- 1Exploration and Development Research Institute, PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gasfield Company, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development, Beijing, China
- 3PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gasfield Company, Chengdu, China
The fifth member of the Xujiahe Formation in the West Sichuan depression of the Sichuan Basin has developed high-quality source rocks and large-scale delta distributary channel sediments, which have good potential for hydrocarbon accumulation, but the reservoir characteristics and genesis remain unclear. Based on the cast thin section, cathodoluminescence, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, and porosity and permeability data, the characteristics and controlling factors of physical properties of the tight sandstone reservoir in the fifth member of the Xujiahe Member were analyzed. The results show that the sandstone in the fifth member of the Xujiahe Formation is mainly being feldspar lithic sandstone and lithic sandstone, with the reservoir space type mainly lithic intragranular dissolution pores. The average porosity and permeability of the reservoir are 2.03% and 0.22 Md, respectively, making it an ultra-low porosity and extra-low permeability reservoir. The reservoir has undergone strong compaction and calcite and clay cementation. The provenance controlled the initial mineral composition of the reservoir, resulting in high rock fragment content and low quartz content in the northwest area. This led to the physical properties of sandstones in the northwest area being generally worse than those in the southwest source area. The sandstone in the delta front underwater distributary channel has low carbonate cements and matrix content, resulting in relatively good reservoir physical properties. Overall, the lithic intragranular dissolution pores and microfractures are the key factors in improving the physical properties of reservoirs.
1 Introduction
Tight sandstone gas, a widely distributed unconventional petroleum resource with significant reserves, has emerged as a promising field in unconventional gas exploration and development (Dai et al., 2012; Jia et al., 2012; Zou et al., 2013). Tight sandstone reservoirs are typically characterized by porosity levels below 10% and in situ permeability of less than 0.1 mD (Law et al., 2004; Zou et al., 2010). Compared to conventional sandstone reservoirs, tight sandstone reservoirs are commonly characterized by poor reservoir properties, small pore throat, and strong heterogeneity, which pose challenges for the tight gas exploration and development (Law et al., 2004; Law et al., 2004; Wang G. et al., 2017). However, many of the successful exploration efforts indicate that local high-quality sandstones control high gas production within tight sandstone reservoirs (Law et al., 2004; Lai et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2020). Therefore, it is crucial to understand the factors affecting reservoir quality and predict the distribution patterns of high-quality sandstones within tight sandstone reservoirs.
Sandstone reservoir quality varies depending on sedimentation and diagenesis (Bjørlykke, 2014; Makeen et al., 2016; Okunuwadje et al., 2020). Sedimentary processes primarily determine the heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs through dual controls of provenance and sedimentary facies (Bjørlykke, 2014; Wang et al., 2020; Munir et al., 2025). Provenance influences the initial composition of the sandstone framework, with different source terrains providing varying proportions of quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments that inherently affect the reservoir’s diagenetic process and pore evolution (Rossi et al., 2002; Sun et al., 2022). Concurrently, sedimentary facies exert architectural control through hydrodynamic sorting processes, generating systematic variations in textural parameters including grain size distribution, sorting, and matrix content across different depositional environments (Bjørlykke, 2014; Yang et al., 2014; Jan et al., 2024). After deposition, diagenesis commonly accentuates the variations in porosity and permeability and significantly affects reservoir quality (Mansurbeg et al., 2008; Morad et al., 2010; Wang Y. et al., 2017). Intense compaction and cementation are commonly responsible for the deterioration of sandstone reservoir properties, while dissolution generally contribute to the formation of high-quality reservoirs (Bjørlykke et al., 1989; Ehrenberg, 1989; Lai et al., 2015; Lai et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2022). These complex diagenetic alterations often result in the formation of strong heterogeneous tight reservoirs.
The Upper Triassic Xujiahe sandstones in the Western Sichuan Depression (China) constitute an important and promising tight gas reservoir (Luo and Tong, 1989; Lai et al., 2015; Li et al., 2025). Previous researchers have conducted extensive studies on the Xujiahe tight reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression. However, they mainly focused on the second and fourth members of the Xujiahe Formation (Liu et al., 2014; Lai et al., 2015; Yu et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2024). Due to the high shale content and low porosity and permeability, the fifth member of the Xujiahe (Xu5) Formation has always been regarded as the main source rock layer for the overlying Jurassic reservoir and the cap rock for the underlying fourth member of the Xujiahe Formation (Liu et al., 2019; Zheng et al., 2019). With further exploration and development, several wells have obtained considerable industrial gas flow in the Xu5 member after fracturing, indicating that the Xu5 member in this area has great exploration potential (Shi et al., 2017; Tian et al., 2021). However, the main controlling factors affecting reservoir quality are unknown and the distribution characteristics of high-quality reservoirs remain unclear, limiting the further exploration and development of tight gas resources in this area. In this study, integrated analyses of thin section, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and cathodoluminescence (CL) are conducted to understand the reservoir characteristics, and the controlling factors affecting reservoir quality are discussed. The outcomes of this research may provide a reference for the exploration and development of tight gas reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression and similar tight sandstone reservoirs elsewhere.
2 Geological settings
The Sichuan Basin is a large superimposed hydrocarbon-bearing basin located in the southwest China (Deng et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020) (Figure 1). It consists of six secondary structural units: the western Sichuan depression (WSD), northern Sichuan depression (NSD), central Sichuan low-gentle slope (CSS), southwestern Sichuan low-gentle slope (SSS), southern Sichuan low-steep-fold zone (SSZ), and eastern Sichuan high-steep-fold zone (ESZ) (Dai et al., 2009; Pang et al., 2020) (Figure 1). Before the Late Triassic, the western Sichuan depression mainly recorded marine carbonate deposits in a passive continental margin (Shi et al., 2020; Deng et al., 2022). During the Late Triassic Indosinian orogeny, the western Sichuan depression emerged as a foreland basin due to tectonic compression within the Longmenshan thrust band in the northwest, and deposited thick continental clastic strata (Zheng et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021). Our study area is situated in the southwestern part of the western Sichuan depression which has rarely been focused on before (Figure 2).

Figure 1. Geographic location of the Sichuan Basin (A) and the location of the study area in the Sichuan Basin (B). WSD, the western Sichuan depression; NSD, northern Sichuan depression; CSS, central Sichuan low-gentle slope; SSS, southwestern Sichuan low-gentle slope; SSZ, southern Sichuan low-steep-fold zone; ESZ, eastern Sichuan high-steep-fold zone.

Figure 2. Stratigraphy Sequence of Xujiahe formation (modified from Yu et al., 2019).
The Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation is a typical layer for tight sandstone gas production in the Sichuan Basin (Lai et al., 2015). The Xujiahe Formation is a set of coal-bearing clastic strata with the maximum thickness of over 3000 m. The Xujiahe Formation can be subdivided into six members from the bottom to the top, namely, Xu6 to Xu1, predominantly characterized by deltaic and lacustrine sedimentary environments (Figure 2). Members Xu1, Xu3, and Xu5 mainly consist of shale and dark mudstone, with locally developed coal and sandstone packages (Liu et al., 2019; Zheng et al., 2019). Members Xu2 and Xu4 are dominated by deltaic sandstone with thin mudstone packages (Liu et al., 2019). The Xu6 member is absent due to denudation in the western Sichuan depression. This study focuses on the Xu5 tight sandstone reservoir which is mainly developed in a delta-front depositional environment.
