- 1School of Energy Resources, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing, China
- 2CAGS/Key Laboratory of Karst Dynamics, MNR&GZAR/International Research Centre on Karst under the Auspices of UNESCO, Institute of Karst Geology, Guilin, Guangxi, China
- 3Pingguo Guangxi, Karst Ecosystem, National Observation and Research Station, Pingguo, Guangxi, China
A set of thick carbonate rocks is developed in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations of Jixian System in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas, with diverse dolomite rock types, complex reservoir space, and large differences in physical properties, which are the main layers of hydrocarbon and geothermal resources. However, it is difficult to identify the paleokarstification, and the paleoenvironmental characteristics are not clear. The major and trace elements, carbon, oxygen and strontium isotopes of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are analyzed based on field geological investigation, core observation, thin section identification and physical property analysis. The results show that dolomite and siliceous bands of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are formed in the warm subtropical climate of seawater environment, which are partially affected by meteoric water, characterized by interactive marine, and the depth of water as a whole is relatively shallow, mainly in an oxidizing environment, affected by different degree of terrestrial fluids. The fluid temperature at the time of formation of the dolomite fillings is significantly higher than that of the seawater in the same period, which is controlled by the high temperature fluid transformation after burial. The calcite fillings exhibit a meteoric water genesis, having precipitated under anoxic reducing conditions at temperatures equivalent to those of dolomite. Four periods of carbonate paleokarstification and depositional environments have been revealed, which are marine syndiagenetic depositional period or eogenetic karst, shallow burial period, medium-deep burial period or high-temperature paleoenvironment and the hypergene period of meteoric water karstification.
1 Introduction
In the 1970s, the discovery of Renqiu oilfield opened the prelude of large-scale oil and gas exploration in Meso-Neoproterozoic carbonate rocks in Jizhong depression (Zhao et al., 2015). So far, the buried hill in Jizhong Depression has experienced nearly half a century of exploration and development, and a series of buried hill reservoirs have been discovered (Guo et al., 2009; Zhao et al., 2012; Liu et al., 2017). The report of proven oil and gas reserves in Jizhong Depression shows that the proven reserves of buried hill reservoirs account for more than half of the total proven reserves (Yang et al., 2009), and these oil and gas resources are mainly hosted in the dolomite reservoirs of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations of Jixian System (Pei et al., 2009; Feng et al., 2020). In addition, the survey results of geothermal resources show that there are abundant karst geothermal resources in the buried hills of Jizhong Depression (Zhang et al., 2017; Wang et al., 2021), among which Xiong ‘an New Area is a typical representative, and its geothermal reservoirs are mainly karst reservoirs of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations (Dai et al., 2023; Qiao et al., 2023a). According to statistics, the geothermal reservoir temperature of buried hill geothermal field in Xiong ‘an New Area can reach more than 110°C, and the single well production of geothermal reservoir can reach more than 120 m3/h (Gao et al., 2023). It can be seen that dolomite reservoirs of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Jixian System of Xiong ‘an New Area not only contain a large amount of oil and gas resources, but also contain abundant geothermal resources, which lays a solid foundation for Xiong ‘an New Area to achieve the goal of zero pollution and zero emission.
The predecessors have carried out seismic and drilling work in Xiong ‘an New Area, and accumulated a large amount of basic data. They have obtained a preliminary understanding of the characteristics of geothermal reservoir distribution, temperature distribution and hydrodynamics in Xiong ‘an New Area (Xiong et al., 1985), and also studied the development and evolution of buried hill structures in Jizhong Depression and its secondary structural units (Gui et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2022). In the past decade, especially since the establishment of Xiong ‘an New Area in 2017, with the exploration and development of geothermal geology, the research on geothermal resources in Xiong ‘an New Area has been increasing, and the results have been fruitful (Yue et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023; Qiao et al., 2023b). Geothermal resources evaluation is mainly carried out around reservoir distribution, temperature and water yield (Guo et al., 2023). In recent years, there have been some breakthroughs in the study of karst reservoirs in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in this area, including the characteristics of fracture development, development pattern of karst reservoir and reservoir formation mechanism (Lu et al., 2021; Yue et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2023). However, due to the ancient geological age, complex evolution process and strong later transformation of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations, it is difficult to identify the paleokarstification that formed the reservoirs in this area, and the lack of constraints of various geochemical means on karst reservoirs, and unclear characteristics of paleoenvironmental differences between bedrock and fracture-cavity fillings, which restricts the exploration and deployment of geothermal resources in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations to a certain extent. Therefore, it is urgent to systematically study the paleokarstification and paleoenvironmental characteristics of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations.
Paleokarstification is one of the key factors in the formation of pore system in carbonate reservoirs (Richard et al., 2005; Li et al., 2008; Sun et al., 2024), which has an important influence on the formation of pores, caves and fractures in reservoirs (Kerans, 1988; Loucks, 1999; Loucks et al., 2004). The elemental composition of marine carbonate rocks is sensitive to the physical and chemical properties of sedimentary water and post-sedimentary paleokarstification. It can be used to trace paleokarstification and paleoenvironmental characteristics. In recent years, it has been widely used in Precambrian strata (Ling et al., 2013; Xiong et al., 2014; Ma et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). Therefore, the study takes the Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas as the research objects. On the basis of field outcrop investigation, core observation, microscopic identification and porosity and permeability analysis, the characteristics of major and trace elements and carbon, oxygen and strontium isotopes are studied to explore the application of geochemical characteristics in characterizing paleokarstification and paleoenvironment, with the aim to provide support for the exploration and development of geothermal resources in the Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area.
2 Geological setting
Xiong ‘an New Area is located in the hinterland of Beijing, Tianjin and Hebei. The administrative scope covers Xiongxian County, Rongcheng County, Anxin County and surrounding areas, with a total area of about 1796 km2. The structure is located in the central part of the Jizhong Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin. There are nine secondary structural units in the Jizhong Depression, including three uplifts, four depressions and two slopes, namely, Niutuozhen uplift, Rongcheng uplift and Gaoyang low uplift. Baxian sag, Raoyang sag, Baoding sag and Xushui sag; Niubei slope and Lixian slope. The faults in the area are widely developed, including the NE-trending Rongcheng fault, Niudong fault, Baoding fault, Gaoyang fault and Renxi fault, and the NWW-trending Rongnan fault and Niunan fault (Figure 1).
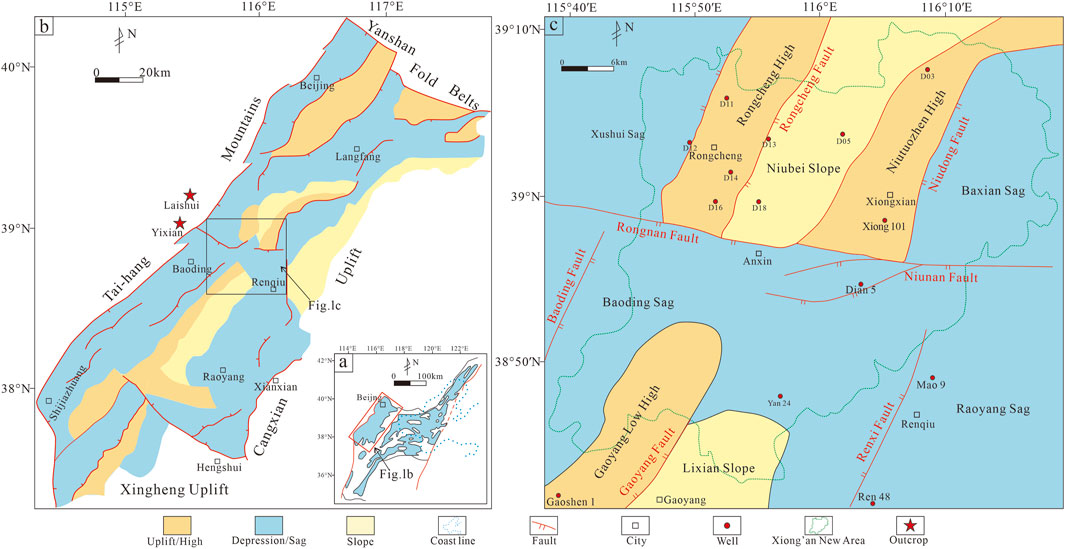
Figure 1. Distribution of tectonic units in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas (modified from Zhao et al., 2015; Dai et al., 2023).
As a part of the Bohai Bay Basin, Xiong ‘an New Area is located on the eastern continental block of the North China Craton in the geotectonic position (Zhao et al., 2005; Chang et al., 2018). Since the Archean, it has mainly experienced five stages of tectonic uplift: Lingyuan, Qinyu, Indosinian, Yanshan and Himalayan (Yang et al., 2002). Under the action of multiple tectonic-thermal activities, the basement continued to proliferate, collage and expand, forming a unified crystalline basement in Archean-Paleoproterozoic. Subsequently, the North China Craton entered a stable stage of caprock evolution (Tang et al., 2013). The Mesoproterozoic North China Craton experienced intracontinental rifting (Zhai et al., 2011), and correspondingly deposited thick carbonate rocks of Changcheng and Jixian Systems. Tectonic activity is dominated by integral ascending and descending movement in the Neoproterozoic-Paleozoic (Lu et al., 2008; Zhai et al., 2011). The southward subduction of the Paleo-Asian Ocean in the late Paleozoic and the collision between South China and North China in the early Mesozoic have had an important impact on the evolution of the North China Craton (Zhu et al., 2017). The nearly north-south extrusion caused the nearly east-west tectonic pattern of the Bohai Bay Basin in the Indosinian movement (Li X. D. et al., 2024). Since the Yanshan movement, the subduction of the ancient Pacific plate has significantly changed the tectonic system of the North China Craton, from the north-south compression to the NWW-SE extension (Li F. et al., 2016; Yu et al., 2023), accompanied by strong magmatic activity (Wang et al., 2019). At the same time, the Bohai Bay Basin began to develop (Chang et al., 2018), and the boundary faults had strong extensional block faulting activities. The tectonic framework of the Jizhong Depression gradually formed, and this process continued until the end of the Paleogene (Allen et al., 1997; Yang et al., 2002; Li et al., 2012). In the Miocene, Niutuozhen and Rongcheng uplifts continued to uplift, and the denudation from Wumishan Formation to Paleogene was further enhanced. In the depositional period of the Minghuazhen Formation in the Pliocene, the Xiong ‘an New Area and the entire Bohai Bay Basin entered the post-rift thermal subsidence stage, and finally formed the current tectonic framework (Li Z. H. et al., 2016).
The Archean and Lower Proterozoic complex metamorphic rock basements are developed in Xiong ‘an New Area. The sedimentary caprocks are mainly Mesoproterozoic and Cenozoic. The Cenozoic clastic rocks in the main area of Xiong ‘an New Area are directly covered on the Wumishan Formation of Jixian System (Lu et al., 2021), and the Paleozoic and Mesozoic are seriously eroded. The Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations of Jixian System are a set of extremely thick dolomite strata of tidal flat facies. The drilling thickness of Gaoyuzhuang Formation is as high as about 1,000 m (Figure 2). Wumishan Formation can be divided into four members from bottom to top, with a total thickness of 760–1,400 m (Dai et al., 2023).
