- 1Hunan Water Resources and Hydropower Survey, Design, Planning and Research Co., Ltd., Changsha, China
- 2Hunan Provincial Water Resources Development and Investment Co., Ltd., Changsha, China
- 3School of Civil Engineering, Central South University of Forestry and Technology, Changsha, China
- 4School of Water Resources and Hydropower, Hunan Polytechnic of Water Resources and Electric Power, Changsha, China
- 5Hunan Engineering Research Center of Intelligent Inspection and Digital Maintenance for Hydraulic Engineering, Changsha, China
Clarifying the mechanism of grouting to block karst water outbursts is essential for ensuring effective sealing. This article studies the grouting blocking problem related to the prevention and control of water surge disasters in karst tunnels, focusing on the grouting blocking mechanism of efficiently plugs expanding material (EPEM) under dynamic water conditions. We propose a grouting diffusion formula and blocking criterion that take into account the self-expanding properties of the slurry. First, based on the equilibrium relationship between the friction force and anti-splitting force between the blocking body and the rock wall, we establish an effective blocking condition. Second, by combining capillary theory with Newton’s fluid constitutive equation, we derive the diffusion distance formula for self-expanding slurry under dynamic water conditions. We then construct a mechanical model that uses the length of the critical blocking body as a criterion, revealing the coupling influences of groundwater pressure, grouting pressure, and grouting time. The results indicate that groundwater pressure is positively correlated with grouting pressure and grouting time, while grouting pressure is negatively correlated with grouting time. Finally, we verify the practicality of the proposed criterion through the project at Quanmutang Reservoir in Hunan Province, successfully implementing a parameter combination of 0.5 MPa grouting pressure and 20 min of grouting time to block surge water. This research provides a theoretical basis and engineering guidance for designing water surge grouting in karst tunnels.
1 Introduction
The construction of transportation infrastructure has entered a phase of rapid growth in China. New projects increasingly exhibit distinctive characteristics due to harsher construction environments, more complex geological conditions, and a higher frequency of disasters and accidents. These challenges are particularly pronounced in tunnel engineering, especially regarding adverse geological conditions. Notably, surge water disasters in karst regions have become a significant bottleneck in the development of China’s transportation infrastructure due to their unpredictable nature, high potential for damage, prolonged duration, and the difficulties associated with post-disaster management. Currently, the grouting method is regarded as the most effective technical solution for preventing and controlling tunnel surge water disasters in karst areas. The key to its effectiveness lies in the careful selection of grouting parameters and the type of grouting materials used.
Extensive engineering practice has shown that surging water disasters not only threaten the safety of life and property for construction personnel but also cause serious damage to groundwater systems. Currently, scholars in China and around the world have conducted extensive research on the mechanisms of grouting and plugging. In terms of model testing, Wanghua et al. (2015) investigated the influence of four factors (fracture width, slurry gelation time, water flow rate, and grouting volume) on grouting plugging and summarized their effects. Chen et al. (2019) established a large-scale visualization experimental system based on similarity criteria, which revealed the plugging mechanism of fibers and particles in hydraulic fracturing. Liu et al. (2024) designed and constructed an experimental system to simulate the grouting plugging of surge water in karst pipelines and analyzed the influence of various factors on the effectiveness of grouting plugging. Pan et al. (2022) developed a pipeline-type grouting plugging simulation experimental system and investigated the mechanism of flowing water grouting plugging under controlled flow conditions. Shucai et al. (2020) derived numerical openness as a function of flow rate in the pipeline after implementing flow control, using their self-developed karst pipeline model test system.