3 Data and methods
A total of twenty-four regular core cylinders (2.5 cm in diameter and 5 cm in length) were collected from the Xu5 Formation in seven drilling wells (QX1, ZJ001-X3, H4, D3, D14, M6, and M7). Before all the tests, each core plug sample was initially washed with a mixture of trichloromethane and alcohol to eliminate residual oil and then dried at about 110 °C for 24 h under vacuum. Porosity and permeability were first measured by a JS100007 Helium Porosimeter and an A-10133 Gas Permeameter, respectively. Following that, casting thin section, CL, XRD, SEM, and fluid inclusion were conducted.
Casting thin sections were prepared under vacuum by impregnating them with blue epoxy to highlight pores. The sandstone’s detrital mineralogy and grain size were determined from thin sections by performing point counting on at least 300 points using a Leica DMLP polarizing microscope. The volumetric content of cements and pores were measured from thin sections photomicrographs following the methodology outlined by Wang et al. (2015). The CL observation was conducted using a CL8200 MK5 detector equipped with a Leica DM2500 optical microscope.
XRD analyses were performed using a X′ Pert PRO MPD X-ray diffractometer with Cu-Ka radiation at 40 Kv and 40 mA. The mineral phases were identified and quantified using RockQuan and ClayQuan softwares. The testing method, process and results meet national standards SY/T 5163-2018 with errors of less than 2%.
SEM observations were conducted with a Quanta 450 FEG scanning electron microscope to investigate the characteristics of authigenic clay minerals. The thin section was initially polished with Ar-ion and then coated with carbon to prevent electrostatic charges. The resolution can reach 1.2 nm with an accelerating voltage of 30 kV under high vacuum. The average resolution applied to the samples in this study is on the micrometer scale.
4 Results
4.1 Framework grain composition
The result of thin section observation shows that the Xu5 sandstone reservoir is dominated by litharenite and feldspar litharenite, accounting for 50% and 36.4%, respectively, and contains a small amount of lithic arkose, accounting for 13.6% (Figure 3A). The quartz in the detrital particles is mainly monocrystalline quartz, with content ranging from 19% to 75% averaging 38.79%. The feldspar content varies from 12% to 32% with an average of 23.1%, being plagioclase and potassium feldspar accounting for 15.2% and 7.8%, respectively. The rock fragments are the most abundant mineral with the content ranging from 14% to 68% and averaging at 43.63%. The rock fragments are composed of volcanic, metamorphic and sedimentary rock fragments with the average content of 10%, 14.4% and 17.21%, respectively (Figure 3B). The metamorphic rock fragments mainly consist of schist and quartzite, while the sedimentary rock fragments are mainly mudstone and carbonate debris. The interstitial materials are dominant by argillaceous matrix, carbonate and authigenic clays with an average content of 6.04%, 8.02% and 4.6%, respectively. The Xu5 tight sandstones are predominantly medium-grained and fine-grained sand with moderate sorting and subangular to subrounded roundness.
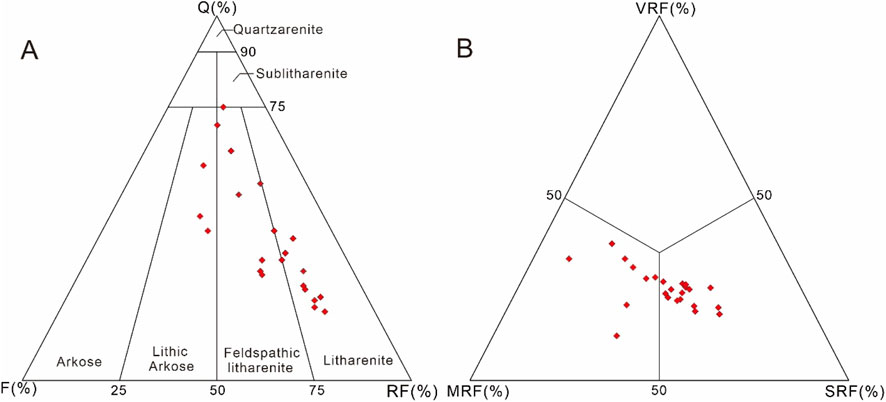
Figure 3. (A) Ternary diagram illustrating the framework compositions of the Xu5 sandstones. Q, quartz; F, feldspar; RF, rock fragments (based on Folk, 1974). (B) Ternary diagram showing rock fragments content of the Xu5 sandstones (based on Folk, 1974). VRF, volcanic rock fragments; MRF, metamorphic rock fragments; SRF, sedimentary rock fragments.
4.2 Porosity and permeability
The porosity measured from 24 sandstone samples ranges from 0.67% to 5.45%, with an average value of 7.49% (Figure 4A). The measured permeability varies from 0.13 mD to 0.77 mD and averaged at 0.22 mD (Figure 4B). Overall, the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs are very tight characterized by ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability. The physical properties of sandstone with different lithology are different. The average porosity of coarse sandstone, medium sandstone, fine sandstone and siltstone is 1.96%, 4.31%, 1.55% and 0.68%, respectively, and the average permeability is 0.25%, 0.46%, 0.16% and 0.15%, respectivel. The porosity and permeability of medium sandstone are the best, followed by coarse sandstone, while fine sandstone and siltstone are the worst (Figure 4C). The permeability shows a relatively good correlation with porosity y (Figure 4D), indicating that the reservoir space is dominated by the pore system, with only a few micro-fractures.
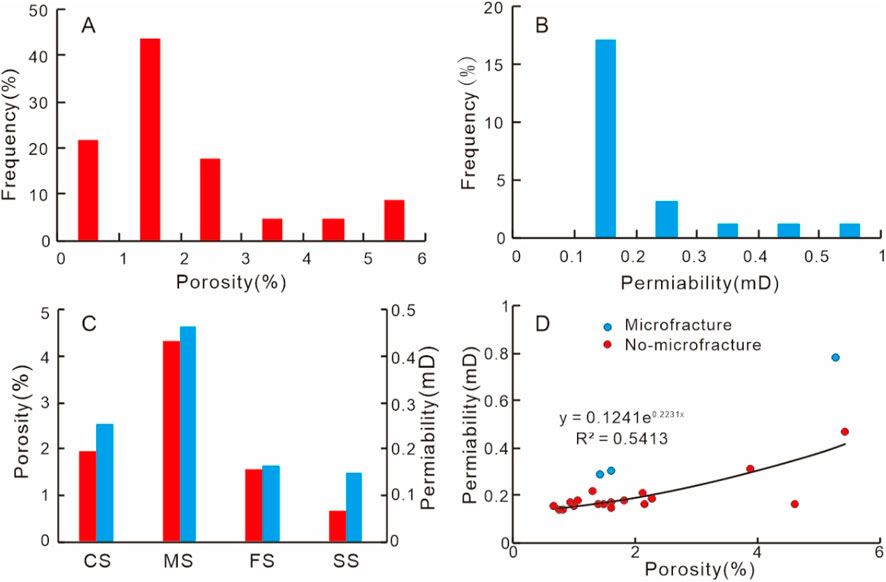
Figure 4. Characteristic of porosity and permeability of the Xu5 sandstones. (A) Histogram of porosity distribution; (B) Histogram of permeability distribution; (C) Histogram of porosity distribution of different lithology (CS, Coarse sandstone; MS, Medium sandstone; FS, Fine sandstone; SS: Siltstone); (D) Correlation of porosity and permeability.