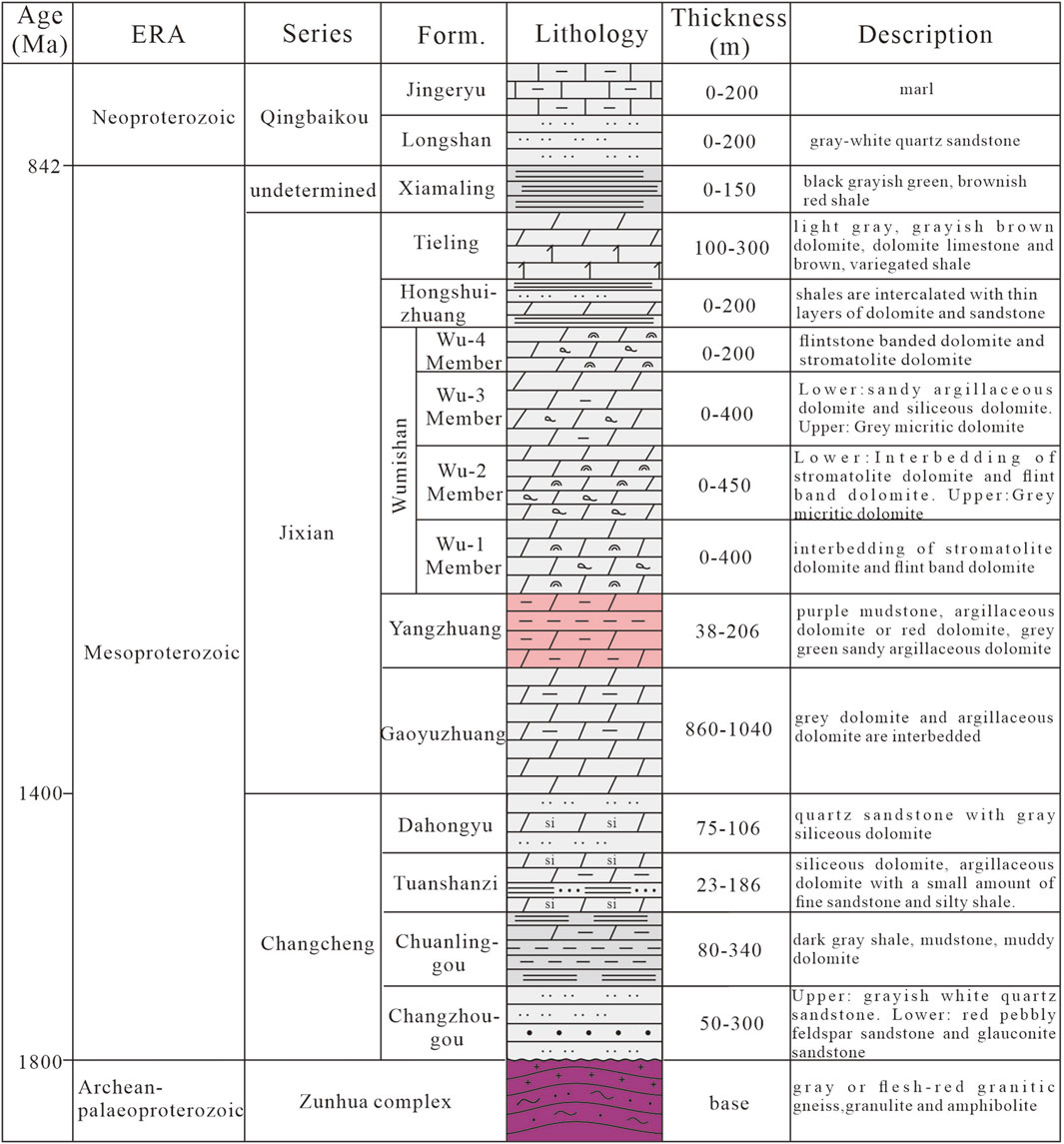
Figure 2. Generalized stratigraphic column of Proterozoic strata in Xiong ‘an New Area (modified from Dai et al., 2023).
3 Sample collection and testing
The experimental samples in the study are from the core data of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Wells D03, D05 and D16 of Xiong ‘an New Area, as well as the outcrop of Yixian and Laishui countries (Figure 1), of which the samples of Wumishan Formation are the main ones. The outcrops of Jixian System dolomite strata in Yixian and Laishui countries are good, and the later tectonic and magmatic activities are relatively weak, and there are few interference factors. Core and field systematic sampling are carried out, and mineralization alteration and strong weathering areas are avoided as far as possible in the sampling process. Bedrock samples of different lithologies from the Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are collected, with sizes of 5–10 cm, and samples of fillings of not less than 30 g. On the basis of naked-eye observation, using field tools such as geological hammers, knives, and hydrochloric acid, the mineralization alteration and weathering of carbonate formation can be roughly judged, such as the hardness of carbonate rocks after weathering decreases, the color is mostly oxidized, the hardness of carbonate rocks changes after mineralization alteration, and the powder drops of hydrochloric acid do not bubble, etc., and reject these samples during sampling. Core sample collection is greatly affected by the harvest rate of coring, and generally core samples are less weathered. Field and core samples will also undergo a second screening indoors, such as cutting bedrock, observing the sample structure with a magnifying glass, and ensuring that samples that are not weathered and mineralized are selected. More than 110 samples are obtained, and thin section identification, porosity and permeability analysis and geochemical analysis are carried out respectively.
The identification of thin section is based on the selection of fresh, unaltered and weathered samples to be made into thin sections, which are observed and photographed under the optical microscope for the characteristics of mineral composition, content, structure and structure, and finally the lithology is accurately named according to the standard of DZ/T0275.1-5-2015. The above process is completed at the Sichuan Keyuan Testing Center of Engineering and Technology and the Karst Geological Resources and Environmental Testing Center. Porosity and permeability analysis are carried out by firstly preparing cylindrical samples with a diameter of about 25 mm and a length of about 50 mm, and then using AP-608 overburden pressure porosimeter to simulate the porosity and permeability under the condition of net overburden pressure, and then using high-pressure air as the source of pressure and helium as the medium of the test.
The samples are processed prior to geochemical testing, i.e., fresh samples are selected indoors, washed with deionized water, pulverized, and ground to 200 mesh. The testing of samples for major elements, trace elements and carbon and oxygen isotopes are done at the Karst Geological Resources and Environmental Testing Center. The testing standards of major elements are GB/T3286-2012 and DZG93-07, and the testing instrument is A-68 atomic absorption spectrophotometer, the testing standards of trace elements are DS21420 and DZ/T0279.32-2016, and the testing instrument is A-17 inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer; and carbon and oxygen isotopes are tested by MAT-253 mass spectrometer. The test is based on GB/T6041-2002, and the reference standard is the argillite of Vienna Pee Dee group (V-PDB), and the test precision is 0.1‰. Strontium isotope testing of the samples is completed at Sichuan Keyuan Testing Center of Engineering and Technology, using a Triton Plus thermal ionization isotope ratio mass spectrometer, using GBW04411 standard for the testing process, with a testing accuracy of better than 0.01%.
4 Characteristics of karst reservoir in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan formations
4.1 Petrological characteristics
On the basis of outcrops, core observation and thin section identification, combined with the results of Lu et al. (2019) and Guo et al. (2023), the main rock types of karst reservoirs in Gaoyuzhuang -Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas are divided into five categories: crystal grain dolomite, particle dolomite, microbial dolomite, siliceous dolomite and breccia dolomite (Figure 3).
(1) Crystal grain dolomite. It mainly includes Micro-powder crystal dolomite, fine crystal dolomite, medium crystal dolomite and coarse crystal dolomite. Among them, micro-powder crystal dolomite is the most important dolomite type in Gaoyuzhuang -Wumishan Formations. The grain size is less than 0.05 mm, and the structure is uniform (Figures 3a,b). The composition of micro-powder crystal dolomite is relatively pure, and the content is more than 90%. The grain size of medium-coarse crystal dolomite is different, up to 1mm, with a high degree of crystal authomorphism, dominated by line contacts and visible mosaic contacts (Figures 3c,d).
(2) Particle dolomite. The content of particles is more than 60%. The microscopic observation results of thin sections show that it is mainly doloarenite and intraclast dolomite (Figures 3e,f), with medium roundedness and different sizes of particle up to 5 mm (Figure 3f). Some particles are point and line contact, and some are not contacted, floating and disorderly distributed. The pore filling between particles is sparry dolomite cement (Figures 3e,f).
(3) Microbial dolomite. Mainly for different forms of stromatolite dolomite (Figure 3g). Outcrop profiles, core and thin section observation show that the Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations mainly develop layered and wavy stromatolite dolomite. Among them, light brown ‘dark layer’ dolomite and sparry ‘bright layer’ dolomite can be seen under the microscope to be distributed in a stacked layer, occasionally a small amount of siliceous, mostly microcrystalline, enriched in siliceous zone bedding distribution (Figure 3g).
(4) Siliceous dolomite. Including primary sedimentary siliceous banded dolomite and secondary metasomatic siliceous dolomite (Figures 3h–j). Siliceous bands and nodular flint are insoluble compound, and basically no dissolution occurs (Figures 3h,i). Dolomite can be dissolved to form dissolution pores (Figure 3h). In the siliceous dolomite of secondary metasomatic origin, there is a phenomenon of incomplete local silicification. Dolomite and siliceous are mixed. Due to the fact that dolomite is more prone to dissolution, dissolution pores are formed. Silica is insoluble and forms a lattice structure, which is conducive to the preservation of pores, while the high brittleness of silica makes it easy to form structural fractures (Figure 3i).
(5) Breccia dolomite. It is mainly breccia dolomite formed by faults and karstification (Figures 3k,l). Fault breccia dolomite is mainly developed in the vicinity of large fault zones. The microscopic observation results show that the breccia is poorly rounded, angular, 0.4–8 mm in size, and poorly sorted. The main component is mud-powder crystal dolomite. The breccia is not in contact with each other and is distributed in a floating. The pore fillings between the breccias are sparry dolomite cements (Figure 3k). The karst breccia dolomite is mostly developed in the vicinity of large karst caves and weathering crusts. The roundness and sorting of the breccia are poor, and the composition of the breccia is complex, including mud-powder crystal dolomite and sandstone, with muddy mixed fillings, and the development of some dissolution cave (Figure 3k).
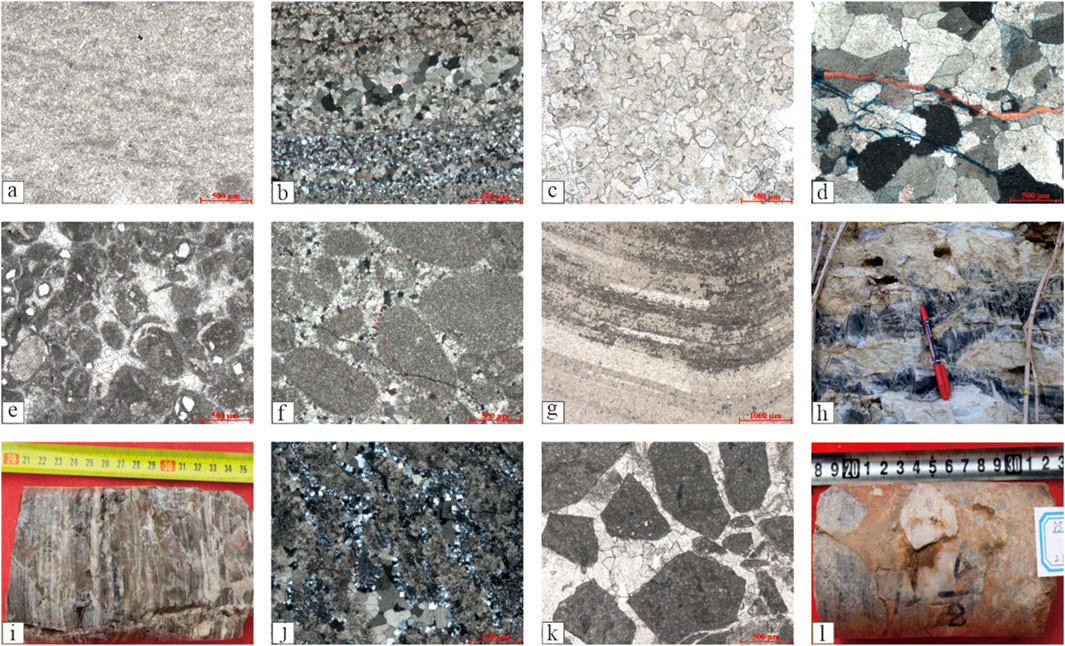
Figure 3. Petrological characteristics of dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas. (a) powder crystal dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Well D05, 3230.28 m; (b) siliceous powder crystal dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Well D03, 2391.2 m; (c) medium crystal dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Well D05, 2157.3 m; (d) coarse crystal dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Yixian county; (e) sparry calcarenite dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Well D05, 3407.57 m; (f) sparry calcarenite dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Yixian county; (g) stromatolite dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Yixian county; (h) siliceous bands dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Yixian county; (i) siliceous dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Well D03, 1679.2 m; (j) siliceous dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Yixian county; (k) breccia dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Laishui county; (l) breccia dolomite of Wumishan Formation, Well D05, 2157.3 m.
4.2 Reservoir space type
The reservoir space of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas can be divided into three categories: pores, caves and fractures based on the observation of field profiles, cores and thin sections. Pores are divided into primary pores and secondary pores, caves are secondary genesis, and fractures include structural fractures, structural dissolution fractures and stylolite according to the genesis. Among them, the most favorable reservoir space is the dissolution pores, caves and fractures by karstification.
(1) Pores. The primary pores are mainly intergranular pores and intercrystalline pores (Figures 4a,b), which are mostly developed in particle dolomite and crystal grain dolomite, with small scale and limited reservoir space. The secondary pores are mainly formed by dissolution. A large number of honeycomb dissolved pores are observed in the core, with a diameter of 1–2 mm (Figure 4c). Thin section observation shows the pores have non-selective dissolution (Figures 4d,e), and the edges are occasionally filled with sparry dolomite (Figure 4e).
