- 1Institute of Geophysics, Space Science and Astronomy, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- 2School of Ocean and Earth Science, University of Southampton, Southampton, United Kingdom
- 3Dipartimento di Scienze Della Terra, Università degli Studi di Firenze, Florence, Italy
The seismotectonics of the Northwestern (NW) Ethiopian plateau and the adjacent rift flanks were studied using local earthquake data recorded by broadband seismic networks. This include stations from the Ethiopian plateau network (2014–2016) as well as seven permanent Ethiopian seismic stations. A total of 800 earthquakes, with magnitudes ranging from ML∼1.1 to 4.6 were located. Seismicity clustered beneath the NW plateau, Fentale volcano, and the Guraghe border fault of the Main Ethiopian Rift (MER). The detected seismic activity beneath the NW plateau is the first observation ever made in the area, supporting recent tomographic investigation results indicating the presence of partial melt and magmatic activity. This result further show that the NW plateau exhibits greater tectonic activity relative to the southeasten plateau of the MER. Moment tensor inversion is conducted using ISOLA software for few earthquakes in the magnitude range Mw 3.7 to 4.6. We obtained a dominantly normal faulting earthquake of magnitude 3.7 at 14 km depth beneath the NW plateau implying extensional tectonics. We interpret that active thermal degradation and crustal heterogeneity contributes to the seismicity beneath the NW plateau, where cumulative observations may indicate distributed extension.
1 Introduction
The Main Ethiopian Rift (MER) is located at the northern end of the East African Rift System (EARS) which is the longest continental rift system on Earth. The MER is known for its volcanic activity and serves as a unique location where magma-rich continental rifting occurs in a young rift setting (Corti, 2009; Ebinger and Casey, 2001; Keir et al., 2006a; Pik et al., 1998; Wolfenden et al., 2004). Previous geological and geophysical studies show that the majority of extension occurs in the MER (e.g., Ebinger and Casey, 2001), with the limited micro-seismicity records showing that the majority of earthquakes are at the rift margins or within the rift (Ayele and Kulhánek, 1997). However, seismic station coverage was previously very sparse on the NW plateau meaning that it is unclear whether the deforming region is solely restricted to the rift.
The MER developed during the Miocene to the present, representing the most recent extensional arm of a triple junction located in central Afar (Maestrelli et al., 2024; Corti, 2009; Wolfenden et al., 2004). The MER accommodates most of the separation between the Nubian and Somalian plates, where GNSS data show a spreading rate of ∼5 mm/yr in an ∼E-W direction (Birhanu et al., 2016; Knappe et al., 2020; Figure 1). However, these data do also indicate that ∼2 mm/yr of the extension is distributed across the NW plateau, hinting at a potentially complex and distributed pattern of strain accumulation (Birhanu et al., 2016; Knappe et al., 2020).
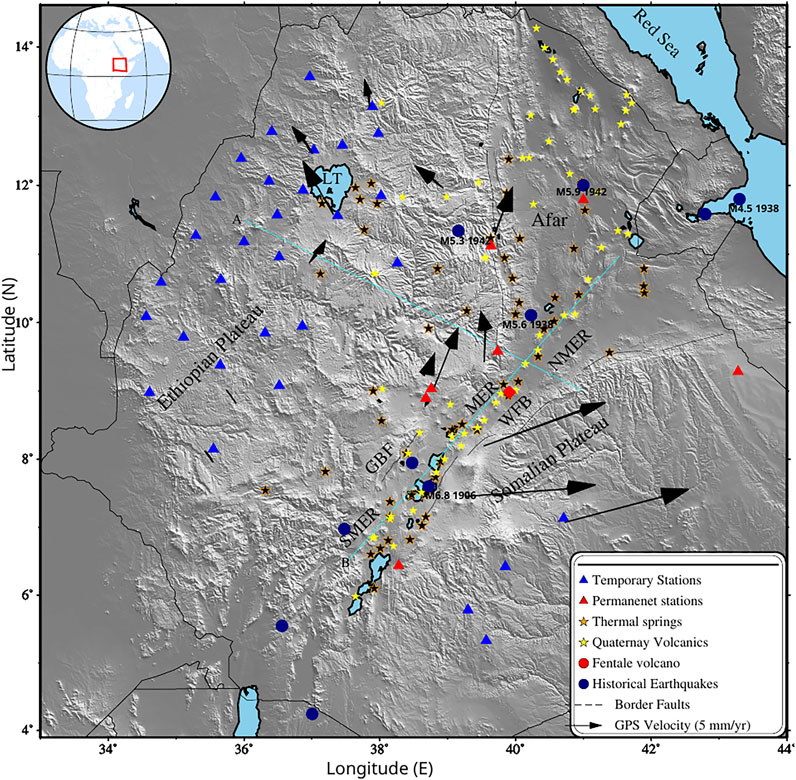
Figure 1. Topographic map (DEM) of the Horn of Africa region where blue triangles represent broadband seismic network consisiting of 30 stations and the red ones are seven permanent Ethiopian stations used in the study. The orange and yellow stars show thermal springs (Keir et al., 2009) and Quaternary-Recent volcanics respectively, the red circle marks Fentale Volcano, the navy blue circles represents historical earthquakes, with major events identified in the text, each labeled by magnitude and year beneath the respective circle. The black vectors show Nubian-fixed reference frame velocities with limits (after Knappe et al., 2020), the broken lines are border faults with GBF, Guraghe Border Fault; MER, Main Ethiopian Rift; NMER, Northern Main Ethiopian Rift; SMER, Southern Main Ethiopian Rift; WFB, Wonji Fault Belt; LT, Lake Tana, the two light cyan lines ,(A and B) are profiles. The inset map shows the location of study area.
Rifting in the region occurs above a broad hotspot where the upper mantle beneath Ethiopia exhibit some of the slowest seismic wave speeds globally, with P-waves traveling approximately 6% slower than in regions with typical mantle structure (Gallacher et al., 2016; Bastow et al., 2008). Isostatic calculations show that the regionally hot and bouyant upper mantle is the most likely cause of the regionally high elevations observed across the region, including dynamically supporting NW plateau (average elevation of 2.5 km) (Moucha et al., 2011; Gauntlett et al., 2024). Understanding the dynamics and characteristics of this region contributes to our broader knowledge of tectonic processes and the Earth’s structure.
