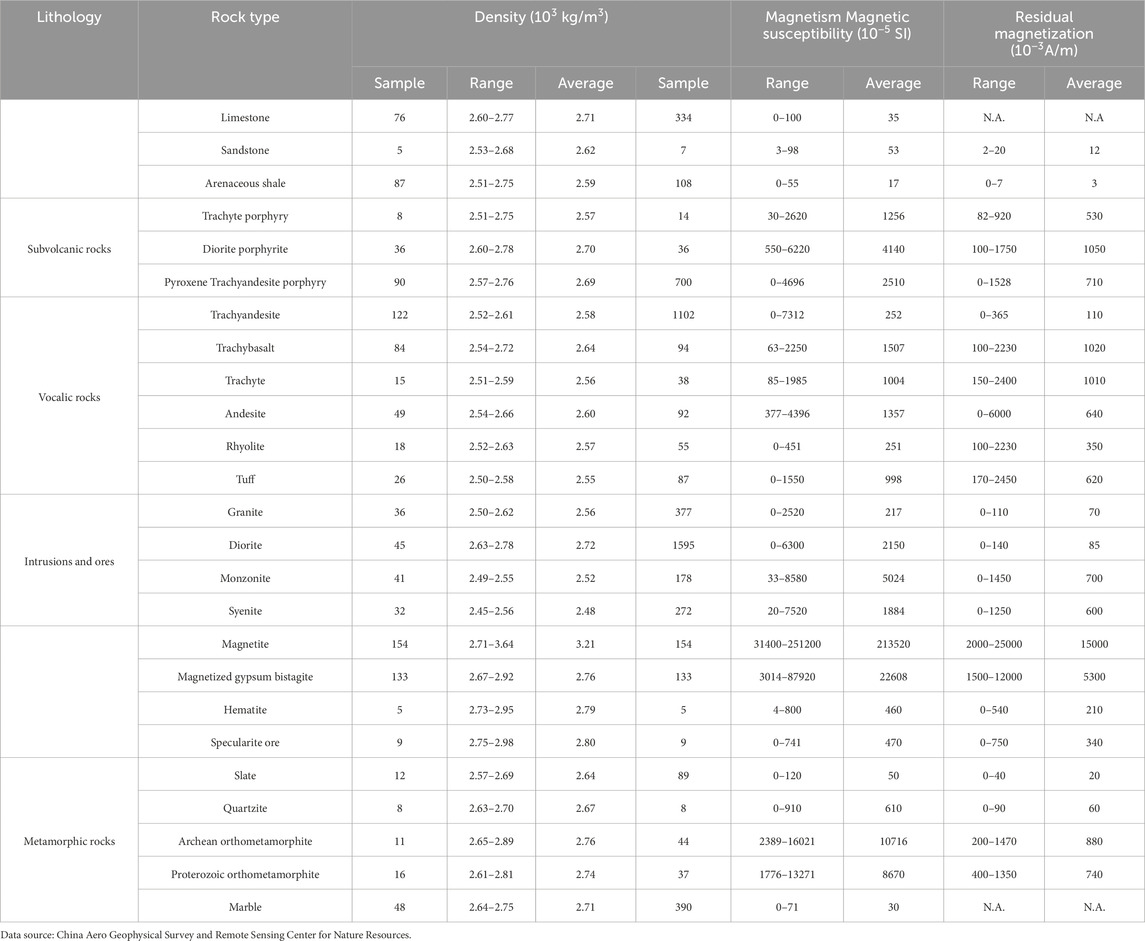
Density and magnetic properties are widely employed to interpret gravity and magnetic data for regional rock units (Guan, 2005; Ge et al., 2020). Accordingly, to facilitate the interpretation of Bouguer gravity and aeromagnetic data, this study summarized the density and magnetic data-including magnetic susceptibility and residual magnetization-based on both sampling and measurements in this study, as well as previous results. The main rock units in the YMB were then further examined, and the results are shown in Table 1.
Tertiary-Quaternary loose sediments in river channels exhibit the lowest density, the weakest magnetism (Zhu, 2018). Therefore, these sediments are generally considered to generate low-amplitude gravity and magnetic anomalies. Common sedimentary rocks such as limestones and sandtones generally have low to moderate density, weak magnetic susceptibility, and low residual magnetization. Therefore, they typically yield low-to moderate-amplitude gravity anomalies and low-amplitude magnetic anomalies. Volcanic and intrusions show significant variability in density and magnetism, and their magnetic susceptibility and residual magnetization depend primarily on their mineralogical composition. Overall, volcanic and intrusive rocks containing higher proportions of magnesian minerals and fewer felsic minerals exhibit higher density, magnetic susceptibility, and residual magnetization (Table 1). Therefore, felsic volcanic rocks and intrusions (i.e., tuffs, porphyries, volcanic breccias, granites, and granodiorites) typically produce relatively low-amplitude gravity and magnetic anomalies, while intermediate volcanic rocks and intrusions (i.e., andesites, diorites, and monzonites) generally yield medium-to high-amplitude gravity and magnetic anomalies. Metamorphic rocks-including gneisses, schists, metamorphic sandstones, marbles, and amphibolites-typically have extremely weak magnetic susceptibility and very low remanence. However, Archean metamorphic rocks, such as certain igneous metamorphic rocks in the Dabie complex, exhibit relatively high magnetic susceptibility. Metamorphic rocks feature moderate to high densities (Table 1), depending primarily on lithology and metamorphic conditions (Zheng et al., 2022). Therefore, metamorphic rocks typically exhibit low-to high-amplitude magnetic anomalies and moderate-to high-amplitude gravity anomalies.