Considering the shortcomings of indoor and outdoor model tests, such as size effects and the difficulty of achieving large sample sizes, researchers have conducted extensive studies on the grouting plugging mechanism of tunnel surge water using numerical simulations, which facilitate the research process. Chengyuan et al. (2021) employed the coupled computational fluid dynamics/discrete element method (CFD-DEM) method to simulate the formation of the fissure blocking zone and revealed the evolution mechanism of its structure. Haiyan et al. (2020) investigated the blocking mechanism of pipelines through numerical simulation, analyzing the changes in the slurry flow rate during the grouting process. Liu et al. (2017) used the multi-physics coupling software COMSOL Multiphysics to establish a numerical model for the diffusion of fissure grouting under dynamic water conditions, examining the influence of initial dynamic water flow rate, grouting rate, and time-varying viscosity on the diffusion process. Yang et al. (2020) utilized a CFD-DEM model for dynamic simulations, revealing the transport behavior, dynamic aggregation, and blocking mechanism of nanoparticles intruding into the pore spaces of shale. Lastly, Xu (Zhenhao et al., 2021) conducted a numerical simulation study on flow control technology for flowing water grouting plugging in karst pipes. The theoretical analysis method is straightforward due to its derivation process, allowing certain assumptions to be avoided in many cases. Consequently, more scholars are adopting this method. For example, Wang et al. (2018) proposed grouting plugging guidelines for conditions of moving water, identifying key construction parameters and processes for tunnel surge water grouting. Haiyan et al. (2021) systematically studied the dynamic water plugging mechanism under conditions of high flow rates in karst pipelines, focusing on flow control and deceleration. Additionally, Shucai et al. (2020) analyzed slurry diffusion processes at various flow rates, exploring the impacts of flow rate, grouting pressure, and countercurrent diffusion distance on slurry behavior under dynamic water conditions. Wang et al. (2018) conducted an in-depth investigation into the mechanisms of slurry diffusion and plugging in dynamic water grouting. Finally, Yalei et al. (2024) established a theoretical analytical model for grouting diffusion decay and examined the effects of the closure mechanism in multi-jointed fissured rock bodies. Scholars have conducted more in-depth research on the mechanism of tunnel surge water grouting and plugging; however, there is a lack of relevant research on the pipeline-type grouting plugging mechanism. Consequently, existing knowledge and research findings cannot directly guide tunnel surge water self-expanding material grouting projects in karst areas.
This article first analyzes the effective conditions for grouting plugging from the perspective of the relationship between the plugging body and the rock wall. It combines the single-pipe flow formula and considers the self-expansion effect of the slurry to derive the formula for the diffusion of self-expanding slurry grouting. Second, the friction between the plugging body and the contact surface of the surge water channel is used as a basis for constructing a mechanical calculation model, which proposes the grouting blocking criterion. Lastly, by examining the influence of groundwater pressure on grouting parameters, this study explores the influence mechanism of the grouting plugging criterion for tunnel surge water in karst areas.
2 The plugging mechanism of dynamic water grouting
2.1 Analysis of effective grouting plugging conditions
The efficiently plugs expanding material (EPEM) injected into the surge water pipeline will quickly undergo gelatinization and solidification to form a blocking body when it contacts water. The success of the grouting process relies primarily on the gelatinization and solidification of the EPEM after it forms the blocking body, as well as the maximum static friction (f) between the blocking body and the rock wall in relation to the water pressure (Pw).
Due to the action of water pressure, the grouting blocking body may experience splitting. Even if the maximum static friction of the blocking body is sufficient to resist the water pressure, if the water pressure exceeds the splitting force of the blocking body, cracks will form, leading to the failure of water plugging. Therefore, the rock wall should be considered in an ideal horizontal state with no bulge, and it should be analyzed under the following two conditions. The schematic diagram of blocking criterion is schematically shown in Figure 1.
(1) When the maximum static friction of the grouted plugging body (f) exceeds the splitting force of the plugging body (fp), the grouted plugging body may crack under the action of water pressure. This cracking can cause the plugging body to split and lead to failure in water blocking. Therefore, the successful criterion for grouted plugging should satisfy the condition of fp > Pw.
(2) When the maximum static friction of the grouting blocking body (f) is less than the cleavage resistance of the blocking body (fp), there will be no water pressure causing cleavage in the blocking body. In this case, the success criterion for grouting blocking should be that f > Pw.
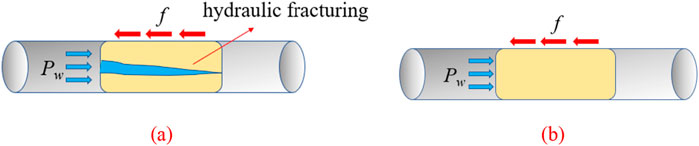
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of blocking criterion. (a) Maximum static friction f > blocking body splitting force
2.2 Derivation of the grout diffusion equation for surge water
2.2.1 Basic assumptions
① EPEM is an incompressible Newtonian fluid, and changes in the fluid flow pattern during the grouting process are not considered
② the fluid movement in the pipeline is assumed to be laminar flow
③ the fluid is immiscible with the water body, and there exists a front at the leading edge of the fluid.