4.3 Pore types
The analysis of cast thin sections and SEM reveals that the pore types of the Xu5 tight sandstone reservoirs primarily include residual intergranular pores, intergranular dissolution pores, intragranular dissolution pores, intercrystalline pores, and microfractures. Residual intergranular pores are preserved primary pores after compaction and cementation, typically displaying regular triangular or polygonal shapes (Figures 5A,C). However, due to intense diagenetic alteration in the study area, primary intergranular pores are relatively scarce. Intergranular dissolution pores are relatively common in the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs, formed by the dissolution of detrital grain edges, cements, or matrix, exhibiting irregular shapes and a wide range of pore size distributions (Figures 5A,B). Intragranular dissolution pores are well-developed in the study area. Given the high rock fragment and low feldspar content, these pores are predominantly lithic intragranular dissolution pores, generally presenting a honeycomb-like structure with isolated distribution and poor connectivity (Figures 5B,D–F). Intercrystalline pores are micropores with authigenic clay minerals such as kaolinite, chlorite, and illite, with relatively small pore sizes, among which kaolinite intercrystalline micropores are the most prevalent (Figure 5I). Microfractures can be categorized into tectonic fractures and diagenetic fractures. Tectonic fractures typically cut across multiple detrital grains and extend over several millimeters in length and tens of micrometers in width (Figure 5G). Diagenetic fractures include grain-edge fractures and intragranular fractures, mainly distributed along the edges or within grains such as quartz (Figure 5H).
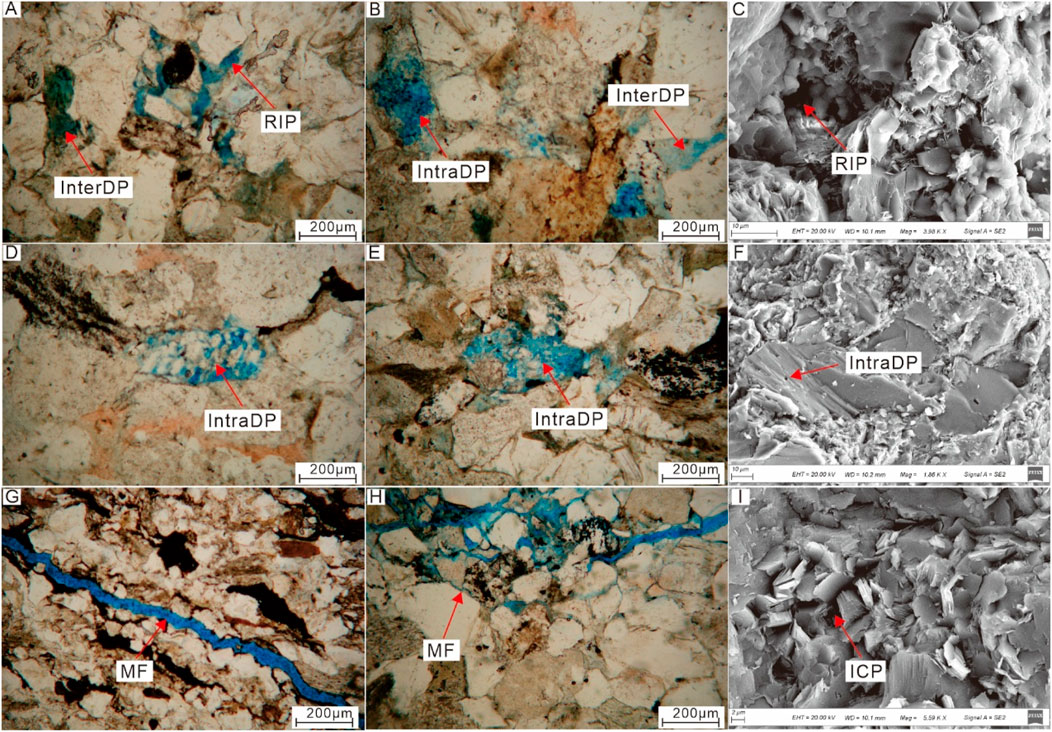
Figure 5. Thin section and SEM microphotographs showing characteristic pore types of Xu5 sandstone reservoir. (A) Intergranular dissolution pore (InterDP) and residual intergranular pore (RIP), well H4, 2,458.1 m; (B) Intergranular dissolution pore (InterDP) and intragranular dissolution pore (IntraDP), well M6, 3,372.27 m; (C) Residual intergranular pore, well M6, 3,361.45 m; (D) Intragranular dissolution pore within rock fragment, well M6, 3,372.27 m; (E) Intragranular dissolution pore within rock fragment, well H4, 2,458.1 m; (F) Intragranular dissolution pore within feldspar, well QX1, 3,271.06 m; (G) Tectonic microfracture (MF), well QX1, 3,285.88 m; (H) Grain-edge microfracture, well H4, 2,453.95 m; (I) Intercrystalline micropores (ICP) within kaolinite, well QX1, 3,273.05 m.
4.4 Diagenetic alterations
4.4.1 Compaction
Thin-section analysis reveals that the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs in the Western Sichuan Depression have undergone intense mechanical compaction. The detrital grains exhibit extremely tight packing, predominantly showing line and concave-convex grain contacts (Figures 6A,B). Compressional deformation and pseudomatrix formation are observed in micas and ductile rock fragments, which fill pore spaces and further reduce reservoir capacity (Figure 6C). Intragranular fractures frequently occur within quartz particles (Figure 6D). The scarcity of concave-convex contacts and absence of stylolitic structures in the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs suggest limited chemical compaction during diagenesis.
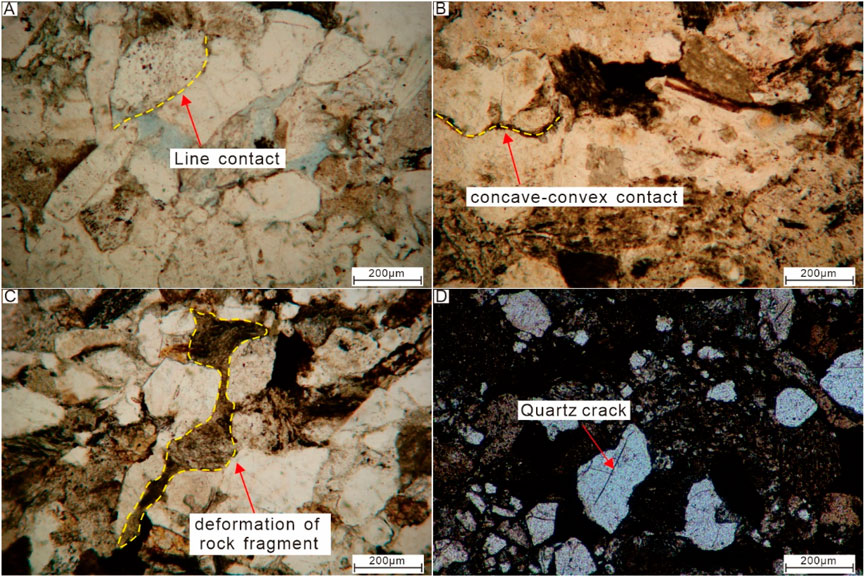

Figure 6. Thin section photomicrograph showing compaction features of Xu5 sandstones. (A) Line grain contact, well QX1, 3,281.59 m; (B) Concave-convex grain contact, well QX1, 3,271.06 m; (C) Deformation of ductile rock fragment, well M7, 3,252.55 m; (D) Cracks within quartz grain, well QX1, 3,274.05 m.