1.1 Seismicity from previous studies
Knowledge of the seismic activity associated with the MER and adjacent NW plateau comes from both instrumental and historical records. Limited earthquake monitoring equipment in the early stages and sparse distribution of monitoring stations have resulted in an incomplete earthquake catalog for the region (Ayele et al., 2004; Ayele and Kulhánek, 1997; Hofstetter and Beyth, 2003; Kebede and Kulhánek, 1994). Regional and local instrumental studies reveal that seismicity is predominantly concentrated in the rift, and in particular most closely associated with major border faults, the Wonji Fault Belt (WFB) and volcanic centres (Kebede and Kulhánek, 1994; Ayele, 2005; Keir et al., 2006a; Asefa and Ayele, 2020; Ogden et al., 2021; Alemayehu and Asefa, 2023). Earthquakes occurrence in the region are characterized by frequent moderate to small-magnitude (Kebede and Kulhánek, 1994; Ayele and Kulhánek, 1997), and commonly occur in episodic swarms (Keir et al., 2006a; Greenfield et al., 2019; Raggiunti et al., 2023). Earthquake depths are mostly within the shallowest 20-km of the crust, with the exception of rare lower crustal microseismic swarms interpretted to be induced by motion of deep magma or volatile fluids (e.g., Ayele et al., 2024; Muluneh et al., 2021). Focal mechanisms from previous studies (Brazier et al., 2008; Hofstetter and Beyth, 2003; Keir et al., 2006a) reveal normal faulting in the MER, which is consistent with the extensional tectonic regime.
In contrast to the seismicity of the MER, the seismicity beneath the NW plateau is less understood. Keir et al. (2009) investigated the seismicity of the MER during 2001–2003 (project EAGLE–Ethiopia Afar Geoscientific Lithospheric Experiment), but also recorded earthquakes outside of the rift. The study showed clusters of seismicity beneath the Yerer-Tullu Wellel Volcanic Lineament (YTVL) which is on the rift margin between the MER and NW plateau. Some of the earthquakes are reliably located in the lower crust and interpreted as induced by magma migration (Keir et al., 2009). In addition, Brazier et al. (2008) analyzed earthquake activity that occurred during the 2000–2002 project period as part of the Ethiopia Broadband Seismic Experiment (EBSE) and identified minor seismic activity along the northwestern edges of the NW plateau.
Pre-instrumental earthquake observations from various sources spanning over 500 years have been compiled, revealing a significant history of seismic activity (Gouin, 1979). Notable events included the 6.8 (MW) Langano earthquake in August 1906, which was felt in Addis Ababa and its surroundings. Ayele and Kulhánek (2000) relocated this event to the eastern shoulder of the MER with a magnitude of MW = 6.6. The NW plateau experiences notable seismic activity, particularly along its eastern escarpment. Historical earthquakes, such as the 1938 (M 5.6, M 4.5) and 1942 (M 5.3–5.9) events, occurred near Debre Berhan and the plateau-Afar escarpment, indicating active faulting. Durham University deployed seismic network in 1974 in the Afar region and recorded 106 low-magnitude earthquakes in the NW plateau (39.5°E−40°E, 10°N-13°N), with seismic clustering in the Guf graben and northwest of Debre Sina. Additionally, a 1971 swarm of 151 microearthquakes (M ∼3.8) near Debre Berhan revealed ongoing fault movement. This seismicity is linked to extensional tectonics along the Plateau-Afar escarpment, where crustal adjustments continue to shape the region.
1.2 Seismic structure of the MER and NW plateau
Previous geophysical studies imaged mantle and crustal seismic structure beneath the MER and adjacent NW plateau, focusing mainly on seismic wavespeeds and crustal thickness. Based on receiver function evaluations, the Moho depth below the MER is between 27 and 38 km, and Poisson’s ratios are between 0.27 and 0.35 (Dugda, 2005). According to surface and body wave research, the greatest Moho depth beneath the Addis Ababa region is 48 km (Searle and Gouin, 1971). Studies of seismic velocity, such as ambient noise tomography (ANT) reveal especially slow S-wave velocities (Vs.) in the lower crust beneath the MER. The observed Vs. (∼3.20 km/s) is suggestive of partial melt influence (Chambers et al., 2019; Ogden et al., 2019).
The Ethiopian plateau is characterized by thicker and relatively stable crust, and shows distinct geophysical features compared to the MER. Receiver function analyses estimate Moho depths of 36–44 km beneath the NW plateau (Kibret et al., 2022). S-wave velocity studies reveal a heterogeneous crustal structure, with low velocities (∼3.6 km/s) in the lower crust of some regions such as Lake Tana (Alemayehu et al., 2023). The uppermost mantle beneath the plateau exhibits Vs. values of 3.9–4.3 km/s, reflecting presence of a thermal anomaly and partial melt (Eshetu et al., 2021).
1.3 Motivation of the study
Previous studies highlight a lack of geophysical constraints due to absence of data on the patterns of seismicity and the mode of deformation in the NW plateau and its surroundings. To address these gaps a new passive seismic network consisting of thirty broadband seismograph stations was deployed in the Ethiopian plateau. This study aims to provide the first observation for understanding of the seismicity, focal mechanisms and the local stress condition covering a larger area and greater depth than previous attempts. We also performed focal mechanisms for selected earthquakes. The majority of the stations were fairly distributed across the NW plateau in order to acquire high resolution coverage. Here we investigate, for the first time, the seismicity, focal mechanisms and related local stress condition of NW plateau and surrounding rift flanks with the rare data set acquired during the aforementioned project period.
2 Data and methods
2.1 Local earthquake hypocenter determination
To investigate the seismicity and focal mechanisms in the NW plateau we utilized data from 30 temporary Guralp CMG-3T seismometers deployed during 2014–2016 by the University of Cornell (Keranen, 2013) in collaboration with the Institute of Geophysics, Space Science, and Astronomy (IGSSA) of Addis Ababa University. These instruments were equipped with three component seismometers and recorded data at a sampling rate of 100 Hz. Additionally, seven permanent Ethiopian seismic stations were included in the analysis (Figure 1).
Earthquake records were identified manually from continuous seismic data recorded at both permanent and temporary seismic stations in the region. To enhance the clarity of the seismic arrivals, we band-pass filtered the data within the range of 0.5 and 15 Hz, utilizing a Butterworth band-pass filtered seismogram as described by Havskov and Ottemoller (1999). We employed manual phase picking to determine the seismic phase arrival times. P-waves were measured on the vertical component due to their sharp onset and S-waves detected on either of the clearer horizontal component. A sample earthquake waveform is plotted on Figure 2. The earthquake location determination was conducted using the HYPO71 routine, which is integrated within the SEISAN software package (Figure 3a). Earthquake epicentral error ellipse are shown in Figure 3b and the distribution of P and S-wave travel time residuals are shown in Figure 3c. The 1D velocity model of Keranen et al. (2009) is used for the location, which was constructed using controlled-source seismic experiment conducted along the rift and across the Ethiopian Plateau. This model gives a high-resolution representation of the shallow crustal structure (less than 15 km deep), which reduces the uncertainty in the hypocenter depths. The 1D models of Alemayehu et al. (2023) and Baranov and Morelli (2014) were used to compute focal mechanism solutions. These include regional and global constraints (receiver functions, surface wave tomography) and best suited for resolving the structure of the deeper crust and upper mantle (>15 km). This makes it possible to do accurate full-waveform modeling needed for moment tensor inversion (Dreger and Helmberger, 1993; Herrmann, 2013). A minimum of three seismic stations was used to calculate the epicenter and depth of the detected earthquakes. In total we located 800 earthquakes.