2.5 Fast discrimination method based on IALM-RPCA algorithm
Robust Principal Component Analysis (RPCA) has been widely applied in data representation, data denoising, and discrimination (Turk and Pentland, 1991; Yang et al., 2004; Zhang et al., 2015). This study separated local anomalies from regional anomalies using a fast discrimination method based on the Inexact Augmented Lagrange Multiplier (IALM) Algorithm (Fan et al., 2025), aiming to identify and extract magnetic anomalies related to iron deposits in the YMB. This method, solving the RPCA model based on the IALM algorithm, can effectively separate accurate, high-amplitude local anomalies from regional anomalies and minimize false anomalies. Furthermore, it overcomes the disadvantage of time-consuming calculations in the time domain, achieving much higher computational efficiency than the Exact Augmented Lagrange Multiplier (EALM) algorithm proposed by previous researchers (Lin et al., 2010; Wright et al., 2009). Therefore, the fast discrimination method is suitable to use in the processing of vast aeromagnetic data. This method is detailed as follows:
Assuming that the given high-dimensional data are located near a low-dimensional linear subspace, the calculations based on principal components analysis (PCA) are to efficiently and accurately estimate this subspace. Provided that the observed data contains matrix
where
where
where
To solve the non-convex optimization problem mentioned above, the objective function is relaxed as follows (Lin et al., 2010):
where
For the convex relaxation of the RPCA problem in Equation 1, it is necessary to construct an augmented Lagrangian function (Wright et al., 2009):
The Lagrangian function can be expressed as follows:
Observation data
① Calculating
② Solving the optimization problem:
③ Solving the optimization problem:
④ Calculating:
⑤ If Equation 2 meets the conditions of convergence,
Parameters
2.6 Curie isothermal surface cauculation
The Curie isothermal surface represents the fundamental lower boundary of the magnetic layer within the Earth’s upper lithosphere. Below this critical interface, where temperatures reach the Curie point (the characteristic demagnetization temperature of ferromagnetic minerals), the magnetization of these minerals progressively diminishes, effectively defining the depth limit of magnetically active crustal materials. As a temperature interface of the lithosphere, the Curie isothermal surface reflects the distribution of magnetic layers and heat flow in the continental crust. It indirectly manifests the undulating nature of the isothermal surface at a certain depth within the crust, playing a crucial role in studies on tectonics, earthquakes, geothermal resources, mineral resources, and volcanic activity (Gao et al., 2021; Ge et al., 2020; Nabi, 2016).
There are two main methods to calculate the depth of the Curie isothermal surface based on magnetic data: the individual magnetic anomaly method (Bhattacharyya and Leu, 1975; Vacquier and Affleck, 1941) and the combined magnetic anomaly method (Spector and Grant, 1970). Both methods establish the relationship between magnetic anomalies and the depths of the magnetic bodies’ bases by converting spatial domain data to the frequency domain. In this study, a power spectrum analysis based on the combined magnetic anomaly method (e.g., Tanaka et al., 1999) was employed using the software Geoprobe 4.1 (Xue et al., 2014).The formula is as follows (Zhang et al., 2023):
where
When calculating the Curie surface depth using the power spectrum method, a sliding window is employed (100 km × 100 km in this paper). Within each window,
3 Results
3.1 Geological interpretation of Bouguer Gravity data
Gravity-derived geophysical features effectively analyze regional geology (Kosaroglu et al., 2016; Mousa et al., 2020; Naveen et al., 2023) and identify mineralization zones, particularly IOA and skarn deposits (Gao et al., 2021; Lü et al., 2020; Yan et al., 2015). The Bouguer gravity anomaly (Ge et al., 2020; Mallick et al., 2012) is derived by subtracting normal gravity from corrected gravimeter readings, accounting for elevation, altitude, middle-layer, and terrain effects. As a key tool in geophysical exploration, it isolates subsurface density variations from local topography, aiding geological interpretation.
While generally independent of surface features, Bouguer anomalies may reflect density changes below the elevation datum. Regionally, they often inversely correlate with terrain due to crustal compensation, linked to lower crustal morphology (Figures 3, 4a). These anomalies combine shallow/localized signals (tens of meters to kilometers deep) with deeper regional components, including lower crustal and Moho density variations.
Regional Bouguer gravity anomalies range from approximately 4 mGal to −62 mGal. The Bouguer anomaly map (Figure 4A) presents local rock mass anomalies with significantly high and low gravity values. The banded high-amplitude gravity anomalies are primarily distributed along the YMB, especially in its east part, while low-amplitude gravity anomalies are found in the southern and western parts of the YMB. Overall, gravity highs correspond to low terrain elevation (along the Yangtze River), while gravity lows are principally related to the mountainous terrain in the western and southern parts of this region (Figures 3, 4a). Changes in the regional Bouguer gravity anomalies are related to the crust-mantle gravity balance, somewhat reflecting the thickening and thinning of the crust.
The Dabie orogenic belt generally exhibits a significant Bouguer gravity low, which is generally negatively correlated with the terrain of this region. The axis of the gravity low is in the NW-SE direction and protrudes southeastward, indicating that this region is subjected to pronounced compression in the NE-SW direction. In contrast, the North China block to the north exhibits moderate-to high-amplitude gravity anomalies, with high-amplitude gravity anomalies corresponding to the Hefei Basin (Figures 3, 4a).
Despite relatively consistent elevations, the YMB exhibits different gravity anomalies, with anomaly amplitude being high in the east and low in the west overall. In fact, this region is covered by extensive alluvium, with rocks exposed including only andesites, sandstones, and conglomerates, all of which have medium to low densities. The strong Bouguer gravity anomalies in this region tend to correspond to the detected basins of volcanic origin and iron deposits in areas including Ningwu, Luzong, and Huaining. They are supposed to represent a comprehensive reflection of deeply buried mafic volcanic rocks, subvolcanic rocks, and iron ores. As these anomalies correspond to the Ningwu and Luzong IOA ore cluster areas locally, they can be interpreted as being genetically associated with the IOA mineralization system. The steep gradients of gravity anomalies in the southern part of the YMB reflect the boundary between the YMB and the Jiangnan orogenic belt, coinciding with the Jiangnan fault zone. The Ningwu and Luzong IOA ore cluster areas exhibit NE-trending gravity anomalies with high gradients. In contrast, the Edongnan skarn ore cluster area lies along the margin of the NW-trending gravity anomalies with medium-to-high gradients. The Jiangnan orogenic belt, to the south of the Jiangnan fault, primarily exhibits low-amplitude Bouguer gravity anomalies, which gradually increase eastward and roughly correlate with the terrain.