4.4.2 Cements
The Xu5 tight sandstones exhibit strong cementation with total cement contents ranging from 6% to 33% (average 13.27%). The primary cements in the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs include carbonates, authigenic clay minerals, and minor silica. Carbonate cementation prevalent, with contents reaching up to 29% and averaging 8.67%. The carbonate cements are mostly calcite (avg. 8.02%), with dolomite being less common (avg. 0.54%). Early-stage calcite cements fill large intergranular pores and show an orange-red color under CL with poikilotopic textures (Figures 7A,B). While this cementation reduces primary porosity significantly, it prevents compaction and maintains grain contacts as floating and point grain textures. Late-stage calcite cements typically replace feldspar and fill dissolution pores in feldspars and lithic fragments, further densifying the sandstone (Figure 7B). Dolomite appears as euhedral rhombohedra, mainly filling intergranular pores and deteriorating reservoir quality (Figures 7C,D).
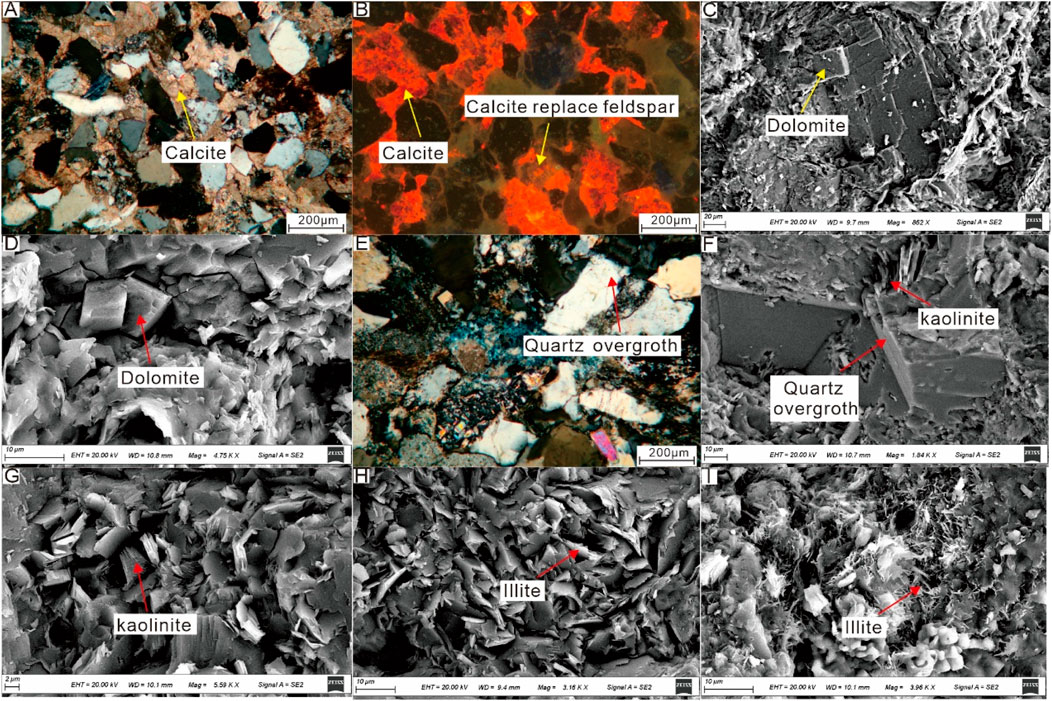
Figure 7. Photomicrographs of sandstones showing cementation features from thin sections, CL and SEM analyses. (A) Thin section photomicrograph showing calcite cements, well H4, 2,525.31 m; (B) CL photomicrograph showing pervasive calcite cementation and replacement of feldspar by calcite, well M6, 3,372.27 m; (C) SEM photomicrograph showing dolomite, well H4, 2,528.11 m; (D) SEM photomicrograph showing dolomite, well QX1, 3,271.58 m; (E) Thin section photomicrograph showing quartz overgrowth, well H4, 2,458.1 m; (F) SEM photomicrograph showing quartz overgrowth and kaolinite, well D3, 2,563.6 m; (G) Authigenic kaolinite, well QX1, 3,273.05 m; (H): Flaky illite, well ZJ001-X3, 2,973.7 m; (I): Filamentous illite, well H4, 2,528.11 m.
Silica cements are rare in the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs with the average content of 0.26%. Quartz overgrowths are occasionally seen, often linked with authigenic kaolinite (Figures 7E,F). Due to low quartz and feldspar content in the study area, pressure dissolution and feldspar dissolution are limited, resulting in inadequate silica sources. As a result, silica cementation has a miniml impact on reservoir quality.
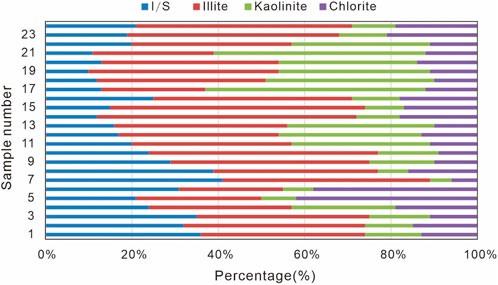
The Xu5 tight sandstones contain authigenic clay minerals, dominated by illite and kaolinite, with average contents of 3.06% and 5.72%, respectively, along with illite-smectite mixed-layer clays (avg. 3.13%) and chlorite (avg. 2.04%) (Figure 8). Petrographic analysis reveals that kaolinite typically occurs as pore-filling booklets and vermicular aggregates, which is formed primarily through feldspar dissolution under acidic conditions and often associated with quartz overgrowths (Figures 7F,G). This pore-filling kaolinite significantly reduces reservoir porosity and permeability. Illite exhibits diverse morphologies including hair-like filaments, flakes, curled sheets, and pore-bridging structures (Figures 7H,I), originating either from detrital mineral alteration or through diagenetic transformation of kaolinite and chlorite. The pervasive pore-bridging and filamentous illite particularly impairs pore connectivity and fluid flow capacity.
4.4.3 Dissolution
Petrographic observations show that dissolution processes are highly developed in the Xu5 Member sandstone reservoirs, primarily involving the dissolution of rock fragments and feldspar grains under acidic fluid conditions. Quantitative analysis reveals that dissolution porosity constitutes 0.5%–1.5% of the total rock volume, with an average value of 0.65%. The dissolution of unstable components in the rock fragments typically forms irregular honeycomb-shaped pores (Figures 5D,E), while feldspar grains preferentially dissolve along cleavage planes (Figure 5F). The dissolution of carbonate cements is not observed in the Xu5 reservoirs. Dissolution processes can potentially improve reservoir quality by generating secondary porosity.
5 Discussions
5.1 Sedimentary controls on reservoir quality
Sedimentary processes primarily control the heterogeneity of tight sandstone reservoirs through two main factors: provenance and sedimentary facies. Provenance and sedimentary facies affect the mineral composition and texture of sediments, which in turn determine the diagenetic type and intensity. These factors ultimately result in variations in reservoir properties.