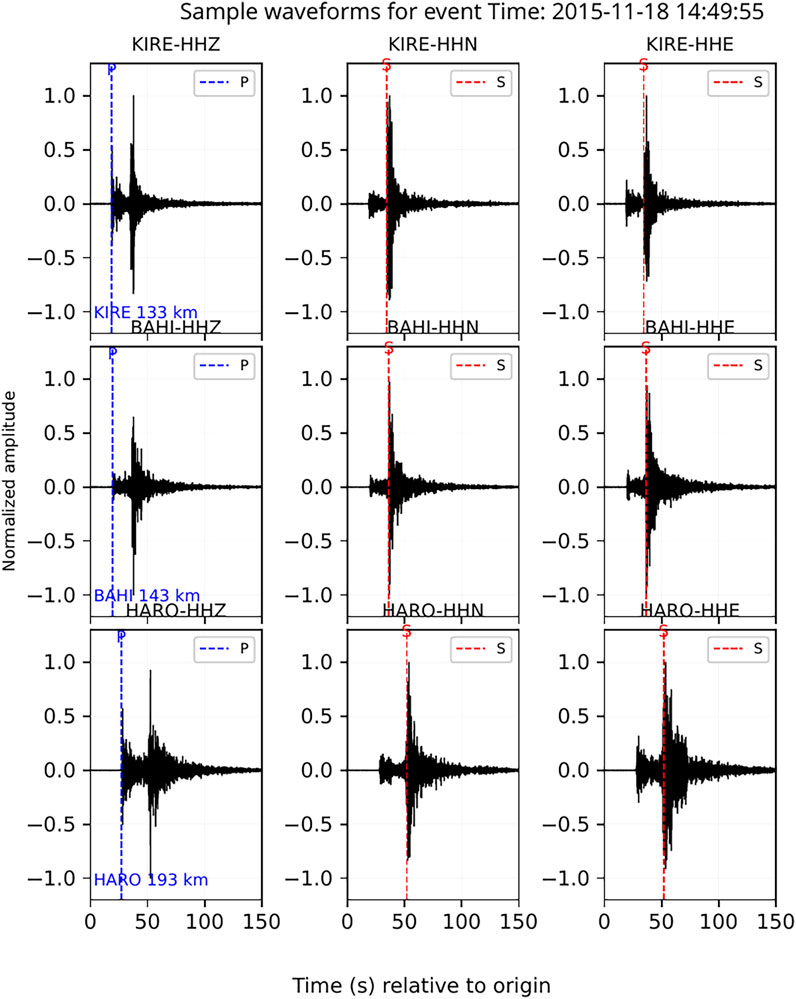
Figure 2. Sample waveform plot for an event that occurred on 2015/11/18 at 14:49:57 and is located at 10.4oN and 37.98oE with MW = 3.7. The stations KIRE, BAHI and HARO are 133 km, 143 km and 193 km respectively away from the earthquake source.
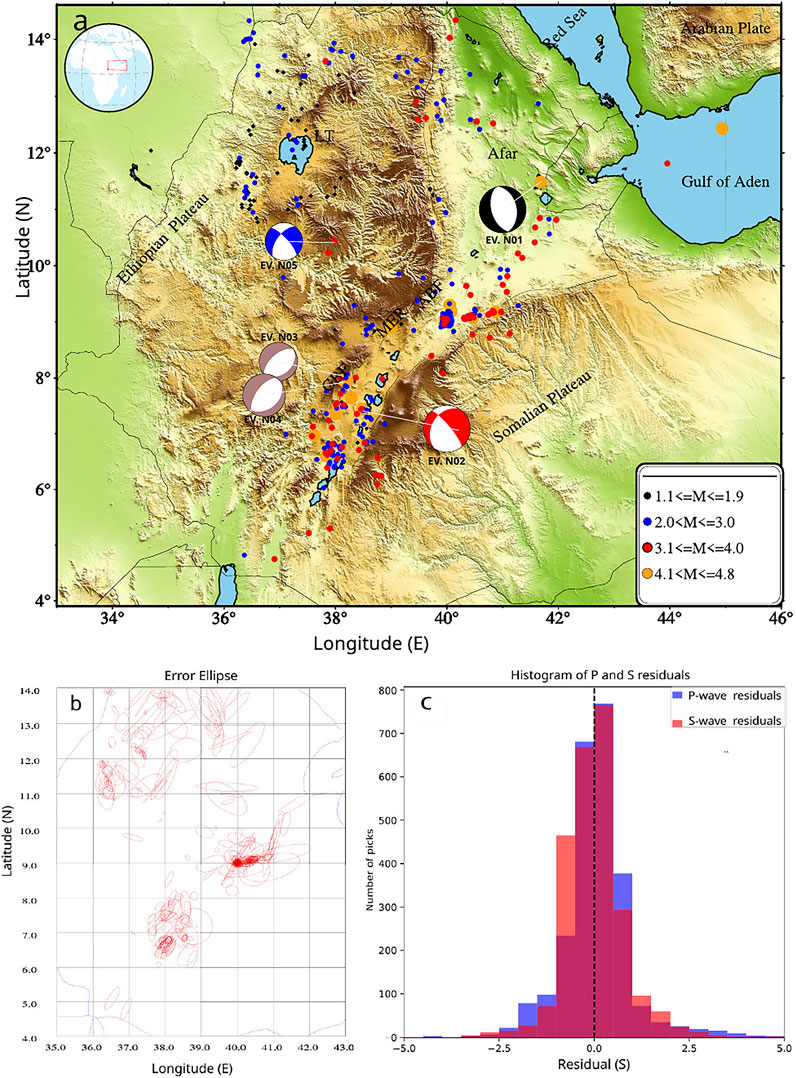
Figure 3. (a) Seismicity of the Ethiopian plateau and its surrounding region observed for the period 2014–2016. Circles represent the earthquakes of different magnitude range, as shown in the legend. GBF, Guraghe Border Fault; MER, Main Ethiopian Rift; NMER, Northern Main Ethiopian Rift; SMER, Southern Main Ethiopian Rift; LT, Lake Tana; ABF, Ankober Border Fault. The focal mechanisms are shown by beachball symbols of various colours. The black beach ball represent event in the Afar region, the blue beach ball represent event in the NW plateau, the brown beach balls represent events along the Guraghe border fault, and the red beach ball represent event in the Main Ethiopian Rift (MER), under each beachball, event numbers are displayed (Table 2). The dots on the map represent the locations of the earthquakes, and the size of each dot is proportional to the magnitude of the corresponding earthquake as shown in the legend. (b) Error ellipse of the earthquakes on NW plateau and its surrounding region. (c) The histogram of P and S wave’s residuals. The blue, orange and red colours depicts histogram of P, S and both P and S waves residuals respectively.
2.2 Earthquake magnitudes
In this study, earthquake magnitudes were determined using the local magnitude (ML) scale of Keir et al., 2006b. ML is a measure of the energy released during an earthquake and is calculated based on the logarithm of the maximum amplitude of the earthquake signal observed on the seismogram taking into account the distance between the earthquake focus and the seismometer. The calculated magnitudes are displayed in Figure 3a and Supplementary Figure S1. The scaling equation (Keir et al., 2006b) read as:
In Equation 1, AWA represents the maximum zero-to-peak amplitude recorded on the horizontal components on a Wood-Anderson seismograph in mm and r is the hypocentral distance in km.