To separate Bouguer gravity anomalies of different wavelengths, this study filtered the Bouguer gravity data through upward continuation (Blakely, 1995), highlighting long-wavelength regional anomalies while filtering out short-wavelength local anomalies. The choice of upward continuation height significantly impacts geophysical data interpretation, with distinct effects observed at lower versus higher elevations. As the upward continuation height increases, high-frequency signals from shallow sources (e.g., small-scale geological structures or near-surface mineralizations) progressively weaken, while low-frequency signals from deep sources (e.g., basement faults or large igneous bodies) become enhanced. We tested various upward continuation parameters and found that when the continuation height reached 10 km, the manifestations of basement faults or large igneous bodies became most prominent (Figure 5). The 10-km upward continuation of Bouguer gravity data of the YMB (Figure 6A) revealed pounced features of deep gravity anomalies, including two distinct gravity highs in the eastern part of the YMB and a gentle gravity high along the YMB. A large, distinct V-shaped gravity high can be observed along the YMB, strong in the east and weak in the west. The long-wavelength, large-scale gravity anomaly is inferred to be caused by large-scale, high-density igneous rocks, corresponding well to the large-scale volcanic activity in the region. The gravity high, also strong in the east and weak in the west, suggests that the deep sources of volcanic rocks should still be reflected in the modern crust-mantle structures. The Tanlu, Jiangnan, Xiangfan-Guangji, and Xiaotian-Mozitan faults feature steep Bouguer gravity gradients, forming the structural boundaries between the North China Plate, the Dabie orogenic belt, the YMB, and the South China Plate Belt. In addition, faults not serving as plate boundaries, such as Huangshi and Changjiang faults, are also distinct in the Bouguer anomaly map, suggesting that these faults might extend to very deep parts. These major faults serve as conduits for deep-seated ore-forming materials and magmas, thereby broadly controlling the distribution of iron-polymetallic deposits. However, gravity data fail to reveal the distribution of smaller ore-hosting fractures and structures. This limitation arises because signals from such minor faults and ore-hosting structures are inherently weaker-often remaining undetected or being filtered out during signal processing-and this phenomenon is likewise manifested in the aeromagnetic data.
3.2 Geological interpretation of aeromagnetic data
Aeromagnetic data effectively reveal subsurface structures and support mineral exploration (e.g., De Oliveira et al., 2008; El-Badrawy et al., 2024; Evans, 2005; Ge et al., 2020; Kosaroglu et al., 2016; Mousa et al., 2020; Naveen et al., 2023; Prasad et al., 2023; Rao et al., 2011; Zhu et al., 2022). Magnetic anomalies originate from induced fields (rock susceptibility-dependent) and residual fields (remanence history), with induced magnetization typically dominant except in volcanic rocks (Hinze et al., 2013; Table 1). High-susceptibility rocks show stronger anomaly variations (Table 1).
In the YMB (inclination 47.7°, declination −5.3°), RTP processing was applied to align anomalies with geological targets (Guan, 2005; Ge et al., 2020). The regional aeromagnetic data reveal complex local magnetic anomalies (Figure 6b), which spatially correlate with known rocks and structures overall. A series of NE-trending magnetic anomalies are observed in the eastern South China Plate (Figure 6), corresponding to Jurassic volcanic rocks with medium to high magnetism. In contrast, the western part of the plate primarily exhibits quiet magnetic fields, corresponding to the exposed Ordovician-Cambrian carbonate rocks and more ancient non-magnetic metamorphic rocks. The North China Plate and the Dabie orogenic belt are mainly characterized by concentrated high-amplitude magnetic anomalies with significantly different orientations. Specifically, the Dabie orogenic belt mainly exhibits NW-trending magnetic anomalies, while the North China Plate manifests E-W trending ones. This reflects the widespread distribution of high magnetic I-type granites, as well as Archean magnetic metamorphic rocks and migmatites, in both regions. Furthermore, the magnetic anomaly trending is consistent with the distribution of the primary faults and magmatic belts in both regions. The most prominent linear aeromagnetic anomalies are observed along the NE-trending Tanlu fault.
The YMB exhibits a relatively weak background magnetic field, with several moderate-to high-amplitude, linear magnetic anomalies present. Each individual anomaly measures about 20–30 km in width and 25–140 km in length. These magnetic anomalies are mostly NE-trending to the east of Jiujiang and are NW-trending to the west of Jiujiang, forming a U-shaped, intermittent anomaly belt parallel to the primary boundary faults in the region. The aeromagnetic anomalies correspond to the distribution of volcanic-subvolcanic rocks in ore cluster areas such as Ningwu, Luzong, and Jinniushan, also highlighting the distribution of intrusions including quartz diorites, granite diorite porphyries, and granites in the Edongnan ore cluster area. These magnetic rocks exhibit isotope ages of around 130 Ma, suggesting that these volcanic and intrusive rocks are the product of magmatic events of the same period.
The aeromagnetic data were also filtered using 10-km upward continuation to highlight long-wavelength aeromagnetic anomalies (Figure 6b). The results reveal a large magnetic anomaly belt on the north side of the Tanlu fault, weak background magnetic fields superimposed by beaded anomalies in the YMB, and a gradually intensifying magnetic field to the south of the Jiangnan Fault. The high-amplitude magnetic anomalies in volcanic basins such as Ningwu and Luzong are consistent with the Bouguer gravity anomalies, indicating that both anomalies are caused by intermediate-basic volcanic rocks. The upward continuation filtered out the short-wavelength anomalies related to shallow Jurassic igneous rocks (Figure 6). The rock magnetization and remanence data indicate that the shallow Jurassic igneous rocks in the YMB exhibit moderate to high magnetism, depending on their content of mafic minerals. The long-wavelength magnetic anomalies in the Ningwu and Luzong basins are related to deep and thick volcanic-subvolcanic rocks. The upward continuation map reveals distinct linear magnetic field characteristics of the Tanlu, Jiangnan, Xiangfan-Guangji, Xiaotian-Mozitan, Huangshi, and Changjiang faults, suggesting that they are crustal faults.