2.2.2 Model construction and derivation
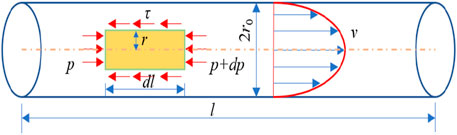
The conduit pipe is idealized as a smooth and undulating pipe, as shown in Figure 2. In the figure, l is the length of the pipe, dl is a microelement segment of the slurry; is the shear stress; r0 is the radius of the pipe; v is the slurry flow rate; p is the driving pressure; r is the radius of the grout’s microelement.
The Newtonian fluid slurry eigenstructure equation is as follows:
where
The force analysis of the EPEM microelement is carried out, and the mechanical equilibrium equation is given.
Equation 2 can be simplified as
Equations 1, 3 are obtained.
Integrating Equation 4 with the boundary condition
Integrating the slurry velocity in the pipe gives the slurry flow rate, Equation 6 is obtained.
Solve for the slurry flow rate in the pipe as:
The joint Equation 3, Equation 7 can be obtained as the pipe wall shear stress:
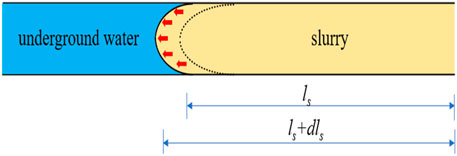
EPEM was injected into the conduit to displace groundwater flow, as shown in Figure 3.
The force on the slurry can be analyzed using Newton’s second law:
where m is the mass of the slurry,
Equation 9 can be written as
EPEM is moving in a laminar flow in the pipe.
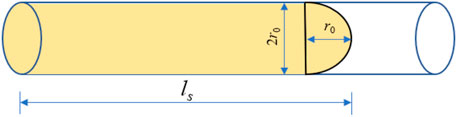
Assuming that EPEM diffuses in the pipe as a column-hemisphere model, and also considering the self-expansion effect of EPEM, as shown in Figure 4, the relationship between the flow rate and the grouting volume is
where v is the slurry flow rate in the injection pipe, m/s; rd is the grouting pipe radius, mm; t is the grouting time, min; K is the volume expansion of slurry, %.
The joint Equations 11, 12 lead to the EPEM diffusion distance equation:
2.3 Derivation of grouting sealing criteria for surge water
2.3.1 Basic assumptions
① The blocking body is a homogeneous and isotropic medium;
② the influence of the gravity of the blocking body is not considered;
③ the wall pressure of the plugging body on the inner wall of the pipe is equal.
2.3.2 Model construction and derivation
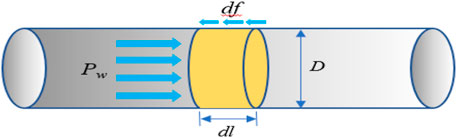
The length of the blocking body is taken as dl, and the diameter of the blocking body is taken as D for analysis, as shown in Figure 3, 5.
The water pressure acting on the micrometric blocking body at the time of successful EPEM blocking is
where
The contact area S of the blocking body with the rock wall (Equation 15) is obtained.
The relationship between friction and water pressure is obtained from the limiting equilibrium state:
where
The critical blocking body segment length required for successful blocking can then be expressed as
From Equations 14, 16 when
According to Equation 17, the minimum blocking body segment length required for successful EPEM blocking can be found. Combining this with Equation 13, the grouting pressure and grouting time required for the critical blocking body length for successful EPEM blocking can be solved.
2.4 Parameterization and conditions of application
2.4.1 Determination of parameters
① EPEM volume expansion rate K.
EPEM volume expansion rate is calculated according to Equation 19:
where V1 is the total volume of raw slurry, L; V2 is the slurry colloid volume, L.
② Slurry viscosity.
Measurement, analysis, and calculation are obtained by using a fluid viscometer, such as a capillary viscometer or a rotational viscometer.
2.4.2 Applicable conditions
Considering that when the maximum static friction of the blocking body f> the anti-splitting force of the blocking body fp, the blocking body may split under the action of water pressure, so the following conditions (Equation 20) should be satisfied:
3 Influence mechanism of grouting sealing criteria of tunnel surge water
3.1 Analysis of the influence law of grouting time
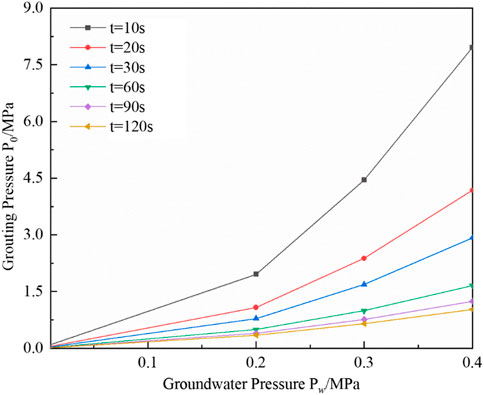
In order to investigate the influence of grouting time on grouting plugging under the criterion model of grouting plugging of surge water, the change rule of groundwater pressure and grouting pressure under different grouting times is quantitatively analyzed. Groundwater pressures of 0.2 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.4 MPa and grouting times of 10 s, 20 s, 30 s, 60 s, 90 s, and 120 s are selected, respectively, and the influence law of grouting time under the surge water grouting blocking criterion model is shown in Figure 6.