2.3 Focal mechanisms
One of the most crucial earthquake source parameters is the focal mechanism solution, which serves as a starting point for understanding the state of stress of a region. Our objective is to determine the focal mechanisms, depth, and size of earthquakes in the study area that are relatively minor in magnitude. To achieve this, we utilized a software package ISOLA, which has been developed and widely used for focal mechanism analysis (Singh et al., 2024; Sokos and Zahradník, 2013; Sokos and Zahradnik, 2008; Zahradník and Sokos, 2018; Zahradník and Sokos, 2025). ISOLA provides advanced capabilities for analyzing earthquake focal mechanisms from the waveform records and extracting valuable information regarding the earthquake source characteristics. By employing ISOLA, we aimed to obtain reasonable estimate of the focal mechanism solutions for selected earthquakes under investigation, allowing us to gain insights into the stress conditions prevailing in the study area.
Assuming a point source, the deviatoric moment tensor was obtained by inverting the low-frequency full waveforms. A fourth-order Butterworth filter was used to band-pass filter the data between 0.02 and 0.09 Hz and cut from the event origin time for about 300 s after removing the instrument response, mean, and trend. The discrete wavenumber (DWN) approach was used in ISOLA to calculate the Green’s functions for the trial point source positions below the epicenter (Bouchon, 2003). The correlation (corr) or variance reduction (VR) parameter of the ISOLA code is used to quantify the waveform agreement between the synthetic and observed seismograms.
The double-couple (DC) percentage of the moment tensor solution of tectonic earthquakes may indicate the quality of the inversion result. The validity of the focal mechanism is significantly compromised when the double-couple percentage falls below 0.5 (DC < 0.5) (Carvalho et al., 2016).
ISOLA employs a grid search technique to determine the optimal moment tensor. Preliminary analyses of a horizontal grid search indicated optimal waveform fit beneath the epicenter. We generated a database of Green’s functions for depths ranging from 1.0 to 36 km in 2.5 km increments, calculated using ISOLA’s default maximum frequency of 1.6667 Hz, the Nyquist frequency. The inversion simultaneously searched for the optimal source depth and centroid time shift relative to the origin time (t = 0). The temporal grid search spanned from −5.0 to 5.0 s, using a step of 0.3 s. Stability of the solution was verified by jack-knifing of stations and components, implemented in ISOLA (Supplementary Figure S2).
3 Results
3.1 Rift valley
Significant seismic activity in the rift valley is highlighted in this study, particularly near the Fentale Volcano and the Guraghe Border Fault (GBF). There were about 600 located earthquakes in the rift, mostly with magnitudes between 2.0 and 3.0 ML and most of the depths are less than 20 km. Of these, 497 were concentrated around the Fentale Volcano, while 27 occurred close to the GBF. We measured earthquake swarms in the Fentale region in March and April 2015 (Figures 4a, b). These were further documented by Ayele et al. (2024). With magnitudes of Mw 3.5 and 4.3, moment tensor inversion for two events in GBF revealed normal faulting (Table 1; Table 2; Supplementary Figures S3-S6). The Afar and Ankober Border Faults (ABF) have seen less seismic activity. A single event that happened on 13 December 2014, at 23:37:19, close to Asayita, had a moment tensor inversion that showed an orientation of NE-SW and a depth of 11 km (Table 1; Table 2; Supplementary Figure S7). The same event was located by the USGS with a body magnitude of 4.4 (Mb).
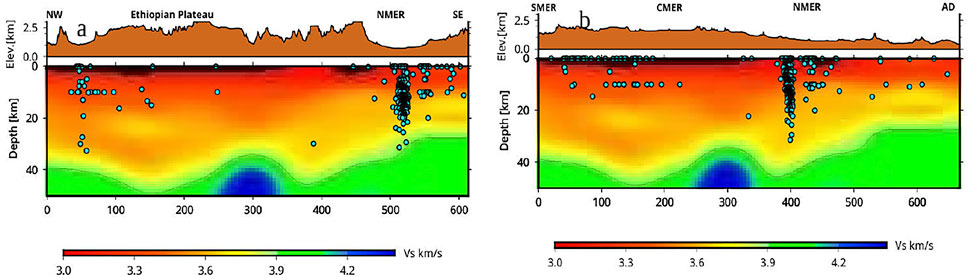
Figure 4. (a) Simplified Moho map of two selected profile in the study area (modified after Alemayehu et al., 2023). (Top panel) Vertical sections through the 3-D shear wave velocity model along the profile orthogonal to the rift axis in Figure 1: (a) (Plateau–NMER). The velocity slice at 3.9 km/s is used as an indicator of crustal thickness. The solid line on the top panel corresponds to the Moho depth. The horizontal lines are distance in km and the vertical lines are depth in km. The cyan circles are depth of the earthquakes in this study. We plotted all the earthquakes within a radius of 50 km from the profile. AD: Afar Depression, NMER, SMER and CMER: Northern Southern and Central Main Ethiopian Rift, NWP and SE: North-Western and southeastern Ethiopian plateau. The concentrated event location beneath Fentale Volcano represents the earthquake swarms in March and April 2015. (b) Same as Figure 4a but for vertical sections through the 3-D shear wave velocity model along the profile parallel to the rift axis showed in Figure 1: (b) (MER-AFAR).
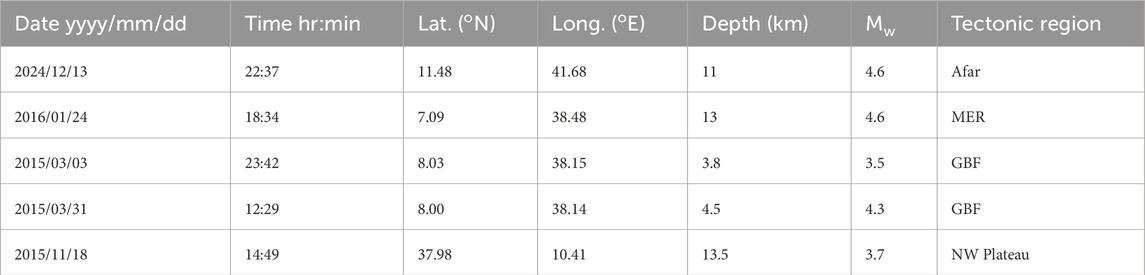
Table 1. Hypo central parameters of five selected earthquakes. Event selection for moment tensor inversion (Table 1) followed two key criteria: First, events were chosen from representative tectonic provinces across Ethiopia (NW Plateau, Afar Depression, and Main Ethiopian Rift) to capture regional variations in focal mechanisms. Second, strict waveform quality requirements were applied: only earthquakes exhibiting unambiguous P- and S-wave arrivals with visually confirmed high signal-to-noise characteristics across ≥4 broadband stations were processed.