3.3 Fast discrimination results based on IALM-RPCA algorithm
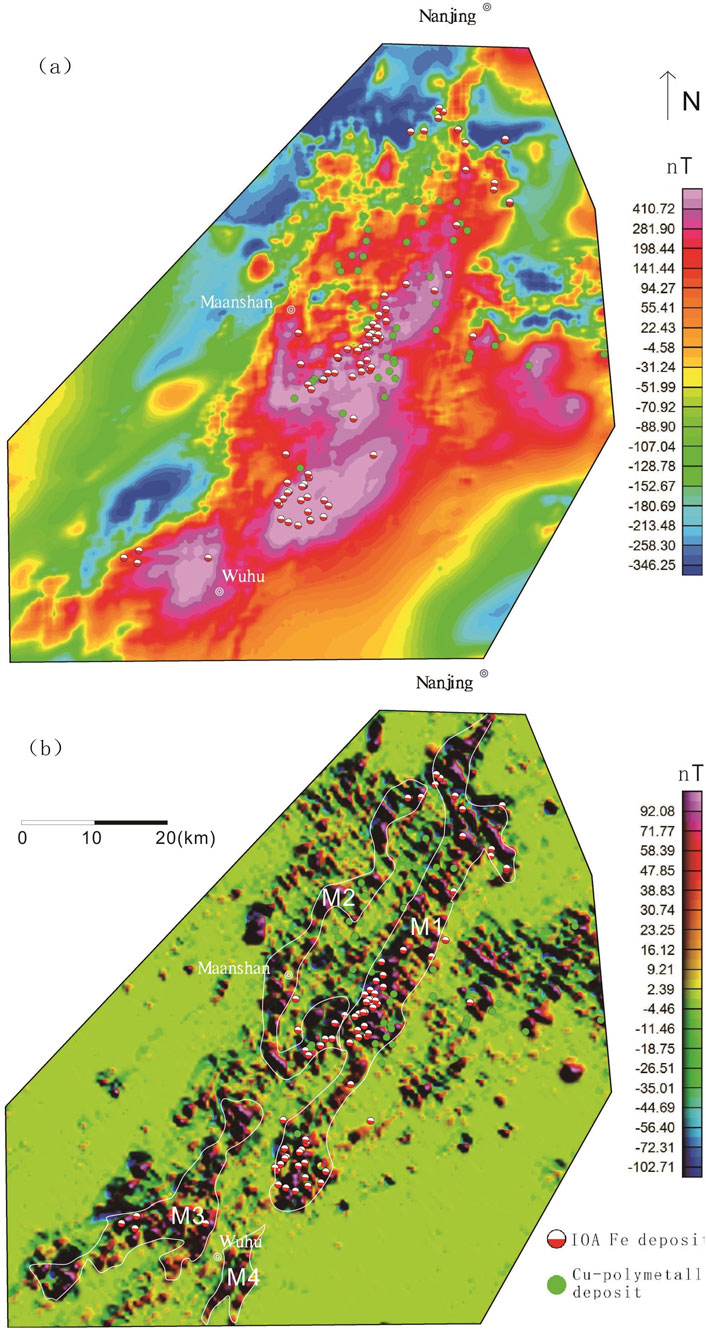
Local magnetic anomalies related to iron deposits in the Ningwu, Luzong, and Edongnan ore cluster areas in the YMB were identified and extracted from the RTP-transformed aeromagnetic data using the fast discrimination method based on the IALM-RPCA algorithm (Figures 7–12). The results indicate that the separated local magnetic anomalies correlated strongly with the distribution of iron deposits (Figures 10–12).
In the Ningwu and Luzong areas, the extracted major magnetic anomalies predominantly exhibit NE-trending linear characteristics, while those in the Edongnan area display clustered block-like features.Within the Ningwu area, the linear magnetic anomalies are primarily located in Wuhu, northeastern Wuhu, and Ma’anshan. These positive anomalies largely reflect subvolcanic structures and hypabyssal intrusive rocks. The background anomalies, distributed in sheet-like patterns from Wuhu to Nanjing, predominantly signify effusive rock types extensively covering volcanic basins.In the Ningwu area, four prominent linear-shaped local anomalies (M1-M4) are observed (Figure 10). Similarly, in the Luzong area, linear magnetic anomalies are predominantly concentrated in the northwestern Tongling region (Figure 11). Among these, the M6 anomaly exhibits an elongated NE-trending distribution, while the M1 anomaly displays a circular-linear pattern, likely linked to volcanic ring fractures. The background anomalies are characterized by sheet-like distributions over extensive areas, closely corresponding to the spatial extent of the Luzong volcanic basin. Nearly all known IOA (iron-oxide-apatite) type metallic deposits exhibit spatial associations with these delineated anomaly zones, with deposits either located within or near the margins of these zones. Isotopic age data further indicate that subvolcanic rocks aged approximately 130 Ma are detectable near the prominent positive anomaly zones (Mao et al., 2011; Zhai et al., 1992; Zhou et al., 2011). This anomaly pattern suggests the potential presence of highly magnetized, fault-controlled intrusive magma sources along these linear anomaly zones, which may be linked to magmatic systems associated with IOA-type iron mineralization. In contrast to the regions hosting IOA-type iron deposits, the local anomalies (Figure 12) (M1–M7) extracted in the southeastern Hubei (Edongnan) area exhibit clustered block-like features with varying orientations, reflecting the geometry of intrusive rock masses in this region. Skarn-type iron deposits are predominantly localized along the margins of these clustered anomalies. Notably, the large-scale volcanic-related magnetic anomalies in the western parts of the M6 and M7 anomalies have been significantly filtered out, highlighting the distinct geophysical signature of intrusive-dominated systems in Edongnan area.
3.4 Curie isothermal surface results
The Curie-point isothermal surface within the study region demonstrates remarkable homogeneity (Figure 13a), with two distinctive dome-shaped uplifts (termed Curie uplifts) identified in: (1) the southeastern sector of the Ningwu metallogenic cluster, and (2) the Huangshi City vicinity within the Edongnan ore district. These Curie uplifts display contrasting depths, measuring approximately 19 km and 21 km for the Ningwu and Huangshi anomalies respectively, significantly shallower than the regional background Curie depth of ∼29 km observed throughout the study area. The dual Curie uplifts demonstratepronounced magmatic processes accompanied by deep crustal thermal conduction, serving as prominent indicators of regional magmatic activity. Moreover, the core zones of these twin Curie uplifts demonstrate pronounced linear gravity-magnetic anomaly signatures, strongly suggesting the existence of deep-seated fault systems beneath these structural highs.