As analyzed in Figure 6, there is a positive correlation between the grouting time and groundwater pressure; that is, with increased groundwater pressure, the grouting time required for grouting and plugging increases. The reason is that with the increase of groundwater pressure, the water flow velocity increases under the same pipe diameter, and the slurry can be easily dispersed by the moving water, which leads to a decrease in the retention rate of the slurry. As a result, it is difficult to form a full-section blocking body in the pipeline, so it needs a longer grouting time to make the retention rate of the slurry increase and form a blocking body with the resistance to be scoured by the moving water inside the pipeline and then successfully block the pipe against a sudden surge of water.
3.2 Analysis of the influence law of grouting pressure
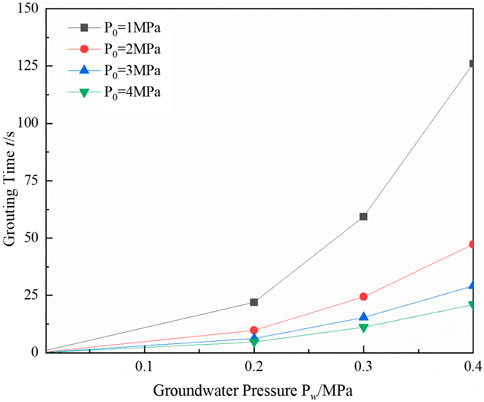
The change rule of groundwater pressure and grouting time under different grouting pressures is analyzed quantitatively to investigate the influence of grouting pressure on grouting plugging under the criterion model. Groundwater pressures of 0.2 MPa, 0.3 MPa, and 0.4 MPa, and grouting pressures of 1 MPa, 2 MPa, 3 MPa, and 4 MPa are selected, and the influence law of grouting pressure under the criterion model is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 shows a positive correlation between grouting pressure and groundwater pressure; that is, with increased groundwater pressure, the grouting pressure required for grouting plugging increases. The reason is that with the increase of groundwater pressure, the friction between the blocking body and the rock wall must be larger to resist the water pressure. The main influencing factor of the friction of the blocking body is the length of the blocking body; therefore, a higher grouting pressure is required to make the amount of grouting per unit of time increase, so that the length of the blocking body formed per unit of time will be longer and the friction will be higher to resist the groundwater pressure.
3.3 Analysis of groundwater pressure impact pattern
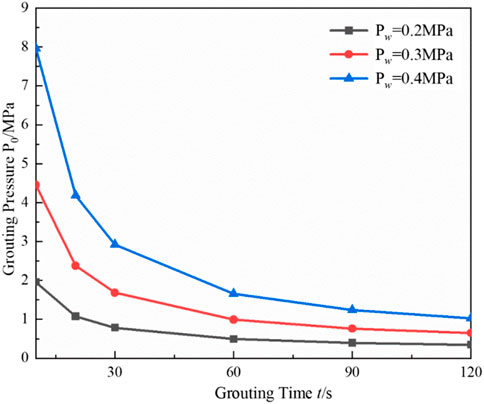
In order to investigate the influence of groundwater pressure on grouting and plugging under the criterion model, the change rule of grouting time and grouting pressure under different groundwater pressures is analyzed quantitatively. Grouting times of 30 s, 60 s, 90 s, and 120 s and grouting pressures of 1 MPa, 2 MPa, 3 MPa, and 4 MPa are selected. The results are shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8 shows that groundwater pressure, grouting pressure, and grouting time are positively correlated, while grouting pressure and grouting time are negatively correlated. That is, with the increase in grouting pressure, the grouting time required for grouting plugging is reduced. The reason is that with the increase in grouting pressure, under the same diameter of grouting pipe, the grouting volume per unit time increases, which makes the length of the blocking body formed per unit time be longer. The growth of the length of the blocking body makes the friction between the blocking body and the rock wall increase, which can realize the blocking in a shorter period of time.