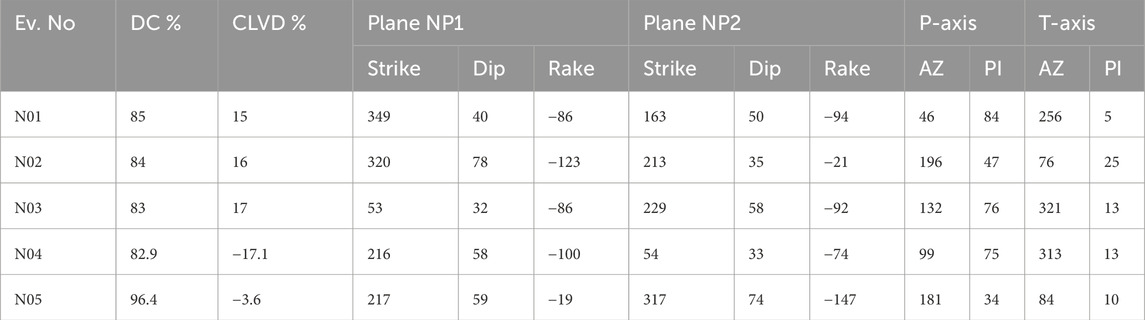
Table 2. List of the focal parameters of the five earthquakes in the selected region during 2014–2016, which are being modeled in the present study. NP1 and NP2 are the two nodal planes of the focal mechanisms obtained using the moment tensor inversion approach.
3.2 Northwestern plateau
We recorded seismic activity across the NW plateau with magnitudes as low as ML 1.1. There were 115 earthquakes in this region, with magnitude ranging from 1.1 to 3.7 ML. Most of these earthquakes are located at depths less than 25 km (Figure 4a; Supplementary Figure S1) while clusters of earthquakes are also observed close to Lake Tana. In contrast, there was no seismic activity reported beneath the southeastern plateau in this monitoring period (Figure 3a).
A normal faulting mechanism with a minor strike-slip component is obtained from the moment tensor inversion for the earthquake that occurred on 18 November 2015, at 14:49:55 GMT (Figures 5, 6a–c; Supplementary Figure S1).
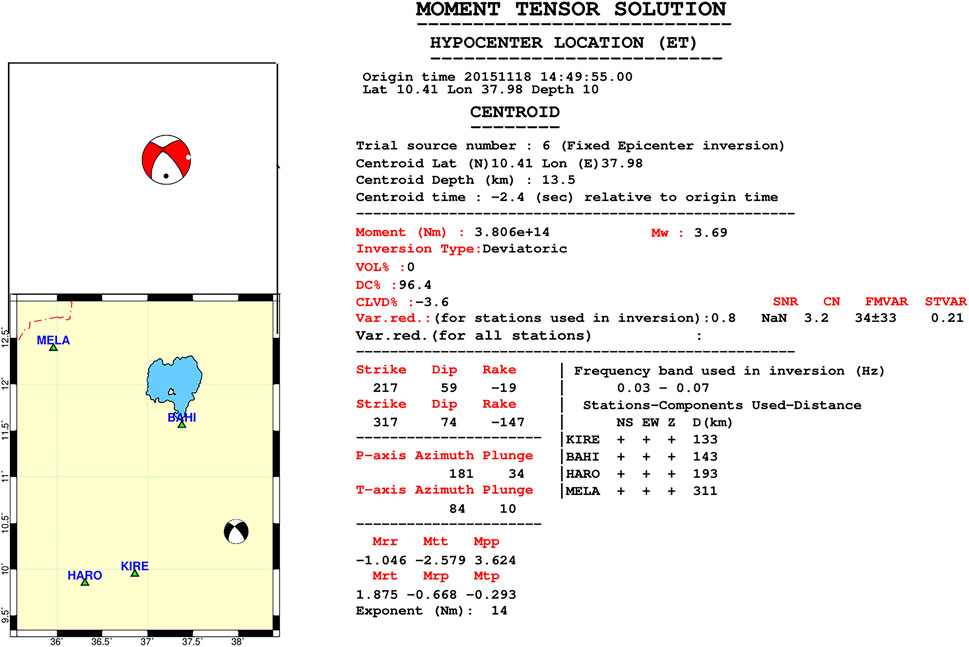
Figure 5. The moment tensor solution and hypocenter location for the event that occurred in the Ethiopian plateau on 18/11/2015 with magnitude of 3.7 Mw: upper left panel shows beach-ball plot, lower left panel the beach-ball and station distributions used for the inversion and right panel show details of the source parameters where all are automatic output of ISOLA software.
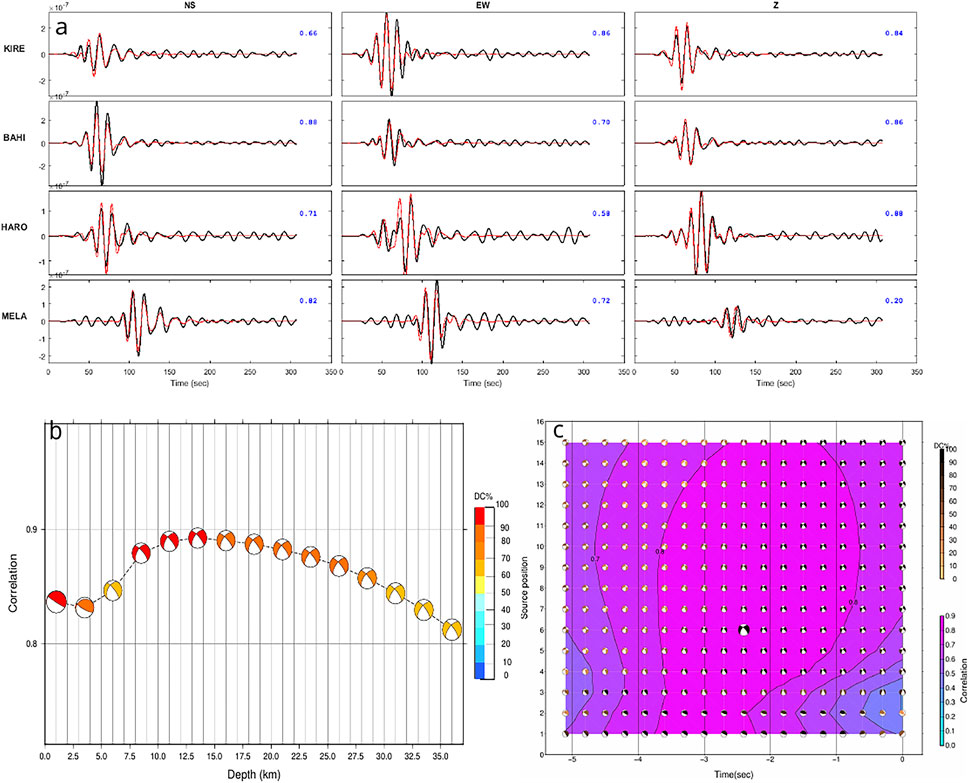
Figure 6. (a) Best waveform fits with the red line showing synthetics and the black line observed data for the event mentioned in Figure 5. The station names for each waveform are displayed on the left, while the Variance Reduction (VR) coefficient for each real-synthetic waveform pair is shown in the upper right corner (blue colour). The frequency range utilized for each inversion is 0.03–0.07 Hz. (b) The correlation between observed and synthetic waveform and focal mechanism as a function of the trial depth. Colours represent the DC %. (c) Plot of correlation vs. time shift, source position and focal mechanism for a single source inversion. Large correlation was obtained for source 6 (13.5 km depth). Focal mechanism shading changes according to double couple percentage, preferred solution is shown by a larger black beach ball. We used a time shift from −5 to 0 s for plotting Figure 6c.