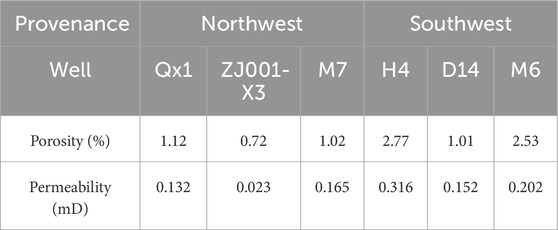
The Xu5 sediments in the study area are primarily derived from the Longmenshan fault zone in the northwest and the Kangdian Oldland in the southwest (Shi et al., 2011; Yu, 2016). The Longmenshan provenance area is characterized by abundant heavy minerals such as rutile and titanite, along with a relatively high carbonate rock fragment content (Yao,2021). Influenced by the Longmenshan source, the sandstone reservoirs in the northern study area exhibit higher rock fragment content but lower quartz content, with lithic sandstone being the dominant rock type (Figure 9A). The rock fragments are dominated by sedimentary rock fragments such as mudstone and carbonate clasts. In contrast, the Kangdian Oldland provenance contains heavy minerals such as zircon, tourmaline, and pyroxene (Yao,2021). Due to the long transport distance and slow but sustained sediment supply, the sandstone reservoirs in the southern study area have higher quartz and feldspar content but lower lithic fragment content (Figure 9A). The dominant rock types are feldspathic litharenite and lithic arkose, with an increased proportion of metamorphic and volcanic rock fragments (Figure 9B). These provenance differences result in distinct reservoir properties between the northern and southern regions. The sandstone reservoirs in the northern wells (QX1, ZJ001-X3, and M7) generally exhibit lower porosity and permeability compared to those in the southern wells (H4, D14, and M6) (Table 1).

Figure 9. The differences in detrital composition of Xu5 sandstones from different source areas. (A) Framework grain composition; (B) Rock fragment composition.
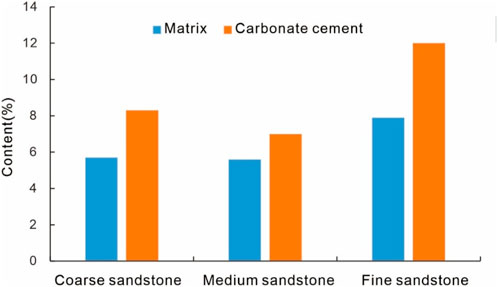
Statistical analysis reveals a significant negative correlation between porosity/permeability and matrix content in the Xu-5 Member sandstones, demonstrating that hydrodynamic conditions during deposition represent a crucial controlling factor for reservoir quality (Figure 10). The Xu5 sandstone reservoirs in the study area are mainly delta-front deposits. The medium-to coarse-grained sandstones deposited in high-energy hydrodynamic environments such as subaqueous distributary channels and mouth bars within the delta front, exhibiting good sorting, low matrix content, low carbonate cement and favorable initial physical properties. In contrast, fine-grained sandstones and siltstones deposited in low-energy hydrodynamic settings such as distal bars and interdistributary bays, and contain higher matrix and carbonate cement content, resulting in inferior reservoir quality (Figure 11).
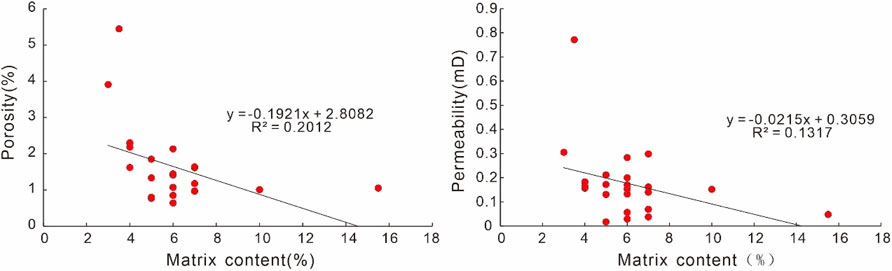
Figure 10. Cross-plots showing the relationship between the matrix content and porosity and permeability.
5.2 Diagenetic controls on reservoir quality
Diagenesis controls the entire pore evolution process in reservoirs and serves as a key controlling factor for reservoir quality. Based on thin-section and SEM analyses, changes in porosity resulting from different diagenetic processes are quantitatively calculated. The quantitative porosity loss through mechanical compaction (COPL), porosity loss by cementation (CEPL) and porosity increase by dissolution (DPI) can be calculated by following equations:
where OP is the original (depositional) porosity, which is assumed as 40% in this study; C is the total cement content; φpm represents the thin section porosity of the intergranular pores; φp is the core measured porosity; φt is total thin section porosity; φd represents the thin section porosity of dissolution pores.
Calculated result shows that compaction-induced porosity loss exceeds 50% of the initial porosity in nearly all samples, with an average of 65.2%, (Equation 1) demonstrating that compaction is a regionally pervasive diagenetic process and the primary cause of porosity reduction in Xu5 sandstone reservoirs (Figure 12). The lithic-rich sandstone derived from northwestern provenance tend to undergo more intense compaction with the porosity loss rate of 68.4%, while that of sandstone from southwestern provenance is 61.8% (Figure 12A). The intensity of compaction is closely related to detrital composition of sandstone from different provenances. Measured porosity and permeability show positive correlation with quartz and rock fragment content, indicating that higher quartz content but lower fragment content corresponds to better reservoir properties (Figure 13). This occurs because quartz can enhance sandstone’s compressibility as a rigid mineral, thereby mitigating the loss of primary intergranular porosity. In contrast, the Xu5 sandstone reservoirs contain abundant ductile rock fragments such as mudstone and schist clasts, which are prone to bending and pseudomatrix deformation under compaction. These processes significantly reduce intergranular porosity and degrade flow capacity.

Figure 12. Plot showing the effects of compaction and cementation on porosity reduction of sandstones from different provenances (A) and different microfacies (B) according to the corrected diagram proposed by Ehrenberg (1989). DC: Underwater distributary channel; MB: Mouth bar; SS: Sheet sand; DB: Underwater distributary bar.
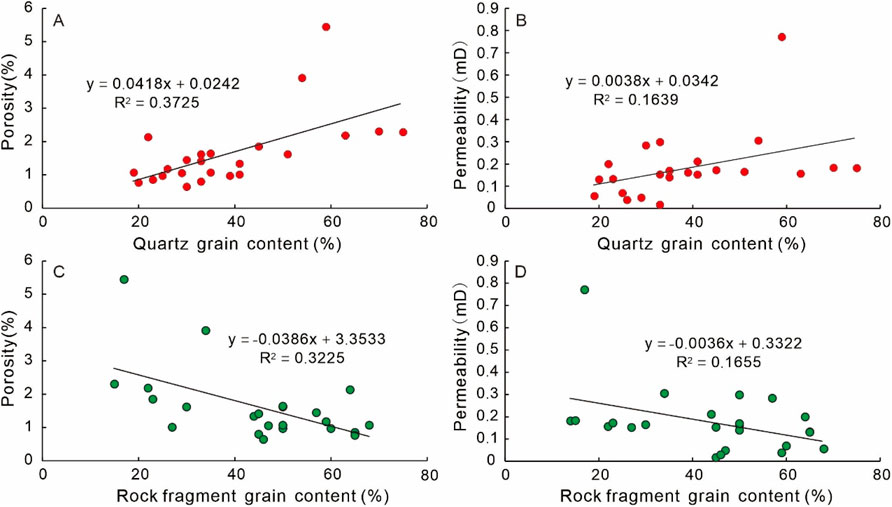
Figure 13. Cross-plots showing the relationship between abundance of quartz grain and (A) porosity and (B) permeability, and relationship between abundance of rock fragment grain and (C) porosity and (D) permeability.