4 Engineering applications
4.1 Engineering geology and hydrogeology
The total length of the Jiulongling Tunnel is 19,261.8 m. The topography is dominated by ridges and low hills and wide valleys, with gentle terrain and ground elevation of 300–350 m, and the undulation is slightly larger in the latter part of the tunnel, with a maximum height of approximately 550 m. The engineering geological conditions are complicated. The main strata traversed are the Devonian (D) and the Carboniferous (C), and the Ordovician (O) strata are traversed at the end of the tunnel. The rock properties are mainly cherts, Dolomitic tuff, dolomite, marl, charcoal shale, sandstone, slate, etc. The thickness of each rock layer ranges from thin to very thick, and there are large differences between the layers. The tunnel traverses complex hydrogeological conditions, including surface water development along the line, a groundwater level that is located above the roof of the cave, and dark rivers distributed near the axis. In terms of tectonic development, the area of the tunnel has a total of 34 faults, most of which intersect with the cave line at a large angle. The level of inclination is relatively gentle, more or less than 30°. In terms of karst development, the construction site experienced the occurrence of a sudden surge of water many times, as shown in Figure 9.
4.2 Construction program and effectiveness evaluation
According to the analysis of the site survey report, it is proposed to carry out curtain grouting on the side wall in the section. The holes are arranged in a plum blossom type, the designed drilling hole diameter is Φ50 mm, the hole depth is 5.0 m, the hole spacing is 1.5 m, and the ring spacing is 1.5 m. There are 10 rings in total. EPEM was chosen as the grouting material. After the field test, the slurry proportions were determined to be an alcohol-ester ratio of 0.9:1, a cement mixing amount of 70%, and a catalyst mixing amount of 3%. Through the above calculation of single-hole water influx combined with the surge water grouting blocking criterion model, the final grouting pressure is 0.5 MPa, and the single-hole grouting time reaches 20 min as the final grouting standard.
After the completion of EPEM grouting, the surge water situation improved significantly, and the flow of surge water in the section was cut off. Through the observation and analysis of the grouting holes, the surface of the grouting holes is dry, and there is no water leakage or seepage in the holes, so the grouting sealing effect is good. Subsequent on-site monitoring shows that there is no water seepage or leakage after construction using the grouting construction parameters discussed herein. The perimeter rock has been stable during subsequent excavation and lining construction, and there have been no accidents, such as a secondary surge of water.
5 Conclusion
(1) This article first analyzes the effective blocking conditions between the blocking body and the surge water pipe, focusing on the relationship between the blocking body and the rock wall, while also considering the water pressure splitting effect of the blocking body. Second, it deduces a formula for the grouting diffusion of the surge water by combining capillary theory with the flow formula for a single pipe. Finally, it constructs a mechanical calculation model based on the relationship between water pressure and the friction force of the blocking body, proposing the concept of grouting blocking.
(2) To reveal the influence mechanism of the grouting plugging criterion, a quantitative analysis was conducted based on the derived tunnel surge water grouting plugging criterion model, focusing on grouting time, grouting pressure, and groundwater pressure. The results indicate a positive correlation between groundwater pressure and grouting pressure; specifically, as groundwater pressure increases, the grouting pressure required for successful plugging also increases. Additionally, there is a positive correlation between groundwater pressure and grouting time, meaning that higher groundwater pressure necessitates a longer grouting time for successful plugging. Conversely, there is a negative correlation between grouting pressure and grouting time; as grouting pressure increases, the time required for successful grouting and plugging decreases.
(3) The research findings on the grouting sealing mechanism for sudden water inflows in karst tunnel areas presented in this article have been successfully applied in the grouting project for the tunnel in the irrigation district of the Quanmutang Reservoir Engineering Project in Hunan Province. Based on on-site applications, a curtain grouting scheme was proposed to seal the water outburst areas. The grouting was completed when the final grouting pressure reached 0.5 MPa and the single-hole grouting time extended to 20 min, ensuring the safe excavation and support of the tunnel.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SZ: writing – review and editing and writing – original draft. LL: data curation, validation, and writing – review and editing. ZL: conceptualization and writing – review and editing. JZ: writing – review and editing and conceptualization. YC: data curation, writing – review and editing. LC: writing – original draft and methodology.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Scientific Research Project of Hunan Education Department (23B1009), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52378426), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (No. 2025JJ60272), the Distinguished Young Scholars of Changsha City Bureau (kq2209017), the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No.2023RC3160), and the Water Resources Science and Technology Program of Hunan Province (XSKJ2022068-07). The corresponding author gratefully acknowledges this financial support.