4 Discussion
4.1 Rift valley seismicity
The seismicity pattern in the Afar region aligns with ongoing extensional deformation. The focal mechanisms in this region predominantly exhibit normal faulting with strikes of more or less NE-SW orientations, aligning with the regional extensional stress regime in Afar. The shallow focal depths (about 11 km) suggest brittle deformation in the upper crust (Table 1; Table 2; Supplementary Figure S7). Focal mechanisms along the MER are predominantly normal faulting in style with a strike-slip component, suggesting complex fault interactions and potential reactivation of pre-existing structures, influenced by diking and regional stress fluctuations (Manighetti et al., 1998; Keir et al., 2006a). Substantial activity has been observed along the GBF and in proximity to the Fentale volcano, where earthquake swarms suggest connections between tectonic and magmatic processes. The Fentale-Dofan region notably displays considerable shallow seismicity and evidence of ongoing dike intrusions, emphasizing the importance of magmatism in strain accommodation (Acton et al., 1991; Temtime et al., 2020). The results show that the Wonji Fault Belt (WFB) traversing the rift floor, is a significant source of seismic activity and facilitates active deformation by fault slip and diking process (Keir et al., 2025; Ayele et al., 2024).
4.2 Plateau seismcity
Numerous micoearthquakes recorded during the operation of extensive broadband seismic networks show that the NW plateau is more seismically active than previously expected. The majority of these earthquakes occur near Lake Tana, with Figure 3a showing are associated with a significant morphological rift valley, known as the Lake Tana Basin and thought to have been mostly active during the late Miocene to Quaternary (Chorowicz et al., 1998). Most of the earthquakes therefore appear to occur on existing lines of past extension, suggesting that pre-existing faults are being reactivated. The single focal mechanism for the NW plateau shows normal faulting with a strike-slip component and yielding a near E-W oriented T-axis, consistent with the extension direction across the MER.
While the dominant cluster of seismicity that occurs north-west of Lake Tana (LT) is spatially separated from the main concentration of hot springs and volcanic features located to the east, our results also reveal a secondary, yet significant, cluster of earthquakes occurring southeast of LT (Figures 1, 3a). This south-eastern cluster is spatially associated with the hot springs and volcanic features located specifically in that region, with the earthquakes also occurring down to lower crustal depths (Figure 4a; Supplementary Figure S1). Both observations point towards fluid involvement in triggering the seismicity. Seismic velocity models and receiver function analysis indicate that the crust beneath the NW plateau has a thickness of 20–35 km and exhibits locally elevated Vp/Vs ratios, suggesting the presence of partial melt zones or magmatic intrusions (Ogden et al., 2019). Low velocity zones in the lower crust suggest that melting and magmatic underplating significantly influence the mechanical properties of the crust (Eilon, 2025; Alemayehu et al., 2023; Chambers et al., 2019; Chambers et al., 2021). These magmatic alteration can locally cause high strain rates and facilitate the onset of micoseismicity in the deep crust.
Seismic activity in the rift valley is predominantly localized along the major fault zones in the rift valley, while it is more dispersed beneath the NW plateau, suggesting a diffuse extension regime. Our observations of seismicity beneath the NW plateau is consistent with recent GNSS findings that show ∼2 mm/yr of near E-W extension across the plateau (Birhanu et al., 2016). The findings are important since they show that deformation is not only localized to the rift valley, but that non insignificant amounts of extension occurs across a broad region outside of the rift. Seismic images of the mantle suggest the broad extension is associated with some limited partial melting (e.g., Asefa and Ayele, 2021; Chambers et al., 2022), linking the distributed extension to fluid involvement in the seismicity. The unique faulting process in the region illustrate how the divergence of the Somalian and Nubian plates within the East African Rift System has led to regional extension (Corti, 2009). The Afar mantle plume induces localized uplift, thermal weakening, and extension, hence enhancing fault activity (Ebinger and Casey, 2001). Tectonic processes are corroborated by seismic and geodetic data regarding extensional strain rates and upper crustal fault slip (Jones et al., 2019). Active magmatism, thermal degradatiation and pre-existing crustal heterogeneity all contributes to seismicity, particularly in the NW plateau, where the hypothesis of early-stage rifting is potentially occurring is supported by the cumulative observations.
5 Conclusion
Seismic data from earthquakes recorded between 2014 and 2016 were employed to examine the seismicity of the NW plateau and the MER. A total of 800 precisely determined epicentral earthquake locations have been generated. The seismic activity and focal mechanisms of the NW plateau and neighboring rifts have been thoroughly examined, yielding significant insights into the tectonics. The detected seismic activity is the first report from that region of the study, supporting recent tomographic analyses indicating the presence of partial melting and magmatic activity. This further suggests that the NW plateau exhibits greater tectonic activity relative to the SE plateau of the MER. Active thermal degradation, and crustal heterogeneity contributes to seismicity, particularly in the NW plateau, where cumulative observations may indicate distributed extension.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SA: Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Software. AA: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Project administration, Visualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision. DK: Supervision, Investigation, Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing, Resources, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The research work is sponsored by the International Center for Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Sandwich Training Educational Program (STEP) and Addis Ababa University. DK is partially supported through NERC grant NE/L013932/1.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the IRIS Data Management Center for providing the seismic data used in this study. The first author also would like to thankful for the support received from the International Center for Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Sandwich Training Educational Program (STEP) and Addis Ababa University. The Ethiopian Seismic Network (ESSN) is supported by the International Science Program (ISP) of Uppsala University. We also acknowledge the valuable contributions of J. Zahradník and E. Sokos, who provided consistent guidance during the utilization of the ISOLA moment tensor software. Maps are plotted using Generic Mapping Tools (GMT) (Wessel and Smith, 1998).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/feart.2025.1643092/full#supplementary-material
References
Acton, G. D., Stein, S., and Engeln, J. F. (1991). Block rotation and Continental extension in Afar: a comparison to oceanic microplate systems. Tectonics 10 (3), 501–526. doi:10.1029/90tc01792
Alemayehu, S., and Asefa, J. (2023). A review of earthquake source parameters in the main Ethiopian rift. Int. J. Geophys. 2023 (1), 1–14. doi:10.1155/2023/8368175
Alemayehu, S., Aoudia, A., Ayele, A., Pachhai, S., Thapa, H. R., Ebinger, C., et al. (2023). Structure of the crust-uppermost mantle beneath the Ethiopian volcanic province using ambient seismic noise and teleseismic P wave coda autocorrelation. Tectonophysics 869, 230092. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2023.230092
Asefa, J., and Ayele, A. (2020). Complex tectonic deformation in circum-tanzania craton: east African rift system. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 170, 103893. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2020.103893
Asefa, J., and Ayele, A. (2021). Seismicity of the east African rift System for the period 2013 to 2016. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 183, 104315. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2021.104315
Ayele, A. (2005). History and operational capability of the ethiopian seismic station network (ESSN). SINET Ethiop. J. Sci. 28 (1), 93–98. doi:10.4314/sinet.v28i1.18236
Ayele, A., and Kulhánek, O. (1997). Spatial and temporal variations of seismicity in the Horn of Africa from 1960 to 1993. Geophys. J. Int. 130 (3), 805–810. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246x.1997.tb01875.x
Ayele, A., and Kulhánek, O. (2000). Reassessment of source parameters for three major earthquakes in the East African rift system from historical seismograms and bulletins.