(2) Caves. Large-scale caves can be seen in the field, mainly distributed near the weathering crust at the top of the Wumishan Formation, mostly distributed in the area of fracture activity, up to several meters in diameter (Figures 4f,g), filled with collapse breccia and sandy-muddy deposits. Dissolved pores are visible in the core, 1–5 cm in diameter, partly half-filled with reddish-brown mud (Figure 4h).
(3) Fractures. The outcrop and core can identify ‘X-type’ joints (Figure 4i) and high-angle structural fractures almost perpendicular to the bedding plane (Figure 4j). The structural fractures are characterized by straight, smooth and uniform width. Fractures under the microscope are common, among which the surface of the dissolution fracture is mostly irregular, uneven, and the width of the fractures changes greatly, with obvious dissolution characteristics (Figure 4k). Occasionally, along the stylolite with dissolution enlargement, mostly filled with mud or asphaltene, and the reservoir space is limited (Figure 4l).

Figure 4. Macroscopic and microscopic characteristics of dolomite karst reservoirs in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas. (a) inter-breccia dissolved pores of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, Laishui county; (b) intergranular (dissolution) pores, Yixian county; (c) honeycomb dissolution pores, Well D16, 1109.52 m; (d) honeycomb dissolved pores of Wumishan Formation, Yixian county; (e) dissolved pores of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, and the edge was filled with sparry dolomite; (f) large cave of Wumishan Formation, Yixian county; (g) caves of Wumishan Formation developed along faults, Yixian county; (h) dissolution pores of Wumishan Formation with reddish brown mud half-filled, Well D05, 2157.3 m; (i) ‘X' type joints of Wumishan Formation, Laishui county; (j) structural fractures of Wumishan Formation, along fractures with dissolution enlarged, Well D03, 1678.7 m; (k) dissolution-enlarged fractures of Wumishan Formation, Well D05, 2888.78 m; (l) dissolution-enlarged along irregular stylolite, Well D03, 810 m.
4.3 Reservoir physical property
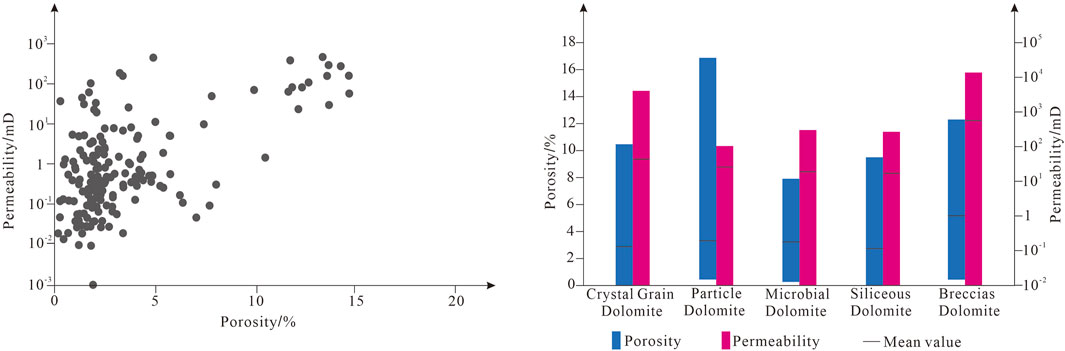
By analyzing the physical properties of the core samples and combined with previous research results, it is found that the physical properties of dolomite karst reservoirs in Wumishan Formation of Jixian System are better, with the porosity of the buried depth in the region of 4,000 m and shallower ranging from 0.5% to 22.4%, the average porosity of 3.39%, the permeability mainly distributed in the range of 0.01 mD–3,000 mD, and the average permeability of 82.3 Md (Dai et al., 2019), and the buried depth in the region below 4,000 m ranging from 2.2% to 19.5%, the average porosity of 6.3%, and the average permeability of 212.82 mD. The porosity in the area below 4,000 m is 2.2%–19.5%, with an average porosity of 6.3%, and the permeability is 0.01–2489 mD, with an average permeability of 212.82 mD (Dai et al., 2023). The porosity of the Gaoyuzhuang Formation is mainly distributed in 1.2%–3.5%, up to 13.2%, and the permeability is mainly distributed in 0.3 mD–7.9 mD, up to 160 mD (Dai et al., 2023). It can be seen that the correlation between porosity and permeability is good according to the crossplot of porosity and permeability, and in local areas, due to the existence of fractures or strong dissolution, the porosity and permeability show abnormally high values, and the physical properties of karst reservoirs are characterized by a strong non-homogeneity (Figure 5). The porosity and permeability of different lithologies varies greatly, and the statistics found that the porosity of crystal grain dolomite is 0.014%–10.47%, with an average of 2.83%, and the permeability is 0.01 mD–3870 mD, with an average of 41.84 mD. The porosity of particle dolomite is 0.51%–16.9%, with an average of 3.26%, and the permeability is 0.01 mD–102 mD, with an average of 24.67 mD (Figure 5). The porosity of microbial dolomite is 0.32%–7.90%, with an average of 3.17%, and the permeability is 0.01 mD–285 mD, with an average of 17.97 mD. The porosity of siliceous dolomite is 0.02%–9.52%, with an average of 2.69%, and the permeability is 0.01 mD–264 mD, with an average of 16.39 mD. The porosity of breccia dolomite is 0.50%–12.32%, with an average of 5.1%, and the permeability is 0.01–13214 mD, with an average of 532.33 mD (Figure 5). Overall the porosity and permeability of breccia dolomite, particle dolomite and crystal grain dolomite are better, and the porosity and permeability of siliceous dolomite are the worst.
5 The results of geological testing
5.1 Major and trace elements
The contents of major and trace elements in 54 samples of the Jixian System from outcrops in Yixian (No. CXD and LYS beginning) and Laishui countries (No. ZJG beginning) and drilling cores (No. D beginning), and some calculation results are shown in Table 1.
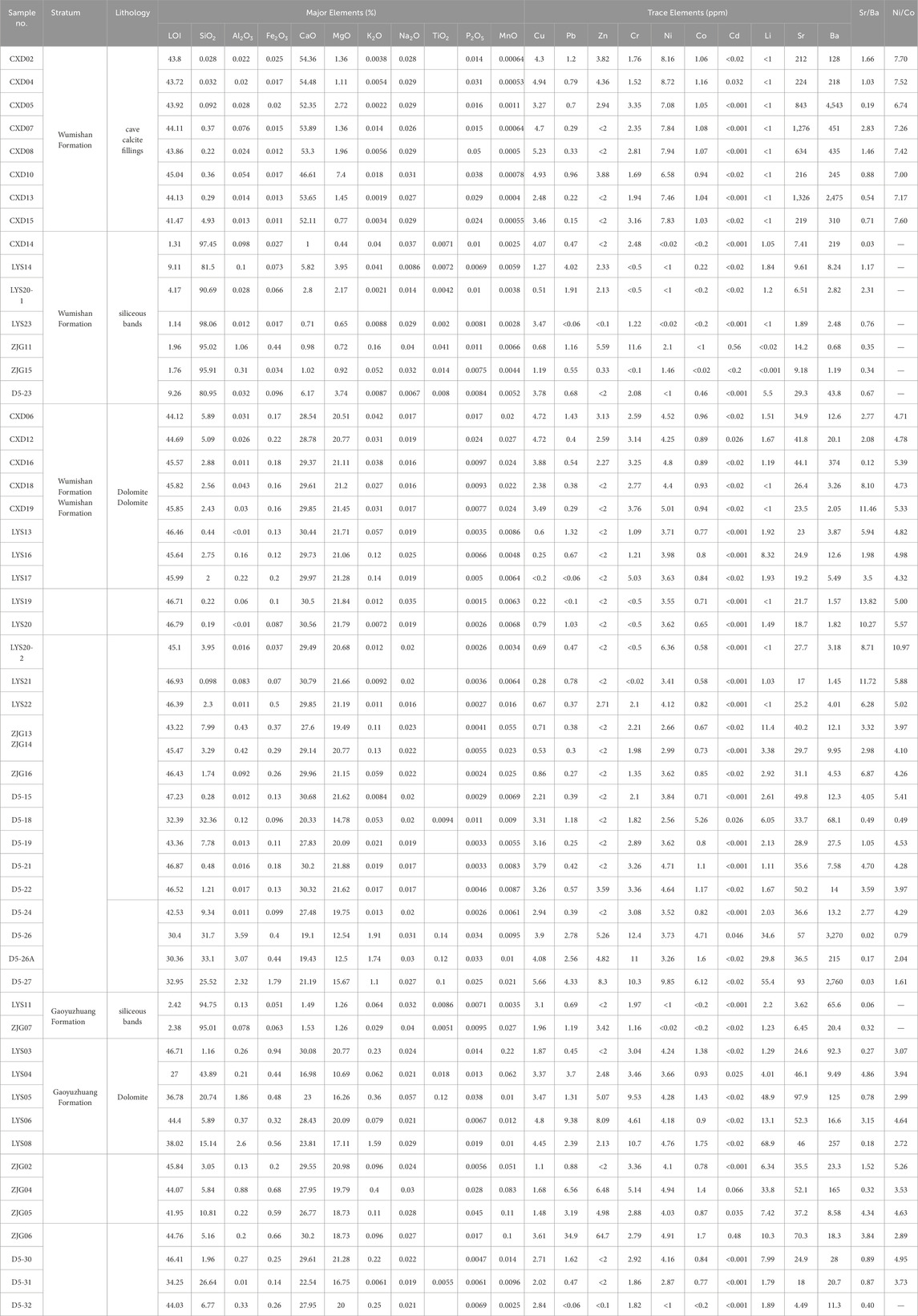
Table 1. Composition and partial calculation results of major and trace elements in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas.
5.1.1 Major elements
(1) CaO, MgO and LOI contents. The contents of CaO, MgO and LOI varied greatly among different lithologies, among which the CaO contents of cave calcite fillings of Wumishan Formation are distributed from 46.61% to 54.48%, with an average of 52.59%, the MgO content ranges from 0.77% to 7.40%, with an average of 2.27%, and the ∑(CaO + MgO + LOI) had a minimum value of 94.35%, with a maximum value of 99.52%, and the average value is 98.62%. The contents of CaO, MgO and LOI in the siliceous bands of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are extremely low, with the content of CaO ranging from 0.71% to 6.17%, with an average of only 2.39%, the content of MgO ranging from 0.44% to 3.95%, with an average of 1.68%, and the ∑(CaO + MgO + LOI) with a minimum value of 2.5%, a maximum value of 18.88%, and an average of 7.79%. The CaO content of dolomite is distributed from 16.98% to 30.79%, with an average of 27.50%, the MgO content is distributed from 10.69% to 21.88%, with an average of 19.44%, and the ∑(CaO + MgO + LOI) content is distributed from 54.67% to 99.53%, with an average of 89.59%. There is a significant correlation between CaO and MgO. Among them, CaO and MgO in cave calcite fillings of Wumishan Formation have a negative correlation, and siliceous bands and dolomite show a positive correlation (Figure 6).
(2) The content of terrestrial elements (SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, TiO2, P2O5). The content of terrestrial elements varies greatly in different lithologies, and the content of terrestrial elements in the same lithology also has some differences. The content of total terrestrial elements in the siliceous bands of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations is the highest, ranging from 81.09% to 97.59%, with an average of 92.47%, and SiO2 is the dominant one. The contents of total terrestrial elements in calcite fillings of caves in Wumishan Formation are the lowest, ranging from 0.089% to 4.98%, with an average of 0.87%, without TiO2. The content of total terrestrial elements in dolomite of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations varies greatly, ranging from 0.25% to 44.57%, with an average of 9.83%, and the terrestrial element content is dominated by SiO2, followed by Al2O3, and only 7 dolomite samples contain TiO2 (Table 1). The analysis found that SiO2 and Al2O3 of dolomite and calcite fillings have a strong positive correlation, and a negative correlation between SiO2 and Al2O3 in siliceous bands. CaO shows a negative correlation with SiO2 and Al2O3, while MgO has a poor correlation with SiO2 and Al2O3 (Figure 6).