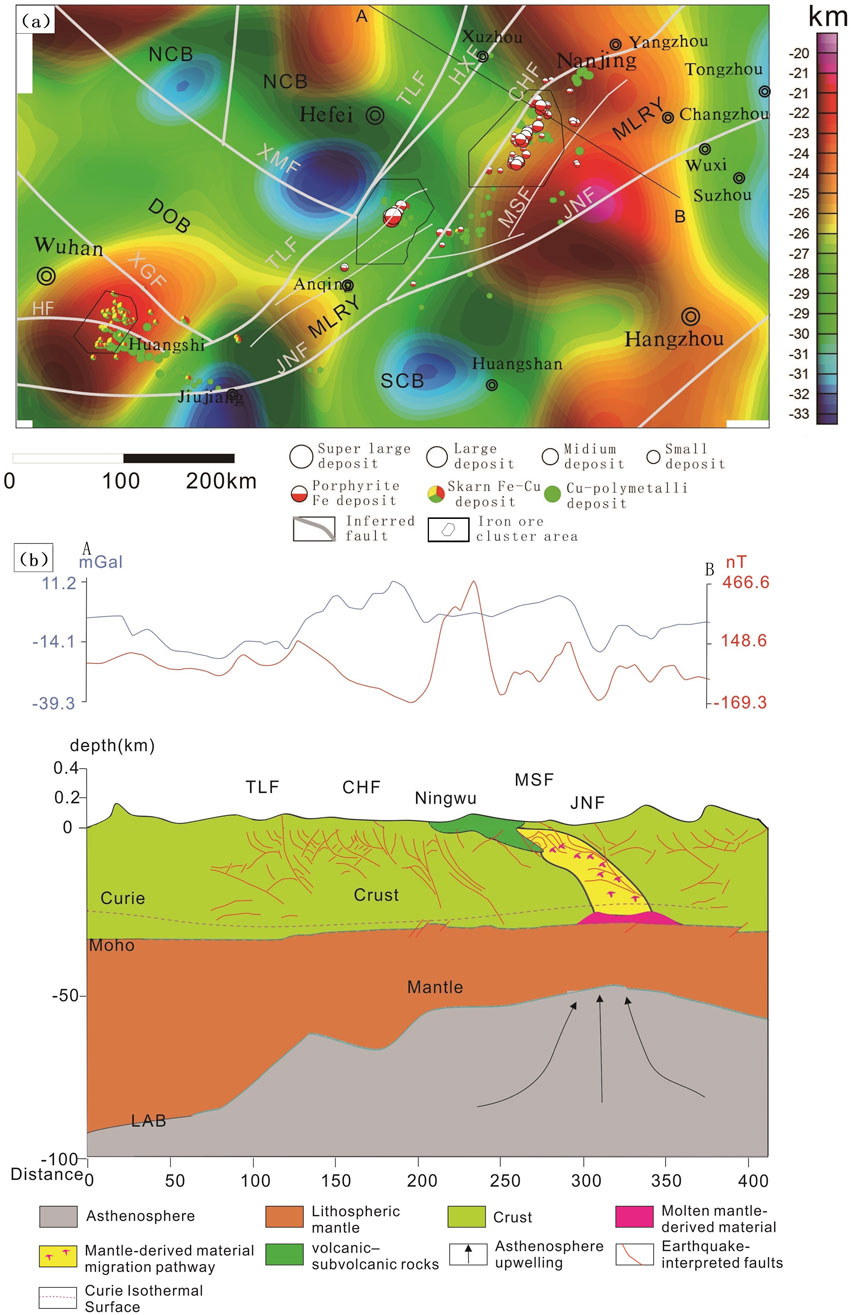
Figure 13. Map showing the Curie depths (a) and geological interpretation section seismic profile (b) (Moho depth and seismic inferred faults after Lü et al., 2014) LAB (the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary).
4 Discussion
4.1 Regional geophysical data and iron deposits
The regional gravity and magnetic data of the YMB obtained in this study serve as a supplement to previous geological understandings of the IOA and skarn-type Fe polymetallic deposits in the region. Furthermore, these data clearly reflect the distribution range of large-scale faults, especially in areas covered by widely distributed river alluvial deposits.
The Bouguer gravity and aeromagnetic data (Figure 4) indicate that IOA iron deposits in the YMB are located in banded Bouguer gravity and aeromagnetic anomalies parallel to the NNE-trending Tanlu, Changjiang, and Jiangnan faults. In contrast, the skarn iron deposits in the region are located in areas with steep changes in E-W-trending gravity and aeromagnetic anomalies. Furthermore, the aeromagnetic data reveal that the IOA and skarn iron ore clusters were positioned at the edges of the intense linear aeromagnetic highs trending NNE and NNW.
The upward continuation (10 km) processing of Bouguer gravity and aeromagnetic datasets (Figure 6) reveals that iron oxide-apatite (IOA) and skarn-type iron deposits consistently occur along the transitional zones of prominent high-amplitude gravity-magnetic anomalies. This spatial correlation strongly suggests genetic linkages between these mineralization systems and deep-seated magmatic bodies exhibiting coupled gravity-magnetic responses characteristic of IOA and skarn ore-forming processes.
4.2 Potential anomalies related to iron deposits
Regarding deposit exploration, local anomalies demonstrate a more significant correspondence with deposits compared to regional anomalies. Regional anomalies, heavily influenced by broader regional background fields, are typically characterized by subdued signals and indistinct boundaries. Conversely, local anomalies exhibit a stronger association with discrete ore bodies after filtering out the regional background field, and typically manifest with more pronounced peak amplitudes and sharper boundary features. In this study, a fast discrimination method based on the IALM-RPCA algorithm was used for the Ningwu, Luzong, and Edongnan ore cluster areas (Figures 7–9). Several NE and NEE-trending linear anomalies were extracted from the Ningwu and Luzong areas (Figures 9b, 10b), with IOA iron deposits found at the peaks of these linear anomalies (Figure 13b). The linear anomalies including anomalies M1-4 marked in Figure 10b and anomalies M1-6 marked in Figure 11b, reflected subvolcanic intrusions with high magnetite content that have intruded along faults, and these subvolcanic intrusions are closely related to iron mineralization. In the Edongnan skarn ore cluster area (Figure 13b), several NE-trending magnetic anomaly belts marked as M1-7 correspond to quartz diorites and granites that are closely related to iron deposits. Skarn iron deposits have been found near the steep-gradient edges of these anomalies, indicating that iron mineralization mostly occurred in the surrounding quartz diorites and granites.
The results of fast discrimination method based on the IALM-RPCA algorithm identify potential exploration locations of IOA and skarn deposits, thus facilitating the exploration of iron deposits. In contrast, copper deposits exhibit a lower correlation with local magnetic anomalies.
4.3 Metallogenic evolution in the YMB
Our Curie point depth (CPD) analysis identifies two thermally anomalous domains within the Yangtze Metallogenic Belt (YMB): (1) the southeastern Ningwu iron ore cluster (31.1°N, 119.2°E) and (2) the Huangshi district of the Edongnan ore cluster (30.2°N, 114.8°E) (Figure 13a), which confirms earlier CPD estimations by Xiong et al. (2016b). Integrated analysis demonstrates remarkable consistency between these thermal anomalies and crust-mantle boundary deformations. The Sino Probe seismic profiles (Lü et al., 2015) document contemporaneous uplift features at both the lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary (LAB) and Moho discontinuity beneath these regions (Figure 13B). The spatial coincidence of these multi-layer uplift structures with: (1) distinct linear gravity/magnetic anomalies, (2) southeast-dipping fault systems (particularly in the Ningwu cluster’s basement), and (3) high-density fracture networks strongly suggests their genetic relationship as potential conduits for mantle-derived fluid migration. This interpretation is further supported by the observed spatial correlation among the Curie isotherm perturbations, deep-crustal fault architectures, and magmato-hydrothermal mineralization systems characteristic of IOA and skarn-type deposits in the YMB.