Ayele, A., Stuart, G., and Kendall, J. M. (2004). Insights into rifting from shear wave splitting and receiver functions: an example from Ethiopia. Geophys. J. Int. 157 (1), 354–362. doi:10.1111/j.1365-246X.2004.02206.x
Ayele, A., Luckett, R., Baptie, B., and Whaler, K. (2024). The 2015 earthquake swarm in the Fentale volcanic complex (FVC): a geohazard risk for Ethiopia's commercial route to the Djibouti port. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 213, 105236. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2024.105236
Baranov, A., and Morelli, A. (2014). “The global moho depth map for continental crust,” in EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts.
Bastow, I. D., Nyblade, A. A., Stuart, G. W., Rooney, T. O., and Benoit, M. H. (2008). Upper mantle seismic structure beneath the Ethiopian hot spot: rifting at the edge of the African low-velocity anomaly. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 9 (12). doi:10.1029/2008gc002107
Birhanu, Y., Bendick, R., Fisseha, S., Lewi, E., Floyd, M., King, R., et al. (2016). GPS constraints on broad scale extension in the Ethiopian Highlands and main Ethiopian rift. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43 (13), 6844–6851. doi:10.1002/2016gl069890
Bouchon, M. (2003). A review of the discrete wavenumber method. Pure Appl. Geophys. 160, 445–465. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-8010-7_2
Brazier, R. A., Miao, Q., Nyblade, A. A., Ayele, A., and Langston, C. A. (2008). Local magnitude scale for the ethiopian Plateau. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 98 (5), 2341–2348. doi:10.1785/0120070266
Carvalho, J., Barros, L., and Portela Fontenele, D. (2016). “Determination of the focal mechanisms of events in Brazil central,” in Conference: Simpósio Brasileiro de Geofísica. Simpósio Brasileiro de Geofísica, 1–4. doi:10.22564/7simbgf2016.057
Chambers, E. L., Harmon, N., Keir, D., and Rychert, C. A. (2019). Using ambient noise to image the northern east African rift. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 20 (4), 2091–2109. doi:10.1029/2018gc008129
Chambers, E. L., Harmon, N., Rychert, C. A., and Keir, D. (2021). Variations in melt emplacement beneath the northern east African rift from radial anisotropy. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 573, 117150. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2021.117150
Chambers, E. L., Harmon, N., Rychert, C. A., Gallacher, R. J., and Keir, D. (2022). Imaging the seismic velocity structure of the crust and upper mantle in the northern East African rift using rayleigh wave tomography. Geophys. J. Int. 230 (3), 2036–2055. doi:10.1093/gji/ggac156
Chorowicz, J., Collet, B., Bonavia, F. F., Mohr, P., Parrot, J. F., and Korme, T. (1998). The tana basin, Ethiopia: intra-plateau uplift, rifting and subsidence. Tectonophysics 295 (3-4), 351–367. doi:10.1016/s0040-1951(98)00128-0
Corti, G. (2009). Continental rift evolution: from rift initiation to incipient break-up in the main Ethiopian rift, East Africa. Earth-Science Rev. 96 (1-2), 1–53. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2009.06.005
Dreger, D. S., and Helmberger, D. V. (1993). Determination of source parameters at regional distances with three-component sparse network data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 98 (B5), 8107–8125. doi:10.1029/93jb00023
Dugda, M. T., Nyblade, A. A., Julia, J., Langston, C. A., Ammon, C. J., and Simiyu, S. (2005). Crustal structure in Ethiopia and Kenya from receiver function analysis: implications for rift development in eastern Africa. J. Geophys. Res. 110 (B1). doi:10.1029/2004jb003065
Ebinger, C. J., and Casey, M. (2001). Continental breakup in magmatic provinces: an Ethiopian example. Geology 29 (6), 527. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0527:Cbimpa>2.0.Co;2
Eilon, Z. C. (2025). Attenuation and velocity tomography of the northern east African rift. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 130 (2), e2024JB030417. doi:10.1029/2024jb030417
Eshetu, A., Mammo, T., and Tilmann, F. (2021). Imaging the Ethiopian rift region using transdimensional hierarchical seismic noise tomography. Pure Appl. Geophys. 178 (11), 4367–4388. doi:10.1007/s00024-021-02880-2
Gallacher, R. J., Keir, D., Harmon, N., Stuart, G., Leroy, S., Hammond, J. O., et al. (2016). The initiation of segmented buoyancy-driven melting during Continental breakup. Nat. Commun. 7, 13110. doi:10.1038/ncomms13110
Gauntlett, M., Stephenson, S., Kendall, J. M., Ogden, C., Hammond, J. O., Hudson, T., et al. (2024). The dynamic crust of northern Afar and adjacent rift margins: new evidence from receiver function analysis in Eritrea and Ethiopia. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 25 (6), e2023GC011314. doi:10.1029/2023gc011314
Greenfield, T., Keir, D., Kendall, J. M., and Ayele, A. (2019). Seismicity of the bora-tullu moye volcanic field, 2016–2017. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 20 (2), 548–570. doi:10.1029/2018gc007648
Havskov, J., and Ottemoller, L. (1999). SEISAN earthquake analysis software. Seismol. Res. Lett. 70 (5), 532–534. doi:10.1785/gssrl.70.5.532
Herrmann, R. B. (2013). Computer programs in seismology: an evolving tool for instruction and research. Seismol. Res. Lett. 84 (6), 1081–1088. doi:10.1785/0220110096
Hofstetter, R., and Beyth, M. (2003). The Afar depression: interpretation of the 1960–2000 earthquakes. Geophys. J. Int. 155 (2), 715–732. doi:10.1046/j.1365-246x.2003.02080.x
Jones, J. R., Stamps, D. S., Wauthier, C., Saria, E., and Biggs, J. (2019). Evidence for slip on a border fault triggered by magmatic processes in an immature Continental rift. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 20 (5), 2515–2530. doi:10.1029/2018gc008165
Kebede, F., and Kulhánek, O. (1994). Spatial and temporal variations of b-values along the East African rift system and the southern Red Sea. Phys. Earth Planet. Interiors 83 (3-4), 249–264. doi:10.1016/0031-9201(94)90092-2
Keir, D., Ebinger, C., Stuart, G., Daly, E., and Ayele, A. (2006a). Strain accommodation by magmatism and faulting as rifting proceeds to breakup: seismicity of the northern Ethiopian rift. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 111 (B5). doi:10.1029/2005jb003748
Keir, D., Stuart, G., Jackson, A., and Ayele, A. (2006b). Local earthquake magnitude scale and seismicity rate for the Ethiopian rift. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 96 (6), 2221–2230. doi:10.1785/0120060051
Keir, D., Bastow, I. D., Whaler, K. A., Daly, E., Cornwell, D. G., and Hautot, S. (2009). Lower crustal earthquakes near the Ethiopian rift induced by magmatic processes. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 10 (6). doi:10.1029/2009gc002382
Keir, D., La Rosa, A., Pagli, C., Wang, H., Ayele, A., Lewi, E., et al. (2025). The 2024 fentale diking episode in a slow extending Continental rift. Geophys. Res. Lett. 52 (5), e2024GL113214. doi:10.1029/2024gl113214
Keranen, K. (2013). Exploring extensional tectonics beyond the Ethiopian rift. Int. Fed. Digital Seismogr. Netw., 10.