Cementation are critical factor responsible for the deterioration of reservoir quality in the Xu5 sandstones, resulting in an average porosity reduction rate of 33.4% (Equation 2). The porosity loss by cementation of sandstone reservoir from different provenances has no obvious differences, but varies as a function of the sedimentary environment (Figure 12). The Xu5 sandstones exhibit notably high abundance of carbonate cement, which shows a significant negative correlation with both porosity and permeability (Figure 14). Statistical analyses further reveal that sandstones with carbonate cement contents exceeding 15% typically exhibit permeability values below 0.1 mD, serving as a key factor in the development of ultra-low permeability characteristics (Figure 14). Carbonate cement abundance is closely related to the sedimentary microfacies. The thin-bedded fine-grained sandstones in underwater distributary bays and sheet sands generally tend to be subjected to more intense cementation, while sandstones in underwater distributary channels and mouth bars typically exhibit lower carbonate cement contents (Figure 12B). It is worth noting that early carbonate cements retard compaction and preserve the pore space by stabilizing gain pack and improving the resistance of rocks to compression (Figures 7A,B). Furthermore, authigenic kaolinite and illite formed during the middle to late diagenetic stages progressively infill the remaining pore spaces and obstruct pore throats, significantly deteriorating reservoir properties (Figure 15).
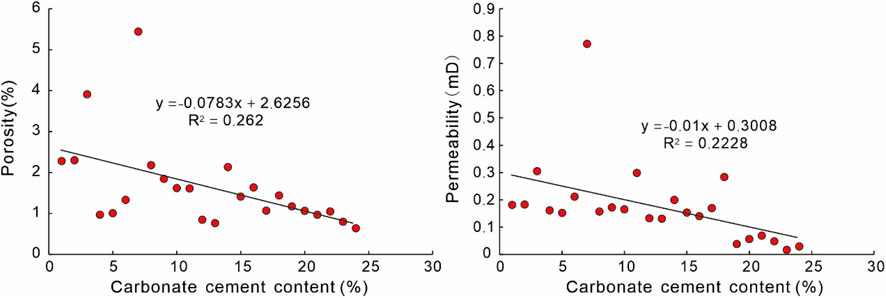
Figure 14. Cross-plots showing the relationship between the abundance of carbonate cement and porosity and permeability.
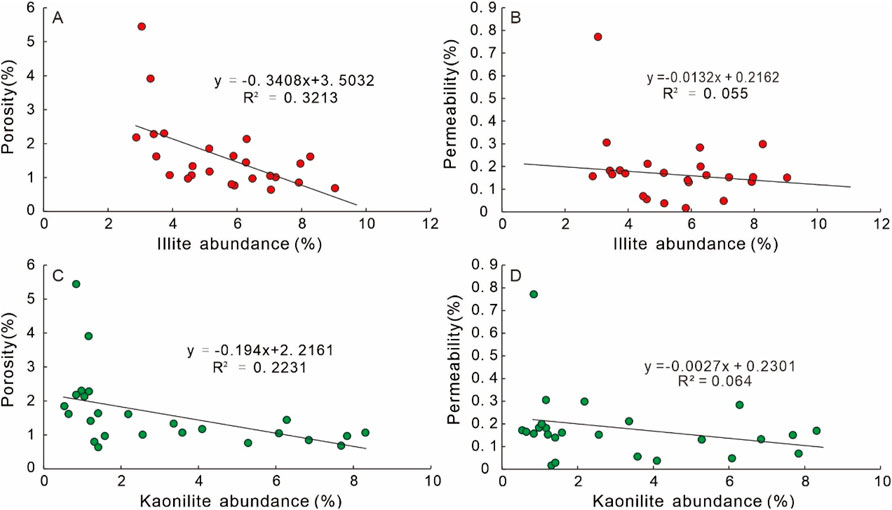
Figure 15. Cross-plots showing the relationship between abundance of illite and (A) porosity and (B) permeability, and relationship between abundance of kaolinite and (C) porosity and (D) permeability.
The dissolution effects induced by acidic fluids play a crucial role in enhancing porosity development within sandstone reservoirs, with the porosity increase rate of 3.1% (Equation 3). In the Xu5 reservoir, the extensive thick shale intervals provide abundant organic acids during the middle diagenetic stage when organic matter reaches thermal maturity. These acidic fluids trigger intensive dissolution of framework minerals (e.g., feldspars and rock fragments), generating substantial secondary porosity that significantly improves reservoir quality. Statistical analyses reveal a distinct positive correlation between porosity/permeability values and dissolution porosity in the Xu5 sandstones, demonstrating that dissolution processes markedly enhance reservoir properties, particularly porosity development (Figure 16). Compared to northwestern provenance, sandstones from southwestern provenance exhibit more intensive dissolution alteration with the porosity increase rate of 3.6%, while that of sandstone from southwestern provenance is 2.4%. This occurs because lithic-rich sandstones from the northwestern provenance experience more rapid loss of intergranular pores, which act as the main pathways for dissolution during the burial. The presence of microfractures especially tectonic microfractures further facilitates these dissolution processes by providing effective migration pathways for acidic fluids, thereby promoting more extensive mineral dissolution and secondary porosity formation (Figures 4D, 5H).
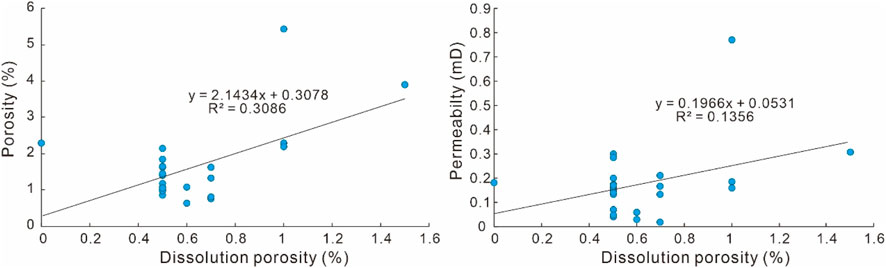
Figure 16. Cross-plots showing the relationship between the dissolution porosity and measured porosity and permeability.
6 Conclusion
1. The Xu5 sandstones display ultra-low porosity and extremely low permeability, with average values of 2.03% and 0.22 mD, respectively. These reservoirs are mainly made up of lithic sandstones and feldspathic lithic sandstones. The pore systems in the Xu5 sandstones are primarily characterized by intergranular dissolution pores, intragranular dissolution pores, and intercrystalline pores, with microfractures being rare.
2. The initial mineral composition of Xu5 sandstone reservoirs is controlled by provenance. Sandstones from the northwestern source area have higher rock fragment and lower quartz content, resulting in inferior reservoir properties compared to those from the southwestern source area. Medium-to coarse-grained sandstones deposited in delta-front subaqueous distributary channels have better reservoir physical properties due to their lower matrix content and reduced carbonate cementation.