The metallogenic processes in the Yangtze Metallogenic Belt (YMB) can be effectively explained by the melting-assimilation-storage-homogenization (MASH) model proposed by Hildreth and Moorbath (1988), Hildreth (2007). From the Middle-Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous, the regional tectonic system underwent a significant transformation, shifting from a nearly-E-W-trending collisional tectonic system to a NW-trending subduction tectonic system (Xu et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2009). This shift was driven by remote compressive stresses resulting from the NW-trending low-angle subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Accordingly, continental subduction and lithospheric delamination occurred in the YMB. These processes caused mantle-derived basaltic melts, generated by the upwelling of asthenospheric materials, underplated the lower crust near the crust-mantle boundary. The interactions between the basaltic melts and crustal materials produced adakite-like magmas. During the Early Cretaceous (approximately 130 Ma), magmas and hydrothermal fluids migrated toward shallower areas within extensional environments. This migration facilitated the formation of shallow magma chambers and the metallogenic explosion of IOA and skarn-type iron deposits in the YMB.
The 2 Curie point uplifts observed in the Yangtze Metallogenic Belt (YMB, Figure 13a) exhibit a strong spatial correlation with regional iron ore clusters, indicating their genetic relationship to mantle upwelling zones associated with continental subduction. The primary subduction event occurred in the southeastern sector of the Ningwu ore cluster, inducing the ascent of mantle-derived magmas. These magmas were subsequently channeled along fault systems into the Ningwu basin, ultimately forming iron oxide-apatite (IOA) type deposits.
A contemporaneous subduction episode developed near Huangshi City within the Edongnan ore cluster, likely influenced by the structural barrier created by the pre-existing Dabie ultra-high-pressure metamorphic belt. Petrogenetic studies suggest the Ningwu IOA deposits originated from the southeastern margin of the cluster, having undergone significant lateral transport exceeding 80 km along fault systems. This extensive migration contrasts sharply with the more localized formation of skarn-type iron deposits in the Edongnan cluster, which show no evidence of comparable lateral displacement. Compared to the known deposits, many anomalies warrant further investigation.
5 Conclusion
This study presents a comprehensive geological interpretation of newly acquired aeromagnetic and gravity data to evaluate the metallogenic potential and evolutionary characteristics of IOA-type and skarn iron deposits in the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Metallogenic Belt (YMB), with particular emphasis on key ore cluster areas including Luzong, Ningwu, and Edongnan. The research yields several significant findings:
1. Distinct spatial patterns were identified: IOA-type iron deposits consistently occur near gravity and magnetic highs, while skarn-type deposits are preferentially located along the margins of steep-gradient gravity and magnetic anomalies.
2. Application of an innovative dimensionality reduction method based on the IALM-RPCA algorithm successfully isolated local magnetic anomalies, enabling precise delineation of potential mineralization zones and associated igneous rocks within the ore cluster areas.
3. Thermal modeling revealed two prominent isothermal uplift zones proximal to the IOA and skarn ore clusters, providing crucial thermodynamic constraints for mineralization processes.
4. Systematic investigation of ore-forming material sources and migration pathways offers critical insights into the genetic processes of iron deposits in IOA-type and skarn-type ore cluster systems in the YMB.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
TG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. XY: Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. ZyF: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. JH: Software, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XG: Software, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. XL: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. LQ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. ZgF: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. XH: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFC2903704) the Ministry-Province Cooperative Project under the Ministry of Natural Resources (2024ZRBSHZ132) and the programs of the China Geological Survey (DD20240119, DD20243245).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their sincere gratitude to the School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China university of Geosciences Beijing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bhattacharyya, B. K., and Leu, L. K. (1975). Analysis of magnetic anomalies over yellowstone National park: mapping of curie point isothermal surface for geothermal reconnaissance. J. Geophys. Res. 80, 4461–4465. doi:10.1029/jb080i032p04461
Blakely, R. J. (1995). Potential theory in gravity and magnetic applications. Cambridge University Press.
Chang, Y. F., Liu, X. P., and Wu, Y. C. (1991). The Middle-Lower Yangtze River valley steel metallogenic belt. Beijing: Geological Publishing House.
De Oliveira, D. C., Dall'Agnol, R., Corrêa da Silva, J. B., and Costa de Almeida, J. A. (2008). Gravimetric, radiometric, and magnetic susceptibility study of the Paleoproterozoic Redenção and Bannach plutons, eastern Amazonian Craton, Brazil: implications for architecture and zoning of A-type granites. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 25, 100–115. doi:10.1016/j.jsames.2007.10.003
Dong, S. W., Ma, L. C., Liu, G., Xue, H. M., Shi, W., and Li, J. H. (2011). The dynamics of the metallogenic belt of Middle-Lower reaches of Yangtze River, Eastern China. Acta Geol. Sin. 85 (5), 612–625. doi:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2011.00516.x
El-Badrawy, H. T., Abbas, A. M., Massoud, U., Abu-Alam, T., Alrefaee, H. A., Abo Khashaba, S. M., et al. (2024). Integratedapproach-based groundwater mapping in sohag governorate, upper Egypt, using remote sensing and aeromagnetic data. Front. Earth Sci. 12, 1456055. doi:10.3389/feart.2024.1456055
Evans, D. M. (2005). Geology and geochemistry of Munali nickel deposit: consulting report (Report No. 1-34). Denbighshire, United Kingdom: Carrog Consulting.
Fan, Z. Y., Xiong, S. Q., Ge, T. F., He, J. Z., Yang, H., and Yang, X. (2025). Identification and extraction of aeromagnetic anomalies based on fast and robust principal component analysis: a case study of sedimentary metamorphic iron deposits. Earth Sci. Frontiers[J/OL]. Earth Sci. Front., 1-16. doi:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2025.3.38
Gao, B. L. (2021). Study on the deep background and geophysical characteristics of the southeastern Hubei mineral concentration area. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences.
Gao, M. G., Lu, Q. M., Wang, J., and Kang, G. F. (2021). Constraining crustal thickness and lithospheric thermal state beneath the northeastern Tibetan Plateau and adjacent regions from gravity, aeromagnetic, and heat flow data. J. Asian Earth Sci. 212, 104743. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104743
Ge, T. F., Qiu, L., He, J. Z., Fan, Z. G., Huang, X. Z., and Xiong, S. Q. (2020). Aeromagnetic identification and modeling of mafic-ultramafic complexes in the Huangshan-Turaergen Ni-Cu metallogenic belt in NW China: magmatic and metallogenic implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 127, 103849. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103849
Hildreth, W. (2007). Quaternary magmatism in the Cascades-Geologic perspectives. Washington, DC: U.S. Geological Survey. U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1744).