(3) The contents of Na2O and K2O. The difference in Na2O content of different lithologies is relatively small, in which the Na2O contents of calcite fillings are 0.026% ∼ 0.031%, with an average of 0.029%. The siliceous bands are 0.0067% ∼ 0.04%, with an average of 0.027%, and dolomite is 0.016% ∼ 0.035%, with an average of 0.023%. The K2O contents of calcite fillings range from 0.0019% to 0.0056%, with an average of 0.0068%. The content of K2O in siliceous bands is 0.0021% ∼ 0.064%, with an average of 0.045%, and the K2O content of dolomite ranges from 0.0061% to 1.91%, with an average value of 0.25%. The average Na contents of calcite fillings, siliceous bands and dolomite are 215.16 × 10−6, 200.32 × 10−6 and 170.65 × 10−6, respectively. Studies have shown that the Na content of calcite formed in modern oceans ranges from 200 × 10−6 to 300 × 10−6, while that of dolomite is less than 110 × 10−6 ∼ 160 × 10−6 (Veizer, 1983), compared to carbonate minerals in normal seawater, dolomite in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations has relatively high Na content. In addition, the correlation analysis showed that Na2O content does not correlate with MgO/CaO, and the Na2O contents of calcite fillings and siliceous bands correlate negatively with Sr content, while the Na2O content of dolomite correlates positively with Sr content. The Na2O contents of calcite fillings do not correlate with SiO2 content, while the Na2O content of siliceous bands and dolomite correlates positively with SiO2 (Figure 6).
(4) The content of Fe2O3 and MnO. The contents of Fe2O3 in calcite fillings, siliceous bands and dolomite are 0.011% ∼ 0.025%, 0.017% ∼ 0.44% and 0.037% ∼ 1.79%, respectively, and the average values are 0.016%, 0.096% and 0.32%, respectively, and the corresponding average values of Fe contents are 112 × 10−6, 672 × 10−6 and 2,240 × 10−6. The contents of MnO range from 0.0004% to 0.0011%, 0.0025%–0.027%, and 0.0025%–0.22%, with average values of 0.00064%, 0.0069%, and 0.028%, respectively, and corresponding average values of Mn content of 4.96 × 10−6, 53.45 × 10−6, and 216.9 × 10−6, respectively. The content of Fe in carbonate minerals formed in normal seawater in different periods is about 50 × 10−6, and the average content of Mn is not more than 1 × 10−6 (Veizer, 1983). The lowest values of Fe and Mn contents in all samples of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations have exceeded the range, and the highest value even exceeds it by about 200 times. In addition, the results show that the Fe2O3 content of the dolomite is positively correlated with the SiO2 and MnO content, and weakly negatively correlated with the CaO content (Figure 6).
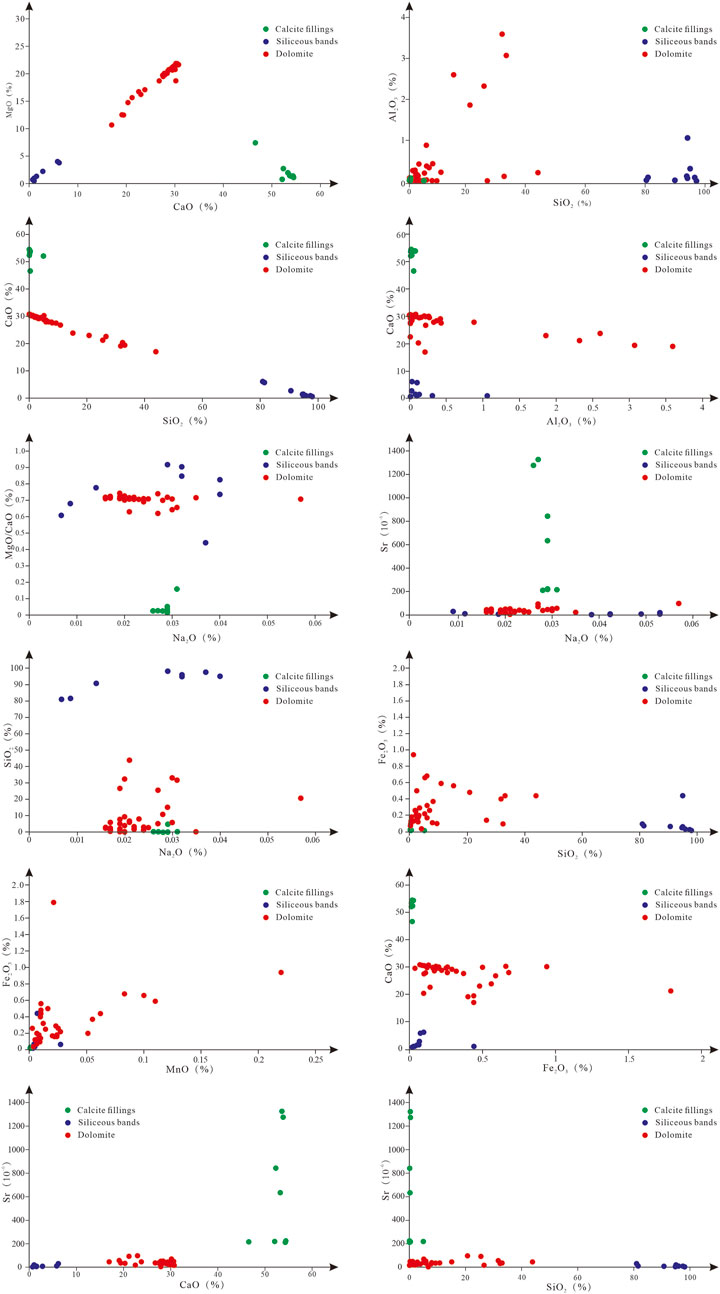
Figure 6. Crossplot of major and trace elements of different lithologies in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations.
5.1.2 Trace elements
The trace element content of the samples varied considerably between lithologies, as evidenced by calcite fillings with significantly higher Cu, Ni, Sr and Ba contents, and lower Pb and Li contents. The siliceous bands have significantly lower Cu, Cr, Ni, Sr and Ba contents, and the overall trace element content is extremely low. Dolomite has relatively high Zn, Cr, Co and Li values, while Sr and Ba contents are low (Table 1). The Sr content of calcite fillings ranges from 212 × 10−6 to 1,326 × 10−6, with an average value of 618.75 × 10−6, and the Sr content of dolomite ranges from 4.49 × 10−6 to 97.9 × 10−6, with an average value of 37.29 × 10−6. Previous studies have found that the Sr content of aragonite formed in modern oceans is greater than (7,740 ± 300)×10−6, the Sr content of high-Mg calcite is in the range of 400–5,000 × 10−6, and the Sr content of primary dolomite is even lower, 245 × 10−6 to 600 × 10−6 (Baker and Brun, 1985). Strong dolomitization reduces Sr content to 155 × 10−6 in marine depositional environments, while sedimentary fluids with extremely high salinity (up to salt rock saturation) can reduce the Sr content to less than 43 × 10−6 ∼ 150 × 10−6 (Lu and Meyers, 1998), in addition, recrystallization and meteoric water leaching also lead to a reduction of Sr content in carbonate rocks. Comparison found that the Sr contents of calcite fillings are much smaller than that of aragonite, and most of them are smaller than the lowest Sr content of high-Mg calcite. The Sr content of dolomite is less than that of carbonate minerals formed by strong dolomitization, and most of them are less than that of carbonate minerals formed under extremely high salinity fluid. The results show that the Sr content of dolomite is positively correlated with the Na content (Figure 6), and weakly negatively correlated and weakly positively correlated with the distributions of authigenic element CaO and terrestrial element SiO2, respectively (Figure 6).
5.2 Carbon and oxygen isotopes
Carbon and oxygen isotope values of 71 samples of the Jixian System from outcrops in Yixian (No. CXD and LYS beginning), Laishui countries (No. ZJG beginning) and drilling cores (No. D beginning) are shown in Table 2. The results show that there are large variations in carbon and oxygen isotope values of different lithologies. The δ13C values of dolomite in Gaoyuzhuang Formation are between −1.72‰ and 1.34‰, with an average of −0.38‰, and the δ18O values range from −9.85‰ to −2.95‰, with an average of −6.36‰. The δ13C values of dolomite fillings in fracture-cavity of Gaoyuzhuang Formation range from −7.44‰ to −1.43‰, with an average of −3.46‰, and the δ18O values differ from the bedrock with a wide range of values, ranging from −17.84‰ to −6.57‰, with an average of −12.99‰, and δ18O values are obviously negatively biased (Figure 7; Table 2) The samples from the Wumishan Formation can be divided into dolomite, siliceous bands, fracture-cavity dolomite fillings and calcite fillings according to lithology, in which the carbon and oxygen isotope values of dolomite in Wumishan Formation are generally similar to those of Gaoyuzhuang Formation, reflecting their generally similar depositional environments. The δ13C values of dolomite are −3.9‰ ∼ 0.96‰, with an average of −0.51‰, and the δ18O values are −9.65‰ ∼ −4.42‰, with an average of −6.41‰. The δ13C values of siliceous bands are −4.25‰ ∼ −0.53‰, with an average of −1.36‰, and the δ18O values are −12.4‰ ∼ −7.07‰, with an average of −8.94‰. The δ13C values of dolomite fillings in fracture-cavity are −1.89‰ ∼ −0.47‰, with an average value of −1.04‰, and the δ18O values are significantly negative, with a large range of changes, ranging from −17.19‰ to −8.48‰, with an average value of-11.87‰. The δ13C values of calcite fillings are significantly negative, ranging from-10.67‰ to-8.13‰, with an average of −9.02‰, and the δ18O values range from −9.81‰ to −7.38‰, with an average of −8.63‰ (Figure 7; Table 2). Overall, the δ13C and δ18O values of different fillings have some differences, and compared with the dolomite and siliceous bands, the carbon and oxygen isotope values of fracture-cavity fillings are negatively biased. Among them, the δ18O values of fracture-cavity dolomite fillings are obviously negatively biased, and the δ13C values of calcite fillings are negatively biased (Figure 7; Table 2), reflecting the characteristics of two types of fracture-cavity fillings with different filling paleoenvironments.
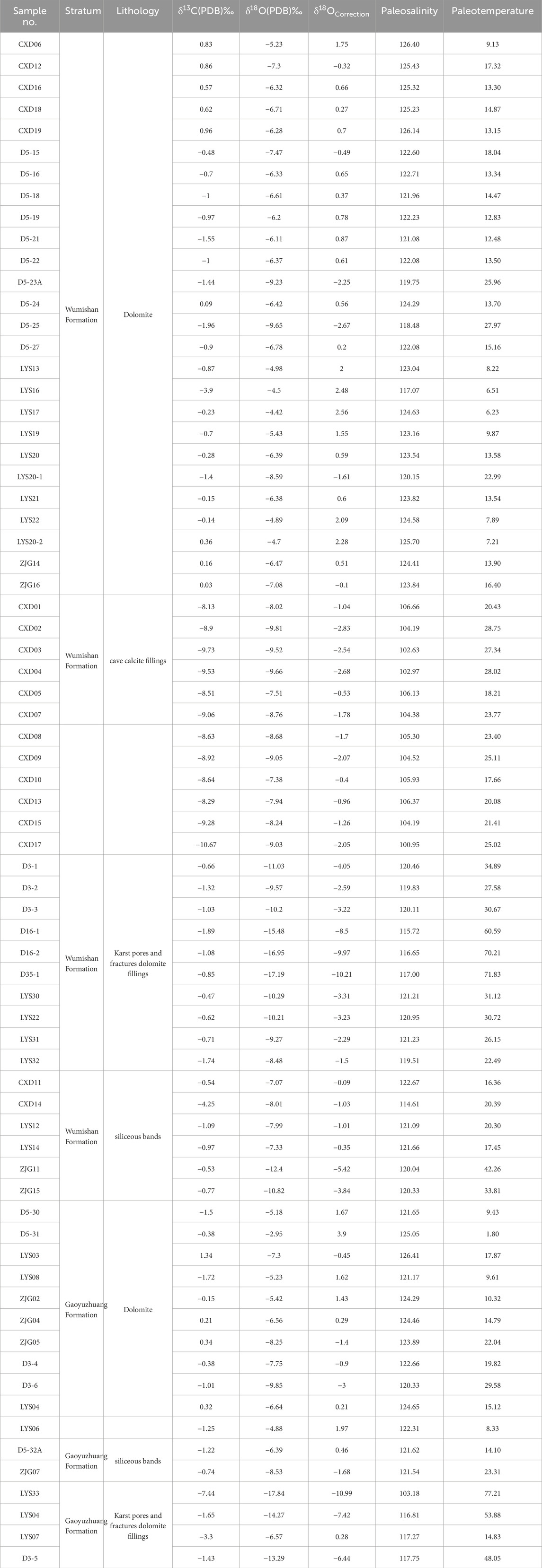
Table 2. The results of carbon and oxygen isotopes of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas.