Conflict of interest
Authors SZ and YC were employed by Hunan Water Resources and Hydropower Survey, Design, Planning and Research Co., Ltd. Authors LL and JZ were employed by Hunan Provincial Water Resources Development and Investment Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Chen, Y., Fujian, Z., Feng, W., Tian, Z., Yuan, L., and Gao, L. (2019). Plugging mechanism of fibers and particulates in hydraulic fracture. J. Petroleum Sci. Eng. 176, 396–402. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2019.01.084
Chengyuan, X. U., Zhang, J., Kang, Y., Xu, F., Lin, C., Yan, X., et al. (2021). Structural formation and evolution mechanisms of fracture plugging zone. Petroleum Explor. Dev. 48 (1), 232–242. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(21)60019-8
Haiyan, L. I., Liu, J., Jing, W. U., Xu, Z., Zhang, X., Zhang, L., et al. (2021). Grouting sealing method of flow-control speed-down in karst pipelines and its engineering application. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 108, 103695. doi:10.1016/j.tust.2020.103695
Haiyan, L. I., Zhang, Y., Jing, W. U., Zhang, X., Zhang, L., and Li, Z. (2020). Grouting sealing mechanism of water gushing in karst pipelines and engineering application. Constr. Build. Mater. 254, 119250. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119250
Liu, J., Liu, S., Wang, M., and Peng, B. (2024). An experimental study on the sealing mechanism of a Karst pipeline by dynamic water grouting. Appl. Sci. 14 (4), 1381. doi:10.3390/app14041381
Liu, R., Zhang, L., Zhang, Q., Yang, L., Li, Z., Sun, Z., et al. (2017). Numerical simulation and experimental validation of diffusion of fast-setting slurry fissure dynamic water grouting. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 36 (S1), 3297–3306. doi:10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2015.0815 (in Chinese)
Pan, D., Bu, Z., Haiyan, L, Xu, Z., and Liu, J. (2022). Experimental investigation of flow control technology for grouting and blocking of flowing water in karst conduits. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 26 (8), 3440–3454. doi:10.1007/s12205-022-2129-3
Shucai, L. I., Pan, D., Zhenhao, X. U., Lin, P., and Zhang, Y. (2020). Numerical simulation of dynamic water grouting using quick-setting slurry in rock fracture:the Sequential Diffusion and Solidification (SDS) method. Comput. Geotechnics 122, 103497. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103497
Wanghua, S. U. I., Jinyuan, L. I. U., Hu, W., Qi, J., and Zhan, K. (2015). Experimental investigation on sealing efficiency of chemical grouting in rock fracture with flowing water. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 50 (08), 239–249. doi:10.1016/j.tust.2015.07.012
Wang, Q., Zhu, Q., Shao, T., Shu-yi, X., Qing-Li, K., Jun-Jie, Z., et al. (2018). The rheological test and application research of glass fiber cement slurry based on plugging mechanism of dynamic water grouting. Constr. Build. Mater., 189–130. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.081
Yalei, Z. H. E., Hou, K., Wang, Z., Shifei, Y., Yunlin, Y., and Yong, Y. (2024). The grouting plugging mechanism of layered jointed rock mass considering the time-varying yield stress of grout. Sci. Rep. 14 (1), 23029. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-74583-2
Yang, X., Cai, J., Jiang, G., Xie, J., Shi, Y., Chen, S., et al. (2020). Nanoparticle plugging prediction of shale pores: a numerical and experimental study. Energy 208, 118337. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2020.118337
Keywords: karst tunnel, surge water, self-expanding slurry, grouting plugging, dynamic water conditions, plugging criterion
Citation: Zhan S, Lu L, Liu Z, Zhou J, Chen Y and Cao L (2025) Mechanism of water plugging by dynamic grouting with self-expanding slurry in karst tunnels. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1633717. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1633717
Received: 23 May 2025; Accepted: 16 June 2025;
Published: 08 August 2025.
Edited by:
Pengfei Liu, CCCC Second Harbor Engineering Co., Ltd., ChinaReviewed by:
Yipeng Xie, Ocean University of China, ChinaZhen Huang, Guangxi University, China
Han Feng, Shijiazhuang Tiedao University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhan, Lu, Liu, Zhou, Chen and Cao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Cao, bTE4ODc0MTc3MjE0QDE2My5jb20=
 Shuangqiao Zhan1
Shuangqiao Zhan1 Lei Cao
Lei Cao