Hildreth, W., and Moorbath, S. (1988). Crustal contributions to arc magmatism in the Andes of Central Chile. Contributions Mineralogy Petrology 98, 455–489. doi:10.1007/bf00372365
Hinze, W. J., Von Frese, R. R., and Saad, A. H. (2013). Gravity and magnetic exploration: principles, practices and applications. Cambridge University Press.
Hu, H., Li, J. W., Harlov, D. E., Lentz, D., McFarlane, C., and Yang, Y. H. (2020). A genetic link between iron oxide apatite and iron skarn mineralization in the Jinniu volcanic basin, Daye district, eastern China: evidence from magnetite geochemistry and multi-mineral U-Pb geochronology. GSA Bull. 132, 899–917. doi:10.1130/b35180.1
Kosaroglu, S., Buyuksarac, A., and Aydemir, A. (2016). Modeling of shallow structures in the Cappadocia region using gravity and aeromagnetic anomalies. J. Asian Earth Sci. 124, 214–226. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.05.005
Li, Z. X. (1994). Collision between the North and South China blocks: a crustal-detachment model for suturing in the region east of the Tanlu fault. Geology 22 (8), 739–742. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0739:cbtnas>2.3.co;2
Lin, Z., Chen, M., and Ma, Y. (2010). The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1009.5055. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1009.5055
Liu, W. J., Zhang, X. Y., Luo, Z. W., Hou, Z. Y., and Xi, J. J. (2021). 1:2,500,000 Bouguer gravity anomaly map of the people’s Republic of China. Inst. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. Ministry Geol. Mineral Resour.
Lü, X. B., Zhao, P. D., and Yao, S. Z. (1998). Geological Anomaly and mineralization in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Geol. Sin. 72 (3), 260–266.
Lü, Q. T., Dong, S. W., Shi, D. N., Tang, J. T., and Jiang, G. M.Sino Probe-03-CJ Group (2014). Lithosphere architecture and geodynamic model of Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze Metallogenic Belt: a review from Sino Probe. Acta Petrol. Sin. 30 (4), 889–906.
Lü, Q. T., Shi, D. N., Liu, Z. D., Zhang, Y. Q., Dong, S. W., and Zhao, J. H. (2015). Crustal structure and geodynamics of the Middle and Lower reaches of Yangtze metallogenic belt and neighboring areas: insights from deep seismic reflection profiling. J. Asian Earth Sci. 114, 704–716. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.022
Lü, Q. T., Meng, G. X., Yan, J. Y., Zhang, K., Gong, X. J., and Gao, F. X. (2020). The geophysical exploration of Mesozoic iron-copper mineral system in the middle and lower reaches of Yangztez River metallogenic belt: a synthesis. Earth Sci. Front. 27 (2), 235–253. doi:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.3.18
Lü, Q. T., Meng, G. X., Zhang, K., Liu, Z. D., Yan, J. Y., Shi, D. N., et al. (2021). The lithospheric architecture of the Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt, East China: insights into an extensive Fe-Cu mineral system. Ore Geol. Rev. 132, 103989. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.103989
Mallick, K., Vasanthi, A., and Sharma, K. K. (2012). Bouguer gravity regional and residual separation: application to geology and environment. Netherlands, New Delhi: Springer.
Mao, J. W., Xie, G. Q., Duan, C., Pirajno, F., Ishiyama, D., and Chen, Y. (2011). A tectono-genetic model for porphyry–skarn–stratabound cu–au–mo–fe and magnetite–apatite deposits along the Middle–Lower Yangtze River Valley, Eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 43 (1), 294–314. doi:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.07.010
Mousa, A. A., Mickus, B. K., and Al-Rahim, A. (2020). The use of gravity and aeromagnetic data to define the structural configuration of the Western Desert, Iraq. J. Asian Earth Sci. 196, 104362. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104362
Nabi, S. H. A. E. (2012). Curie point depth beneath the Barramiya-Red Sea coast area estimated from spectral analysis of aeromagnetic data. J. Asian Earth Sci. 43 (1), 254–266. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.09.015
National Standardization Administration of China (2019). Specifications for national gravity control survey (GB/T 20256-2019). Beijing: Standards Press of China.
Naveen, P. U., Sathapathy, S. K., Giri, Y., Singh, A. P., Radhakrishna, M., and Rao, C. V. (2023). Crustal structure across the Central part of Narmada-Son Lineament, India based on the interpretation of aeromagnetic and gravity data: geological implications. J. Asian Earth Sci. 255, 105765. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105765
Prasad, K. N. D., Patel, V. C., Bansal, A. R., and Singh, A. P. (2023). New insights into the crustal magnetization of the eastern Indian shield inferred from the aeromagnetic data-based depth to the bottom of the magnetic sources (DBMS). J. Asian Earth Sci. 245, 105544. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105544
Rao, C. R., Kishore, R. K., Kumar, V. P., Kumar, V. P., and Babu, B. B. (2011). Delineation of intra crustal horizon in Eastern Dharwar Craton - an aeromagnetic evidence. J. Asian Earth Sci. 40 (2), 534–541. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.10.006
Shahabpour, J. (1999). The role of deep structures in the distribution of some major ore deposits in Iran, NE of the Zagros thrust zone. J. Geodyn. 28, 237–250. doi:10.1016/s0264-3707(98)00040-4
Shang, S. G., Zhang, Q. M., Gao, C. S., and Fan, Y. (2014). Characteristic of gravity-magnetic field in Luohe-Xiaobaozhuang iron ore district in Lujiang-Zongyang ore district in Anhui Province and prospecting prediction. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. 6 (19), 730–735.
Spector, A., and Grant, F. S. (1970). Statistical models for interpreting aeromagnetic data. Geophysics 35 (2), 293–302. doi:10.1190/1.1440092
Tanaka, A., Okubo, Y., and Matsubayashi, O. (1999). Curie point depth based on spectrum analysis of the magnetic anomaly data in east and southeast Asia. Tectonophysics 306 (3-4), 461–470. doi:10.1016/s0040-1951(99)00072-4
Turk, M., and Pentland, A. (1991). Eigenfaces for recognition. J. Cognitive Neurosci. 3 (1), 71–86. doi:10.1162/jocn.1991.3.1.71
Tweto, O., and Case, J. E. (1972). “Gravity and magnetic features as related to geology in Leadville 30-minute quadrangle, Colorado,” in Geophysical field investigations. Washington, D.C.: United States Department of the Interior Rodgers, 1–38.