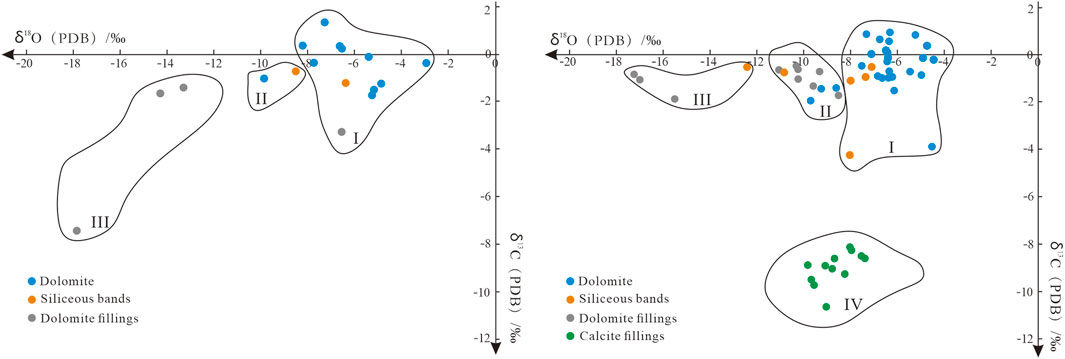
Figure 7. Carbon and oxygen isotope crossplot of Gaoyuzhuang Formation (left) and Wumishan Formation (right).
5.3 Strontium isotope
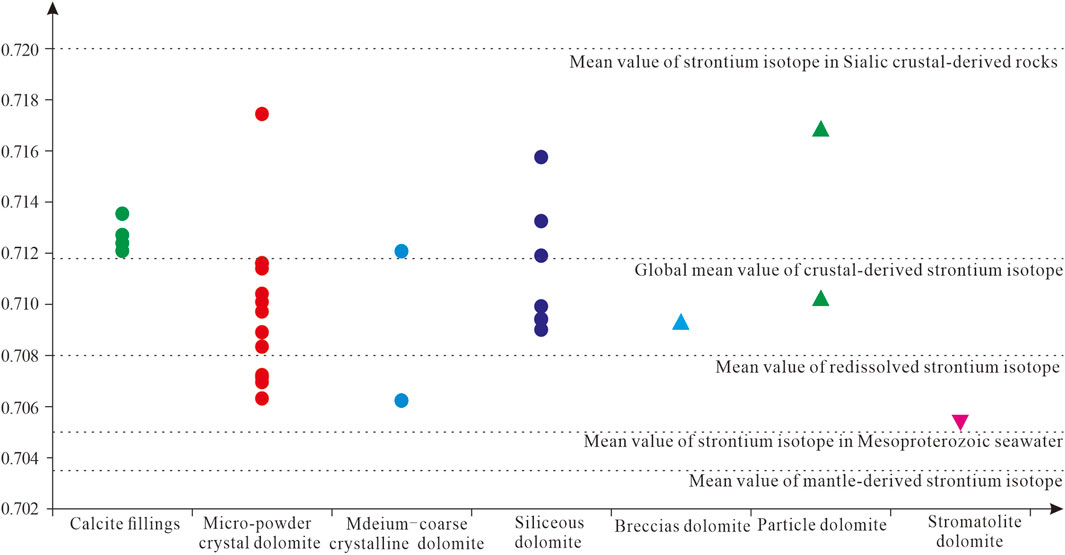
A total of 30 carbonate rock samples are analyzed by strontium isotope analysis in this study, including calcite fillings, siliceous bands, mud-powder crystal dolomite, medium-coarse crystal dolomite, siliceous dolomite, breccia dolomite and stromatolite dolomite, and the results of the tests are shown in Table 3 and Figure 8. The 87Sr/86Sr values of different lithologies vary widely (Figure 8), with the 87Sr/86Sr values of the four calcite filling samples ranging from 0.712112 to 0.713570, with an average value of 0.712676. The 87Sr/86Sr values of the micro-powder crystal dolomite vary greatly, ranging from 0.706345 to 0.717464, with an average value of 0.709785. The 87Sr/86Sr values of two medium-coarse crystal dolomite samples are 0.706235 and 0.712081. The 87Sr/86Sr values of siliceous dolomite are 0.709042∼0.715747, with an average of 0.711237. The 87Sr/86Sr values of the two particle dolomites are 0.710245 and 0.716808. Breccia dolomite and stromatolite dolomite have only one sample each, with 87Sr/86Sr values of 0.709235 and 0.705305, respectively. On the whole, the 87Sr/86Sr values of calcite fillings, siliceous dolomites and particle dolomites are significantly higher than those of the other lithologies.
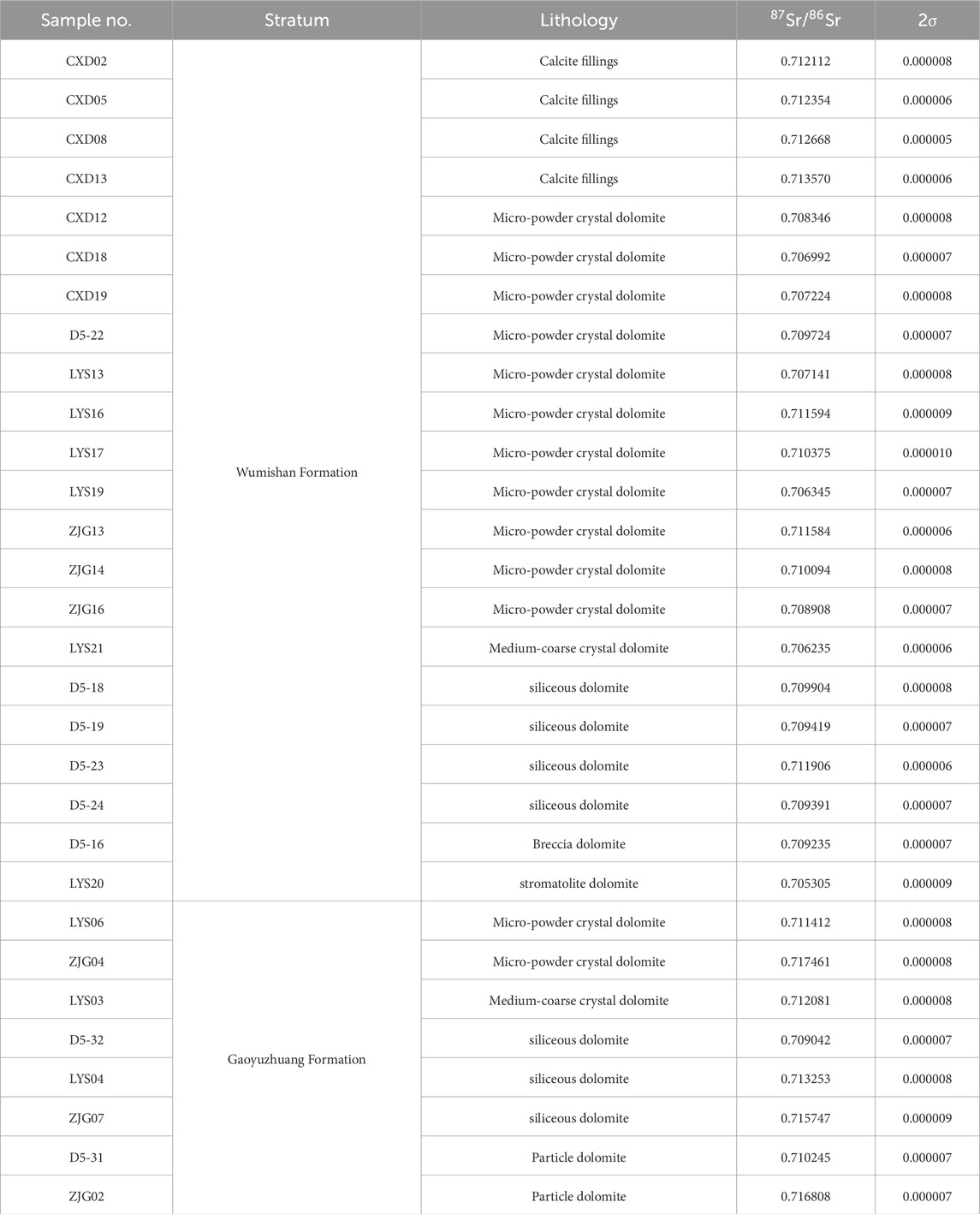
Table 3. The results of87Sr/86Sr from Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas.
6 Discussion
6.1 Paleosalinity and paleotemperature of seawater
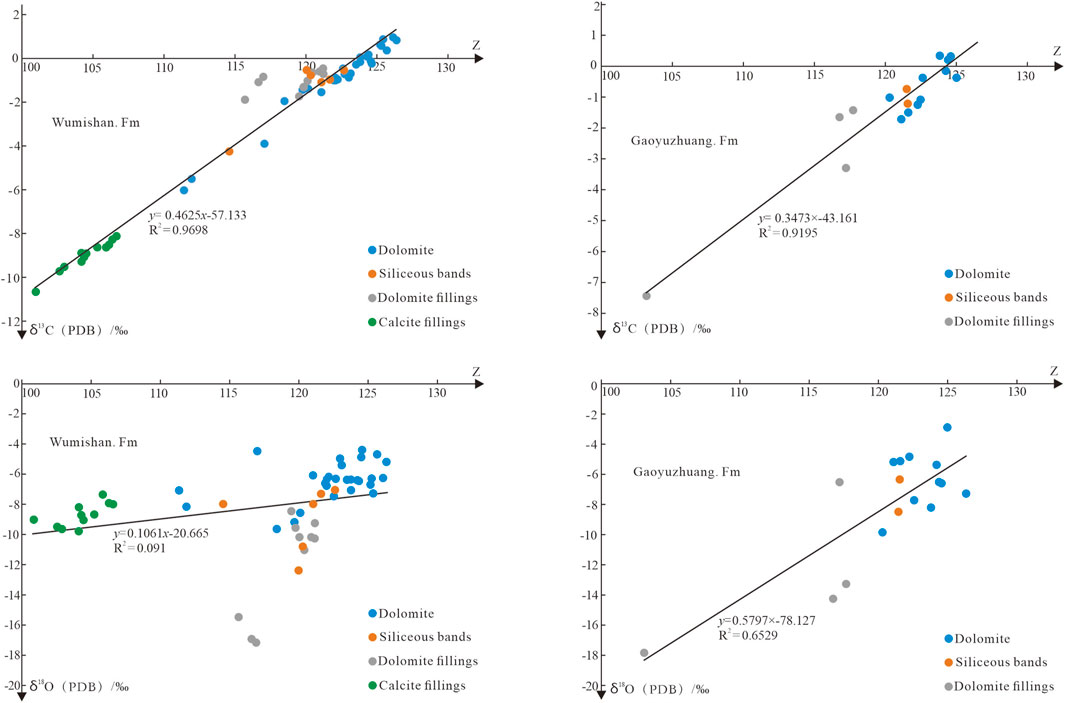
The carbon and oxygen isotope compositions of carbonate rocks are controlled by sedimentary water, and the carbon and oxygen isotope compositions of sedimentary water are affected by water salinity (Li et al., 2023). Keith and Weber (1964) proposed an equation to calculate the salinity index Z of sedimentary water by using δ13C value and δ18O value (which is not the absolute value of the salinity, but only positively correlates with the paleosalinity, and a value of Z less than 120 is freshwater, and more than 120 is marine environment): Z = 2.048 × (δ13C + 50) + 0.498 × (δ18O + 50), where δ13C and δ18O are both standardized values of the PDB, and the paleosalinity is calculated by using the equation, and the results are shown in Table 2.
The Z values of different lithologies in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations vary greatly, reflecting different formation environments. The Z values of dolomite in Gaoyuzhuang Formation range from 120.33 to 126.41, with an average of 123.35, indicating that the dolomite in Gaoyuzhuang Formation is mainly deposited in the marine environment. The Z values of the two siliceous band samples are 121.62 and 121.54, respectively, indicating that the siliceous band is formed in the same environment as the dolomite. The Z values of dolomite fillings are 103.18∼117.75, all of which are less than 120, and are of freshwater genesis. The Z values of different lithologies in the Wumishan Formation are similar to those in the Gaoyuzhuang Formation. The Z values of dolomite are 117.07∼126.4, with an average value of 123.07, indicating that the dolomite of the Wumishan Formation, like that of the Gaoyuzhuang Formation, is dominated by marine deposits, and locally affected by the injection of freshwater. The Z values of calcite fillings range from 100.95 to 106.66, with an average value of 104.52, reflecting that calcite fillings are of typical freshwater genesis. The Z values of dolomite fillings are 115.72∼121.23, with an average of 119.27, and the Z values of half of the samples are less than 120, indicating that the dolomite fillings are mixed with freshwater and seawater. The Z values of the siliceous bands range from 114.61 to 122.67, with an average of 120.07, and only one of the six samples has a Z value of less than 120, reflecting that the siliceous bands, like dolomite, is mainly marine deposits, and locally affected by freshwater.