3. Compaction is the main factor responsible for the densification of Xu5 Member sandstones, while carbonate cementation significantly degrades reservoir quality. The development of rock fragment dissolution pores and microfractures are crucial positive factors that enhance reservoir properties.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XiW: Writing – original draft. ZW: Writing – review and editing. LL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. HM: Writing – original draft, Investigation. ZS: Writing – original draft, Data curation. SL: Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. AZ: Writing – original draft. XuW: Investigation, Writing – original draft. KY: Investigation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was financially supported by the PetroChina Scientific Research and technological project “Main controlling factors and domain evaluation of different types of large gas fields” (No. 2021DJ0605).
Conflict of interest
Authors XiW, LL, AZ, and KY were employed by PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gasfield Company. Authors HM, ZS, SL, and XuW were employed by PetroChina Southwest Oil and Gasfield Company.
Author ZW was employed by PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development.
The authors declare that this study received funding from PetroChina. The funder had the following involvement in the study: the funder provided drilling cores and basic data.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bjørlykke, K. (2014). Relationships between depositional environments, burial history and rock properties. Some principal aspects of diagenetic process in sedimentary basins. Sediment. Geol. 301, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2013.12.002
Bjørlykke, K., Ramm, M., and Saigal, G. C. (1989). Sandstone diagenesis and porosity modification during basin evolution. Geol. Rundsch. 78, 243–268. doi:10.1007/bf01988363
Dai, J., Ni, Y., Zou, C., Tao, S., Hu, G., Hu, A., et al. (2009). Stable carbon isotopes of alkane gases from the Xujiahe coal measures and implication for gas-source correlation in the Sichuan Basin, SW China. Org. Geochem. 40, 638–646. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.01.012
Dai, J., Ni, Y., and Wu, X. (2012). Tight gas in China and its significance in exploration and exploitation. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 39, 277–284. doi:10.1016/s1876-3804(12)60043-3
Deng, T., Li, Y., Wang, Z., Yu, Q., Dong, S., Yan, L., et al. (2019). Geochemical characteristics and organic matter enrichment mechanism of black shale in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in the Sichuan basin: implications for paleoweathering, provenance and tectonic setting. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 109, 698–716. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.057
Deng, J., Liu, M., Ji, Y., Tang, D., Zeng, Q., Song, L., et al. (2022). Controlling factors of tight sandstone gas accumulation and enrichment in the slope zone of foreland basins: the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation in Western Sichuan foreland basin, China. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 214, 110474. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110474
Ehrenberg, S. N. (1989). Assessing the relative importance of compaction processes and cementation to reduction of porosity in sandstones: discussion; compaction and porosity evolution of Pliocene sandstones, Ventura basin, California: discussion. AAPG Bull. 73, 1274–1276. doi:10.1306/44b4aa1e-170a-11d7-8645000102c1865d
Jan, J. A., Shah, M. M., Rahim, H. U., Iqbal, S., Jahandad, S., Jamil, M., et al. (2024). Depositional and diagenetic studies of clastic reservoirs zone in the Cretaceous lower Goru formation, Sindh monocline, south Pakistan. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 133, 115. doi:10.1007/s12040-024-02333-z
Jia, C., Zou, C., Li, J., Li, D., and Zheng, M. (2012). Assessment criteria, main types, basic features and resource prospects of the tight oil in China. Acta Pet. Sin. 33, 343–350. doi:10.7623/syxb201203001
Lai, J., Wang, G., Ran, Y., and Zhou, Z. (2015). Predictive distribution of high-quality reservoirs of tight gas sandstones by linking diagenesis to depositional facies: evidence from Xu-2 sandstones in the penglai area of the central sichuan Basin, China. J. Nat. Gas. Sci. Eng. 23, 97–111. doi:10.1016/j.jngse.2015.01.026
Lai, J., Wang, G. W., Ran, Y., Zhou, Z. L., and Cui, Y. F. (2016). Impact of diagenesis on the reservoir quality of tight oil sandstones: the case of Upper Triassic Yanchang formation Chang 7 oil layers in Ordos basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 145, 54–65. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2016.03.009
Law, B. E., Curtis, S. K. W., Cluff, R. M., and Robinson, J. W. (2004). Factors controlling prolific gas production from low-permeability sandstone reservoirs: implications for resource assessment, prospect development, and risk analysis. AAPG Bull. 88, 1083–1121. doi:10.1306/03250403051
Li, Y., Zhang, Z., and Wu, X. (2025). Identifying gas and water in low-resistivity fractured-porous gas reservoirs of Xujiahe formation, Xinchang area, western Sichuan basin. Nat. Gas Explor. Dev. 48 (2), 14–25. doi:10.12055/gaskk.issn.1673-3177.2025.02.002
Liu, S. B., Huang, S. J., Shen, Z. M., Lv, Z. X., and Song, R. C. (2014). Diagenetic fluid evolution and water-rock interaction model of carbonate cements in sandstone: an example from the reservoir sandstone of the fourth member of the Xujiahe formation of the Xiaoquan-Fenggu area, Sichuan Province, China. Sci. China (Earth Sci.) 57 (5), 1077–1092. doi:10.1007/s11430-014-4851-2
Liu, Y., Hu, W., Cao, J., Wang, X., Zhu, F., Tang, Q., et al. (2019). Fluid-rock interaction and its effects on the Upper Triassic tight sandstones in the sichuan Basin, China: insights from petrographic and geochemical study of carbonate cements. Sediment. Geol. 383, 121–135. doi:10.1016/j.sedgeo.2019.01.012
Liu, J., Cao, J., Hu, G., Wang, Y., Yang, R., and Liao, Z. (2020). Water-level and redox fluctuations in a sichuan basin lacustrine system coincident with the Toarcian OAE. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 558, 109942. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109942
Liu, K., Wang, R., Shi, W., Travé, A., Martín-Martín, J., Baqués, V., et al. (2022). Diagenetic controls on reservoir quality and heterogeneity of the Triassic chang 8 tight sandstones in the binchang area (Ordos basin, China). Mar. Petroleum Geol. 146, 105974. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105974
Luo, Z., and Tong, C. (1989). Plate tectonics and petroliferous basin in China. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press.