Vacquier, V., and Affleck, J. (1941). A computation of the average depth to the bottom of the earth’s magnetic crust, based on a statistical study of local magnetic anomalies. EOS 22 (2), 446–450.
Wright, J., Ganesh, A., Rao, S., and Ma, Y. (2009). Robust principal component analysis: exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices via convex optimization. Adv. neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2080–2088.
Wu, F. Y., Ge, W. C., Sun, D. y., and Guo, C. L. (2003). Several issues in the study of lithospheric thinning in eastern China. Earth Sci. Front. 2003 (03), 51–60. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xiong, S. Q., Tong, J., Ding, Y. Y., and Li, Z. K. (2016). Aeromagnetic data and geological structure of continental China: a review. Appl. Geophys. 13, 227–237. doi:10.1007/s11770-016-0552-2
Xiong, S. Q., Yang, H., Ding, Y. Y., and Li, Z. K. (2016b). Characteristics of Chinese continent Curie point isotherm. Chin. J. Geophys. 59(10), 3604–3617. doi:10.6038/cjg20161008
Xu, X. B., Zhang, Y. O., Jia, D., Shu, L. S., and Wang, R. R. (2009). Early Mesozoic geotectonic processes in South China. Geol. China 36 (3), 573–593.
Xue, D. J., Wang, L. F., He, H., and Guo, Z. H. (2014). Development and application of the geophysical platform (geoprobe). China Sci. Technol. Achiev. 8, 45–47.
Yan, J. Y., Lü, Q. T., Chen, M. C., Deng, Z., Qi, G., Zhang, K., et al. (2015). Identification and extraction of geological structure information based on multi-scale edge detection of gravity and magnetic fields: an example of the Tongling ore concentration area. Chin. J. Geophys. 58(12), 4450–4464. doi:10.6038/cjg20151210
Yang, W. C. (2023). Origin of the mid-lower-yangtze tectonic belt and Yanshanian ocean subduction. Geol. Rev. 69 (5), 1619–1627. doi:10.16509/j.georeview.2023.07.015
Yang, J., Zhang, D., Frangi, A. F., and Jing-yu Yang, (2004). Two-dimensional PCA: a new approach to appearance-based face representation and recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analysis Mach. Intell. 26 (1), 131–137. doi:10.1109/tpami.2004.1261097
Yin, A., and Nie, S. Y. (1993). An indentation model for the North and South China collision and the development of the Tan-Lu and Honam Fault Systems, eastern Asia. Tectonics 12 (4), 801–813. doi:10.1029/93tc00313
Zhai, Y. S., Yao, S. Z., Lin, X. D., Zhou, X. M., Wan, T. L., and Zhou, Z. G. (1992). Metallogenic regularity of iron copper deposits in the middle and lower valley of the Yangtze River. Geological Publishing House, Beijing.
Zhang, Y. Q., Xu, X. B., Jia, D., and Shu, L. S. (2009). Deformation record of the change from Indosinian collision-related tectonic system to Yanshanian subduction-related tectonic system in South China during the Early Mesozoic. Earth Sci. Front. 16 (1), 234–247. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, F., Yang, J., Qian, J., and Xu, Y. (2015). Nuclear norm-based 2-DPCA for extracting features from images. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 26 (10), 2247–2260. doi:10.1109/tnnls.2014.2376530
Zhang, J., He, Y. B., and Fan, Y. X. (2023). Crustal thermal structure and deep heat source conditions in the Songliao Basin. J. Earth Sci. Environ. 45(2), 157–167 doi:10.13745/j.esf.sf.2022.1.20
Zhao, J. X., Wang, Y. J., Fu, X. X., and Ward, S. H. (1989). An overview of exploration geophysics in China-1988. Tulsa, OK: Society of Exploration Geophysicists.
Zheng, Q. F., Zheng, Y. Z., and Zhao, R. (2022). Gravity and magnetic anomaly in the southern Tanlu fault zone and its geological interpretation. Earth Sci. Front. 29 (3), 292–303. doi:10.13745/i.esf.sf.2022.1.55 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou, T. F., Fan, Y., Yuan, F., Song, C. Z., Zhang, L. J., Qian, C. C., et al. (2010). Temporal-spatial framework of magmatic intrusions in the Luzong volcanic basin in East China and their constraints on mineralization. Acta Petrol. Sin. 26 (9), 2694–2714. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou, T. F., Fan, Y., Yuan, F., Zhang, L. J., Ma, L., Qian, B., et al. (2011). Petrogenesis and metallogeny study of the volcanic basins in the Middle and Lower Yangtze Metallogenic Belt. Acta Geol. Sin. 78 (2), 422–435. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhou, T. F., Fan, Y., Wang, S. W., and White, N. C. (2017). Metallogenic regularity and metallogenic model of the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrol. Sin. 33 (11), 3353–3372. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu, J. B. (2018). Discussion on distribution characteristics of huangmaqing Formation bottom burial depth in Zhonggu Orefield. Nonferrous Met. Abstr. 33 (5), 43–44. doi:10.19534/j.cnki.zyxxygc.2018.05.019 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu, G., Liu, G. S., Niu, M. L., Xie, C. L., Wang, Y. S., and Xiang, B. W. (2009). Syn-collisional transform faulting of the Tan-Lu fault zone, East China. Int. J. Earth Sci. (Geol Rundsch) 98 (1), 135–155. doi:10.1007/s00531-007-0225-8
Keywords: aeromagnetic anomaly, curie isothermal surface, Yangtze, iron deposit, RPCA algorithm
Citation: Ge T, Yang X, Fan Z, He J, Gao X, Li X, Qiu L, Fan Z and Huang X (2025) Geological interpretation of aeromagnetic data in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze river metallogenic belt, China: implications for iron oxide-apatite (IOA) and skarn iron deposit exploration. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1620818. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1620818
Received: 30 April 2025; Accepted: 18 September 2025;
Published: 02 October 2025.
Edited by:
Costanza Bonadiman, University of Ferrara, ItalyReviewed by:
Ameha Atnafu Muluneh, University of Bremen, GermanyVsevolod Yutsis, Instituto Potosino de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (IPICYT), Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Ge, Yang, Fan, He, Gao, Li, Qiu, Fan and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xue Yang, MzQ0MTg5NzU1QHFxLmNvbQ==; Zhenyu Fan, Znp5MzAxMDE3MDAyMUAxNjMuY29t
 Tengfei Ge
Tengfei Ge Xue Yang1*
Xue Yang1* Zhenyu Fan
Zhenyu Fan Liang Qiu
Liang Qiu