The correlation analysis of δ13C and δ18O with Z shows that the δ13C of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations correlate well with Z values, with correlation coefficients of 0.9195 and 0.9698, respectively, However, the correlation between δ18O and Z is poor, and the correlation coefficients are 0.6529 and 0.091, respectively (Figure 9). It indicates that δ13C and δ18O of carbonate rocks are affected differently by the salinity of sedimentary water, and δ13C is more affected by the salinity of sedimentary water.
The δ18O value is closely related to the temperature of the deposition medium (Leng, 2006). When the salinity of the deposition medium remains constant, the higher the temperature, the lower the δ18O value (Zhang et al., 2023). Therefore, the δ18O value can reflect the relative level of paleotemperature. Some predecessors proposed and calibrated the equation: T (°C) = 15.976-4.2 × δ18O + 0.13 × (δ18O+0.22)2 to calculate the paleo-seawater temperature (Yang et al., 2017; Ren et al., 2018). It is worth noting that the equation is more applicable to post-Mesozoic strata, and for the Jixian System, a correction for age effects is required before applying the equation. The average δ18O values of the samples of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are −8.05‰ and −8.18‰, respectively, and the average δ18O value of the Quaternary marine carbonate rocks is −1.2‰ as the standard. The δ18O values of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are corrected to be equivalent to that of the Quaternary samples with 6.85‰ and 6.98‰, respectively, and then the paleo-seawater temperatures of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are obtained by using the equation. The results are shown in Table 2.
It shows that paleo-seawater temperature of the Gaoyuzhuang Formation (dolomite and siliceous bands deposition period) ranges from 1.8°C to 29.58°C, with an average of 15.09°C, and the dolomite fillings are 14.83°C ∼ 77.21°C, with an average of 48.49°C. Paleo-seawater temperature of the Wumishan Formation (dolomite and siliceous bands deposition period) ranges from 6.23°C to 42.26°C, with an average of 16°C. The calcite fillings range from 17.66°C to 28.75°C, with an average of 23.27°C, and the dolomite fillings is 22.49 ∼ 71.83°C, with an average of 40.63°C. On the whole, the average temperature of the paleo-seawater during the deposition period of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations is 15°C ∼ 16°C, which is generally the temperature of seawater in a warm climate. Pesonen et al. (2021) indicated that the North China Plate was in the low latitude area north of the equator in the Mesoproterozoic Jixian Epoch, which shows that Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are formed in the warm subtropical climate of seawater environment. The fluid temperature at the time of formation of the dolomite fillings in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations is significantly higher than the seawater temperature of the same period, suggesting that the pre-existing dissolution pores are modified by high-temperature fluids at a later stage.
6.2 Paleowater depth and offshore distance
The relative depth of paleowater and the relative distance from the shore are mainly estimated by different geochemical characterization parameters, and the common characterization parameters include Sr/Ba value and 87Sr/86Sr value (Ren et al., 2018). It is generally believed that Sr tends to be enriched in the deep sea, while Ba is mostly enriched in coastal water and its corresponding sediments, so the Sr/Ba value of freshwater sediments is less than 1, and that of marine sediments is greater than 1 (Ren et al., 2018; Dan et al., 2021). It can be seen that the Sr/Ba values of the dolomite of the Gaoyuzhuang Formation range from 0.18 to 4.86, with an average value of 1.78, and only 5 out of 12 samples have Sr/Ba greater than 1, the Sr/Ba values of the dolomite of the Wumishan Formation range from 0.02 to 13.82, with an average value of 4.67, and 5 out of 25 samples have Sr/Ba less than 1 according to Table 1, indicating that the paleowater depth of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations is relatively shallow, with the characteristics of interactive marine, and Gaoyuzhuang Formation is slightly more modified by freshwater. Only two of the nine samples of siliceous bands from Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations have Sr/Ba greater than 1, indicating the siliceous bands is deposited close to the shore and is greatly affected by freshwater injection.
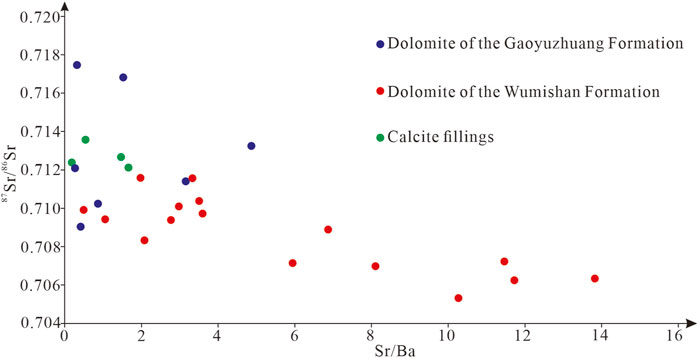
The magnitude of river injection in the ocean can indirectly determine the offshore distance of the depositional environment, and the strontium isotope can reflect the relative magnitude of river injection to a certain extent. The strontium isotopic composition of seawater is independent of latitude and depth, and is mainly controlled by three sources of crustal, mantle, and redissolved strontium, in which crustal-derived strontium is mainly from weathering material of paleocontinental sialic rock, mantle strontium from mantle-derived material brought out by hydrothermal activity at mid-ocean ridges, and redissolved strontium from chemical weathering of marine carbonate rocks (Banner, 1995; Guacaneme et al., 2021). The mean strontium isotope value of crustal-derived sialic rock is 0.720, the global mean of crustal-derived strontium isotope is 0.7119 (Li Z. T. et al., 2024), the value of redissolved strontium isotope is 0.708 (Liu et al., 2007), the mean strontium isotope value of Mesoproterozoic seawater is about 0.705 (Shield and Veizer, 2002; Chen et al., 2022), and mantle-derived strontium of 0.7035 (Li X. D. et al., 2024) (Figure 8). The continental weathering products with high 87Sr/86Sr are transported to the ocean via rivers, which leads to the increase of 87Sr/86Sr value in seawater. The 87Sr/86Sr values vary considerably between lithologies, and are all greater than the mean value of the Mesoproterozoic seawater (Figure 8), suggesting Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations were modified by crustal-derived strontium, including large amounts of river injection and supergene karstification. It is found that the 87Sr/86Sr values of dolomite in Gaoyuzhuang Formation are mostly greater than 0.71, the dolomite in Wumishan Formation is mostly less than 0.71, and the 87Sr/86Sr values of calcite fillings in Wumishan Formation are all greater than 0.712 (Table 3), showing that Gaoyuzhuang Formation is more affected than Wumishan Formation by crust-derived strontium, which further reveals the closer offshore distance and environmental characteristics of interactive marine. The calcite fillings are of meteoric water genesis, which is greatly affected by crust-derived strontium. The result shows that 87Sr/86Sr values are negatively correlated with Sr/Ba (Figure 10). As mentioned above, Ba is mostly enriched in coastal water and its corresponding sediments. The smaller the Sr/Ba reflects the greater influence of freshwater, and the closer the offshore, the greater river injection, i.e., the greater the influence of crustal-derived strontium, resulting in the increase of 87Sr/86Sr.
In addition, the contents of major and trace elements can also reflect the relative magnitude of river injection. Figure 6 and Table 1 show that Na2O content does not correlate with MgO/CaO, and the Na2O contents of calcite fillings and siliceous bands correlate negatively with Sr content, while the Na2O content of dolomite correlates positively with Sr content. The Na2O contents of calcite fillings do not correlate with SiO2 content, while the Na2O content of siliceous bands and dolomite correlates positively with SiO2, indicating that siliceous bands and dolomite samples are jointly controlled by marine fluids and terrestrial fluids during the depositional period, with the siliceous bands being more significantly affected by terrestrial fluids. As mentioned earlier, the Fe and Mn contents of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are much greater than carbonate minerals formed in normal seawater, indicating Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are injected with exogenous fluids rich in Fe and Mn during the depositional period.
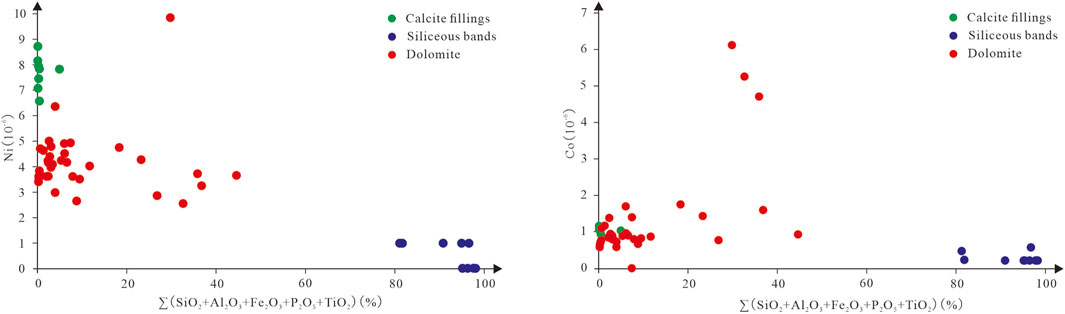
6.3 Redox environment
Previous studies of redox conditions in the paleocean have relied on redox-sensitive elements, and Ni/Co is commonly used to characterize the redox environment of sedimentary water. Before applying redox-sensitive elements to the study of redox environment, the extent to which each element is influenced by non-autogenous factors (e.g., detrital sources and diagenesis) needs to be assessed. The contents of Ni and Co in the samples are weakly correlated with the contents of terrestrial elements (∑SiO2 + Al2O3 + Fe2O3 + P2O5 + TiO2) (Figure 11), indicating that the contents of Ni and Co in the samples are less affected by terrestrial elements. When Ni/Co value is greater than 7, it indicates that the sedimentary water is an anoxic reducing environment, when Ni/Co value is less than 5, it indicates that the sedimentary water is an oxidizing environment, and when the ratio is between 5 and 7 it indicates a weakly oxidizing environment (Jones and Manning, 1994). The Ni/Co values of Gaoyuzhuang and Wumishan Formation are 2.72 ∼ 5.26 and 0.49 ∼ 10.97, with the average values of 3.85 and 4.45, respectively, of which only one sample of the dolomites of Gaoyuzhuang Formation has Ni/Co greater than 5, which is 5.26, and the other samples are less than 5. Among the 25 dolomite samples of Wumishan Formation, only one sample has Ni/Co greater than 7, and there are seven samples whose Ni/Co is between 5 and 7, and the remaining 17 samples are less than 5. The siliceous bands of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations all have Ni/Co less than 5. The above characteristics indicate that Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are in an oxidizing environment during the depositional period, and the paleowater depth is shallow, which is consistent with the conclusion drawn from the analysis of the previous analysis of paleowater depth and the distance to the offshore. It is worth noting that the Ni/Co values of calcite fillings range from 6.74 to 7.70, only one sample is 6.74, and the Ni/Co values of the other seven samples are greater than 7 (Table 1), indicating an anoxic reduction environment. As mentioned earlier, the samples belong to the calcite fillings of caves in the Wumishan Formation, and the caves are formed in a period of exposure to strong oxidizing, low-temperature meteoric water leaching. When the vertical infiltration of meteoric water along the dolomite of the Wumishan Formation, due to water-rock interactions and degassing of dissolved CO2 in the water, the unsaturated, open-atmosphere freshwater gradually turns into a relatively closed, oxygen-deficient, supersaturated fluid, thus precipitating calcite.
6.4 Filling paleoenvironment and paleokarst developmental periods
Carbon and oxygen isotopes of Carbonate rocks are characterized by different abundances with different geological background conditions, and have smaller late-stage alteration and good regional comparability, making them good indicators for studying paleoclimate and recovering paleoenvironments (Brasier et al., 1990; Tribovillard et al., 2006; Pu et al., 2016). Carbon and oxygen isotopes of bedrock can reflect changes in depositional environments and Chronostratigraphic boundaries (Brasier et al., 1990), and fracture-cavity dolomite or calcite fillings are formed by the precipitation of later karst fluid after the transformation of parent rock. Due to the different dissolution environments such as fluid properties, temperature and pressure conditions, the δ13C and δ18O values from which the dolomite is precipitated are different, and thus can be used to indicate paleokarst environments. The δ13C-δ18O relationship diagrams of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are drawn respectively based on the test data Table 2.