Makeen, Y. M., Abdullah, W. H., Ayinla, H. A., Hakimi, M. H., and Sia, S. (2016). Sedimentology, diagenesis and reservoir quality of the upper abu gabra formation sandstones in the Fula Sub-basin, Muglad Basin, Sudan. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 77, 1227–1242. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.08.015
Mansurbeg, H., Morad, S., Salem, A., Marfil, R., El-Ghali, M. A. K., Nystuen, J. P., et al. (2008). Diagenesis and reservoir quality evolution of palaeocene deep-water, marine sandstones, the Shetland- Faroes Basin, British continental shelf. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 25, 514–543. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2007.07.012
Morad, S., Al-Ramadan, K., Ketzer, J. M., and Ros, L. F. D. (2010). The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs: a review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy. AAPG Bull. 94, 1267–1309. doi:10.1306/04211009178
Munir, M. N., Zafar, M., Ehsan, M., Chen, R., Abdelrahman, K., Ullah, J., et al. (2025). Diagenetic and mineralogical impacts on clastic reservoir; A case study from the lower Indus Basin, Pakistan. J. Asian Earth Sci. 283, 106539. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2025.106539
Okunuwadje, S., MacDonald, D., and Bowden, S. (2020). Diagenetic and reservoir quality variation of Miocene sandstone reservoir analogues from three basins of southern California, USA. Earth Sci. 31 (5), 930–949. doi:10.1007/s12583-020-1289-7
Pang, X., Zheng, T., Ma, X., Zheng, D., Wang, W., Wang, X., et al. (2020). Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion features of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation source rocks and their controlling effects on hydrocarbon accumulation in the Sichuan basin, Central China. Geol. J. 55, 4977–4996. doi:10.1002/gj.3653
Rossi, C., Kälin, O., Arribas, J., and Tortosa, A. (2002). Diagenesis, provenance and reservoir quality of Triassic TAGI sandstones from Ourhoud field, Berkine (Ghadames) Basin, Algeria. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 19 (2), 117–142. doi:10.1016/S0264-8172(02)00004-1
Shi, Z., Wang, X., and Wu, C. (2011). The heavy minerals and provenances of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation in Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas. Geosci. 22 (4), 619–627. doi:10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2011.04.618
Shi, H., Yang, K., and Wang, T. (2017). Characteristics and controlling factors of tight sandstone and shale reservoirs of the fifth member of Xujiahe formation in the Western sichuan depression. Lithol. Reserv. 29 (4), 38–46. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2017.04.005
Shi, C., Cao, J., Selby, D., Tan, X., Luo, B., and Hu, W. (2020). Hydrocarbon evolution of the over-mature sinian dengying reservoir of the neoproterozoic sichuan basin, China: insights from Re–Os geochronology. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 122, 104726. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104726
Sun, X., Tan, X., Tang, Y., Tian, J., Lei, T., Wang, J., et al. (2022). Diagenetic–porosity evolution and reservoir evaluation in multiprovenance tight sandstones: insight from the Lower Shihezi formation in Hangjinqi area, northern Ordos Basin. Lithosphere 2022 (Special 13), 6411000. doi:10.2113/2022/6411000
Tian, Y., Zhu, H., Ye, S., Zhuo, J., Xie, R., and Xiong, J. (2021). Main controlling factors and models of hydrocarbon accumulation in the source of Western sichuan Depression: taking Xu 5th member of xujiahe formation in Xiaoquan-Fenggu structural belt as an example. Earth Sci. 46 (7), 2494–2506. doi:10.3799/dqkx.2020.257
Wang, G., Li, P., Hao, F., Zou, H., Zhang, L., and Yu, X. (2015). Impact of sedimentology, diagenesis, and solid bitumen on the development of a tight gas grainstone reservoir in the feixianguan formation, Jiannan area, China: implications for gas exploration in tight carbonate reservoirs. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 64, 250–265. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.02.045
Wang, G., Chang, X., Yin, W., Li, Y., and Song, T. (2017). Impact of diagenesis on reservoir quality and heterogeneity of the Upper Triassic Chang 8 tight oil sandstones in the Zhenjing area, Ordos Basin, China. China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 83, 84–96. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.03.008
Wang, Y., Liu, L., Li, S., Ji, H., Xu, Z., Luo, Z., et al. (2017). The forming mechanism and process of tight oil sand reservoirs: a case study of Chang 8 oil layers of the Upper Triassic Yanchang formation in the western Jiyuan area of the Ordos basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 158, 29–46. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2017.08.026
Wang, E., Liu, G., Pang, X., Wu, Z., Li, C., Bai, H., et al. (2020). Sedimentology, diagenetic evolution, and sweet spot prediction of tight sandstone reservoirs: a case study of the third member of the upper Paleogene Shahejie formation, Nanpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 186, 106718. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106718
Yang, R. C., Fang, A. P., Van Loon, A. J., Han, Z. Z., and Wang, X. P. (2014). Depositional and diagenetic controls on sandstone reservoirs with low porosity and low permeability in the eastern sulige gas field, China. Acta Geol. Sin. Engl. 88, 1513–1534. doi:10.1111/1755-6724.12315
Yang, P., Zhang, L., Liu, K., Cao, B., Gao, J., and Qiu, G. (2021). Diagenetic history and reservoir evolution of tight sandstones in the second member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation, western Sichuan Basin, China. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 201, 108451. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108451
Yang, Q., Xu, S., Yuan, Q., and Zhang, Y. (2024). Microscopic characteristics and sedimentary paleoenvironment of tight sandstone: examples from Xujiahe 3 and Xujiahe 2 members, Zitong-Qiulin area, northwestern Sichuan Basin. Nat. Gas Explor. Dev. 47 (5), 1–8. doi:10.12055/gaskk.issn.1673-3177.2024.05.001
Yao, W. (2021). Reservoir control of tight sandstone provenance system in Xujiahe formation, Sichuan basin. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 40 (5), 224–230. doi:10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0036
Yu, S. (2016). Provenance analysis of Late Triassic Xujiahe formation in western sichuan basin and its tectonic significance. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Yu, Y., Lin, L., Zhai, C., Chen, H., Wang, W., Li, Y., et al. (2019). Impacts of lithologic characteristics and diagenesis on reservoir quality of the 4th member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation tight gas sandstones in the western Sichuan basin, southwest China. China. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 107, 1–19. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.04.040
Zheng, D., Pang, X., Ma, X., Li, C., Zheng, T., and Zhou, L. (2019). Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of the source rocks in the third member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe formation and its effect on conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resource potential in the Sichuan basin. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 109, 175–192. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.014
Zou, C., Zhang, G., Tao, S., Hu, S., Li, X., Li, J., et al. (2010). Geological features, major discoveries and unconventional petroleum geology in the global petroleum exploration. Petrol. Explor. Dev. 37, 129–145. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(10)60021-3
Zou, C. N., Yang, Z., Tao, S. Z., Yuan, X. J., Zhu, R. K., Hou, L. H., et al. (2013). Continuous hydrocarbon accumulation over a large area as a distinguishing characteristic of unconventional petroleum: the Ordos Basin, north-central China. Earth Sci. Rev. 126, 358–369. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.08.006
Keywords: tight sandstone, digenesis, reservoir quality, Xujiahe formation, western Sichuan depression
Citation: Wang X, Wang Z, Li L, Ma H, Sun Z, Li S, Zhang A, Wang X and Yang K (2025) Characteristics and controlling factors of the Triassic Xu5 tight sandstone reservoirs, Western Sichuan depression, China. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1635249. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1635249
Received: 26 May 2025; Accepted: 27 August 2025;
Published: 24 September 2025.
Edited by:
Ruyue Wang, State Key Laboratory of Shale Oil and Gas Enrichment Mechanisms and Efficient Development, ChinaReviewed by:
Hongjian Zhu, Yanshan University, ChinaShaoke Feng, SINOPEC, China
Hamad Ur Rahim, Pakistan Museum of Natural History, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Wang, Li, Ma, Sun, Li, Zhang, Wang and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhihong Wang, d2FuZ3poaWhvbmc2OUBwZXRyb2NoaW5hLmNvbS5jbg==
 Xiaojuan Wang1
Xiaojuan Wang1 Ke Yang
Ke Yang