Keranen, K. M., Klemperer, S. L., Julia, J., Lawrence, J. F., and Nyblade, A. A. (2009). Low lower crustal velocity across Ethiopia: is the main Ethiopian rift a narrow rift in a hot craton? Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 10 (5). doi:10.1029/2008gc002293
Kibret, B. A., Ayele, A., and Keir, D. (2022). Modelling S-Wave velocity structure beneath the central main Ethiopian rift using receiver functions. Front. Earth Sci. 10, 773783. doi:10.3389/feart.2022.773783
Knappe, E., Bendick, R., Ebinger, C., Birhanu, Y., Lewi, E., Floyd, M., et al. (2020). Accommodation of east African rifting across the Turkana depression. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 125 (2), e2019JB018469. doi:10.1029/2019jb018469
Maestrelli, D., Sani, F., Keir, D., Pagli, C., Rosa, A. L., Muluneh, A. A., et al. (2024). Reconciling plate motion and faulting at a rift-rift-rift triple junction. Geology 52 (5), 362–366. doi:10.1130/g51909.1
Manighetti, I., Tapponnier, P., Gillot, P. Y., Jacques, E., Courtillot, V., Armijo, R., et al. (1998). Propagation of rifting along the arabia-somalia plate boundary: into Afar. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 103 (B3), 4947–4974. doi:10.1029/97jb02758
Moucha, R., and Forte, A. M. (2011). Changes in African topography driven by mantle convection. Nat. Geosci. 4 (10), 707–712. doi:10.1038/ngeo1235
Muluneh, A. A., Keir, D., and Corti, G. (2021). Thermo-rheological properties of the Ethiopian lithosphere and evidence for transient fluid induced lower crustal seismicity beneath the Ethiopian rift. Front. Earth Sci. 9, 610165. doi:10.3389/feart.2021.610165
Ogden, C., Bastow, I. D., Gilligan, A., and Rondenay, S. (2019). A reappraisal of the H–κ stacking technique: implications for global crustal structure. Geophys. J. Int. 219 (3), 1491–1513. doi:10.1093/gji/ggz364
Ogden, C. S., Keir, D., Bastow, I. D., Ayele, A., Marcou, S., Ugo, F., et al. (2021). Seismicity and crustal structure of the southern main Ethiopian rift: new evidence from Lake abaya. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 22 (8), e2021GC009831. doi:10.1029/2021gc009831
Pik, R., Deniel, C., Coulon, C., Yirgu, G., Hofmann, C., and Ayalew, D. (1998). The northwestern ethiopian Plateau flood basalts: classification and spatial distribution of magma types. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 81 (1-2), 91–111. doi:10.1016/s0377-0273(97)00073-5
Raggiunti, M., Keir, D., Pagli, C., and Lavayssière, A. (2023). Evidence of fluid induced earthquake swarms from high resolution earthquake relocation in the main Ethiopian rift. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 24 (4), e2022GC010765. doi:10.1029/2022gc010765
Searle, R., and Gouin, P. (1971). An analysis of some local earthquake phases originating near the Afar triple junction. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 61 (4), 1061–1071. doi:10.1785/bssa0610041061
Singh, A., Kumar, R., Rai, A., Singh, S., Singh, R., Prakash, S., et al. (2024). “Determination and identification of focal mechanism solutions for the 2016 Kumamoto earthquake from waveform inversion using ISOLA software,” in Recent developments in earthquake seismology: present and future of seismological analysis (Springer), 165–178.
Sokos, E. N., and Zahradnik, J. (2008). ISOLA a fortran code and a matlab GUI to perform multiple-point source inversion of seismic data. Comput. and Geosciences 34 (8), 967–977. doi:10.1016/j.cageo.2007.07.005
Sokos, E., and Zahradník, J. (2013). Evaluating centroid-moment-tensor uncertainty in the new version of ISOLA software. Seismol. Res. Lett. 84 (4), 656–665. doi:10.1785/0220130002
Temtime, T., Biggs, J., Lewi, E., and Ayele, A. (2020). Evidence for active rhyolitic dike intrusion in the northern main Ethiopian rift from the 2015 fentale seismic swarm. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 21 (6), e2019GC008550. doi:10.1029/2019gc008550
Wessel, P., and Smith, W. H. (1998). New, improved version of generic mapping tools released. Eos, Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 79 (47), 579. doi:10.1029/98eo00426
Wolfenden, E., Ebinger, C., Yirgu, G., Deino, A., and Ayalew, D. (2004). Evolution of the northern main Ethiopian rift: birth of a triple junction. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 224 (1-2), 213–228. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.04.022
Zahradník, J., and Sokos, E. (2018). “ISOLA code for multiple-point source modeling”, in Moment tensor solutions: a useful tool for seismotectonics, 1–28.
Keywords: seismtectonics, Ethiopian plateau, Guraghe border fault, Fentale volcano, focal mechanisms
Citation: Alemayehu S, Ayele A and Keir D (2025) The first observation of seismicity beneath the northwestern Ethiopian plateau and its seismotectonic implications. Front. Earth Sci. 13:1643092. doi: 10.3389/feart.2025.1643092
Received: 08 June 2025; Accepted: 23 September 2025;
Published: 02 October 2025.
Edited by:
Kelly Hong Liu, Missouri University of Science and Technology, United StatesReviewed by:
Titi Anggono, National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), IndonesiaNagaraju Kanna, Pondicherry University, India
Tuo Wang, Hunan Institute of Geophysics and Geochemistry, China
Copyright © 2025 Alemayehu, Ayele and Keir. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sisay Alemayehu, c2lzYXkuYWxlbWF5ZWh1QGFhdS5lZHUuZXQ=
 Sisay Alemayehu
Sisay Alemayehu Atalay Ayele
Atalay Ayele Derek Keir
Derek Keir