The results show that the Gaoyuzhuang Formation (bedrock and fillings) mainly has three different types of paleokarst environments (Figure 7). Type I is syndiagenetic or eogenetic karst environment, which mainly forms marine with δ13C ranging from −3.3‰ to 1.34‰, and δ18O ranging from −8.25‰ to −2.95‰. The siliceous bands and dolomite fillings in the range of carbon and oxygen isotopes abundance of bedrock are the results of syngenetic deposition and filling, respectively. Type II is the karst environment of shallow burial. The samples have relatively low δ18O, which is negative than bedrock of Type I, while the δ13C is basically the same as the bedrock, and having no obvious negative bias. The δ13C ranges from −1.01‰ to −0.74‰, and δ18O ranging from −9.85‰ to −8.53‰. Only one dolomite and one siliceous band samples fall into the interval. The temperature in the shallow burial environment is slightly higher than that in the syngenetic or eogenetic karst environment, and δ18O is sensitive to the temperature, when the temperature rises, 16O is active, resulting in a negative deviation of δ18O, and only 1 out of 11 dolomite samples in the Gaoyuzhuang Formation falls into this interval, indicating the shallow burial karst environment is not the main period for the formation of dolomite in the Gaoyuzhuang Formation. Type III is the medium-deep burial or high-temperature paleoenvironment, which is mainly characterized by the obvious negative deviation of δ18O value (less than-12‰). The study suggests that δ18O value less than −12‰ can’t be formed in the low-temperature meteoric water, while it reflects that the formation of dolomite fillings has relationship with the medium-deep buried or high-temperature paleoenvironment. The dolomite fillings of the Gaoyuzhuang Formation mainly fall into this interval, reflecting that the dolomite fillings are mainly formed in the medium-deep burial and high temperature conditions.
Based on the δ13C-δ18O relational diagram shown in Figure 7, the Wumishan Formation (bedrock and fillings) can be divided based on their paleokarst depositional environments into 4 different types. Type I is syndiagenetic or eogenetic karst environment, with δ13C and δ18O distributions range basically the same as the background value area of bedrock, indicating that the karst environment is similar to that of carbonate deposition, and reflects a short exposure karstification after carbonate deposition, which is the characteristics of eogenetic karst. The δ13C is −4.25‰ ∼ 0.96‰ and δ18O is −8.01‰ ∼ −4.42‰ in the syngenetic period. Four out of six siliceous bands fall into the interval, reflecting that the siliceous bands are mainly formed by syngenetic or quasi-syngenetic deposition. Type II is shallow buried karst environment, δ13C is −1.96‰ ∼ −0.47‰, δ18O is −11.03‰ ∼ −8.48‰. Dolomite fillings mainly fall into the interval, and only one siliceous band and three dolomite samples fall into the interval, indicating that shallow buried karst environment is the main period for the formation of dolomite fillings, while siliceous bands and dolomite are mainly formed in the syngenetic period. Type III is a medium-deep burial or high-temperature paleoenvironment, with δ18O significantly negative deviation, less than −12‰. It shows that three dolomite fillings and a siliceous band samples are found in the interval, indicating that some dolomite fillings are formed in medium-deep burial environment. The results show that siliceous bands are developed in syngenetic period, shallow burial and medium-deep burial or high-temperature paleoenvironment, but mainly in syngenetic period, indicating that the siliceous bands are subject to different degrees of thermal disturbance in the burial process. Type IV is meteoric water karst environment, affected by meteoric water, δ13C and δ18O have obvious negative bias. δ13C is less than −6‰, and δ18O is −9.81‰ ∼ -7.38‰. It is found that all calcite fillings fall into the interval, which is obviously different from dolomite fillings and bedrock. The calcite filled in the cave wall is mainly composed of meteoric water, which gradually changes from unsaturated to supersaturated in the vertical infiltration process, thus precipitating and forming cave calcite fillings, similar to the genesis of modern cave stalactite.
7 Conclusion
Based on outcrops and cores observations, major and trace elements, carbon and oxygen isotopes and strontium isotope in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations, the following conclusions can be drawn.
(1) The Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are predominantly composed of crystal grain dolomite, particle dolomite, microbial dolomite, siliceous dolomite and breccia dolomite. The physical properties of different lithologies vary greatly, crystal grain dolomite, particle dolomite and breccia dolomite reservoirs having better physical properties, and siliceous dolomite reservoirs having the worst physical properties.
(2) Dolomite, siliceous bands and fillings have different paleoenvironmental characteristics. The dolomite and siliceous bands are formed in a warm subtropical climate of seawater environment, which are partially influenced by meteoric water. They have the characteristics of interactive marine, and the depth of water as a whole is relatively shallow, mainly in an oxidizing environment, affected by different degrees of terrestrial fluids. The fluid temperature at the time of formation of the dolomite fillings is significantly higher than that of the seawater in the same period, indicating that the pre-existing fracture-cavity is transformed by the high-temperature fluid after burial. The calcite fillings exhibit a meteoric water genesis, having precipitated under anoxic reducing conditions at temperatures equivalent to those of dolomite.
(3) Four periods of carbonate paleokarstification and depositional environments have been revealed: the first period is marine syndiagenetic depositional period or eogenetic karst, during which the dolomite is dominated by dissolution and the filling is relatively weak. The second period is shallow burial period, which is the main period for the formation of dolomite fillings in Wumishan Formation. The third period is the medium-deep burial period or high-temperature paleoenvironment, and the dolomite fillings of Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations are mainly formed in the period. The fourth stage is the hypergene period of meteoric water karstification, which is characterized by the formation of cave calcite fillings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GN: Supervision, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. QZ: Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Funding acquisition. DH: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Conceptualization. XL: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation. SJ: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Basic Research expenses of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (Nos. JKYQN202368 and JKYQN202372), Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi, China (No. 2022GXNSFBA035454), Basic Research Fund of Institute of Karst Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (No. 2022011).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express sincere gratitude to the reviewers and editors for their valuable comments on this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Allen, M. B., Macdonald, D. I. M., Xun, Z., Vincent, S. J., and Brouet-Menzies, C. (1997). Early Cenozoic two-phase extension and late Cenozoic thermal subsidence and inversion of the Bohai Basin, northern China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 14, 951–972. doi:10.1016/S0264-8172(97)00027-5
Baker, P. A., and Brun, S. J. (1985). Occurrence and formation of dolomite in organic-rich continental margin sediments. AAPG Bull. 69, 1917–1930. doi:10.1306/94885570-1704-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Banner, J. L. (1995). Application of the trace element and isotope geochemistry of strontium to studies of carbonate diagenesis. Sedimentology 42, 805–824. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3091.1995.tb00410.x
Brasier, M. D., Magaritz, M., Corfield, R., Huilin, L., Xiche, W., Lin, O., et al. (1990). The carbon- and oxygen-isotope record of the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary interval in China and Iran and their correlation. Geol. Mag. 127, 319–332. doi:10.1017/S0016756800014886
Chang, J., Qiu, Q. S., Zhao, X. Z., Shen, F. Y., Liu, N., and Xu, W. (2018). Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectono-thermal reconstruction of the western Bohai Bay Basin (East China) with implications for hydrocarbon generation and migration. J. Asian. Earth Sci. 160, 380–395. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.09.008
Chen, X., Zhou, Y., and Shields, G. A. (2022). Progress towards an improved Precambrian seawater 87Sr/86Sr curve. Earth Sci. Rev. 224, 103869. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103869
Dai, M. G., Sun, P. G., Lei, H. F., Xing, Q., and Bao, Z. D. (2023). Spatial distribution characteristics of strata and main thermal reservoirs and geothermal water resource potential in Xiong'an New Area. Chin. J. Geol. 58, 412–437. doi:10.12017/dzkx.2023.026
Dai, M. G., Wang, X. W., Liu, J. X., Lei, H. F., and Bao, Z. D. (2019). Characteristics and influence factors of starting and adjacent zone of geothermal resources in the xiong’an new area. Chin. J. Geol. 54, 176–191. doi:10.1017/dzkx.2019.011
Dan, Y., Nie, G. Q., Liang, B., Zhang, Q. Y., Li, J. R., Dong, H. Q., et al. (2021). The source of fracture-cave mud fillings of the Ordovician yingshan Formation and its paleokarst environment in the northern slope of the tazhong uplift, Tarim Basin, China: based on petrology and geochemical analysis. Miner 11, 1329. doi:10.3390/min11121329
Feng, W. P., Wang, F. Y., Jiang, T., Zhao, X. Z., Guan, J., Ma, X. F., et al. (2020). Origin and accumulation of petroleum in deep Precambrian reservoir in Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 120, 104541. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104541
Gao, J., Li, Y. Y., Wang, G. L., Zhang, B. J., and Xing, Y. F. (2023). Geothermal reservoirs characteristics and resource assessment of jixian System in gaoyang geothermal field, Xiongan new area. Acta Geosci. Sin. 44, 133–144. doi:10.3975/cagsb.2022.100902
Guacaneme, C., Babinski, M., Bedoya-Rueda, C., Paula-Santos, G. M., Caetano-Filho, S., Kuchenbecker, M., et al. (2021). Tectonically-induced strontium isotope changes in ancient restricted seas: the case of the Ediacaran-Cambrian Bambuí foreland basin system, east Brazil. Gondwana Res. 93, 275–290. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2021.02.007
Gui, B. L., He, D. F., Zhang, Y. S., Sun, Y. P., and Zhang, W. J. (2021). 3D geometry and kinematics of the Niudong fault, Baxian Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, Eastern China—Insights from high-resolution seismic data. J. Struct. Geol. 146, 104307. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2021.104307
Guo, J. H., Guo, Y. C., and Wang, L. S. (2009). Features of buried hill reservoirs in Hexiwu structural belt, Langgu Sag, Jizhong Depression. Pet. Explor. Dev. 36, 701–708. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60004-3
Guo, R. J., J, Y. L., Ma, Z. T., Wan, H. F., Yang, D. J., Ji, H. C., et al. (2023). Mechanism and development model of karst reservoir in the Wumishan Formation in Xiong'an New Area. J. Palaeogeogr. 25, 180–197. doi:10.7605/gdlxb.2023.01.012
Jones, B., and Manning, D. A. (1994). Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones. Chem. Geol. 111, 111–129. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X
Keith, M. H., and Weber, J. N. (1964). Carbon and oxygen isotopic composition of selected limestones and fossils. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta. 28, 1787–1816. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(64)90022-5
Kerans, C. (1988). Karst-controlled reservoir heterogeneity in ellenburger group carbonates of West Texas. AAPG Bull. 72, 1160–1183. doi:10.1306/703c996f-1707-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Leng, M. J. (2006). Isotopes in palaeoenvironmental research. Nertherlands Dordrecht: Springer, 227–257. doi:10.1007/1-4020-2504-1
Li, C. W., Liu, K. Y., and Liu, J. L. (2023). A petroliferous Ediacaran microbial-dominated carbonate reservoir play in the central Sichuan Basin, China: characteristics and diagenetic evolution. Precambrian Res. 384, 106937. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2022.106937
Li, F., Li, S. L., Zeng, J. H., Liu, J. W., Liu, J., Ge, D. W., et al. (2016a). Feature of paleofluids and present fluids in the inner buried hill of Niutuozhen uplift, Baxian sag. Geosci 30, 1115–1133. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2016.05.016
Li, H. Q., Carbonell, R., Gao, R., Huang, X. F., Zhang, J., Deng, X. F., et al. (2023). Geophysical constraints on the deep structure beneath the Xiong'an New Area geothermal field, North China. Tectonophysics 869, 230125. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2023.230125
Li, J., Zhang, W. Z., Luo, X., and Hu, G. Y. (2008). Paleokarst reservoirs and gas accumulation in the Jingbian field, ordos Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 25, 401–415. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.01.005
Li, S. Z., Zhao, G. C., Dai, L. M., Zhou, L. H., Liu, X., Suo, Y. H., et al. (2012). Cenozoic faulting of the Bohai Bay Basin and its bearing on the destruction of the eastern North China craton. Asian. Earth Sci. 47, 80–93. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.06.011
Li, X. D., Wei, Z. Y., He, Y. B., and Zhong, J. W. (2024a). Strontium isotope and restricted marine basin analysis from thin bedded limestone at the top of Xujiajuan Formation, Xiangshan group in Ningxia, China. Acta Geol. Sin. 98 (4), 1229–1243. doi:10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2023284
Li, Z. H., Qu, H. J., and Gong, W. B. (2016b). Late Mesozoic basin development and tectonic setting of the northern North China Craton. J. Asian. Earth Sci. 114, 115–139. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.029
Li, Z. T., Liu, B., Liu, Y. J., Yuan, J. L., Zhou, Q. J., Li, S. Z., et al. (2024b). Mesozoic to Cenozoic tectonic evolution in the central Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 136, 4965–4984. doi:10.1130/B37427.1
Ling, H. F., Chen, X., Li, D., Wang, D., Zhou, G. S., and Zhu, M. Y. (2013). Cerium anomaly variations in Ediacaran-earliest Cambrian carbonates from the Yangtze Gorges area, South China: implications for oxygenation of coeval shallow seawater. Precambrian Res. 225, 110–127. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.10.011
Liu, C. G., Li, G. R., Zhang, Y. W., Han, Y. Q., Lv, H. T., Yang, X. Y., et al. (2007). Application of strontium isotope to the study of Paleokarst—an case from Ordovician in the Tahe oilfield, Tarim Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. 81 (10), 1398–1406. doi:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.10.010
Liu, N., Qiu, N. S., Chang, J., Shen, F. Y., Wu, H., Lu, X. S., et al. (2017). Hydrocarbon migration and accumulation of the Suqiao buried-hill zone in Wen'an Slope, Jizhong Subbasin, Bohai Bay Basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 86, 512–525. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.05.040
Loucks, R. G. (1999). Paleocave carbonate reservoirs: origins, burial-depth modification, spatial complexity, and reservoir implications. AAPG Bull. 83 (11), 1795–1834. doi:10.1306/E4FD426F-1732-11D7-8645000102C1865D
Loucks, R. G., Mescher, P. K., and McMechan, G. (2004). Three-dimensional architecture of a coalesced, collapsed-paleocave system in the Lower Ordovician ellenburger group, central Texas. AAPG Bull. 88 (5), 545–564. doi:10.1306/12220303072
Lu, F. H., and Meyers, W. J. (1998). Massive dolomitization of a late Miocene carbonate platform: a case of mixed evaporative brines with meteoric water, Nijar, Spain. Sedimentology 45, 263–277. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3091.1998.0142e.x
Lu, K., Bao, Z. D., Ji, H. C., Liu, J. X., Wang, G. L., Ma, F., et al. (2019). Characteristics,main controlling factors and favorable area prediction of karstic geothermal reservoirs of the jixianian wumishan formation in Xiong'an New Area. J. Palaeogeogr. 21 (6), 885–900. doi:10.7605/gdlxb.2019.06.060
Lu, K., Bao, Z. D., Sheng, M., Bao, Y. F., Dai, Q. Q., Cao, Y. Z., et al. (2021). Influence of internal textures in fracture development in dolostones: a case study in the Mesoproterozoic wumishan formation in the Jizhong depression, Bohai Bay Basin, north China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 125, 104877. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104877
Lu, S. N., Zhao, G. C., Wang, H. C., and Hao, G. J. (2008). Precambrian metamorphic basement and sedimentary cover of the North China Craton: a review. Gondwana Res. 160, 77–93. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.04.017
Ma, F., Li, T. X., Zhou, Y., Cai, J., and Cai, Y. F. (2022). Paleoenvironment of Mesoproterozoic gaoyuzhuang and wumishan formations, North China: new insights from geochemistry and carbon and oxygen isotopes of dolostones. Miner 12, 1111. doi:10.3390/min12091111
Pei, Z. P., Han, B. P., Feng, Q. Y., Jin, X. Y., Han, Y. L., and Mao, Q. (2009). Karst developmemt of buried dolomite hill reservoir in wumishan formation of Renqiu oilfield. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 1, 1247–1252. doi:10.1016/j.proeps.2009.09.192
Pesonen, L. J., Evans, D., Veikkolainen, T., Salminen, J., and Elming, S. K. (2021). Chapter 1-Precambrian supercontinents and supercycles-An overview. Anc. Supercont. Palaeogeogr. Earth., 2021. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-818533-9.00020-5
Pu, J. B., Wang, A. Y., Shen, L. C., Yin, J. J., Yuan, D. X., and Zhao, H. P. (2016). Factors controlling the growth rate, carbon and oxygen isotope variation in modern calcite precipitation in a subtropical cave, Southwest China. J. Asian. Earth Sci. 119, 167–178. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.12.010
Qiao, Y., Li, M., Du, L., and Li, S. H. (2023a). Simulation study on seepage patterns of geothermal reinjection in carbonate thermal reservoir and geothermal doublet well patterns in Xiong'an new area. Water 15, 2683. doi:10.3390/w15152683
Qiao, Y., Li, S. H., Yan, K. N., Zuo, Y. H., Zhang, T., Tian, L. X., et al. (2023b). Karst thermal reservoir tracer test and seepage characteristics analysis in niutuozhen geothermal field in Xiong’an New Area. Front. Earth Sci. 11, 1132092. doi:10.3389/feart.2023.1132095
Ren, Y., Zhong, D. K., Liu, H. L., Liang, T., Sun, H. T., Gao, C. L., et al. (2018). Isotopic and elemental evidence for paleoenvironmental evolution of Cambrian stage 4 longwangmiao formation, east chongqing. China. Earth Sci. 43, 4066–4095. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2017.590
Richard, S., Kathy, R. B., and Ronald, A. R. (2005). Paleokarst and reservoir porosity in the Ordovician Beekmantown dolomite of the central appalachian Basin. Carbonates Evaporites 20, 50–63. doi:10.1007/BF03175448
Shields, G., and Veizer, J. (2002). Precambrian marine carbonate isotope database: version 1.1. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 3 (6), 1 of 12–12 of 12. doi:10.1029/2001gc000266
Sun, Q. Q., Holdsworth, R. E., Fan, T. L., Mccaffrey, K. J. W., Gao, Z. Q., Yang, D. B., et al. (2024). The spatial and geological characteristics of fault-and paleokarst-controlled carbonate-hosted reservoirs in the tabei uplift, tarim Basin, China. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 36 (11-12), 4985–5008. doi:10.1130/B37444.1
Tang, Y. J., Zhang, H. F., Santosh, M., and Ying, J. F. (2013). Differential destruction of the North China Craton: a tectonic perspective. J. Asian. Earth Sci. 78, 71–82. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.047
Tribovillard, N., Algeo, T., Lyons, T., and Riboulleau, A. (2006). Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: an update. Chem. Geol. 232, 12–32. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.02.012
Veizer, J. (1983). Chemical diagenesis of carbonates: theory and application of trace element technique. Stable Isot. Sediment. Geol. 1983, 10. doi:10.2110/scn.83.01.0000
Wang, Q., Sun, Y. H., Zhang, W. F., Wang, Y. G., Cao, L. Z., and Li, X. W. (2022). Structural characteristics and mechanism of the Hengshui accommodation zone in the southern Jizhong subbasin, Bohai Bay basin, China. Mar. Pet. Geol. 138, 105558. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105558
Wang, Y., Zhang, Y. S., Cheng, H., and Chen, F. K. (2019). Complex magma sources of late Mesozoic granites along the southern margin of the North China Craton: constraints from geochemistry and geochronology of the massive Heyu and Lantian plutons. Int. Geol. Rev. 62, 1862–1882. doi:10.1080/00206814.2019.1669078
Wang, Z. T., Rao, S., Xiao, H. P., Wang, Y. B., Jiang, G. Z., Hu, S. B., et al. (2021). Terrestrial heat flow of Jizhong depression, China, Western Bohai Bay basin and its influencing factors. Geothermics 96, 102210. doi:10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102210
Xiong, G. Q., Wang, J., Wu, H., Zhang, H. Q., Yu, Q., Yan, J. F., et al. (2014). Trace element and REE geochemistry of the ediacaran doushantuo formation from Fanjingshan area, northeast Guizhou province, China. Carbonates Evaporites 29, 363–394. doi:10.1007/s13146-014-0217-2
Xiong, L. P., Zhang, J. M., and Sun, H. W. (1985). Mathematical simulation of geo⁃temperature and heat flow patterns. J. Geodyn. 4, 45⁃61. doi:10.1016/0264⁃3707(85)90051⁃1
Yang, G. R., Cui, Z. Q., Cui, J. F., and Tian, F. Q. (2009). Distribution characteristics of gas and oil reserves and analysis of the future reserves in Jizhong depression. Nat. Gas. Geosci. 20, 923–929.
Yang, H. M., Liu, C. Y., Sun, D. S., and Cui, Y. Q. (2002). Extensional tectonic system and its deep-seated setting of Jizhong Basin, China. Geotecton. Metallog. 26, 113–120. doi:10.1007/s11769-002-0045-5
Yang, X. Q., Zhong, D. K., Ren, Y., Xie, R., Jiang, Y. J. F., Pu, Q., et al. (2017). Characteristics and significance of carbon and oxygen isotopes of the Cambrian longwangmiao formation, eastern Chongqing. J. Palaeogeogr. 19 (5), 865–878.
Yu, H. T., Xu, Z. J., Cheng, R. H., Zhang, Z., and Gao, D. (2023). Late Mesozoic transformation from the compressive to extensional tectonic regime of the Eastern North China Craton: sedimentary records from the North Yellow Sea Basin. J. Asian. Earth Sci. 256, 105809. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2023.105809
Yue, G. F., Wang, G. L., Ma, F., Zhu, X., Zhang, H. X., Zhou, J. W., et al. (2022). Fracture characteristics and reservoir inhomogeneity prediction of the Gaoyuzhuang formation in the Xiong'an new area: insights from a 3D discrete fracture network model. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 849361. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.849361
Zhai, M. G., Santosh, M., and Zhang, L. C. (2011). Precambrian geology and tectonic evolution of the North China craton. Gondwana Res. 20, 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2011.04.004
Zhang, B. J., Wang, S. Q., Kang, F. X., Li, Y. Y., Zhuo, L. Y., Gao, J., et al. (2022). Flow path of the carbonate geothermal water in Xiong’an new area, North China: constraints from 14C dating and H-O isotopes. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 782273. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.782273
Zhang, Q. Y., Liang, B., Ji, S. C., and Li, J. R. (2023). Isotopic characteristics of carbon and oxygen within ordovician carbonate paleokarst in the tazhong region and their paleoenvironmental significance. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 1047535. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.1047535
Zhang, Y. M., Chang, J., Liu, N., Liu, J. W., Ma, X. F., Zhao, S. F., et al. (2017). Present-day temperature–pressure field and its implications for the geothermal resources development in the Baxian area, Jizhong depression of the Bohai Bay Basin. Nat. Gas. Ind. 5, 226–234. doi:10.1016/j.ngib.2017.10.006
Zhao, G., Sun, M., Wilde, S. A., and Li, S. Z. (2005). Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the north China craton: key issues revisited. Precambrian Res. 136, 177–202. doi:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
Zhao, X. Z., Jin, F. M., Cui, Z. Q., Han, C. Y., Zeng, J. H., Wang, Q., et al. (2012). Types of subtle buried-hill oil reservoirs and their accumulation simulation in Jizhong depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 39, 147–154. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(12)60027-5
Zhao, X. Z., Lin, F. M., Wang, Q., and Bai, G. P. (2015). Buried-hill play, Jizhong subbasin, Bohai Bay basin: a review and future prospectivity. AAPG Bull. 99, 1–26. doi:10.1306/07171413176
Zhu, R. X., Zhang, H. F., Zhu, G., Meng, Q. R., Fan, H. R., Yang, J. H., et al. (2017). Craton destruction and related resources. Int. J. Earth Sci. 106, 2233–2257. doi:10.1007/s00531-016-1441-x
Keywords: karst reservoir, gaoyuzhuang-wumishan formations, geochemical characteristics, palaeoenvironment, Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas
Citation: Nie G, Zhang Q, He D, Li X and Ji S (2025) Geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironmental significance of karst reservoirs in Gaoyuzhuang-Wumishan Formations of Jixian System in Xiong ‘an New Area and its adjacent areas. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1624161. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1624161
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 10 July 2025;
Published: 31 July 2025.
Edited by:
Huan Li, Central South University, ChinaReviewed by:
Fuchuan Chen, Kunming University of Science and Technology, ChinaGuanxiong Ren, Southwest Petroleum University, China
Copyright © 2025 Nie, Zhang, He, Li and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qingyu Zhang, enFpbmd5dUBtYWlsLmNncy5nb3YuY24=
 Guoquan Nie
Guoquan Nie Qingyu Zhang2,3*
Qingyu Zhang2,3* Shaocong Ji
Shaocong Ji